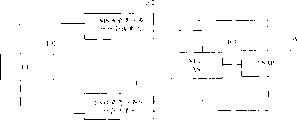CN101166364A - A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service - Google Patents
A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101166364A CN101166364A CNA2007100875291A CN200710087529A CN101166364A CN 101166364 A CN101166364 A CN 101166364A CN A2007100875291 A CNA2007100875291 A CN A2007100875291A CN 200710087529 A CN200710087529 A CN 200710087529A CN 101166364 A CN101166364 A CN 101166364A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- emergency
- vcc
- domain
- call
- psap
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/90—Services for handling of emergency or hazardous situations, e.g. earthquake and tsunami warning systems [ETWS]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/50—Connection management for emergency connections
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
The method includes steps: (1) urgent call center PSAP and one party in user equipment (UE) in source domain initiates urgency traffic request to the other party; (2) network entity determines whether the condition for triggering service of urgent call continuity is satisfied; if yes, the urgency traffic is anchored to voice call continuity (VCC) application server (AS); and the UE in source domain establishes talking connection with PSAP; (3) based on anchored the urgency traffic, VCC AS implements VCC service. The invention also discloses the system in use for implementing VCC in urgency traffic. Thus, the invention realizes VCC in switching time between source domain and target domain when urgency traffic is carrying on.
Description
Technical Field
The present invention relates to network communication technologies, and in particular, to a method and a system for implementing voice call continuity in emergency services.
Background
Currently, the communications community proposes the concept of Voice Call Continuity (VCC), which is a subscription IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) application service for the user's home domain. IMS is an IP multimedia subsystem defined by the third generation mobile communication standardization partnership project (3GPP) standard, and is a target network for the third generation mobile communication system (3G) mobile network to implement packet voice and packet data, providing unified multimedia services and applications.
A user with simultaneous access capability to the IMS domain and the Circuit Switched (CS) domain is called a VCC user terminal (UE). In the normal voice call continuity service, all the calls initiated or received by the UE must be anchored to a VCC Application Server (AS) having a domain switching control function in the IMS domain to which the UE belongs, and anchoring to the VCC AS here means storing all the call information initiated or received by the UE on the VCC AS. When the connection between the UE and the 3GPP system is switched between the CS domain and the IMS domain, the VCC AS realizes the switching between the IMS domain and the CS domain, thereby ensuring that the voice call of the UE is kept uninterrupted in the switching and ensuring that the user experience of the voice service is not influenced by the change of the connection of the UE.
Currently, emergency services are services that provide emergency calls to users. For example, when the user dials the emergency call number 119, the network does not route the emergency call request according to a normal voice call, but routes the emergency call request directly to an emergency call center (PSAP) through a pre-established call session unit, which provides service to the user.
When realizing the emergency service, when the UE initiates the emergency service in the IMS domain, the UE initiates an emergency service request through an IMS domain call session unit and a special user identifier, and the IMS domain call session unit routes the emergency service to an emergency call center to establish the call connection between the UE and the PSAP. When the UE initiates the emergency service in the CS domain, the UE initiates an emergency service request to a CS domain call session unit, and the CS domain call session unit routes the emergency service to a PSAP (public safety access point), so as to establish a call connection between the UE and the PSAP.
It can be seen that in the prior art, when the UE initiates an emergency service in the IMS domain, since the emergency service initiated by the user in the visited domain is processed by a special call session unit or the user does not have a card or the card-holding user is unregistered and cannot acquire the subscription information of the user, the session unit cannot anchor the voice call to the VCC AS of the IMS domain to which the user belongs through an initial filter rule (iFC); when the UE initiates an emergency voice call service in the CS domain, the UE cannot touch the intelligent service, and thus cannot anchor the emergency call to the VCC AS in the IMS domain to which the user belongs. When a UE initiating an emergency service is handed over between an IMS domain and a CS domain, since an emergency call cannot be anchored to a VCC AS, voice call continuity for the emergency service being handed over between a source domain and a destination domain cannot be achieved.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, an object of the embodiments of the present invention is to provide a method and a system for implementing voice call continuity in emergency services, which ensure that voice call continuity can be implemented when a UE switches between a source domain and a destination domain.
The invention provides a method for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service, which comprises the following steps:
A. one of a PSAP (emergency call center) and a UE (user equipment) in a source domain initiates an emergency service request to the other party;
B. the network entity judges whether the emergency service meets the condition of triggering the emergency call continuity service; when the condition is met, anchoring the emergency service to a Voice Call Continuity (VCC) Application Server (AS) and establishing a call connection between the UE and a PSAP in a source domain;
C. and the VCC AS realizes the voice call continuity service according to the anchored emergency service.
To achieve the second objective, the present invention further provides a system for implementing voice call continuity during an emergency service call, the system comprising: UE, an emergency service call session unit in a source domain, PSAP and VCC AS; wherein,
the UE initiates an emergency service request or a switching request carrying emergency call continuity information in a source domain or a PSAP initiates an emergency service request carrying the emergency call continuity information;
the emergency service call session unit in the source domain anchors the emergency service request to a VCC AS and establishes a call connection between the UE and the PSAP;
and the VCC AS anchors the emergency service according to the switching request sent by the UE, establishes a call connection with a PSAP in a target domain by acting the UE and releases the session resource of the UE in the source domain.
According to the technical scheme, the method and the system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service are provided by the invention. And a VCC AS and an emergency service call session unit are added in the system, the emergency service call session control unit routes the emergency service to a PSAP, and the emergency service is anchored to the VCC AS according to the acquired call continuity information. When UE switches between source domain and target domain, VCC AS finds out anchored conversation, and proxy UE and PSAP to negotiate again, and set up new conversation connection, then release conversation resource of UE in source domain, thus when emergency service is carried out, it can realize continuity of voice call when switching between source domain and target domain.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for implementing voice call continuity in emergency services according to an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency services according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 2a is a message interaction flow diagram of the method for implementing voice call continuity in emergency service shown in fig. 2;
fig. 3 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency services according to a second preferred embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 3a is a message interaction flowchart of the method for implementing voice call continuity in emergency service shown in fig. 3;
fig. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency services according to a third preferred embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 4a is a message interaction flowchart of the method for implementing voice call continuity in emergency service shown in fig. 4;
fig. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency services according to a fourth preferred embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 5a is a message interaction flowchart of the method for implementing voice call continuity in emergency service shown in fig. 5.
Detailed Description
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more apparent, the present invention is further described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing voice call continuity during emergency service.A UE or an emergency call center (PSAP) in a source domain judges whether the emergency service meets the condition for triggering the call continuity service when initiating an emergency service request in the source domain, when the condition for triggering the call continuity service is met, a network entity anchors the emergency call to a VCC AS, and the VCC AS realizes the continuity of the anchored emergency service. Thus, when UE is switched between the source domain and the target domain, VCC AS can find the anchored session, and the session resource in the source domain is released after the proxy UE and the emergency call center are reconnected, thereby realizing the continuity of the emergency service call.
The emergency service comprises the following steps: and initiating an emergency service request to the PSAP by the UE in the source domain and initiating the emergency service request to the UE in the source domain by the PSAP, wherein the emergency service request can carry emergency call continuity information.
The network entity judges whether the condition of triggering the call continuity service is met or not according to the emergency call continuity information; the emergency call continuity information includes emergency service information that may be explicit, such as an emergency service indication, an emergency subscriber identification, an emergency number, etc.; or the implicit emergency service information includes: the call is routed to a session control unit E-CSCF, etc., which handles emergency services, and may also include terminal call continuity information, which includes: terminal capabilities, user preferences, etc., and may also include network call continuity information, such as roaming status, access network type, subscription data, etc.
The subscription data in the network call continuity information is subscription data of the UE initiating the emergency service request, and the subscription data includes the VCC service. The subscription data may be subscription data of an emergency user identifier of the UE initiating the emergency service request, or subscription data of a common public user identifier of the emergency user identifier of the UE initiating the emergency service request, or subscription data of a wildcard form to which the emergency user identifier of the UE initiating the emergency service request conforms.
When the emergency service is an emergency service request initiated by the UE in the source domain to the PASP, the method for the network entity to trigger to the VCC AS is AS follows:
1. the network entity judges whether the emergency service request includes the displayed or hidden emergency service information, and if the emergency service request includes the displayed or hidden emergency service information, the network entity triggers the emergency service request to VCC AS.
2. The network entity judges whether the emergency service request carries the displayed or hidden emergency service information, if so, and judges that the emergency service request carries at least one of the terminal call continuity information and the network call continuity information, and triggers the emergency service request to VCC AS. The terminal call continuity information and the network call continuity information may be reported by the terminal, or carried in the service request message, or obtained by the network entity querying the third-party node.
Further comprising, before triggering the emergency service request to the VCC AS: the network entity obtains the address of the vcc as. The acquisition method comprises the following steps: the network entity obtains the address of VCC AS from the emergency service request; or inquiring a third-party node to obtain the address of the VCC AS; or obtain the address of the VCC AS from its own configuration. The third party node may be a HSS, Home Location Register (HLR), device management/client provisioning (DM/CP), etc.
The network needs to notify the UE of the obtained address of the VCC AS in the following, for example, the address may be sent to the UE by the network entity or the VCC AS in a following emergency service request response message, or returned to the UE in the form of a message or the like.
When the emergency service is an emergency service request initiated by the PSAP to the UE in the source domain, such AS an emergency service callback, the method for the network entity to trigger the VCC AS is AS follows:
the network entity may trigger the emergency service request to the VCC AS based on the PSAP identity carried in the emergency service request, the emergency call continuity information, e.g., UE capability or emergency subscriber identity, or other emergency service flags.
When PSAP sends an emergency service request to a registered user, the emergency service request is firstly routed to a network entity registered in a home domain by the user, the network entity anchors the emergency service request to a VCC AS signed by the home domain of the user according to subscription data in the emergency call continuity information, and then the emergency service request is further routed to UE to establish call connection.
When the PSAP initiates an emergency service request to an unregistered user, the address of the VCC AS is first obtained from the emergency call continuity information, and then the emergency service request is anchored to the VCC AS. The VCC AS establishes a call between the PSAP and the user terminal according to the obtained latest user routing information.
The emergency call continuity information may be emergency call continuity information set in advance in the PSAP; or, PSAP inquires HSS, HLR, or DM/CP where user data is located according to the emergency call continuity information obtained by the emergency user identification; or, the PSAP obtains the emergency call continuity information according to the emergency service request carrying the emergency call continuity information that the UE initiated. The subscription data in the network call continuity information may be downloaded to the subscription data of the network entity when the subscriber identity is registered, or obtained in other manners. The subscription data contains initial filtering rules (ifcs) and information contained in the ifcs indicating that the ifcs can be used in emergency services, which information may be an emergency public identity (EMPU) or a wildcard form of the EMPU, and which information may also be an emergency service flag, e.g. the network entity matches the ifcs using a normal PU, so that the network entity can recognize that the current call is an emergency service to match the emergency service flag.
Wherein, the source domain may be any one of an IMS domain, a CS domain, and a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN); the destination domain may also be any one of an IMS domain, a CS domain, and a WLAN. The UE or PSAP firstly initiates an emergency service request in a source domain, the UE is then switched to a destination domain according to the requirement, and the combination mode of the UE or PSAP during switching between the source domain and the destination domain can be as follows: the UE or the PSAP can firstly initiate an emergency call request in an IMS domain, and when the UE needs to be switched from a source domain to a target domain, the UE or the PSAP can be switched to any one of the IMS domain, the CS domain and the WLAN; the UE or the PSAP can also initiate an emergency call request in the CS domain at first, and when the UE needs to be switched from the source domain to the target domain, the UE can be switched to any one of the IMS domain, the CS domain and the WLAN; the UE or PSAP may also first initiate an emergency call request in the WLAN, and may switch to any of the IMS domain, CS domain, and WLAN when the UE needs to switch from the source domain to the destination domain.
Referring to fig. 1, fig. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for implementing voice call continuity in emergency service according to an embodiment of the present invention. The system includes a UE101, an IMS domain emergency services call session element 102, a CS domain emergency services call session element 103, a VCC AS104, and a PSAP 105.
The UE101 is connected to the IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102 and the CS domain emergency service call session unit 103, respectively, and the UE101 first initiates an emergency service request in one of the IMS domain or the CS domain, where the emergency service request refers to an emergency call initiated by the UE 101. The IMS domain emergency services call session unit 102 and the CS domain emergency services call session unit 103 are both one of the network entities.
When UE101 initiates an emergency call in IMS domain, IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102 is connected to UE101, VCC AS104, and PSAP105, respectively, and anchors the emergency call to VCC AS104 according to the emergency call continuity information, where IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102 may be an emergency call session control function (E-CSCF), an inquiry call session control function (I-CSCF), a service call session control function (S-CSCF), a proxy call session control function (P-CSCF), an Access Gateway Control Function (AGCF), a Border Gateway Control Function (BGCF), an Interconnection Border Control Function (IBCF), an AS, or a Media Gateway Control Function (MGCF) of IMS domain.
When UE101 initiates an emergency call in CS domain, CS domain emergency service call session unit 103 is connected to UE101, VCC AS104 and PSAP105, respectively, and anchors the call to VCC AS104 according to the emergency call continuity information; wherein the CS domain emergency services call session unit 103 may be a visited mobile services switching center (VMSC) or a mobile Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC).
The VCC AS104 receives the emergency call anchor from the IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102 or the CS domain emergency service call session unit 103 or the PSAP105, and the VCC AS104 routes the emergency service request initiated by the UE101 to the PSAP105 or routes the emergency service request initiated by the PSAP105 to the UE101 in a proxy or redirection manner, mainly responsible for the control function of completing the emergency call continuity service. When the UE101 switches between the IMS domain and the CS domain, the VCC AS104 finds the anchored session, proxies the UE101 to renegotiate with the PSAP105, establishes a new access leg, and releases the session resources in the source domain, implementing the handover of the emergency call between the IMS domain and the CS domain.
PSAP105 is connected to IMS domain emergency services call session element 102, CS domain emergency services call session element 103, and VCC AS104, respectively. Can receive a call request initiated by UE101 and store emergency call continuity information; while the PSAP105 may initiate an emergency service request to the UE101 containing an emergency user identification. The emergency user identity is a user identity, including a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Uniform Resource Identity (URI) or a Telephony (TEL) URI, when the UE101 is registered, or a temporary emergency public user identity assigned to the UE101 in the IMS domain when the UE101 is unregistered. When the PSAP105 initiates an emergency service request to the UE101, the PSAP105 carries the emergency call continuity information, and the emergency service call session unit 102 or 103 anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS104 of the UE home domain, routes the emergency service to the UE101, and establishes a call connection between the PASP105 and the UE 101.
UE101 or PASP105 initiates a call request in any domain of IMS domain and CS domain, if UE101 or PASP105 first initiates an emergency call to IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102, IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102 is used as the emergency service call session unit of the source domain, CS domain emergency service call session unit 103 is used as the emergency service call session unit of the destination domain; after the UE101 is switched from the IMS domain to the CS domain, the UE101 initiates an emergency call request to the CS domain emergency service call session unit 103. If the UE101 or the PASP105 first initiates an emergency call to the CS domain emergency service call session unit 103, the CS domain emergency service call session unit 103 serves as an emergency service call session unit of the source domain, and the IMS domain emergency service call session unit 104 serves as an emergency service call session unit of the destination domain. After the UE101 is switched from the IMS domain to the CS domain, the UE101 initiates an emergency call request to the IMS domain emergency service call session unit 102.
Referring to fig. 2, fig. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency service according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention. In the embodiment, the UE firstly initiates an emergency service request in an IMS domain, and then the UE is switched to a CS domain according to the requirement; the E-CSCF, MGCF, I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain and the VMSC of the CS domain serve as network entities, the IMS domain serves as the source domain of this embodiment, and the CS serves as the destination domain of this embodiment. The realization of the service comprises the following steps:
In this step 201, the emergency call request may carry emergency call continuity information.
The method for acquiring the emergency call continuity information comprises the following steps: the network entity obtains the emergency call continuity information from the UE or the PSAP or obtains the emergency call continuity information from the emergency service request; or, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain directly or indirectly obtains the emergency call continuity information from the HSS, the HLR, or the DM/CP server, or the UE may report the terminal call continuity information and the network call continuity information to the network entity in the form of a message.
The above-mentioned emergency call continuity information includes explicit emergency service information and terminal call continuity information, or one of them;
further, the emergency call continuity information may also include network call continuity information obtained by querying a subscriber subscription database.
Wherein, in the IMS domain, if the emergency call is routed to the E-CSCF of the IMS domain, the implicit emergency service information is obtained. The explicit emergency service information comprises an emergency service indication, an emergency user identification, an emergency number and the like, and the terminal call continuity information at least comprises one of terminal capability, user preference and a VCCAS address; the network call continuity information includes at least one of roaming status, access network type, subscription data.
The subscription data is subscription data of the UE initiating the emergency service request, and at least comprises one of the following data: the subscription data of the emergency user identifier of the UE carrying the subscription VCC service information, the subscription data of the common public identifier of the emergency user identifier of the UE carrying the subscription VCC service information and the subscription data of the emergency user identifier of the UE carrying the subscription VCC service information conforming to the wildcard form. These subscription data include an initial filter rule (iFC), the EMPU carried in the iFC, the wildcard form of the EMPU, or the emergency service flag indicates that the iFC can be used in the emergency service, and the iFC may be downloaded during emergency registration or during normal registration. The subscription information may be downloaded to the network entity if the UE is a registered UE.
The emergency user identity mentioned in the previous paragraph, wherein when the UE is registered, the emergency user identity includes a public user identity, and the public user identity includes a SIP URI or a TEL URI; when the UE is not registered, the emergency user identity may further include a temporary emergency public user identity, which is an emergency public user identity temporarily allocated when an emergency call is initiated in the IMS domain, and which may be a SIP URI or a TEL URI.
The E-CSCF of the IMS domain judges whether the service meets the condition of triggering the call continuity service according to the emergency call continuity information, and the judging mode comprises the following steps: the E-CSCF of the IMS domain judges whether the service meets the condition of triggering the call continuity service according to the explicit emergency service information or the implicit emergency service information; further comprising according to the explicit emergency service information and the terminal call continuity information; or explicit emergency service information and network call continuity information; or implicit emergency service information and terminal call continuity information; or implicit emergency service information and network call continuity information; or explicit emergency service information, network call continuity information, and terminal call continuity information; or implicit emergency service information, network call continuity information and terminal call continuity information judge whether the service meets the condition of triggering the call continuity service.
The E-CSCF of the IMS domain routes the emergency call to the VCC AS, anchoring the call to the designated VCC AS, which routes the request to the PSAP in a proxy or redirect manner, step 203.
There are three cases of implementing the emergency call anchoring to the VCC AS in this step 203, and any one of the following ways may be adopted in this embodiment:
configuring a VCC AS address on UE in advance; or in step 201, the UE carries the VCC AS address in the initiated emergency service request; or inquiring a third-party node to obtain the address of the VCC AS, or obtaining the address of the VCC AS from the terminal call continuity information or the network call continuity information. Thus, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain anchors the emergency service request to the VCC AS according to the acquired VCC AS address. The third party node can be HSS, HLR, DM/CP
When UE initiates an emergency service request, it acquires and stores a VCC AS address issued in advance from the network, and the E-CSCF of IMS domain anchors the emergency service request to the VCC AS according to the VCC AS address carried by the emergency service request initiated by UE in step 201;
the method for acquiring and storing the VCC AS address issued in advance by the UE from the network comprises the following steps: when UE is in IMS domain, VCC AS or HSS or HLR or DM/CP server or E-CSCF in IMS domain returns VCC AS address to UE in form of short message or instant message or subscription notice in advance, or VCC AS address is carried in response to UE registration or calling in advance; when the UE is in the CS domain, the address of the VCC AS is carried in the connection number of the response message ANM in advance, or is returned to the UE in the form of short message.
And configuring a VCC AS address on an E-CSCF of the IMS domain in advance, and anchoring the emergency service request to the VCC AS by the E-CSCF of the IMS domain according to the VCC AS address configured by the E-CSCF of the IMS domain.
Implementation of this step referring to fig. 2a, 3-5, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain puts the VCC AS and its own address into the routing (Route) header domain, and forwards the call request to the selected VCC AS, thereby implementing the anchoring of the call to the selected VCC AS. The VCC AS then routes the request back to the E-CSCF of the IMS domain by sending invite (invite) information to the E-CSCF of the IMS domain, which then routes the emergency call request to the PSAP.
The specific steps are shown in fig. 2a at 6-14. PSAP carries on conversation description agreement (SDP) media negotiation with UE at first, PSAP sends conversation establishment information to E-CSCF of IMS field, then E-CSCF of IMS field sends conversation establishment information to VCC AS and UE, and receives their acknowledgement message, E-CSCF of IMS field finally sends acknowledgement message to PSAP, set up conversation with PSAP.
In step 205, the VCC AS returns its address to the UE.
In this step, the VCC AS returns its address to the UE in the form of short message, instant message, or subscription notification, or in the anchored session response message, and the UE saves it, while the PSAP saves the emergency call continuity information containing the VCC AS address; when the UE is unregistered UE, the VCC AS, HSS, HLR, DM/CP server or network entity stores the routing information of the UE.
Referring to fig. 2a at 15-16, this step is implemented when the UE determines that the emergency call needs to be handed over to the CS domain due to a degraded wireless environment or other reasons, and the UE initiates a call request in the CS domain with the vcc as address as the called number.
In step 207, the VMSC of the CS domain routes the handover request to the VCC AS.
The specific operation is accomplished by 17-19 in fig. 2a, first, the VMSC in the CS domain forwards an Initial Address Message (IAM) to the MGCF, which then routes the emergency call to the I/S-CSCF in the IMS domain together with the invite message, and finally routes the emergency call to the VCC AS by the I/S-CSCF in the IMS domain.
The switching request is a switching request carrying an emergency service indication, which indicates that the switching is the switching of the emergency call. The handover request may be: the handover request carrying the emergency indication in the message header field, or the parameter field, or the message body of the handover request, the handover request carrying the emergency service indication in the VCC domain handover number (VDN) and/or the VCC handover uniform resource identifier (VDI) number, or the handover request carrying the emergency call continuity information including the emergency service indication.
Referring to fig. 2a at 20-28, the method for the VCC AS to find the anchor session in this step is:
in step 203, the E-CSCF in the IMS domain has anchored the emergency call request carrying the emergency user identity to the VCC AS, where the emergency user identity is the emergency user identity described in step 201. In this step 208, the VCC AS finds the anchored session according to the emergency user identity; or the VCC AS sends the session to the UE according to the session identifier, and finds the anchored session by the anchor index stored by the UE. The VCC AS may return the anchor index to the UE in the form of a short message, an instant message, or a subscription notification, or in a session response message after anchoring, and store the anchor index by the UE. And the latest emergency subscriber identity is maintained by one or both of the PSAP and VCC AS.
The specific operation of the VCC AS finding the anchored session according to the emergency user identity is AS follows, when the UE is a registered UE, the emergency user identity is a public user identity, including an SIP URI or a TEL URI, and the VCC AS finds the anchored session according to the user identity. When the UE is unregistered UE, the emergency user identifier is a temporary emergency public user identifier (SIP URI or TEL URI) distributed for the UE in an IMS domain, when the temporary emergency public user identifier is the TEL URI, a VCC AS finds an anchored session according to the emergency public user identifier or the VCC AS designates an anchored index number on the VCC AS for the call and returns the anchored index number to the UE, and the VCC AS finds the anchored session according to the index number and records the route of a switching request; when the temporary emergency public user identifier is SIP URI, the VCC AS appoints an anchoring index number on the VCC AS for the call and returns the anchoring index number to the UE, and the VCC AS finds out an anchoring session according to the index number. During or after the call connection between the UE in the VCC AS proxy destination domain and the PSAP is established, the routing information of the UE in the destination domain is saved by VCC AS or HSS or HLR or DM/CP server or network entity.
The VCC AS agent UE and PSAP negotiate, and the realization process of reestablishing the call connection is roughly described AS follows: VCC AS agent UE initiates a call request to PSAP again, and receives session establishment information of PSAP, VCC AS tells MGCF the connection information through I/S-CSCF of IMS domain, MGCF tells VMSC, VMCS sends connection request information to UE after receiving the connection information, UE returns confirmation information, and sends the confirmation information to VCC AS, thus establishing the call connection between UE and PSAP in CS domain.
Detailed operation referring to fig. 2a at 29-30, the VCC AS informs the UE of the session end in the IMS domain by sending a BYE message to the E-CSCF of the IMS domain, and then forwarding the BYE message to the UE by the E-CSCF of the IMS domain.
Referring to fig. 3, fig. 3 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency service according to a second preferred embodiment of the present invention. The PSAP first initiates an emergency service request to the UE of the IMS domain in the IMS domain, where the emergency service request is an emergency call request or a callback request for an emergency call. When the UE judges that the emergency call needs to be switched to the CS domain according to the wireless environment, the PSAP establishes emergency call connection with the UE in the CS domain again in the CS domain; wherein, the E/S-CSCF, MGCF, I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain and the VMSC of the CS domain are used as network entities, the IMS domain is used as the source domain of this embodiment, and the CS is used as the destination domain of this embodiment.
In this step, the step of the E/S-CSCF obtaining the emergency call continuity information includes: the E/S-CSCF of the IMS domain acquires the continuity information of the emergency call from the emergency service request initiated by the PSAP; alternatively, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain obtains the emergency call continuity information directly or indirectly from the subscriber subscription database or the DM/CP server.
When the PSAP carries the emergency call continuity information in the initiated emergency service request, the method for the PSAP to acquire the information comprises the following steps: setting emergency call continuity information on a PSAP (public safety access point) in advance, or acquiring the emergency call continuity information by the PSAP from an emergency service request initiated by a UE (user equipment), or inquiring an HSS (home subscriber server), an HLR (home location register) and a DM/CP (direct memory access/content provider) server where user data are located according to a user identification by the PSAP; or emergency call continuity information otherwise obtained.
In this step 302, the method for the E/S-CSCF in the IMS domain to determine whether the immediate service satisfies the condition for triggering the call continuity service is completely the same as the method for the E-CSCF in the IMS domain to determine whether the service satisfies the condition for triggering the call continuity service in step 202.
In this step 303, the method for the E/S-CSCF in the IMS domain to anchor the emergency call request or the callback request of the emergency call to the VCC AS is: the E/S-CSCF obtains the emergency call continuity information and the PSAP identification, and anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS according to the emergency call continuity information or the PSAP identification.
The E/S-CSCF of the IMS domain anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS based on the emergency call continuity information containing the emergency user identity.
When the emergency service request initiated by the PSAP is an emergency call request, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain anchors the emergency call request to the VCC AS according to the emergency call continuity information.
When the emergency service request initiated by the PSAP is a callback request of an emergency call, the E-CSCF of the IMS domain realizes the specific operation of anchoring to the VCC AS AS: when UE is registered UE, the emergency user identification is user identification comprising SIP URI or TEL URI, E/S-CSCF of IMS domain inquires user signing database according to user identification to obtain VCC AS address signed by user, anchors emergency service between PSAP and UE to home domain VCC AS signed by user, and then routes the emergency service to UE; when the UE is unregistered UE, the emergency user identity is a temporary emergency public user identity allocated to the UE in the IMS domain, and includes SIP URI or TEL URI, the E/S-CSCF in the IMS domain anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS according to the VCC AS address acquired in the emergency call, and simultaneously routes the routing information between the UE and the VCC AS, which is stored in the callback routing information unit, to the UE, where the callback routing information unit in this embodiment refers to VCC AS, HSS, HLR, or DM/CP server, or network entity. And the VCC AS appoints the index number on the VCC AS for the emergency service according to the temporary emergency public user identifier distributed for the UE and returns the index number to the UE for storage, and the VCC AS routes the callback request of the emergency call to the UE according to the routing information.
When the routing information of the UE is saved by a VCC AS, routing the callback information of the emergency call to the UE according to the saved information of the UE; when the routing information of the UE is stored by the HSS, the HLR, the DM/CP server or the network entity, the VCC AS can obtain the routing information of the UE from the HSS, the HLR, the DM/CP server or the network entity in the emergency call callback, and routes the callback of the emergency call to the UE according to the routing information of the UE; the routing information is destination domain information after UE switching.
The following steps 304 to 309 are substantially the same as all descriptions of the steps 204 to 209 in the first embodiment, except that the E-CSCF of the IMS domain is replaced with the E/S-CSCF of the IMS domain.
See figure 3a for a specific operation.
Referring to fig. 4, fig. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency service according to a third preferred embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the UE initiates an emergency call service in the CS domain, anchors a session with the PSAP to the VCC AS, and after the UE moves to the IMS domain, the VCC AS proxies the UE to initiate a new session connection to the PSAP, where the I/S-CSCF, MGCF, and VMSC of the CS domain of the IMS domain are used AS network entities, the CS domain is used AS the source domain of this embodiment, and the IMS is used AS the destination domain of this embodiment. The method comprises the following steps:
in step 401, the UE initiates an emergency call request to the VMSC of the CS domain in the CS domain.
In this step 401, the emergency call request may carry emergency call continuity information.
The method for the VMSC of the CS domain to obtain the emergency call continuity information and determine whether the service meets the condition for triggering the call continuity service is completely the same as the corresponding method in step 202.
In step 403, AS described in step 207, the VMSC of the CS domain anchors the call to the VCC AS by means of a special prefix or the like, and the VCC AS routes the emergency call request to the PSAP in a proxy or redirect manner.
Detailed operation referring to steps 3-5 in fig. 4a, the VMSC of the CS domain first routes the emergency call request to the VCC AS through the MGCF of the IMS domain and the I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain, anchoring the emergency call to the designated VCC AS.
The case of anchoring an emergency call to a designated VCC AS mentioned in the preceding paragraph is exactly the same AS the case of implementing the anchoring to the VCC AS in step 203, except that the operation of anchoring the emergency call to the VCC AS is done by the VMSC of the CS domain in this step.
Detailed implementation of step 404 referring to fig. 4a, 6-14, the technique for establishing a session connection between a UE and a PSAP is prior art, and therefore can be described as follows: the VCC AS initiates an emergency call request to the PSAP, the PSAP performs SDP media negotiation with the MGCF of the IMS domain after receiving the emergency call request, and sends session establishment information to the VCC AS. Finally, the I/S-CFCS and VCCAS of the IMS domain return acknowledgement information to the PSAP, thereby establishing a call connection between the PSAP and the UE, while the PSAP stores emergency call continuity information.
The address of the VCC AS can inform the UE in forms of instant message, etc., and is stored by the UE, and the PSAP stores the emergency call continuity information containing the VCC AS address; when the UE is unregistered UE, the VCC AS, HSS, HLR, DM/CP server or network entity stores the routing information of the UE.
Implementation of this step 406 referring to fig. 4a, 15-16, when the UE determines that the call needs to be handed over to the IMS domain according to the wireless environment, the UE initiates an emergency call request to the I/S-CFCS in the IMS domain with the VCC AS address AS the called number.
In step 407, the I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain routes the handover request to the VCC AS.
The specific operation of step 408 is shown in fig. 4a at 18-21, where the VCC AS finds an anchored session, and the method for the VCC AS to find an anchored session in this step is: VCC AS finds the anchored conversation by registering the user identification of UE; or the VCC AS finds the anchored session according to the anchor index which is sent to the UE and stored by the UE, wherein the anchor index is an index identifier.
The VCC AS agent UE re-initiates a session request to the PSAP, and after receiving the request, the PSAP informs the UE of session establishment information through the VCC AS and the I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain, and establishes a call connection between the UE and the PSAP; during or after the call connection is established, when the UE is unregistered, the VCC AS, HSS, HLR, DM/CP server or network entity stores the routing information of the UE in the IMS domain.
Step of VCC AS releasing UE session resource in IMS domain referring to 22-24 in fig. 4a, VCC AS sends BYE information to I/S-CSCF in IMS domain, I/S-CSCF in IMS domain notifies MGCF in IMS domain of BYE information, MGCF in IMS domain receives BYE information and sends Release (REL) information to VMSC in CS domain, and VMSC in CS domain notifies UE of REL information, thereby releasing UE session resource in CS domain.
See figure 4a for a specific operation.
Referring to fig. 5, fig. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a method for implementing voice call continuity during emergency service according to a fourth preferred embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, a PSAP initiates an emergency service request to a UE in a CS domain, where the emergency service request is an emergency call request or a callback request of an emergency call, and anchors a session with the PSAP to a VCC AS, and after the UE moves to an IMS domain, the VCC AS proxies the UE to initiate a new session connection to the PSAP, where S-CSCF, MGCF, I/S-CSCF of the IMS domain and VMSC of the CS domain are used AS network entities, the CS domain is used AS a source domain of this embodiment, and the IMS is used AS a destination domain of this embodiment. The method comprises the following steps:
in step 501, the PSAP initiates an emergency service request to the S-CSCF of the IMS domain, where the emergency service request is a callback request for an emergency call request or live emergency call.
In this step 502, the method for the S-CSCF in the IMS domain to obtain the emergency call continuity information is exactly the same as the method for the E/S-CSCF in the IMS domain to obtain the emergency call continuity information described in step 302.
The method for the S-CSCF of the IMS domain to obtain the emergency call continuity information is the same as the method described in step 302.
The method for the S-CSCF in the IMS domain to determine whether the service satisfies the condition for triggering the call continuity service is completely the same as the method for the E-CSCF in the IMS domain to determine whether the service satisfies the condition for triggering the call continuity service in step 202.
The method for the E/S-CSCF of the IMS domain to anchor the emergency service to the VCC AS is the same AS described in step 303.
The steps for establishing a session connection between the PSAP and the UE are prior art and are only briefly described here. Referring specifically to fig. 5a, 3-14, the VCC AS receives the emergency call request routed by the S-CSCF, the VCC AS address may be notified to the UE in the form of short message, instant message, etc., the UE sends a response message to the PSAP via 6-11 in fig. 5a, the PSAP receives the session establishment information and then sends an acknowledgement message to the S-CSCF, and finally sends the response message to the VCC AS and the MGCF via 13, 14 in fig. 5a, respectively, thereby establishing the session between the PSAP and the UE.
In all the above embodiments, the IMS domain and the CS domain are taken as the source domain and the destination domain, respectively, for description, wherein in the embodiment shown in fig. 1, any one of the IMS domain emergency service call session unit and the CS domain emergency service call session unit is the emergency service call session unit of the source domain, and when the UE is handed over from the source domain to the destination domain, any one of the IMS domain emergency service call session unit and the CS domain emergency service call session unit may be the emergency service call session unit of the destination domain. In the embodiment shown in fig. 2, the UE uses the IMS domain as the source domain for initiating the emergency call request, and uses the CS domain as the destination domain for handover; in the embodiment shown in fig. 3, the PSAP initiates an emergency service request to the UE in the IMS domain, where the IMS domain is the source domain and the CS domain is the destination domain for handover; in the embodiment shown in fig. 4, the UE uses the CS domain as the source domain for initiating the emergency call request, and uses the IMS domain as the destination domain for handover; in the embodiment shown in fig. 5, the PSAP initiates an emergency service request to the UE in the CS domain, which is the source domain and the IMS domain which is the destination domain for handover.
In addition to the above, other cases include: an IMS domain is used as a source domain, and the IMS domain is used as a target domain; or, the IMS domain is used as the source domain, and the WLAN is used as the destination domain; or, the CS domain is used as a source domain and the CS domain is used as a target domain; or, the CS domain is used as the source domain, and the WLAN is used as the destination domain; or taking WLAN as a source domain and IMS domain as a target domain; or taking WLAN as a source domain and CS domain as a target domain; or the case of using WLAN as the source domain and WLAN as the destination domain is basically the same as the execution method described in the above embodiment, and for the sake of simplicity, the description is omitted here.
In short, the above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and is not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
Claims (36)
1. A method for implementing voice call continuity in emergency services, the method comprising:
A. one of a PSAP (emergency call center) and a UE (user equipment) in a source domain initiates an emergency service request to the other party;
B. the network entity judges whether the emergency service meets the condition of triggering the emergency call continuity service; when the condition is met, anchoring the emergency service to a Voice Call Continuity (VCC) Application Server (AS) and establishing a call connection between the UE and a PSAP in a source domain;
C. and the VCC AS realizes the voice call continuity service according to the anchored emergency service.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein step a comprises:
the UE in the source domain initiates an emergency service request to the PSAP.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein step a comprises:
the PSAP initiates an emergency service request to the UE in the source domain.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the step B, before the network entity determining whether the service satisfies the condition for triggering the emergency call continuity service, further comprises: the network entity obtains emergency call continuity information,
in step B, the network entity determines whether the emergency service satisfies the condition for triggering the emergency call continuity service according to the acquired emergency call continuity information.
5. The method of claim 4, wherein the step of the network entity obtaining the emergency call continuity information comprises:
a network entity acquires emergency call continuity information from a UE or a PSAP;
or, the network entity obtains the emergency call continuity information from the emergency service request;
alternatively, the network entity obtains emergency call continuity information from a third party node.
6. The method of claim 5, wherein the step of the network entity obtaining emergency call continuity information from a third party node comprises: the network entity obtains the emergency call continuity information directly or indirectly from a home subscriber server, or a local location register, or a device management/client provisioning DM/CP server.
7. The method according to claim 1, wherein the source domain is any one of an IP multimedia subsystem, IMS, a circuit switched, CS, and a wireless local area network, WLAN.
8. The method of claim 3, wherein step A is preceded by the further step of: PSAP obtains the continuity information of the emergency call;
the emergency service request is initiated by the PSAP to the UE in the source domain, either as an emergency call request or as a callback request for an emergency call, in step a.
9. The method of claim 8, wherein said PSAP obtaining emergency call continuity information comprises: setting the emergency call continuity information in the PSAP in advance; or, the PSAP queries a Home Subscriber Server (HSS) or a Home Location Register (HLR) or a DM/CP server where the UE data is located according to the emergency user identification to acquire the emergency call continuity information; or, the PSAP obtains the emergency call continuity information according to an emergency service request which is sent by the UE and carries the emergency call continuity information.
10. The method of claim 4, wherein the emergency call continuity information comprises: explicit emergency service information or implicit emergency service information.
11. The method of claim 10, wherein the emergency call continuity information further comprises: terminal call continuity information and/or network call continuity information.
12. The method of claim 10, wherein the explicit emergency services information comprises: an emergency service indication, an emergency subscriber identity or an emergency number.
13. The method of claim 10, wherein the implicit emergency service information is information generated by a network entity routing emergency service to an E-CSCF.
14. The method of claim 11, wherein the terminal call continuity information comprises: one or more of terminal capability, user preference and VCC AS address.
15. The method of claim 11, wherein the network call continuity information comprises: one or more of roaming status, access network type and subscription data.
16. The method of claim 15,
the subscription data is subscription data of the UE initiating the emergency service request.
17. The method of claim 2,
step B, the step of anchoring the emergency service request to the VCC AS by the network entity according to the emergency call continuity information comprises:
the network entity obtains the VCC AS address, and anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS according to the obtained VCC AS address.
18. The method of claim 17, wherein step a further comprises: UE acquires the address of VCC AS;
in step A, UE carries VCC AS address in the initiated emergency service request;
in step B, the network entity anchors the emergency service to the VCC AS according to the VCC AS address carried in the emergency service request.
19. The method of claim 18, wherein the step of the UE acquiring the address of VCC AS comprises: configuring an address of VCC AS on UE in advance; or, the VCC AS address is issued to the UE in advance.
20. The method of claim 19, wherein the step of issuing the VCC AS address to the UE in advance comprises:
when UE is in IMS domain, the address of VCC AS is returned to UE in the form of short message or instant message or subscription notice, or the VCC AS address is carried in the response to UE registration or call;
when the UE is in the CS domain, the address of the VCC AS is carried in the connection number of the response message ANM or returned to the UE in the form of short message.
21. The method of claim 19 wherein the step of issuing the VCC AS address to the UE is performed by a VCC AS, a HSS, a HLR, a DM/CP server, or a network entity.
22. The method of claim 17, wherein the method for the network entity to obtain the VCC AS address comprises:
the network entity inquires a third party node to obtain the address of the VCC AS;
or, configuring the address of the VCC AS on the network entity, and the network entity acquires the address of the VCC AS according to the configuration.
23. The method according to claim 2, wherein in step B, after establishing the call connection between the UE in the source domain and the PSAP, further comprising: and sending the VCC AS address to the UE for storage.
24. The method of claim 1, wherein the network entity anchoring the emergency service after VCC AS according to emergency call continuity information when the UE is unregistered further comprises:
the callback routing information element stores the routing information of the UE.
25. The method of claim 3, wherein the network entity obtains emergency call continuity information and/or PSAP identification;
in step B, the step of anchoring the emergency service request to the VCC AS by the network entity includes:
the network entity anchors the emergency service request to a VCC AS according to the acquired emergency call continuity information;
or anchoring the emergency service request to a VCC AS according to the obtained PSAP identifier;
or the network entity anchors the emergency service request to VCC AS according to the obtained emergency call continuity information and PSAP identification.
26. The method according to claim 1, wherein when the UE needs to handover to the destination domain, the step C comprises:
cl and UE initiate a switching request by taking the acquired VCC AS address AS a called number;
c2, VCC AS receives the switch request, finds the anchored conversation, agent UE and PSAP to negotiate again, and establishes the conversation connection in the target domain after the negotiation.
27. The method of claim 26, wherein the VCC AS finds an anchored session method comprising: the VCC AS finds the anchored session according to the emergency user identification or anchor index.
28. The method of claim 26, wherein the handover request is a handover request carrying an emergency service indication.
29. The method AS claimed in claim 2, wherein in step C, during or after the VCC AS proxy UE establishes the call connection with the PSAP, further comprising: when the UE is unregistered, routing information of the UE in the destination domain is held by the callback routing information element.
30. The method of claim 24 or 29, wherein the callback routing information element comprises VCC AS, HSS, HLR, DM/CP server or network entity, and wherein the routing information of the UE comprises UE destination domain information.
31. The method of claim 27, wherein the anchor index is an index id sent by VCC AS to UE.
32. The method of claim 1,
when the source domain or the destination domain is an IMS domain, the network entity is: any one of an emergency call session control function E-CSCF, a service call session control function S-CSCF, an inquiry call session control function I-CSCF, a proxy call session control function P-CSCF, an access gateway control function AGCF, a border gateway control function BGCF, an interconnection border control function IBCF, a media gateway control function MGCF and an application server AS of the IMS domain;
when the source domain or the destination domain is a CS domain, the network entity is: a visited mobile services switching centre VMSC or a mobile gateway services switching centre GMSC of the CS domain.
33. A system for implementing voice call continuity in an emergency services call, the system comprising: UE, an emergency service call session unit in a source domain, PSAP and VCC AS; wherein,
the UE initiates an emergency service request or a switching request carrying emergency call continuity information in a source domain or a PSAP initiates an emergency service request carrying the emergency call continuity information;
the emergency service call session unit in the source domain anchors the emergency service request to a VCC AS and establishes a call connection between the UE and the PSAP;
and the VCC AS anchors the emergency service according to the switching request sent by the UE, establishes a call connection with a PSAP in a target domain by acting the UE and releases the session resource of the UE in the source domain.
34. The system of claim 33, further comprising:
and the emergency service call session unit in the destination domain routes the switching request sent by the UE to the VCCAS.
35. The system of claim 33 or 34,
when the domain is an IMS domain, the emergency call session unit is: E-CSCF, S-CSCF, I-CSCF, P-CSCF, AGCF, BGCF, IBCF, MGCF, or AS.
36. The system of claim 33 or 34,
and when the domain is the CS domain, the emergency call session unit is VMSC or GMSC.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2007100875291A CN101166364A (en) | 2006-10-21 | 2007-03-16 | A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service |
| PCT/CN2007/070236 WO2008046319A1 (en) | 2006-10-21 | 2007-07-04 | A method and system to realize voice call continuity when dealing with emergency business |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200610137242.0 | 2006-10-21 | ||
| CN200610137242 | 2006-10-21 | ||
| CNA2007100875291A CN101166364A (en) | 2006-10-21 | 2007-03-16 | A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101166364A true CN101166364A (en) | 2008-04-23 |
Family
ID=39313613
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2007100875291A Pending CN101166364A (en) | 2006-10-21 | 2007-03-16 | A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101166364A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2008046319A1 (en) |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010022611A1 (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, system and mobile switching center for voice continuity call handover |
| CN101784027A (en) * | 2009-01-19 | 2010-07-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for switching emergent session |
| WO2010091573A1 (en) * | 2009-02-10 | 2010-08-19 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for emergency service session handover and emergency service system thereof |
| WO2010105563A1 (en) * | 2009-03-17 | 2010-09-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and apparatus for implementing emergency call service |
| CN101854583A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-06 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Location service providing method |
| CN101938728A (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-05 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A method and system for implementing emergency session switching |
| WO2011020427A1 (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2011-02-24 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method, device and system for ensuring continuity of emergency service |
| CN101998330A (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2011-03-30 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Switching method, device and system |
| CN102045897A (en) * | 2009-10-10 | 2011-05-04 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Group identification reporting method and device |
| CN101577890B (en) * | 2008-11-11 | 2011-08-10 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for transferring emergency service sessions, and emergency service system |
| CN101668273B (en) * | 2008-09-05 | 2011-11-23 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Emergency service switching method |
| CN102273236A (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2011-12-07 | 爱立信电话股份有限公司 | Emergency call support during roaming |
| CN101772128B (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2012-05-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for processing information of unrestricted service in network switch |
| US8345635B2 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2013-01-01 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Access control method, access control apparatus and communication system |
| CN103416100A (en) * | 2011-03-03 | 2013-11-27 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | Methods, devices, system and computer program products for supporting the re-establishment of an emergency communication |
| CN102111922B (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2014-01-01 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Management method and system for M2M service signing data, and user signing data memory |
| CN105659576A (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2016-06-08 | 微软技术许可有限责任公司 | Voice call continuity in hybrid networks |
| CN108141451A (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2018-06-08 | 莱尔德波鸿有限责任公司 | For the method, equipment and network of data transmission |
| CN109121130A (en) * | 2017-06-23 | 2019-01-01 | 现代自动车株式会社 | Vehicle and for control from vehicle generate urgent call signal method |
| CN111213406A (en) * | 2017-09-29 | 2020-05-29 | 萨基姆宽带连接公司 | Method for assisting roaming of mobile terminal between community wireless local area networks |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI802114B (en) * | 2021-11-29 | 2023-05-11 | 財團法人工業技術研究院 | Method for assisting unregistered user device to access private network service and communication system |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1801998A (en) * | 2004-12-31 | 2006-07-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Conversation switching method from multimedia subsystem domain to circuit subsystem domain |
| CA2595077C (en) * | 2005-01-19 | 2015-08-25 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | A method and apparatus for handling emergency calls |
| CN1802022B (en) * | 2005-09-30 | 2010-05-05 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for establishing initial call in voice service continuity service |
-
2007
- 2007-03-16 CN CNA2007100875291A patent/CN101166364A/en active Pending
- 2007-07-04 WO PCT/CN2007/070236 patent/WO2008046319A1/en not_active Ceased
Cited By (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010022611A1 (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, system and mobile switching center for voice continuity call handover |
| CN101668273B (en) * | 2008-09-05 | 2011-11-23 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Emergency service switching method |
| US9532202B2 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2016-12-27 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Access control method, access control apparatus and communication system |
| US9001785B2 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2015-04-07 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Access control method, access control apparatus and communication system |
| US8345635B2 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2013-01-01 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Access control method, access control apparatus and communication system |
| CN101577890B (en) * | 2008-11-11 | 2011-08-10 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for transferring emergency service sessions, and emergency service system |
| CN102273236B (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2015-09-09 | 爱立信电话股份有限公司 | Urgent call support during roaming |
| CN101772128B (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2012-05-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for processing information of unrestricted service in network switch |
| CN102273236A (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2011-12-07 | 爱立信电话股份有限公司 | Emergency call support during roaming |
| CN101784027B (en) * | 2009-01-19 | 2014-03-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for switching emergent session |
| CN101784027A (en) * | 2009-01-19 | 2010-07-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for switching emergent session |
| WO2010091573A1 (en) * | 2009-02-10 | 2010-08-19 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for emergency service session handover and emergency service system thereof |
| CN101800960B (en) * | 2009-02-10 | 2014-03-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司南京分公司 | Method for transferring emergent service session and emergent service system |
| WO2010105563A1 (en) * | 2009-03-17 | 2010-09-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and apparatus for implementing emergency call service |
| CN101854583A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-06 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Location service providing method |
| CN101938728A (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-05 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A method and system for implementing emergency session switching |
| CN101938728B (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2015-05-20 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for realizing emergency session handover |
| CN101998330A (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2011-03-30 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Switching method, device and system |
| WO2011020427A1 (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2011-02-24 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method, device and system for ensuring continuity of emergency service |
| CN101998330B (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2014-06-04 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Switching method, device and system |
| CN102045897A (en) * | 2009-10-10 | 2011-05-04 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Group identification reporting method and device |
| CN102045897B (en) * | 2009-10-10 | 2014-08-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Group identification reporting method and device |
| CN102111922B (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2014-01-01 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Management method and system for M2M service signing data, and user signing data memory |
| CN103416100A (en) * | 2011-03-03 | 2013-11-27 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | Methods, devices, system and computer program products for supporting the re-establishment of an emergency communication |
| CN103416100B (en) * | 2011-03-03 | 2017-02-15 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | Methods, devices, system and computer program products for supporting the re-establishment of an emergency communication |
| CN105659576A (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2016-06-08 | 微软技术许可有限责任公司 | Voice call continuity in hybrid networks |
| CN105659576B (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2019-03-19 | 微软技术许可有限责任公司 | Method for Voice Call Continuity in Hybrid Networks |
| CN108141451A (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2018-06-08 | 莱尔德波鸿有限责任公司 | For the method, equipment and network of data transmission |
| CN109121130A (en) * | 2017-06-23 | 2019-01-01 | 现代自动车株式会社 | Vehicle and for control from vehicle generate urgent call signal method |
| CN109121130B (en) * | 2017-06-23 | 2021-04-23 | 现代自动车株式会社 | Vehicle and method for controlling emergency call signal generated from vehicle |
| CN111213406A (en) * | 2017-09-29 | 2020-05-29 | 萨基姆宽带连接公司 | Method for assisting roaming of mobile terminal between community wireless local area networks |
| CN111213406B (en) * | 2017-09-29 | 2021-05-18 | 萨基姆宽带连接公司 | Method for assisting mobile terminal roaming between community wireless local area networks |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2008046319A1 (en) | 2008-04-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101166364A (en) | A method and system for realizing voice call continuity in emergency service | |
| CN101297531B (en) | Providing IMS service through circuit switching access | |
| US8542672B2 (en) | Call handling for IMS registered user | |
| EP1972100A1 (en) | Mobile communications method and system for signalling information relating to network's capabilities | |
| EP1881689A1 (en) | A method and device for perceiving the user triggering a supplementary service | |
| CN101330736A (en) | Method and device for providing call forwarding service for users | |
| EP2716001B1 (en) | Routing of calls in ip multimedia subsystem centralized services networks | |
| EP1974519B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing ims services to circuit-switched controlled terminals | |
| CN100553219C (en) | Method for message intercommunication between IMS domain and CS domain | |
| US8416723B2 (en) | Method, system, and device for establishing association-control relations | |
| WO2007025473A1 (en) | A cs domain call terminating system, method and network device | |
| US20090270064A1 (en) | Method and system architecture for establishing a specific communication session in a communication network | |
| KR20060113284A (en) | IMS system supporting voice service between heterogeneous networks and call setting method accordingly | |
| CN101102615B (en) | An implementation method for final call in IP multimedia subsystem centrally controlled service | |
| CN102547651B (en) | User roaming method and ICS (internet connection sharing) enhanced network | |
| CN102595372B (en) | User's loaming method and ICS enhancing networks | |
| KR20090009925A (en) | Selecting S-CPF for Application Server Outgoing Requests | |
| CN1997201A (en) | Method and device for call processing in the phone service continuity | |
| CN102572785B (en) | User's loaming method and ICS strengthen network | |
| KR20080069881A (en) | Method and system for providing voice call continuous service in internet protocol multimedia subsystem | |
| CN102036205A (en) | Method and system for realizing emergency location | |
| WO2011020390A1 (en) | Number conversion method and service continuity application server | |
| CN101455052A (en) | S-cscf selection for application server originated requests |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Open date: 20080423 |