CN101698552B - Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system - Google Patents
Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101698552B CN101698552B CN200910212796A CN200910212796A CN101698552B CN 101698552 B CN101698552 B CN 101698552B CN 200910212796 A CN200910212796 A CN 200910212796A CN 200910212796 A CN200910212796 A CN 200910212796A CN 101698552 B CN101698552 B CN 101698552B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- water
- artificial soil
- earthworm
- capillary infiltration
- pedosphere
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Treatment Of Biological Wastes In General (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了一种强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统处理生活污水的方法,生活污水先进入水解酸化池进行预处理,预处理出水进入依次由土壤层、砂土层、人工土层和导水层构成的强化型毛细管渗滤沟进行处理,收集出水并排出;其中在所述强化型毛细管渗滤沟的土壤层和人工土层中均接种蚯蚓。本发明的强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统具有较强的耐冲击负荷能力,日处理污水量大幅度提高,其CODcr、氨氮、总磷的去除效率达到90%以上。在目前村镇污水进水水质条件下,出水可以达到《GB8978-1996国家污水排放标准》要求。
The invention discloses a method for treating domestic sewage by an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system. The domestic sewage first enters a hydrolysis acidification tank for pretreatment, and the pretreated effluent enters successively from the soil layer, the sandy soil layer, the artificial soil layer and the aquifer The formed enhanced capillary infiltration ditch is processed, and the effluent is collected and discharged; wherein both the soil layer and the artificial soil layer of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch are inoculated with earthworms. The enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system of the present invention has strong impact load resistance, greatly increases the daily sewage treatment volume, and the removal efficiency of COD cr , ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus reaches over 90%. Under the current water quality conditions of village and town sewage inflow, the effluent can meet the requirements of "GB8978-1996 National Sewage Discharge Standard".
Description
技术领域 technical field
本发明属于农村生活污水处理领域,具体涉及一种强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统及利用其处理生活污水的方法。The invention belongs to the field of domestic sewage treatment in rural areas, and in particular relates to an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system and a method for treating domestic sewage by using it.
背景技术 Background technique
全国农村每年产生生活污水80多亿吨,严重污染了农村地区居住环境,农村大部分地区河、湖等水体普遍受到污染,富营养化现象越来越严重,污染事件频繁爆发。饮用水水质安全受到严重威胁,直接危害农民的身体健康,严重影响农村地区的环境卫生,极易导致一些流行性疾病的发生与传播。据估算,农村环境问题每年造成的经济损失已超过千亿元,我国农村环境与生态状况令人担忧。目前农村生活污水的治理存在一个较大的难点,即基建投资以及运行费用较大,农村经济实力以及技术力量很难满足常规城市生活污水处理厂技术要求等。Rural areas across the country produce more than 8 billion tons of domestic sewage every year, seriously polluting the living environment in rural areas. Water bodies such as rivers and lakes in most rural areas are generally polluted, eutrophication is becoming more and more serious, and pollution incidents frequently break out. The safety of drinking water quality is seriously threatened, directly endangering the health of farmers, seriously affecting the environmental sanitation in rural areas, and easily leading to the occurrence and spread of some epidemic diseases. It is estimated that the annual economic loss caused by rural environmental problems has exceeded 100 billion yuan, and the rural environment and ecological conditions in my country are worrying. At present, there is a big difficulty in the treatment of rural domestic sewage, that is, the capital investment and operating costs are relatively large, and the rural economic strength and technical strength are difficult to meet the technical requirements of conventional urban domestic sewage treatment plants.
因而,农村生活污水治理技术必须具备投资省、处理效率高、运行费用少、管理简单等特点。现行的毛细管渗滤沟技术,从上到下依次由表层土壤层、砂土层、人工土层和导水层组成;其中在表层土壤层上种植有植物,在表层土壤层和人工土层内分别设有与水解酸化池或化粪池相通的表层布水管和深层布水管,布水管周围是用土工布包裹的青石子;在导水层内设有与排水池相通的排水管;设有用拔风原理来自然强制通风的拔风管。水力负荷较高,对生活污水中的COD、BOD5、TP、NH3-N、TN去除效率较高,出水可达国家污水综合排放标准,但是渗滤沟水流速度慢,日处理量少,限制了此种技术的广泛运用。Therefore, the rural domestic sewage treatment technology must have the characteristics of low investment, high treatment efficiency, low operating cost, and simple management. The current capillary infiltration ditch technology consists of surface soil layer, sandy soil layer, artificial soil layer and aquifer layer from top to bottom; plants are planted on the surface soil layer, and in the surface soil layer and artificial soil layer There are surface water distribution pipes and deep water distribution pipes connected with the hydrolytic acidification tank or septic tank respectively, and the water distribution pipes are surrounded by bluestones wrapped with geotextiles; the drainage pipes connected with the drainage tank are arranged in the aquifer; The principle of pulling out the wind comes from the pulling out of the wind pipe for natural forced ventilation. The hydraulic load is high, and the removal efficiency of COD, BOD 5 , TP, NH 3 -N, TN in domestic sewage is high, and the effluent can reach the national comprehensive sewage discharge standard, but the water flow speed of the infiltration ditch is slow, and the daily treatment capacity is small. This limits the widespread application of this technique.
发明内容 Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是对现行毛细管渗滤沟系统的一种改进和强化,从而提供一种处理效率更高、运行更稳定、处理能力更强的强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统处理生活污水的方法。The purpose of the present invention is to improve and strengthen the existing capillary infiltration ditch system, so as to provide a method for treating domestic sewage with an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system with higher treatment efficiency, more stable operation and stronger processing capacity.
本发明的另一目的是提供一种强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统。Another object of the present invention is to provide an enhanced capillary infiltration trench system.
本发明的目的可以通过以下措施达到:The purpose of the present invention can be achieved through the following measures:
一种强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统处理生活污水的方法,生活污水先进入水解酸化池进行预处理,预处理出水进入依次由土壤层、砂土层、人工土层和导水层构成的强化型毛细管渗滤沟进行处理,收集出水并排出;其中在所述强化型毛细管渗滤沟的土壤层和人工土层中均接种蚯蚓。A method for treating domestic sewage with an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system. The domestic sewage first enters a hydrolysis acidification tank for pretreatment, and the pretreated water enters an enhanced sewage treatment system consisting of soil layer, sandy soil layer, artificial soil layer and water-conducting layer in sequence. The capillary infiltration ditch is treated, and the effluent is collected and discharged; wherein, both the soil layer and the artificial soil layer of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch are inoculated with earthworms.
本发明的方法在强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统中进行,该系统由水解酸化池和强化型毛细管渗滤沟组成,所述水解酸化池的出水口与所述强化型毛细管渗滤沟内的土壤层和人工土层中铺设的布水管的进水口相通;其中在强化型毛细管渗滤沟的土壤层和人工土层中均设有蚯蚓。The method of the present invention is carried out in an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system, which system is composed of a hydrolytic acidification tank and an enhanced capillary infiltration ditch, the water outlet of the hydrolytic acidification tank is connected to the soil in the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch The layer communicates with the water inlet of the water distribution pipe laid in the artificial soil layer; earthworms are arranged in both the soil layer and the artificial soil layer of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch.
本发明先因地制宜采用水解酸化池(也可以采用化粪池-水解酸化池的一种)作为前置的预处理技术,与毛细管渗滤沟形成组合工艺;其次,在毛细管渗滤沟的表层土壤层和人工土层添加蚯蚓,利用蚯蚓具有吞食有机物、提高土壤通气透水性能和与微生物的协同作用强化对水中有机物和氮磷的去除。The present invention first adopts hydrolytic acidification tank according to local conditions (also can adopt a kind of septic tank-hydrolytic acidification tank) as the pretreatment technology of front, forms combined process with capillary infiltration ditch; Secondly, in the surface layer soil of capillary infiltration ditch Add earthworms to the layer and artificial soil layer, and use earthworms to swallow organic matter, improve soil aeration and water permeability, and strengthen the removal of organic matter and nitrogen and phosphorus in water through the synergistic effect with microorganisms.
采用水解酸化池作为污水毛细管渗滤系统的预处理装置,可以为后续系统提供污染物浓度较低、生化降解性较高的进水,其出水BOD5为30-80mg/L,CODCr约为50-150mg/L。同时,粪便中的寄生虫卵和病原微生物在厌氧环境中受生物拮抗作用而被杀死,污水中的粪便也得到了一定的无害化处理。水解酸化池为一有进水口、出水口和检查口的埋地池,结构如图1所示。水解酸化池设有砖混结构的挡板,以防止发生短流。出水通过潜水电泵,流经表层布水管和深层布水管进入毛细管渗滤沟。水解酸化池的体积大小,根据处理水量和提留时间确定。Using the hydrolytic acidification tank as the pretreatment device of the sewage capillary infiltration system can provide the follow-up system with low pollutant concentration and high biodegradability influent. The BOD 5 of the effluent is 30-80mg/L, and the COD Cr is about 50-150mg/L. At the same time, the parasite eggs and pathogenic microorganisms in the feces are killed by biological antagonism in the anaerobic environment, and the feces in the sewage have also been harmlessly treated to a certain extent. The hydrolytic acidification tank is a buried tank with a water inlet, a water outlet and an inspection port. The structure is shown in Figure 1. The hydrolytic acidification tank is equipped with a brick-concrete structure baffle to prevent short flow. The outlet water passes through the submersible electric pump, flows through the surface water distribution pipe and the deep water distribution pipe and enters the capillary infiltration ditch. The volume of the hydrolytic acidification tank is determined according to the amount of treated water and the retention time.
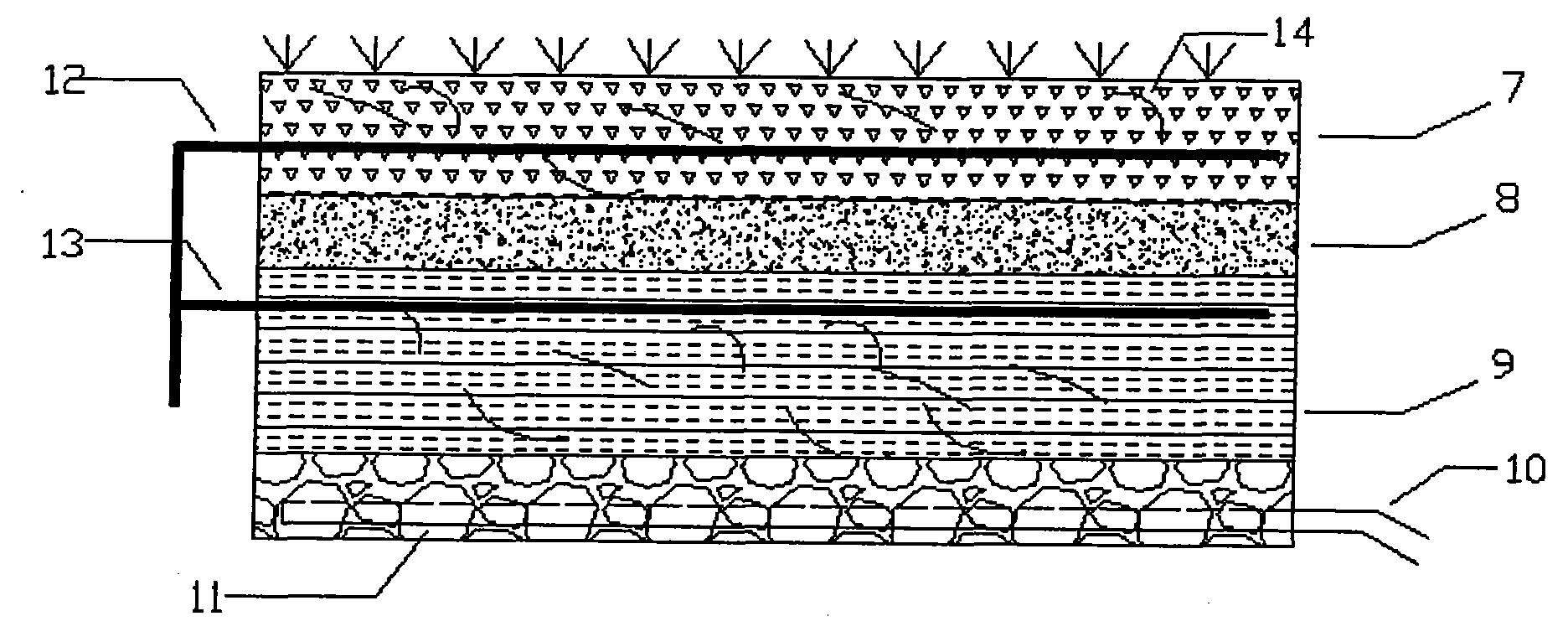
强化型毛细管渗滤沟,由多种填料组成。从上到下,依次为土壤层、砂土层、人工土层和导水层(各层采用常规厚度)。其中在表层土壤层和人工土层中铺设布水管,布水管为双排孔的PVC布水管,布水孔直径为4~5mm,孔间距为45~55mm,埋设深度15~20cm。表层种植草坪植物,植物通过根系的作用吸收大量的氮磷物质,是污水净化的重要途径。同时,植物的生长也极大的改变了污水处理的环境条件。由于植物根系深入土壤,既提高了土壤的水力渗透速率,还有助于创造一个良好的植物根区的微环境,有利于微生物对污染物的降解。砂土层主要为粒径不大于2mm的细砂,由于巨大比表面积从而聚集了大量的微生物,可对污染物质进行吸附、降解。同时,细砂较大的渗透系数可保证正常的水力负荷。砂土层下面是人工土层,由土壤与木屑和/或稻壳(即土壤与木质纤维的比例)按2.5~3.5∶1的比例进行混合配制。这种富含有机物的土壤,有利于蚯蚓活动具有较强的新陈代谢作用,同时多种细菌和微生物的活性也得到加强。这层对有机物和氮磷的去除起主要作用。最下面一层是导水层,由鹅卵石填充,由卵石组层起承托和过滤作用。导水层内铺设的排水管,经过卵石过滤的水,流到排水管内。通过排水系统将深度处理后的污水排出,从而增大系统处理污水能力。排水管采用波纹导水管,管材为4″,PVC管材;考虑到排水效率,管网不宜过稀。导水管的间距为0.6~0.8m,集水管周围,由鹅卵石组成的隔离层,能防人工土层土壤堵塞集水管影响排水。Enhanced capillary percolation ditch, composed of various fillers. From top to bottom, there are soil layer, sand layer, artificial soil layer and aquifer layer (each layer adopts conventional thickness). Among them, the water distribution pipes are laid in the surface soil layer and the artificial soil layer. The water distribution pipes are PVC water distribution pipes with double rows of holes. The diameter of the water distribution holes is 4-5mm, the hole spacing is 45-55mm, and the buried depth is 15-20cm. Lawn plants are planted on the surface, and the plants absorb a large amount of nitrogen and phosphorus substances through the action of the root system, which is an important way for sewage purification. At the same time, the growth of plants has greatly changed the environmental conditions of sewage treatment. Because the plant root system goes deep into the soil, it not only improves the hydraulic infiltration rate of the soil, but also helps to create a good microenvironment of the plant root zone, which is conducive to the degradation of pollutants by microorganisms. The sandy soil layer is mainly fine sand with a particle size not greater than 2mm. Due to the huge specific surface area, a large number of microorganisms are gathered, which can adsorb and degrade pollutants. At the same time, the large permeability coefficient of fine sand can ensure normal hydraulic load. Below the sandy soil layer is an artificial soil layer, which is prepared by mixing soil with sawdust and/or rice husk (that is, the ratio of soil to wood fiber) in a ratio of 2.5 to 3.5:1. This kind of soil rich in organic matter is beneficial to the activities of earthworms with strong metabolism, and at the same time the activity of various bacteria and microorganisms is also strengthened. This layer plays a major role in the removal of organic matter and nitrogen and phosphorus. The bottom layer is the water-conducting layer, which is filled with pebbles and supported and filtered by the pebble layer. The drainage pipe laid in the aquifer, the water filtered by the pebbles flows into the drainage pipe. The sewage after advanced treatment is discharged through the drainage system, thereby increasing the sewage treatment capacity of the system. The drainage pipe adopts corrugated aqueduct, and the pipe material is 4″, PVC pipe material; considering the drainage efficiency, the pipe network should not be too thin. The distance between the aqueduct is 0.6-0.8m, and the isolation layer composed of pebbles around the water collection pipe can prevent artificial The soil in the soil layer clogs the water collection pipe and affects the drainage.
本技术的关键在于蚯蚓的投加。蚯蚓喜欢温暖、潮湿和安静的环境。在土壤中穴居以生活在土壤上层15-20厘米深度以内者居多,越往下层越少,这主要是由蚯蚓的食性决定的。实际上,几乎所有的蚯蚓都参与环境中有机物的降解过程,在其生命活动中,它们大量吞食有机残落物质,并将其与土壤混合,通过砂囊的机械研磨作用和肠道内的生物化学作用进行分解和转化。除此之外,蚯蚓还通过本身和其对土壤微生物群落的影响而推动土壤中碳和氮的转化。它们的作用包括直接的和偶尔的吞食,疏松,竞争和潜在共生关系。强化型毛细管渗滤沟土壤层的表层土壤和人工土层的人工配土中均要投放一定数量、种类的蚯蚓,接种蚯蚓的密度为8g~12g(蚯蚓)/(L填料)。其中土壤层接种的蚯蚓为大平2号蚯蚓,投放深度为5~8cm(从土壤层上表面开始计);人工土层中接种的蚯蚓为威廉环毛蚯蚓,投放深度为15~20cm(从人工土层上表面开始计)。The key of this technology lies in the addition of earthworms. Earthworms like warm, moist and quiet environments. In the soil, burrows live in the upper layer of the soil within a depth of 15-20 cm, and the lower the layer, the less it is, which is mainly determined by the feeding habits of earthworms. In fact, almost all earthworms are involved in the degradation of organic matter in the environment. During their life activities, they devour a large amount of organic debris and mix them with the soil. function for decomposition and transformation. In addition, earthworms also promote the transformation of carbon and nitrogen in the soil through themselves and their impact on the soil microbial community. Their roles include direct and occasional cannibalism, loosening, competition and potential symbiosis. The surface soil of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch soil layer and the artificial soil layer of the artificial soil layer must be put in a certain number and type of earthworms, and the density of inoculated earthworms is 8g-12g (earthworms)/(L filler). The earthworms inoculated in the soil layer are Daping No. 2 earthworms, and the depth of feeding is 5 to 8 cm (from the upper surface of the soil layer); counting from the upper surface of the soil layer).
通过研究发现,在强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统中蚯蚓能与微生物发生协同作用,促进C、N、P的转化和矿化,同时蚯蚓的运动形成了较多空隙,加快了水流速度。因此,加入蚯蚓的强化型毛细管渗滤沟对生活污水中的COD、BOD5、TP、NH3-N、TN去除效率更高,日处理能力增强。这种充分利用土壤-微生物-动物-植物系统的陆地生态系统的自我调控机制和对污染物的综合净化功能来处理污水,使水质得到不同程度的改善,实现了污水的资源化与无害化。Through research, it is found that in the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system, earthworms can cooperate with microorganisms to promote the transformation and mineralization of C, N, and P. At the same time, the movement of earthworms forms more gaps and speeds up the water flow. Therefore, the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch with earthworms has higher removal efficiency for COD, BOD 5 , TP, NH 3 -N, and TN in domestic sewage, and the daily treatment capacity is enhanced. This fully utilizes the self-regulation mechanism of the terrestrial ecosystem of the soil-microbe-animal-plant system and the comprehensive purification function of pollutants to treat sewage, which improves the water quality to varying degrees and realizes the recycling and harmlessness of sewage. .
经过上诉技术方案的实施,强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统具有较强的耐冲击负荷能力,日处理污水量大幅度提高。CODcr、氨氮、总磷的去除效率达到90%以上。在目前村镇污水进水水质条件下,出水可以达到《GB8978-1996国家污水排放标准》要求。After the implementation of the appeal technical plan, the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system has a strong impact load resistance capacity, and the daily sewage treatment volume has been greatly increased. The removal efficiency of COD cr , ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus can reach over 90%. Under the current water quality conditions of village and town sewage inflow, the effluent can meet the requirements of "GB8978-1996 National Sewage Discharge Standard".
附图说明 Description of drawings
图1为水解酸化池结构示意图。Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the hydrolytic acidification tank.
其中:1为进水管;2为检查口;3为挡板;4为表层土壤布水管出口;5为人工配土的布水管出口;6为潜水泵。Among them: 1 is the water inlet pipe; 2 is the inspection port; 3 is the baffle; 4 is the outlet of the surface soil distribution pipe; 5 is the outlet of the water distribution pipe for artificial soil distribution; 6 is the submersible pump.
图2为强化型毛细管渗滤沟示意图。Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of an enhanced capillary percolation ditch.
其中:7为表层土壤;8为砂土层;9为人工配土层;10为导水层排水管;11为导水层;12为表层土壤布水管;13为深层土壤(人工配土)布水管;14为投加的蚯蚓。Among them: 7 is the surface soil; 8 is the sand layer; 9 is the artificial soil layer; 10 is the drainage pipe of the aquifer; 11 is the aquifer; 12 is the surface soil water distribution pipe; 13 is the deep soil (artificial soil) Water distribution pipe; 14 is the earthworm that adds.
具体实施方式 Detailed ways
实施例1:日处理能力为15t的强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统Example 1: Enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system with a daily processing capacity of 15 tons
设计处理水量:Q=15t/d。Design treatment water volume: Q=15t/d.
水解酸化池的结构如图1所示,长5米,宽3米,有效深度为1.5m,超高0.2m,总深度为1.7m,池子安装采取地埋式,池面铺水泥板,板厚20mm。进水管嵌入位置距池墙底部高度35cm,与池墙夹角成25°向下。出水通过潜水电泵进入到强化型毛细管渗滤沟的表层土壤层中的布水管和人工土层中的布水管。强化型毛细管渗滤沟的结构如图2所示,占地20m2,池体结构采取砖混结构:The structure of the hydrolytic acidification tank is shown in Figure 1, with a length of 5 meters, a width of 3 meters, an effective depth of 1.5m, a super height of 0.2m, and a total depth of 1.7m. 20mm thick. The water inlet pipe is embedded at a height of 35cm from the bottom of the pool wall, and is downward at an angle of 25° with the pool wall. The outlet water enters the water distribution pipe in the surface soil layer of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch and the water distribution pipe in the artificial soil layer through the submersible electric pump. The structure of the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch is shown in Figure 2, covering an area of 20m 2 , and the pool structure adopts brick-concrete structure:
处理单元总体积15m3,表面积18m2。取长为6m,宽为3m,高为1m(其中有效高度0.9m)。表层土壤深度25cm,砂土深15cm,人工配土40cm(土壤与木屑质量比3∶1),导水层深10cm。其中在表层土壤铺设布水管深度15cm,人工配土层铺设布水管深度20cm,导水层铺设导水管(即排水管)。布水管孔径5mm左右,孔间距为50mm左右;导水管孔径8mm,间距为0.7m左右;布水管和导水管的管材均为PVC材料。表层土壤中投放大平2号蚯蚓,投放深度8-10cm,投放密度8g(蚯蚓)/(L填料);人工配土中投放威廉环毛蚯蚓,深度为15-20cm,投放密度12g(蚯蚓)/(L填料)。The processing unit has a total volume of 15m 3 and a surface area of 18m 2 . The length is 6m, the width is 3m, and the height is 1m (the effective height is 0.9m). The depth of the surface soil is 25cm, the depth of the sandy soil is 15cm, the artificial soil is 40cm (the mass ratio of soil to sawdust is 3:1), and the depth of the aquifer is 10cm. Among them, the depth of water distribution pipes is 15cm in the surface soil, the depth of water distribution pipes in the artificial soil layer is 20cm, and the drainage pipes (ie drainage pipes) are laid in the aquifer layer. The aperture of the water distribution pipe is about 5mm, and the hole spacing is about 50mm; the aperture of the aqueduct pipe is 8mm, and the spacing is about 0.7m; the pipe materials of the water distribution pipe and the aqueduct are all PVC materials. Put Daping No. 2 earthworms in the surface soil at a depth of 8-10cm and a density of 8g (earthworms)/(L filler); put the William Ringworm in the artificial soil with a depth of 15-20cm and a density of 12g (earthworms)/(L filler). (L packing).
在环境温度为28℃的条件下,将村镇污水引入强化型毛细管渗滤沟系统中,先在水解酸化池中进行预处理,预处理出水的BOD5为30-80mg/L,CODCr约为50-150mg/L。Under the condition of an ambient temperature of 28°C, the sewage from villages and towns is introduced into the enhanced capillary infiltration ditch system, and pretreated in the hydrolytic acidification tank first. The BOD 5 of the pretreated water is 30-80mg/L, and the COD Cr is about 50-150mg/L.
预处理出水再进入不加蚯蚓的上述毛细管渗滤沟中进行处理,处理后的水最后从导水层中的导水管中排出。处理效果如表1:The pretreated effluent enters the above-mentioned capillary infiltration ditch without adding earthworms for treatment, and the treated water is finally discharged from the aqueduct in the aquifer. The treatment effect is shown in Table 1:
表1常规毛细管渗滤沟处理污水Table 1 Treatment of sewage by conventional capillary infiltration ditch
预处理出水再进入上述投加蚯蚓的强化型毛细管渗滤沟中进行处理,处理后的水最后从导水层中的导水管中排出。处理效果如表2:The pretreated effluent enters the above-mentioned enhanced capillary infiltration ditch where earthworms are added for treatment, and the treated water is finally discharged from the aqueduct in the aquifer. The treatment effect is shown in Table 2:
表2强化型毛细管渗滤沟处理污水Table 2 Enhanced capillary infiltration ditch treatment of sewage
投加蚯蚓的强化型毛细管渗滤沟,对有机物、TN、NH3-N和TP有着更高的去除率和较强的稳定性,去除率分别达到了82.86%、87.72%、92.28%和95.87%,是对原有技术的大幅度提升。其中,蚯蚓的加入对有机物的去除影响最大CODcr去除率增加了11%,对TP去除影响较小。The enhanced capillary infiltration ditch with earthworms has a higher removal rate and stronger stability for organic matter, TN, NH 3 -N and TP, and the removal rates reached 82.86%, 87.72%, 92.28% and 95.87%, respectively. %, which is a substantial improvement on the original technology. Among them, the addition of earthworms had the greatest effect on the removal of organic matter, and the removal rate of CODcr increased by 11%, but had little effect on the removal of TP.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910212796A CN101698552B (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2009-11-09 | Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910212796A CN101698552B (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2009-11-09 | Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101698552A CN101698552A (en) | 2010-04-28 |
| CN101698552B true CN101698552B (en) | 2012-08-29 |
Family
ID=42147012
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910212796A Expired - Fee Related CN101698552B (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2009-11-09 | Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101698552B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111272965B (en) * | 2020-03-10 | 2022-05-10 | 广东通达检测技术有限公司 | Remote multi-parameter water quality testing equipment and water quality testing method |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0483593A (en) | 1990-07-26 | 1992-03-17 | Meidensha Corp | Apparatus for simultaneously removing nitrogen and phosphorus in waste water |
| CN1320568A (en) * | 2000-04-25 | 2001-11-07 | 同济大学 | Physiological microbe-earthworm filter pool system for treating household sewage |
| CN101284705A (en) * | 2008-01-23 | 2008-10-15 | 南京大学 | A tower type earthworm ecological filter for treating domestic sewage |
-
2009
- 2009-11-09 CN CN200910212796A patent/CN101698552B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0483593A (en) | 1990-07-26 | 1992-03-17 | Meidensha Corp | Apparatus for simultaneously removing nitrogen and phosphorus in waste water |
| CN1320568A (en) * | 2000-04-25 | 2001-11-07 | 同济大学 | Physiological microbe-earthworm filter pool system for treating household sewage |
| CN101284705A (en) * | 2008-01-23 | 2008-10-15 | 南京大学 | A tower type earthworm ecological filter for treating domestic sewage |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101698552A (en) | 2010-04-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101973637B (en) | River channel purification system for processing rural domestic sewage | |
| CN103951067B (en) | System and method for treating rural sewage by using ecological system based on multi-submerged plant combinations | |
| CN101445297B (en) | Method for deeply treating papermaking wastewater | |
| CN104058545B (en) | A method for treating aquaculture sewage by combining biological carrier and ecological restoration technology | |
| CN103359825A (en) | Method for treating pig farm wastewater by using straw | |
| CN106966547A (en) | A kind of rural domestic sewage treating device of hypsography larger area | |
| CN101229937A (en) | High load capillary infiltration ditch system for domestic sewage treatment | |
| CN206486407U (en) | A kind of livestock breeding wastewater processing system | |
| CN102951736B (en) | Garden wetland purifying technology and garden wetland | |
| CN110183037A (en) | A kind of farmland irrigating drainage purified treatment circulatory system | |
| CN202148222U (en) | Processing device for denitrification and phosphorous removal of high-load reciprocating type undercurrent artificial wetland | |
| CN111704241A (en) | A zonal circulation type soil infiltration system | |
| CN110092531A (en) | A kind of multifunctional assembled Tailwater Depth denitrogenation dephosphorizing artificial wet land system | |
| CN102515434A (en) | Method for sewage treatment in compound tower-type ecological filtering pool | |
| CN202054672U (en) | Solar greenhouse wetland sewage treatment system | |
| CN107500486A (en) | A kind of method and system of domestic sewage in rural areas ecological management | |
| CN201587887U (en) | A non-powered single-family rural domestic sewage treatment device | |
| CN105692905B (en) | A kind of land disposal method and device of ecotype landscape water body | |
| CN101698552B (en) | Method for treating domestic sewage with reinforced capillary infiltration trench system | |
| CN203144243U (en) | System for treating breeding wastewater through combination of biological carrier and ecological restoration technology | |
| CN202080988U (en) | Natural-aeration percolation type land treatment device for rural domestic sewage | |
| CN205528280U (en) | Freshwater aquaculture advanced waste treatment recycling system | |
| CN102897976B (en) | Method for in-situ ecological treatment of town domestic waste water by using river and creek converging | |
| CN107529524A (en) | A kind for the treatment of method for rural sewage and system | |
| CN222556753U (en) | Resource utilization system for rural domestic sewage |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C53 | Correction of patent of invention or patent application | ||
| CB03 | Change of inventor or designer information |
Inventor after: Zhang Jibiao Inventor after: Luo Yan Inventor after: Guo Feihong Inventor after: Fang Caixia Inventor after: Zheng Zheng Inventor after: Zheng Binguo Inventor after: Luo Xingzhang Inventor after: Wang Longmian Inventor after: Wang Xixi Inventor after: Wang Zhengfang Inventor before: Zheng Zheng Inventor before: Luo Yan Inventor before: Guo Feihong Inventor before: Fang Caixia Inventor before: Zhang Jibiao Inventor before: Luo Xingzhang Inventor before: Wang Longmian Inventor before: Zheng Binguo Inventor before: Wang Xixi Inventor before: Wang Zhengfang |
|
| COR | Change of bibliographic data |
Free format text: CORRECT: INVENTOR; FROM: ZHENG ZHENG GUO FEIHONG FANG CAIXIA ZHANG JIBIAO LUO XINGZHANG WANG LONGMIAN ZHENG BINGUO WANG XIXI WANG ZHENGFANG LUO YAN TO: ZHANG JIBIAO GUO FEIHONG FANG CAIXIA ZHENG ZHENG ZHENG BINGUO LUO XINGZHANG WANG LONGMIAN WANG XIXI WANG ZHENGFANG LUO YAN |
|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20120829 Termination date: 20121109 |