WO2020137433A1 - Couche jetable - Google Patents
Couche jetable Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020137433A1 WO2020137433A1 PCT/JP2019/047707 JP2019047707W WO2020137433A1 WO 2020137433 A1 WO2020137433 A1 WO 2020137433A1 JP 2019047707 W JP2019047707 W JP 2019047707W WO 2020137433 A1 WO2020137433 A1 WO 2020137433A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- region
- longitudinal direction
- basis weight
- disposable diaper
- edge
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/496—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers in the form of pants or briefs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/494—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/494—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means
- A61F13/49406—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means the edge leakage prevention means being at the crotch region
- A61F13/49413—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means the edge leakage prevention means being at the crotch region the edge leakage prevention means being an upstanding barrier
- A61F13/4942—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means the edge leakage prevention means being at the crotch region the edge leakage prevention means being an upstanding barrier the barrier not being integral with the top- or back-sheet
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/531—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having a homogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/532—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having a homogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/494—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means
- A61F2013/49493—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers characterised by edge leakage prevention means the edge leakage prevention means being or forming three-dimensional barrier with raised lateral side-or end-wall
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
- A61F2013/5355—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes with terraced core
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a disposable diaper.
- Patent Document 1 discloses an absorbent core containing an absorbent material.
- the absorbent core is used in absorbent articles such that the absorbent material is substantially free of cellulosic fibers and forms a pattern of discrete areas of absorbent material.
- the pattern includes a dot formation region and at least one of a region extending in the width direction and a region extending in the longitudinal direction.
- an absorbent body containing a relatively large amount of superabsorbent polymer When applying an absorbent body containing a relatively large amount of superabsorbent polymer to a disposable diaper, it is possible to use an absorbent body in which the superabsorbent polymer is arranged approximately uniformly in a plane.
- the superabsorbent polymer absorbs a liquid (example: urine) and swells after being worn, the rigidity of the absorbent body is increased, and the absorbent body becomes relatively straight in the longitudinal direction. Become. Then, on both sides in the width direction of the absorbent body, the pair of leak-proof walls extending in the longitudinal direction along the absorbent body are pulled so as to be stretched from both sides in the longitudinal direction, and toward the wearer's skin surface. It becomes difficult to stand up. As a result, the height of the leak preventive wall becomes low, and there is a risk that the liquid may leak across the pair of leak preventive walls in the width direction.
- the absorber (absorbent core) of Patent Document 1 is divided into a plurality of regions in a plan view in order to improve wearing comfort.
- the absorbent body may absorb liquid and have a shape that pops out.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a disposable diaper that can suppress leakage of liquid in the width direction in a disposable diaper containing a super absorbent polymer.
- the disposable diaper of the present invention is as follows. (1) Absorption that has a longitudinal direction, a width direction, and a thickness direction that are orthogonal to each other, is located between a ventral side portion, a back side portion, the abdominal side portion and the back side portion, and includes an absorber A disposable diaper, comprising: an absorbent body, wherein the absorbent body contains a superabsorbent polymer, is adjacent to a crotch region and a rear side in the longitudinal direction of the crotch region, the back side portion and the thickness.
- the absorbent main body is located on both sides in the width direction on the skin side surface, and A pair of side sheets extending in a direction, each of the pair of side sheets being located at the front and rear ends of the side sheet in the longitudinal direction, and being fixed to the surface of the absorbent main body.
- an elastic member extending along the longitudinal direction, located between the fixing regions on the front side and the rear side of the side sheet in the longitudinal direction, and on the surface of the absorbent main body, the outer end in the width direction.
- An edge is fixed, and a leak preventive wall that does not fix the inner edge in the width direction is provided, and the edge on the central side in the longitudinal direction in the fixed area has the low basis weight area and the thickness. Disposable diapers that overlap in the vertical direction.
- the absorbent body since the absorbent body has a low basis weight region having a low basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer in the ventral region and/or the dorsal region in the longitudinal direction, the low basis weight region and the high absorbency are provided.
- a starting point for changing the basis weight can be formed at a position between the crotch region where the basis weight of the polymer is high. That is, in the absorbent body, a starting point where the rigidity is changed can be formed at a position between the low basic weight region having low rigidity and the crotch region having high rigidity in the longitudinal direction.
- Such a starting point becomes a folding starting point at which the end of the absorbent body is broken when the contracting force in the longitudinal direction of the leak preventive wall is applied to the end of the absorbent body as a force toward the center side in the longitudinal direction.
- the folding starting point that is, the edge on the crotch region side in the low basis weight region is located in the center side rather than the edge on the center side in the longitudinal direction of the fixed region in plan view. ..
- the super absorbent polymer absorbs liquid and swells after mounting, the rigidity of the absorbent body increases and the shape becomes relatively straight in the longitudinal direction. Is pulled to increase the contraction force in the longitudinal direction of the leak preventive wall.
- the contraction force in the longitudinal direction of the leak-proof wall causes the longitudinal center edge of the fixing region to be strongly pulled toward the central side, and the folding start point is set as described above. Therefore, the absorber can be folded at the folding start point so that the end portion in the longitudinal direction of the absorber stands up toward the skin surface of the wearer. As a result, it is possible to reduce the degree to which the leakproof wall is pulled toward both sides in the longitudinal direction by the longitudinal ends of the standing absorber, and to make the leakproof wall stand up toward the wearer's skin surface. You can That is, it is possible to prevent the height of the leakproof wall from being lowered, and to prevent the liquid from leaking in the width direction beyond the leakproof wall.
- the disposable diaper of the present invention has the above (1), in which (2) the edge of the effective region of the elastic member on the fixing region side in the effective portion that overlaps the low basis weight region in the thickness direction.
- the disposable diaper described in 1. may be used.
- the edge of the effective portion of the elastic member on the side of the fixed region overlaps the low basis weight region in the thickness direction. That is, the distance between the fixed region and the effective portion can be reduced in plan view. This makes it possible to easily pull the fixed region at the effective portion, so that the absorbent body can be more easily folded at the folding start point so that the longitudinal end of the absorbent body stands up toward the skin surface of the wearer.
- the position of the edge on the central side in the longitudinal direction in the fixing region is opposite to the crotch region side than the edge on the crotch region side in the low basis weight region.
- the disposable diaper according to (1) or (2) above, which is close to the side edge, may be used.
- the position of the edge on the center side in the longitudinal direction in the fixed region is on the opposite side (dorsal region or ventral region side) from the crotch region side edge in the low basis weight region. Near the edge.
- the position of the edge on the central side in the longitudinal direction in the fixed region is the position where the contraction force of the leak preventive wall acts.
- the edge on the crotch region side in the low grammage region is the position where the folding starts. Therefore, in the present disposable diaper, the position where the contraction force acts is configured to be farther from the position of the folding start point. That is, in the present disposable diaper, the distance between the fixing region where the contracting force acts and the folding start point is made larger.
- a force F in a direction perpendicular to the arm member is applied to the object fixed to the rotation axis by the arm member to rotate the object around the rotation axis, when the forces F are equal, The longer the length r, the larger the torque N for rotating the object.
- the folding start point corresponds to the rotation axis
- the member between the fixed region and the folding start point corresponds to the arm member
- the distance between the fixed region and the folding start point corresponds to the length r of the arm member
- the end of the absorber including the fixing member corresponds to an object
- the contraction force of the leak preventive wall corresponds to force F. Therefore, in the present disposable diaper, the end portion of the absorbent body is rotated by the contraction force of the leak preventive wall around the folding start point, that is, when the absorbent core is folded, the contraction force of the leak preventive wall is the same and the fixed region and the folding start point are the same. By increasing the distance, it is possible to increase the force for breaking the end portion of the absorbent body.
- the leak preventive wall can be made to stand up toward the wearer's skin surface. That is, it is possible to further suppress the height of the leakproof wall from being lowered, and it is possible to further suppress liquid from leaking in the width direction beyond the leakproof wall.
- the disposable diaper of the present invention further comprises (4) at least one of the back side region and the ventral side region, wherein the region including the low basis weight region further includes a non-arrangement region that does not include the superabsorbent polymer. Including, the non-arranged region is adjacent to the side opposite to the crotch region side in the low basis weight region in the longitudinal direction, and in the longitudinal direction, at least a part of the fixed region is the non-arranged region.
- the disposable diaper according to any one of (1) to (3) above, which overlaps in the thickness direction, may be used.
- the fixing region extends to the non-arrangement region in the longitudinal direction, and at least a part of the fixing region overlaps in the thickness direction.
- the leak-proof wall pulls the fixed region by contraction, the portion outside the low basis weight region in the longitudinal direction can be pulled together with the fixed region. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the absorbent body from being broken at a place other than (the starting point of the folding) of the low basis weight region. This makes it easier to fold the absorbent body at the folding start point in the low basis weight region, and makes it easier for the leak preventive wall to stand up toward the wearer's skin surface. As a result, it is possible to further suppress the height of the leakproof wall from being lowered, and it is possible to further suppress liquid from leaking in the width direction beyond the leakproof wall.
- an edge of the fixed region on the side opposite to the leak-proof wall side is an end on the side opposite to the low basis weight region in the non-arranged region.
- the disposable diaper according to (4) above, which is located outside the edge may be used.
- the fixing region extends outside the non-disposition region to the outside of the absorbent body in the longitudinal direction. Therefore, when the leak-proof wall pulls the fixed region by contraction, the region outside the low basis weight region in the longitudinal direction and including the outer portion of the absorber can be pulled together with the fixed region. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the absorbent body from being broken at a place other than (the starting point of the folding) of the low basis weight region.
- the leak preventive wall has a first wall portion whose outer edge is fixed to a surface of the absorbent main body in the width direction, and an inner edge of the first wall portion.
- the disposable diaper according to any one of (1) to (5) above, further comprising: a second wall portion having an inner edge connected to the edge and an outer edge not fixed. May be.
- the leak-proof wall has a V-shaped (convex inward) shape which is lateral when viewed in the longitudinal direction. Therefore, the leak preventive wall can be made to stand higher toward the wearer's skin surface. As a result, it is possible to further suppress the height of the leakproof wall from being lowered, and it is possible to further suppress liquid from leaking in the width direction beyond the leakproof wall.
- the back side region has a back side low basis weight region as the low basis weight region, and the ventral side region is adjacent to the crotch region in the longitudinal direction
- the superabsorbent polymer has a basal high grammage region equivalent to that of the crotch region, and the longitudinal center edge of the fixed region on the rear side of the longitudinal direction is the back side.
- the low basis weight area overlaps with the thickness direction, and the edge of the fixing area on the front side in the longitudinal direction on the center side in the longitudinal direction overlaps with the abdominal high basis weight area in the thickness direction.
- the disposable diaper described in 1) to (6) may be used.
- the starting point where the weighing is changed to a position between the back side low basis weight region and the crotch region. That is, it is possible to form a starting point where the rigidity changes.
- a starting point is a folding starting point at which the end of the absorbent body is broken when a force toward the center in the longitudinal direction, which is a contracting force in the longitudinal direction of the leak preventive wall, is applied to the end of the absorbent body.
- the folding starting point that is, the edge on the crotch region side in the back side low basis weight region is located in the center side rather than the center side edge of the back side fixing region in plan view. ing.
- the central edge of the dorsal fixing region is strongly pulled toward the central side by the contracting force in the longitudinal direction of the leak preventive wall, and the longitudinal end portion of the absorbent body is The absorber can be folded at the folding start point so that the person stands up toward the wearer's skin surface.
- the abdominal region of the absorbent body does not have a low basis weight region, but has an abdominal high basis weight region, so that it is between the abdominal high basis weight region and the crotch region.
- the position does not have a starting point where the weighing changes, that is, a starting point where the rigidity changes. Therefore, the end portion of the absorbent body does not break near the center-side end edge in the longitudinal direction in the abdominal fixed region, the abdominal side fit can be improved, and transmission leakage from the abdominal region can be suppressed. .. In this way, it is possible to suppress the height of the leak preventive wall from decreasing, to prevent the liquid from leaking in the width direction beyond the leak preventive wall, to suppress the transmission leak from the ventral side, and to improve the fit. Can be improved.
- the present invention it is possible to provide a disposable diaper that can suppress leakage of liquid in the width direction in the disposable diaper containing a super absorbent polymer.
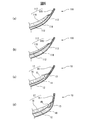
- FIG. 2 is a sectional view taken along line II-II in FIG. 1. It is a top view and a sectional view showing an example of composition of an absorber concerning an embodiment. It is the top view which expanded a part of back side part of the disposable diaper which concerns on embodiment. It is the top view which expanded a part of ventral side part of the disposable diaper which concerns on embodiment. It is a schematic diagram explaining the effect of the disposable diaper which concerns on embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a sectional view taken along line II-II of FIG. 1 according to another embodiment. It is the top view which expanded a part of back side part of the disposable diaper which concerns on another embodiment.
- the disposable diaper according to the embodiment will be described by taking a pants-type disposable diaper as an example.
- the type of disposable diaper is not limited to this example, and other types of disposable diapers may be used without departing from the scope of the present invention. Examples of such disposable diapers include tape-type disposable diapers.
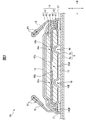
- FIG. 1 and 2 are diagrams showing a configuration example of a disposable diaper 1 according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a plan view showing a state where the disposable diaper 1 is unfolded
- FIG. 2 is a sectional view taken along line II-II of FIG.
- the disposable diaper 1 has a longitudinal direction L, a width direction W, and a thickness direction T that are orthogonal to each other, and a longitudinal center line CL that passes through the center of the width direction W and extends in the longitudinal direction L, It has a width direction center line CW extending in the width direction W through the center of the longitudinal direction L.
- the direction and the side approaching the longitudinal centerline CL are respectively inward and inward in the width direction W, and the direction and the side away are respectively outward and outward in the width direction W.
- the direction and the side approaching the width direction center line CW are defined as the inner direction and the inner side in the longitudinal direction L, and the direction and the side facing away are the outer direction and the outer side in the longitudinal direction L, respectively.
- the side of the disposable diaper 1 corresponding to the abdomen of the wearer in the longitudinal direction L is also referred to as the front side in the longitudinal direction L of the disposable diaper 1 that corresponds to the wearer's back.
- the side toward the edge (the edge on the back side) is also referred to as the rear side of the longitudinal direction L.
- the “plan view” means that the disposable diaper 1 in a state of being developed on a plane including the longitudinal direction L and the width direction W is viewed from above in the thickness direction T, and the “planar shape” is grasped in the plan view.
- the “planar direction” is an arbitrary direction parallel to the plane including the width direction W and the longitudinal direction L.
- the “skin side” and “non-skin side” mean the side relatively closer to the wearer's skin surface and the side farther away in the thickness direction T when the disposable diaper 1 is worn by the wearer, respectively. .. These definitions are commonly used not only for the disposable diaper 1 but also for the absorbent body of the disposable diaper 1 and each material arranged therein.
- a member or the like being parallel to the longitudinal direction L means that a member, a structure, a shape or the like is along the longitudinal direction L, but a component Dx of the member or the like in the longitudinal direction L is a component of the member or the like in the width direction W.
- Dy Dy
- the member and the like extending in the width direction W are not limited to the case where the member and the like are parallel to the width direction W, and the component Dy of the member and the like in the width direction W is greater than the component Dx of the member and the like in the longitudinal direction L. It also includes a large value (Dy>Dx).
- the member or the like is evaluated as described above with respect to the tangent line of each point on the curve or the like.
- the disposable diaper 1 has a ventral side portion (ventral waist belt) 2, a back side portion (dorsal waist belt) 3, a ventral side portion 2 and a back side portion 3 in the longitudinal direction L. And an absorbent body 10 located between and.
- the disposable diaper 1 further includes a crotch portion 4 located between the abdominal side portion 2 and the back side portion 3.
- the abdominal part 2 is a part that comes into contact with the abdomen of the wearer.
- the back side portion 3 is a portion that contacts the wearer's hip or back.
- the absorbent main body 10 is a portion that comes into contact with the wearer's crotch, and one end portion in the longitudinal direction L is laminated on the abdominal side portion 2 and the other end portion is laminated on the back side portion 3.
- the crotch portion 4 is a portion that supports the absorbent main body 10 from the non-skin side. Both ends 2a, 2a of the abdominal part 2 in the width direction W and both ends 3a, 3a of the back part 3 in the width direction W overlap in the thickness direction T and are joined along the longitudinal direction L. Thus, the disposable diaper 1 is formed.
- the waist opening through which the wearer's waist passes is defined by the outer end 2e of the abdominal part 2 in the longitudinal direction L and the outer end 3e of the dorsal part 3 in the longitudinal direction L.
- the pair of leg openings through which the wearer's legs pass is defined by the side portions 5e and 5e on both sides of the crotch portion 4 in the width direction W.
- the abdominal part (abdominal waist belt) 2 and the dorsal part (dorsal waist belt) 3 are defined in the range of the longitudinal direction L where both ends 2a, 2a and both ends 3a, 3a are joined. Can be said.
- the abdominal part 2 and the dorsal part 3 each have a rectangular shape that extends substantially in the width direction W and are separated from each other in the longitudinal direction L.
- the crotch portion 4 is located between the ventral side portion 2 and the back side portion 3, and both side edges in the width direction W are recessed inward in the width direction W.
- the abdominal part 2, the crotch part 4, and the back part 3 are integrally formed with each other.
- the ventral portion 2, crotch portion 4 and dorsal portion 3 are formed separately from each other.
- the disposable diaper 1 comprises an abdominal part 2 and a dorsal part 3 and no crotch part 4.
- the abdominal part 2, the dorsal part 3 and the crotch part 4 are provided with a liquid-impermeable cover sheet (sheet member) 5.
- the cover sheet 5 includes a cover sheet 5a located on the skin side and a cover sheet 5b located on the non-skin side.
- the cover sheet 5a and the cover sheet 5b are laminated in the thickness direction T and are bonded to each other with an adhesive or the like. Both ends in the longitudinal direction L of the cover sheet 5b are folded back to the skin side so as to cover both ends in the longitudinal direction L of the cover sheet 5a.
- the cover sheets 5b at the folding positions on the abdominal part 2 and the back part 3 form the end 2e of the abdominal part 2 and the end 3e of the back part 3, respectively.
- cover sheet 5 examples include any liquid-impermeable sheet such as a liquid-impermeable nonwoven fabric, a synthetic resin film, a composite sheet of these, an SB nonwoven fabric, and an SMS nonwoven fabric.
- material of the cover sheet 5 include polyolefin-based materials such as polypropylene and polyethylene.
- the basis weight of the cover sheet 5 is, for example, 5 to 100 g/m 2 , and preferably 10 to 50 g/m 2 .
- the dimension (thickness) of the cover sheet 5 in the thickness direction T is, for example, 0.1 to 5 mm, preferably 0.1 to 2 mm.
- the number of cover sheets 5 is one, or three or more (not shown).
- the cover sheet 5b is not folded back (not shown).
- the abdomen 2 and the back 3 are provided with a plurality of elastic members 6a and 6b for waist gather and a plurality of elastic members 7a and 7b between the cover sheet 5a and the cover sheet 5b, respectively. ..
- the plurality of elastic members 6a and 6b are arranged on the outside and inside of the abdominal side portion 2 in the longitudinal direction L, respectively.
- the plurality of elastic members 6a are arranged along the width direction W at intervals in the longitudinal direction L in the respective predetermined regions on both sides of the longitudinal center line CL.
- the predetermined region is a region from the end portion 2a to a portion inside the end edge of the absorbent main body 10 facing the end portion 2a in the width direction W.
- the plurality of elastic members 6b extend from one end 2a to the other end 2a along the width direction W, and are arranged at intervals in the longitudinal direction L.
- the plurality of elastic members 7 a and 7 b are arranged on the outer side and the inner side of the back side portion 3 in the longitudinal direction L, respectively.
- the plurality of elastic members 7a are arranged along the width direction W in the respective predetermined regions on both sides of the longitudinal centerline CL so as to be spaced from each other in the longitudinal direction L.
- the predetermined region is a region from the end portion 3a to a portion inside the end edge of the absorbent main body 10 facing the end portion 3a in the width direction W.
- the plurality of elastic members 7b extend from one end 3a to the other end 3a along the width direction W, and are arranged at intervals in the longitudinal direction L.
- the plurality of elastic members 6a, 6b, 7a, 7b expand and contract the waist opening, and are exemplified by rubber thread. It can be said that the abdominal part (abdominal waist belt) 2 and the dorsal part (dorsal waist belt) 3 are defined in the range of the longitudinal direction L in which the plurality of elastic members 6a, 6b, 7a, 7b are arranged. ..
- the disposable diaper 1 includes a plurality of elastic members 8 for leg gathers from the crotch portion 4 to the back side portion 3 and the abdominal side portion 2.
- the plurality of elastic members 8 mainly extend along both ends of the crotch portion 4 in the width direction W along the longitudinal direction L.
- the plurality of elastic members 8 respectively expand and contract the pair of leg openings, and are exemplified by a rubber thread.
- the absorbent main body 10 has a substantially rectangular shape, and is positioned between the liquid-permeable topsheet 12, the liquid-impermeable backsheet 13, and the topsheet 12 and the backsheet 13. And an absorber 14 that absorbs and retains the liquid.
- the surface sheet 12 include a liquid-permeable nonwoven fabric or woven fabric, a synthetic resin film having liquid-permeable holes formed therein, and a composite sheet of these.
- the back sheet 13 include liquid impermeable nonwoven fabrics, synthetic resin films, composite sheets of these, SMS nonwoven fabrics, and the like.
- the absorbent body 14 includes an absorbent core that absorbs and holds the liquid, and a core wrap that contains the absorbent core. Details of the absorber 14 will be described later.
- the absorber 14 and the topsheet 12 and the backsheet 13 are bonded with an adhesive, respectively, and the topsheet 12 and the backsheet 13 are bonded with an adhesive at their peripheral portions.
- the adhesive include materials known for disposable diapers, for example, hot melt adhesive.
- the shape of the absorbent main body 10 is not limited to the above example as long as it is a shape that is long in the longitudinal direction L, and may be, for example, a rectangle with rounded corners, a rectangle with a convex curve outward on the short side, or an hourglass shape.
- the back sheet 13 is omitted, and the non-skin side surface of the absorber 14 and the non-skin side surface of the peripheral portion of the top sheet 12 are joined to the cover sheet 5.
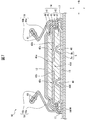
- the absorbent main body 10 includes a pair of side sheets 17, 17 located on both sides in the width direction W on the skin side surface and extending in the longitudinal direction L.
- Each side sheet 17 has a leak preventive wall 16 and fixing regions 15 and 15.
- the fixing regions 15 and 15 are located at the front and rear ends of the side seat 17 in the longitudinal direction L, and are fixed to the skin-side surface of the absorbent main body 10.
- the leak preventive wall 16 is located between and adjacent to the front and rear fixing regions 15 in the longitudinal direction L of the side sheet 17, is adjacent to the fixing regions 15, and is provided on the skin side surface of the absorbent main body 10 in the width direction W.
- the outer edge is fixed, and the inner edge in the width direction W is not fixed.
- the leak-proof wall 16 and the fixing regions 15 and 15 are formed, for example, at the inner side portion of the side seat 17 in the width direction W, and the outer side portion of the side seat 17 in the width direction W is fixed to the absorbent main body 10.
- the absorbent main body 10 includes the pair of leak-proof walls 16, 16.
- the pair of leak preventive walls 16 and 16 are arranged at both ends in the width direction W on the skin side of the absorbent main body 10 so as to face each other, and continuously extend along the longitudinal direction L.
- Each leak preventive wall 16 includes two elastic members 61 extending in the longitudinal direction L at the inner end in the width direction W.
- the elastic member 61 is exemplified by rubber thread.
- each of the pair of leak preventive walls 16 and 16 has an inner end in the width direction W folded back to the outer side in the width direction W (described later).
- the number of elastic members 61 is one or three or more.
- Each of the pair of leakproof walls 16 and 16 is formed of a hydrophobic sheet, for example, a hydrophobic nonwoven fabric. In another embodiment, it is formed of a hydrophilic sheet, such as a hydrophilic nonwoven.
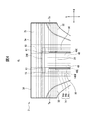
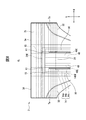
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a configuration example of the absorber 14 according to the embodiment, (a) is a plan view, and (b) is a cross-sectional view taken along line IIIb-IIIb in (a).
- the absorber 14 is a layer having a liquid absorption performance and a liquid retention performance, and in the present embodiment, the first absorption layer 41 located on the skin side, the second absorption layer 42 located on the non-skin side, and the first And an intermediate layer 43 located between the absorption layer 41 and the second absorption layer 42.
- the absorber 14 has a two-layer structure in which the first absorption layer 41, the intermediate layer 43, and the second absorption layer 42 are laminated in this order in the thickness direction T.
- the absorber 14 has a single-layer structure in which the intermediate layer 43 does not exist and the first absorption layer 41 and the second absorption layer 42 are integrated in the thickness direction.
- the absorber 14 has a multilayer structure of three or more layers in which another intermediate layer and another absorbing layer are further laminated between the first absorbing layer 41 and the second absorbing layer 42.
- the first absorbent layer 41 is located on the skin side and the second absorbent layer 42 is located on the non-skin side.
- the absorber 14 has a substantially rectangular planar shape extending in the longitudinal direction L.
- the absorber 14 can be regarded as having a first water absorbent material 45 and a second water absorbent material 47 as an absorbent core and a first base material 44 and a second base material 46 as core wraps.
- the shape is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a rectangle with a short side protruding in an arc shape, a rounded rectangle, an ellipse, and an hourglass.
- the thickness of the absorber 14 is, for example, 0.5 to 20 mm, and preferably 1 to 10 mm.
- the basis weight of the absorbent body 14 can be appropriately adjusted depending on the absorption performance required for the pants-type diaper 1, and is, for example, 60 to 1600 g/m 2 .
- the first absorbent layer 41 is disposed on the intermediate layer 43 side of the first base material 44 and the first base material 44, which is formed of a sheet having liquid permeability, and absorbs water containing a water-absorbing polymer.
- the first absorbent layer 41 can be regarded as having the first water absorbent material 45 as the absorbent core and the first base material 44 (and the intermediate layer 43) as the core wrap.
- a core wrap sheet made of, for example, a tissue is provided that wraps the first water absorbing material 45 inside them.
- the first water-absorbing material 45 is formed by applying an adhesive to at least one of the surface of the first base material 44 on the side of the intermediate layer 43 and the surface of the intermediate layer 43 on the side of the first base material 44. It is fixed to at least one of the layers 43.
- the water absorbent material of the first water absorbent material 45 is arranged in the first absorbent layer 41 with a substantially uniform basis weight.
- the basis weight of the end portion in the longitudinal direction L and/or the width direction W may be gradually reduced toward the edge.
- the end portions are areas within 10% of the maximum dimension in the longitudinal direction L and/or the width direction W at both ends in the longitudinal direction L and/or the width direction W, for example.
- the water absorbent material of the first water absorbent material 45 is arranged in the first absorbent layer 41 in a predetermined distribution having a portion having a large basis weight and a portion having a small basis weight.
- the first water absorbent material 45 has a substantially rectangular planar shape.
- the first base material 44 has a substantially rectangular planar shape and covers the first water absorbent material 45 from the skin side in a plan view, and the peripheral portion of the first base material 44 is slightly around the first water absorbent material 45. Extend outwards.
- the outer dimension (outer edge) of the first absorbent layer 41 in the plane direction is, for example, the outer dimension (outer edge) of the first water absorbent material 45 in the plane direction.
- the outer dimension (outer edge) is measured, for example, at a half position in the thickness direction T of the first water absorbent material 45.
- the second absorbent layer 42 is disposed on the second base material 46 formed of a sheet having water retention and liquid diffusibility and on the intermediate layer 43 side with respect to the second base material 46, and the water absorbent polymer.
- the second absorbent layer 42 can be regarded as having the second water absorbent material 47 as an absorbent core and the second base material 46 (and the intermediate layer 43) as a core wrap.
- a core wrap sheet made of, for example, a tissue that wraps the second water absorbing material 47 inside them is provided.
- the second water-absorbing material 47 is formed on the intermediate layer 43 side of the second base material 46 and the adhesive applied to at least one of the surface of the intermediate layer 43 on the second base material 46 side. It is fixed to at least one of the layers 43.
- the water absorbing material of the second water absorbing material 47 is arranged in the second absorbing layer 42 with a substantially uniform basis weight except for the pair of channels 48, 48 (described later). However, the basis weight of the end portion in the longitudinal direction L and/or the width direction W may be gradually reduced toward the edge. In this case, the ends are as described above.
- the water absorbing materials of the second water absorbing material 47 are arranged in the second absorbing layer 42 in a predetermined distribution having a portion having a large basis weight and a portion having a small basis weight.
- the second water absorbent material 47 has a substantially rectangular planar shape that is slightly larger than the first water absorbent material 45 in the width direction W and the longitudinal direction L.
- the second base material 46 has a substantially rectangular planar shape and covers the second water absorbent material 47 from the non-skin side in a plan view, and the peripheral edge portion of the second base material 46 is surrounded by the second water absorbent material 47. It extends slightly outside.
- both ends of the second base material 46 in the width direction W cover both side surfaces of the second water absorbent material 47, and also cover the skin-side surface of both ends of the first base material 44 in the width direction W. That is, on the skin-side surface of the end portion of the first absorbent layer 41 in the width direction W, the end portion of the second base material 46 in the width direction W and the end portion of the first base material 44 in the width direction W overlap each other. Are joined together.
- the outer dimension (outer edge) of the second absorbent layer 42 in the plane direction is, for example, the outer dimension (outer edge) of the second water absorbent material 47 in the plane direction.
- the outer size (outer edge) is measured at, for example, a half position in the thickness direction T of the second water absorbent material 47.
- both ends of the second base material 46 in the width direction W cover the side surfaces of the second water absorbent material 47 in the width direction W, and further cover the side surfaces of the first base material 44 in the width direction W.
- the second water absorbent material 47 is sealed in the second absorbent layer 42 in the width direction W
- the first water absorbent material 45 is sealed in the first absorbent layer 41 in the width direction W.
- both ends of the first base material 44 in the width direction W cover both ends of the second base material 46 in the width direction W.
- the first base material 44, the intermediate layer 43, and the second base material 46 are stacked in the thickness direction T and joined.
- the first base material 44, the intermediate layer 43, and the second base material 46 are laminated and joined in the thickness direction T at both ends in the longitudinal direction L of the absorber 14.
- the second water absorbent material 47 is enclosed in the second absorbent layer 42 by the first base material 44 and the intermediate layer 43 in the longitudinal direction L
- the first water absorbent material 45 is intermediate with the second base material 46 in the longitudinal direction L. It is enclosed by the layer 43 in the second absorption layer 42.
- both ends of the absorbent body 14 in the longitudinal direction L are not covered with the first base material 44 and the second base material 46.
- the intermediate layer 43 is a liquid-permeable sheet and has a substantially rectangular planar shape.
- the intermediate layer 43 includes an upper layer 43a and a pair of lower layers 43b and 43b adjacent to both sides in the width direction W on the non-skin side surface of the upper layer 43a.
- the intermediate layer 43 is formed by folding a pair of side portions located on both sides of the central portion in the width direction W back to the non-skin side of the central portion and stacking them on a sheet member having a substantially rectangular planar shape. At that time, the central portion of the sheet member becomes the upper layer 43a, and the pair of side portions of the sheet member becomes the pair of lower layers 43b, 43b.
- the portions on both sides of the intermediate layer 43 in the width direction W each have a two-layer structure in which the upper layer 43a and the lower layer 43b are stacked, and have a substantially rectangular shape extending in the longitudinal direction L.
- a portion 43d of the intermediate layer 43 near the center in the width direction W has a single-layer structure including only the upper layer 43a and has a substantially rectangular shape extending along the longitudinal direction L.
- the upper layer 43a and the lower layer 43b of the two-layer structure are joined by a pair of heat seal portions 43c, 43c extending along the longitudinal direction L on both sides in the width direction W of the portion 43d.
- the heat seal portion 43c is formed by squeezing while heating.
- the upper layer 43a and the lower layer 43b having a two-layer structure are joined by embossed portions extending along the longitudinal direction L on both sides in the width direction W of the portion 43d.
- the embossed portion is formed by pressing.
- the heat-sealing portion and the embossing portion have a plurality of points, a plurality of curved lines or a pattern.
- the intermediate layer 43 is sandwiched between both end edges in the width direction W by both end portions in the width direction W of the first base material 44 and the second base material 46, and both end edges in the longitudinal direction L are connected to the first base material 44 and the first base material 44.
- the two base materials 46 are sandwiched between both ends in the longitudinal direction L and are joined to each other.
- both end edges in the longitudinal direction L are not sandwiched between the ends of the first base material 44 and the second base material 46 in the longitudinal direction L, and are not joined.
- the absorber 14 has a pair of channels 48, 48 extending along the longitudinal direction L.
- the pair of channels 48, 48 are band-shaped regions that are located in the second absorption layer 42, extend in the longitudinal direction L, and are arranged at predetermined intervals on both sides in the width direction W with the longitudinal centerline CL interposed therebetween.
- the channel 48 is formed in at least the central portion in the longitudinal direction L so as to straddle the width-direction center line CW.
- the channel 48 is formed so as to reach at least one of both edges in the longitudinal direction L.
- the pattern of the pair of channels 48 in the plan view is, for example, a pattern formed such that the interval between the two is constant along the longitudinal direction L.
- the pattern of the pair of channels 48, 48 is, for example, a pattern formed to be narrow near the center in the longitudinal direction L and expand toward both outer sides in the longitudinal direction L.
- the channel 48 is an area in which the basis weight of the water absorbing material is smaller than the area around the channel in the absorber 14, and, for example, compared with the area around the channel 48 in the second absorbent layer 42. , A region where the basis weight of the water-absorbent material is small, including a case where the basis weight is zero.
- the channel 48 is formed such that the second base material 46 is recessed toward the intermediate layer 43 side, that is, the second water absorbing material 47 is recessed toward the intermediate layer 43 side.
- the second water absorbing material 47 is formed so as to be recessed toward the second base material 46 side.
- the pair of channels 48, 48 overlaps the pair of heat seal portions 43c, 43c in the thickness direction T.
- at least a part of the channel 48 does not overlap the heat seal portion 43c in the thickness direction T.
- the channel 48 extends not only in the longitudinal direction L but also in the width direction W as well as in the longitudinal direction L.
- the channels 48 are one or more than two.
- the channel 48 is formed in the first absorbent layer 41 instead of, or in addition to, the second absorbent layer 42.
- the channel 48 is not formed.
- the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 include a super absorbent polymer (SAP).
- SAP super absorbent polymer
- the super absorbent polymer is not particularly limited as long as it is a polymer capable of absorbing and retaining water, and examples thereof include particulate or fibrous super absorbent polymers.
- the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer of the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 can be appropriately adjusted according to the absorption performance required for the disposable diaper 1, and for example, each is 10 to 500 g/m 2. , Preferably 100 to 400 g/m 2 .
- One of the basis weights of the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 may be larger than the other, or may be the same.
- the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 may further include hydrophilic fibers such as pulp fibers and water absorbent fibers.
- the ratio of the super absorbent polymer to the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 is, for example, 80 to 100% by mass, preferably 90 to 100% by mass, and more preferably 95 to 100% by mass. .. Therefore, it can be said that the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 contain the super absorbent polymer as a main component, and the absorber 14 can be called a so-called SAP sheet.
- the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 are made of only a super absorbent polymer and do not contain hydrophilic fibers.
- the first water absorbent material 45 and the second water absorbent material 47 include pulp fibers and/or water absorbent fibers in addition to the super absorbent polymer.
- superabsorbent polymers examples include starch-based, cellulose-based, and synthetic polymer-based polymer absorbents.
- examples of the starch-based or cellulose-based superabsorbent polymer include starch-acrylic acid (salt) graft copolymer, saponified starch-acrylonitrile copolymer, and crosslinked sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
- examples of synthetic polymer-based superabsorbent polymers include polyacrylic acid salt-based, polysulfonic acid salt-based, maleic acid anhydride-based, polyacrylamide-based, polyvinyl alcohol-based, polyethylene oxide-based, polyaspartate-based, polyglutamic acid.
- Examples thereof include salt-based, polyalginate-based, starch-based, cellulose-based and the like.
- a polyacrylic acid salt-based (particularly, sodium polyacrylate-based) superabsorbent polymer is preferable.
- 90 to 100% by mass of the superabsorbent polymer in the absorber 14 is composed of superabsorbent polymer particles having a particle diameter of 150 to 500 ⁇ m.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles having such a particle size distribution have a small particle size and are uniform, so that they are easily held by the adhesive.
- the particle size of the super absorbent polymer particles is measured according to the sieving test method described in JIS R 6002:1998.
- the adhesive is not particularly limited as long as it can fix the superabsorbent polymer, and examples thereof include hot melt adhesives.
- the application pattern of the adhesive is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a continuous or intermittent omega pattern, a spiral pattern, and a line pattern.
- the basis weight of the adhesive can be appropriately adjusted so that the liquid absorbency of the absorbent body 14 is not significantly lowered, and for example, 3 to 50 g/m 2 for each layer can be mentioned.
- each layer means an adhesive layer between the first water absorbent material 45 and the first base material 44, an adhesive layer between the first water absorbent material 45 and the intermediate layer 43, and a second water absorbent material 47.
- the adhesive layer is between the second base material 46 and the second water absorbing material 47 and the intermediate layer 43.
- the first base material 44 is not particularly limited as long as it is a sheet having liquid permeability.
- the first base material 44 include liquid-permeable nonwoven fabrics, hydrophilic nonwoven fabrics, and laminated nonwoven fabrics thereof. Among them, nonwoven fabrics having high water permeability are preferable.
- it is formed from polyolefin fibers such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyester fibers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), or a combination thereof. Spunbonded non-woven fabric and air-through non-woven fabric. These fibers are preferably hydrophilized by a known method.
- an air-laid nonwoven fabric in which hydrophilic fibers such as pulp fibers and rayon fibers are coated with a hydrophilic binder, and a spunlace nonwoven fabric in which the above hydrophilic fibers and the above synthetic fibers are combined are included.
- an air-laid non-woven fabric having liquid permeability and liquid retention property, in which pulp fibers are coated with a hydrophilic binder is used.
- the first base material 44 one or a plurality of types of non-woven fabrics may be laminated in multiple layers.
- the basis weight of the first base material 44 is, for example, 10 to 100 g/m 2 , and preferably 20 to 80 g/m 2 .
- the thickness of the first base material 44 is, for example, 0.1 to 5 mm, and preferably 0.15 to 3 mm.
- the second base material 46 is not particularly limited as long as it is a sheet having water retention and liquid diffusion properties.
- the second base material 46 include synthetic fibers such as polyamide fibers, recycled fibers such as rayon fibers and acetate fibers, natural fibers such as cotton, silk, hemp, and pulp (cellulose) fibers, or a combination thereof.
- the spunlace nonwoven fabric containing rayon fibers and/or pulp fibers may contain polyolefin fibers and/or polyester fibers.
- a spunlace nonwoven fabric containing rayon fibers and pulp fibers, which has liquid retaining properties and liquid diffusing properties is used.
- the second base material 46 one or a plurality of types of non-woven fabrics may be laminated in a plurality of layers.
- the basis weight of the second base material 46 is, for example, 10 to 200 g/m 2 , and preferably 35 to 150 g/m 2 .
- the thickness of the second base material 46 is, for example, 0.1 to 5 mm, and preferably 0.15 to 3 mm.
- the intermediate layer 43 is not particularly limited as long as it is a sheet having liquid permeability.
- As the intermediate layer 43 for example, a sheet similar to the first base material 44 can be used.
- the basis weight of the intermediate layer 43 is, for example, 10 to 100 g/m 2 , and preferably 15 to 80 g/m 2 .
- the thickness of the intermediate layer 43 is, for example, 0.1 to 5 mm, and preferably 0.15 to 3 mm.
- the absorbent body 14 includes a dorsal region BA, a ventral region FA, and a crotch region MA, which are arranged along the longitudinal direction L.
- the back side region BA is a region overlapping the back side portion 3 of the absorber 14 in the thickness direction T.
- the abdominal area FA is an area that overlaps the abdominal portion 2 of the absorber 14 in the thickness direction T.
- the crotch region MA is a region located between the back region BA and the abdominal region FA of the absorber 14, that is, a region overlapping the crotch portion 4 in the thickness direction T.
- the absorbent body 14 is divided along the longitudinal direction L into a dorsal region BA overlapping the dorsal part 3, an abdominal region FA overlapping the abdominal part 2, and a crotch region MA overlapping the crotch part 4. To be done.
- the absorber 14 also includes a high basis weight area 14a, a low basis weight area 14b, and a non-arranged area 14c.
- the high basis weight region 14a is a region in which the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer is high, and is a region in which the first absorbent layer 41 and the second absorbent layer 42 overlap in the thickness direction T.
- the boundary between the high grammage region 14a and the low grammage region 14b is, for example, the outer edge of the first absorption layer 41.
- the low basis weight region 14b is a region in which the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer is low, and the first absorbent layer 41 does not exist in the thickness direction T and only the second absorbent layer 42 exists.
- the boundary between the low basis weight area 14b and the non-arranged area 14c is, for example, the outer edge of the second absorbent layer.
- the non-arranged region 14c is a region that does not contain the superabsorbent polymer, and is a region in which the first absorption layer 41 and the second absorption layer 42 do not exist in the thickness direction T.
- not including the super absorbent polymer includes a case where the super absorbent polymer exists but its basis weight is very small. “Very low” means that the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer is 5% or less of the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer in the high basis weight region 14a.
- the high basis weight area 14a, the low basis weight area 14b, and the non-arrangement area 14c have a substantially rectangular shape.
- the shape is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a rectangle with a short side protruding in an arc shape, a rounded rectangle, an ellipse, and an hourglass.
- the low basis weight region 14b is a region that surrounds the high basis weight region 14a in a substantially frame shape (encloses at least three sides), and the low basis weight region 14b.
- the outer size is, for example, 5 to 25% larger than the outer size of the high basis weight region 14a.
- the non-arrangement area 14c is an area that surrounds the low basis weight area 14b in a substantially frame shape, and the outer dimension of the non-arrangement area 14c is, for example, 3 to 15% larger than the outer dimension of the low basis weight area 14b.
- the basic weight of the low basic weight area 14b is, for example, 40 to 60% of the basic weight of the high basic weight area 14a
- the basic weight of the non-arranged area 14c is, for example, 0% of the basic weight of the high basic weight area 14a. -5% is included.
- the high basis weight region is a water absorbing material (including an adhesive). Is the region of the maximum value to 50% of the maximum value.
- the low basis weight part is a region where the thickness of the water absorbing material (including the adhesive) is in the range of 50% to 5% of the maximum value, and the non-arranged region is the thickness of the water absorbing material (including the adhesive). Is the range of 5% to 0% of the maximum value.
- the thickness is the arithmetic average height (Ra: JIS B 0601-2001).
- the back side area BA is the back side high basis weight area BAa as the high basis weight area 14a, the back side low basis weight area BAb as the low basis weight area 14b, and the non-arrangement area 14c.
- the abdominal area FA includes an abdominal high basis weight area FAa as the high grammage area 14a and an abdominal non-arrangement area FAc as the non-arrangement area 14c.
- the crotch region MA has only the high basis weight region 14a. Therefore, the basis weight of the super absorbent polymer in the back side high basis weight region BAa and the abdominal side high basis weight region FAa is equivalent to the basis weight of the super absorbent polymer in the crotch region MA.
- the abdominal area FA includes the abdominal low basis weight area FAb as the low basis weight area 14b in addition to the abdominal high basis weight area FAa and the abdominal non-arrangement area FAc.
- the second absorption layer 42 includes, at a rear end in the longitudinal direction L, a protrusion that protrudes outward from the edge of the first absorption layer 41 in a plan view.
- the protrusion includes the back side low basis weight region BAb, and in the present embodiment, the protrusion is the same as the back side low basis weight region BAb.
- the second absorbent layer 42 is covered with the intermediate layer 43, and thus the protruding portion, that is, the back side low basis weight region BAb is covered with the intermediate layer 43 and the first base material 44 on the skin side.
- the second absorbent layer 42 includes, in a plan view, the width-direction protrusions that protrude outward from the end edges of the first absorption layer 41 at both ends in the width direction W.
- the width direction protrusion is covered with the intermediate layer 43 and the first base material 44 on the skin side.
- the second absorbent layer 42 includes, at a front end in the longitudinal direction L, another protruding portion that protrudes outward from the edge of the first absorbent layer 41 in a plan view.
- Other protrusions include the ventral low basis weight area.
- the protruding portion that is, the back low-basis-weight area BAb is covered on the skin side by one of the intermediate layer 43 and the first base material 44 and not by the other.
- the second absorbent layer 42 does not include a widthwise protruding portion that protrudes outward from the end edge of the first absorbent layer 41 at both end portions in the width direction W in a plan view.
- the disposable diaper 1 of the present embodiment has a low basis weight region (example: back side low) in which the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer is low in the ventral side area FA and/or the back side area BA in the longitudinal direction L.
- the basis weight area BAb is provided. Therefore, a starting point where the weighing is changed can be formed between the low grammage region and the crotch region MA where the grammage of the superabsorbent polymer is high. That is, in the absorbent body 14, the starting point where the rigidity changes can be formed in the longitudinal direction L at a position between the low basic weight region having low rigidity and the crotch region having high rigidity.
- the starting point where the weighing is changed can be formed at the boundary between the back side low basis weight area BAb and the back side high basis weight area BAa.
- the starting point is the end portion of the absorbent body 14 when a force directed substantially inward in the substantially longitudinal direction L is applied to the end portion (low grammage area; portion including the back side low grammage area BAb) of the absorber 14.
- the basis weight of the superabsorbent polymer in the crotch region MA is relatively high, and the low basis weight region of at least one of the back side region BA and the abdominal side region FA (example. : The basis weight of the water-absorbent polymer in the back side low basis weight region BAb) is relatively low. Therefore, since a relatively large amount of the super absorbent polymer is arranged in the crotch region MA that needs to absorb the liquid, the absorber 14 ensures the absorption performance and does not leak the liquid (example: urine) without fail. Can be absorbed.
- the region becomes thin, so that it corresponds to the region.
- the absorber can be less likely to bite into the skin surface. This makes it difficult for the wearer to feel uncomfortable and improves the fit of the disposable diaper 1. Therefore, in the disposable diaper 1 containing the super absorbent polymer, it is possible to improve the fit while ensuring the absorption performance.
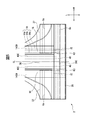
- FIG. 4 is an enlarged plan view of a part including the back side portion 3 of the disposable diaper according to the embodiment.
- the back portion 3 has a low back elastic region 31 having low elasticity in the width direction W and a pair of high elastic regions 32, 32 having high elasticity in the width direction W.
- the back side low expansion/contraction region 31 is located in the center portion of the back side portion 3 in the width direction W and extends from the front edge in the longitudinal direction L to the rear side.
- the pair of back side high expansion/contraction regions 32, 32 are adjacent to both sides of the back side low expansion/contraction region 31 in the width direction W.
- the elongation ratio ((length after expansion-original length)/(original length)) for a predetermined tensile force in the width direction W is the width of the back side high expansion/contraction region 32. It is a region of 1/3 or less of the elongation in the direction W, preferably 1/5 or less, and more preferably 1/10 or less.
- the back low expansion/contraction region 31 is a region in which there is no elastic member that expands/contracts in the width direction W, or a region in which an elastic member exists but the elastic member does not function as an elastic member (does not expand or contract much). ..
- the back side high expansion/contraction region 32 is a region where the elastic member 7a that expands/contracts in the width direction W exists. Therefore, the back high expansion/contraction area 32 and the back low expansion/contraction area 31 are defined by the area where the elastic member 7a that can function as the elastic member exists and the area where the elastic member that can function as the elastic member does not exist. ..
- the term “low elasticity” includes the case where elasticity does not occur. The elasticity of each elastic area is determined by the elasticity of the elastic member.
- the back side part 3 further has another back side high expansion/contraction region 34 that exhibits high elasticity in the width direction W.
- the other back high-elasticity region 34 is adjacent to the rear side of the pair of back high-elasticity regions 32, 32 and the back low-elasticity region 31 in the longitudinal direction L in plan view.
- the stretch ratio in the width direction W of the other back-side high stretch regions 34 is substantially the same as the stretch ratio in the width direction W of the back-side high stretch regions 32.
- Another back side high expansion/contraction region 34 is defined as a region where the elastic member 7b exists. Therefore, the rear end portion of the back side portion 3 in the longitudinal direction L is easily pressed against the wearer's back by the other back side high elasticity region 34.
- the rear portion of the channel 48 in the longitudinal direction L overlaps with the back low-elasticity region 31 in the thickness direction T.
- the inner edge K1 in the width direction W of each of the pair of back side high-elasticity regions 32, 32 is an edge of the absorber 14 facing the back side high-elasticity region 32 in the width direction W. 14 EW and the channel 48 (the edge 48E in the width direction W thereof).
- the edge K1 is an inner edge in the width direction W of the elastic member 7a. Therefore, of the absorbent body 14 including the portion on the rear side of the longitudinal direction L of the channel 48, the central portion in the width direction W is hardly expanded in the width direction W by the back side low elastic region 31, and both end portions in the width direction W are formed. Is extended in the width direction W by the pair of back side high elastic regions 32, 32.
- FIG. 5 is an enlarged plan view of a part including the ventral side portion 2 of the disposable diaper according to the embodiment.
- the ventral side portion 2 is substantially the same as the back side portion 3. That is, the abdominal part 2 has a low abdominal expansion/contraction region 36 in which the elasticity in the width direction W is low, and a pair of abdominal high expansion/contraction regions 37, 37 in which the elasticity in the width direction W is high.
- the belly-side low expansion/contraction region 36 is located at the center of the belly-side portion 2 in the width direction W, and extends from the rear edge of the longitudinal direction L to the front side.
- the pair of belly-side high stretch regions 37, 37 are adjacent to both sides of the belly-side low stretch region 36 in the width direction W.
- the abdominal side low expansion/contraction region 36 has an elongation rate ((length after expansion-original length)/(original length)) with respect to a predetermined tensile force in the width direction W, and is a width of the abdominal side high expansion/contraction region 37. It is a region of 1/3 or less of the elongation in the direction W, preferably 1/5 or less, and more preferably 1/10 or less.
- the belly-side low expansion/contraction region 36 is a region in which there is no elastic member that expands/contracts in the width direction W, or a region in which an elastic member exists but the elastic member does not function as an elastic member (does not expand or contract very much). ..
- the abdominal high expansion/contraction region 37 is a region where the elastic member 6a that expands/contracts in the width direction W exists. Therefore, the region in which the elastic member 6a that can function as the elastic member exists and the region in which the elastic member that can function as the elastic member does not exist define the belly-side high expansion/contraction region 37 and the belly-side low expansion/contraction region 36.
- the elasticity of each elastic area is determined by the elasticity of the elastic member.
- the abdominal side portion 2 further has another abdominal side high elastic region 39 that exhibits high elasticity in the width direction W.
- the other abdominal high-elasticity region 39 is adjacent to the front side in the longitudinal direction L of the pair of abdominal high-elasticity regions 37, 37 and the abdominal low-elasticity region 36.
- the expansion ratio in the width direction W of the other abdominal high expansion/contraction region 39 is substantially the same as the expansion ratio of the abdominal high expansion/contraction region 37 in the width direction W.
- the other high-side elastic region 39 is defined as a region where the elastic member 6b exists. Therefore, the front end of the abdominal part 2 in the longitudinal direction L is easily pressed against the abdomen of the wearer by the other abdominal high elastic region 39.
- the end edge 61e of the elastic member 61 on the fixed region 15 side overlaps with the low grammage region (example: back side low grammage region BAb) in the thickness direction T.
- the edge 61e of the elastic member 61 is an edge of an effective portion of the elastic member 61 that can exert an elastic force.
- a portion that cannot exert an elastic force for example, a portion that does not substantially expand and contract (elongation rate with respect to a predetermined tensile force ((length after extension-original length)/(original length))) Is less than or equal to 1 ⁇ 5 of the original elongation, preferably less than or equal to 1/10) at the end of the elastic member 61, the effective portion does not include that portion. Therefore, the distance between the fixed region 15 and the elastic member 61 (effective portion thereof) can be reduced in a plan view.
- the portion of the channel 48 on the front side in the longitudinal direction L overlaps with the abdominal low expansion/contraction region 36 in the thickness direction T.
- the inner edge K2 in the width direction W of each of the pair of ventral high-elasticity regions 37, 37 is an edge of the absorber 14 facing the ventral high-elasticity region 37 in the width direction W. 14 EW and the channel 48 (the edge 48E in the width direction W thereof).
- the edge K2 is an inner edge in the width direction W of the elastic member 6a.
- the central portion in the width direction W is hardly expanded or contracted in the width direction W by the belly-side low expansion/contraction region 36, and both end portions in the width direction W are It is extended in the width direction W by the pair of ventral high-stretch regions 37, 37.
- the channel 48 of the absorbent body 14 reaches at least one of the back side part 3 (back side waist belt) and the abdominal side part 2 (abdominal waist belt) in the longitudinal direction L.
- the liquid example: urine
- the liquid can be transported and distributed to the dorsal side (rear side of the longitudinal direction L) and/or the ventral side (front side of the longitudinal direction L) of the absorbent body 14.
- the liquid can be absorbed by the superabsorbent polymer at the rear end or front end of the longitudinal direction L of the absorbent body 14 that hardly contributes to the absorption, and the superabsorbent polymer can be effectively utilized.
- this disposable diaper 1 WHEREIN The inner side edge part of the width direction W in the high expansion/contraction area (back side high expansion/contraction area 32, abdominal side high expansion/contraction area 37) of at least one of the back side part 3 and the abdominal side part 2, It is located between the end edge 14WE and the channel 48 that face the high expansion/contraction region in the width direction W of the absorber 14. That is, the central portion of the absorbent body 14 in the width direction W overlaps with the low elasticity region (back low elasticity region 31, abdominal low elasticity region 36) in the thickness direction T.
- the contraction force for contracting the absorbent body 14 in the width direction W is not too strong, so that the back-side end of the absorbent body 14 in the longitudinal direction L contracts in the width direction W and becomes a convex shape before mounting. Can be suppressed. Further, the portions on both sides of the absorbent body 14 in the width direction W overlap the high elasticity region in the thickness direction T. Therefore, the absorber 14 can be pulled from both sides of the channel 48 in the width direction W by the contraction force in the high expansion/contraction region. As a result, it is possible to suppress the phenomenon that the end portion of the absorbent body 14 in the longitudinal direction L has a convex shape and the end portion of the absorbent main body 10 in the longitudinal direction L jumps out of the wearer's body.
- the flatness of at least one of the back side portion 3 and the abdominal side portion 2 can be maintained before and after the attachment. As a result, it is possible to prevent the liquid from leaking from the gap between at least one of the back side portion 3 and the abdominal side portion 2 and the skin surface. As a result, it is possible to suppress the leakage of the liquid while suppressing the deterioration of the fitting property of the disposable diaper 1.
- the hot-melt adhesive is applied onto the sheet for the second base material 46 while moving the sheet for the second base material 46 in the longitudinal direction L.
- the super absorbent polymer is supplied from the super absorbent polymer supply device along the longitudinal direction L on both end portions and the central portion in the width direction W of the sheet for the second base material 46 coated with the hot melt adhesive. And spray. At this time, a small amount of superabsorbent polymer migrates to a region (corresponding to a channel) between both end portions and the central portion.
- the sheet for the intermediate layer 43, the hot melt adhesive of which is applied on both sides is laminated on the super absorbent polymer on the sheet for the second base material 46.
- a superabsorbent polymer is supplied from another superabsorbent polymer supply device to the central portion in the width direction W of the intermediate layer 43 sheet coated with the hot melt adhesive. Spray along the longitudinal direction L.
- the sheet for the first base material 44 in which the hot melt adhesive is applied is laminated on the super absorbent polymer on the sheet for the intermediate layer 43, with the hot melt adhesive being on the super absorbent polymer side.
- both sides of the sheet for the second base material 46 in the width direction W are folded back to both sides of the sheet for the first base material 44 in the width direction W to obtain a laminate.
- the thickness of the laminate is adjusted by passing the laminate through a pair of press rolls, that is, by pressing, and the absorber 14 is obtained.
- the liquid-permeable surface sheet 12 is attached to the upper surface (the surface of the first base material 44) of the absorbent body 14 manufactured as described above, and the liquid is not applied to the lower surface of the absorbent body 14 (the surface of the second base material 46).
- the transparent back sheet 13 is attached to obtain a laminated body.
- the side sheets 17 with the leak preventive wall 16 are attached to both sides of the laminate in the width direction W to obtain the absorbent main body 10.
- the absorptive main body 10 is pasted on the cover sheet 5 (including the elastic members 6, 7, and 8), and the abdominal portion 2 in the width direction W at both ends 2a, 2a and the back side portion 3 in the width direction W is attached.
- the both ends 3a, 3a are joined. Thereby, the disposable diaper 1 is manufactured.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram for explaining one effect of the disposable diaper according to the embodiment.
- 6A and 6B show a conventional pants-type diaper
- FIGS. 6C and 6D show the pants-type diaper of the present embodiment (the cover sheet is not shown).
- the topsheet 112, the absorber 114, and the backsheet 113 are laminated in this order in the thickness direction.
- a pair of leakproof walls 116, 116 extending in the longitudinal direction along the absorber 114 are arranged on both sides of the absorber 114 in the width direction. It is fixed at 112.
- the absorbent body 114 When an absorbent body containing a relatively large amount of superabsorbent polymer is applied to such a disposable diaper, it is usual to use the absorbent body 114 in which the superabsorbent polymer is arranged substantially uniformly in a plane. Immediately after mounting the disposable diaper, that is, before the superabsorbent polymer absorbs a liquid (eg, urine), the rigidity of the absorbent body 114 is low. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 6A, the absorbent body 114 bends relatively gently, and the leak preventive wall 116 can stand up toward the wearer's skin surface relatively easily. However, when the super absorbent polymer absorbs the liquid and swells after mounting, the rigidity of the absorbent body 114 increases. Therefore, as shown in FIG.
- the absorber has a relatively straight shape in the longitudinal direction, and the leak-proof wall 116 is pulled so as to be stretched from both sides in the longitudinal direction, so that the wearer's It becomes difficult to stand up toward the skin. As a result, the height of the leakproof wall 116 becomes low, and there is a possibility that the liquid may leak in the width direction beyond the pair of leakproof walls 116.
- the rigidity of the absorber 14 is low before the superabsorbent polymer absorbs the liquid (example: urine), as in the conventional pants-type diaper. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 6(c), the absorber 14 bends relatively gently, and the leak preventive wall 16 can stand up toward the wearer's skin surface relatively easily.
- the rigidity of the absorber 14 is increased, and the absorbent body 14 has a relatively straight shape in the longitudinal direction L. Therefore, the contraction force of the leakproof wall 16 in the longitudinal direction L is increased by being pulled so as to be stretched from both sides in the longitudinal direction L.
- the contraction force of the leak preventive wall 16 in the longitudinal direction L causes the end of the fixed region 15 on the central side in the longitudinal direction L to be strongly pulled toward the central side. Therefore, even in the disposable diaper 1, it may be difficult for the leak-proof wall 16 to stand up toward the wearer's skin surface, as shown in FIG. 6B, like the conventional disposable diaper.
- the absorbent body 14 has the folding start point FL at which the end of the absorbent body 14 is bent toward the central portion of the absorbent body 14.
- the folding start point FL is the starting point at which the weighing amount changes at the boundary between the back-side low basis weight area BAb and the back-side high basis weight area BAa. Therefore, as shown in FIG.
- the end portion in the longitudinal direction L of the absorbent body 14 stands up toward the wearer's skin surface.
- the absorber 14 can be folded at the folding start point FL.
- the edge 61e of the elastic member 61 on the fixed region 15 side in the effective portion has a low basic weight region (eg, back low basic weight region BAb) and a thickness direction T. Overlap with. That is, the distance between the fixed region 15 and the effective portion can be reduced in a plan view. As a result, the fixing region 15 can be easily pulled at the effective portion, so that the absorbent body 14 is more easily folded at the folding starting point so that the end portion of the absorbent body 14 in the longitudinal direction L stands up toward the wearer's skin surface. be able to.
- a low basic weight region eg, back low basic weight region BAb
- T thickness direction
- the position of the end edge 15E on the center side in the longitudinal direction L in the fixed area 15 is closer to that of the edge on the crotch area MA side in the low grammage area (example: back side low grammage area BAb). Is close to the edge on the side opposite to the crotch region MA side (eg, the back side region BA side).
- the position of the end edge 15E on the center side in the longitudinal direction L in the fixed region 15 is the position where the contracting force of the leak prevention wall 16 acts.
- the edge on the crotch region side in the low basis weight region is a position that becomes the folding start point FL.
- the disposable diaper 1 is configured such that the position where the contracting force acts is farther away from the position of the folding start point FL. That is, in the disposable diaper 1, the distance between the fixed region 15 on which the contracting force acts and the folding starting point FL is made larger.
- the force F in a direction perpendicular to the arm member is applied to the object fixed to the rotation axis by the arm member to rotate the object around the rotation axis, when the forces F are equal, The longer the member length r, the larger the torque N for rotating the object.
- the folding start point FL corresponds to the rotation axis
- the member between the fixed region 15 and the folding start point FL corresponds to the arm member
- the distance between the fixed region 15 and the folding start point FL is the length of the arm member.
- the end portion of the absorber 14 including the fixed region 15 corresponds to the object r
- the contracting force of the leak preventive wall 16 corresponds to the force F.
- the contraction force of the leak preventive wall 16 is the same and the fixing region 15
- the force for folding the end of the absorber 14 can be increased.
- the leak preventive wall 16 can be further raised toward the wearer's skin surface.
- the fixing region 15 extends to the non-arrangement region (eg, back non-arrangement region BAc) in the longitudinal direction L, and at least a part of the fixing region 15 overlaps in the thickness direction T. Therefore, when the leak preventive wall 15 pulls the fixed region 15 due to contraction, a portion outside the low grammage region (example: back side low grammage region BAb) in the longitudinal direction L can be pulled together with the fixed region 15. .. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the absorber 14 from being broken at a place other than (the folding start point FL) of the low basis weight region. Thereby, the absorber 14 can be more easily folded at the folding start point FL in the low basis weight region, and the leak preventive wall 16 can be more easily raised toward the wearer's skin surface.
- the non-arrangement region eg, back non-arrangement region BAc
- the fixing region 15 overlaps in the thickness direction T. Therefore, when the leak preventive wall 15 pulls the fixed region 15 due to contraction, a portion outside the
- the fixed region 15 extends to the outside of the absorbent body 14 in the longitudinal direction L beyond the non-arrangement region (exemplification: back non-arrangement region BAc). Therefore, when the leak-proof wall 16 pulls the fixed region 15 by contraction, it is an outer side portion in the longitudinal direction L with respect to the low basis weight region (example: back side low basis weight region BAb) and outside the absorber 14.
- the region including the portion of can be pulled together with the fixing region 15. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the absorber 14 from being folded at a location other than (the fold starting point FL) of the low basis weight region. Thereby, the absorber 14 can be more easily folded at the folding starting point FL in the low basis weight region, and the leak preventive wall 16 can be more easily erected toward the wearer's skin surface.
- FIG. 7 is a sectional view taken along line II-II of FIG. 1 according to another embodiment.
- the leak preventive wall 16 has a V-shaped (convex inward) shape which is lateral when viewed in the longitudinal direction L.
- the leak preventive wall 16 includes a first wall portion 16a and a second wall portion 16b located between the front and rear fixing regions 15 and 15 of the side seat 17 in the longitudinal direction L.
- the outer edge of the first wall portion 16a in the width direction W is fixed to the surface of the absorbent main body 10.
- the second wall portion 16b has an inner edge in the width direction W connected to an inner edge in the width direction W of the first wall portion 16a, and an outer edge in the width direction W is not fixed.
- At least the second wall portion 16b of the first wall portion 16a and the second wall portion 16b includes an elastic member 61 extending along the longitudinal direction. Due to the first wall portion 16a and the second wall portion 16b, it can be said that the leak preventive wall 16 has a V-shaped (convex inward) shape which is laterally inclined when viewed in the longitudinal direction L. In this case, the leak preventive wall 16 can be raised in the thickness direction T. Therefore, the leak preventive wall 16 can be made to stand higher toward the wearer's skin surface. As a result, it is possible to further suppress the height of the leak preventive wall 16 from decreasing.
- FIG. 8 is the top view which expanded a part of back side part of the disposable diaper which concerns on another embodiment.
- the edge 15E (see FIG. 1) on the center side (inside) in the longitudinal direction L in the fixed region 15 on the rear side (dorsal portion 3 side) in the longitudinal direction L is the back side low basis weight region. It overlaps with BAb in the thickness direction T.
- the edge 15E on the central side (inner side) in the longitudinal direction L in the fixed region 15 on the front side (the ventral side portion 2 side) in the longitudinal direction L is the abdominal side high basis weight area FAa.
- the thickness direction T is the thickness direction T.
- the longitudinal direction L of the absorber 14 is increased.
- the absorber 14 can be folded at the folding start point FL so that the end portion of the absorber stands up toward the wearer's skin surface.
- the abdominal region of the absorbent body 14 since the abdominal region of the absorbent body 14 does not have the low basis weight region but the abdominal high basis weight region FAa, it is between the abdominal high basis weight region FAa and the crotch region MA. Does not have a starting point where the weighing changes, that is, a starting point where the rigidity changes. Therefore, the end portion of the absorbent body 14 does not break near the end edge 15E on the central side in the longitudinal direction L in the abdominal side fixed region 15, the fit of the abdominal side portion 2 is enhanced, and the abdominal region FA is removed. Can be suppressed.
- the disposable diaper 1 is a tape type diaper.
- the tape-type diaper includes a pair of locking members located on both outer sides in the width direction W of the back side portion of the absorbent main body 10.
- the tape-type diaper preferably further comprises an elastic member so as to straddle the longitudinal centerline CL at the center of the back side portion of the absorbent main body 10 in the width direction W, and more preferably between the pair of locking members.
- Prepare The structure of the absorbent main body 10 is as described above. Also in this case, the above-mentioned effects can be obtained.
- the disposable diaper and the absorbent body of the present invention are not limited to the above-described embodiments, and the object and the purpose of the present invention are combined and the known techniques are applied within a range not departing from the gist of the present invention. It is possible.
- Disposable diaper 1
- Ventral region 3
- Dorsal part (dorsal waist belt) 10
- Absorbent body 14
- Fixing area 15E
- Leakage prevention wall 17
- Side sheet BA
- Dorsal area FA
- Abdominal area MA Crotch area
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
La présente invention concerne une couche jetable qui est capable de réduire la fuite de liquide dans son sens de la largeur. Ladite couche jetable est pourvue d'une section ventrale (2), d'une section dorsale (3), et d'un corps absorbant (10) comprenant un agent absorbant (14). L'agent absorbant comprend un polymère superabsorbant, et est pourvu d'une zone d'entrejambe (MA), d'une zone côté dorsal (BA) qui chevauche la section dorsale dans le sens de l'épaisseur, et d'une zone côté ventral (FA) qui chevauche la section ventrale dans le sens de l'épaisseur. La zone côté dorsal et/ou la zone côté ventral comprennent une zone de bas poids de base dans laquelle le poids de base du polymère superabsorbant est inférieur à celui dans la zone d'entrejambe. Le corps absorbant comprend une paire de feuilles latérales (17, 17). Chacune des feuilles latérales présente : une zone fixe (15) qui est fixée à la surface du corps absorbant ; et une paroi antifuite (16) qui présente un bord externe dans le sens de la largeur fixé à la surface du corps absorbant avec un bord interne dans le sens de la largeur qui est laissé non fixé. Les bords (15E) des zones fixes sur le côté du centre dans le sens longitudinal chevauchent la zone de bas poids de base dans le sens de l'épaisseur.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811630673 | 2018-12-29 | ||
| CN201811630673.X | 2018-12-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020137433A1 true WO2020137433A1 (fr) | 2020-07-02 |
Family
ID=71129070
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/047707 WO2020137433A1 (fr) | 2018-12-29 | 2019-12-05 | Couche jetable |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6818119B2 (fr) |
| CN (2) | CN212166012U (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2020137433A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN212166012U (zh) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-12-18 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 一次性尿布 |
| JP7409996B2 (ja) * | 2020-08-18 | 2024-01-09 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012016435A (ja) * | 2010-07-07 | 2012-01-26 | Kao Corp | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2013188437A (ja) * | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-26 | Daio Paper Corp | パンツタイプ使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2016112208A (ja) * | 2014-12-15 | 2016-06-23 | 花王株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3737725B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-31 | 2006-01-25 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 開放型の使い捨て着用物品 |
| AU2002328060A1 (en) * | 2001-09-21 | 2003-04-07 | Kao Corporation | Disposable diaper |
| JP3769545B2 (ja) * | 2003-02-10 | 2006-04-26 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 使い捨て紙おむつ |
| DE10326022A1 (de) * | 2003-06-02 | 2004-12-23 | Paul Hartmann Ag | Hygieneartikel zum einmaligen Gebrauch |
| US20070208319A1 (en) * | 2006-03-06 | 2007-09-06 | Kao Corporation | Flat type disposable diaper |
| JP5997944B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-11 | 2016-09-28 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6278434B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-28 | 2018-02-14 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP6371152B2 (ja) * | 2014-07-22 | 2018-08-08 | 花王株式会社 | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ |
| JP6412899B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-06 | 2018-10-24 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN212166012U (zh) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-12-18 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 一次性尿布 |
-
2019
- 2019-12-02 CN CN201922125791.1U patent/CN212166012U/zh not_active Withdrawn - After Issue
- 2019-12-02 CN CN201911216046.6A patent/CN111374831B/zh active Active
- 2019-12-05 WO PCT/JP2019/047707 patent/WO2020137433A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2019-12-10 JP JP2019223233A patent/JP6818119B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012016435A (ja) * | 2010-07-07 | 2012-01-26 | Kao Corp | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2013188437A (ja) * | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-26 | Daio Paper Corp | パンツタイプ使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2016112208A (ja) * | 2014-12-15 | 2016-06-23 | 花王株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020108742A (ja) | 2020-07-16 |
| CN111374831A (zh) | 2020-07-07 |
| CN212166012U (zh) | 2020-12-18 |
| CN111374831B (zh) | 2022-10-28 |
| JP6818119B2 (ja) | 2021-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2020137424A1 (fr) | Couche de type culotte | |
| WO2020137433A1 (fr) | Couche jetable | |
| JP7304800B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2020137426A1 (fr) | Couche de type bande | |
| WO2020137427A1 (fr) | Couche de type culotte | |
| WO2020137430A1 (fr) | Couche de type culotte | |
| JP7170622B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| CN111374835B (zh) | 吸收性物品用的吸收体以及吸收性物品 | |
| JP7213789B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品用の吸収体、及び吸収性物品 | |
| JP6847188B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2020108747A (ja) | 吸収体と吸収性物品 | |
| JP2022089470A (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19903391 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19903391 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: JP |