WO2012046207A1 - Anti-parasitic substituted ring fused azine compounds - Google Patents
Anti-parasitic substituted ring fused azine compounds Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012046207A1 WO2012046207A1 PCT/IB2011/054414 IB2011054414W WO2012046207A1 WO 2012046207 A1 WO2012046207 A1 WO 2012046207A1 IB 2011054414 W IB2011054414 W IB 2011054414W WO 2012046207 A1 WO2012046207 A1 WO 2012046207A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- compound
- alkyl
- benzofuran
- propanediamine
- quinazolinyl
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K45/00—Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
- A61K45/06—Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P33/00—Antiparasitic agents
- A61P33/10—Anthelmintics
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/70—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D239/72—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines
- C07D239/86—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines with hetero atoms directly attached in position 4
- C07D239/94—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
Abstract
The present invention relates to substituted ring fused azine compounds for treating parasitic infections, in particular helminth infections. The present invention also relates to veterinary compositions comprising the compounds, uses of the compounds in the manufacture of medicaments, and methods of treating parasitic infections.
Description
ANTI-PARASITIC SUBSTITUTED RING FUSED AZINE COMPOUNDS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the use of substituted ring fused azine compounds with anti-parasitic activity for treating parasitic infections, in particular helminth infections. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Parasites are responsible for a variety of diseases detrimental to animal health. In production livestock, infection by parasites such as helminths, most notably gastrointestinal nematodes, can lead to significantly decreased productivity and in some cases, animal death. The economic cost can be enormous, such that treatments against nematodes are considered to be of the highest economic importance in sheep and cattle-producing regions of the world.
Effective control of nematode parasites is essential not only on welfare grounds, but as a means of enabling the intensification of livestock agriculture to provide food and fibre at a practical economic cost. Parasite control relies almost exclusively on the regular application of antiparasitic agents, for example anthelmintics, such as milbemycin or thiabendazole to the animal. For production livestock, such as sheep or cattle, these anti -parasitic agents are commonly applied on a regular basis to most or all animals on a property to ensure acceptable productivity gains are met.
The sustained and widespread application of chemotherapeutic agents characteristically results in the selection of organisms resistant to the applied chemical. This has been the case with gastrointestinal nematodes in grazing livestock. Resistance to the three established anthelmintic classes (benzimidazoles, imidithiazoles and macrocyclic lactones) is now widespread throughout the world in small ruminants, and is a rapidly growing problem in cattle. While two new anthelmintic families have recently been introduced to the market, history suggests resistance will develop following a few years of use. Accordingly, there is an ongoing need for the development and registration of new anti-parasitic agents to ensure long-term sustainability of pastoral agriculture. It is an object of at least preferred embodiments of this invention to go some way towards meeting this need; and/or to at least provide the public with a useful choice.
Other objects of the invention may become apparent from the following description which is given by way of example only.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In one aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
(I) wherein:
D is NR R2, wherein R and R2 are each independently selected from H, C\-C alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl, wherein CI-CQ alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring;
X is selected from H, C -Ce alkyl and C -Ce cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, CHR3, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein C C6 alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl or methoxy groups;
Z and Q are each independently selected from N and CH, provided that at least one of Z and Q is N;
J is selected from N and CR5;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Q-C4 alkyl, Q-C4 alkenyl, C1-C4 alkynyl, OR8, SR8, NR8R9, CH2R8, COR8, SOR8, S02R8, S02NR8R9, C02R8, CONR8R9, CF3, CN, and N02; and
R¾, R8, and R9 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein CI-CQ alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups.
In another aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
D is NRiR2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, C\-Ce alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, and Ci-C6 alkyl;
Z and Q are both N;
J is selected from N and CR5;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6; R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkenyl, C C4 alkynyl, OR8, and CF3; and
R5 and R8 are each independently selected from H, C I-CQ alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl.
In another aspect, the invention relates to a veterinary composition comprising a compound of formula (I) or a veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof and a veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent.
In another aspect, the invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (I) or a
pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof in the manufacture of a medicament for treating a parasitic infection in an animal. In another aspect, the invention relates to a method of treating a parasitic infection in an animal, comprising administering to the animal a therapeutically effect amount of a compound of formula (I).
In another aspect, the invention provides a kit comprising a compound of formula (I) and one or more additional anti-parasitic agents. In the above aspects:
In one embodiment the parasitic infection is an endo-parasite infection, preferably a helminth infection, more preferably a nematode infection.
In one embodiment the animal is a production animal selected from the group comprising cattle, sheep, swine, deer and goats. Preferably, the animal is cattle or sheep.
In one embodiment the animal is a companion animal.
Any discussion of documents, acts, materials, devices, articles or the like which has been included in the present specification is solely for the purpose of providing a context for the present invention. It is not to be taken as an admission that any or all of these matters form part of the prior art base or were common general knowledge in the field relevant to the present invention as it existed before the priority date.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The term "comprising" as used in this specification means "consisting at least in part of. When interpreting each statement in this specification that includes the term "comprising", features other than that or those prefaced by the term may also be present. Related terms such as "comprise" and "comprises" are to be interpreted in the same manner.
The term "alkyl," as used herein means, unless otherwise stated, a straight or branched chain, noncyclic fully saturated hydrocarbon radical, and may have the number of carbon atoms designated (i.e. Ci-Cio means one to ten carbons).
Examples of straight chain alkyls include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl and the like. Examples of branched chain alkyls include isopropyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, test-butyl, isopentyl and the like.
The term "alkenyl", as used herein means, unless otherwise stated, a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon radical having at least one double bond including, but not limited to, ethenyl, propenyl, 1 -butenyl, 2-butenyl and the like. The term "alkynyl", as used herein means, unless otherwise stated, a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon radical having at least one triple bond including, but not limited to, ethynyl, propynyl, 1 -butynyl, 2-butynyl and the like.
The term "cycloalkyl" as used herein means, unless otherwise stated, a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon radical. Representative cycloalkyls include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, and the like.
The term "N-containing heterocyclic ring", as used herein means, unless otherwise stated, a monocyclic non-aromatic 3-, 4-, 5-, 6- or 7- membered heterocyclic ring containing a nitrogen atom and optionally one or more heteroatoms independently selected from the group consisting
of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur in the ring. Examples of N-containing heterocyclic rings include, but are not limited to: morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methylpiperazine.
In one aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
D is NR1R2, wherein R4 and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and CI-CQ cycloalkyl, wherein CI-CQ alkyl and CI-Q cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, CHR3, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-; R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein
Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl or methoxy groups;
Z and Q are each independently selected from N and CH, provided that at least one of Z and Q is N; J is selected from N and CR¾;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
P 6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkenyl, C1-C4 alkynyl, OR8, SR8, NR8R9, CH2R8, COR8, SOR8, S02R8, S02NR8R9, C02R8, CONR8R9, CF3, CN, and N02; and R¾, R8, and R9 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups.
Preferred embodiments of compounds of the invention are described below.
In one embodiment Q is N. In another embodiment Z is CH and Q is N. Preferably, both Z and Q are both N.
In one embodiment Y is independently selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N- and -C(R3)=CR4-. In another embodiment, Y is independently selected from O, NR4, -C(R3)=N- and -C(R3)=CR4-. In another embodiment, Y is independently selected from O, -C(R3)=N- and -C(R3)=CR4-. In another embodiment, Y is independently selected from O, S, and NR4. In another embodiment, Y is O or NR4. In another embodiment, Y is O.
In one embodiment D is NRiR2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H and Ci-C6 alkyl, preferably methyl or ethyl. In another embodiment D is a N- containing heterocyclic ring. Preferably, the N-containing heterocyclic ring is selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine.
In one embodiment the N-containing heterocyclic ring is
wherein p is an integer from 1 to 4 and R10 is branched or unbranched Ci-C6 alkyl. Preferably p = 1 and Rio is methyl.
In one embodiment J is CR5. Preferably R5 is hydrogen. In one embodiment X is H. In one embodiment m is 2 or 3, preferably 2.
In one embodiment n is 0.
In one embodiment R6 and R7 are independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, CF3 and OR8. In another embodiment R6 and R7 are independently selected from H, Ct¾, F, CI, Br, OCH3, OEt, O'Pr, and CF3. In another embodiment, R6 and R7 are independently selected from H, CH3, Br, OCH3 and CF3.
In one embodiment R3, R4, R5, R8 and R9 are independently selected from H and Ci-C6 alkyl, preferably H or methyl.
In one embodiment, Y is selected from O, S, and NR4; and J is CH. In another embodiment, Y is O or NR4; and J is CH. In another embodiment, Y is O; and J is CH. In another embodiment, Y is S; and J is CH. In another embodiment, Y is NR4; and J is CH.
In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is -C(R3)=CR4-; J is CR¾; and X is H. In another embodiment, R3 and R4 are independently selected from H and Ci-C^ alkyl. In another embodiment, R3 and R4 are each H.
In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is O; J is CR5, wherein R5 is H or C1-C5 alkyl; and X is H.
In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is NR4; J is CR5, wherein R5 is H or C -C5 alkyl; and X is H. In one embodiment, R4 is H or C1-C5 alkyl. In another embodiment, R4 is H.
In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is -C(R3)=N-; J is CR5, wherein R5 is H or C1-C5 alkyl; and X is H. In one embodiment, R3 is H or Ci-C^ alkyl. In another embodiment, R3 is H. In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is S; J is CR5, wherein R5 is H or C -C5 alkyl; and X is H.
In one embodiment, Z and Q are both N; Y is -C(R)3=CR4-; J is N; and X is H. In one embodiment, R3 and R4 are independently selected from H and Ci-C^ alkyl. In another embodiment, R3 and R4 are each H. In another aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
(I) wherein:
D is NR1R2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-; R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, and Ci-C6 alkyl; Z and Q are both N; J is CR5;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Ci-C4 alkyl, Ci-C4 alkenyl, Ci-C4 alkynyl, OR8, and CF3; and
R¾ and R8 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and cycloalkyl.
In another aspect, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
D is NR R2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, and Ci-C6 alkyl;
Z and Q are both N;
J is selected from N and CR¾;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Ci-C4 alkyl, Ci-C4 alkenyl, Ci-C4 alkynyl, OR8, and CF3; and
R¾ and R8 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and cycloalkyl. In one embodiment, n is 0. In one embodiment m is 2 or 3.
In one embodiment Y is selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, and -C(R3)=CR4-. In one embodiment Y is selected from O, S, and NR4. In one embodiment Y is selected from O and NR4. In one embodiment Y is selected from O.
In one embodiment, J is CR5. In another embodiment, J is CH.
In one embodiment, X is H.
In one embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein: D is NR1R2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine; X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is 0;
Y is selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, and -C(R3)=CR(-; R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, and Ci-C6 alkyl; Z and Q are both N; J is selected from N and CR5;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is 2 or 3;
R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Ci-C4 alkyl, Ci-C4 alkenyl, Ci-C4 alkynyl, OR8, and CF3; and
R¾ and R8 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof.
In one embodiment Y is selected from O, S, and NR4. In one embodiment Y is selected from O and NR4. In one embodiment Y is selected from O. In one embodiment, J is CR5. In another embodiment, J is CH.
In one embodiment, X is H.
In one embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein:
D is NRiR2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl or methyl groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring;
X is H; n is 1 , Y is O, Z and Q are both N, J is CR5 wherein R5 is H, A is (CH2)m wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Ci-C4 alkyl, or OR8 where R8 is Ci-C6 alkyl, and CF3; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof.
In one embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein:
D is NRiR2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl or methyl groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring;
X is H; n is 0, Y is O, Z and Q are both N, J is CR5 wherein R5 is H, A is (CH2)m wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, or OR8 where R8 is Ci-C6 alkyl, and CF3; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof. Preferably, the N-containing heterocyclic ring is selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine.
Preferably, the compound of formula (I) is in the form of a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt; more preferably, a hydrochloride salt.
The compounds of the invention may be prepared in accordance with the methods described in WO 2007/1 17161 and US 20090318479, which are incorporated herein by reference. The compounds may be purified by any suitable method known in the art.
In one embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) selected from the group consisting of:
1 2 2
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,2-ethanediamine;
1 1 2 2
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N ,N -trimethyl- 1,2-ethanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1, 3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N4,N4-dimethyl-l,4-butanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -diethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dipropyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -bis(2-hydroxyethyl)- 1,3 -propanediamine; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]-4-quinazolinamine; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N- [3 -(4-methyl- l -piperazinyl)propyl]-4-quinazolinamine; 2-( 1 -benzofuran-2-yl)-N- [3 -( 1 -pyrrolidinyl)propyl] -4-quinazolinamine;
N 1 -[2-( 1 -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl] -N 3 -cyclopropyl- 1 ,3 -propanediamine;
1 3
N -[2-(l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N -methyl- 1 ,3 -propanediamine;
1 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N -ethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N ,2,2-tetramethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-5-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-5-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-5-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-5-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4,5-quinazolinediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4-{[3-(-dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-5- quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-fluoro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-bromo-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4,6-quinazolinediamine; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-6-quinazolinecarbonitrile; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-6-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-fluoro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-bromo-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7 -amino-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-7-quinazolinecarbonitrile;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-7-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl-]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-phenyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8 -amino-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-8-quinazolinecarbonitrile;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-8-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,7-dichloro-4-quinazoliny-l]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,8-dichloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,8-dibromo-4-quinazolinyl-]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(3-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
N1-[2-(4-chloro-5-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3- propanediamine;
N1 - [2-(5 -methoxy- 1 -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl] -N 1 ,Ν1 -dimethyl- 1 ,3 -propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(5-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(5-chloro-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(5-bromo-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(6-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(7-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(7-methoxy-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l ,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[8-methyl-2-(3-methyl-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(5-methoxy-lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1,N1-dimethyl-N3-[2-(5-methoxy-l-methyl-lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3- propanediamine;
N1-[2-(6-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]amine;
N N1-dimethyl-N3-[2-(l -methyl-l H-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l ,3-propanediaminei
N1-[2-(l-benzothien-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,N3-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
N1,N1-dimethyl-N3-[2-(3-quinolinyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
N1,N1-diniethyl-N3-[2-(2-naphthyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l ,3-propanediamine;
2-(l -benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethyl-N-[2-(l-methyl-2-pyiTolidinyl)ethyl]-4-quinazolinamine
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinolinyl]-N3,N3-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
N1-[3-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-l-isoquinolinyl]-N3,N3-dimethyl-l ,3-propanediamine; and
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,N3-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof is a hydrochloride salt.
In another embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) selected from the group consisting of:
N^P-Cl -benzofuran^-y^^-quinazolinylj-^^-dimethyl-l ^-ethanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N2,N2-trimethyl-l,2-ethanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,N3-dimethyl-l ,3-propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N4,N4-dimethyl-l ,4-butanediamine;
N1-[2-(l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,NJ-diethyl-l ,3-propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,N3-dipropyl-l ,3-propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N3,N3-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-l,3-propanediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]-4-quinazolinamine;
2-(l -benzofuran-2-yl)-N-[3-(4-methyl-l -piperazinyl)propyl]-4-quinazolinamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N- 3 -( 1 -pyrrolidinyl)propyl] -4-quinazolinamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■4-quinazolinyl]-N -cyclopropyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■4-quinazolinyl]-N -methyl- 1 ,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■4-quinazolinyl]-N -ethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N ,2,2-tetramethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 5-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 5-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 5-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 5-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■N -[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4,5-quinazolinediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-N- 3 -(dimethylamino)propyl] -4- { [3 -(-dimethylamino)propyl] amino} -i quinazolinecarboxamide;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■6-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-fluoro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-bromo-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl 6-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1-[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl ■N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4,6-quinazolinediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4- [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-6-quinazolinecarbonitrile;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-6-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-fluoro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-bromo-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7 -amino-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-7-quinazolinecarbonitrile;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-7-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl-]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-methyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-phenyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-chloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8-nitro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-8 -amino-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-8-quinazolinecarbonitrile;
2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-{[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino}-8-quinazolinecarboxamide;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,7-dichloro-4-quinazoliny-l]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,8-dichloro-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6,8-dibromo-4-quinazolinyl-]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethyl-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(3-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
N1-[2-(4-chloro-5-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3- propanediamine;
N1 - [2-(5 -methoxy- 1 -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl] -N 1 ,Ν1 -dimethyl- 1 ,3 -propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(5-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(5-chloro-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(5-bromo-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(6-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(7-methyl-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(7-methoxy-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l ,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[8-methyl-2-(3-methyl-l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3- propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(5-methoxy-lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
N1,N1-dimethyl-N3-[2-(5-methoxy-l-methyl-lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3- propanediamine;
N1-[2-(6-methoxy-l -benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N1,N1-dimethyl-l,3-propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; N1-[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]amine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(l -methyl-lH-indol-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzothien-2-yl)-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(3-quinolinyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 1 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(2-naphthyl)-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine; 2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-7,8-dimethyl-N-[2-(l-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]-4-quinazolinamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-4-quinolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[3-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-l-isoquinolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(5-methoxy-lH-indol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(2-naphthyl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-prop-2-yloxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzothien-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(2-quinolinyl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine; and
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-ethoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof is a
hydrochloride salt.
In another embodiment, the invention provides a compound of formula (I) selected from the group consisting of:
1 3 3
N -[2-(lH-indol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(5-methoxy-lH-indol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3- propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(2-naphthyl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine;
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-prop-2-yloxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzothien-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine;
I I 3
N ,N -dimethyl-N -[2-(2-quinolinyl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-l,3-propanediamine; and
1 3 3
N -[2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-ethoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1,3 -propanediamine; or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt thereof is a
hydrochloride salt.
Asymmetric centers may exist in the compounds of formula (I). The asymmetric centers may be designated by the symbols "R" or "S", depending on the configuration of substituents in three dimensional space at the chiral carbon atom. All stereochemical isomeric forms, including diastereomeric, enantiomeric, and epimeric forms, as well as d-isomers and 1-isomers, and mixtures thereof of the compounds are contemplated herein. Individual enantiomers of the compounds can be prepared synthetically from commercially available enantiopure starting materials or by preparing enantiomeric mixtures of the compounds and resolving the mixture into individual enantiomers. Resolution methods include conversion of the enantiomeric mixture into a mixture of diastereomers and separation of the diastereomers by, for example,
recrystallization or chromatography; direct separation of the enantiomers on chiral
chromatographic columns; and any other appropriate method known in the art. Starting materials of defined stereochemistry may be commercially available or made and resolved by techniques well known in the art.
The compounds may also exist as geometric isomers. All cis, trans, syn, anti, entgegen (E), and zusammen (Z) isomers, as well as the appropriate mixtures thereof of the compounds are contemplated herein.
The compounds may also exist as tautomers, for example, keto/enol; imine/enamine;
amide/imino alcohol; nitroso/oxime; thioketone/enethiol; N- nitroso/hyroxyazo; and nitro/aci- nitro. All tautomeric isomers of the compounds are contemplated herein.
The compounds may exist in solvated or unsolvated forms. If the solvent is water, the solvate may be referred to as a hydrate, for example, a mono-hydrate, a di-hydrate, or a tri-hydrate. All solvates of the compounds are contemplated herein. Salts of the compounds are also contemplated herein. Salts of the compounds include, for example, acid addition salts, base addition salts, and quaternary salts of basic nitrogen-containing groups.
Acid addition salts can be prepared by reacting compounds, in free base form, with inorganic or organic acids. Examples of inorganic acids include, but are not limited to, hydrochloric;
hydrobromic; hydroiodic; nitric; carbonic; sulfuric; and phosphoric acid. Examples of organic acids include, but are not limited to, cholic; sorbic; lauric; acetic; trifluoroacetic; formic;
propionic; succinic; glycolic; gluconic; digluconic; lactic; malic; tartaric; citric; ascorbic;
glucuronic; maleic; fumaric; pyruvic; aspartic; glutamic; aryl carboxylic; anthranilic acid;
mesylic; stearic; salicylic; phenylacetic; mandelic; embonic (pamoic); alkylsulfonic;
ethanesulfonic; arylsulfonic; benzenesulfonic; pantothenic; sulfanilic; cyclohexylaminosulfonic; β-hydroxybutyric; galactaric; galacturonic; adipic, alginic; butyric; camphoric; camphorsulfonic; cyclopentanepropionic; dodecylsulfic; glycoheptanoic; glycerophosphic; heptanoic; hexanoic; nicotinic; 2-naphthalesulfonic; oxalic; palmoic; pectinic; 3-phenylpropionic; picric; pivalic; thiocyanic; tosylic; and undecanoic acid. Base addition salt can be prepared by reacting compounds, in free acid form, with inorganic or organic bases. Examples of base addition salts include metal salts and organic salts. Preferred metal salts include alkali metal salts, alkaline earth metal salts, and other physiologically acceptable metal salts. Preferably the metal salt comprises aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, or zinc. Organic salts may be made from amines, such as
trimethylamine, diethylamine, N^-dibenzylethylenediamine, chloroprocaine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, ethylenediamine, meglumine (N-methylglucamine), and procaine.
It may be convenient or desirable to prepare, purify, and/or handle the active compound in a chemically protected form. The term "chemically protected form," as used herein, pertains to a compound in which one or more reactive functional groups are protected from undesirable chemical reactions, that is, are in the form of a protected or protecting group (also known as masked or masking group). By protecting a reactive functional group, reactions involving other unprotected reactive functional groups can be performed, without affecting the protected group; the protecting group may be removed, usually in a subsequent step, without substantially affecting the remainder of the molecule (see, for example, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis; T. Green and P. Wuts; Wiley; 1991).
The compounds of formula (I) have anti-parasitic activity and are therefore useful in treating parasite infections in animals.
The term "treatment", and related terms, such as "treating" and "treat" as used herein, in the context of treating a parasitic infection, relates generally to treatment, of either a human or a non-human animal, in which some desired therapeutic effect is achieved. The therapeutic effect may, for example, be the inhibition of progress of a parasitic infection, including a reduction in the rate of progress; a halt in the rate of progress of the infection; amelioration of the infection; and cure of the infection. Treatment as a prophylactic measure (i.e., prophylaxis) is also included. Treatment also includes combination treatments and therapies, in which two or more treatments or therapies are used, for example, sequentially or simultaneously, in combination. For example, a therapeutically effective amount of an anti-parasitic agent of formula (I) could be combined with or used in conjunction with a known anthelmintic agent.
The term "parasitic infection", as used herein, means an infection or infestation of external parasites (ecto-parasites) or internal parasites (endo-parasites) in or on an animal.
The parasitic infection may be an ecto-parasite infection or infestation. Ecto-parasites include, but are not limited to, bedbugs, fleas, flies, gnats, ticks, lice, and mites, such as, Bovicola ovis (sheep louse); Bovicola bovis; Haematopinus eurysternus (short-nosed cattle louse); Hypoderma spp.; Lucilia sericata (sheep blowfly); Lucilia cuprina (Australian sheep blow fly); Haematobia irritans exigua; Cochliomyia spp.; Chrysomya spp.; Linognathus vituli (long nosed cattle louse);
Solenopotes capillatus (tubercule-bearing louse); Sar copies spp. (mange mites), including Sarcoptes scabiei cams, Sarcoptes scabiei suis, Sarcoptes scabiei bovis, Sarcoptes scabiei var. humani; Psoroptes spp., including Psoroptes ovis and Dermatophgoides spp.; Boophilus microplus; and Damaliniabovis . Alternatively, the parasitic infection may be an endo-parasite infection or infestation.
Endoparasites include, but are not limited to, protozoan parasites, such as Plasmodium spp.; Trypanosoma spp. and Eimeria spp., and parasitic worms (helminths). Helminths include, but are not limited to, cestodes (flatworms), nematodes (roundworms), and trematodes (flukes), such as, Trichostrongyloidea, including Haemonchus contortus; Trichostrongylus spp.; Teladorsagia circumcinta; Dictyocaulus spp.; Ascaridoidea, including Toxocara spp.; Strongylus spp.;
Filarioidea, including Diro filar iaimmitis and Onchocerca spp.: Trematoda, including
Fasciolahepatica and Schistosoma spp.; Taenia spp.; and Moniezia spp.; Ostertagia spp.;
Nematodirus spp.; Cooper ia spp.; Bunostomum spp.; Oesophagostomum spp.; Chabertia spp, Trichuris spp.; Trichonema spp.; Capillar ia spp.; Heterakis spp.; Toxocara spp.; Oxyuris spp.; Ancylostoma spp.; Uncinaria spp.; Toxascaris spp.; and Parascaris spp.
Preferably, the parasitic infection is an endo-parasite infection or infestation; more preferably a helminth infection or infestation; most preferably a Haemonchus spp.; Ostertagia spp.;
Trichostrongylus spp.; Nematodirus spp.; or Cooperia spp. infection or infestation.
The animal may be human or non-human. Non-human animals include, for example, production animals such as cattle, sheep, swine, deer, and goats; companion animals such as dogs, cats, and horses; zoo animals such as zebras, elephants, giraffes, and large cats; research animals such as mice, rats, rabbits, and guinea pigs; fur-bearing animals such as mink; birds such as ostriches, emus, hens, geese, turkeys, and ducks; and fresh- and salt-water fish such as, trout, salmon, carp, and eels. The term "therapeutically effective amount", as used herein, means the amount of an active compound, or a material, composition, formulation, or dosage form comprising an active compound, which is effective for producing some desired therapeutic or prophylactic effect, commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio. Therapeutically effective amounts can be determined using routine optimization techniques well known in the art. The amount may depend on, for example, the type of parasitic infection; the type of animal; the condition of the animal; the weight of the animal; and the mode of administration.
In another aspect, the invention relates to a veterinary composition comprising a compound for formula (I) or a veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof and a veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent.
The composition may comprise more than one compound of formula (I). The composition may also comprise one or more additional therapeutic agents. In one embodiment, in addition to a compound of formula (I), the composition comprises one or more additional anti-parasitic agents.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a method of manufacturing a veterinary composition comprising combining a compound of formula (I) or a veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof and a veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a method of manufacturing a veterinary composition for treating a parasitic infection in an animal comprising combining a compound of formula (I) or a veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof and a veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent. The compound of formula (I) and the veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent may be combined in accordance with any suitable method known in the art. For example, the compound may be mixed, admixed, or blended with or dissolved, suspended, or emulsified in the veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent.
The methods may also comprise combining one or more additional anti-parasitic agents. The compounds of the invention can be administered alone or in admixture with a
pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent selected with regard to the intended route of administration and standard pharmaceutical practice.
The pharmaceutical and veterinary compositions formed by combining the compound of the invention and the pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable carriers are then readily
administered in a variety of dosage forms suitable for the disclosed routes of administration. The formulations may conveniently be presented in unit dosage form by methods known in the art of pharmacy.
The term "pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable" as used herein refers to compounds, ingredients, materials, compositions, dosage forms and the like, which are within the scope of sound medical judgment, suitable for use in contact with the tissues of the animal in question (whether human or non-human) without excessive toxicity, irritation, allergic response, or other problem or complication, commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio. Each carrier, diluent, excipient, etc., must also be "acceptable" in the sense of being compatible with the other ingredients of the formulation. A pharmaceutically acceptable substance should be suitable for use in humans, while a veterinarily acceptable substance should be suitable for use in non-human animals. Suitable pharmaceutical carriers include inert solid diluents or fillers, sterile aqueous solution and various organic solvents. Examples of solid carriers are lactose, terra alba, sucrose, cyclodextrin, talc, gelatine, agar, pectin, acacia, magnesium stearate, stearic acid, lower alkyl ethers of cellulose, corn starch, potato starch, gums and the like. Examples of liquid carriers are syrup, peanut oil, olive oil, phospho lipids, fatty acids, fatty acid amines, polyoxyethylene and water. The compounds of the invention may be administered orally, including sublingually, in the form of tablets containing excipients, such as, starch or lactose; in capsules or ovules either alone or in admixture with excipients; in the form of elixirs, solutions, or suspensions optionally containing flavouring or colouring agents. Compositions for oral administration may be prepared with enteric coatings to provide controlled release. For example, the compounds may be incorporated into capsules, tablets, or boluses formulated to dissolve in, for example, the colon or duodenum.
For oral administration, capsules, boluses, or tablets may be prepared by mixing the active ingredient with a suitable finely divided diluent or carrier, additionally containing a
disintegrating agent and/or binder such as starch, lactose, talc, or magnesium stearate. A drench formulation may be prepared by dispersing the active ingredients in an aqueous solution together with dispersing or wetting agents.
The compounds may also be administered with animal feedstuffs by mixing concentrated feed additives or premixes comprising the compounds with normal animal feeds.
The compounds may also be administered with animal drinking water by, for example, dissolving, suspending, or dispersing the compounds or formulations comprising the compounds in the water.
The compounds may be injected parenterally, for example, intravenously, intramuscularly or subcutaneously. For parenteral administration, the compounds are preferably in the form of a sterile aqueous solution, suspension or emulsion that may contain other substances, such as, salt or glucose (to make the solution isotonic with blood). The compounds may be administered topically, in the form of sterile creams, gels, pour-on or spot-on formulations, suspensions, emulsions, shampoos, jetting fluid, lotions, ointments, dips, dusting powders, sprays, drug-incorporated dressings, or skin patches.
For example the compounds may be incorporated into a cream comprising an aqueous or oily emulsion of polyethylene glycols or liquid paraffin; an ointment comprising a white wax soft paraffin base; a hydrogel with cellulose or polyacrylate derivatives or other suitable viscosity modifiers; a dry powder; liquid spray; aerosol with butane, propane, HFA, or CFC propellants; a dressing, such as, a tulle dressing, with white soft paraffin or polyethylene glycol impregnated gauze dressings or with hydrogel, hydrocolloid, or alginate film dressings. The compounds may also be administered intra-ocularly as an eye drop with appropriate buffers, viscosity modifiers (for example, cellulose derivatives), and preservatives (for example, benzalkonium chloride).
Pour-on or spot-on formulations may be prepared by dissolving the compound in an acceptable liquid carrier vehicle, such as butyl digol, liquid paraffin or non- volatile ester with or without addition of a volatile component such as isopropanol. The formulation can be in a form suitable for direct application or in the form of a concentrate that requires dilution with a suitable quantity of water or other diluent before application. Pour-on, spot-on or, spray formulations can be prepared by encapsulation to leave a residue of active agent on the surface of the animal.
The formulations can be incorporated into collars, harnesses, or tags, to be worn by the animal.
The compounds of the invention may be used in conjunction with other anti-parasitic agents to, for example, widen the spectrum of activity or prevent the buildup of resistance. Examples of other suitable anti-parasitic agents include paraherquamide and its derivatives, such as derquantel (in Pfizer Animal Health's STARTECT® product); avermectins and milbemycins, such as, abamectin, cydectin, doramectin, eprinomectin, ivermectin, and milbemycin;
benzimidazoles, such as, albendazole, cambendazole, fenbendazole, flubendazole, mebendazole, oxfendazole, parbendazole, and oxibendazole; pro-benzimidazoles, such as, febantel,
thiophanate, and netobimin; salicylanilides, such as, closantel and niclosamide; imidazothiazoles,
such as, butamisole and levamisole; tetrahydropyrimidines, such as morantel; and hexahydropyrazinoisoquinolines, such as, praziquantel; amino-acetonitrile derivatives (AADs), such as monepantel (in Norvartis Animal Health's ZOLVIX® product). The compounds may be administered in combination with the other anti-parasitic agents separately, simultaneously, or sequentially.
In one embodiment, the compound and other anti-parasitic agent are administered in separate dosage forms. In another embodiment, the compound and other anti-parasitic agent are administered together in a single dosage form.
A person skilled in the art can readily determine the appropriate dosage and frequency of administration for treating an animal with a parasitic infection.
The exact dosage will depend upon the frequency and mode of administration, the sex, age, weight and general condition of the animal treated, the nature and severity of the condition treated and any concomitant diseases to be treated and other factors evident to those skilled in the art. A typical oral dosage is in the range of form about 0.001 to about 100 mg/kg body weight per day, preferably from about 0.01 to about 50 mg/kg body weight per day, and more preferably from about 0.05 to about 10 mg/kg body weight per day administered in one or more dosages such as 1 to 3 dosages.
The amount may be lowered or increased depending on the response of the treated animal. The invention also provides a kit comprising a compound of the invention. The kit may also contain one or more anti-parasitic agents. Kits of the invention are suitable for administering different dosage forms of more than one anti-parasitic agent by separating the agents using, for example, a container, divided bottle or divided foil package.
The following non-limiting examples are provided to illustrate the present invention and in no way limit the scope thereof.
EXAMPLES
Example 1
Compounds of the invention were screened for anthelmintic activity against the nematode parasite Haemonchus contortus using an EC10o assay. The EC10o of a compound is the concentration at which 100% of the nematodes present were killed. Haemonchus contortus were recovered from faeces using the method set out in Coles, G. C, Bauer, C, Borgsteede, F. H. M., Geerts, S., Klei, T. R., Taylor, M. A., Waller, P. J. (1992) World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology (W.A.A.V.P.) methods for the detection of anthelmintic resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance. Veterinary Parasitology, 44 (1-2), pp. 35-44. The Falcon tube containing the eggs was shaken well and a 100 μΐ aliquot of the egg solution taken. The eggs were counted using the McMaster Chamber in accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions.
Distilled water was added or removed (by centrifuging and removing the appropriate quantity of water) to obtain an egg solution with a concentration of 100 eggs per 100 μΐ. Working stock solutions of each compound (100 ppm) were prepared by dissolving and/or diluting each compound, in free base form or salt form (for example, a hydrochloride salt) as appropriate, in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Additional dilutions were performed with DMSO, as required.
The compounds were assayed using 96 well Nunc tissue culture plates. Agar (Merck-101614) was prepared as a 2% solution and then heated by microwave before cooling to ~45 °C. 0.85% Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution was prepared by dissolving one PBS tablet (Sigma P4417) in 125 ml of distilled water. Earle's balanced salt solution (IX) was prepared from 10 x Earle's balanced salt solution (Sigma E7510). 1% Yeast solution was prepared from 0.25 g Yeast extract (Sigma Y-1000), 22.5 ml of 0.85% PBS solution, and 2.5ml of Earle's balanced salt solution (IX). Larval development assay (LDA) media was prepared by mixing 15 ml of a 0.015% solution of lyophilised E. coli (strain W (ATCC) 9637; Sigma Ec9637); 15 ml of a 1% yeast solution; and 45 ul of a 5 mg/ml solution of amphotericin B (Sigma A-9528) in distilled water and either used immediately or stored overnight at 4 °C.
Test compound or water as a negative control (2 μΐ) was added to each well, followed by agar (100 μΐ). The concentration of compound in the 2 μΐ sample was varied to determine the EC 100 of each compound. The agar was allowed to set at room temperature, then a solution of nematode eggs (60 μΐ; 100 eggs per 100 μΐ) and LDA media (40 μΐ) were added to each well.
The plates were incubated for up to 10 days at 25 °C in a plastic container with appropriate aeration and humidity. The larvae were aerated by blowing air over the plate after 24 hours and on every third day until the plates were evaluated.
Each well was then assessed for larval viability microscopically. If larval motility was absent, the compound was scored as having the maximum potency against the larvae.
The results are shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1
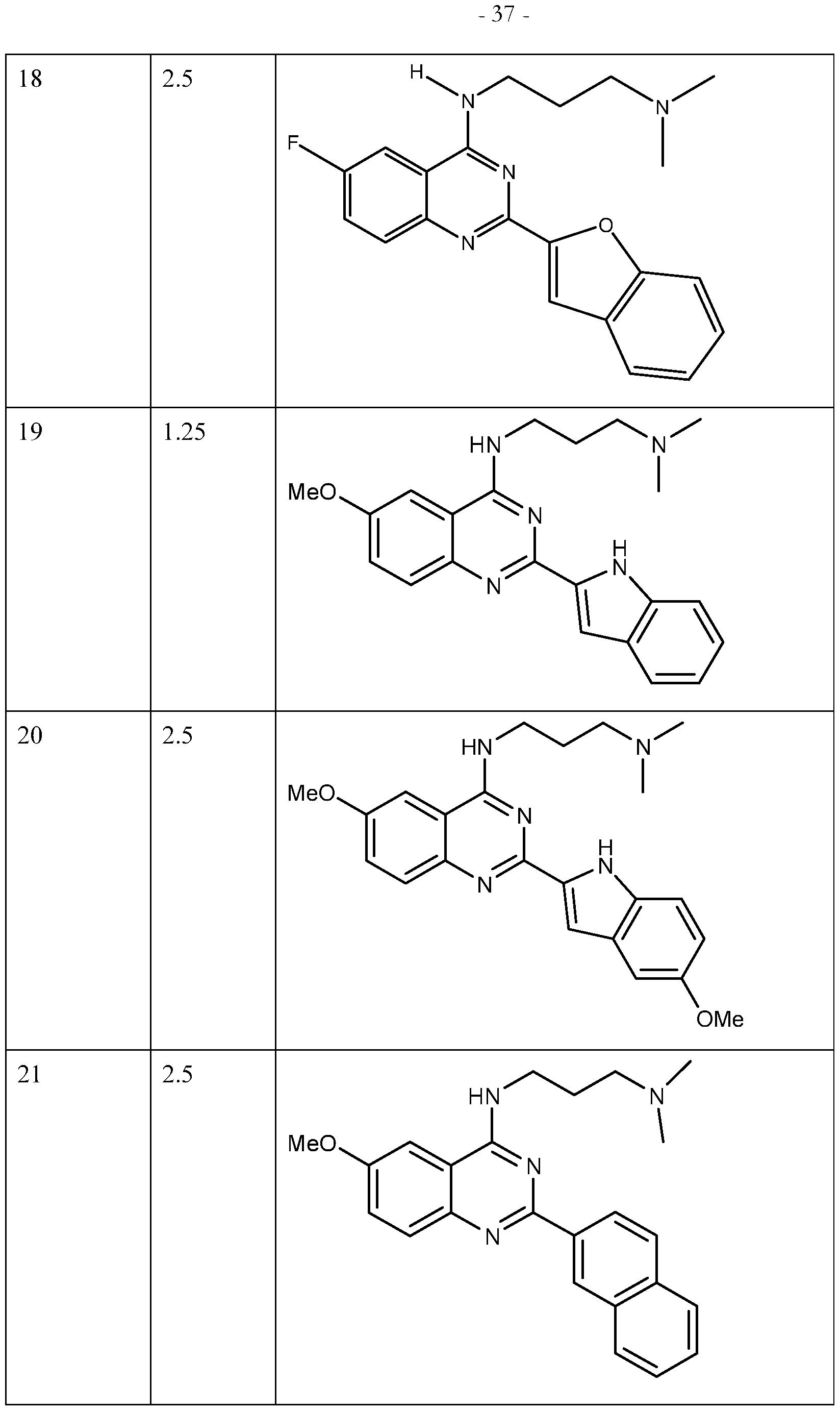
Compound ECIOO Structure
(ppm)
1 2.5
Example 2
Mice were infected with 100 Heligmosoides polygyrus L3 larvae by oral gavage. Approximately 10 days later, infection was confirmed by faecal egg count. Mice were dosed with 100 ppm N1- [2-(l-benzofuran-2-yl)-6-methoxy-4-quinazolinyl]-N ,N -dimethyl- 1, 3 -propanediamine hydrochloride (compound 15) by oral gavage based on body weight. 7 days later, the mice were euthanized and their intestines removed or the carcasses frozen for long term storage. The contents of the small intestine were flushed out with 5ml of water, using a syringe, into a petri dish. Adult worms were identified and counted using a dissecting microscope.
The results are shown in Table 2 below. Table 2
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The substituted ring fused azine compounds described herein have anti-parasitic activity and can, therefore, be used to treat a variety of parasitic infections in animals. The compounds are especially useful for the treatment of endoparasitic infections, in particular helminth infections in production animals.
Where in the forgoing description reference has been made to integers or compounds having known equivalents then such equivalents are herein incorporated as if individually set forth.
It is not the intention to limit the scope of the invention to the abovementioned examples only. As would be appreciated by a skilled person in the art, many variations are possible without departing from the scope of the invention as set out in the accompanying claims.
Claims
1. A compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
D is NR1R2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N- containing heterocyclic ring;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, CHR3, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl or methoxy groups;
Z and Q are each independently selected from N and CH, provided that at least one of Z and Q is N;
J is selected from N and CR¾;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6; R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkenyl, C1-C4 alkynyl, OR8, SR8, NR8R9, CH2R8, COR8, SOR8, S02R8, S02NR8R9, C02R8, CONR8R9, CF3, CN, and N02; and
R¾, R8, and R9 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups.
2. A compound of claim 1 wherein Q is N.
3. A compound of claim 1 or 2 wherein Z is CH and Q is N.
4. A compound of any one of claims 1 to 3 wherein both Z and Q are both N.
5. A compound of any preceding claim wherein Y is independently selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, and -C(R3)=C(R4)-.
6. A compound of any preceding claim wherein Y is independently selected from O, NR4, -C(R3)=N- and -C(R3)=C(R4)-.
7. A compound of any one of claims 1 to 5 wherein Y is independently selected from O, S, and NR4
8. A compound of any one of claims 1 to 7 wherein Y is O or NR4.
9. A compound of any one of claims 1 to 8 wherein Y is O.
10. A compound of any preceding claim wherein D is NRiR2 wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H and C -Ce alkyl.
1 1. A compound of any one of claims 1 to 9 wherein D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring.
12. A compound of claim 1 1 wherein the N-containing heterocyclic ring is selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine
13. A compound of claim 1 1 wherein the N-containing heterocyclic ring is
C6 alkyl.
14. A compound of any preceding claim wherein J is CR¾.
15. A compound of claim 14 wherein R5 is hydrogen.
16. A compound of any preceding claim wherein X is H.
17. A compound of any preceding claim wherein m is 2 or 3.
18. A compound of any preceding claim wherein n is 0.
19. A compound of any preceding claim wherein R6 and R7 are independently selected from H, halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, CF3 and OR8.
20. A compound of any preceding claim wherein R3, R4, R5, R8 and R9 are independently selected from H and C\-Ce alkyl.
21. A compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically or veterinarily acceptable salt or solvate thereof for treating a parasitic infection in an animal:
(I) wherein: D is NR1R2, wherein Ri and R2 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl may each be optionally substituted with one or more amino, hydroxyl, or methoxy groups; or D is a N-containing heterocyclic ring selected from morpholine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, imidazole and 4-methyl piperazine;
X is selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and Ci-C6 cycloalkyl; n is an integer selected from 0 to 2;
Y is selected from O, S, NR4, -C(R3)=N-, -N=CR3-, and -C(R3)=CR4-;
R3 and R4 are independently selected from H, and Ci-C6 alkyl;
Z and Q are both N;
J is selected from N and CR5;
A is (CH2)m, wherein m is an integer selected from 2 to 6;
R6 and R7, at one or more of the available positions on rings T and W respectively, at each occurrence are each independently selected from H, halogen, Ci-C4 alkyl, Ci-C4 alkenyl, Ci-C4 alkynyl, OR8, and CF3; and
R5 and R8 are each independently selected from H, Ci-C6 alkyl and cycloalkyl.
22. A compound of claim 21 wherein m is 2 or 3.
23. A compound of claim 21 or 22 wherein n is 0.
24. A compound of any preceding claim wherein the parasitic infection is an endo-parasite infection.
25. A compound of any preceding claim wherein the parasitic infection is a helminth
infection or infestation.
26. A compound of any preceding claim wherein the animal is a production animal selected from the group consisting of cattle and sheep.
27. A veterinary composition comprising a compound of any one of claims 1 to 23 and a veterinarily acceptable excipient, carrier, or diluent.
28. A use of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 23 in the manufacture of a medicament for treating a parasitic infection in an animal.
29. A method of treating a parasitic infection in an animal, comprising administering to the animal a therapeutically effect amount of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 23.
30. A kit comprising a compound of any one of claims 1 to 23 and one or more additional anti-parasitic agents.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US39125810P | 2010-10-08 | 2010-10-08 | |
| US61/391,258 | 2010-10-08 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012046207A1 true WO2012046207A1 (en) | 2012-04-12 |
Family
ID=45927288
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/IB2011/054414 WO2012046207A1 (en) | 2010-10-08 | 2011-10-07 | Anti-parasitic substituted ring fused azine compounds |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2012046207A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107721982A (en) * | 2017-10-16 | 2018-02-23 | 中山大学 | A kind of antiobesity compounds and its preparation method and application |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000076982A1 (en) * | 1999-06-16 | 2000-12-21 | University Of Iowa Research Foundation | Antagonism of immunostimulatory cpg-oligonucleotides by 4-aminoquinolines and other weak bases |
| WO2002062767A1 (en) * | 2001-02-07 | 2002-08-15 | Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals Company, Limited | Novel quinazoline derivatives |
| WO2004014873A1 (en) * | 2002-08-09 | 2004-02-19 | Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 4-substituted quinazoline-8-carboxyamide derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable addition salt thereof |
| WO2007117161A1 (en) * | 2006-04-07 | 2007-10-18 | Auckland Uniservices Limited | Substituted ring fused azines and their use in cancer therapy |
-
2011
- 2011-10-07 WO PCT/IB2011/054414 patent/WO2012046207A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000076982A1 (en) * | 1999-06-16 | 2000-12-21 | University Of Iowa Research Foundation | Antagonism of immunostimulatory cpg-oligonucleotides by 4-aminoquinolines and other weak bases |
| WO2002062767A1 (en) * | 2001-02-07 | 2002-08-15 | Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals Company, Limited | Novel quinazoline derivatives |
| WO2004014873A1 (en) * | 2002-08-09 | 2004-02-19 | Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 4-substituted quinazoline-8-carboxyamide derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable addition salt thereof |
| WO2007117161A1 (en) * | 2006-04-07 | 2007-10-18 | Auckland Uniservices Limited | Substituted ring fused azines and their use in cancer therapy |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| CHAIRES, J.B. ET AL.: "Triplex Selective 2-(2-Naphthyl)quinoline Compounds: Origins of Affinity and New Design Principles", JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, vol. 125, no. 24, 2003, pages 7272 - 7283, XP002759812, DOI: doi:10.1021/ja034181r * |
| LIN, Z. ET AL.: "Quinazolines as novel anti-inflammatory histone deacetylase inhibitors", MUTATION RESEARCH, vol. 690, no. 1-2, August 2010 (2010-08-01), pages 81 - 88, XP027188410 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107721982A (en) * | 2017-10-16 | 2018-02-23 | 中山大学 | A kind of antiobesity compounds and its preparation method and application |
| CN107721982B (en) * | 2017-10-16 | 2019-12-03 | 中山大学 | A kind of antiobesity compounds and its preparation method and application |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2013312882B2 (en) | Spirocyclic isoxazoline parasiticidal combinations | |
| EP0819000B1 (en) | Nodulisporic acid derivatives | |
| EP2892902A1 (en) | Spirocyclic derivatives as antiparasitic agents | |
| CN104603140A (en) | Spirocyclic isoxazolines as antiparasitic agents | |
| JP2023506303A (en) | Anthelmintic Compounds Containing Azaindole Structures | |
| EP4077281A1 (en) | Anthelmintic compounds comprising a quinoline structure | |
| JP3862938B2 (en) | Anthelmintic composition | |
| US20080287511A1 (en) | Anthelmintic Imidazol-Thiazole Derivates | |
| EP2900065A1 (en) | Spirocyclic isoxazoline derivatives for treatment of sea lice | |
| WO2012046207A1 (en) | Anti-parasitic substituted ring fused azine compounds | |
| AU2002338201B2 (en) | Anthelmintic composition | |
| US20090291977A1 (en) | Chromane Derivatives Useful As Acid Pump Antagonists | |
| EP3313837B1 (en) | Carboline antiparasitics | |
| CN100496244C (en) | Nodulisporic acid derivative spot-on formulations for killing parasites | |
| WO2008152081A2 (en) | Anthelmintic benzo[d]isoxazolyl benzamide derivatives | |
| CA3098151A1 (en) | Endoparasitic depsipeptides | |
| WO2010126857A1 (en) | Parasiticidal combinations of macrocyclic lactones and polyether antibiotics | |
| AU2009246600A1 (en) | Naphthylmethylimidizoles for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence | |
| NZ580761A (en) | Compositions comprising C-13 alkoxyether macrolide compounds and phenylpyrazole compounds | |
| NO300136B1 (en) | Analogous Process for Preparation of Therapeutically Active Stable Salts of 4 '' - Deoxy-4 '' - Epimethylaminoavermectin B1a / B1b |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11830281 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11830281 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |