WO2017154484A1 - 暗号通信システム、暗号通信方法、セキュリティチップ、通信装置およびその制御方法と制御プログラム - Google Patents
暗号通信システム、暗号通信方法、セキュリティチップ、通信装置およびその制御方法と制御プログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017154484A1 WO2017154484A1 PCT/JP2017/005311 JP2017005311W WO2017154484A1 WO 2017154484 A1 WO2017154484 A1 WO 2017154484A1 JP 2017005311 W JP2017005311 W JP 2017005311W WO 2017154484 A1 WO2017154484 A1 WO 2017154484A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- common key
- security chip
- encryption
- decryption
- key
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0819—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s)
- H04L9/0825—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s) using asymmetric-key encryption or public key infrastructure [PKI], e.g. key signature or public key certificates
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09C—CIPHERING OR DECIPHERING APPARATUS FOR CRYPTOGRAPHIC OR OTHER PURPOSES INVOLVING THE NEED FOR SECRECY
- G09C1/00—Apparatus or methods whereby a given sequence of signs, e.g. an intelligible text, is transformed into an unintelligible sequence of signs by transposing the signs or groups of signs or by replacing them by others according to a predetermined system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09C—CIPHERING OR DECIPHERING APPARATUS FOR CRYPTOGRAPHIC OR OTHER PURPOSES INVOLVING THE NEED FOR SECRECY
- G09C5/00—Ciphering apparatus or methods not provided for in the preceding groups, e.g. involving the concealment or deformation of graphic data such as designs, written or printed messages
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/04—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks
- H04L63/0428—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/04—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks
- H04L63/0428—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload
- H04L63/0435—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload wherein the sending and receiving network entities apply symmetric encryption, i.e. same key used for encryption and decryption
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H04L63/061—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network for key exchange, e.g. in peer-to-peer networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H04L63/062—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network for key distribution, e.g. centrally by trusted party
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/06—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols the encryption apparatus using shift registers or memories for block-wise or stream coding, e.g. DES systems or RC4; Hash functions; Pseudorandom sequence generators
- H04L9/0618—Block ciphers, i.e. encrypting groups of characters of a plain text message using fixed encryption transformation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/06—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols the encryption apparatus using shift registers or memories for block-wise or stream coding, e.g. DES systems or RC4; Hash functions; Pseudorandom sequence generators
- H04L9/0618—Block ciphers, i.e. encrypting groups of characters of a plain text message using fixed encryption transformation
- H04L9/0637—Modes of operation, e.g. cipher block chaining [CBC], electronic codebook [ECB] or Galois/counter mode [GCM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0838—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these
- H04L9/0841—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these involving Diffie-Hellman or related key agreement protocols
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0861—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0877—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords using additional device, e.g. trusted platform module [TPM], smartcard, USB or hardware security module [HSM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2209/00—Additional information or applications relating to cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communication H04L9/00
- H04L2209/12—Details relating to cryptographic hardware or logic circuitry
- H04L2209/127—Trusted platform modules [TPM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2463/00—Additional details relating to network architectures or network communication protocols for network security covered by H04L63/00
- H04L2463/061—Additional details relating to network architectures or network communication protocols for network security covered by H04L63/00 applying further key derivation, e.g. deriving traffic keys from a pair-wise master key
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2463/00—Additional details relating to network architectures or network communication protocols for network security covered by H04L63/00
- H04L2463/062—Additional details relating to network architectures or network communication protocols for network security covered by H04L63/00 applying encryption of the keys
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an encryption communication system, an encryption communication method, a security chip, a communication device, a control method thereof, and a control program.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technique in which a public key and a private key corresponding to the public key are embedded in a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) so that information is not inadvertently leaked. Also, on page 13 of Non-Patent Document 1, a technique for encrypting (wrapping) a common key with a public key in the TPM and storing a secret key for decryption (unwrapping) in the TPM to protect data. Proposed.
- TPM Trusted Platform Module
- the common key is used outside the TPM at the time of encryption / decryption with the common key, or the common key generated in the TPM is resident, so that the common key is leaked. could not prevent.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a technique for solving the above-described problems.
- an encryption communication system provides: An encryption communication system that uses a pair of a first secret part and a first public part and a pair of a second secret part and a second public part in an encryption key pre-distribution system (KPS), In a first security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of the first communication device, the first security chip held in the first security chip using the second public unit transmitted from the second communication device which is a communication partner.
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution system
- a ciphertext generating means for generating a common key by a secret part and generating a ciphertext by encrypting a plaintext based on the common key in the first security chip;
- the second secret unit held in the second security chip using the first public unit transmitted from the first communication device that is a communication partner uses a common key.
- decrypting means for decrypting the ciphertext received from the first communication device based on the common key in the second security chip and generating plaintext; Is provided.
- an encryption communication method includes: An encryption communication method using a pair of a first secret part and a first public part and a pair of a second secret part and a second public part in an encryption key pre-distribution system (KPS: Key Predistribution System), In a first security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of the first communication device, the first security chip held in the first security chip using the second public unit transmitted from the second communication device which is a communication partner.
- KPS Key Predistribution System
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- the second secret unit held in the second security chip using the first public unit transmitted from the first communication device that is a communication partner uses a common key.
- a communication device provides: A communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module),
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- the security chip is A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS);
- KPS key predistribution system
- a common key generating means for generating a common key by the held secret part
- Ciphertext generating means for encrypting plaintext and generating ciphertext based on the common key
- a method for controlling a communication device includes: A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, a ciphertext generating step of generating a ciphertext by encrypting a plaintext based on the common key; including.
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- KPS key predistribution system
- a control program for a communication device includes: A control program for a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, a ciphertext generating step of generating a ciphertext by encrypting a plaintext based on the common key; Is executed on the computer.
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- KPS key predistribution system
- a communication device provides: A communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module),
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- the security chip is A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS);
- KPS key predistribution system
- a common key generating means for generating a common key by the held secret part;
- Decryption means for decrypting the ciphertext received from the communication partner based on the common key to generate plaintext; Is provided.
- a method for controlling a communication device includes: A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, based on the common key, a decryption step of decrypting a ciphertext received from the communication partner to generate a plaintext; including.
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- KPS key predistribution system
- a control program for a communication device includes: A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, based on the common key, a decryption step of decrypting a ciphertext received from the communication partner to generate a plaintext; Is executed on the computer.
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
- KPS key predistribution system
- a security chip comprises: A security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of a communication device, A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Based on the held secret part and the public part in the encryption key pre-distribution system transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution system; An encryption command to which a plaintext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached is received, the common key generation means generates the common key, and the plaintext is encrypted based on the common key.
- a security chip comprises: A security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of a communication device, A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Based on the held secret part and the public part in the encryption key pre-distribution system transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution system; Receiving a decryption command to which a ciphertext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached, causing the common key generating means to generate the common key, and decrypting the ciphertext based on the common key Decryption means for generating plaintext; Is provided.
- TMP Trusted Platform Module
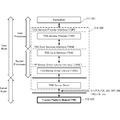
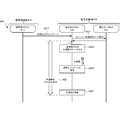
- a cryptographic communication system 100 as a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
- the cryptographic communication system 100 includes a communication device using a pair of a first secret part and a first public part and a pair of a second secret part and a second public part in a key predistribution system (KPS). It is a system that performs cryptographic communication between them.
- KPS key predistribution system
- the cryptographic communication system 100 includes a ciphertext generation unit 101 and a decryption unit 102.
- the ciphertext generation unit 101 uses the second disclosure unit 113 transmitted from the second communication device 120, which is the communication partner, to perform the first.
- a common key 130 is generated by the first secret unit 112 held in the security chip 111, and a plaintext is encrypted based on the common key 130 in the first security chip 111 to generate a ciphertext.
- the decryption unit 102 uses the first disclosure unit 123 transmitted from the first communication device 110 that is the communication partner, and the second security chip 121 holds the second security chip 121.
- a secret key 122 is generated by the secret unit 122, and the ciphertext received from the first communication device 110 is decrypted by the second security chip 121 based on the common key 130 to generate plaintext.
- the first communication device generates a common key from the first secret part and the second public part in the TPM at the time of encryption, performs encryption in the TPM, and the second communication apparatus at the time of decryption.
- the cryptographic communication system according to the present embodiment embeds the secret part in the distributed encryption key pre-distribution method in the TPM and transmits the public part to the communication partner. Then, a common key is generated in the TPM at the time of encryption or decryption, encryption or decryption is performed in the TPM, and the common key is discarded after completion.
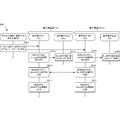
- FIG. 6A is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of encryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 600 according to the prerequisite technology.
- step S611 the encryption side CPU 611 of the encryption side device 610 requests the encryption side TPM 612 to load a common key.
- the encryption side TPM 612 of the encryption side device 610 passes the common key to the encryption side CPU 611 in step S613.
- the common key is disclosed to the encryption CPU 611.
- the encryption side CPU 611 encrypts the plaintext message with the loaded common key. Then, the encryption CPU 611 transmits the encrypted message to the decryption CPU 621 of the decryption device 620 in step S617. In step S619, the encryption side CPU 611 discards the loaded common key. During this time (see 601 in FIG. 6A), since the common key continues to exist in the encryption CPU 611, the common key leakage probability increases.
- FIG. 6B is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of decryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 600 according to the base technology.
- the encryption CPU 611 of the encryption device 610 transmits the encrypted message to the decryption CPU 621 of the decryption device 620 in step S617.
- the decryption-side CPU 621 of the decryption-side device 620 receives the encrypted message and requests the decryption-side TPM 622 to load the common key in step S621. In step S623, the decryption-side TPM 622 of the decryption-side device 620 passes the common key to the decryption-side CPU 621.
- the common key is disclosed to the decryption CPU 621.
- the decryption-side CPU 621 decrypts the ciphertext message using the loaded common key.
- the decryption-side CPU 621 discards the loaded common key.
- the common key leakage probability increases.
- FIG. 6C is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a security chip (TMP) 630/640 according to the prerequisite technology.
- TMP security chip
- FIG. 6C shows a configuration 630 of TPMv1.2 specifications and a configuration 640 of TPMv2.0 specifications by TCG (Trusted Computing Group).
- a function for holding the KPS secret part in the nonvolatile memory, a common key generation and encryption function by the encryption command Encrypt, and a common key generation and decryption function by the decryption command Decrypt Is added.
- FIG. 6D is a diagram illustrating an example of the algorithm 650 of the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS) according to the base technology.
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- FIG. 6D is a diagram illustrating an example of the algorithm 650 of the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS) according to the base technology.
- the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS) algorithm 650 shown in FIG. 6D is an example called a Blom algorithm, and the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS) algorithm that can be used in this embodiment is not limited to FIG. 6D. .
- the upper half (theory) of FIG. 6D proves that a large number of pairs with (KPS public part, KPS secret part) are generated based on the Blom algorithm. That is, in the algorithm 650 of the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS), the KPS secret part is calculated corresponding to the KSP public part, and this KSP public part is transmitted to the communication destination. A common key is calculated.
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- FIG. 6D The lower half (specific example) of FIG. 6D shows that the above theory is correct based on the Blom algorithm according to simple specific values.
- a KPS secret part secret value
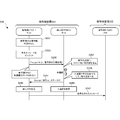
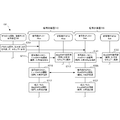
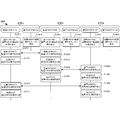
- FIG. 2A is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of operation preparation processing of the cryptographic communication system 200 according to the present embodiment.
- step S201 the distribution device 230 that distributes a set of KPS (public part and secret part) and encryption side CPU 211 of the encryption side device 210 (hereinafter also abbreviated as Alice) and decryption side device 220 (hereinafter also abbreviated as Bob). ) Of the KPS (public part, secret part) is distributed to the decryption-side CPU 221.
- 2A shows an example in which a set of KPS (public part and secret part) is distributed from the distribution device 230, but the public part is transmitted from the encryption CPU 211 or the decryption CPU 221 and the secret part is received. May be.
- step S211 the encryption side CPU 211 instructs the encryption side TPM 212 to embed the received KPS secret part and hold the secret part.
- step S213 the encryption side TPM 212 securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S 215 the encryption side CPU 211 transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the decryption side CPU 221 and receives the decryption side KPS disclosure unit transmitted from the decryption side CPU 221.
- step S217 the encryption-side CPU 211 stores the received decryption-side KPS disclosure unit.
- the decryption CPU 221 instructs the decryption TPM 222 to embed the received KPS secret part in step S221.
- the decryption side TPM 222 securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S225 the decryption-side CPU 221 transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the encryption-side CPU 211, and receives the encryption-side KPS disclosure unit transmitted from the encryption-side CPU 211.
- step S227 the decryption-side CPU 221 stores the received encryption-side KPS disclosure unit.
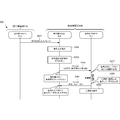
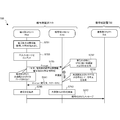
- FIG. 2B is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of encryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 200 according to the present embodiment.
- step S231 the encryption CPU 211 reads the stored public information (public part) on the decryption side.
- step S233 the encryption-side CPU 211 acquires a plaintext message and inputs it to the encryption-side TPM 212. That is, in step S235, the encryption-side CPU 211 transmits an encryption command Encrypt (plaintext, decryption-side public information) attached with plaintext and decryption-side public information to the encryption-side TPM 212.
- Encrypt plaintext, decryption-side public information
- the encryption side TPM 212 analyzes the received encryption command Encrypt (plaintext, public information on the decryption side) and uses the attached public information on the decryption side to generate a common key by the secret part held in the encryption side TPM 212. It is determined that the plaintext generated and encrypted with the common key is encrypted, and the ciphertext is returned to the encryption side CPU 211. In step S237, the encryption side TPM 212 generates a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS), and in step S239, encrypts the plaintext with the common key to generate a ciphertext.
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- step S241 the encryption side TPM 212 returns an encryption response command Encrypt (cipher text, status) to which the cipher text encrypted with the common key and the processing status in the encryption side TPM 212 are attached to the encryption side CPU 211. Also, the encryption side TPM 212 discards the common key generated for encryption in step S243.
- step S245 the encryption side CPU 211 transmits the ciphertext returned from the encryption side TPM 212 to the decryption side CPU 221 of the decryption side device 220.
- step S247 the ciphertext is transmitted as an encrypted message to the decryption CPU 221.
- FIG. 2C is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of decryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 200 according to the present embodiment.
- step S251 the decryption side CPU 221 receives the ciphertext from the encrypted message transmitted from the encryption side CPU 211 in step S247.
- step S253 the decryption-side CPU 221 reads the stored encryption-side public information (public part).
- step S ⁇ b> 255 the decryption-side CPU 221 transmits a decryption command Decrypt (ciphertext, encryption-side public information) attached with the ciphertext and encryption-side public information to the decryption-side TPM 222.
- Decrypt decryption command Decrypt
- the decryption-side TPM 222 analyzes the received decryption command Encrypt (ciphertext, encryption-side public information), and uses the attached encryption-side public information to obtain a common key from the secret part held in the decryption-side TPM 222.
- the ciphertext generated and decrypted with the common key is decrypted, and the plaintext is returned to the decryption side CPU 221 ”.
- the decryption-side TPM 222 generates a common key in accordance with the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS).
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- the decryption TPM 222 decrypts the ciphertext with the common key and generates plaintext.
- step S 261 the decryption side TPM 222 returns a decryption response command Decrypt (plain text, status) attached with the plaintext decrypted with the common key and the processing status in the decryption side TPM 222 to the decryption side CPU 221. Further, the decryption-side TPM 222 discards the common key generated for decryption in step S263.
- Decrypt plain text, status
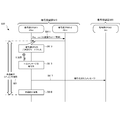
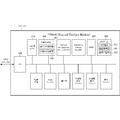
- FIG. 3A is a block diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of the cryptographic communication system 200 according to the present embodiment.
- the configuration outside the communication control in each communication device is omitted.
- the encryption side device 210 includes the CPU 211 and the TPM 212 described above.
- the CPU 211 includes an application 311, a cryptographic function module 312, and an I2C (Inter Integrated Circuit) 313.
- the application 311 mainly includes software that provides a service including communication with the decryption-side device 220.
- the cryptographic function module 312 includes software for performing encryption processing using the TPM 212 in accordance with the operation of the application 311.
- the I2C 313 operates as a GPIO (General Purpose Input / Output) connected to the TPM 212 via a serial interface.
- GPIO General Purpose Input / Output
- the decryption side device 220 includes the CPU 221 and the TPM 222 described above.
- the CPU 221 includes an application 321, a decryption function module 322, and an I2C 323.
- the application 321 mainly includes software that provides a service including communication with the encryption-side apparatus 210.
- the decryption function module 322 includes software for performing decryption processing using the TPM 222 according to the operation of the application 321.
- the I2C 323 operates as a GPIO connected by a serial interface by the TPM 222 and two signal lines (SCL: Serial: Clock and SDA: Serial Data).
- Communication device A communication apparatus including the encryption side apparatus 210 and the decryption side apparatus 220 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 3B to 4D.
- FIG. 3B is a block diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of the communication device 210/220 according to the present embodiment. Note that FIG. 3B shows a general configuration of a communication device on which the TPM 212/222 is mounted, and the communication device of the present embodiment is not limited to the configuration of FIG. 3B.
- the communication device 210/220 includes a CPU 211/221, a ROM 320, a RAM 340, a control unit (Controller) 360, a display unit (Display) 361, and an operation unit (Keyboard) 362. Detailed descriptions of other illustrated configurations are omitted.
- the CPU 211/221 is a central processing unit that controls the communication device 210/220.
- the ROM 320 is a storage unit that holds a boot program and a fixed value in a nonvolatile manner.
- the RAM 340 is a storage unit used as temporary storage that can be rewritten by the CPU 211/221.
- the control unit (Controller) 360 connects the CPU bus and the IO bus to control the peripheral device (ID device).
- FIG. 3C is a block diagram showing a software layer configuration of the communication device 210/220 according to the present embodiment.
- 3C shows a general software configuration of a communication device in which the TPM 212/222 is mounted, and the communication device of the present embodiment is not limited to the software layer configuration of FIG. 3C.
- the software configuration of the communication device 210/220 roughly includes an application 311/321 and an encryption function module 312 / decryption function module 322 as shown in FIG. 3A.
- the encryption function module 312 / decryption function module 322 has a TSP (TCG service provider) connected to the application 311/321 via TSPI (TCG service provider interface).
- the encryption function module 312 / decryption function module 322 has a TCS (TSS Core Services) connected to the TSP via a TCSI (TSS Core Services Interface).
- TCS TCS Core Services
- TCSI TCSI
- the encryption function module 312 / decryption function module 322 includes TDDL (TCGTCDevice Driver Library) connected via TCSI and TDDLI (TPM Device Driver Library Interface).
- TDD TDD
- the encryption function module 312 / decryption function module 322 has a TDD (TPMTPDevice Driver) that drives and controls the TPM 212/222.
- FIG. 4A is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of the communication device 210/220 according to the present embodiment.
- CPUs 211/221 are processors for arithmetic control, and realize the functional components shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C by executing a program.
- the ROM 320 stores fixed data and programs such as initial data and programs.
- the communication control unit 430 controls communication with a server and other communication devices via a network.
- the input / output interface 360 controls input / output of the display unit and the operation unit.
- the RAM 340 is a random access memory used by the CPU 211/221 as a work area for temporary storage.
- the RAM 340 has an area for storing data necessary for realizing the present embodiment.
- the plain text is a text before encryption in the case of the encryption side device 210.
- the ciphertext from the variation is an encrypted text generated by the encryption processing of the present embodiment from the plaintext in the case of the encryption side device 210.
- the received ciphertext is an encrypted text transmitted from the encryption device 210 in the case of the decryption device 220.
- the plaintext decrypted from the ciphertext is a text decrypted from the ciphertext by the decryption processing of the present embodiment in the case of the decryption side device 220.
- the transmission / reception data is message data exchanged with a server or another communication device via the communication control unit 430.
- the input / output data is data exchanged with the input / output device via the input / output interface 360.
- the storage 450 stores a database, various parameters, or the following data or programs necessary for realizing the present embodiment.
- the communication partner public information holding unit 451 holds a KPS public unit which is transmitted from the communication device of the communication partner and used to generate a shared key at the time of encryption or decryption.
- the storage 450 holds the following programs.
- the communication device control program is a program for controlling the entire communication device 210/220.
- the KPS secret part embedding module is a module for embedding the distributed KPS secret part in the TMP.
- the KPS public part transmission module is a module for transmitting the distributed KPS public part to the communication apparatus of the communication partner.
- the KPS secret part embedding module and the KPS public part transmission module may be collectively used as an operation preparation module.
- the ciphertext transmission module generates a common key from the KPS secret key and the KPS public key transmitted from the communication partner in the TPM, encrypts the plaintext with the common key, and transmits the ciphertext to the communication device of the communication partner. It is a module.
- the plaintext decryption module generates a common key from the KPS private key and the KPS public key transmitted from the communication partner in the TPM, decrypts the ciphertext received from the communication partner with this common key, and generates the original plaintext. It is a module.
- the display unit 361, the operation unit 362, and the TPM 212/222 are connected to the input / output interface 360.
- the TPM 212/222 may be connected by another interface.
- RAM 340 and the storage 450 in FIG. 4A do not show programs and data related to general-purpose functions and other realizable functions of the communication device 210/220.
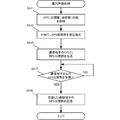
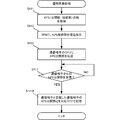
- FIG. 4B is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of operation preparation processing of the communication device 210/220 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the CPU 211/221 in FIG. 4A using the RAM 340, and implements the functional components shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C. The following processing procedure of the communication device 210/220 will be described assuming that the communication device 210/220 has both encryption and decryption processing functions. There are also devices, and these are included.
- step S411 the communication device 210/220 acquires a set of (public part, secret part) in KPS. As described above, the secret part may be acquired based on the public part.
- step S413 the communication device 210/220 instructs the TPM to embed a KPS secret part.
- step S415 the communication device 210/220 transmits the KPS disclosure unit to the communication partner CPU.
- step S417 the communication device 210/220 waits for reception of the KPS disclosure unit from the communication partner, and if there is reception of the KPS disclosure unit, stores the KPS disclosure unit of the received communication partner in step S419.
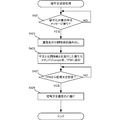
- FIG. 4C is a flowchart showing a procedure of ciphertext transmission processing of the communication device 210/220 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the CPU 211/221 in FIG. 4A using the RAM 340, and implements the functional components shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C.
- step S421 the communication device 210/220 determines whether there is a plaintext message to be encrypted. If there is a plaintext message to be encrypted, the communication device 210/220 reads the stored public information (public part) of the transmission destination in step S423. In step S425, the communication device 210/220 sends an encryption command Encrypt to which the plain text and the public information are attached to the TPM.
- step S427 the communication device 210/220 waits for a ciphertext reply from the TPM. If there is a ciphertext reply from the TPM, the communication device 210/220 sends the ciphertext to the destination in step S429.
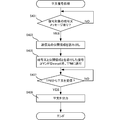
- FIG. 4D is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of plaintext decryption processing of the communication device 210/220 according to the second embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the CPU 211/221 in FIG. 4A using the RAM 340, and implements the functional components shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C.
- step S437 the communication device 210/220 waits for a plaintext response from the TPM. If there is a plaintext response from the TPM, the communication device 210/220 outputs the plaintext in step S439.
- TMP security chip
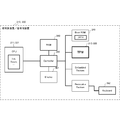
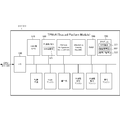
- FIG. 5A is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 according to the present embodiment.
- FIG. 5A is a configuration example of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 of the present embodiment, and is not limited to this. That is, various functions can be added.
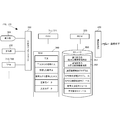
- the security chip (TMP) 212/222 includes a TMP CPU 510, a nonvolatile memory 520, an input / output interface (I / O) 530, a RAM 540, and a program 550.
- the TMP CPU 510 controls the entire TMP to realize each function.
- the nonvolatile memory 520 is a memory that maintains stored contents even without a power source, and a storage area of the KPS secret part 521 is secured. Note that the storage area of the KPS secret part 521 may be fixed or may be changed as long as it can be read at the time of encryption or decryption.
- the input / output interface (I / O) 530 is an interface for connecting the TMP and the CPUs 211/221 of the apparatus.
- the RAM 540 is a storage unit that the TMP CPU 510 uses for temporary storage.
- the program 550 holds a program corresponding to a function realized by TMP. In this embodiment, the program 550 holds a KPS calculation module 551, a secret part embedding module 552, and an encryption module and a decryption module 553.
- the KPS calculation module 551 is a module that receives an encryption command and a decryption command and generates a common key by a secret part using a public part of a communication partner.
- the secret part embedding module 552 is a module that holds the KPS secret part in the nonvolatile memory in accordance with an instruction from the apparatus CPU.
- the encryption module and the decryption module 553 are modules that convert plaintext into ciphertext and ciphertext into plaintext using the common key generated by the KPS calculation module 551.
- constituent elements other than those described with reference numerals are blocks that indicate functions generally provided in the TPM, and description thereof is omitted here.
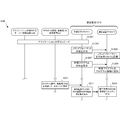
- FIG. 5B is a flowchart showing the procedure of the secret part embedding process of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the TMP CPU 510 of FIG. 5A using the RAM 540, and implements the functional configuration unit of FIG. 5A.
- the following processing procedure of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 will be described assuming that the security chip (TMP) 212/222 is used in a communication device having both encryption and decryption processing functions. Includes a security chip (TMP) dedicated to the encryption side device or the decryption side device, and includes these.
- step S511 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 waits for reception of an embedded command for the KPS secret part.
- the security chip (TMP) 212/222 acquires the KPS secret part from the embedded command in step S513. Then, in step S515, the security chip (TMP) 212/222 stores the acquired KPS secret part in the nonvolatile memory.
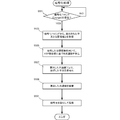
- FIG. 5C is a flowchart showing the procedure of the encryption processing of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the TMP CPU 510 of FIG. 5A using the RAM 540, and implements the functional configuration unit of FIG. 5A.
- TMP security chip
- step S521 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 waits for reception of the encryption command Encrypt. If the encrypted command Encrypt is received, the security chip (TMP) 212/222 acquires the plaintext attached from the encrypted command and the public information (public part) in step S523. In step S525, the security chip (TMP) 212/222 calculates a common key based on the KSP secret part in the TMP using the acquired public information.
- step S527 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 encrypts the plaintext acquired using the calculated common key.
- step S529 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 discards the calculated common key.
- step S531 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 attaches the ciphertext and status, and returns the encrypted command from the apparatus CPU.
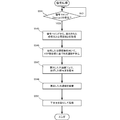
- FIG. 5D is a flowchart showing the decryption processing procedure of the security chip (TMP) 212/222 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the TMP CPU 510 of FIG. 5A using the RAM 540, and implements the functional configuration unit of FIG. 5A.
- TMP security chip
- step S541 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 waits for reception of the decryption command Decrypt.
- the security chip (TMP) 212/222 acquires the ciphertext and public information (public part) attached from the decryption command in step S543.
- the security chip (TMP) 212/222 calculates a common key based on the KSP secret part in the TMP using the acquired public information.
- step S547 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 decrypts the ciphertext obtained using the calculated common key.
- the security chip (TMP) 212/222 discards the calculated common key.
- step S551 the security chip (TMP) 212/222 returns the decryption command from the device CPU with the plaintext and status attached.
- a common key is generated in the TPM at the time of encryption or decryption, encryption or decryption is performed in the TPM, and the common key is discarded after the completion, thereby preventing leakage of the common key,
- the confidentiality of communication information can be improved.
- the cryptographic communication system according to the present embodiment further includes an initial vector (Cipher Block Chaining Mode) or an initial vector used in a CFB mode (Cipher Feedback Mode).
- an initial vector Cipher Block Chaining Mode
- CFB mode Cipher Feedback Mode
- IV Initialization Vector
- the secret algorithm part of the KPS for the initial vector is hidden in the TPM, and the public part is freely disclosed. Since other configurations and operations are the same as those of the second embodiment, the same configurations and operations are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
- FIG. 7A is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of operation preparation processing of the cryptographic communication system 700 according to the present embodiment. Each step in FIG. 7A is obtained by extending the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 2A to share the initial value vector (IV).
- step S701 the distribution device 730 that distributes the KPS (public part, secret part) pair to the initial value vector (IV) also decrypts the encryption side CPU 711 of the encryption side device 710 and the decryption side device 720.
- a pair of KPS (public part, secret part) is distributed to the side CPU 721.
- 7A shows an example in which a pair of KPS (public part, secret part) is distributed from the distribution device 730. However, the public part is transmitted from the encryption CPU 711 or the decryption CPU 721, and the secret part is received. May be.
- step S711 the encryption CPU 711 instructs the encryption TPM 712 to embed the received KPS secret part.
- step S713 the encryption side TPM 712 securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S715 the encryption side CPU 711 transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the decryption side CPU 721, and receives the decryption side KPS disclosure unit transmitted from the decryption side CPU 721.
- step S717 the encryption side CPU 711 stores the received decryption side KPS disclosure unit.
- step S721 the decryption-side CPU 721 instructs the decryption-side TPM 722 to embed the received KPS secret part.
- step S723 the decryption side TPM 722 securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S725 the decryption-side CPU 721 transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the encryption-side CPU 711, and receives the encryption-side KPS disclosure unit transmitted from the encryption-side CPU 711.
- step S727 the decryption-side CPU 721 stores the received encryption-side KPS disclosure unit.
- FIG. 7B is a sequence diagram illustrating an operation procedure of encryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 700 according to the present embodiment.
- Each step in FIG. 7B is obtained by extending the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 2B to the sharing of the initial value vector (IV).
- the initial value vector (IV) the encryption CPU 711 reads the stored decryption side public information (public part) in step S731.
- the encryption side CPU 711 acquires a plaintext message and inputs it to the encryption side TPM 712.
- step S735 the encryption-side CPU 711 transmits the encryption command Encrypt (plaintext, decryption-side key public information, decryption-side IV public information) attached with plaintext and decryption-side public information to the encryption-side TPM 712. To do.
- Encrypt plaintext, decryption-side key public information, decryption-side IV public information
- the encryption-side TPM 712 analyzes the received encryption command Encrypt (plain text, decryption-side key public information, decryption-side IV public information), and “attached decryption-side key public information and IV-publication”
- Encrypt plain text, decryption-side key public information, decryption-side IV public information
- Attached decryption-side key public information and IV-publication A common key is generated by the secret part held in the encryption side TPM 712 using the information, the plaintext attached with the common key is repeatedly encrypted for each block, and the ciphertext is returned to the encryption side CPU 711.
- the encryption side TPM 712 generates a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS).
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- the encryption side TPM 712 generates a ciphertext by encrypting the plaintext with the common key.
- step S241 the encryption side TPM 712 returns to the encryption side CPU 711 an encryption response command Encrypt (encrypted text, status) attached with the encrypted text encrypted with the common key and the status of the processing in the encryption side TPM 712. Also, the encryption side TPM 712 discards the common key generated for encryption in step S743.
- step S245 the encryption CPU 711 transmits the ciphertext returned from the encryption TPM 712 to the decryption CPU 721 of the decryption device 720.
- step S247 the ciphertext is transmitted to the decryption CPU 721 as an encrypted message.
- FIG. 7C is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of decryption processing of the cryptographic communication system 700 according to this embodiment.
- Each step in FIG. 7C is obtained by extending the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 2B to share the initial value vector (IV).
- the same step numbers are assigned to the same steps as in FIG. 2C.
- the decryption side CPU 721 receives the ciphertext from the encrypted message transmitted from the encryption side CPU 211 in step S247.
- step S753 the decryption-side CPU 721 reads the stored encryption-side public information (public part).
- step S755 the decryption-side CPU 721 transmits the decryption command Decrypt (ciphertext, encryption-side key public information, encryption-side IV public information) attached with the ciphertext and encryption-side public information to the decryption-side TPM 722. .
- the decryption-side TPM 722 analyzes the received decryption command Encrypt (encrypted text, encryption-side key public information, encryption-side IV public information), and “attached encryption-side key public information and IV-publication” It is determined that a secret key stored in the decryption-side TPM 722 is generated using the information, a ciphertext attached with the common key is decrypted, and a plaintext is returned to the decryption-side CPU 721.
- the decryption-side TPM 722 generates a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution method (KPS), and in step S759, decrypts the ciphertext using the common key to generate plaintext.
- KPS encryption key pre-distribution method
- step S 261 the decryption side TPM 722 returns a decryption response command Decrypt (plain text, status) attached with the plaintext decrypted with the common key and the status of processing in the decryption side TPM 222 to the decryption side CPU 721. Also, the decryption-side TPM 722 discards the common key generated for decryption in step S763.
- Decrypt plain text, status
- Communication device With reference to FIG. 8A and FIG. 8B, a structure and operation
- FIG. 8A is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of the communication device 710/720 according to the present embodiment.
- the same components as those in FIG. 4A are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted.
- a CPU 711/721 is a processor for arithmetic control, and implements the functional components shown in FIGS. 7A to 7C by executing a program.
- the storage 850 stores a database, various parameters, or the following data or programs necessary for realizing the present embodiment.
- the communication partner key public information holding unit 851 holds a KPS public unit for generating a common key that is transmitted from the communication device of the communication partner and used to generate a shared key at the time of encryption or decryption.
- the communication partner IV public information holding unit 852 holds a KPS public unit for IV generation that is transmitted from the communication device of the communication partner and used to generate a shared key at the time of encryption or decryption.
- the input / output interface 360 is connected to the TPM 712/722.
- the TPM 712/722 may be connected by another interface.
- FIG. 8B is a flowchart showing a procedure of operation preparation processing of the communication device 710/720 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the CPU 711/721 in FIG. 8A using the RAM 340, and implements the functional components shown in FIGS. 7A to 7C. The following processing procedure of the communication device 710/720 will be described on the assumption that the communication device 710/720 has both encryption and decryption processing functions. There are also devices, and these are included.
- Each step in FIG. 8B is an extension of the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 4B to the sharing of the initial value vector (IV).
- step S811 the communication device 710/720 acquires a set of (public part, secret part) in KPS including the initial value vector (IV). As described above, the secret part may be acquired based on the public part.
- step S813 the communication device 710/720 instructs the TPM to embed a KPS secret part.
- step S815 communication device 710/720 transmits the KPS disclosure unit to the communication partner CPU.
- step S817 the communication device 710/720 waits for reception of the KPS disclosure unit from the communication partner, and if there is reception of the KPS disclosure unit, stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the communication partner in step S819.
- TMP security chip
- FIG. 9A is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a security chip (TMP) 712/722 according to the present embodiment.
- TMP security chip
- the non-volatile memory 920 holds a key KPS secret part 921 and an IV KPS secret part 922.
- the program 950 holds a program corresponding to the function realized by the TMP.
- the program 950 holds a KPS calculation module 951, a secret part embedding module 952, and an encryption module and a decryption module 953. To do.
- the KPS calculation module 951 is a module that receives an encryption command and a decryption command and generates a common key and an IV by a secret part using a public part of a communication partner.
- the secret part embedding module 952 is a module that holds, in a nonvolatile memory, a KPS secret part that generates a common key and an IV in accordance with an instruction from the device CPU.
- the encryption module and decryption module 953 are modules for converting plaintext into ciphertext and ciphertext into plaintext using the common key and IV generated by the KPS calculation module 951.
- FIG. 9B is a flowchart showing the procedure of the secret part embedding process of the security chip (TMP) 712/722 according to the present embodiment. This flowchart is executed by the TMP CPU 510 of FIG. 9A using the RAM 540, and implements the functional component of FIG. 9A.
- the following processing procedure of the security chip (TMP) 712/722 will be described assuming that the security chip (TMP) 712/722 is used in a communication device having both encryption and decryption processing functions. Includes a security chip (TMP) dedicated to the encryption side device or the decryption side device, and includes these.
- each step in FIG. 9A is an extension of the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 5B to the sharing of the initial value vector (IV).
- step S911 the security chip (TMP) 712/722 waits for reception of an embedded command of the KPS secret part including the initial value vector (IV).
- the security chip (TMP) 712/722 acquires the KPS secret part from the embedded command in step S913. Then, in step S915, the security chip (TMP) 712/722 stores the acquired common key and IV KPS secret part in the nonvolatile memory.
- the initial vector used for encryption or decryption after the second block is updated in the TPM in the CBC mode and the CFB mode.
- the present embodiment it is possible to further prevent the leakage of the initial vector (IV) used in the CBC mode or the CFB mode of the common key encryption, and improve the confidentiality of the communication information.
- the cryptographic communication system according to the present embodiment generates a common key or an initialization vector from a secret part and each public part among three or more communication devices. It is different in point. Since other configurations and operations are the same as those of the second embodiment or the third embodiment, the same configurations and operations are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
- FIG. 10 is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of operation preparation processing of the cryptographic communication system according to the present embodiment.
- Each step in FIG. 10 extends the KPS public part and the KPS secret part in FIG. 2A to share each other among three or more communication devices. Also, in FIG. 10, the step of distributing the KPS (public part, secret part) set by the distribution device 230 to the CPU of each communication device is not shown in order to avoid duplication.
- step S1011 the CPU 1011 of the device U instructs the TPM 1012 of the device U to embed the received KPS secret part.
- step S1013 the TPM 1012 of the apparatus U securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S1015 the CPU 1011 of the device U transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1021 of the device V, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the device V transmitted from the CPU 1021 of the device V. Then, the CPU 1011 of the device U stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the device V in step S1017.
- the CPU 1021 of the device V instructs the TPM 1022 of the device V to embed the received KPS secret part in step S1031.
- the TPM 1022 of the device V securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S1035 the CPU 1021 of the device V transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1011 of the device U, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the device U transmitted from the CPU 1011 of the device U. Then, the CPU 1021 of the device V stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the device U in step S1037.
- step S1039 the CPU 1021 of the device V transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1031 of the device W, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the device W transmitted from the CPU 1031 of the device W. Then, the CPU 1021 of the device V stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the device W in step S1041.
- step S1051 the CPU 1031 of the device W instructs the TPM 1032 of the device W to embed the received KPS secret part.
- step S1053 the TPM 1032 of the apparatus W securely holds the KPS secret part at a predetermined position in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S1055 the CPU 1031 of the device W transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1021 of the device V, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the device V transmitted from the CPU 1021 of the device V.
- step S1057 the CPU 1031 of the apparatus W stores the received encryption-side KPS disclosure unit.
- step S1019 the CPU 1011 of the device U transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1031 of the device W, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the device W transmitted from the CPU 1031 of the device W.
- step S1021 the CPU 1011 of the apparatus U stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the apparatus W.
- step S1059 the CPU 1031 of the apparatus W transmits the received KPS disclosure unit to the CPU 1011 of the apparatus U, and receives the KPS disclosure unit of the apparatus U transmitted from the CPU 1011 of the apparatus U.
- step S1061 the CPU 1031 of the device W stores the received KPS disclosure unit of the device U.
- Communication device With reference to FIGS. 11A to 11D, the configuration and operation of the communication apparatus U / V / W of the present embodiment will be described.
- FIG. 11A is a diagram showing a configuration of a public information table 1110/1120/1130 stored in the communication device U / V / W according to the present embodiment.
- the public information table 1110 is held by the device U.
- the public information table 1120 is held by the device V.
- the public information table 1130 is held by the device W.
- the specific values in FIG. 11A correspond to the specific example of the Blom algorithm shown in FIG. 6D.
- the public information table 1110 stores the public information (public part) 1112 of the transmission partner transmitted from the transmission partner in association with the device ID 1111 of the transmission partner.
- public information (public part) 1112 is transmitted from the devices V and W, and is stored in association with the transmission partner.
- the device U encrypts the plaintext and transmits the ciphertext, or decrypts the received ciphertext and generates the plaintext
- the communication partner is the device V
- the public information table 1120 stores the public information (public part) 1122 of the transmission partner transmitted from the transmission partner in association with the device ID 1121 of the transmission partner. That is, in the public information table 1120, public information (public part) 1122 is transmitted from the device U and the device W, and is stored in association with the transmission partner.
- the public information table 1130 stores the public information (publication unit) 1132 of the transmission partner transmitted from the transmission partner in association with the device ID 1131 of the transmission partner. That is, in the public information table 1130, public information (public part) 1132 is transmitted from the device U and the device V, and is stored in association with the transmission partner.
- processing of the device V using the public information table 1120 and the processing of the device W using the public information table 1130 are the same as the processing of the device U using the public information table 1110, and thus description thereof is omitted. .
- FIG. 11B is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of operation preparation processing of the communication device U / V / W according to the present embodiment.
- the same steps as those in FIG. 4B are denoted by the same step numbers, and redundant description is omitted.
- step S1119 the communication device U / V / W associates the device ID of the communication partner with the received KPS disclosure unit of the communication partner and stores them in the public information table.
- FIG. 11C is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of ciphertext transmission processing of the communication device U / V / W according to the present embodiment.
- the same steps as those in FIG. 4C are denoted by the same step numbers, and redundant description is omitted.
- step S1123 the communication device U / V / W reads the public information associated with the ciphertext transmission destination from the public information table.
- FIG. 11D is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of plaintext decryption processing of the communication device U / V / W according to the present embodiment.
- the same steps as those in FIG. 4D are denoted by the same step numbers, and redundant description is omitted.
- step S1133 the communication device U / V / W reads the public information associated with the ciphertext transmission source from the public information table.
- a common key is generated in the TPM at the time of encryption or decryption in each communication device, and encryption is performed in the TPM.
- the cryptographic communication system according to the present embodiment is different from the second to fourth embodiments in that the TPM does not have a memory corresponding to the application.
- the TPM acquires the function of the above-described embodiment by an application downloaded from a server or a storage medium. Since other configurations and operations are the same as those in the second to fourth embodiments, the same configurations and operations are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
- FIG. 12 is a sequence diagram showing an operation procedure of application download processing of the cryptographic communication system 1200 according to the present embodiment.
- the communication device 1210 does not have the encryption communication function according to the present embodiment.
- this corresponds to the case where the TPM 1212 does not have the encryption communication function according to the present embodiment.
- the same steps as those in FIG. 2A are denoted by the same step numbers, and redundant description is omitted.
- step S1201 the CPU 1211 of the communication device 1210 logs in to the server or storage medium 1220 that provides the application for encrypted communication according to the present embodiment, and downloads the application for encrypted communication according to the present embodiment.
- step S1203 the CPU 1211 of the communication device 1210 instructs to embed a new command format that is not prepared in the TPM 1212.
- step S1205 the TPM 1212 stores the new command format in the nonvolatile memory.
- step S1207 the CPU 1211 of the communication device 1210 instructs to embed a new processing program that is not prepared in the TPM 1212.
- step S1209 the TPM 1212 stores a new processing program in the program area.
- the TPM 1212 can realize holding of the secret part, generation of the common key, encryption and decryption according to the processing program in response to the Encrypt command and Decrypt command of the present embodiment.
- the communication device or the TPM even if the communication device or the TPM does not have a function necessary for realizing the present embodiment in advance, it can be realized by downloading those function assignments to the communication device or the TPM.
- the configuration is shown in which the KPS secret part distributed by the communication device is embedded in the TMP.
- the KPS secret part is embedded in advance when the TMP is manufactured, and the corresponding KSP public part is acquired. Even if it is the structure which transmits to a communicating party, there can exist an effect similar to this invention.
- the present invention may be applied to a system composed of a plurality of devices, or may be applied to a single device. Furthermore, the present invention can also be applied to a case where an information processing program that implements the functions of the embodiments is supplied directly or remotely to a system or apparatus. Therefore, in order to realize the functions of the present invention on a computer, a program installed on the computer, a medium holding the program, and a WWW (World Wide Web) server that downloads the program are also included in the scope of the present invention. . In particular, at least a non-transitory computer readable medium storing a program for causing a computer to execute the processing steps included in the above-described embodiments is included in the scope of the present invention.
- a ciphertext generating means for generating a common key by a secret part and generating a ciphertext by encrypting a plaintext based on the common key in the first security chip;
- the second secret unit held in the second security chip using the first public unit transmitted from the first communication device that is a communication partner uses a common key.
- decrypting means for decrypting the ciphertext received from the first communication device based on the common key in the second security chip and generating plaintext;
- a cryptographic communication system comprising: (Appendix 2) The encryption communication system according to appendix 1, wherein the ciphertext generation unit and the decryption unit discard the common key after encryption or decryption based on the common key.
- the cryptographic communication system according to appendix 1 or 2, further comprising operation preparation means.
- the ciphertext generation means and the decryption means further include an initial vector (IV: Initialization Vector) when encryption and decryption are performed for each block, a secret part for the initial vector held in the security chip,
- the encryption communication system according to any one of appendices 1 to 3, wherein the encryption communication system is generated from the initial vector public part transmitted from the communication partner and used for the encryption and the decryption, respectively.
- Secret part holding means for receiving and holding the secret part; Based on the held secret part and the public part transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution method, An encryption command to which a plaintext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached is received, the common key generation means generates the common key, and the plaintext is encrypted based on the common key.
- a ciphertext generating means for generating a sentence Receiving a decryption command to which a ciphertext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached, causing the common key generating means to generate the common key, and decrypting the ciphertext based on the common key Decryption means for generating plaintext;
- the encryption communication system according to any one of appendices 1 to 4, further comprising a function granting unit that stores a program for granting at least one of the above and data.
- the second secret unit held in the second security chip using the first public unit transmitted from the first communication device that is a communication partner uses a common key.
- An encryption communication method including: (Appendix 7) The encryption communication method according to appendix 6, wherein, in the ciphertext generation step and the decryption step, the common key is discarded after encryption or decryption based on the common key.
- a communication device having a security chip TMP: Trusted Platform Module
- the security chip is A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key by the held secret part; Ciphertext generating means for encrypting plaintext and generating ciphertext based on the common key;
- a communication device comprising: (Appendix 9) The communication apparatus according to appendix 8, wherein the ciphertext generating unit discards the common key after encryption based on the common key.
- (Appendix 10) A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, a ciphertext generating step of generating a ciphertext by encrypting a plaintext based on the common key; A method for controlling a communication device including: (Appendix 11) A control program for a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner,
- a communication device having a security chip TMP: Trusted Platform Module
- the security chip is A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key by the held secret part; Decryption means for decrypting the ciphertext received from the communication partner based on the common key to generate plaintext;
- a communication device comprising: (Appendix 13) The communication apparatus according to appendix 12, wherein the decryption unit discards the common key after encryption or decryption based on the common key.
- (Appendix 14) A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generation step of generating a common key by the held secret part; In the security chip, based on the common key, a decryption step of decrypting a ciphertext received from the communication partner to generate a plaintext; A method for controlling a communication device including: (Appendix 15) A method for controlling a communication device having a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module), A secret part holding step for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS) in a secret part holding means of the security chip; In the security chip, using a public part in the encryption key pre-distribution method transmitted from the communication
- a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of a communication device A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Based on the held secret part and the public part in the encryption key pre-distribution system transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution system; An encryption command to which a plaintext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached is received, the common key generation means generates the common key, and the plaintext is encrypted based on the common key.
- a security chip (TMP: Trusted Platform Module) of a communication device A secret part holding means for holding a secret part in a key predistribution system (KPS); Based on the held secret part and the public part in the encryption key pre-distribution system transmitted from the communication partner, a common key generating means for generating a common key according to the encryption key pre-distribution system; Receiving a decryption command to which a ciphertext and a public part transmitted from the communication partner are attached, causing the common key generating means to generate the common key, and decrypting the ciphertext based on the common key Decryption means for generating plaintext; Security chip with.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/083,557 US11070365B2 (en) | 2016-03-11 | 2017-02-14 | Encryption communication system, encryption communication method, security chip, communication apparatus, and control method and control program of communication apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016048244A JP6728799B2 (ja) | 2016-03-11 | 2016-03-11 | 暗号通信システム、暗号通信方法、セキュリティチップ、通信装置およびその制御方法と制御プログラム |
| JP2016-048244 | 2016-03-11 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017154484A1 true WO2017154484A1 (ja) | 2017-09-14 |
Family
ID=59790474
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/005311 Ceased WO2017154484A1 (ja) | 2016-03-11 | 2017-02-14 | 暗号通信システム、暗号通信方法、セキュリティチップ、通信装置およびその制御方法と制御プログラム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11070365B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6728799B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017154484A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10877806B2 (en) * | 2017-06-14 | 2020-12-29 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for securely binding a first processor to a second processor |
| US11169935B2 (en) | 2018-06-20 | 2021-11-09 | Intel Corporation | Technologies for low-latency cryptography for processor-accelerator communication |
| CN113037764B (zh) * | 2021-03-19 | 2022-06-07 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | 一种业务执行的系统、方法及装置 |
| CN114640510B (zh) * | 2022-03-02 | 2023-07-04 | 宁波三星医疗电气股份有限公司 | 一种采用分离的加密服务器进行通信的方法 |
| CN114785503B (zh) * | 2022-06-16 | 2022-09-23 | 北京智芯半导体科技有限公司 | 密码卡及其根密钥保护方法、计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN115913794B (zh) * | 2023-03-09 | 2023-05-19 | 鹏城实验室 | 数据安全传输方法、设备及介质 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09238132A (ja) * | 1996-02-29 | 1997-09-09 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 携帯用端末通信システム及びその通信方法 |
| JP2010508576A (ja) * | 2006-10-31 | 2010-03-18 | ヒューレット−パッカード デベロップメント カンパニー エル.ピー. | 装置間でのデータオブジェクトの転送 |
| JP2012506658A (ja) * | 2008-10-24 | 2012-03-15 | ジエマルト・エス・アー | 暗号アルゴリズムの弱点保護 |
| JP2014050038A (ja) * | 2012-09-03 | 2014-03-17 | West Japan Railway Co | 無線システム及び列車制御システム |
| JP2015233201A (ja) * | 2014-06-09 | 2015-12-24 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 通信システム、通信装置及び通信方法 |
| JP2017060031A (ja) * | 2015-09-17 | 2017-03-23 | Kddi株式会社 | 車載制御システム、車両、管理装置、車載コンピュータ、データ共有方法、及びコンピュータプログラム |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08185445A (ja) * | 1994-12-28 | 1996-07-16 | Advance Co Ltd | 認証方式及び同方式による取引システム |
| JP2005140823A (ja) * | 2003-11-04 | 2005-06-02 | Sony Corp | 情報処理装置、制御方法、プログラム、並びに記録媒体 |
| JP2006148614A (ja) * | 2004-11-22 | 2006-06-08 | Hitachi Ltd | コンテンツ受信装置、コンテンツ送信装置、コンテンツ受信方法、コンテンツ送信方法及びネットワークシステム |
| JP2008035449A (ja) | 2006-08-01 | 2008-02-14 | Hitachi Software Eng Co Ltd | 自己復号ファイルによるデータ配布方法および該方法を用いた情報処理システム |
| WO2008147577A2 (en) * | 2007-01-22 | 2008-12-04 | Spyrus, Inc. | Portable data encryption device with configurable security functionality and method for file encryption |
| JP2010011400A (ja) * | 2008-06-30 | 2010-01-14 | National Institute Of Advanced Industrial & Technology | 共通鍵方式の暗号通信システム |
| US9122893B1 (en) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-09-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Trusted platform module switching |
-
2016
- 2016-03-11 JP JP2016048244A patent/JP6728799B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-02-14 WO PCT/JP2017/005311 patent/WO2017154484A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2017-02-14 US US16/083,557 patent/US11070365B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09238132A (ja) * | 1996-02-29 | 1997-09-09 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 携帯用端末通信システム及びその通信方法 |
| JP2010508576A (ja) * | 2006-10-31 | 2010-03-18 | ヒューレット−パッカード デベロップメント カンパニー エル.ピー. | 装置間でのデータオブジェクトの転送 |
| JP2012506658A (ja) * | 2008-10-24 | 2012-03-15 | ジエマルト・エス・アー | 暗号アルゴリズムの弱点保護 |
| JP2014050038A (ja) * | 2012-09-03 | 2014-03-17 | West Japan Railway Co | 無線システム及び列車制御システム |
| JP2015233201A (ja) * | 2014-06-09 | 2015-12-24 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 通信システム、通信装置及び通信方法 |
| JP2017060031A (ja) * | 2015-09-17 | 2017-03-23 | Kddi株式会社 | 車載制御システム、車両、管理装置、車載コンピュータ、データ共有方法、及びコンピュータプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6728799B2 (ja) | 2020-07-22 |
| JP2017163470A (ja) | 2017-09-14 |
| US11070365B2 (en) | 2021-07-20 |
| US20190081776A1 (en) | 2019-03-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6728799B2 (ja) | 暗号通信システム、暗号通信方法、セキュリティチップ、通信装置およびその制御方法と制御プログラム | |
| US20220078024A1 (en) | State synchronization for post-quantum signing facilities | |
| CN109768862B (zh) | 一种密钥管理方法、密钥调用方法及密码机 | |
| US10951402B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for encryption | |
| US20130003966A1 (en) | Cryptographic hardware module and method for updating a cryptographic key | |
| CN109564553A (zh) | 多阶段存储器完整性方法和装置 | |
| CN115065472B (zh) | 基于多密钥加密解密的安全芯片加密解密方法及装置 | |
| CN110166236B (zh) | 密钥处理方法、装置和系统及电子设备 | |
| CN113904808B (zh) | 一种私钥分发、解密方法、装置、设备及介质 | |
| JP6026017B2 (ja) | データ処理システム及び暗号装置及び復号装置及びプログラム | |
| US20230299953A1 (en) | Quantum cryptographic communication system, key management device, and key management method | |
| US8804953B2 (en) | Extensive ciphertext feedback | |
| US20200374275A1 (en) | Key-ladder protected personalization data conversion from global to unique encryption | |
| CN112291268A (zh) | 信息的传输方法、装置、设备以及存储介质 | |
| KR20200135127A (ko) | 무선 데이터 통신용 대칭형 양자 암호화 키 기반 암호화 장치 | |
| JP5586758B1 (ja) | 動的暗号化鍵生成システム | |
| KR20160024504A (ko) | 암호화 키 생성 장치 및 방법과 복호화 키 생성 장치 및 방법 | |
| KR102794226B1 (ko) | 전자 장치 및 암호화 방법 | |
| JP5043421B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置およびその方法 | |
| CN115361132B (zh) | 密钥生成方法、装置、片上系统、设备及存储介质 | |
| KR101999209B1 (ko) | 가상 함수 테이블 포인터 암호화 시스템 및 그 방법 | |
| JP2017021144A (ja) | 翻訳システムおよび翻訳方法 | |
| WO2020144758A1 (ja) | 秘密計算装置及びクライアント装置 | |
| CN110780884B (zh) | 一种信息处理方法、装置及设备 | |
| KR20170019679A (ko) | 효율적인 화이트박스 암호 기반 암복호화 방법, 및 인증코드 생성 및 검증 방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17762827 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17762827 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |