WO2022074992A1 - 医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 - Google Patents
医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022074992A1 WO2022074992A1 PCT/JP2021/032880 JP2021032880W WO2022074992A1 WO 2022074992 A1 WO2022074992 A1 WO 2022074992A1 JP 2021032880 W JP2021032880 W JP 2021032880W WO 2022074992 A1 WO2022074992 A1 WO 2022074992A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- image
- medical
- images
- switching
- image processing
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 47
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title abstract description 10
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 238000013527 convolutional neural network Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000013441 quality evaluation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000740 bleeding effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001839 endoscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002604 ultrasonography Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0012—Biomedical image inspection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
- A61B1/045—Control thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/94—Hardware or software architectures specially adapted for image or video understanding
- G06V10/945—User interactive design; Environments; Toolboxes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/98—Detection or correction of errors, e.g. by rescanning the pattern or by human intervention; Evaluation of the quality of the acquired patterns
- G06V10/987—Detection or correction of errors, e.g. by rescanning the pattern or by human intervention; Evaluation of the quality of the acquired patterns with the intervention of an operator
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/20—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for handling medical images, e.g. DICOM, HL7 or PACS
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/40—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for processing medical images, e.g. editing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/20—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for computer-aided diagnosis, e.g. based on medical expert systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10024—Color image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10068—Endoscopic image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20092—Interactive image processing based on input by user
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30096—Tumor; Lesion
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30168—Image quality inspection
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V2201/03—Recognition of patterns in medical or anatomical images
- G06V2201/034—Recognition of patterns in medical or anatomical images of medical instruments
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a medical image processing device for acquiring a key image for a report and a method for operating the medical image processing device.
- doctors diagnose patients while operating equipment during endoscopy and ultrasonography. After the diagnosis, a key image including a region of interest to be included in the report is acquired from the acquired inspection image. Since the criteria and rules for the key images to be included in the report differ depending on the facility or doctor, the doctor himself selects the key images from the inspection images taken in large quantities at the time of diagnosis.
- Patent Document 1 describes that the frame image of a site such as bleeding is automatically highlighted, and that the image frame before and after the image frame selected by the user in the list display is reproduced.
- the frame image of a site such as bleeding is automatically highlighted to make it easier for the user to identify a key image candidate. Further, by displaying before and after the image frame selected by the user, it is easy to identify a similar image suitable for the key image more than the key image candidate selected by the user. However, if there is no image having the characteristics desired by the user among the automatically displayed images, the burden may not be reduced.
- the medical image processing apparatus of the present invention comprises a processor, which acquires a plurality of medical images, classifies the medical images into at least one of a plurality of categories, and is among a plurality of medical images based on the result of the classification. At least one image of Instead, a non-automatically selected image other than the automatically selected image among a plurality of medical images classified into categories is switched and displayed as a switching image.
- the processor is characterized in that the switching image is switched and displayed from the selected image according to a plurality of categories.
- the processor is characterized in that the switching images classified into the same category as the selected images are switched and displayed.
- the processor displays a plurality of switching candidate images that are candidates for switching images on the screen and accepts user input for determining a switching image from the displayed plurality of switching candidate images.
- the switching candidate image includes an image of the same category as the selected image.
- the processor is characterized in that when the switching image is selected from a plurality of medical images according to the category of the automatically selected images, the imaging conditions of the medical images are taken into consideration.
- the processor is characterized in that the diagnostic usefulness of the medical image is added when the switching image is selected from a plurality of medical images according to the category of the automatically selected image.
- the processor displays each image with character or symbol information according to the category.
- the processor changes the display mode of each image according to the category.
- the processor displays the switching image and the automatically selected image in different modes.
- the processor accepts an input for approving each image displayed on the screen as a key image and displays it in a different manner depending on whether or not the approval is accepted.
- the processor classifies images according to a trained CNN model obtained by learning using an image group including a plurality of medical images.
- the category is preferably information about the part of the subject.
- the category is preferably information regarding whether or not the image includes a region of interest.
- the category is preferably information regarding whether or not the image contains the treatment tool or the type of the treatment tool included.
- the category is preferably information about the spraying state of the dye or dye in the image.
- the method of operating the medical image processing apparatus of the present invention includes a step of acquiring a plurality of medical images, a step of classifying the medical image into at least one of a plurality of categories, and a plurality of medical images based on the result of the classification.
- a step of displaying at least one of the images on the screen as an automatically selected image a step of accepting an input for the user to select an image requiring reselection as a key image from the displayed automatically selected images, and a selected image.
- it has a step of switching and displaying a non-automatically selected image other than the automatically selected image among a plurality of medical images classified into categories as a switching image.
- the present invention reduces the burden on the user when the user selects an image to be used as a report from a large number of medical images, and supports the creation of a report.
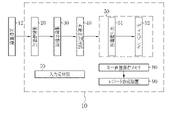
- the medical image processing apparatus 10 programs related to various processes are incorporated in a program memory (not shown).
- the medical image processing apparatus 10 is provided with a central control unit (not shown) configured by a processor.
- the central control unit By executing the program in the program memory by the central control unit, the image acquisition unit 20, the image classification unit 30, the usefulness determination unit 40, the image display unit 50, the display control unit 51, the input reception unit 70, and the key image storage are executed.
- the functions of the memory 80 and the report creation device 90 are realized.
- the image acquisition unit 20 acquires a plurality of medical images 12 from the endoscope system 11 and transmits them to the image classification unit 30. Find the key image 13 used to create the report from the medical images 12.
- the key image 13 is an image to be posted in the report so that the test results can be conveyed at a glance, and it is preferable that the features such as lesions are clear.
- the image classification unit 30 extracts the image information of the medical image 12 transmitted from the image acquisition unit 20, acquires category information, and calculates image quality information.
- the medical images 12 are classified into each category according to the acquired category information.
- the categories to be classified are any or a combination of the imaging site, the presence / absence and type of lesion, the state of use of the treatment tool, the state of spraying the pigment agent, and the like.
- image quality information information such as image brightness, noise, and degree of blurring is acquired and attached to the medical image 12.
- Image information is extracted using a trained CNN (Convolutional neural network) model.
- the trained CNN model is obtained by training with an image group containing at least a plurality of medical images 12.
- the category information and the image quality information acquired at the time of photographing by the endoscope system 11 and attached to the medical image 12 have priority over the information extracted by the trained CNN model.
- the medical image 12 after categorization is transmitted to the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the usefulness determination unit 40 determines the diagnostic usefulness of the medical image 12 based on the classification result and the image quality information obtained by the image classification unit 30. The higher the diagnostic usefulness, the more likely it is that the image is suitable for the key image 13.
- the evaluation of usefulness is expressed by, for example, a graded evaluation. It can be evaluated that the medical image 12 having an item such as a lesion in the classification result of the category and having a low degree of blur in the image quality evaluation is highly useful. If there is no category information, the degree of blurring is large, the brightness is too high, or the brightness is too low, the usefulness is low.
- the medical image 12 whose usefulness has been determined is transmitted to the image display unit 50. The usefulness is evaluated, and the evaluation threshold can be set arbitrarily by the user.
- the medical image 12 transmitted from the usefulness determination unit 40 by the display control unit 51 is displayed on the display 52 according to the classified categories.
- the input receiving unit 70 accepts user input such as image selection for switching display, page change, embodiment switching, category display switching, layout change, and key image saving.
- the key image storage memory 80 stores the key image 13 used for the report.
- the report creation device 90 creates a report of inspection results using the key image 13. It is preferable that the report is automatically created after the key image 13 is acquired.
- the endoscope system 11 acquires a large amount of medical images 12 by the light source device 11a, the endoscope 11b, and the processor device 11c.
- the endoscope system 11 is connected to the medical image processing device 10, and the acquired medical image 12 is transmitted to the medical image processing device 10.
- the medical image 12 transmitted from the endoscope system 11 is received by the image acquisition unit 20 and sent to the image display unit 50 via the image classification unit 30 and the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the image display unit 50 includes a display control unit 51 and a display 52.
- the image display unit 50 at least one image of the medical images 12 classified by category in the image classification unit 30 is selected as the automatically selected image 54.
- the automatically selected image 54 is an image selected according to the results of categorization and usefulness determination, and is an image that can be a candidate for the key image 13 to be posted in the report.
- the automatically selected image 54 is displayed on the display 52.
- the displayed automatically selected image 54 is approved as the key image 13 by the user input received by the input receiving unit 70, and is stored in the key image storage memory 80.
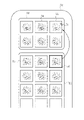
- the acquired medical image 12 is displayed as an automatically selected image 54 according to the category classified in the display 52.
- the display 52 is provided with an image display field 53, in which the automatically selected images 54 are displayed in a list.
- the automatically selected image 54 is preferably selected so as to include all the predetermined categories, and the automatically selected image 54 displayed in the list is evaluated to have a certain degree of usefulness or more, and the image was acquired. It is preferably in chronological order.
- the display 52 has a cursor 71, a display switching button 73, and an approval button 74 that reflect user operations such as mouse operations.
- the key image 13 when the key image 13 has an image requiring reselection from the automatically selected images 54 listed in the image display field 53 of the display 52, the image needs to be reselected by operating the mouse or the like.
- the selected image 55 is set via the cursor 71.
- the selected image 55 switches and displays an image automatically selected from the image group not displayed in the list as the switching image 56 based on the category information.
- the image requiring reselection for the key image 13 is an image in which the approval of the key image 13 is suspended at the user's discretion and is temporarily hidden. In some cases, the switching image 56 and the switching display are displayed, and then the original image is restored.
- the image selected as the switching image 56 is "an image of the same imaged part as the selected image 55", “an image of a part close to the imaged part of the selected image 55", and "if the selected image 55 is using the treatment tool, the treatment tool is not used”. "Image”, “an image in which the dye is not sprayed if the selected image 55 is being dyed”, “an image in the same light source mode as the selected image 55", and the like.
- the switching image 56 may be selected in consideration of information on the imaging time of the image, the imaging mode (enlarged or non-enlarged, etc.), or diagnostic usefulness by image quality evaluation. Specifically, there are “images with close shooting time”, “images with a low degree of blur”, “images with appropriate brightness”, and the like.
- the switching image 56 emphasizes the frame of the image so that the switching display can be discriminated at a glance.
- the approval of the key image 13 by selecting the approval button 74 is performed collectively for the displayed images. When it is not necessary to switch and display, all the automatically selected images 54 displayed first are approved as the key images 13 as they are.
- FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing changes in display switching between the selected image 55 and the switching image 56.
- the display control unit 51 detects the switching image 56 to be switched and displayed from the category in which the selected image 55 is classified, the attached image quality information, and the like.
- the switching image 56 is detected from among the non-automatically selected images 57 other than the automatically selected image 54 among the medical images 12 classified by category by the image classification unit 30.
- the category-classified image group 58 is composed of an automatically selected image group 59 including an automatically selected image 54 obtained by automatic selection and a non-automatically selected image group 60 not selected as the automatically selected image 54. ..
- the switching image 56 is automatically selected from the non-automatic selection image group 60.
- the approval button 74 is pressed.
- the images displayed in the list are collectively saved as the key image 13 in the key image storage memory 80, and are also sent to the report creation device 90, and each key image 13 is sent. Used for reporting.
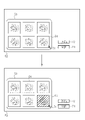
- FIG. 6 describes a display mode of the automatically selected image 54 and the switching image 56 displayed in the image display field 53.
- the display control unit 51 visualizes the category information and displays it along with each image. Further, the display may be turned on / off or the information to be displayed may be switched by the display switching button 73. For example, assuming that the normal display is "display a", in “display b", the image information display field 61 is expanded at the bottom of each image displayed in the image display field 53, and the category in which each image is classified is displayed as characters. Display with. Further, in the "display c", the evaluation of the usefulness calculated by the usefulness determination unit 40 is displayed in the image information display column 61. By utilizing the above display form, a more appropriate key image 13 can be selected. Further, a form in which the above display forms are combined may be provided and displayed.
- FIG. 7 describes another pattern of approval processing by the approval button 74.
- the approval process for the key image 13 is collectively performed for the image 4 in the image display field 53, but the displayed images may be individually approved one by one. In that case, it is necessary to display the approved image and the unapproved image so as to distinguish them. For example, it is possible to know at a glance that an image that has undergone approval processing has been approved by using a display pattern such as a shaded display, surrounding the image, or placing a mark on the image.
- the approved key image 13 is transmitted to the report creating device 90 and used for creating the report 91.
- the screen display of the display 52 is switched from the image display field 53 to the report 91, and the user can create the report 91 immediately after the approval of the key image 13.
- patient information, user information, etc. that have been input in advance are automatically input.
- the user inputs the findings in the finding input field 92 and creates a report.
- the user selects the selected image 55 that needs to be reselected in the categorized state.
- a switching candidate image display field 62 for displaying a list of a plurality of switching candidate images 63 on the display 52 instead of switching and displaying the switching image 56 is expanded, and the user switches a plurality.
- the switching image 56 is selected from the candidate images 63.
- the expansion of the switching candidate image display field 62 ends, and the selection image 55 and the switching image 56 are switched.
- the key image 13 that reflects the user's preference can be selected for the report as compared with the first embodiment.
- the switching candidate image 63 does not display all the medical images 12 that are not displayed in the list, but is a part of the image group selected based on the category of the selected images 55.
- the image group of the switching candidate image 63 displayed in the switching candidate image display field 62 is "an image group of the same shooting area as the selected image 55", “an image group of a part close to the selected image 55 and the shooting part", and "selected image”. Examples include “an image group in which the treatment tool is not used if 55 is in use of the treatment tool” and “an image group in which the dye is not sprayed if the selected image 55 is being dyed”. Further, the image group to be displayed as the switching candidate image 63 may not display all the medical images 12 that match the above conditions, but may be configured to display only a predetermined number of them. As a result, the number of sheets to be confirmed at the time of selection is limited, so that the work load can be further reduced. Further, a predetermined number of images may be selected in consideration of the image shooting time, the shooting mode, and the diagnostic usefulness by the image quality evaluation.
- the switching candidate image 63 displayed in a list displays another switching candidate image 63 by operating the page switching button 75 provided on the switching candidate image display field 62 in the same manner. Can be done.
- the page switching button 75 has two "forward" and “back", and the user can arbitrarily operate the page switching button 75 to switch pages. Further, it is preferable to describe the displayed page number in the center of the page switching button. It is preferable that the page switching is displayed in the same category as the switching candidate image 63, starting with the one judged to be highly useful.
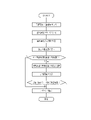
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing a series of flow of switching and displaying the selected image to the switching image.
- the medical image processing device 10 acquires a medical image 12 taken by the endoscope system 11 at the image acquisition unit 20.
- the acquired medical image 12 is transmitted to the image classification unit 30 to classify the categories.
- the image classification unit 30 extracts the image information of the medical image 12, attaches it to the original medical image 12 as category information and image quality information, and classifies each medical image 12 into a predetermined category based on the category information.
- Image information is extracted by a trained CNN (Convolutional neural network) model.
- the medical image 12 after categorization is transmitted to the usefulness determination unit 40.
- the usefulness determination unit 40 determines the usefulness from the category information and the image quality information of the medical image 12, and attaches the determination result to the original medical image 12.
- the medical image 12 after the usefulness determination is transmitted to the image display unit 50.
- the image display unit 50 displays a list of medical images 12 on the display 52 as automatically selected images 54 according to the results of categorization and usefulness determination. It is preferable that the images to be listed are selected so as to include all the predetermined categories and have a high evaluation in the determination of usefulness.
- the user observes whether there is an image requiring reselection in the key image 13 from the automatically selected images 54 displayed in the list, selects the image if there is, and switches and displays the image to another image. If not, select the approval button 74.
- the switching image 56 that has been switched and displayed is preferably selected according to the category and usefulness of the selected image 55, and is highly useful.
- the reselection of the switching image 56 is repeated until the switching image 56 can be approved by the key image 13.
- the approval button 74 is selected.
- the key image 13 is transmitted to the key image storage memory 80 and transmitted to the report creation device 90.
- various processes such as an image acquisition unit 20, an image classification unit 30, a usefulness determination unit 40, an image display unit 50, a display control unit 51, an input reception unit 70, a key image storage memory 80, and a report creation device 90.
- the hardware structure of the processing unit that executes the above is various processors as shown below.
- Various processors include CPU (Central Processing Unit), GPU (Graphical Processing Unit), FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), which are general-purpose processors that execute software (programs) and function as various processing units.
- PLD Programmable Logic Device
- a processing unit may be composed of one of these various processors, or a combination of two or more processors of the same type or different types (for example, a plurality of FPGAs, a combination of a CPU and an FPGA, or a CPU and a combination of two or more processors. It may be composed of a combination of GPUs, etc.). Further, a plurality of processing units may be configured by one processor. As an example of configuring a plurality of processing units with one processor, first, as represented by a computer such as a client or a server, one processor is configured by a combination of one or more CPUs and software. There is a form in which this processor functions as a plurality of processing units.
- SoC System On Chip
- the various processing units are configured by using one or more of the above-mentioned various processors as a hardware-like structure.
- the hardware-like structure of these various processors is, more specifically, an electric circuit (circuitry) in which circuit elements such as semiconductor elements are combined.
- the hardware structure of the storage unit is a storage device such as an HDD (hard disk drive) or SSD (solid state drive).
- Medical image processing device 11 Endoscope system 11a Light source device 11b Endoscope 11c Processor device 12 Medical image 13 Key image 20 Image acquisition unit 30 Image classification unit 40 Usefulness determination unit 50 Image display unit 51 Display control unit 52 Display 53 Image display field 54 Automatic selection image 55 Selected image 56 Switching image 57 Non-automatic selection image 58 Category classified image group 59 Automatic selection image group 60 Non-automatic selection image group 61 Image information display field 62 Switching candidate image display field 63 Switching candidate image 70 Input reception unit 71 Cursor 73 Display switching button 74 Approval button 75 Page switching button 80 Key image storage memory 90 Report creation device 91 Report 92 Findings input field
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Abstract
レポートに載せるキー画像を自動選定した場合において、選定結果に対して医師が行う作業を軽減することができる医療画像処理装置及びその作動方法を提供することを目的とする。複数の医療画像(12)を取得する画像取得部(20)と、医療画像(12)を複数のカテゴリに分類する画像分類部(30)、分類結果に基づいて医療画像(12)の内少なくとも1枚を自動選定画像(54)として画面表示する画像表示部(50)、表示された自動選定画像(54)の中から、キー画像(13)に要再選定する画像を選択画像(55)としてユーザが選択する入力を受け付ける入力受付部(70)、選択画像(55)を表示することに代えて、カテゴリごとに分類された複数の医療画像(12)のうち自動選定画像(54)以外の非自動選定画像(57)を、切替画像(56)として切替表示する表示制御部(51)とを有する医療画像処理装置(10)による。
Description
本発明は、レポート用キーイメージ画像の取得を行う医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法に関する。
医療分野においては、内視鏡や超音波検査時に医師は機器を操作しながら患者を診断する。診断後に、取得した検査画像からレポートに載せる注目領域等を含むキー画像を取得する。レポートに載せるキー画像は施設又は医師によって基準やルールが異なるため、診断時に大量に撮影した検査画像からキー画像を医師自身が選定している。
取得した検査画像を1枚ずつ確認し、病変等の注目領域を含むキー画像の特定を行うことは時間や労力がかかり、医師の負担となるため、キー画像を容易に取得することを支援する技術が開発されつつある。
具体的には、特許文献1では、出血等の部位のフレーム画像は自動的に強調表示すること、及び、一覧表示においてユーザ選択した画像フレームの前後を再生することが記載されている。
特許文献1では、出血等の部位のフレーム画像は自動的に強調表示することでユーザがキー画像候補の特定をしやすくしている。また、ユーザ選択した画像フレームの前後を表示することで類似した、ユーザが選択したキー画像候補以上にキー画像に適した画像を特定しやすくしている。しかし、自動で表示される画像の中にユーザが求める特徴を有する画像が無い場合、負担の軽減にはならないことがある。
医師による検査終了後に、検査中に撮影された画像群からレポート向けに複数枚の画像を自動選定された場合を想定する。診断上の有用性やレポートの様式を学習して自動でキー画像候補を選定するが、推論ミスによる不適切な画像を選定する、医師の嗜好を反映できない、特殊な検査などへの対応ができないといった問題がある。そのため、選定結果に対して医師が確認を行う作業が必須となるが、この作業の負担が大きければ結果的に作業負担が軽減されないという問題が発生する。
本発明は、レポートに載せるキー画像を自動選定した場合において、選定結果に対して医師が行う作業を軽減することができる医療画像処理装置及びその作動方法を提供することを目的とする。
本発明の医療画像処理装置は、プロセッサを備え、プロセッサは、複数の医療画像を取得し、医療画像を複数のカテゴリの少なくとも1つに分類し、分類の結果に基づいて複数の医療画像の内の少なくとも1枚を自動選定画像として画面表示し、表示された自動選定画像の中から、キー画像に要再選定の画像を選択画像としてユーザが選択する入力を受け付け、選択画像を表示することに代えて、カテゴリに分類された複数の医療画像のうち自動選定画像以外の非自動選定画像を、切替画像として切替表示する。
プロセッサは、複数のカテゴリに応じて、選択画像から切替画像を切替表示することを特徴とすることが好ましい。
プロセッサは、選択画像と同一のカテゴリに分類された切替画像を切替表示することを特徴とすることが好ましい。
プロセッサは、切替画像の候補である複数の切替候補画像を画面表示し、表示された複数の切替候補画像から切替画像を決定するユーザ入力を受け付けることが好ましい。
切替候補画像は、選択画像と同一のカテゴリの画像を含むことを特徴とすることが好ましい。
プロセッサは、自動選定画像のカテゴリに応じて、切替画像を複数の医療画像から選択する際に、医療画像の撮影条件を加味することを特徴とすることが好ましい。
プロセッサは、自動選定画像のカテゴリに応じて、切替画像を複数の医療画像から選択する際に、医療画像の診断上の有用性を加味することを特徴とすることが好ましい。
プロセッサは、各画像をカテゴリに応じた文字または記号情報を付与して表示することが好ましい。
プロセッサは、各画像の表示態様をカテゴリに応じて変更することが好ましい。
プロセッサは、切替画像と自動選定画像を異なる態様で表示することが好ましい。
プロセッサは、画面表示する各画像をキー画像に承認する入力を受け付け、承認を受け付けたか否かに応じて異なる態様で表示することが好ましい。
プロセッサは、複数の医療画像を含む画像群を用いて学習することにより得られた学習済CNNモデルによって画像を分類することが好ましい。
カテゴリは、被写体の部位に関する情報であることが好ましい。
カテゴリは、画像に注目領域が含まれるか否かに関する情報であることが好ましい。
カテゴリは、画像に処置具が含まれるか否かまたは含まれる処置具の種類に関する情報であることが好ましい。
カテゴリは、画像内の色素剤または染色剤の散布状態に関する情報であることが好ましい。
本発明の医療画像処理装置の作動方法は、複数の医療画像を取得するステップと、医療画像を複数のカテゴリの少なくとも1つに分類するステップと、分類の結果に基づいて複数の医療画像の内の少なくとも1枚を自動選定画像として画面表示するステップと、表示された自動選択画像の中から、キー画像に要再選定の画像を選択画像としてユーザが選択する入力を受け付けるステップと、選択画像を表示することに代えて、カテゴリに分類された複数の医療画像のうち自動選定画像以外の非自動選定画像を、切替画像として切替表示するステップとを有する。
本発明は、大量の医療画像の中からユーザがレポート使用する画像を選択する際にユーザの負担を減らし、レポート作成の支援を行う。
[第1実施形態]
医療画像処理装置10は、各種処理に関するプログラムがプログラム用メモリ(図示しない)に組み込まれている。医療画像処理装置10には、プロセッサによって構成される中央制御部(図示しない)が設けられている。中央制御部によってプログラムメモリ内のプログラムが実行されることによって、画像取得部20、画像分類部30、有用性判定部40、画像表示部50、表示制御部51、入力受付部70、キー画像保存メモリ80、レポート作成装置90の機能が実現する。
医療画像処理装置10は、各種処理に関するプログラムがプログラム用メモリ(図示しない)に組み込まれている。医療画像処理装置10には、プロセッサによって構成される中央制御部(図示しない)が設けられている。中央制御部によってプログラムメモリ内のプログラムが実行されることによって、画像取得部20、画像分類部30、有用性判定部40、画像表示部50、表示制御部51、入力受付部70、キー画像保存メモリ80、レポート作成装置90の機能が実現する。
画像取得部20は、内視鏡システム11から複数の医療画像12を取得し、画像分類部30に送信する。医療画像12の中からレポート作成に用いるキー画像13を見つける。キー画像13とは、レポートに掲載する、検査結果が一目で伝わるような画像であり、病変などの特徴が明確であることが好ましい。
画像分類部30は、画像取得部20から送信された医療画像12の画像情報を抽出し、カテゴリ情報の取得や画質情報の算出を行う。取得したカテゴリ情報に従い、医療画像12をそれぞれのカテゴリに分類する。分類するカテゴリは撮影部位、病変の有無や種類、処置具の使用状態、色素剤の散布状態などのいずれかまたはそれらの組み合わせである。画質情報においては、画像の明るさやノイズ、ボケ度合いなどの情報を取得し、医療画像12に付属させる。画像情報の抽出には学習済みCNN(Convolutional neural network)モデルで行う。学習済みCNNモデルは複数の医療画像12を少なくとも含む画像群を用いて学習することによって得られる。内視鏡システム11での撮影時に取得し、医療画像12に付属したカテゴリ情報や画質情報は学習済みCNNモデルで抽出した情報よりも優先することが好ましい。カテゴリ分類後の医療画像12は有用性判定部40に送信される。
有用性判定部40では、画像分類部30で得た分類結果や画質情報を基に医療画像12の診断上の有用性の判定を行う。診断上の有用性が高いほど、キー画像13に適した画像である可能性が高くなる。有用性の評価は例えば、段階評価などで表される。カテゴリの分類結果では病変などの項目を有し、画質評価ではボケ度合いが低い医療画像12は有用性が高いと評価できる。カテゴリ情報が無い、ボケ度合いが大きい、明度が高すぎる、もしくは、明度が低すぎる場合では、有用性は低くなる。有用性の判定が終わった医療画像12は、画像表示部50に送信される。有用性は評価し、評価の閾値はユーザが任意に設定できる。
画像表示部50では、表示制御部51により有用性判定部40から送信された医療画像12は、分類されたカテゴリに従ってディスプレイ52に表示される。
入力受付部70は、切替表示するための画像選択、ページ変更、実施形態の切替、カテゴリ表示切替、レイアウト変更、キー画像保存といったユーザ入力を受け付ける。
キー画像保存メモリ80では、レポートに使用するキー画像13が保存される。
レポート作成装置90では、キー画像13を用いて、検査結果のレポートを作成する。レポートの作成はキー画像13の取得後、自動的に行われることが好ましい。
図1に示すように、内視鏡システム11は、光源装置11a、内視鏡11b、およびプロセッサ装置11cにより大量の医療画像12を取得する。内視鏡システム11は医療画像処理装置10に接続しており、取得した医療画像12を医療画像処理装置10に送信する。
図2に示すように、内視鏡システム11から送信された医療画像12は、画像取得部20が受け取り、画像分類部30、有用性判定部40を介して画像表示部50に送られる。画像表示部50は表示制御部51と、ディスプレイ52を備える。画像表示部50において、画像分類部30でカテゴリごとに分類された医療画像12のうちの少なくとも1枚の画像が自動選定画像54として選定される。自動選定画像54は、カテゴリ分類や有用性判定の結果に応じて選定される画像であって、レポートに掲載するキー画像13の候補となり得る画像である。自動選定画像54は、ディスプレイ52に表示される。表示された自動選定画像54は、入力受付部70が受け付けるユーザ入力によりキー画像13とする承認を行い、キー画像保存メモリ80に保存される。
図3に示すように、取得した医療画像12は、ディスプレイ52に分類されたカテゴリに応じ、自動選定画像54として表示される。ディスプレイ52では、画像表示欄53が設けられ、その中に自動選定画像54が一覧表示される。自動選定画像54は、所定のカテゴリを全て含むように選定されることが好ましく、また、一覧表示される自動選定画像54は一定以上の有用性があると評価されたものであり、画像取得した時間順であることが好ましい。ディスプレイ52には、マウス操作等によるユーザ操作を反映するカーソル71、表示切替ボタン73、承認ボタン74を有する。
図4に示すように、第1実施形態ではディスプレイ52の画像表示欄53に一覧表示された自動選定画像54の中からキー画像13に要再選定の画像がある場合、それをマウス操作等でカーソル71を介して選択画像55とする。選択画像55はカテゴリ情報に基づいて、一覧表示されていない画像群から自動で選択された画像を切替画像56として切替表示する。なお、キー画像13に要再選定の画像は、ユーザの判断でキー画像13の承認を保留とし、一旦非表示にする画像である。また、切替画像56と切替表示をした後、元に戻す場合もある。
切替画像56として選択する画像は「選択画像55と同じ撮影部位の画像」、「選択画像55の撮影部位と近い部位の画像」、「選択画像55が処置具使用中であれば処置具未使用の画像」、「選択画像55が色素散布中であれば色素散布していない画像」、「選択画像55と同じ光源モードの画像」、などが挙げられる。他にも、画像の撮影時間や撮影モード(拡大または非拡大など)、または画質評価による診断上の有用性の情報を加味して切替画像56選択してもよい。具体的には「撮影時間が近い画像」、「ボケ度合いが低い画像」、「明度が適切な画像」などである。画像表示欄53において、切替画像56は、画像の枠を強調することで、切替表示したことを一目で判別可能にすることが好ましい。なお、承認ボタン74を選択することによるキー画像13の承認は表示されてる画像に対して一括で行われる。切替表示する必要のない場合は、最初に表示された自動選定画像54全部をそのままキー画像13として承認する。
図5は選択画像55と、切替画像56の表示切替の変化を示す概念図である。選択画像55がユーザに選択されると、表示制御部51は、選択画像55が分類されているカテゴリや付属している画質情報などから切替表示する切替画像56を検出する。切替画像56は、画像分類部30でカテゴリごとに分類された医療画像12のうち、自動選定画像54以外の非自動選定画像57の中から検出される。図5では、カテゴリ分類済画像群58は、自動選定により得られる自動選定画像54を含む自動選定画像群59と、自動選定画像54として選定されなかった非自動選定画像群60とから構成される。切替画像56は、非自動選定画像群60の中から自動的に選定される。
ディスプレイ52の画像表示欄53に一覧表示された自動選定画像54および、切替画像56のいずれもキー画像13と承認する場合、承認ボタン74をする。承認ボタン74が選択されると、一覧表示されている画像は一括でキー画像13としてキー画像保存メモリ80への保存処理が行われるとともに、レポート作成装置90にも送信され、各キー画像13はレポート作成に使用される。
図6では画像表示欄53に表示される、自動選定画像54および切替画像56の表示態様について説明する。表示制御部51がカテゴリ情報を視覚化して各画像に付随して表示する。また、表示切替ボタン73によって、表示on/offしてもよいし、表示する情報を切り替えてもよい。例えば、通常の表示を「表示a」とすると、「表示b」では画像表示欄53に表示してる各画像の下部に画像情報表示欄61を展開し、それぞれの画像が分類されたカテゴリを文字で表示する。また、「表示c」では、有用性判定部40で算出された有用性の評価を画像情報表示欄61に表示する。上記表示形態を活用することでより適切なキー画像13の選定ができる。また、上記の表示形態を組み合わせた形態を設けて表示してもよい。
図7では、承認ボタン74による承認処理の別パターンについて説明する。キー画像13の承認処理は画像表示欄53の画像4に対して一括で行うが、表示している画像を1枚ずつ個別に承認処理を行ってもよい。その場合、承認済み画像と未承認画像の区別をつくように表示する必要がある。例えば、承認処置を行った画像に対して、網掛け表示や、画像の周りを囲む、マークを乗せる、といった表示パターンを用いて一目で承認処理したとわかるようにする。
図8に示すように、承認処理したキー画像13はレポート作成装置90に送信されてレポート91の作成に使用される。承認処理終了後、ディスプレイ52の画面表示は画像表示欄53からレポート91に切り替わり、ユーザはキー画像13の承認後すぐにレポート91を作成できる。レポート91はあらかじめ入力された患者の情報、ユーザ情報、などが自動で入力される。ユーザは所見入力欄92に所見の入力等を行い、レポートを作成する。
[第2実施形態]
第2実施形態には選択画像55から切替画像56への切り替えにおいて、自動での切り替えではなく、選択画像55を選択した際に、複数の切替候補画像63を表示し、ユーザがその中から任意の切替画像56を選択する。なお、第1実施形態と共通する内容に関しては省略する。
第2実施形態には選択画像55から切替画像56への切り替えにおいて、自動での切り替えではなく、選択画像55を選択した際に、複数の切替候補画像63を表示し、ユーザがその中から任意の切替画像56を選択する。なお、第1実施形態と共通する内容に関しては省略する。
図9に示すように、第2実施形態では、第1実施形態同様に、カテゴリ分類された状態でユーザが再選定を要する選択画像55を選択する。ユーザが選択画像55を選択した際に、切替画像56を切替表示するのではなくディスプレイ52に複数の切替候補画像63を一覧表示する切替候補画像表示欄62が展開され、ユーザは、複数の切替候補画像63の中から切替画像56を選択する。切替画像56が選択されると、切替候補画像表示欄62の展開は終わり、選択画像55と切替画像56が切り替えられる。これにより、第1実施形態に比べてよりユーザの嗜好を反映させたキー画像13をレポート向けに選択できる。切替候補画像63は一覧表示されていない全ての医療画像12を表示するのではなく、選択画像55のカテゴリに基づいて選択された一部の画像群である。
切替候補画像表示欄62に表示される切替候補画像63の画像群は、「選択画像55と同じ撮影部位の画像群」、「選択画像55と撮影部位が近い部位の画像群」、「選択画像55が処置具使用中であれば処置具未使用の画像群」、「選択画像55が色素散布中であれば色素散布していない画像群」などが挙げられる。また、切替候補画像63として表示する画像群は上記条件に一致する全ての医療画像12を表示するのではなく、それらの中から所定枚数に制限して表示する構成にしてもよい。これにより選択時に確認すべき枚数が制限されるため、より作業負担を軽減できる。さらに、画像の撮影時間や撮影モード、または画質評価による診断上の有用性を加味して所定の枚数の画像を選択してもよい。
図10に示すように、一覧表示される切替候補画像63は、同様に切替候補画像表示欄62上に設けられたページ切替ボタン75を操作することで更に他の切替候補画像63を表示することができる。ページ切替ボタン75は「進む」、「戻る」の2つがあり、ユーザが任意に操作してページ切替が行われる。また、ページ切替ボタンの中央部では表示しているページ番号を記載することが好ましい。ページ切替で表示されるのは、切替候補画像63とカテゴリが同じで、有用性が高いと判定されたものから表示されるのが好ましい。
図11は、選択画像を切替画像に切替表示する一連の流れを示すフローチャートである。医療画像処理装置10は、画像取得部20にて内視鏡システム11が撮影した医療画像12を取得する。取得した医療画像12は、画像分類部30に送信し、カテゴリの分類を行う。
画像分類部30では医療画像12の画像情報を抽出し、もとの医療画像12にカテゴリ情報と画質情報として付属させ、カテゴリ情報をもとに各医療画像12を所定のカテゴリに分類する。画像情報の抽出は学習済みCNN(Convolutional neural network)モデルによって行う。カテゴリ分類後の医療画像12は有用性判定部40に送信される。
有用性判定部40では、医療画像12のカテゴリ情報及び画質情報から有用性を判定し、判定結果を元の医療画像12に付属させる。有用性判定後の医療画像12は画像表示部50に送信される。
画像表示部50では、医療画像12をカテゴリ分類及び有用性判定の結果に従って、自動選定画像54としてディスプレイ52に一覧表示する。一覧表示する画像は、所定のカテゴリを全て含むように選定されること、および有用性の判定で評価が高いことが好ましい。
ユーザは、一覧表示された自動選定画像54の中からキー画像13に要再選定の画像があるかを観察し、ある場合はその画像を選択し、他の画像に切替表示する。ない場合は承認ボタン74を選択する。
切替表示した切替画像56は、選択画像55のカテゴリや有用性に応じたものが選択され、有用性が高いことが好ましい。
切替画像56がキー画像13に承認できるまで、切替画像56の再選定を繰り返す。一覧表示した画像で再選定となる画像が無くなったら承認ボタン74を選択する。
承認ボタンの選択後、キー画像13は、キー画像保存メモリ80に送信及びレポート作成装置90に送信される。
上記実施形態において、画像取得部20、画像分類部30、有用性判定部40、画像表示部50、表示制御部51、入力受付部70、キー画像保存メモリ80、レポート作成装置90といった各種の処理を実行する処理部(processing unit)のハードウェア的な構造は、次に示すような各種のプロセッサ(processor)である。各種のプロセッサには、ソフトウエア(プログラム)を実行して各種の処理部として機能する汎用的なプロセッサであるCPU(Central Processing Unit)、GPU(Graphical Processing Unit)、FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) などの製造後に回路構成を変更可能なプロセッサであるプログラマブルロジックデバイス(Programmable Logic Device:PLD)、各種の処理を実行するために専用に設計された回路構成を有するプロセッサである専用電気回路などが含まれる。
1つの処理部は、これら各種のプロセッサのうちの1つで構成されてもよいし、同種または異種の2つ以上のプロセッサの組み合せ(例えば、複数のFPGA、CPUとFPGAの組み合わせ、またはCPUとGPUの組み合わせ等)で構成されてもよい。また、複数の処理部を1つのプロセッサで構成してもよい。複数の処理部を1つのプロセッサで構成する例としては、第1に、クライアントやサーバなどのコンピュータに代表されるように、1つ以上のCPUとソフトウエアの組み合わせで1つのプロセッサを構成し、このプロセッサが複数の処理部として機能する形態がある。第2に、システムオンチップ(System On Chip:SoC)などに代表されるように、複数の処理部を含むシステム全体の機能を1つのIC(Integrated Circuit)チップで実現するプロセッサを使用する形態がある。このように、各種の処理部は、ハードウェア的な構造として、上記各種のプロセッサを1つ以上用いて構成される。
さらに、これらの各種のプロセッサのハードウェア的な構造は、より具体的には、半導体素子などの回路素子を組み合わせた形態の電気回路(circuitry)である。また、記憶部のハードウェア的な構造はHDD(hard disc drive)やSSD(solid state drive)等の記憶装置である。
10 医療画像処理装置
11 内視鏡システム
11a 光源装置
11b 内視鏡
11c プロセッサ装置
12 医療画像
13 キー画像
20 画像取得部
30 画像分類部
40 有用性判定部
50 画像表示部
51 表示制御部
52 ディスプレイ
53 画像表示欄
54 自動選定画像
55 選択画像
56 切替画像
57 非自動選定画像
58 カテゴリ分類済画像群
59 自動選定画像群
60 非自動選定画像群
61 画像情報表示欄
62 切替候補画像表示欄
63 切替候補画像
70 入力受付部
71 カーソル
73 表示切替ボタン
74 承認ボタン
75 ページ切替ボタン
80 キー画像保存メモリ
90 レポート作成装置
91 レポート
92 所見入力欄
11 内視鏡システム
11a 光源装置
11b 内視鏡
11c プロセッサ装置
12 医療画像
13 キー画像
20 画像取得部
30 画像分類部
40 有用性判定部
50 画像表示部
51 表示制御部
52 ディスプレイ
53 画像表示欄
54 自動選定画像
55 選択画像
56 切替画像
57 非自動選定画像
58 カテゴリ分類済画像群
59 自動選定画像群
60 非自動選定画像群
61 画像情報表示欄
62 切替候補画像表示欄
63 切替候補画像
70 入力受付部
71 カーソル
73 表示切替ボタン
74 承認ボタン
75 ページ切替ボタン
80 キー画像保存メモリ
90 レポート作成装置
91 レポート
92 所見入力欄
Claims (17)
- プロセッサを備え、前記プロセッサは、
複数の医療画像を取得し、
前記医療画像を複数のカテゴリの少なくとも1つに分類し、
前記分類の結果に基づいて複数の前記医療画像の内の少なくとも1枚を自動選定画像として画面表示し、
表示された前記自動選定画像の中から、キー画像に要再選定の画像を選択画像としてユーザが選択する入力を受け付け、
前記選択画像を表示することに代えて、前記カテゴリに分類された複数の前記医療画像のうち前記自動選定画像以外の非自動選定画像を、切替画像として切替表示する医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
複数の前記カテゴリに応じて、前記選択画像から前記切替画像を切替表示することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
前記選択画像と同一の前記カテゴリに分類された前記切替画像を切替表示することを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
前記切替画像の候補である複数の切替候補画像を画面表示し、
表示された複数の前記切替候補画像から前記切替画像を決定するユーザ入力を受け付ける請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記切替候補画像は、
前記選択画像と同一の前記カテゴリの画像を含むことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
前記自動選定画像の前記カテゴリに応じて、前記切替画像を複数の前記医療画像から選択する際に、前記医療画像の撮影条件を加味することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
前記自動選定画像の前記カテゴリに応じて、前記切替画像を複数の前記医療画像から選択する際に、前記医療画像の診断上の有用性を加味することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
各画像を前記カテゴリに応じた文字または記号情報を付与して表示する請求項1ないし3、5ないし7いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
各画像の表示態様を前記カテゴリに応じて変更する請求項1ないし3、5ないし8いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
前記切替画像と前記自動選定画像を異なる態様で表示する請求項1、6または7いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
画面表示する各画像を前記キー画像に承認する入力を受け付け、
承認を受け付けたか否かに応じて異なる態様で表示する請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記プロセッサは、
複数の医療画像を含む画像群を用いて学習することにより得られた学習済CNNモデルによって画像を分類する請求項1に記載の医療画像処理装置。 - 前記カテゴリは、被写体の部位に関する情報である請求項1ないし3、5ないし9いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。
- 前記カテゴリは、画像に注目領域が含まれるか否かに関する情報である請求項1ないし3、5ないし9いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。
- 前記カテゴリは、画像に処置具が含まれるか否かまたは含まれる処置具の種類に関する情報である請求項1ないし3、5ないし9いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。
- 前記カテゴリは、画像内の色素剤または染色剤の散布状態に関する情報である請求項1ないし3、5ないし9いずれか1項に記載の医療画像処理装置。
- 複数の医療画像を取得するステップと、
前記医療画像を複数のカテゴリの少なくとも1つに分類するステップと、
前記分類の結果に基づいて複数の前記医療画像の内の少なくとも1枚を自動選択画像として画面表示するステップと、
表示された前記自動選択画像の中から、キー画像に要再選定の画像を選択画像としてユーザが選択する入力を受け付けるステップと、
前記選択画像を表示することに代えて、前記カテゴリに分類された複数の前記医療画像のうち前記自動選定画像以外の非自動選定画像を、切替画像として切替表示するステップとを有する医療画像処理装置の作動方法。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202180068968.6A CN116324572A (zh) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | 医疗图像处理装置及其工作方法 |
| EP21877295.2A EP4227725A4 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | MEDICAL IMAGE PROCESSING DEVICE AND METHOD OF OPERATING THE SAME |
| JP2022555314A JPWO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | |
| US18/297,402 US20230245312A1 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2023-04-07 | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020171577 | 2020-10-09 | ||
| JP2020-171577 | 2020-10-09 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US18/297,402 Continuation US20230245312A1 (en) | 2020-10-09 | 2023-04-07 | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022074992A1 true WO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2022-04-14 |
Family
ID=81126460
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/032880 WO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2020-10-09 | 2021-09-07 | 医療画像処理装置およびその作動方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230245312A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP4227725A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2022074992A1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN116324572A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2022074992A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114724669A (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2022-07-08 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009008125A1 (ja) | 2007-07-12 | 2009-01-15 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | 画像処理装置、該動作方法及び該プログラム |
| WO2018225448A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-09 | 2018-12-13 | 智裕 多田 | 消化器官の内視鏡画像による疾患の診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム及びこの診断支援プログラムを記憶したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| WO2019039354A1 (ja) * | 2017-08-23 | 2019-02-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 光源装置及び内視鏡システム |
| WO2019064704A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-04 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡画像観察支援システム、内視鏡画像観察支援装置、内視鏡画像観察支援方法 |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10482313B2 (en) * | 2015-09-30 | 2019-11-19 | Siemens Healthcare Gmbh | Method and system for classification of endoscopic images using deep decision networks |
| CN113543694B (zh) * | 2019-03-08 | 2024-02-13 | 富士胶片株式会社 | 医用图像处理装置、处理器装置、内窥镜系统、医用图像处理方法、及记录介质 |
-
2021
- 2021-09-07 CN CN202180068968.6A patent/CN116324572A/zh active Pending
- 2021-09-07 EP EP21877295.2A patent/EP4227725A4/en active Pending
- 2021-09-07 JP JP2022555314A patent/JPWO2022074992A1/ja active Pending
- 2021-09-07 WO PCT/JP2021/032880 patent/WO2022074992A1/ja unknown
-
2023
- 2023-04-07 US US18/297,402 patent/US20230245312A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009008125A1 (ja) | 2007-07-12 | 2009-01-15 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | 画像処理装置、該動作方法及び該プログラム |
| WO2018225448A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-09 | 2018-12-13 | 智裕 多田 | 消化器官の内視鏡画像による疾患の診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム及びこの診断支援プログラムを記憶したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| WO2019039354A1 (ja) * | 2017-08-23 | 2019-02-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 光源装置及び内視鏡システム |
| WO2019064704A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-04 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡画像観察支援システム、内視鏡画像観察支援装置、内視鏡画像観察支援方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP4227725A4 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114724669A (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2022-07-08 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
| CN114724669B (zh) * | 2022-05-07 | 2023-08-22 | 丹阳慧创医疗设备有限公司 | 用于近红外脑功能成像装置的医学报告生成方法及装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2022074992A1 (ja) | 2022-04-14 |
| EP4227725A1 (en) | 2023-08-16 |
| CN116324572A (zh) | 2023-06-23 |
| EP4227725A4 (en) | 2024-04-10 |
| US20230245312A1 (en) | 2023-08-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8442280B2 (en) | Method and system for intelligent qualitative and quantitative analysis of digital radiography softcopy reading | |
| EP1662415A1 (en) | Digital medical image analysis | |
| US20210295510A1 (en) | Heat map based medical image diagnostic mechanism | |
| US20220044147A1 (en) | Teaching data extending device, teaching data extending method, and program | |
| US20230245312A1 (en) | Medical image processing apparatus and operation method thereof | |
| JP2022190920A (ja) | 情報処理装置、クラス判定方法、プログラム | |
| US20240013524A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus, method of operating information processing apparatus, and program for operating information processing apparatus | |
| US20230298178A1 (en) | Medical image display system, medical image display method, and recording medium | |
| US20230100147A1 (en) | Diagnosis support system, diagnosis support method, and storage medium | |
| EP4226840A1 (en) | Medical image processing device and operation method for same | |
| JP6903041B2 (ja) | 表示制御装置、表示制御方法、及び表示制御プログラム | |
| US8433112B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for processing chest X-ray images | |
| JP7109910B2 (ja) | 読影レポート作成支援装置及び読影レポート作成支援方法 | |
| JP6336252B2 (ja) | レポート作成支援装置、その制御方法、及びプログラム | |
| JPWO2020105248A1 (ja) | 医用画像表示制御装置、方法及びプログラム | |
| US20230222663A1 (en) | Medical imaging apparatus and operation method for medical imaging apparatus | |
| JP2019200770A (ja) | 表示制御装置、表示制御方法、及び表示制御プログラム | |
| JP7388284B2 (ja) | 類似症例検索プログラム、類似症例検索方法及び類似症例検索システム | |
| EP4123501A1 (en) | Medical diagnosis assistance system and method | |
| US20230317249A1 (en) | Medical support device, and operation method and operation program of medical support device | |
| US20230177690A1 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium | |
| JP2023029106A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、およびプログラム | |
| JP2021087729A (ja) | 医用画像処理装置及びプログラム | |
| JP2023075195A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理装置の制御方法、及びプログラム | |
| CN114947912A (zh) | 医用图像显示装置、医用图像显示方法以及存储介质 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21877295 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022555314 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021877295 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20230509 |