WO2021029382A1 - Ue及びsmf - Google Patents
Ue及びsmf Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021029382A1 WO2021029382A1 PCT/JP2020/030441 JP2020030441W WO2021029382A1 WO 2021029382 A1 WO2021029382 A1 WO 2021029382A1 JP 2020030441 W JP2020030441 W JP 2020030441W WO 2021029382 A1 WO2021029382 A1 WO 2021029382A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- pdu session
- information
- session
- smf
- 3gpp access
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 409
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 109
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 34
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 253
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 139
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 85
- JLTPSDHKZGWXTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[6-(dicyanomethylidene)naphthalen-2-ylidene]propanedinitrile Chemical compound N#CC(C#N)=C1C=CC2=CC(=C(C#N)C#N)C=CC2=C1 JLTPSDHKZGWXTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 65
- 102100025683 Alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme Human genes 0.000 description 65
- 101710161969 Alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme Proteins 0.000 description 65
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 22
- 239000004820 Pressure-sensitive adhesive Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 9
- 101000579423 Homo sapiens Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102100028287 Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 102100021087 Regulator of nonsense transcripts 2 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 101710028540 UPF2 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 6
- 101150102131 smf-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- GVVPGTZRZFNKDS-JXMROGBWSA-N geranyl diphosphate Chemical compound CC(C)=CCC\C(C)=C\CO[P@](O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O GVVPGTZRZFNKDS-JXMROGBWSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000013256 coordination polymer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005641 tunneling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000007516 Chrysanthemum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 244000189548 Chrysanthemum x morifolium Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100038254 Cyclin-F Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101000884183 Homo sapiens Cyclin-F Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000004378 air conditioning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013475 authorization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012508 change request Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004321 preservation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/12—Setup of transport tunnels
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/08—Load balancing or load distribution
- H04W28/09—Management thereof
- H04W28/0925—Management thereof using policies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/02—Processing of mobility data, e.g. registration information at HLR [Home Location Register] or VLR [Visitor Location Register]; Transfer of mobility data, e.g. between HLR, VLR or external networks
- H04W8/08—Mobility data transfer
- H04W8/14—Mobility data transfer between corresponding nodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/18—Selecting a network or a communication service
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/15—Setup of multiple wireless link connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/30—Connection release
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/0252—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control per individual bearer or channel
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/11—Allocation or use of connection identifiers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/15—Setup of multiple wireless link connections
- H04W76/16—Involving different core network technologies, e.g. a packet-switched [PS] bearer in combination with a circuit-switched [CS] bearer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/30—Connection release
- H04W76/32—Release of transport tunnels
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/30—Connection release
- H04W76/34—Selective release of ongoing connections
Definitions
- the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) is studying the system architecture of 5GS (5G System), which is a 5th generation (5G) mobile communication system, and discussions are being held to support new procedures and new functions.
- 5GS 5G System
- 5GC 5G Core Network
- ATSSS Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting
- 5GS Non-Patent Document 1, Non-Patent Document 2).
- Non-Patent Document 3 Non-Patent Document 3
- ATSSS In the discussion on ATSSS, it is not the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) session (also called single access PDU session, SA PDU session, SA PDU Session) that has already been defined, but the multi-access PDU session (MA PDU session, MA PDU Session). Communication using a special PDU session called) is under consideration and discussion.
- PDU Protocol Data Unit
- PDU session anchor also called PDU Session Anchor, PSA
- PSA PDU Session Anchor
- SSC Session and Service Continuity
- SSC Session and Service Continuity
- One aspect of the present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object thereof is a procedure for changing the PSA of an MA PDU session in which SSC mode 2 or SSC mode 3 is set, or a MA PDU.
- the purpose is to clarify the behavior.
- the UE of one embodiment of the present invention is a UE (User Equipment) including a control unit and a transmission / reception unit, and the transmission / reception unit is from an AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function) and the network is ATSSS (Access Traffic Steering, Upon receiving the first information indicating whether or not to support Switching, Splitting), the control unit identifies whether or not ATSSS is supported by the network based on the first information, and the above-mentioned If the network does not support ATSSS, the control unit does not start the PDU session establishment procedure in order to establish an MA (Multi-Access) PDU (Protocol Data Unit) session.
- MA Multi-Access
- PDU Protocol Data Unit
- the communication control method is a communication control method executed by a UE (User Equipment), and the UE is from AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function) and the network is ATSSS (Access Traffic). It receives a first piece of information indicating whether it supports Steering, Switching, Splitting), and based on the first piece of information, identifies whether ATSSS is supported by the network, and the network is ATSSS. If the above is not supported, the PDU session establishment procedure is not started in order to establish the MA (Multi-Access) PDU (Protocol Data Unit) session.
- MA Multi-Access
- PDU Protocol Data Unit
- a procedure for changing the PSA of the MA PDU session in which SSC mode 2 or SSC mode 3 is set or a procedure for changing a part of the PSA of the MA PDU session to the PSA of the SA PDU session. It is also possible to clarify the procedure for changing a part of the PSA of the SA PDU session to the PSA of the MA PDU session and the behavior of each device when those procedures are executed.
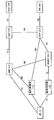
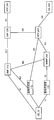
- FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining the outline of the mobile communication system 1
- FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the detailed configuration of the mobile communication system 1 and the first communication state.
- FIG. 14 is a diagram for explaining a second communication state.
- FIG. 15 is a diagram for explaining a third communication state.
- FIG. 1 shows that the mobile communication system 1 is composed of UE (User Equipment) _10, access network _100, access network _102, core network _200, and DN (Data Network) _300.
- UE User Equipment
- DN Data Network
- these devices / networks may be described by omitting symbols such as UE, access network, core network, DN and the like.
- Fig. 2 shows UE_10, base station device_110, base station device_120, AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function) _210, SMF (Session Management Function) _220, UPF (User Plane Function) _230, N3IWF (Non). -3GPP InterWorking Function) _240, PCF (Policy Control Function) _250, DN_300 and other device / network functions, and interfaces for connecting these devices / network functions to each other are described.
- AMF Access and Mobility Management Function
- SMF Session Management Function
- UPF User Plane Function
- N3IWF Non
- PCF Policy Control Function
- devices / network functions such as UE_10, base station device_112, base station device_122, AMF_210, SMF_220, UPF_232, N3IWF_242, PCF_250, DN_300, and these devices / network functions are connected to each other.
- the interface is described.
- devices / network functions such as UE_10, base station device_110, base station device_122, AMF_210, SMF_220, UPF_230, UPF_232, N3IWF_242, PCF_250, DN_300, and these devices / network functions are shown to each other.
- the interface to connect is described. Note that these devices / network functions may be described by omitting symbols such as UE, base station device, AMF, SMF, UPF, N3IWF, PCF, DN, etc.
- 5GS which is a 5G system, is configured to include a UE, an access network, and a core network, but may further include a DN.
- the UE is a device that can connect to network services via 3GPP access (3GPP access network, also called 3GPP AN) and / or non-3GPP access (non-3GPP access network, also called non-3GPP AN). is there.
- the UE may be a terminal device capable of wireless communication such as a mobile phone or a smartphone, and may be a terminal device capable of connecting to EPS (Evolved Packet System), which is a 4G system, or 5GS.
- EPS Evolved Packet System
- the UE may be provided with UICC (Universal Integrated Circuit Card) or eUICC (Embedded UICC).
- the UE may be expressed as a user device or a terminal device.
- the UE is a device that can use the ATSSS (Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting) function, that is, an ATSSS capable UE.
- ATSSS Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting
- the access network may also be referred to as a 5G access network (5G AN).
- 5GAN is composed of NG-RAN (NG Radio Access Network) and / or non-3GPP access network (non-3GPPAN).
- NG-RAN NG Radio Access Network
- non-3GPPAN non-3GPP access network
- One or more base chrysanthemum devices are installed in NG-RAN.
- the base station device may be gNB.
- gNB is a node that provides the NR (New Radio) user plane and control plane to the UE, and is a node that connects to 5GC via an NG interface (including an N2 interface or an N3 interface). That is, gNB is a newly designed base station device for 5GS and has a different function from the base station device (eNB) used in EPS.
- eNB base station device
- each gNB is connected to each other by, for example, an Xn interface.
- NG-RAN may be referred to as 3GPP access.
- wireless LAN access network and non-3GPP AN may be referred to as non-3GPP access.
- the nodes arranged in the access network may be collectively referred to as NG-RAN nodes.
- the device included in the access network and / or the device included in the access network may be referred to as an access network device.
- access network_100 supports 3GPP access
- access network_102 supports non-3GPP access.
- base station equipment_110 and / or base station equipment_112 is arranged in access network_100
- base station equipment_120 and / or base station equipment_122 and / or TNAP are arranged in access network_102.
- the base station device_110 and / or the base station device_112 and / or the base station device_120 and / or the base station device_122 and / or TNAP may be able to use the ATSSS function.
- access network_102 may be referred to as Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP Access.
- the base station device 120 and N3IWF in FIG. 2 describe the case of Untrusted Non-3GPP Access. That is, when the access network_102 is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access, the base station device_120 or the base station device_122 and N3IWF are used.
- the access network_102 is Trusted Non-3GPP Access (also referred to as Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network, TNAN), instead of base station device _120 or base station device _122 and N3IWF, Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point (also called TNAP) and Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function (also called TNGF) are used.
- TNAP and TNGF are located on access network _102 or core network _200.
- the core network is compatible with 5GC (5G Core Network).
- 5GC 5G Core Network
- AMF, UPF, SMF, PCF and the like are arranged in 5GC.
- 5GC may be expressed as 5GCN.
- the AMF, UPF, SMF, and PCF may be able to use the ATSSS function.
- N3IWF is located in access network_102 or core network_200.
- the core network and / or the device included in the core network may be referred to as a core network device.
- the core network may be an IP mobile communication network operated by a mobile network operator (MNO) that connects the access network and the DN, or a mobile network operator 1 that operates and manages the mobile communication system 1. It may be a core network for a mobile network operator, or a core network for a virtual mobile network operator such as MVNO (Mobile Virtual Network Operator) or MVNE (Mobile Virtual Network Enabler) or a virtual mobile communication service provider. ..
- MNO mobile network operator
- MVNE Mobile Virtual Network Enabler
- the DN may be a DN that provides a communication service to the UE.
- the DN may be configured as a packet data service network or may be configured for each service.
- the DN may include a connected communication terminal. Therefore, connecting to the DN may be connecting to a communication terminal or server device arranged in the DN. Further, sending and receiving user data to and from the DN may be sending and receiving user data to and from a communication terminal or server device arranged in the DN.
- At least a part of an access network, a core network, a DN, and / or one or more devices included in these may be referred to as a network or a network device. That is, a network and / or network device sending and receiving messages and / or performing a procedure means that an access network, a core network, at least a portion of a DN, and / or one or more devices contained therein. , Sending and receiving messages, and / or performing procedures.
- the UE can connect to the access network.
- the UE can also connect to the core network via the access network.
- the UE can connect to the DN via the access network and the core network. That is, the UE can send / receive (communicate) user data with the DN.
- IP Internet Protocol
- non-IP communication may be used.
- IP communication is data communication using IP, and data is transmitted and received by IP packets.
- An IP packet is composed of an IP header and a payload part.
- the payload section may include devices / functions included in EPS and data transmitted / received by devices / functions included in 5GS.
- non-IP communication is data communication that does not use IP, and data is transmitted and received in a format different from the structure of IP packets.
- non-IP communication may be data communication realized by sending and receiving application data to which an IP header is not added, or a UE can add another header such as a Mac header or an Ethernet (registered trademark) frame header.
- User data to be sent and received may be sent and received.
- each device may be configured as physical hardware, may be configured as logical (virtual) hardware configured on general-purpose hardware, or may be configured as software. May be done. Further, at least a part (including all) of the functions of each device may be configured as physical hardware, logical hardware, or software.
- each storage unit (storage unit_330, storage unit_440, storage unit_540) in each device / function appearing below is, for example, a semiconductor memory, SSD (Solid State Drive), HDD (Hard Disk Drive). ) Etc.
- each storage unit has not only the information originally set from the shipping stage, but also devices / functions other than its own device / function (for example, UE and / or access network device, and / or core network device, and /.
- various information transmitted / received to / from PDN and / or DN can be stored.
- each storage unit can store identification information, control information, flags, parameters, and the like included in control messages transmitted and received in various communication procedures described later. Further, each storage unit may store such information for each UE.
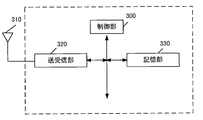
- the UE is composed of a control unit_300, an antenna_310, a transmission / reception unit_320, and a storage unit_330.
- the control unit_300, the transmission / reception unit_320, and the storage unit_330 are connected via a bus.
- the transmitter / receiver_320 is connected to the antenna_310.
- Control unit_300 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire UE.
- the control unit_300 may process all the functions that the other functional units (transmission / reception unit_320, storage unit_330) in the UE do not have.
- the control unit _300 realizes various processes in the UE by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _330 as needed.
- the transmission / reception unit_320 is a functional unit for wireless communication with a base station device or the like in the access network via the antenna_310. That is, the UE can transmit / receive user data and / or control information to / from the access network device and / or the core network device and / or the DN by using the transmission / reception unit_320.
- the UE can communicate with the base station device_110, the base station device_120, and TNAP by using the transmission / reception unit_320. That is, the UE communicates with the base station device_110 when communicating via 3GPP access. The UE also communicates with base station device_120 or TNAP when communicating via non-3GPP access. More specifically, the UE communicates with the base station device_120 when communicating via Untrusted non-3GPP Access, and the UE communicates with TNAP when communicating via Trusted non-3GPP Access. .. In this way, the UE can change the connection destination according to the access network to be used.
- the UE can communicate with the core network device (AMF, SMF, UPF, etc.) by using the transmitter / receiver _320.
- AMF core network device
- SMF SMF
- UPF User Plane Function
- the UE can send and receive AMF and NAS (Non-Access-Stratum) messages via the N1 interface (the interface between the UE and AMF).
- the N1 interface is a logical interface
- the communication between the UE and AMF is actually base station device_110, base station device_112, base station device_120, base station device_122, It is done via TNAP.
- the UE may communicate with AMF via base station device_110 or base station device_112 when communicating via 3GPP access.
- non-3GPP access Untrusted non-3GPP Access
- the UE can communicate with the base station device_120 or the base station device_122 via N3IWF with AMF.
- the UE can communicate with AMF via TNAP and TNGF.
- the information exchanged between the UE and AMF is mainly control information.
- the UE can communicate with the SMF using the N1 interface and the N11 interface (the interface between the AMF and the SMF). Specifically, the UE can communicate with the SMF via the AMF. As described above, the communication path between the UE and AMF may follow three types of routes depending on the access (3GPP access, Untrusted Non-3GPP Access, Trusted Non-3GPP Access).
- the information exchanged between the UE and SMF is mainly control information.
- the UE can communicate with the UPF using the N3 interface (the interface between the access network and the UPF). Specifically, the UE may communicate with the UPF via base station device_110 or base station device_112 when communicating via 3GPP access. Further, when communicating via non-3GPP access (Untrusted non-3GPP Access), the UE can communicate with the UPF via base station device_120 or base station device_122 and N3IWF. In addition, the UE can communicate with the UPF via TNAP and TNGF when communicating via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP Access).
- the communication path between the UE and UPF is mainly used to send and receive user data.
- the UE can communicate with the PCF using the N1 interface, the N11 interface, and the N7 interface (the interface between the SMF and the PCF). Specifically, the UE can communicate with the PCF via AMF and SMF. As described above, the communication path between the UE and AMF may follow three types of routes depending on the access (3GPP access, Untrusted Non-3GPP Access, Trusted Non-3GPP Access). The information exchanged between the UE and the PCF is mainly control information.
- UE can communicate with DN using N3 interface and N6 interface (interface between UPF and DN). Specifically, when communicating via 3GPP access, the UE can communicate with base station device_110 or base station device_112 and DN via UPF. Further, when communicating via non-3GPP access (Untrusted non-3GPP Access), the UE can communicate with the DN via the base station device_120 or the base station device_122, N3IWF, and UPF. In addition, when communicating via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP Access), the UE can communicate with DN via TNAP, TNGF, and UPF.
- the communication path between the UE and DN that is, the PDU session or MAPDU session, is mainly used to send and receive user data.
- the above only describes the communication between the UE and a typical device / function in the present specification, and the UE can communicate with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. Needless to say.
- the storage unit_330 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the UE.
- the UE is a UE that supports the ATSSS function, and it is desirable that the control information received from the core network side be stored in the storage unit_330. Then, the control unit _300 performs communication using the MA PDU session or performs communication using the SA PDU session according to the control information received from the core network side or the control information stored in the storage unit _330. It may have a function of determining whether or not. Also, when communicating using a MAPDU session, determine whether to communicate via 3GPP access only, non-3GPP access only, or 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. can do. In addition, when communicating using the SA PDU session, it is possible to determine whether to communicate only via 3GPP access or only non-3GPP access. The control unit_300 controls the transmission / reception unit 320 so that it can communicate appropriately according to these decisions.
- the UE when communicating using a MAPDU session, the UE may have a function of deciding which access the uplink traffic should be routed to according to the ATSSS rules received from the SMF.
- the UE may have a function of requesting the establishment of a MA PDU session based on the URSP rules received from the PCF.
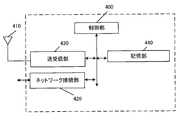
- Base station device_110 is a base station device located in 3GPP access.
- the base station device_110 is composed of a control unit_400, an antenna_410, a network connection unit_420, a transmission / reception unit_430, and a storage unit_440.
- the control unit_400, network connection unit_420, transmission / reception unit_430, and storage unit_440 are connected via a bus.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is connected to the antenna_410.
- the base station device_110 may be a base station device that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_400 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire base station device_110. Note that the control unit_400 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_420, transmission / reception unit_430, storage unit_440) in the base station device_110 do not have. The control unit _400 realizes various processes in the base station device _110 by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _440 as needed.
- the network connection unit_420 is a functional unit for the base station device_110 to communicate with the AMF and / or the UPF. That is, the base station apparatus_110 can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from the AMF and / or the UPF or the like by using the network connection unit_420.
- the base station device_110 can communicate with the AMF via the N2 interface (the interface between the access network and the AMF) by using the network connection unit_420. Further, the base station device_110 can communicate with the UPF via the N3 interface by using the network connection unit_420.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is a functional unit for wireless communication with the UE via the antenna_410. That is, the base station device_110 can transmit / receive user data and / or control information between the UE and the UE by using the transmission / reception unit_430 and the antenna_410.
- the base station device_110 has a function of transmitting user data and / or control information to the core network device when the user data and / or control information addressed to the core network device is received from the UE. Further, the base station apparatus_110 has a function of transmitting the user data and / or the control information to the UE when the user data and / or the control information addressed to the UE is received from the core network apparatus.
- the above only describes the communication between the base station device_110 and a typical device / function, and the base station device_110 communicates with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. It goes without saying that you can do it.
- the storage unit_440 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the base station device_110.
- Base station device_120 is a base station device located in non-3GPP access (Untrusted non-3GPP Access).
- the base station device_120 is composed of a control unit_400, an antenna_410, a network connection unit_420, a transmission / reception unit_430, and a storage unit_440.
- the control unit_400, network connection unit_420, transmission / reception unit_430, and storage unit_440 are connected via a bus.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is connected to the antenna_410.
- the base station device_120 may be a base station device that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_400 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire base station device_120.
- the control unit _400 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit _420, transmission / reception unit _430, storage unit _440) in the base station device _120 do not have.
- the control unit _400 realizes various processes in the base station apparatus _120 by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _440 as needed.
- the network connection unit_420 is a functional unit for the base station device_120 to communicate with the N3IWF, and is a functional unit for communicating with the AMF and / or UPF via the N3IWF. That is, the base station device_120 can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from the N3IWF by using the network connection unit_420. Further, the base station device_120 can transmit / receive control information and / or user data to / from the AMF and / or the UPF or the like by using the network connection unit_420.
- the base station device_120 can communicate with the N3IWF via the Y2 interface (the interface between the access network and the N3IWF) by using the network connection unit_420.
- the base station device_120 can communicate with the AMF via the N2 interface (the interface between the N3IWF and the AMF) via the N3IWF.
- the base station device_120 can communicate with the UPF via the N3 interface (the interface between the N3IWF and the UPF) via the N3IWF.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is a functional unit for wireless communication with the UE via the antenna_410. That is, the base station apparatus_120 uses the transmitter / receiver _430 and the antenna_410 to transmit user data and / or control information to and from the UE via the Y1 interface (interface between the access network and the UE). You can send and receive.
- the base station device_120 has a function of transmitting the user data and / or the control information to the core network device when the user data and / or the control information addressed to the core network device is received from the UE. Further, the base station apparatus_120 has a function of transmitting the user data and / or the control information to the UE when the user data and / or the control information addressed to the UE is received from the core network apparatus.
- the base station device_120 only describes the communication between the base station device_120 and a typical device / function, and the base station device_120 communicates with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. It goes without saying that you can do it.
- the storage unit_440 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the base station device_120.
- TNAP is a base station device (also referred to as an access point) located in non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP Access).
- TNAP is composed of a control unit_400, an antenna_410, a network connection unit_420, a transmission / reception unit_430, and a storage unit_440.
- the control unit_400, network connection unit_420, transmission / reception unit_430, and storage unit_440 are connected via a bus.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is connected to the antenna_410.
- the TNAP may be a TNAP that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_400 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire TNAP.
- the control unit_400 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_420, transmission / reception unit_430, storage unit_440) in TNAP do not have.
- the control unit _400 realizes various processes in TNAP by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _440 as needed.
- the network connection unit_420 is a functional unit for TNAP to communicate with TNGF, and is a functional unit for communicating with AMF and / or UPF via TNGF. That is, TNAP can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from TNGF using the network connection unit_420. In addition, TNAP can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from AMF and / or UPF, etc. using the network connection unit_420.
- TNAP can communicate with TNGF via the Ta interface (the interface between TNAP and TNGF) by using the network connection part_420.
- TNAP can communicate with AMF via N2 interface (interface between TNGF and AMF) via TNGF.
- TNAP can communicate with UPF via N3 interface (interface between TNGF and UPF) via TNGF.
- the transmitter / receiver_430 is a functional unit for wireless communication with the UE via the antenna_410. That is, TNAP can send and receive user data and / or control information to and from the UE via the Yt interface (interface between TNAP and UE) using the transmitter / receiver _430 and antenna_410. ..
- TNAP has a function of transmitting user data and / or control information to the core network device when receiving user data and / or control information addressed to the core network device from the UE. Further, TNAP has a function of transmitting user data and / or control information to the UE when the user data and / or control information addressed to the UE is received from the core network device.
- TNAP can communicate with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. ..
- the storage unit_440 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of TNAP.
- N3IWF is a device and / or function that is placed between non-3GPP access and 5GC when the UE connects to 5GS via non-3GPP access (Untrusted non-3GPP Access). It is located in non-3GPP access (Untrusted non-3GPP Access) or core network.
- N3IWF consists of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540. The control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus. Further, the N3IWF may be an N3IWF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire N3IWF. Note that the control unit_500 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the N3IWF do not have. The control unit_500 realizes various processes in the N3 IWF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit_540 as needed.
- the network connection unit_520 is a functional unit for N3IWF to communicate with the base station device_120 or the base station device_122, and / or the AMF, and / or the UPF. That is, the N3IWF can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from the base station device _120 or the base station device _122 by using the network connection unit _520. In addition, N3IWF can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from AMF and / or UPF, etc. using the network connection unit_520.
- the N3IWF can communicate with the base station device _120 or the base station device _122 via the Y2 interface by using the network connection unit _520.
- the N3IWF can also communicate with the AMF via the N2 interface.
- N3IWF can also communicate with UPF via the N3 interface.
- the above only describes the communication between the N3IWF and a typical device / function, and it goes without saying that the N3IWF can communicate with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. ..
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of N3IWF.
- N3IWF has a function to establish an IPsec tunnel between the UE and an IPsec tunnel, a function to terminate the N2 interface for the control plane, a function to terminate the N3 interface for the user plane, a function to relay NAS signaling between the UE and AMF, and a PDU session.
- Ability to process N2 signaling from SMF with respect to and QoS a function to establish IPsec SA (Security Association) to support PDU session traffic, a function to relay userplane packets between UE and UPF (IPsec) Includes packet encapsulation / decapsulation for N3 tunnels), functions as a local mobility anchor within an untrusted non-3GPP access network, and the ability to select AMF. All of these functions are controlled by control unit_500.
- TNGF is a device and / or function that is placed between non-3GPP access and 5GC when the UE connects to 5GS via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP Access). It is located in non-3GPP Access (Trusted non-3GPP Access) or in the core network.
- the TNGF is composed of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540. The control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus. Also, the TNGF may be a TNGF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire TNGF.
- the control unit_500 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the TNGF do not have.
- the control unit _500 realizes various processes in the TNGF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _540 as needed.
- Network connection _520 is a functional unit for TNGF to communicate with TNAP and / or AMF and / or UPF. That is, the TNGF can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from TNAP using the network connection unit_520. In addition, the TNGF can send and receive control information and / or user data to and from the AMF and / or the UPF, etc. using the network connection unit_520.
- TNGF can communicate with TNAP via the Y2 interface by using the network connection part_520.
- the TNGF can also communicate with the AMF via the N2 interface.
- TNGF can also communicate with UPF via the N3 interface.
- the above only describes the communication between the TNGF and a typical device / function, and it goes without saying that the TNGF can communicate with a device / function other than the above, that is, a core network device other than the above. ..
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of TNGF.
- TNGF has a function to terminate N2 interface and N3 interface, a function to act as an approver when UE registers with 5GC via TNAN, a function to select AMF, and a NAS message between UE and AMF.
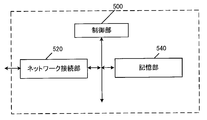
- the AMF consists of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540.
- the control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus.
- the AMF may be a node that handles the control plane. Further, the AMF may be an AMF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire AMF.
- the control unit_500 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the AMF do not have.
- the control unit_500 realizes various processes in AMF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit_540 as needed.
- the network connection part_520 is a functional part for AMF to connect to the base station equipment in 5GAN and / or SMF and / or PCF, and / or UDM, and / or SCEF. That is, the AMF uses the network connection _520 to communicate with the base station equipment in 5GAN and / or SMF and / or PCF, and / or UDM, and / or SCEF. Alternatively, control information can be transmitted and received.
- the AMF in the 5GC can communicate with the base station device via the N2 interface by using the network connection _520, and the N8 interface (AMF and UDM). Can communicate with UDM via interface between), can communicate with SMF via N11 interface, and can communicate with PCF via N15 interface (interface between AMF and PCF) it can.
- AMF can send and receive NAS messages to and from the UE via the N1 interface by using the network connection unit_520.
- the N1 interface is logical, communication between the UE and AMF is actually done via 5GAN.
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of AMF.
- AMF has a function to exchange control messages with RAN using the N2 interface, a function to exchange NAS messages with UE using the N1 interface, a function to encrypt and protect the integrity of NAS messages, and registration management.
- the RM status for each UE is managed.
- the RM state may be synchronized between the UE and AMF.
- the RM state includes a non-registered state (RM-DEREGISTERED state) and a registered state (RM-REGISTERED state).
- RM-DEREGISTERED state the UE is not registered in the network, so the UE context in the AMF does not have valid location information or routing information for the UE, so the AMF cannot reach the UE.
- the RM-REGISTERED state the UE is registered in the network, so the UE can receive services that require registration with the network.
- the RM state may be expressed as a 5GMM state (5GMM state).
- the RM-DEREGISTERED state may be expressed as 5GMM-DEREGISTERED state
- the RM-REGISTERED state may be expressed as 5GMM-REGISTERED state.
- the 5GMM-REGISTERED state may be a state in which each device has established a 5GMM context or a PDU session context.
- UE_10 may start sending and receiving user data and control messages, or may respond to paging. Further, when each device is in the 5GMM-REGISTERED state, UE_10 may execute a registration procedure other than the registration procedure for initial registration and / or a service request procedure.
- each device may be in a state where the 5GMM context has not been established, the location information of UE_10 may not be known to the network, or the network may be in the state of UE_10. It may be in an unreachable state.
- UE_10 may start the registration procedure or establish the 5GMM context by executing the registration procedure.
- the CM state may be synchronized between the UE and AMF.
- the CM state includes a non-connected state (CM-IDLE state) and a connected state (CM-CONNECTED state).
- CM-IDLE state the UE is in the RM-REGISTERED state, but does not have a NAS signaling connection established with the AMF via the N1 interface.
- N2 connection N2 connection
- N3 connection N3 interface connection
- the CM-CONNECTED state has a NAS signaling connection established with the AMF via the N1 interface.
- the CM-CONNECTED state the UE may have an N2 interface connection (N2 connection) and / or an N3 interface connection (N3 connection).
- the CM state in 3GPP access and the CM state in non-3GPP access may be managed separately.
- the CM state in 3GPP access may be a non-connected state in 3GPP access (CM-IDLE state over 3GPP access) and a connected state in 3GPP access (CM-CONNECTED state over 3GPP access).
- the CM state in non-3GPP access includes the non-connection state (CM-IDLE state over non-3GPP access) in non-3GPP access and the connection state (CM-CONNECTED state over non-3GPP access) in non-3GPP access. ) May be there.
- the disconnected state may be expressed as an idle mode
- the connected state mode may be expressed as a connected mode.
- the CM state may be expressed as 5GMM mode (5GMM mode).
- the non-connected state may be expressed as 5GMM non-connected mode (5GMM-IDLE mode)
- the connected state may be expressed as 5GMM connected mode (5GMM-CONNECTED mode).
- the disconnected state in 3GPP access may be expressed as 5GMM non-connection mode (5GMM-IDLE mode over 3GPP access) in 3GPP access
- the connection state in 3GPP access is 5GMM connection mode (5GMM- It may be expressed as CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access).
- non-connection state in non-3GPP access may be expressed as 5GMM non-connection mode (5GMM-IDLE mode over non-3GPP access) in non-3GPP access, and the connection state in non-3GPP access is non. It may be expressed as 5GMM connection mode (5GMM-CONNECTED mode over non-3GPP access) in -3GPP access.
- the 5GMM non-connection mode may be expressed as an idle mode, and the 5GMM connection mode may be expressed as a connected mode.
- AMF may be placed in the core network.
- AMF may be an NF that manages one or more NSIs (Network Slice Instances).
- the AMF may be a shared CP function (CCNF; Common CPNF (Control Plane Network Function)) shared among a plurality of NSIs.
- CCNF Common CPNF (Control Plane Network Function)
- the SMF consists of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540.
- the control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus.
- the SMF may be a node that handles the control plane. Further, the SMF may be an SMF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire SMF. Note that the control unit_500 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the SMF do not have. The control unit _500 realizes various processes in the SMF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _540 as needed.
- the network connection part_520 is a functional part for SMF to connect with AMF and / or UPF and / or PCF and / or UDM. That is, the SMF can send and receive user data and / or control information between the AMF and / or the UPF and / or the PCF and / or the UDM by using the network connection part_520.
- the SMF in the 5GC can communicate with the AMF via the N11 interface by using the network connection _520, and the N4 interface (between the SMF and UPF). It can communicate with the UPF via the interface), with the PCF via the N7 interface, and with the UDM via the N10 interface (the interface between the SMF and UDM).
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the SMF.
- SMF has session management functions such as establishment, modification, and release of PDU sessions, IP address allocation and management functions for UEs, UPF selection and control functions, and appropriate destinations (appropriate destinations).
- SMF has a function to create ATSSS rules and N4 rules from PCC rules received from PCF.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling MAPDU sessions sent from SMF to UE.
- N4 rules are information for controlling the MA PDU session sent from SMF to UPF.
- SMF has a function of associating and managing PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules (also referred to as mapping). All of these functions are controlled by control unit_500.
- the UPF consists of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540.
- the control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus.
- the UPF may be a node that handles the user plane.
- the UPF may be a UPF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire UPF. Note that the control unit_500 may process all the functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the UPF do not have. The control unit _500 realizes various processes in the UPF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _540 as needed.
- the network connection unit_520 is a functional unit for the UPF to connect to the base station equipment in 5GAN and / or the SMF and / or the DN. That is, the UPF can send and receive user data and / or control information between the base station device in 5GAN and / or the SMF and / or the DN by using the network connection part_520.
- the UPF in the 5GC can communicate with the base station equipment via the N3 interface by using the network connection _520, via the N4 interface. It can communicate with SMF, can communicate with DN via N6 interface, and can communicate with other UPFs via N9 interface (interface between UPFs).
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the UPF.
- the UPF functions as an anchor point for intra-RAT mobility or inter-RAT mobility, and as an external PDU session point for interconnecting to the DN (that is, as a gateway between the DN and the core network, as a user.
- Data transfer function
- packet routing and transfer function
- UL CL Uplink Classifier
- It has a branching point function, a QoS (Quality of Service) processing function for userplane, a function for verifying uplink traffic, a function for buffering downlink packets, and a function for triggering downlink data notification (Downlink Data Notification).
- the UPF also has the function of deciding which access the downlink traffic should be routed to when the MAPDU session is established, based on the N4 rules received from the SMF. All of these functions are controlled by control unit_500.
- the UPF may also be a gateway for IP communication and / or non-IP communication.
- the UPF may have a function of transferring IP communication, or may have a function of converting non-IP communication and IP communication.
- the plurality of gateways arranged may be gateways connecting the core network and a single DN.
- the UPF may have connectivity with other NFs, or may be connected to each device via the other NFs.
- the user plane is user data sent and received between the UE and the network.
- the user plane may be sent and received using a PDU session. Further, in the case of 5GS, the user plane may be transmitted and received via the interface between the UE and NG RAN and / or the N3 interface and / or the N9 interface and / or the N6 interface.
- the user plane may be expressed as a U-Plane.
- control plane is a control message sent and received to control the communication of the UE.
- the control plane may be transmitted and received using a NAS (Non-Access-Stratum) signaling connection between the UE and AMF.
- NAS Non-Access-Stratum
- control plane may be transmitted and received using the interface between the UE and NG RAN and the N2 interface.
- the control plane may be expressed as a control plane or a C-Plane.
- the U-Plane (User Plane; UP) may be a communication path for transmitting and receiving user data, and may be composed of a plurality of bearers.
- the C-Plane (Control Plane; CP) may be a communication path for transmitting and receiving control messages, and may be composed of a plurality of bearers.
- the PCF is composed of a control unit_500, a network connection unit_520, and a storage unit_540.
- the control unit_500, network connection unit_520, and storage unit_540 are connected via a bus.
- the PCF may be a PCF that supports the ATSSS function.
- Control unit_500 is a functional unit that controls the operation and functions of the entire PCF. Note that the control unit_500 may process all functions that the other functional units (network connection unit_520, storage unit_540) in the PCF do not have. The control unit _500 realizes various processes in the PCF by reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit _540 as needed.
- the network connection part_520 is a functional part for the PCF to connect with the SMF and / or AF (Application Function). That is, the PCF can send and receive control information to and from the SMF and / or AF by using the network connection unit_520.
- the PCF can communicate with the SMF via the N7 interface by using the network connection part_520.
- the PCF can communicate with the AF (Application Function) via the N5 interface (the interface between the PCF and the AF) by using the network connection unit_520.
- the storage unit_540 is a functional unit for storing programs, user data, control information, etc. required for each operation of the UPF.
- PCF has a function to support a unified policy framework, a function to provide policy rules to a control function (control plane function) to enforce them, a function to access registration information, etc. have.
- the PCF also has the ability to generate policies for MA PDU sessions (also called PCC rules), policies for SA PDU sessions, and URSP rules. These are sent to the SMF, at least some of which may be sent to the UE or to the UPF. All of these functions are controlled by control unit_500.
- the network refers to at least a part of the access network, core network, and DN. Further, one or more devices included in at least a part of the access network, the core network, and the DN may be referred to as a network or a network device. That is, the fact that the network executes the transmission / reception and / or processing of messages may mean that the devices (network devices and / or control devices) in the network execute the transmission / reception and / or processing of messages. .. Conversely, the fact that a device in the network executes message transmission / reception and / or processing may mean that the network executes message transmission / reception and / or processing.
- SM session management
- NAS Non-Access-Stratum
- SM messages may be NAS messages used in procedures for SM, and are sent and received between UE and SMF via AMF. It may be a control message to be executed.
- SM messages include PDU session establishment request messages, PDU session establishment acceptance messages, PDU session completion messages, PDU session rejection messages, PDU session change request messages, PDU session change acceptance messages, PDU session change response messages, and the like. You may.
- the procedure for SM may include a PDU session establishment procedure.
- the 5GS (5G System) service may be a connection service provided using the core network. Further, the 5GS service may be a service different from the EPS service or a service similar to the EPS service.
- non 5GS service may be a service other than the 5GS service, and may include an EPS service and / or a non EPS service.
- DNN Data Network Name
- DN DN
- DNN can also be used as information for selecting a gateway such as UPF that connects the core network.
- the DNN may correspond to the APN (Access Point Name) in EPS.
- a PDU session can be defined as a relationship between a DN that provides a PDU connectivity service and a UE.
- a PDU session is between a UE and an external gateway or DN. It may be the connectivity established in.
- the UE can send and receive user data to and from the DN using the PDU session.
- the external gateway may be UPF, SCEF, or the like.
- the UE can use the PDU session to send and receive user data to and from devices such as application servers located in the DN.
- the PDU connectivity service is a service that provides PDU exchange between the UE and DN.
- this PDU session is composed of only userplane resources in one access network (3GPP access network or non-3GPP access network), and may be referred to as an SA PDU session. That is, the SA PDU session may be a PDU session that, unlike the MA PDU session, is not simultaneously composed of user plane resources in the 3GPP access network and user plane resources in the non-3GPP access network.
- each device may manage one or more identification information in association with each other for the PDU session.
- these identification information may include one or more of DNN, TFT, PDU session type, application identification information, NSI identification information, access network identification information, and SSC mode, and other information may be further included. May be included. Further, when a plurality of PDU sessions are established, the identification information associated with the PDU session may have the same content or different contents.
- the MA PDU session may be a PDU session that provides a PDU connectivity service capable of using one 3GPP access network and one non-3GPP access network at the same time.
- the MA PDU session may also be a PDU session that provides a PDU connectivity service that can use one 3GPP access network or one non-3GPP access network at any given time.
- the MAPDU session may consist only of userplane resources in the 3GPP access network, may consist only of userplaneresources in the non-3GPP access network, userplaneresources in the 3GPP access network and It may be configured at the same time by userplane resources in the non-3GPP access network.
- the fact that the UE communicates with the DN using the MAPDU session may mean that the UE communicates with the DN using only userplane resources in the 3GPP access network, or the UE communicates with the DN using the non-3GPP access network. It may be possible to communicate with the DN using only the userplane resources in the 3GPP access network, or it may be to communicate with the DN using the userplane resources in the 3GPP access network and the userplane resources in the non-3GPP access network. ..
- the UE can execute the transmission / reception of user data with a device such as an application server arranged in the DN by using the MAPDU session.
- each device may manage one or more identification information in association with each MA PDU session.
- these identification information may include one or more of DNN, TFT, PDU session type, application identification information, NSI identification information, access network identification information, and SSC mode, and other information may be further included. May be included. Further, when a plurality of MA PDU sessions are established, the identification information associated with the MA PDU session may have the same content or different contents.
- the PDU (Protocol Data Unit or Packet Data Unit) session type indicates the type of PDU session, and includes IPv4, IPv6, Ethernet (registered trademark), and Unstructured.
- IPv4 indicates that data is sent and received using IPv4.
- IPv6 indicates that data is sent and received using IPv6.
- Ethernet registered trademark
- Ethernet registered trademark
- Ethernet may indicate that communication using IP is not performed.
- Unstructured it indicates that data is sent and received to the application server etc. in the DN by using the point-to-point (P2P) tunneling technology.
- the PDU session type may include an IP in addition to the above.
- IP can be specified if the UE can use both IPv4 and IPv6.
- IP may also be expressed as IPv4 v6.
- a network slice is a logical network that provides specific network capabilities and network characteristics.
- UEs and / or networks can support network slices (NW slices; NS) in 5GS.
- a network slice instance is composed of an instance (entity) of a network function (NF) and a set of necessary resources, and forms a network slice to be arranged.
- NF is a processing function in a network and is adopted or defined in 3GPP.
- NSI is an entity of NS that consists of one or more in the core network.
- NSI may be composed of a virtual NF (Network Function) generated by using NST (Network Slice Template).
- NST Network Slice Template
- NST Network Slice Template
- NSI may be a logical network configured to divide user data delivered by services or the like.
- One or more NFs may be configured in NS.
- the NF configured in NS may or may not be a device shared with other NS.
- UE and / or devices in the network are 1 or more based on NSSAI and / or S-NSSAI and / or UE usage type and / or registration information such as 1 or more NSI IDs and / or APN.
- the UE usage type is a parameter value included in the UE registration information used to identify the NSI.
- the UE usage type may be stored in the HSS.
- AMF may select SMF and UPF based on UE usage type.
- S-NSSAI Single Network Slice Selection Assistance Information
- S-NSSAI may be composed of only SST (Slice / Service type), or may be composed of both SST and SD (Slice Differentiator).
- SST is information indicating the operation of NS expected in terms of functions and services.
- SD may be information for interpolating SST when selecting one NSI from a plurality of NSIs represented by SST.
- the S-NSSAI may be information peculiar to each PLMN, or may be standard information shared among PLMNs.
- the network may store one or more S-NSSAI in the UE registration information as the default S-NSSAI. If the S-NSSAI is the default S-NSSAI and the UE does not send a valid S-NSSAI to the network in the registration request message, the network may provide the NS related to the UE.
- NSSAI Network Slice Selection Assistance Information
- S-NSSAI Network Slice Selection Assistance Information
- Each S-NSSAI included in NSSAI is information that assists the access network or core network in selecting NSI.
- the UE may memorize the NSSAI permitted from the network for each PLMN.
- NSSAI may also be the information used to select AMF.
- SSC Session and Service Continuity
- SSC mode indicates the mode of session service continuity (Session and Service Continuity) supported by the system and / or each device in the 5G system (5GS). More specifically, it may be a mode indicating the types of session service continuation supported by the PDU session established between the UE and UPF.
- SSC mode may be a mode indicating the type of session service continuation set for each PDU session.
- the SSC mode may be composed of three modes, SSC mode 1, SSC mode 2, and SSC mode 3. Note that the SSC mode associated with the PDU session does not have to be changed for the life of the PDU session.
- SSC mode1 is a mode in which the network maintains the connectivity service provided to the UE.
- the PDU session type associated with the PDU session is IPv4 or IPv6, the IP address may be maintained when the session service is continued.
- SSC mode1 may be a session service continuation mode in which the same UPF is maintained regardless of the access technology used when the UE connects to the network. More specifically, SSC mode1 is a mode that realizes session service continuation even when UE mobility occurs, without changing the UPF used as the PDU session anchor of the established PDU session. Good.
- SSC mode2 is a mode in which the network releases the connectivity service provided to the UE and the corresponding PDU session.
- the PDU session type associated with the PDU session is IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4v6, even if the IP address assigned to the UE is released when changing the anchor of the PDU session. Good.
- SSC mode2 may be a session service continuation mode in which the same UPF is maintained only within the serving area of the UPF. More specifically, SSC mode 2 may be a mode that realizes session service continuation without changing the UPF used by the established PDU session as long as the UE is within the serving area of the UPF. Furthermore, SSC mode2 is a mode that realizes session service continuation by changing the UPF used by the established PDU session when UE mobility occurs, such as leaving the serving area of the UPF. Good.
- the serving area of the UPF may be an area where one UPF can provide the session service continuation function, or a subset of the access network such as RAT and cells used when the UE connects to the network. It may be. Further, the subset of access networks may be a network composed of one or more RATs and / or cells.
- the change of the anchor point of the PDU session of SSC mode 2 may be realized by each device executing the procedure of changing the PSA of SSC mode 2.
- the anchor or the anchor point may be expressed as an end point.
- SSC mode 3 is a mode in which changes in the user plane are revealed to the UE while the network guarantees that connectivity will not be lost.
- SSC mode3 in order to realize better connectivity service, a PDU session passing through a new PDU session anchor point may be established before the established PDU session is disconnected.
- the PDU session type associated with the PDU session is IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4v6, the IP address assigned to the UE is not maintained when changing the anchor of the PDU session. May be good.
- SSC mode 3 has a PDU session established between the UE and the UPF, and / or a new PDU session via the new UPF for the same DN before disconnecting the communication path, and / Alternatively, the mode may be a session service continuation mode that allows the establishment of a communication path. Further, SSC mode 3 may be a session service continuation mode that allows the UE to become multihoming. Furthermore, SSC mode 3 may be a mode in which session service continuation using a plurality of PDU sessions and / or UPFs associated with PDU sessions is permitted. In other words, in the case of SSC mode 3, each device may realize the session service continuation by using a plurality of PDU sessions, or may realize the session service continuation by using a plurality of UPFs.
- the selection of the new UPF may be carried out by the network, and the new UPF is where the UE connects to the network. It may be the most suitable UPF.
- the UE immediately implements the mapping of the application and / or flow communication to the newly established PDU session. It may be carried out based on the completion of communication.
- the change of the anchor point of the PDU session of SSC mode 3 may be realized by each device executing the procedure of changing the PSA of SSC mode 3.
- the default SSC mode is the SSC mode used by the UE and / or the network when a specific SSC mode is not determined.
- the default SSC mode is the SSC mode used by the UE when there is no SSC mode request from the application and / or when there is no UE policy to determine the SSC mode for the application. May be good.
- the default SSC mode may be the SSC mode used by the network when there is no request for the SSC mode from the UE.
- the default SSC mode may be set for each DN, may be set for each PDN, or may be set for each PDN, based on the subscriber information and / or the operator policy and / or the UE policy. , And / or may be set for each subscriber. Further, the default SSC mode may be information indicating SSC mode 1, SSC mode 2, or SSC mode 3.
- IP address preservation is a technology that allows you to continue to use the same IP address. If IP address maintenance is supported, the UE can continue to use the same IP address for user data communication even when moving out of the TA. In other words, if IP address maintenance is supported, each device may be able to continue to use the same IP address for user data communication even when the anchor point of the PDU session changes. ..
- the steering feature also allows ATSSS-enabled UEs to steer, switch, and split traffic in MAPDU sessions via 3GPP and non-3GPP access. It may be a function.
- the steering function may include an MPTCP (Multi-Path Transmission Control Protocol) function and an ATSSS (Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting) -LL (Low-Layer) function.
- MPTCP Multi-Path Transmission Control Protocol
- ATSSS Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting
- -LL Low-Layer
- the MPTCP function is a steering function for layers above the IP layer and is applied to TCP traffic. Traffic to which the MPTCP function is applied may be referred to as an MPTCP flow.
- the MPTCP function of the UE can communicate with the MPTCP proxy function of the UPF using the user plane of 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access. Also, if the UE requests a MAPDU session and provides MPTCP capability, the MPTCP function may be enabled, and if the UPF agrees to enable the MPTCP function, the UPF will enable the MPTCP Proxy function. You can be.
- the network also assigns one IP address / prefix and two IP addresses / prefixes (also called link-specific multipath addresses) for MAPDU sessions.
- One of the link-specific multipath addresses is used to establish a subflow via 3GPP access and the other is used to establish a subflow via non-3GPP access.
- the link-specific multicast address is used only for the MPTCP function of the UE. Cannot route via N6.
- the network can send MPTCP proxy information (which may include the IP address, port number, and type of MPTCP proxy) to the UE.
- the type may be Type 1 (transport converter).
- the network may show the UE a list of apps to which the MPTCP function should be applied.
- the ATSSS-LL function is a steering function for layers below the IP layer, and is applied to all types of traffic (TCP traffic, UDP (User Data Protocol) traffic, ethernet traffic, etc.). Traffic to which the ATSSS-LL function is applied may be referred to as Non-MPTCP flow.
- the UPF may also support steering functions that are the same as or similar to the ATSSS-LL function.
- the ATSSS-LL function of the UE determines the steering, switch, and split of upstream traffic based on the ATSSS rules and local conditions.
- the ATSSS-LL function may be enabled, and if the UE provides ATSSS-LL capability, the ATSSS-LL function in UPF is enabled. May become.
- ATSSS rules is a list of one or more ATSSS rules.
- the ATSSS rule may be composed of a rule priority (Rule Precedence) and / or a traffic descriptor (Traffic Descriptor) and / or an access selection descriptor (Access Selection Descriptor).
- Rule Precedence in ATSSS rule defines the order of ATSSS rules evaluated in UE.
- the UE may refer to the Rule Precedence in each ATSSS rule and evaluate in order from the highest priority ATSSS rule.
- the Traffic Descriptor in the ATSSS rule indicates when to apply the ATSSS rule.
- the Traffic Descriptor in the ATSSS rule may be composed of an application descriptor and / or an IP descriptor and / or a non-IP descriptor.
- the Application descriptors may also indicate information that identifies the application that generates the traffic.
- IP descriptors may indicate information that identifies the destination of IP traffic.
- non-IP descriptors may indicate information that identifies the destination of non-IP traffic (for example, ethernet traffic or unstructured traffic).
- the Access Selection Descriptor in the ATSSS rule may be composed of a steering mode and / or a steering function.
- the steering mode may be information indicating whether the traffic of the service data flow (also referred to as SDF) should be distributed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. Further, the steering mode may include four modes of Active-Standby, Smallest Delay, Load-Balancing, and Priority-based.
- Active-Standby sets active access and standby access, and when active access is available, steers the service data flow (SDF) for that access, and that active access is used. When it becomes impossible, it may be a mode to switch SDF to standby access.
- Active-Standby sets only active access, and if standby access is not set, it steers the service data flow (SDF) for that access when active access is available. The mode may be such that the SDF cannot be switched to standby access even if active access becomes unavailable.
- Smallest Delay may be a mode in which the service data flow (SDF) is steered for an access having the minimum RTT (Round-Trip Time). Also, when this mode is set, the UE and UPF may make measurements to determine the RTT when communicating via 3GPP access and the RTT when communicating via non-3GPP access.
- SDF service data flow
- RTT Red-Trip Time
- Load-Balancing may be a mode that separates the service data flow (SDF) for both accesses. If Load-Balancing is specified, it may also include information indicating the percentage of service data flow (SDF) that should be sent via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- SDF service data flow
- Priority-based is also used to steer all traffic in the service data flow (SDF) for high priority access until it is determined to be congested. Mode may be used. If it is determined that the access is congested, the SDF traffic will be sent not only to the high-priority access but also to the low-priority access. Mode may be. Further, when high priority access becomes unavailable, all the traffic of SDF may be sent to low priority access.
- SDF service data flow
- the steering function may also indicate whether the MPTCP function or the ATSSS-LL function should be used to steer the traffic of the service data flow (also referred to as SDF). It may also be the information used if the UE supports both the MPTCP and ATSSS-LL features.
- the URSP (UE Route Selection Policy) rules may be composed of one or more URSP (UE Route Selection Policy Rule) rules paste.
- each URSP rule may be composed of a rule priority (Rule Precedence) and / or a traffic descriptor (Traffic descriptor) and / or a route selection descriptor list (List of Route Selection Descriptors).
- Rule Precedence in URSP rule indicates the order of URSP rules enforced in UE.
- the UE may refer to the Rule Precedence in each URSP rule and apply the URSP rules in order from the highest priority.
- Traffic descriptor in the URSP rule indicates when to apply the URSP rule.
- Traffic descriptors in the URSP rule are Application descriptors and / or IP descriptors, and / or Domain descriptors, and / or Non-IP descriptors. ), And / or DNN (Data Network Name), and / or Connection Capabilities.
- Application descriptors may include an OS ID and an OS application ID.
- IP descriptors indicate information that identifies a destination of IP traffic, and may include, for example, an IP address, an IPv6 network prefix, a port number, a protocol number, and the like.
- domain descriptors may indicate the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) of the destination.
- non-IP descriptors may indicate information that identifies the destination of non-IP traffic (for example, ethernet traffic or unstructured traffic).
- the DNN may also be information about the DNN provided by the application. Connection Capabilities may also indicate the information provided by the UE's application when the UE requests a connection to the network using its capabilities.
- the List of Route Selection Descriptors in the URSP rule may be composed of one or more route selection descriptors (Route Selection Descriptors).
- Each Route Selection Descriptor may be composed of the priority of the rule selection descriptor (Route Selection Descriptor Precedence) and / or the components of the route selection (Route selection components).
- RouteSelectionDescriptorPrecedence indicates the order in which RouteSelectionDescriptors are applied.
- the UE may refer to the Rule Precedence in each Route Selection Descriptor and apply the Route Selection Descriptors in order from the highest priority.
- RouteSelectionDescriptor is SSC mode selection (SSC Mode Selection) and / or network slice selection (Network Slice Selection) and / or DNN selection (DNN Selection) and / or PDU session type selection (PDU Session Type Selection). ), And / or a non-seamless offload indication, and / or an access type preference.
- SSCModeSelection may indicate that application traffic is routed through a specified SSC mode PDU session.
- Network Slice Selection may also indicate that it routes application traffic using the indicated PDU sessions that support one or more S-NSSAI.
- DNN Selection may also indicate that it routes application traffic using a PDU session that supports one or more of the indicated DNNs.
- this Route Selection Descriptor does not have to include DNN Selection.
- PDU session type selection may indicate that application traffic is routed using PDU sessions that support the indicated PDU session types.
- Non-Seamless Offload indication may indicate offloading application traffic for non-3GPP access.
- the AccessType preference may indicate the access type for establishing the PDU session when the UE needs to establish the PDU session.
- the access type may be 3GPP, non-3GPP, or multi-access. Multi-access may also indicate that the PDU session should be established as a MA PDU session with both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- the first identification information is DNN. Further, the first identification information may be information indicating the DNN required by the UE. Further, the first identification information may be a DNN that identifies the DN to which the MA PDU session or the SA PDU session that requests establishment is connected.
- the second identification information is information indicating whether or not the UE supports the ATSSS function.
- the information indicating whether or not the UE supports the ATSSS function may be expressed as ATSSS capability.
- the second identification information also supports information indicating whether the UE supports the MPTCP function, which is one of the ATSSS functions, and / or the ATSSS-LL function, which is another function of the ATSSS function. It may be information indicating whether or not.
- the information indicating whether or not the MPTCP function is supported may be expressed as MPTCP capability
- the information indicating whether or not the ATSSS-LL function is supported may be expressed as ATSSS-LL capability.
- the UE can include MPTCP capability in the second identification information.
- the UE can include the ATSSS-LL capability in the second identification information.
- the second identification information can include the MPTCP capability and the ATSSS-LL capability.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID. Further, the third identification information may be information indicating the PDU session ID requested by the UE (information for identifying the PDU session). Specifically, when the UE requests the establishment of a MA PDU session, the third identification information may be a PDU session ID for identifying the MA PDU session. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the SA PDU session, the third identification information may be the PDU session ID for identifying the SA PDU session.
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type. Further, the fourth identification information may be information indicating the PDU session type requested by the UE. Also, when the UE requests the establishment of a MA PDU session, the fourth identification information may be the PDU session type for the MA PDU session. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the SA PDU session, the fourth identification information may be the PDU session type for identifying the SA PDU session. Further, the fourth identification information may be any one of IPv4, IPv6, IPv4v6, Unstructured, and Ethernet (registered trademark).
- the fifth identification information is SSC mode. Further, the fifth identification information may be information indicating the SSC mode requested by the UE. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the MA PDU session, the fifth identification information may be the SSC mode for the MA PDU session. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the SA PDU session, the fifth identification information may be the SSC mode for the SA PDU session. Further, the fifth identification information may be any one of SSC mode 1, SSC mode 2, and SSC mode 3.
- the sixth identification information is S-NSSAI. Further, the sixth identification information may be information indicating S-NSSAI requested by the UE. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the MA PDU session, the sixth identification information may be S-NSSAI for the MA PDU session. Further, when the UE requests the establishment of the SA PDU session, the sixth identification information may be S-NSSAI for the SA PDU session. Also, when the UE requests the establishment of a MAPDU session, the sixth identity may be S-NSSAI, which is allowed for both accesses (3GPP access and non-3GPP access). Further, even when the UE requests the establishment of the SA PDU session, when the MA PDU session is established, specifically, the sixth identification information is registered by the UE for 5GS. It may be one or more S-NSSAI included in Allowed NSSAI (NSSAI permitted by the network) included in the Registration Accept message received from AMF in the Registration procedure executed in.
- Allowed NSSAI NSSAI permitted by the network
- the seventh identification information is Request type.
- the seventh identification information is an initial request, an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session), an emergency request (Emergency Request), or an existing emergency PDU session (Existing Emergency PDU Session), or Any of the MA PDU request may be indicated.
- Initial request may be specified when requesting the establishment of a new PDU session.
- the Existing PDU Session may also be specified when switching an existing PDU session between 3GPP access and non-3GPP access, or when handing over from an existing PDN connection in an EPC to a 5G PDU session.
- EmergencyRequest may be specified when requesting the establishment of a new PDU session for an emergency service.
- the Existing Emergency PDU Session is also 5G from the existing PDN connection for emergency services in EPC, when switching an existing PDU session for emergency service between 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. It may be specified when handing over to a PDU session.
- the MAPDURequest may also be specified to indicate that the UE requests the establishment of a MAPDU session. If a network that does not support the MAPDU session receives it, the MAPDURequest may be interpreted as an initial request. In addition, MAPDURequest may be expressed as MAPDURequest indication.
- the eighth identification information is the PDU session ID. Further, the eighth identification information may indicate a PDU session ID (also referred to as an old PDU session ID) indicating an old PDU session. Specifically, the 8th identification information is scheduled to be released in the procedure for changing the PSA of SSC mode 3 (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure). It may indicate the PDU session ID that is present. For example, the eighth identification information may indicate the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session when the MA PDU session is scheduled to be released. In addition, the eighth identification information may indicate the PDU session ID that identifies the SA PDU session when the SA PDU session is scheduled to be released.
- the ninth identification information is information indicating the access type. Also, the ninth identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access. Further, the ninth identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access) and / or non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access). Specifically, the 9th identification information is scheduled to be released in the procedure for changing the PSA of SSC mode 3 (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure). It may indicate the access corresponding to the user plane resources in the MA PDU session.
- the eighth identification information may be transmitted together with the ninth identification information.
- the 9th identifier modifies the PSA of SSC mode 3 when the 8th identity indicates 3GPP access.
- the procedure to be performed (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure)
- user plane resources via 3GPP access will be released in the established MAPDU session. It may be shown that there is.
- the 9th identification information indicates the PSA of SSC mode 3 when the 8th identification information indicates non-3GPP access.
- the procedure to change (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure)
- userplane resources via non-3GPP access It may indicate that it will be released.
- the eighth identification information indicates the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session
- the ninth identification information indicates that the eighth identification information indicates non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access). Is a non-3GPP access in the established MAPDU session in the procedure for changing the PSA of SSC mode 3 (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure). It may indicate that the userplane resources will be released via (untrusted non-3GPP access).
- the eighth identification information indicates the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session
- the ninth identification information indicates that the eighth identification information indicates non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access). Is a non-3GPP access in the established MAPDU session in the procedure for changing the PSA of SSC mode 3 (4th PSA change procedure, 5th PSA change procedure, 6th PSA change procedure). It may indicate that the userplane resources will be released via (Trusted non-3GPP access).
- the tenth identification information may be information having a content obtained by combining the contents of two or more identification information among the above-mentioned first to ninth identification information.
- the eleventh identification information is DNN. Further, the eleventh identification information may be information indicating the DNN determined by the network.
- the eleventh identification information includes the identification information of the first to eighth and / or the ability information of the network, and / or the operator policy, and / or the state of the network, and / or the user registration information, etc., depending on the network. The information may be determined based on the information. Further, the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information is information indicating whether or not the network supports the ATSSS function.
- information indicating whether or not the network supports the ATSSS function may be expressed as ATSSS capability.
- the twelfth identification information supports information indicating whether or not the network supports the MPTCP function, which is one function of the ATSSS function, and / or the ATSSS-LL function, which is another function of the ATSSS function. It may be information indicating whether or not.
- the information indicating whether or not the MPTCP function is supported may be expressed as MPTCP capability
- the information indicating whether or not the ATSSS-LL function is supported may be expressed as ATSSS-LL capability.
- MPTCP capability can be included in the twelfth identification information.
- the twelfth identification information can include the ATSSS-LL capability.
- the twelfth identification information can include the MPTCP capability and the ATSSS-LL capability.
- the twelfth identification information includes the identification information of the first to eighth and / or the capability information of the network, and / or the operator policy, and / or the state of the network, and / or the user registration information, etc., depending on the network.
- the information may be determined based on the information.
- the thirteenth identification information is the PDU session ID. Further, the thirteenth identification information may be information indicating the PDU session ID determined by the network (information for identifying the PDU session). Specifically, the thirteenth identification information may be the PDU session ID for the SA PDU session or the PDU session ID for the MA PDU session. More specifically, when the network allows the establishment of a MA PDU session, the thirteenth identifying information may be a PDU session ID for identifying the MA PDU session. Further, when the network permits the establishment of the SA PDU session, the thirteenth identification information may be the PDU session ID for identifying the SA PDU session.
- the thirteenth identification information may be used for the first to eighth identification information and / or the network capability information, and / or the operator policy, and / or the network status, and / or the user registration information, etc., depending on the network.
- the information may be determined based on the information.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information is the PDU session type. Further, the 14th identification information may be information indicating the PDU session type determined by the network. The 14th identification information may be any of IPv4, IPv6, IPv4v6, Unstructured, and Ethernet (registered trademark). Further, the 14th identification information may be information indicating the PDU session type corresponding to the PDU session to be established. Also, when the network allows the establishment of an SA PDU session, the 14th identifying information may be the PDU session type for the SA PDU session. Also, when the network allows the establishment of a MA PDU session, the 14th identifying information may be the PDU session type for the MA PDU session.
- the 14th identification information may be used in the 1st to 8th identification information and / or the network capability information and / or the operator policy and / or the network status and / or the user registration information depending on the network. The information may be determined based on the information. Further, the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the 15th identification information is SSC mode. Further, the fifteenth identification information may be information indicating the SSC mode determined by the network. Further, the fifteenth identification information may be any one of SSC mode 1, SSC mode 2, and SSC mode 3. Further, the fifteenth identification information may be information indicating the SSC mode corresponding to the established PDU session. Further, when the network allows the establishment of the SA PDU session, the fifteenth identification information may be the SSC mode for the SA PDU session. Further, when the network permits the establishment of the MA PDU session, the fifteenth identification information may be the SSC mode for the MA PDU session.
- the fifteenth identification information may be used in the first to eighth identification information and / or the network capability information and / or the operator policy and / or the network status, and / or the user registration information, etc., depending on the network.
- the information may be determined based on the information. Further, the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information.
- the 16th identification information is S-NSSAI. Further, the 16th identification information may be information indicating S-NSSAI determined by the network. Further, the 16th identification information may be information indicating S-NSSAI corresponding to the established PDU session. Also, when the network allows the establishment of MAPDU sessions, the 16th identity may be S-NSSAI, which is allowed for both accesses (3GPP access and non-3GPP access). Also, when the network allows the establishment of an SA PDU session, the 16th identification information may be S-NSSAI permitted for one access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access). Specifically, the 16th identification information is Allowed NSSAI (Network) included in the Registration Accept message received from AMF in the Registration procedure executed by the UE to register with 5GS. It may be one or more S-NSSAI included in NSSAI) permitted by.
- NSSAI Network
- the 16th identification information may be used in the 1st to 8th identification information and / or the network capability information and / or the operator policy and / or the network status, and / or the user registration information, etc., depending on the network.
- the information may be determined based on the information.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 17th identification information is information indicating whether or not the establishment of the MAPDU session is permitted by the network. Further, the 17th identification information may be information indicating that the establishment of the MA PDU session is permitted by the network. The 17th identification information is based on the 1st to 8th identification information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information. It may be the information to be determined.
- the 18th identification information is information indicating whether or not the establishment of the SA PDU session is permitted by the network. Further, the 18th identification information may be information indicating that the establishment of the SA PDU session is permitted by the network. The 18th identification information is based on the 1st to 8th identification information and / or the network capability information and / or the operator policy, and / or the network status, and / or the user registration information. It may be the information to be determined.
- the 19th identification information is information indicating the access type. Also, the 19th identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access. Further, the 19th identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access (untrusted 3GPP access) and / or non-3GPP access (Trusted 3GPP access). In addition, the 19th identification information indicates the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which the establishment is permitted when the network permits the establishment of the MA PDU session (the establishment of the user plane resources for both accesses is permitted). It may be the information to be shown. Here, the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment is permitted may be 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- the 19th identification information is based on the 1st to 8th identification information and / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information. It may be the information to be determined.
- the 20th identification information is ATSSS rules.
- the 20th identification information is based on the 1st to 8th identification information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information. It may be the information to be determined.
- the 21st identification information may be information having a content obtained by combining the contents of two or more identification information out of the above 11th to 20th identification information.
- the procedure for changing this PSA may include a first PSA change procedure and a second PSA change procedure.
- the first PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA (all PSAs) used in the first MAPDU session.
- the first PSA change procedure is the PSA used by userplane resources via 3GPP access and the userplane via non-3GPP access among the PSAs used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure to change the PSA used in resources.
- the second PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA (some PSAs) used in the first MAPDU session.
- the second PSA change procedure is only the PSA used in the user plane resources via one of the accesses (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) of the PSA used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure to change.
- the second PSA change procedure is the PSA used by user plane resources via one of the access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) of the PSA used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure that does not change the PSA used by userplane resources via the remaining access (non-3GPP access or 3GPP access).
- the first PSA change procedure is the establishment of a first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. This is a procedure to change the PSA (all PSAs) used in the first MA PDU session when SSC mode 2 is applied to one MA PDU session.
- the first PSA change procedure each device transitions from the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 to the second communication state shown in FIG. Also, by executing the first PSA change procedure, all PSAs are changed from UPF_230 to UPF_232.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 6 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE is in a state where it can send and receive user data to and from DN_300 using the first MAPDU session (S600).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in the S600.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_230 (also called the serving UPF) in use in the first MAPDU session needs to be reassigned (S602). SMF, for example, if it becomes unable to maintain userplane resources and / or userplaneresources via 3GPP access, and / or communicates via 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access. If the throughput of communication via is extremely low, and / or if UPF_230 is in an overflow state, and / or if the UE is moved, and / or if the operator policy or network policy is changed, and / or etc. It may be determined that UPF_230 needs to be reassigned when requested by the NF of.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S604. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 needs to be reassigned, each device may perform steps S604 and beyond. Here, the case where it is determined that the UPF_230 needs to be reassigned will be described. Next, the PDU session release procedure of S604 will be described with reference to FIG.
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF. The SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released by the user plane resources of the first MAPDU session, and here, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also releases the first MA PDU session of its UE by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230, and / or userplane resources and / or user plane resources and / or in the first MA PDU session via 3GPP access. You may request the release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session.
- the SMF does not have to send the access type to UPF_230.
- UPF_230 when UPF_230 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_230 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first MA PDU session of its UE and / or in the first MA PDU session. , Userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access, and / or the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session may be released.
- UPF_230 received the N4 session release request message by sending the N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first MA PDU session of the UE, and / or the first.
- SMF that released userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access and / or released the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session in the MAPDU session of You may tell (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_230 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF.
- UPF_230 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. When including access types, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_230 has received an N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_230 is the UE's first MA PDU.
- the session was released and / or UPF_230 released userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session, and / or UPF_230 was the first. It may be recognized that the N4 session corresponding to the MA PDU session of is released.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type and / or a reason value.
- the N2SM resource release request message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first MA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released, and here, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value may also indicate that the MA PDU session needs to be reestablished for the same DN.
- the SMF may instruct the release of the first MA PDU session of its UE by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message.
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. By receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the N2SM resource release request message, the AMF recognizes that the release of the first MA PDU session of the UE is instructed. You can do it.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via the access network (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, NAS messages are sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the NAS message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the NAS message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the base station device_110, and the base station device_110 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the destination depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP Access. Is different.
- AMF sends a NAS message to N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends NAS to base station device_120.
- the base station device_120 that sends a message and receives it may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends a NAS message to TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends a NAS message to TNAP.
- the TNAP that sends and receives this may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF releases the first MAPDU session of its UE and / or via userplane resources and non-3GPP access via 3GPP access in the first MAPDU session. You may notify the UE that you are instructed to release user plane resources.
- the UE When the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. The UE may recognize that the release of the first MA PDU session of the UE is instructed by receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message. The UE may then release the first MA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the UE cannot communicate with DN_300 because the first MA PDU session has been released.
- the UE is also registered in 5GS via 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- each device performs the PDU session establishment procedure of S606 in order to establish a new (second) MA PDU session for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the first communication state.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the MA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- each device can establish a new (second) MAPDU session when the MAPDU session establishment procedure is completed normally. Specifically, each device can establish a second MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- each device cannot establish a second MAPDU session if the MAPDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure may be a procedure initiated by the UE.
- each device may establish a plurality of MAPDU sessions by executing the MAPDU session establishment procedure a plurality of times.
- 3GPP access is assuming that they are managed / operated by the same operator, they are operated by different operators. It is possible to apply in some cases.
- the UE is the information stored in the UE in advance and / or the information received in advance from the access network and / or the information received in advance from the core network (identification information received in the registration procedure and / or from the PCF). It may be determined to start the MAPDU session establishment procedure in order to establish the second MAPDU session based on the URSP rules etc. received in advance).
- the UE starts the MA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access (also referred to as 3GPP access network) and non-3GPP access (also referred to as non-3GPP access network). That is, when the UE sends a NAS message via 3GPP access, the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via base station device_110. Also, when the UE transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the UE transmits a NAS message to AMF via base station device_120 and N3IWF. Also, when the UE sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via TNAP and TNGF. In this way, the communication route to AMF changes depending on which access the UE sends the NAS message from, but the communication route from AMF to SMF may be the same. Here, it is assumed that the NAS message is transmitted via 3GPP access.
- 3GPP access also referred to as
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN to be connected to the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the DN that was communicating in the first MA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN to be identified.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. It may have different PDU session IDs or the same PDU session ID.
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the same as the PDU session type set for the first MA PDU session. It is preferably set to the PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the SSC mode set for the first MA PDU session, that is, SSC mode 2. It is preferable to set it to, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and both access (3GPP access and non-) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for 3GPP access).
- the UE also includes the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message with the seventh identification information indicating the MAPDURequest, so that the PDU session establishment request message is the second. Being sent to establish a (new) MAPDU session and / or applying ATSSS-LL and / or MPTCP functionality to steer traffic in a second MAPDU session. May be notified to the network side.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the second if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses. You may refuse to establish a MA PDU session. The AMF may also refuse to establish a second MAPDU session if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when the establishment of the second MAPDU session is refused, it may be the case that the MAPDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- the AMF may send a NAS message to the UE containing information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session is rejected. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- the AMF when refusing to establish a second MAPDU session, the AMF sends information to the SMF indicating that it refuses to establish a second MAPDU session, and the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message.
- a NAS message containing an N1 SM container containing may be sent to the UE.
- the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message may contain information indicating that the establishment of the second MA PDU session is rejected.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request.
- the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, it may start the procedure of (A) and / or (B) of FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. Also, if the network refuses to establish a second MAPDU session (userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access refuses to establish a second MAPDU session. In the case of), the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF.
- the SMF may say that if the seventh identity indicates an initial request or MAPDURequest, that is, if this procedure is performed to establish a new (second) MAPDU session.
- SMF may select an appropriate PCF based on the information received from AMF and the like. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature.
- the SMF can also use the PCF already selected, that is, the PCF used in the first MA PDU session, when the seventh identity is an existing PDU session or an existing emergency PDU session. Good. That is, it is not necessary to select a PCF, but a different PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (S1306).
- the SMF decides to allow the establishment of the second MAPDU session, it further "information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session is permitted" and / or "user via 3GPP access".
- PCF for "information indicating that the establishment of user plane resources is permitted via plane resources and non-3GPP access” and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment is permitted (access type)”. May be sent to.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which the establishment is permitted (access type)" may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- the PCF when the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF, the UE requests the establishment of a second MAPDU session, and / or the information received from the SMF, etc. Can recognize the contents of (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF will tell the SMF "information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session has been permitted” and / Or "information indicating that the establishment of user plane resources via 3GPP access and non-3 GPP access is permitted” and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources that is permitted to be established”.
- (Access type) may be sent (S1306).
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which the establishment is permitted (access type)” may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- the PCF is permitted to establish a second MAPDU session based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) (via userplane resources via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access).
- a second MAPDU session was allowed to be established using the user plane resources), or based on the information (messages, containers, information) received from the SMF.
- PCC rules may be generated.
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF may also explicitly indicate to the SMF that it has allowed the establishment of the second MAPDU session by sending information indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the second MAPDU session.
- sending PCC rules may imply that the establishment of a second MAPDU session has been permitted.
- the PCF when the PCF generates a policy for the SA PDU session, it may send the policy to the SMF.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling the second MAPDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UE
- N4 rules are the information for controlling the second MAPDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UPF. It is information for controlling.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the second MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the second MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the second MAPDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the second MAPDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1308).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status. And / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF. Also, if multiple UPFs are selected, the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF. Also, if the establishment of a second MAPDU session is permitted, the SMF may select a UPF that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function. Here, it is assumed that UPF_232 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1308), the UPF can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the second MAPDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF may configure whether downlink traffic in the second MAPDU session to be established should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- the application of N4 rules in UPF may be performed after S1318.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the second MAPDU session. (S1310).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) passes through the access network. And send a NAS message to the UE (S1314) (S1316).
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network that receives the N2 PDU session request message sends a NAS message to the UE (S1316).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. That is, when the AMF transmits the NAS message via 3GPP access, the AMF transmits the NAS message to the UE via the base station device_110. When the AMF transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the AMF transmits the NAS message to the UE via the N3IWF and the base station device_120. Also, when AMF sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), it sends a NAS message to the UE via TNGF and TNAP.
- the AMF preferably transmits the NAS message to the UE via the same access as the access received from the UE, but may transmit the NAS message via a different access. Absent. Here, the explanation will be continued assuming that the NAS message is transmitted via 3GPP access (base station device_110).
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request. Also, the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the establishment of the second MA PDU session has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance is accepted.
- Messages and / or N1 SM containers and / or PDU session IDs (13th identification) and / or access types (19th identification) and / or NAS messages and / or N2SM information, and / or / Or the N2 PDU session request message may contain at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 17th identification information may indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of a second MAPDU session.
- the 19th identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the second MA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- / or the establishment of userplane resources via 3GPP access and / or the establishment of userplaneresources via non-3GPP access was permitted, and / or the establishment of userplaneresources was permitted.
- the corresponding access type may be notified to the UE.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1316).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE was allowed to establish a second MAPDU session and / or userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplane resources via non-3GPP access, and / Or can recognize the access type corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment is permitted.
- the UE is in a state where user plane resources have been established via 3GPP access.
- the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using a second MAPDU session with user plane resources via 3GPP access. That is, the UE may be communicable with the DN via 3GPP access and UPF_232.
- user plane resources via non-3GPP access may not yet be established.
- the SMF may send an N4 session correction request message to the already selected UPF_232 via the N4 interface (S1318).
- the N4 session correction request message does not need to be sent including the N4 rules, but may be included.
- UPF_232 when UPF_232 receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from SMF. UPF_232 may then send an N4 session corrective response message to the SMF via the N4 interface (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session correction response message, it can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF.
- the SMF then sends the N2SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification) and / or the access type (19th identification) to the AMF via the N11 interface (S1322). ).
- the SMF does not need to transmit the N1SM container transmitted in S1312 to the AMF, but may transmit it.
- the AMF receives the N2SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information).
- AMF may send an N2PDU session request message to N3IWF. Further, when the second MAPDU session uses Trusted non-3GPP access, AMF may send an N2PDU session request message to TNGF and / or TNAP.
- the N2 PDU session request message may include N2 SM information.
- the N2 PDU session request message does not have to include the NAS message, but may be included.
- N3IWF S1324.
- N3IWF executes the procedure for establishing IPsec child SA (security association) with the UE via the access network (S1326).
- N3IWF describes IKEv2 in RFC 7296 to establish an IPsec Child SA for the second MA PDU session (user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the second MA PDU session).
- the IKE Create_Child_SA request message may indicate that the requested IPsec Child SA operates in tunnel mode.
- the IKE Create_Child_SA request message may include the PDU session ID associated with this Child SA.
- the UE when it accepts IPsec Child SA, it sends an IKE Create_Child_SA response message to N3IWF.
- SMF and / or AMF can be used in the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or access type (19th identification information), and / or N2 SM information, and / or N2 PDU session request message. At least one of the 11th to 21st identification information may be included and transmitted.
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE and / or N3IWF and / or the access network of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the contents of the identification information of the 11th to 21st may be the same as the contents in the procedure of (A).
- the 19th identification information in the procedure (A) indicates only 3GPP access
- the 19th identification information in the procedure (B) may indicate only non-3GPP access.
- the UE may recognize that user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access based on the receipt of the IKE Create_Child_SA request message and / or the transmission of the IKE Create_Child_SA response message.
- N4 rules in UPF may be performed after S1318, and the application of ATSSS rules in UE may be performed at this stage.
- the UE When the procedure (B) in Fig. 13 is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access. That is, the UE may be communicable with the DN via non-3GPP access and UPF_232.
- the UE when the procedures (A) and (B) in Fig. 13 are completed normally, the UE will have a second MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via 3GPP access. It may be used to enable communication with the DN.
- normally completing the procedures (A) and (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure is normally completed.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if it refuses to establish a second MAPDU session, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish a second MAPDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed). In this case, a second (new) MAPDU session cannot be established. Further, in this case, since the first MAPDU session has already been released and the second MAPDU session could not be established, the UE may be in a state where it cannot communicate with the DN. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 6 may be skipped.
- the UE When the PDU session establishment procedure is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where a second MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access has been established. It is ready to communicate with DN_300 using 2 MA PDU sessions (S608).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_232.
- the first PSA change procedure When the first PSA change procedure is completed, the first MA PDU session using the first communication state shown in Fig. 2 (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access) From the established state), a second MA PDU session is established using the second communication state shown in FIG. 14 (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access). Transition to the current state). In addition, the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_232 by executing the first PSA change procedure.
- the second PSA change procedure is the establishment of a first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. This is the procedure to change the PSA (some PSAs) used in the first MA PDU session when SSC mode 2 is applied to the first MA PDU session.
- the case where only the PSA used in user plane resources via non-3GPP access is changed and the PSA used in user plane resources via 3GPP access is not changed will be described.
- each device transitions from the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 to the third communication state shown in FIG.
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_230 and UPF_232 by executing the second PSA change procedure.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 7 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE is in a state where it can send and receive user data to and from DN_300 using the first MAPDU session (S700).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in the S700.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_230 (also called the serving UPF) in use in the first MAPDU session needs to be reassigned (S702).
- SMF for example, when it becomes unable to maintain user plane resources via non-3GPP access and / or when the throughput of communication via non-3GPP access drops significantly, and / or when UPF_230 overflows.
- UPF_230 needs to be reassigned. Good.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S704. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 needs to be reassigned, each device may perform steps S704 and beyond. Here, the case where it is determined that the UPF_230 needs to be reassigned will be described. Next, the PDU session release procedure of S704 will be described with reference to FIG.
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF. The SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released by the user plane resources of the first MAPDU session, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also releases the first MA PDU session of its UE by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230, and / or a user plane via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may request the release of resources and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first MA PDU session (or user plane resources via non-3GPP access).
- UPF_230 when UPF_230 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_230 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first MA PDU session of its UE and / or in the first MA PDU session. , Release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access, and / or release of N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session (or userplaneresources via non-3GPP access).
- UPF_230 received the N4 session release request message by sending the N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first MA PDU session of the UE, and / or the first. Released userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or released N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session (or userplaneresources via non-3GPP access). You may tell SMF what you have done (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_230 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF. In addition, UPF_230 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. If you include an access type, you may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_230 has received an N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_230 is the UE's first MA PDU.
- the session was released and / or UPF_230 released userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session, and / or UPF_230 released the first MAPDU session (or non-3GPP). It may be recognized that the N4 session corresponding to userplane resources) via access has been released.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type and / or a reason value.
- the N2SM resource release request message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first MA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value may also indicate that it is necessary to establish an SA PDU session for the same DN.
- the SMF releases the first MA PDU session and / or the first MA of its UE by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1SM container and / or an N2SM resource release request message. You may instruct the release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the PDU session.
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. Upon receiving the N1SM container and / or N2SM resource release request message, the AMF releases the first MAPDU session of its UE and / or provides non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session. You may recognize that you are instructed to release user plane resources through it.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via the access network (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, NAS messages may be sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the NAS message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the NAS message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the base station device_110, and the base station device_110 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the destination depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP access. Is different.
- AMF sends a NAS message to N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends NAS to base station device_120.
- the base station device_120 that sends a message and receives it may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends a NAS message to TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends a NAS message to TNAP.
- the TNAP that sends and receives this may send a NAS message to the UE.
- the AMF By sending a NAS message, the AMF is instructed to release the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or release the user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may notify the UE that you are.
- the UE When the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. The UE releases the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or / or the user via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message. You may recognize that the release of plane resources is instructed. The UE may then release the user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the UE releases user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session, but the UE uses user plane resources via 3GPP access. Since the MA PDU session of 1 is maintained, it is possible to communicate with DN_300 using the first MA PDU session.
- the UE is also registered in 5GS via 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- each device establishes a new (first) SA PDU session via non-3GPP access for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the first communication state.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the SA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the SA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- non-3GPP access is untrusted non-3GPP access
- the base station device _120 and N3IWF with TNAP and TNGF, it can be applied even when non-3GPP access is Trusted non-3GPP access.
- the UE Before executing this SA PDU session establishment procedure, the UE is registered in 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the state of being registered with 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the IPsec SA for NAS signaling with N3IWF. May be in an established state.
- the UE starts the SA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (base station device_120) (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface (S1300).
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the PDU session establishment request message is sent to N3IWF using IPsec SA for NAS signaling, and N3IWF forwards the received PDU session establishment request message to AMF.
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN that is the connection destination of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the DN that was communicating in the first MA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN to be identified.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. Must be set to a different PDU session ID.
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the same as the PDU session type set for the first MA PDU session. It is preferably set to the PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the SSC mode set for the first MA PDU session, that is, SSC mode 2. It is preferable to set it to, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and both access (3GPP access and non-) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for 3GPP access).
- the UE also includes in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message a seventh identification information indicating an initial request or an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session).
- the PDU session establishment request message was sent to establish the first (new) SA PDU session, and / or the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU.
- the network may be notified that the ATSSS-LL function and / or the MPTCP function will be applied to steer the traffic of the session.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the first if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses. You may refuse to establish a SA PDU session. The AMF may also refuse to establish a first SA PDU session if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused, it may be the case that the SA PDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- the AMF may send a NAS message to the UE containing information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- the AMF when refusing to establish the first SA PDU session, the AMF sends information to the SMF indicating that it refuses to establish the first SA PDU session, and the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message.
- a NAS message containing an N1 SM container containing may be sent to the UE.
- the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message may contain information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is rejected.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request. In the third condition determination, the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, the SMF may start the procedure (B) in FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. If the network allows the establishment of the first SA PDU session, the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network refuses to establish the first SA PDU session, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. The condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF. For example, if the 7th identity indicates an Initial request, that is, if this procedure is performed to establish a new (1st) SA PDU session, the SMF will An appropriate PCF may be selected based on the information received from the AMF. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature. Further, when the seventh identification information indicates an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session), the SMF may use the PCF already selected, that is, the PCF used in the first MA PDU session. .. That is, it is not necessary to select a new PCF, but a new PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (not shown).
- the SMF decides to permit the establishment of the first SA PDU session, it further "information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted" and / or "the first that permits the establishment".
- Information indicating the access corresponding to the SA PDU session of (access type) may be sent to the PCF.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF when the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF, the UE requests the establishment of the first SA PDU session, and / or the information received from the SMF, etc. Can recognize the contents of (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF decides to allow the establishment of the first SA PDU session, the PCF tells the SMF "information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted" and / Alternatively, "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)" may be transmitted.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)" may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF detects that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information), or the information received from the SMF (message, message, information). If you allow the establishment of the first SA PDU session based on the container, information), you may generate PCC rules (also called policies, routing rules) for the first SA PDU session.
- PCC rules also called policies, routing rules
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF may also explicitly indicate to the SMF that it has allowed the establishment of the first SA PDU session by sending information indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the first SA PDU session.
- sending PCC rules may imply that the establishment of the first SA PDU session has been permitted.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information transmitted from the PCF, it can recognize the contents of the information. Then, when the SMF receives the PCC rules from the PCF, the SMF may generate ATSSS rules (20th identification information) and N4 rules from the PCC rules.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session transmitted from SMF to UE
- N4 rules are information sent from SMF to UPF. Information for controlling the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session transmitted.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the first SA PDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the first SA PDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the first SA PDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the first SA PDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1318).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status.
- / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF.
- the SMF may select the UPF that supports the first SA PDU session and / or the ATSSS function.
- UPF_232 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the first SA PDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF may configure whether downlink traffic in an established SA PDU session should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the first SA PDU session. (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) is the N3IWF and the access network.
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the N3 IWF (S1324)
- the N3 IWF that receives the N2 PDU session request message is sent to the UE via the access network (base station device_120).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request. Also, the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the PDU session establishment has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the ATSSS container IE and / or the PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or the N1SM container and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or The access type (19th identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information and / or N2PDU session request message contains at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. Good.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 18th identification information may indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of the first SA PDU session.
- the 19th identification information may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the first SA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- the UE may be notified of the access type corresponding to the first SA PDU session that was allowed to establish and / or was allowed to establish.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1326).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE can recognize that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted and / or the access type corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted.
- the UE When the procedure (B) in Fig. 13 is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where the first SA PDU session is established via non-3GPP access. That is, the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access. That is, the UE may be communicable with the DN via non-3GPP access and UPF_232.
- normally completing the procedure (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure is normally completed.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish the SA PDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- the first SA PDU session cannot be established via non-3GPP access.
- the UE cannot communicate with the DN using this first MAPDU session because the first MAPDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access is still maintained. It is in a state where it can be done. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 7 may be skipped.
- the UE Upon successful completion of the PDU session establishment procedure, the UE will be in a state where the first MA PDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access have been established. , It is possible to communicate with DN_300 using these 1st MA PDU session and 1st SA PDU session (S708) (S710).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230 and UPF_232.
- the first MA PDU session using the first communication state (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access) shown in Fig. 2 is started. From the established state), the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 (the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU via non-3GPP access). Transition to the state where the session is established).
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_230 and UPF_232 by executing the second PSA change procedure.
- the procedure for changing this PSA may include a third PSA change procedure.
- the third PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA of the first SA PDU session.
- the third PSA modification procedure consists of a first MA PDU session using only user plane resources via one access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) and the other access (non-).
- the first SA PDU session is established via 3GPP access or 3GPP access
- SSC mode 2 is applied to those first MA PDU session and first SA PDU session.
- the procedure for changing the PSA of the first SA PDU session is established.
- the case where the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access) are established. explain.
- the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access (Trusted non) It is also applicable when a first SA PDU session is established via 3GPP access).
- a case where each device transitions from the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 to the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 by executing the third PSA change procedure will be described.
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 and UPF_232 to UPF_230 by executing the third PSA change procedure.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 8 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE sends and receives user data to and from DN_300 using the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via the above 3GPP access and the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access. It is in a state where it is possible (S800) (S802).
- the PSAs at this time are UPF_230 and UPF_232 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in the S800 and S802.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_232 (also called the serving UPF) in use in the first SA PDU session needs to be reassigned (S804).
- SMF for example, when it becomes unable to maintain user plane resources via non-3GPP access and / or when the throughput of communication via non-3GPP access drops significantly, and / or when UPF_230 overflows.
- UPF_232 needs to be reassigned. Good.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S806. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 needs to be reassigned, each device may perform the steps from S806 onwards. Here, the case where it is determined that the UPF_232 needs to be reassigned will be described. Next, the PDU session release procedure of S806 will be described with reference to FIG.
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_232 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF.
- the SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released in the first SA PDU session, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also requests the release of the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first SA PDU session by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230. May be good.
- the SMF does not have to send the access type to UPF_232.
- UPF_232 when UPF_232 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_232 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first SA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session of that UE. You may release the corresponding N4 session.
- UPF_232 then received the N4 session release request message by sending an N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first SA PDU session of its UE, and / or the first. You may tell the SMF that you have released the N4 session that corresponds to your SA PDU session (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_232 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF.
- UPF_232 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. If you include an access type, you may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_232 has received the N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_232 is the UE's first SA PDU. It may be recognized that the session has been released and / or UPF_232 has released the N4 session corresponding to the first SA PDU session.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type and / or a reason value.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first SA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value is that it is necessary to reestablish the MAPDU session for the same DN, add it to the MAPDU session for the same DN, or add userplane resources to the MAPDU session for the same DN. May be shown.
- the SMF releases the first SA PDU session of its UE and / or to the same DN by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message. You may instruct to add user plane resources to the MA PDU session.
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. By receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the N2SM resource release request message, the AMF releases the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or for the same DN. You may be aware that you are instructed to add userplane resources to your MAPDU session.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via non-3GPP access (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the AMF sends a NAS message to the N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends a NAS message to the base station device_120, and the base station device_120 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the AMF sends a PDU session release command message and / or an N1SM container and / or a NAS message to release the first SA PDU session of its UE and / or to a MA PDU session for the same DN. You may notify the UE that you are instructed to add user plane resources.
- the UE when it receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. Then, by receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message, the UE releases the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or MAPDU for the same DN. You may be aware that you are instructed to add userplane resources to your session. The UE may then release the first SA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the UE has released the first SA PDU session.
- the UE since the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access is maintained, the UE is in a state where it can communicate with DN_300 using the first MA PDU session.
- the UE is also registered in 5GS via 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- each device establishes user plane resources via non-3GPP access for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the third communication state, that is, via 3GPP access.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the MA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- non-3GPP access is untrusted non-3GPP access
- the base station device _120 and N3IWF with TNAP and TNGF, it can be applied even when non-3GPP access is Trusted non-3GPP access.
- the UE Before executing this MAPDU session establishment procedure, the UE is registered in 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the state of being registered with 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the IPsec SA for NAS signaling with N3IWF. May be in an established state.
- 3GPP access is assuming that they are managed / operated by the same operator, they are operated by different operators. It is possible to apply in some cases.
- the UE is the information stored in the UE in advance and / or the information received in advance from the access network and / or the information received in advance from the core network (identification information received in the registration procedure and / or from the PCF Start the MA PDU session establishment procedure to add user plane resources via non-3GPP access to the first MA PDU session based on (including URSP rules etc. received in advance) etc. You may judge that.
- the UE starts the MA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access (also referred to as 3GPP access network) and non-3GPP access (also referred to as non-3GPP access network). That is, when the UE sends a NAS message via 3GPP access, the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via base station device_110. Also, when the UE transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the UE transmits a NAS message to AMF via base station device_120 and N3IWF. Also, when the UE sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via TNAP and TNGF. In this way, the communication route to AMF changes depending on which access the UE sends the NAS message from, but the communication route from AMF to SMF may be the same. Here, it is assumed that the NAS message is transmitted via non-3GPP access.
- 3GPP access also referred to
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN to which the user plane resources that request establishment (addition) are connected, and communicates in the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN that identifies the existing DN.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session of userplane resources that requests establishment (addition), and is different from the PDU session ID set for the first SA PDU session. It may be a PDU session ID, or it may be the same PDU session ID as the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. Here, if the third identification information is set to the same PDU session ID as the PDU session ID of the first MA PDU session, it may mean that the UE requests addition to the first MA PDU session. ..
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the MA PDU session of userplane resources that requests establishment (addition), and is set for the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set the same PDU session type as the existing PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the MA PDU session of the user plane resources requesting establishment (addition), and is set for the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to SSC mode, that is, SSC mode 2, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the MA PDU session of user plane resources that requests establishment (addition), and both access (3GPP access and non-3GPP) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for access).
- the UE also includes the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container, and / or the NAS message with the seventh identification information indicating the MAPDURequest, so that the PDU session establishment request message is a new MA.
- ATSSS-LL feature and / or MPTCP to be sent to establish a PDU session (to add user plane resources) and / or to steer the traffic of the first MA PDU session You may notify the network side that the function will be applied.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the first if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses.
- MA PDU session establishment (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) may be rejected.
- the AMF may also refuse to establish a first MAPDU session (add user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when rejecting the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), it may be the case that the MA PDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- AMF when refusing to establish a first MA PDU session (adding user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), AMF will also establish a first MA PDU session (to the first MA PDU session). A NAS message containing information indicating that the addition of user plane resources) may be rejected may be sent to the UE. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- AMF when refusing to establish a first MA PDU session (adding userplane resources to the first MA PDU session), AMF tells the SMF to establish a first MA PDU session (first).
- the SMF may send a NAS message containing the N1SM container containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE by sending information indicating that the user plane resources will be rejected to the MA PDU session.
- the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) is rejected for the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request. In the third condition determination, the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, the SMF may start the procedure (B) in FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network refuses to establish the first MA PDU session (adding user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF. For example, in the SMF, when the seventh identification information indicates an initial request or MAPDURequest, that is, the establishment of a new first MAPDU session (user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) If this procedure is performed to add), SMF may select an appropriate PCF based on the information received from AMF and so on. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature. The SMF can also use the PCF already selected, that is, the PCF used in the first SA PDU session, when the seventh identity is an existing PDU session or an existing emergency PDU session. Good. That is, it is not necessary to select a PCF, but a different PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (not shown).
- the SMF decides to allow the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session)
- it further “establishes the first MA PDU session (first).
- information indicating access (access type) corresponding to user planet resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted may be sent to the PCF.
- “information indicating access corresponding to user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) sent from the SMF
- the UE establishes the first MAPDU session (adds user plane resources to the first MAPDU session). Can recognize what you are requesting and / or the content of information (messages, containers, information) received from SMF.
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF decides to allow the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session)
- the PCF tells the SMF that "the first MA Information indicating that the establishment of the PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) was permitted "and / or” the establishment (addition) of user plane resources via non-3GPP access was permitted.
- Information indicating that, and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)" may be transmitted.
- “information indicating access corresponding to user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF was allowed to establish the first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) based on the information received from the SMF (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF was allowed to establish the first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) based on the information received from the SMF (messages, containers, information).
- PCC rules for the first MAPDU session may be generated.
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF also sends information to the SMF indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), thereby sending the first MA.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling the first MA PDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UE
- N4 rules are the information for controlling the first MA PDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UPF. It is information for controlling.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the first MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the first MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the first MAPDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the first MAPDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1318).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status.
- / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF. Also, if multiple UPFs are selected, the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF.
- the SMF selects the UPF that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function. You can. Here, it is assumed that UPF_230 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the first MAPDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF sets whether downlink traffic in the first MA PDU session, including the established (added) user plane resources, should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. Good.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the first MA PDU session. (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) is the N3IWF and the access network.
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the N3 IWF (S1324)
- the N3 IWF that receives the N2 PDU session request message is sent to the UE via the access network (base station device_120).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- And / or PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or access type (19th identification information), and / or NAS message, and / or N2 SM information, and / or N2 PDU session request message May include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 17th identification information may indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session).
- the 19th identification information may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the first MA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- (Addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) was allowed, and / or establishment (addition) of userplaneresources via non-3GPP access was allowed, and / or The UE may be notified of the access type corresponding to the userplane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1326).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE is allowed to establish a first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) and / or establish userplane resources via non-3GPP access. It is possible to recognize the access type corresponding to the user plane resources that has been permitted and / or has been permitted to be established (added).
- the UE When the procedure (B) in Fig. 13 is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access. In other words, the UE is in a state where user plane resources via non-3GPP access are established (added) for the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access that has already been established. It becomes. That is, the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using the first MA PDU session with user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- normally completing the procedure (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure is normally completed.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) is rejected, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish the SA PDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- user plane resources cannot be established via non-3GPP access. That is, the UE cannot establish (add) user plane resources via non-3GPP access for the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access that has already been established. ..
- the UE can communicate with the DN using the first MAPDU session because the first MAPDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access is still maintained. It is in a state. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 8 may be skipped.
- the UE When the PDU session establishment procedure is completed normally, the UE is in a state where the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access is established, and the first MA PDU session is established. It is in a state where it can communicate with DN_300 using the MA PDU session of (S810).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230.
- the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first MA PDU session via non-3GPP access.
- the first MA PDU using the first communication state shown in Fig. 2 (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access). Transition to the state where the session is established).
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 and UPF_232 to UPF_230 by executing the third PSA change procedure.
- the procedure for changing this PSA may include a fourth PSA change procedure and a fifth PSA change procedure.
- the fourth PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA (all PSAs) used in the first MAPDU session.
- the fourth PSA change procedure is the PSA used by userplane resources via 3GPP access and the userplane via non-3GPP access among the PSAs used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure to change the PSA used in resources.
- the fifth PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA (some PSAs) used in the first MAPDU session.
- the fifth PSA change procedure is only the PSA used in the user plane resources via one access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) of the PSA used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure to change.
- the fifth PSA change procedure is the PSA used by user plane resources via access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) of one of the PSAs used in the first MAPDU session. It can be said that it is a procedure that does not change the PSA used by userplane resources via the remaining access (non-3GPP access or 3GPP access).
- the fourth PSA change procedure is the establishment of a first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. This is a procedure to change the PSA (all PSAs) used in the first MA PDU session when SSC mode 3 is applied to one MA PDU session.
- the fourth PSA change procedure each device transitions from the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 to the second communication state shown in FIG. Also, by executing the fourth PSA change procedure, all PSAs will be changed from UPF_230 to UPF_232.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 9 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE is in a state where it can send and receive user data to and from DN_300 using the first MAPDU session (S900).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in the S900.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_230 (also referred to as the serving UPF) and / or the SMF in use in the first MAPDU session needs to be reassigned (S902).
- SMF for example, if it becomes unable to maintain userplane resources and / or userplaneresources via 3GPP access, and / or communicates via 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access. If the throughput of communication via is extremely low, and / or if UPF_230 is in an overflow state, and / or if the UE is moved, and / or if the operator policy or network policy is changed, and / or etc. It may be determined that reassignment of UPF_230 and / or SMF is necessary when requested by the NF of.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S904. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 and / or SMF need to be reassigned, each device may perform the steps S904 and beyond.
- the case where it is determined that the reassignment of SMF is unnecessary and the reassignment of UPF_230 is necessary will be described.
- the SMF transmits the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information to the AMF (S904).
- the N1SM container may contain a PDU session change command message.
- the PDU session change command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type and / or reason value.
- the N2SM information may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID included in the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information is information that identifies the PDU session (first MA PDU session) to be reassigned.
- the access type may indicate the access to be changed, and here, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value may also indicate that the MA PDU session needs to be reestablished for the same DN.
- the SMF sends a PDU session change command message and / or N1SM container and / or N2SM information to change the settings of the UE's first MA PDU session and / or the first MA PDU session.
- a PDU session change command message and / or N1SM container and / or N2SM information to change the settings of the UE's first MA PDU session and / or the first MA PDU session.
- the AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information from the SMF (S904).
- the AMF changes the settings of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or the first MA PDU session. It may be recognized that instructed to change the settings of userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access, and / or to reestablish the MAPDU session for the same DN.
- AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the access network (S906).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID and / or an N1SM container.
- the access network that receives the N2 session request message sends a NAS message to the UE (S906).
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, the N2 PDU session request message may be sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the N2 PDU session request message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the N2 PDU session request message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends the N2 PDU session request message to the base station device _110, and the base station device _110 that receives this is sent to the UE. Send a NAS message.
- the N2PDU session request message is sent via non-3GPP access, it depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP access. , The destination is different.
- AMF sends an N2PDU session request message to N3IWF_240, and N3IWF_240 that receives this sends the base station device_
- a NAS message may be sent to 120, and the base station device_120 that receives the NAS message may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends an N2PDU session request message to the TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends the TNAP.
- a NAS message may be sent, and the TNAP that receives it may send the NAS message to the UE.
- the AMF changes the settings of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or in the first MA PDU session, user plane resources and non-3 GPP via 3GPP access. You may notify the UE that you are instructed to change the settings of userplane resources via access and / or reestablish the MAPDU session for the same DN.
- the UE when the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. Then, based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message, the UE changes the setting of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or performs non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may recognize that you are instructed to change the settings of userplane resources and / or reestablish the MAPDU session for the same DN. The UE may then decide to initiate the PDU session establishment procedure based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message (S908).
- each device performs the PDU session establishment procedure of S908 in order to establish a second (new) MA PDU session for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the first communication state.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the MA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- each device can establish a second (new) MAPDU session when the MAPDU session establishment procedure is completed normally. Specifically, each device can establish a second MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- each device cannot establish a second (new) MAPDU session if the MAPDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure may be a procedure initiated by the UE.
- each device may establish a plurality of MAPDU sessions by executing the MAPDU session establishment procedure a plurality of times.
- 3GPP access is assuming that they are managed / operated by the same operator, they are operated by different operators. It is possible to apply in some cases.
- the UE is the information stored in the UE in advance and / or the information received in advance from the access network and / or the information received in advance from the core network (identification information received in the registration procedure and / or from the PCF). It may be determined to start the MAPDU session establishment procedure in order to establish the second MAPDU session based on the URSP rules etc. received in advance).
- the UE starts the MA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access (also referred to as 3GPP access network) and non-3GPP access (also referred to as non-3GPP access network). That is, when the UE sends a NAS message via 3GPP access, the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via base station device_110. Also, when the UE transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the UE transmits a NAS message to AMF via base station device_120 and N3IWF. Also, when the UE sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via TNAP and TNGF. In this way, the communication route to AMF changes depending on which access the UE sends the NAS message from, but the communication route from AMF to SMF may be the same. Here, it is assumed that the NAS message is transmitted via 3GPP access.
- 3GPP access also referred to as
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN to which the MA PDU session requesting establishment (second MA PDU session) is connected, and the DN communicating in the first MA PDU session is used. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN to be identified.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. Must be set to a different PDU session ID.
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the same as the PDU session type set for the first MA PDU session. It is preferably set to the PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the SSC mode set for the first MA PDU session, that is, SSC mode 2. It is preferable to set it to, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the MA PDU session (second MA PDU session) that requests establishment, and both access (3GPP access and non-) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for 3GPP access).
- the UE also includes the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message with the seventh identification information indicating the MAPDURequest, so that the PDU session establishment request message is the second. Being sent to establish a (new) MAPDU session and / or applying ATSSS-LL and / or MPTCP functionality to steer traffic in a second MAPDU session. May be notified to the network side.
- the eighth identification information may indicate the PDU session ID indicating the PDU session (first MA PDU session) scheduled to be released. It may also indicate that the first MAPDU session will be released by transmitting the eighth identification information.
- the ninth identification information may indicate the access corresponding to the user plane resources in the PDU session (first MA PDU session) scheduled to be released. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. Further, the ninth identification information may be notified separately for untrusted non-3GPP access and Trusted non-3GPP access for non-3GPP access. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), or 3GPP access and non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access). In addition, by including both the 8th identification information and the 9th identification information, userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the 1st MAPDU session. May indicate that you plan to release.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the second if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses. You may refuse to establish a MA PDU session. The AMF may also refuse to establish a second MAPDU session if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when the establishment of the second MAPDU session is refused, it may be the case that the MAPDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- the AMF may send a NAS message to the UE containing information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session is rejected. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- the AMF when refusing to establish a second MAPDU session, the AMF sends information to the SMF indicating that it refuses to establish a second MAPDU session, and the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message.
- a NAS message containing an N1 SM container containing may be sent to the UE.
- the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message may contain information indicating that the establishment of the second MA PDU session is rejected.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request.
- the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, it may start the procedure of (A) and / or (B) of FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. Also, if the network refuses to establish a second MAPDU session (userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access refuses to establish a second MAPDU session. In the case of), the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF.
- the SMF may say that if the seventh identity indicates an initial request or MAPDURequest, that is, if this procedure is performed to establish a new (second) MAPDU session.
- SMF may select an appropriate PCF based on the information received from AMF and the like. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature. Further, when the 7th identification information indicates an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session), the SMF may use the already selected PCF, that is, the PCF used in the 1st MA PDU session. .. That is, it is not necessary to select a new PCF, but a new PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (S1306).
- the SMF decides to allow the establishment of the second MAPDU session, it further "information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session is permitted" and / or "user via 3GPP access".
- PCF for "information indicating that the establishment of user plane resources is permitted via plane resources and non-3GPP access” and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment is permitted (access type)”. May be sent to.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which the establishment is permitted (access type)" may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- the PCF when the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF, the UE requests the establishment of a second MAPDU session, and / or the information received from the SMF, etc. Can recognize the contents of (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF will tell the SMF "information indicating that the establishment of the second MAPDU session has been permitted” and / Or "information indicating that the establishment of user plane resources via 3GPP access and non-3 GPP access is permitted” and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources that is permitted to be established”.
- (Access type) may be sent (S1306).
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the user plane resources for which the establishment is permitted (access type)” may indicate 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- the PCF is permitted to establish a second MAPDU session based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) (via userplane resources via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access).
- a second MAPDU session was allowed to be established using the user plane resources), or based on the information (messages, containers, information) received from the SMF.
- PCC rules may be generated.
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF may also explicitly indicate to the SMF that it has allowed the establishment of the second MAPDU session by sending information indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the second MAPDU session.
- sending PCC rules may imply that the establishment of a second MAPDU session has been permitted.
- the PCF when the PCF generates a policy for the SA PDU session, it may send the policy to the SMF.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling the second MAPDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UE
- N4 rules are the information for controlling the second MAPDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UPF. It is information for controlling.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the second MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the second MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the second MAPDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the second MAPDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1308).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status. And / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF. Also, if multiple UPFs are selected, the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF. Also, if the establishment of a second MAPDU session is permitted, the SMF may select a UPF that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function. Here, it is assumed that UPF_232 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1308), the UPF can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the second MAPDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF may configure whether downlink traffic in the second MAPDU session to be established should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- the application of N4 rules in UPF may be performed after S1318.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the second MAPDU session. (S1310).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) passes through the access network. And send a NAS message to the UE (S1314) (S1316).
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network that receives the N2 PDU session request message sends a NAS message to the UE (S1316).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. That is, when the AMF transmits the NAS message via 3GPP access, the AMF transmits the NAS message to the UE via the base station device_110. When the AMF transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the AMF transmits the NAS message to the UE via the N3IWF and the base station device_120. Also, when AMF sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), it sends a NAS message to the UE via TNGF and TNAP.
- the AMF preferably transmits the NAS message to the UE via the same access as the access received from the UE, but may transmit the NAS message via a different access. Absent. Here, the explanation will be continued assuming that the NAS message is transmitted via 3GPP access (base station device_110).
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request. Also, the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the PDU session establishment has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance is accepted.
- Messages and / or N1 SM containers and / or PDU session IDs (13th identification) and / or access types (19th identification) and / or NAS messages and / or N2SM information, and / or / Or the N2 PDU session request message may contain at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 17th identification information may indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of a second MAPDU session.
- the 19th identification information may indicate 3GPP access and / or non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the second MA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- / or the establishment of userplane resources via 3GPP access and / or the establishment of userplaneresources via non-3GPP access was permitted, and / or the establishment of userplaneresources was permitted.
- the corresponding access type may be notified to the UE.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1316).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE was allowed to establish a second MAPDU session and / or userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplane resources via non-3GPP access, and / Or can recognize the access type corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment is permitted.
- the UE is in a state where user plane resources have been established via 3GPP access.
- the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using a new (second) MAPDU session with user plane resources via 3GPP access. That is, the UE is newly established by the procedure (A) in FIG. 13 in addition to the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- it may be possible to communicate with the DN using the second MAPDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access.
- user plane resources via non-3GPP access may not yet be established.
- the SMF may send an N4 session correction request message to the already selected UPF_232 via the N4 interface (S1318).
- the N4 session correction request message does not need to be sent including the N4 rules, but may be included.
- UPF_232 when UPF_232 receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from SMF. UPF_232 may then send an N4 session corrective response message to the SMF via the N4 interface (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session correction response message, it can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF.
- the SMF then sends the N2SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification) and / or the access type (19th identification) to the AMF via the N11 interface (S1322). ).
- the SMF does not need to transmit the N1SM container transmitted in S1312 to the AMF, but may transmit it.
- the AMF receives the N2SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information).
- AMF may send an N2PDU session request message to N3IWF. Further, when the second MAPDU session uses Trusted non-3GPP access, AMF may send an N2PDU session request message to TNGF and / or TNAP.
- the N2 PDU session request message may include N2 SM information.
- the N2 PDU session request message does not have to include the NAS message, but may be included.
- N3IWF S1324.
- N3IWF executes the procedure for establishing IPsec child SA (security association) with the UE via the access network (S1326).
- N3IWF describes IKEv2 in RFC 7296 to establish an IPsec Child SA for the second MA PDU session (user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the second MA PDU session).
- the IKE Create_Child_SA request message may indicate that the requested IPsec Child SA operates in tunnel mode.
- the IKE Create_Child_SA request message may include the PDU session ID associated with this Child SA.
- the UE when it accepts IPsec Child SA, it sends an IKE Create_Child_SA response message to N3IWF.
- SMF and / or AMF can be used in the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or access type (19th identification information), and / or N2 SM information, and / or N2 PDU session request message. At least one of the 11th to 21st identification information may be included and transmitted.
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE and / or N3IWF and / or the access network of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the contents of the identification information of the 11th to 21st may be the same as the contents in the procedure of (A).
- the 19th identification information in the procedure (A) indicates only 3GPP access
- the 19th identification information in the procedure (B) may indicate only non-3GPP access.
- the UE may recognize that user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access based on the receipt of the IKE Create_Child_SA request message and / or the transmission of the IKE Create_Child_SA response message.
- N4 rules in UPF may be performed after S1318, and the application of ATSSS rules in UE may be performed at this stage.
- the UE is in a state where user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access.
- the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using a new (second) MAPDU session with user plane resources via 3GPP access. That is, the UE is newly established by the procedure (A) in FIG. 13 in addition to the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. Also, using the second MAPDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access newly established by the procedure (B) in Fig. 13. It may be in a state where it can communicate with the DN.
- the UE may be in a state of being able to communicate with the DN using the first MAPDU session and the second MAPDU session. (S910) (S912).
- normally completing the procedures (A) and (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure is normally completed.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if it refuses to establish a second MAPDU session, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish a second MAPDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- a second (new) MAPDU session cannot be established.
- the second (new) MAPDU session could not be established, but since the first MAPDU session is maintained, the UE uses the first MAPDU session with the DN. It is in a state where it can communicate. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 9 may be skipped.
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF. The SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released by the user plane resources of the first MAPDU session, and here, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also releases the first MA PDU session of its UE by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230, and / or userplane resources and / or user plane resources and / or in the first MA PDU session via 3GPP access. You may request the release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session.
- the SMF does not have to send the access type to UPF_230.
- UPF_230 when UPF_230 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_230 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first MA PDU session of its UE and / or in the first MA PDU session. , Userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access, and / or the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session may be released.
- UPF_230 received the N4 session release request message by sending the N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first MA PDU session of the UE, and / or the first.
- SMF that released userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access and / or released the N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session in the MAPDU session of You may tell (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_230 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF.
- UPF_230 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. When including access types, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_230 has received an N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_230 is the UE's first MA PDU.
- the session was released and / or UPF_230 released userplane resources via 3GPP access and userplaneresources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session, and / or UPF_230 was the first. It may be recognized that the N4 session corresponding to the MA PDU session of is released.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type.
- the N2SM resource release request message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first MA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released, and here, 3GPP access and non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF may also instruct the release of the UE's first MA PDU session by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message. ..
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. By receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the N2SM resource release request message, the AMF recognizes that the release of the first MA PDU session of the UE is instructed. You can do it.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via the access network (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, NAS messages are sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the NAS message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the NAS message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the base station device_110, and the base station device_110 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the destination depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP access. Is different.
- AMF sends a NAS message to N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends NAS to base station device_120.
- the base station device_120 that sends a message and receives it may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends a NAS message to TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends a NAS message to TNAP.
- the TNAP that sends and receives this may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF releases the first MAPDU session of its UE and / or via userplane resources and non-3GPP access via 3GPP access in the first MAPDU session. You may notify the UE that you are instructed to release user plane resources.
- the UE When the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. The UE may recognize that the release of the first MA PDU session of the UE is instructed by receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message. The UE may then release the first MA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the fourth PSA change procedure When the fourth PSA change procedure is completed, the first MA PDU session using the first communication state shown in Fig. 2 (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access) From the established state), a second MA PDU session is established using the second communication state (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access) shown in FIG. Transition to the current state).
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_232 by executing the fourth PSA change procedure.
- the fifth PSA change procedure is the first MA PDU session established using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. This is the procedure to change the PSA (some PSAs) used in the first MA PDU session when SSC mode 3 is applied to one MA PDU session.
- the case where only the PSA used in user plane resources via non-3GPP access is changed and the PSA used in user plane resources via 3GPP access is not changed will be described.
- each device transitions from the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 to the third communication state shown in FIG.
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_230 and UPF_232 by executing the fifth PSA change procedure.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 9 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE is in a state where it can send and receive user data to and from DN_300 using the first MAPDU session described above (S1000).
- the PSA at this time is UPF_230 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in the S1000.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_230 (also referred to as the serving UPF) and / or the SMF in use in the first MAPDU session needs to be reassigned (S1002).
- SMF for example, when it becomes unable to maintain user plane resources via non-3GPP access and / or when the throughput of communication via non-3GPP access drops significantly, and / or when UPF_230 overflows.
- UPF_230 and / or SMF reassignment is required in some cases, and / or when the UE has moved, and / or when the operator policy or network policy has changed, and / or when requested by another NF. May be determined.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1004. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 and / or SMF need to be reassigned, each device may perform the steps after S1004.
- the case where it is determined that the reassignment of SMF is unnecessary and the reassignment of UPF_230 is necessary will be described.
- the SMF transmits the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information to the AMF (S1004).
- the N1SM container may contain a PDU session change command message.
- the PDU session change command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type and / or reason value.
- the N2SM information may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID included in the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information is information that identifies the PDU session (first MA PDU session) to be reassigned.
- the access type may indicate the access to be changed, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value may also indicate that it is necessary to establish an SA PDU session for the same DN.
- the SMF sends a PDU session change command message and / or N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information to change the settings of the UE's first MA PDU session and / or the first MA PDU session. You may instruct to change the settings of userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or establish an SA PDU session for the same DN.
- AMF receives N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information from SMF (S1004).
- SMF SMF
- the AMF changes the settings of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or the first MA PDU session. You may be aware that you are instructed to change the settings of userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or establish an SA PDU session for the same DN.
- AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the access network (S1006).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID and / or an N1SM container.
- the access network that receives the N2 session request message sends a NAS message to the UE (S1006).
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, the N2 PDU session request message may be sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the N2 PDU session request message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the N2 PDU session request message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends the N2 PDU session request message to the base station device _110, and the base station device _110 that receives this is sent to the UE. Send a NAS message.
- the N2PDU session request message is sent via non-3GPP access, it depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP access. , The destination is different.
- AMF sends an N2PDU session request message to N3IWF_240, and N3IWF_240 that receives this sends the base station device_
- a NAS message may be sent to 120, and the base station device_120 that receives the NAS message may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends an N2PDU session request message to the TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends the TNAP.
- a NAS message may be sent, and the TNAP that receives it may send the NAS message to the UE.
- AMF changes the settings of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or sets user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may notify the UE that you are instructed to make changes and / or establish an SA PDU session for the same DN.
- the UE when it receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. Then, based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message, the UE changes the setting of the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or performs non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may be aware that you are instructed to change the settings of userplane resources and / or establish an SA PDU session for the same DN. The UE may then decide to initiate the PDU session establishment procedure based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message (S1008).
- each device establishes a first (new) SA PDU session via non-3GPP access for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the first communication state.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the SA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the SA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- non-3GPP access is untrusted non-3GPP access
- the base station device _120 and N3IWF with TNAP and TNGF, it can be applied even when non-3GPP access is Trusted non-3GPP access.
- the UE Before executing this SA PDU session establishment procedure, the UE is registered in 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the state of being registered with 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the IPsec SA for NAS signaling with N3IWF. May be in an established state.
- the UE starts the SA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (base station device_120) (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface (S1300).
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the PDU session establishment request message is sent to N3IWF using IPsec SA for NAS signaling, and N3IWF forwards the received PDU session establishment request message to AMF.
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN to which the SA PDU session requesting establishment (first SA PDU session) is connected, and the DN communicating in the first MA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN to be identified.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. Must be set to a different PDU session ID.
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and is the same as the PDU session type set for the first MA PDU session. It is preferably set to the PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and the SSC mode set for the first MA PDU session, that is, SSC mode 2. It is preferable to set it to, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the SA PDU session (first SA PDU session) that requests establishment, and both access (3GPP access and non-) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for 3GPP access).
- the UE also includes in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message a seventh identification information indicating an initial request or an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session).
- the PDU session establishment request message was sent to establish a new (first) SA PDU session, and / or the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU.
- the network may be notified that the ATSSS-LL function and / or the MPTCP function will be applied to steer the traffic of the session.
- the eighth identification information may indicate the PDU session ID indicating the PDU session (first MA PDU session) scheduled to be released. It may also indicate that the first MAPDU session will be released by transmitting the eighth identification information.
- the ninth identification information may indicate the access corresponding to the user plane resources in the PDU session (first MA PDU session) scheduled to be released. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate non-3GPP access. Further, the ninth identification information may be notified separately for untrusted non-3GPP access and Trusted non-3GPP access for non-3GPP access. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access) or non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access). In addition, by including both the 8th identification information and the 9th identification information, it is shown that the user plane resources via non-3GPP access will be released in the 1st MAPDU session. You can.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the first if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses. You may refuse to establish a SA PDU session. The AMF may also refuse to establish a first SA PDU session if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused, it may be the case that the SA PDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- the AMF may send a NAS message to the UE containing information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- the AMF when refusing to establish the first SA PDU session, the AMF sends information to the SMF indicating that it refuses to establish the first SA PDU session, and the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message.
- a NAS message containing an N1 SM container containing may be sent to the UE.
- the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message may contain information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is rejected.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request. In the third condition determination, the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, the SMF may start the procedure (B) in FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. If the network allows the establishment of the first SA PDU session, the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network refuses to establish the first SA PDU session, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. The condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF. For example, if the 7th identity indicates an Initial request, that is, if this procedure is performed to establish a new (1st) SA PDU session, the SMF will An appropriate PCF may be selected based on the information received from the AMF. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature. Further, when the 7th identification information indicates an existing PDU session (Existing PDU Session), the SMF may use the already selected PCF, that is, the PCF used in the 1st MA PDU session. .. That is, it is not necessary to select a new PCF, but a new PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (not shown).
- the SMF decides to permit the establishment of the first SA PDU session, it further "information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted" and / or "the first that permits the establishment".
- Information indicating the access corresponding to the SA PDU session of (access type) may be sent to the PCF.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF when the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF, the UE requests the establishment of the first SA PDU session, and / or the information received from the SMF, etc. Can recognize the contents of (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF decides to allow the establishment of the first SA PDU session, the PCF tells the SMF "information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted" and / Alternatively, "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)" may be transmitted.
- the "information indicating the access corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted (access type)" may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF detects that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information), or the information received from the SMF (message, message, information). If you allow the establishment of the first SA PDU session based on the container, information), you may generate PCC rules (also called policies, routing rules) for the first SA PDU session.
- PCC rules also called policies, routing rules
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF may also explicitly indicate to the SMF that it has allowed the establishment of the first SA PDU session by sending information indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the first SA PDU session.
- sending PCC rules may imply that the establishment of the first SA PDU session has been permitted.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information transmitted from the PCF, it can recognize the contents of the information.
- the SMF is "information indicating that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted" from the PCF and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the first SA PDU session that is permitted to be established (access type).
- the SMF may recognize that the establishment of the first SA PDU session has been permitted.
- the SMF may generate ATSSS rules (20th identification information) and N4 rules from the PCC rules.
- the ATSSS rules may be information for controlling the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UE
- the N4 rules may be the information transmitted from the SMF to the UPF. It may be information for controlling the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session transmitted to.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the first SA PDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the first SA PDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the first SA PDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the first SA PDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1318).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status. And / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF. Also, if multiple UPFs are selected, the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF. Also, if the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted, the SMF may select a UPF that supports the MA PDU session and / or the ATSSS function. Here, it is assumed that UPF_232 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the first SA PDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF may configure whether downlink traffic in the first SA PDU session to be established should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the first SA PDU session. (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) is the N3IWF and the access network.
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the N3 IWF (S1324)
- the N3 IWF that receives the N2 PDU session request message is sent to the UE via the access network (base station device_120).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request. Also, the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the PDU session establishment has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- the ATSSS container IE and / or the PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or the N1SM container and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or The access type (19th identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information and / or N2PDU session request message contains at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. Good.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the eighteenth identifier may also indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of a SAPDU session.
- the 19th identification information may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the first SA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- the UE may be notified of the access type corresponding to the first SA PDU session that was allowed to establish and / or was allowed to establish.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1326).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE can recognize that the establishment of the first SA PDU session is permitted and / or the access type corresponding to the first SA PDU session for which establishment is permitted.
- the UE When the procedure (B) in Fig. 13 is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where the first SA PDU session is established via non-3GPP access.
- the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using a new (first) SA PDU session via non-3GPP access.
- the UE is in the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access, which has been established before the start of the fifth PSA change procedure.
- it may be able to communicate with the DN using the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access newly established by the procedure (B) in FIG.
- normally completing the procedure (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure of S1008 is completed normally.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if the establishment of the first SA PDU session is refused, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish the SA PDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- the first SA PDU session cannot be established via non-3GPP access.
- the UE can communicate with the DN using the first MAPDU session because the first MAPDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access is still maintained. It is in a state. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 10 may be skipped.
- the UE Upon successful completion of the S1008's PDU session establishment procedure, the UE will add to the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access, as described above. It may be possible to communicate with the DN using the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access (S1010) (S1012).
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF. The SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released by the user plane resources of the first MAPDU session, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also releases the first MA PDU session of its UE by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_230, and / or a user plane via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may request the release of resources and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first MA PDU session (or user plane resources via non-3GPP access).
- UPF_230 when UPF_230 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_230 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first MA PDU session of its UE and / or in the first MA PDU session. , Release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access, and / or release of N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session (or userplaneresources via non-3GPP access).
- UPF_230 received the N4 session release request message by sending the N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first MA PDU session of the UE, and / or the first. Released userplane resources via non-3GPP access and / or released N4 session corresponding to the first MAPDU session (or userplaneresources via non-3GPP access). You may tell SMF what you have done (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_230 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF. In addition, UPF_230 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. If you include an access type, you may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_230 has received an N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_230 is the UE's first MA PDU.
- the session was released and / or UPF_230 released userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session, and / or UPF_230 released the first MAPDU session (or non-3GPP). It may be recognized that the N4 session corresponding to userplane resources) via access has been released.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type.
- the N2SM resource release request message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first MA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also releases the first MA PDU session of its UE and / or its UE by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1SM container and / or an N2SM resource release request message. You may instruct the release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MAPDU session of.
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. Upon receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the N2SM resource release request message, the AMF releases the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or the first of the UE. It may be recognized that the release of userplane resources via non-3GPP access in 1 MAPDU session is instructed.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via the access network (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the access network may be 3GPP access or non-3GPP access. That is, NAS messages are sent via 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- SMF or AMF may decide which access to send the NAS message. If the SMF decides, the SMF may inform the AMF about the access to send the NAS message and identify the access that the AMF should send accordingly. When the AMF is determined, it may be arbitrarily specified from the accesses included in the access type received from the SMF.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the base station device_110, and the base station device_110 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the destination depends on whether the non-3GPP access used in the first MAPDU session is Untrusted Non-3GPP Access or Trusted Non-3GPP access. Is different.
- AMF sends a NAS message to N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends NAS to base station device_120.
- the base station device_120 that sends a message and receives it may send a NAS message to the UE.
- AMF sends a NAS message to TNGF, and the TNGF that receives this sends a NAS message to TNAP.
- the TNAP that sends and receives this may send a NAS message to the UE.
- the AMF By sending a NAS message, the AMF is instructed to release the first MA PDU session of the UE and / or release the user plane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session. You may notify the UE that you are.
- the UE When the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. Upon receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message, the UE releases the UE's first MAPDU session and / or the UE's first MAPDU. You may be aware that the session is instructed to release userplane resources via non-3GPP access. The UE may then release the first MA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the UE releases the userplane resources via non-3GPP access in the first MA PDU session, but the first MA using userplane resources via 3GPP access. Since the PDU session and the first SA PDU session have been established, it is possible to communicate with the DN_300 using the first MA PDU session and the first SA PDU session (S1016) (S1018). ..
- the first MA PDU session using the first communication state (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access) shown in Fig. 2 is started. From the established state), the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 (the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU via non-3GPP access). Transition to the state where the session is established). In addition, the PSA is changed from UPF_230 to UPF_230 and UPF_232 by executing the fifth PSA change procedure.
- the procedure for changing this PSA may include the sixth PSA change procedure.
- the sixth PSA change procedure is a procedure for changing the PSA of the first SA PDU session.
- the sixth PSA change procedure consists of a first MA PDU session using only user plane resources via one access (3GPP access or non-3GPP access) and the other access (non-).
- the first SA PDU session is established via 3GPP access or 3GPP access
- SSC mode 3 is applied to those first MA PDU session and first SA PDU session.
- the procedure for changing the PSA of the first SA PDU session is established.
- the case where the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access) are established. explain.
- the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access (Trusted non) It is also applicable when a first SA PDU session is established via 3GPP access).
- a case where each device transitions from the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 to the first communication state shown in FIG. 2 by executing the sixth PSA change procedure will be described.
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 and UPF_232 to UPF_230 by executing the sixth PSA change procedure.
- UPF1, UPF2, and SMF1 in FIG. 11 correspond to UPF_230, UPF_232, and SMF_220, respectively.
- the UE can send and receive user data to and from DN_300 using the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access. It is in a possible state (S1100) (S1102).
- the PSAs at this time are UPF_230 and UPF_232 as described above.
- the UE may or may not actually send and receive user data in S1100 and S1102.
- the SMF determines whether the UPF_232 (also referred to as the serving UPF) and / or the SMF in use in the first SA PDU session needs to be reassigned (S1104).
- SMF for example, when it becomes unable to maintain user plane resources via non-3GPP access and / or when the throughput of communication via non-3GPP access drops significantly, and / or when UPF_230 overflows.
- UPF_232 and / or SMF reassignment is required in some cases, and / or when the UE has moved, and / or when the operator policy or network policy has changed, and / or when requested by another NF. May be determined.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S806. If the SMF determines that UPF_230 and / or SMF need to be reassigned, each device may perform the steps from S806 onwards.
- the case where it is determined that the reassignment of SMF is unnecessary and the reassignment of UPF_232 is necessary will be described.
- the SMF transmits the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information to the AMF (S1106).
- the N1SM container may contain a PDU session change command message.
- the PDU session change command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type and / or reason value.
- the N2SM information may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID included in the N1 SM container and / or the N2 SM information is information that identifies the MA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be changed, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the reason value is that it is necessary to reestablish the MAPDU session for the same DN, add it to the MAPDU session for the same DN, or add userplane resources to the MAPDU session for the same DN. May be shown.
- the SMF sends a PDU session change command message and / or N1SM container and / or N2SM information to change the settings of the UE's first SA PDU session and / or MAPDU for the same DN. You may instruct to add userplane resources to the session.
- the AMF receives the N1SM container and / or the N2SM information from the SMF (S1106).
- the AMF changes the settings of the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or MAPDU for the same DN. You may be aware that you are instructed to add userplane resources to your session.
- AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the access network (non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access)) (S1108).
- AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to N3IWF_240, and N3IWF_240 that receives this sends a NAS message to base station device _120 and receives this message from base station device _120. May send a NAS message to the UE.
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID and / or an N1SM container.
- the access network that receives the N2 session request message sends a NAS message to the UE (S1108).
- the AMF By sending an N2 PDU session request message, the AMF is instructed to change the settings of the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or add user plane resources to the MA PDU session for the same DN. May be notified to the UE.
- the UE when the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. Then, the UE changes the settings of the first SA PDU session of the UE based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message, and / or of the user plane resources to the MA PDU session for the same DN. You may recognize that the addition is instructed. The UE may then decide to initiate the PDU session establishment procedure based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message (S1110).
- each device establishes user plane resources via non-3GPP access for the same DN (DN_300) as the DN (DN_300) in the third communication state, that is, via 3GPP access.
- the PDU session establishment procedure is also referred to as the MA PDU session establishment procedure.
- the MA PDU session establishment procedure will be described with reference to FIG.
- non-3GPP access is untrusted non-3GPP access
- the base station device _120 and N3IWF with TNAP and TNGF, it can be applied even when non-3GPP access is Trusted non-3GPP access.
- the UE Before executing this MAPDU session establishment procedure, the UE is registered in 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the state of being registered with 5GS via non-3GPP access, so the UE is in the IPsec SA for NAS signaling with N3IWF. May be in an established state.
- 3GPP access is assuming that they are managed / operated by the same operator, they are operated by different operators. It is possible to apply in some cases.
- the UE is the information stored in the UE in advance and / or the information received in advance from the access network and / or the information received in advance from the core network (identification information received in the registration procedure and / or from the PCF Start the MA PDU session establishment procedure to add user plane resources via non-3GPP access to the first MA PDU session based on (including URSP rules etc. received in advance) etc. You may judge that.
- the UE starts the MA PDU session establishment procedure by sending a NAS message containing the N1SM container including the PDU session establishment request message to the AMF via the access network (S1300).
- NAS messages are sent via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be an uplink NAS transport (UL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the access network includes 3GPP access (also referred to as 3GPP access network) and non-3GPP access (also referred to as non-3GPP access network). That is, when the UE sends a NAS message via 3GPP access, the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via base station device_110. Also, when the UE transmits a NAS message via non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access), the UE transmits a NAS message to AMF via base station device_120 and N3IWF. Also, when the UE sends a NAS message via non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access), the UE sends a NAS message to AMF via TNAP and TNGF. In this way, the communication route to AMF changes depending on which access the UE sends the NAS message from, but the communication route from AMF to SMF may be the same. Here, it is assumed that the NAS message is transmitted via non-3GPP access.
- 3GPP access also referred to
- the UE also requests the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message by including at least one of the identification information 1 to 10. This can be notified to the network side.
- the first identification information is a DNN that identifies the DN to which the user plane resources that request establishment (addition) are connected, and communicates in the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to the same DNN as the DNN that identifies the existing DN.
- the UE also includes the second identification in the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container and / or the NAS message to determine whether the UE supports the ATSSS function and / or.
- the network side may be notified whether or not the MPTCP function and / or the ATSSS-LL function is supported.
- the third identification information is the PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session of userplane resources that requests establishment (addition), and is different from the PDU session ID set for the first SA PDU session. It may be a PDU session ID, or it may be the same PDU session ID as the PDU session ID set for the first MA PDU session. Here, if the third identification information is set to the same PDU session ID as the PDU session ID of the first MA PDU session, it may mean that the UE requests addition to the first MA PDU session. ..
- the fourth identification information is the PDU session type of the MA PDU session of userplane resources that requests establishment (addition), and is set for the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set the same PDU session type as the existing PDU session type.
- the fifth identification information is the SSC mode of the MA PDU session of the user plane resources requesting establishment (addition), and is set for the first MA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session. It is preferable to set it to SSC mode, that is, SSC mode 2, but it may be set to SSC mode 1 or 3.
- the sixth identification information is the S-NSSAI of the MA PDU session of user plane resources that requests establishment (addition), and both access (3GPP access and non-3GPP) by the network in the registration procedure. It is preferable to set to S-NSSAI that is permitted for access).
- the UE also includes the PDU session establishment request message and / or the N1SM container, and / or the NAS message with the seventh identification information indicating the MAPDURequest, so that the PDU session establishment request message is a new MA.
- ATSSS-LL feature and / or MPTCP to be sent to establish a PDU session (to add user plane resources) and / or to steer the traffic of the first MA PDU session You may notify the network side that the function will be applied.
- the eighth identification information may indicate the PDU session ID indicating the PDU session (first SA PDU session) scheduled to be released. It may also indicate that it intends to release the first SA PDU session by transmitting the eighth identification information.
- the ninth identification information may indicate the access corresponding to the user plane resources in the PDU session (first MA PDU session) scheduled to be released. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate non-3GPP access. Further, the ninth identification information may be notified separately for untrusted non-3GPP access and Trusted non-3GPP access for non-3GPP access. That is, the ninth identification information may indicate non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access) or non-3GPP access (Trusted non-3GPP access). It may also indicate that the inclusion of both the 8th and 9th identification information will release the 1st SA PDU session via non-3GPP access.
- the ninth identification information may indicate non-3GPP access or non-3GPP access (untrusted non-3GPP access). It may also indicate that the established first SA PDU session is to be released by including both the eighth identification information and the ninth identification information.
- the UE sends the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer (for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer) and the control message of the layer higher than the NAS layer. It may be included and sent.
- the control message of the layer lower than the NAS layer for example, RRC layer, MAC layer, RLC layer, PDCP layer
- the AMF when the AMF receives the NAS message, it can recognize what the UE is requesting and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message.
- the AMF is the first if the UE is registered for both accesses, but the S-NSSAI indicated by the sixth identification information received from the UE is not allowed for both accesses.
- MA PDU session establishment (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) may be rejected.
- the AMF may also refuse to establish a first MAPDU session (add user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) if it does not support the ATSSS feature.
- each device may skip, that is, cancel the steps after S1302. Further, when rejecting the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), it may be the case that the MA PDU session establishment procedure is not completed normally.
- AMF when refusing to establish a first MA PDU session (adding user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), AMF will also establish a first MA PDU session (to the first MA PDU session). A NAS message containing information indicating that the addition of user plane resources) may be rejected may be sent to the UE. At this time, the AMF does not need to send at least a part of the information (message, container, information) included in the NAS message received from the UE to the SMF.
- AMF when refusing to establish a first MA PDU session (adding userplane resources to the first MA PDU session), AMF tells the SMF to establish a first MA PDU session (first).
- the SMF may send a NAS message containing the N1SM container containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE by sending information indicating that the user plane resources will be rejected to the MA PDU session.
- the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) is rejected for the PDU session establishment refusal message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message.
- AMF selects SMF as the transfer destination of at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE (S1302).
- AMF includes information (messages, containers, information) contained in NAS messages, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and /.
- the transfer destination SMF may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the AMF.
- the AMF may also select an SMF that supports MAPDU sessions and / or ATSSS functionality. Here, it is assumed that SMF_220 that supports the MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function is selected.
- the AMF sends at least a part of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message received from the UE to the selected SMF via the N11 interface (S1304).
- the AMF may also send information to the SMF indicating that the UE is registered for both accesses.
- the SMF when the SMF receives the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the AMF, the UE requests and / or the content of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. Can be recognized.
- the SMF may or may not determine the third condition.
- the third condition determination may be for determining whether or not to accept the UE request. In the third condition determination, the SMF determines whether the third condition determination is true or false. If the SMF determines that the third condition determination is true, the SMF may start the procedure (B) in FIG. If the third condition determination is determined to be false, the procedure for rejecting the UE request may be started.
- the third condition determination is information received from AMF (messages, containers, information) and / or subscription information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and /. Alternatively, it may be executed based on the state of the network and / or the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network does not allow the UE request, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Also, if the network to which the UE is connected and / or the devices in the network support the functions required by the UE, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and the functions required by the UE are supported. If not, the third condition determination may be determined to be false. Further, when the transmitted / received identification information is permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be true, and when the transmitted / received identification information is not permitted, the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the third condition determination may be determined to be true. If the network refuses to establish the first MA PDU session (adding user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), the third condition determination may be determined to be false.
- the condition for determining the authenticity of the third condition determination is not limited to the above-mentioned condition.
- SMF may select PCF. For example, in the SMF, when the seventh identification information indicates an initial request or MAPDURequest, that is, the establishment of a new first MAPDU session (user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) If this procedure is performed to add), SMF may select an appropriate PCF based on the information received from AMF and so on. For example, the SMF may select a PCF that supports the ATSSS feature. The SMF can also use the PCF already selected, that is, the PCF used in the first SA PDU session, when the seventh identity is an existing PDU session or an existing emergency PDU session. Good. That is, it is not necessary to select a PCF, but a different PCF may be selected.
- the SMF may send at least a part of the information (messages, containers, information) received from the AMF to the PCF (not shown).
- the SMF decides to allow the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session)
- it further “establishes the first MA PDU session (first).
- information indicating access (access type) corresponding to user planet resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted may be sent to the PCF.
- “information indicating access corresponding to user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF receives the information (message, container, information) sent from the SMF
- the UE establishes the first MAPDU session (adds user plane resources to the first MAPDU session). Can recognize what you are requesting and / or the content of information (messages, containers, information) received from SMF.
- the PCF further makes the same judgment as the above judgment in the SMF based on the information received from the SMF (message, container, information) and / or the operator policy and / or the subscriber information (subscription information). You may go.
- the same information as the information transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be transmitted from the PCF to the SMF.
- the above judgment may be made only by the PCF without making the above judgment in the SMF.
- the information (message, container, information) transmitted from the SMF to the PCF may be at least a part of the information (message, container, information) received from the AMF. That is, when the SMF makes the above determination, the above information generated by the SMF and additionally transmitted to the PCF need not be transmitted.
- the PCF decides to allow the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session)
- the PCF tells the SMF that "the first MA Information indicating that the establishment of the PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session) was permitted "and / or” the establishment (addition) of user plane resources via non-3GPP access was permitted.
- Information indicating that, and / or "information indicating access corresponding to the user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)" may be transmitted.
- “information indicating access corresponding to user plane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted (access type)” may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the PCF was allowed to establish the first MAPDU session (adding userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) based on the information received from the SMF (messages, containers, information).
- the PCF may generate PCC rules for MA PDU sessions.
- the PCF may be sent to the SMF.
- the PCF also sends information to the SMF indicating that it has allowed the establishment of the first MA PDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MA PDU session), thereby sending the first MA.
- ATSSS rules are information for controlling the first MA PDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UE
- N4 rules are the information for controlling the first MA PDU session transmitted from the SMF to the UPF. It is information for controlling.
- SMF may manage PCC rules, ATSSS rules, and N4 rules in association with each other (mapped).
- the SMF may assign an IP address or IP prefix to the first MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates unstructured, the SMF may assign an IPv6 address for the first MAPDU session. Further, when the fourth identification information indicates ethernet (registered trademark), the SMF does not have to assign a MAC address or an IP address to the first MAPDU session.
- the SMF selects the UPF to establish the first MAPDU session, and sends an N4 session establishment request message to the selected UPF via the N4 interface (S1318).
- SMF refers to information received from AMF and / or information received from PCF, and / or subscriber information, and / or network capability information, and / or operator policy, and / or network status.
- / or one or more UPFs may be selected based on the user's registration information and / or the context held by the SMF. Also, if multiple UPFs are selected, the SMF may send an N4 session establishment request message to each UPF.
- the SMF will support the first MAPDU session and / or the ATSSS function. May be selected.
- UPF_230 is selected.
- the N4 session establishment request message may be sent including the N4 rules.
- the UPF when the UPF receives the N4 session establishment request message (S1318), it can recognize the content of the information received from the SMF.
- the UPF also creates a context for the first MAPDU session.
- the UPF may be set to operate according to the N4 rules when the N4 rules are received from the SMF. That is, the UPF may set whether downlink traffic in the first MAPDU session to be established (added) should be routed to 3GPP access or non-3GPP access.
- the UPF may send an N4 session establishment response message to the SMF via the N4 interface based on receiving the N4 session establishment request message and / or creating a context for the first MA PDU session. (S1320).
- the SMF when the SMF receives the N4 session establishment response message as the response message to the N4 session establishment request message, the SMF can recognize the content of the information received from the UPF. Further, the SMF may assign an address to be assigned to the UE based on the reception of the PDU session establishment request message, / or the selection of the UPF, and / or the reception of the N4 session establishment response message.
- the SMF then receives the PDU session establishment request message and / or selects the UPF and / or receives the N4 session establishment response message and / or completes the address assignment of the address assigned to the UE, etc.
- the N1SM container may include a PDU session establishment acceptance message
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may include an ATSSS container IE (Information Element).
- the AMF that receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM information and / or the PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or the access type (19th identification information) is the N3IWF and the access network.
- the NAS message is transmitted via the N1 interface.
- the NAS message may be a downlink NAS transport (DL NAS TRANSPORT) message.
- the AMF sends an N2 PDU session request message to the N3 IWF (S1324)
- the N3 IWF that receives the N2 PDU session request message is sent to the UE via the access network (base station device_120).
- the N2 PDU session request message may include a NAS message and / or N2 SM information.
- the NAS message may also include a PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or an access type (19th identification information) and / or an N1 SM container.
- the N1 SM container may contain a PDU session establishment acceptance message.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may be a response message to the PDU session establishment request.
- the PDU session establishment acceptance message may indicate that the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) has been accepted.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message and / or N1 SM container and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (13th identification information).
- 19 identification information) and / or NAS message, and / or N2SM information, and / or N2PDU session request message may include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information. ..
- the SMF and / or AMF may notify the UE of the content of these identifications by transmitting at least one of these identifications.
- And / or PDU session ID (13th identification information) and / or access type (19th identification information), and / or NAS message, and / or N2 SM information, and / or N2 PDU session request message May include at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information.
- SMF and / or AMF are ATSSS container IE and / or PDU session establishment acceptance message, and / or N1 SM container, and / or PDU session ID (13th identification information), and / or access type (No. 13). 19 identification information) and / or NAS message and / or N2SM information, and / or which identification information is included in the N2PDU session request message, each identification information received, and / or subscriber information, and Select and make decisions based on / or network capability information and / or operator policy, and / or network status, and / or user registration information, and / or context held by SMF and / or AMF. You may.
- the eleventh identification information may be the same as the first identification information.
- the twelfth identification information may indicate MPTCP capability and / or ATSSS-LL capability in the network.
- the thirteenth identification information may be the same as the third identification information.
- the 14th identification information may be the same as the 4th identification information.
- the fifteenth identification information may be the same as the fifth identification information, and may be, for example, SSC mode 2.
- the 16th identification information may be the same as the 6th identification information.
- the 17th identification information may indicate that the network has allowed the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session).
- the 19th identification information may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the 20th identification information may indicate ATSSS rules.
- the first MA PDU session is transmitted by including at least one of the 11th to 21st identification information in the / or NAS message and / or the N2SM information and / or the N2PDU session request message.
- (Addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) was allowed, and / or establishment (addition) of userplaneresources via non-3GPP access was allowed, and / or The UE may be notified of the access type corresponding to the userplane resources for which establishment (addition) is permitted.
- the UE receives the NAS message via the N1 interface (S1326).
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been accepted and / or the contents of the information (message, container, information) contained in the NAS message. it can. That is, the UE is allowed to establish a first MAPDU session (addition of userplane resources to the first MAPDU session) and / or establish userplane resources via non-3GPP access. It is possible to recognize the access type corresponding to the user plane resources that has been permitted and / or has been permitted to be established (added).
- the UE When the procedure (B) in Fig. 13 is completed normally, the UE will be in a state where user plane resources have been established via non-3GPP access. In other words, the UE is in a state where user plane resources via non-3GPP access are established (added) for the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access that has already been established. It becomes. That is, the UE may be ready to communicate with the DN using the first MA PDU session with user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- normally completing the procedure (B) in FIG. 13 may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure is normally completed.
- each step of the procedure for rejecting the UE request which is executed when the third condition determination is false, will be described.
- This procedure may be initiated if the establishment of the first MAPDU session (addition of user plane resources to the first MAPDU session) is rejected, as described above.
- the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE via the AMF. Specifically, the SMF sends a PDU session establishment refusal message to the AMF via the N11 interface.
- the AMF receives the PDU session establishment request message from the SMF, it uses the N1 interface to send a NAS message containing the PDU session establishment refusal message to the UE.
- the SMF may indicate that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected by transmitting the PDU session establishment refusal message.
- the UE can recognize that the UE request by the PDU session establishment request message has been rejected. That is, the UE can recognize that the request to establish the SA PDU session has been rejected by the network.
- the completion of the procedure for rejecting the UE request may mean that the PDU session establishment procedure was not completed normally (abnormally completed).
- user plane resources cannot be established via non-3GPP access. That is, the UE cannot establish (add) user plane resources via non-3GPP access for the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access that has already been established. ..
- the UE can communicate with the DN using the first MAPDU session because the first MAPDU session using userplane resources via 3GPP access is still maintained. It is in a state. Also, in this case, the remaining steps in FIG. 11 may be skipped.
- the UE Upon successful completion of the S1110 PDU session establishment procedure, the UE will in addition to the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access, as described above. It may be possible to communicate with the DN using the first SA PDU session via non-3GPP access (S1112) (S1114).
- the PDU session release procedure is started by SMF sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_232 (S1200).
- the N4 session release request message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type.
- the N4 session ID is the N4 session and / or N4 session that the SMF generates and provides to the UPF when establishing a new PDU session or changing the UPF for an already established PDU session. It may be an identifier for identifying the context of.
- the N4 session ID is information stored in SMF and UPF. The SMF may also remember the relationship between the N4 session ID and the PDU session ID for a UE.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released by the user plane resources of the MAPDU session, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF also requests the release of the first SA PDU session of the UE and / or the release of the N4 session corresponding to the first SA PDU session by sending an N4 session release request message to UPF_232. May be good.
- the SMF does not have to send the access type to UPF_232.
- UPF_232 when UPF_232 receives the N4 session release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release request message. UPF_232 is based on the N4 session release request message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release request message, and SMF releases the first SA PDU session and / or the first SA PDU session of that UE. You may release the corresponding N4 session.
- UPF_232 then received the N4 session release request message by sending an N4 session release response message to the SMF, and / or released the first SA PDU session of its UE, and / or the first. You may tell the SMF that you have released the N4 session that corresponds to your SA PDU session (S1202).
- the N4 session release response message may include the N4 session ID and / or access type contained in the N4 session release request message.
- UPF_232 does not need to include the access type when the access type is not received from SMF.
- UPF_232 may include an access type even when the access type is not received from the SMF. If you include an access type, you may indicate non-3GPP access.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_232 has received the N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_232 is the UE's first SA PDU. It may be recognized that the session has been released and / or UPF_232 has released the N4 session corresponding to the first SA PDU session.
- the SMF receives the N4 session release response message, it confirms the information contained in the N4 session release response message.
- the SMF is that UPF_232 has received the N4 session release request message based on the N4 session release response message and / or the information contained in the N4 session release response message, and / or UPF_232 is the UE's first SA PDU. It may be recognized that the session has been released and / or UPF_232 has released the N4 session corresponding to the first SA PDU session.
- the SMF sends an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message to the AMF (S1204). Further, the SMF sends a PDU session release command message, and the PDU session release command message may be included in the N1SM container and transmitted.
- the PDU session release command message may include a PDU session ID and / or access type.
- the N2SM resource release request message may include a PDU session ID and / or an access type.
- the PDU session ID is information for identifying the first SA PDU session.
- the access type may indicate the access to be released in the first SA PDU session, and here, non-3GPP access may be indicated.
- the SMF may also instruct the release of the UE's first SA PDU session by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1 SM container and / or an N2 SM resource release request message. ..
- AMF when AMF receives the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message, it confirms the information contained in the N1 SM container and / or N2 SM resource release request message. By receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or the N2SM resource release request message, the AMF recognizes that the release of the first SA PDU session of the UE is instructed. You can do it.
- AMF sends a NAS message to the UE via non-3GPP access (S1206, S1208).
- the NAS message includes the N1SM container. That is, the PDU session release command message received from the SMF may be included in the NAS message and transmitted.
- the AMF sends a NAS message to the N3IWF_240, and the N3IWF_240 that receives this sends a NAS message to the base station device_120, and the base station device_120 that receives this sends the NAS message to the UE.
- the AMF notifies the UE that the UE is instructed to release the first SA PDU session by sending a PDU session release command message and / or an N1SM container and / or NAS message. You can.
- the UE When the UE receives the NAS message, it confirms the information contained in the NAS message. The UE may recognize that the release of the first SA PDU session of the UE is instructed by receiving the PDU session release command message and / or the N1SM container and / or NAS message. The UE may then release the first SA PDU session based on the NAS message and / or the information contained in the NAS message.
- the UE releases the first SA PDU session, but the first MA PDU using user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access. Since the session has been established, it is possible to communicate with DN_300 using the first MAPDU session (S1118).
- the third communication state shown in FIG. 15 the first MA PDU session using user plane resources via 3GPP access and the first MA PDU session via non-3GPP access.
- the first MA PDU using the first communication state shown in Fig. 2 (user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access). Transition to the state where the session is established).
- the PSA is changed from UPF_230 and UPF_232 to UPF_230 by executing the sixth PSA change procedure.
- the UE (User Equipment) of the embodiment is a UE including a control unit and a transmission / reception unit, and the control unit uses user plane resources via 3GPP access and user plane resources via non-3GPP access.
- the transmission / reception unit indicates a first PDU session ID that identifies the MA PDU session, and an access type indicating the non-3GPP access.
- the control unit Upon receiving a PDU session release command message containing a reason value indicating that an SA PDU session needs to be established for the same DN, the control unit uses the non-3GPP access in the MA PDU session. Releasing user plane resources, the transmitter / receiver assigns a second PDU session ID that identifies the SA PDU session to be established in the PDU session establishment procedure initiated via the non-3GPP access indicated by the access type. Sending a PDU session establishment request message including, the control unit establishes an SA PDU session via the non-3GPP access, and the transmission / reception unit uses the user plane resources via the 3GPP access. Communication using the PDU session and the SA PDU session via the non-3GPP access is feasible, and the PDU session anchor of the MA PDU session and the PDU session anchor of the SA PDU session are different. It is a feature.
- the UE (User Equipment) of the embodiment is a UE including a control unit and a transmission / reception unit, and the control unit is a MAPDU session using only userplane resources via 3GPP access and a non-3GPP access.
- SSC mode 2 is applied to the MA PDU session and the SA PDU session, and the SA PDU session is changed.
- the transmitter / receiver needs to reestablish the second PDU session ID that identifies the SA PDU session and the userplane resources for the same DN.
- the transmission / reception unit Upon receiving the PDU session release command message including the reason value indicating that the control unit releases the SA PDU session, the transmission / reception unit starts the MA PDU session via the non-3GPP access.
- the control unit transmits the MAPDU session establishment request message including the first PDU session ID that identifies the MAPDU session and the Request type set in the MAPDURequest, and the control unit accesses the 3GPP.
- the MAPDU session using only userplane resources via add userplaneresources via non-3GPP access, and add userplaneresources via 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. It is characterized in that communication by the MAPDU session using the user planet resources via the user becomes possible.
- the program that operates in the device according to one aspect of the present invention is a program that controls a central processing unit (CPU) or the like to operate a computer so as to realize the functions of the embodiment according to one aspect of the present invention. Is also good.
- the program or the information handled by the program is temporarily stored in a volatile memory such as Random Access Memory (RAM), a non-volatile memory such as a flash memory, a Hard Disk Drive (HDD), or another storage device system.
- RAM Random Access Memory
- HDD Hard Disk Drive
- the program for realizing the function of the embodiment according to one aspect of the present invention may be recorded on a computer-readable recording medium. It may be realized by loading the program recorded on this recording medium into a computer system and executing it.
- the term "computer system” as used herein is a computer system built into a device, and includes hardware such as an operating system and peripheral devices.
- the "computer-readable recording medium” is a semiconductor recording medium, an optical recording medium, a magnetic recording medium, a medium that dynamically holds a program for a short time, or another recording medium that can be read by a computer. Is also good.
- each functional block or various features of the device used in the above-described embodiment can be implemented or executed in an electric circuit, for example, an integrated circuit or a plurality of integrated circuits.
- Electrical circuits designed to perform the functions described herein are general purpose processors, digital signal processors (DSPs), application specific integrated circuits (ASICs), field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), or others. Programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic, discrete hardware components, or a combination thereof may be included.
- the general purpose processor may be a microprocessor, a conventional processor, a controller, a microcontroller, or a state machine.
- the electric circuit described above may be composed of a digital circuit or an analog circuit. Further, when an integrated circuit technology that replaces the current integrated circuit appears due to the progress of semiconductor technology, one or a plurality of aspects of the present invention can use a new integrated circuit according to the technology.
- the invention of the present application is not limited to the above-described embodiment.
- an example of the device has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the present invention is not limited to this, and a stationary or non-movable electronic device installed indoors or outdoors, for example, an AV device or a kitchen device. , Cleaning / washing equipment, air conditioning equipment, office equipment, vending machines, and other terminal devices or communication devices such as living equipment.
- Mobile communication system 10 UE 100 access network 102 Access network 110 Base station equipment 112 Base station equipment 120 base station equipment 122 Base station equipment 200 core network 210 AMF 220 SMF 230 UPF 232 UPF 240 N3IWF 242 N3IWF 250 PCF 300 DN
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
本発明の一態様によれば、制御部と送受信部とを備えるUE(User Equipment)であって、前記送受信部は、AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)から、ネットワークがATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)をサポートするか否かを示す第1の情報を受信し、前記制御部は、前記第1の情報に基づいて、ATSSSが前記ネットワークによってサポートされているか否かを特定し、前記制御部は、前記ネットワークがATSSSをサポートしていない場合、MA(Multi-Access) PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッションを確立するために、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始しない、ことを特徴とする。
Description
本出願は、UE及びSMFに関する。本出願は、2019年8月9日に出願された日本国特許出願である特願2019-147898号に対して優先権の利益を主張するものであり、それを参照することにより、その内容の全てが本願に含まれる。
3GPP(3rd Generation Partnership Project)では、第5世代(5G)の移動通信システムである5GS(5G System)のシステムアーキテクチャが検討されており、新しい手続きや新しい機能のサポートするための議論が行われている。5GS(5G System)では、多種多様なサービスを提供するために、新たなコアネットワークである5GC(5G Core Network)が検討されている。さらに、高信頼性、及び/又は低遅延の通信が必要されるATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting)を5GSでサポートするための議論も開始されている(非特許文献1、非特許文献2、及び非特許文献3を参照)。ATSSSに関する議論では、すでに規定されている、PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッション(シングルアクセスPDUセッション、SA PDUセッション、SA PDU Sessionとも称する)ではなく、マルチアクセスPDUセッション(MA PDUセッション、MA PDU Sessionとも称する)という特別なPDUセッションを用いて通信することが検討議論されている。
3GPP TS 23.501 V16.1.0 (2019-06); 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2 (Release 16)
3GPP TS 23.502 V16.1.1 (2019-06); 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Procedures for the 5G System; Stage 2 (Release 16)
3GPP TR 23.793 V16.0.0 (2018-12); 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Study on access traffic steering, switch and splitting support in the 5G system architecture (Release 16)
しかしながら、SSC(Session and Service Continuity) mode 2やSSC mode 3が設定されている、MA PDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカー(PDU Session Anchor、PSAとも称する)を変更する手続きや、MA PDUセッションのPSAの一部をSA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きや、SA PDUセッションのPSAをMA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きについては、まだ明らかになっていない。
本発明の一態様は、以上のような事情を鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、SSC mode 2又はSSC mode 3が設定された、MA PDUセッションのPSAを変更する手続きや、MA PDUセッションのPSAの一部をSA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きや、SA PDUセッションのPSAの一部をMA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きや、それらの手続きが実行された場合の各装置の挙動を明確化することにある。
本発明の一実施形態のUEは、制御部と送受信部とを備えるUE(User Equipment)であって、前記送受信部は、AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)から、ネットワークがATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)をサポートするか否かを示す第1の情報を受信し、前記制御部は、前記第1の情報に基づいて、ATSSSが前記ネットワークによってサポートされているか否かを特定し、前記制御部は、前記ネットワークがATSSSをサポートしていない場合、MA(Multi-Access) PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッションを確立するために、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始しない、
ことを特徴とするUE。
ことを特徴とするUE。
また、本発明の一実施形態の通信制御方法は、UE(User Equipment)によって実行される通信制御方法であって、前記UEは、AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)から、ネットワークがATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)をサポートするか否かを示す第1の情報を受信し、前記第1の情報に基づいて、ATSSSが前記ネットワークによってサポートされているか否かを特定し、前記ネットワークがATSSSをサポートしていない場合、MA(Multi-Access) PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッションを確立するために、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始しない、ことを特徴とする。
本発明の一態様によれば、SSC mode 2又はSSC mode 3が設定された、MA PDUセッションのPSAを変更する手続きや、MA PDUセッションのPSAの一部をSA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きや、SA PDUセッションのPSAの一部をMA PDUセッションのPSAに変更する手続きや、それらの手続きが実行された場合の各装置の挙動を明確化することができる。
以下では、各実施形態で共通する部分の多い、移動通信システム、各装置の構成、実施形態で用いられる用語・識別情報や手続きについて説明した後、本発明を実施する為の実施形態について説明する。
[1. 移動通信システムの概要]
ここでは、移動通信システムについて説明する。
ここでは、移動通信システムについて説明する。
まず、図1は、移動通信システム1の概略を説明する為の図であり、図2は、その移動通信システム1の詳細構成、及び第1の通信状態を説明する為の図である。図14は、第2の通信状態を説明する為の図である。図15は、第3の通信状態を説明する為の図である。
図1には、移動通信システム1は、UE(User Equipment)_10、アクセスネットワーク_100、アクセスネットワーク_102、コアネットワーク_200、DN(Data Network)_300により構成されることが記載されている。尚、これらの装置・ネットワークについて、UE、アクセスネットワーク、コアネットワーク、DN等のように、記号を省略して記載する場合がある。
また、図2には、UE_10、基地局装置_110、基地局装置_120、AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)_210、SMF(Session Management Function)_220、UPF(User Plane Function)_230、N3IWF(Non-3GPP InterWorking Function)_240、PCF(Policy Control Function)_250、DN_300等の装置・ネットワーク機能、及びこれらの装置・ネットワーク機能を互いに接続するインターフェースが記載されている。
また、図14には、UE_10、基地局装置_112、基地局装置_122、AMF_210、SMF_220、UPF_232、N3IWF_242、PCF_250、DN_300等の装置・ネットワーク機能、及びこれらの装置・ネットワーク機能を互いに接続するインターフェースが記載されている。
また、図15には、UE_10、基地局装置_110、基地局装置_122、AMF_210、SMF_220、UPF_230、UPF_232、N3IWF_242、PCF_250、DN_300等の装置・ネットワーク機能、及びこれらの装置・ネットワーク機能を互いに接続するインターフェースが記載されている。尚、これらの装置・ネットワーク機能について、UE、基地局装置、AMF、SMF、UPF、N3IWF、PCF、DN等のように、記号を省略して記載する場合がある。
尚、5Gシステムである5GS(5G System)は、UE、アクセスネットワーク及びコアネットワークを含んで構成されるが、さらにDNが含まれても良い。
UEは、3GPPアクセス(3GPPアクセスネットワーク、3GPP ANとも称する)及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセス(non-3GPPアクセスネットワーク、non-3GPP ANとも称する)を介して、ネットワークサービスに対して接続可能な装置である。UEは、携帯電話やスマートフォン等の無線通信が可能な端末装置であってよく、4GシステムであるEPS(Evolved Packet System)にも5GSにも接続可能な端末装置であってよい。UEは、UICC(Universal Integrated Circuit Card)やeUICC(Embedded UICC)を備えてもよい。尚、UEのことをユーザ装置と表現してもよいし、端末装置と表現してもよい。尚、UEは、ATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching and Splitting)機能を利用可能な装置、すなわち、ATSSS capable UEである。
また、アクセスネットワークは、5Gアクセスネットワーク(5G AN)と呼称してもよい。5G ANは、NG-RAN(NG Radio Access Network)及び/又はnon-3GPP アクセスネットワーク(non-3GPP AN)で構成される。NG-RANには、1以上の基地菊装置が配置されている。その基地局装置はgNBであってよい。gNBは、NR(New Radio)ユーザプレーンと制御プレーンをUEに提供するノードであり、5GCに対してNGインターフェース(N2インターフェース又はN3インターフェースを含む)を介して接続するノードである。すなわち、gNBは、5GSのために新たに設計された基地局装置であり、EPSで使用されていた基地局装置(eNB)とは異なる機能を有する。また、複数のgNBがある場合は、各gNBは、例えばXnインターフェースにより、互いに接続している。尚、基地局装置_110、基地局装置_112は、gNBに対応する。
また、以下では、NG-RANは、3GPPアクセスと称することがある。また、無線LANアクセスネットワークやnon-3GPP ANは、non-3GPPアクセスと称することがある。また、アクセスネットワークに配置されるノードを、まとめてNG-RANノードとも称することがある。
また、以下では、アクセスネットワーク、及び/又はアクセスネットワークに含まれる装置に含まれる装置は、アクセスネットワーク装置と呼称する場合がある。
なお、アクセスネットワーク_100は3GPPアクセスに対応し、アクセスネットワーク_102はnon-3GPPアクセスに対応する。
また、アクセスネットワーク_100には基地局装置_110及び/又は基地局装置_112が配置され、アクセスネットワーク_102には基地局装置_120及び/又は基地局装置_122及び/又はTNAPが配置されている。尚、基地局装置_110及び/又は基地局装置_112及び/又は基地局装置_120及び/又は基地局装置_122及び/又はTNAPは、ATSSS機能を利用可能であってよい。
また、アクセスネットワーク_102はUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessまたはTrusted Non-3GPP Accessと称する場合もある。図2の基地局装置120とN3IWFはUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合について記載している。すなわち、アクセスネットワーク_102がUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合には、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122とN3IWFが用いられる。また、アクセスネットワーク_102がTrusted Non-3GPP Access(Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network、TNANとも称する)の場合には、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122とN3IWFの代わりに、Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point(TNAPとも称する)とTrusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function(TNGFとも称する)が使用される。TNAPおよびTNGFは、アクセスネットワーク_102またはコアネットワーク_200に配置される。
また、コアネットワークは、5GC(5G Core Network)に対応する。5GCには、例えば、AMF、UPF、SMF、PCF等が配置されている。ここで、5GCは、5GCNと表現されてもよい。尚、AMF、UPF、SMF、PCFは、ATSSS機能を利用可能であってよい。
また、N3IWFは、アクセスネットワーク_102またはコアネットワーク_200に配置される。
また、以下では、コアネットワーク、及び/又はコアネットワークに含まれる装置は、コアネットワーク装置と称する場合がある。
コアネットワークは、アクセスネットワークとDNとを接続した移動体通信事業者(Mobile Network Operator; MNO)が運用するIP移動通信ネットワークの事であってもよいし、移動通信システム1を運用、管理する移動体通信事業者の為のコアネットワークでもよいし、MVNO(Mobile Virtual Network Operator)、MVNE(Mobile Virtual Network Enabler)等の仮想移動通信事業者や仮想移動体通信サービス提供者の為のコアネットワークでもよい。
また、DNは、UEに通信サービスを提供するDNであってよい。DNは、パケットデータサービス網として構成されてもよいし、サービス毎に構成されてもよい。さらに、DNは、接続された通信端末を含んでもよい。従って、DNと接続する事は、DNに配置された通信端末やサーバ装置と接続する事であってもよい。さらに、DNとの間でユーザデータを送受信する事は、DNに配置された通信端末やサーバ装置とユーザデータを送受信する事であってもよい。
また、以下では、アクセスネットワーク、コアネットワーク、DNの少なくとも一部、及び/又はこれらに含まれる1以上の装置を、ネットワーク又はネットワーク装置と呼称する場合がある。つまり、ネットワーク及び/又はネットワーク装置が、メッセージを送受信する、及び/又は手続きを実行するということは、アクセスネットワーク、コアネットワーク、DNの少なくとも一部、及び/又はこれらに含まれる1以上の装置が、メッセージを送受信する、及び/又は手続きを実行することを意味する。
また、UEは、アクセスネットワークに接続することができる。また、UEは、アクセスネットワークを介して、コアネットワークと接続する事ができる。さらに、UEは、アクセスネットワーク及びコアネットワークを介して、DNに接続する事ができる。すなわち、UEは、DNとの間で、ユーザデータを送受信(通信)する事ができる。ユーザデータを送受信する際は、IP(Internet Protocol)通信だけでなく、non-IP通信を用いてもよい。
ここで、IP通信とは、IPを用いたデータ通信の事であり、IPパケットにより、データの送受信が行われる。IPパケットは、IPヘッダとペイロード部で構成される。ペイロード部には、EPSに含まれる装置・機能や、5GSに含まれる装置・機能が送受信するデータが含まれてよい。
また、non-IP通信とは、IPを用いないデータ通信の事であり、IPパケットの構造とは異なる形式により、データの送受信が行われる。例えば、non-IP通信は、IPヘッダが付与されていないアプリケーションデータの送受信によって実現されるデータ通信でもよいし、マックヘッダやEthernet(登録商標)フレームヘッダ等の別のヘッダを付与してUEが送受信するユーザデータを送受信してもよい。
[2. 各装置の構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用される各装置(UE、及び/又はアクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置)の構成について、図を用いて説明する。尚、各装置は、物理的なハードウェアとして構成されても良いし、汎用的なハードウェア上に構成された論理的な(仮想的な)ハードウェアとして構成されても良いし、ソフトウェアとして構成されても良い。また、各装置の持つ機能の少なくとも一部(全部を含む)が、物理的なハードウェア、論理的なハードウェア、ソフトウェアとして構成されても良い。
次に、各実施形態で使用される各装置(UE、及び/又はアクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置)の構成について、図を用いて説明する。尚、各装置は、物理的なハードウェアとして構成されても良いし、汎用的なハードウェア上に構成された論理的な(仮想的な)ハードウェアとして構成されても良いし、ソフトウェアとして構成されても良い。また、各装置の持つ機能の少なくとも一部(全部を含む)が、物理的なハードウェア、論理的なハードウェア、ソフトウェアとして構成されても良い。
尚、以下で登場する各装置・機能内の各記憶部(記憶部_330、記憶部_440、記憶部_540)は、例えば、半導体メモリ、SSD(Solid State Drive)、HDD(Hard Disk Drive)等で構成されている。また、各記憶部は、出荷段階からもともと設定されていた情報だけでなく、自装置・機能以外の装置・機能(例えば、UE、及び/又はアクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置、及び/又はPDN、及び/又はDN)との間で、送受信した各種の情報を記憶する事ができる。また、各記憶部は、後述する各種の通信手続き内で送受信する制御メッセージに含まれる識別情報、制御情報、フラグ、パラメータ等を記憶することができる。また、各記憶部は、これらの情報をUE毎に記憶してもよい。
[2.1. UE_10の装置構成]
まず、各実施形態で使用されるUEの装置構成例について、図3を用いて説明する。UEは、制御部_300、アンテナ_310、送受信部_320、記憶部_330で構成されている。制御部_300、送受信部_320、記憶部_330は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_320は、アンテナ_310と接続している。
まず、各実施形態で使用されるUEの装置構成例について、図3を用いて説明する。UEは、制御部_300、アンテナ_310、送受信部_320、記憶部_330で構成されている。制御部_300、送受信部_320、記憶部_330は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_320は、アンテナ_310と接続している。
制御部_300は、UE全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_300は、UEにおける他の機能部(送受信部_320、記憶部_330)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_300は、必要に応じて、記憶部_330に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、UEにおける各種の処理を実現する。
送受信部_320は、アンテナ_310を介して、アクセスネットワーク内の基地局装置等と無線通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、UEは、送受信部_320を用いて、アクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置、及び/又はDNとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
具体的には、UEは、送受信部_320を用いることにより、基地局装置_110、基地局装置_120、TNAPと通信することができる。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_110と通信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_120またはTNAPと通信する。より詳細には、UEは、Untrusted non-3GPP Accessを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_120と通信し、UEは、Trusted non-3GPP Accessを介して通信するときは、TNAPと通信する。このように、UEは、利用するアクセスネットワークに応じて、接続先を変更することができる。
また、UEは、送受信部_320を用いることにより、コアネットワーク装置(AMF、SMF、UPF等)と通信することができる。
UEは、N1インターフェース(UEとAMF間のインターフェース)を介して、AMFとNAS(Non-Access-Stratum)メッセージを送受信することができる。ただし、N1インターフェースは論理的なインターフェースであるため、実際には、UEとAMFの間の通信は、基地局装置_110、基地局装置_112、基地局装置_120、基地局装置_122、TNAPを介して行われる。具体的には、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_110又は基地局装置_112を介してAMFと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122とN3IWFを介してAMFと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、TNAPとTNGFを介してAMFと通信することができる。UEとAMFとの間で交換される情報は主に制御情報である。
また、UEは、N1インターフェースとN11インターフェース(AMFとSMF間のインターフェース)を用いて、SMFと通信することができる。具体的には、UEは、AMFを介して、SMFと通信することができる。尚、UEとAMFとの間の通信路は、上述の通り、アクセス(3GPPアクセス、Untrusted Non-3GPP Access、Trusted Non-3GPP Access)に応じて、3種類の経路を辿る場合があり得る。UEとSMFとの間で交換される情報は主に制御情報である。
また、UEは、N3インターフェース(アクセスネットワークとUPF間のインターフェース)を用いて、UPFと通信することができる。具体的には、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_110又は基地局装置_112を介してUPFと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122とN3IWFを介してUPFと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、TNAPとTNGFを介してUPFと通信することができる。UEとUPFとの間の通信路は、主にユーザデータを送受信するために使用される。
また、UEは、N1インターフェースとN11インターフェースとN7インターフェース(SMFとPCF間のインターフェース)を用いて、PCFと通信することができる。具体的には、UEは、AMFおよびSMFを介して、PCFと通信することができる。尚、UEとAMFとの間の通信路は、上述の通り、アクセス(3GPPアクセス、Untrusted Non-3GPP Access、Trusted Non-3GPP Access)に応じて、3種類の経路を辿る場合があり得る。UEとPCFとの間で交換される情報は主に制御情報である。
また、UEは、N3インターフェースとN6インターフェース(UPFとDN間のインターフェース)を用いて、DNと通信することができる。具体的には、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介して通信するときは、基地局装置_110又は基地局装置_112とUPFを介してDNと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122とN3IWFとUPFを介してDNと通信することができる。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)を介して通信するときは、TNAPとTNGFとUPFを介してDNと通信することができる。UEとDNとの間の通信路、すなわちPDUセッション又はMA PDU セッションは、主にユーザデータを送受信するために使用される。
尚、上記は、UEと本明細書において代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、UEが、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_330は、UEの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
また、UEは、ATSSS機能をサポートするUEであり、コアネットワーク側から受信した制御情報は、記憶部_330に記憶されることが望ましい。そして、制御部_300は、コアネットワーク側から受信した制御情報、あるいは記憶部_330に記憶された制御情報に従って、MA PDUセッションを用いた通信を行うのか、SA PDUセッションを用いた通信を行うのかを決定する機能を有してよい。また、MA PDUセッションを用いて通信する場合は、3GPPアクセスだけを介して通信するか、non-3GPPアクセスだけを介して通信するか、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介して通信するかを決定することができる。また、SA PDUセッションを用いて通信する場合は、3GPPアクセスだけを介して通信するか、non-3GPPアクセスだけを介して通信するかを決定することができる。制御部_300は、これらの決定に従って、適切に通信できるように、送受信部320を制御する。
また、UEは、MA PDUセッションを用いて通信する場合、SMFから受信したATSSS rulesに従って、上りリンクトラフィックをどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを決定する機能を有してよい。
また、UEは、PCFから受信したURSP rulesに基づいて、MA PDUセッションの確立を要求する機能を有してよい。
[2.2. 基地局装置_110、基地局装置_112の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用される基地局装置_110、基地局装置_112の装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。尚、基地局装置_112と基地局装置_110は、同一の装置構成であってよいため、以下、基地局装置_110の装置構成を説明する。
次に、各実施形態で使用される基地局装置_110、基地局装置_112の装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。尚、基地局装置_112と基地局装置_110は、同一の装置構成であってよいため、以下、基地局装置_110の装置構成を説明する。
基地局装置_110は、3GPPアクセスに配置される基地局装置である。基地局装置_110は、制御部_400、アンテナ_410、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440で構成されている。制御部_400、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410と接続している。また、基地局装置_110は、ATSSS機能をサポートする基地局装置であってよい。
制御部_400は、基地局装置_110全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_400は、基地局装置_110における他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_400は、必要に応じて、記憶部_440に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、基地局装置_110における各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_420は、基地局装置_110が、AMF及び/又はUPFと通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、基地局装置_110は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いて、AMF及び/又はUPF等との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。
具体的には、基地局装置_110は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いることにより、N2インターフェース(アクセスネットワークとAMF間のインターフェース)を介して、AMFと通信することができる。また、基地局装置_110は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いることにより、N3インターフェースを介して、UPFと通信することができる。
送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410を介して、UEと無線通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、基地局装置_110は、送受信部_430とアンテナ_410を用いて、UEとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
また、基地局装置_110は、UEからコアネットワーク装置宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのコアネットワーク装置にユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。また、基地局装置_110は、コアネットワーク装置からUE宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのUEにユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。
尚、上記は、基地局装置_110と代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、基地局装置_110が、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_440は、基地局装置_110の各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
[2.3. 基地局装置_120、基地局装置_122の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用される基地局装置_120、基地局装置_122の装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。尚、基地局装置_122と基地局装置_120は、同一の装置構成であってよいため、以下、基地局装置_110の装置構成を説明する。
次に、各実施形態で使用される基地局装置_120、基地局装置_122の装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。尚、基地局装置_122と基地局装置_120は、同一の装置構成であってよいため、以下、基地局装置_110の装置構成を説明する。
基地局装置_120は、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)に配置される基地局装置である。基地局装置_120は、制御部_400、アンテナ_410、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440で構成されている。制御部_400、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410と接続している。また、基地局装置_120は、ATSSS機能をサポートする基地局装置であってよい。
制御部_400は、基地局装置_120全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_400は、基地局装置_120における他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_400は、必要に応じて、記憶部_440に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、基地局装置_120における各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_420は、基地局装置_120が、N3IWFと通信する為の機能部であり、N3IWFを介してAMF及び/又はUPFと通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、基地局装置_120は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いて、N3IWFとの間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。また、基地局装置_120は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いて、AMF及び/又はUPF等との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。
つまり、基地局装置_120は、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いることにより、Y2インターフェース(アクセスネットワークとN3IWF間のインターフェース)を介して、N3IWFと通信することができる。また、基地局装置_120は、N3IWFを介して、N2インターフェース(N3IWFとAMF間のインターフェース)を介して、AMFと通信することができる。また、基地局装置_120は、N3IWFを介して、N3インターフェース(N3IWFとUPF間のインターフェース)を介して、UPFと通信することができる。
送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410を介して、UEと無線通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、基地局装置_120は、送受信部_430とアンテナ_410を用いて、Y1インターフェース(アクセスネットワークとUE間のインターフェース)を介して、UEとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
また、基地局装置_120は、UEからコアネットワーク装置宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのコアネットワーク装置にユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。また、基地局装置_120は、コアネットワーク装置からUE宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのUEにユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。
尚、上記は、基地局装置_120と代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、基地局装置_120が、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_440は、基地局装置_120の各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
[2.4. TNAPの装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるTNAPの装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。TNAPは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)に配置される基地局装置(アクセスポイントとも称する)である。TNAPは、制御部_400、アンテナ_410、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440で構成されている。制御部_400、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410と接続している。また、TNAPは、ATSSS機能をサポートするTNAPであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるTNAPの装置構成例について、図4を用いて説明する。TNAPは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)に配置される基地局装置(アクセスポイントとも称する)である。TNAPは、制御部_400、アンテナ_410、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440で構成されている。制御部_400、ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440は、バスを介して接続されている。送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410と接続している。また、TNAPは、ATSSS機能をサポートするTNAPであってよい。
制御部_400は、TNAP全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_400は、TNAPにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_420、送受信部_430、記憶部_440)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_400は、必要に応じて、記憶部_440に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、TNAPにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_420は、TNAPが、TNGFと通信する為の機能部であり、TNGFを介してAMF及び/又はUPFと通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、TNAPは、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いて、TNGFとの間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。また、TNAPは、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いて、AMF及び/又はUPF等との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。
つまり、TNAPは、ネットワーク接続部_420を用いることにより、Taインターフェース(TNAPとTNGF間のインターフェース)を介して、TNGFと通信することができる。また、TNAPは、TNGFを介して、N2インターフェース(TNGFとAMF間のインターフェース)を介して、AMFと通信することができる。また、TNAPは、TNGFを介して、N3インターフェース(TNGFとUPF間のインターフェース)を介して、UPFと通信することができる。
送受信部_430は、アンテナ_410を介して、UEと無線通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、TNAPは、送受信部_430とアンテナ_410を用いて、Ytインターフェース(TNAPとUE間のインターフェース)を介して、UEとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
また、TNAPは、UEからコアネットワーク装置宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのコアネットワーク装置にユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。また、TNAPは、コアネットワーク装置からUE宛のユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を受信した場合、そのUEにユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送信する機能を有している。
尚、上記は、TNAPと代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、TNAPが、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_440は、TNAPの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
[2.5. N3IWF_240の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるN3IWFの装置/機能構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。N3IWFは、UEが5GSに対してnon-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)を介して接続する場合に、non-3GPPアクセスと5GCとの間に配置される装置及び/又は機能であり、具体的には、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)またはコアネットワークに配置される。N3IWFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。また、N3IWFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするN3IWFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるN3IWFの装置/機能構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。N3IWFは、UEが5GSに対してnon-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)を介して接続する場合に、non-3GPPアクセスと5GCとの間に配置される装置及び/又は機能であり、具体的には、non-3GPPアクセス(Untrusted non-3GPP Access)またはコアネットワークに配置される。N3IWFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。また、N3IWFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするN3IWFであってよい。
制御部_500は、N3IWF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、N3IWFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、N3IWFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、N3IWFが、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122、及び/又はAMF、及び/又はUPFと通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、N3IWFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。また、N3IWFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、AMF及び/又はUPF等との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。
つまり、N3IWFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、Y2インターフェースを介して、基地局装置_120又は基地局装置_122と通信することができる。また、N3IWFは、N2インターフェースを介して、AMFと通信することができる。また、N3IWFは、N3インターフェースを介して、UPFと通信することができる。
尚、上記は、N3IWFと代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、N3IWFが、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_540は、N3IWFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、N3IWFは、UEとIPsecトンネルを確立する機能、control planeについてN2インターフェースを終端する機能、user planeについてN3インターフェースを終端する機能、UEとAMFとの間のNASシグナリングをリレーする機能、PDUセッションやQoSに関してSMFからのN2シグナリングを処理する機能、PDUセッションのトラフィックをサポートするために、IPsec SA(Security Association)を確立する機能、UEとUPFとの間でuser planeパケットをリレーする機能(IPsecやN3トンネルのためにパケットをカプセル化/カプセル除去する機能を含む)、untrusted non-3GPPアクセスネットワーク内のローカルモビリティアンカーとしての機能、AMFを選択する機能などを有している。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
[2.6. TNGFの装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるTNGFの装置/機能構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。TNGFは、UEが5GSに対してnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)を介して接続する場合に、non-3GPPアクセスと5GCとの間に配置される装置及び/又は機能であり、具体的には、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)またはコアネットワークに配置される。TNGFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。また、TNGFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするTNGFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるTNGFの装置/機能構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。TNGFは、UEが5GSに対してnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)を介して接続する場合に、non-3GPPアクセスと5GCとの間に配置される装置及び/又は機能であり、具体的には、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP Access)またはコアネットワークに配置される。TNGFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。また、TNGFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするTNGFであってよい。
制御部_500は、TNGF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、TNGFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、TNGFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、TNGFが、TNAP及び/又はAMF及び/又はUPFと通信する為の機能部である。すなわち、TNGFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、TNAPとの間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。また、TNGFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、AMF及び/又はUPF等との間で、制御情報及び/又はユーザデータを送受信することができる。
つまり、TNGFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、Y2インターフェースを介して、TNAPと通信することができる。また、TNGFは、N2インターフェースを介して、AMFと通信することができる。また、TNGFは、N3インターフェースを介して、UPFと通信することができる。
尚、上記は、TNGFと代表的な装置/機能との通信を記載しただけであり、TNGFが、上記以外の装置/機能、すなわち上記以外のコアネットワーク装置と通信することができるのは言うまでもない。
記憶部_540は、TNGFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、TNGFは、N2インターフェースとN3インターフェースを終端する機能、UEがTNANを介して5GCに登録する場合に、承認者として振舞う機能、AMFを選択する機能、UEとAMFとの間のNASメッセージを透過的に(処理せずに)リレーする機能、PDUセッションやQoSをサポートするためSMFとN2シグナリングを処理する機能、UEとUPFとの間のPDUを透過的に(処理せずに)リレーする機能、TNAN内のローカルモビリティアンカーとしての機能などを有している。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
[2.7. AMF_210の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるAMFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。AMFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。AMFは、制御プレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするAMFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるAMFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。AMFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。AMFは、制御プレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするAMFであってよい。
制御部_500は、AMF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、AMFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、AMFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、AMFが、5G AN内の基地局装置、及び/又はSMF、及び/又はPCF、及び/又はUDM、及び/又はSCEFと接続する為の機能部である。すなわち、AMFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、5G AN内の基地局装置、及び/又はSMF、及び/又はPCF、及び/又はUDM、及び/又はSCEFとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
図2を参照して詳細に説明すると、5GC内にあるAMFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N2インターフェースを介して、基地局装置と通信することができ、N8インターフェース(AMFとUDM間のインターフェース)を介して、UDMと通信することができ、N11インターフェースを介して、SMFと通信することができ、N15インターフェース(AMFとPCF間のインターフェース)を介して、PCFと通信することができる。また、AMFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N1インターフェースを介して、UEとNASメッセージの送受信をすることができる。ただし、N1インターフェースは論理的なものであるため、実際には、UEとAMFの間の通信は、5G ANを介して行われる。
記憶部_540は、AMFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、AMFは、N2インターフェースを用いたRANとの制御メッセージを交換する機能、N1インターフェースを用いたUEとのNASメッセージを交換する機能、NASメッセージの暗号化及び完全性保護を行う機能、登録管理(Registration management; RM)機能、接続管理(Connection management; CM)機能、到達可能性管理(Reachability management)機能、UE等の移動性管理(Mobility management)機能、UEとSMF間のSM(Session Management)メッセージを転送する機能、アクセス認証(Access Authentication、Access Authorization)機能、セキュリティアンカー機能(SEA; Security Anchor Functionality)、セキュリティコンテキスト管理(SCM; Security Context Management)機能、N3IWF(Non-3GPP Interworking Function)に対するN2インターフェースをサポートする機能、N3IWFを介したUEとのNAS信号の送受信をサポートする機能、N3IWFを介して接続するUEの認証する機能等を有している。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
また、登録管理では、UEごとのRM状態が管理される。RM状態は、UEとAMFとの間で同期がとられていてもよい。RM状態としては、非登録状態(RM-DEREGISTERED state)と、登録状態(RM-REGISTERED state)がある。RM-DEREGISTERED状態では、UEはネットワークに登録されていないため、AMFにおけるUEコンテキストが、そのUEに対する有効な位置情報やルーティング情報を持っていない為、AMFはUEに到達できない状態である。また、RM-REGISTERED stateでは、UEはネットワークに登録されているため、UEはネットワークとの登録が必要なサービスを受信することができる。尚、RM状態は、5GMM状態(5GMM state)と表現されてもよい。この場合、RM-DEREGISTERED stateは、5GMM-DEREGISTERED stateと表現されてもよいし、RM-REGISTERED stateは、5GMM-REGISTERED stateと表現されてもよい。
言い換えると、5GMM-REGISTERED stateは、各装置が、5GMMコンテキストを確立した状態であってもよいし、PDUセッションコンテキストを確立した状態であってもよい。尚、各装置が5GMM-REGISTERED stateである場合、UE_10は、ユーザデータや制御メッセージの送受信を開始してもよいし、ページングに対して応答してもよい。さらに、尚、各装置が5GMM-REGISTERED stateである場合、UE_10は、初期登録のための登録手続き以外の登録手続き、及び/又はサービス要求手続きを実行してもよい。
さらに、5GMM-DEREGISTERED stateは、各装置が、5GMMコンテキストを確立していない状態であってもよいし、UE_10の位置情報がネットワークに把握されていない状態であってもよいし、ネットワークがUE_10に到達不能である状態であってもよい。尚、各装置が5GMM-DEREGISTERED stateである場合、UE_10は、登録手続きを開始してもよいし、登録手続きを実行することで5GMMコンテキストを確立してもよい。
また、接続管理では、UEごとのCM状態が管理される。CM状態は、UEとAMFとの間で同期がとられていてもよい。CM状態としては、非接続状態(CM-IDLE state)と、接続状態(CM-CONNECTED state)がある。CM-IDLE状態では、UEはRM-REGISTERED stateにあるが、N1インターフェースを介したAMFとの間で確立されるNASシグナリング接続(NAS signaling connection)を持っていない。また、CM-IDLE状態では、UEはN2インターフェースの接続(N2 connection)、及びN3インターフェースの接続(N3 connection)を持っていない。一方、CM-CONNECTED stateでは、N1インターフェースを介したAMFとの間で確立されるNASシグナリング接続(NAS signaling connection)を持っている。また、CM-CONNECTED stateでは、UEはN2インターフェースの接続(N2 connection)、及び/又はN3インターフェースの接続(N3 connection)を持っていてもよい。
さらに、接続管理では、3GPPアクセスにおけるCM状態と、non-3GPPアクセスにおけるCM状態とで分けて管理されてもよい。この場合、3GPPアクセスにおけるCM状態としては、3GPPアクセスにおける非接続状態(CM-IDLE state over 3GPP access)と、3GPPアクセスにおける接続状態(CM-CONNECTED state over 3GPP access)とがあってよい。さらに、non-3GPPアクセスにおけるCM状態としては、non-3GPPアクセスにおける非接続状態(CM-IDLE state over non-3GPP access)と、non-3GPPアクセスにおける接続状態(CM-CONNECTED state over non-3GPP access)とがあってよい。尚、非接続状態はアイドルモード表現されてもよく、接続状態モードはコネクテッドモードと表現されてもよい。
尚、CM状態は、5GMMモード(5GMM mode)と表現されてもよい。この場合、非接続状態は、5GMM非接続モード(5GMM-IDLE mode)と表現されてもよいし、接続状態は、5GMM接続モード(5GMM-CONNECTED mode)と表現されてもよい。さらに、3GPPアクセスにおける非接続状態は、3GPPアクセスにおける5GMM非接続モード(5GMM-IDLE mode over 3GPP access)と表現されてもよいし、3GPPアクセスにおける接続状態は、3GPPアクセスにおける5GMM接続モード(5GMM-CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access)と表現されてもよい。さらに、non-3GPPアクセスにおける非接続状態は、non-3GPPアクセスにおける5GMM非接続モード(5GMM-IDLE mode over non-3GPP access)と表現されてもよいし、non-3GPPアクセスにおける接続状態は、non-3GPPアクセスにおける5GMM接続モード(5GMM-CONNECTED mode over non-3GPP access)と表現されてもよい。尚、5GMM非接続モードはアイドルモード表現されてもよく、5GMM接続モードはコネクテッドモードと表現されてもよい。
また、AMFは、コアネットワーク内に1以上配置されてもよい。また、AMFは、1以上のNSI(Network Slice Instance)を管理するNFでもよい。また、AMFは、複数のNSI間で共有される共有CPファンクション(CCNF; Common CPNF(Control Plane Network Function))でもよい。
[2.8. SMF_220の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるSMFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。SMFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。SMFは、制御プレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするSMFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるSMFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。SMFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。SMFは、制御プレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするSMFであってよい。
制御部_500は、SMF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、SMFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、SMFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、SMFが、AMF、及び/又はUPF、及び/又はPCF、及び/又はUDMと接続する為の機能部である。すなわち、SMFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、AMF、及び/又はUPF、及び/又はPCF、及び/又はUDMとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
図2を参照して詳細に説明すると、5GC内にあるSMFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFと通信することができ、N4インターフェース(SMFとUPF間のインターフェース)を介して、UPFと通信することができ、N7インターフェースを介して、PCFと通信することができ、N10インターフェース(SMFとUDM間のインターフェース)を介して、UDMと通信することができる。
記憶部_540は、SMFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、SMFは、PDUセッションの確立・修正・解放等のセッション管理(Session Management)機能、UEに対するIPアドレス割り当て(IP address allocation)及びその管理機能、UPFの選択と制御機能、適切な目的地(送信先)へトラフィックをルーティングする為のUPFの設定機能、NASメッセージのSM部分を送受信する機能、下りリンクのデータが到着したことを通知する機能(Downlink Data Notification)、AMF経由でN2インターフェースを介してANに送信される、AN特有の(ANごとの)SM情報を提供する機能、セッションに対するSSCモード(Session and Service Continuity mode)を決定する機能、ローミング機能等を有している。また、SMFは、PCFから受信したPCC rulesから、ATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを作成する機能を有する。ATSSS rulesはSMFからUEに対して送信されるMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信されるMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて管理する(マッピングとも称する)機能を有する。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
[2.9. UPF_230の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるUPFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。UPFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。UPFは、ユーザプレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、UPFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするUPFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるUPFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。UPFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。UPFは、ユーザプレーンを扱うノードであってよい。また、UPFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするUPFであってよい。
制御部_500は、UPF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、UPFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、UPFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、UPFが、5G AN内の基地局装置、及び/又はSMF、及び/又はDNと接続する為の機能部である。すなわち、UPFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、5G AN内の基地局装置、及び/又はSMF、及び/又はDNとの間で、ユーザデータ及び/又は制御情報を送受信することができる。
図2を参照して詳細に説明すると、5GC内にあるUPFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N3インターフェースを介して、基地局装置と通信することができ、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFと通信することができ、N6インターフェースを介して、DNと通信することができ、N9インターフェース(UPF間のインターフェース)を介して、他のUPFと通信することができる。
記憶部_540は、UPFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、UPFは、intra-RAT mobility又はinter-RAT mobilityに対するアンカーポイントとしての機能、DNに相互接続するための外部PDUセッションポイントとしての機能(つまり、DNとコアネットワークとの間のゲートウェイとして、ユーザデータを転送する機能)、パケットのルーティング及び転送する機能、1つのDNに対して複数のトラフィックフローのルーティングをサポートするUL CL(Uplink Classifier)機能、マルチホーム(multi-homed)PDUセッションをサポートするBranching point機能、user planeに対するQoS(Quality of Service) 処理機能、上りリンクトラフィックの検証機能、下りリンクパケットのバッファリング、下りリンクデータ通知(Downlink Data Notification)をトリガする機能等を有している。また、UPFは、SMFから受信したN4 rulesに基づいて、MA PDUセッションが確立されている場合に、下りリンクトラフィックをどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを決定する機能も有している。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
また、UPFは、IP通信及び/又はnon-IP通信の為のゲートウェイでもよい。また、UPFは、IP通信を転送する機能を持ってもよく、non-IP通信とIP通信を変換する機能を持っていてもよい。さらに複数配置されるゲートウェイは、コアネットワークと単一のDNを接続するゲートウェイでもよい。尚、UPFは、他のNFとの接続性を備えてもよく、他のNFを介して各装置に接続してもよい。
尚、ユーザプレーン(user plane)は、UEとネットワークとの間で送受信されるユーザデータ(user data)のことである。ユーザプレーンは、PDUセッションを用いて送受信されてもよい。さらに、5GSの場合、ユーザプレーンは、UEとNG RANとの間のインターフェース、及び/又はN3インターフェース、及び/又はN9インターフェース、及び/又はN6インターフェースを介して送受信されてもよい。以下、ユーザプレーンは、U-Planeと表現されてもよい。
さらに、制御プレーン(control plane)は、UEの通信制御等を行うために送受信される制御メッセージのことである。制御プレーンは、UEとAMFとの間のNAS(Non-Access-Stratum)シグナリングコネクションを用いて送受信されてもよい。さらに、5GSの場合、制御プレーンは、UEとNG RANとの間のインターフェース、及びN2インターフェースを用いて送受信されてもよい。以下、制御プレーンは、コントロールプレーンと表現されてもよいし、C-Planeと表現されてもよい。
さらに、U-Plane(User Plane; UP)は、ユーザデータを送受信する為の通信路でもよく、複数のベアラで構成されてもよい。さらに、C-Plane(Control Plane; CP)は、制御メッセージを送受信する為の通信路でもよく、複数のベアラで構成されてもよい。
[2.10. PCF_250の装置構成]
次に、各実施形態で使用されるPCFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。PCFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。 また、PCFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFであってよい。
次に、各実施形態で使用されるPCFの装置構成例について、図5を用いて説明する。PCFは、制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540で構成されている。制御部_500、ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540は、バスを介して接続されている。 また、PCFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFであってよい。
制御部_500は、PCF全体の動作・機能を制御する機能部である。尚、制御部_500は、PCFにおける他の機能部(ネットワーク接続部_520、記憶部_540)が有さない全ての機能を処理してもよい。制御部_500は、必要に応じて、記憶部_540に記憶されている各種プログラムを読み出して実行する事により、PCFにおける各種の処理を実現する。
ネットワーク接続部_520は、PCFが、SMF、及び/又はAF(Application Function)と接続する為の機能部である。すなわち、PCFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いて、SMF及び/又はAFとの間で、制御情報を送受信することができる。
PCFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N7インターフェースを介して、SMFと通信することができる。また、PCFは、ネットワーク接続部_520を用いることにより、N5インターフェース(PCFとAF間のインターフェース)を介して、AF(Application Function)と通信することができる。
記憶部_540は、UPFの各動作に必要なプログラム、ユーザデータ、制御情報等を記憶する為の機能部である。
尚、PCFは、統一されたポリシーフレームワークをサポートする機能、それらを強制するために制御機能(control plane function)に対してポリシールールを提供する機能、登録情報(subscription information)にアクセスする機能などを有している。また、PCFは、MA PDUセッションのためのポリシー(PCC rulesとも称する)、SA PDUセッションのためのポリシー、及びURSP rulesを生成する機能も有している。これらはSMFに送信され、その少なくとも一部はUEに送信される場合もあるし、UPFに送信される場合もある。これらの機能は、全て制御部_500によって制御される。
[3. 各実施形態で用いられる、専門性の高い用語や識別情報の説明]
次に、各実施形態で用いられる、専門性の高い用語や識別情報について、予め説明する。
次に、各実施形態で用いられる、専門性の高い用語や識別情報について、予め説明する。
[3.1. 各実施形態で用いられる専門性の高い用語の説明]
まず、各実施形態で用いられる専門性の高い用語について説明する。
まず、各実施形態で用いられる専門性の高い用語について説明する。
ネットワークとは、アクセスネットワーク、コアネットワーク、DNのうち、少なくとも一部を指す。また、アクセスネットワーク、コアネットワーク、DNのうち、少なくとも一部に含まれる1以上の装置を、ネットワーク又はネットワーク装置と称してもよい。つまり、ネットワークがメッセージの送受信及び/又は処理を実行するということは、ネットワーク内の装置(ネットワーク装置、及び/又は制御装置)がメッセージの送受信及び/又は処理を実行することを意味してもよい。逆に、ネットワーク内の装置がメッセージの送受信及び/又は処理を実行するということは、ネットワークがメッセージの送受信及び/又は処理を実行することを意味してもよい。
また、SM(セッションマネジメント)メッセージ(NAS(Non-Access-Stratum) SMメッセージとも称する)は、SMのための手続きで用いられるNASメッセージであってよく、AMFを介してUEとSMFの間で送受信される制御メッセージであってよい。さらに、SMメッセージには、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、PDUセッション完了メッセージ、PDUセッション拒絶メッセージ、PDUセッション変更要求メッセージ、PDUセッション変更受諾メッセージ、PDUセッション変更応答メッセージ等が含まれてもよい。また、SMのための手続きには、PDUセッション確立手続きが含まれてもよい。
また、5GS(5G System)サービスは、コアネットワークを用いて提供される接続サービスでよい。さらに、5GSサービスは、EPSサービスと異なるサービスでもよいし、EPSサービスと同様のサービスでもよい。
また、non 5GSサービスは、5GSサービス以外のサービスでよく、EPSサービス、及び/又はnon EPSサービスが含まれてもよい。
また、DNN(Data Network Name)は、コアネットワーク及び/又はDN等の外部ネットワークを識別する識別情報でよい。さらに、DNNは、コアネットワークを接続するUPF等のゲートウェイを選択するための情報として用いることもできる。DNNは、EPSにおけるAPN(Access Point Name)に相当するものであってもよい。
また、PDUセッションとは、PDU接続性サービス(PDU connectivity service)を提供するDNとUEとの間の関連性として定義することができるが、具体的には、UEと外部ゲートウェイ又はDNとの間で確立される接続性であってもよい。UEは、5GSにおいて、アクセスネットワーク及びコアネットワークを介したPDUセッションを確立することにより、PDUセッションを用いて、DNとの間のユーザデータの送受信を行うことができる。ここで、この外部ゲートウェイとは、UPF、SCEF等であってよい。UEは、PDUセッションを用いて、DNに配置されるアプリケーションサーバー等の装置と、ユーザデータの送受信を実行する事ができる。また、PDU接続性サービスとは、UEとDNとの間でPDUの交換を提供するサービスである。また、このPDUセッションは、1つのアクセスネットワーク(3GPPアクセスネットワークまたはnon-3GPPアクセスネットワーク)におけるuser plane resourcesのみによって構成され、SA PDUセッションと称する場合もある。つまり、SA PDUセッションは、MA PDUセッションとは異なり、3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesによって同時に構成されることはないPDUセッションであってよい。
尚、各装置(UE、及び/又はアクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置)は、PDUセッションに対して、1以上の識別情報を対応づけて管理してもよい。尚、これらの識別情報には、DNN、TFT、PDUセッションタイプ、アプリケーション識別情報、NSI識別情報、アクセスネットワーク識別情報、及びSSC modeのうち1以上が含まれてもよいし、その他の情報がさらに含まれてもよい。さらに、PDUセッションを複数確立する場合には、PDUセッションに対応づけられる各識別情報は、同じ内容でもよいし、異なる内容でもよい。
また、MA PDUセッションとは、1つの3GPPアクセスネットワークと1つのnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークを同時に使用することが可能なPDU接続性サービスを提供するPDUセッションであっても良い。また、MA PDUセッションは、ある時点では、1つの3GPPアクセスネットワーク、または1つのnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークを使用することが可能なPDU接続性サービスを提供するPDUセッションであっても良い。言い換えると、MA PDUセッションは、3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesだけで構成されてもよいし、non-3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesだけで構成されてもよいし、3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesによって同時に構成される場合がある。
つまり、UEがMA PDUセッションを用いてDNと通信するということは、UEが3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesのみを用いてDNと通信することであってもよいし、UEがnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesのみを用いてDNと通信することであってもよいし、3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスネットワークにおけるuser plane resourcesを用いてDNと通信することであってもよい。このような手法により、UEは、MA PDUセッションを用いて、DNに配置されるアプリケーションサーバー等の装置と、ユーザデータの送受信を実行する事ができる。
尚、各装置(UE、及び/又はアクセスネットワーク装置、及び/又はコアネットワーク装置)は、MA PDUセッションに対して、1以上の識別情報を対応づけて管理してもよい。尚、これらの識別情報には、DNN、TFT、PDUセッションタイプ、アプリケーション識別情報、NSI識別情報、アクセスネットワーク識別情報、及びSSC modeのうち1以上が含まれてもよいし、その他の情報がさらに含まれてもよい。さらに、MA PDUセッションを複数確立する場合には、MA PDUセッションに対応づけられる各識別情報は、同じ内容でもよいし、異なる内容でもよい。
また、PDU(Protocol Data Unit又はPacket Data Unit)セッションタイプは、PDUセッションのタイプを示すものであり、IPv4、IPv6、Ethernet(登録商標)、Unstructuredがある。IPv4が指定された場合、IPv4を用いてデータの送受信を行うことを示す。IPv6が指定された場合は、IPv6を用いてデータの送受信を行うことを示す。Ethernet(登録商標)が指定された場合は、Ethernet(登録商標)フレームの送受信を行うことを示す。また、Ethernet(登録商標)は、IPを用いた通信を行わないことを示してもよい。Unstructuredが指定された場合は、Point-to-Point(P2P)トンネリング技術を用いて、DNにあるアプリケーションサーバー等にデータを送受信することを示す。P2Pトンネリング技術としては、例えば、UDP/IPのカプセル化技術を用いても良い。尚、PDUセッションタイプには、上記の他にIPが含まれても良い。IPは、UEがIPv4とIPv6の両方を使用可能である場合に指定する事ができる。尚、IPはIPv4v6とも表現されてもよい。
また、ネットワークスライス(NS)とは、特定のネットワーク能力及びネットワーク特性を提供する論理的なネットワークである。UE及び/又はネットワークは、5GSにおいて、ネットワークスライス(NWスライス; NS)をサポートすることができる。
また、ネットワークスライスインスタンス(NSI)とは、ネットワーク機能(NF)のインスタンス(実体)と、必要なリソースのセットで構成され、配置されるネットワークスライスを形成する。ここで、NFとは、ネットワークにおける処理機能であって、3GPPで採用又は定義されたものである。NSIはコアネットワーク内に1以上構成される、NSの実体である。また、NSIはNST(Network Slice Template)を用いて生成された仮想的なNF(Network Function)により構成されてもよい。ここで、NSTとは、要求される通信サービスや能力(capability)を提供する為のリソース要求に関連付けられ、1以上のNFの論理的表現である。つまり、NSIとは、複数のNFにより構成されたコアネットワーク内の集合体でよい。また、NSIはサービス等によって配送されるユーザデータを分ける為に構成された論理的なネットワークでよい。NSには、1以上のNFが構成されてよい。NSに構成されるNFは、他のNSと共有される装置であってもよいし、そうでなくてもよい。UE、及び/又ネットワーク内の装置は、NSSAI、及び/又はS-NSSAI、及び/又はUE usage type、及び/又は1以上のNSI ID等の登録情報、及び/又はAPNに基づいて、1以上のNSに割り当てられることができる。尚、UE usage typeは、NSIを識別するための使用される、UEの登録情報に含まれるパラメータ値である。UE usage typeはHSSに記憶されていてよい。AMFはUE usage typeに基づきSMFとUPFを選択してもよい。
また、S-NSSAI(Single Network Slice Selection Assistance Information)は、NSを識別するための情報である。S-NSSAIは、SST(Slice/Service type)のみで構成されてもよいし、SSTとSD(Slice Differentiator)の両方で構成されてもよい。ここで、SSTとは、機能とサービスの面で期待されるNSの動作を示す情報である。また、SDは、SSTで示される複数のNSIから1つのNSIを選択する際に、SSTを補間する情報であってもよい。S-NSSAIは、PLMNごとに特有な情報であってもよいし、PLMN間で共通化された標準の情報であってもよい。また、ネットワークは、デフォルトS-NSSAIとして、UEの登録情報に1以上のS-NSSAIを記憶してもよい。尚、S-NSSAIがデフォルトS-NSSAIである場合において、UEが登録要求メッセージにおいて有効なS-NSSAIをネットワークに送信しないときは、ネットワークは、UEに関係するNSを提供してもよい。
また、NSSAI(Network Slice Selection Assistance Information)は、S-NSSAIの集まりである。NSSAIに含まれる、各S-NSSAIはアクセスネットワーク又はコアネットワークがNSIを選択するのをアシストする情報である。UEはPLMNごとにネットワークから許可されたNSSAIを記憶してもよい。また、NSSAIは、AMFを選択するのに用いられる情報であってよい。
また、SSC(Session and Service Continuity) modeは、5Gシステム(5GS)において、システム、及び/又は各装置がサポートするセッションサービス継続(Session and Service Continuity)のモードを示すものである。より詳細には、UEとUPFとの間で確立されたPDUセッションがサポートするセッションサービス継続の種類を示すモードであってもよい。なお、SSC modeはPDUセッション毎に設定されるセッションサービス継続の種類を示すモードであってもよい。さらに、SSC modeは、SSC mode 1、SSC mode 2、SSC mode 3の3つのモードから構成されていてもよい。尚、PDUセッションに対応づけられたSSC modeは、PDUセッションが存続している間は、変更されなくてもよい。
また、SSC mode 1は、ネットワークが、UEに提供する接続性サービスを維持するモードである。尚、PDUセッションに対応づけられたPDUセッションタイプが、IPv4又はIPv6である場合、セッションサービス継続の際に、IPアドレスは維持されてもよい。
さらに、SSC mode 1は、UEがネットワークに接続する際に用いるアクセステクノロジーに関わらず、同じUPFが維持され続けるセッションサービス継続のモードであってもよい。より詳細には、SSC mode 1は、UEのモビリティが発生しても、確立しているPDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカーとして用いられるUPFを変更せずに、セッションサービス継続を実現するモードであってもよい。
また、SSC mode 2は、ネットワークが、UEに提供された接続性サービスと、対応するPDUセッションとを解放するモードである。尚、SSC mode 2では、PDUセッションに対応づけられたPDUセッションタイプが、IPv4、IPv6又はIPv4v6である場合、PDUセッションのアンカーを変更する際に、UEに割り当てられたIPアドレスは解放されてもよい。
さらに、SSC mode 2は、UPFのサービングエリア内でのみ、同じUPFが維持され続けるセッションサービス継続のモードであってもよい。より詳細には、SSC mode 2は、UEがUPFのサービングエリア内にいる限り、確立しているPDUセッションが用いるUPFを変更せずに、セッションサービス継続を実現するモードであってもよい。さらに、SSC mode 2は、UPFのサービングエリアから出るような、UEのモビリティが発生した場合に、確立しているPDUセッションが用いるUPFを変更して、セッションサービス継続を実現するモードであってもよい。
ここで、UPFのサービングエリアとは、1つのUPFがセッションサービス継続機能を提供することができるエリアであってもよいし、UEがネットワークに接続する際に用いるRATやセル等のアクセスネットワークのサブセットであってもよい。さらに、アクセスネットワークのサブセットとは、1又は複数のRAT、及び/又はセルから構成されるネットワークであってもよい。
尚、SSC mode 2のPDUセッションのアンカーポイント(以下、PDUセッションアンカー、PSAとも呼称する)の変更は、各装置が、SSC mode 2のPSAを変更する手続きを実行することによって実現されてよい。尚、アンカー又はアンカーポイントを、端点と表現してもよい。
また、SSC mode 3は、接続性が消失しないことを、ネットワークが担保しつつ、ユーザプレーンの変更がUEに明らかになるモードである。尚、SSC mode 3の場合、よりよい接続性サービスを実現するために、確立しているPDUセッションが切断される前に、新しいPDUセッションアンカーポイントを通るPDUセッションが確立されてもよい。さらに、SSC mode 3では、PDUセッションに対応づけられたPDUセッションタイプが、IPv4、IPv6又はIPv4v6である場合、PDUセッションのアンカーを変更する際に、UEに割り当てられたIPアドレスは維持されなくてもよい。
さらに、SSC mode 3は、UEとUPFとの間で確立されたPDUセッション、及び/又は通信路を切断する前に、同じDNに対して、新たなUPFを介した新たなPDUセッション、及び/又は通信路を確立することを許可するセッションサービス継続のモードであってもよい。さらに、SSC mode 3は、UEがマルチホーミングになることを許可するセッションサービス継続のモードであってもよい。さらに、SSC mode 3は、複数のPDUセッション、及び/又はPDUセッションに対応づけられたUPFを用いたセッションサービス継続が許可されたモードであってもよい。言い換えると、SSC mode 3の場合、各装置は、複数のPDUセッションを用いてセッションサービス継続を実現してもよいし、複数のUPFを用いてセッションサービス継続を実現してもよい。
ここで、各装置が、新たなPDUセッション、及び/又は通信路を確立する場合、新たなUPFの選択は、ネットワークによって実施されてもよいし、新たなUPFは、UEがネットワークに接続した場所に最適なUPFであってもよい。さらに、複数のPDUセッション、及び/又はPDUセッションが用いるUPFが有効である場合、UEは、アプリケーション、及び/又はフローの通信の新たに確立されたPDUセッションへの対応づけを、即座に実施してもよいし、通信の完了に基づいて実施してもよい。
尚、SSC mode 3のPDUセッションのアンカーポイントの変更は、各装置が、各装置が、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続きを実行することによって実現されてよい。
また、デフォルトSSC modeは、特定のSSC modeが定まらない場合に、UE及び/又はネットワークが用いるSSC modeである。具体的には、デフォルトSSC modeは、アプリケーションからのSSC modeの要求がない場合、及び/又はアプリケーションに対してSSC modeを決めるためのUEのポリシーがない場合に、UEが用いるSSC modeであってもよい。また、デフォルトSSC modeは、UEからのSSC modeの要求がない場合に、ネットワークが用いるSSC modeであってもよい。
なお、デフォルトSSC modeは、加入者情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はUEのポリシーに基づいて、DN毎に設定されていてもよいし、PDN毎に設定されていてもよいし、UE、及び/又は加入者毎に設定されていてもよい。さらに、デフォルトSSC modeは、SSC mode 1、SSC mode 2又はSSC mode 3を示す情報であってもよい。
また、IPアドレス維持(IP address preservation) は、同じIPアドレスを使い続けることができる技術である。IPアドレス維持がサポートされている場合、UEは、TA外へ移動した場合においても、ユーザデータの通信に対して同じIPアドレスを用い続けることが可能である。言い換えると、IPアドレス維持がサポートされている場合、各装置は、PDUセッションのアンカーポイントが変更される際においても、ユーザデータの通信に対して同じIPアドレスを用い続けることが可能であってよい。
また、ステアリング機能は、ATSSSを使用可能なUEが、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介して、MA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリング(steering)したり、切り替えたり(switching)、分けたり(splitting)する機能であってよい。ここで、ステアリング機能には、MPTCP(Multi-Path Transmission Control Protocol)機能と、ATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)-LL(Low-Layer)機能とが含まれてよい。
また、MPTCP機能は、IP層より上の層のステアリング機能であり、TCPトラフィックに適用される。MPTCP機能が適用されるトラフィックは、MPTCPフローと称する場合がある。また、UEのMPTCP機能は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスのuser planeを使って、UPFのMPTCPプロキシ機能と通信することができる。また、UEは、MA PDUセッションを要求し、MPTCP capabilityを提供すると、MPTCP 機能がenabledになってよいし、UPFは、MPTCP 機能をenableすることに合意すると、UPFは、MPTCP Proxy 機能をenabledになってよい。また、ネットワークは、MA PDUセッションのための1つのIPアドレス/プレフィックスと、2つのIPアドレス/プレフィックス(link-specific multipathアドレスとも称する)を割り当てる。link-specific multipathアドレスのうちの1つは、3GPPアクセスを介したsubflowを確立するために使用され、もう1つは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したsubflowを確立するために使用される。また、link-specific multicastアドレスは、UEのMPTCP 機能でのみ使用。N6を介してroutingできない。また、ネットワークは、MPTCP proxy情報(MPTCP proxyのIPアドレス、port number、typeを含んでよい)をUEに送信することができる。ここで、typeはType 1(transport converter)であってよい。また、ネットワークは、MPTCP 機能を適用するべきアプリのリストをUEに示す場合がある。
また、ATSSS-LL機能は、IP層より下の層のステアリング機能であり、全てのタイプのトラフィック(TCPトラフィック、UDP(User Data Protocol)トラフィック、ethernetトラフィック等)に適用される。ATSSS-LL機能が適用されるトラフィックを、Non-MPTCP flowと称する場合がある。また、UPFでは、ATSSS-LL機能と同じであるか、又は似たステアリング機能がサポートされてよい。また、UEのATSSS-LL機能は、ATSSS rulesとlocal conditionsに基づいて、上りトラフィックのsteering, switch, splitを決定する。また、UEは、MA PDUセッションを要求し、ATSSS-LL capabilityを提供すると、ATSSS-LL機能がenabledになってよいし、UEがATSSS-LL capabilityを提供すると、UPFにおけるATSSS-LL機能がenabledになってよい。
また、ATSSS rulesは、1以上のATSSS ruleをリスト化したものである。ATSSS ruleは、ルール優先度(Rule Precedence)、及び/又はトラフィック記述子(Traffic Descriptor)、及び/又はアクセス選択記述子(Access Selection Descriptor)で構成されてよい。ここで、ATSSS ruleにおけるRule Precedenceは、UEにおいて評価されるATSSS rulesの順番を定義するものである。UEは、ATSSS rulesを受信した場合、つまり、1以上のATSSS ruleを受信した場合、各ATSSS ruleにおけるRule Precedenceを参照し、優先度の高いATSSS ruleから順番に評価してよい。
また、ATSSS ruleにおけるTraffic Descriptorは、ATSSS ruleをいつ適用するかを示すものである。ATSSS ruleにおけるTraffic Descriptorは、アプリケーション記述子(Application descriptors)、及び/又はIP記述子(IP descriptors)、及び/又はnon-IP記述子(Non-IP descriptors)で構成されてよい。また、Application descriptorsは、トラフィックを生成するアプリケーションを識別する情報を示してよい。また、IP descriptorsは、IPトラフィックの送信先(destination)を識別する情報を示してよい。また、non-IP descriptorsは、non-IPトラフィック(例えば、ethernetトラフィックやunstructuredトラフィック)の送信先(destination)を識別する情報を示してよい。
また、ATSSS ruleにおけるAccess Selection Descriptorは、ステアリングモード、及び/又はステアリング機能で構成されてよい。ステアリングモードは、サービスデータフロー(SDFとも称する)のトラフィックを3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらに分配するべきかを示す情報であって良い。また、ステアリングモードには、Active-Standby、Smallest Delay、Load-Balancing、Priority-basedの4つのモードが含まれてよい。
また、Active-Standbyは、activeなアクセスとstandbyアクセスとを設定し、activeなアクセスが利用可能なときは、そのアクセスに対して、サービスデータフロー(SDF)をステアリングし、そのactiveなアクセスが利用不能になったときは、standbyアクセスにSDFを切り替えるモードであってよい。また、Active-Standbyは、activeなアクセスのみを設定し、standbyアクセスを設定しない場合は、activeなアクセスが利用可能なときは、そのアクセスに対して、サービスデータフロー(SDF)をステアリングし、そのactiveなアクセスが利用不能になったとしても、standbyアクセスにSDFを切り替えることはできないモードであってよい。
また、Smallest Delayは、最小のRTT(Round-Trip Time)を持つアクセスに対して、サービスデータフロー(SDF)をステアリングするモードであってよい。また、このモードが設定された場合、UEとUPFは、3GPPアクセスを介して通信した場合のRTT、およびnon-3GPPアクセスを介して通信した場合のRTTを決定するための測定を行ってよい。
また、Load-Balancingは、両方のアクセスに、サービスデータフロー(SDF)を分けるモードであってよい。また、Load-Balancingが指定される場合は、さらに、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されるべきサービスデータフロー(SDF)の割合を示す情報も含んでよい。
また、Priority-basedは、優先度の高いアクセス(high priority access)に対して、そのアクセスが混雑していると判断されるまで、サービスデータフロー(SDF)の全てのトラフィックをステアリングするために使用するモードであってよい。また、そのアクセスが混雑している判断された場合は、そのSDFのトラフィックは、優先度の高いアクセスだけでなく、優先度の低いアクセス(low priority access)に対しても、SDFのトラフィックが送信されるモードであってよい。さらに、high priority accessが利用不能になった場合、SDFの全てのトラフィックがlow priority accessに対して送信されるモードであってよい。
また、ステアリング機能は、サービスデータフロー(SDFとも称する)のトラフィックをステアリングするために、MPTCP機能とATSSS-LL機能のどちらを使用するべきかを示してよい。また、これは、UEがMPTCP機能とATSSS-LL機能のどちらもサポートする場合に、使用される情報であってよい。
また、URSP(UE Route Selection Policy) rulesとは、1以上のURSP(UE Route Selection Policy Rule) ruleのりストで構成されてよい。また、各URSP ruleは、ルール優先度(Rule Precedence)、及び/又はトラフィック記述子(Traffic descriptor)、及び/又はルート選択記述子リスト(List of Route Selection Descriptors)で構成されてよい。ここで、URSP ruleにおけるRule Precedenceは、UEにおいて強制されるURSP rulesの順番を示す。UEは、URSP rulesを受信した場合、つまり、1以上のURSP ruleを受信した場合、各URSP ruleにおけるRule Precedenceを参照し、優先度の高いURSP ruleから順番に適用してよい。
また、URSP ruleにおけるTraffic descriptorは、URSP ruleをいつ適用するかを示すものである。URSP ruleにおけるTraffic descriptorは、アプリケーション記述子(Application descriptors)、及び/又はIP記述子(IP descriptors)、及び/又はドメイン記述子(Domain descriptors)、及び/又はnon-IP記述子(Non-IP descriptors)、及び/又はDNN(Data Network Name)、及び/又は接続能力(Connection Capabilities)で構成されてよい。また、Application descriptorsは、OSのIDと、OSのアプリケーションIDを含んでよい。また、IP descriptorsは、IPトラフィックの送信先(destination)を識別する情報を示し、例えば、IPアドレス、IPv6ネットワークプレフィックス、ポート番号、プロトコル番号などを含んでよい。また、ドメイン記述子(Domain descriptors)は、送信先のFQDN(Fully Qualified Domain Name)を示してよい。また、non-IP descriptorsは、non-IPトラフィック(例えば、ethernetトラフィックやunstructuredトラフィック)の送信先(destination)を識別する情報を示してよい。また、DNNは、アプリケーションによって提供されるDNNに関する情報であって良い。また、Connection Capabilitiesは、UEがある能力(capability)を用いてネットワークへの接続を要求するときに、UEのアプリケーションによって提供される情報を示してよい。
また、URSP ruleにおけるList of Route Selection Descriptorsは、1以上のルート選択記述子(Route Selection Descriptor)で構成されてよい。各Route Selection Descriptorは、ルール選択記述子の優先度(Route Selection Descriptor Precedence)、及び/又はルート選択の構成要素(Route selection components)で構成されてよい。Route Selection Descriptor Precedenceは、Route Selection Descriptorsが適用される順番を示す。UEは、Route Selection Descriptorsを受信した場合、つまり、1以上のRoute Selection Descriptorを受信した場合、各Route Selection DescriptorにおけるRule Precedenceを参照し、優先度の高いRoute Selection Descriptorから順番に適用してよい。また、Route Selection Descriptorは、SSCモード選択(SSC Mode Selection)、及び/又はネットワークスライス選択(Network Slice Selection)、及び/又はDNN選択(DNN Selection)、及び/又はPDUセッションタイプ選択(PDU Session Type Selection)、及び/又はノンシームレスオフロード指示(Non-Seamless Offload indication)、及び/又はアクセスタイプの好み(Access Type preference)で構成されてよい。また、SSC Mode Selectionは、アプリケーションのトラフィックを、指定されたSSCモードのPDUセッションを介して、ルーティングすることを示してよい。また、Network Slice Selectionは、示された1以上のS-NSSAIをサポートするPDUセッションを使って、アプリケーションのトラフィックをルーティングすることを示してよい。また、DNN Selectionは、示された1以上のDNNをサポートするPDUセッションを使って、アプリケーションのトラフィックをルーティングすることを示してよい。尚、DNNがTraffic descriptorで使用されている場合は、このRoute Selection Descriptorは、DNN Selectionを含まなくてよい。また、PDUセッションタイプ選択は、示されたPDUセッションタイプをサポートするPDUセッションを使って、アプリケーションのトラフィックをルーティングすることを示してよい。また、Non-Seamless Offload indicationは、アプリケーションのトラフィックを、non-3GPPアクセスに対するオフロードすることを示してよい。また、Access Type preferenceは、UEがPDUセッションを確立する必要がある場合、PDUセッションを確立するアクセスタイプを示してよい。ここでアクセスタイプとは、3GPP又はnon-3GPP又はマルチアクセス(Multi-Access)であってよい。また、マルチアクセスは、PDUセッションは3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスの両方を用いたMA PDUセッションとして確立されるべきであることを示してよい。
[3.2. 各実施形態で用いられる識別情報の説明]
次に、各実施形態で用いられる識別情報について説明する。
次に、各実施形態で用いられる識別情報について説明する。
まず、第1の識別情報は、DNNである。また、第1の識別情報は、UEが要求するDNNを示す情報であってよい。また、第1の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション又はSA PDUセッションの接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであってよい。
また、第2の識別情報は、UEがATSSS機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報である。また、UEがATSSS機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、ATSSS capabilityと表現されてよい。また、第2の識別情報は、UEがATSSS機能の1つの機能であるMPTCP機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報、及び/又はATSSS機能のもう1つの機能であるATSSS-LL機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報であってよい。また、MPTCP機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、MPTCP capabilityと表現されてよいし、ATSSS-LL機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、ATSSS-LL capabilityと表現されてよい。また、UEは、MPTCP機能のみをサポートする場合、第2の識別情報にMPTCP capabilityを含めることができる。また、UEは、ATSSS-LL機能のみをサポートする場合、第2の識別情報にATSSS-LL capabilityを含めることができる。また、UEは、MPTCP機能およびATSSS-LL機能をサポートする場合、第2の識別情報にMPTCP capabilityおよびATSSS-LL capabilityを含めることができる。
また、第3の識別情報は、PDUセッションIDである。また、第3の識別情報は、UEが要求するPDUセッションIDを示す情報(PDUセッションを特定するための情報)であってよい。具体的には、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第3の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するためのPDUセッションIDであってよい。また、UEがSA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第3の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションを識別するためのPDUセッションIDであってよい。
また、第4の識別情報は、PDUセッションタイプである。また、第4の識別情報は、UEが要求するPDUセッションタイプを示す情報であってもよい。また、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第4の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションに対するPDUセッションタイプであってよい。また、UEがSA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第4の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションを識別するためのPDUセッションタイプであってよい。また、第4の識別情報は、IPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6、Unstructured、Ethernet(登録商標)のいずれかであってよい。
また、第5の識別情報は、SSC modeである。また、第5の識別情報は、UEが要求するSSC modeを示す情報であってよい。また、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第5の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションに対するSSC modeであってよい。また、UEがSA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第5の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションに対するSSC modeであってよい。また、第5の識別情報は、SSC mode 1、SSC mode 2、SSC mode 3のいずれかであってよい。
また、第6の識別情報は、S-NSSAIである。また、第6の識別情報は、UEが要求するS-NSSAIを示す情報であってよい。また、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第6の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションに対するS-NSSAIであってよい。また、UEがSA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第6の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションに対するS-NSSAIであってよい。また、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときは、第6の識別情報は、両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIであってよい。また、UEがSA PDUセッションの確立を要求するときであっても、MA PDUセッションを確立しているときは、具体的には、第6の識別情報は、UEが5GSに対して登録するために実行される登録手続き(Registration procedure)においてAMFから受信した登録受諾(Registration Accept)メッセージに含まれるAllowed NSSAI(ネットワークによって許可されたNSSAI)に含まれる1以上のS-NSSAIであってよい。
また、第7の識別情報は、Request typeである。ここで、第7の識別情報は、初期要求(Initial request)、又は既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)、又は緊急要求(Emergency Request)、又は既存の緊急PDUセッション(Existing Emergency PDU Session)、又はMA PDU requestのいずれかを示してよい。また、Initial requestは、新しいPDUセッションの確立を要求する場合に、指定されてよい。また、Existing PDU Sessionは、既存のPDUセッションを3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスの間で切り替える場合、又はEPCにおける既存のPDNコネクションから5GのPDUセッションにハンドオーバする場合に、指定されてよい。また、Emergency Requestは、緊急サービス(Emergency service)のために新たにPDUセッションの確立を要求する場合に、指定されてよい。また、Existing Emergency PDU Sessionは、緊急サービス(Emergency service)のための既存のPDUセッションを3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスの間で切り替えるとき、又はEPCにおける緊急サービスのための既存のPDNコネクションから5GのPDUセッションにハンドオーバする場合に、指定されてよい。また、MA PDU Requestは、UEがMA PDUセッションの確立を要求することを示す場合に、指定されてよい。尚、MA PDUセッションをサポートしないネットワークが受信した場合は、MA PDU Requestは、初期要求として解釈されてよい。尚、MA PDU Requestは、MA PDU Request indicationと表現する場合がある。
また、第8の識別情報は、PDUセッションIDである。また、第8の識別情報は、古いPDUセッションを示すPDUセッションID(old PDUセッションIDとも称する)を示してもよい。具体的には、第8の識別情報は、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、解放を予定しているPDUセッションIDを示してよい。例えば、第8の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションの解放を予定しているときは、MA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示してよい。また、第8の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションの解放を予定しているときは、SA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示してよい。
また、第9の識別情報は、アクセスタイプを示す情報である。また、第9の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第9の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を示してもよい。具体的には、第9の識別情報は、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、解放を予定しているMA PDUセッションにおけるuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、第9の識別情報と共に送信されてよい。
例えば、第8の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示すときに、第9の識別情報は、第8の識別情報が3GPPアクセスを示すときは、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、確立しているMA PDUセッションの中で、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示すときに、第9の識別情報は、第8の識別情報がnon-3GPPアクセスを示すときは、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、確立しているMA PDUセッションの中で、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示すときに、第9の識別情報は、第8の識別情報がnon-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を示すときは、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、確立しているMA PDUセッションの中で、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDを示すときに、第9の識別情報は、第8の識別情報がnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を示すときは、SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き(第4のPSA変更手続き、第5のPSA変更手続き、第6のPSA変更手続き)において、確立しているMA PDUセッションの中で、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第10の識別情報は、上記第1~9の識別情報のうちの2以上の識別情報の内容を組み合わせた内容を持つ情報であって良い。
また、第11の識別情報は、DNNである。また、第11の識別情報は、ネットワークによって決定されたDNNを示す情報であってよい。
また、第11の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。また、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってもよい。
また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークがATSSS機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報である。また、ネットワークがATSSS機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、ATSSS capabilityと表現されてよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークがATSSS機能の1つの機能であるMPTCP機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報、及び/又はATSSS機能のもう1つの機能であるATSSS-LL機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報であってよい。また、MPTCP機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、MPTCP capabilityと表現されてよいし、ATSSS-LL機能をサポートするか否かを示す情報は、ATSSS-LL capabilityと表現されてよい。また、ネットワークは、MPTCP機能のみをサポートする場合、第12の識別情報にMPTCP capabilityを含めることができる。また、ネットワークは、ATSSS-LL機能のみをサポートする場合、第12の識別情報にATSSS-LL capabilityを含めることができる。また、ネットワークは、MPTCP機能およびATSSS-LL機能をサポートする場合、第12の識別情報にMPTCP capabilityおよびATSSS-LL capabilityを含めることができる。
また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。
また、第13の識別情報は、PDUセッションIDである。また、第13の識別情報は、ネットワークによって決定されたPDUセッションIDを示す情報(PDUセッションを特定するための情報)であってよい。具体的には、第13の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションのためのPDUセッションIDまたはMA PDUセッションのためのPDUセッションIDであってよい。より具体的には、ネットワークがMA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第13の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションを識別するためのPDUセッションIDであってよい。また、ネットワークがSA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第13の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションを識別するためのPDUセッションIDであってよい。
さらに、第13の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってもよい。
また、第14の識別情報は、PDUセッションタイプである。また、第14の識別情報は、ネットワークによって決定されたPDUセッションタイプを示す情報であってよい。第14の識別情報は、IPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6、Unstructured、Ethernet(登録商標)のいずれかであってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、確立されるPDUセッションに対応するPDUセッションタイプを示す情報であってもよい。また、ネットワークがSA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第14の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションに対するPDUセッションタイプであってよい。また、ネットワークがMA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第14の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションに対するPDUセッションタイプであってよい。
さらに、第14の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってもよい。
また、第15の識別情報は、SSC modeである。また、第15の識別情報は、ネットワークによって決定されたSSC modeを示す情報であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、SSC mode 1、SSC mode 2、SSC mode 3のいずれかであってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、確立されるPDUセッションに対応するSSC modeを示す情報であってもよい。また、ネットワークがSA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第15の識別情報は、SA PDUセッションに対するSSC modeであってよい。また、ネットワークがMA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第15の識別情報は、MA PDUセッションに対するSSC modeであってよい。
さらに、第15の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってもよい。
また、第16の識別情報は、S-NSSAIである。また、第16の識別情報は、ネットワークによって決定されたS-NSSAIを示す情報であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、確立されるPDUセッションに対応するS-NSSAIを示す情報であってよい。また、ネットワークがMA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第16の識別情報は、両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIであってよい。また、ネットワークがSA PDUセッションの確立を許可するときは、第16の識別情報は、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスまたはnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIであってよい。具体的には、第16の識別情報は、UEが5GSに対して登録するために実行される登録手続き(Registration procedure)においてAMFから受信した登録受諾(Registration Accept)メッセージに含まれるAllowed NSSAI(ネットワークによって許可されたNSSAI)に含まれる1以上のS-NSSAIであってよい。
さらに、第16の識別情報は、ネットワークによって、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってもよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってもよい。
また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによってMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたか否かを示す情報である。また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによってMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示す情報であってよい。また、第17の識別情報は、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってよい。
また、第18の識別情報は、ネットワークによってSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたか否かを示す情報である。また、第18の識別情報は、ネットワークによってSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示す情報であってよい。また、第18の識別情報は、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってよい。
また、第19の識別情報は、アクセスタイプを示す情報である。また、第19の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセス(untrusted 3GPP access)及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted 3GPP access)を示してもよい。また、第19の識別情報は、ネットワークによってMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された(両方のアクセスに対するuser plane resourcesの確立が許可された)場合、確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報であってよい。ここで、確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスは、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。
また、第19の識別情報は、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってよい。
また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesである。また、第20の識別情報は、第1~8の識別情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報等に基づいて、決定される情報であってよい。
また、第21の識別情報は、上記第11~20の識別情報のうちの2以上の識別情報の内容を組み合わせた内容を持つ情報であって良い。
[4. SSC mode 2のPSAを変更する手続き1]
次に、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_110、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)およびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_120、N3IWF_240、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース、又はUEが、TNAP、TNGF、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)を用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、PSA(本実施形態ではUPF_230)を変更する手続きを説明する。
次に、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_110、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)およびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_120、N3IWF_240、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース、又はUEが、TNAP、TNGF、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)を用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、PSA(本実施形態ではUPF_230)を変更する手続きを説明する。
このPSAを変更する手続きには、第1のPSA変更手続きと、第2のPSA変更手続きがあってよい。
ここで、第1のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。言い換えると、第1のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAと、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAとを変更する手続きであるとも言える。
また、第2のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。言い換えると、第2のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAのみを変更する手続きであるとも言える。さらに言い換えると、第2のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAを変更し、残りのアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAを変更しない手続きであるとも言える。
[4.1. 第1のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第1のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第1のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。各装置は、第1のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図14に示される第2の通信状態に遷移する。また、第1のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは全て、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第1のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第1のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。各装置は、第1のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図14に示される第2の通信状態に遷移する。また、第1のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは全て、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
以下、第1のPSA変更手続きについて、図6を用いて説明する。ここで、図6におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S600)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230である。UEは、S600において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_230(serving UPFとも称する)の再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S602)。SMFは、例えば、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介した通信及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_230の再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S604以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S604以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。次に、S604のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のMA PDUセッションのuser plane resourcesで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。尚、SMFは、UPF_230にアクセスタイプを送信しなくてもよい。
次に、UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_230は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_230がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_230がそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値(cause value)が含まれてよい。また、N2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のMA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立が必要であることを示してよい。SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。また、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、NASメッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される。また、NASメッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはNASメッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、NAS メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP Accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、NASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UEは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションを解放してよい。
以上で、S604のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションが解放されているため、DN_300と通信することができない状態となる。また、UEは、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態である。
次に、各装置は、第1の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、新たな(第2の)MA PDUセッションを確立するため、S606のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをMA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。MA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了した場合、新たな(第2の)MA PDUセッションを確立することができる。具体的には、各装置は、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを確立することができる。
また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)場合、第2のMA PDUセッションを確立することはできない。
また、MA PDUセッション確立手続きは、UEが主導して開始される手続きであってよい。また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを複数回実行することにより、複数のMA PDUセッションを確立してもよい。
また、ここでは、3GPPアクセス、及びnon-3GPPアクセス、及び5GC(5G Core Network)は、全て同一のオペレータが管理/運営している場合を想定して説明するが、これらが異なるオペレータが運用する場合に適用することは可能である。
UEは、UE内に予め記憶されている情報、及び/又はアクセスネットワークから事前に受信した情報、及び/又はコアネットワークから事前に受信した情報(登録手続きで受信した識別情報、及び/又はPCFから事前に受信しているURSP rules等を含む)などに基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションを確立するためにMA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを判断してよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワークを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス(3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)及びnon-3GPPアクセス(non-3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)が含まれる。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_110を介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_120およびN3IWFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、TNAPおよびTNGFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。このように、UEがどのアクセスからNASメッセージを送信するかによって、AMFまでの通信経路が変わるが、AMFからSMFまでの通信経路は同一であってよい。ここでは、NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信されたものとして、説明する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)の接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッションで通信していたDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)を識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDにしてもよいし、同一のPDUセッションIDにしてもよい。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、MA PDU Requestを示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立するために送信されたものであること、及び/又は第2のMA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してもよい。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するときは、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(A)及び/又は(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合)は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合)は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(A)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)またはMA PDU Requestを示す場合、つまり、新たに(第2の)MA PDUセッションを確立するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッションまたは既存の緊急PDUセッションであるときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のMA PDUセッションで使用していたPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、PCFを選択しなくてよいが、異なるPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(S1306)。
また、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい(S1306)。ここで、「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された)ことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する)場合、第2のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成してよい。
そして、PCFが第2のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
また、PCFは、SA PDUセッションのためのポリシーを生成した場合は、SMFに対して、そのポリシーを送信してよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成する。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される第2のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であり、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される第2のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1308)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合は、SMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_232が選択されたものとする。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1308)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第2のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立される第2のMA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。尚、UPFにおけるN4 rulesの適用は、S1318の後に行われてもよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第2のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1310)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1312)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1314)(S1316)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、アクセスネットワークに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1314)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したアクセスネットワークは、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1316)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスが含まれる。すなわち、AMFは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するとき、基地局装置_110を介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。また、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、N3IWFおよび基地局装置_120を介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。また、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、TNGFおよびTNAPを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、AMFは、UEからNASメッセージを受信したアクセスと同一のアクセスを介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信することが好ましいが、異なるアクセスを介して、NASメッセージを送信しても構わない。ここでは、NASメッセージが3GPPアクセス(基地局装置_110)を介して送信されるものとして、説明を続ける。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された(3GPPアクセスに対するuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスに対するuser plane resourcesの確立が許可された)場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによって第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1316)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(A)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
この段階で、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスおよびUPF_232を介して、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。しかし、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesはまだ確立されていない状態であってよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、すでに選択されているUPF_232に、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション修正要求メッセージを送信してよい(S1318)。ここで、N4セッション修正要求メッセージは、N4 rulesを含めて送信する必要はないが、含めてもよい。
次に、UPF_232は、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、UPF_232は、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFに対して、N4セッション修正応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション修正応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。
次に、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、N2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、SMFは、AMFに対して、S1312で送信したN1 SMコンテナを送信する必要はないが、送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信する。
次に、第2のMA PDUセッションがuntrusted non-3GPP accessを利用する場合、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信してよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションがTrusted non-3GPP accessを利用する場合、AMFは、TNGF及び/又はTNAPに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信してよい。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、N2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージが含まれる必要はないが、含めてもよい。ここでは、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージがN3IWFに送信されるとする(S1324)。
次に、N3IWFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEとの間で、IPsec child SA(セキュリティアソシエーション)の確立手続きを実行する(S1326)。
具体的には、N3IWFは、第2のMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッションにおけるnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対するIPsec Child SAを確立するために、RFC 7296に記載されるIKEv2規格に従って、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージをUEに送信する。ここで、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージは、要求したIPsec Child SAがトンネルモードで動作することを示してよい。また、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージには、このChild SAに関連するPDUセッションIDが含まれてよい。
次に、UEは、IPsec Child SAを受諾すると、IKE Create_Child_SA応答メッセージを、N3IWFに送信する。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UE及び/又はN3IWF及び/又はアクセスネットワークに通知することができる。
尚、第11から21の識別情報の内容は、(A)の手続きにおける内容と同一でよい。
ただし、(A)の手続きにおいて、第19の識別情報が3GPPアクセスのみを示した場合は、(B)の手続きにおける第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスのみを示してよい。
UEは、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はIKE Create_Child_SA応答メッセージの送信に基づいて、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立されたことを認識してもよい。
尚、UPFにおけるN4 rulesの適用は、S1318の後に行われてもよいし、UEにおけるATSSS rulesの適用は、この段階で行われてもよい。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。すなわち、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスおよびUPF_232を介して、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。
また、図13の(A)及び(B)の手続きを正常に完了すると、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及び3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。また、図13の(A)及び(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションは確立できない。また、この場合、第1のMA PDUセッションはすでに解放済みであり、また、第2のMA PDUセッションを確立できなかったため、UEは、DNと通信できない状態となってよい。また、この場合、図6の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S606のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesとnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションが確立された状態となり、この第2のMA PDUセッションとを用いて、DN_300と通信することが可能な状態にある(S608)。尚、このときのPSAは、UPF_232となっている。
以上で、第1のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第1のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図14に示される第2の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第1のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
[4.2. 第2のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第2のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第2のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合を説明する。各装置は、第2のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図15に示される第3の通信状態に遷移する。また、第2のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第2のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第2のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合を説明する。各装置は、第2のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図15に示される第3の通信状態に遷移する。また、第2のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第2のPSA変更手続きについて、図7を用いて説明する。ここで、図7におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S700)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230である。UEは、S700において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_230(serving UPFとも称する)の再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S702)。SMFは、例えば、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_230の再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S704以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S704以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。次に、S704のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のMA PDUセッションのuser plane resourcesで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。
次に、UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_230は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_230がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_230がそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値(cause value)が含まれてよい。また、N2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のMA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が必要であることを示してよい。SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。また、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、NASメッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されてよい。また、NASメッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはNASメッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、NAS メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、NASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを、認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放してよい。
以上で、S604のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションにおけるnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが解放されているが、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されたままであるため、その第1のMA PDUセッションを用いてDN_300と通信することはできる状態となる。また、UEは、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態である。
次に、各装置は、第1の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介した新たな(第1の)SA PDUセッションを確立するため、S706のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをSA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。SA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
尚、以下では、non-3GPPアクセスがuntrusted non-3GPP accessの場合を説明する。ただし、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、non-3GPPアクセスがTrusted non-3GPP accessの場合にも適用可能である。
このSA PDUセッション確立手続きを実行する前の段階で、UEはnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態であるため、UEは、N3IWFとの間で、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAは確立されている状態であってよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、SA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される(S1300)。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。具体的には、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージは、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAを用いて、N3IWFに送信され、N3IWFは、受信したPDUセッション確立要求メッセージをAMFに転送する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)の接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッションで通信していたDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)を識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDに設定する必要がある。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、初期要求(Initial request)又は既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)を示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、 第1の(新たな)SA PDUセッションを確立するために送信されたものであること、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してもよい。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するときは、SA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)を示す場合、つまり、新たに(第1の)SA PDUセッションを確立するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)を示すときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のMA PDUセッションで使用していたPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、新たなPCFを選択しなくてよいが、新たなPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(図示せず)。
また、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい。ここで、「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合、第1のSA PDUセッションのためのPCC rules(ポリシー、ルーティングルールとも称する)を生成してよい。
そして、PCFが第1のSA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成してよい。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であり、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1318)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合は、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_232が選択されたものとする。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第1のSA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立されるSA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、N3IWF及びアクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1324)(S1326)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1324)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したN3IWFは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1326)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッションの確立が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、SA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第18の識別情報は、ネットワークによって第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可された第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1326)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可された第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立された状態となる。つまり、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。すなわち、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスおよびUPF_232を介して、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。
また、図13の(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、SA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションは確立できない。ただし、この場合、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されたままであるため、UEは、この第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信することはできる状態である。また、この場合、図7の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S706のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションとnon-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立された状態となり、これらの第1のMA PDUセッションと第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することが可能な状態にある(S708)(S710)。尚、このときのPSAは、UPF_230およびUPF_232となっている。
以上で、第2のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第2のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図15に示される第3の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第2のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
尚、本4.2章では、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合について説明したが、PSAを変更するアクセスが逆の場合に対しても適用可能である。すなわち、各装置間で情報を交換したアクセスタイプを、non-3GPPアクセスから3GPPアクセスに置き換えることで、適用可能である。
[5. SSC mode 2のPSAを変更する手続き2]
次に、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、PSAを変更する手続きを説明する。
次に、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、PSAを変更する手続きを説明する。
このPSAを変更する手続きには、第3のPSA変更手続きがあってよい。ここで、第3のPSA変更手続きは、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAが変更される手続きである。
[5.1. 第3のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第3のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第3のPSA変更手続きは、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAを変更される手続きである。ここでは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合を説明する。尚、以下の説明は、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合に対しても、適用可能である。特に、各装置は、第3のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図15に示される第3の通信状態から、図2に示される第1の通信状態に遷移する場合を説明する。また、第3のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
次に、第3のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第3のPSA変更手続きは、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されている場合に、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAを変更される手続きである。ここでは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合を説明する。尚、以下の説明は、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合に対しても、適用可能である。特に、各装置は、第3のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図15に示される第3の通信状態から、図2に示される第1の通信状態に遷移する場合を説明する。また、第3のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
次に、第3のPSA変更手続きについて、図8を用いて説明する。ここで、図8におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、上記の3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S800)(S802)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230およびUPF_232である。UEは、S800、S802において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_232(serving UPFとも称する)の再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S804)。SMFは、例えば、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_232の再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_232の再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S806以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S806以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、UPF_232の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。次に、S806のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_232にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のSA PDUセッションで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。尚、SMFは、UPF_232にアクセスタイプを送信しなくてもよい。
次に、UPF_232は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_232は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_232は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_232は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_232は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_232がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_232がそのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_232が第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値(cause value)が含まれてよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のSA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立、または同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへの追加、または、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が必要であることを示してよい。SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセスを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
次に、UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。そして、UEは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションを解放してよい。
以上で、S604のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のSA PDUセッションが解放されている。しかし、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されているため、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することができる状態でなる。また、UEは、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態である。
次に、各装置は、第3の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを確立するため、つまり、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを追加するため、S808のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをMA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。MA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
尚、以下では、non-3GPPアクセスがuntrusted non-3GPP accessの場合を説明する。ただし、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、non-3GPPアクセスがTrusted non-3GPP accessの場合にも適用可能である。
このMA PDUセッション確立手続きを実行する前の段階で、UEはnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態であるため、UEは、N3IWFとの間で、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAは確立されている状態であってよい。
また、ここでは、3GPPアクセス、及びnon-3GPPアクセス、及び5GC(5G Core Network)は、全て同一のオペレータが管理/運営している場合を想定して説明するが、これらが異なるオペレータが運用する場合に適用することは可能である。
UEは、UE内に予め記憶されている情報、及び/又はアクセスネットワークから事前に受信した情報、及び/又はコアネットワークから事前に受信した情報(登録手続きで受信した識別情報、及び/又はPCFから事前に受信しているURSP rules等を含む)などに基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを追加するため、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを判断してよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワークを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス(3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)及びnon-3GPPアクセス(non-3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)が含まれる。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_110を介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_120およびN3IWFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、TNAPおよびTNGFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。このように、UEがどのアクセスからNASメッセージを送信するかによって、AMFまでの通信経路が変わるが、AMFからSMFまでの通信経路は同一であってよい。ここでは、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されたものとして、説明する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesの接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションで通信していたDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDにしてもよいし、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションIDと同一のPDUセッションIDにしてもよい。ここで、第3の識別情報を第1のMA PDUセッションのPDUセッションIDと同一のPDUセッションIDに設定する場合、UEが第1のMA PDUセッションへの追加を要求することを意味してよい。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、MA PDU Requestを示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、新たなMA PDUセッションを確立するために(user plane resourcesを追加するために)送信されたものであること、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶してもよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するときは、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する場合は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶する場合は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)またはMA PDU Requestを示す場合、つまり、新たに第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッションまたは既存の緊急PDUセッションであるときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のSA PDUセッションで使用していたPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、PCFを選択しなくてよいが、異なるPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(図示せず)。
また、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい。ここで、「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する場合、第1のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成してよい。
そして、PCFが第1のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成する。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される第1のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であり、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される第1のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1318)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可された場合は、SMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_230が選択されたものとする。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第1のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立(追加)されるuser plane resourcesを含む第1のMA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、N3IWF及びアクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1324)(S1326)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1324)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したN3IWFは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1326)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可された場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによって第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立(追加)が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1326)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立(追加)が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。言い換えると、UEは、すでに確立している3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立(追加)された状態となる。つまり、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。
また、図13の(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、SA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを確立できない。すなわち、UEは、すでに確立している3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立(追加)することができない。ただし、この場合、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されたままであるため、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信することはできる状態である。また、この場合、図8の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S808のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立された状態となり、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することが可能な状態にある(S810)。尚、このときのPSAは、UPF_230となっている。
以上で、第3のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第3のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図15に示される第3の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第3のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
尚、本4.2章では、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合について説明したが、PSAを変更するアクセスが逆の場合に対しても適用可能である。すなわち、各装置間で情報を交換したアクセスタイプを、non-3GPPアクセスから3GPPアクセスに置き換えることで、適用可能である。
[6. SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き1]
次に、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_110、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)およびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_120、N3IWF_240、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース、又はUEが、TNAP、TNGF、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)を用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、PSA(本実施形態ではUPF_230)を変更する手続きを説明する。
次に、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_110、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)およびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources(UEが、基地局装置_120、N3IWF_240、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース、又はUEが、TNAP、TNGF、UPF_230を介して、DN_300と通信するためのリソース)を用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、PSA(本実施形態ではUPF_230)を変更する手続きを説明する。
このPSAを変更する手続きには、第4のPSA変更手続きと、第5のPSA変更手続きがあってよい。
ここで、第4のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。言い換えると、第4のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAと、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAとを変更する手続きであるとも言える。
また、第5のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。言い換えると、第5のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAのみを変更する手続きであるとも言える。さらに言い換えると、第5のPSA変更手続きとは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSAのうち、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAを変更し、残りのアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesで使用されるPSAを変更しない手続きであるとも言える。
[6.1. 第4のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第4のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第4のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。各装置は、第4のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図14に示される第2の通信状態に遷移する。また、第4のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは全て、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第4のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第4のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(全てのPSA)を変更する手続きである。各装置は、第4のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図14に示される第2の通信状態に遷移する。また、第4のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは全て、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
以下、第4のPSA変更手続きについて、図9を用いて説明する。ここで、図9におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S900)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230である。UEは、S900において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_230(serving UPFとも称する)及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S902)。SMFは、例えば、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介した通信及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S904以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S904以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、SMFの再割り当ては不要と判断し、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。
次に、SMFは、AMFに対して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信する(S904)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージを含んでよい。また、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値を含んでよい。また、N2 SM情報は、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、N1 SMコンテナ及び/又はN2 SM情報に含まれるPDUセッションIDは、再割り当てを行うPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)を識別する情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、変更したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立が必要であることを示してよい。
SMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、SMFから、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信する(S904)。AMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立が指示されていることを認識してよい。
次に、AMFは、アクセスネットワークに、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信する(S906)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を含んでよい。また、NASメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナを含んでよい。N2セッション要求メッセージを受信したアクセスネットワークは、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S906)。
ここで、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されてよい。また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
次に、UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立が指示されていることを、認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを決定してもよい(S908)。
次に、各装置は、第1の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立するため、S908のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをMA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。MA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了した場合、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立することができる。具体的には、各装置は、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを確立することができる。
また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)場合、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立することはできない。
また、MA PDUセッション確立手続きは、UEが主導して開始される手続きであってよい。また、各装置は、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを複数回実行することにより、複数のMA PDUセッションを確立してもよい。
また、ここでは、3GPPアクセス、及びnon-3GPPアクセス、及び5GC(5G Core Network)は、全て同一のオペレータが管理/運営している場合を想定して説明するが、これらが異なるオペレータが運用する場合に適用することは可能である。
UEは、UE内に予め記憶されている情報、及び/又はアクセスネットワークから事前に受信した情報、及び/又はコアネットワークから事前に受信した情報(登録手続きで受信した識別情報、及び/又はPCFから事前に受信しているURSP rules等を含む)などに基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションを確立するためにMA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを判断してよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワークを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス(3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)及びnon-3GPPアクセス(non-3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)が含まれる。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_110を介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_120およびN3IWFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、TNAPおよびTNGFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。このように、UEがどのアクセスからNASメッセージを送信するかによって、AMFまでの通信経路が変わるが、AMFからSMFまでの通信経路は同一であってよい。ここでは、NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信されたものとして、説明する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)の接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッションで通信しているDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)を識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDに設定する必要がある。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立を要求するMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッション)のS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、MA PDU Requestを示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立するために送信されたものであること、及び/又は第2のMA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)を示すPDUセッションIDを示してよい。また、第8の識別情報を送信することにより、第1のMA PDUセッションを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第9の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)におけるuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示してよい。すなわち、第9の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスについて、untrusted non-3GPP accessとTrusted non-3GPP accessに分けて通知してもよい。つまり、第9の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)、または3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を示してもよい。また、第8の識別情報と第9の識別情報とがともに含められることにより、第1のMA PDUセッションの中で、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してもよい。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するときは、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(A)及び/又は(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合)は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合)は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(A)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)またはMA PDU Requestを示す場合、つまり、新たに(第2の)MA PDUセッションを確立するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)を示すときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のMA PDUセッションで使用しているPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、新たなPCFを選択しなくてよいが、新たなPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(S1306)。
また、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい(S1306)。ここで、「確立を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された)ことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可する)場合、第2のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成してよい。
そして、PCFが第2のMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
また、PCFは、SA PDUセッションのためのポリシーを生成した場合は、SMFに対して、そのポリシーを送信してよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成する。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される第2のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であり、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される第2のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1308)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合は、SMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_232が選択されたものとする。
また、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1308)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第2のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立される第2のMA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。尚、UPFにおけるN4 rulesの適用は、S1318の後に行われてもよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第2のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1310)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1312)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1314)(S1316)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、アクセスネットワークに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1314)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したアクセスネットワークは、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1316)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスが含まれる。すなわち、AMFは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するとき、基地局装置_110を介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。また、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、N3IWFおよび基地局装置_120を介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。また、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、TNGFおよびTNAPを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、AMFは、UEからNASメッセージを受信したアクセスと同一のアクセスを介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信することが好ましいが、異なるアクセスを介して、NASメッセージを送信しても構わない。ここでは、NASメッセージが3GPPアクセス(基地局装置_110)を介して送信されるものとして、説明を続ける。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッションの確立が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可された(3GPPアクセスに対するuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスに対するuser plane resourcesの確立が許可された)場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによって第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、3GPPアクセス及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1316)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(A)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
この段階で、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた新たな(第2の)MA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。つまり、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに加えて、図13の(A)の手続きによって新たに確立された、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。しかし、第2のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesはまだ確立されていない状態であってよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、すでに選択されているUPF_232に、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション修正要求メッセージを送信してよい(S1318)。ここで、N4セッション修正要求メッセージは、N4 rulesを含めて送信する必要はないが、含めてもよい。
次に、UPF_232は、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、UPF_232は、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFに対して、N4セッション修正応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション修正応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。
次に、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、N2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、SMFは、AMFに対して、S1312で送信したN1 SMコンテナを送信する必要はないが、送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信する。
次に、第2のMA PDUセッションがuntrusted non-3GPP accessを利用する場合、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信してよい。また、第2のMA PDUセッションがTrusted non-3GPP accessを利用する場合、AMFは、TNGF及び/又はTNAPに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信してよい。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、N2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージが含まれる必要はないが、含めてもよい。ここでは、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージがN3IWFに送信されるとする(S1324)。
次に、N3IWFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEとの間で、IPsec child SA(セキュリティアソシエーション)の確立手続きを実行する(S1326)。
具体的には、N3IWFは、第2のMA PDUセッション(第2のMA PDUセッションにおけるnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対するIPsec Child SAを確立するために、RFC 7296に記載されるIKEv2規格に従って、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージをUEに送信する。ここで、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージは、要求したIPsec Child SAがトンネルモードで動作することを示してよい。また、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージには、このChild SAに関連するPDUセッションIDが含まれてよい。
次に、UEは、IPsec Child SAを受諾すると、IKE Create_Child_SA応答メッセージを、N3IWFに送信する。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UE及び/又はN3IWF及び/又はアクセスネットワークに通知することができる。
尚、第11から21の識別情報の内容は、(A)の手続きにおける内容と同一でよい。
ただし、(A)の手続きにおいて、第19の識別情報が3GPPアクセスのみを示した場合は、(B)の手続きにおける第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスのみを示してよい。
UEは、IKE Create_Child_SA要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はIKE Create_Child_SA応答メッセージの送信に基づいて、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立されたことを認識してもよい。
尚、UPFにおけるN4 rulesの適用は、S1318の後に行われてもよいし、UEにおけるATSSS rulesの適用は、この段階で行われてもよい。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。
この段階で、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた新たな(第2の)MA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。つまり、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに加えて、図13の(A)の手続きによって新たに確立された、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources、及び図13の(B)の手続きによって新たに確立された、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。
また、図13の(A)及び(B)の手続きを正常に完了すると、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッション及び第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい(S910)(S912)。また、図13の(A)及び(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第2のMA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションは確立できない。また、この場合、第2の(新たな)MA PDUセッションを確立できなかったが、第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されているため、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信できる状態である。また、この場合、図9の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S908のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
次に、S914のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のMA PDUセッションのuser plane resourcesで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。尚、SMFは、UPF_230にアクセスタイプを送信しなくてもよい。
次に、UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_230は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_230がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_230がそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。また、N2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のMA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、3GPPアクセス及びnon-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。また、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、NASメッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される。また、NASメッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはNASメッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、NAS メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、NASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UEは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションを解放してよい。
以上で、S914のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションが解放されるが、第2のMA PDUセッションは確立されているため、第2のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することができる状態である(S916)。
以上で、第4のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第4のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図14に示される第2の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第2のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第4のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230からUPF_232に変更される。
[6.2. 第5のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第5のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第5のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合を説明する。各装置は、第5のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図15に示される第3の通信状態に遷移する。また、第5のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第5のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第5のPSA変更手続きとは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されており、その第1のMA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用されるPSA(一部のPSA)を変更する手続きである。ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAのみを変更し、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesで使用されているPSAを変更しない場合を説明する。各装置は、第5のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図2に示される第1の通信状態から、図15に示される第3の通信状態に遷移する。また、第5のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
次に、第5のPSA変更手続きについて、図10を用いて説明する。ここで、図9におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、上記の第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S1000)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230である。UEは、S1000において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_230(serving UPFとも称する)及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S1002)。SMFは、例えば、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S1004以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S1004以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、SMFの再割り当ては不要と判断し、UPF_230の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。
次に、SMFは、AMFに対して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信する(S1004)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージを含んでよい。また、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値を含んでよい。また、N2 SM情報は、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、N1 SMコンテナ及び/又はN2 SM情報に含まれるPDUセッションIDは、再割り当てを行うPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)を識別する情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、変更したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が必要であることを示してよい。
SMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、SMFから、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信する(S1004)。AMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が指示されていることを認識してよい。
次に、AMFは、アクセスネットワークに、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信する(S1006)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を含んでよい。また、NASメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナを含んでよい。そして、N2セッション要求メッセージを受信したアクセスネットワークは、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1006)。
ここで、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されてよい。また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
次に、UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が指示されていることを、認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを決定してもよい(S1008)。
次に、各装置は、第1の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1の(新たな)SA PDUセッションを確立するため、S1008のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをSA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。SA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
尚、以下では、non-3GPPアクセスがuntrusted non-3GPP accessの場合を説明する。ただし、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、non-3GPPアクセスがTrusted non-3GPP accessの場合にも適用可能である。
このSA PDUセッション確立手続きを実行する前の段階で、UEはnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態であるため、UEは、N3IWFとの間で、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAは確立されている状態であってよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、SA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される(S1300)。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。具体的には、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージは、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAを用いて、N3IWFに送信され、N3IWFは、受信したPDUセッション確立要求メッセージをAMFに転送する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)の接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッションで通信しているDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)を識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDに設定する必要がある。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立を要求するSA PDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)のS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、初期要求(Initial request)又は既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)を示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、新たな(第1の)SA PDUセッションを確立するために送信されたものであること、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)を示すPDUセッションIDを示してよい。また、第8の識別情報を送信することにより、第1のMA PDUセッションを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第9の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)におけるuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示してよい。すなわち、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスについて、untrusted non-3GPP accessとTrusted non-3GPP accessに分けて通知してもよい。つまり、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)、またはnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を示してもよい。また、第8の識別情報と第9の識別情報とがともに含められることにより、第1のMA PDUセッションの中で、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶してもよい。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するときは、SA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)を示す場合、つまり、新たに(第1の)SA PDUセッションを確立するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッション(Existing PDU Session)を示すときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のMA PDUセッションで使用しているPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、新たなPCFを選択しなくてよいが、新たなPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(図示せず)。
また、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい。ここで、「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可する場合、第1のSA PDUセッションのためのPCC rules(ポリシー、ルーティングルールとも称する)を生成してよい。
そして、PCFが第1のSA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PCFから「第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立を許可した第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」、及び/又はPCC rulesを受信することにより、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを認識してよい。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成してよい。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であってよく、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であってよい。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1318)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合は、SMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_232が選択されたものとする。
また、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第1のSA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立される第1のSA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、N3IWF及びアクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1324)(S1326)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1324)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したN3IWFは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1326)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッションの確立が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、SA PDUセッションの確立が許可された場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第18の識別情報は、ネットワークによってSAPDUセッションの確立が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可された第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1326)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立が許可された第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立された状態となる。UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介した新たな(第1の)SA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。つまり、UEは、第5のPSA変更手続きを開始する前から確立している、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに加えて、図13の(B)の手続きによって新たに確立された、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい。
また、図13の(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、S1008のPDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第1のSA PDUセッションの確立を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、SA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションは確立できない。ただし、この場合、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されたままであるため、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信することはできる状態である。また、この場合、図10の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S1008のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
S1008のPDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了すると、上述のように、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに加えて、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい(S1010)(S1012)。
次に、S1014のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のMA PDUセッションのuser plane resourcesで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_230にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。
次に、UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_230は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_230は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_230は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_230がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_230がそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_230が第1のMA PDUセッション(又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources)に対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。また、N2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のMA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、アクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。また、アクセスネットワークとは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスであってよい。すなわち、NASメッセージは、3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される。また、NASメッセージをどちらのアクセスを介して送信するかは、SMFまたはAMFが決定してもよい。SMFが決定する場合、SMFはNASメッセージを送信するべきアクセスに関する情報をAMFに伝え、AMFがそれに従って送信するべきアクセスを特定してよい。また、AMFが決定する場合は、SMFから受信したアクセスタイプに含まれるアクセスの中から任意に特定してよい。
NASメッセージが3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合、AMFは、基地局装置_110に対して、NAS メッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_110が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
また、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信される場合は、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP AccessかTrusted Non-3GPP accessであるかによって、送信先が異なる。
第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがUntrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションで使用するnon-3GPPアクセスがTrusted Non-3GPP Accessの場合、AMFは、TNGFに対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNGFは、TNAPにNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したTNAPが、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。
AMFは、NASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UEは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又はそのUEの第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションを解放してよい。
以上で、S1014のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションにおける、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesは解放されるが、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、第1のSA PDUセッションが確立されているため、第1のMA PDUセッションと第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することができる状態である(S1016)(S1018)。
以上で、第5のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第5のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図15に示される第3の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第5のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230から、UPF_230及びUPF_232に変更される。
[7. SSC mode 3のPSAを変更する手続き2]
次に、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、PSAを変更する手続きを説明する。
次に、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、PSAを変更する手続きを説明する。
このPSAを変更する手続きには、第6のPSA変更手続きがあってよい。ここで、第6のPSA変更手続きは、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAが変更される手続きである。
[7.1. 第6のPSA変更手続き]
次に、第6のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第6のPSA変更手続きは、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAを変更される手続きである。ここでは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合を説明する。尚、以下の説明は、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合に対しても、適用可能である。特に、各装置は、第6のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図15に示される第3の通信状態から、図2に示される第1の通信状態に遷移する場合を説明する。また、第6のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
次に、第6のPSA変更手続きについて説明する。上述のように、第6のPSA変更手続きは、片方のアクセス(3GPPアクセス又はnon-3GPPアクセス)を介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、もう一方のアクセス(non-3GPPアクセス又は3GPPアクセス)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されており、それらの第1のMA PDUセッション及び第1のSA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 3が適用されている場合に、第1のSA PDUセッションのPSAを変更される手続きである。ここでは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合を説明する。尚、以下の説明は、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介した第1のSA PDUセッションとが確立されている場合に対しても、適用可能である。特に、各装置は、第6のPSA変更手続きを実行することにより、図15に示される第3の通信状態から、図2に示される第1の通信状態に遷移する場合を説明する。また、第6のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
次に、第6のPSA変更手続きについて、図11を用いて説明する。ここで、図11におけるUPF1、UPF2、SMF1は、それぞれUPF_230、UPF_232、SMF_220に対応する。
まず、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300とユーザデータを送受信することが可能な状態にある(S1100)(S1102)。このときのPSAは、上述のようにUPF_230およびUPF_232である。UEは、S1100、S1102において、実際にユーザデータを送受信していてもよいし、送受信していなくてもよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のSA PDUセッションで使用中のUPF_232(serving UPFとも称する)及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要か否かを判定する(S1104)。SMFは、例えば、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを維持できなくなった場合、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介した通信のスループットが極端に低下した場合、及び/又はUPF_230がオーバーフロー状態である場合、及び/又はUEが移動した場合、及び/又はオペレータポリシーやネットワークポリシーが変更された場合、及び/又は他のNFから要求された場合等に、UPF_232及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定してよい。
SMFがUPF_232及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが不要と判定した場合、各装置は、S806以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してよい。SMFがUPF_230及び/又はSMFの再割り当てが必要と判定した場合、各装置は、S806以降のステップを実行してよい。ここでは、SMFの再割り当ては不要と判断し、UPF_232の再割り当てが必要と判断した場合を説明する。
次に、SMFは、AMFに対して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信する(S1106)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージを含んでよい。また、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプ、及び/又は理由値を含んでよい。また、N2 SM情報は、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、N1 SMコンテナ及び/又はN2 SM情報に含まれるPDUセッションIDは、MA PDUセッションを識別する情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、変更したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、理由値は、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションの再確立、または同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへの追加、または、同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が必要であることを示してよい。
SMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、SMFから、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信する(S1106)。AMFは、PDUセッション変更コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を受信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを認識してよい。
次に、AMFは、アクセスネットワーク(non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access))に、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信する(S1108)。具体的には、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信してよい。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報を含んでよい。また、NASメッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナを含んでよい。N2セッション要求メッセージを受信したアクセスネットワークは、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1108)。
AMFは、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
次に、UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの設定変更、及び/又は同一のDNに対するMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加が指示されていることを、認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを決定してもよい(S1110)。
次に、各装置は、第3の通信状態におけるDN(DN_300)と同一のDN(DN_300)に対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを確立するため、つまり、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを追加するため、S1110のPDUセッション確立手続きを実行する。尚、本章では、PDUセッション確立手続きをMA PDUセッション確立手続きとも称する。MA PDUセッション確立手続きについて、図13を用いて説明する。
尚、以下では、non-3GPPアクセスがuntrusted non-3GPP accessの場合を説明する。ただし、基地局装置_120とN3IWFを、TNAPとTNGFに置き換えることで、non-3GPPアクセスがTrusted non-3GPP accessの場合にも適用可能である。
このMA PDUセッション確立手続きを実行する前の段階で、UEはnon-3GPPアクセスを介して5GSに登録されている状態であるため、UEは、N3IWFとの間で、NASシグナリングのためのIPsec SAは確立されている状態であってよい。
また、ここでは、3GPPアクセス、及びnon-3GPPアクセス、及び5GC(5G Core Network)は、全て同一のオペレータが管理/運営している場合を想定して説明するが、これらが異なるオペレータが運用する場合に適用することは可能である。
UEは、UE内に予め記憶されている情報、及び/又はアクセスネットワークから事前に受信した情報、及び/又はコアネットワークから事前に受信した情報(登録手続きで受信した識別情報、及び/又はPCFから事前に受信しているURSP rules等を含む)などに基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを追加するため、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始することを判断してよい。
まず、UEは、アクセスネットワークを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを送信することにより(S1300)、MA PDUセッション確立手続きを開始する。NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。NASメッセージは、アップリンクNASトランスポート(UL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
ここで、アクセスネットワークには、3GPPアクセス(3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)及びnon-3GPPアクセス(non-3GPPアクセスネットワークとも称する)が含まれる。すなわち、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_110を介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、基地局装置_120およびN3IWFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。また、UEは、non-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を介してNASメッセージを送信するときは、UEは、TNAPおよびTNGFを介して、AMFにNASメッセージを送信する。このように、UEがどのアクセスからNASメッセージを送信するかによって、AMFまでの通信経路が変わるが、AMFからSMFまでの通信経路は同一であってよい。ここでは、NASメッセージがnon-3GPPアクセスを介して送信されたものとして、説明する。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第1から10の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信することにより、UEが要求することを、ネットワーク側に通知することができる。
また、第1の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesの接続先となるDNを識別するDNNであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションで通信していたDNを識別するDNNと同一のDNNに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、第2の識別情報を含めることにより、UEがATSSS機能をサポートしているか否か、及び/又はMPTCP機能及び/又はATSSS-LL機能をサポートしているか否かを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第3の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションを識別するPDUセッションIDであり、第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションIDと異なるPDUセッションIDにしてもよいし、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して設定されているPDUセッションIDと同一のPDUセッションIDにしてもよい。ここで、第3の識別情報を第1のMA PDUセッションのPDUセッションIDと同一のPDUセッションIDに設定する場合、UEが第1のMA PDUセッションへの追加を要求することを意味してよい。
また、第4の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのPDUセッションタイプであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたPDUセッションタイプと同一のPDUセッションタイプに設定することが好ましい。
また、第5の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのSSC modeであり、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対して設定されていたSSC mode、すなわちSSC mode 2に設定することが好ましいが、SSC mode 1や3に設定しても構わない。
また、第6の識別情報は、確立(追加)を要求するuser plane resourcesのMA PDUセッションのS-NSSAIであり、登録手続き(Registration procedure)において、ネットワークによって両方のアクセス(3GPPアクセスおよびnon-3GPPアクセス)に対して許可されているS-NSSAIに設定することが好ましい。
また、UEは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージに、MA PDU Requestを示す第7の識別情報を含めることにより、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージが、新たなMA PDUセッションを確立するために(user plane resourcesを追加するために)送信されたものであること、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションのトラフィックをステアリングするために、ATSSS-LL機能及び/又はMPTCP機能を適用することを、ネットワーク側に通知してよい。
また、第8の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のSA PDUセッション)を示すPDUセッションIDを示してよい。また、第8の識別情報を送信することにより、第1のSA PDUセッションを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第9の識別情報は、解放を予定しているPDUセッション(第1のMA PDUセッション)におけるuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示してよい。すなわち、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスについて、untrusted non-3GPP accessとTrusted non-3GPP accessに分けて通知してもよい。つまり、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)、またはnon-3GPPアクセス(Trusted non-3GPP access)を示してもよい。また、第8の識別情報と第9の識別情報とがともに含められることにより、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを解放する予定であることを示してよい。
また、第9の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセス、又はnon-3GPPアクセス(untrusted non-3GPP access)を示してよい。また、第8の識別情報と第9の識別情報とがともに含められることにより、確立している第1のSA PDUセッションを解放する予定であることを示してもよい。
尚、UEは、第1から10の識別情報について、NASレイヤよりも下位レイヤ(例えば、RRCレイヤ、MACレイヤ、RLCレイヤ、PDCPレイヤ)の制御メッセージや、NASレイヤよりも上位レイヤの制御メッセージに含めて送信してもよい。
次に、AMFは、NASメッセージを受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、AMFは、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されているが、UEから受信した第6の識別情報で示されるS-NSSAIが両方のアクセスに対して許可されていない場合には、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶してよい。また、AMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートしない場合、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶してもよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、各装置は、S1302以降のステップをスキップ、すなわち中止してもよい。また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するときは、MA PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった場合であってよい。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、AMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報を含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。また、このとき、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、SMFに送信する必要はない。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶するとき、AMFは、SMFに対して、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報を送信し、SMFが、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むN1 SMコンテナを含むNASメッセージを、UEに送信してもよい。このとき、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージには、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶することを示す情報が含まれてよい。
次に、AMFは、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部の転送先として、SMFを選択する(S1302)。尚、AMFは、NASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、転送先のSMFを選択してもよい。また、AMFは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMFを選択してもよい。ここでは、MA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするSMF_220が選択されたものとする。
次に、AMFは、選択されたSMFに、N11インターフェースを介して、UEから受信したNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を送信する(S1304)。また、AMFは、SMFに対して、UEが両方のアクセスに登録されていることを示す情報を送信してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが要求していること、及び/又はAMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
ここで、SMFは、第3の条件判別をしてもよいし、しなくてもよい。第3の条件判別は、UEの要求を受諾するか否かを判断する為のものであってよい。第3の条件判別において、SMFは、第3の条件判別が真か偽かを判定する。SMFは、第3の条件判別が真と判定した場合、図13の(B)の手続きを開始してよい。また、第3の条件判別が偽と判定した場合、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きを開始してよい。
尚、第3の条件判別は、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、実行されてもよい。
例えば、UEの要求をネットワークが許可する場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、UEの要求をネットワークが許可しない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、UEの接続先のネットワーク、及び/又はネットワーク内の装置が、UEが要求する機能をサポートしている場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、UEが要求する機能をサポートしていない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、送受信された識別情報が許可される場合、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよく、送受信された識別情報が許可されない場合、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する場合は、第3の条件判別は真と判定してよい。また、ネットワークが、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶する場合は、第3の条件判別は偽と判定してよい。尚、第3の条件判別の真偽を判定する条件は、前述した条件に限らなくてよい。
次に、図13の(B)の手続きの各ステップを説明する。
まず、SMFは、PCFを選択してもよい。例えば、SMFは、第7の識別情報が初期要求(Initial request)またはMA PDU Requestを示す場合、つまり、新たに第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)するために本手続きが実行された場合は、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報などに基づき、適切なPCFを選択してよい。例えば、SMFは、ATSSS機能をサポートするPCFを選択してもよい。また、SMFは、第7の識別情報が既存のPDUセッションまたは既存の緊急PDUセッションであるときは、すでに選択済みのPCF、つまり第1のSA PDUセッションで使用していたPCFを使用してもよい。すなわち、PCFを選択しなくてよいが、異なるPCFを選択してもよい。
次に、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部を、PCFに送信してよい(図示せず)。
また、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する判断をする場合、さらに「第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、PCFに送信してもよい。ここで、「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、PCFは、SMFから送信された情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)を受信すると、UEが第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を要求していること、及び/又はSMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。
尚、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又は加入者情報(subscription information)等に基づいて、SMFにおける上記判断と同様の判断をさらに行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信された情報と同様の情報を、PCFからSMFに対して送信してよい。
また、PCFは、SMFにおいて上記判断が行われていることを検出したときは、この判断を行わなくてもよい(スキップしてもよい)。
また、SMFにおいて上記判断を行わず、PCFでのみ上記判断を行ってもよい。この場合、SMFからPCFに対して送信される情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)は、AMFから受信した等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の少なくとも一部だけでよい。すなわち、SMFが上記判断をした場合に、SMFが生成してPCFに追加で送信していた上記の情報は、送信しなくてよい。この場合において、PCFが第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する判断をする場合、PCFは、SMFに対して、「第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)を許可したことを示す情報」、及び/又は「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」を、送信してよい。ここで、「確立(追加)を許可したuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスを示す情報(アクセスタイプ)」は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
そして、PCFは、SMFから受信した情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたことを検出した場合、あるいは、SMFから受信した情報(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)に基づいて、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可する場合、MA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成してよい。
そして、PCFがMA PDUセッションのためのPCC rulesを生成した場合は、PCC rulesをSMFに対して送信してよい。また、PCFは、SMFに対して、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを示す情報を送信することで、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを明示的に示してもよいし、PCC rulesを送信することで、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を許可したことを暗示的に示してもよい。
次に、SMFは、PCFから送信された情報を受信すると、それらの情報の内容を認識することができる。そして、SMFは、PCFからPCC rulesを受信した場合、PCC rulesから、ATSSS rules(第20の識別情報)とN4 rulesを生成する。ここで、ATSSS rulesは、SMFからUEに対して送信される第1のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報であり、N4 rulesは、SMFからUPFに対して送信される第1のMA PDUセッションを制御するための情報である。また、SMFは、PCC rulesとATSSS rulesとN4 rulesを対応付けて(マッピングして)管理してよい。
また、第4の識別情報がIPv4、IPv6、IPv4v6のいずれかを示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対するIPアドレスまたはIPプレフィックスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がunstructuredを示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対するIPv6アドレスを割り当ててよい。また、第4の識別情報がethernet(登録商標)を示すときは、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、MACアドレスもIPアドレスも割り当てなくてよい。
次に、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立先のUPFを選択し、選択されたUPFに、N4インターフェースを介して、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信する(S1318)。ここで、SMFは、AMFから受信した情報等、及び/又はPCFから受信した情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、1以上のUPFを選択してもよい。また、複数のUPFが選択された場合、SMFは、各々のUPFに対してN4セッション確立要求メッセージを送信してもよい。また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可された場合は、SMFは、第1のMA PDUセッション及び/又はATSSS機能をサポートするUPFを選択してよい。ここでは、UPF_230が選択されたものとする。
また、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたときは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージには、N4 rulesを含めて送信してよい。
次に、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると(S1318)、SMFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、UPFは、第1のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストを作成する。また、UPFは、SMFからN4 rulesを受信した場合には、N4 rulesに従って動作するように設定してよい。すなわち、UPFは、確立(追加)される第1のMA PDUセッションにおける下りリンクトラフィックについて、3GPPアクセスとnon-3GPPアクセスのどちらのアクセスに対してルーティングするべきかを設定してよい。さらに、UPFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又は第1のMA PDUセッションのためのコンテキストの作成に基づいて、N4インターフェースを介して、SMFにN4セッション確立応答メッセージを送信してよい(S1320)。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション確立要求メッセージに対する応答メッセージとして、N4セッション確立応答メッセージを受信すると、UPFから受信した情報の内容を認識することができる。また、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信などに基づいて、UEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当てを行ってもよい。
次に、SMFは、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージの受信、及び/又はUPFの選択、及び/又はN4セッション確立応答メッセージの受信、及び/又はUEに割り当てるアドレスのアドレス割り当ての完了などに基づいて、N11インターフェースを介して、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を、AMFに送信する(S1322)。ここで、N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよく、さらに、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージには、ATSSSコンテナIE(Information Element)が含まれてよい。
次に、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)を受信したAMFは、N3IWF及びアクセスネットワークを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1324)(S1326)。ここで、NASメッセージは、N1インターフェースを介して、送信される。また、NASメッセージは、ダウンリンクNASトランスポート(DL NAS TRANSPORT)メッセージであってよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWFに対して、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信すると(S1324)、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを受信したN3IWFは、アクセスネットワーク(基地局装置_120)を介して、UEに対して、NASメッセージを送信する(S1326)。ここで、N2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、NASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報が含まれてよい。また、NASメッセージには、PDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナが含まれてよい。N1 SMコンテナには、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージが含まれてよい。
また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、PDUセッション確立要求に対する応答メッセージであってよい。また、PDUセッション確立受諾メッセージは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が受諾されたことを示してよい。
ここで、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求の少なくとも一部が受諾されたことを示してもよい。
また、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11から21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを含めて送信してもよい。SMF及び/又はAMFは、これらの識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つを送信することにより、これらの識別情報の内容を、UEに通知することができる。
例えば、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可された場合、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージには、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれてよい。
尚、SMF及び/又はAMFは、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージにどの識別情報を含めるかを、受信した各識別情報、及び/又は加入者情報、及び/又はネットワークの能力情報、及び/又はオペレータポリシー、及び/又はネットワークの状態、及び/又はユーザの登録情報、及び/又はSMF及び/又はAMFが保持するコンテキスト等に基づいて、選択、決定をしてもよい。
ここで、第11の識別情報は、第1の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第12の識別情報は、ネットワークにおけるMPTCP capability及び/又はATSSS-LL capabilityを示してよい。また、第13の識別情報は、第3の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第14の識別情報は、第4の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第15の識別情報は、第5の識別情報と同一であってよく、例えばSSC mode 2であってよい。また、第16の識別情報は、第6の識別情報と同一であってよい。また、第17の識別情報は、ネットワークによって第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたことを示してよい。また、第19の識別情報は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、第20の識別情報は、ATSSS rulesを示してよい。
また、ATSSSコンテナIE、及び/又はPDUセッション確立受諾メッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はPDUセッションID(第13の識別情報)、及び/又はアクセスタイプ(第19の識別情報)、及び/又はNASメッセージ、及び/又はN2 SM情報、及び/又はN2 PDUセッション要求メッセージに、第11~21の識別情報のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれて送信されることにより、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立(追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立(追加)が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを、UEに通知してもよい。
次に、UEは、N1インターフェースを介して、NASメッセージを受信する(S1326)。UEは、NASメッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が受諾されたこと、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報等(メッセージ、コンテナ、情報)の内容を認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)が許可されたこと、及び/又はnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesの確立が許可されたこと、及び/又は確立(追加)が許可されたuser plane resourcesに対応するアクセスタイプを認識することができる。
以上で、図13の(B)の手続きは、正常に完了する。
図13の(B)の手続きが正常に完了すると、UEは、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立された状態となる。言い換えると、UEは、すでに確立している3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立(追加)された状態となる。つまり、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesおよびnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態となってよい。
また、図13の(B)の手続きを正常に完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了することを意味してよい。
次に、図13において、第3の条件判別が偽の場合に実行される、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きの各ステップを説明する。この手続きは、上述のように、第1のMA PDUセッションの確立(第1のMA PDUセッションへのuser plane resourcesの追加)を拒絶する場合に開始されてよい。
まず、SMFは、AMFを介して、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。具体的には、SMFは、N11インターフェースを介して、AMFにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信する。AMFは、SMFからPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを受信すると、N1インターフェースを用いて、UEにPDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを含むNASメッセージを送信する。
ここで、SMFは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを送信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを示してもよい。
UEは、PDUセッション確立拒絶メッセージを受信することで、PDUセッション確立要求メッセージによるUEの要求が拒絶されたことを認識することができる。すなわち、UEは、SA PDUセッションの確立要求が、ネットワークによって拒絶されたことを認識することができる。
以上で、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了する。また、UEの要求を拒絶する手続きが完了することは、PDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了しなかった(異常に完了した)ことを意味してよい。この場合、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを確立できない。すなわち、UEは、すでに確立している3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに対して、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesが確立(追加)することができない。ただし、この場合、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションは維持されたままであるため、UEは、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信することはできる状態である。また、この場合、図11の残りのステップは、スキップしてよい。
以上で、S1110のPDUセッション確立手続きが完了する。
S1110のPDUセッション確立手続きが正常に完了すると、上述のように、UEは、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションに加えて、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションを用いて、DNと通信可能な状態であってよい(S1112)(S1114)。
次に、S1116のPDUセッション解放手続きについて、図12を用いて説明する。
PDUセッション解放手続きは、SMFが、UPF_232にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって開始される(S1200)。N4セッション解放要求メッセージには、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。N4セッションIDは、新たにPDUセッションを確立する際や、すでに確立されているPDUセッションに対するUPFを変更する際に、SMFが生成して、UPFに対して提供されるN4セッション及び/又はN4セッションのコンテキストを識別するための識別子であってよい。また、N4セッションIDは、SMFとUPFにおいて記憶されている情報である。また、SMFは、あるUEについての、N4セッションIDとPDUセッションIDとの関係も記憶していてよい。また、アクセスタイプは、MA PDUセッションのuser plane resourcesで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、UPF_232にN4セッション解放要求メッセージを送信することによって、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放を要求してもよい。尚、SMFは、UPF_232にアクセスタイプを送信しなくてもよい。
次に、UPF_232は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UPF_232は、N4セッション解放要求メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、SMFは、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションの解放をしてよい。
そして、UPF_232は、SMFにN4セッション解放応答メッセージを送信することにより、N4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はそのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又は第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことをSMFに伝えてよい(S1202)。N4セッション解放応答メッセージには、N4セッション解放要求メッセージに含まれていた、N4セッションID及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。尚、UPF_232は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合、アクセスタイプを含めなくてよい。また、UPF_232は、SMFからアクセスタイプを受信していない場合であっても、アクセスタイプを含めてもよい。アクセスタイプを含める場合は、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_232がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_232がそのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_232が第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
次に、SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージを受信すると、N4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。SMFは、N4セッション解放応答メッセージ、及び/又はN4セッション解放応答メッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、UPF_232がN4セッション解放要求メッセージを受信したこと、及び/又はUPF_232がそのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションを解放したこと、及び/又はUPF_232が第1のSA PDUセッションに対応するN4セッションを解放したことを認識してよい。
そして、SMFは、AMFに、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信する(S1204)。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを送信するが、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、N1 SMコンテナに含まれて送信されてよい。PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージには、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプが含まれてよい。また、N2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージは、PDUセッションID、及び/又はアクセスタイプを含んでよい。ここで、PDUセッションIDは、第1のSA PDUセッションを識別するための情報である。また、アクセスタイプは、第1のSA PDUセッションで解放したいアクセスを示してよく、ここでは、non-3GPPアクセスを示してよい。また、SMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放を指示してもよい。
次に、AMFは、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信すると、N1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はN2 SMリソース解放要求メッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。
そして、AMFは、non-3GPPアクセスを介して、UEにNASメッセージを送信する(S1206、S1208)。ここで、NASメッセージには、N1 SMコンテナが含まれる。つまり、SMFから受信したPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージは、NASメッセージに含まれて送信されてよい。
具体的には、AMFは、N3IWF_240に対して、NASメッセージを送信し、これを受信したN3IWF_240は、基地局装置_120にNASメッセージを送信し、これを受信した基地局装置_120が、UEにNASメッセージを送信する。
AMFは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを送信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを、UEに通知してよい。
UEは、NASメッセージを受信すると、NASメッセージに含まれる情報を確認する。UEは、PDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージ、及び/又はN1 SMコンテナ、及び/又はNASメッセージを受信することで、そのUEの第1のSA PDUセッションの解放が指示されていることを認識してよい。そして、UEは、NASメッセージ、及び/又はNASメッセージに含まれる情報に基づいて、第1のSA PDUセッションを解放してよい。
以上で、S1116のPDUセッション解放手続きを完了する。PDUセッション解放手続きが完了すると、UEは、第1のSA PDUセッションは解放されるが、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されているため、第1のMA PDUセッションを用いて、DN_300と通信することができる状態である(S1118)。
以上で、第6のPSA変更手続きを完了する。
第6のPSA変更手続きが完了すると、図15に示される第3の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介した第1のSA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)から、図2に示される第1の通信状態(3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resources及びnon-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた第1のMA PDUセッションが確立されている状態)に遷移する。また、第6のPSA変更手続きが実行されることにより、PSAは、UPF_230及びUPF_232から、UPF_230に変更される。
[実施形態の要旨]
実施形態のUE(User Equipment)は、制御部と送受信部を備えるUEであって、前記制御部は、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesと、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesとを用いたMA PDUセッションを確立しており、前記MA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されており、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesに対応するPDUセッションアンカーのみを変更する手続きにおいて、前記送受信部は、前記3GPPアクセス又は前記non-3GPPアクセスを介して実行されるMA PDUセッション解放手続きにおいて、前記MA PDUセッションを識別する第1のPDUセッションID、前記non-3GPPアクセスを示すアクセスタイプ、および同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が必要であることを示す理由値を含むPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを受信して、前記制御部は、前記MA PDUセッションにおける前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放し、前記送受信部は、前記アクセスタイプで示されるnon-3GPPアクセスを介して開始されるPDUセッション確立手続きにおいて、確立されるSA PDUセッションを識別する第2のPDUセッションIDを含むPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを送信して、前記制御部は、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したSA PDUセッションを確立し、前記送受信部は、前記3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた前記MA PDUセッションと、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介した前記SA PDUセッションとを用いた通信とが実行可能であり、前記MA PDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカーと、前記SA PDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカーは異なることを特徴とする。
実施形態のUE(User Equipment)は、制御部と送受信部を備えるUEであって、前記制御部は、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesと、non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesとを用いたMA PDUセッションを確立しており、前記MA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されており、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesに対応するPDUセッションアンカーのみを変更する手続きにおいて、前記送受信部は、前記3GPPアクセス又は前記non-3GPPアクセスを介して実行されるMA PDUセッション解放手続きにおいて、前記MA PDUセッションを識別する第1のPDUセッションID、前記non-3GPPアクセスを示すアクセスタイプ、および同一のDNに対するSA PDUセッションの確立が必要であることを示す理由値を含むPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを受信して、前記制御部は、前記MA PDUセッションにおける前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを解放し、前記送受信部は、前記アクセスタイプで示されるnon-3GPPアクセスを介して開始されるPDUセッション確立手続きにおいて、確立されるSA PDUセッションを識別する第2のPDUセッションIDを含むPDUセッション確立要求メッセージを送信して、前記制御部は、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したSA PDUセッションを確立し、前記送受信部は、前記3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを用いた前記MA PDUセッションと、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介した前記SA PDUセッションとを用いた通信とが実行可能であり、前記MA PDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカーと、前記SA PDUセッションのPDUセッションアンカーは異なることを特徴とする。
また、実施形態のUE(User Equipment)は、制御部と送受信部を備えるUEであって、前記制御部は、3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いたMA PDUセッションと、non-3GPPアクセスを介したSA PDUセッションとを確立しており、前記MA PDUセッションおよび前記SA PDUセッションに対してSSC mode 2が適用されており、前記SA PDUセッションに対応するPDUセッションアンカーを変更する手続きにおいて、前記送受信部は、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介して実行されるPDUセッション解放手続きにおいて、前記SA PDUセッションを識別する第2のPDUセッションID、および同一のDNに対するuser plane resourcesの再確立が必要であることを示す理由値を含むPDUセッション解放コマンドメッセージを受信して、前記制御部は、前記SA PDUセッションを解放し、前記送受信部は、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介して開始されるMA PDUセッション確立手続きにおいて、前記MA PDUセッションを識別する前記第1のPDUセッションID、およびMA PDU RequestにセットされたRequest typeを含むMA PDUセッション確立要求メッセージを送信して、前記制御部は、前記3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesのみを用いた前記MA PDUセッションに対して、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesを追加し、前記3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesと、前記non-3GPPアクセスを介したuser plane resourcesとを用いた前記MA PDUセッションによる通信が可能となることを特徴とする。
[8. その他]
本発明の一態様に関わる装置で動作するプログラムは、本発明の一態様に関わる実施形態の機能を実現するように、Central Processing Unit(CPU)等を制御してコンピュータを機能させるプログラムであっても良い。プログラムあるいはプログラムによって取り扱われる情報は、一時的にRandom Access Memory(RAM)等の揮発性メモリあるいはフラッシュメモリ等の不揮発性メモリやHard Disk Drive(HDD)、あるいはその他の記憶装置システムに格納される。
本発明の一態様に関わる装置で動作するプログラムは、本発明の一態様に関わる実施形態の機能を実現するように、Central Processing Unit(CPU)等を制御してコンピュータを機能させるプログラムであっても良い。プログラムあるいはプログラムによって取り扱われる情報は、一時的にRandom Access Memory(RAM)等の揮発性メモリあるいはフラッシュメモリ等の不揮発性メモリやHard Disk Drive(HDD)、あるいはその他の記憶装置システムに格納される。
尚、本発明の一態様に関わる実施形態の機能を実現する為のプログラムをコンピュータが読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録しても良い。この記録媒体に記録されたプログラムをコンピュータシステムに読み込ませ、実行する事によって実現しても良い。ここでいう「コンピュータシステム」とは、装置に内蔵されたコンピュータシステムであって、オペレーティングシステムや周辺機器等のハードウェアを含むものとする。また、「コンピュータが読み取り可能な記録媒体」とは、半導体記録媒体、光記録媒体、磁気記録媒体、短時間動的にプログラムを保持する媒体、あるいはコンピュータが読み取り可能なその他の記録媒体であっても良い。
また、上述した実施形態に用いた装置の各機能ブロック、または諸特徴は、電気回路、たとえば、集積回路あるいは複数の集積回路で実装または実行され得る。本明細書で述べられた機能を実行するように設計された電気回路は、汎用用途プロセッサ、デジタルシグナルプロセッサ(DSP)、特定用途向け集積回路(ASIC)、フィールドプログラマブルゲートアレイ(FPGA)、またはその他のプログラマブル論理デバイス、ディスクリートゲートまたはトランジスタロジック、ディスクリートハードウェア部品、またはこれらを組み合わせたものを含んでよい。汎用用途プロセッサは、マイクロプロセッサでもよいし、従来型のプロセッサ、コントローラ、マイクロコントローラ、またはステートマシンであっても良い。前述した電気回路は、デジタル回路で構成されていてもよいし、アナログ回路で構成されていてもよい。また、半導体技術の進歩により現在の集積回路に代替する集積回路化の技術が出現した場合、本発明の一又は複数の態様は当該技術による新たな集積回路を用いる事も可能である。
なお、本願発明は上述の実施形態に限定されるものではない。実施形態では、装置の1例を記載したが、本願発明は、これに限定されるものではなく、屋内外に設置される据え置き型、または非可動型の電子機器、たとえば、AV機器、キッチン機器、掃除・洗濯機器、空調機器、オフィス機器、自動販売機、その他生活機器等の端末装置もしくは通信装置に適用出来る。
以上、この発明の実施形態に関して図面を参照して詳述してきたが、具体的な構成はこの実施形態に限られるものではなく、この発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲の設計変更等も含まれる。また、本発明は、請求項に示した範囲で種々の変更が可能であり、異なる実施形態にそれぞれ開示された技術的手段を適宜組み合わせて得られる実施形態についても本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。また、上記各実施形態に記載された要素であり、同様の効果を奏する要素同士を置換した構成も含まれる。
1 移動通信システム
10 UE
100 アクセスネットワーク
102 アクセスネットワーク
110 基地局装置
112 基地局装置
120 基地局装置
122 基地局装置
200 コアネットワーク
210 AMF
220 SMF
230 UPF
232 UPF
240 N3IWF
242 N3IWF
250 PCF
300 DN
10 UE
100 アクセスネットワーク
102 アクセスネットワーク
110 基地局装置
112 基地局装置
120 基地局装置
122 基地局装置
200 コアネットワーク
210 AMF
220 SMF
230 UPF
232 UPF
240 N3IWF
242 N3IWF
250 PCF
300 DN
Claims (2)
- 制御部と送受信部とを備えるUE(User Equipment)であって、
前記送受信部は、AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)から、ネットワークがATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)をサポートするか否かを示す第1の情報を受信し、
前記制御部は、前記第1の情報に基づいて、ATSSSが前記ネットワークによってサポートされているか否かを特定し、
前記制御部は、前記ネットワークがATSSSをサポートしていない場合、MA(Multi-Access) PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッションを確立するために、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始しない、
ことを特徴とするUE。 - UE(User Equipment)によって実行される通信制御方法であって、
前記UEは、
AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)から、ネットワークがATSSS(Access Traffic Steering, Switching, Splitting)をサポートするか否かを示す第1の情報を受信し、
前記第1の情報に基づいて、ATSSSが前記ネットワークによってサポートされているか否かを特定し、
前記ネットワークがATSSSをサポートしていない場合、MA(Multi-Access) PDU(Protocol Data Unit)セッションを確立するために、PDUセッション確立手続きを開始しない、
ことを特徴とする通信制御方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202080065695.5A CN114521335B (zh) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-08-07 | Ue以及通信控制方法 |
| EP20851974.4A EP4013075A4 (en) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-08-07 | EU AND SMF |
| US17/632,594 US20220279384A1 (en) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-08-07 | Ue and smf |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019-147898 | 2019-08-09 | ||
| JP2019147898A JP7555183B2 (ja) | 2019-08-09 | 2019-08-09 | Ue |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021029382A1 true WO2021029382A1 (ja) | 2021-02-18 |
Family
ID=74570320
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/030441 WO2021029382A1 (ja) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-08-07 | Ue及びsmf |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20220279384A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP4013075A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7555183B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN114521335B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2021029382A1 (ja) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115278861A (zh) * | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-01 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | 协议数据单元会话建立异常处理方法及用户设备 |
| WO2022257644A1 (zh) * | 2021-06-07 | 2022-12-15 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 数据断流恢复方法、终端及存储介质 |
| EP4221445A1 (en) * | 2022-01-31 | 2023-08-02 | Nokia Technologies Oy | Access traffic steering, switching, and splitting with branching point or uplink classifier on the path |
| WO2023185558A1 (zh) * | 2022-03-31 | 2023-10-05 | 华为技术有限公司 | 通信方法及装置 |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20220353941A1 (en) * | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-03 | Mediatek Inc. | Ma pdu reactivation requested handling |
| US12069515B2 (en) * | 2021-12-08 | 2024-08-20 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Techniques for managing access combinations for multiple access protocol data unit sessions |
| WO2024010230A1 (ko) * | 2022-07-07 | 2024-01-11 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 연합 학습 |
| WO2024149743A1 (en) * | 2023-01-09 | 2024-07-18 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Network nodes, user equipment and methods performed therein |
| WO2024172519A1 (en) * | 2023-02-17 | 2024-08-22 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System and method to handle slice deregistration inactivity timer of on-demand s-nssais |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017135052A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-04 | 2017-08-10 | シャープ株式会社 | 端末装置、基地局装置、通信方法、および、集積回路 |
| WO2018030474A1 (ja) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-15 | シャープ株式会社 | 端末装置、ゲートウェイ、及び通信制御方法 |
| JP2019147898A (ja) | 2018-02-27 | 2019-09-05 | トッパン・フォームズ株式会社 | 擬似接着積層体 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11116028B2 (en) * | 2017-07-10 | 2021-09-07 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Multi-access data connection in a mobile network |
| CN118433934A (zh) * | 2017-08-11 | 2024-08-02 | 交互数字专利控股公司 | 多个接入网络之间的业务引导和切换 |
| EP3755116B1 (en) * | 2018-02-13 | 2024-07-31 | LG Electronics Inc. | Method of processing establishment of ma pdu session, and amf node and smf node |
| US10750406B2 (en) * | 2018-04-01 | 2020-08-18 | Industrial Technology Research Institute | Method of distributing uplink data flow between different access networks in 5G communication system and user equipment using the same |
| EP3777251A4 (en) * | 2018-04-04 | 2021-05-26 | Guangdong Oppo Mobile Telecommunications Corp., Ltd. | DEVICE AND PROCEDURE FOR ACCESS TO ROUTING, BROKERING AND / OR SPLITTING OPERATIONS |
| WO2019197016A1 (en) * | 2018-04-09 | 2019-10-17 | Lenovo (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Data packet steering on a multi-access data connection |
| JP7189316B2 (ja) * | 2018-07-20 | 2022-12-13 | オッポ広東移動通信有限公司 | セッション管理方法、端末装置とネットワーク装置 |
| US20200260401A1 (en) * | 2019-02-12 | 2020-08-13 | Zte Corporation | Session management policy support for session establishment |
| US11228997B2 (en) * | 2019-06-18 | 2022-01-18 | Mediatek Inc. | Handling of multi-access PDU session when inter-system change |
-
2019
- 2019-08-09 JP JP2019147898A patent/JP7555183B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-08-07 WO PCT/JP2020/030441 patent/WO2021029382A1/ja unknown
- 2020-08-07 CN CN202080065695.5A patent/CN114521335B/zh active Active
- 2020-08-07 EP EP20851974.4A patent/EP4013075A4/en active Pending
- 2020-08-07 US US17/632,594 patent/US20220279384A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017135052A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-04 | 2017-08-10 | シャープ株式会社 | 端末装置、基地局装置、通信方法、および、集積回路 |
| WO2018030474A1 (ja) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-15 | シャープ株式会社 | 端末装置、ゲートウェイ、及び通信制御方法 |
| JP2019147898A (ja) | 2018-02-27 | 2019-09-05 | トッパン・フォームズ株式会社 | 擬似接着積層体 |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| "Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Procedures for the 5G system; Stage 2 (Release 16", 3GPP TS 23.502, June 2019 (2019-06-01) |
| "Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Study on access traffic steering, switch and splitting support in the 5G system architecture (Release 16", 3GPP TR 23.793, December 2018 (2018-12-01) |
| "Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2 (Release 16", 3GPP TS 23.501, June 2019 (2019-06-01) |
| 3GPP: "Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; System Architecture for the 5G System; Stage 2 (Release 16)", 3GPP TS 23.501 V16.1.0, 11 June 2019 (2019-06-11), pages 266 - 275, XP051751775 * |
| See also references of EP4013075A4 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115278861A (zh) * | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-01 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | 协议数据单元会话建立异常处理方法及用户设备 |
| CN115278861B (zh) * | 2021-04-29 | 2023-10-13 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | 协议数据单元会话建立异常处理方法及用户设备 |
| WO2022257644A1 (zh) * | 2021-06-07 | 2022-12-15 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 数据断流恢复方法、终端及存储介质 |
| EP4221445A1 (en) * | 2022-01-31 | 2023-08-02 | Nokia Technologies Oy | Access traffic steering, switching, and splitting with branching point or uplink classifier on the path |
| WO2023185558A1 (zh) * | 2022-03-31 | 2023-10-05 | 华为技术有限公司 | 通信方法及装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114521335A (zh) | 2022-05-20 |
| EP4013075A1 (en) | 2022-06-15 |
| US20220279384A1 (en) | 2022-09-01 |
| CN114521335B (zh) | 2024-08-27 |
| EP4013075A4 (en) | 2022-12-21 |
| JP7555183B2 (ja) | 2024-09-24 |
| JP2021029031A (ja) | 2021-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021029382A1 (ja) | Ue及びsmf | |
| WO2020255954A1 (ja) | Ue及びsmf | |
| CN110915293B (zh) | 用户装置及用户装置的通信控制方法 | |
| JP7441596B2 (ja) | ユーザ装置、セッション管理機能及び通信制御方法 | |
| JP7045808B2 (ja) | Ue及びueの通信制御方法 | |
| CN110754114B (zh) | 终端装置以及核心网装置 | |
| WO2018207837A1 (ja) | ユーザ装置 | |
| JP7283868B2 (ja) | ユーザ装置、制御装置、及び通信制御方法 | |
| WO2010098146A1 (en) | Method for a communication node with a plurality of communication interfaces to notify dynamic path setup and associated apparatus thereof | |
| JP7283869B2 (ja) | ユーザ装置、制御装置、及び通信制御方法 | |
| US11576219B2 (en) | User equipment, control apparatus, and communication control method | |
| JP2020088472A (ja) | ユーザ装置 | |
| CN110892780A (zh) | 用户装置、用户装置的通信控制方法、核心网装置、核心网的通信控制方法、smf、smf的通信控制方法、upf以及upf的通信控制方法 | |
| WO2020100719A1 (ja) | ユーザ装置、制御装置、及び通信制御方法 | |
| CN112714506B (zh) | 数据传输方法和装置 | |
| JP2020088473A (ja) | ユーザ装置 | |
| JP7539402B2 (ja) | Ue | |
| WO2021132193A1 (ja) | Ue | |
| JP2020061610A (ja) | ユーザ装置、制御装置、及び通信制御方法 | |
| JP7251936B2 (ja) | ユーザ装置、制御装置、及び通信制御方法 | |
| WO2021132192A1 (ja) | Ue | |
| WO2021132190A1 (ja) | Ue | |
| WO2022059627A1 (ja) | UE(User Equipment) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20851974 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2020851974 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20220309 |