WO2024116366A1 - 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 - Google Patents
移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024116366A1 WO2024116366A1 PCT/JP2022/044354 JP2022044354W WO2024116366A1 WO 2024116366 A1 WO2024116366 A1 WO 2024116366A1 JP 2022044354 W JP2022044354 W JP 2022044354W WO 2024116366 A1 WO2024116366 A1 WO 2024116366A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- still image
- information
- unit
- image
- mobile terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/14—Digital output to display device ; Cooperation and interconnection of the display device with other functional units
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01C—CONSTRUCTION OF, OR SURFACES FOR, ROADS, SPORTS GROUNDS, OR THE LIKE; MACHINES OR AUXILIARY TOOLS FOR CONSTRUCTION OR REPAIR
- E01C23/00—Auxiliary devices or arrangements for constructing, repairing, reconditioning, or taking-up road or like surfaces
- E01C23/01—Devices or auxiliary means for setting-out or checking the configuration of new surfacing, e.g. templates, screed or reference line supports; Applications of apparatus for measuring, indicating, or recording the surface configuration of existing surfacing, e.g. profilographs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T1/00—General purpose image data processing
- G06T1/60—Memory management
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
Definitions
- the present invention relates to mobile terminals and the like that process video captured while moving.
- Non-Patent Document 1 there was a technology that had participants record and collect information such as photos of manholes and their deterioration status using a map game application that showed the locations of manholes, and awarded points according to the number of photos collected (for example, see Non-Patent Document 1).
- Patent Document 1 discloses an information processing device that mounts an imaging device on a mobile object moving along a road, captures an image of an area including the surface of the road, analyzes the captured image, determines defects in the road in the image, and identifies and outputs images that contain defects.
- the present invention therefore aims to provide a video utilization system that allows both image providers and users to provide and use images without any hindrance.
- the mobile terminal of the first invention is a mobile terminal that includes a location acquisition unit that acquires location information, a shooting unit that acquires video including still images while moving and that corresponds to the location information, a determination unit that determines whether or not a still image included in the video acquired by the shooting unit satisfies a selection condition, and an image transmission unit that transmits a still image that the determination unit determines satisfies the selection condition in association with the location information acquired by the location acquisition unit.
- still images that meet certain conditions can be selected from videos captured by a mobile terminal and used.
- the mobile terminal of the second invention is different from the mobile terminal of the first invention in that the judgment unit is equipped with judgment means for acquiring one or more attribute values corresponding to a still image, judging whether or not the one or more attribute values match a test condition, and judging whether or not a still image judged to match the test condition satisfies a selection condition.
- the mobile terminal of the third invention is different from the mobile terminal of the first or second invention in that the determination unit determines whether or not a still image satisfies each of a plurality of selection conditions, and further includes a tag acquisition unit that acquires a tag corresponding to a selection condition that the determination unit determines is satisfied, and the image transmission unit is a mobile terminal that transmits the still image in association with the tag and location information.
- the mobile terminal of the fourth invention is the mobile terminal of any one of the first to third inventions, in which the determination unit also obtains analysis results for still images included in the video, and further includes a tag acquisition unit that acquires tags using the analysis results for still images that the determination unit determines satisfy the selection conditions, and the image transmission unit transmits the still images in association with the tags and location information.
- This configuration allows appropriate tags to be added to still images that meet the conditions.
- the mobile terminal of the fifth invention is the same as any one of the first to fourth inventions in that the camera constituting the imaging unit is installed in a position to capture an image of the moving surface of the mobile terminal or the vicinity of the moving surface, and the imaging unit is a mobile terminal that captures images of the moving surface or the vicinity while moving and obtains video.
- the mobile terminal of the sixth invention is a mobile terminal in which the selection conditions for any one of the first to fifth inventions are that there is a crack in the road in the still image, that there is damage to the bridge in the still image, that there is damage to a manhole in the road in the still image, and that there is a fallen object on the road in the still image.
- the information processing device of the seventh invention is an information processing device that includes a receiving unit that receives a still image associated with location information from any one of the first to sixth mobile terminals, and a storage unit that stores the still image received by the receiving unit in pairs with the location information.
- the information processing device of the eighth invention is an information processing device that includes a receiving unit that receives a video that is a video shot by a mobile terminal while moving and has a plurality of still images that correspond to location information, a determining unit that determines whether or not a still image included in the video received by the receiving unit satisfies a selection condition, and a storage unit that stores the still image that the determining unit determines satisfies the selection condition in association with the location information that corresponds to the still image.
- the information processing device of the ninth invention is an information processing device according to the seventh or eighth invention, further comprising a transmitter that corresponds to the still image with a tag, corresponds to notification destination information that specifies the notification destination of the still image, and transmits the still image to the notification destination specified by the notification destination information that corresponds to the tag that corresponds to the still image.
- the information processing device of the tenth invention is an information processing device according to any one of the seventh to ninth inventions, further comprising a rights holder processing unit that corresponds a still image or video received by the receiving unit to a rights holder identifier that identifies the rights holder of the still image or video, and performs rights holder processing, which is processing related to the rights holder identified by the rights holder identifier.
- This configuration allows for appropriate processing regarding the rights holders of still images.
- the information processing device of the eleventh invention is an information processing device according to the tenth invention, in which the rights holder identifier is a rights holder identifier corresponding to the video that is the source of the still image, and the rights holder processing unit is an information processing device equipped with a reward means that performs reward processing, which is processing for giving a reward to the rights holder identified by the rights holder identifier.
- This configuration makes it possible to provide compensation to the rights holder of videos captured by the mobile terminal.
- the information processing device of the twelfth invention is an information processing device in which, compared to the tenth invention, the rights holder processing unit is equipped with a first preservation means that performs a first preservation process in which the still image is stored in association with a set of attribute values corresponding to the still image.
- This configuration allows still images that meet the selection conditions to be preserved.
- the information processing device of the thirteenth invention is an information processing device in which, compared to the ninth invention, the rights holder processing unit is equipped with a second security means that performs a second security process in which the still image is stored in association with a rights holder identifier corresponding to the still image.
- This configuration allows the rights holder of still images that meet the selection conditions to be the appropriate rights holder.
- the information processing device of the fourteenth invention is an information processing device that, compared to the ninth invention, further includes a transmission unit that transmits the still image to a user terminal, and the rights holder processing unit includes a third security means that stores the still image in association with a rights holder identifier corresponding to the user terminal.
- the information processing device of the fifteenth invention is an information processing device according to any one of the twelfth to fourteenth inventions, in which the rights holder processing unit is provided with a fourth preservation means for performing a fourth preservation process that accumulates preservation information, including access information for accessing the still image, in the blockchain.
- This configuration makes it possible to store preservation information for still images that require preservation.
- still images that meet certain conditions can be efficiently selected and used from videos captured by a mobile terminal.
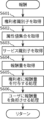
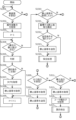
- Block diagram of information system A A flowchart illustrating an example of the operation of the information processing device 1.
- a flowchart for explaining an example of the operation of the mobile terminal 2 A flowchart illustrating an example of the determination process
- a diagram showing the compensation management table The inspection conditions management table
- Block diagram of information system B in embodiment 2 A flowchart illustrating an example of the operation of the information processing device 3.
- a mobile terminal transmits still images that make up a video captured by the mobile terminal and that satisfy a selection condition, along with location information, etc.
- the mobile terminal determines, for example, whether a still image that satisfies a detection condition satisfies the selection condition.
- the selection condition may be, for example, a road with cracks, a damaged bridge, a damaged manhole, or an object that has fallen onto the road.
- a still image may also be referred to as a field or frame.
- the rights holder processing is, for example, a compensation processing described below, and various types of preservation processing described below.
- information X corresponding to information Y means that information Y can be obtained from information X, or information X can be obtained from information Y, and the method of the correspondence is not important.
- Information X and information Y may be linked, may exist in the same buffer, information X may be included in information Y, or information Y may be included in information X, etc.
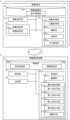
- FIG. 1 is a conceptual diagram of an information system A in this embodiment.
- Information system A includes an information processing device 1 and one or more mobile terminals 2.
- the information processing device 1 is a server that accumulates still images and the like transmitted by one or more mobile terminals 2.
- the information processing device 1 is, for example, a cloud server or an ASP server, but the type is not important.
- the information processing device 1 may also be a device that constitutes a blockchain.
- the information processing device 1 mainly performs image-related processing, and therefore may also be called an image processing device.
- the mobile terminal 2 is a terminal installed on a moving body and is a terminal that shoots videos.
- the mobile terminal 2 is, for example, a drive recorder, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, a camera with a communication function, or a glasses-type camera. Installation usually means that it is fixed, but it may also be considered to include being in contact with or held.
- the mobile terminal 2 may be, for example, a terminal held by a person.
- the mobile terminal 2 may also have a driving means such as an engine or a moving means such as wheels.
- the mobile terminal 2 is a terminal that is not fixed to a building or the ground.
- the mobile body is a moving object, for example, a terrestrial moving device, a water moving device, an underwater moving device, an aerial moving device, a space moving device, or a living thing.
- the terrestrial moving device is, for example, a vehicle or a robot.
- the aerial moving device is, for example, a ship.
- the aerial moving device is, for example, a submarine.
- the aerial moving device is, for example, an aircraft or a drone.
- the space moving device is, for example, a rocket or an artificial satellite.
- the information processing device 1 and one or more mobile terminals 2 can usually communicate with each other via a network such as the Internet.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram of information system A in this embodiment.
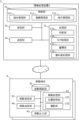
- Information processing device 1 constituting information system A includes a storage unit 11, a receiving unit 12, a processing unit 13, and a transmitting unit 14.
- Storage unit 11 includes a terminal management unit 111, and a remuneration management unit 112.
- Processing unit 13 includes an accumulation unit 131, and rights holder processing unit 132.
- Rights holder processing unit 132 includes first maintenance means 1321, second maintenance means 1322, third maintenance means 1323, fourth maintenance means 1324, and remuneration means 1325.
- the mobile terminal 2 includes a mobile storage unit 21, a mobile receiving unit 22, a mobile processing unit 23, and a mobile transmitting unit 24.
- the mobile storage unit 21 includes a condition management unit 211.
- the mobile processing unit 23 includes a position acquisition unit 231, a photographing unit 232, a determination unit 233, and a tag acquisition unit 234.
- the mobile transmitting unit 24 includes an image transmission unit 241.
- Various types of information are stored in the storage unit 11. Examples of the various types of information include terminal information, still images and location information, one or more pieces of notification destination information, and one or more sets of tags and notification destination information, as described below.
- Destination information is information that specifies the destination to which the still image is to be sent.
- Destination information can be, for example, an email address, a phone number, a user identifier for a communication app, or an IP address of the destination device.
- a tag is information that identifies the characteristics of a still image.
- a tag is information that is the result of analyzing a still image.
- a tag is information that indicates the classification of a still image.
- a tag is information that indicates characteristic elements contained in a still image. For example, tags are "manhole damage,” “road cracks,” “bridge damage,” and “ fallen objects.” Tags are also called metadata.
- the terminal management unit 111 stores one or more pieces of terminal information.
- the terminal information is information related to the mobile terminal 2.
- the terminal information includes, for example, a terminal identifier and an attribute value set.
- the terminal information may correspond to a video captured by the mobile terminal 2.
- the terminal identifier may be included in the attribute value set.
- the terminal identifier is information that identifies the mobile terminal 2.
- the terminal identifier may be a rights holder identifier that identifies the rights holder who is the user of the mobile terminal 2.
- the terminal identifier is, for example, the ID of the mobile terminal 2, the user identifier of the user of the mobile terminal 2, the name of the mobile terminal 2, the IP address of the mobile terminal 2, or the MAC address of the mobile terminal 2.
- the right holder is a person who has some right to a video shot by the mobile terminal 2 or a still image transmitted by the mobile terminal 2.
- the right holder is, for example, the owner of the still image, the copyright holder of the still image, the owner of the mobile terminal 2 that shot the still image, or the person with the right to dispose of the still image.
- the right holder is, for example, the initial right holder of the still image.
- the right holder is usually the owner of the mobile terminal 2, but it may be any person who has the right to a video shot by the mobile terminal 2 or a still image transmitted by the mobile terminal 2.
- the rights holder identifier is the identifier of the rights holder of the selected still image.
- the rights holder identifier may be a terminal identifier.
- the rights holder identifier is, for example, the rights holder's ID, the rights holder's name, the rights holder's email address, or the rights holder's phone number.
- the rights holder ID is, for example, a user identifier.
- An attribute value set is a set of one or more attribute values.
- the attribute values are those of a still image.
- the attribute values may also be those of a video that includes still images.
- the attribute values are, for example, environmental information, tags, and scores.
- Environmental information is information about the environment in which the video was shot. Examples of environmental information include location information, road type identifier, point information, direction information, camera information, time information, weather information, temperature information, and season information.
- Location information is information that identifies the shooting location. The shooting location is the position of the camera that shoots. Location information is, for example, (latitude, longitude), (latitude, longitude, altitude). However, location information may also be an area identifier that identifies an area on a map, an address, a road identifier that identifies a road, a lane identifier that identifies a lane on a road, and the like. Location information is usually associated with a still image.
- Road type identifier is information that identifies the type of road on which the mobile object traveled. Examples of road type identifiers are "expressway,” "national highway,” and “prefectural road.” Point information is information that identifies a point. Examples of point information are place names, bridge names, and road names. Direction information is information that identifies the direction of shooting. Examples of direction information are the angle from true north. Camera information is information about the camera. Examples of camera information are the angle of view and resolution. Time information is information that specifies the time when the video was shot. The time when the video was shot may be a time around the time when the video was shot, and accuracy is not required.
- Time information is, for example, the time, year/month/date/time, year/month/date/time/minute, year/month/date/time/minute/second, year/month/date, and month/day. In other words, the granularity of the time indicated by the time information does not matter.
- Weather information is information that specifies the weather at the location where the video was shot. Examples of weather information are “sunny,” “rain,” “snow,” and “cloudy.”
- Temperature information is information that specifies the outside temperature at the location where the video was shot. Examples of temperature information are “25 degrees” and “above 30 degrees.”
- Season information is information that specifies the season at the location where the video was shot. Examples of season information are “spring,” “summer,” “early summer,” and "winter.”
- the score is, for example, information indicating the certainty of the judgment or the degree of the situation.
- the scores are, for example, the score when it is determined that the manhole is damaged, the score when it is determined that there is a crack in the road, the score when it is determined that the bridge is damaged, the score when it is determined that there is a fallen object on the road, the degree of damage to the manhole, the degree or size of the crack in the road, and the degree of damage to the bridge.
- the reward management unit 112 manages one or more pieces of reward information. It is preferable that the reward information corresponds to a tag. That is, for example, it is preferable that the reward corresponding to providing a still image of road damage is different from the reward corresponding to providing a still image of manhole damage. It is preferable that the reward information corresponds to a score. That is, it is preferable that the higher the score, the higher the reward.
- the reward information is information for determining the reward.
- the reward information is, for example, a monetary amount, points, or an arithmetic formula for determining the reward amount.
- the receiving unit 12 receives various information and instructions from the mobile terminal 2 or a terminal not shown.
- the various information and instructions are, for example, a still image, location information, an attribute value set, an output instruction, a purchase instruction, inspection conditions described below, and selection conditions described below.
- the terminals not shown are, for example, a user terminal and an operator terminal.
- a user terminal is a terminal to which a still image is transmitted, a terminal of a user requesting a still image, or a terminal of a user using a still image.
- An operator terminal is a terminal of the operator of the information processing device 1.
- the receiving unit 12 receives a still image associated with the location information from the mobile terminal 2.
- the receiving unit 12 receives one or more still images from the mobile terminal 2.
- Such still images are still images that satisfy the selection conditions.
- the receiving unit 12 may usually receive a video that includes a still image that satisfies the selection conditions. When receiving a video, the still image included in the video is also received, so this may be considered as receiving a still image.
- the still images received by the receiving unit 12 may include still images that do not satisfy the selection conditions.
- the receiving unit 12 receives, for example, output instructions or purchase instructions from a user terminal.
- An output instruction is an instruction to output a still image or the like.
- An output instruction is an instruction to cause a user terminal to output a still image or the like.
- An output instruction corresponds to, for example, location information.
- a still image or the like is, for example, a still image and a set of attribute values.
- a purchase instruction is an instruction to purchase a still image.
- the purchase instruction is associated with a user identifier.
- the purchase instruction typically includes information that identifies the still image.
- the purchase instruction has, for example, a still image identifier.
- the purchase instruction includes, for example, the conditions of the purchase.
- the conditions of the purchase are, for example, the purchase amount.
- the conditions of the purchase include, for example, information that identifies the rights period.
- the receiving unit 12 receives the inspection conditions, for example, from a user terminal or an operator terminal (not shown) of the operator of the information processing device 1.
- the receiving unit 12 receives the selection conditions, for example, from a user terminal or an operator terminal.
- the processing unit 13 performs various types of processing. For example, various types of processing are performed by the storage unit 131 and the rights holder processing unit 132.
- the storage unit 131 stores the still images received by the receiving unit 12 in pairs with the received location information.
- the rights holder processing unit 132 performs rights holder processing.
- Rights holder processing is processing related to a rights holder identified by a rights holder identifier.
- the rights holder identifier is, for example, a rights holder identifier associated with a video that is the source of a still image that satisfies the selection conditions.
- the rights holder identifier is, for example, a rights holder identifier received in pairs with a still image.
- the rights holder identifier is, for example, information that identifies a person who uses a still image that satisfies the selection conditions.
- a person who uses the still image is, for example, a user who downloaded the still image from a user terminal, or a user identified by a user identifier for the user terminal to which the still image was transmitted.
- the user may also be an organization that uses the still image.
- the organization is, for example, a company, a local government, or a national agency.
- Rights holder processing is processing related to the rights of a still image. Examples of rights holder processing include a first protection processing described below, a second protection processing described below, a third protection processing described below, a fourth protection processing described below, and a compensation processing described below.
- the first maintenance means 1321 performs a first maintenance process to store still images that satisfy the selection conditions in association with a set of attribute values corresponding to the still images.
- the still images that satisfy the selection conditions are still images received by the receiving unit 12, or still images selected by the information processing device 3 described below.
- the set of attribute values corresponding to the still images may also be a set of attribute values corresponding to the video that is the source of the still images.
- the second security means 1322 performs a second security process to store still images that satisfy the selection conditions in association with a rights holder identifier corresponding to the still image.
- the rights holder identifier corresponding to the still image may be the rights holder identifier corresponding to the video that is the source of the still image.
- the third security means 1323 stores still images that satisfy the selection conditions in association with the rights holder identifier corresponding to the user terminal.
- the fourth security means 1324 performs a fourth security process that accumulates security information including access information for accessing the still images.
- the fourth security means 1324 accumulates the security information in the blockchain. That is, it is preferable that the fourth security means 1324 accumulates the security information in the distributed ledger of the blockchain. It is preferable that the fourth security means 1324 registers the security information as a non-fungible token (NFT). It is preferable that the fourth security means 1324 registers the security information in a distributed file system in an IPFS (Inter Planetary File System) network.
- NFT non-fungible token
- the preservation information is information for ensuring the originality of a still image. It can be said that the preservation information is header information for a still image.
- the preservation information is, for example, access information and a set of attribute values. It is preferable that the preservation information has, for example, one or more rights holder identifiers.
- the preservation information has multiple rights holder identifiers, the rights holder of the video may be shared, and the multiple rights holder identifiers may be rights holder history information.
- the rights holder history information is a set of rights holder identifiers and is information that indicates the history of the rights holder.
- the fourth preservation process can ensure the originality of the preservation information of a registered still image.
- the access information is information for accessing the video.
- the access information is information that identifies the storage destination of the video.
- the access information is, for example, a URL or a URI.
- the compensation means 1325 performs compensation processing, which is processing for giving compensation to a right holder identified by a right holder identifier.
- the compensation means 1325 usually performs compensation processing for a right holder who has the rights to the mobile terminal 2 that transmitted the still image.
- the reward means 1325 performs reward processing, which is, for example, a process of acquiring reward information corresponding to a tag paired with a still image that satisfies a selection condition from the reward management unit 112 and granting a reward corresponding to the reward information.
- the reward means 1325 performs reward processing, which is, for example, a process of acquiring reward information corresponding to a score paired with a still image that satisfies a selection condition from the reward management unit 112 and granting a reward corresponding to the reward information.
- the reward means 1325 performs reward processing, which is, for example, a process of acquiring reward information corresponding to a tag and a score that are paired with a still image that satisfies a selection condition from the reward management unit 112 and granting a reward corresponding to the reward information.
- the reward process is a process for giving a reward.
- the reward process is, for example, a process for increasing points managed in pair with one or more rights holder identifiers corresponding to a still image.
- the reward process is, for example, a process for making a payment to a rights holder identified by one or more rights holder identifiers corresponding to a still image.
- the reward process is, for example, a process for transmitting a still image or other content to a user terminal of a rights holder identified by one or more rights holder identifiers corresponding to a still image.
- the reward process may be of any kind as long as it gives a merit to a rights holder identified by one or more rights holder identifiers corresponding to a still image.
- the reward may be, for example, money, points, goods, content, etc., and the content is not important.
- the reward means 1325 acquires a set of attribute values corresponding to the still image transmitted by the transmission unit 14, and performs reward processing, which is processing for determining rewards for one or more rights holders using the set of attribute values and providing the rewards.
- the reward means 1325 preferably performs reward processing, which is a process of acquiring a reward amount corresponding to a service identifier that identifies a service provided for a still image, and giving a reward corresponding to the reward amount.
- the service identifier is, for example, "output” or "purchase.”
- reward information corresponding to the service identifier is stored in the storage unit 11.
- the reward means 1325 performs reward processing, which is processing for obtaining a reward amount using, for example, one or more pieces of information from the attribute value set and the service identifier, and granting a reward corresponding to the reward amount.
- reward processing is processing for obtaining a reward amount using, for example, one or more pieces of information from the attribute value set and the service identifier, and granting a reward corresponding to the reward amount.
- an arithmetic formula or reward correspondence table corresponding to each of the multiple service identifiers is stored in the storage unit 11.
- the arithmetic formula is a formula for calculating the reward amount using one or more video attribute values included in the attribute value set as a parameter.
- the reward correspondence table is a table having multiple pieces of reward correspondence information that manage reward amounts corresponding to one or more video attribute values.
- the compensation means 1325 typically performs a process of charging compensation to users who have enjoyed services related to still images.
- the process of charging the reward is, for example, a process of charging the amount of reward acquired and the amount of profit obtained by the operator of the information processing device 1.
- the process of charging the reward is, for example, a process of deducting points corresponding to the user who enjoyed the service, a settlement process using the user's credit card number, etc.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the still image to the user terminal. For example, in response to receiving an output instruction from a user terminal, the transmission unit 14 transmits a still image corresponding to the output instruction to the user terminal.
- the transmitting unit 14 transmits the still image to the notification destination specified by the notification destination information corresponding to the tag corresponding to the still image. In this case, the transmitting unit 14 automatically transmits the still image. In addition, when a still image is received, the transmitting unit 14 preferably acquires the tag corresponding to the still image, acquires the notification destination information corresponding to the tag from the storage unit 11, and transmits the still image to the notification destination specified by the notification destination information. When a still image is received, the transmitting unit 14 preferably immediately transmits the still image. ⁇ Details of components of mobile terminal 2>
- the various types of information are stored in the mobile storage unit 21 that constitutes the mobile terminal 2.
- the various types of information are, for example, videos, still images that satisfy selection conditions, attribute value sets, rights holder identifiers, one or more inspection conditions, one or more pairs of selection conditions and tags, and map information.
- one or more attribute values that make up an attribute value set correspond to one or more still images that make up a video.
- the one or more attribute values may correspond to all still images, to one still image, or to multiple still images.
- the condition management unit 211 stores one or more selection conditions.
- One or more inspection conditions may be stored in the condition management unit 211. It is preferable that the selection conditions correspond to tags. Examples of tags are “crack in road,” “damage to bridge,” “damage to manhole,” “ fallen object,” and “identifier of fallen object.” Examples of “identifier of fallen object” are “tire,” “wood,” “unknown,” etc.
- Inspection conditions are conditions for determining still images that are used to determine whether or not they satisfy the selection conditions. By using inspection conditions, the number of times the selection condition judgment process is performed can be reduced, and overall processing costs can be reduced. Inspection conditions are conditions based on one or more attribute values corresponding to still images.
- the one or more attribute values are, for example, environmental information and attribute values of the road on which the mobile object is traveling.
- Environmental information here is, for example, position information, time information, weather information, temperature information and seasonal information.
- Road attribute values are, for example, road type identifiers (e.g., expressways) and point information.
- Position information is, for example, information identifying the location of a manhole and information identifying the location of a bridge.
- a selection condition is a condition for selecting a still image from a video.
- a selection condition is a condition related to the content of a still image.
- a selection condition may be that there is a crack in the road in the still image, that there is damage to a bridge in the still image, that there is damage to a manhole in the road in the still image, or that there is a fallen object on the road in the still image.
- the selection conditions for example, have a learning model for determining whether or not the selection conditions are met.
- the selection conditions for example, have an image for determining whether or not the selection conditions are met. It is preferable that the selection conditions, for example, have an image for determining whether or not the selection conditions are met and a similarity threshold.
- the similarity threshold is a similarity threshold between the still image and an image included in the selection conditions.
- the selection condition is, for example, that the similarity is within a threshold or greater than a threshold.
- a learning model is information constructed by the learning process of machine learning, and is information used in the prediction process of machine learning.
- a learning model is information obtained by executing a machine learning learning module using, for example, one or more positive example teacher data and one or more negative example teacher data.
- a learning model may also be called a learner, classification model, classifier, etc.
- Machine learning algorithms can be deep learning, random forest, decision tree, SVM, etc.
- various machine learning functions such as the TensorFlow library, the random forest module of the R language, TinySVM, and various existing libraries can be used.
- the training data for positive examples includes still images that meet the selection conditions.
- the training data for negative examples includes still images that do not meet the selection conditions.
- Still images that meet the selection conditions are, for example, still images that include a road with a crack, a damaged bridge, a damaged manhole, and a road with fallen objects.
- the images used to determine whether they meet the selection criteria are, for example, still images including a road with a crack, a damaged bridge, a damaged manhole, and a road with fallen objects.
- the mobile receiving unit 22 receives various types of information.
- the various types of information are, for example, one or more inspection conditions, and one or more combinations of selection conditions and tags.
- the movement processing unit 23 performs various types of processing.
- the various types of processing are, for example, processing performed by the position acquisition unit 231, the photographing unit 232, the determination unit 233, and the tag acquisition unit 234.
- the movement processing unit 23, for example, stores information received by the movement receiving unit 22 in the movement storage unit 21.
- the movement processing unit 23, for example, creates a data structure for outputting the information received by the movement receiving unit 22.
- the movement processing unit 23 may, for example, perform all the functions that a navigation terminal can perform.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires an attribute value set during shooting.
- the movement processing unit 23 stores the acquired attribute value set in the movement storage unit 21.
- the movement processing unit 23 also associates the acquired attribute value set with a moving image, for example.
- Associating with a moving image usually means associating with still images that make up the moving image. It is preferable that the attribute value set and the still images are synchronized in time.
- the attribute value set is, for example, one or more pieces of environmental information.
- the environmental information is, for example, location information, time information, weather information, temperature information, and seasonal information.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires time information from a clock (not shown), for example, during shooting.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires time information, for example, constantly, at predetermined intervals, or when a selection condition is met.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires time information from a clock (not shown) and acquires seasonal information corresponding to the time information.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires weather information, for example, during shooting.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires weather information corresponding to location information, for example, from a server not shown.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires weather information, for example, constantly, at predetermined intervals, or when acquisition conditions are met.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires temperature information, for example, during shooting.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires temperature information corresponding to location information, for example, from a server not shown.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires temperature information, for example, from a temperature sensor installed on a moving object.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires temperature information, for example, constantly, at predetermined intervals, or when a selection condition is met.
- the movement processing unit 23 is equipped with a microphone, for example, acquires sound information, and stores the sound information in association with the video acquired by the image capturing unit 232.
- a function is, for example, the function of a drive recorder.
- the location acquisition unit 231 acquires location information.
- the location acquisition unit 231 normally acquires location information during shooting.
- the location acquisition unit 231 acquires location information, for example, by using a GPS receiver that is held by the location acquisition unit 231.
- the location acquisition unit 231 acquires location information, for example, constantly, at predetermined intervals.
- the image capturing unit 232 captures video including still images while moving, and captures video that corresponds to the location information. It is preferable that the image capturing unit 232 captures the moving surface or the surrounding area while moving, and captures the video.
- the surrounding area is the range that the camera can capture. The surrounding area is, for example, a range within a threshold from the position indicated by the location information.
- the determination unit 233 determines whether or not a still image included in the video captured by the shooting unit 232 satisfies the selection conditions.
- the determination unit 233 determines whether some of the still images in the video satisfy the selection condition.
- the determination unit 233 determines whether only one still image out of N still images (N is a natural number equal to or greater than 2) in the video satisfies the selection condition.
- the judgment unit 233 acquires one or more attribute values corresponding to still images included in the video acquired by the image capture unit 232, judges whether or not the one or more attribute values match the inspection conditions, and judges whether or not the still images judged to match the inspection conditions satisfy the selection conditions.
- the judgment unit 233 extracts, for example, still images included in the video acquired by the image capture unit 232, and judges whether or not they match the inspection conditions.
- the attribute values here are, for example, location information, an identifier of a specific object in the still image, a road type identifier of the road on which the mobile object traveled, and location information specifying the location on which the mobile object traveled.
- the location information is, for example, information indicating the location of a manhole.
- the inspection condition is, for example, that the distance between the location information indicating the location of the manhole and the location information corresponding to the still image, which is the location information acquired by the location acquisition unit 231, is within a threshold value or is smaller than the threshold value.
- the determination unit 233 determines whether a still image included in the video acquired by the image capture unit 232 matches the inspection conditions. Next, the determination unit 233 may determine whether each of a plurality of consecutive still images including the still image determined to match the inspection conditions, for example, satisfies a selection condition. In such a case, when the determination unit 233 detects a plurality of still images that satisfy the selection condition, it may select a specific still image from the plurality of still images, or may acquire the plurality of consecutive still images.
- the specific still image is, for example, a still image in a specific order (for example, the middle) from among the plurality of consecutive still images, or a still image in which an object (for example, damage, a fallen object) is most prominently shown.
- each of the multiple consecutive still images including the still image determined to match the inspection conditions may be a still image following the still image determined to match the inspection conditions, or may be a still image preceding the still image determined to match the inspection conditions.
- the judgment unit 233 for example, provides a still image included in the video acquired by the imaging unit 232 and a learning model included in the selection conditions to a machine learning prediction module, executes the prediction module, and acquires a judgment result indicating whether or not the selection conditions are met. It is preferable that the judgment unit 233 also acquires a score here.
- the score is information output by the prediction module. It can be said that the score is, for example, the likelihood of the judgment result.
- the judgment result is, for example, "1" indicating that the selection conditions are met, or "0" indicating that the selection conditions are not met.
- the still image included in the video acquired by the imaging unit 232 is a still image that meets the inspection conditions.
- the judgment unit 233 also obtains an analysis result for a still image included in the video.
- the analysis result is, for example, an identifier of an object on a road in a still image.
- the identifier of the object is, for example, an identifier of a falling object.
- the identifier of a falling object is, for example, the name of the falling object or the ID of the falling object.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether or not a specific object is included in a still image included in the video, and judges whether or not a still image judged to include a specific object satisfies a selection condition.
- the specific object is, for example, a manhole or a fallen object.
- the fallen object is, for example, a tire, wood, or a plastic bottle, but is not limiting.
- the inclusion of a specific object may be considered to match the inspection condition.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether the still image satisfies each of the multiple selection conditions.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires a tag corresponding to the selection condition that the judgment unit 233 judges to be satisfied.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires the tag from the condition management unit 211. Note that the tag may also be considered as an attribute value.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires a tag, for example, by using the analysis result for the still image that the judgment unit 233 judges to satisfy the selection condition.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires, for example, an object identifier that is the analysis result.
- the mobile transmission unit 24 transmits various types of information to the information processing device 1.
- the various types of information are, for example, still images, videos, and sets of attribute values.
- the mobile transmission unit 24 may transmit videos including still images that the determination unit 233 has determined to satisfy the selection conditions to the information processing device 1.
- the image transmission unit 241 transmits the still image that the determination unit 233 determines satisfies the selection condition in association with the location information acquired by the location acquisition unit 231. It is preferable that the image transmission unit 241 transmits the still image that the determination unit 233 determines satisfies the selection condition in association with the location information and the rights holder identifier.
- the image transmission unit 241 may also transmit attribute values other than the location information in association with the still image.
- the attribute values other than the location information may be, for example, a tag, location information, a road type identifier, or time information, but are not limiting.
- the image transmitting unit 241 may transmit a video including a still image that the determining unit 233 has determined to satisfy the selection condition to the information processing device 1.
- a video is a still image that is consecutive to the still image that satisfies the selection condition, and preferably includes one or more still images before the still image that satisfies the selection condition and/or one or more still images after the still image that satisfies the selection condition.
- the image transmitting unit 241 normally transmits still images, etc. to the information processing device 1.
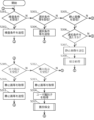
- the receiving unit 12 determines whether or not inspection conditions, etc. have been received from a terminal (not shown). If inspection conditions, etc. have been received, the process proceeds to S302, and if inspection conditions, etc. have not been received, the process proceeds to S303. Note that the inspection conditions, etc. are, for example, the inspection conditions and a tag.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the inspection conditions, etc. received in S301 to one or more mobile terminals 2 managed by the terminal management unit 111. Return to S301. Note that the processing unit 13 may store the inspection conditions, etc. in the storage unit 11.
- the receiving unit 12 judges whether or not selection conditions, etc. have been received from a terminal not shown. If selection conditions, etc. have been received, the process proceeds to S304, and if selection conditions, etc. have not been received, the process proceeds to S305.
- the selection conditions, etc. are, for example, selection conditions and tags.
- the selection conditions may include usage information used for selection. Usage information is, for example, a learning model and an image.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the selection conditions, etc. received in S303 to one or more mobile terminals 2 managed by the terminal management unit 111. Return to S301. Note that the processing unit 13 may store the selection conditions, etc. in the storage unit 11.
- the receiving unit 12 judges whether or not a still image or the like has been received from the mobile terminal 2. If a still image or the like has been received, the process proceeds to S306. If a still image or the like has not been received, the process proceeds to S309. Note that a still image or the like is, for example, a still image, a tag, a set of attribute values, and a rights holder identifier.
- the processing unit 13 determines whether the still image etc. received in S305 satisfies the notification condition. If the notification condition is met, the process proceeds to S307, and if the notification condition is not met, the process proceeds to S301.
- the processing unit 13 acquires notification destination information corresponding to the still image, etc. received in S305.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the still image, etc. received in S305 to the destination indicated by the notification destination information.
- the rights holder processing unit 132 performs preservation processing. Return to S301. An example of preservation processing will be explained using the flowchart in FIG. 4.
- the receiving unit 12 determines whether or not an output instruction has been received from the user terminal. If an output instruction has been received, the process proceeds to S311; if an output instruction has not been received, the process proceeds to S312.
- the processing unit 13 acquires access information for a still image or the like that corresponds to the output instruction. Next, the processing unit 13 acquires the still image or the like from the access destination indicated by the access information.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the still image etc. acquired in S310 to the user terminal that transmitted the output instruction.
- the receiving unit 12 determines whether or not a purchase instruction has been received from the user terminal. If a purchase instruction has been received, the process proceeds to S313, and if no purchase instruction has been received, the process returns to S301. Note that the purchase instruction is associated with the user identifier of the user who is the purchaser.
- the processing unit 13 acquires access information for a still image or the like corresponding to the purchase instruction. Next, the processing unit 13 acquires the still image or the like from the access destination indicated by the access information.
- the processing unit 13 acquires a user identifier corresponding to the purchase instruction.
- This user identifier is the identifier of the user who will purchase the still image.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 performs the fourth maintenance process. Return to S301. An example of the fourth maintenance process will be explained using the flowchart in FIG. 5.
- processing ends when the power is turned off or an interrupt occurs to end processing.
- the first security means 1321 acquires a rights holder identifier.
- a rights holder identifier is usually a rights holder identifier that is paired with the received still image.
- the rights holder identifier is a rights holder identifier that is paired with a tag that is paired with the received still image, and may be a rights holder identifier stored in the storage unit 11.
- Such a rights holder identifier is an identifier of a user who requires a still image.
- the first security means 1321 stores the received still images, etc., in association with the rights holder identifier acquired in S401.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 performs a fourth maintenance process.
- An example of the fourth maintenance process will be explained using the flowchart in FIG. 5.
- the reward means 1325 performs reward processing. Return to S301. An example of the reward processing will be explained using the flowchart in FIG. 6.
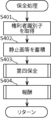
- the fourth security means 1324 acquires access information that identifies the storage destination of still images, etc.
- the fourth preservation means 1324 acquires a set of attribute values corresponding to the stored still images, etc.
- the fourth security means 1324 constructs security information having the access information acquired in S501, the attribute value set acquired in S502, and the right holder identifier of the still image, etc. If a new right holder identifier has been acquired, the fourth security means 1324 constructs security information including, for example, the new right holder identifier and the original right holder identifier. The new right holder identifier is usually the identifier of the user who needs the still image.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 accumulates the maintenance information configured in S503. The process returns to the upper level process. The fourth maintenance means 1324 accumulates the maintenance information in, for example, a block chain.
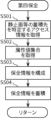
- the compensation means 1325 acquires one or more rights holder identifiers for the target still image, etc.
- the compensation means 1325 may also acquire the rights holder identifiers of the previous rights holders for the target still image, etc.
- the reward means 1325 acquires a set of attribute values of the target still image, etc.
- the reward means 1325 acquires a service identifier that identifies the service provided for the target still image, etc.
- the service identifier is, for example, "output” or "purchase.”
- the reward means 1325 obtains the reward amount using one or more pieces of information from the attribute value set obtained in S602 and the service identifier obtained in S603.
- the compensation means 1325 obtains a compensation amount for each rights holder identifier. If rights holder history information including multiple rights holder identifiers is obtained, the compensation means 1325 may obtain a compensation amount for each rights holder identifier.
- the reward means 1325 performs processing to give a reward to the rights holder identified by the rights holder identifier obtained in S601, in the amount of reward obtained in S604.
- the remuneration means 1325 performs a process of charging the user who has enjoyed the service related to the target still image, etc. with a remuneration. The process returns to the upper level process.
- the target still image, etc. is usually a video sent to the user terminal.
- the profits earned by the operator of the information processing device 1 may be acquired and accumulated.
- the reward means 1325 may obtain reward information corresponding to the tag paired with the target still image from the reward management unit 112, and use the reward information to obtain the reward amount.
- the mobile receiving unit 22 determines whether or not inspection conditions, etc. have been received from the information processing device 1. If inspection conditions, etc. have been received, the process proceeds to S702, and if inspection conditions, etc. have not been received, the process proceeds to S703. Note that the inspection conditions, etc. are, for example, the inspection conditions and a tag.
- the movement processing unit 23 stores the inspection conditions, etc. received in S701 in the condition management unit 211. Return to S701.
- selection conditions, etc. are, for example, selection conditions and tags. Selection conditions, etc. are, for example, selection conditions, usage information, and tags.
- the movement processing unit 23 stores the selection conditions and the like received in S703 in the condition management unit 211. Return to S701.
- the movement processing unit 23 judges whether or not the start of movement has been detected. If the start of movement has been detected, the process proceeds to S706, and if not, the process returns to S701. Note that the start of movement is determined, for example, by the engine of the moving object on which the mobile terminal 2 is installed being turned on, or the power supply of the mobile terminal 2 being turned on.
- the image capture unit 231 starts capturing images.
- the image capture unit 231 acquires the video and stores it in the mobile storage unit 21.
- the movement processing unit 23 acquires a set of attribute values of the mobile terminal 2. That is, the position acquisition unit 231 acquires current position information. The movement processing unit 23 also acquires other attribute values.
- the other attribute values are, for example, time information, weather information, temperature information, and season information.
- the movement processing unit 23 determines whether or not the i-th still image is present in the video acquired in S707. If the i-th still image is present, the process proceeds to S711; if not, the process proceeds to S716.
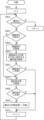
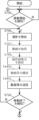
- the determination unit 233 performs a determination process for the i-th still image. An example of the determination process is described using the flowchart in FIG. 8.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires tags that are paired with one or more matching selection conditions from the mobile storage unit 21.
- the movement processing unit 23 composes information including still images and one or more tags. Note that here, the movement processing unit 23 may compose information having a plurality of still images including a still image that matches the selection conditions. It is preferable that all of the plurality of still images match the selection conditions, but it is also possible to include still images that do not match the selection conditions. It is preferable that the plurality of still images are still images that are consecutive in time.
- N is a natural number equal to or greater than 2. In other words, it is preferable to perform the determination process of FIG. 8 on the thinned still images.
- the movement processing unit 23 determines whether or not the information was configured in S714. If the information was configured, the process proceeds to S717; if not, the process proceeds to S720.
- the transfer processing unit 23 obtains the rights holder identifier from the transfer storage unit 21.
- the movement processing unit 23 uses the rights holder identifier and the information constructed in S714 to construct the information to be transmitted.
- the image transmission unit 241 transmits the information constructed in S718 to the information processing device 1.
- the movement processing unit 23 judges whether or not the end of the movement has been detected. If the end of the movement has been detected, the process returns to S701. If the end of the movement has not been detected, the process returns to S709. Note that the movement processing unit 23 detects the end of the movement by, for example, detecting the engine being turned off, the power supply being turned off of the mobile terminal 2, or the arrival at the destination.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether the i-th tag exists. If the i-th tag exists, the process proceeds to S803; if it does not exist, the process returns to the upper process.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether or not an inspection condition corresponding to the i-th tag exists. If the inspection condition exists, the process proceeds to S804; if it does not exist, the process proceeds to S807.
- the judgment unit 233 obtains the inspection conditions corresponding to the i-th tag.
- the judgment unit 233 acquires one or more attribute values from the attribute value set to be used for judging the inspection conditions acquired in S804.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether or not one or more attribute values acquired in S805 match the inspection conditions acquired in S804. If they match the inspection conditions, the process proceeds to S807, and if they do not match the inspection conditions, the process proceeds to S810.
- the judgment unit 233 acquires the selection conditions, etc., corresponding to the i-th tag.
- the selection conditions, etc. are, for example, the selection conditions and the usage information.
- the judgment unit 233 judges whether the still image being judged matches the selection condition acquired in S807. If the selection condition is met, the process proceeds to S809, and if the selection condition is not met, the process proceeds to S810.
- the still image to be judged here may be only the still image that matches the inspection conditions, but may also be multiple surrounding still images that include the still image that matches the inspection conditions.
- the multiple surrounding still images are usually multiple still images that are consecutive in time within a specified period of time, but may also be still images arbitrarily extracted within the specified period of time.
- the specified period is, for example, 10 seconds or 5 seconds.
- the judgment unit 233 assigns the value "match” to the variable "i-th judgment result” corresponding to the i-th tag. Note that the initial value of the "i-th judgment result” is "mismatch.”
- the terminal management unit 111 of the information processing device 1 stores terminal information including a terminal identifier and communication destination information for each of one or more mobile terminals 2. It is also assumed that the information processing device 1 transmits inspection conditions, selection conditions, etc. to the mobile terminal 2, and that the mobile terminal 2 receives and stores the inspection conditions, selection conditions, etc.
- the reward management unit 112 stores a reward management table having the structure shown in FIG. 9.
- the reward management table is a table that manages one or more pieces of reward management information.
- the reward management information has an "ID”, “tag”, “reward conditions”, “reward information”, and “notification destination information”.
- the "ID” is information that identifies a record.
- the “reward conditions” are the conditions under which a reward is generated.
- the “reward information” is an amount or points in this case.
- the “notification destination information” is information that indicates the notification destination of the user to whom a still image or the like corresponding to the tag is sent.
- the "notification destination information" is, for example, an email address, a telephone number, a fax number, a notification app ID, or an IP address of the user terminal used by the user.
- the notification destination is, for example, a person in a local government organization that develops measures against cracks in roads, damage to bridges, and damage to manholes, or a person in the Japan Highway Public Corporation that removes fallen objects from highways.
- the reward condition "first location” means that the location information corresponding to the selected still image is the first location information among one or more location information corresponding to still images that have already been received. Note that the location information that is not the first may be only location information that matches one or more location information corresponding to still images that have already been received, or may include location information where the difference between the two location information is within a threshold or less than a threshold.
- the score included in the reward condition is a score obtained by a machine learning prediction module.
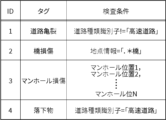
- the condition management unit 211 of the mobile terminal 2 stores the inspection condition management table shown in FIG. 10.
- the inspection condition management table stores one or more records having an "ID", "tag”, and "inspection condition”.
- the "ID” is information that identifies the record. It is preferable that the "inspection condition” is managed for each tag.
- the inspection condition is a collection of location information that indicates the location of each manhole.
- the test condition "Road type identifier "Expressway”” indicates that it applies only to expressways.
- the condition management unit 211 also stores a selection condition management table shown in FIG. 11.
- the selection condition management table stores one or more records having an "ID", "tag”, "usage information", and "selection condition”.
- the "usage information” is information used to determine whether or not a selection condition is met.
- the "usage information” is, for example, a learning model or an image.
- the image is an image from which the similarity to a still image included in a captured video is obtained.
- the "selection condition” is, for example, a condition based on a prediction result, a condition based on a prediction result and a score, or a condition based on the similarity between two images.
- the prediction result is the execution result (objective variable) of a machine learning prediction module.
- the score is a value obtained as a result of the execution of a prediction module.
- learning model 1 is information obtained by providing a machine learning learning module with a plurality of positive example images of a road portion with a crack and a plurality of negative example images of a road portion without a crack, and executing the learning module.
- Learning model 2 is information obtained by providing a machine learning learning module with a plurality of positive example images of a damaged bridge portion and a plurality of negative example images of a undamaged bridge portion, and executing the learning module.
- Learning model 3 is information obtained by providing a machine learning learning module with a plurality of positive example images of a damaged manhole and a plurality of negative example images of an undamaged manhole, and executing the learning module.
- the mobile terminal 2 when a mobile terminal 2 mounted on a vehicle detects a crack in the road, damage to a bridge, damage to a manhole, or a fallen object while the vehicle is traveling on a national road or expressway, the mobile terminal 2 transmits a still image of the detection, a rights holder identifier, and a set of attribute values to the information processing device 1.
- the image capture unit 232 of the mobile terminal 2 captures video. Then, while the car is traveling, the position acquisition unit 231 constantly acquires position information. Also, while the car is traveling, the movement processing unit 23 acquires a set of attribute values.
- the set of attribute values includes a road type identifier and location information. Note that the set of attribute values may also include other attribute values, such as time information. Note that the technology of acquiring the road type identifier and location information while traveling using the car's navigation function is a publicly known technology.
- the judgment unit 233 refers to the inspection condition management table (FIG. 10) according to the flowchart of FIG. 8, and judges whether each still image included in the captured video satisfies the inspection condition of any record. If the inspection condition of any record is satisfied, the judgment unit 233 refers to the selection condition management table (FIG. 11) according to the flowchart of FIG. 8, and acquires the usage information and selection conditions that are paired with the tag corresponding to the satisfied inspection condition. Next, the judgment unit 233 judges whether the selection conditions are satisfied using the still image that satisfies the inspection conditions and the acquired usage information and selection conditions.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires a tag that pairs with the matched selection condition.
- the movement processing unit 23 composes information including the still image that satisfies the selection condition, the attribute value set, the tag, and the rights holder identifier of the movement storage unit 21 (here, "U001").
- the image transmission unit 241 transmits the composed information to the information processing device 1.
- the attribute value set includes, for example, a tag, a road type identifier, point information, location information, etc.
- the information processing device 1 operates as follows, in accordance with the processing of the flowchart in FIG. 3. That is, the receiving unit 12 of the information processing device 1 receives still images, etc. from the mobile terminal 2.
- the still images, etc. include a rights holder identifier, a still image, and a set of attribute values including a tag.
- the received tag is, for example, "falling object, tire.”
- the processing unit 13 judges whether the still image etc. received in S305 satisfies the notification condition.
- the notification condition is that there is notification destination information corresponding to the received tag (not NULL "-").
- the processing unit 13 acquires the notification destination information "notification destination S4" that pairs with the tag "falling object, tire” from the reward management table (Fig. 9).
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the received still image etc. to the notification destination indicated by the notification destination information.
- the notification destination indicated by "notification destination S4" is a terminal (not shown) of a person in charge of the Japan Highway Public Corporation who is responsible for ensuring the safety of the expressway.
- the terminal of the person in charge receives and outputs the still image etc.
- the person in charge looks at the still image etc., heads to the position indicated by the position information that pairs with the still image, and performs the task of removing the fallen object from the expressway.
- the rights holder processing unit 132 of the information processing device 1 performs the preservation process as follows, in accordance with the operation of the flowchart in FIG. 4.
- the first security means 1321 acquires the rights holder identifier "U001" that transmitted the still image.
- the first security means 1321 stores the received still image etc. in the storage unit 11 in association with the rights holder identifier "U001.”
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 performs the fourth maintenance process as follows, according to the operation of the flowchart in FIG. 5. That is, first, the fourth maintenance means 1324 acquires access information (here, URL) that specifies the storage destination of the still images, etc. The fourth maintenance means 1324 also acquires a set of attribute values corresponding to the stored still images, etc. The fourth maintenance means 1324 also configures maintenance information having the URL, the set of attribute values, and the right holder identifier "U001" of the still images, etc. The fourth maintenance means 1324 also acquires the right holder identifier "X001" corresponding to the Japan Highway Public Corporation that requires the still images, etc.
- access information here, URL
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 also acquires a set of attribute values corresponding to the stored still images, etc.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 also configures maintenance information having the URL, the set of attribute values, and the right holder identifier "U001" of the still images, etc.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 also acquires the right holder
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 configures maintenance information including the right holder identifier "X001" and the original right holder identifier "U001", for example.
- the fourth maintenance means 1324 accumulates the constructed maintenance information in the blockchain. Note that the preservation information does not have to include the original rights holder identifier "U001".
- the remuneration means 1325 performs remuneration processing as follows, according to the operation of the flowchart in FIG. 6. First, the remuneration means 1325 acquires the right holder identifier "U001" of the target still image, etc. Next, the remuneration means 1325 acquires an attribute value set that is an attribute value set of the target still image, etc., and that includes the tag "falling object, tire”. Next, the remuneration means 1325 refers to the remuneration management table (FIG. 9) and acquires remuneration information "100 yen" corresponding to the tag "falling object, tire".
- the remuneration means 1325 performs processing to give the remuneration information "100 yen" to the right holder identified by the right holder identifier "U001".
- the remuneration means 1325 performs processing to have the organization of notification destination S4 (the organization corresponding to the right holder identifier "X001") that has enjoyed the service related to the target still image, etc., pay the remuneration "100 yen”.
- still images that meet the selection conditions can be selected from videos captured by the mobile terminal 2 and used. Also, according to this embodiment, still images that meet two or more selection conditions can be selected from videos captured by the mobile terminal 2 and used.
- still images that meet the inspection conditions are used as the selection conditions, making it possible to efficiently obtain the necessary still images.
- tags can be added to still images that meet the conditions.
- still images that meet certain conditions can be selected and used from videos captured on the surface on which the mobile terminal 2 is moving or in the vicinity of the surface on which the mobile terminal 2 is moving.
- still images that can confirm defects on the surface of the mobile terminal 2 or in the vicinity of the surface of the mobile terminal 2, such as cracks in the road, damage to a bridge, damage to a manhole, or fallen objects, can be selected and used.
- still images that meet the selection criteria can be received from videos captured by the mobile terminal 2 and stored.
- a still image can be automatically sent to a person who needs the still image.
- a still image can be automatically sent to a person who needs the still image immediately in response to receiving the still image, etc.
- the party providing the image is paid a fee, and the party using the image is granted rights, so that both parties can provide and use images without hindrance.
- the various processes in the various devices in this specification may be realized by software.
- This software may be distributed by software download or the like.
- This software may also be recorded on a recording medium such as a CD-ROM and distributed.
- the software that realizes the information processing device 1 in this embodiment is a program such as the one described below.
- this program causes a computer to function as a receiving unit that receives still images associated with location information from a mobile terminal 2, and as a storage unit that stores the still images received by the receiving unit in pairs with the location information.
- the software that realizes the mobile terminal 2 in this embodiment is the following program. That is, this program causes a computer to function as a location acquisition unit that acquires location information, a shooting unit that acquires, while moving, a video that includes still images and that corresponds to the location information, a determination unit that determines whether or not a still image included in the video acquired by the shooting unit satisfies a selection condition, and an image transmission unit that transmits the still image that the determination unit determines satisfies the selection condition, in association with the location information acquired by the location acquisition unit.
- the present embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that the information processing device receives a moving image from a mobile terminal and performs a determination process for selecting a still image that satisfies a selection condition from the moving image.
- the information processing device receives a moving image from a mobile terminal and performs a determination process for selecting a still image that satisfies a selection condition from the moving image.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram of information system B in this embodiment.
- Information system B includes an information processing device 3 and one or more mobile terminals 4.
- the information processing device 3 is, for example, a cloud server or an ASP server, but the type is not important.
- the information processing device 3 may also be a device that constitutes a blockchain.
- the information processing device 3 mainly performs processing related to images, so it may also be called an image processing device.
- the mobile terminal 4 is, for example, a drive recorder, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, a camera with communication functions, or a glasses-type camera.
- the information processing device 3 includes a storage unit 31, a receiving unit 32, a processing unit 33, and a transmitting unit 14.
- the storage unit 31 includes a terminal management unit 111, a reward management unit 112, and a condition management unit 211.
- the processing unit 33 includes a judgment unit 233, a tag acquisition unit 234, an accumulation unit 131, and a rights holder processing unit 132.
- the mobile terminal 4 includes a movement storage unit 41, a movement receiving unit 42, a movement processing unit 43, a movement transmitting unit 44, and a movement output unit 45.
- the movement processing unit 43 includes a position acquisition unit 231 and an imaging unit 232.
- the storage unit 31 constituting the information processing device 3 stores various types of information.
- the various types of information are, for example, sets of attribute values such as terminal information, reward information, detection conditions, selection conditions, videos, still images, and location information.
- the receiving unit 32 receives a video that includes multiple still images and is a video captured by the mobile terminal 4 while it is moving. Normally, a still image is associated with a set of attribute values that includes location information. However, a video may contain still images that are not associated with location information, etc.
- the processing unit 33 performs various types of processing. For example, the various types of processing are performed by the determination unit 233, the tag acquisition unit 234, the storage unit 131, and the rights holder processing unit 132.
- the determination unit 233 performs a determination process.
- the determination unit 233 determines whether or not a still image included in a video received by the receiving unit 32 satisfies a selection condition. The process of determining whether or not a selection condition is satisfied has been described in the first embodiment.
- the storage unit 131 stores the still image that the determination unit 233 has determined to satisfy the selection condition in association with an attribute value set including position information associated with the still image. Details of the storage unit 131 have been described in the first embodiment. ⁇ Details of components of mobile terminal 4>
- the mobile storage unit 41 that constitutes the mobile terminal 4 stores various types of information.
- the various types of information are, for example, videos, attribute value sets, rights holder identifiers, and map information.
- the mobile receiving unit 42 receives various types of information.
- the mobile receiving unit 42 receives information from the information processing device 3.
- the various types of information are, for example, reward information.
- the movement processing unit 43 performs various types of processing.
- the various types of processing are, for example, processing performed by the position acquisition unit 231 and the photographing unit 232.
- the movement processing unit 43 acquires a set of attribute values. This processing is the same as that of the movement processing unit 23, and has been described above.
- the movement processing unit 43 performs, for example, processing for a navigation terminal.
- Processing for a navigation terminal includes, for example, acquiring a road type identifier and acquiring location information corresponding to the current position.
- the mobile transmission unit 44 transmits various types of information to the information processing device 1.
- the various types of information are, for example, a video, a set of attribute values, and a rights holder identifier.
- the movement output unit 45 outputs various types of information.
- the various types of information include, for example, map information and video.
- output is a concept that includes displaying on a display, projecting using a projector, printing on a printer, outputting sound, sending to an external device, storing on a recording medium, and passing on the processing results to other processing devices or other programs, etc.
- the storage unit 31 and the mobile storage unit 41 are preferably non-volatile recording media, but can also be realized using volatile recording media.
- information may be stored in the storage unit 31, etc. via a recording medium, information transmitted via a communication line, etc. may be stored in the storage unit 31, etc., or information inputted via an input device may be stored in the storage unit 31, etc.
- the receiving unit 32 and the mobile receiving unit 42 are typically implemented using wireless or wired communication means, but may also be implemented using means for receiving broadcasts.
- the processing unit 33 and the movement processing unit 43 can usually be realized by a processor, memory, etc.
- the processing procedure of the processing unit 33, etc. is usually realized by software, and the software is recorded in a recording medium such as a ROM. However, they may also be realized by hardware (dedicated circuitry).
- the processor may be a CPU, MPU, GPU, etc., and the type is not important.
- the mobile transmitter 44 is typically implemented using wireless or wired communication means, but may also be implemented using broadcasting means.
- the movement output unit 45 may be considered to include or not include an output device such as a display, a speaker, etc.
- the movement output unit 45 may be realized by driver software for an output device, or a combination of driver software for an output device and an output device, etc. ⁇ Operation>
- the receiving unit 32 judges whether or not a video or the like has been received from the mobile terminal 4. If a video or the like has been received, the process proceeds to S1302. If a video or the like has not been received, the process proceeds to S309. Note that a video or the like is, for example, a video, a set of attribute values, and a rights holder identifier.
- the processing unit 33 obtains a set of attribute values associated with the video.
- the processing unit 23 determines whether or not the i-th still image is present in the video received in S1301. If the i-th still image is present, the process proceeds to S1305; if not, the process proceeds to S1310.
- the determination unit 233 performs a determination process for the i-th still image. An example of the determination process was explained using the flowchart in FIG. 8.
- the tag acquisition unit 234 acquires tags that are paired with each of the one or more matching selection conditions from the storage unit 31.
- the processing unit 33 composes information including still images and one or more tags. Note that here, the processing unit 33 may compose information having a plurality of still images including a still image that matches the selection conditions. It is preferable that all of the plurality of still images match the selection conditions, but it is also possible to include still images that do not match the selection conditions. It is preferable that the plurality of still images are still images that are consecutive in time.
- N is a natural number equal to or greater than 2. In other words, it is preferable to perform the judgment process on the thinned still images.
- the processing unit 33 determines whether or not information was configured in S1308. If information was configured, the process proceeds to S1311; if information was not configured, the process returns to S1301.
- the processing unit 33 configures the still images, etc. to be stored.
- the still images, etc. are, for example, one or more still images, a set of attribute values including tags, and a rights holder identifier.
- the processing unit 33 determines whether the stored still images, etc., match the notification conditions. If they match, the process proceeds to S1313; if they do not match, the process proceeds to S1314.
- the processing unit 13 acquires notification destination information corresponding to the still image, etc.
- the transmission unit 14 transmits the still image, etc. to the destination indicated by the notification destination information.
- the rights holder processing unit 132 performs preservation processing. Return to S1301. Note that an example of preservation processing was explained using the flowchart in FIG. 4.
- processing ends when the power is turned off or an interrupt occurs to end processing.
- the movement processing unit 43 composes information to be transmitted.
- This information includes video and the like.
- the video and the like is, for example, a video, a set of attribute values, and a rights holder identifier.
- the mobile transmission unit 44 transmits the information constructed in S1401 to the information processing device 3. Go to S720.
- processing ends when the power is turned off or an interrupt occurs to end processing.
- still images that meet the selection conditions can be selected from videos captured by the mobile terminal 4 and used. Also, according to this embodiment, still images that meet two or more selection conditions can be selected from videos captured by the mobile terminal 4 and used.
- still images that meet the inspection conditions are used as the selection conditions, making it possible to efficiently obtain the necessary still images.
- tags can be added to still images that meet the conditions.
- still images that meet certain conditions can be selected and used from videos captured on the surface on which the mobile terminal 4 is moving or in the vicinity of the surface on which the mobile terminal 4 is moving.
- still images that can confirm defects on the surface of the mobile terminal 4 or in the vicinity of the surface of the mobile terminal 4, such as cracks in the road, damage to a bridge, damage to a manhole, or fallen objects, can be selected and used.
- still images that meet the selection criteria can be received and stored from videos captured by the mobile terminal 4.
- a still image can be automatically sent to a person who needs the still image.
- a still image can be automatically sent to a person who needs the still image immediately in response to receiving a still image, etc.
- FIG. 15 also shows the appearance of a computer that executes the programs described in this specification to realize the information processing device 1, mobile terminal 2, information processing device 3, and mobile terminal 4 of the various embodiments described above.
- the above-mentioned embodiments can be realized by computer hardware and a computer program executed thereon.
- FIG. 15 is an overview of this computer system 300
- FIG. 16 is a block diagram of system 300.
- computer system 300 includes computer 301, which includes a CD-ROM drive, keyboard 302, mouse 303, and monitor 304.
- computer 301 in addition to CD-ROM drive 3012, computer 301 includes MPU 3013, bus 3014 connected to CD-ROM drive 3012 etc., ROM 3015 for storing programs such as a boot-up program, RAM 3016 connected to MPU 3013 for temporarily storing application program instructions and providing temporary storage space, and hard disk 3017 for storing application programs, system programs, and data.
- computer 301 may further include a network card that provides connection to a LAN.
- a program that causes computer system 300 to execute the functions of information processing device 1 and the like of the above-mentioned embodiment may be stored on CD-ROM 3101, inserted into CD-ROM drive 3012, and then transferred to hard disk 3017.
- the program may be sent to computer 301 via a network (not shown) and stored on hard disk 3017.
- the program is loaded into RAM 3016 when executed.
- the program may be loaded directly from CD-ROM 3101 or the network.
- the program does not necessarily have to include an operating system (OS) that causes the computer 301 to execute the functions of the information processing device 1 of the above-mentioned embodiment, or a third-party program, etc.
- OS operating system
- the program only needs to include an instruction portion that calls appropriate functions (modules) in a controlled manner to obtain the desired results. How the computer system 300 operates is well known, and a detailed description will be omitted.
- the steps of transmitting information and receiving information do not include processing performed by hardware, such as processing performed by a modem or interface card in the transmission step (processing that can only be performed by hardware).
- the computer that executes the above program may be a single computer or multiple computers. In other words, it may perform centralized processing or distributed processing.
- multiple communication means present in one device may be realized physically by one medium.
- each process may be realized by centralized processing in a single device, or may be realized by distributed processing in multiple devices.
- the mobile terminal of the present invention has the effect of being able to select and use still images that meet certain conditions from videos captured by the mobile terminal, making it useful as a drive recorder installed in an automobile, etc.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/044354 WO2024116366A1 (ja) | 2022-12-01 | 2022-12-01 | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 |
| JP2024561092A JP7654174B2 (ja) | 2022-12-01 | 2022-12-01 | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 |
| US19/096,721 US12360718B1 (en) | 2022-12-01 | 2025-04-01 | Mobile terminal, information processing device and information processing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/044354 WO2024116366A1 (ja) | 2022-12-01 | 2022-12-01 | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024116366A1 true WO2024116366A1 (ja) | 2024-06-06 |
Family
ID=91323461
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/044354 Ceased WO2024116366A1 (ja) | 2022-12-01 | 2022-12-01 | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US12360718B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7654174B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2024116366A1 (enExample) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018018461A (ja) * | 2016-07-29 | 2018-02-01 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | 情報処理装置、表示装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2020184322A (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2020-11-12 | トヨタ モーター ノース アメリカ,インコーポレイティド | 利害関係者との間における車両データの共有 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6647171B2 (ja) | 2016-07-29 | 2020-02-14 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| US10783600B2 (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2020-09-22 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Method and system using a blockchain database for data exchange between vehicles and entities |
| US20220187847A1 (en) * | 2019-11-05 | 2022-06-16 | Strong Force Vcn Portfolio 2019, Llc | Robot Fleet Management for Value Chain Networks |
| JP2022072963A (ja) | 2020-10-30 | 2022-05-17 | ダイナミックマップ基盤株式会社 | 情報処理方法、プログラム、及び情報処理装置 |
-
2022
- 2022-12-01 WO PCT/JP2022/044354 patent/WO2024116366A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2022-12-01 JP JP2024561092A patent/JP7654174B2/ja active Active
-
2025
- 2025-04-01 US US19/096,721 patent/US12360718B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018018461A (ja) * | 2016-07-29 | 2018-02-01 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | 情報処理装置、表示装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2020184322A (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2020-11-12 | トヨタ モーター ノース アメリカ,インコーポレイティド | 利害関係者との間における車両データの共有 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US12360718B1 (en) | 2025-07-15 |
| US20250231727A1 (en) | 2025-07-17 |
| JPWO2024116366A1 (enExample) | 2024-06-06 |
| JP7654174B2 (ja) | 2025-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9898810B2 (en) | Digital media enhancement system, method, and apparatus | |
| CN102509310B (zh) | 一种结合地理信息的视频追踪分析方法及系统 | |
| US10943135B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, image delivery system, information processing method, and computer-readable recording medium | |
| Barnas et al. | A pilot (less) study on the use of an unmanned aircraft system for studying polar bears (Ursus maritimus) | |
| US20200066146A1 (en) | Information system, information processing method, and non-transitory storage medium | |
| US9852343B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, display method, and storage medium | |
| Patterson et al. | Evaluation of an unmanned aircraft system for detecting surrogate caribou targets in Labrador | |
| JP6849256B1 (ja) | 3次元モデル構築システム、および3次元モデル構築方法 | |
| US20200117941A1 (en) | Real-time micro air-quality indexing | |
| JP7654174B2 (ja) | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 | |
| Pedersen et al. | Geolocating traffic signs using crowd-sourced imagery | |
| JP7667921B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 | |
| JP7733427B2 (ja) | 情報システム | |
| JP2008242682A (ja) | メタ情報自動付与システム、メタ情報自動付与方法、及びメタ情報自動付与プログラム | |
| JP7738782B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、ユーザ端末、および情報処理方法 | |
| JP7681812B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、ユーザ端末、および情報処理方法 | |
| US20250252753A1 (en) | Information processing device, mobile terminal, user terminal and information processing method | |
| JP7717434B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、移動端末、情報処理方法、およびプログラム | |
| WO2024195107A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 | |
| WO2024161606A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、ユーザ端末、および情報処理方法 | |
| WO2024134861A1 (ja) | 移動端末、情報処理装置、および情報処理方法 | |
| JP2025085532A (ja) | マップ更新装置、マップ更新方法、およびプログラム | |
| WO2024161605A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、ユーザ端末、および情報処理方法 | |
| WO2023084809A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び、情報処理プログラム | |
| CN117319785A (zh) | 车载短视频拍摄生成方法、装置、设备及存储介质 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22967199 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2024561092 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 22967199 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |