WO2012028925A2 - An improved process for the preparation of telmisartan - Google Patents
An improved process for the preparation of telmisartan Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012028925A2 WO2012028925A2 PCT/IB2011/001973 IB2011001973W WO2012028925A2 WO 2012028925 A2 WO2012028925 A2 WO 2012028925A2 IB 2011001973 W IB2011001973 W IB 2011001973W WO 2012028925 A2 WO2012028925 A2 WO 2012028925A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- methyl
- formula
- propyl
- telmisartan
- sodium
- Prior art date
Links
- RMMXLENWKUUMAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N telmisartan Chemical compound CCCC1=NC2=C(C)C=C(C=3N(C4=CC=CC=C4N=3)C)C=C2N1CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(O)=O RMMXLENWKUUMAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 58
- 239000005537 C09CA07 - Telmisartan Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 32
- 229960005187 telmisartan Drugs 0.000 title claims abstract description 32
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 30
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 52
- IGCBUUTXGYCQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(butanoylamino)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate Chemical compound CCCC(=O)NC1=C(C)C=C(C(=O)OC)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O IGCBUUTXGYCQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- -1 Telmisartan ester Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000005864 Sulphur Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 78
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 62
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 42
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 26
- JVBXVOWTABLYPX-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium dithionite Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)S([O-])=O JVBXVOWTABLYPX-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 21
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 13
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000006210 cyclodehydration reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Substances C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000011181 potassium carbonates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium sulfite Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])=O GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 4
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- MFGOFGRYDNHJTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-1-(2-fluorophenyl)ethanol Chemical compound NCC(O)C1=CC=CC=C1F MFGOFGRYDNHJTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bicarbonate Chemical class OC([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-DEQYMQKBSA-M Sodium bicarbonate-14C Chemical compound [Na+].O[14C]([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-DEQYMQKBSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- RQPZNWPYLFFXCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L barium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Ba+2] RQPZNWPYLFFXCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001863 barium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- FJDQFPXHSGXQBY-UHFFFAOYSA-L caesium carbonate Chemical compound [Cs+].[Cs+].[O-]C([O-])=O FJDQFPXHSGXQBY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000024 caesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- HUCVOHYBFXVBRW-UHFFFAOYSA-M caesium hydroxide Inorganic materials [OH-].[Cs+] HUCVOHYBFXVBRW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- NKWPZUCBCARRDP-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].OC([O-])=O.OC([O-])=O NKWPZUCBCARRDP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000020 calcium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- AXCZMVOFGPJBDE-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Ca+2] AXCZMVOFGPJBDE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000920 calcium hydroxide Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001861 calcium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004649 carbonic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000006184 cosolvent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- DKEONVNYXODZRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydron;2-n-methylbenzene-1,2-diamine;dichloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.CNC1=CC=CC=C1N DKEONVNYXODZRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000347 magnesium hydroxide Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001862 magnesium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000028 potassium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000015497 potassium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011736 potassium bicarbonate Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium hydrogencarbonate Chemical compound [K+].OC([O-])=O TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- GRVFOGOEDUUMBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium sulfide (anhydrous) Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[S-2] GRVFOGOEDUUMBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UUCCCPNEFXQJEL-UHFFFAOYSA-L strontium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Sr+2] UUCCCPNEFXQJEL-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001866 strontium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004178 (C1-C4) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylacetamide Chemical compound CN(C)C(C)=O FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000010 aprotic solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- HRZFUMHJMZEROT-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium disulfite Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)S([O-])(=O)=O HRZFUMHJMZEROT-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940001584 sodium metabisulfite Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010262 sodium metabisulphite Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052979 sodium sulfide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010265 sodium sulphite Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- HXJUTPCZVOIRIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfolane Chemical compound O=S1(=O)CCCC1 HXJUTPCZVOIRIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 2
- ZTHYODDOHIVTJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propyl gallate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1 ZTHYODDOHIVTJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 125000003158 alcohol group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- DEFDQXCQBZEOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 7-methyl-2-propyl-3h-benzimidazole-5-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=C(C(=O)OC)C=C2NC(CCC)=NC2=C1C DEFDQXCQBZEOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 27
- XWAJTVCEILFDGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-methyl-2-propyl-3h-benzimidazole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C1=C(C(O)=O)C=C2NC(CCC)=NC2=C1C XWAJTVCEILFDGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 15
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 57
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 19
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 16
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 11
- ILXRSCZVHSZGCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-6-(1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-2-propyl-1h-benzimidazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(C)C(C3=CC(C)=C4N=C(NC4=C3)CCC)=NC2=C1 ILXRSCZVHSZGCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium on carbon Substances [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 6
- IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen chloride Substances Cl.Cl IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910000041 hydrogen chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 235000011054 acetic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- WNAFVJVEADYQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-phenylbenzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 WNAFVJVEADYQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- RPKCLSMBVQLWIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-n-methylbenzene-1,2-diamine Chemical compound CNC1=CC=CC=C1N RPKCLSMBVQLWIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ILYSAKHOYBPSPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylbenzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ILYSAKHOYBPSPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylbenzene Natural products C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical class [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000004305 biphenyl Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000009903 catalytic hydrogenation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 3
- 238000007363 ring formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium chloride Substances [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [NH4+].[OH-] VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrazine Chemical compound NN OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Raney nickel Chemical compound [Al].[Ni] NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001860 alkaline earth metal hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000287 alkaline earth metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonia Natural products N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000011114 ammonium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000001448 anilines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 description 2
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylselenoniopropionate Natural products CCC(O)=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000011167 hydrochloric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002050 international nonproprietary name Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- UITANFWKOFOWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-amino-4-(butanoylamino)-5-methylbenzoate Chemical compound CCCC(=O)NC1=C(C)C=C(C(=O)OC)C=C1N UITANFWKOFOWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920000137 polyphosphoric acid Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000001117 sulphuric acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011149 sulphuric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- JRMUNVKIHCOMHV-UHFFFAOYSA-M tetrabutylammonium bromide Chemical compound [Br-].CCCC[N+](CCCC)(CCCC)CCCC JRMUNVKIHCOMHV-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 238000010626 work up procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- JIHQDMXYYFUGFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,5-triazine Chemical compound C1=NC=NC=N1 JIHQDMXYYFUGFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RHXSYTACTOMVLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(C(=O)O)=NC2=C1 RHXSYTACTOMVLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XABKVLSJTCMEDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-6-[4-[[4-methyl-6-(1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-2-propylbenzimidazol-1-yl]methyl]phenyl]benzoic acid Chemical compound CCCc1nc2c(C)cc(cc2n1Cc1ccc(cc1)-c1cccc(c1C(O)=O)C(C)(C)C)-c1nc2ccccc2n1C XABKVLSJTCMEDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTJGVAJYTOXFJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-aminonaphthalene-1,5-disulfonic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C2=CC(N)=CC(S(O)(=O)=O)=C21 MTJGVAJYTOXFJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000497 Amalgam Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003125 aqueous solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001556 benzimidazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonic acid Chemical class OC(O)=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004494 ethyl ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000001035 gastrointestinal tract Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N mercury Chemical compound [Hg] QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052753 mercury Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- VBEGHXKAFSLLGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-phenylnitramide Chemical class [O-][N+](=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 VBEGHXKAFSLLGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003472 neutralizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002828 nitro derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 238000010534 nucleophilic substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005580 one pot reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000011007 phosphoric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019260 propionic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N quinbolone Chemical compound O([C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4CC3)C)CC[C@@]21C)C1=CCCC1 IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000011946 reduction process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052703 rhodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N teixobactin Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](CCC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H]1C(N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C[C@@H]2NC(=N)NC2)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@H]1C)[C@@H](C)CC)=O)NC)C1=CC=CC=C1 LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 231100000331 toxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000002588 toxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035899 viability Effects 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D235/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, condensed with other rings
- C07D235/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, condensed with other rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D235/04—Benzimidazoles; Hydrogenated benzimidazoles
- C07D235/18—Benzimidazoles; Hydrogenated benzimidazoles with aryl radicals directly attached in position 2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D235/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, condensed with other rings
- C07D235/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, condensed with other rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D235/04—Benzimidazoles; Hydrogenated benzimidazoles
- C07D235/20—Two benzimidazolyl-2 radicals linked together directly or via a hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radical
Definitions
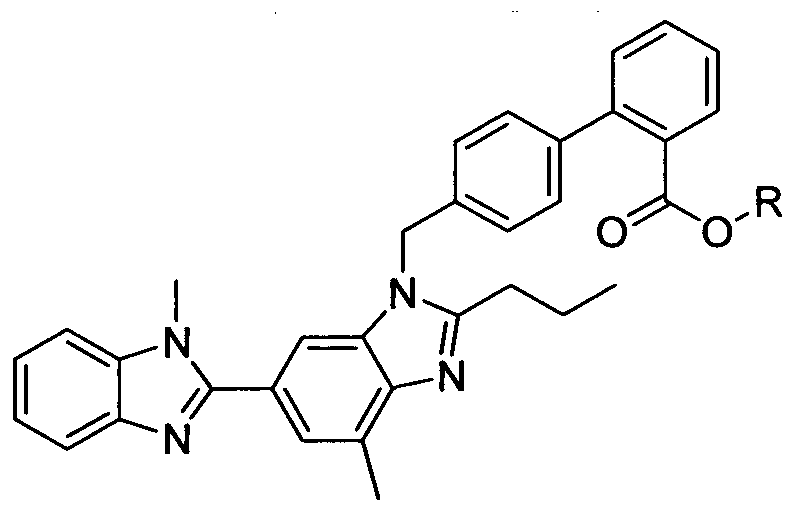
- the present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2- n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan) of Formula I.
- Telmisartan is the INN (International Nonproprietary Name) for the compound 4'- [2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid. (CAS Registry No. 144701-48-4)
- the empirical formula of telmisartan is C3 3 H 3 oN 4 02 and its molecular weight is 514.63.
- the molecular structure of telmisartan is represented by Formula I.
- Chinese patent application CN 1412183 (hereinafter the ⁇ 83 application) describes a process for preparing Telmisartan, which includes reacting 2-n-propyl-4-methyl- 6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 4'-(bromomethyl)-[l,l '- biphenyl]-2 -carbonitrile to afford the carbonitrile derivative of Telmisartan, i.e., 4'- [ 1 ,4 ' -dimethyl-2 ' -propyl [2,6' -bi- 1 H-benzimidazol] - 1 ' -yl-)methyl] -[1,1 '-biphenyl] - -carbonitrile, followed by hydrolysis of the cyano group to afford Telmisartan.
- Chinese patent application CN 1344712 (hereinafter the '712 application) describes the preparation of Telmisartan by reacting 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 4'-(bromomethyl)-[l,r-biphenyl]-2- carboxylic acid methyl or ethyl ester via nucleophilic substitution, to give the carboxylic ester derivatives of Telmisartan, followed by hydrolysis to afford Telmisartan.
- WO 2006/044648 describes synthetic route, which is similar to- the synthesis described in the '712 application, using a low boiling solvent and a PTC.
- Telmisartan In general, Telmisartan is manufactured and supplied in its free acid form. However, as described in US 6,410,742 crystalline Telmisartan apparently exists in two polymorphic forms A and B, which have different melting points. Both of these forms are apparently very poorly soluble in aqueous systems at the physiological pH range 1 to 7, in the gastro-intestinal tract.
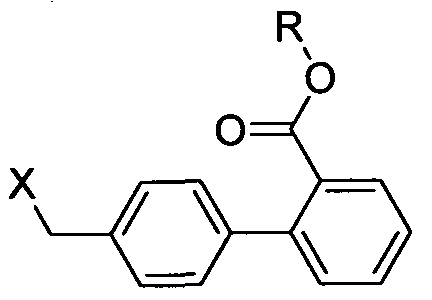
- the critical step in the manufacturing process of Telmisartan is the n-alkylation of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)- 1 H-benzimidazole (DMPBB) of formula VII with 4'-halomethylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid alkyl ester of formula VIII.
- DMPBB dimethylbenzimidazol-2-yl
- the synthesis of substituted benzimidazoles is desirably carried out by first reducing methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate of formula III under various catalytic hydrogenation conditions to yield methyl-3-amino-4- (butyramido)-5-methylbenzoate.
- the reduction step is carried out under different conditions using Raney Ni/H 2 , Pd-C/H 2 , Sn(II)chloride and Fe/HCl, Sn/HCl as per the literature known procedures.
- Methyl-3-amino-4-(butyramido)-5-methylbenzoate of formula III is cyclized under variety of basic and acidic conditions to yield methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate of formula IV as per the prior art methods.
- DMPBB dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH,3'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol
- US 5,591,762 describes methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate is reduced under catalytic hydrogenation condition using Pd/C in methanol to give the substituted aniline derivative.
- This aniline derivative is converted to methyl-4- methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate using acetic acid.
- the crude product obtained is hydrolyzed and recrystallized from isopropanol to give benzimidazole carboxylic acid, which is then converted into the desired 2-n-propyl- 4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 2-methylamino- aniline by cyclization.
- US 2007/0037986 describes a process for preparing l,7'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-2,5'- bi-lH-benzimidazole, by reacting N-methyl-o-phenylenediamine with 2-propyl-4- methyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylic acid wherein the coupling and cyclization is achieved using 1,3,5-triazine and tertiary amine.
- DMPBB may be prepared by mixing 2-propyl-4-methyl-lH-benzimidazole-6- carboxylic acid with N-methyl-o-phenylene-diamine dihydrochloride with polyphospharic acid as disclosed in J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36(25), 4040-51, international patent application WO 2000/0063158, and US 2003/0139608, are hereby incorporated by reference for their disclosure of processes, which involves two-step process involving tedious work-up and purification procedures.
- WO 2009/133122 describes the method for the preparation of l,7'-dimethyl-2'- propyl-2,5'-bi-lH-benzimidazole by the conversion of N-methyl-o-phenylene- diamine with 2-propyl-4-methyl-lH-benzimidazol-6-carboxylic acid using phosphourus pentoxide in methane sulphonic acid solvent, at a temperature range from 110-160 °C.
- Reduction of nitro groups which is the first step in the above mentioned syntheses is achieved with a wide variety of reagents namely catalytic hydrogenation using metal supported catalysts like Pd/C, Rh C, Pt/C and dissolved metal reductions like Sn/HCl, Mercury amalgam, Sn(II) Chloride etc.
- the main objective of the present invention is to provide an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2- yl)benzimidazol-l-ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan), which is simple, industrially applicable and economically viable.
- the present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2- n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmeth l]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan) of formula I,
- step (a) converting the isolated ester of formula IV from step (a) with an aqueous base in presence or absence of an organic co-solvent at a temperature ranging 20-100 °C, preferably in the range of 80-100 °C to corresponding acid of formula V;
- N-Ortho nitro anilines are cyclized to 2-substituted benzimidazoles in one pot using reagents like Pd-C/methanol/H 2 gas as described in Organic Process Research & Development 2007, 11, 81-85, Sn/HCl in Chemische Berichte 1872, 5, 920, Fe/HCl in WO 2004/108686 and Hydrazine/Raney Ni in Journal of Heterocyclic chemistry 2003, 40, 1107-1112. These reductions suffer from major draw backs of toxic inorganic byproducts and random purification procedures using column chromatography.
- methyl-4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate (II) is reacted with reducing agent selected from derivatives of sulphur like sodium sulfite, sodium sulphide, sodium dithionite, sodium metabisulfite etc. in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent with a temperature ranging 20-120 °C.
- reducing agent selected from derivatives of sulphur like sodium sulfite, sodium sulphide, sodium dithionite, sodium metabisulfite etc.
- Insitu reduction and cyclodehydration takes place in one-step giving methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (IV).
- the cyclizing agent is sodium dithionite, a cheap alternate to the costly catalysts used in the reduction process of nitro compound.
- the insitu reduction and cyclization is carried out in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent, wherein an organic solvent selected from alcohol such as methanol, IP A, ethanol, butanol or ether such as dioxane or THF or dipolar aprotic solvent such as DMF, DMA, DMSO, NMP, sulfolane.
- an organic solvent selected from alcohol such as methanol, IP A, ethanol, butanol or ether such as dioxane or THF or dipolar aprotic solvent such as DMF, DMA, DMSO, NMP, sulfolane.
- the above mentioned process can be carried out in presence of acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, benzoic acid etc., in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent.
- acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, benzoic acid etc.
- the above mentioned process can also be carried out in presence of bases selected from alkali earth metal or alkaline earth metal hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate etc., in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent.
- bases selected from alkali earth metal or alkaline earth metal hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate etc.
- insitu reduction-cyclodehydration process of compound of formula II is treated with hydrose (Sodium dithionite), in aqueous solvent system as previously described at a temperature ranging from 20-120 °C, preferably 80-100 °C for a period of 20-48 hrs.
- hydrose sodium dithionite
- the acid, 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole which is obtained by the above process is cyclized with N-methyl-o- phenylenediamine in presence of an acid selected from polyphosphoric acid, p- toluenesulfonic acid, sulphuric acid, acetic acid, preferably polyphosphoric acid at a temperature ranging 80-130 °C, preferably 120-130 °C, gives l,4'-dimethyl-2'- propyl- 1 H,3 'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (VII).
- reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (150 ml) and the pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X60 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2 -propyl- 1H- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (1 gm, Yield: 40.2 %) of formula IV.
- Methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (40 gms, 0.172 moles) was suspended in methanol (200 ml) and stirred for few minutes.
- Sodium hydroxide 13.76 gms, 0.344 moles
- water 50 ml
- methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure and water (100 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-10 °C.
- the solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50 °C under vacuum (700 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl- 6-carboxy benzimidazole (30gms, Yield: 80 %).
- Aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (1.68 gms, 0.042 moles, 10 ml) was added to a solution of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (5 gms, 0.021 moles) in isopropanol (20 ml) and stir for few minutes. Then the temperature was raised to 85 °C. After reaction complies, isopropanol was evaporated under reduced pressure and water (75 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-15 °C. Then the pH of the crude mass was adjusted to 6-6.5 and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50 °C under vacuum (600 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (2.81 gms, Yield: 60%).
- Orthophosphoric acid (210 gms) was taken in round bottomed flask and ⁇ 2 0 5 (210 gms) was added in portions with vigorous stirring. (Note: Sharp increase in temperature > 200 °C). The above mass is allowed to cool to 70 °C and 2-n-propyl- 4-methyl-benzimidazole-6-carboxylic acid (70 gms, 0.321 mol) was added slowly. Then N-methylbenzene-l,2-diamine hydrochloride (62.3 gms, 0.321 mol) was added in small portions at same temperature and then the temperature was raised to 125-130 °C.
- reaction was quenched with ice cold water (1 Lt), adjusted pH of the reaction mixture to 9-10 by the addition of aqueous ammonia solution. Obtained solid was filtered and washed with cold water until the pH of the filtrate becomes neutral. Then the crude solid was washed with hot water until colorless filtrate was observed. The crude solid was boiled in ethyl acetate (700 ml) for 2-3 hrs. The reaction mass was cooled and the suspension was filtered off and dried to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH- benzimidazole (V) (80 gms, Yield : 82 %).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
- Nitrogen Condensed Heterocyclic Rings (AREA)
Abstract
Methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate is treated with sulphur containing reducing agent to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate, which is further hydrolyzed to the corresponding acid, 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6- carboxy benzimidazole. The critical intermediate l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH,3'H- 2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (DMPBB) is prepared by treating the above acid with N- mehtyl-o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride under acidic conditions. Reaction of 4'-halomethylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid alkyl ester with DMPBB in presence of base to give Telmisartan ester which is further converted to Telmisartan of Formula (I).
Description
AN IMPROVED PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF
TELMISARTAN FIELD OF INVENTION
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2- n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan) of Formula I.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Telmisartan is the INN (International Nonproprietary Name) for the compound 4'- [2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid. (CAS Registry No. 144701-48-4) The empirical formula of telmisartan is C33H3oN402 and its molecular weight is 514.63. The molecular structure of telmisartan is represented by Formula I.
The synthesis of Telmisartan was first described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,591,762 (hereinafter the '762 patent) by hydrolysis of the tertiary-butyl ester precursor of Telmisartan, in particular, tert-butyl 4'[2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 -ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid using trifluoroacetic acid in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF).
Telmisartan
Chinese patent application CN 1412183 (hereinafter the Ί83 application) describes a process for preparing Telmisartan, which includes reacting 2-n-propyl-4-methyl- 6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 4'-(bromomethyl)-[l,l '- biphenyl]-2 -carbonitrile to afford the carbonitrile derivative of Telmisartan, i.e., 4'- [ 1 ,4 ' -dimethyl-2 ' -propyl [2,6' -bi- 1 H-benzimidazol] - 1 ' -yl-)methyl] -[1,1 '-biphenyl] - -carbonitrile, followed by hydrolysis of the cyano group to afford Telmisartan.
Chinese patent application CN 1344712 (hereinafter the '712 application) describes the preparation of Telmisartan by reacting 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-
methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 4'-(bromomethyl)-[l,r-biphenyl]-2- carboxylic acid methyl or ethyl ester via nucleophilic substitution, to give the carboxylic ester derivatives of Telmisartan, followed by hydrolysis to afford Telmisartan.
WO 2006/044648 describes synthetic route, which is similar to- the synthesis described in the '712 application, using a low boiling solvent and a PTC.
In general, Telmisartan is manufactured and supplied in its free acid form. However, as described in US 6,410,742 crystalline Telmisartan apparently exists in two polymorphic forms A and B, which have different melting points. Both of these forms are apparently very poorly soluble in aqueous systems at the physiological pH range 1 to 7, in the gastro-intestinal tract.
The critical step in the manufacturing process of Telmisartan is the n-alkylation of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)- 1 H-benzimidazole (DMPBB) of formula VII with 4'-halomethylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid alkyl ester of formula VIII.
The synthesis of substituted benzimidazoles is desirably carried out by first reducing methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate of formula III under various catalytic hydrogenation conditions to yield methyl-3-amino-4- (butyramido)-5-methylbenzoate. The reduction step is carried out under different conditions using Raney Ni/H2, Pd-C/H2, Sn(II)chloride and Fe/HCl, Sn/HCl as per the literature known procedures.
Methyl-3-amino-4-(butyramido)-5-methylbenzoate of formula III is cyclized under variety of basic and acidic conditions to yield methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate of formula IV as per the prior art methods.
The critical intermediate l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH,3'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (DMPBB) of Formula VII is prepared in the prior art as per the following methods: US 5,591,762 describes methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate is reduced under catalytic hydrogenation condition using Pd/C in methanol to give the substituted aniline derivative. This aniline derivative is converted to methyl-4- methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate using acetic acid. The crude product obtained is hydrolyzed and recrystallized from isopropanol to give benzimidazole carboxylic acid, which is then converted into the desired 2-n-propyl- 4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazole with 2-methylamino- aniline by cyclization.
US 2007/0037986 describes a process for preparing l,7'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-2,5'- bi-lH-benzimidazole, by reacting N-methyl-o-phenylenediamine with 2-propyl-4- methyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylic acid wherein the coupling and cyclization is achieved using 1,3,5-triazine and tertiary amine.
DMPBB may be prepared by mixing 2-propyl-4-methyl-lH-benzimidazole-6- carboxylic acid with N-methyl-o-phenylene-diamine dihydrochloride with polyphospharic acid as disclosed in J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36(25), 4040-51,
international patent application WO 2000/0063158, and US 2003/0139608, are hereby incorporated by reference for their disclosure of processes, which involves two-step process involving tedious work-up and purification procedures. WO 2009/133122 describes the method for the preparation of l,7'-dimethyl-2'- propyl-2,5'-bi-lH-benzimidazole by the conversion of N-methyl-o-phenylene- diamine with 2-propyl-4-methyl-lH-benzimidazol-6-carboxylic acid using phosphourus pentoxide in methane sulphonic acid solvent, at a temperature range from 110-160 °C.
Reduction of nitro groups, which is the first step in the above mentioned syntheses is achieved with a wide variety of reagents namely catalytic hydrogenation using metal supported catalysts like Pd/C, Rh C, Pt/C and dissolved metal reductions like Sn/HCl, Mercury amalgam, Sn(II) Chloride etc.
However, these methods suffer from the disadvantage that the catalysts used are very expensive and manufacturing methods involve workup using organic solvents. These facts affect the commercial viability of manufacturing process substantially. There is a need for better synthetic methodologies for the manufacture of 1,4'- dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH,3'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (DMPBB) of formula VII.
We have now realized an alternate method for the synthesis of methyl-4-methyl-2- propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate of formula IV involving a single pot reduction and cyclodehydration as per Scheme given below:
Scheme
The main objective of the present invention is to provide an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2- yl)benzimidazol-l-ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan), which is simple, industrially applicable and economically viable.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of [4'-(2- n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - ylmeth l]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (Telmisartan) of formula I,
a) treating methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate of formula II,
Formula II
with sulphur containing reducing agent in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent to give a compound of formula IV,
Formula IV
which is formed by insitu reduction and cyclodehydration process at temperature ranging 20-120 °C, preferably in the range of 80-100 °C; b) reaction mass from step (a) is basified with an inorganic base to pH 1 1 -12 and heated at temperature ranging from 20-100 °C preferably in the range of 80-100 °C to convert ester of formula IV to the corresponding acid of formula V,
(OR)
converting the isolated ester of formula IV from step (a) with an aqueous base in presence or absence of an organic co-solvent at a temperature ranging 20-100 °C, preferably in the range of 80-100 °C to corresponding acid of formula V;
Formula V
c) cyclizing the corresponding acid of formula V with N-methyl-o- phenylenediamine dihydrochloride in the presence of an acid to give a compound of formula VII
Formula VII
alkylation of compound of formula VII with 4'-halomethylbiphenyl-2- carboxylic acid alkyl ester of formula VIII,
Formula VIII
wherein X represents Br, CI, I and R represents straight or branched chain C,-C4 alkyl;
to give Telmisartan ester (IX),
e) hydrolysis of Telmisartan ester (IX) to give Telmisartan.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
N-Ortho nitro anilines are cyclized to 2-substituted benzimidazoles in one pot using reagents like Pd-C/methanol/H2 gas as described in Organic Process Research & Development 2007, 11, 81-85, Sn/HCl in Chemische Berichte 1872, 5, 920, Fe/HCl in WO 2004/108686 and Hydrazine/Raney Ni in Journal of Heterocyclic chemistry 2003, 40, 1107-1112. These reductions suffer from major draw backs of toxic inorganic byproducts and random purification procedures using column chromatography.
We have now realized methyl-4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate (II) is reacted with reducing agent selected from derivatives of sulphur like sodium sulfite, sodium sulphide, sodium dithionite, sodium metabisulfite etc. in water or an
organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent with a temperature ranging 20-120 °C. Insitu reduction and cyclodehydration takes place in one-step giving methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (IV). The cyclizing agent is sodium dithionite, a cheap alternate to the costly catalysts used in the reduction process of nitro compound. The insitu reduction and cyclization is carried out in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent, wherein an organic solvent selected from alcohol such as methanol, IP A, ethanol, butanol or ether such as dioxane or THF or dipolar aprotic solvent such as DMF, DMA, DMSO, NMP, sulfolane.
The above mentioned process can be carried out in presence of acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, benzoic acid etc., in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent.
The above mentioned process can also be carried out in presence of bases selected from alkali earth metal or alkaline earth metal hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate etc., in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent.
According to a particular embodiment, insitu reduction-cyclodehydration process of compound of formula II is treated with hydrose (Sodium dithionite), in aqueous solvent system as previously described at a temperature ranging from 20-120 °C, preferably 80-100 °C for a period of 20-48 hrs.
After completion of the insitu reduction-cyclodehydration, product is isolated from the reaction mass by neutralizing.
Hydrolysis of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (IV) with base selected from inorganic bases of alkali earth metal or alkaline earth metal hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate etc., preferably sodium hydroxide, in a solvent selected from ethanol, methanol, isopropyl alcohol, preferably methanol at a temperature of 80 °C gives 2-n-propyl- 4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole. The acid, 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole which is obtained by the above process is cyclized with N-methyl-o- phenylenediamine in presence of an acid selected from polyphosphoric acid, p- toluenesulfonic acid, sulphuric acid, acetic acid, preferably polyphosphoric acid at a temperature ranging 80-130 °C, preferably 120-130 °C, gives l,4'-dimethyl-2'- propyl- 1 H,3 'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (VII).
Condensation of l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH,3'H-2,6'-bisbenzimidazol (VII) with 4'-halomethylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid alkyl ester (VIII) in presence of base selected from potassium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, preferably sodium hydroxide in a solvent selected from DMF, DMSO, THF, preferably DMF at a temperature ranging 0-60 °C, preferably 20-30 °C, to produce 4'-(l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH-[2,5']benzimidazolyl-3'- ylmethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (IX) (Telmisartan ester).
Further hydrolysis of 4,-(l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH-[2,5']benzimidazolyl-3'- ylmethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (IX) in presence of base preferably sodium hydroxide and a solvent preferably methanol to produce Telmisartan.
The following examples illustrate the nature of the invention and are provided for illustrative purposes only and should not be construed to limit the scope of the invention.
Experiments:
Experiment I: Preparation of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6- carboxylate (Imidazole Ester).
Example 1:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (50 gm, 0.178 moles), was suspended in water (300 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. A suspension of sodium dithionite (108.7 gm, 0.536 moles) in water (300 ml) was added gradually to the above mass and the temperature is raised to 90-100 °C. After the reaction completed, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (3x200 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6- carboxylate (40 gms, Yield : 96.6 %) of formula IV.
Example 2:
To a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles) in methanol (20 ml) was added a suspension of sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) in water (15 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature was raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. Water (100 ml) was added to the residue and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (70 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl- lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3.9 gms, Yield: 95%) of formula IV.
Example 3:
A suspension of sodium dithionite (108.7 gm, 0.536 moles) in water (150 ml) was added gradually to a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (50 gm, 0.178 moles) in isopropanol (200 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature was raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, Isopropanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. To the residue was added water (500 ml) and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (600 ml), and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-
methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (33 gms, Yield: 79.6 %) of formula IV.
Example 4:
A suspension of sodium dithionite (108.7 gm, 0.536 moles) in water (150 ml) was added gradually to a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (50 gm, 0.178 moles) in n-butanol (200 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature was raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, n-butanol was distilled out under reduced pressure. Water (400 ml) was added to the residue and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (3x200 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford methyl-4-methyl- 2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (31 gm, Yield: 75 %) of formula IV.
Example 5:
To a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles) in toluene (20 ml), was gradually added sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) in water (20 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature is raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, toluene was evaporated under reduced pressure. Water (100 ml) was added to the residue and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2x60 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to provide methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (1 gm, Yield: 24 %) of formula IV.
Example 6:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles), was suspended in MeOH (25 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. Sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) was added gradually to the reaction mixture and the temperature was raised to 60-65 °C. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. To the residue was added water (70 ml) and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2x50 ml) and the combined
organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2- propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3 gm, Yield: 96.6 %) of formula IV.
Example 7:
Sodium dithionite (6.52 gm, 0.0375 moles) was added gradually to a solution of 4- butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (3 gm, 0.0107moles) in DMF (15 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature was maintained at 90-100 °C. After the reaction completed, the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (150 ml) and the pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2x50 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (1.8 gm, Yield: 72.4 %) of formula IV.
Example 8:
Sodium dithionite (6.52 gm, 0.0375 moles) was added gradually to a solution of 4- butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (3 gm, 0.0107moles) in DMSO (10 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. Then the temperature of the reaction was raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (150 ml) and the pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X75 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford methyl -4-methyl-2 -propyl- \H- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (2.2 gms, Yield: 90 %) of formula IV.
Example 9:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (3 gm, 0.0107 moles), was suspended in DMA (15 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. Sodium dithionite (6.52 gm, 0.0375 moles) was added gradually to the reaction mixture and the temperature was raised to 90-100 °C. After reaction complies, the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (150 ml) and the pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X60 ml) and the combined organic layer was
concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2 -propyl- 1H- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (1 gm, Yield: 40.2 %) of formula IV.
Example 10:
To a suspension of sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) in water (50 ml) was added 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles) in 10% DMF/H20 (100 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature was maintained at 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (200 ml) and the reaction mass pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X50 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford methyl -4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3.5 gms, Yield: 84.5 %) of formula IV.
Example 11:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (3 gm, 0.0107 moles), was suspended in 10% DMSO/H20 (100 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. Sodium dithionite (6.52 gm, 0.0375 moles) suspended in water (20 ml) was added gradually to the above reaction mass and the temperature maintained at 90-100 °C. After reaction complies, the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water (150 ml) and the reaction mass pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X50 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (2.1gms, Yield: 84.4 %) of formula IV. Example 12:
To a suspension of sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) in water (40 ml) was gradually added to a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles) in Toluene (50 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature of the reaction mixture was maintained at 90-100 °C. Tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.5 gm) was added to the reaction mass as a PTC. After completion of the reaction, toluene was evaporated under reduced pressure.
To the residue water (100 ml) was added and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X60 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3 gms, Yield: 72.4 %) of formula IV.
Example 13:
To a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gm, 0.0178 moles) in methanol (50 ml) at 70-80 °C, was gradually added a suspension of sodium dithionite (10.87 gm, 0.0536 moles) in water (40 ml). Then the temperature of the reaction mixture was maintained at 90-100 °C. Tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.5 gm) was added as a PTC to the above reaction mass. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. Water (100 ml) was added to the residue and pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2x60 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl -4-methyl -2 -propyl- \H- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3 gms, Yield: 72.4 %) of formula IV.
Example 14:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (3 gm, 0.0107 moles), was suspended in 10 % aqueous acetic acid (50 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. A suspension of sodium dithionite (6.52 gm, 0.0375 moles) in water (20 ml) was added gradually to the reaction mixture and the temperature was raised to 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X60 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH- benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (2.1 gms, Yield: 84.4 %) of formula IV.
Example 15:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (20 gm, 0.071 moles), was suspended in methanol (100 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. Sodium dithionite (43.5 gm, 0.248 moles) was suspended in saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (60 ml)
was added gradually to the reaction mixture and the temperature was raised to 90- 100 °C. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. The pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2X75 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (16 gms, Yield: 96.5 %) of formula IV.
Example 16:
To a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (20 gm, 0.071 moles) in isopropanol (80 ml) at 70-80 °C was added sodium dithionite (43.5 gm, 0.248 moles) in saturated bicarbonate solution (60 ml) and the temperature of the reaction mass was maintained at 90-100 °C. After reaction complies, isopropanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. The reaction mass pH was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (2x75 ml) and the combined organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give methyl -4-methyl-2- propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (10 gm, Yield: 60.3 %) of formula IV.
Example 17:
A solution of sodium sulfide (1.39 gm, 0.536 moles) in water (80 ml) was added gradually to a suspension of 4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (5 gms, 0.0178 moles) in water (30 ml) at 70-80 °C. Then the temperature of the reaction mass was maintained at 90-100 °C. After completion of the reaction, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 9-10 and extracted with ethyl acetate (500 ml) and the combined extracts were concentrated and the pure methyl-4- methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (2 gms, Yield : 51.4 %) of formula IV was isolated by column chromatography.
Experiment II: Preparation of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (V).
Example 1:
Methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (40 gms, 0.172 moles) was suspended in methanol (200 ml) and stirred for few minutes. Sodium hydroxide (13.76 gms, 0.344 moles) dissolved in water (50 ml) was added to the reaction mass and the temperature is maintained at 80°C. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure and water (100 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-10 °C. Then adjusted the pH of the crude mass to 6- 6.5 and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50 °C under vacuum (700 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl- 6-carboxy benzimidazole (30gms, Yield: 80 %).
Example 2:
To a suspension of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazoIe-6-carboxylate (2 gms, 0.0086 moles) in water (10 ml) was added aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (0.69 gms, 0.017 moles) and the temperature is maintained at 85-95 °C. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mass was cooled to room temperature and pH was adjusted to 6-6.5 with aqueous hydrogen chloride and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45- 50 °C under vacuum (700 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (1.1 gms, Yield: 59 %).
Example 3:
Aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (1.68 gms, 0.042 moles, 10 ml) was added to a solution of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (5 gms, 0.021 moles) in isopropanol (20 ml) and stir for few minutes. Then the temperature was raised to 85 °C. After reaction complies, isopropanol was evaporated under reduced pressure and water (75 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-15 °C. Then the pH of the crude mass was adjusted to 6-6.5 and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50 °C under
vacuum (600 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (2.81 gms, Yield: 60%).
Example 4:
4-butyramido-3-methyl-5-nitro methyl benzoate (II) (10 gm, 0.036 moles), was suspended in water (60 ml) and heated to 70-80 °C. A suspension of sodium dithionite (21.75 gm, 0.124 moles) in water (60 ml) was added gradually to the above mass and the temperature is raised to 90-100 °C. After the reaction complies, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 10-11 and continued to stir at same temperature until the methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate disappears in TLC. Then the pH of the reaction mass adjusted to pH 6-6.5. The solid obtained was filtered and dried at 45-50 °C to afford 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6- carboxy benzimidazole (7.5 gms, Yield: 96.4 %). Example 5:
To a solution of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (2 gms, 0.0086 moles) in methanol (10 ml) was added aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (0.95 gms, 0.017 moles, in 5 ml) and the temperature is maintained at 80 °C. After completion of the reaction, methanol was evaporated under reduced pressure and water (50 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-15 °C. Then adjusted the pH of the crude mass to 6-6.5 and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50 °C under vacuum (600 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (1.22 gms, 64 %). Example 6:
An aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate (2.1 gms, 0.026 moles, in 10 ml) was added to a solution of methyl-4-methyl-2-propyl-lH-benzimidazole-6-carboxylate (3 gms, 0.013 moles) in methanol (15 ml) and the temperature is maintained at 80 °C. After reaction complies, methanol was distilled off under reduced pressure and water (100 ml) was added to the crude mass at 5-15 °C. Then the pH of the crude mass was adjusted to 6-6.5 and the obtained solid was filtered. The solid was
washed with water and dried at temperature of 45-50°C under vacuum (600 mm) to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-carboxy benzimidazole (0.56gms, Yield: 20 %).
Experiment III: Preparation of 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-methylbenzimidazol- 2-yl)-lH-benzimidazoIe (VII).
Example 1:
Orthophosphoric acid (210 gms) was taken in round bottomed flask and Ρ205 (210 gms) was added in portions with vigorous stirring. (Note: Sharp increase in temperature > 200 °C). The above mass is allowed to cool to 70 °C and 2-n-propyl- 4-methyl-benzimidazole-6-carboxylic acid (70 gms, 0.321 mol) was added slowly. Then N-methylbenzene-l,2-diamine hydrochloride (62.3 gms, 0.321 mol) was added in small portions at same temperature and then the temperature was raised to 125-130 °C. After completion, reaction was quenched with ice cold water (1 Lt), adjusted pH of the reaction mixture to 9-10 by the addition of aqueous ammonia solution. Obtained solid was filtered and washed with cold water until the pH of the filtrate becomes neutral. Then the crude solid was washed with hot water until colorless filtrate was observed. The crude solid was boiled in ethyl acetate (700 ml) for 2-3 hrs. The reaction mass was cooled and the suspension was filtered off and dried to yield 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH- benzimidazole (V) (80 gms, Yield : 82 %).
Example 2:
2-n-Propyl-4-methyl-benzimidazole-6-carboxylic acid (7 gms) was taken in acetic acid at 70 °C. Then N-methylbenzene-l,2-diamine hydrochloride (6.3 gms) was added in portion wise at same temperature and then the temperature was raised to 1 10 °C. After completion, reaction was quenched with ice cold water (200 ml) and pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 9-10 by the addition of aqueous ammonia solution. The obtained solid was filtered and washed with cold water (3 x 100 ml) until the pH of the filtrate becomes neutral. The residue was dried at 50-55 °C under vacuum (700 mm) to give 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazole (V) (2 gms, Yield : 20 %).
Experiment IV: Preparation of 4'-(l,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-lH- [2,5']benzimidazolyl-3'-ylmethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (IX).
Sodium hydroxide (10 gms, mol) dissolved in water (11 ml) was added to a round bottomed flask containing DMF (20 ml) at 0-5 °C. 2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)-lH-benzimidazole (55 gms, 0.181 mol) dissolved in DMF (200 ml) was added slowly to the above mass at same temperature and stirring was continued at the same temperature for 30 min. 4'-(bromomethyl)-[l,l'- biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (55 gms, 0.181 mol) in 100 ml of DMF was added slowly to the above reaction mass at same temperature for 30 min. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mass was poured into ice cold water (1 Lt) with continuous stirring. The obtained precipitate was filtered and the wet cake was washed with cold water (1 Lt) and dried at room temperature to yield 4'-(l,4'- dimethyl-2' -propyl- 1 H-[2,5 ' ]benzimidazolyl-3 ' -ylmethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (88 gms, Yield : 92.1%).
Experiment V: Preparation of [4'-(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazoI-2-yI)benzimidazoI-l-yImethyI]biphenyI-2-carboxyIic acid (I).
4' -( 1 ,4' -dimethyl-2 ' -propyl- 1 H- [2,5 ' ]benzimidazolyl-3 ' -ylmethyl)biphenyl-2- carboxylic acid methyl ester (90 gms, 0.170 mol) was taken in methanol (500 ml). 100 ml of 4 M sodium hydroxide solution was added and raised the temperature up to 80 °C. After the reaction was completed, methanol was distilled under vacuum and 500 ml of DM water was added to the reaction mass and extracted with ethyl acetate (3X150 ml). Entire aqueous layers were collected and cooled to 5-10 °C. The pH of above aqueous solution was adjusted to 6-6.5 using aqueous hydrochloric acid (IN HCl). The precipitated solid was filtered, washed with water and wet product was dried at 40-45 °C to yield [4'-(2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-(l- methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 -ylmethyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (I). The crude solid was recrystallized from DMF and MeOH/H20 system, to give pure telmisartan. (81 gms, Yield: 92.4 %).
Claims
Claim
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation (2-n-propyl-4-methyl-6-( 1 -methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzimidazol- 1 - y ) of formula I,
Formula I
a) treating methyl-4-(butyramido)-3-methyl-5-nitrobenzoate of formula II,
Formula II
with sulphur containing reducing agent in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent to give a compound of formula IV,
Formula IV
which is formed by insitu reduction and cyclodehydration process at temperature ranging 20-120 °C, preferably in the range of 80-100 °C; b) reaction mass from step (a) is basified with an inorganic base to pH 11-12 and heated at temperatures ranging 20-100 °C, preferably in the range of
80-100 °C to convert ester of formula IV to the corresponding acid of formula V,
(OR)
converting the isolated ester of formula IV from step (a) with an aqueous base in presence or absence of an organic co-solvent at a temperature ranging 20-100 °C, preferably in the range of 80-100 °C to corresponding acid of formula V;
Formula V
c) cyclizing the corresponding acid of formula V with N-methyl-o- phenylenediamine dihydrochloride in the presence of an acid to give a compound of formula VII;
carboxylic acid alk l ester of formula VIII,
Formula VIII
wherein X represents Br, CI, I and R represents straight or branched chain C,-C4 alkyl;
in the presence of base in an organic solvent to give Telmisartan ester (IX),
Formula IX
wherein R represents straight or branched chain C1-C4 alkyl;
e) hydrolysis of Telmisartan ester (IX) to give Telmisartan.
A process according to claim 1, sulphur containing reducing agent used in step (a) is selected from sodium sulfite, sodium sulfide, sodium dithionite, sodium metabisulfite.
A process according to claim 1, insitu reduction and cyclodehydration is carried out in water or an organic solvent or a mixture of water and an organic solvent, wherein organic solvent is selected from alcohol such as methanol, IP A, ethanol, butanol or ether such as dioxane, THF or dipolar aprotic solvent such as DMF, DMA, DMSO, NMP, sulfolane.
A process according to claim 1, insitu reduction and cyclodehydration is carried at a temperature ranging 20-120°C, preferably 80-100°C.
A process according to claim 1, wherein a base used in step (b) and (d) is inorganic base selected from alkali earth metals or alkaline earth metals hydroxides, carbonates, bicarbonates such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, barium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, calcium bicarbonate etc., preferably sodium hydroxide.
6. A process according to claim 1, wherein an organic co-solvent used in step (b) is selected from ethanol, methanol, and isopropyl alcohol.
7. A process according to claim 1, wherein an acid in step (c) is selected from PPA, PTSA, H2S04> CH3COOH.
8. A process according to claim 1, wherein a solvent used in step (d) is selected from DMF, DMSO, THF. 9. A process according to claim 1, Telmisartan ester is hydrolyzed in presence of base and a solvent to produce Telmisartan.
10. According to claim 1 or 9, wherein base is sodium hydroxide and a solvent is methanol.
(MANAGING DIRECTOR)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN2561CHE2010 | 2010-09-03 | ||
| IN2561CH2010 | 2010-09-03 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012028925A2 true WO2012028925A2 (en) | 2012-03-08 |
| WO2012028925A3 WO2012028925A3 (en) | 2012-04-26 |
Family
ID=44801033
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/IB2011/001973 WO2012028925A2 (en) | 2010-09-03 | 2011-08-29 | An improved process for the preparation of telmisartan |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2012028925A2 (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014067237A1 (en) * | 2012-10-31 | 2014-05-08 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Telmisartan preparation method and intermediate thereof |
| JP2015160810A (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-07 | 株式会社トクヤマ | Process for producing 4-methyl-6 (1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl) -2-n-propyl-1H-benzimidazole |
| CN104974096A (en) * | 2015-07-07 | 2015-10-14 | 威海迪嘉制药有限公司 | Preparation method of telmisartan intermediate |
| CN106008356A (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2016-10-12 | 浙江华海药业股份有限公司 | Preparation method for telmisartan |
| CN108250148A (en) * | 2017-12-29 | 2018-07-06 | 江苏中邦制药有限公司 | A kind of process for purification of Telmisartan key intermediate |
| CN111041516A (en) * | 2019-12-19 | 2020-04-21 | 湖南大学 | A new method for the preparation of intermediates of antihypertensive drug telmisartan |
| CN111808027A (en) * | 2020-05-25 | 2020-10-23 | 重庆康刻尔制药有限公司 | Purification method of telmisartan intermediate |
| CN112441984A (en) * | 2019-08-29 | 2021-03-05 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Benzimidazole substituted phenyl n-butylamide-based compound and preparation method thereof |
| WO2021077351A1 (en) * | 2019-10-23 | 2021-04-29 | 江苏中邦制药有限公司 | Method for preparing telmisartan impurity j |
| US11053203B2 (en) | 2017-11-13 | 2021-07-06 | Ecolab Usa Inc. | One-pot homogeneous process for the large scale manufacture of 2-substituted benzimidazoles |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5591762A (en) | 1991-02-06 | 1997-01-07 | Dr. Karl Thomae Gmbh | Benzimidazoles useful as angiotensin-11 antagonists |
| WO2000063158A1 (en) | 1999-04-17 | 2000-10-26 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Kg | Method for nitrating aniline derivatives |
| CN1344712A (en) | 2001-07-30 | 2002-04-17 | 中国科学院上海药物研究所 | Synthesis path of Timisatem |
| US6410742B1 (en) | 1999-01-19 | 2002-06-25 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Kg | Polymorphs of telmisartan |
| CN1412183A (en) | 2001-10-15 | 2003-04-23 | 中国科学院上海药物研究所 | New preparation method of timixatan |
| US20030139608A1 (en) | 2002-01-18 | 2003-07-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Gmbh & Co. Kg | Process for preparing and purifying 1,7' -dimethyl-2' -propyl-2,5'-bi-1H-benzimidazole |
| WO2004108686A2 (en) | 2003-06-06 | 2004-12-16 | Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Benzimidazole compounds having hypoglycemic activity |
| WO2006044648A1 (en) | 2004-10-15 | 2006-04-27 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Process for preparing telmisartan |
| US20070037986A1 (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2007-02-15 | Helmut Heitger | Preparation of 1,7,'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-2,5'-bi-1H-benzimidazole |
| WO2009133122A1 (en) | 2008-05-02 | 2009-11-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Production of 1,7´-dimethyl-2´-propyl-2,5´-bi-1h-benzimidazole |
-
2011
- 2011-08-29 WO PCT/IB2011/001973 patent/WO2012028925A2/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5591762A (en) | 1991-02-06 | 1997-01-07 | Dr. Karl Thomae Gmbh | Benzimidazoles useful as angiotensin-11 antagonists |
| US6410742B1 (en) | 1999-01-19 | 2002-06-25 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Kg | Polymorphs of telmisartan |
| WO2000063158A1 (en) | 1999-04-17 | 2000-10-26 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Kg | Method for nitrating aniline derivatives |
| CN1344712A (en) | 2001-07-30 | 2002-04-17 | 中国科学院上海药物研究所 | Synthesis path of Timisatem |
| CN1412183A (en) | 2001-10-15 | 2003-04-23 | 中国科学院上海药物研究所 | New preparation method of timixatan |
| US20030139608A1 (en) | 2002-01-18 | 2003-07-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma Gmbh & Co. Kg | Process for preparing and purifying 1,7' -dimethyl-2' -propyl-2,5'-bi-1H-benzimidazole |
| WO2004108686A2 (en) | 2003-06-06 | 2004-12-16 | Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Benzimidazole compounds having hypoglycemic activity |
| WO2006044648A1 (en) | 2004-10-15 | 2006-04-27 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Process for preparing telmisartan |
| US20070037986A1 (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2007-02-15 | Helmut Heitger | Preparation of 1,7,'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-2,5'-bi-1H-benzimidazole |
| WO2009133122A1 (en) | 2008-05-02 | 2009-11-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Production of 1,7´-dimethyl-2´-propyl-2,5´-bi-1h-benzimidazole |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| HYDRAZINE/RANEY NI, JOURNAL OF HETEROCYCLIC CHEMISTRY, vol. 40, 2003, pages 1107 - 1112 |
| J. MED. CHEM., vol. 36, no. 25, 1993, pages 4040 - 51 |
| ORGANIC PROCESS RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT, vol. 11, 2007, pages 81 - 85 |
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104768936B (en) * | 2012-10-31 | 2017-07-28 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Prepare the method and its intermediate of Telmisartan |
| CN103787982A (en) * | 2012-10-31 | 2014-05-14 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Telmisartan preparation method and intermediate of telmisartan |
| CN104768936A (en) * | 2012-10-31 | 2015-07-08 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Enzalutamide polymorphic forms and its preparation |
| WO2014067237A1 (en) * | 2012-10-31 | 2014-05-08 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Telmisartan preparation method and intermediate thereof |
| JP2015160810A (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-07 | 株式会社トクヤマ | Process for producing 4-methyl-6 (1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl) -2-n-propyl-1H-benzimidazole |
| CN104974096B (en) * | 2015-07-07 | 2019-02-01 | 威海迪素制药有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of telmisartan intermediate |
| CN104974096A (en) * | 2015-07-07 | 2015-10-14 | 威海迪嘉制药有限公司 | Preparation method of telmisartan intermediate |
| CN106008356A (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2016-10-12 | 浙江华海药业股份有限公司 | Preparation method for telmisartan |
| CN106008356B (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2023-02-28 | 浙江华海药业股份有限公司 | Preparation method of telmisartan |
| US11053203B2 (en) | 2017-11-13 | 2021-07-06 | Ecolab Usa Inc. | One-pot homogeneous process for the large scale manufacture of 2-substituted benzimidazoles |
| CN108250148A (en) * | 2017-12-29 | 2018-07-06 | 江苏中邦制药有限公司 | A kind of process for purification of Telmisartan key intermediate |
| CN108250148B (en) * | 2017-12-29 | 2021-06-08 | 江苏中邦制药有限公司 | Refining method of telmisartan key intermediate |
| CN112441984A (en) * | 2019-08-29 | 2021-03-05 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Benzimidazole substituted phenyl n-butylamide-based compound and preparation method thereof |
| CN112441984B (en) * | 2019-08-29 | 2024-04-19 | 上海特化医药科技有限公司 | Benzimidazole-substituted phenyl n-butyramide-based compound and preparation method thereof |
| WO2021077351A1 (en) * | 2019-10-23 | 2021-04-29 | 江苏中邦制药有限公司 | Method for preparing telmisartan impurity j |
| CN111041516A (en) * | 2019-12-19 | 2020-04-21 | 湖南大学 | A new method for the preparation of intermediates of antihypertensive drug telmisartan |
| CN111808027A (en) * | 2020-05-25 | 2020-10-23 | 重庆康刻尔制药有限公司 | Purification method of telmisartan intermediate |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2012028925A3 (en) | 2012-04-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2012028925A2 (en) | An improved process for the preparation of telmisartan | |
| KR101461291B1 (en) | Process for the manufacture of pharmaceutically active compounds | |
| CN105283442B (en) | Method for synthesizing 1 (2 ((2,4 3,5-dimethylphenyl) is thio) phenyl) piperazine | |
| CN100418953C (en) | The method for preparing telmisartan | |
| US7799916B2 (en) | Process for the preparation of 5-(4-[4-(5-cyano-3-indolyl)butyl]-1-piperazinyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide | |
| CN101538224A (en) | Process for preparing xanthine phosphodiesterase V inhibitors and precursors thereof | |
| US11332460B2 (en) | Process for the preparation of a sulfonamide structured kinase inhibitor | |
| WO2014026657A2 (en) | A process for the preparation of a derivative of 2-methyl-2'-phenylpropionic acid using new intermediates | |
| US10392364B2 (en) | Process for synthesis of lenalidomide | |
| CN105001169B (en) | A kind of synthetic method of 3 aminoquinoxaline 2 (1H) ketone compounds | |
| US20130303781A1 (en) | Process for preparation of triclabendazole | |
| JP2008531642A (en) | Method for obtaining pharmaceutically active compound irbesartan and synthetic intermediates thereof | |
| US20170145001A1 (en) | Processes for preparing brexpiprazole | |
| CA2693513A1 (en) | An improved process for the preparation of candesartan cilexetil | |
| US9024040B2 (en) | Processes for preparing benzimidazole compounds | |
| WO2009116089A2 (en) | Novel intermediates and method for synthesis of 4'-[(1,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-[2,6'- bi-1hbenzimidazol]-l-yl)methyl]-1,1-biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid. | |
| JP2015038053A (en) | Method for producing 4-(2-methyl-1-imidazolyl)-2,2-phenylbutane amide | |
| WO2013171643A1 (en) | An improved process for preparation of irbesartan | |
| EP2217585A2 (en) | Process for the preparation of 2h-chromene-3-carbamate derivatives | |
| US9499491B2 (en) | One pot process for the preparation of telmisartan | |
| HK40081621A (en) | Process for the preparation of a sulfonamide structured kinase inhibitor | |
| KR101421032B1 (en) | Method for preparing (2-methyl-1-(3-methylbenzyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)(piperidin-1-yl)methanone | |
| CN117362314A (en) | Preparation method of 2-aryl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1, 4-epoxy benzazepine compound | |
| HK40021800A (en) | Process for the preparation of a sulfonamide structured kinase inhibitor | |
| HK40021800B (en) | Process for the preparation of a sulfonamide structured kinase inhibitor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11770155 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11770155 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |