WO2015098384A1 - 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 - Google Patents
携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015098384A1 WO2015098384A1 PCT/JP2014/080843 JP2014080843W WO2015098384A1 WO 2015098384 A1 WO2015098384 A1 WO 2015098384A1 JP 2014080843 W JP2014080843 W JP 2014080843W WO 2015098384 A1 WO2015098384 A1 WO 2015098384A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- biometric authentication
- biometric
- context
- key device
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/34—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards
- G06F21/35—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards communicating wirelessly
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/32—User authentication using biometric data, e.g. fingerprints, iris scans or voiceprints
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/34—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/30—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass
- G07C9/32—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass in combination with an identity check
- G07C9/37—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass in combination with an identity check using biometric data, e.g. fingerprints, iris scans or voice recognition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H04L63/061—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network for key exchange, e.g. in peer-to-peer networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0853—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities using an additional device, e.g. smartcard, SIM or a different communication terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0861—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities using biometrical features, e.g. fingerprint, retina-scan
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/06—Authentication
- H04W12/065—Continuous authentication
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus control technique using a portable key device using a biometric authentication technique.
- the mobile device is locked, for example, with a password or pattern lock.
- the personal identification number or pattern may be analyzed and the portable device may be used illegally.
- biometric authentication there are cases where authentication fails due to changes in biometric input methods, biometric information, etc., regardless of the identity of the individual, as defined as the rejection rate of the individual. Also, in order to prevent impersonation, every time the mobile device is unlocked, a biometric input is required. For this reason, it may be less convenient than a password or pattern lock.
- the device can be miniaturized and can be built in a portable device, but the finger vein authentication device using the vein pattern inside the finger, the palm vein authentication device using the palm, Compared with fingerprint authentication, iris authentication devices that use the iris of the eye use internal information of the living body, so it is difficult to duplicate, less affected by the state of the living body such as hand shake, and the amount of information is larger than fingerprint authentication
- it is difficult to reduce the size of the apparatus it is difficult to incorporate it into a portable device.
- the present invention incorporates a wireless communication function, and device control technology using a portable key device using a biometric authentication technology that can reduce the number of authentications while taking advantage of biometric authentication. I will provide a.
- the portable device When wireless communication between the two portable key devices is established, the portable device enters the unlock signal transmission state, and when wireless communication is disconnected, the biometric authentication success context is discarded and the unlock signal transmission is performed. Transition to the stop state and requesting biometric authentication is required to send the unlock signal again.
- the biometric authentication success context is retained to reduce the number of times the user performs biometric authentication, and when the key device is misplaced or the like, the authentication success context is discarded to restrict use by others, thereby improving usability and safety. Can be improved.
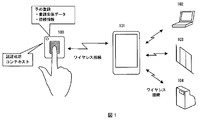
- 1 is a device control system using wireless communication according to an embodiment of the present invention.
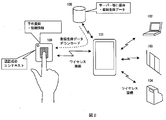
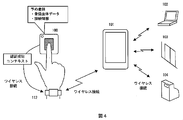
- 1 is a device control system using a server-use type biometric authentication device according to an embodiment of the present invention. It is an apparatus control system using the wearable biometric authentication apparatus concerning the Example of this invention. It is an apparatus control system using the wearable device concerning the Example of this invention.
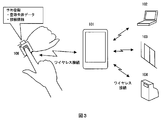
- 1 is a wearable biometric authentication device according to an embodiment of the present invention. 1 is an example of a wearable device according to an example of the present invention. 1 is a circuit example of a wearable device according to an embodiment of the present invention. It is an operation
- Fig. 1 shows an overall conceptual diagram of this embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 the portable device 101, and the control target devices 102 to 104 are used.
- the biometric authentication device 100 includes a communication unit and a biometric information input unit, and registers registered biometric data used for collation and connection information of the connection destination portable device 101 in advance. Registered biometric data and connection information are registered by connecting to a biometric authentication device alone or a host device such as a PC (Personal Computer).
- a biometric authentication device alone or a host device such as a PC (Personal Computer).
- the biometrics to be authenticated will be described using finger veins, but other biometrics such as fingerprints, palm prints, palm veins, irises and faces may be used.
- connection information with the mobile device 101 corresponds to pairing information between devices in a wireless standard such as Bluetooth (registered trademark), for example, and only a specific biometric authentication device and a specific mobile device are secured one-to-one. Connection information for enabling a wireless connection to be established.
- the biometric authentication device 100 is a device that incorporates a battery or the like and can be used on a mobile.
- the portable device 101 includes a communication unit, an input / output unit (for example, a display with a touch panel), and a calculation unit (processor).
- a communication unit for example, a communication unit, an input / output unit (for example, a display with a touch panel), and a calculation unit (processor).
- the control target devices 102 to 104 are devices controlled by the biometric authentication device.
- control targets for example, login control of the PC 102, door locking / opening / closing of the entrance / exit management device 103, and the settlement terminal 104 Payment processing is applicable.
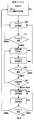
- FIG. 8 shows an operation flow diagram of the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 After the user turns the biometric authentication device 100 from OFF to ON (S701 to 702), the biometric authentication device 100 starts connection with the portable device 101 by wireless communication (S703). If the wireless communication is not established for a certain period, the biometric authentication device shifts to a power OFF state (S701). When the wireless communication is established, the biometric authentication device 100 prompts the user to input biometric information and performs biometric authentication (S704). If the biometric authentication is successful, the biometric authentication device 100 stores the authentication success context in the device, and the portable device 101 that has received the authentication success information shifts to the unlocked state (S705, 706). If the authentication fails, the biometric authentication device 100 shifts to the power OFF state (S701).
- the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 continue to monitor the wireless communication state (S708). While the wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is established, the portable device 101 continues to maintain the unlocked state (S709).
- the user can use the portable device without performing unlocking operation such as password entry by always carrying the biometric authentication device and the portable device at a distance that allows wireless communication.
- step S710 the biometric authentication apparatus 101 discards the authentication success context (S711), and shifts to the power OFF state.
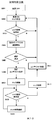
- FIG. 9 shows a flowchart regarding the operation of the mobile device 101.
- the biometric authentication device 100 When the power of the mobile device 101 is turned on (S801) and it is brought close to the biometric authentication device 100 registered in the connection information in advance, the mobile device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 automatically establish a connection by wireless communication, The biometric authentication device 100 enters a biometric input waiting state (S802, S803).
- the wireless connection is assumed to be a one-to-one connection between the specific biometric authentication device 100 and the specific portable device 101 securely by encryption key exchange or the like.
- the biometric authentication device 100 measures the biometric information of the input biometric and creates authentication biometric data, which is registered in advance with the authentication biometric data.
- Biometric authentication is performed by checking the registered biometric data. As a result of the verification, if it is determined that the authentication biometric data and the registered biometric data are the same, the authentication is successful, the authentication success context is generated and stored in the apparatus, and the wireless device authentication is successful. Send with. If the authentication fails, the biometric authentication device shifts to a power-off state in order to reduce battery consumption.
- the portable device waits for reception of authentication success while monitoring wireless communication (S804, S805). At this time, if the wireless communication is interrupted, the wireless communication device 100 returns to the wireless communication monitoring state and the biometric authentication device 100 stops the biometric authentication (S806, S802). When the biometric authentication is successful, the portable device 101 that has received the authentication success starts to send an unlock signal for changing the control target measure from the locked state to the unlocked state (S807).
- the portable device 101 keeps the unlock signal transmission state, and the biometric authentication device 101 keeps the context of the authentication success.
- the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 monitor the state of wireless communication (S809), and if the wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is disconnected even once, the biometric authentication device 100 is in the context of successful authentication. And the portable device 101 shifts to the stop state.
- FIG. 10 shows a flowchart regarding the operation of the control target devices 102 to 104.
- control target device is turned on from power OFF (S901, S902).
- the device to be controlled is in a locked state, that is, no operation is accepted. Then, it waits for an unlock signal from the mobile device 101.
- the unlock signal When the unlock signal is received, authentication of the portable device is started. If it is determined that the unlock signal is for the control target device, the authentication is successful, and the authentication context is stored (S904 to S906). At this time, it may further communicate with the portable device 101 to request information. Here, even if the context of biometric authentication information is further requested from the portable device 101, the user is not requested to input biometric information anew. If the authentication fails, the lock state is continued (S902).
- the device to be controlled is unlocked and becomes operable (S907).
- the user can use the control target device.
- the device to be controlled continues to monitor the unlock signal from the portable device 101, and continues to be operable and unlocked while receiving the unlock signal (S909).
- the lock release signal is not received, the lock state is entered, the operation becomes impossible, the authentication context is discarded, and the process returns to the lock release signal wait (S910, S911, S902).
- the operations of the biometric authentication device 100, the portable device 101, and the control target devices 102 to 104 have the following effects.
- biometric information is required in order to unlock the control target devices 102 to 104 and make them operable. As a result, only the user himself / herself can unlock the control target device, so that safety can be increased.
- the device to be controlled is unlocked depending on the presence or absence of a lock release signal, and does not require new biometric information to be read from the user's body when the lock is released.
- the user holds the biometric authentication success context by establishing wireless communication by carrying the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 in the pockets of clothes or the like. Since wireless communication remains established, the mobile device continues to transmit the unlock signal, and the user can release the lock when approaching the device to be controlled, and it is necessary to read biometric information each time the lock is released. No.
- the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101 is separated due to theft or misplacement, the distance between the portable device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 exceeds the communication distance, and wireless communication is disconnected, and the biometric authentication device 100 discards the context of successful authentication and shifts to the power-off state, and the portable device 101 stops issuing the unlock signal.
- the biometric authentication device 100 In order to recover from this state, the biometric authentication device 100 must be turned on to communicate with the mobile device to perform biometric authentication. That is, only the user can be in a state of transmitting the unlock signal again. Even if only one or both are separately acquired by a third party, there is no biometric information, so it cannot be used.
- an authentication application is installed on a smartphone as the portable device 101.
- the mobile device 101 can be used as a smartphone having functions other than the mobile key.
- a notebook PC or tablet PC may be used as long as the user can carry it.
- the portable device 101 is put in a place where it can be easily taken out such as a breast pocket or a bag. Since the biometric authentication device 100 does not need to be used by the user after successful authentication and only needs to maintain the establishment of wireless communication with the portable device 101, the biometric authentication device 100 is not easily dropped with the user such as a pants pocket. It is desirable to keep it. If the biometric authentication terminal used exclusively for the portable key is combined with the portable device 101 used for other purposes, the user can easily remove the portable device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 is not easily disturbed or dropped. Carrying in difficult places and in different places, the possibility of losing them together can be reduced.
- the radio wave output of the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101 may be an output that can establish a connection only at a short distance of about 1 to 3 m.
- the device to be controlled to be unlocked can be used in combination with the PC 102 equipped with the wireless function, the door entrance / exit management device 103, the settlement terminal 104, or the like.
- the portable device 101 in the lock release signal transmission state approaches the PC 102 in the logout state, and the PC 102 and the portable device 101 are connected by wireless communication, and when mutual authentication is completed, the PC 102 is set in the logon state.
- the user can log on to the PC 102 without performing biometric authentication for each logon, as in the case of performing identity verification for each logon with a single biometric authentication.
- the portable device 101 in the lock release signal transmission state approaches the door entry / exit management device, connects with wireless communication, and when the mutual authentication is completed, the door is unlocked.
- PC it is possible to enter and leave the room in the same way as when confirming the identity of each room with a single biometric authentication, without performing a biometric for each room (entrance or exit). Become.
- the mobile device that is in the lock release signal transmission state at the time of payment is brought close to the payment terminal 104, so that the mobile device 101 and the payment terminal 104 are connected by wireless communication, and mutual authentication is completed and payment is completed. I do.
- a simple operation on the payment terminal 104 may be requested to confirm the payment.
- the user can make a payment in the same manner as in the case of performing identity verification for each payment with a single biometric authentication without performing the biometric authentication for each payment.
- the user may be able to set the valid time of the authentication success context for the biometric authentication device 100. Counts the time since biometric authentication succeeds and generates a context. When the time set by the user has elapsed, the authentication success context stored in biometric authentication device 100 is discarded and the power is turned off. Migrate to Alternatively, a clock is built in the biometric authentication device 100, and when the time set by the user comes, the authentication success context in the authentication device is discarded, and the power-off state is entered.
- the user If the user sets the context destruction time to night, the user authenticates in the morning and uses the mobile device 101 until the night. After leaving work, the biometric authentication device 100 and the mobile device can be left together. At this time, the context of successful authentication can be discarded and the portable device 101 can be shifted to the locked state.
- the lost location can be estimated when the biometric authentication device or the portable device is lost.
- the time at which the wireless connection between the biometric authentication device and the portable device is interrupted is recorded on the biometric authentication device or the portable device, or the portable device 101 is recorded on a server on the network and lost due to misplacement of the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101.
- the time at which the wireless connection is interrupted can be confirmed, and the location where the other device is lost can be estimated from the user's behavior at that time (for example, location information based on GPS or entry / exit records).
- two portable key devices biometric authentication device 100 and portable device 101 that perform wireless communication with each other are provided, and at least one of them has a function of holding a biometric authentication success context. If so, the function of inputting biometric information, the registered biometric data, and the biometric authentication function may be provided so as to communicate with a device different from the two portable key devices.
- Example 2 will be described.
- the second embodiment is mostly the same as the first embodiment and will not be described in detail, but the differences are as follows.
- the registered biometric data is registered in the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 is lost, the registered biometric data in the biometric authentication device 100 is also lost.
- the registered biometric data is stored in a place other than the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 such as the server 105, and wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is established.
- the portable device 101 communicates with the server 105 to download the registered biometric data from the server 105.
- the portable device 101 transmits the downloaded registered biometric data to the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 uses the received registered biometric data to collate with the input biometric information and perform biometric authentication.
- the biometric authentication device 100 When the authentication is successful, the biometric authentication device 100 creates a biometric authentication success context, stores it in the biometric authentication device 100, and then discards the received registered biometric data. The subsequent processing is the same as in the first embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 discards the received registered biometric data and shifts to the power OFF state.
- the registered biometric data can be protected by the above method even if the biometric authentication device 100 is lost.
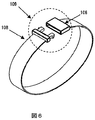
- the biometric authentication device 106 may be a wearable biometric authentication device 106 that is worn by the user, such as a wristwatch or a bracelet. In the first and second embodiments, it is detected that the key device is separated from the user because wireless communication is interrupted. However, in this embodiment, the wearable device worn on the body is separated from the user's body. Is detected.
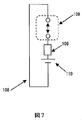
- FIG. 3 shows a conceptual diagram of the wearable biometric authentication device 106.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 includes a biometric detection function 107 such as a pulse meter, and can detect that it has been removed from the human body.
- the circuit configuration shown in FIG. 7 having the shape shown in FIG. 6 and the opening / closing mechanism 109 need to be opened in order to remove it from the human body, such as detecting the removal from the living body by the opening / closing mechanism 109.
- the removal from the human body may be detected by detecting the change in shape.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 performs biometric authentication only in a state worn by the user as in the first and second embodiments. If the authentication is successful, a context for successful authentication is generated and stored in the device.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 since the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is completely integrated with the user, even if the wireless connection between the wearable biometric authentication device 106 and the portable device 101 is disconnected, the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is not lost. Therefore, there is no need to discard the context of successful authentication in the biometric authentication device 100.
- the context of successful authentication in the wearable biometric authentication device 106 can be discarded only by the user removing the wearable biometric authentication device 106 or instructing it with a switch or the like provided in the wearable biometric authentication device 106.
- the wireless communication between the wearable biometric authentication device and the portable device is again performed after the wireless communication between the wearable biometric authentication device and the portable device is disconnected. Is established, the wearable biometric authentication device retains the context of successful authentication, and the portable device can be unlocked again without performing biometric authentication.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 may transmit a lock release signal while holding the biometric authentication success context without using the portable device 101. Even in this case, when the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is removed from the user's human body, this is detected, the biometric authentication success context is discarded, and the transmission of the unlock signal is stopped, which is effective.
- the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 is an embodiment in the case where the authentication success context generated by the biometric authentication apparatus is transferred to another device and used.
- another wearable device 111 such as a wristwatch or a bracelet having a wireless communication function is used.
- the wearable device 111 is assumed to have a function of detecting what the user wears through a living body detection function, a shape change detection, or the like, as in the third embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 generates a context of successful authentication upon successful authentication, and transmits it to the wearable device 111.
- the wearable device 111 receives and holds the context, and further returns a successful reception to the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 discards the context of the authentication success when it is received.
- the wearable device 111 monitors what the user wears using the biometric detection function, and discards the context of authentication success when the wearable device 111 is removed from the user.
- the wearable device 111 When the wearable device 111 that holds the context of the authentication success approaches the mobile device 101 such as a mobile phone or smartphone that is locked with a wireless function, it establishes a wireless connection between the wearable device and the mobile device, and Perform device authentication. If the device authentication is successful, the portable device 101 shifts to an unlock signal transmission state, and thereafter, the wireless device 101 continues to maintain the lock release signal transmission state while the wireless connection with the wearable device is established.
- the mobile device 101 such as a mobile phone or smartphone that is locked with a wireless function
- the mobile device 101 When the mobile device 101 is in the lock release signal transmission state, the mobile device 101 can be used for the PC 102, the door entrance / exit management 103, and the settlement terminal 104 as in the first embodiment.
- the mobile device 101 If the mobile device 101 is lost due to theft or misplacement, if the wireless connection is disconnected due to the distance between the wearable device 111 and the mobile device 101 exceeding the wireless communication distance, the mobile device 101 A third party becomes unusable after shifting to the outgoing call suspension state.
- the wearable device 111 since the wearable device 111 has a function of detecting what the user wears, the wearable device 111 can be worn even after the wireless connection with the mobile device 101 is disconnected. As long as you continue to detect it, you do n’t need to discard the authentication success context stored inside the wearable device, and wireless connectivity with the mobile device is re-established. When established, the portable device shifts to a lock release signal transmission state.
- the biometric authentication success context may be discarded, or the wireless connection disconnection and the wearable device removal may be used as the context discarding condition.
- the wearable device worn by the user does not include a biometric authentication device, it is possible to use a biometric authentication device that has a large casing size but high authentication accuracy, such as a vein authentication device or an iris authentication device. it can.
- the wearable device since the wearable device only needs to incorporate a wireless communication function, it is possible to reduce the size and power consumption.
- Biometric Authentication Device 101 Mobile Device 102 PC 103 Door entry / exit management 104 Payment terminal 105 Server 106 Wearable biometric authentication 107 Biometric detection function 108 Wristband 109 Open / close detection mechanism 110 Battery 111 Wearable device
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
- Lock And Its Accessories (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/021,014 US20160224779A1 (en) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | Portable key device and device control method |
| EP14874447.7A EP3089062B1 (en) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | Portable key device and device control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013264833A JP6063859B2 (ja) | 2013-12-24 | 2013-12-24 | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 |
| JP2013-264833 | 2013-12-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015098384A1 true WO2015098384A1 (ja) | 2015-07-02 |
Family
ID=53478256
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/080843 Ceased WO2015098384A1 (ja) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20160224779A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3089062B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6063859B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015098384A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3118764A1 (en) * | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-18 | Biowatch SA | A biometric sensor apparatus for authenticating a user, and a user authenticating method |
| JP2017111730A (ja) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報処理システム、処理装置、端末装置、認証結果提供方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US11297479B2 (en) | 2018-01-10 | 2022-04-05 | Sony Corporation | Portable wireless device, communication method, and server |
| US11323450B2 (en) | 2017-09-11 | 2022-05-03 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, client system, and control method of client system |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12418794B2 (en) * | 2011-07-15 | 2025-09-16 | Omnissa, Llc | Mobile device authentication |
| EP3128453B1 (en) * | 2015-08-06 | 2021-11-03 | Nokia Technologies Oy | An apparatus comprising a biometric sensor |
| JP6077077B1 (ja) * | 2015-09-14 | 2017-02-08 | ヤフー株式会社 | 認証装置、認証方法及び認証プログラム |
| JP6380360B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-10 | 2018-08-29 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 画像処理システム、画像出力装置、端末装置、画像出力方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US20170300678A1 (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2017-10-19 | Motorola Solutions, Inc | Method and apparatus for using a biometric template to control access to a user credential for a shared wireless communication device |
| US10127926B2 (en) * | 2016-06-10 | 2018-11-13 | Google Llc | Securely executing voice actions with speaker identification and authentication input types |
| JP6801251B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-16 | 2020-12-16 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報機器管理システム、個人識別装置およびプログラム |
| JP6798169B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-13 | 2020-12-09 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 認証システム、制御方法およびプログラム |
| CN106878344A (zh) * | 2017-04-25 | 2017-06-20 | 北京洋浦伟业科技发展有限公司 | 一种生物特征认证、注册方法及装置 |
| JP6902225B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-13 | 2021-07-14 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 認証システム |
| WO2020018940A1 (en) * | 2018-07-20 | 2020-01-23 | The Trustees Of Dartmouth College | Token-based authentication for digital devices |
| US11093659B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2021-08-17 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling content visibility on a computing device based on wearable device proximity |
| US11455411B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2022-09-27 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling content visibility on a computing device based on computing device location |
| US11082402B2 (en) * | 2019-04-25 | 2021-08-03 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling computing device virtual private network usage with a wearable device |
| US11562051B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2023-01-24 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Varying computing device behavior for different authenticators |
| US11431514B1 (en) * | 2019-05-06 | 2022-08-30 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Systems for determining authenticated transmissions of encrypted payloads |
| JP2020201805A (ja) * | 2019-06-12 | 2020-12-17 | 国立大学法人福井大学 | 認証プログラム、認証装置及び認証システム |
| US12495042B2 (en) * | 2021-08-16 | 2025-12-09 | Capital One Services, Llc | Systems and methods for resetting an authentication counter |
| JP7531190B2 (ja) * | 2022-02-15 | 2024-08-09 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 顔認証機および顔認証方法 |
| JP7173648B1 (ja) | 2022-05-02 | 2022-11-16 | 久米機電工業株式会社 | ログイン管理システム |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003058509A (ja) * | 2001-08-15 | 2003-02-28 | Sony Corp | 認証処理システム、認証処理方法、および認証デバイス、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| JP2003085150A (ja) * | 2001-09-12 | 2003-03-20 | Sony Corp | 個人認証システム及び個人認証方法、携帯情報端末、携帯認証媒体、認証装置、並びに記憶媒体 |
| JP2005071225A (ja) * | 2003-08-27 | 2005-03-17 | Sony Corp | 電子機器および認証方法 |
| JP2008073462A (ja) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-04-03 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 認証装置、及び認証方法 |
| US20090094681A1 (en) * | 2007-10-03 | 2009-04-09 | Sadler Daniel J | Method and system for providing extended authentication |
| JP2009286343A (ja) | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 遠隔車両制御システム、乗員認証装置および遠隔車両制御方法 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001195145A (ja) * | 2000-01-07 | 2001-07-19 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 情報処理装置、個人認証方法およびその方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| US8674804B2 (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2014-03-18 | Deadman Technologies, Llc | Control of equipment using remote display |
| US9443071B2 (en) * | 2010-06-18 | 2016-09-13 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Proximity based device security |
| JP2013078175A (ja) * | 2011-09-29 | 2013-04-25 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 電子機器 |
-
2013
- 2013-12-24 JP JP2013264833A patent/JP6063859B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-11-21 EP EP14874447.7A patent/EP3089062B1/en active Active
- 2014-11-21 US US15/021,014 patent/US20160224779A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-11-21 WO PCT/JP2014/080843 patent/WO2015098384A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003058509A (ja) * | 2001-08-15 | 2003-02-28 | Sony Corp | 認証処理システム、認証処理方法、および認証デバイス、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| JP2003085150A (ja) * | 2001-09-12 | 2003-03-20 | Sony Corp | 個人認証システム及び個人認証方法、携帯情報端末、携帯認証媒体、認証装置、並びに記憶媒体 |
| JP2005071225A (ja) * | 2003-08-27 | 2005-03-17 | Sony Corp | 電子機器および認証方法 |
| JP2008073462A (ja) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-04-03 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 認証装置、及び認証方法 |
| US20090094681A1 (en) * | 2007-10-03 | 2009-04-09 | Sadler Daniel J | Method and system for providing extended authentication |
| JP2009286343A (ja) | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 遠隔車両制御システム、乗員認証装置および遠隔車両制御方法 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3118764A1 (en) * | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-18 | Biowatch SA | A biometric sensor apparatus for authenticating a user, and a user authenticating method |
| US10659456B2 (en) | 2015-07-15 | 2020-05-19 | Biowatch SA | Method, device and computer program for authenticating a user |
| JP2017111730A (ja) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報処理システム、処理装置、端末装置、認証結果提供方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US11323450B2 (en) | 2017-09-11 | 2022-05-03 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, client system, and control method of client system |
| US11297479B2 (en) | 2018-01-10 | 2022-04-05 | Sony Corporation | Portable wireless device, communication method, and server |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6063859B2 (ja) | 2017-01-18 |
| EP3089062A4 (en) | 2017-06-21 |
| EP3089062A1 (en) | 2016-11-02 |
| JP2015121910A (ja) | 2015-07-02 |
| EP3089062B1 (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| US20160224779A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6063859B2 (ja) | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 | |
| US11720656B2 (en) | Live user authentication device, system and method | |
| US9349235B2 (en) | Preauthorized wearable biometric device, system and method for use thereof | |
| US11451536B2 (en) | User state monitoring system and method using motion, and a user access authorization system and method employing same | |
| EP3078157B1 (en) | A wearable device and a method for storing credentials associated with an electronic device in said wearable device | |
| US20240098491A1 (en) | Cryptographic process for portable devices, and user presence and/or access authorization system and method employing same | |
| US11605255B2 (en) | User activity-related monitoring system and method, and a user access authorization system and method employing same | |
| KR101219957B1 (ko) | 바이오메트릭스를 이용한 사용자 인증 방법, 장치 및 시스템, 이를 위한 기록 매체 | |
| KR102291715B1 (ko) | 웨어러블 단말기와의 상호 작용에 의한 도어락 제어 시스템 | |
| US20170286655A1 (en) | Wearable device, system including the same, and operation methods thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14874447 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014874447 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014874447 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15021014 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |