WO2022074992A1 - 医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 - Google Patents
医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022074992A1 WO2022074992A1 PCT/JP2021/032880 JP2021032880W WO2022074992A1 WO 2022074992 A1 WO2022074992 A1 WO 2022074992A1 JP 2021032880 W JP2021032880 W JP 2021032880W WO 2022074992 A1 WO2022074992 A1 WO 2022074992A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- image
- medical
- images
- switching
- image processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0012—Biomedical image inspection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
- A61B1/045—Control thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/94—Hardware or software architectures specially adapted for image or video understanding
- G06V10/945—User interactive design; Environments; Toolboxes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/98—Detection or correction of errors, e.g. by rescanning the pattern or by human intervention; Evaluation of the quality of the acquired patterns
- G06V10/987—Detection or correction of errors, e.g. by rescanning the pattern or by human intervention; Evaluation of the quality of the acquired patterns with the intervention of an operator
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/20—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for handling medical images, e.g. DICOM, HL7 or PACS
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/40—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for processing medical images, e.g. editing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/20—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for computer-aided diagnosis, e.g. based on medical expert systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10024—Color image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10068—Endoscopic image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20092—Interactive image processing based on input by user
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30096—Tumor; Lesion
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30168—Image quality inspection
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V2201/03—Recognition of patterns in medical or anatomical images
- G06V2201/034—Recognition of patterns in medical or anatomical images of medical instruments
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a medical image processing device for acquiring a key image for a report and a method for operating the medical image processing device.
- doctors diagnose patients while operating equipment during endoscopy and ultrasonography. After the diagnosis, a key image including a region of interest to be included in the report is acquired from the acquired inspection image. Since the criteria and rules for the key images to be included in the report differ depending on the facility or doctor, the doctor himself selects the key images from the inspection images taken in large quantities at the time of diagnosis.
- Patent Document 1 describes that the frame image of a site such as bleeding is automatically highlighted, and that the image frame before and after the image frame selected by the user in the list display is reproduced.
- the frame image of a site such as bleeding is automatically highlighted to make it easier for the user to identify a key image candidate. Further, by displaying before and after the image frame selected by the user, it is easy to identify a similar image suitable for the key image more than the key image candidate selected by the user. However, if there is no image having the characteristics desired by the user among the automatically displayed images, the burden may not be reduced.
- the medical image processing apparatus of the present invention comprises a processor, which acquires a plurality of medical images, classifies the medical images into at least one of a plurality of categories, and is among a plurality of medical images based on the result of the classification. At least one image of Instead, a non-automatically selected image other than the automatically selected image among a plurality of medical images classified into categories is switched and displayed as a switching image.
- the processor is characterized in that the switching image is switched and displayed from the selected image according to a plurality of categories.
- the processor is characterized in that the switching images classified into the same category as the selected images are switched and displayed.
- the processor displays a plurality of switching candidate images that are candidates for switching images on the screen and accepts user input for determining a switching image from the displayed plurality of switching candidate images.
- the switching candidate image includes an image of the same category as the selected image.
- the processor is characterized in that when the switching image is selected from a plurality of medical images according to the category of the automatically selected images, the imaging conditions of the medical images are taken into consideration.
- the processor is characterized in that the diagnostic usefulness of the medical image is added when the switching image is selected from a plurality of medical images according to the category of the automatically selected image.
- the processor displays each image with character or symbol information according to the category.
- the processor changes the display mode of each image according to the category.
- the processor displays the switching image and the automatically selected image in different modes.
- the processor accepts an input for approving each image displayed on the screen as a key image and displays it in a different manner depending on whether or not the approval is accepted.
- the processor classifies images according to a trained CNN model obtained by learning using an image group including a plurality of medical images.
- the category is preferably information about the part of the subject.
- the category is preferably information regarding whether or not the image includes a region of interest.
- the category is preferably information regarding whether or not the image contains the treatment tool or the type of the treatment tool included.
- the category is preferably information about the spraying state of the dye or dye in the image.
- the method of operating the medical image processing apparatus of the present invention includes a step of acquiring a plurality of medical images, a step of classifying the medical image into at least one of a plurality of categories, and a plurality of medical images based on the result of the classification.
- a step of displaying at least one of the images on the screen as an automatically selected image a step of accepting an input for the user to select an image requiring reselection as a key image from the displayed automatically selected images, and a selected image.
- it has a step of switching and displaying a non-automatically selected image other than the automatically selected image among a plurality of medical images classified into categories as a switching image.
- the present invention reduces the burden on the user when the user selects an image to be used as a report from a large number of medical images, and supports the creation of a report.
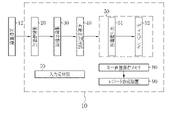
- the medical image processing apparatus 10 programs related to various processes are incorporated in a program memory (not shown).
- the medical image processing apparatus 10 is provided with a central control unit (not shown) configured by a processor.
- the central control unit By executing the program in the program memory by the central control unit, the image acquisition unit 20, the image classification unit 30, the usefulness determination unit 40, the image display unit 50, the display control unit 51, the input reception unit 70, and the key image storage are executed.
- the functions of the memory 80 and the report creation device 90 are realized.
- the image acquisition unit 20 acquires a plurality of medical images 12 from the endoscope system 11 and transmits them to the image classification unit 30. Find the key image 13 used to create the report from the medical images 12.
- the key image 13 is an image to be posted in the report so that the test results can be conveyed at a glance, and it is preferable that the features such as lesions are clear.
- the image classification unit 30 extracts the image information of the medical image 12 transmitted from the image acquisition unit 20, acquires category information, and calculates image quality information.
- the medical images 12 are classified into each category according to the acquired category information.
- the categories to be classified are any or a combination of the imaging site, the presence / absence and type of lesion, the state of use of the treatment tool, the state of spraying the pigment agent, and the like.
- image quality information information such as image brightness, noise, and degree of blurring is acquired and attached to the medical image 12.
- Image information is extracted using a trained CNN (Convolutional neural network) model.
- the trained CNN model is obtained by training with an image group containing at least a plurality of medical images 12.
- the category information and the image quality information acquired at the time of photographing by the endoscope system 11 and attached to the medical image 12 have priority over the information extracted by the trained CNN model.
- the medical image 12 after categorization is transmitted to the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the usefulness determination unit 40 determines the diagnostic usefulness of the medical image 12 based on the classification result and the image quality information obtained by the image classification unit 30. The higher the diagnostic usefulness, the more likely it is that the image is suitable for the key image 13.
- the evaluation of usefulness is expressed by, for example, a graded evaluation. It can be evaluated that the medical image 12 having an item such as a lesion in the classification result of the category and having a low degree of blur in the image quality evaluation is highly useful. If there is no category information, the degree of blurring is large, the brightness is too high, or the brightness is too low, the usefulness is low.
- the medical image 12 whose usefulness has been determined is transmitted to the image display unit 50. The usefulness is evaluated, and the evaluation threshold can be set arbitrarily by the user.
- the medical image 12 transmitted from the usefulness determination unit 40 by the display control unit 51 is displayed on the display 52 according to the classified categories.
- the input receiving unit 70 accepts user input such as image selection for switching display, page change, embodiment switching, category display switching, layout change, and key image saving.
- the key image storage memory 80 stores the key image 13 used for the report.
- the report creation device 90 creates a report of inspection results using the key image 13. It is preferable that the report is automatically created after the key image 13 is acquired.
- the endoscope system 11 acquires a large amount of medical images 12 by the light source device 11a, the endoscope 11b, and the processor device 11c.
- the endoscope system 11 is connected to the medical image processing device 10, and the acquired medical image 12 is transmitted to the medical image processing device 10.
- the medical image 12 transmitted from the endoscope system 11 is received by the image acquisition unit 20 and sent to the image display unit 50 via the image classification unit 30 and the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the image display unit 50 includes a display control unit 51 and a display 52.
- the image display unit 50 at least one image of the medical images 12 classified by category in the image classification unit 30 is selected as the automatically selected image 54.
- the automatically selected image 54 is an image selected according to the results of categorization and usefulness determination, and is an image that can be a candidate for the key image 13 to be posted in the report.
- the automatically selected image 54 is displayed on the display 52.
- the displayed automatically selected image 54 is approved as the key image 13 by the user input received by the input receiving unit 70, and is stored in the key image storage memory 80.
- the acquired medical image 12 is displayed as an automatically selected image 54 according to the category classified in the display 52.
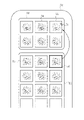
- the display 52 is provided with an image display field 53, in which the automatically selected images 54 are displayed in a list.
- the automatically selected image 54 is preferably selected so as to include all the predetermined categories, and the automatically selected image 54 displayed in the list is evaluated to have a certain degree of usefulness or more, and the image was acquired. It is preferably in chronological order.
- the display 52 has a cursor 71, a display switching button 73, and an approval button 74 that reflect user operations such as mouse operations.
- the key image 13 when the key image 13 has an image requiring reselection from the automatically selected images 54 listed in the image display field 53 of the display 52, the image needs to be reselected by operating the mouse or the like.
- the selected image 55 is set via the cursor 71.
- the selected image 55 switches and displays an image automatically selected from the image group not displayed in the list as the switching image 56 based on the category information.
- the image requiring reselection for the key image 13 is an image in which the approval of the key image 13 is suspended at the user's discretion and is temporarily hidden. In some cases, the switching image 56 and the switching display are displayed, and then the original image is restored.
- the image selected as the switching image 56 is "an image of the same imaged part as the selected image 55", “an image of a part close to the imaged part of the selected image 55", and "if the selected image 55 is using the treatment tool, the treatment tool is not used”. "Image”, “an image in which the dye is not sprayed if the selected image 55 is being dyed”, “an image in the same light source mode as the selected image 55", and the like.
- the switching image 56 may be selected in consideration of information on the imaging time of the image, the imaging mode (enlarged or non-enlarged, etc.), or diagnostic usefulness by image quality evaluation. Specifically, there are “images with close shooting time”, “images with a low degree of blur”, “images with appropriate brightness”, and the like.
- the switching image 56 emphasizes the frame of the image so that the switching display can be discriminated at a glance.
- the approval of the key image 13 by selecting the approval button 74 is performed collectively for the displayed images. When it is not necessary to switch and display, all the automatically selected images 54 displayed first are approved as the key images 13 as they are.
- FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing changes in display switching between the selected image 55 and the switching image 56.
- the display control unit 51 detects the switching image 56 to be switched and displayed from the category in which the selected image 55 is classified, the attached image quality information, and the like.
- the switching image 56 is detected from among the non-automatically selected images 57 other than the automatically selected image 54 among the medical images 12 classified by category by the image classification unit 30.
- the category-classified image group 58 is composed of an automatically selected image group 59 including an automatically selected image 54 obtained by automatic selection and a non-automatically selected image group 60 not selected as the automatically selected image 54. ..
- the switching image 56 is automatically selected from the non-automatic selection image group 60.
- the approval button 74 is pressed.
- the images displayed in the list are collectively saved as the key image 13 in the key image storage memory 80, and are also sent to the report creation device 90, and each key image 13 is sent. Used for reporting.
- FIG. 6 describes a display mode of the automatically selected image 54 and the switching image 56 displayed in the image display field 53.
- the display control unit 51 visualizes the category information and displays it along with each image. Further, the display may be turned on / off or the information to be displayed may be switched by the display switching button 73. For example, assuming that the normal display is "display a", in “display b", the image information display field 61 is expanded at the bottom of each image displayed in the image display field 53, and the category in which each image is classified is displayed as characters. Display with. Further, in the "display c", the evaluation of the usefulness calculated by the usefulness determination unit 40 is displayed in the image information display column 61. By utilizing the above display form, a more appropriate key image 13 can be selected. Further, a form in which the above display forms are combined may be provided and displayed.
- FIG. 7 describes another pattern of approval processing by the approval button 74.
- the approval process for the key image 13 is collectively performed for the image 4 in the image display field 53, but the displayed images may be individually approved one by one. In that case, it is necessary to display the approved image and the unapproved image so as to distinguish them. For example, it is possible to know at a glance that an image that has undergone approval processing has been approved by using a display pattern such as a shaded display, surrounding the image, or placing a mark on the image.
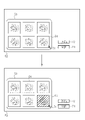
- the approved key image 13 is transmitted to the report creating device 90 and used for creating the report 91.
- the screen display of the display 52 is switched from the image display field 53 to the report 91, and the user can create the report 91 immediately after the approval of the key image 13.
- patient information, user information, etc. that have been input in advance are automatically input.
- the user inputs the findings in the finding input field 92 and creates a report.
- the user selects the selected image 55 that needs to be reselected in the categorized state.
- a switching candidate image display field 62 for displaying a list of a plurality of switching candidate images 63 on the display 52 instead of switching and displaying the switching image 56 is expanded, and the user switches a plurality.
- the switching image 56 is selected from the candidate images 63.
- the expansion of the switching candidate image display field 62 ends, and the selection image 55 and the switching image 56 are switched.
- the key image 13 that reflects the user's preference can be selected for the report as compared with the first embodiment.
- the switching candidate image 63 does not display all the medical images 12 that are not displayed in the list, but is a part of the image group selected based on the category of the selected images 55.
- the image group of the switching candidate image 63 displayed in the switching candidate image display field 62 is "an image group of the same shooting area as the selected image 55", “an image group of a part close to the selected image 55 and the shooting part", and "selected image”. Examples include “an image group in which the treatment tool is not used if 55 is in use of the treatment tool” and “an image group in which the dye is not sprayed if the selected image 55 is being dyed”. Further, the image group to be displayed as the switching candidate image 63 may not display all the medical images 12 that match the above conditions, but may be configured to display only a predetermined number of them. As a result, the number of sheets to be confirmed at the time of selection is limited, so that the work load can be further reduced. Further, a predetermined number of images may be selected in consideration of the image shooting time, the shooting mode, and the diagnostic usefulness by the image quality evaluation.
- the switching candidate image 63 displayed in a list displays another switching candidate image 63 by operating the page switching button 75 provided on the switching candidate image display field 62 in the same manner. Can be done.
- the page switching button 75 has two "forward" and “back", and the user can arbitrarily operate the page switching button 75 to switch pages. Further, it is preferable to describe the displayed page number in the center of the page switching button. It is preferable that the page switching is displayed in the same category as the switching candidate image 63, starting with the one judged to be highly useful.
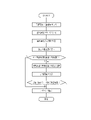
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing a series of flow of switching and displaying the selected image to the switching image.
- the medical image processing device 10 acquires a medical image 12 taken by the endoscope system 11 at the image acquisition unit 20.
- the acquired medical image 12 is transmitted to the image classification unit 30 to classify the categories.
- the image classification unit 30 extracts the image information of the medical image 12, attaches it to the original medical image 12 as category information and image quality information, and classifies each medical image 12 into a predetermined category based on the category information.
- Image information is extracted by a trained CNN (Convolutional neural network) model.
- the medical image 12 after categorization is transmitted to the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the usefulness determination unit 40 determines the usefulness from the category information and the image quality information of the medical image 12, and attaches the determination result to the original medical image 12.
- the medical image 12 after the usefulness determination is transmitted to the image display unit 50.
- the image display unit 50 displays a list of medical images 12 on the display 52 as automatically selected images 54 according to the results of categorization and usefulness determination. It is preferable that the images to be listed are selected so as to include all the predetermined categories and have a high evaluation in the determination of usefulness.
- the user observes whether there is an image requiring reselection in the key image 13 from the automatically selected images 54 displayed in the list, selects the image if there is, and switches and displays the image to another image. If not, select the approval button 74.
- the switching image 56 that has been switched and displayed is preferably selected according to the category and usefulness of the selected image 55, and is highly useful.
- the reselection of the switching image 56 is repeated until the switching image 56 can be approved by the key image 13.
- the approval button 74 is selected.
- the key image 13 is transmitted to the key image storage memory 80 and transmitted to the report creation device 90.
- various processes such as an image acquisition unit 20, an image classification unit 30, a usefulness determination unit 40, an image display unit 50, a display control unit 51, an input reception unit 70, a key image storage memory 80, and a report creation device 90.
- the hardware structure of the processing unit that executes the above is various processors as shown below.
- Various processors include CPU (Central Processing Unit), GPU (Graphical Processing Unit), FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), which are general-purpose processors that execute software (programs) and function as various processing units.
- PLD Programmable Logic Device
- a processing unit may be composed of one of these various processors, or a combination of two or more processors of the same type or different types (for example, a plurality of FPGAs, a combination of a CPU and an FPGA, or a CPU and a combination of two or more processors. It may be composed of a combination of GPUs, etc.). Further, a plurality of processing units may be configured by one processor. As an example of configuring a plurality of processing units with one processor, first, as represented by a computer such as a client or a server, one processor is configured by a combination of one or more CPUs and software. There is a form in which this processor functions as a plurality of processing units.
- SoC System On Chip
- the various processing units are configured by using one or more of the above-mentioned various processors as a hardware-like structure.
- the hardware-like structure of these various processors is, more specifically, an electric circuit (circuitry) in which circuit elements such as semiconductor elements are combined.
- the hardware structure of the storage unit is a storage device such as an HDD (hard disk drive) or SSD (solid state drive).
- Medical image processing device 11 Endoscope system 11a Light source device 11b Endoscope 11c Processor device 12 Medical image 13 Key image 20 Image acquisition unit 30 Image classification unit 40 Usefulness determination unit 50 Image display unit 51 Display control unit 52 Display 53 Image display field 54 Automatic selection image 55 Selected image 56 Switching image 57 Non-automatic selection image 58 Category classified image group 59 Automatic selection image group 60 Non-automatic selection image group 61 Image information display field 62 Switching candidate image display field 63 Switching candidate image 70 Input reception unit 71 Cursor 73 Display switching button 74 Approval button 75 Page switching button 80 Key image storage memory 90 Report creation device 91 Report 92 Findings input field
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202180068968.6A CN116324572A (zh) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | 医疗图像处理装置及其工作方法 |
| EP21877295.2A EP4227725A4 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | MEDICAL IMAGE PROCESSING DEVICE AND METHOD OF OPERATING THE SAME |
| JP2022555314A JPWO2022074992A1 (enExample) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | |
| US18/297,402 US20230245312A1 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2023-04-07 | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-171577 | 2020-10-09 | ||
| JP2020171577 | 2020-10-09 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US18/297,402 Continuation US20230245312A1 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2023-04-07 | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022074992A1 true WO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2022-04-14 |
Family
ID=81126460
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/032880 Ceased WO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | 医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230245312A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP4227725A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2022074992A1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN116324572A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2022074992A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114724669A (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2022-07-08 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009008125A1 (ja) | 2007-07-12 | 2009-01-15 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | 画像処理装置、該動作方法及び該プログラム |
| WO2018225448A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-09 | 2018-12-13 | 智裕 多田 | 消化器官の内視鏡画像による疾患の診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム及びこの診断支援プログラムを記憶したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| WO2019039354A1 (ja) * | 2017-08-23 | 2019-02-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 光源装置及び内視鏡システム |
| WO2019064704A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-04 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡画像観察支援システム、内視鏡画像観察支援装置、内視鏡画像観察支援方法 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015076004A1 (ja) * | 2013-11-21 | 2015-05-28 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | 画像表示装置 |
| CN106455947A (zh) * | 2014-09-22 | 2017-02-22 | 奥林巴斯株式会社 | 图像显示装置、图像显示方法以及图像显示程序 |
| US10482313B2 (en) * | 2015-09-30 | 2019-11-19 | Siemens Healthcare Gmbh | Method and system for classification of endoscopic images using deep decision networks |
| JP6975241B2 (ja) * | 2017-08-24 | 2021-12-01 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 医療画像処理装置及び医療画像処理装置の作動方法 |
| CN113543694B (zh) * | 2019-03-08 | 2024-02-13 | 富士胶片株式会社 | 医用图像处理装置、处理器装置、内窥镜系统、医用图像处理方法、及记录介质 |
-
2021
- 2021-09-07 EP EP21877295.2A patent/EP4227725A4/en active Pending
- 2021-09-07 WO PCT/JP2021/032880 patent/WO2022074992A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2021-09-07 JP JP2022555314A patent/JPWO2022074992A1/ja active Pending
- 2021-09-07 CN CN202180068968.6A patent/CN116324572A/zh active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-04-07 US US18/297,402 patent/US20230245312A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009008125A1 (ja) | 2007-07-12 | 2009-01-15 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | 画像処理装置、該動作方法及び該プログラム |
| WO2018225448A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-09 | 2018-12-13 | 智裕 多田 | 消化器官の内視鏡画像による疾患の診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム及びこの診断支援プログラムを記憶したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| WO2019039354A1 (ja) * | 2017-08-23 | 2019-02-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 光源装置及び内視鏡システム |
| WO2019064704A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-04 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡画像観察支援システム、内視鏡画像観察支援装置、内視鏡画像観察支援方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP4227725A4 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114724669A (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2022-07-08 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
| CN114724669B (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2023-08-22 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP4227725A1 (en) | 2023-08-16 |
| JPWO2022074992A1 (enExample) | 2022-04-14 |
| CN116324572A (zh) | 2023-06-23 |
| EP4227725A4 (en) | 2024-04-10 |
| US20230245312A1 (en) | 2023-08-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101203747B (zh) | 用于数字x光影像软拷贝解读的智能化定性与定量分析的方法和系统 | |
| US20210295510A1 (en) | Heat map based medical image diagnostic mechanism | |
| US20060291708A1 (en) | Digital medical image analysis | |
| KR20200118502A (ko) | 초음파 검사를 주석화하기 위한 방법 및 장치 | |
| US20230100147A1 (en) | Diagnosis support system, diagnosis support method, and storage medium | |
| US20240013524A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus, method of operating information processing apparatus, and program for operating information processing apparatus | |
| US20230245312A1 (en) | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof | |
| JP2022190920A (ja) | 情報処理装置、クラス判定方法、プログラム | |
| JP2011215680A (ja) | 病理診断支援装置、病理診断支援方法、病理診断支援のための制御プログラムおよび該制御プログラムを記録した記録媒体 | |
| US20230245758A1 (en) | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof | |
| JP6336252B2 (ja) | レポート作成支援装置、その制御方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP6903041B2 (ja) | 表示制御装置、表示制御方法、及び表示制御プログラム | |
| JP7109910B2 (ja) | 読影レポート作成支援装置及び読影レポート作成支援方法 | |
| US20230222663A1 (en) | Medical imaging apparatus and operation method for medical imaging apparatus | |
| JP7642585B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置及び画像処理方法 | |
| US20250139773A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program | |
| JP7388284B2 (ja) | 類似症例検索プログラム、類似症例検索方法及び類似症例検索システム | |
| US20230317249A1 (en) | Medical support device, and operation method and operation program of medical support device | |
| US20230025181A1 (en) | Medical diagnosis assistance system and method | |
| JP7409211B2 (ja) | 類似症例検索プログラム、類似症例検索方法及び類似症例検索システム | |
| JP2023075195A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理装置の制御方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP2023029106A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、およびプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21877295 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022555314 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021877295 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20230509 |