WO2022045238A1 - 光照射システム、ウェアラブル装置、設置型の光照射装置、および光照射方法 - Google Patents
光照射システム、ウェアラブル装置、設置型の光照射装置、および光照射方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022045238A1 WO2022045238A1 PCT/JP2021/031307 JP2021031307W WO2022045238A1 WO 2022045238 A1 WO2022045238 A1 WO 2022045238A1 JP 2021031307 W JP2021031307 W JP 2021031307W WO 2022045238 A1 WO2022045238 A1 WO 2022045238A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- light
- irradiation
- subject
- intensity
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B47/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light sources in general, i.e. where the type of light source is not relevant
- H05B47/10—Controlling the light source
- H05B47/105—Controlling the light source in response to determined parameters
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N5/0613—Apparatus adapted for a specific treatment
- A61N5/0622—Optical stimulation for exciting neural tissue
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B47/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light sources in general, i.e. where the type of light source is not relevant
- H05B47/10—Controlling the light source
- H05B47/105—Controlling the light source in response to determined parameters
- H05B47/11—Controlling the light source in response to determined parameters by determining the brightness or colour temperature of ambient light
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B47/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light sources in general, i.e. where the type of light source is not relevant
- H05B47/10—Controlling the light source
- H05B47/16—Controlling the light source by timing means
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N2005/0626—Monitoring, verifying, controlling systems and methods
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N2005/0626—Monitoring, verifying, controlling systems and methods
- A61N2005/0627—Dose monitoring systems and methods
- A61N2005/0628—Dose monitoring systems and methods including a radiation sensor
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N2005/0635—Radiation therapy using light characterised by the body area to be irradiated
- A61N2005/0643—Applicators, probes irradiating specific body areas in close proximity
- A61N2005/0645—Applicators worn by the patient
- A61N2005/0647—Applicators worn by the patient the applicator adapted to be worn on the head
- A61N2005/0648—Applicators worn by the patient the applicator adapted to be worn on the head the light being directed to the eyes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N2005/0658—Radiation therapy using light characterised by the wavelength of light used
- A61N2005/0662—Visible light
- A61N2005/0663—Coloured light
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
- A61N2005/0664—Details
- A61N2005/0667—Filters
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to a light irradiation system, a wearable device, a stationary light irradiation device, and a light irradiation method.
- ganglion cells such as intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (iPRGC) in the eye, which have photoacceptive ability but do not have a direct relationship with visual function.
- iPRGC intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells
- Non-Patent Document 1 reports that acute and chronic pain is alleviated by irradiating light in a wavelength band corresponding to green light.
- the light irradiation system includes an irradiation unit that irradiates the eyes of a subject with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band, and at least the predetermined wavelength band contained in light different from the irradiation light. It is equipped with a shielding mechanism that reduces the illuminance of light in different wavelength bands.
- the wearable device is a wearable device worn on the head of the subject, and includes an irradiation unit that irradiates the eyes of the subject with irradiation light of a predetermined wavelength band and the eyes of the subject. It is provided with a shielding mechanism for reducing the illuminance of light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band, which is contained in the light different from the irradiation light.
- the stationary light irradiation device includes a support portion that supports a sitting or lying user, an irradiation portion that irradiates the eyes of a subject with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band, and the subject.
- the irradiation unit includes a shielding mechanism that reduces the illuminance of light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band, which is contained in light different from the irradiation light and reaches the human eye. It is installed at a position facing the subject's eyes.
- the intensity and the second intensity of the return light detected in the closed state are acquired, and based on the comparison result between the first intensity and the second intensity, the subject's eyelids are in the open state.
- the light irradiation step to irradiate, whether or not the subject's eyelids are closed, and whether or not a predetermined time has elapsed in the closed state are determined, and the intensity of the irradiation light is determined from the first reference intensity.
- the first intensity change step for changing to the second reference intensity and whether or not the eyelids of the subject are in the open state are determined, and the intensity of the irradiation light is changed from the second reference intensity to the first reference intensity. Includes a second intensity change step, which changes to.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of a main part of the light irradiation system 100 according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
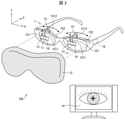
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a configuration example of the light irradiation system 100 according to one aspect of the present disclosure.
- the light irradiation system 100 includes a light irradiation device 1 which is a device for irradiating the eyes of a subject with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band.
- the light irradiation device 1 may be an installation type device that is difficult to carry, or may be a wearable device.
- the light irradiation system 100 may further include a display device 14 that displays images and various information acquired from the light irradiation device 1 in addition to the light irradiation device 1.
- a display device 14 that displays images and various information acquired from the light irradiation device 1 in addition to the light irradiation device 1.
- the light irradiation system 100 including the display device 14 will be described as an example.
- the light irradiation device 1 When the light irradiation device 1 is a stationary device (see FIG. 5), the light irradiation device 1 includes a support portion 50 that supports a subject in a sitting or lying position.
- the support 50 may be, for example, a chair and a bed.
- the display device 14 may be integrated with the light irradiation device 1, and for example, the display device 14 may be arranged in the light irradiation device 1.
- the light irradiation device 1 when the light irradiation device 1 is a wearable device (see FIG. 2), the light irradiation device 1 has an arbitrary shape (for example, glasses type, goggles type, and headgear) that can be attached to the head of the subject. It may be a mold, etc.).
- the light irradiation device 1 may be provided with a mounting mechanism for mounting on the body of the subject.
- the wearing mechanism may be a nose pad, a temple (a so-called “vine” portion that is hooked on the ear), or the like.
- the wearing mechanism in the case of the goggle type light irradiation device 1 may be a head strap (fixed band) or the like.
- the display device 14 may be a separate body from the light irradiation device 1.
- the display device 14 may be a display unit or a display of a computer (not shown) capable of communicating with the light irradiation device 1.
- the light irradiation device 1 includes an irradiation unit 11 and a shielding mechanism 12. Although not essential, the light irradiation device 1 may further include an image pickup unit 13, a moving mechanism 15, a light receiving unit 16, and a control unit 10. 1 and 2 show a light irradiation device 1 including an image pickup unit 13, a moving mechanism 15, a light receiving unit 16, and a control unit 10 in addition to the irradiation unit 11 and the shielding mechanism 12. Further, the light irradiation device 1 includes a storage unit (not shown) in which various computer programs read by the control unit 10 and data used in various processes executed by the control unit 10 are stored. May be good.
- a light irradiation system a wearable device and an installation capable of irradiating a subject's eyes with light in a predetermined wavelength band to bring about a non-visual effect on the subject's mind and body.
- a type of light irradiation device can be realized.
- the light irradiation device 1 is a glasses-type wearable device.
- the irradiation unit 11 includes one or more light sources for irradiating the eyes of the subject with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band.
- the irradiation unit 11 may include, for example, a light emitting element such as a light emitting diode (LED) and a semiconductor laser (LD) as a light source. By using these light emitting elements, the irradiation unit 11 can selectively irradiate monochromatic light having a narrow wavelength width of the light emitting wavelength.
- the irradiation unit 11 may include a light source that emits white light and an optical filter (for example, a bandpass filter) that transmits only light in a predetermined wavelength band. By selecting and using an appropriate optical filter, the irradiation unit 11 can selectively irradiate the irradiation light in a desired wavelength band.
- the light irradiation device 1 shown in FIG. 2 can irradiate both eyes of a subject with light in a predetermined wavelength band, but is not limited to this.
- the light irradiation device 1 may be configured to irradiate one eye of the subject with light in a predetermined wavelength band. In this case, only one light source of the irradiation unit 11 may be turned on.
- the irradiation unit 11 may be detachably attached to the light irradiation device 1 so that the irradiation unit 11 on the unused side can be removed.
- the irradiation unit 11 is arranged in a moving mechanism 15 described later, and the position of the irradiation unit 11 with respect to the position of the eyes of the subject can be changed by using the moving mechanism 15. You may.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light may be any wavelength band of light that is expected to have an effect of improving the physical and mental condition of the subject by irradiating the eyes of the subject.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light may be the wavelength band of the green light.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light is, for example, 450 to 600 nm, and may be 500 to 550 nm.
- the irradiation light may be green light having a peak top of 525 nm.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light may be the wavelength band of purple light.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light may be 350 to 410 nm.
- the wavelength band of the irradiation light may be the wavelength band of blue light.
- an optical filter that blocks ultraviolet rays and near-ultraviolet rays may be further provided in order to reduce the damage to the eyes of the subject as much as possible.
- the irradiation light may be continuous light continuously applied to the eyes of the subject, or pulsed light emitted intermittently. May be.
- the light irradiation device 1 includes a shielding mechanism 12.
- a shielding mechanism 12 thereby, when the irradiation light of a predetermined wavelength band is irradiated to the eyes of the subject, the illuminance of the light reaching the eyes of the subject and having a wavelength band different from that of the irradiation light can be reduced.
- the light irradiation device 1 provided with the shielding mechanism 12 can improve the pain relief effect obtained by irradiating the eyes of the subject with green light.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may reduce the illuminance of light different from the irradiation light or the illuminance of light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band contained in the light different from the irradiation light.
- the light different from the irradiation light may be, for example, sunlight or light from indoor lighting.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may be made of a cloth or resin having a light-shielding property, or may be made of a metal having a light-shielding property or a light reflecting property.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may include an optical filter that selectively transmits light in a predetermined wavelength band and does not transmit light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band.
- the shielding mechanism 12 can reduce the illuminance of the light from the outside of the light irradiation device 1 over the entire wavelength band.
- the shielding mechanism 12 can reduce the illuminance of the light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band contained in the light from the outside of the light irradiation device 1.
- the shielding mechanism 12 is made of a light-reflecting material, it is possible to reduce the light from the outside of the light irradiation device 1, while it is also possible to reflect the light inside the light irradiation device 1 to the irradiation target. Is.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may be arranged so that there is no gap between the subject wearing the light irradiation device 1 and the light irradiation device 1. Further, the shielding mechanism 12 may be integrated with the light irradiation device 1 or may be a separate body.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may have a goggle-like shape that covers the entire frame portion of the light irradiation device 1.
- the shielding mechanism 12 can cover the frame portion of the light irradiation device 1.
- the shielding mechanism 12 may be configured to cover the entire head of the subject.
- the target person wearing the light irradiation device 1 shown in FIG. 2, the head of the target person, or the like may be covered with a separate shielding mechanism 12.
- the shielding mechanism 12 shown in FIG. 2 shields the light that reaches both eyes of the subject from the outside of the light irradiation device 1, but is not limited to this.
- the light irradiation device 1 may be configured to include a shielding mechanism 12 for the right eye and a shielding mechanism 12 for the left eye.
- the shielding mechanism 12 on the same side may be used. According to this configuration, the field of view of the eye on the side not irradiated with the irradiation light is not blocked by the shielding mechanism 12. This allows the subject to visually recognize the surrounding situation with the eyes on the side not irradiated with the irradiation light.
- the image pickup unit 13 is a camera for taking an image of a subject, and may be a digital camera or a digital video.
- the image pickup unit 13 may image the face of the subject who is irradiated with the irradiation light, or may image the eyes of the subject who is irradiated with the irradiation light and its surroundings.
- the image data (still image data or moving image data) captured by the image pickup unit 13 may be transmitted from the light irradiation device 1 to the display device 14.
- the image pickup unit 13 may be arranged anywhere as long as it can image the eyes of the subject irradiated with the irradiation light and its surroundings.
- the imaging unit 13 may be arranged in the vicinity of the irradiation unit 11 as shown in FIG. In this case, the position of the imaging unit 13 may be changed by using the moving mechanism 15 together with the irradiation unit 11.
- the moving mechanism 15 accepts an operation for changing the position of the irradiation unit 11 with respect to the position of the subject's eyes (particularly, the pupil).
- the moving mechanism 15 is a mechanism provided for moving the position of the irradiation unit 11 so that the light from the irradiation unit 11 can be irradiated toward the eyes of the subject, particularly the pupil.
- the moving mechanism 15 may have any configuration as long as it is possible to change the position of the irradiation unit 11 with respect to the position of the pupil of the subject's eye.
- the moving mechanism 15 has a holding portion 151 for holding the irradiation portion 11 at the first end 1511 and a guide rail 152 for moving the holding portion 151 in the X-axis direction (left-right direction).
- the direction parallel to the anterior-posterior axis of the eyeball that is, the axis connecting the cornea and the retina
- the direction parallel to the left-right axis that is, the axis connecting the left ear and the right ear
- Is the X-axis direction, and the direction parallel to the vertical axis is the Y-axis direction.
- the guide rail 152 may be, for example, a groove provided in the upper part of the frame of the light irradiation device 1.
- the second end 1512 opposite to the first end 1511 of the holding portion 151 may be slidably abutted on the inner surface of the groove. As a result, the holding portion 151 can move in the X-axis direction along the guide rail 152.
- the moving mechanism 15 may be able to move the position of the irradiation unit 11 in the Y-axis direction (vertical direction).
- the holding portion 151 may have a structure that can be expanded and contracted in the Y-axis direction.
- a fixing member (not shown) that fixes the irradiation unit 11 to the holding portion 151 may be slidable along the holding portion 151, and the irradiation unit 11 may be movable along the holding portion 151.
- a medical person such as a doctor or a nurse in charge of the subject can manually change the position of the irradiation unit 11 along the guide rail 152. Further, the position of the irradiation unit 11 may be automatically changed along the guide rail 152 based on the image data of the image pickup unit 13.
- the light irradiation device 1 can accurately irradiate the eyes of the subject, particularly the pupil, with the irradiation light to reach the fovea centralis of the retina.
- the light receiving unit 16 detects the intensity of the return light of the irradiation light.
- the return light is intended to be light that is reflected on the surface of the eyelid or the like and returns to the irradiation unit 11 when the irradiation light is applied to the eyes or eyelids of the subject from the irradiation unit 11.
- the light receiving unit 16 may be installed at any position as long as it can receive the return light.
- the light receiving unit 16 may include one or more light receiving elements.
- the light receiving unit 16 may include a plurality of light receiving elements in order to detect the intensity of the return light with higher accuracy.
- the light receiving element is an avalanche photodiode.
- an intensity signal output unit (not shown) may be connected to the light receiving unit 16, and the intensity signal output unit is configured to output an intensity signal indicating the intensity of the reflected light detected by the light receiving unit 16. There may be.
- the light receiving unit 16 may be arranged anywhere as long as it can receive the return light.
- the light receiving unit 16 may be provided in the vicinity of the irradiation unit 11 as shown in FIG. In this case, the position of the light receiving unit 16 may be changed by using the moving mechanism 15 together with the irradiation unit 11.
- the display device 14 displays the image captured by the image pickup unit 13.
- the display device 14 may be, for example, a liquid crystal display device or an organic EL display attached to a terminal operated by a medical personnel.
- the display device 14 and the image pickup unit 13 may be connected by wire or wirelessly, but the image captured by the image pickup unit 13 may be displayed on the display device 14 in real time.
- the display device 14 may display an image of the target person captured by the image pickup unit 13. Based on the image displayed on the display device 14, the medical personnel can know the position where the irradiation light is irradiated and the open / closed state of the eyelid of the subject.
- the control unit 10 controls to execute the processing of each function included in the light irradiation device 1.
- the control unit 10 may be a CPU included in the light irradiation device 1.
- the control unit 10 includes an eyelid open / close determination unit 17, a light intensity adjustment unit 18, a calibration unit 19, a time management unit 20, and an output unit 21.
- the light irradiation system 100 can irradiate the eyes of a subject with closed eyes with irradiation light having a predetermined wavelength.
- the illuminance of the irradiation light when it reaches the subject's retina through the eyelids differs depending on whether the eyelids are in the open state or the closed state. Therefore, the light irradiation system 100 may include a control unit 10 and can adjust the illuminance of the irradiation light according to the open / closed state of the eyelids of the subject.
- the eyelid open / close determination unit 17 determines the open / closed state of the target person's eyelids based on the intensity of the return light received by the light receiving unit 16.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 may determine the open / closed state of the eyelid of the subject and measure the duration of each of the open state and the closed state of the eyelid of the subject.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 Based on the determination result by the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17, the light intensity adjusting unit 18 irradiates the irradiation unit 11 when the subject's eyelids are closed, as compared with the case where the subject's eyelids are open. The intensity of the irradiation light may be increased.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 has a first reference intensity (for example, see the intensity L4 shown in FIG. 3) and a second reference intensity (for example, the intensity shown in FIG. 3), which are predetermined by the calibration process performed by the calibration unit 19 described later. (See L3) may be applied to adjust the intensity of the irradiation light.
- the first reference intensity is the intensity of the irradiation light applied when the subject's eyelids are open
- the second reference intensity is the intensity of the irradiation light applied when the subject's eyelids are in the closed state. It is strength.
- the first reference strength and the second reference strength may be determined for each subject.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 may be configured not to increase the intensity of the irradiation light when the subject's eyelids are not closed for a predetermined time or longer.
- an arbitrary fixed value for example, 1 second may be set in advance in seconds.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 may be configured to weaken the intensity of the irradiation light when the subject's eyelids are closed for a predetermined time or longer and then opened.
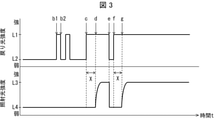
- FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing an example of time-dependent changes in the intensity of the return light received by the light receiving unit 16 and the intensity of the irradiation light irradiated by the irradiation unit 11.
- the intensity of the irradiation light and the intensity of the return light are constant until the point b1 in FIG.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the target person's eyelids are in an open state, and the irradiation unit 11 irradiates irradiation light having a predetermined intensity (for example, 4 to 100 Lux).
- a predetermined intensity for example, 4 to 100 Lux.
- the intensity of the irradiation light is 4 to 100 Lux, it is possible to continuously relieve physical pain such as pain felt by the subject without causing the subject to feel glare.
- the predetermined time X in which the subject's eyelids remain closed is preset to 5 seconds as an example.
- the intensity of the return light increased from the intensity L2 to the intensity L1, and at the time of b2, it returned to the intensity L2.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are in the closed state at the time of b1, and starts measuring the time for which the eyelids are kept closed.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are in the open state at the time of b2. Further, the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 measures the time from the time b1 to the time b2 as the time during which the subject's eyelids are kept closed.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 compares the time measured by the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 (the time during which the subject's eyelids are closed) with the preset predetermined time X (5 seconds). ..
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 does not change the intensity of the irradiation light at the intensity L4 (first reference intensity) when the time during which the subject's eyelids remain closed is shorter than 5 seconds, which is the predetermined time X. ..
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 does not change the intensity of the irradiation light when the subject blinks and the eyelids are closed for a very short time.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are in the closed state, and starts measuring the duration of the eyelid closing state. Next, the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the target person's eyelids are in the closed state at the time d. Further, the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 measures the time from the time c to the time d as the time during which the subject's eyelids are closed.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 compares the time measured by the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 (the time during which the subject's eyelids are closed) with the predetermined time X.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 changes the intensity of the irradiation light from the intensity L4 to the intensity L3 (second reference intensity) when the subject's eyelids are kept closed for a longer time than the predetermined time X.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 determines the light intensity irradiated by the irradiation unit 11. Make it stronger.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 adjusts the intensity of the irradiation light so that the illuminance of the irradiation light reaching the subject's retina can be increased. It is possible to avoid a significant decrease.
- the e-point corresponds to, for example, when the subject wakes up and opens his eyelids. That is, at the time e, the intensity of the return light is reduced from the intensity L1 to the intensity L2 again.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are in the open state, and starts measuring the duration of the eyelid open state.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 immediately weakens the light intensity irradiated by the irradiation unit 11.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 reduces the intensity of the irradiation light from the intensity L3 to the intensity L4 when the subject's eyelids are closed for a predetermined time or longer and then opened. As a result, it is possible to prevent the intense irradiation light from being applied to the eyes of the awakened subject.
- the intensity of the return light has increased again from the intensity L2 to the intensity L1.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the target person's eyelids are in the closed state at the time f, and starts measuring the time for which the eyelid is kept closed.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 changes the light intensity irradiated by the irradiation unit 11 from the intensity L4 to the intensity L3.
- the calibration unit 19 performs the above-mentioned processing for determining the first reference strength and the second reference strength. Specifically, the calibration unit 19 continuously irradiates the eyes of the subject with irradiation light of a predetermined intensity for a certain period of time, and sets the first intensity of the return light detected when the eyelids of the subject are open. , The second intensity of the return light detected in the closed state is acquired.
- the calibration unit 19 has a first reference intensity of irradiation light when the subject's eyelids are open and when the subject's eyelids are closed, based on the results of comparison with the first intensity and the second intensity.
- the second reference intensity of the irradiation light of the above may be determined in advance.
- the first intensity is the intensity of the return light detected by the light receiving unit 16 when the target person's eyelids are open
- the second intensity is the light receiving unit when the target person's eyelids are closed.
- 16 is the intensity of the return light detected.
- the first reference intensity is the intensity of the irradiation light emitted by the irradiation unit 11 to the subject when the subject's eyelids are open
- the second reference intensity is the intensity of the irradiation light when the subject's eyelids are closed. It is the intensity of the irradiation light that the irradiation unit 11 sometimes irradiates the subject.
- the illuminance of the irradiation light that reaches the subject's retina when the subject closes the eyelids differs depending on the condition of the subject's eyelids.
- the state of the eyelid is, for example, the thickness of the eyelid, the presence or absence of a substance present on the surface of the eyelid, and the like. Further, since the thickness of the eyelids varies from subject to subject, the illuminance of the irradiation light reaching the subject's retina differs from subject to subject. Therefore, the first reference strength and the second reference strength may be determined for each subject.
- the calibration unit 19 may determine the first reference strength for each subject. It is known that there are individual differences in the conditions of the cornea, crystalline lens, eyeball, and iris. For example, the curvature of the cornea, the curvature of the crystalline lens, the length of the axis of the eyeball, the accommodation power of the iris, and the degree of turbidity of the crystalline lens are different for each subject. Therefore, even if the irradiation light of the same intensity is irradiated, the illuminance of the irradiation light reaching the retina may differ from subject to subject.
- the calibration unit 19 may determine the first reference intensity to irradiate each subject based on the condition of at least one of the cornea, lens, eyeball, and iris of the subject's eye. For example, in a subject with a large degree of turbidity of the crystalline lens, it is highly possible that the irradiation light of a predetermined intensity does not reach the retina, so that the calibration unit 19 increases the first reference intensity to irradiate the subject. You may decide.
- the calibration unit 19 determines the illuminance of the irradiation light that reaches the subject's retina when each subject is irradiated with the reference irradiation light of a predetermined intensity, the intensity of the irradiation light, and the cornea, crystalline lens, and eyeball of the subject's eye. And may be calculated based on at least one of the states of the iris. Further, the calibration unit 19 may determine the intensity of the irradiation light to be applied to the subject from the relationship between the intensity of the irradiation light and the calculated illuminance. For example, the calibration unit 19 may have data showing the relationship between the intensity of the irradiation light, the state of the cornea, the crystalline lens, the eyeball, and the iris and the illuminance of the irradiation light reaching the retina.
- the state of at least one of the subject's cornea, lens, eyeball, and iris may be, for example, configured to be acquired from the subject's ophthalmic chart information. According to this, it is possible to irradiate the irradiation light of an appropriate intensity for each subject.
- the time management unit 20 measures the intensity of the irradiation light irradiated to the eyes of the subject by the irradiation unit 11 and the integrated time irradiated to the eyes of the subject for each subject.
- the time management unit 20 may be configured to acquire information indicating the time from a timer (not shown) included in the light irradiation device 1, for example.
- the intensity of the irradiation light radiated to the eyes of the subject is, for example, the intensity of the irradiation light when the eyelids of the subject are open (first reference intensity) and the intensity of the irradiation light when the eyelids of the subject are closed. Strength (second standard strength) and the like.
- the integrated time of irradiating the irradiation light may be the integrated time of irradiating the subject with the irradiation light within a predetermined period such as one day, one month, or half a year, and is the integrated time of irradiation in one treatment. You may.
- the output unit 21 outputs, for example, to an external terminal, a server, a storage device, or the like, information indicating the intensity of the irradiation light and the integrated time of irradiation to the eyes of the subject, respectively, measured by the time management unit 20.
- the light irradiation system 100 includes an irradiation unit 11 that irradiates the eyes of a subject with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band, and at least a predetermined wavelength band included in light different from the irradiation light. It is provided with a shielding mechanism 12 that reduces the illuminance of light in a wavelength band different from that of the above.
- the light irradiation system 100 can irradiate the eyes of the subject with irradiation light of a predetermined wavelength band, and at the same time, light in a wavelength band different from the predetermined wavelength band penetrates into the eyes of the subject. Can be prevented.
- the light irradiation system 100 it is possible to irradiate the eyes of a subject with a predetermined wavelength band to effectively bring about an action on the mind and body of the subject.
- the light irradiation system 100 further includes an imaging unit 13 that captures an image of the subject, and a display device 14 that allows a medical person or the subject to visually recognize an image of the subject's eyes imaged by the imaging unit 13. You may. Further, the light irradiation system 100 may further include a moving mechanism 15 for receiving an operation for changing the position of the irradiation unit 11 with respect to the position of the eyes of the subject.
- the irradiation light is applied to the fovea centralis of the subject's eye where the pyramidal cells are concentrated. It may be incident.
- the light irradiation system 100 includes an imaging unit 13, a display device 14, and a moving mechanism 15, so that the medical personnel or the subject can check the position of the irradiation unit while checking the displayed image of the subject's eyes. , Can be moved to an appropriate position using the moving mechanism 15. As a result, the medical personnel or the subject can efficiently inject the irradiation light into the fovea centralis.
- the light irradiation system 100 may further include a light receiving unit 16 that detects the intensity of the return light of the irradiation light, and an eyelid open / close determination unit 17 that determines the open / closed state of the eyelid of the subject based on the intensity of the return light. .. Further, the light irradiation system 100 determines the intensity of the irradiation light when the subject's eyelids are closed, as compared with the case where the subject's eyelids are open, based on the determination result by the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17. A light intensity adjusting unit 18 for intensifying may be further provided.
- the magnitude of the effect of irradiating the subject's eye with irradiation light in a predetermined wavelength band depends on the illuminance when the irradiation light reaches the retina of the subject's eye.
- the illuminance of the irradiation light reaching the subject's retina is extremely reduced.
- the irradiation light is blocked by the eyelids, so that the illuminance when reaching the retina may be significantly reduced.
- the light irradiation system 100 includes a light receiving unit 16, an eyelid open / close determination unit 17, and a light intensity adjusting unit 18 to determine the open / closed state of the target person's eyelids based on the intensity of the return light of the irradiation light.
- the intensity of the irradiation light can be adjusted based on the determination result of the open / closed state.
- the light irradiation system 100 has a time management unit 20 that measures the intensity of the irradiation light radiated to the eyes of the subject and the integrated time of irradiation for each subject, and the measured intensity of the irradiation light and the integrated time.
- An output unit 21 for outputting the respective indicated information may be further provided.
- the medical personnel manages the integrated illuminance of the irradiation light received by the subject for each subject, and determines the magnitude of the effect of irradiating the subject's eyes with the irradiation light for each subject. Can be evaluated.
- the configuration shown in FIG. 1 is an example and is not limited to this.
- the light irradiation system 100 may further include a server device that receives and manages the ID of each subject and the information measured by the time management unit 20.
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing executed by the light irradiation system 100 according to the present embodiment.
- the calibration unit 19 performs the above-mentioned calibration process, and determines the first reference intensity and the second reference intensity, which are the intensities of the irradiation light irradiated by the irradiation unit 11 (calibration step).
- the irradiation unit 11 irradiates light of the first reference intensity and proceeds to S103 (light irradiation step).
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines whether or not the target person's eyelids are in the closed state. When the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the target person's eyelids are in the closed state (YES in S103), the process proceeds to S104. When the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are not in the closed state, that is, in the open state (NO in S103), the process returns to S102, and the irradiation unit 11 irradiates light of the first reference intensity. continue.
- the eyelid open / close determination unit 17 starts time measurement and proceeds to S105.
- the time management unit 20 may perform the time measurement as an example.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines whether or not a predetermined time has elapsed since the time measurement was started in S104 (time determination step). At this time, the time management unit 20 may determine whether or not the predetermined time has elapsed. When the predetermined time has elapsed (YES in S105), the process proceeds to S106. If the predetermined time has not elapsed (NO in S105), the process returns to S102, and the irradiation unit 11 continues to irradiate the light of the first reference intensity.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 changes the intensity of the irradiation light irradiated by the irradiation unit 11 from the first reference intensity to the second reference intensity, and proceeds to S107 (first intensity change step). That is, it is conceivable that the subject fell asleep, for example, because the subject's eyelids were closed for a predetermined time or longer.
- the irradiation unit 11 irradiates the retina of the subject with light having a second reference intensity, which is stronger than the first reference intensity, so that the light having the same illuminance as in the open state reaches the retina of the subject.
- the irradiation unit 11 continues the light irradiation of the second reference intensity and proceeds to S108.
- the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines whether or not the target person's eyelids are in the open state. When the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the target person's eyelids are in the open state (YES in S108), the process proceeds to S109. When the eyelid opening / closing determination unit 17 determines that the subject's eyelids are not in the open state, that is, in the closed state (NO in S108), the process returns to S107, and the irradiation unit 11 irradiates light of the second reference intensity. continue.
- the light intensity adjusting unit 18 changes the intensity of the irradiation light irradiated by the irradiation unit 11 from the second reference intensity to the first reference intensity (second intensity change step).
- the light irradiation system 100 determines whether or not to end the light irradiation, and if the end of the light irradiation is accepted (YES in S110), the irradiation unit 11 ends the light irradiation.
- the irradiation unit 11 returns to S102 and continues the processing from S102 to S110.
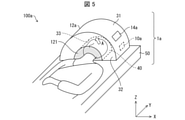
- FIG. 5 is a perspective view showing a configuration example of the light irradiation system 100a according to the second embodiment.
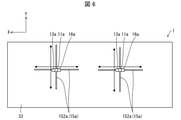
- FIG. 6 is a bottom view showing a configuration example of the light irradiation system 100a according to the second embodiment.
- the light irradiation device 1a is a stationary device.
- the light irradiation device 1a includes an irradiation unit 11a and a shielding mechanism 12a, similarly to the light irradiation device 1. Further, the light irradiation device 1a further includes a support portion 50 for supporting the subject in the sitting position or the lying position.
- the irradiation unit 11a will be described later with reference to FIG.
- the light irradiation device 1a may further include a display device 14a and a control unit 10a as shown in FIG. Further, the light irradiation device 1a may further include an image pickup unit 13a, a moving mechanism 15a, and a light receiving unit 16a. The image pickup unit 13a, the moving mechanism 15a, and the light receiving unit 16a will be described later with reference to FIG.
- the support portion 50 of the light irradiation device 1a is a bed as an example.
- the shielding mechanism 12a is a half-pipe type in which an insertion hole 40, which is a hole, is provided inside.
- the insertion hole 40 is a portion surrounded by the inner peripheral surface 33 and the support portion 50, and is a hole for the subject to insert the head.
- a shielding portion 121 is installed at the entrance of the insertion hole 40 into which the subject inserts the head, and the shielding portion 121 is installed on the same surface as the outer surface 32 of the shielding mechanism 12a and is joined to the end portion of the outer surface 32.
- the shielding portion 121 may be made of a cloth having a light-shielding property so that the subject can easily move the head in and out.
- the display device 14a corresponds to the display device 14 in the first embodiment.
- the display device 14a may be installed on the outer peripheral surface 31 of the light irradiation device 1a.
- the control unit 10a corresponds to the control unit 10 in the first embodiment, and controls to execute the processing of each function included in the light irradiation device 1a.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic view showing an inner peripheral surface 33 ahead of the line of sight A seen from the subject when the subject inserts his / her head into the insertion hole 40 of the light irradiation device 1a of FIG.
- the irradiation unit 11a, the image pickup unit 13a, the moving mechanism 15a, and the light receiving unit 16a are installed on the inner peripheral surface 33 of the shielding mechanism 12a.
- the irradiation unit 11a corresponds to the irradiation unit 11 of the first embodiment.
- the irradiation unit 11a is installed at a position facing the eyes of the subject in the shielding mechanism 12a. Specifically, if the irradiation unit 11a is installed on the inner peripheral surface 33 of the shielding mechanism 12a and is installed at a position facing the eyes of the subject when the subject inserts the head into the insertion hole 40. good.
- the image pickup unit 13a corresponds to the image pickup unit 13 of the first embodiment.
- the image data captured by the image pickup unit 13a may be transmitted to the display device 14a installed on the outer peripheral surface 31 described above. As shown in FIG.
- the image pickup unit 13a may be arranged in the vicinity of the irradiation unit 11a, and in this case, the position of the image pickup unit 13a can be changed together with the irradiation unit 11a by using the moving mechanism 15a. It may be.
- the moving mechanism 15a may be a guide rail 152a for moving the irradiation unit 11a in the X-axis direction (horizontal direction) and the Y-axis direction (vertical direction).
- the direction parallel to the anterior-posterior axis of the eyeball is the Z-axis direction
- the left-right axis that is, the axis connecting the left ear and the right ear
- the direction parallel to the X-axis direction is defined as the X-axis direction
- the direction parallel to the vertical axis that is, the axis connecting the head and the side portion
- the Y-axis direction is defined as the Y-axis direction.
- the irradiation unit 11a is held by the first end (corresponding to the first end 1511 of the first embodiment and FIG. 2) of the holding portion (not shown), and the second holding portion is held.
- the end (corresponding to the second end 1512 of the first embodiment and the second embodiment) may be configured to move on the guide rail 152a.
- the light receiving unit 16a corresponds to the light receiving unit 16 of the first embodiment. As shown in FIG. 6, the light receiving unit 16a may be provided in the vicinity of the irradiation unit 11a, or may be changed by using the moving mechanism 15a together with the irradiation unit 11a.
- control blocks (control units 10, 10a) of the light irradiation systems 100 and 100a may be realized by a logic circuit (hardware) formed in an integrated circuit (IC chip) or the like, or may be realized by software. ..
- the light irradiation systems 100 and 100a include a computer that executes a program command that is software that realizes each function.
- the computer includes, for example, one or more processors and a computer-readable recording medium that stores the program. Then, in the computer, the processor reads the program from the recording medium and executes the program, thereby achieving the object of the present disclosure.
- the processor for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) can be used.
- the recording medium in addition to a “non-temporary tangible medium” such as a ROM (Read Only Memory), a tape, a disk, a card, a semiconductor memory, a programmable logic circuit, or the like can be used.
- a RAM RandomAccessMemory
- the program may be supplied to the computer via any transmission medium (communication network, broadcast wave, etc.) capable of transmitting the program.
- transmission medium communication network, broadcast wave, etc.
- One aspect of the present disclosure may also be realized in the form of a data signal embedded in a carrier wave, in which the program is embodied by electronic transmission.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Radiation-Therapy Devices (AREA)
- Eye Examination Apparatus (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US18/023,131 US20230293905A1 (en) | 2020-08-27 | 2021-08-26 | Light irradiation system, wearable device, installation-type light irradiation device, and light irradiation method |
| JP2022545695A JP7483899B2 (ja) | 2020-08-27 | 2021-08-26 | 光照射システム、ウェアラブル装置、および設置型の光照射装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-143867 | 2020-08-27 | ||
| JP2020143867 | 2020-08-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022045238A1 true WO2022045238A1 (ja) | 2022-03-03 |
Family
ID=80353371
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/031307 Ceased WO2022045238A1 (ja) | 2020-08-27 | 2021-08-26 | 光照射システム、ウェアラブル装置、設置型の光照射装置、および光照射方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230293905A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7483899B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2022045238A1 (enExample) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010076708A1 (en) * | 2008-12-30 | 2010-07-08 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | System and method for administering light therapy |
| WO2015011589A1 (en) * | 2013-07-25 | 2015-01-29 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | System and method for providing light therapy and modifying circadian rhythm |
| US20160067086A1 (en) * | 2014-09-09 | 2016-03-10 | LumiThera, Inc. | Devices and methods for non-invasive multi-wavelength photobiomodulation for ocular treatments |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3863243A (en) * | 1972-01-19 | 1975-01-28 | Max Skolnick | Sleep inhibiting alarm |
| RU2567263C2 (ru) * | 2009-04-24 | 2015-11-10 | Конинклейке Филипс Электроникс Н.В. | Система для доставки электромагнитного излучения в глазное яблоко субъекта |
| US9081416B2 (en) * | 2011-03-24 | 2015-07-14 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Device, head mounted display, control method of device and control method of head mounted display |
| EP2802381A4 (en) * | 2012-01-12 | 2015-02-18 | Goodlux Technology Llc | PHOTOTHERAPY SURVEILLANCE |
| US10394057B2 (en) * | 2016-02-08 | 2019-08-27 | Verily Life Sciences Llc | Eyes closed interface |
-
2021
- 2021-08-26 JP JP2022545695A patent/JP7483899B2/ja active Active
- 2021-08-26 US US18/023,131 patent/US20230293905A1/en active Pending
- 2021-08-26 WO PCT/JP2021/031307 patent/WO2022045238A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010076708A1 (en) * | 2008-12-30 | 2010-07-08 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | System and method for administering light therapy |
| WO2015011589A1 (en) * | 2013-07-25 | 2015-01-29 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | System and method for providing light therapy and modifying circadian rhythm |
| US20160067086A1 (en) * | 2014-09-09 | 2016-03-10 | LumiThera, Inc. | Devices and methods for non-invasive multi-wavelength photobiomodulation for ocular treatments |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2022045238A1 (enExample) | 2022-03-03 |
| US20230293905A1 (en) | 2023-09-21 |
| JP7483899B2 (ja) | 2024-05-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2580983C2 (ru) | Система для фототерапии, включающая оправы очков и контактные линзы | |
| RU2545904C2 (ru) | Система и способ для проведения фототерапии | |
| US20230064792A1 (en) | Illumination of an eye fundus using non-scanning coherent light | |
| US20250057420A1 (en) | Method and device for remote optical monitoring of intraocular pressure | |
| US20060200013A1 (en) | Systems and methods for maintaining optical fixation and alignment | |
| JP2000512520A (ja) | 対話型光フィールド装置 | |
| CN114272519B (zh) | 一种自适应调节医疗装置光能量源位置的方法及其装置 | |
| EP3884737B1 (en) | Head worn electronic device | |
| CN114224598B (zh) | 一种自适应调节医疗装置光能量源输出功率的方法及其装置 | |
| CN112912041B (zh) | 对直接选择性激光小梁成形术的保护 | |
| CN114306946B (zh) | 一种施加光能量于眼睛的医疗装置 | |
| US9131837B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for imaging the choroid | |
| CA2840124C (en) | Method and apparatus for imaging the choroid | |
| CN114209990B (zh) | 一种实时分析医疗装置的入眼有效功的方法及装置 | |
| JP7483899B2 (ja) | 光照射システム、ウェアラブル装置、および設置型の光照射装置 | |
| JP7752872B2 (ja) | 網膜への放射線治療装置 | |
| US20060181677A1 (en) | Method or apparatus for inhibiting myopia development in humans | |
| US20070025118A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for reducing visual aberrations | |
| JP7631510B2 (ja) | 光照射システム | |
| JP2013003075A (ja) | 糖濃度測定装置、糖濃度測定システム、及び糖濃度測定方法 | |
| WO2018201008A1 (en) | Non-mydriatic mobile retinal imager | |
| Delori et al. | Light levels in ophthalmic diagnostic instruments | |
| CN110267584A (zh) | 用于有效抑制内部反射的偏光眼底照相机 | |
| KR102877512B1 (ko) | 당뇨망막병증 치료용 다파장 광 조사 장치 및 방법 | |
| CN223248626U (zh) | 一种哺光眼镜 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21861660 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022545695 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 21861660 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |