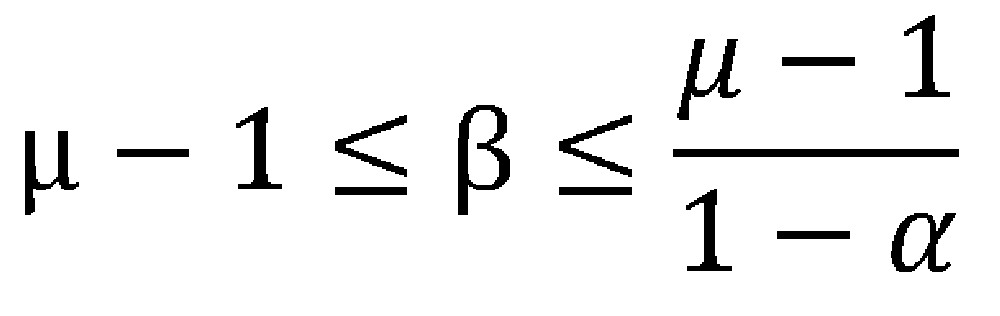WO2016122138A1 - Back-off counter selection device for random channel access and method therefor - Google Patents
Back-off counter selection device for random channel access and method therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016122138A1 WO2016122138A1 PCT/KR2016/000255 KR2016000255W WO2016122138A1 WO 2016122138 A1 WO2016122138 A1 WO 2016122138A1 KR 2016000255 W KR2016000255 W KR 2016000255W WO 2016122138 A1 WO2016122138 A1 WO 2016122138A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- equation
- value
- random
- state information
- distribution function
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/04—Error control
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access, e.g. scheduled or random access
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access, e.g. scheduled or random access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled or contention based access, e.g. random access, ALOHA, CSMA [Carrier Sense Multiple Access]
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus and method for selecting a back-off counter for random channel access. More particularly, the present invention relates to a back-off counter in a wireless network system using a random back-off counter. A technique for selecting a counter value.
- all wireless devices access the wireless media on a contention-based basis to transmit data packets, wait for Distributed Inter Frame Space (DIFS) time after the data transmission from other wireless devices is terminated, and then The transmission time is determined by a randomly selected counter value in the (Contention Widow: CW) section.
- DIFS Distributed Inter Frame Space
- each WLAN device In the medium access method of the conventional WLAN system, a random backoff value is obtained from a random variable having a uniform distribution.
- each WLAN device initially sets the range of the initial uniform distribution to the minimum value (CW -0 ) and then increases the uniform distribution range according to the collision result of the transmitted data.
- the wireless device may increase the transmission delay time due to the large backoff value compared to other wireless devices having a relatively small contention window size.
- the average transmission rate and packet transmission delay time of each terminal may be increased, which may result in deterioration of overall system performance or decrease in fair channel access opportunity of each wireless device.
- the WLAN increases the size of the competing window of each wireless device from the minimum value according to the collision result, it is possible to reduce the probability of collision at a certain moment.
- short term fairness Short Term Fairness (STF) problems.
- the wireless devices without transmission collisions select a random backoff value from the relatively small competition window. Failure to occupy the channel for a period of time may occur.
- An embodiment of the present invention is to provide a random backoff counter selection apparatus and method that can improve the transmission rate and short term fairness due to collision between wireless devices in a dense environment.
- Random backoff counter selection apparatus comprises the steps of obtaining network state information in a wireless network system; Calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function.
- the network state information includes at least one of data transmission probability, number of network wireless devices, average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and average time (Idle Time) when no wireless device occupies a channel. It may include.
- the calculating of the random backoff counter value may use a binomial distribution function or a Poisson distribution function as the distribution function.
- a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function may be set as a backoff counter value.
- the data transmission probability may be calculated using the number of network wireless devices and an average value of packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices.
- a data transmission probability may be calculated using Equation 1 or Equation 2 below.
- N is the number of network radios
- ⁇ * is the optimal data transmission probability
- Is the average packet transmission collision time
- N ⁇ is the average network transmission rate
- a value between 0 and 1 at which Equation 1 or Equation 2 becomes minimum may be calculated as the data transmission probability.
- the average value of the random backoff value may be calculated using the data transmission probability.
- the calculating of the random backoff counter value may include:
- the average value of the random backoff value may be calculated using Equation 3 below.
- the binomial distribution function may be defined as in Equation 4 below.
- the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ may be defined using Equation 5 below.
- N is the number of network radios and ⁇ is the average of the random backoff values.
- Binomial distribution parameter ⁇ can be defined using Equation 6 below.
- Binomial distribution parameter ⁇ can be defined using Equation 7 below.
- the Poisson distribution function may be defined as in Equation 8 below.
- the Poisson distribution average value ⁇ may be calculated using Equation 9 below.
- An apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access includes a network state information obtaining unit for obtaining network state information in a wireless network system; And a control unit calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function.
- the network state information obtaining unit may include at least one of a data transmission probability, a number of network wireless devices, an average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and an average time when no wireless device occupies a channel. The above can be obtained.
- the controller may calculate a random value of the network state information using a binomial distribution function or a Poisson distribution function.
- the controller may set a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function as a backoff counter value.
- the network state information obtaining unit may calculate a packet transmission collision time average value using the data transmission probability.
- This technology can achieve the highest throughput and short term fairness, and can coexist with existing homogeneous or heterogeneous systems based on uniform distribution.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining a binomial distribution characteristic and a binomial distribution parameter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for calculating a parameter of a binomial distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining characteristics and average values of a Poisson distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a method of calculating an average of Poisson distributions according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of calculating a data transmission probability ( ⁇ ) in the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution determination process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram of a computer system to which a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention is applied.
- An embodiment of the present invention proposes a new distribution function and a distribution function characteristic determination method for random backoff selection in order to solve a problem of lowering transmission rate and short term fairness caused by collision between wireless devices in a dense environment. .
- a binomial distribution and Poisson distribution function are used as the selection distribution function.
- the data transmission probability ( ⁇ ), the number of wireless devices in the network (N), and the average value of packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices Disclosed is a method for deriving a binomial distribution function and a Poisson distribution function.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the backoff counter selection apparatus 110 for random channel access includes a network state information acquisition unit 110, a storage unit 120, a control unit 130, and an output buffer 140.
- the network state information obtaining unit 110 obtains network state information in the wireless network system.
- the network state information includes data transmission probability ( ⁇ ), number of network wireless devices (N), and packet transmission collision time average values due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ), The average time that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ).
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 may determine the packet transmission collision time average value due to the number N of network radio devices and simultaneous transmission of different radio devices.
- the data transmission probability ⁇ is calculated using the following equation, and the specific equations are as shown in Equations 1 and 2 below. However, the data transmission probability ⁇ may be obtained through measurement.
- N is the number of network radios
- ⁇ * is the optimal data transmission probability
- Is the average packet transmission collision time
- N ⁇ is the average network transmission rate
- the network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates a value between 0 and 1 at which Equation 1 or Equation 2 becomes the minimum as a data transmission probability.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 may calculate an average value m of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability ⁇ . That is, the network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates an average value m of random backoff values using Equation 3 below.
- ⁇ is the average value of the random backoff and ⁇ is the optimal data transmission probability.
- the storage unit 120 stores the network state information obtained from the network state information obtaining unit 110 and the random value calculated by the control unit 130.
- the controller 130 calculates a random value by applying the network state information to the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function, and calculates a random backoff counter value by adding 1 to the random value. In this case, the controller 130 selects one of the binomial distribution function and the Poisson distribution function according to the situation of the wireless network or the wireless device. At this time, the controller 130 selects one of the Poisson and binomial distribution to generate random numbers according to hardware performance.
- the binomial distribution function may be defined as in Equation 4 below.
- ⁇ , ⁇ , and ⁇ are binomial distribution parameters, where ⁇ is the probability that all other devices except for any one of the N wireless devices will not attempt to transmit, and b is a binomial distribution whose average is. Means the number of different modified binomial distributions, and the value is defined as a positive integer value within the range below. g is a constant value used for the modified binomial distribution such that the mean of the binomial random variable X is ⁇ .
- the controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using Equation 5 below.
- the controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using Equation 6 below.
- the controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using Equation 7 below.
- Poisson distribution function may be defined as shown in Equation 8.
- ⁇ is the Poisson distribution mean value
- ⁇ is the mean value of the random backoff value
- the controller 130 may calculate the Poisson distribution average value ⁇ using Equation 9 below.
- ⁇ is the data transmission probability
- the controller 130 calculates the backoff counter value X by adding 1 to the random value Y calculated through the distribution function, and the wireless device transmits data when the channel is not occupied for the slot time of the backoff counter X. Done.
- the apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access having such a configuration determines the optimal random backoff counter selection distribution function according to the network conditions and selects the backoff counter value using the optimal selection distribution function to yield the highest yield. And short term fairness.
- the network state information obtaining unit 110 obtains network state information in a wireless network system (S100).
- the network state information includes data transmission probability ( ⁇ ), number of network wireless devices (N), and packet transmission collision time average values due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ), The average time that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ).
- the controller 130 selects one of the binomial distribution function and the Poisson distribution function according to the situation of the wireless network or the wireless device (S200). At this time, the controller 130 selects one of the Poisson and binomial distribution to generate random numbers according to hardware performance.
- the controller 130 calculates a random value by applying the binomial distribution function when the binomial distribution function is selected according to the selection of the process S200 (S300), and applies the Poisson distribution function when the Poisson distribution function is selected, and then applies a random value. To calculate (S400).
- controller 130 sets the backoff counter value by adding 1 to the random value calculated by applying the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function (S500).
- Network state information acquisition unit 110 is a packet transmission collision time average value ( ) Is a known value (S301), and if it is a known value, the average packet transmission collision time ( ) Is applied to the binomial distribution (S305).
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 is the average value of the packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ) Is estimated (S302).
- the network management device for example, the AP collects relevant information from each terminal and averages the packet transmission collision time of the network. ) Value can be determined and passed to each terminal have.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 determines whether the number of wireless devices (N) of the network is already known (S303), and if the value is already known, the wireless device number (N) of the network is applied to the binomial distribution. (S305).
- the binomial distribution function is the same as Equation 4 described above.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 is the average time (Idle Time) that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ) Can be used to estimate the number of wireless devices (N) of the network (S304).
- the estimated number of radio devices (N) of the network is applied to the binomial distribution function (S305).
- the packet transmission collision time average value ( ) And the number of wireless devices (N) of the network are used to calculate the data transmission probability ( ⁇ ) for applying the binomial distribution function.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates a data transmission probability ⁇ (S311).
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates an average value ⁇ of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability ⁇ (S312).
- the equation for calculating the average value ( ⁇ ) of the random backoff value is the same as the above equation (3).
- the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using the average value ⁇ of the random backoff values (S313), and calculates the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ as shown in Equation 5 above.
- the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ (S314) and calculates the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ as shown in Equation 6 above.
- the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ using the binomial distribution parameters ⁇ and ⁇ (S315), and the equation for calculating the binomial distribution parameter ⁇ is shown in Equation 7 above.
- FIG. 5 a method of determining a characteristic of the Poisson distribution and an average value ⁇ of a random backoff value according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
- the controller 130 determines whether the packet transmission collision time average value ( ⁇ ) and the number of wireless devices (N) of the network are already known (S401, 403). If it is estimated (S402, S404).
- the packet transmission collision time average value ( ) And a random value is calculated by applying the number of wireless devices (N) of the network to the Poisson distribution function (S405).
- the Poisson distribution function may be defined as in Equation 8 described above.
- FIG. 6 illustrates a method of calculating an average value ( ⁇ ) of a Poisson distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates a data transmission probability ⁇ (S411).
- the network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates an average value ⁇ of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability ⁇ (S412).
- the equation for calculating the average value ( ⁇ ) of the random backoff value is the same as the above equation (3).
- Data transmission probability ( ⁇ ) is measured by N, It can be determined by Equation 1 or Equation 2 using the value.
- the network state information obtaining unit 110 selects one of Equation 1 or Equation 2 (S421). In this case, the network state information acquisition unit 110 may select one of the equations (1) and (2) to speed up the calculation.
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates the average value of the packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of the wireless device number (N) of the network and different wireless devices (Equation 1 or 2). ) To calculate the optimal data transmission probability ⁇ * (S422, S423.)
- the network state information acquisition unit 110 determines the optimal data transmission probability ⁇ * as the data transmission probability ⁇ (S424).
- the present invention applies the network state information when determining the backoff counter value, thereby improving the average transmission rate of the terminal and minimizing the packet transmission delay time, thereby improving the performance of the communication system and accessing the common channel of each wireless device. Give opportunities to improve equity.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram of a computer system to which a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention is applied.
- the computing system 1000 may include at least one processor 1100, a memory 1300, a user interface input device 1400, a user interface output device 1500, and storage connected through a bus 1200. 1600, and network interface 1700.
- the processor 1100 may be a central processing unit (CPU) or a semiconductor device that executes processing for instructions stored in the memory 1300 and / or the storage 1600.
- the memory 1300 and the storage 1600 may include various types of volatile or nonvolatile storage media.
- the memory 1300 may include a read only memory (ROM) and a random access memory (RAM).
- the steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein may be embodied directly in hardware, software module, or a combination of the two executed by the processor 1100.
- the software module resides in a storage medium (ie, memory 1300 and / or storage 1600), such as RAM memory, flash memory, ROM memory, EPROM memory, EEPROM memory, registers, hard disks, removable disks, CD-ROMs. You may.
- An exemplary storage medium is coupled to the processor 1100, which can read information from and write information to the storage medium.
- the storage medium may be integral to the processor 1100.
- the processor and the storage medium may reside in an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC).
- ASIC application specific integrated circuit
- the ASIC may reside in a user terminal.
- the processor and the storage medium may reside as discrete components in a user terminal.
Abstract
A random back-off counter selection device according to one embodiment of the present invention can comprise the steps of: acquiring network state information in a wireless network system; and calculating a random back-off counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function.
Description
본 발명은 랜덤 채널 접속의 백-오프 카운터 선택 장치 및 그 방법에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는 랜덤 백오프(Back-off) 카운터(counter)를 이용하는 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 고려하여 백오프 카운터 값을 선택하는 기술에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for selecting a back-off counter for random channel access. More particularly, the present invention relates to a back-off counter in a wireless network system using a random back-off counter. A technique for selecting a counter value.
IEEE802.11 기반 무선랜 시스템에서 모든 무선기기는 데이터 패킷을 전송하기 위하여 경쟁기반으로 무선매체에 접근을 하며 다른 무선 기기의 데이터 전송이 종료되고 나서 Distributed Inter Frame Space (DIFS) 시간 동안 기다린 후 경쟁윈도우(Contention Widow: CW) 구간에서 랜덤하게 선택한 카운터 값으로 전송 시점을 결정한다.In an IEEE802.11 based wireless LAN system, all wireless devices access the wireless media on a contention-based basis to transmit data packets, wait for Distributed Inter Frame Space (DIFS) time after the data transmission from other wireless devices is terminated, and then The transmission time is determined by a randomly selected counter value in the (Contention Widow: CW) section.
기존의 무선랜 시스템의 매체접근 방식에서 랜덤 백오프 값은 균일분포(Uniform Distribution)를 가지는 랜덤변수로부터 획득된다. 이때 각 무선랜 기기는 최초 균일분포의 범위를 최소값(CW-0)으로 초기에 설정한 뒤 전송 데이터의 충돌 결과에 따라 균일분포의 범위를 증대 시킨다. In the medium access method of the conventional WLAN system, a random backoff value is obtained from a random variable having a uniform distribution. In this case, each WLAN device initially sets the range of the initial uniform distribution to the minimum value (CW -0 ) and then increases the uniform distribution range according to the collision result of the transmitted data.
이는 네트워크의 현재상태 정보를 이용하지 않고 무선접속 최초시도에서는 무선기기의 수가 적을 것이라는 가정에서 분포 범위를 최소값으로 설정하고 충돌 결과에 따라 네트워크 내 무선기기 수가 많다고 가정하여 충돌확률을 낮추기 위해 분포 범위를 증가 시키기 때문이다. This is based on the assumption that the number of wireless devices will be small at the initial attempt of wireless access without using the network's current state information. Because it increases.
따라서 초기에 많은 수의 무선기기가 존재하는 경우 초기 작은 분포 범위로 인한 높은 충돌확률로 다수의 무선기기의 전송성공확률이 낮아지게 되고, 충돌에 의해 증가된 큰 범위의 균일분포를 가지게 되는 경우 이 무선기기는 랜덤 백오프 값이 상대적으로 작은 경쟁윈도우 크기를 갖는 다른 무선기기에 비하여 큰 백오프 값에 의해 전송 지연시간이 증대될 수 있다. Therefore, when a large number of wireless devices exist in the early stage, the transmission probability of many wireless devices is lowered due to a high collision probability due to the initial small distribution range, and when a large range of uniform distributions is increased due to collision, The wireless device may increase the transmission delay time due to the large backoff value compared to other wireless devices having a relatively small contention window size.
이에, 이러한 경우 각 단말의 평균 전송률 및 패킷전송지연 시간이 증대되어 전체 시스템 성능 저하의 원인이 되거나 각 무선기기의 공평한 채널접속 기회를 저하시키는 원인이 될 수 있다.In this case, the average transmission rate and packet transmission delay time of each terminal may be increased, which may result in deterioration of overall system performance or decrease in fair channel access opportunity of each wireless device.
이와 같이 무선랜은 각 무선기기의 경쟁윈도우 크기를 최소값에서부터 충돌 결과에 따라 증가시키게 되므로 일정 순간에서 충돌 확률을 감소 시킬 수 있지만 충돌에 따라 경쟁윈도우를 증가시킨 일부 무선기기에 대해서는 단기간 공평성(Short Term Fairness;STF) 문제를 야기할 수 있다. As described above, since the WLAN increases the size of the competing window of each wireless device from the minimum value according to the collision result, it is possible to reduce the probability of collision at a certain moment. However, for some wireless devices that increase the competing window according to the collision, short term fairness (Short Term Fairness (STF) problems.
즉, 일부 무선기기들의 전송이 충돌 되어 경쟁윈도우를 증대 시키고 랜덤 백오프 카운터로 큰 값을 선택하는 경우 전송충돌이 없는 무선기기들이 상대적으로 작은 크기의 경쟁윈도우에서 랜덤 백오프 값을 선택하게 되므로 일정 기간 동안 채널을 점유하지 못하는 경우가 발생할 수 있다.In other words, when the transmission of some wireless devices collide with each other to increase the competition window and select a large value as the random backoff counter, the wireless devices without transmission collisions select a random backoff value from the relatively small competition window. Failure to occupy the channel for a period of time may occur.
본 발명의 실시예는 밀집한 환경에서의 무선기기 사이의 충돌에 의한 전송률 및 단기간 공평성(Short Term Fairness)을 향상시킬 수 있는 랜덤 백오프 카운터 선택장치 및 그 방법을 제공하고자 한다.An embodiment of the present invention is to provide a random backoff counter selection apparatus and method that can improve the transmission rate and short term fairness due to collision between wireless devices in a dense environment.
본 발명의 기술적 과제들은 이상에서 언급한 기술적 과제들로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 기술적 과제들은 아래의 기재들로부터 당업자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.Technical problems of the present invention are not limited to the technical problems mentioned above, and other technical problems not mentioned will be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following descriptions.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤 백오프 카운터 선택장치는 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계; 상기 네트워크 상태정보를 분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Random backoff counter selection apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises the steps of obtaining network state information in a wireless network system; Calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function.
상기 네트워크 상태정보는 데이터 전송확률, 네트워크 무선기기의 수, 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값, 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간(Idle Time) 중 적어도 하나 이상을 포함할 수 있다.The network state information includes at least one of data transmission probability, number of network wireless devices, average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and average time (Idle Time) when no wireless device occupies a channel. It may include.
상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, 상기 분포함수로서 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용할 수 있다. The calculating of the random backoff counter value may use a binomial distribution function or a Poisson distribution function as the distribution function.
또한, 상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, 상기 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 산출된 랜덤값에 1을 가산한 값을 백오프 카운터값으로 설정 할 수 있다. In the calculating of the random backoff counter value, a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function may be set as a backoff counter value.
또한, 상기 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계는, 상기 네트워크 무선기기의 수 및 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값을 이용하여 상기 데이터 전송확률을 산출 할 수 있다. In the obtaining of the network state information, the data transmission probability may be calculated using the number of network wireless devices and an average value of packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices.
또한, 상기 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계는, 아래 수학식 1 또는 수학식 2를 이용하여 데이터 전송확률을 산출할 수 있다. In the obtaining of the network state information, a data transmission probability may be calculated using Equation 1 or Equation 2 below.
[수학식 1][Equation 1]
[수학식 2][Equation 2]
여기서, N은 네트워크 무선기기의 수, τ*는 최적 데이터 전송확률, 는 패킷 전송 충돌시간 평균값이고, Nτ는 평균 네트워크 전송률이다.Where N is the number of network radios, τ * is the optimal data transmission probability, Is the average packet transmission collision time, and Nτ is the average network transmission rate.
상기 수학식 1 또는 상기 수학식 2가 최소가 되는 0과 1 사이의 값을 상기 데이터 전송확률로 산출할 수 있다. A value between 0 and 1 at which Equation 1 or Equation 2 becomes minimum may be calculated as the data transmission probability.
또한, 상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, 상기 데이터 전송확률을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값을 산출할 수 있다. In the calculating of the random backoff counter value, the average value of the random backoff value may be calculated using the data transmission probability.
또한, 상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, The calculating of the random backoff counter value may include:
[수학식 3][Equation 3]
(여기서 μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값이고, τ는 최적 데이터 전송확률을 의미함)(Where μ is the average value of the random backoff values and τ is the optimal data transmission probability)
상기 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값을 아래 수학식 3을 이용하여 산출 할 수 있다. The average value of the random backoff value may be calculated using Equation 3 below.
또한, 상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, 상기 이항분포함수를 아래 수학식 4와 같이 정의 할 수 있다. In the calculating of the random backoff counter value, the binomial distribution function may be defined as in Equation 4 below.
[수학식 4] [Equation 4]
(여기서, α,β,γ는 이항분포 파라미터임)(Where α, β, γ are binomial distribution parameters)
이항분포 파라미터 α는 아래 수학식 5를 이용하여 정의 할 수 있다. The binomial distribution parameter α may be defined using Equation 5 below.
[수학식 5] [Equation 5]
(여기서 N은 네트워크 무선기기의 수, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)Where N is the number of network radios and μ is the average of the random backoff values.
이항분포 파라미터 β는 아래 수학식 6을 이용하여 정의 할 수 있다. Binomial distribution parameter β can be defined using Equation 6 below.
[수학식 6][Equation 6]
(여기서, α는 이항분포 파라미터, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)(Where α is the binomial distribution parameter and μ is the average value of the random backoff values)
이항분포 파라미터 γ는 아래 수학식 7을 이용하여 정의 할 수 있다. Binomial distribution parameter γ can be defined using Equation 7 below.
[수학식 7] [Equation 7]
(여기서, α, β는 이항분포 파라미터, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)(Where α and β are binomial distribution parameters, μ is the average value of the random backoff values)
상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, 상기 포아송 분포함수를 아래 수학식 8과 같이 정의할 수 있다. In calculating the random backoff counter value, the Poisson distribution function may be defined as in Equation 8 below.
[수학식 8] [Equation 8]
(여기서, e는 오일러의 수(자연상수), λ는 포아송분포 평균값, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)(Where e is Euler's number (natural constant), λ is the Poisson distribution mean value, μ is the average value of the random backoff value)
또한, 상기 포아송분포 평균값 λ는 아래 수학식 9를 이용하여 산출할 수 있다.In addition, the Poisson distribution average value λ may be calculated using Equation 9 below.
[수학식 9][Equation 9]
(여기서, τ는 데이터 전송확률을 의미함)Where τ is the probability of data transmission
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치는 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 네트워크 상태정보 획득부; 및 상기 네트워크 상태정보를 분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 제어부를 포함할 수 있다.An apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a network state information obtaining unit for obtaining network state information in a wireless network system; And a control unit calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function.
상기 네트워크 상태정보 획득부는, 데이터 전송확률, 네트워크 무선기기의 수, 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값, 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간(Idle Time) 중 적어도 하나 이상을 획득할 수 있다.The network state information obtaining unit may include at least one of a data transmission probability, a number of network wireless devices, an average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and an average time when no wireless device occupies a channel. The above can be obtained.
상기 제어부는, 상기 네트워크 상태정보를 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 랜덤값을 산출할 수 있다.The controller may calculate a random value of the network state information using a binomial distribution function or a Poisson distribution function.
상기 제어부는, 상기 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 산출된 랜덤값에 1을 가산한 값을 백오프 카운터값으로 설정할 수 있다.The controller may set a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function as a backoff counter value.
상기 네트워크 상태정보 획득부는, 상기 데이터 전송확률을 이용하여 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값을 산출할 수 있다.The network state information obtaining unit may calculate a packet transmission collision time average value using the data transmission probability.
본 기술은 최고 수율(Throughput) 및 단기간 공평성(Short term fairness)를 확보할 수 있고, 기존 균일분포 기반의 동종 또는 이종 시스템과 상호 공존 가능한 효과가 있다.This technology can achieve the highest throughput and short term fairness, and can coexist with existing homogeneous or heterogeneous systems based on uniform distribution.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치의 구성도이다.1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포 특성과 이항분포 파라미터를 결정하는 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.3 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining a binomial distribution characteristic and a binomial distribution parameter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포의 모수 계산 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for calculating a parameter of a binomial distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 5는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 포아송분포의 특성 및 평균값을 결정하는 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.5 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining characteristics and average values of a Poisson distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 포아송분포의 평균 계산 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.6 is a flowchart illustrating a method of calculating an average of Poisson distributions according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포 및 포아송분포 결정과정에서의 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 계산하는 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of calculating a data transmission probability (τ) in the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution determination process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 8은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법을 적용한 컴퓨터 시스템의 구성도이다.8 is a block diagram of a computer system to which a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention is applied.
이하, 본 발명의 일부 실시예들을 예시적인 도면을 통해 상세하게 설명한다. 각 도면의 구성요소들에 참조부호를 부가함에 있어서, 동일한 구성요소들에 대해서는 비록 다른 도면상에 표시되더라도 가능한 한 동일한 부호를 가지도록 하고 있음에 유의해야 한다. 또한, 본 발명의 실시예를 설명함에 있어, 관련된 공지 구성 또는 기능에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 실시예에 대한 이해를 방해한다고 판단되는 경우에는 그 상세한 설명은 생략한다.Hereinafter, some embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail through exemplary drawings. In adding reference numerals to the components of each drawing, it should be noted that the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components as much as possible even though they are shown in different drawings. In addition, in describing the embodiments of the present invention, if it is determined that the detailed description of the related well-known configuration or function interferes with the understanding of the embodiments of the present invention, the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
본 발명의 실시예의 구성 요소를 설명하는 데 있어서, 제 1, 제 2, A, B, (a), (b) 등의 용어를 사용할 수 있다. 이러한 용어는 그 구성 요소를 다른 구성 요소와 구별하기 위한 것일 뿐, 그 용어에 의해 해당 구성 요소의 본질이나 차례 또는 순서 등이 한정되지 않는다. 또한, 다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가진다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가진 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.In describing the components of the embodiments of the present invention, terms such as first, second, A, B, (a), and (b) may be used. These terms are only for distinguishing the components from other components, and the nature, order or order of the components are not limited by the terms. In addition, unless otherwise defined, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art. Terms such as those defined in the commonly used dictionaries should be construed as having meanings consistent with the meanings in the context of the related art, and shall not be construed in ideal or excessively formal meanings unless expressly defined in this application. Do not.
본 발명의 실시예는 밀집한 환경에서의 무선기기 사이의 충돌에 의한 전송률 저하 및 단기간 공평성(Short Term Fairness) 문제를 해결하기 위하여 랜덤 백오프 선택을 위한 새로운 분포함수 및 분포함수 특성 결정 방법을 제시한다. An embodiment of the present invention proposes a new distribution function and a distribution function characteristic determination method for random backoff selection in order to solve a problem of lowering transmission rate and short term fairness caused by collision between wireless devices in a dense environment. .
이에 본 발명에서는 선택분포함수로 이항분포함수(Binomial Distribution) 및 포아송분포함수를 사용한다. 특히, 데이터전송확률(τ), 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자(N), 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷전송충돌시간의 평균값()으로부터 이항분포함수 및 포아송 분포함수를 도출하는 방법을 개시한다.Accordingly, in the present invention, a binomial distribution and Poisson distribution function are used as the selection distribution function. In particular, the data transmission probability (τ), the number of wireless devices in the network (N), and the average value of packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( Disclosed is a method for deriving a binomial distribution function and a Poisson distribution function.
이하, 도 1 내지 도 8을 참조하여, 본 발명의 실시예들을 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 1 to 8.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속(random channel access)의 백오프 카운터(backoff counter) 선택장치의 구성도이다.1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 램덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치(110)는 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110), 저장부(120), 제어부(130), 출력버퍼(140)를 포함한다.The backoff counter selection apparatus 110 for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a network state information acquisition unit 110, a storage unit 120, a control unit 130, and an output buffer 140.
네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득한다. 이때, 네트워크 상태정보는 데이터 전송확률(τ), 네트워크 무선기기의 수(N), 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값(), 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간(Idle Time) ()을 포함한다.The network state information obtaining unit 110 obtains network state information in the wireless network system. In this case, the network state information includes data transmission probability (τ), number of network wireless devices (N), and packet transmission collision time average values due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ), The average time that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ).
네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 네트워크 무선기기의 수(N) 및 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값()을 이용하여 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 산출하여 그 구체적인 수학식은 아래 수학식 1 및 수학식 2와 같다. 다만, 데이터 전송확률(τ)은 측정을 통해 획득될 수도 있다.The network state information acquisition unit 110 may determine the packet transmission collision time average value due to the number N of network radio devices and simultaneous transmission of different radio devices. The data transmission probability τ is calculated using the following equation, and the specific equations are as shown in Equations 1 and 2 below. However, the data transmission probability τ may be obtained through measurement.
수학식 1 및 수학식 2에서, N은 네트워크 무선기기의 수, τ*는 최적 데이터 전송확률, 는 패킷 전송 충돌시간 평균값이고, Nτ는 평균 네트워크 전송률이다.In Equations 1 and 2, N is the number of network radios, τ * is the optimal data transmission probability, Is the average packet transmission collision time, and Nτ is the average network transmission rate.
네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 상기 수학식 1 또는 상기 수학식 2가 최소가 되는 0과 1 사이의 값을 데이터 전송확률로 산출한다. The network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates a value between 0 and 1 at which Equation 1 or Equation 2 becomes the minimum as a data transmission probability.
또한, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(m)을 산출할 수 있다. 즉, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 아래 수학식 3을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(m)을 산출한다.In addition, the network state information acquisition unit 110 may calculate an average value m of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability τ. That is, the network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates an average value m of random backoff values using Equation 3 below.
여기서 μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값이고, τ는 최적 데이터 전송확률을 의미한다.Where μ is the average value of the random backoff and τ is the optimal data transmission probability.
저장부(120)는 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)로부터 획득된 네트워크 상태정보 및 제어부(130)를 통해 산출된 랜덤값을 저장한다.The storage unit 120 stores the network state information obtained from the network state information obtaining unit 110 and the random value calculated by the control unit 130.
제어부(130)는 네트워크 상태정보를 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤값을 산출하고, 그 랜덤값에 1을 가산하여 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출한다. 이때, 제어부(130)는 무선 네트워크 또는 무선 기기의 상황에 따라 선택분포함수를 이항분포함수와 포아송분포함수 중 하나를 선택한다. 이때, 제어부(130)는 하드웨어 성능에 따라 포아송과 이항분포중 난수생성이 용이한 쪽으로 선택한다.The controller 130 calculates a random value by applying the network state information to the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function, and calculates a random backoff counter value by adding 1 to the random value. In this case, the controller 130 selects one of the binomial distribution function and the Poisson distribution function according to the situation of the wireless network or the wireless device. At this time, the controller 130 selects one of the Poisson and binomial distribution to generate random numbers according to hardware performance.
이항분포함수는 아래 수학식 4와 같이 정의될 수 있다.The binomial distribution function may be defined as in Equation 4 below.
여기서, α,β,γ는 이항분포 파라미터임로서, α는 N개의 무선기기 중 임의의 기기 이외의 다른 모든 기기가 전송을 시도하지 않을 확률을 의미하고, b는 평균이 이 되는 이항분포를 만들기 위한 서로 다른 수정이항분포(Modified binomial distribution)의 개수를 의미하며, 그 값은 아래의 범위 내의 양의 정수 값으로 정한다. g는 이항분포 랜덤변수 X의 평균이 μ가 되도록 수정이항분포에 사용되는 상수 값을 의미한다. Here, α, β, and γ are binomial distribution parameters, where α is the probability that all other devices except for any one of the N wireless devices will not attempt to transmit, and b is a binomial distribution whose average is. Means the number of different modified binomial distributions, and the value is defined as a positive integer value within the range below. g is a constant value used for the modified binomial distribution such that the mean of the binomial random variable X is μ.
제어부(130)는 이항분포 파라미터 α를 아래 수학식 5를 이용하여 정의할 수 있다.The controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter α using Equation 5 below.
제어부(130)는 이항분포 파라미터 β를 아래 수학식 6을 이용하여 정의할 수 있다.The controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter β using Equation 6 below.
제어부(130)는 이항분포 파라미터 γ를 아래 수학식 7을 이용하여 정의할 수 있다.The controller 130 may define the binomial distribution parameter γ using Equation 7 below.
한편, 포아송분포함수는 아래 수학식 8과 같이 정의될 수 있다.On the other hand, Poisson distribution function may be defined as shown in Equation 8.
여기서, e는 오일러의 수(자연상수), λ는 포아송분포 평균값, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값이다.Where e is the Euler number (natural constant), λ is the Poisson distribution mean value, and μ is the mean value of the random backoff value.
제어부(130)는 포아송분포 평균값 λ을 아래 수학식 9를 이용하여 산출할 수 있다.The controller 130 may calculate the Poisson distribution average value λ using Equation 9 below.
여기서, τ는 데이터 전송확률을 의미한다.Where τ is the data transmission probability.
제어부(130)는 이와 같이 분포함수를 통해 산출된 랜덤값 Y에 1을 가산하여 백오프 카운터 값 X를 산출하고, 백오프 카운터 X개의 슬롯타임동안 채널이 점유되지 않은 경우 무선기기는 데이터를 전송하게 된다.The controller 130 calculates the backoff counter value X by adding 1 to the random value Y calculated through the distribution function, and the wireless device transmits data when the channel is not occupied for the slot time of the backoff counter X. Done.
이러한 구성을 가지는 본 발명의 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치는 네트워크 상황에 따라 최적의 랜덤 백오프 카운터 선택분포함수를 결정하고 최적의 선택분포함수를 이용하여 백오프 카운터 값을 선택함으로써 최고 수율 및 단기간 공평성(short term fairness)을 확보할 수 있다.The apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to the present invention having such a configuration determines the optimal random backoff counter selection distribution function according to the network conditions and selects the backoff counter value using the optimal selection distribution function to yield the highest yield. And short term fairness.
이하, 도 2를 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법을 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, a method of selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 2.
먼저, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득한다(S100). 이때, 네트워크 상태정보는 데이터 전송확률(τ), 네트워크 무선기기의 수(N), 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값(), 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간 (Idle Time) ()을 포함한다.First, the network state information obtaining unit 110 obtains network state information in a wireless network system (S100). In this case, the network state information includes data transmission probability (τ), number of network wireless devices (N), and packet transmission collision time average values due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ), The average time that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ).
제어부(130)는 무선 네트워크 또는 무선 기기의 상황에 따라 선택분포함수를 이항분포함수와 포아송분포함수 중 하나를 선택한다(S200). 이때, 제어부(130)는 하드웨어 성능에 따라 포아송과 이항분포중 난수생성이 용이한 쪽으로 선택한다.The controller 130 selects one of the binomial distribution function and the Poisson distribution function according to the situation of the wireless network or the wireless device (S200). At this time, the controller 130 selects one of the Poisson and binomial distribution to generate random numbers according to hardware performance.
그 후, 제어부(130)는 상기 과정 S200의 선택에 따라 이항분포함수가 선택되면 이항분포함수를 적용하여 랜덤값을 산출하고(S300), 포아송분포함수가 선택되면 포아송분포함수를 적용하여 랜덤값을 산출한다(S400). Thereafter, the controller 130 calculates a random value by applying the binomial distribution function when the binomial distribution function is selected according to the selection of the process S200 (S300), and applies the Poisson distribution function when the Poisson distribution function is selected, and then applies a random value. To calculate (S400).
이 후, 제어부(130)는 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 적용하여 산출된 랜덤값에 1을 가산하여 백오프 카운터 값을 설정한다(S500).Thereafter, the controller 130 sets the backoff counter value by adding 1 to the random value calculated by applying the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function (S500).
이하, 도 3을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포 특성과 이항분포 파라메터를 결정하는 방법을 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다. Hereinafter, a method of determining the binomial distribution characteristic and the binomial distribution parameter according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 3.
네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값()이 이미 알고 있는 값인지 판단하여(S301), 이미 알고 있는 값인 경우엔 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값()을 이항분포에 적용한다(S305). Network state information acquisition unit 110 is a packet transmission collision time average value ( ) Is a known value (S301), and if it is a known value, the average packet transmission collision time ( ) Is applied to the binomial distribution (S305).
한편, 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값()이 이미 알고 있는 값이 아닌 경우, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷전송충돌시간의 평균값()을 추정한다(S302). 평균값 추정의 일 실시예는 각 단말이 전송한 신호에 대한 ACK 응답신호가 없을 경우 충돌로 판단하고 해당 패킷의 전송시간을 평균하여 추정한다. 또한, 평균값 추정의 일 실시예로 네트워크에서 동일한 패킷전송충돌시간의 평균값()을 적용하기 위하여 네트워크 관리기기(예를 들어, AP)에서 각 단말로부터 관련 정보를 수집하여 네트워크 공동의 패킷전송충돌시간의 평균값() 값을 결정하고 각 단말에 전달할 수 있다.On the other hand, the average packet transmission collision time ( ) Is not a known value, the network state information acquisition unit 110 is the average value of the packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices ( ) Is estimated (S302). In an embodiment of estimating the average value, if there is no ACK response signal for a signal transmitted by each terminal, it is determined as a collision and is estimated by averaging the transmission time of the corresponding packet. Also, as an example of estimating the average value, the average value of the same packet transmission collision time in the network ( In order to apply), the network management device (for example, the AP) collects relevant information from each terminal and averages the packet transmission collision time of the network. ) Value can be determined and passed to each terminal have.
한편, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)이 이미 알고 있는 값인지 판단하여(S303), 이미 알고 있는 값인 경우엔 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)을 이항분포에 적용한다(S305). 이때 이항분포함수는 앞서 기술한 수학식 4와 같다.On the other hand, the network state information acquisition unit 110 determines whether the number of wireless devices (N) of the network is already known (S303), and if the value is already known, the wireless device number (N) of the network is applied to the binomial distribution. (S305). In this case, the binomial distribution function is the same as Equation 4 described above.
네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)이 이미 알고 있는 값이 아닌 경우, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간 (Idle Time) ()을 이용하여 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)를 추정할 수 있다(S304).If the number of wireless devices (N) of the network is not a known value, the network state information acquisition unit 110 is the average time (Idle Time) that no wireless device occupies the channel ( ) Can be used to estimate the number of wireless devices (N) of the network (S304).
이에 추정된 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)를 이항분포함수에 적용한다(S305).The estimated number of radio devices (N) of the network is applied to the binomial distribution function (S305).
이때, 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값() 및 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)은 이항분포함수 적용을 위한 데이터 전송확률(τ) 산출시 이용된다.At this time, the packet transmission collision time average value ( ) And the number of wireless devices (N) of the network are used to calculate the data transmission probability (τ) for applying the binomial distribution function.
이하, 도 4를 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포의 파라미터 계산 방법을 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다. Hereinafter, a method for calculating a parameter of a binomial distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 4.
먼저, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 산출한다(S311).First, the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates a data transmission probability τ (S311).
이어, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 산출한다(S312). 이때, 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 산출하는 식은 위에서 상술한 수학식 3과 같다.Subsequently, the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates an average value μ of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability τ (S312). At this time, the equation for calculating the average value (μ) of the random backoff value is the same as the above equation (3).
이에, 제어부(130)는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 이용하여 이항분포 파라미터 α를 산출하고(S313), 이항분포 파라미터 α를 산출하는 식은 상기 수학식 5와 같다.Accordingly, the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter α using the average value μ of the random backoff values (S313), and calculates the binomial distribution parameter α as shown in Equation 5 above.
이어, 제어부(130)는 이항분포 파라미터 α를 이용하여 이항분포 파라미터 β를 산출하고(S314) 이항분포 파라미터 β 산출하는 식은 상기 수학식 6과 같다.Subsequently, the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter β using the binomial distribution parameter α (S314) and calculates the binomial distribution parameter β as shown in Equation 6 above.
이후, 제어부(130)는 이항분포 파라미터 α, β 이용하여 이항분포 파라미터 γ를 산출하며(S315) 이항분포 파라미터 γ를 산출하는 식은 상기 수학식 7과 같다.Thereafter, the controller 130 calculates the binomial distribution parameter γ using the binomial distribution parameters α and β (S315), and the equation for calculating the binomial distribution parameter γ is shown in Equation 7 above.
이하, 도 5를 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 포아송분포의 특성 및 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 결정하는 방법을 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, referring to FIG. 5, a method of determining a characteristic of the Poisson distribution and an average value μ of a random backoff value according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail. FIG.
먼저, 제어부(130)는 이항분포함수 적용시와 마찬가지로, 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값(μ) 및 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)가 이미 아는 정보인지를 판단하여(S401, 403), 알지 못하는 정보인 경우 추정을 한다(S402, S404).First, as in the case of applying the binomial distribution function, the controller 130 determines whether the packet transmission collision time average value (μ) and the number of wireless devices (N) of the network are already known (S401, 403). If it is estimated (S402, S404).
이후, 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값() 및 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)를 포아송분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤값을 산출한다(S405). 이때, 포아송분포함수는 상술한 수학식 8과 같이 정의될 수 있다.After that, the packet transmission collision time average value ( ) And a random value is calculated by applying the number of wireless devices (N) of the network to the Poisson distribution function (S405). In this case, the Poisson distribution function may be defined as in Equation 8 described above.
이하, 도 6은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 포아송분포의 평균값(μ) 계산 방법을 구체적으로 설명한다.6 illustrates a method of calculating an average value (μ) of a Poisson distribution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
먼저, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 산출한다(S411).First, the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates a data transmission probability τ (S411).
이어, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 산출한다(S412). 이때, 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값(μ)을 산출하는 식은 위에서 상술한 수학식 3과 같다.Subsequently, the network state information obtaining unit 110 calculates an average value μ of the random backoff values using the data transmission probability τ (S412). At this time, the equation for calculating the average value (μ) of the random backoff value is the same as the above equation (3).
이하, 도 7을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이항분포 및 포아송분포 함수 적용 시 필요한 데이터 전송확률(τ)을 계산하는 방법을 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다. Hereinafter, a method of calculating the data transmission probability τ required when applying the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution function according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 7.
데이터 전송확률(τ)은 측정을 하거나 네트워크의 N, 값을 이용한 수학식 1 또는 수학식 2에 의해 결정될 수 있다.Data transmission probability (τ) is measured by N, It can be determined by Equation 1 or Equation 2 using the value.
네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 수학식 1 또는 수학식 2 중 하나를 선택한다(S421). 이때, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 수학식 1 및 수학식 2 중 계산이 빠르게 되는 것을 선택할 수 있다.The network state information obtaining unit 110 selects one of Equation 1 or Equation 2 (S421). In this case, the network state information acquisition unit 110 may select one of the equations (1) and (2) to speed up the calculation.
이후 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 수학식 1 또는 수학식 2에 네트워크의 무선기기 숫자 (N)와 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷전송충돌시간의 평균값()를 적용하여 최적 데이터 전송확률 τ*을 산출한다(S422, S423.)Thereafter, the network state information acquisition unit 110 calculates the average value of the packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of the wireless device number (N) of the network and different wireless devices (Equation 1 or 2). ) To calculate the optimal data transmission probability τ * (S422, S423.)
이어서, 네트워크 상태정보 획득부(110)는 최적 데이터 전송확률 τ*을 데이터 전송확률(τ)로 결정한다(S424).Subsequently, the network state information acquisition unit 110 determines the optimal data transmission probability τ * as the data transmission probability τ (S424).
이와 같이 본 발명은 백오프 카운터값 결정 시 네트워크의 상태정보를 적용하여 결정함으로써, 단말의 평균 전송률을 향상시키고 패킷 전송지연시간을 최소화하여 통신 시스템의 성능을 개선하고 각 무선기기의 공편한 채널 접속 기회를 주어 공평성을 향상시킬 수 있다.As described above, the present invention applies the network state information when determining the backoff counter value, thereby improving the average transmission rate of the terminal and minimizing the packet transmission delay time, thereby improving the performance of the communication system and accessing the common channel of each wireless device. Give opportunities to improve equity.
도 8은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법을 적용한 컴퓨터 시스템의 구성도이다.8 is a block diagram of a computer system to which a method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access according to an embodiment of the present invention is applied.
도 8을 참조하면, 컴퓨팅 시스템(1000)은 버스(1200)를 통해 연결되는 적어도 하나의 프로세서(1100), 메모리(1300), 사용자 인터페이스 입력 장치(1400), 사용자 인터페이스 출력 장치(1500), 스토리지(1600), 및 네트워크 인터페이스(1700)를 포함할 수 있다. Referring to FIG. 8, the computing system 1000 may include at least one processor 1100, a memory 1300, a user interface input device 1400, a user interface output device 1500, and storage connected through a bus 1200. 1600, and network interface 1700.
프로세서(1100)는 중앙 처리 장치(CPU) 또는 메모리(1300) 및/또는 스토리지(1600)에 저장된 명령어들에 대한 처리를 실행하는 반도체 장치일 수 있다. 메모리(1300) 및 스토리지(1600)는 다양한 종류의 휘발성 또는 불휘발성 저장 매체를 포함할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 메모리(1300)는 ROM(Read Only Memory) 및 RAM(Random Access Memory)을 포함할 수 있다. The processor 1100 may be a central processing unit (CPU) or a semiconductor device that executes processing for instructions stored in the memory 1300 and / or the storage 1600. The memory 1300 and the storage 1600 may include various types of volatile or nonvolatile storage media. For example, the memory 1300 may include a read only memory (ROM) and a random access memory (RAM).
따라서, 본 명세서에 개시된 실시예들과 관련하여 설명된 방법 또는 알고리즘의 단계는 프로세서(1100)에 의해 실행되는 하드웨어, 소프트웨어 모듈, 또는 그 2 개의 결합으로 직접 구현될 수 있다. 소프트웨어 모듈은 RAM 메모리, 플래시 메모리, ROM 메모리, EPROM 메모리, EEPROM 메모리, 레지스터, 하드 디스크, 착탈형 디스크, CD-ROM과 같은 저장 매체(즉, 메모리(1300) 및/또는 스토리지(1600))에 상주할 수도 있다. Thus, the steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the embodiments disclosed herein may be embodied directly in hardware, software module, or a combination of the two executed by the processor 1100. The software module resides in a storage medium (ie, memory 1300 and / or storage 1600), such as RAM memory, flash memory, ROM memory, EPROM memory, EEPROM memory, registers, hard disks, removable disks, CD-ROMs. You may.
예시적인 저장 매체는 프로세서(1100)에 커플링되며, 그 프로세서(1100)는 저장 매체로부터 정보를 판독할 수 있고 저장 매체에 정보를 기입할 수 있다. 다른 방법으로, 저장 매체는 프로세서(1100)와 일체형일 수도 있다. 프로세서 및 저장 매체는 주문형 집적회로(ASIC) 내에 상주할 수도 있다. ASIC는 사용자 단말기 내에 상주할 수도 있다. 다른 방법으로, 프로세서 및 저장 매체는 사용자 단말기 내에 개별 컴포넌트로서 상주할 수도 있다.An exemplary storage medium is coupled to the processor 1100, which can read information from and write information to the storage medium. In the alternative, the storage medium may be integral to the processor 1100. The processor and the storage medium may reside in an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC). The ASIC may reside in a user terminal. In the alternative, the processor and the storage medium may reside as discrete components in a user terminal.
이상의 설명은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 예시적으로 설명한 것에 불과한 것으로서, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 본 발명의 본질적인 특성에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능할 것이다. The above description is merely illustrative of the technical idea of the present invention, and those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains may make various modifications and changes without departing from the essential characteristics of the present invention.
따라서, 본 발명에 개시된 실시예들은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 한정하기 위한 것이 아니라 설명하기 위한 것이고, 이러한 실시예에 의하여 본 발명의 기술 사상의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다. 본 발명의 보호 범위는 아래의 청구범위에 의하여 해석되어야 하며, 그와 동등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 기술 사상은 본 발명의 권리범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다.Therefore, the embodiments disclosed in the present invention are not intended to limit the technical idea of the present invention but to describe the present invention, and the scope of the technical idea of the present invention is not limited by these embodiments. The protection scope of the present invention should be interpreted by the following claims, and all technical ideas within the equivalent scope should be interpreted as being included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (20)
- 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계;Obtaining network state information in a wireless network system;상기 네트워크 상태정보를 분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계 Calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function를 포함하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The method of selecting a backoff counter for random channel access comprising a.
- 청구항 1에 있어서, The method according to claim 1,상기 네트워크 상태정보는 데이터 전송확률, 네트워크 무선기기의 수, 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값, 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간(Idle Time) 중 적어도 하나 이상을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The network state information includes at least one of data transmission probability, number of network wireless devices, average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and average time (Idle Time) when no wireless device occupies a channel. And a backoff counter selection method for random channel access.
- 청구항 2에 있어서, The method according to claim 2,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는,Computing the random backoff counter value,상기 분포함수로서 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.And a binomial distribution function or Poisson distribution function as the distribution function.
- 청구항 3에 있어서, The method according to claim 3,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는,Computing the random backoff counter value,상기 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 산출된 랜덤값에 1을 가산한 값을 백오프 카운터값으로 설정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.And a backoff counter value is set to a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function.
- 청구항 3에 있어서, The method according to claim 3,상기 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계는, Acquiring the network state information,상기 네트워크 무선기기의 수 및 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값을 이용하여 상기 데이터 전송확률을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.And calculating the data transmission probability by using the number of the network wireless devices and the average value of packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices.
- 청구항 3에 있어서, The method according to claim 3,상기 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 단계는, Acquiring the network state information,아래 수학식 1 또는 수학식 2를 이용하여 데이터 전송확률을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.A method for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access, comprising calculating a data transmission probability using Equation 1 or Equation 2 below.[수학식 1][Equation 1][수학식 2][Equation 2]
- 청구항 6에 있어서, The method according to claim 6,상기 수학식 1 또는 상기 수학식 2가 최소가 되는 0과 1 사이의 값을 상기 데이터 전송확률로 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.And a value between 0 and 1 at which Equation 1 or Equation 2 becomes the minimum as the data transmission probability.
- 청구항 4에 있어서, The method according to claim 4,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, Computing the random backoff counter value,상기 데이터 전송확률을 이용하여 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.And calculating an average value of a random backoff value using the data transmission probability.
- 청구항 8에 있어서, The method according to claim 8,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는, Computing the random backoff counter value,[수학식 3][Equation 3](여기서 μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값이고, τ는 최적 데이터 전송확률을 의미함)(Where μ is the average value of the random backoff values and τ is the optimal data transmission probability)상기 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값을 아래 수학식 3을 이용하여 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The method of selecting a backoff counter for random channel access, characterized in that the average value of the random backoff value is calculated using Equation 3 below.
- 청구항 3에 있어서, The method according to claim 3,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는,Computing the random backoff counter value,상기 이항분포함수를 아래 수학식 4와 같이 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The binomial distribution function is defined as shown in Equation 4 below.[수학식 4][Equation 4](여기서,α,β,γ는 이항분포 파라미터임)Where α, β and γ are binomial distribution parameters
- 청구항 10에 있어서, The method according to claim 10,이항분포 파라미터 α는 아래 수학식 5를 이용하여 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The binomial distribution parameter α is defined using Equation 5 below.[수학식 5][Equation 5](여기서 N은 네트워크 무선기기의 수, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)Where N is the number of network radios and μ is the average of the random backoff values.
- 청구항 10에 있어서, The method according to claim 10,이항분포 파라미터 β는 아래 수학식 6을 이용하여 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The binomial distribution parameter β is defined using Equation 6 below.[수학식 6][Equation 6](여기서, α는 이항분포 파라미터, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)(Where α is the binomial distribution parameter and μ is the average value of the random backoff values)
- 청구항 10에 있어서, The method according to claim 10,이항분포 파라미터 γ는 아래 수학식 7을 이용하여 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The binomial distribution parameter γ is defined using Equation 7 below.[수학식 7] [Equation 7](여기서, αβ는 이항분포 파라미터, μ는 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)Where αβ is the binomial distribution parameter and μ is the average value of the random backoff values.
- 청구항 3에 있어서, The method according to claim 3,상기 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 단계는,Computing the random backoff counter value,상기 포아송 분포함수를 아래 수학식 8과 같이 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택방법.The Poisson distribution function is defined as shown in Equation (8) below.[수학식 8][Equation 8](여기서, e는 오일러의 수(자연상수), λ는 포아송분포 평균값, μ 랜덤 백오프값의 평균값)(Where e is Euler's number (natural constant), λ is Poisson distribution mean value, μ random backoff value mean)
- 무선 네트워크 시스템에서 네트워크 상태정보를 획득하는 네트워크 상태정보 획득부; 및A network state information obtaining unit obtaining network state information in a wireless network system; And상기 네트워크 상태정보를 분포함수에 적용하여 랜덤 백오프 카운터 값을 산출하는 제어부A control unit calculating a random backoff counter value by applying the network state information to a distribution function를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.The apparatus for selecting a backoff counter for random channel access, comprising: a.
- 청구항 16에 있어서,The method according to claim 16,상기 네트워크 상태정보 획득부는,The network state information acquisition unit,데이터 전송확률, 네트워크 무선기기의 수, 서로 다른 무선기기의 동시 전송에 의한 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값, 어떠한 무선기기도 채널을 점유하지 않은 평균시간(Idle Time) 중 적어도 하나 이상을 획득하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.At least one of data transmission probability, number of network wireless devices, average packet transmission collision time due to simultaneous transmission of different wireless devices, and average time (Idle Time) that no wireless device occupies a channel. A backoff counter selector for random channel connection.
- 청구항 17에 있어서, The method according to claim 17,상기 제어부는, The control unit,상기 네트워크 상태정보를 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 랜덤값을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.And calculating a random value from the network state information by using a binomial distribution function or a Poisson distribution function.
- 청구항 18에 있어서, The method according to claim 18,상기 제어부는, The control unit,상기 이항분포함수 또는 포아송분포함수를 이용하여 산출된 랜덤값에 1을 가산한 값을 백오프 카운터값으로 설정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.And a backoff counter value is set to a value obtained by adding 1 to a random value calculated using the binomial distribution function or the Poisson distribution function.
- 청구항 18에 있어서, The method according to claim 18,상기 네트워크 상태정보 획득부는,The network state information acquisition unit,상기 데이터 전송확률을 이용하여 패킷 전송충돌시간 평균값을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 랜덤채널접속의 백오프 카운터 선택장치.And a packet transmission collision time average value is calculated using the data transmission probability.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150015598 | 2015-01-30 | ||
| KR10-2015-0015598 | 2015-01-30 | ||
| KR1020150178793A KR20160094263A (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2015-12-15 | Device and Method for selecting the back-off counter of random channel access |
| KR10-2015-0178793 | 2015-12-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016122138A1 true WO2016122138A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
Family
ID=56543698
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2016/000255 WO2016122138A1 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2016-01-11 | Back-off counter selection device for random channel access and method therefor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2016122138A1 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030161340A1 (en) * | 2001-10-31 | 2003-08-28 | Sherman Matthew J. | Method and system for optimally serving stations on wireless LANs using a controlled contention/resource reservation protocol of the IEEE 802.11e standard |
| EP2131535A1 (en) * | 2001-01-02 | 2009-12-09 | AT & T Corp. | random medium access methods with backoff adaptation to traffic |
| US20090303887A1 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2009-12-10 | Vasan Arunchandar | Method and system for timestep stochastic simulation for networks |
| WO2013191448A1 (en) * | 2012-06-18 | 2013-12-27 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for initial access distribution over wireless lan |
| WO2014061992A1 (en) * | 2012-10-16 | 2014-04-24 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for accessing channel in wireless lan |
-
2016
- 2016-01-11 WO PCT/KR2016/000255 patent/WO2016122138A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2131535A1 (en) * | 2001-01-02 | 2009-12-09 | AT & T Corp. | random medium access methods with backoff adaptation to traffic |
| US20030161340A1 (en) * | 2001-10-31 | 2003-08-28 | Sherman Matthew J. | Method and system for optimally serving stations on wireless LANs using a controlled contention/resource reservation protocol of the IEEE 802.11e standard |
| US20090303887A1 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2009-12-10 | Vasan Arunchandar | Method and system for timestep stochastic simulation for networks |
| WO2013191448A1 (en) * | 2012-06-18 | 2013-12-27 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for initial access distribution over wireless lan |
| WO2014061992A1 (en) * | 2012-10-16 | 2014-04-24 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for accessing channel in wireless lan |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| KIM, YUN BAE ET AL.: "Design and Analysis of Medium Access Protocol: Throughput and Short-Term Fairness Perspective", IEEE /ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, vol. 23, no. 3, 12 June 2015 (2015-06-12), pages 959 - 972, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_a.l.jsp?arnumber=6778811&tag=1> * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2020226462A1 (en) | Frame transmission method and device using multiple random backoff operation in broadband wireless communication network | |
| WO2019177272A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for beam failure recovery in communication system | |
| WO2015093892A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for terminal cell search in beamforming system | |
| WO2016182387A1 (en) | Method for transmitting and receiving data in wireless communication system using shared band, and device therefor | |
| WO2011132847A1 (en) | Method and system for multi-user transmit opportunity for multi-user multiple-input-multiple-output wireless networks | |
| WO2013073784A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for supporting a service for the simultaneous transmission of multiple network-based data | |
| WO2017171531A1 (en) | Wireless communication method and wireless communication terminal for spatial reuse of overlapped basic service set | |
| EP2491739A2 (en) | Communication system of detecting victim terminal and performing interference coordination in multi-cell environments | |
| WO2010140742A1 (en) | Method for providing information of access point selection | |
| WO2015182969A1 (en) | Wireless communication method and wireless communication device for broadband link configuration | |
| WO2016089069A1 (en) | Wireless communication terminal and wireless communication method for clear channel allocation | |
| WO2021182667A1 (en) | Wireless intrusion prevention system, wireless network system comprising same, and method for operating wireless network system | |
| WO2015194917A1 (en) | Wireless communication method for saving power and wireless communication terminal using same | |
| WO2012105803A2 (en) | Network reentry method and apparatus in a mobile communication system | |
| WO2021145601A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for str in wireless lan that supports multi-links | |
| WO2018159992A1 (en) | Method for avoiding collision in synchronous wireless communication system | |
| WO2015167298A1 (en) | Method and device for real time transmission power control in wireless communication system | |
| WO2017115907A1 (en) | Transmission device and method for measuring dynamic path state in various network environments | |
| WO2016122138A1 (en) | Back-off counter selection device for random channel access and method therefor | |
| WO2015023079A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for random access in virtual cell network system | |
| WO2011053067A2 (en) | Method and apparatus of requiring uplink resources for transmitting ranging request message in communication system | |
| WO2012043954A1 (en) | Cognitive radio transmitter and cognitive radio receiver for improving data transfer rate | |
| WO2016137115A1 (en) | Distributed control method and device for wireless communication system | |
| WO2016186478A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for random access for multiple devices in wireless communication system | |
| WO2014003504A1 (en) | Method and device for avoiding macro interference |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16743616 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16743616 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |