WO2018199289A1 - 燃料噴射器及びガスタービン - Google Patents
燃料噴射器及びガスタービン Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018199289A1 WO2018199289A1 PCT/JP2018/017189 JP2018017189W WO2018199289A1 WO 2018199289 A1 WO2018199289 A1 WO 2018199289A1 JP 2018017189 W JP2018017189 W JP 2018017189W WO 2018199289 A1 WO2018199289 A1 WO 2018199289A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cooling air
- fuel
- plenum
- cooling
- supply tube
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23R—GENERATING COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OF HIGH PRESSURE OR HIGH VELOCITY, e.g. GAS-TURBINE COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
- F23R3/00—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel
- F23R3/28—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply
- F23R3/286—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply having fuel-air premixing devices
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23R—GENERATING COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OF HIGH PRESSURE OR HIGH VELOCITY, e.g. GAS-TURBINE COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
- F23R3/00—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel
- F23R3/28—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply
- F23R3/30—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply comprising fuel prevapourising devices
- F23R3/32—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply comprising fuel prevapourising devices being tubular
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02C—GAS-TURBINE PLANTS; AIR INTAKES FOR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS; CONTROLLING FUEL SUPPLY IN AIR-BREATHING JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F02C7/00—Features, components parts, details or accessories, not provided for in, or of interest apart form groups F02C1/00 - F02C6/00; Air intakes for jet-propulsion plants
- F02C7/12—Cooling of plants
- F02C7/16—Cooling of plants characterised by cooling medium
- F02C7/18—Cooling of plants characterised by cooling medium the medium being gaseous, e.g. air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02C—GAS-TURBINE PLANTS; AIR INTAKES FOR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS; CONTROLLING FUEL SUPPLY IN AIR-BREATHING JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F02C7/00—Features, components parts, details or accessories, not provided for in, or of interest apart form groups F02C1/00 - F02C6/00; Air intakes for jet-propulsion plants
- F02C7/22—Fuel supply systems
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02C—GAS-TURBINE PLANTS; AIR INTAKES FOR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS; CONTROLLING FUEL SUPPLY IN AIR-BREATHING JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F02C7/00—Features, components parts, details or accessories, not provided for in, or of interest apart form groups F02C1/00 - F02C6/00; Air intakes for jet-propulsion plants
- F02C7/22—Fuel supply systems
- F02C7/222—Fuel flow conduits, e.g. manifolds
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23R—GENERATING COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OF HIGH PRESSURE OR HIGH VELOCITY, e.g. GAS-TURBINE COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
- F23R3/00—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel
- F23R3/28—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply
- F23R3/283—Attaching or cooling of fuel injecting means including supports for fuel injectors, stems, or lances
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23R—GENERATING COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OF HIGH PRESSURE OR HIGH VELOCITY, e.g. GAS-TURBINE COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
- F23R3/00—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel
- F23R3/28—Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the fuel supply
- F23R3/34—Feeding into different combustion zones
- F23R3/346—Feeding into different combustion zones for staged combustion
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2240/00—Components
- F05D2240/35—Combustors or associated equipment
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2260/00—Function
- F05D2260/20—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling
- F05D2260/201—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling by impingement of a fluid
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2260/00—Function
- F05D2260/20—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling
- F05D2260/213—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling by the provision of a heat exchanger within the cooling circuit
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2260/00—Function
- F05D2260/20—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling
- F05D2260/221—Improvement of heat transfer
- F05D2260/2212—Improvement of heat transfer by creating turbulence
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2260/00—Function
- F05D2260/20—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling
- F05D2260/232—Heat transfer, e.g. cooling characterized by the cooling medium
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a fuel injector and a gas turbine.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a fuel injector that ejects a mixed gas of compressed air and fuel gas from a plurality of ejection holes regularly formed in a circular substrate. .
- the flame may become an attached flame that adheres to the outlet of the injection hole. This causes the substrate to become high temperature, and thus requires cooling of the substrate.
- the fuel injector described in Patent Document 1 the fuel injector is kept at a low temperature by reviewing the shape of the baffle provided inside the casing into which the fuel gas is introduced. As countermeasures, further countermeasures are desired.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a fuel injector and a gas turbine capable of efficiently cooling a high temperature substrate.
- the fuel injector has a tubular shape centered on the axis, and a fuel supply tube into which fuel gas is introduced from the upstream side in the axial direction in which the axis extends, and the axial direction
- a cylindrical outer surface that connects the plate, a substrate that supports downstream ends of the plurality of premixing tubes, the support plate and the substrate, and forms a plenum inside the support plate and the substrate;
- a cooling air plenum is divided into an upstream side cooling air plenum and a downstream side cooling air plenum disposed downstream of the upstream
- the cooling air introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum is jetted toward the substrate through the cooling holes of the baffle, so that the high temperature substrate can be efficiently cooled.
- At least some of the plurality of cooling holes may be impingement holes.
- the baffle is formed between the baffle body, the cooling hole being formed, and a baffle body provided radially inward with the axis as a center, and the baffle body and the outer wall. And an inclined portion that is inclined toward the downstream side toward the outer side in the radial direction with the cooling hole not formed.
- the cooling air introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum is jetted downstream from the plurality of cooling holes, and then cools the substrate, while radially cooling along the inclined portion. Flowing into. Cooling air introduced into the downstream cooling air plenum is directed radially outward along the baffle ramp. Accordingly, not only the substrate but also the premixing tube in the downstream side cooling air plenum can be cooled.
- the fuel injector may include a plurality of cooling air discharge holes formed in the substrate and discharging the cooling air from the downstream cooling air plenum to the downstream side of the substrate.
- a cooling air introduction hole penetrating the premixing tube in and out may be formed in a portion of the premixing tube located in the downstream side cooling air plenum.
- the cooling air supply tube may be disposed coaxially with the fuel supply tube on a radially inner side of the fuel supply tube.
- the cooling air supply tube can be connected to the plenum without being exposed to the compressed air.
- the fuel injector has a tubular shape centered on the axis, a fuel supply tube into which fuel gas is introduced from the upstream side in the axial direction in which the axis extends, and the axis
- a plurality of premixing tubes that form a tubular shape extending in the direction and into which air is introduced from the upstream side, and a support plate that supports the downstream side of the fuel supply tube and the upstream side end portions of the plurality of premixing tubes
- a substrate that supports downstream ends of the plurality of premix tubes, a cylindrical outer wall that connects the support plate and the substrate, and forms a plenum inside the support plate and the substrate;
- a partition plate that divides the plenum into a fuel plenum, the fuel plenum, and a cooling air plenum disposed downstream of the fuel plenum, and a cooling plate that supplies cooling air to the cooling air plenum.
- An air supply tube and an expansion tube provided downstream of the downstream end of the cooling air supply tube and inclined toward the downstream side toward the radially outer side centered on the axis and connected to the outer wall.
- a baffle having a diameter part, and a cooling air inflow hole into which the cooling air supplied from the cooling air supply tube is formed at a center in a radial direction centering on the axis of the enlarged diameter part, And a fuel introduction hole penetrating the premixing tube in and out is formed in a portion of the premixing tube located in the fuel plenum.
- the cooling air that has flowed into the downstream side of the baffle from the cooling air inflow hole flows radially outward along the enlarged diameter portion while cooling the vicinity of the center of the substrate. That is, the cooling air is directed radially outward along the enlarged diameter portion of the baffle.
- a gas turbine includes a compressor that generates compressed air obtained by compressing air, and any one of the fuel injectors described above, and fuel is mixed with the compressed air to produce combustion gas. , A bleed portion for extracting compressed air generated by the compressor, a forced air-cooled compressor for further compressing the extracted compressed air, and cooling air generated by the forced air-cooled compressor A cooling air introduction part for introducing the fuel into the fuel injector.
- the gas turbine may include a cooler that cools the compressed air extracted by the extraction unit. According to such a configuration, cooling air having a temperature lower than that of the extracted compressed air can be supplied by cooling the compressed air using a cooler.
- the cooling air introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum is jetted toward the substrate through the cooling holes of the baffle, so that the high temperature substrate can be efficiently cooled.
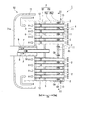
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG. 2, illustrating a fuel injector according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
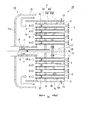
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG. 2, illustrating a fuel injector according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
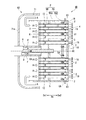
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG. 2, illustrating a fuel injector according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG.
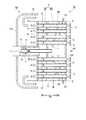
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG. 2, illustrating a fuel injector according to a fifth embodiment of the present invention. It is the front view which looked at another form of the fuel injector of this invention from the downstream.
- the gas turbine 100 of the present embodiment combusts a mixed gas of a compressor 51 that compresses outside air Ao to generate compressed air A, and compressed air A and fuel gas F, thereby producing combustion gas.
- a plurality of combustors 52 that generate G, a turbine 53 that is driven by the combustion gas G, and a cooling device 54 that cools a cooling target of the gas turbine 100 are provided.
- the compressor 51 includes a compressor rotor 56 that rotates about the gas turbine axis Ar, a compressor casing 57 that rotatably covers the compressor rotor 56, and a plurality of compressor vane rows 58. .
- the compressor rotor 56 includes a compressor rotor shaft 59 extending along the gas turbine axis Ar and a plurality of compressor blade rows 60 attached to the compressor rotor shaft 59.
- the plurality of compressor rotor cascades 60 are arranged in the axial direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- Each compressor moving blade row 60 is composed of a plurality of moving blades arranged in the circumferential direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- a compressor stationary blade row 58 is disposed on each downstream side of the plurality of compressor moving blade rows 60.
- Each compressor stationary blade row 58 is fixed inside the compressor casing 57.
- Each compressor stationary blade row 58 is composed of a plurality of stationary blades arranged in the circumferential direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- the turbine 53 includes a turbine rotor 61 that rotates about the gas turbine axis Ar, a turbine casing 62 that rotatably covers the turbine rotor 61, and a plurality of turbine stationary blade rows 63.
- the turbine rotor 61 includes a turbine rotor shaft 64 extending along the gas turbine axis Ar, and a plurality of turbine rotor blade rows 65 attached to the turbine rotor shaft 64.
- the plurality of turbine rotor blade rows 65 are arranged in the axial direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- Each turbine rotor blade row 65 is composed of a plurality of rotor blades arranged in the circumferential direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- a turbine stationary blade row 63 is arranged on each upstream side of the plurality of turbine blade rows 65.
- Each turbine stationary blade row 63 is fixed inside the turbine casing 62.
- Each turbine stationary blade row 63 is composed of a plurality of stationary blades arranged in the circumferential direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- the gas turbine 100 further includes a cylindrical intermediate casing 67 around the gas turbine axis Ar.
- the intermediate casing 67 is disposed between the compressor casing 57 and the turbine casing 62 in the axial direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- the compressor rotor 56 and the turbine rotor 61 are located on the same gas turbine axis Ar, and are connected to each other to form a gas turbine rotor 68.
- the rotor of the generator G is connected to the gas turbine rotor 68.
- the combustor 52 generates a high-temperature and high-pressure combustion gas G by supplying the fuel gas F to the compressed air A compressed by the compressor 51.
- the plurality of combustors 52 are fixed to the intermediate casing 67 at intervals in the circumferential direction of the gas turbine axis Ar.
- the combustor 52 includes a fuel injector 1 and a combustion cylinder 69 that combusts a gas in which compressed air A and fuel gas F injected from the fuel injector 1 are mixed and guides the combustion gas G to the turbine 53. ing.
- the outside air Ao taken into the compressor 51 passes through the plurality of compressor stationary blade rows 58 and the compressor moving blade row 60 and is compressed to become high-temperature and high-pressure compressed air A.
- the compressed gas A is mixed with the fuel gas F in the combustor 52 and burned, whereby a high-temperature and high-pressure combustion gas G is generated.
- the combustion gas G passes through the turbine stationary blade row 63 and the turbine rotor blade row 65 of the turbine 53, so that the turbine rotor shaft 64 is rotationally driven, and rotational power is supplied to the generator G connected to the gas turbine rotor 68. Power is generated by granting.
- the cooling device 54 is a device that extracts a part of the compressed air A supplied to the combustor 52 and compresses it again to cool the cooling target of the gas turbine 100.
- the object to be cooled is a component that is exposed to a high temperature.
- the cooling device 54 includes an extraction unit 72 that extracts a part of the compressed air A, a cooler 73 that cools the extracted compressed air A, and further compresses the compressed air A that has been cooled by the cooler 73 to generate cooling air CA.
- the cooling air introduction part 76 is connected to the cooling air supply tube 9 of the fuel injector 1.
- one cooling system 54 is provided for one gas turbine 100, but multiple cooling systems 54 may be provided for one gas turbine 100.
- Compressed air A compressed again by the forced air-cooled compressor 74 is supplied as cooling air CA to the fuel injector 1 of the combustor 52 through the cooling air introduction section 76.
- the cooling air CA may be supplied to another cooling target of the gas turbine 100, for example, a stationary blade.
- the combustor 52 includes a cylindrical outer cylinder 71 and the fuel injector 1 disposed inside the outer cylinder 71.
- the compressed air A that has flowed in between the outer cylinder 71 and the fuel injector 1 turns 180 ° at the end wall 71 a of the outer cylinder 71 and is supplied to the fuel injector 1.
- the fuel injector 1 of the present embodiment includes a fuel supply tube 8 that supplies a fuel gas F, a plurality of premixing tubes 2, and a support plate 3 that supports an end of the upstream Da1 of the plurality of premixing tubes 2. , A substrate 4 that supports the ends of the downstream Da2 of the plurality of premixing tubes 2, a cylindrical outer wall 5 that forms a plenum P therein, and a plenum P divided into a fuel plenum PF and a cooling air plenum PA And a baffle 7 disposed on the downstream side Da2 of the partition plate 6, and a cooling air supply tube 9 for supplying the cooling air CA to the cooling air plenum PA.
- the baffle 7 divides the cooling air plenum PA into an upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 and a downstream side cooling air plenum PA2 disposed on the downstream side Da2 of the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1.
- the main surface of the support plate 3, the main surface of the partition plate 6, the main surface of the baffle 7, and the main surface of the substrate 4 are orthogonal to the axis At of the fuel supply tube 8.
- the direction in which the axis At of the fuel supply tube 8 extends is defined as the axis direction Da.
- a direction perpendicular to the axis At is defined as a radial direction, a side away from the axis At in the radial direction is referred to as a radially outer side, and a side closer to the axis At in the radial direction is referred to as a radially inner side.
- the side where the fuel gas F in the axial direction Da is introduced (the left side in FIG. 2) is the upstream side Da1
- the side where the fuel gas F in the axial direction Da is injected is the downstream side Da2. That is, in the fuel injector 1 of the present embodiment, the fuel gas F and the compressed air A circulate from the upstream Da1 toward the downstream Da2.
- the fuel gas F is introduced from the upstream side Da ⁇ b> 1 by the fuel supply tube 8.
- the fuel injector 1 mixes the introduced fuel gas F with the compressed air A through the premixing tube 2, and then injects and discharges the fuel gas F toward the downstream Da2.
- the fuel supply tube 8 distributes the fuel gas F supplied from the upstream side Da1 to the fuel plenum PF.
- the fuel supply tube 8 extends in a tubular shape centered on the axis At.
- the fuel supply tube 8 is connected to the support plate 3 on the downstream side Da2.
- the end of the downstream side Da2 of the fuel supply tube 8 opens into the fuel plenum PF. That is, the position in the axial direction Da of the end portion of the downstream side Da 2 of the fuel supply tube 8 is the downstream side Da 2 of the support plate 3 and the upstream side Da 1 of the partition plate 6.
- the cooling air supply tube 9 distributes the cooling air CA supplied from the cooling device 54 (upstream Da1) to the upstream cooling air plenum PA1.
- the cooling air supply tube 9 is arranged on the radially inner side of the fuel supply tube 8 so as to be coaxial with the fuel supply tube 8. That is, the fuel gas F flows through the radial gap between the cooling air supply tube 9 and the fuel supply tube 8.
- the end portion of the downstream side Da2 of the cooling air supply tube 9 opens into the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1. That is, the position in the axial direction Da of the end portion of the downstream side Da2 of the cooling air supply tube 9 is the downstream side Da2 of the partition plate 6 and the upstream side Da1 of the baffle 7.
- the support plate 3 has a disc shape centered on the axis At, and a circular through hole is formed at the center.
- the through hole is formed with the same diameter as the outer diameter of the fuel supply tube 8.
- the support plate 3 is connected to the fuel supply tube 8 in a state where the end of the fuel supply tube 8 is inserted into the through hole so as to protrude to the downstream side Da2.
- the support plate 3 is formed with a plurality of through holes for inserting and supporting the plurality of premixing tubes 2.
- the substrate 4 has substantially the same outer diameter as the support plate 3 and is formed in a disc shape with the axis At as the center.
- the substrate 4 is connected to the support plate 3 via the outer wall 5, thereby defining a plenum P that is a space inside with the support plate 3.
- a plurality of through holes for inserting and supporting the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are formed at positions corresponding to the through holes formed in the support plate 3.
- the outer wall 5 connects the outer periphery of the support plate 3 and the outer periphery of the substrate 4.
- the outer side wall 5 has a cylindrical shape formed with an inner diameter that is the same as the outer diameter of the support plate 3 and the substrate 4.
- the outer wall 5 is connected to the support plate 3 on the upstream side Da1.
- the outer wall 5 is connected to the substrate 4 at the end of the downstream side Da2. Therefore, a plenum P is provided as a defined space inside the support plate 3 and the substrate 4 connected by the outer wall 5.
- the partition plate 6 is a plate that partitions the plenum P into a fuel plenum PF, a fuel plenum PF, and a cooling air plenum PA disposed on the downstream side Da2 of the fuel plenum PF.
- the partition plate 6 has substantially the same outer diameter as the support plate 3 and is formed in a disc shape with the axis At as the center.
- the partition plate 6 is disposed on the downstream side Da ⁇ b> 2 of the support plate 3 and on the upstream side Da ⁇ b> 1 of the substrate 4.
- a circular through hole is formed at the center of the partition plate 6.
- the through hole is formed with the same diameter as the outer diameter of the cooling air supply tube 9.
- the partition plate 6 is connected to the cooling air supply tube 9 in a state where the end of the cooling air supply tube 9 is inserted into the through hole so as to protrude to the downstream side Da2.
- a plurality of through holes for inserting and supporting the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are formed in the partition plate 6 at positions corresponding to the through holes formed in the support plate 3.
- the baffle 7 is a plate that divides the cooling air plenum PA into an upstream cooling air plenum PA1 and a downstream cooling air plenum PA2 disposed on the downstream Da2 of the upstream cooling air plenum PA1.
- the baffle 7 has the same outer diameter as the partition plate 6 and is formed in a disc shape with the axis At as the center.
- the baffle 7 is disposed on the downstream side Da ⁇ b> 2 of the partition plate 6 and on the upstream side Da ⁇ b> 1 of the substrate 4.
- a plurality of through holes for inserting and supporting the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are formed at positions corresponding to the through holes formed in the support plate 3.
- the baffle 7 is formed with a plurality of cooling holes 11 for communicating the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 and the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2.
- the cooling hole 11 is a hole extending in the axial direction Da. That is, the cooling air CA introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 through the cooling air supply tube 9 is introduced into the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2 through the plurality of cooling holes 11.
- the premixing tube 2 is a tube material having a cylindrical shape extending in the axial direction Da. Compressed air A is introduced into the premixing tube 2 from the upstream side Da1, and a mixed gas of the compressed air A and the fuel gas F is discharged from the downstream side Da2. In the premixing tube 2, the end of the upstream Da 1 is supported by the support plate 3, and the end of the downstream Da 2 is supported by the substrate 4.
- the premixing tube 2 of the present embodiment is fixed so that the end of the upstream side Da1 is substantially flush without protruding from the support plate 3 to the upstream side Da1.
- the premixing tube 2 is fixed so that the end portion of the downstream side Da2 does not protrude from the substrate 4 to the downstream side Da2 and is substantially flush.
- a fuel introduction hole 12 that penetrates the premixing tube 2 inward and outward in the radial direction is formed in a portion located in the fuel plenum PF.
- the fuel introduction hole 12 is a through hole through which the fuel gas F flows into the premixing tube 2 by the plenum P.
- the fuel introduction hole 12 has a circular cross-sectional shape and penetrates the premixing tube 2 in the radial direction.
- the fuel introduction hole 12 is formed on the upstream side Da ⁇ b> 1 with respect to the partition plate 6.
- the position of the fuel introduction hole 12 in the axial direction Da is the same in all the premixing tubes 2.
- the outer wall 5 is formed with a plurality of cooling air discharge holes 13 penetrating into and out of the plenum P.
- the cooling air discharge hole 13 is formed in a portion located in the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2.
- the plurality of cooling air discharge holes 13 are formed at equal intervals in the circumferential direction around the axis At.
- a plurality of premix tubes 2 are provided for the support plate 3 and the substrate 4.
- the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are formed to have the same cross-sectional shape and the same length.
- the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are arranged such that, when viewed from the axial direction Da, the cross-sectional area of the plenum P orthogonal to the axial line At is spread with a plurality of virtual equilateral triangles T about the axial line At. When partitioned, the virtual equilateral triangle T is arranged at the vertex position.
- the virtual equilateral triangle T is an equilateral triangle that is arranged in a plurality so as to spread radially around the axis At on a virtual plane that is a cross-sectional area of the plenum P orthogonal to the axis At.
- the length of one side in the virtual equilateral triangle T is determined from the distance from the axis At where the premixing tube 2 is arranged and the distance between the premixing tubes 2 adjacent to each other.
- virtual equilateral triangles T having the same side length and the same shape are spread in the cross-sectional area of the plenum P.
- the plurality of premixing tubes 2 are arranged at the vertices of the virtual equilateral triangle T, and are arranged so that the number gradually increases in the radial direction from the axis At toward the center. .
- the plurality of cooling holes 11 are arranged at the center position of the virtual equilateral triangle T when viewed from the axial direction Da.
- the fuel gas F is introduced into the fuel plenum PF from the upstream side Da1 via the fuel supply tube 8.
- the fuel gas F introduced into the fuel plenum PF is taken into the premixing tube 2 through the fuel introduction hole 12.
- the premixing tube 2 into which the fuel gas F flows the compressed air A introduced from the upstream side Da1 and the fuel gas F are mixed, and the mixed gas is injected from the downstream side Da2.
- the cooling air CA is introduced from the upstream side Da1 to the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 via the cooling air supply tube 9.
- the cooling air CA introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum PA ⁇ b> 1 is jetted from the plurality of cooling holes 11 and collides with the substrate 4.
- substrate 4 can be cooled similarly to impingement cooling by injecting the cooling air CA by the cooling hole 11.
- the cooling air CA used for cooling the substrate 4 is discharged radially outward from the cooling air discharge hole 13.
- the cooling air CA introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 is jetted toward the substrate 4 through the cooling holes 11 of the baffle 7 to efficiently cool the substrate 4 that reaches a high temperature.
- the flame generated by the injection of the fuel gas F and the compressed air A becomes an adhering flame that adheres to the outlet (injection hole) of the premixing tube 2, and the substrate 4 is actively cooled when the temperature of the substrate 4 becomes high. be able to.
- the compressed air A generated by the compressor 51 is extracted, and the compressed air A extracted by using the forced air-cooled compressor 74 of the cooling device 54 is re-pressurized, so that the pressure is higher than that of the extracted compressed air.
- Air CA can be supplied. Further, by cooling the compressed air A using the cooler 73, it is possible to supply cooling air CA having a temperature lower than that of the extracted compressed air A.
- cooling air supply tube 9 is arranged on the radially inner side of the fuel supply tube 8 so as to be coaxial with the fuel supply tube 8, an increase in the temperature of the cooling air CA can be suppressed. That is, the cooling air supply tube 9 can be connected to the plenum P without being exposed to the compressed air A that is higher in temperature than the fuel gas F.
- the fuel injector 1B of the second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
- differences from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described, and description of similar parts will be omitted.
- the fuel injector 1B of the present embodiment is different from the fuel injector of the first embodiment in the shape of the baffle.
- the baffle 7 ⁇ / b> B of the present embodiment has a baffle body 15 disposed on the radially inner side and an inclined portion 16 disposed on the radially outer side of the baffle body 15.
- the diameter of the baffle body 15 is smaller than the diameter of the substrate 4.
- the diameter of the baffle body 15 can be set to about 1/3 of the diameter of the substrate 4.
- the baffle body 15 is formed with a plurality of cooling holes 11 similar to the baffle 7 of the first embodiment.
- the inclined portion 16 is a plate-like member formed so as to connect the outer periphery of the baffle body 15 and the inner peripheral surface of the outer wall 5.
- the inclined portion 16 is inclined toward the downstream side Da2 as it goes outward in the radial direction. In other words, the inclined portion 16 is formed so as to gradually increase in diameter toward the downstream side Da2.
- the cooling hole 11 is not formed in the inclined portion 16.
- the cooling air CA introduced into the upstream side cooling air plenum PA1 is jetted from the plurality of cooling holes 11 to the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2, and then cools the vicinity of the center of the substrate 4, It flows radially outward along the inclined portion 16. That is, the cooling air CA introduced into the downstream side cooling air plenum PA ⁇ b> 2 is directed radially outward along the inclined portion 16 of the baffle 7. As a result, not only the substrate 4 but also the premixing tube 2 in the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2 can be cooled.
- a fuel injector 1C according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
- differences from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described, and description of similar parts will be omitted.
- a second cooling air discharge hole 17 is formed in the substrate 4C of the present embodiment. That is, the fuel injector 1 of the present embodiment has the second cooling air discharge hole 17 formed in the substrate 4 in addition to the cooling air discharge hole 13 formed in the outer wall 5.
- the cooling air discharge hole 13 in the outer wall 5 may be omitted.
- the second cooling air discharge hole 17 is a through hole extending in the axial direction Da.
- the position of the second cooling air discharge hole 17 of the present embodiment viewed from the axial direction Da is different from the position of the cooling hole 11 of the baffle 7.
- the cooling air CA is discharged without colliding with the substrate 4. Can be suppressed.
- the premixing tube 2 of the fuel injector 1D of the present embodiment has a cooling air introduction hole 18 that penetrates the premixing tube 2 in and out of the premixing tube 2 at a portion located in the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2. Is formed.
- the cooling air introduction hole 18 is a through hole through which the cooling air CA flows into the premixing tube 2 by the downstream side cooling air plenum PA2.
- the cooling air introduction hole 18 has a circular cross-sectional shape and penetrates the premixing tube 2 in the radial direction.
- the fuel introduction hole 12 is formed on the downstream side Da ⁇ b> 2 with respect to the baffle 7.
- the position of the cooling air introduction hole 18 in the axial direction Da is the same in all the premixing tubes 2.
- the cooling air introduction hole 18 is oriented such that the cooling air CA flows toward the downstream side Da2. In other words, the central axis of the cooling air introduction hole 18 is inclined from the outer peripheral surface of the premixing tube 2 toward the downstream Da2 toward the inner peripheral surface of the premixing tube 2.
- a fuel injector 1E according to a fifth embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
- differences from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described, and description of similar parts will be omitted.
- the baffle 7 ⁇ / b> E of the present embodiment is provided on the downstream Da ⁇ b> 2 rather than the downstream Da ⁇ b> 2 end of the cooling air supply tube 9.
- the baffle 7E is not formed so as to partition the cooling air plenum PA, and a cooling air inflow hole 19 is formed at the center thereof.
- the baffle 7E is formed at the center of the diameter-enlarged portion 20 and the diameter-enlarged portion 20 that is inclined to the downstream Da2 and connected to the outer wall 5 toward the outer side in the radial direction centered on the axis At. And a cooling air inflow hole 19.
- the position in the axial direction Da of the end portion (cooling air inflow hole 19) on the upstream side Da1 of the enlarged diameter portion 20 is the same as the position of the end portion on the downstream side Da2 of the cooling air supply tube 9, or slightly downstream side Da2. .
- the diameter of the cooling air inflow hole 19 is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the cooling air supply tube 9.
- the cooling air inflow hole 19 has a circular shape, and the center is disposed on the axis At.
- the cooling air CA supplied from the cooling air supply tube 9 flows into the cooling air inflow hole 19 and then collides with the substrate 4.
- the cooling air CA introduced into the cooling air plenum PA flows from the cooling air inflow hole 19 to the downstream Da2 of the baffle 7.
- the inflowing cooling air CA flows radially outward along the enlarged diameter portion 20 while cooling the vicinity of the center of the substrate 4. That is, the cooling air CA is directed radially outward along the enlarged diameter portion 20 of the baffle 7.
- the fuel supply tube 8 and the cooling air supply tube 9 were set as the structure arrange
- the cooling air supply tube 9 may be connected to the outer wall 5 and the cooling air CA may be introduced into the cooling air plenum PA through a through hole formed in the outer wall 5.
- the one fuel injector 1 is arrange
- a plurality of fuel injectors having a cylindrical outer wall may be disposed in the combustion cylinder 69.
- the cross-sectional shape of each fuel injector need not be circular.
- a cylindrical outer wall 5A and a plurality of walls 5B that divide the inside of the outer wall 5A in the circumferential direction are provided, and a plurality of fan-like shapes are provided in one combustor 52A.
- a fuel injector 1A may be provided.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Gas Burners (AREA)
- Turbine Rotor Nozzle Sealing (AREA)
- Fuel-Injection Apparatus (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112018002222.6T DE112018002222B4 (de) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-04-27 | Brennstoffinjektor und Gasturbine |
| CN201880026932.XA CN110573801B (zh) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-04-27 | 燃料喷射器及燃气轮机 |
| KR1020197031286A KR102190537B1 (ko) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-04-27 | 연료 분사기 및 가스 터빈 |
| US16/607,968 US11079113B2 (en) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-04-27 | Fuel injector and gas turbine |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017090705A JP6822894B2 (ja) | 2017-04-28 | 2017-04-28 | 燃料噴射器及びガスタービン |
| JP2017-090705 | 2017-04-28 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018199289A1 true WO2018199289A1 (ja) | 2018-11-01 |
Family
ID=63918439
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/017189 Ceased WO2018199289A1 (ja) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-04-27 | 燃料噴射器及びガスタービン |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11079113B2 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| JP (1) | JP6822894B2 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| KR (1) | KR102190537B1 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| CN (1) | CN110573801B (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| DE (1) | DE112018002222B4 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| WO (1) | WO2018199289A1 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112594734A (zh) * | 2019-10-01 | 2021-04-02 | 三菱动力株式会社 | 燃气轮机燃烧器 |
| EP3896341A1 (en) * | 2020-04-15 | 2021-10-20 | Marvel-Tech Ltd | Gas turbine combustor |
| CN119802674A (zh) * | 2025-02-12 | 2025-04-11 | 清华大学 | 冷却微混喷嘴、燃烧器及燃气轮机 |
Families Citing this family (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6979343B2 (ja) * | 2017-11-30 | 2021-12-15 | 三菱パワー株式会社 | 燃料噴射器、燃焼器、及びガスタービン |
| JP7489759B2 (ja) | 2018-11-20 | 2024-05-24 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 燃焼器及びガスタービン |
| JP7254540B2 (ja) | 2019-01-31 | 2023-04-10 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | バーナ及びこれを備えた燃焼器及びガスタービン |
| KR102433673B1 (ko) | 2021-01-11 | 2022-08-18 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연료 노즐, 이를 포함하는 연료 노즐 모듈 및 연소기 |
| EP4027059A1 (en) * | 2021-01-12 | 2022-07-13 | Crosstown Power GmbH | Burner, combustor, and method for retrofitting a combustion appliance |
| KR102403750B1 (ko) * | 2021-01-15 | 2022-05-30 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 멀티 튜브를 갖는 연소기용 노즐, 연소기, 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
| KR102437977B1 (ko) | 2021-01-18 | 2022-08-30 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 노즐 어셈블리, 연소기 및 이를 포함하는 가스터빈 |
| KR102415892B1 (ko) | 2021-01-27 | 2022-06-30 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 마이크로 믹서 및 이를 포함하는 연소기 |
| KR102460001B1 (ko) * | 2021-02-17 | 2022-10-26 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 마이크로 믹서모듈 및 이를 포함하는 연소기 |
| DE102021110614A1 (de) * | 2021-04-26 | 2022-10-27 | Rolls-Royce Deutschland Ltd & Co Kg | Brennkammerbaugruppe für ein Triebwerk mit mindestens einem Wärmetauscherkanal für einzudüsenden Kraftstoff |
| CN113091094B (zh) * | 2021-05-13 | 2023-05-23 | 中国联合重型燃气轮机技术有限公司 | 燃气轮机燃烧室喷嘴及喷嘴中预混燃料和空气的方法 |
| CN113091095B (zh) * | 2021-05-13 | 2023-05-23 | 中国联合重型燃气轮机技术有限公司 | 燃气轮机燃烧室喷嘴及喷嘴中预混燃料和空气的方法 |
| KR102595333B1 (ko) * | 2021-09-17 | 2023-10-27 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기 및 이를 포함하는 가스터빈 |
| KR20230091605A (ko) * | 2021-12-16 | 2023-06-23 | 한화에어로스페이스 주식회사 | 직교 배열되는 채널을 포함하는 연소 장치 |
| KR102663869B1 (ko) | 2022-01-18 | 2024-05-03 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기용 노즐, 연소기 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
| US11828465B2 (en) * | 2022-01-21 | 2023-11-28 | General Electric Company | Combustor fuel assembly |
| KR102619152B1 (ko) * | 2022-02-21 | 2023-12-27 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기용 노즐, 연소기, 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
| KR102599921B1 (ko) | 2022-03-21 | 2023-11-07 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기용 노즐, 연소기, 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
| JP2023148761A (ja) * | 2022-03-30 | 2023-10-13 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 燃焼器及びガスタービン |
| JP7650843B2 (ja) * | 2022-03-30 | 2025-03-25 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 燃焼器及びガスタービン |
| US11867400B1 (en) * | 2023-02-02 | 2024-01-09 | Pratt & Whitney Canada Corp. | Combustor with fuel plenum with mixing passages having baffles |
| DE112024000649T5 (de) * | 2023-03-29 | 2025-11-13 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Brenneranordnung, gasturbinenbrennkammer und gasturbine |
| KR102814686B1 (ko) * | 2023-05-02 | 2025-05-28 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기용 노즐, 연소기, 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
| KR102863421B1 (ko) * | 2023-12-15 | 2025-09-22 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | 연소기용 노즐, 연소기, 및 이를 포함하는 가스 터빈 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011069602A (ja) * | 2009-09-25 | 2011-04-07 | General Electric Co <Ge> | 燃料噴射器用の内部バッフル |
| JP2013139993A (ja) * | 2012-01-03 | 2013-07-18 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービンエンジンで使用する燃焼器アセンブリ及びその組立方法 |
| JP2013250046A (ja) * | 2012-05-30 | 2013-12-12 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービンエンジンに使用するための燃料注入組立体及びそれを組み立てる方法 |
| JP2015222023A (ja) * | 2014-05-22 | 2015-12-10 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | ガスタービン設備、及び冷却装置の運転方法 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4969384B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-25 | 2012-07-04 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | ガスタービン燃焼器の冷却構造 |
| US8112999B2 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2012-02-14 | General Electric Company | Turbomachine injection nozzle including a coolant delivery system |
| US8157189B2 (en) * | 2009-04-03 | 2012-04-17 | General Electric Company | Premixing direct injector |
| JP5653705B2 (ja) | 2010-09-30 | 2015-01-14 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 回収式空気冷却ガスタービン燃焼器冷却構造 |
| US8955327B2 (en) | 2011-08-16 | 2015-02-17 | General Electric Company | Micromixer heat shield |
| US9243803B2 (en) * | 2011-10-06 | 2016-01-26 | General Electric Company | System for cooling a multi-tube fuel nozzle |
| US8904798B2 (en) * | 2012-07-31 | 2014-12-09 | General Electric Company | Combustor |
-
2017
- 2017-04-28 JP JP2017090705A patent/JP6822894B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-04-27 US US16/607,968 patent/US11079113B2/en active Active
- 2018-04-27 KR KR1020197031286A patent/KR102190537B1/ko active Active
- 2018-04-27 CN CN201880026932.XA patent/CN110573801B/zh active Active
- 2018-04-27 DE DE112018002222.6T patent/DE112018002222B4/de active Active
- 2018-04-27 WO PCT/JP2018/017189 patent/WO2018199289A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011069602A (ja) * | 2009-09-25 | 2011-04-07 | General Electric Co <Ge> | 燃料噴射器用の内部バッフル |
| JP2013139993A (ja) * | 2012-01-03 | 2013-07-18 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービンエンジンで使用する燃焼器アセンブリ及びその組立方法 |
| JP2013250046A (ja) * | 2012-05-30 | 2013-12-12 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービンエンジンに使用するための燃料注入組立体及びそれを組み立てる方法 |
| JP2015222023A (ja) * | 2014-05-22 | 2015-12-10 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | ガスタービン設備、及び冷却装置の運転方法 |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112594734A (zh) * | 2019-10-01 | 2021-04-02 | 三菱动力株式会社 | 燃气轮机燃烧器 |
| JP2021055973A (ja) * | 2019-10-01 | 2021-04-08 | 三菱パワー株式会社 | ガスタービン燃焼器 |
| US11339969B2 (en) | 2019-10-01 | 2022-05-24 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Gas turbine combustor |
| JP7270517B2 (ja) | 2019-10-01 | 2023-05-10 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | ガスタービン燃焼器 |
| DE102020212361B4 (de) | 2019-10-01 | 2025-03-20 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Gasturbinenverbrennungsvorrichtung |
| EP3896341A1 (en) * | 2020-04-15 | 2021-10-20 | Marvel-Tech Ltd | Gas turbine combustor |
| US11365885B2 (en) | 2020-04-15 | 2022-06-21 | Marvel-Tech Ltd. | Gas turbine combustor with fuel injector including a downstream guide member |
| CN119802674A (zh) * | 2025-02-12 | 2025-04-11 | 清华大学 | 冷却微混喷嘴、燃烧器及燃气轮机 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE112018002222T5 (de) | 2020-02-20 |
| JP6822894B2 (ja) | 2021-01-27 |
| JP2018189285A (ja) | 2018-11-29 |
| US20210102703A1 (en) | 2021-04-08 |
| KR102190537B1 (ko) | 2020-12-14 |
| US11079113B2 (en) | 2021-08-03 |
| DE112018002222B4 (de) | 2024-03-14 |
| CN110573801B (zh) | 2021-04-06 |
| KR20190128232A (ko) | 2019-11-15 |
| CN110573801A (zh) | 2019-12-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018199289A1 (ja) | 燃料噴射器及びガスタービン | |
| EP3062022B1 (en) | Gas turbine engine mixer assembly with cooling holes | |
| US10995954B2 (en) | Gas turbine engine with igniter stack or borescope mount having noncollinear cooling passages | |
| JP4818895B2 (ja) | 燃料混合気の噴射装置と、このような装置を備えた燃焼室およびタービンエンジン | |
| EP1524471A1 (en) | Methods and apparatus for cooling turbine engine combuster exit temperatures | |
| US10794595B2 (en) | Stepped heat shield for a turbine engine combustor | |
| JP2008008612A (ja) | 空気と燃料の混合物を噴射するための装置と、このような装置を備える燃焼室およびターボ機械 | |
| US11274830B2 (en) | Combustor nozzle, combustor, and gas turbine | |
| KR101752114B1 (ko) | 노즐, 연소기, 및 가스 터빈 | |
| JP2018189285A5 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) | ||
| JP2008275308A (ja) | 燃料ノズル及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2010223577A6 (ja) | スワーラ、少なくとも1つのスワーラを備えたバーナにおける逆火の防止方法およびバーナ | |
| JP2010223577A (ja) | スワーラ、少なくとも1つのスワーラを備えたバーナにおける逆火の防止方法およびバーナ | |
| US11242994B2 (en) | Combustion chamber for a turbomachine | |
| KR20150020135A (ko) | 버너 장치 및 버너 장치를 작동하기 위한 방법 | |
| US10215410B2 (en) | Turbine engine combustor heat shield with multi-angled cooling apertures | |
| EP3130855B1 (en) | Combustor liner for a gas turbine with a hole arrangement | |
| KR20200002970A (ko) | 연소기 및 그 연소기를 구비하는 가스 터빈 | |
| US20180266690A1 (en) | Combustion chamber of a turbine engine | |
| US20220373182A1 (en) | Pilot fuel nozzle assembly with vented venturi | |
| US11092076B2 (en) | Turbine engine with combustor | |
| US11300296B2 (en) | Combustion chamber of a turbomachine | |
| JP6326205B2 (ja) | 燃料ノズル、燃焼器、及びガスタービン |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18789979 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20197031286 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18789979 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |