CN101882644A - 具有ⅳ/ⅲ-ⅴ族混合合金的多结太阳能电池 - Google Patents
具有ⅳ/ⅲ-ⅴ族混合合金的多结太阳能电池 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101882644A CN101882644A CN2010101479778A CN201010147977A CN101882644A CN 101882644 A CN101882644 A CN 101882644A CN 2010101479778 A CN2010101479778 A CN 2010101479778A CN 201010147977 A CN201010147977 A CN 201010147977A CN 101882644 A CN101882644 A CN 101882644A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- band gap
- battery
- layer
- sub
- gesisn
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims abstract description 11
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 11
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 38
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 33
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910000530 Gallium indium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 17
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 185
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 18
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 16
- 229910000980 Aluminium gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 11
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 9
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 6
- -1 GaInP Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000005357 flat glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 4
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium Chemical compound [Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052787 antimony Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N antimony atom Chemical compound [Sb] WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052785 arsenic Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- RQNWIZPPADIBDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N arsenic atom Chemical compound [As] RQNWIZPPADIBDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910002056 binary alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052797 bismuth Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JCXGWMGPZLAOME-UHFFFAOYSA-N bismuth atom Chemical compound [Bi] JCXGWMGPZLAOME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000001451 molecular beam epitaxy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002978 peroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052716 thallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BKVIYDNLLOSFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N thallium Chemical compound [Tl] BKVIYDNLLOSFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000927 vapour-phase epitaxy Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/072—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN heterojunction type
- H01L31/0725—Multiple junction or tandem solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/068—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN homojunction type, e.g. bulk silicon PN homojunction solar cells or thin film polycrystalline silicon PN homojunction solar cells
- H01L31/0687—Multiple junction or tandem solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/068—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN homojunction type, e.g. bulk silicon PN homojunction solar cells or thin film polycrystalline silicon PN homojunction solar cells
- H01L31/0693—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN homojunction type, e.g. bulk silicon PN homojunction solar cells or thin film polycrystalline silicon PN homojunction solar cells the devices including, apart from doping material or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds, e.g. GaAs or InP solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/072—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN heterojunction type
- H01L31/0735—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN heterojunction type comprising only AIIIBV compound semiconductors, e.g. GaAs/AlGaAs or InP/GaInAs solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
- H01L31/1804—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof comprising only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L31/1812—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof comprising only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table including only AIVBIV alloys, e.g. SiGe
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
- H01L31/184—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof the active layers comprising only AIIIBV compounds, e.g. GaAs, InP
- H01L31/1844—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof the active layers comprising only AIIIBV compounds, e.g. GaAs, InP comprising ternary or quaternary compounds, e.g. Ga Al As, In Ga As P
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
- H01L31/184—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof the active layers comprising only AIIIBV compounds, e.g. GaAs, InP
- H01L31/1852—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof the active layers comprising only AIIIBV compounds, e.g. GaAs, InP comprising a growth substrate not being an AIIIBV compound
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/544—Solar cells from Group III-V materials
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P70/00—Climate change mitigation technologies in the production process for final industrial or consumer products
- Y02P70/50—Manufacturing or production processes characterised by the final manufactured product
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Photovoltaic Devices (AREA)
Abstract
本发明涉及具有IV/III-V族混合合金的多结太阳能电池。一种通过以下步骤制造太阳能电池的方法:提供锗半导体生长衬底;及在所述半导体生长衬底上沉积形成太阳能电池的半导体材料层的序列,其包含由IV/III-V族混合合金构成的子电池。
Description
技术领域
本发明涉及半导体装置的领域及其制作工艺及装置,例如基于IV/III-V族混合半导体化合物的多结太阳能电池。
背景技术
已主要通过硅半导体技术提供来自光伏打电池(也称作太阳能电池)的太阳能电力。然而,在过去几年中,大量制造用于太空应用的III-V族化合物半导体多结太阳能电池已加速此技术不仅用于太空中而且用于陆地太阳能电力应用的发展。与硅相比,尽管III-V族化合物半导体多结装置往往制造起来更复杂,但其具有更高的能量转换效率且通常更抗辐照。典型的商用III-V族化合物半导体多结太阳能电池在一个太阳、0气团(AM0)照明条件下具有超过27%的能量效率,而即使是最有效的硅技术在相当的条件下通常仅达到约18%的效率。在高太阳能会聚(例如,500倍)的情况下,陆地应用(AM处于1.5D)中的市场可购得III-V族化合物半导体多结太阳能电池具有超过37%的能量效率。与硅太阳能电池相比,III-V族化合物半导体太阳能电池的较高转换效率部分地基于能够实现通过使用具有不同带隙能量的多个光伏打区域进行对入射辐照的光谱分离且积累来自所述区域中的每一者的电流。
在卫星及其它太空相关的应用中,卫星电力系统的大小、质量及成本依赖于所使用的太阳能电池的功率及能量转换效率。换句话说,有效负载的大小及机载服务的可用性与所提供的功率量成比例。因此,随着有效负载变得更加成熟,太阳能电池的功率对重量比变得越来越重要,且越发关注具有高效率及低质量的重量较轻、“薄膜”型太阳能电池。
典型的III-V族化合物半导体太阳能电池以垂直、多结结构制作于半导体晶片上。然后,将个别太阳能电池或晶片安置成水平阵列,其中个别太阳能电池以串联电路方式连接在一起。阵列的形状及结构以及其包含的电池数目部分地取决于所需要的输出电压及电流。
发明内容
简要且概括地,本发明的一个方面包括制造太阳能电池的方法,所述方法包括:提供锗半导体生长衬底;在所述半导体生长衬底上沉积形成太阳能电池的半导体材料层的序列,其包含由IV/III-V族混合合金构成的子电池。
在另一方面中,本发明包括通过以下步骤制造太阳能电池的方法:提供半导体生长衬底;及在所述半导体生长衬底上沉积形成太阳能电池的半导体材料层的序列,其包含由GeSiSn构成的至少一个层及生长在所述GeSiSn层由Ge构成的一个层。
在另一方面中,提供根据本发明一个方面的一种太阳能电池,其包括:由GeSiSn构成且具有第一带隙的第一太阳能子电池;由GaAs、InGaAsP或InGaP构成且安置在所述第一太阳能子电池上方的第二太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第一带隙的第二带隙且与所述第一太阳能子电池晶格匹配;及由GaInP构成且安置在所述第二太阳能子电池上方的第三太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第二带隙的第三带隙且相对于所述第二子电池晶格匹配。
本发明的一些实施方案可并入或实施上述发明内容中所述的各个方面及特征中的数者。
依据本发明(包含下文详细说明)及通过实践本发明,所属领域的技术人员将明了本发明的另外方面、优点及新颖特征。虽然下文参照优选实施例来描述本发明,但应了解,本发明并不限于此。所属领域的技术人员通过阅读本文中的教示将会认识到本发明在其它领域中的另外应用、修改及实施例,这些应用、修改及实施例均属于本文所揭示并请求的发明范围内且本发明对于这些应用、修改及实施例可具有实用性。
附图说明
结合附图考虑并参照以下详细说明将更好且更全面地理解本发明,附图中:
图1是表示某些二进制材料的带隙及其晶格常数的图表;
图2A是在根据本发明一个实施例于生长衬底上沉积半导体层之后的本发明太阳能电池的横截面视图;
图2B是在根据本发明另一实施例于生长衬底上沉积半导体层之后的发明本太阳能电池的横截面视图;
图2C是在根据本发明另一实施例在生长衬底上沉积半导体层之后的本发明太阳能电池的横截面视图;
图3是图2A、2B或者2C的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的高度简化横截面视图;
图4是图3的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图;
图5是图4的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图;
图6A是在其中制作有四个太阳能电池的晶片的俯视平面图;
图6B是图6A的晶片的仰视平面图;
图6C是在其中制作有两个太阳能电池的晶片的俯视平面图;
图7是图5的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图;
图8是图7的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图,在所述下一工艺步骤中附接盖片玻璃;及
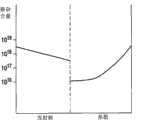
图9是根据本发明的太阳能电池中子电池的基极层及发射极层的掺杂分布的图表。
具体实施方式
现在将描述本发明的细节,包含其实例性方面及实施例。参照图式及下文说明,相同的参考编号用于识别相同或功能上相似的元件,且打算以高度简化的图示方式图解说明实例性实施例的主要特征。此外,这些图式既不打算描绘实际实施例的每一特征,也不打算描绘所描绘元件的相对尺寸,且这些图式并非按比例绘制。
制作多结太阳能电池的基本概念是在衬底上以有序序列生长太阳能电池的子电池。即,直接在半导体生长衬底(例如,GaAs或Ge)上外延生长低带隙子电池(即,具有介于0.7到1.2eV范围中的带隙的子电池),且因此,此类子电池与此衬底晶格匹配。然后,可在低带隙子电池上生长一个或一个以上中等带隙的中间子电池(即,具有介于1.0到2.4eV范围中的带隙)。
在所述中间子电池上方形成顶部子电池或上部子电池,以使得顶部子电池相对于中间子电池大致晶格匹配且以使得所述顶部子电池具有第三较高带隙(即,介于1.6到2.4eV范围中的带隙)。
在上述相关申请案中,揭示了多结太阳能电池的各种不同特征及方面。此类特征中的一些特征或所有特征可包含在与本发明太阳能电池相关联的结构及工艺中。
半导体结构中的层的晶格常数及电特性优选地通过规定适当反应器生长温度及时间且通过使用适当化学组成及掺杂剂来控制。使用气相沉积方法(例如,有机金属气相外延(OMVPE)、金属有机化学气相沉积(MOCVD)、或其它气相沉积方法)或用于逆向生长的其它沉积技术(例如分子束外延(MBE))可使单块半导体结构中形成电池的层能够生长为具有所需厚度、元素组成、掺杂剂浓度及粒度和传导性类型。
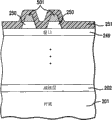
图2A描绘在锗生长衬底上顺序形成三个子电池A、B及C之后的根据本发明的多结太阳能电池。更特定来说,其显示衬底201,所述衬底优选地为锗(Ge)或其它适合材料。
在Ge衬底的情况下,可在衬底201上直接沉积成核层202。在衬底201上,或在成核层202上方(在Ge衬底的情况下),进一步沉积缓冲层203。在Ge衬底的情况下,缓冲层203优选地为p+型Ge。然后,在层203上沉积p+型GeSiSn的BSF层204。然后,在BSF层204上外延沉积由p型基极层205及n+型发射极层206构成的子电池A,所述基极层及发射极层由锗构成。子电池A通常与生长衬底201晶格匹配。子电池A可具有大约为0.67eV的带隙。
BSF层204从基极/BSF界面表面附近的区域驱动少数载流子,以使复合损失效应最小化。换句话说,BSF层204减少太阳能子电池A背侧处的复合损失且从而减少基极中的复合。
应注意,多结太阳能电池结构可由周期表中所列的III到V族元素的满足晶格常数及带隙要求的任何适合组合形成,其中III族包含硼(B)、铝(Al)、镓(Ga)、铟(In)及铊(T)。所述IV族包含碳(C)、硅(Si)、锗(Ge)及锡(Sn)。所述V族包含氮(N)、磷(P)、砷(As)、锑(Sb)及铋(Bi)。
在基极层206的顶部上,沉积窗口层207,其优选地为n+型GeSiSn,且所述窗口层用于减少复合损失。
在窗口层207的顶部上,沉积形成隧道二极管(即,将子电池A连接到子电池B的欧姆电路元件)的重掺杂p型及n型层208a及208b的序列。层208a优选地由n++GaAs构成,且层208b优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
在隧道二极管层208a/208b的顶部上,沉积BSF层209,其优选地为p+型InGaAs。更大体来说,子电池B中所使用的BSF层209操作以减少界面复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除一个或多个额外层。
在BSF层209的顶部上,沉积子电池B的各个层:p型基极层210及n+型发射极层211。这些层优选地由InGaAs构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。因此,子电池B可由GaAs、GaInP、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN发射极区域及GaAs、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN基极区域构成。子电池B的带隙可大约为1.25到1.4eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层210及211的掺杂分布。
在子电池B的顶部上,沉积窗口层212,其与窗口层207执行相同的功能。在窗口层212上方分别沉积类似于层208a及208b的p++/n++隧道二极管层213a及213b,所述隧道二极管层形成将子电池B连接到子电池C的欧姆电路元件。层213a优选地由n++GaInP构成,且层213b优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
然后,在隧道二极管层213b上方沉积优选地由p+型InGaAlP构成的BSF层214。此BSF层操作以减少子电池“C”中的复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除额外层。
在BSF层214的顶部上,沉积子电池C的各个层:p型基极层215及n+型发射极层216。这些层优选地分别由p型InGaAs或InGaP及n+型InGaAs或InGaP构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。子电池C的带隙可大约为1.75eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层215及216的掺杂分布。
然后,在子电池C的顶部上沉积窗口层217,其优选地由n+型InAlP构成,所述窗口层与窗口层207及212执行相同功能。
将以对图3及后续图的说明为开始来描述对制作图2A的实施例中的太阳能电池的后续处理步骤的说明。同时,将描述多结太阳能电池半导体结构的其它实施例。
图2B描绘在根据本发明的另一实施例中在锗生长衬底上顺序形成四个子电池A、B、C及D之后的多结太阳能电池。更特定来说,其显示衬底201,所述衬底优选地为锗(Ge)或其它适合材料。
图2B的实施例中的层202到212的组成类似于图2A的实施例中所述的那些层,但具有实现不同带隙所必要的不同元素组成或掺杂剂浓度,且因此此处不需重复对此类层的说明。特定来说,在图2B的实施例中,子电池A的带隙可大约为0.73eV,且子电池B的带隙可大约为1.05eV。
在窗口层212的顶部上,沉积形成隧道二极管(即,将子电池B连接到子电池C的欧姆电路元件)的重掺杂p型及n型层213c及213d的序列。层213c优选地由n++GaAs构成,且层213d优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
在隧道二极管层213c/213d的顶部上,沉积BSF层214,其优选地为p+型AlGaAs。更大体来说,子电池C中所使用的BSF层214操作以减少界面复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除一个或多个额外层。
在BSF层214的顶部上,沉积子电池C的各个层:p型基极层215及n+型发射极层216。这些层优选地分别由InGaAs及InGaAs或InGaP构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。因此,子电池C可由GaAs、GaInP、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN发射极区域及GaAs、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN基极区域构成。子电池C的带隙可大约为1.25到1.4eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层215及216的掺杂分布。
在子电池C的顶部上,沉积由InAlP构成的窗口层217,所述窗口层与窗口层212执行相同的功能。在窗口层217上方分别沉积类似于层213c及213d的p++/n++隧道二极管层218a及218b,所述隧道二极管层形成将子电池C连接到子电池D的欧姆电路元件。层218a优选地由n++InGaP构成,且层218b优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
然后,在隧道二极管层218b上方沉积优选地由p+型AlGaAs构成的BSF层219。此BSF层操作以减少子电池“D”中的复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除额外层。
在BSF层219的顶部上,沉积子电池D的各个层:p型基极层220及n+型发射极层221。这些层优选地分别由p型InGaP及n+型InGaP构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。子电池D的带隙可大约为1.85eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层220及221的掺杂分布。
然后,在子电池D的顶部上沉积优选地由n+型InAlP构成的窗口层222,所述窗口层与窗口层207、212及217执行相同的功能。
图2C描绘在根据本发明的另一实施例中在锗生长衬底上顺序形成五个子电池A、B、C、D及E之后的多结太阳能电池。更特定来说,其显示衬底201,所述衬底优选地为锗(Ge)或其它适合材料。
图2C的实施例中的层201到212的组成类似于图2A的实施例中所述的那些层,但其具有实现不同带隙所必要的不同元素组成或掺杂剂浓度,且因此此处不需重复对此类层的说明。特定来说,在图2C的实施例中,子电池A的带隙可大约为0.73eV,子电池B的带隙可大约为0.95eV,且子电池C的带隙可大约为1.24eV。因此,以窗口层212的顶部上的层来继续对图2C的实施例的说明。
在窗口层212的顶部上,沉积形成隧道二极管(即,将子电池A连接到子电池B的欧姆电路元件)的重掺杂p型及n型层213e及213f的序列。层213e优选地由n++GeSiSn构成,且层213f优选地由p++GeSiSn构成。
在隧道二极管层213e/213f的顶部上,沉积BSF层214a,其优选地为p+型GeSiSn。更大体来说,子电池C中所使用的BSF层214a操作以减少界面复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除一个或多个额外层。
在BSF层214a的顶部上,沉积子电池C的各个层:p型基极层215a及n+型发射极层216a。这些层优选地由GeSiSn构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。因此,子电池C可由GaAs、GaInP、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN发射极区域及GaAs、GaInAs、GaAsSb或GaInAsN基极区域构成。子电池C的带隙可大约为1.24eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层215a及216a的掺杂分布。
在子电池C的顶部上,沉积由InAlP构成的窗口层217a,所述窗口层与窗口层207及212执行相同的功能。在窗口层217a上方分别沉积类似于层208a及208b以及213e及213f的p++/n++隧道二极管层218e及218d,所述隧道二极管层形成将子电池C连接到子电池D的欧姆电路元件。层218c优选地由n++InGaAsP构成,且层218d优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
然后,在隧道二极管层218d上方沉积优选地由p+型AlGaAs构成的BSF层219a。此BSF层操作以减少子电池“D”中的复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除额外层。
在BSF层219a的顶部上,沉积子电池D的各个层:p型基极层220a及n+型发射极层221a。这些层优选地分别由p型InGaAsP或AlGaAs及n+型InGaAsP或AlGaInAs构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。子电池D的带隙可大约为1.6eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层220a及221a的掺杂分布。
然后,在子电池D的顶部上沉积优选地由n+型InAlP、InGaAsP或AlGaInAs构成的窗口层222a,所述窗口层与窗口层207、212及217a执行相同的功能。
在窗口层222a上方分别沉积类似于层218c及218d的p++/n++隧道二极管层223a及223b,所述隧道二极管层形成将子电池D连接到子电池E的欧姆电路元件。层223a优选地由n++InGaAsP构成且层223b优选地由p++AlGaAs构成。
然后,在隧道二极管层223b上方沉积优选地由p+型AlGaAs或InGaAlP构成的BSF层224。此BSF层操作以减少子电池“E”中的复合损失。所属领域的技术人员应明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中添加或删除额外层。
在BSF层224的顶部上,沉积子电池E的各个层:p型基极层225及n+型发射极层226。这些层优选地分别由p型AlGaInP及n+型AlGaInP构成,但也可使用与晶格常数及带隙要求相一致的任何其它适合材料。子电池E的带隙可大约为2.0eV。将结合图9论述根据本发明的层224及225的掺杂分布。
然后,在子电池E的顶部上沉积优选地由n+型InAlP构成的窗口层227,所述窗口层227与窗口层207、212、217a及222a执行相同的功能。
图3是图2A、2B或2C中的任一者的太阳能电池的高度简化横截面视图,其显示其中在窗口层249上沉积优选地由n+型InGaAs构成的高带隙接触层250的下一工艺步骤,所述窗口层可根据情况分别表示图2A、2B及2C的窗口层217、222或227。后续图将利用此图3的高度简化横截面视图,应理解,对太阳能电池的后续制作的说明可以涉及所描绘的图2A、2B或2C实施例中的任一者,或本文上文所述的额外或类似实施例中的任一者。
所属领域的技术人员应明了,除了接触层250,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下在所述电池结构中于子电池结构的顶部上添加或删除一个或多个额外层。
图4是图3的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤的序列之后的横截面视图,在所述下一工艺步骤的序列中,将光致抗蚀剂层(未显示)置于半导体接触层318上方。借助掩模以光刻方式图案化光致抗蚀剂层以形成栅格线501的位置,移除光致抗蚀剂层的其中将要形成栅格线的部分,且然后通过蒸气或类似工艺将金属接触层319既沉积到光致抗蚀剂层上方又沉积到光致抗蚀剂层中的其中将要形成栅格线的开口中。然后,剥离覆盖接触层318的光致抗蚀剂层部分以留下完成的金属栅格线501,如图中所描绘。栅格线501优选地由层Pd/Ge/Ti/Pd/Au的序列构成,但也可使用其它适合序列及材料。
图5是图4的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图,在所述下一工艺步骤中将所述栅格线用作掩膜来使用柠檬酸/过氧化物蚀刻混合物向下蚀刻所述表面到达窗口层249。
图6A是在其中实施四个太阳能电池的100mm(或4英寸)晶片的俯视平面图。对四个电池的描绘仅出于说明的目的,且本发明并不限于每一晶片的任何特定电池数目。
在每一电池中,存在栅格线501(更具体地显示于图5的横截面图中)、互连总线502及接触垫503。栅格线及总线以及接触垫的几何形状及数目为说明性的,且本发明并不限于所图解说明的实施例。
图6B是图6A的晶片的仰视平面图,其概括地显示四个太阳能电池的位置。
图6C是在其中实施两个太阳能电池的100mm(或4英寸)晶片的俯视平面图。尽管可利用各种多边形几何形状来界定太阳能电池在晶片内的边界,但在所图解说明的几何配置中,每一太阳能电池具有26.3cm2的面积。
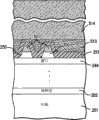
图7是图5的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图,在所述下一工艺步骤中在晶片的具有栅格线501的“顶部”侧的整个表面上方施加抗反射(ARC)电介质涂布层。
图8是在本发明第二实施例中图7的太阳能电池在下一工艺步骤之后的横截面视图,在所述下一工艺步骤中,通过粘合剂513将盖片玻璃514固定到电池的顶部。盖片玻璃514通常约为4密耳厚,且优选地覆盖整个通道510、在平台516的一部分上方延伸,但不延伸到通道511。尽管对于众多环境条件及应用,期望使用盖片玻璃,但其对于所有实施方案并非为必要,且也可利用额外的层或结构来向太阳能电池提供额外的支撑或环境保护。
图9是本发明的多结太阳能电池的一个或一个以上子电池中发射极层及基极层中的掺杂分布的图表。在2007年12月13日提出申请的第11/956,069号共同未决美国专利申请案(其以引用的方式并入本文中)中更具体描述本发明范围内的各种掺杂分布及此类掺杂分布的优点。本文中所描绘的掺杂分布仅为说明性,且如所属领域的技术人员所明了,可在不背离本发明的范围的前提下使用其它更复杂的分布。
应了解,上文所述元件中的每一者或者两个或两个以上元件一起,也可有用地应用于不同于上文所述类型的构造的其它类型的构造中。
另外,尽管所图解说明的实施例配置有顶部及底部电触点,但替代地子电池可借助金属触点与子电池之间的横向传导性半导体层接触。此类布置可用于形成3-端子装置、4-端子装置且大体来说,n-端子装置。可使用这些额外端子将所述子电池互连成电路,以使得可有效地使用每一子电池中的大多数可用光生电流密度,从而导致多结电池的高效性,尽管在各种子电池中光生电流密度通常为不同。
如上文所述,本发明可利用一个或一个以上或者全部为单质结的电池或子电池(即,其中在两者均具有相同化学组成及相同带隙而仅在掺杂剂种类及类型上有所不同的p型半导体与n型半导体之间形成p-n结的电池或子电池)的布置。具有p型及n型InGaP的子电池是单质结子电池的一个实例。另一选择是,如在美国专利7,071,407中更具体地描述,本发明可利用一个或一个以上或全部为异质结的电池或子电池,即其中在p型半导体与n型半导体之间形成p-n结的电池或子电池,所述两种半导体除了在形成p-n结的p型及n型区域中利用不同的掺杂剂种类及类型之外,还在n型区域中具有半导体材料的不同化学组成及/或在p型区域中具有不同的带隙能量。
在一些电池中,可将薄的所谓“本征层”置于发射极层与基极层之间,其具有与发射极层或者基极层相同或不同的组成。所述本征层可用于抑制空间电荷区域中的少数载流子复合。类似地,基极层或发射极层也可以是本征的或在其厚度的一部分或全部上为非故意掺杂的(“NID”)。在2008年10月16日提出申请的第12/253,051号共同未决美国专利申请案中更具体地描述了一些此类配置。
窗口或BSF层的组成可利用满足晶格常数及带隙要求的其它半导体化合物,且可包含AlInP、AlAs、AlP、AlGaInP、AlGaAsP、AlGaInAs、AlGaInPAs、GaInP、GaInAs、GaInPAs、AlGaAs、AlInAs、AlInPAs、GaAsSb、AlAsSb、GaAlAsSb、AlInSb、GaInSb、AlGaInSb、AIN、GaN、InN、GaInN、AlGaInN、GaInNAs、AlGaInNAs、ZnSSe、CdSSe及类似材料,且此仍归属于本发明的精神内。
Claims (20)
1.一种制造太阳能电池的方法,其包括:
提供锗半导体生长衬底;
在所述半导体生长衬底上沉积形成太阳能电池的半导体材料层的序列,其包含由IV/III-V族混合合金构成的子电池。
2.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中所述IV/III-V族混合合金为GeSiSn。
3.如权利要求2所述的方法,其中所述GeSiSn子电池具有介于0.8eV到1.2eV范围中的带隙。
4.如权利要求3所述的方法,其进一步包括在所述GeSiSn子电池与所述锗衬底之间沉积由锗构成的子电池。
5.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中所述层的序列包含具有介于0.91eV到0.95eV范围中的带隙的第一GeSiSn子电池及具有介于1.13eV到1.24eV范围中的带隙的第二GeSiSn子电池。
6.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中所述沉积半导体材料层的序列的步骤包含:在所述衬底上形成由GeSiSn构成且具有第一带隙的第一太阳能子电池;在所述第一子电池上方形成由InGaAs构成的第二太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第一带隙的第二带隙;及在所述第二太阳能子电池上方形成由GaInP构成的第三太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第二带隙的第三带隙。
7.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中所述沉积半导体材料层的序列的步骤包含:在所述衬底上形成由Ge构成且具有第一带隙的第一太阳能子电池;在所述第一子电池上方形成由GeSiSn构成的第二太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第一带隙的第二带隙;及在所述第二太阳能子电池上方形成由InGaAs构成的第三太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第二带隙的第三带隙;及形成由GaInP构成的第四太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第三带隙的第四带隙且与所述第三太阳能子电池晶格匹配。
8.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中所述沉积半导体材料层的序列的步骤包含:在所述衬底上形成由Ge构成且具有第一带隙的第一太阳能子电池;在所述第一子电池上方形成由GeSiSn构成的第二太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第一带隙的第二带隙;及在所述第二太阳能子电池上方形成由GeSiSn构成的第三太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第二带隙的第三带隙;及形成由InGaAs构成的第四太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第三带隙的第四带隙且与所述第三太阳能子电池晶格匹配;形成由GaInP构成的第五太阳能子电池,其具有大于所述第四带隙的第五带隙且与所述第四太阳能子电池晶格匹配。
9.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中借助金属有机化学气相沉积工艺在约700℃的温度下沉积所述层中的一些层。
10.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中适当地匹配所述生长衬底与所述半导体材料层之间的热膨胀系数以避免破裂。
11.如权利要求7所述的方法,其进一步包括在由Ge构成的所述第一子电池与由GeSiSn构成的所述第二子电池之间形成由GeSiSn构成的隧道二极管。
12.如权利要求1所述的方法,其进一步包括在所述生长衬底上方沉积由GeSiSn构成的BSF层。
13.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中通过化学气相沉积在约300℃的温度下沉积所述IV/III-V族混合合金。
14.如权利要求1所述的方法,其进一步包括在所述锗生长衬底上方沉积Ge缓冲层。
15.如权利要求4所述的方法,其进一步包括在邻近于所述锗子电池处形成GeSiSin BSF层及GeSiSn窗口层。
16.如权利要求4所述的方法,其中所述锗子电池具有大约0.73eV的带隙。
17.如权利要求1所述的方法,其中通过将As及/或P扩散到混合合金层中而在所述IV/III-V族混合合金中形成结以形成光伏子电池。
18.如权利要求1所述的方法,其进一步包括在邻近于由所述IV/III-V族混合合金构成的所述子电池处形成由所述IV/III-V族混合合金构成的窗口层及BSF层。
19.一种制造太阳能电池的方法,其包括:
提供半导体生长衬底;及
在所述半导体生长衬底上沉积形成太阳能电池的半导体材料层的序列,其包含由GeSiSn构成的至少一个层及生长在所述GeSiSn层上方由Ge构成的一个层。
20.一种多结太阳能电池,其包括:
第一太阳能子电池,其由GeSiSn构成且具有第一带隙;
第二太阳能子电池,其由GaAs、InGaAsP或InGaP构成且安置在所述第一太阳能子电池上方,所述第二太阳能子电池具有大于所述第一带隙的第二带隙且与所述第一太阳能子电池晶格匹配;及
第三太阳能子电池,其由GaInP构成且安置在所述第二太阳能子电池上方,所述第三太阳能子电池具有大于所述第二带隙的第三带隙且相对于所述第二子电池晶格匹配。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/463,216 US20100282306A1 (en) | 2009-05-08 | 2009-05-08 | Multijunction Solar Cells with Group IV/III-V Hybrid Alloys |
| US12/463,216 | 2009-05-08 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101882644A true CN101882644A (zh) | 2010-11-10 |
Family
ID=43054598
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101479778A Pending CN101882644A (zh) | 2009-05-08 | 2010-04-08 | 具有ⅳ/ⅲ-ⅴ族混合合金的多结太阳能电池 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20100282306A1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP2010263222A (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN101882644A (zh) |
| TW (1) | TW201044625A (zh) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102751389A (zh) * | 2012-07-19 | 2012-10-24 | 厦门市三安光电科技有限公司 | 一种高效多结太阳能电池的制备方法 |
| CN102790121A (zh) * | 2012-08-09 | 2012-11-21 | 厦门大学 | 具有两结锗子电池的四结太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103151414A (zh) * | 2013-04-03 | 2013-06-12 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 正装三结级联太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103280483A (zh) * | 2013-05-08 | 2013-09-04 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 一种三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103337548A (zh) * | 2013-06-19 | 2013-10-02 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 含Bi热光伏电池的结构及其制备方法 |
| CN103346189A (zh) * | 2013-05-10 | 2013-10-09 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN104201231A (zh) * | 2014-09-11 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种混合三子结化合物光伏电池 |
| CN104201230A (zh) * | 2014-09-10 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种三子结化合物光伏电池 |
| CN104201249A (zh) * | 2014-09-15 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种倒置生长InAlAsP/InGaAs/Ge三结光伏电池的制备方法 |
| CN105870240A (zh) * | 2011-06-02 | 2016-08-17 | 光城公司 | 具有用于集中光伏应用的铜格栅的隧道结太阳能电池 |
| CN106663714A (zh) * | 2014-07-11 | 2017-05-10 | 株式会社理光 | 化合物‑半导体光伏电池及化合物‑半导体光伏电池的制造方法 |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100319764A1 (en) * | 2009-06-23 | 2010-12-23 | Solar Junction Corp. | Functional Integration Of Dilute Nitrides Into High Efficiency III-V Solar Cells |
| US20110114163A1 (en) * | 2009-11-18 | 2011-05-19 | Solar Junction Corporation | Multijunction solar cells formed on n-doped substrates |
| TW201137944A (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2011-11-01 | Sumitomo Chemical Co | Semiconductor substrate, method for making a semiconductor substrate, and method for making a photo-electric conversion device |
| US20110232730A1 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-09-29 | Solar Junction Corp. | Lattice matchable alloy for solar cells |
| US9214580B2 (en) | 2010-10-28 | 2015-12-15 | Solar Junction Corporation | Multi-junction solar cell with dilute nitride sub-cell having graded doping |
| US8962991B2 (en) | 2011-02-25 | 2015-02-24 | Solar Junction Corporation | Pseudomorphic window layer for multijunction solar cells |
| CN103875079B (zh) * | 2011-08-29 | 2017-12-12 | Iqe公司 | 光伏器件 |
| WO2013074530A2 (en) * | 2011-11-15 | 2013-05-23 | Solar Junction Corporation | High efficiency multijunction solar cells |
| KR101918737B1 (ko) * | 2012-03-19 | 2019-02-08 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 태양 전지 |
| US9153724B2 (en) | 2012-04-09 | 2015-10-06 | Solar Junction Corporation | Reverse heterojunctions for solar cells |
| KR20150006452A (ko) * | 2012-04-23 | 2015-01-16 | 난양 테크놀러지컬 유니버시티 | 전지 배열 |
| US8647439B2 (en) | 2012-04-26 | 2014-02-11 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation |
| US11495705B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2022-11-08 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| US11646388B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2023-05-09 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| US9099595B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2015-08-04 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| US9985160B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2018-05-29 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| US10903383B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2021-01-26 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| US9997659B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2018-06-12 | The Boeing Company | Group-IV solar cell structure using group-IV or III-V heterostructures |
| TWI602315B (zh) | 2013-03-08 | 2017-10-11 | 索泰克公司 | 具有經組構成效能更佳之低帶隙主動層之感光元件及相關方法 |
| CN103258906B (zh) * | 2013-04-27 | 2017-02-01 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 一种三结级联太阳能电池结构及其制备方法 |
| CN103258907B (zh) * | 2013-04-27 | 2016-09-07 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 一种三结级联太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103311353B (zh) * | 2013-05-29 | 2016-09-07 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 三结级联太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
| TWI656651B (zh) | 2014-02-05 | 2019-04-11 | 美商太陽光電公司 | 單片多接面換能器 |
| WO2015198117A1 (en) | 2014-06-26 | 2015-12-30 | Soitec | Semiconductor structures including bonding layers, multijunction photovoltaic cells and related methods |
| JP6702673B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-11 | 2020-06-03 | ソレアロ テクノロジーズ コーポレイション | 複数の変成層を備える反転変成多接合型ソーラーセル |
| US20170110613A1 (en) | 2015-10-19 | 2017-04-20 | Solar Junction Corporation | High efficiency multijunction photovoltaic cells |
| US10930808B2 (en) | 2017-07-06 | 2021-02-23 | Array Photonics, Inc. | Hybrid MOCVD/MBE epitaxial growth of high-efficiency lattice-matched multijunction solar cells |
| WO2019067553A1 (en) | 2017-09-27 | 2019-04-04 | Solar Junction Corporation | SHORT-LENGTH WAVELENGTH INFRARED OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICES HAVING DILUTED NITRIDE LAYER |
| WO2020185528A1 (en) | 2019-03-11 | 2020-09-17 | Array Photonics, Inc. | Short wavelength infrared optoelectronic devices having graded or stepped dilute nitride active regions |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6340788B1 (en) * | 1999-12-02 | 2002-01-22 | Hughes Electronics Corporation | Multijunction photovoltaic cells and panels using a silicon or silicon-germanium active substrate cell for space and terrestrial applications |
| US20040200523A1 (en) * | 2003-04-14 | 2004-10-14 | The Boeing Company | Multijunction photovoltaic cell grown on high-miscut-angle substrate |
| US20070137695A1 (en) * | 2005-12-19 | 2007-06-21 | The Boeing Company | Reduced band gap absorber for solar cells |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5548128A (en) * | 1994-12-14 | 1996-08-20 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Air Force | Direct-gap germanium-tin multiple-quantum-well electro-optical devices on silicon or germanium substrates |
| JP2003282439A (ja) * | 2002-03-27 | 2003-10-03 | Seiko Epson Corp | デバイス用基板およびデバイス用基板の製造方法 |
| US8067687B2 (en) * | 2002-05-21 | 2011-11-29 | Alliance For Sustainable Energy, Llc | High-efficiency, monolithic, multi-bandgap, tandem photovoltaic energy converters |
| US7126052B2 (en) * | 2002-10-02 | 2006-10-24 | The Boeing Company | Isoelectronic surfactant induced sublattice disordering in optoelectronic devices |
| AU2003297649A1 (en) * | 2002-12-05 | 2004-06-30 | Blue Photonics, Inc. | High efficiency, monolithic multijunction solar cells containing lattice-mismatched materials and methods of forming same |
| US7598513B2 (en) * | 2003-06-13 | 2009-10-06 | Arizona Board Of Regents, Acting For And On Behalf Of Arizona State University, A Corporate Body Organized Under Arizona Law | SixSnyGe1-x-y and related alloy heterostructures based on Si, Ge and Sn |
| WO2006034025A1 (en) * | 2004-09-16 | 2006-03-30 | Arizona Board Of Regents | MATERIALS AND OPTICAL DEVICES BASED ON GROUP IV QUANTUM WELLS GROWN ON Si-Ge-Sn BUFFERED SILICON |
| EP1856721A2 (en) * | 2005-03-11 | 2007-11-21 | The Arizona Board of Regents, A Body Corporate Acting on Behalf of Arizona State University | NOVEL GeSiSn-BASED COMPOUNDS, TEMPLATES, AND SEMICONDUCTOR STRUCTURES |
| US20090229662A1 (en) * | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-17 | Emcore Corporation | Off-Cut Substrates In Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells |
| US7741146B2 (en) * | 2008-08-12 | 2010-06-22 | Emcore Solar Power, Inc. | Demounting of inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells |
| US20100282305A1 (en) * | 2009-05-08 | 2010-11-11 | Emcore Solar Power, Inc. | Inverted Multijunction Solar Cells with Group IV/III-V Hybrid Alloys |
-
2009
- 2009-05-08 US US12/463,216 patent/US20100282306A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2010
- 2010-03-22 TW TW099108399A patent/TW201044625A/zh unknown
- 2010-04-08 CN CN2010101479778A patent/CN101882644A/zh active Pending
- 2010-05-07 JP JP2010107410A patent/JP2010263222A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6340788B1 (en) * | 1999-12-02 | 2002-01-22 | Hughes Electronics Corporation | Multijunction photovoltaic cells and panels using a silicon or silicon-germanium active substrate cell for space and terrestrial applications |
| US20040200523A1 (en) * | 2003-04-14 | 2004-10-14 | The Boeing Company | Multijunction photovoltaic cell grown on high-miscut-angle substrate |
| US20070137695A1 (en) * | 2005-12-19 | 2007-06-21 | The Boeing Company | Reduced band gap absorber for solar cells |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105870240A (zh) * | 2011-06-02 | 2016-08-17 | 光城公司 | 具有用于集中光伏应用的铜格栅的隧道结太阳能电池 |
| CN102751389A (zh) * | 2012-07-19 | 2012-10-24 | 厦门市三安光电科技有限公司 | 一种高效多结太阳能电池的制备方法 |
| WO2014012442A1 (zh) * | 2012-07-19 | 2014-01-23 | 厦门市三安光电科技有限公司 | 一种高效多结太阳能电池的制备方法 |
| CN102790121A (zh) * | 2012-08-09 | 2012-11-21 | 厦门大学 | 具有两结锗子电池的四结太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
| CN102790121B (zh) * | 2012-08-09 | 2015-12-16 | 厦门大学 | 具有两结锗子电池的四结太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103151414A (zh) * | 2013-04-03 | 2013-06-12 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 正装三结级联太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103280483B (zh) * | 2013-05-08 | 2015-10-28 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 一种三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103280483A (zh) * | 2013-05-08 | 2013-09-04 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 一种三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103346189A (zh) * | 2013-05-10 | 2013-10-09 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103346189B (zh) * | 2013-05-10 | 2015-12-09 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 三结太阳电池及其制备方法 |
| CN103337548A (zh) * | 2013-06-19 | 2013-10-02 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 含Bi热光伏电池的结构及其制备方法 |
| CN103337548B (zh) * | 2013-06-19 | 2016-12-07 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | 含Bi热光伏电池的结构及其制备方法 |
| CN106663714A (zh) * | 2014-07-11 | 2017-05-10 | 株式会社理光 | 化合物‑半导体光伏电池及化合物‑半导体光伏电池的制造方法 |
| CN104201230A (zh) * | 2014-09-10 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种三子结化合物光伏电池 |
| CN104201231A (zh) * | 2014-09-11 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种混合三子结化合物光伏电池 |
| CN104201249A (zh) * | 2014-09-15 | 2014-12-10 | 六安市大宇高分子材料有限公司 | 一种倒置生长InAlAsP/InGaAs/Ge三结光伏电池的制备方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW201044625A (en) | 2010-12-16 |
| JP2010263222A (ja) | 2010-11-18 |
| US20100282306A1 (en) | 2010-11-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101882644A (zh) | 具有ⅳ/ⅲ-ⅴ族混合合金的多结太阳能电池 | |
| CN101740647B (zh) | 具有两个变质层的四结倒置变质多结太阳能电池 | |
| CN101499495B (zh) | 倒置变形多结太阳能电池中的异质结子电池 | |
| US7741146B2 (en) | Demounting of inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells | |
| US8969712B2 (en) | Four junction inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cell with a single metamorphic layer | |
| CN101882645B (zh) | 具有iv族合金的反向多结太阳能电池 | |
| US8753918B2 (en) | Gallium arsenide solar cell with germanium/palladium contact | |
| US10700232B1 (en) | Inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells with doped alpha layer | |
| US20100122764A1 (en) | Surrogate Substrates for Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells | |
| US20120211047A1 (en) | String interconnection of inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells on flexible perforated carriers | |
| US20100229913A1 (en) | Contact Layout and String Interconnection of Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells | |
| US20090272430A1 (en) | Refractive Index Matching in Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells | |
| US20100282307A1 (en) | Multijunction Solar Cells with Group IV/III-V Hybrid Alloys for Terrestrial Applications | |
| US20100229933A1 (en) | Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells with a Supporting Coating | |
| US20130228216A1 (en) | Solar cell with gradation in doping in the window layer | |
| US20150104898A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells | |
| US20150034152A1 (en) | Solar cell with passivation on the window layer | |
| US10170656B2 (en) | Inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cell with a single metamorphic layer | |
| CN112563354A (zh) | 四结太阳能电池及其制备方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Application publication date: 20101110 |