WO2014163257A1 - Novel infectious bursal disease (ibd) virus k7 strain and vaccine against infectious bursal disease using same - Google Patents
Novel infectious bursal disease (ibd) virus k7 strain and vaccine against infectious bursal disease using same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014163257A1 WO2014163257A1 PCT/KR2013/007945 KR2013007945W WO2014163257A1 WO 2014163257 A1 WO2014163257 A1 WO 2014163257A1 KR 2013007945 W KR2013007945 W KR 2013007945W WO 2014163257 A1 WO2014163257 A1 WO 2014163257A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- virus
- infectious
- vaccine
- cystic
- ibd
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/12—Viral antigens
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N7/00—Viruses; Bacteriophages; Compositions thereof; Preparation or purification thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2720/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA dsRNA viruses
- C12N2720/00011—Details
- C12N2720/10011—Birnaviridae
- C12N2720/10021—Viruses as such, e.g. new isolates, mutants or their genomic sequences
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2720/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA dsRNA viruses
- C12N2720/00011—Details
- C12N2720/10011—Birnaviridae
- C12N2720/10034—Use of virus or viral component as vaccine, e.g. live-attenuated or inactivated virus, VLP, viral protein
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a novel infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain and an infectious F cystic vaccine using the same.
- IBD infectious bursal disease
- IBDV Gumboro disease in chickens
- IBD virus IBDV
- IBDV belongs to the family Birnaviridae. The genome consists of two strands of double-stranded A and B RNA, segment A contains VP5, VP2, VP4 and VP3 genes, and segment B contains the VP1 gene.
- IBDV has two serotypes, type 1 and type 2, which can be classified by viral neutralization (VN) tests. Serotype 1 virus has been shown to be pathogenic for chickens, whereas serotype 2 IBDV causes subacute disease only in turkey.
- VN viral neutralization
- Infectious F cystic disease is an important target that causes infection of the F sac (Bursa of Fabricius) cells to cause immunosuppression.
- Infection of chickens at 3-6 weeks of age leads to clinically infectious F-cysts with high morbidity and mortality, and if infected before 3 weeks of age, rapid immunodepression occurs due to the rapid destruction of lymphocytes in the antibody-producing F-cysts.
- Immunity against various vaccines is reduced and resistance to infectious diseases is weakened. Therefore, diseases that were not observed due to uncontrollable or latent infections in normal chickens show clinical symptoms or more severe clinical symptoms in chickens infected with infectious F cystic disease, causing enormous economic losses to the poultry industry.
- Infectious F-cytopathic live vaccines used at home and abroad to prevent illness are severely toxic (M; mild) and intermediate (I; intermediate) depending on their ability to overcome virulence and maternal antibody levels. It is classified as intermediate plus (I +), which has a strong virulence of intermediate and intermediate poison vaccines that can overcome maternal antibodies in order to prevent early infectious infectious F cystic disease. .
- Korean Patent Publication No. 1020110116315 describes a novel non-pathogenic infectious FDR virus (BP-IBDVac) having excellent vaccine efficacy against infectious FDR disease, an infectious FBD disease vaccine comprising the same, and a method of preparing the same.
- BP-IBDVac non-pathogenic infectious FDR virus
- the present invention has been made in view of the above problems and the need for the above, and an object of the present invention is to provide a novel infectious F cystic virus.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a novel infectious F cystic vaccine.
- the present invention provides infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain deposited with accession number KCTC 12376BP.
- the strain was deposited on March 11, 2013 with the accession number KCTC 12376BP to the Gene Bank of Korea Biotechnology Institute (Yeoseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea) as an international depositing institution.
- the virus is preferably isolated from domestic broilers, and the segments A and B of the virus preferably have the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2, respectively, but are not limited thereto.
- segment A of the virus has amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 3 (VP 5) and 4 (VP2-VP4-VP3) and segment B has amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 5 (VP 1) , 45, 74, 133 in SEQ ID NO: 3, 222, 242, 256, 279, 284, 294, 299, 451, 680, 715, and 751 in SEQ ID NO: 4 , 981, 1005 residues, and 4, 13, 61, 145, 146, 147, 242, 287, 390, 393, 508, 511, 562 in SEQ ID NO: 5 Times, 687, 695th residue is preferably different from other strains, but is not limited thereto.
- the present invention also provides a vaccine for poultry protection against diseases caused from infectious F cystic virus infection, comprising the virus of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
- the virus is in live form, it is preferred that the vaccine further comprises an adjuvant, and that the vaccine further comprises one or more vaccine components of other pathogens infectious to poultry.
- the vaccine further comprises one or more vaccine components of other pathogens infectious to poultry.
- the present invention comprises the steps of a) inoculating a substrate susceptible to infection with an infectious F cystic virus as defined in any one of claims 1 to 3; b) propagating said infectious F cystic virus; And c) provides a method for producing an infectious F-Cyst virus comprising the step of collecting the infectious F-Cyst virus-containing material.
- the substrate is one cell selected from the group consisting of embryonic liver cells (CEL), chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF), chicken kidney cells (CK), and Vero cell lines. But is not limited thereto.
- the present invention also provides a method of controlling a disease caused from an infectious F cystic infection in poultry comprising administering the vaccine of the present invention to birds.
- Vaccines of the invention containing live virus are prepared and marketed in the form of lyophilized or (frozen) suspensions.
- the vaccine further comprises a diluent or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier commonly used in the composition.
- Carriers include stabilizers, preservatives and buffers. Suitable stabilizers are, for example, SPGA, hydrocarbons (eg sorbitol, mannitol, starch, sucrose, dextran, glutamate, or glucose), proteins (eg dried milk serum, albumin or casein) or degradation products thereof. .
- Suitable buffers are for example alkali metal phosphates.
- the live vaccine of the present invention may contain an adjuvant.
- suitable compounds and compositions with adjuvant activity are the same as mentioned below for the preparation of inactivated vaccines.
- the live vaccines of the present invention can be administered, for example, by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, but the live vaccines are preferably administered by low-cost mass administration techniques commonly used for infectious F cystic virus vaccination. This technique includes drinking water and spray vaccination.
- Another method for the administration of live vaccines includes in ovo administration, eye drop administration and beak dipping administration.
- the vaccine of the invention is an active ingredient in an amount effective to immunize an infectious F follicular virus substance, ie an infectious F follicular virus substance that will induce immunity in a vaccinated bird or their offspring against an attack by an toxic virus (antigen administration).
- an infectious F follicular virus substance ie an infectious F follicular virus substance that will induce immunity in a vaccinated bird or their offspring against an attack by an toxic virus (antigen administration).
- Immunity is defined herein to induce a significantly higher level of protection in avian populations after vaccination compared to the non-vaccinated group.
- the live vaccine of the present invention can be administered at a dose of 10 2 -10 9 TCID 50, preferably 10 2 -10 6 TCID 50 per bird.
- the infectious F cystic virus vaccine of the present invention can be used effectively in chickens, but other poultry such as turkey, guinea fowl and quail can also be effectively vaccinated.
- Chickens include edible chickens, cloned cattle, and laying eggs.
- the age of the animals receiving the live vaccine according to the present invention is the same as the age of the animals receiving the currently available live infectious F cystic virus vaccine.
- edible chickens are directly vaccinated with the live vaccine of the present invention from day 1 of birth.
- Vaccination of parental livestock, such as breeders of edible chickens can be performed with the live vaccine of the present invention.
- the advantages of this type of vaccine program include the direct protection of one day old offspring provided by antibodies from the maternal line that are delivered vertically to the offspring.
- a typical breeder's vaccination program includes two to three weeks old livestock inoculated with live, weakened vaccines followed by 14 to 18 weeks old inactivated vaccines.
- Figure 2 is a graph showing the sales ratio of the infectious F cyst live vaccine type in Korea
- Example 1 Isolation of infectious bursal disease virus IBD K7 strain , identification of other pathogens
- IBV Infectious bronchitis virus
- NDV Newcastle disease
- Fowl adeno virus to check for the presence of other pathogens capable of proliferation in the ureteral fluid of the chick embryo , FAdV
- FAdV Chicken infectious anemia virus
- CIAV Chicken infectious anemia virus
- Mycoplasma Mycoplasma
- RT-PCR reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- PCR polymerase chain reaction
- dNTPs deoxynucleotide triphosphates
- the cDNA thus obtained was mixed with 1 ⁇ l of 4-fold diluted cDNA solution, 1 ⁇ l of 10x PCR buffer, 0.2 ⁇ l of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 2 ⁇ l of each primer, 1 ⁇ l of Taq polymerase and 7.2 ⁇ l of DW.
- the PCR product obtained using the reaction solution was purified, and the nucleotide sequence was determined using an ABI3100 autobase sequencer.
- the genome sequence of IBD K7 (Segment A base of IBD K7 virus and Segment B base of IBD K7 virus represented by Segment A and Segment B) is SEQ ID NO: 1, respectively.
- Table 1 shows the sequence and position of the primer set used in the Segment A base analysis
- Table 2 is a table showing the nucleotide sequence and position of the primer set used in Segment B nucleotide analysis
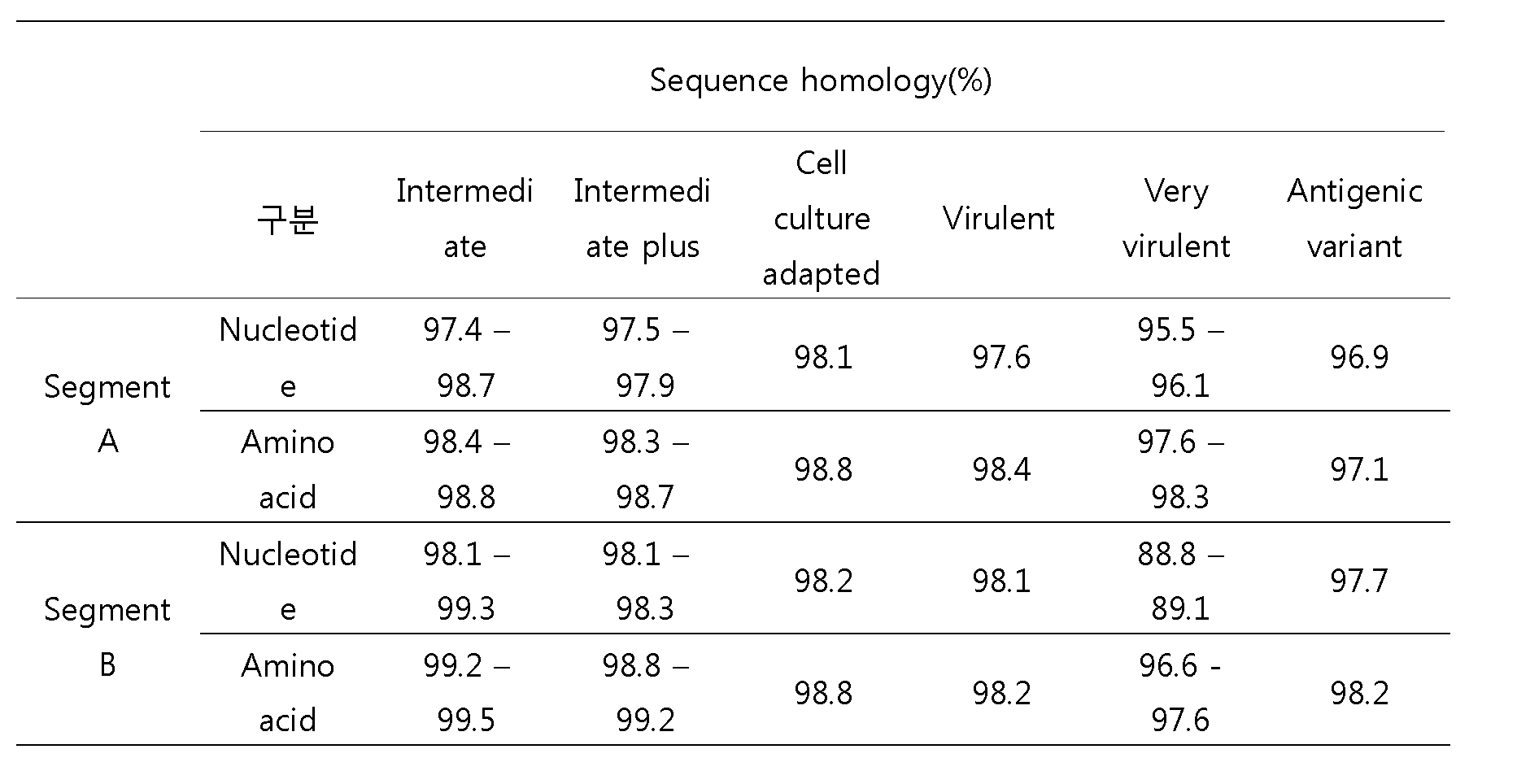
- IBD K7 The entire gene of IBD K7 virus was compared with domestic and foreign infectious F cystic virus registered on GenBank using BLAST search (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast) and Bioedit program. As a result, IBD K7 showed relatively higher homology to the attenuated virus than to the virulent virus (Table 3).
- VP2 hypervariable region analysis applied to phylogenetic analysis revealed that it is a new type that does not belong to any existing type.
- IBD K7 is a very unique antigen with both toxic and attenuated viral motifs.
- IBD K7 had a typical attenuated viral motif (Tables 4 and 5).
- IBD K7 is a novel recombinant IBD virus compared to existing viruses with some of the virogenic viral antigen motif.
- Table 3 shows overall gene homology with IBD K7 and conventional IBDV strain.
- Table 4 shows the comparative analysis of VP5, VP2, VP4 and VP3 of IBD K7 and vaccine and field strains.
- Table 5 shows the comparative analysis of IBD K7, VP1 and vaccine strains.
- IBD K7 strain at 3 weeks of age of SPF chicken and Winterfield strain and D78 strain of IBDV vaccine were administered orally at 103 ELD50 / dose to 8 chickens in each group.
- the rest was euthanized and subjected to body weight and BB-rate [(F-bag weight (g) / weight (g)) ⁇ 1000] and antibody response test.
- body weight and BB-rate [(F-bag weight (g) / weight (g)) ⁇ 1000] and antibody response test.
- IBD K7 strain group each of them died within 4 days, and the remaining groups survived for 7 days.
- body weight and BB-rate it was found to have intermediate pathogenicity between intermediate poisoning and intermediate poisoning.
- the ELISA titer of serum isolated from 4 and 7 days after vaccination showed that the immune response was somewhat lower than that of medium poisoning plus. It was found to be low but stronger than medium poisons (Tables 6 and 7).
- Table 6 shows body weight and BB rate after 4 and 7 days of IBD K7 strain, medium poison plus, medium poison vaccination
- Table 7 shows ELISA titers 4 and 7 days after IBD K7 strain, intermediate poison plus, intermediate poison vaccination
- IBD K7 As a live vaccine, three-week-old SPF chickens were orally vaccinated with IBD K7 strain and the existing vaccine strain Winterfield strain and D78 at 10 3 ELD 50 per dose, and 2 weeks after vaccination.
- the highly infectious F cynovirus was challenged by instillation of 10 5 ELD 50 per dose.
- the control group was also challenged with the same virus in the same manner. Five days after inoculation, clinical symptoms such as depression, feather inversion, and mortality were observed.
- Table 8 is a table showing the protective capacity and immunogenicity against toxic IBDV challenge in IBD K7 strain vaccine chicken.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention relates to a novel infectious bursal disease (IBD) virus K7 strain and a vaccine against an infectious bursal disease using the same.
Description
본 발명은 신규 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주 및 이를 이용한 전염성 F낭병 백신에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a novel infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain and an infectious F cystic vaccine using the same.
닭의 전염성 F낭병(infectious bursal disease, IBD) 또는 감보로병(Gumboro disease)로 불리는 이 병은, IBD 바이러스(IBDV)에 의하여 발병되는 전염병이다. IBDV는 Family Birnaviridae에 속하며 genome은 두 가닥(double-stranded)의 A와 B 2개의 RNA 분절로 이루어져 있으며 분절 A에는 VP5, VP2, VP4, VP3 유전자가 있고, 분절 B에는 VP1 유전자가 있다. IBDV는 1형과 2형 두 개의 혈청형이 존재하는데 이들 두 가지 혈청형은 바이러스 중화(VN) 테스트에 의해 분류될 수 있다. 혈청형 1형 바이러스는 닭에 대해 병원성을 나타내는 것으로 확인된 반면, 혈청형 2형 IBDV는 칠면조에서만 아급성 질병을 유발한다. 전염성 F낭병은 주요 표적으로서 F낭(Bursa of Fabricius) 세포에 감염이 일어나 면역억제를 일으키는 병이다. 3~6주령의 닭에 감염되면 높은 이환율과 폐사율을 보이는 임상형 전염성 F낭병이 유발되며, 3주령 이전에 감염될 경우 항체를 생산하는 F낭 내 림프구를 급격히 파괴시켜 면역억제가 심하게 나타나며, 이로 인하여 각종 백신에 대한 면역효과가 저하되고 전염성 질병에 대한 저항성도 약화된다. 따라서 정상계군에서는 불현성 또는 잠복감염으로 증상이 관찰되지 않던 질병들이 전염성 F낭병에 감염된 계군에서는 임상증상을 나타내거나 더욱 심한 임상증상을 일으켜 양계산업에 막대한 경제적 손실을 가져오고 있다.This disease, called infectious bursal disease (IBD) or Gumboro disease in chickens, is an infectious disease caused by IBD virus (IBDV). IBDV belongs to the family Birnaviridae. The genome consists of two strands of double-stranded A and B RNA, segment A contains VP5, VP2, VP4 and VP3 genes, and segment B contains the VP1 gene. IBDV has two serotypes, type 1 and type 2, which can be classified by viral neutralization (VN) tests. Serotype 1 virus has been shown to be pathogenic for chickens, whereas serotype 2 IBDV causes subacute disease only in turkey. Infectious F cystic disease is an important target that causes infection of the F sac (Bursa of Fabricius) cells to cause immunosuppression. Infection of chickens at 3-6 weeks of age leads to clinically infectious F-cysts with high morbidity and mortality, and if infected before 3 weeks of age, rapid immunodepression occurs due to the rapid destruction of lymphocytes in the antibody-producing F-cysts. Immunity against various vaccines is reduced and resistance to infectious diseases is weakened. Therefore, diseases that were not observed due to uncontrollable or latent infections in normal chickens show clinical symptoms or more severe clinical symptoms in chickens infected with infectious F cystic disease, causing enormous economic losses to the poultry industry.
이 병은 1962년 Cosgrove에 의해 처음 보고된 이후 전 세계에서 이 병이 존재하고 있음이 확인되었고, 우리나라에서는 1979년에 가축위생연구소의 연구팀에 의해 50% 이상의 닭이 감염되어 있음이 확인되었다. 그 후 유럽에서 1987년 처음으로 강독형 전염성 F낭병(very virulent IBD)이 출현하여 심각한 병증을 일으켰으며, 우리나라에서는 1992년 충남 성환 지역 9주령 산란계에서 처음으로 보고되었다. 그 당시 발생농장은 심한 임상증상과 함께 30% 이상의 높은 폐사율을 보이는 것으로 보고되었다. 강독형 전염성 F낭병은 기존 고전형과 달리 3주령 이하나 6주령 이후 주령에서도 높은 폐사를 유발하고 면역장기인 F낭에서 부종이나 충혈 등의 염증반응 없이 곧바로 위축됨으로써 병증이 빠르게 진행되는 특징을 나타냈다.Since the disease was first reported by Cosgrove in 1962, it has been found worldwide. In 1979, it was confirmed that more than 50% of chickens were infected by a team of animal hygiene research institutes. Then, in 1987, the very first very virulent IBD appeared in Europe, causing serious illness. In 1992, it was first reported in 9-week-old laying hens in Seonghwan, Chungnam. The farms at that time were reported to have a high mortality rate of more than 30% with severe clinical symptoms. Unlike the existing classic type, the highly toxic infectious F cyst causes high mortality even after 3 weeks or 6 weeks of age, and the disease progresses rapidly due to atrophy of inflammatory reactions such as swelling or hyperemia in the F organ, which is an immune organ. .
현재 발생하는 야외 전염성 F낭병은 고전형이나 변이형 전염성 F낭병이 거의 없고 사실상 모두 강독형 전염성 F낭병(79%)이다. 병증이 심각하게 나타나는 강독형 감보로 병을 예방하기 위하여 국내외에서 사용되고 있는 전염성 F낭병 생독백신은 독력과 모체이행항체 수준을 극복하는 능력에 따라 약독(M; mild), 중간독(I; intermediate), 중간독 플러스(I+; intermediate plus)로 구별되는데, 조기 감염이 되는 강독형 전염성 F낭병을 예방하기 위해 모체이행항체를 극복할 수 있는 독력이 강한 중간독 및 중간독 플러스 백신이 현재 주로 사용되고 있다.Currently, open field infectious F cysts have few classic or variant infectious F cysts and virtually all are toxic infectious F cysts (79%). Infectious F-cytopathic live vaccines used at home and abroad to prevent illness are severely toxic (M; mild) and intermediate (I; intermediate) depending on their ability to overcome virulence and maternal antibody levels. It is classified as intermediate plus (I +), which has a strong virulence of intermediate and intermediate poison vaccines that can overcome maternal antibodies in order to prevent early infectious infectious F cystic disease. .
*동물약품협회의 자료에 근거하여 연도별 전염성 F낭병 백신 스트레인별 판매비율을 살펴보면 중간독 플러스형 백신(전체의 74~79%), 중간독형 백신(16~22%), 약독형(4~9%) 순서로 나타났다. 이는 강독형 전염성 F낭병의 조기감염을 예방하기 위해 보다 빨리 모체이행항체를 극복할 수 있는 중간독 플러스 백신 사용을 선호하고 있는 것을 나타낸다고 할 수 있다. (그림 2) 중간독 플러스 백신이 강한 면역반응을 일으켜 효과적인 전염성 F낭병 예방을 가능하게 하지만 강한 백신 반응으로 강독형 전염성 F낭병에 감염된 것과 유사한 증상을 일으키고, 면역장기인 F낭에 심각한 손상을 일으키는 것으로 알려져 있다. (Rautenschlein S et al., Protective efficacy of intermediate and intermediate plus infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) vaccines against very virulent IBDV in commercial broilers, Avian Dis. 2005 Jun;49(2):231-7)* Based on the data of the Animal Drug Association, the annual sales rate of infectious F-cystic vaccine vaccine strain by strain is medium-plus vaccine (74-79% of the total), intermediate-type vaccine (16-22%), and attenuated drug (4 ~ 9%). This may indicate a preference for the use of intermediate poisoning plus vaccines that can overcome maternally-transduced antibodies more quickly to prevent premature infection of highly infectious F-cystic disease. (Figure 2) Medium Poison Plus Vaccine Produces a Strong Immune Response That Effectively Prevents Infectious F-Cysts, but Strong Vaccine Responds to Similar Symptoms of Infectious F-Cysts It is known. (Rautenschlein S et al., Protective efficacy of intermediate and intermediate plus infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) vaccines against very virulent IBDV in commercial broilers, Avian Dis. 2005 Jun; 49 (2): 231-7)
현재 국내에서 주로 사용되고 있는 중간독 플러스 백신주들은 전염성 F낭병에 대한 강한 면역력을 형성하지만 면역장기인 F낭에 심각한 손상을 일으켜 다른 질병에 대한 저항성을 저하시킬 수 있기 때문에 기존의 중간독 플러스형 백신의 독력에 비해 낮은 독력을 나타내며, 중간독형 전염성 F낭병 백신보다 높은 면역원성을 지닌 백신 개발이 절실히 요구되고 있는 실정이다.Currently, the intermediate poisonous plus vaccine strains used in Korea form a strong immunity against infectious F cystic disease but can cause severe damage to F organ, which is an immune organ, and thus lower resistance to other diseases. Compared to virulence, low virulence and development of a vaccine with higher immunogenicity than an intermediate infectious F follicular vaccine are urgently needed.
관련 특허로 대한민국 특허공개번호 제1020110116315호는 전염성 F낭병에 대하여 백신 효능이 우수한 신규한 비병원성 전염성 F낭병 바이러스(BP-IBDVac), 이를 포함하는 전염성 F낭병 백신, 및 이의 제조 방법이 기재되어 있다. As a related patent, Korean Patent Publication No. 1020110116315 describes a novel non-pathogenic infectious FDR virus (BP-IBDVac) having excellent vaccine efficacy against infectious FDR disease, an infectious FBD disease vaccine comprising the same, and a method of preparing the same.
본 발명은 상기의 문제점을 해결하고 상기의 필요성에 의하여 안출된 것으로서 본 발명의 목적은 신규 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made in view of the above problems and the need for the above, and an object of the present invention is to provide a novel infectious F cystic virus.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 신규한 전염성 F낭병 백신을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a novel infectious F cystic vaccine.
상기의 목적을 달성하기 위하여 본 발명은 기탁번호 KCTC 12376BP로 기탁된 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주를 제공한다. In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain deposited with accession number KCTC 12376BP.
상기 균주는 2013년 3월 11일자로 국제기탁기관인 한국생명공학연구원 유전자은행(대한민국 대전시 유성구 소재)에 수탁번호 KCTC 12376BP로 기탁되었다. The strain was deposited on March 11, 2013 with the accession number KCTC 12376BP to the Gene Bank of Korea Biotechnology Institute (Yeoseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea) as an international depositing institution.
일 구현예에 상기 바이러스는 국내 육계로부터 분리한 것이 바람직하고, 상기 바이러스의 시그먼트 A 및 B는 각각 서열번호 1 및 2에 기재된 염기서열을 가지는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정되지 아니한다.In one embodiment, the virus is preferably isolated from domestic broilers, and the segments A and B of the virus preferably have the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2, respectively, but are not limited thereto.
일 구현예에 상기 바이러스의 시그먼트 A는 서열번호 3(VP 5) 및 4(VP2-VP4-VP3)에 기재된 아미노산 서열을 가지며 시그먼트 B는 서열번호 5(VP 1)에 기재된 아미노산 서열을 가지며, 서열번호 3에서는 45번, 74번, 133번, 서열번호 4에서는 222번, 242번, 256번, 279번, 284번, 294번, 299번, 451번, 680번, 715번, 751번, 981번, 1005번째 잔기, 그리고 서열번호 5에서는 4번, 13번, 61번, 145번, 146번, 147번, 242번, 287번, 390번, 393번, 508번, 511번, 562번, 687번, 695번째 잔기가 다른 균주들과 차이가 있는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정되지 아니한다.In one embodiment segment A of the virus has amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 3 (VP 5) and 4 (VP2-VP4-VP3) and segment B has amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 5 (VP 1) , 45, 74, 133 in SEQ ID NO: 3, 222, 242, 256, 279, 284, 294, 299, 451, 680, 715, and 751 in SEQ ID NO: 4 , 981, 1005 residues, and 4, 13, 61, 145, 146, 147, 242, 287, 390, 393, 508, 511, 562 in SEQ ID NO: 5 Times, 687, 695th residue is preferably different from other strains, but is not limited thereto.
또한 본 발명은 상기 본 발명의 바이러스 및 약학적 허용 담체 또는 희석제를 포함하는, 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 감염으로부터 유발된 질병에 대한 가금 보호용 백신을 제공한다.The present invention also provides a vaccine for poultry protection against diseases caused from infectious F cystic virus infection, comprising the virus of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
일 구현예에 있어서, 상기 바이러스가 살아있는 형태임이 바람직하고, 상기 백신이 보조제를 추가로 포함하는 것을 바람직하며, 상기 백신이 가금에 감염성이 있는 다른 병원균의 백신성분을 하나 이상 추가로 포함하는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정되지 아니한다.In one embodiment, it is preferred that the virus is in live form, it is preferred that the vaccine further comprises an adjuvant, and that the vaccine further comprises one or more vaccine components of other pathogens infectious to poultry. One is not limited thereto.
또 본 발명은 a) 감염되기 쉬운 기질에 제1항 내지 제3항의 어느 한 항에 정의된 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 접종하는 단계; b) 상기 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 증식시키는 단계; 및 c) 상기 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 함유 물질을 수거하는 단계를 포함하는 전염성 F낭병 바이러스의 제조 방법을 제공한다.In another aspect, the present invention comprises the steps of a) inoculating a substrate susceptible to infection with an infectious F cystic virus as defined in any one of claims 1 to 3; b) propagating said infectious F cystic virus; And c) provides a method for producing an infectious F-Cyst virus comprising the step of collecting the infectious F-Cyst virus-containing material.
일 구현예에 있어서, 상기의 기질은 닭 간의 배세포(CEL), 닭의 배 섬유아세포(CEF), 닭의 신장세포(CK), 및 베로(Vero) 세포주로 구성된 군으로부터 선택된 하나의 세포인 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정되지 아니한다.In one embodiment, the substrate is one cell selected from the group consisting of embryonic liver cells (CEL), chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF), chicken kidney cells (CK), and Vero cell lines. But is not limited thereto.
또 본 발명은 상기 본 발명의 백신을 조류에 투여하는 것을 포함하는 가금에서 전염성 F낭병 감염으로부터 유발된 질병을 제어하는 방법을 제공한다.The present invention also provides a method of controlling a disease caused from an infectious F cystic infection in poultry comprising administering the vaccine of the present invention to birds.
살아있는 바이러스를 함유하는 본 발명의 백신은 동결건조된 형태나 (동결된) 현탁액의 형태로 제조되어 시판된다. 백신은 상기 조성물에 통상적으로 사용되는 희석제 또는 약학적 허용 담체를 추가로 포함한다. 담체는 안정화제, 보존제 및 완충액을 포함한다. 적당한 안정화제는 예를 들어 SPGA, 탄화수소(예로, 소비톨, 만니톨, 전분, 자당, 덱스트란, 글루타메이트, 또는 글루코스), 단백질(예로, 건조된 우유혈청, 알부민 또는 카세인)또는 그것의 분해 산물이다. 적당한 완충액은 예를 들어 알칼리 금속 포스페이트이다. 적당한 보존제는 티메로살, 메티올레이트, 겐타마이신이다. 희석액은 물, 수성 완충액(예로 완충 염수), 알코올 및 폴리올(예로 글리세롤)이다.Vaccines of the invention containing live virus are prepared and marketed in the form of lyophilized or (frozen) suspensions. The vaccine further comprises a diluent or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier commonly used in the composition. Carriers include stabilizers, preservatives and buffers. Suitable stabilizers are, for example, SPGA, hydrocarbons (eg sorbitol, mannitol, starch, sucrose, dextran, glutamate, or glucose), proteins (eg dried milk serum, albumin or casein) or degradation products thereof. . Suitable buffers are for example alkali metal phosphates. Suitable preservatives are thimerosal, methiolate, gentamicin. Dilutions are water, aqueous buffers (eg buffered saline), alcohols and polyols (eg glycerol).
필요한 경우, 본 발명의 살아있는 백신은 보조제를 함유할 수 있다. 보조적 활성을 가진 적당한 화합물과 조성물의 예는 불활성화된 백신의 제조를 위해 아래에 언급된 것과 동일하다.If necessary, the live vaccine of the present invention may contain an adjuvant. Examples of suitable compounds and compositions with adjuvant activity are the same as mentioned below for the preparation of inactivated vaccines.
본 발명의 살아있는 백신은 예를 들어 근육내, 피하내 주사에 의한 투여가 가능하지만, 살아있는 백신은 전염성F낭병 바이러스 백신접종에 통상적으로 사용되는 저가의 대량 투여 기법에 의해 투여되는 것이 바람직하다. 이 기법은 음료수 및 분무 백신접종을 포함한다.The live vaccines of the present invention can be administered, for example, by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, but the live vaccines are preferably administered by low-cost mass administration techniques commonly used for infectious F cystic virus vaccination. This technique includes drinking water and spray vaccination.
살아있는 백신의 투여를 위한 또 다른 방법은 난내(in ovo) 투여, 점안 투여 및 부리를 담그는 투여(beak dipping administration)를 포함한다.Another method for the administration of live vaccines includes in ovo administration, eye drop administration and beak dipping administration.
본 발명의 백신은 활성 성분으로서 전염성F낭병 바이러스를 유효량, 즉 독성 바이러스에 의한 공격(항원 투여)에 대항하여 백신 접종된 조류 또는 그들의 자손에서 면역을 유도할 전염성F낭병 바이러스 물질을 면역화시키는 양으로 포함한다. 본원에서 면역은 백신접종되지 않은 군에 비해 백신접종 후 조류 집단에서 상당히 높은 레벨의 보호를 유도하는 것으로 정의된다.The vaccine of the invention is an active ingredient in an amount effective to immunize an infectious F follicular virus substance, ie an infectious F follicular virus substance that will induce immunity in a vaccinated bird or their offspring against an attack by an toxic virus (antigen administration). Include. Immunity is defined herein to induce a significantly higher level of protection in avian populations after vaccination compared to the non-vaccinated group.
통상적으로, 본 발명의 살아있는 백신은 조류 1 마리 당 102-109TCID50 , 바람직하게는 102-106 TCID50의 용량으로 투여될 수 있다. Typically, the live vaccine of the present invention can be administered at a dose of 10 2 -10 9 TCID 50, preferably 10 2 -10 6 TCID 50 per bird.
본 발명의 전염성F낭병 바이러스 백신은 닭에 효과적으로 사용될 수 있으나, 칠면조, 기니아 파울(guinea fowl) 및 메추라기와 같은 기타의 가금도 효과적으로 백신으로 접종될 수 있다. 닭은 식용 닭, 복제 가축, 및 알을 낳는 가축을 포함한다.The infectious F cystic virus vaccine of the present invention can be used effectively in chickens, but other poultry such as turkey, guinea fowl and quail can also be effectively vaccinated. Chickens include edible chickens, cloned cattle, and laying eggs.
본 발명에 따른 살아있는 백신을 투여받은 동물의 나이는 현재 시판되는 살아있는 전염성F낭병 바이러스 백신을 투여받은 동물의 나이와 동일하다. 예를 들면, 식용 닭은 생후 1일부터, 본 발명의 살아있는 백신으로 직접 백신접종된다. 식용 닭의 종축과 같은 부모 가축의 백신접종은 본 발명의 살아있는 백신으로 수행될 수 있다. 이런 유형의 면역주사 프로그램의 장점은 수직적으로 새끼에게 전달되는 모계 유래의 항체에 의해 제공된 생후 1일된 자손의 직접적인 보호를 포함한다. 전형적인 종축의 백신접종 프로그램은 생후 2~3주의 종축에게 살아있는 약화된 백신을 접종한 후 생후 14-18주에 불활성화된 백신을 접종하는 것을 포함한다. The age of the animals receiving the live vaccine according to the present invention is the same as the age of the animals receiving the currently available live infectious F cystic virus vaccine. For example, edible chickens are directly vaccinated with the live vaccine of the present invention from day 1 of birth. Vaccination of parental livestock, such as breeders of edible chickens, can be performed with the live vaccine of the present invention. The advantages of this type of vaccine program include the direct protection of one day old offspring provided by antibodies from the maternal line that are delivered vertically to the offspring. A typical breeder's vaccination program includes two to three weeks old livestock inoculated with live, weakened vaccines followed by 14 to 18 weeks old inactivated vaccines.
본 발명에서는 새로운 전염성 F낭병 바이러스, 이를 포함하는 백신 및 이들의 제조 방법을 제공함으로써 전염성 F낭병으로부터 유효하게 가금을 보호할 수 있다.In the present invention, it is possible to effectively protect poultry from infectious F cystic disease by providing a novel infectious F cystic virus, a vaccine comprising the same, and a method for preparing the same.
도 1은 국내 분리 전염성 F낭병 바이러스의 독력 유형별 분류 <출처: 농림수산검역검사본부>1 is classified by virulence type of infectious F cystic virus isolated in Korea <Source: Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Headquarters>
도 2는 국내 전염성 F낭병 생독백신 종류별 판매비율을 나타낸 그래프,Figure 2 is a graph showing the sales ratio of the infectious F cyst live vaccine type in Korea,
도 3-7은 타 병원체 오염여부 시험 사진,3-7 is another pathogen contamination test photograph,
도 8은 VP2 초가변 부위의 계통학적 분석8 is a systematic analysis of the VP2 hypervariable region
이하 비한정적인 실시예를 통하여 본 발명을 더욱 상세하게 설명한다. 단 하기 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 의도로 기재한 것으로서 본 발명의 범위는 하기 실시예에 의하여 제한되는 것으로 해석되지 아니한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to non-limiting examples. However, the following examples are intended to illustrate the present invention and the scope of the present invention is not to be construed as limited by the following examples.
실시예 1:국내 야외농장에서의 infectious bursal disease virus IBD K7주 분리, 동정 기타병원체 부정 시험 Example 1: Isolation of infectious bursal disease virus IBD K7 strain , identification of other pathogens
2007년 충남소재 육계 농장으로부터 의뢰된 육계로부터 F낭을 채취하여 멸균 인산완충용액(pH7.2)을 넣어 10중량%의 유제액을 만들었다. 이를 3,000g에서 15분간 원심분리하여 세포와 조직을 침전시키고, 상층액을 0.45㎛의 주사기 여과기로 여과하였다. 11일령 SPF 발육란의 장뇨막(chorioallantoic membrane: CAM) 접종법으로 분리하여 역전사 중합효소연쇄반응(RT-PCR)을 통해 IBD K7 스트레인을 최종 동정하였다.In 2007, F bags were collected from broilers from Chungnam broiler farms and sterile phosphate buffer solution (pH7.2) was added to make 10% by weight emulsion. Cells and tissues were precipitated by centrifugation at 3,000 g for 15 minutes, and the supernatant was filtered with a 0.45 μm syringe filter. IBD K7 strain was finally identified by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and isolated by chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) inoculation of 11-day-old SPF embryonated eggs.
실시예 2:신규한 IBDV 야외분리주 내 기타병원체 부정 시험 Example 2: Other Pathogen Negative Tests in New IBDV Field Isolates
계태아란의 장요막강액 및 장뇨막에서 증식이 가능한 기타 병원체의 존재 유무를 확인하기 위하여 전염성 기관지염 바이러스 (Infectious bronchitis virus, IBV), 뉴캣슬병 바이러스 (Newcastle disease, NDV), 조류아데노바이러스(Fowl adeno virus, FAdV), 닭전염성빈혈증 바이러스(Chicken infectious anemia virus, CIAV), 마이코플라스마(Mycoplasma)에 대한 역전사 중합효소연쇄반응 (RT-PCR) 및 중합효소연쇄반응(PCR)을 실시하여 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 분리주(IBD K7) 외에 기타 병원체가 없음을 확인하였다.Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), Newcastle disease (NDV), Fowl adeno virus to check for the presence of other pathogens capable of proliferation in the ureteral fluid of the chick embryo , FAdV), Chicken infectious anemia virus (CIAV), Mycoplasma, and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were carried out It was confirmed that there was no other pathogen other than (IBD K7).
실시예 3:게놈 염기서열 분석Example 3: Genome Sequencing
11일령 SPF 발육란에 바이러스를 접종하고 5일 후 수확한 장뇨막액 150 ㎕를 활용하여 RNA를 추출하였다. 상기에서 추출한 RNA 1 ㎍, 랜덤 헥사머(random hexamer) 10 pmol, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) 20pmol, Superscript II reverse transcriptase(Invitrogen) 200 units 의 농도로 섞어서 42℃에서 60분간 반응시키고, 역전사 효소는 70℃에서 15분 동안 처리하여 불활성화시켰다.RNA was extracted by inoculating the 11-day-old SPF embryonated eggs with 150 μl of the urinary membrane solution harvested 5 days later. 1 ㎍ of RNA extracted above, random hexamer 10 pmol, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) 20pmol, Superscript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) at a concentration of 200 units and mixed at 42 ℃ for 60 minutes, the reverse transcriptase is 70 ℃ Inactivated by treatment for 15 minutes at.
이와 같이 얻어진 cDNA를 4배 희석한 cDNA 용액 1 ㎕, 10x PCR 버퍼 1 ㎕, 2.5 mM dNTPs 0.2 ㎕, 각각의 프라이머 2 ㎕, Taq 중합효소 1 ㎕ 및 DW 7.2 ㎕를 혼합하였다. (I. Lojkic et al., Sequence Analysis of Both Genome Segments of Three Croatian Infectious Bursal Disease Field Viruses, AVIAN DISEASES 52:513-519, 2008)The cDNA thus obtained was mixed with 1 µl of 4-fold diluted cDNA solution, 1 µl of 10x PCR buffer, 0.2 µl of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 2 µl of each primer, 1 µl of Taq polymerase and 7.2 µl of DW. (I. Lojkic et al., Sequence Analysis of Both Genome Segments of Three Croatian Infectious Bursal Disease Field Viruses, AVIAN DISEASES 52: 513-519, 2008)
상기 반응액을 활용하여 얻은 PCR 산물을 정제하여 ABI3100 자동염기서열분석기를 사용하여 염기서열을 결정하였다. 그 결과 분절 A(Segment A)와 분절 B(segment B)로 표시되는 본 발명의 IBD K7의 게놈 염기 서열(IBD K7 바이러스의 Segment A 염기서열과 IBD K7 바이러스의 Segment B 염기서열은 각각 서열번호 1 및 2)을 얻었으며 VP1, VP5-VP2-VP4-VP3의 단백질의 아미노산 서열을 얻었다.The PCR product obtained using the reaction solution was purified, and the nucleotide sequence was determined using an ABI3100 autobase sequencer. As a result, the genome sequence of IBD K7 (Segment A base of IBD K7 virus and Segment B base of IBD K7 virus represented by Segment A and Segment B) is SEQ ID NO: 1, respectively. And 2) to obtain the amino acid sequence of the proteins VP1, VP5-VP2-VP4-VP3.
표 1은 Segment A 염기 분석에 사용된 primer set의 염기 서열 및 위치를 나타낸 표Table 1 shows the sequence and position of the primer set used in the Segment A base analysis
표 2는 Segment B 염기 분석에 사용된 primer set의 염기 서열 및 위치를 나타낸 표Table 2 is a table showing the nucleotide sequence and position of the primer set used in Segment B nucleotide analysis
실시예 4:IBD K7 바이러스의 분자생물학적 특성Example 4: Molecular Biology of IBD K7 Virus
IBD K7 바이러스 전체 유전자를 GenBank 상에 등록된 국내외 전염성 F낭병 바이러스들과 BLAST 검색(www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast)과 Bioedit 프로그램을 사용하여 비교 분석하였다. 그 결과 IBD K7는 강독형 바이러스보다 약독형 바이러스에 상동성이 상대적으로 높은 것으로 나타났다.(표 3)The entire gene of IBD K7 virus was compared with domestic and foreign infectious F cystic virus registered on GenBank using BLAST search (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast) and Bioedit program. As a result, IBD K7 showed relatively higher homology to the attenuated virus than to the virulent virus (Table 3).
또한 계통 분석에 적용하는 VP2 초가변 부위 분석결과 기존의 어느 타입에도 속하지 않는 새로운 타입임이 밝혀졌으며 방어단백질 VP2의 병원성관련 모티브의 경우 IBD K7은 강독형과 약독형 바이러스 모티브를 동시에 가지고 있는 매우 독특한 항원구조를 가지고 있는 것으로 나타났다.(도 4 및 표 4) 그러나 VP2단백질 이외의 다른 구조단백질의 경우 IBD K7은 전형적인 약독형 바이러스 모티브를 가지고 있었다.(표 4 및 5)In addition, the VP2 hypervariable region analysis applied to phylogenetic analysis revealed that it is a new type that does not belong to any existing type. In the case of pathogenic motifs of protective protein VP2, IBD K7 is a very unique antigen with both toxic and attenuated viral motifs. However, for other structural proteins other than VP2 protein, IBD K7 had a typical attenuated viral motif (Tables 4 and 5).
결론적으로 IBD K7은 강독형 바이러스 항원모티브를 일부 가진 기존의 바이러스와 비교하여 신규한 재조합 IBD 바이러스임을 나타내고 있다.In conclusion, IBD K7 is a novel recombinant IBD virus compared to existing viruses with some of the virogenic viral antigen motif.
표 3은 IBD K7와 기존 IBDV 스트레인과 전체 유전자 상동성 비교Table 3 shows overall gene homology with IBD K7 and conventional IBDV strain.
표 4는 IBD K7와 백신주 및 야외주의 VP5, VP2, VP4, VP3 비교분석Table 4 shows the comparative analysis of VP5, VP2, VP4 and VP3 of IBD K7 and vaccine and field strains.
표 5는 IBD K7와 백신주 및 야외주의 VP1 비교분석Table 5 shows the comparative analysis of IBD K7, VP1 and vaccine strains.
실시예 5:IBD K7 스트레인의 병원성 실험Example 5 Pathogenicity Experiments of IBD K7 Strain
백신 스트레인으로서의 가능성을 조사하고자 SPF 닭 3주령에 IBD K7 스트레인과 기존 IBDV 백신주인 Winterfield 스트레인, D78 스티레인을 각 그룹당 8수의 닭에 103ELD50/dose로 경구접종을 실시한 후 4일째 4수, 7일째 나머지를 안락사시켜 체중 및 BB-율[(F-낭 중량(g)/체중(g))x1000] 및 항체반응 검사를 실시하였다. 그 결과 Winterfield 스트레인 접종군과 IBD K7 스트레인 접종군에서 4일이내 각각 1수씩 폐사하였고 나머지 그룹은 모두 7일간 생존하였다. 체중과 BB-율을 비교분석한 결과 중간독 플러스와 중간독 중간의 병원성을 가진 것으로 조사되었으며 백신 접종 후 4일과 7일에 채혈하여 분리한 혈청의 ELISA 역가 확인 결과 면역반응은 중간독 플러스보다는 다소 낮지만 중간독 보다는 강한 것으로 확인되었다.(표 6 및 7)To investigate the possibility of vaccine strain, IBD K7 strain at 3 weeks of age of SPF chicken and Winterfield strain and D78 strain of IBDV vaccine were administered orally at 103 ELD50 / dose to 8 chickens in each group. The rest was euthanized and subjected to body weight and BB-rate [(F-bag weight (g) / weight (g)) × 1000] and antibody response test. As a result, in Winterfield strain group and IBD K7 strain group, each of them died within 4 days, and the remaining groups survived for 7 days. As a result of comparing body weight and BB-rate, it was found to have intermediate pathogenicity between intermediate poisoning and intermediate poisoning. The ELISA titer of serum isolated from 4 and 7 days after vaccination showed that the immune response was somewhat lower than that of medium poisoning plus. It was found to be low but stronger than medium poisons (Tables 6 and 7).
표 6은 IBD K7 스트레인, 중간독 플러스, 중간독 백신 접종 4일 및 7일 후 체중 및 BB율Table 6 shows body weight and BB rate after 4 and 7 days of IBD K7 strain, medium poison plus, medium poison vaccination
표 7은 IBD K7 스트레인, 중간독 플러스, 중간독 백신 접종 4일 및 7일 후 ELISA 역가Table 7 shows ELISA titers 4 and 7 days after IBD K7 strain, intermediate poison plus, intermediate poison vaccination
실시예 6:SPF 닭에서의 면역원성 및 방어능 실험Example 6: Immunogenicity and Protective Activity in SPF Chickens
IBD K7의 생독백신으로써의 효능을 알아보기 위하여, 3주령 SPF 닭에 IBD K7 스트레인과 기존 백신 스트레인 Winterfield 스트레인 및 D78을 1수당 103ELD50씩 경구로 백신접종하고, 백신접종 2주 후 최근 유행 강독형 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 1수당 105ELD50씩 점안으로 공격접종하였다. 대조군도 동일한 바이러스를 동일한 방법으로 공격접종하였다. 접종 후 5일간 침울이나 깃털 역립, 폐사등의 임상증상을 관찰하였으며 체중 변화를 측정하였다. To determine the efficacy of IBD K7 as a live vaccine, three-week-old SPF chickens were orally vaccinated with IBD K7 strain and the existing vaccine strain Winterfield strain and D78 at 10 3 ELD 50 per dose, and 2 weeks after vaccination. The highly infectious F cynovirus was challenged by instillation of 10 5 ELD 50 per dose. The control group was also challenged with the same virus in the same manner. Five days after inoculation, clinical symptoms such as depression, feather inversion, and mortality were observed.
백신 2주 후 공격접종 전 ELISA 항체가 및 임상증상을 볼 때 중간독 백신인 D78에 비하여 우수한 면역원성을 나타냈으며 중간독 플러스 백신인 Winterfield 스트레인 접종군과 유의적인 차이를 나타내지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.(표 8)After 2 weeks of vaccination, the ELISA antibody and the clinical symptoms showed better immunogenicity than the mid-dose vaccine D78 and no significant difference from the mid-dose plus vaccine Winterfield strain inoculation group. Table 8
표 8은 IBD K7 스트레인 백신 닭에서의 강독형 IBDV 공격접종에 대한 방어능 및 면역원성을 나타낸 표이다.Table 8 is a table showing the protective capacity and immunogenicity against toxic IBDV challenge in IBD K7 strain vaccine chicken.
Claims (11)
- 기탁번호 KCTC 12376BP로 기탁된 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주. Infectious F cystic virus IBD K7, deposited under accession number KCTC 12376BP.
- 제 1항에 있어서, 상기 바이러스는 국내 육계로부터 분리한 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주.The strain of infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 according to claim 1, wherein the virus is isolated from domestic broilers.
- 제 1항에 있어서, 상기 바이러스의 시그먼트 A 및 B는 각각 서열번호 1 및 2에 기재된 염기서열을 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주.The infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain according to claim 1, wherein the segments A and B of the virus have the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 1 and 2, respectively.
- 제 1항에 있어서, 상기 바이러스의 시그먼트 A는 서열번호 3 및 4에 기재된 아미노산 서열을 가지며 시그먼트 B는 서열번호 5에 기재된 아미노산 서열을 가지며, 서열번호 3에서는 45번, 74번, 133번, 서열번호 4에서는 222번, 242번, 256번, 279번, 284번, 294번, 299번, 451번, 680번, 715번, 751번, 981번, 1005번째 잔기, 그리고 서열번호 5에서는 4번, 13번, 61번, 145번, 146번, 147번, 242번, 287번, 390번, 393번, 508번, 511번, 562번, 687번, 695번째 잔기가 다른 균주들과 차이가 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 IBD K7주.The method of claim 1, wherein Sigma A of the virus has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 and 4, Segment B has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 5, 45, 74, 133 in SEQ ID NO: In SEQ ID NO: 4, 222, 242, 256, 279, 284, 294, 299, 451, 680, 715, 751, 981, 1005 residues, and in SEQ ID NO: 5 Residues 4, 13, 61, 145, 146, 147, 242, 287, 390, 393, 508, 511, 562, 687 and 695 were different from other strains. Infectious F cystic virus IBD K7 strain, characterized by a difference.
- 제1항 내지 제4항의 어느 한 항의 바이러스 및 약학적 허용 담체 또는 희석제를 포함하는, 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 감염으로부터 유발된 질병에 대한 가금 보호용 백신. A vaccine for poultry protection against a disease resulting from an infectious follicular virus infection comprising the virus of any one of claims 1 to 4 and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
- 제5항에 있어서, 상기 전염성 F낭병 바이러스가 살아있는 형태임을 특징으로 하는 백신.6. The vaccine of claim 5 wherein said infectious F cystic virus is in live form.
- 제5항에 있어서, 상기 백신이 보조제를 추가로 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 백신.6. The vaccine of claim 5 wherein said vaccine further comprises an adjuvant.
- 제5항에 있어서, 상기 백신이 가금에 감염성이 있는 다른 병원균의 백신성분을 하나 이상 추가로 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 백신.The vaccine of claim 5, wherein said vaccine further comprises one or more vaccine components of other pathogens infectious to poultry.
- a) 감염되기 쉬운 기질에 제1항 내지 제4항의 어느 한 항에 정의된 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 접종하는 단계; a) inoculating a substrate susceptible to infection with the infectious F cystic virus as defined in any one of claims 1 to 4;b) 상기 전염성 F낭병 바이러스를 증식시키는 단계; 및 b) propagating said infectious F cystic virus; Andc) 상기 전염성 F낭병 바이러스 함유 물질을 수거하는 단계를 포함하는 전염성 F낭병 바이러스의 제조 방법.c) A method for producing an infectious FLA virus comprising the step of collecting the infectious F disease virus-containing material.
- 제9항에 있어서, 상기의 기질은 닭 간의 배세포(CEL), 닭의 배 섬유아세포(CEF), 닭의 신장세포(CK), 및 베로(Vero) 세포주로 구성된 군으로부터 선택된 하나의 세포인 것을 특징으로 하는 전염성 F낭병 바이러스의 제조 방법.The method of claim 9, wherein the substrate is one cell selected from the group consisting of embryonic liver cells (CEL), chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF), chicken kidney cells (CK), and Vero cell line. A method for producing an infectious F cystic virus, characterized in that.
- 제5항의 백신을 조류에 투여하는 것을 포함하는 가금에서 전염성 F낭병 감염으로부터 유발된 질병을 제어하는 방법.A method for controlling a disease resulting from an infectious F cystic infection in poultry comprising administering the vaccine of claim 5 to a bird.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR10-2013-0036421 | 2013-04-03 | ||
| KR1020130036421A KR101511712B1 (en) | 2013-04-03 | 2013-04-03 | Novel infectious bursal disease virus IBD K7 and infectious bursal disease vaccine using the same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014163257A1 true WO2014163257A1 (en) | 2014-10-09 |
Family
ID=51658522
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2013/007945 WO2014163257A1 (en) | 2013-04-03 | 2013-09-03 | Novel infectious bursal disease (ibd) virus k7 strain and vaccine against infectious bursal disease using same |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101511712B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2014163257A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106008535A (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2016-10-12 | 河南大学 | Controllable preparation method for one-dimensional porphyrin nano-material applied to hydrogen production through visible photolysis of water |
| WO2017174414A1 (en) | 2016-04-05 | 2017-10-12 | Bayer Cropscience Aktiengesellschaft | Naphthaline-derivatives as pest control agents |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102421251B1 (en) * | 2020-08-24 | 2022-07-15 | 대한민국 | Chinese type Antigen variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus isolated in South Korea and Vaccine composition comprising the same |
| KR102421249B1 (en) * | 2020-08-24 | 2022-07-15 | 대한민국 | American type Antigen variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus isolated in South Korea and Vaccine composition comprising the same |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0600723A2 (en) * | 1992-12-01 | 1994-06-08 | Abic Limited | Infectious bursal disease vaccine |
| KR20050090888A (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2005-09-14 | 권혁무 | Dna vaccine comprising ibdv antigenic determinant sequence for preventing infectious bursal disease |
| KR20050115929A (en) * | 2003-03-24 | 2005-12-08 | 악조 노벨 엔.브이. | Infectious bursal disease virus mutants and vaccines |
| US20060121567A1 (en) * | 2004-12-08 | 2006-06-08 | Vikram Vakharia | Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) variant from Georgia |
| KR20060130726A (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2006-12-19 | 와이어쓰 | Infectious bursal disease virus antigenic isolates and vaccines |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100825503B1 (en) * | 2007-01-26 | 2008-04-25 | 강원대학교산학협력단 | Vaccine composition for preventing infectious bursal disease |
| KR101104911B1 (en) * | 2010-04-19 | 2012-01-12 | 주식회사 바이오포아 | Avirulent infectious bursal disease virus and use thereof as a vaccine |
| JP2013116869A (en) * | 2011-12-02 | 2013-06-13 | Vaxxinova Kk | Live vaccine against infectious bursal disease containing cell internal virus as main component |
-
2013
- 2013-04-03 KR KR1020130036421A patent/KR101511712B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2013-09-03 WO PCT/KR2013/007945 patent/WO2014163257A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0600723A2 (en) * | 1992-12-01 | 1994-06-08 | Abic Limited | Infectious bursal disease vaccine |
| KR20050115929A (en) * | 2003-03-24 | 2005-12-08 | 악조 노벨 엔.브이. | Infectious bursal disease virus mutants and vaccines |
| KR20050090888A (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2005-09-14 | 권혁무 | Dna vaccine comprising ibdv antigenic determinant sequence for preventing infectious bursal disease |
| KR20060130726A (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2006-12-19 | 와이어쓰 | Infectious bursal disease virus antigenic isolates and vaccines |
| US20060121567A1 (en) * | 2004-12-08 | 2006-06-08 | Vikram Vakharia | Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) variant from Georgia |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017174414A1 (en) | 2016-04-05 | 2017-10-12 | Bayer Cropscience Aktiengesellschaft | Naphthaline-derivatives as pest control agents |
| CN106008535A (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2016-10-12 | 河南大学 | Controllable preparation method for one-dimensional porphyrin nano-material applied to hydrogen production through visible photolysis of water |
| CN106008535B (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2017-11-24 | 河南大学 | Controllable method for preparing for the one-dimensional porphyrin nano material of visible ray photolysis water hydrogen |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101511712B1 (en) | 2015-04-13 |
| KR20140120533A (en) | 2014-10-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Alvarado et al. | Genetic characterization, pathogenicity, and protection studies with an avian adenovirus isolate associated with inclusion body hepatitis | |
| JP5508252B2 (en) | Recombinant turkey herpesvirus containing avian influenza gene | |
| US11090377B2 (en) | Avian reovirus vaccines | |
| US20120251564A1 (en) | Reovirus compositions and methods of use | |
| KR20150001559A (en) | A novel Fowl Adenovirus and vaccine thereof | |
| WO2014163257A1 (en) | Novel infectious bursal disease (ibd) virus k7 strain and vaccine against infectious bursal disease using same | |
| US6951650B1 (en) | Antigenic class of avian reoviruses | |
| US9273287B2 (en) | Avian reoviridae and vaccines thereof | |
| Popowich et al. | Broad spectrum protection of broiler chickens against inclusion body hepatitis by immunizing their broiler breeder parents with a bivalent live fowl adenovirus vaccine | |
| JP3756219B2 (en) | Reovirus strain 2177 and vaccine comprising the strain | |
| CN114395536B (en) | Avian adenovirus type 4, 8 and 11 trivalent vaccine and preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP2002045175A (en) | Ibdv strain for in ovo administration | |
| WO2009143332A2 (en) | Poultry viral materials and methods related thereto | |
| WO2014061914A1 (en) | Infectious bronchitis virus k40/09 strain, and vaccine for infectious bronchitis using same | |
| WO2014208822A1 (en) | Novel fowl adenovirus and vaccine thereof | |
| PL209994B1 (en) | An infectious bursal disease virus variant | |
| NZ272548A (en) | Attenuated strain of mareks disease virus (a herpes virus) and its use in poultry vaccines | |
| KR20200061508A (en) | An attenuated avian metapneumovirus and a vaccine composition including the same | |
| KR100913425B1 (en) | Influenza virus and immunogenic composition comprising the same | |
| KR101694607B1 (en) | An Attenuated Infectious bronchitis virus and An Infectious bronchitis vaccine using the same | |
| KR101360112B1 (en) | A novel airborn transmissible low pathogenic avian Influenza virus (H9N2) K040110/2010 and vaccine for low pathogenic avian Influenza comprising the same | |
| CN114395535B (en) | Avian adenovirus I group type 1 and type 4 bivalent vaccine, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| KR102656435B1 (en) | Novel fowl adenovirus and Fowl adenovirus polyvalent vaccine comprising the same as effective component | |
| Saif et al. | Other Viral Infections | |
| Abd El-Ghany | Forms of avian reovirus in poultry production: An overview |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13881304 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13881304 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |