WO2017212665A1 - 熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 - Google Patents
熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017212665A1 WO2017212665A1 PCT/JP2016/081340 JP2016081340W WO2017212665A1 WO 2017212665 A1 WO2017212665 A1 WO 2017212665A1 JP 2016081340 W JP2016081340 W JP 2016081340W WO 2017212665 A1 WO2017212665 A1 WO 2017212665A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- heat medium
- header space
- heating device
- inlet
- outlet
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 93
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000498 cooling water Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003507 refrigerant Substances 0.000 description 2
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/22—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices the heat being derived otherwise than from the propulsion plant
- B60H1/2215—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices the heat being derived otherwise than from the propulsion plant the heat being derived from electric heaters
- B60H1/2221—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices the heat being derived otherwise than from the propulsion plant the heat being derived from electric heaters arrangements of electric heaters for heating an intermediate liquid
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/22—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices the heat being derived otherwise than from the propulsion plant
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24H—FLUID HEATERS, e.g. WATER OR AIR HEATERS, HAVING HEAT-GENERATING MEANS, e.g. HEAT PUMPS, IN GENERAL
- F24H3/00—Air heaters
- F24H3/002—Air heaters using electric energy supply
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24H—FLUID HEATERS, e.g. WATER OR AIR HEATERS, HAVING HEAT-GENERATING MEANS, e.g. HEAT PUMPS, IN GENERAL
- F24H3/00—Air heaters
- F24H3/02—Air heaters with forced circulation
- F24H3/04—Air heaters with forced circulation the air being in direct contact with the heating medium, e.g. electric heating element
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24H—FLUID HEATERS, e.g. WATER OR AIR HEATERS, HAVING HEAT-GENERATING MEANS, e.g. HEAT PUMPS, IN GENERAL
- F24H3/00—Air heaters
- F24H3/02—Air heaters with forced circulation
- F24H3/06—Air heaters with forced circulation the air being kept separate from the heating medium, e.g. using forced circulation of air over radiators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24H—FLUID HEATERS, e.g. WATER OR AIR HEATERS, HAVING HEAT-GENERATING MEANS, e.g. HEAT PUMPS, IN GENERAL
- F24H9/00—Details
- F24H9/18—Arrangement or mounting of grates or heating means
- F24H9/1854—Arrangement or mounting of grates or heating means for air heaters
- F24H9/1863—Arrangement or mounting of electric heating means
- F24H9/1872—PTC
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B1/00—Details of electric heating devices
- H05B1/02—Automatic switching arrangements specially adapted to apparatus ; Control of heating devices
- H05B1/0227—Applications
- H05B1/023—Industrial applications
- H05B1/0236—Industrial applications for vehicles
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B3/00—Ohmic-resistance heating
- H05B3/20—Heating elements having extended surface area substantially in a two-dimensional plane, e.g. plate-heater
- H05B3/22—Heating elements having extended surface area substantially in a two-dimensional plane, e.g. plate-heater non-flexible
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24H—FLUID HEATERS, e.g. WATER OR AIR HEATERS, HAVING HEAT-GENERATING MEANS, e.g. HEAT PUMPS, IN GENERAL
- F24H2250/00—Electrical heat generating means
- F24H2250/04—Positive or negative temperature coefficients, e.g. PTC, NTC
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B2203/00—Aspects relating to Ohmic resistive heating covered by group H05B3/00
- H05B2203/02—Heaters using heating elements having a positive temperature coefficient
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a heat medium heating device for heating a heat medium using a PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heater, and a vehicle air conditioner using the same.
- PTC Physical Temperature Coefficient
- a heat medium engine cooling water, brine, etc. supplied to the radiator for air heating in the vehicle
- the liquid is heated by a dedicated heating medium heating device.
- a heating medium heating device one to which a PTC heater as disclosed in Patent Documents 1 to 3 is applied is known.
- the PTC heater has a positive characteristic thermistor element, that is, a so-called PTC element as a heat generating element, and can be formed in a thin flat plate shape, so that there is an advantage that the heat medium heating device can be configured thin and compact.
- a PTC heater is interposed between a first heat medium flow box and a second heat medium flow box, each having a heat medium flow passage formed therein. In close contact with each other.
- the heat medium flows from the one end to the other end of the heat medium flow passage of the first heat medium flow box, and then U-turned to make a heat medium flow passage of the second heat medium flow box from one end to the other end, By flowing so as to make a U-turn from the other end to one end, it exchanges heat with both sides of the PTC heater and is heated.
- the substrate for controlling the PTC heater and the substrate accommodation unit for accommodating the heat generating electronic parts are in the form of a housing.
- the heat generated from the electronic component is cooled by heat exchange between the electronic component and the heat medium contained therein.
- an inlet for letting the heat medium flow into the heat medium flow passage of the first heat medium flow box and an outlet for letting the heat medium flow out of the heat medium flow passage of the second heat medium flow box are respectively Alternatively, it is formed on the side of the second heat medium distribution box.
- the inlet portion and the outlet portion are configured to be able to connect hose members constituting the heat medium circulation circuit.
- the thickness of the first or second heat medium distribution box has to be increased, which causes a problem that the compactness of the thickness (height) dimension of the heat medium heating device is impaired.
- the present invention has been made to solve such problems, and it reduces the pressure loss of the heat medium inside the heat medium heater, as well as increases the heat exchange efficiency, and at the same time, makes the heat medium heater compact. It is an object of the present invention to provide a heat medium heating device capable of achieving the same and an air conditioner for a vehicle using the same.
- the heat medium heating device comprises a PTC heater and a first heat medium circulation box in which a first heat medium flow passage is formed in close contact with one surface side of the PTC heater.
- a second heat medium flow box closely formed in close contact with the other surface side of the PTC heater and having a second heat medium flow passage formed therein, and joined to the first heat medium flow box;
- An inlet header space and an outlet header space for connecting the upstream ends and the downstream ends of the first and second heat medium flow passages, an inlet for flowing the heat medium into the inlet header space, and the outlet And an outlet for flowing out the heat medium from the header space.
- the heat medium flowing from the inlet portion into the inlet header space is the first heat medium flow passage formed in the first heat medium flow box, and the second heat medium flow passage. It is divided into the second heat medium flow passage formed in the box, flows in the same direction respectively and heats by exchanging heat with the PTC heater, then merges in the outlet header space and flows out from the outlet part and heat medium It flows to the radiator connected downstream of the heating device.
- the heat medium flows linearly and in the same direction through the first and second heat medium flow passages formed inside the heat medium heating device, and there is no U-turn flow, so Pressure loss can be reduced.
- the inlet header space and the outlet header space are respectively formed along the flow passage width direction of the first and second heat medium flow passages, and the first and second heat medium flow passages. It may be configured to extend over the entire width of the flow passage width of the heat medium flow passage.
- the heat medium flowing into the inlet header space from the inlet portion spreads quickly to the entire width of the first heat medium flow passage and the second heat medium flow passage without being reduced or diverted. Flow. Further, the heat medium having flowed through the first heat medium flow passage and the second heat medium flow passage is quickly collected in the outlet header space and flows out from the outlet portion. Therefore, the pressure loss of the heat medium can be further reduced.
- a protrusion extending in a direction intersecting the inflow direction of the heat medium from the inlet portion is formed at a position near the inlet portion on the inner surface of the inlet header space. Good.
- the heat medium when a part of the heat medium flowing from the inlet to the inlet header space abuts on the protrusion, the heat medium can easily flow into the relatively near side of the first and second heat medium flow passages. Therefore, the heat medium can be more evenly flowed over the entire area of the passage widths of the first and second heat medium flow passages, whereby the heat exchange efficiency can be enhanced.
- the inlet portion and the outlet portion are arranged such that their axial directions in plan view are substantially on the extension of the axial direction of the inlet header space and the outlet header space.
- the projection may be formed on the inner surface of the inlet header space on the side away from the first and second heat medium flow passages.
- the heat medium heating device can be made compact in the longitudinal direction.
- a part of the heat medium which flows from the inlet portion and tries to flow straight to the back side of the inlet header space as it strikes the projection portion the direction of the flow is changed, and the first and second heats are generated. It is guided to a range relatively near the medium flow passage. For this reason, the heat medium can be more uniformly flowed over the entire area of the passage widths of the first and second heat medium flow passages, whereby the heat exchange efficiency can be enhanced.
- any one of the first heat medium circulation box and the second heat medium circulation box is an electronic component storage box member for housing an electronic component for controlling the PTC heater.
- the inlet portion and the outlet portion may be provided in the electronic component storage box member.
- the electronic component housing box member having the largest thickness (height) dimension among the plurality of box constituent members constituting the first or second heat medium distribution box is provided with the inlet portion and the outlet portion. Provided. For this reason, even if a certain diameter is given to the inlet part and the outlet part in order to make it possible to connect a hose member of a predetermined thickness, the thickness of the first or second heat medium circulation box due to this There is no increase in size. Thus, the thickness (height) of the heat medium heating device can be made compact.
- an inflow temperature detection sensor detecting an inflow temperature of the heat medium flowing in the inlet header space, or an outflow temperature detection sensor detecting an outflow temperature of the heat medium flowing in the outlet header space At least one may be provided.
- the inflow temperature detection sensor and the outflow temperature detection sensor are provided in the inlet header space and the outlet header space disposed in the vicinity of the electronic component storage chamber. Therefore, it is possible to increase the temperature detection accuracy by these temperature detection sensors, and to store these temperature detection sensors together with other electronic components in the electronic component storage room, thereby bringing together the electronic components into one.
- the heat medium heating device can be made compact.
- At least one of the inflow temperature detection sensor or the outflow temperature detection sensor may be provided in the vicinity of a sloped wall surface on which the heat medium flows.
- the temperature detection sensor is provided at a portion where the temperature of the heat medium is favorably transmitted by the flow of the heat medium, the temperature detection accuracy of the heat medium can be enhanced. Since the portion to which the flow of the heat transfer medium strikes is sloped, the flow of the heat transfer medium does not have a large resistance.
- a vehicle air conditioner includes a blower for circulating external air or cabin air, a cooler provided downstream of the blower, and a radiator provided downstream of the cooler.
- the heat medium according to any one of the above-described heat medium heating devices can be circulated in the radiator, and the above-described actions and effects can be achieved.
- the heat medium heating device As described above, according to the heat medium heating device and the vehicle air conditioner using the same according to the present invention, the pressure loss of the heat medium in the heat medium heating device is reduced, and the heat exchange efficiency is enhanced. Thus, the heat medium heating device can be made compact.
- FIG. 5 is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the heat medium heating device along the line VV of FIG. 4;
- FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view of the heat medium heating device, taken along line VI-VI of FIG. 5;
- FIG. 7 is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the heat medium heating device, taken along line VII-VII of FIG. 5;
- FIG. 8 is a longitudinal sectional view of the heat medium heating device, taken along the line VIII-VIII in FIGS. 4 and 5;
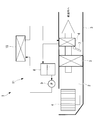
- FIG. 1 shows a schematic configuration diagram of a vehicle air conditioner according to the present embodiment.
- the vehicle air conditioner 1 is, for example, an air conditioner of a hybrid vehicle or an electric vehicle, and is a casing for forming an air flow path 2 for taking in the outside air or the air in the passenger compartment, controlling the temperature, and guiding it into the passenger compartment. It has three.
- outside air or cabin air is taken in sequentially from the upstream side to the downstream side of the air flow path 2, and the blower 4 that feeds it downstream and the air pumped by the blower 4 are cooled Adjusting a ratio of a cooler 5, a radiator 6 for heating air cooled by passing through the cooler 5, an amount of air passing through the radiator 6, and an amount of air flowing bypassing the radiator 6;
- An air mix damper 7 is provided to adjust the temperature of the air mixed downstream of the air mix damper 7.
- the downstream side of the casing 3 is connected to a plurality of blowout ports (not shown) for blowing out the temperature-controlled air into the vehicle interior via a blowout mode switching damper and a duct (not shown).
- the cooler 5 constitutes a refrigerant circuit together with a compressor, a condenser, and an expansion valve (not shown), and cools the air passing therethrough by evaporating the adiabatically expanded refrigerant by the expansion valve.
- the radiator 6 constitutes a heat medium circulation circuit 11 together with a tank 8, a pump 9, an engine (not shown) and a heat medium heating device 10 according to the present invention.
- a heat medium flowing through the heat medium circulation circuit 11 engine cooling water of a hybrid vehicle is used. In the case of an electrically powered vehicle without an engine, brine or the like is used.
- the heating medium circulation circuit 11 heats the engine cooling water by the heating medium heating device 10 when the temperature of the engine cooling water which is the heating medium does not rise so much at the time of hybrid operation or the like, and the heated engine cooling water is By circulating the heat medium circulation circuit 11, the air passing through the radiator 6 in the casing 3 is heated.
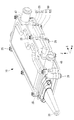
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view of the heating medium heating device 10
- FIG. 3 is a front view of the heating medium heating device 10
- FIG. 4 is a plan view of the heating medium heating device 10 taken along line IV-IV in FIG. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the thermal-medium heating apparatus 10 in alignment with the VV line
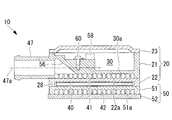
- the X, Y, and Z directions shown in FIG. 2 are defined as the “longitudinal direction”, the “short side direction”, and the “thickness direction” of the heating medium heating device 10, respectively.
- the heat medium heating device 10 is configured such that, for example, three box component members 21, 22 and 23 are overlapped to form a casing.
- a second heat medium distribution box 20 and two box component members 51 and 52 are stacked to form a casing, and a second heat medium distribution box 20 is joined to the lower surface of the first heat medium distribution box 20 in a fluid-tight manner.
- the heat medium flow box 50 and the PTC heater 40 interposed between the first and second heat medium flow boxes 20 and 50 are configured.
- the upper heat medium distribution box 22 similarly having a rectangular shape is liquid-tightly joined to the lower surface of the rectangular electronic component storage box 21 in plan view.
- the upper lid member 23 is liquid-tightly coated on the upper surface.
- the second heat medium distribution box 50 has a configuration in which the lower cover member 52 is liquid-tightly covered on the lower surface of the lower heat medium distribution box 51 having the same rectangular shape as the upper heat medium distribution box 22.
- These box component members 21, 22, 23, 51, 52 are formed of a heat conductive material such as an aluminum alloy.
- the upper cover member 23 is fastened to the upper surface of the electronic component storage box 21 by a plurality of fixing bolts 25, and the upper heat medium distribution box 22, the lower heat medium distribution box 51, and the lower cover member 52 are formed in plurality.
- the fixing bolt 26 is fastened to the lower surface of the electronic component storage box 21.
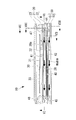
- the PTC heater 40 has a rectangular shape and a flat plate shape smaller than the upper heat medium flow box 22 and the lower heat medium flow box 51. As shown in FIGS. 5 and 7, the PTC heater accommodating chamber 28 is formed by sealing the tray-shaped concave portion formed on the lower surface of the upper heat medium distribution box 22 by the flat upper surface of the lower heat medium distribution box 51. The PTC heater 40 is accommodated here. The upper surface and the lower surface of the PTC heater 40 are in close contact with the lower surface of the upper heat medium distribution box 22 and the upper surface of the lower heat medium distribution box 51 via thin heat transfer sheets, heat transfer paste or the like.
- the inside of the electronic component storage box 21 is an electronic component storage chamber 30, and a control board (electronic component) 31 for controlling the PTC heater 40 is stored and installed therein.
- the control substrate 31 is a heat-generating electronic component 32 such as an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) or an FET (Field Effect Transistor), and other electronic components 33, and a control circuit, A power supply circuit or the like is incorporated.
- the bottom surface of the electronic component storage box 21 is a flat electronic component cooling wall portion 30a.
- the control substrate 31 is fixed at a position higher than the electronic component cooling wall portion 30 a by a fixing structure (not shown), and the heat generating electronic component 32 is disposed on the lower surface side of the control substrate 31. Heat is transferred to the electronic component cooling wall portion 30a through an insulating layer (not shown).
- a wire lead-out portion 35 is formed on one end surface of the electronic component housing box 21, and a wiring member 36 extending from the control substrate 31 is lead out from the wire lead-out portion 35.
- the tray-like concave portion formed on the lower surface of the electronic component storage box 21 constituting the first heat medium distribution box 20 is the flat upper surface of the upper heat medium distribution box 22.
- the first heat medium flow passage 41 is formed in the first heat medium flow box 20 by being hermetically sealed.
- a plurality of heat radiation fins 22a are formed on the upper surface of the upper heat medium circulation box 22 along the longitudinal direction (see FIGS. 6 to 8), and these heat radiation fins 22a form a first heat medium flow passage 41. Are divided into a plurality of parallel flow channels.
- the tray-shaped concave portion formed on the lower surface of the lower heat medium distribution box 51 constituting the second heat medium distribution box 50 is sealed by the flat upper surface of the lower lid member 52, whereby the second heat medium distribution is conducted.
- a second heat medium flow passage 42 is formed inside the box 50.
- a plurality of heat radiation fins 51a are formed along the longitudinal direction (see FIG. 7 and FIG. 8), and the second heat medium flow passage 42 is formed by these heat radiation fins 51a. Are divided into a plurality of parallel flow channels.
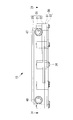
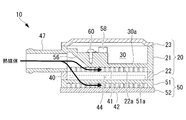
- the first heat medium flow passage 41 and the second heat medium flow passage 42 having the flat shape are formed so as to sandwich the PTC heater storage chamber 28 and the PTC heater 40 having the flat shape. ing. Then, as shown in FIG. 5, FIG. 6, and FIG. 8, the inlets connecting the upstream end portions and the downstream end portions of the first heat medium flow passage 41 and the second heat medium flow passage 42 respectively. A header space 44 and an outlet header space 45 are formed. These header spaces 44, 45 are formed at both ends in the longitudinal direction of the heat medium heating device 10 in plan view, as shown by a two-dot chain line in FIG. 6, and the first and second heat medium flows, respectively. It extends along the flow passage width direction (short direction) of the passages 41 and 42 and over the entire width of the flow passage width W of the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42.
- an inlet portion 47 and an outlet portion 48 are provided to enable connection of the heat medium circulation circuit 11 (see FIG. 1) through which the heat medium circulates in the inlet header space 44 and the outlet header space 45, respectively.
- the inlet portion 47 and the outlet portion 48 are in the form of a union joint to which a hose member constituting the heat medium circulation circuit 11 can be connected, and as shown in FIGS. Is formed integrally with the electronic component storage box 21 so as to overlap with the thickness (height) range of the electronic component storage chamber 30 formed inside the electronic component storage box 21 (see FIGS. 5, 7 and 8). .
- the axial directions 47 a and 48 a are substantially extensions of the axial directions 44 a and 45 a of the inlet header space 44 and the outlet header space 45 in plan view. It is arranged to be located. That is, in plan view, the inlet portion 47 is linearly connected to the inlet header space 44, and the outlet portion 48 is linearly connected to the outlet header space 45.
- first and second heat medium flow passages 41 are provided on the inner surface of the inlet header space 44 at a position near the inlet portion 47 and on the side away from the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42. , 42 are formed.
- the height of the projection 55 is set to, for example, about 10 to 40% of the inner diameter of the inlet 47 or the passage width of the inlet header space 44.
- the inlet portion 47 is positioned so that the axial direction 47 a thereof passes above the inlet header space 44.
- a sloped portion 56 which is a sloped wall surface is formed in the passage on the inner back side of the inlet portion 47, and the heat medium flowing from the inlet portion 47 strikes the sloped portion 56 and the flow is diverted downward, and the inlet header It is designed to flow into the space 44.
- the outlet portion 48 is also positioned such that its axial direction passes above the outlet header space 45, and a sloped portion (not shown) is formed in the passage on the inner back side of the outlet portion 48. It is done. The heat medium flows upward from the outlet header space 45 and strikes the slope, and the flow is diverted to flow out of the outlet 48.
- an inlet temperature detection sensor 58 is provided in the inlet header space 44, and an outlet temperature detection sensor 59 is provided in the outlet header space 45.
- the temperature detection sensors 58 and 59 are fixed by screws 60 in the vicinity of the above-described sloped portion 56, respectively.
- the inflow temperature detection sensor 58 detects the inflow temperature of the heat medium flowing in the inlet header space 44
- the outflow temperature detection sensor 59 detects the outflow temperature of the heat medium flowing in the outlet header space 45.
- the heat medium flowing through the heat medium circulation circuit 11 shown in FIG. 1 flows from the inlet portion 47 of the heat medium heating device 10 as shown in FIGS. Then, it is guided to the inlet header space 44. Thereafter, the heat medium is divided into the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42, and further divided into the flow paths between the radiation fins 22a and 51a of the respective heat medium flow passages 41 and 42 in the same direction ( It flows from the right side to the left side in FIGS. 5 and 6).
- the heat medium exchanges heat with the PTC heater 40 and is heated.
- the heat mediums having passed through the first and second heat medium flow passages 41, 42 join in the outlet header space 45, flow out from the outlet portion 48, and are thermally released connected to the downstream side of the heat medium heating device 10.
- the heat of the heated heat medium is supplied to the passenger compartment to heat the passenger compartment.
- the heat-generating electronic component 32 mounted on the control substrate 31 housed in the electronic component housing chamber 30 of the electronic component housing box 21 and in contact with the electronic component cooling wall portion 30a is the electronic component cooling wall portion 30a.
- the heat medium flowing through the first heat medium flow passage 41 the heat is cooled. Therefore, the heat medium is heated by the PTC heater 40 and also heated by the heat of the electronic component 32.
- the heat medium heating device 10 of this configuration the heat medium flows linearly and in the same direction through the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42 formed inside the heat medium heating device 10. Since there is no flow to turn, the pressure loss of the heat transfer medium can be reduced.
- the inlet header space 44 and the outlet header space 45 extend in the direction of the flow passage width W of the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42 and extend over the entire width of the flow passage W, respectively. There is. For this reason, the heat medium flowing from the inlet portion 47 into the inlet header space 44 is swiftly extended to the entire width of the first heat medium flow passage 41 and the second heat medium flow passage 42 without being reduced or diverted. It spreads and flows. Further, the heat medium having flowed through the first heat medium flow passage 41 and the second heat medium flow passage 42 is promptly collected in the outlet header space 45 and flows out from the outlet portion 48. Therefore, the pressure loss of the heat medium can be further reduced.
- the inlet portion 47 and the outlet portion 48 are arranged such that their axial directions 47a and 48a are located on a substantially extension of the axial directions 44a and 45a of the inlet header space 44 and the outlet header space 45 in plan view (see FIG. 6) It is done. For this reason, the inlet portion 47 and the outlet portion 48 do not protrude in the longitudinal direction from both end portions of the heat medium heating device 10, thereby achieving downsizing of the heat medium heating device 10 in the longitudinal direction. it can.
- the heat medium flowing from the inlet portion 47 tries to flow straight to the back of the inlet header space 44 as it is, but flows from the inlet portion 47 by the projection 55 formed on the inner surface of the inlet header space 44 A part of the heat transfer medium is diverted in flow and is guided to a range relatively near to the first and second heat transfer medium flow passages 41 and 42. Therefore, the heat medium can be more evenly flowed over the entire area of the flow channel width W of the first and second heat medium flow passages 41 and 42, whereby the heat medium is efficiently heat-exchanged with the PTC heater 40. Thus, the heat exchange efficiency of the heat medium heating device 10 can be enhanced.
- the electronic component storage chamber 30 is provided inside the three box components 21, 22, 23 constituting the first heat medium distribution box 20, and the thickness (height) is set.
- the inlet portion 47 and the outlet portion 48 are provided in the electronic component storage box 21 having the largest dimensions, and as shown in FIGS. 5, 7 and 8, the inlet portion 47 (outlet portion 48) is an electronic component storage chamber. Over 30 thickness (height) ranges.
- An inlet 47 and an outlet 48 are provided in the component housing box 21. For this reason, even if the inlet 47 and the outlet 48 are given a certain diameter so as to allow connection of a hose member of a predetermined thickness, the first or second heat medium distribution box 20, There is no increase in the 50 thickness dimension. Thereby, the thickness (height) dimension of the heat medium heating device 10 can be made compact.
- the heat medium heating device 10 also has an inflow temperature detection sensor 58 for detecting the inflow temperature of the heat medium flowing through the inlet header space 44 and an outflow temperature detection sensor 59 for detecting the outflow temperature of the heat medium flowing through the outlet header space 45.
- the inflow temperature detection sensor 58 and the outflow temperature detection sensor 59 are provided in the inlet header space 44 and the outlet header space 45 disposed in the vicinity of the electronic component storage chamber 30. Therefore, it is possible to increase the temperature detection accuracy by the temperature detection sensors 58 and 59, and to store the temperature detection sensors 58 and 59 in the electronic component storage chamber 30 together with other electronic components.
- the heat medium heating device can be made compact by combining the two into one.
- the inflow temperature detection sensor 58 and the outflow temperature detection sensor 59 are provided in the vicinity of the slope portion 56 to which the flow of the heat medium impinges. That is, since the temperature detection sensors 58 and 59 are provided at a portion where the temperature of the heat medium is favorably transmitted by the flow of the heat medium without stagnation, the temperature detection accuracy of the heat medium can be enhanced. Since the slope portion 56 to which the flow of the heat transfer medium is shaped like a slope, the flow of the heat transfer medium is not greatly resisted.
- the pressure loss of the heat medium in the heat medium heating device 10 is reduced and the heat is also reduced.
- the exchange efficiency can be enhanced and, at the same time, the heat medium heating device 10 can be made compact.
- the present invention is not limited to only the configuration of the above-described embodiment, and modifications and improvements can be made as appropriate. Embodiments in which such modifications and improvements are added are also included in the scope of the present invention. I assume. For example, the internal shape, layout, and the like of the heat medium heating device 10 according to the present invention may be changed as long as it does not deviate from the scope of the claims. Further, the configuration of the vehicle air conditioner 1 according to the present invention does not necessarily have to be the same as the configuration described in FIG. 1, and its component parts and layout can be changed as appropriate.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
- Resistance Heating (AREA)
Abstract
熱媒体加熱装置(10)は、PTCヒータ(40)と、このPTCヒータ(40)の一面側に密着して内部に第1の熱媒体流通路(41)が形成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックス(20)と、PTCヒータ(40)の他面側に密着して内部に第2の熱媒体流通路(42)が形成され、且つ第1の熱媒体流通ボックス(20)に接合される第2の熱媒体流通ボックス(50)と、前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路(41,42)の上流側端部同士および下流側端部同士をそれぞれ連通させるインレットヘッダ空間(44)およびアウトレットヘッダ空間(45)と、前記インレットヘッダ空間(44)に熱媒体を流入させるインレット部(47)と、前記アウトレットヘッダ空間(45)から前記熱媒体を流出させるアウトレット部(48)と、を備えて構成されている。
Description
本発明は、PTC(Positive Temperature Coefficient:正温度特性)ヒータを用いて熱媒体を加熱する熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置に関するものである。
エンジンの排熱を車内暖房に利用することが難しいハイブリッド車両や、エンジンを備えない電動車両等においては、車内にある空気加温用の放熱器に供給する熱媒体(エンジン冷却水やブライン等の液体)を専用の熱媒体加熱装置で加熱している。この熱媒体加熱装置として、特許文献1~3に開示されているようなPTCヒータを適用したものが知られている。PTCヒータは、正特性サーミスタ素子、所謂PTC素子を発熱要素としており、薄い平板状に形成できるため、熱媒体加熱装置を薄くコンパクトに構成できるという利点がある。
特許文献1~3に開示されている熱媒体加熱装置は、それぞれ内部に熱媒体流通路が形成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックスと第2の熱媒体流通ボックスとの間にPTCヒータを挟んで密着させたものである。熱媒体は、まず第1の熱媒体流通ボックスの熱媒体流通路を一端から他端まで流れた後、Uターンして第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの熱媒体流通路を一端から他端、そして他端から一端にUターンするように流れることにより、PTCヒータの両面と熱交換して加熱されるようになっている。
また、第1の熱媒体流通ボックスと第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの一方に、PTCヒータを制御する基板および発熱性のある電子部品(IGBT,FET等)を収容する基板収容部が筐体状に形成され、ここに収容された電子部品と熱媒体との間で熱交換させることにより、当該電子部品から発される熱が冷却されるようになっている。
さらに、第1の熱媒体流通ボックスの熱媒体流通路に熱媒体を流入させるインレット部と、第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの熱媒体流通路から熱媒体を流出させるアウトレット部とが、それぞれ第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの側面に形成されている。このインレット部とアウトレット部は、熱媒体循環回路を構成するホース部材を接続可能な形状となっている。
特許文献1~3に開示されている熱媒体加熱装置は、上述のように、その内部で熱媒体が2度Uターンするように流れる構造であるため、熱媒体の圧力損失が大きい。したがって、熱媒体の流量を確保するために、例えば熱媒体を熱媒体加熱装置に圧送するポンプを大型化しなければならないという課題があった。
また、第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの側面に形成されたインレット部とアウトレット部には、所定の太さのホース部材を接続可能にするべく、ある程度の径を付与する必要があり、このために第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの厚さを大きくせざるを得ず、これによって熱媒体加熱装置の厚さ(高さ)寸法のコンパクト性が損なわれてしまうという課題があった。
本発明は、このような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、熱媒体加熱装置の内部における熱媒体の圧力損失を低減させるとともに、熱交換効率を高め、併せて熱媒体加熱装置のコンパクト化を図ることのできる熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置を提供することを目的とする。
上記課題を解決するため、本発明は、以下の手段を採用する。
即ち、本発明の第1態様に係る熱媒体加熱装置は、PTCヒータと、前記PTCヒータの一面側に密着して内部に第1の熱媒体流通路が形成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックスと、前記PTCヒータの他面側に密着して内部に第2の熱媒体流通路が形成され、且つ前記第1の熱媒体流通ボックスに接合される第2の熱媒体流通ボックスと、前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の上流側端部同士および下流側端部同士をそれぞれ連通させるインレットヘッダ空間およびアウトレットヘッダ空間と、前記インレットヘッダ空間に熱媒体を流入させるインレット部と、前記アウトレットヘッダ空間から前記熱媒体を流出させるアウトレット部と、を備えたものである。
即ち、本発明の第1態様に係る熱媒体加熱装置は、PTCヒータと、前記PTCヒータの一面側に密着して内部に第1の熱媒体流通路が形成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックスと、前記PTCヒータの他面側に密着して内部に第2の熱媒体流通路が形成され、且つ前記第1の熱媒体流通ボックスに接合される第2の熱媒体流通ボックスと、前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の上流側端部同士および下流側端部同士をそれぞれ連通させるインレットヘッダ空間およびアウトレットヘッダ空間と、前記インレットヘッダ空間に熱媒体を流入させるインレット部と、前記アウトレットヘッダ空間から前記熱媒体を流出させるアウトレット部と、を備えたものである。
上記構成の熱媒体加熱装置によれば、インレット部からインレットヘッダ空間に流入した熱媒体は、第1の熱媒体流通ボックスに形成された第1の熱媒体流通路と、第2の熱媒体流通ボックスに形成された第2の熱媒体流通路とに分流し、それぞれ同一方向に流れてPTCヒータと熱交換して加熱された後、アウトレットヘッダ空間で合流し、アウトレット部から流出して熱媒体加熱装置の下流側に接続された放熱器に流れる。
本構成によれば、熱媒体加熱装置の内部に形成された第1および第2の熱媒体流通路を熱媒体が直線的且つ同一方向に流れ、Uターンする流れが存在しないため、熱媒体の圧力損失を低減させることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記インレットヘッダ空間および前記アウトレットヘッダ空間は、それぞれ前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の流路幅方向に沿って形成され、且つ前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の流路幅の全幅に亘って延在する構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、インレット部からインレットヘッダ空間に流入した熱媒体は、縮流や変向されることなく、速やかに第1の熱媒体流通路と第2の熱媒体流通路の全幅まで広がって流れる。また、第1の熱媒体流通路と第2の熱媒体流通路を流れ終わった熱媒体は、速やかにアウトレットヘッダ空間に纏められてアウトレット部から流出する。このため、熱媒体の圧力損失をより低減させることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記インレットヘッダ空間の内面の、前記インレット部寄りの位置に、前記インレット部からの前記熱媒体の流入方向と交わる向きに延びる突起部が形成された構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、インレット部からインレットヘッダ空間に流れる熱媒体の一部が突起部に当たることにより、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の比較的手前側の範囲に流れ込みやすくなる。このため、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の通路幅の全域に亘ってより均等に熱媒体を流し込むことができ、これによって熱交換効率を高めることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記インレット部および前記アウトレット部は、平面視でそれぞれの軸線方向が前記インレットヘッダ空間および前記アウトレットヘッダ空間の軸線方向の略延長線上に位置するように配置されるとともに、前記突起部は、前記インレットヘッダ空間の内面における前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路に対して離反する側に形成された構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、インレット部およびアウトレット部が熱媒体加熱装置の両端部から長手方向に向かって突出しない構成となるため、熱媒体加熱装置の長手方向のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
また、インレット部から流入し、そのまま直線的にインレットヘッダ空間の奥側に流れようとする熱媒体の一部が突起部に当たることにより、その流れの向きを変えられて第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の比較的手前側の範囲に誘導される。このため、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の通路幅の全域に亘って熱媒体をより均等に流し込むことができ、これによって熱交換効率を高めることができる。
また、インレット部から流入し、そのまま直線的にインレットヘッダ空間の奥側に流れようとする熱媒体の一部が突起部に当たることにより、その流れの向きを変えられて第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の比較的手前側の範囲に誘導される。このため、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の通路幅の全域に亘って熱媒体をより均等に流し込むことができ、これによって熱交換効率を高めることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記第1の熱媒体流通ボックスまたは前記第2の熱媒体流通ボックスのいずれか一方は、前記PTCヒータの制御用の電子部品を収容する電子部品収容ボックス部材を備え、前記インレット部および前記アウトレット部は、前記電子部品収容ボックス部材に設けられている構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックスを構成する複数のボックス構成部材のうち、最も厚さ(高さ)寸法の大きな電子部品収容ボックス部材にインレット部とアウトレット部とが設けられる。このため、所定の太さのホース部材を接続可能にするべく、インレット部およびアウトレット部にある程度の径を付与しても、これに起因して第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックスの厚さ寸法が大きくなることはない。これにより、熱媒体加熱装置の厚さ(高さ)寸法のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記インレットヘッダ空間を流れる前記熱媒体の流入温度を検知する流入温度検知センサ、または前記アウトレットヘッダ空間を流れる前記熱媒体の流出温度を検知する流出温度検知センサの少なくとも一方を備えた構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、電子部品収容室の近傍に配置されたインレットヘッダ空間およびアウトレットヘッダ空間に流入温度検知センサおよび流出温度検知センサが設けられる。このため、これらの温度検知センサによる温度検知精度を高めるとともに、これらの温度検知センサを電子部品収容室に他の電子部品と一緒に収容することができ、電子部品類を1つに纏めることによって熱媒体加熱装置のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
前記構成の熱媒体加熱装置において、前記流入温度検知センサまたは前記流出温度検知センサの少なくとも一方は、前記熱媒体の流れが当たる斜面状の壁面の近傍に設けられた構成としてもよい。
本構成によれば、熱媒体の流れが当たることによって該熱媒体の温度が良好に伝達なされる部位に温度検知センサが設けられるため、熱媒体の温度検知精度を高めることができる。熱媒体の流れが当たる部位は斜面状であるため、熱媒体の流れに大きな抵抗が付与されることはない。
本発明の第2態様に係る車両用空調装置は、外気または車室内空気循環させるブロアと、該ブロアの下流側に設けられる冷却器と、該冷却器の下流側に設けられる放熱器と、を備え、前記放熱器に、前記のいずれかに記載の熱媒体加熱装置により加熱された前記熱媒体が循環可能に構成されたものであり、これによって前述の作用・効果を奏することができる。
以上のように、本発明に係る熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置によれば、熱媒体加熱装置の内部における熱媒体の圧力損失を低減させるとともに、熱交換効率を高め、併せて熱媒体加熱装置のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
以下、本発明の実施形態について図面を参照しながら説明する。
図1には、本実施形態に係る車両用空調装置の概略構成図が示されている。この車両用空調装置1は、例えばハイブリッド車両、あるいは電動車両の空調装置であり、外気または車室内空気を取り込んで温調し、それを車室内へと導く空気流路2を形成するためのケーシング3を備えている。
図1には、本実施形態に係る車両用空調装置の概略構成図が示されている。この車両用空調装置1は、例えばハイブリッド車両、あるいは電動車両の空調装置であり、外気または車室内空気を取り込んで温調し、それを車室内へと導く空気流路2を形成するためのケーシング3を備えている。
ケーシング3の内部には、空気流路2の上流側から下流側にかけて順次、外気または車室内空気を吸い込み、それを下流側へと圧送するブロア4と、ブロア4により圧送される空気を冷却する冷却器5と、冷却器5を通過して冷却された空気を加熱する放熱器6と、放熱器6を通過する空気量と放熱器6をバイパスして流れる空気量との割合を調整し、その下流側でミックスされる空気の温度を調節するエアミックスダンパ7と、が設置される。
ケーシング3の下流側は、図示省略の吹き出しモード切替ダンパおよびダクトを介して温調された空気を車室内に吹き出す、図示省略の複数の吹き出し口へと接続される。冷却器5は、図示省略の圧縮機、凝縮器、膨張弁と共に冷媒回路を構成し、膨張弁で断熱膨張された冷媒を蒸発させることにより、そこを通過する空気を冷却するものである。
放熱器6は、タンク8、ポンプ9、図示省略のエンジンおよび本発明に係る熱媒体加熱装置10と共に熱媒体循環回路11を構成している。この熱媒体循環回路11を流れる熱媒体としては、ハイブリッド車両のエンジン冷却水が利用されている。エンジンを備えない電動車両の場合はブライン等が用いられる。熱媒体循環回路11は、ハイブリッド運転時等、熱媒体であるエンジン冷却水の温度がさほど上昇しない時に、熱媒体加熱装置10によってエンジン冷却水を加熱し、この加熱したエンジン冷却水をポンプ9により熱媒体循環回路11に循環させることによって、ケーシング3内にて放熱器6を通過する空気を加温するものである。
図2は熱媒体加熱装置10の斜視図、図3は熱媒体加熱装置10の正面図、図4は図3のIV-IV矢視による熱媒体加熱装置10の平面図であり、図5は図4のV-V線に沿う熱媒体加熱装置10の縦断面図である。なお、以下の説明では、図2中に示すX,Y,Z方向が、それぞれ熱媒体加熱装置10の「長手方向」、「短手方向」、「厚さ方向」と定義付けられている。
図2~図5、および図6~図8にも示すように、この熱媒体加熱装置10は、例えば3つのボックス構成部材21,22,23が重ね合わせられて筐体状に構成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20と、2つのボックス構成部材51,52が重ね合わせられて筐体状に構成され、かつ第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20の下面に液密的に接合された第2の熱媒体流通ボックス50と、これら第1および第2の熱媒体流通ボックス20,50の間に挟装されたPTCヒータ40とを備えて構成されている。
第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20は、平面視で長方形状の電子部品収容ボックス21の下面に、同じく長方形状を有する上部熱媒体流通ボックス22が液密的に接合され、電子部品収容ボックス21の上面に上部蓋部材23が液密的に被装された構成である。また、第2の熱媒体流通ボックス50は、上部熱媒体流通ボックス22と同じく長方形状を有する下部熱媒体流通ボックス51の下面に下部蓋部材52が液密的に被装された構成である。これらのボックス構成部材21,22,23,51,52は、アルミニウム合金等の熱伝導性材料により形成されている。
図2に示すように、上部蓋部材23は複数の固定ボルト25で電子部品収容ボックス21の上面に締結され、上部熱媒体流通ボックス22と下部熱媒体流通ボックス51と下部蓋部材52は複数の固定ボルト26で電子部品収容ボックス21の下面に締結されている。これにより、各ボックス構成部材21,22,23,51,52が一体化されている。各ボックス構成部材21,22,23,51,52の接合面には液状ガスケットが塗布されてシールされている。
PTCヒータ40は、上部熱媒体流通ボックス22および下部熱媒体流通ボックス51よりも小さい長方形状かつ平板形状を有している。図5および図7に示すように、上部熱媒体流通ボックス22の下面に形成されたトレー状の凹部が下部熱媒体流通ボックス51の平坦な上面によって密閉されることでPTCヒータ収容室28が形成され、ここにPTCヒータ40が収容されている。PTCヒータ40の上面と下面は、それぞれ薄い熱伝達シートや熱伝達ペースト等を介して上部熱媒体流通ボックス22の下面と下部熱媒体流通ボックス51の上面とに熱伝達可能に密着している。
図5、図7、図8に示すように、電子部品収容ボックス21の内部は電子部品収容室30とされ、ここにPTCヒータ40を制御する制御基板(電子部品)31が格納設置される。制御基板31は、IGBT(Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor:絶縁ゲート型バイポーラトランジスタ)や、FET(Field effect transistor:電界効果トランジスター)といった発熱性のある電子部品32や、他の電子部品33、および制御回路、電源回路等が組み込まれたものである。
電子部品収容ボックス21(電子部品収容室30)の底面は平坦な電子部品冷却壁部30aとなっている。図5に示すように、制御基板31は、図示しない固定構造によって電子部品冷却壁部30aよりも高い位置に固定され、発熱性のある電子部品32は制御基板31の下面側に配設され、図示しない絶縁層を介して電子部品冷却壁部30aに熱伝達可能に接触している。図2に示すように、電子部品収容ボックス21の一端面には配線導出部35が形成され、制御基板31から延出する配線部材36が、この配線導出部35から外部に導出される。
図5、図7、図8に示すように、第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20を構成する電子部品収容ボックス21の下面に形成されたトレー状の凹部が上部熱媒体流通ボックス22の平坦な上面によって密閉されることで第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20の内部に第1の熱媒体流通路41が形成されている。上部熱媒体流通ボックス22の上面には、その長手方向に沿って複数の放熱フィン22aが形成されており(図6~図8参照)、これらの放熱フィン22aによって第1の熱媒体流通路41が複数の平行する流路に区切られている。
また、第2の熱媒体流通ボックス50を構成する下部熱媒体流通ボックス51の下面に形成されたトレー状の凹部が下部蓋部材52の平坦な上面によって密閉されることで第2の熱媒体流通ボックス50の内部に第2の熱媒体流通路42が形成されている。下部熱媒体流通ボックス51の下面には、その長手方向に沿って複数の放熱フィン51aが形成されており(図7、図8参照)、これらの放熱フィン51aによって第2の熱媒体流通路42が複数の平行する流路に区切られている。
上記のように、平坦な形状をしたPTCヒータ収容室28およびPTCヒータ40を挟むようにして、同じく平坦な形状をした第1の熱媒体流通路41と第2の熱媒体流通路42とが形成されている。そして、図5、図6、および図8に示すように、第1の熱媒体流通路41と第2の熱媒体流通路42の上流側端部同士および下流側端部同士をそれぞれ連通させるインレットヘッダ空間44およびアウトレットヘッダ空間45が形成されている。これらのヘッダ空間44,45は、図6中に二点鎖線で示すように、平面視で熱媒体加熱装置10の長手方向両端部に形成されており、それぞれ第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42の流路幅方向(短手方向)に沿い、且つ第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42の流路幅Wの全幅に亘って延在している。
さらに、インレットヘッダ空間44とアウトレットヘッダ空間45とに、それぞれ熱媒体が循環する熱媒体循環回路11(図1参照)を接続可能にするインレット部47およびアウトレット部48が設けられている。これらのインレット部47およびアウトレット部48は、熱媒体循環回路11を構成するホース部材を接続可能なユニオンジョイント状であり、図2および図7、図8等に示すように、電子部品収容ボックス21に一体的に形成され、電子部品収容ボックス21の内部に形成された電子部品収容室30の厚さ(高さ)範囲と重なるように設けられている(図5、図7、図8参照)。
また、図6に示すように、インレット部47およびアウトレット部48は、平面視で、それぞれの軸線方向47a,48aがインレットヘッダ空間44およびアウトレットヘッダ空間45の軸線方向44a,45aの略延長線上に位置するように配置されている。つまり、平面視で、インレット部47はインレットヘッダ空間44に直線的に繋がり、アウトレット部48はアウトレットヘッダ空間45に直線的に繋がっている。
さらに、インレットヘッダ空間44の内面の、インレット部47寄りの位置、且つ第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42に対して離反する側に、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42に向かって延びる突起部55が形成されている。この突起部55の高さは、例えばインレット部47の内径、あるいはインレットヘッダ空間44の通路幅の10~40%程度に設定されている。
図8に示すように、側面視でインレット部47は、その軸線方向47aがインレットヘッダ空間44の上方を通過するように位置付けられている。インレット部47の内部奥側の通路内には斜面状の壁面である斜面部56が形成されており、インレット部47から流入した熱媒体は斜面部56に当たって下方に流れを変向され、インレットヘッダ空間44に流入するようになっている。
図示しないが、アウトレット部48も同様に、その軸線方向がアウトレットヘッダ空間45の上方を通過するように位置付けられており、アウトレット部48の内部奥側の通路内に斜面部(非図示)が形成されている。熱媒体はアウトレットヘッダ空間45から上方に流れて斜面部に当たり、その流れの向きを変えられてアウトレット部48から流出する。
図4および図7、図8に示すように、インレットヘッダ空間44には流入温度検知センサ58が設けられ、アウトレットヘッダ空間45には流出温度検知センサ59が設けられている。これらの温度検知センサ58,59は、それぞれビス60で前述の斜面部56の近傍に固定されている。流入温度検知センサ58はインレットヘッダ空間44を流れる熱媒体の流入温度を検知し、流出温度検知センサ59はアウトレットヘッダ空間45を流れる熱媒体の流出温度を検知するセンサである。
以上のように構成された熱媒体加熱装置10において、図1に示す熱媒体循環回路11を流れる熱媒体は、図6および図8に示すように、熱媒体加熱装置10のインレット部47から流入してインレットヘッダ空間44に導かれる。その後、熱媒体は第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42に分流し、さらにそれぞれの熱媒体流通路41,42の放熱フィン22a,51aの間の流路に分流して同一方向(図5および図6中で右側から左側)に流れる。
この時に熱媒体はPTCヒータ40と熱交換して加熱される。このように第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42を通過した熱媒体はアウトレットヘッダ空間45で合流し、アウトレット部48から流出して熱媒体加熱装置10の下流側に接続された放熱器6に流れ、加熱された熱媒体の熱が車室内の暖房に供される。
一方、電子部品収容ボックス21の電子部品収容室30に収容された制御基板31に搭載されて電子部品冷却壁部30aに接している発熱性のある電子部品32は、電子部品冷却壁部30aを介して第1の熱媒体流通路41を流れる熱媒体と熱交換することにより、その熱を冷却される。したがって、熱媒体は、PTCヒータ40によって加熱されると同時に、電子部品32の熱によっても加熱される。
本構成の熱媒体加熱装置10によれば、熱媒体加熱装置10の内部に形成された第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42を、熱媒体が直線的且つ同一方向に流れ、Uターンする流れが存在しないため、熱媒体の圧力損失を低減させることができる。
インレットヘッダ空間44およびアウトレットヘッダ空間45は、それぞれ第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42の流路幅Wの方向に沿い、且つその流路幅Wの全幅に亘って延在している。このため、インレット部47からインレットヘッダ空間44に流入した熱媒体は、縮流や変向されることなく、速やかに第1の熱媒体流通路41と第2の熱媒体流通路42の全幅まで広がって流れる。また、第1の熱媒体流通路41と第2の熱媒体流通路42を流れ終わった熱媒体は、速やかにアウトレットヘッダ空間45に纏められてアウトレット部48から流出する。このため、熱媒体の圧力損失をより低減させることができる。
インレット部47およびアウトレット部48は、平面視(図6参照)でそれぞれの軸線方向47a,48aがインレットヘッダ空間44およびアウトレットヘッダ空間45の軸線方向44a,45aの略延長線上に位置するように配置されている。このため、インレット部47およびアウトレット部48が熱媒体加熱装置10の両端部から長手方向に向かって突出しない構成となっており、これによって熱媒体加熱装置10の長手方向のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
また、インレット部47から流入した熱媒体は、そのまま直線的にインレットヘッダ空間44の奥まで流れようとするが、インレットヘッダ空間44の内面に形成された突起部55により、インレット部47から流入した熱媒体の一部が流れの向きを変えられて第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42の比較的手前側の範囲に誘導される。このため、第1および第2の熱媒体流通路41,42の流路幅Wの全域に亘ってより均等に熱媒体を流し込むことができ、これによって熱媒体をPTCヒータ40と効率良く熱交換させて熱媒体加熱装置10の熱交換効率を高めることができる。
さらに、この熱媒体加熱装置10では、第1の熱媒体流通ボックス20を構成する3つのボックス構成部材21,22,23のうち、内部に電子部品収容室30が設けられて厚み(高さ)寸法の最も大きな電子部品収容ボックス21にインレット部47とアウトレット部48とが設けられており、図5、図7、図8に示すように、インレット部47(アウトレット部48)が電子部品収容室30の厚さ(高さ)範囲に重なっている。
本構成によれば、第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックス20,50を構成する複数のボックス構成部材21,22,23,51,52のうち、最も厚さ(高さ)寸法の大きな電子部品収容ボックス21にインレット部47とアウトレット部48とが設けられる。このため、所定の太さのホース部材を接続可能にするべくインレット部47およびアウトレット部48にある程度の径を付与しても、これに起因して第1または第2の熱媒体流通ボックス20,50の厚さ寸法が大きくなることはない。これにより、熱媒体加熱装置10の厚さ(高さ)寸法のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
また、この熱媒体加熱装置10は、インレットヘッダ空間44を流れる熱媒体の流入温度を検知する流入温度検知センサ58と、アウトレットヘッダ空間45を流れる熱媒体の流出温度を検知する流出温度検知センサ59を備えている。即ち、電子部品収容室30の近傍に配置されたインレットヘッダ空間44およびアウトレットヘッダ空間45に流入温度検知センサ58および流出温度検知センサ59が設けられている。このため、これらの温度検知センサ58,59による温度検知精度を高めるとともに、これらの温度検知センサ58,59を電子部品収容室30に他の電子部品と一緒に収容することができ、電子部品類を1つに纏めることによって熱媒体加熱装置のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
流入温度検知センサ58および流出温度検知センサ59は、熱媒体の流れが当たる斜面部56の近傍に設けられている。即ち、熱媒体の流れが澱みなく当たることによって該熱媒体の温度が良好に伝達なされる部位にこれらの温度検知センサ58,59が設けられるため、熱媒体の温度検知精度を高めることができる。熱媒体の流れが当たる斜面部56は斜面状であるため、熱媒体の流れに大きな抵抗が付与されることはない。
以上説明したように、本実施形態に係る熱媒体加熱装置10、およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置1によれば、熱媒体加熱装置10の内部における熱媒体の圧力損失を低減させるとともに、熱交換効率を高め、併せて熱媒体加熱装置10のコンパクト化を図ることができる。
なお、本発明は上記実施形態の構成のみに限定されるものではなく、適宜変更や改良を加えることができ、このように変更や改良を加えた実施形態も本発明の権利範囲に含まれるものとする。
例えば、本発明に係る熱媒体加熱装置10の内部形状やレイアウト等は、特許請求の範囲を逸脱しない範囲であれば変更してもよい。
また、本発明に係る車両用空調装置1の構成は、必ずしも図1に記載された構成の通りである必要はなく、その構成部品やレイアウトは適宜変更することができる。
例えば、本発明に係る熱媒体加熱装置10の内部形状やレイアウト等は、特許請求の範囲を逸脱しない範囲であれば変更してもよい。
また、本発明に係る車両用空調装置1の構成は、必ずしも図1に記載された構成の通りである必要はなく、その構成部品やレイアウトは適宜変更することができる。
1 車両用空調装置
4 ブロア
5 冷却器
6 放熱器
10 熱媒体加熱装置
11 熱媒体循環回路
20 第1の熱媒体流通ボックス
21 電子部品収容ボックス
31 制御基板(電子部品)
32 電子部品
33 電子部品
40 PTCヒータ
41 第1の熱媒体流通路
42 第2の熱媒体流通路
44 インレットヘッダ空間
45 アウトレットヘッダ空間
47 インレット部
48 アウトレット部
50 第2の熱媒体流通ボックス
55 突起部
56 斜面部(斜面状の壁面)
58 流入温度検知センサ
59 流出温度検知センサ
W 熱媒体流通路の流路幅
4 ブロア
5 冷却器
6 放熱器
10 熱媒体加熱装置
11 熱媒体循環回路
20 第1の熱媒体流通ボックス
21 電子部品収容ボックス
31 制御基板(電子部品)
32 電子部品
33 電子部品
40 PTCヒータ
41 第1の熱媒体流通路
42 第2の熱媒体流通路
44 インレットヘッダ空間
45 アウトレットヘッダ空間
47 インレット部
48 アウトレット部
50 第2の熱媒体流通ボックス
55 突起部
56 斜面部(斜面状の壁面)
58 流入温度検知センサ
59 流出温度検知センサ
W 熱媒体流通路の流路幅
Claims (8)
- PTCヒータと、
前記PTCヒータの一面側に密着して内部に第1の熱媒体流通路が形成された第1の熱媒体流通ボックスと、
前記PTCヒータの他面側に密着して内部に第2の熱媒体流通路が形成され、且つ前記第1の熱媒体流通ボックスに接合される第2の熱媒体流通ボックスと、
前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の上流側端部同士および下流側端部同士をそれぞれ連通させるインレットヘッダ空間およびアウトレットヘッダ空間と、
前記インレットヘッダ空間に熱媒体を流入させるインレット部と、
前記アウトレットヘッダ空間から前記熱媒体を流出させるアウトレット部と、
を備えた熱媒体加熱装置。 - 前記インレットヘッダ空間および前記アウトレットヘッダ空間は、それぞれ前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の流路幅方向に沿って形成され、且つ前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路の流路幅の全幅に亘って延在している請求項1に記載の熱媒体加熱装置。
- 前記インレットヘッダ空間の内面の、前記インレット部寄りの位置に、前記インレット部からの前記熱媒体の流入方向と交わる向きに延びる突起部が形成された請求項1または2に記載の熱媒体加熱装置。
- 前記インレット部および前記アウトレット部は、平面視でそれぞれの軸線方向が前記インレットヘッダ空間および前記アウトレットヘッダ空間の軸線方向の略延長線上に位置するように配置されるとともに、
前記突起部は、前記インレットヘッダ空間の内面における前記第1および第2の熱媒体流通路に対して離反する側に形成されている請求項3に記載の熱媒体加熱装置。 - 前記第1の熱媒体流通ボックスまたは前記第2の熱媒体流通ボックスのいずれか一方は、前記PTCヒータの制御用の電子部品を収容する電子部品収容ボックス部材を備え、
前記インレット部および前記アウトレット部は、前記電子部品収容ボックス部材に設けられている請求項1から4のいずれかに記載の熱媒体加熱装置。 - 前記インレットヘッダ空間を流れる前記熱媒体の流入温度を検知する流入温度検知センサ、または前記アウトレットヘッダ空間を流れる前記熱媒体の流出温度を検知する流出温度検知センサの少なくとも一方を備えた請求項5に記載の熱媒体加熱装置。
- 前記流入温度検知センサまたは前記流出温度検知センサの少なくとも一方は、前記熱媒体の流れが当たる斜面状の壁面の近傍に設けられた請求項6に記載の熱媒体加熱装置。
- 外気または車室内空気循環させるブロアと、該ブロアの下流側に設けられる冷却器と、該冷却器の下流側に設けられる放熱器と、を備え、
前記放熱器に、請求項1から7のいずれかに記載の熱媒体加熱装置により加熱された前記熱媒体が循環可能に構成された車両用空調装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201680084057.1A CN109311368A (zh) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-10-21 | 热介质加热装置及使用其的车辆用空调装置 |
| US16/087,482 US20190135078A1 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-10-21 | Heating medium heating device and vehicle air conditioner using same |
| DE112016006954.5T DE112016006954T5 (de) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-10-21 | Heizmedium-Heizvorrichtung und Fahrzeugklimaanlage, die diese verwendet |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-116317 | 2016-06-10 | ||
| JP2016116317A JP6698434B2 (ja) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-06-10 | 熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017212665A1 true WO2017212665A1 (ja) | 2017-12-14 |
Family
ID=60577684
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/081340 WO2017212665A1 (ja) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-10-21 | 熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20190135078A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6698434B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN109311368A (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112016006954T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017212665A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3722124B1 (en) * | 2019-04-08 | 2023-12-13 | Borgwarner Emissions Systems Spain, S.L.U. | Heating device for use thereof in a vehicle |
| CN112895846B (zh) * | 2021-02-02 | 2022-04-26 | 镇江海姆霍兹传热传动系统有限公司 | 电动车辆、电加热器及其电加热腔总成 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011152907A (ja) * | 2010-01-28 | 2011-08-11 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 電気式加熱装置及び車両用空気調和装置 |
| JP2012131433A (ja) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-07-12 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置 |
| JP2013056641A (ja) * | 2011-09-09 | 2013-03-28 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 |
| JP2014129090A (ja) * | 2014-02-10 | 2014-07-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5535740B2 (ja) | 1972-04-25 | 1980-09-16 | ||
| JPS5535742B2 (ja) | 1972-09-30 | 1980-09-16 | ||
| KR101082474B1 (ko) * | 2004-12-28 | 2011-11-11 | 한라공조주식회사 | 열교환기 |
| US20080023185A1 (en) * | 2006-07-25 | 2008-01-31 | Henry Earl Beamer | Heat exchanger assembly |
| JP4981386B2 (ja) | 2006-08-30 | 2012-07-18 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 |
| JP2013180690A (ja) * | 2012-03-02 | 2013-09-12 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 |
-
2016
- 2016-06-10 JP JP2016116317A patent/JP6698434B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-10-21 DE DE112016006954.5T patent/DE112016006954T5/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2016-10-21 WO PCT/JP2016/081340 patent/WO2017212665A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2016-10-21 US US16/087,482 patent/US20190135078A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2016-10-21 CN CN201680084057.1A patent/CN109311368A/zh active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011152907A (ja) * | 2010-01-28 | 2011-08-11 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 電気式加熱装置及び車両用空気調和装置 |
| JP2012131433A (ja) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-07-12 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置 |
| JP2013056641A (ja) * | 2011-09-09 | 2013-03-28 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 |
| JP2014129090A (ja) * | 2014-02-10 | 2014-07-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109311368A (zh) | 2019-02-05 |
| DE112016006954T5 (de) | 2019-02-21 |
| JP2017218117A (ja) | 2017-12-14 |
| JP6698434B2 (ja) | 2020-05-27 |
| US20190135078A1 (en) | 2019-05-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5535742B2 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP5535740B2 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP5979892B2 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| US20140050465A1 (en) | Heat medium heating device and vehicular air-conditioning device including the same | |
| WO2013157357A1 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| US9186956B2 (en) | Heat medium heating unit and vehicle air conditioning apparatus provided with the same | |
| US20120237192A1 (en) | Heat medium heating apparatus and vehicular air-conditioning system including the same | |
| US20140037277A1 (en) | Heat medium heating device and vehicular air-conditioning device including the same | |
| JP6675937B2 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2014129090A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP5951205B2 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2012017031A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを用いた車両用空気調和装置 | |
| WO2017212665A1 (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびこれを用いた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2013060098A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2013075616A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2013163440A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2013159134A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2012081803A (ja) | 熱媒体加熱装置およびそれを備えた車両用空調装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16904698 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16904698 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |