WO2012017589A1 - 顔画像登録装置および方法 - Google Patents
顔画像登録装置および方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012017589A1 WO2012017589A1 PCT/JP2011/003146 JP2011003146W WO2012017589A1 WO 2012017589 A1 WO2012017589 A1 WO 2012017589A1 JP 2011003146 W JP2011003146 W JP 2011003146W WO 2012017589 A1 WO2012017589 A1 WO 2012017589A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- face
- person
- image
- registered
- characteristic
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V40/00—Recognition of biometric, human-related or animal-related patterns in image or video data
- G06V40/10—Human or animal bodies, e.g. vehicle occupants or pedestrians; Body parts, e.g. hands
- G06V40/16—Human faces, e.g. facial parts, sketches or expressions
- G06V40/168—Feature extraction; Face representation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V40/00—Recognition of biometric, human-related or animal-related patterns in image or video data
- G06V40/10—Human or animal bodies, e.g. vehicle occupants or pedestrians; Body parts, e.g. hands
- G06V40/16—Human faces, e.g. facial parts, sketches or expressions
- G06V40/172—Classification, e.g. identification
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/70—Determining position or orientation of objects or cameras
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V40/00—Recognition of biometric, human-related or animal-related patterns in image or video data
- G06V40/50—Maintenance of biometric data or enrolment thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30196—Human being; Person
- G06T2207/30201—Face
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a technique applied to a face image registration apparatus and method that can select a registered face with a high matching rate even when the installation environment of the face recognition apparatus changes.
- FIG. 27 is a block configuration diagram of a conventional face authentication device described in Patent Document 1.
- an image photographed by the imaging means 9 is displayed on the display device 11, and an image to be registered is selected and registered by the input device 12.
- a face image suitable for collation is when a face image of a person or the like is registered in the face database, a new face image of the person is input, and the face image registered in the face database is collated.
- the misinformation property that it is not mistaken and the correct property that it is recognized as the person is good.
- the present invention has been made to solve these problems, and to provide a face image registration apparatus and method that can select a face image suitable for face authentication when there are a plurality of face images of the same person. To do.
- the face image registration device is held in an image input unit that inputs a plurality of face images of another person, an other person face holding unit that holds a plurality of other person faces, and the other person face image and the other person face holding unit.
- a false alarm characteristic calculation unit for calculating a false alarm characteristic of the face image of the principal by collating with the other person's face, and a comparison between the face images of the plurality of principals to calculate a correct characteristic of the facial image of the principal
- a registered face image selection unit that selects a registered face image from among the plurality of face images of the person using the false information characteristic of the face image of the person and the correct characteristic of the face image of the person Part.
- This configuration makes it possible to select a registered image that can reduce the false alarm rate and increase the correct alarm rate from a plurality of face images of the person.
- the misinformation characteristic calculation unit calculates a collation result between the person's face image and another person's face held in the other person's face holding unit as a false alarm rate, and the correct characteristic
- the calculation unit calculates a correct report characteristic of the person's face image as a correct report rate
- the registered face image selection unit has a correct report rate of the person's face image out of the plurality of person's face images.
- the registered face image is selected using the difference between the correct report rate of the person's face image and the false report rate of the person's face image.
- This configuration makes it possible to select a registered image that can reduce the false alarm rate and increase the correct alarm rate when the correct report rate is a predetermined threshold.
- the misinformation characteristic calculating unit calculates a result of matching the face image of the person and the face of the other person held in the other person's face holding unit as a false alarm rate, and the correct characteristic
- the calculation unit calculates the correct report characteristic of the face image of the person as the correct rate
- the registered face image selection unit has a predetermined false report rate of the face image of the person from the plurality of face images of the person.
- the registered face image is selected using the difference between the correct report rate of the face image of the person and the false report rate of the face image of the person when the threshold value is set.
- the face image registration apparatus of the present invention has a face orientation calculation unit that calculates the face orientation of the person's face image input from the image input unit, and the stranger face holding unit is a stranger face for each face orientation.
- the misinformation characteristic calculation unit, the correct report characteristic calculation unit, and the registered face image selection unit calculate the misinformation characteristic and the correct report characteristic for each face orientation calculated by the face orientation calculation unit,
- the registered face image selecting unit has a configuration for selecting the registered image for each face orientation calculated by the face orientation calculating unit.
- This configuration makes it possible to select a registered image for each face-oriented image.
- the face image registration apparatus of the present invention has position acquisition means for acquiring the person's photographing position with respect to the image input unit when inputting the person's face image from the image input unit,
- the unit holds a face of another person for each shooting position, and the misinformation characteristic calculation unit, the correct report characteristic calculation unit, and the registered face image selection unit calculate the misreport characteristic and the correct report characteristic for each shooting position,
- the registered face image selection unit is configured to select the registered image for each shooting position.
- This configuration makes it possible to select a registered image for each image shooting position.
- the face image registration device of the present invention has a stranger face update unit for updating a stranger face held in the stranger face holding unit, and the false alarm characteristic calculation unit is a predetermined predetermined latest updated by the stranger face update unit.
- the misinformation characteristic is calculated using another person's face.
- the face image registration device of the present invention has an image input unit for inputting an image, a registered image, a matching threshold value of the registered image, and a misreport rate characteristic indicating a correspondence relationship between the similarity of the registered image and a misreport rate.
- a registered face image holding unit that holds the image, the image input from the image input unit and the face image held in the registered face image holding unit are collated to obtain the similarity of the input image, and the similarity of the input image and the collation
- an individual determination unit that determines an individual by comparing threshold values, and the image input from the image input unit is determined to be the face of the same person as the plurality of registered images held in the registered face image holding unit.
- the faces of multiple registered images are the same person Luke and a determining configure whether.
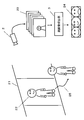
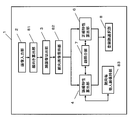
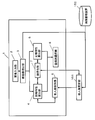
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing Embodiment 1 of a face image registration apparatus of the present invention.
- a face image is cut out by a face image cutout unit 3 from a person image photographed by the image input unit 2, and is sent to a false report characteristic calculation unit 4 and a correct report characteristic calculation unit 6. It is done.
- the false alarm characteristic calculation unit 4 calculates the false alarm characteristic using the face matching unit 7 while referring to the other person face holding unit 5. Further, the correct report characteristic calculation unit 6 calculates the correct report characteristic from the face image cut out by the face image cutout unit 3 using the face collation unit 7. Finally, the registered face image selection unit 8, which is a registered face image selection unit, uses the false report characteristic calculated by the false report characteristic calculation unit 4 and the correct report characteristic calculated by the correct report characteristic calculation unit 6. A face image suitable for the registered face image is selected from the face images cut out by the output unit 3.
- FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram showing the operation of the first embodiment of the present invention.
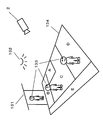
- FIG. 2 shows the person 22 entering the store from the entrance 21 such as a convenience store. The person 22 proceeds according to the trajectory 25.
- the image input unit 2 captures a plurality of images 23 of the person, and the face image cutout unit 3 cuts out the face image 24 of the person.
- the misinformation characteristic calculation unit 4 collates each face image of the person cut out by the face image cutout unit 3 with a face collation unit 7 with another person face holding unit 5.
- the face matching unit 7 calculates the similarity between the other person's face held in the other person's face holding unit 5 and the person's face image. At this time, a threshold is determined, and when the similarity is smaller than the threshold, it is determined that the person is another person, and when the similarity is higher than the threshold, the person is determined.
- the threshold when the threshold is set to a large value, it is rarely determined that the person is the person, so the false alarm rate decreases.However, when the threshold is set to a small value, the person is often determined to be the person, and the false alarm rate is low. Go up.
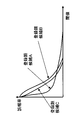
- FIG. 3 shows the false alarm rate when the threshold is changed when the face images of the person cut out by the face image cutout unit 3 are registered face candidates A, B, and C, respectively.
- FIG. 3 shows that the registered face candidate A has a lower false alarm rate when compared with other registered face candidates when the threshold is small, but the false alarm rate does not decrease much even when the threshold is increased. Further, in the registered face candidate B, the false alarm rate is high when the threshold value is small, but the false alarm rate is rapidly lowered when the threshold value is slightly increased.
- the registered face candidate C is in the middle.
- the face image of the person cut out by the face image cutout unit 3 is input to the correct report characteristic calculation unit 6.
- the face verification unit 7 is used to calculate the correct report rate between the face images of the person himself / herself.
- the accuracy rate When calculating the accuracy rate, first, one of the person's face images is collated with all the other person's face images, and the similarity is calculated.
- the number of similarities calculated is a value obtained by subtracting 1 from the total number of the person's face images. Therefore, a threshold value is set, and a correct rate is obtained by dividing the number of face images of other persons whose similarity is equal to or higher than the set threshold value by the total number of similarities calculated.
- the threshold value is changed, the number of face images of other persons whose similarity exceeds the threshold value changes, so that the accuracy rate for one of the face images of each person varies depending on the threshold value.
- the accuracy rate of one face image of the input person's face image is less than the threshold value among the similarities with other person's face images. If the value is reduced, the number of images that exceed the threshold of similarity with the face image of another person increases, so the correct report rate increases.
- FIG. 4 shows the change in the correct report rate when the threshold is changed for the registered face candidates A, B, and C described above.
- the registered face candidate A indicates that the correct report rate is high when the threshold value is small, and the correct report rate gradually decreases as the threshold value is increased. This indicates that the registered face candidate A is evenly distributed from an object with a low similarity to an object with a high similarity when the similarity with another person's face image is obtained.
- the registered face candidate B indicates that the correct report rate rapidly decreases when the threshold value reaches a certain value. This indicates that there are few face images of other persons with high similarity.
- the registered face candidate C has a lower correct report rate than other registered face candidates, and indicates that the correct report rate changes unstable when the threshold value is changed. This indicates that the face image of another person with a low degree of similarity and the face image of another person with a high degree of similarity are uneven.
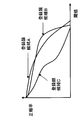
- 5, 6, and 7 are graphs in which the change of the correct report rate and the false report rate when the threshold value is changed is written in the same graph for the registration candidate images A, B, and C.
- the difference between the correct report rate and the false report rate (correct report rate standard) 53 is the largest.
- the registered image with a larger difference between the accuracy rate and the error rate matches the registered image against the newly entered person's face, the accuracy rate for correctly identifying the person is higher, and the misinformation that determines the other person is the person. Since the rate is considered to be low, the registered image A is most suitable as the registered image.
- a threshold when the false alarm rate 51 is 1% is obtained, and a correct report rate 52 is obtained at this threshold, and when the difference is taken, the difference between the correct report rate and the false alarm rate (false report) Rate reference) 54 can be obtained.
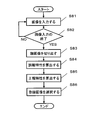
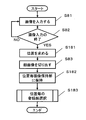
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a processing flow of the first embodiment.
- An image of the person is input from the image input unit 2 (S81). Normally, as shown in FIG. 2, the image 22 is tracked for a certain period after the image of the person 22 is started, and the images 23 are sequentially input.
- FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing the second embodiment.
- the second embodiment is substantially the same as the first embodiment, and has a face orientation calculation unit 81 that calculates the face orientation of the image input from the image input unit 2, and is further cut out by the face image cutout unit 3.
- a face image holding unit 82 for holding the face image for each face.
- it is different in that it has an other person face holding unit 83 for each face direction that holds face images of other people for each face direction.
- FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram explaining how to divide faces. Face orientation detection can be obtained by using an algorithm such as AAM (Active Appearance Model). Depending on the face orientation angle obtained by this, for example, when the vertical direction is 20 degrees or more and the horizontal direction is less than -20 degrees Is classified as a face image at the upper right 30 degrees. Although the face orientation is divided into nine types in total, it can be divided into more types or fewer types.
- AAM Active Appearance Model
- reference numeral 101 denotes a registered face candidate in which an image input by the image input unit 2 has a face orientation calculated by the face direction calculation unit 81 and cut out by the face image cutout unit 3.
- Ten candidate images A to J are obtained because the registration candidate person looks at the front and right direction while moving. These face images are held in the face image holding unit 82 for each face direction.
- the same processing as in the first embodiment is executed for each face direction.
- three images A, B, and I are registered face image candidates, and the face image of the other person is held for each face direction in the other person face holding unit 83 for each face direction.
- the correct report rate and false report rate are calculated and the most suitable for the registered face is selected.
- Method 1 and Method 2 will be described as a method for selecting a registered image corresponding to an angle that is not input from the image input unit 2 among the registered images of the person's face.
- Method 1 for all the faces of the person held in the face-oriented image holding unit 82, false reports are made on the images of the corresponding face orientation among the images held in the other-person face holding unit 83 for each face direction. Calculate the rate.
- the correction coefficient according to the face orientation is corrected by applying this similarity. The correction coefficient is determined for one face direction of the person's face image, the face direction of the other person's face image, and the face direction of the registered face to be obtained. The similarity is calculated and calculated.
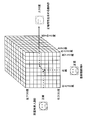
- FIG. 13 shows a data structure in which correction coefficients are held.
- the horizontal axis of the front surface is the face direction of one of the face images of the person (registered face candidate), and is divided into nine from upper right 30 degrees to lower left 30 degrees.
- the vertical axis indicates the face direction of the other person's face image (calculation face), and is similarly divided into nine stages from the upper right 30 degrees to the lower left 30 degrees.
- the depth direction is the face orientation of the face image to be obtained, and is divided into nine stages, similarly from 30 degrees on the upper right to 30 degrees on the lower left.
- Similarity between the registered face candidates A to J is obtained, and the degree of similarity is corrected by applying a correction coefficient selected from the registered face candidate, the calculation face, and the face orientation of the registered face to be obtained. If the similarity between the person's faces is obtained, the correct report characteristic for each person's face can be obtained, so that the registered face candidate can be selected as in the first embodiment.
- the degree of similarity between the face for calculation, for example, B is obtained. If the face orientation of the face image to be obtained is 30 degrees upward, the face orientation of the registered face candidate A is front, the face orientation of the calculation person face B is front, and the face orientation of the registered face to be obtained is upward. Since it is 30 degrees, as shown in FIG. 13, it is possible to select a correction coefficient F corresponding to the registered face candidate being the front face, the calculation face being the front face, and the face orientation to be obtained being the upper 30 degrees.
- the similarity obtained between the registered face candidate A and the calculation principal face B is multiplied by the correction coefficient F to obtain the similarity after the registration face candidate is corrected.
- the correct characteristic for the registered face candidate A can be obtained.
- the correct report characteristic can be calculated for other registered face candidates. Then, the registered face candidate having the largest difference between the correct report characteristic and the false report characteristic is registered as a registered image of the corresponding angle.
- the face of the person in the corresponding face direction is calculated using the three-dimensional model estimated by AAM on the face images of all other persons who are collation partners.
- a method for synthesizing images and calculating the similarity using this face will be described. In this case, it is not necessary to correct the similarity.
- a face image other than the face image of the person who wants to obtain the accuracy rate (referred to as the calculation person's face as in Method 1) is synthesized at an angle for which the accuracy rate is to be obtained, and the synthesized face image, The similarity is obtained with the registered face candidates.
- the calculation person faces BJ are combined to 30 degrees above. Then, the correctness characteristic of A can be obtained by obtaining the similarity between A and the combined face image.
- the same processing is calculated for registered face candidates B to J. That is, when calculating the accuracy rate of the registered face candidate B, the face images of A, C to J are synthesized at the top 30 degrees as the calculation face, and the unregistered registered face candidate B and the post-synthesis
- the accuracy of the registered face candidate B is calculated by calculating the similarity to the calculation person faces A, C to J.
- the same processing is performed for C and below, and the correct rate of each image is obtained.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing according to the second embodiment.
- the process up to the end of image input (S82) is the same as in the first embodiment.
- the face position of each image is obtained to calculate the face orientation (S131).
- the face image is cut out (S83).
- a face image is held for each face direction in the face image holding unit 82 (S132). Further, registered face selection is performed for each face direction (S133).
- FIG. 16 shows the flow of processing of registered face candidate selection (S133) for each face direction.
- the registered face is selected for all nine angles shown in FIG. 10 from the upper right 30 degrees to the lower left 30 degrees. If registered images are selected for all face orientations, the process ends (S141, YES). If the registered faces have not been selected for all face orientations, one face orientation that has not been selected is selected (S142).
- the correct report characteristic is calculated for the corresponding face orientation (S145). Then, a registered image is selected for the corresponding face orientation (S146). When there is one face image of the person for the corresponding face direction, the face image is set as the registered image for the corresponding face direction when the number is two.
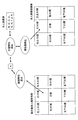
- FIG. 17 is a block configuration diagram of Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
- a position calculation unit 121 is provided instead of the face orientation calculation unit 81, and an image storage unit 122 for each position is provided instead of the face direction image storage unit 82.
- the misreporting characteristic calculation unit 4 there is provided a misreporting characteristic calculation unit 123 for each face position and a correct reporting characteristic calculation unit 124 for each face position instead of the correct reporting characteristic calculation unit 6.
- a face-holding unit 125 for each position is provided in place of the face-other holding unit 83 for each face direction.
- FIG. 18 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the operation of the third embodiment.
- the image input unit 2 captures a place where the person 133 is at the entrance 131 or the floor 134. At this time, images with various conditions are obtained depending on the lighting 132 and the positional relationship between the image input unit 2 and the person.
- FIG. 19 shows what kind of image is input depending on the positional relationship between the image input unit 2 and the person or the illumination 132. As shown in FIG. A: Downlight B: Small face size C: Normal D: Face downward E: Face is likely to face sideways
- an image is held for each positional relationship between the image input unit 2 and a person, a correct report characteristic and a false report characteristic are calculated, and a registered image is determined for each position.
- 20 and 21 are flowcharts showing the flow of processing of the third embodiment. 20 and FIG. 21 are different from FIG. 15 and FIG. 16 which are the flowcharts of the second embodiment, except that the face orientation is changed to the position, and the other points are the same.
- S181 corresponds to S131
- S182 corresponds to S132
- S183 corresponds to S133
- S191 to S198 correspond to S141 to S148, respectively.
- the solid in FIG. 13 is regarded as a solid having a vertical and horizontal depth of 5 ⁇ 5 ⁇ 5, and processing is performed assuming that 30 degrees on the upper right is B: downlight, and 30 degrees on the upper side is B: small face size.
- Embodiment 4 Next, Embodiment 4 according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
- the face image registration device 1 is the same as that of the first embodiment, but in order to update the data of the other person's face held in the other person's face holding unit 5, the other person's face update unit 151 and the image storage unit 152. have.
- the other person face update unit 151 updates the other person's face held in the other person's face holding unit with the face image of the other person input from the image cutout unit 3 or the image storage unit 152.
- the conditions for updating the other person's face held in the other person's face holding unit include the following cases. (1) Using only the face image of the latest visitor When a moving image is input from the image input unit 2, the faces of the 1000 most recent visitors are held in the other person's face holding unit, and old ones are sequentially deleted. Thereby, the influence of time fluctuation can be reduced.
- FIG. 23 shows a block diagram of the fifth embodiment of the present invention.
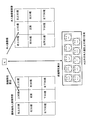
- the individual determination unit 161, the registered face holding unit 162, and the result output unit 167 are provided for the components of the first embodiment.
- the individual face information 163 is held for each individual inside the registered face holding unit 162.
- a registered image 164, a matching threshold value 165, and a false alarm characteristic 166 are held inside the individual information 163.
- a different matching threshold 165 is set for each registered image 164 so that even a registered image person whose degree of similarity is likely to be low can be determined as the person himself / herself.
- the misinformation characteristic 166 is used to make it easier to determine the person.
- the misreporting characteristic calculation unit 4 determines whether or not each of the images cut out by the image cutout unit 3 and the other person's face held in the other person's face holding unit 5. The false alarm characteristics are calculated between.
- the registered face is selected in the same manner as in the first embodiment. However, when the registered face selecting unit 8 selects a registered face and holds it in the registered image holding unit 162, in addition to the registered image 164 and the matching threshold value 165, an erroneous report is made. Preserve characteristics.
- the false alarm characteristic is a probability (false alarm rate) when a person's face is compared with a plurality of other persons' faces and a person is mistaken for the person.
- the degree of similarity is obtained by comparing with the face of another person.
- the degree of similarity is larger than the collation threshold, the person is determined, and when the degree of similarity is smaller, the person is determined as the other person. For this reason, the smaller the verification threshold, the more often the person is erroneously determined to be the person, and the false alarm rate increases.
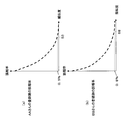
- FIGS. 24A and 24B show the false alarm characteristics when the registered images are AA and BB. In the case of Mr. AA, when the similarity is 53, the false alarm rate is 0.5%. For Mr. BB, when the similarity is 58, the false alarm rate is 0.8%.
- the collation threshold is a value for determining that the input image is AA when the similarity between the registered face of AA and the input image is equal to or greater than the collation threshold, for example.
- the determination unit 161 determines that the unknown face No1 is Mr. AA. Further, the result is output to the result output unit 167.
- the degree of similarity with AA or the like is 40, 58, 38, or 45, so the unknown face No2 is determined to be BB.
- the degree of similarity with AA and the like when the unknown face No. 3 (actually AA) is input is 53, 58, 42, and 43.
- both the matching threshold value 50 of Mr. AA and the matching threshold value 55 of Mr. BB are exceeded, it is impossible to distinguish between Mr. AA and Mr. BB.
- the false alarm rate with Mr. AA when the similarity is 53 is 0.3%
- the false alarm rate with Mr. BB when the similarity is 58 is 0.8%. Since it is found that there is a low possibility of being another person, the unknown face No3 is determined to be AA.
- FIG. 26 is a flowchart showing a processing flow of the fifth embodiment of the present invention.
- a face image is cut out by the face image cutting unit 3 from the image input from the image input unit 2 and sent to the individual determination unit 161.
- the image input step (S81) is performed by the image input unit 2
- the image cutout step (S82) is performed by the face image cutout unit 3.
- the individual determination unit 161 obtains a similarity between the input face image and the registered image 164 of the individual information 163 held in the registered image holding unit 162 (S221).
- the false alarm rate is obtained from the false alarm characteristics by the method described with reference to FIGS. 24 (a) and 24 (b) (S226). This process is performed for all registered images that have exceeded the collation threshold (S227).
- the present invention relates to a face authentication apparatus that can select and register an optimum registered image of the person even when the installation environment of the face authentication apparatus changes.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Collating Specific Patterns (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011800386177A CN103080975A (zh) | 2010-08-05 | 2011-06-03 | 面部图像注册设备和方法 |
| US13/813,793 US9092660B2 (en) | 2010-08-05 | 2011-06-03 | Face image registration device and method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010-175950 | 2010-08-05 | ||
| JP2010175950A JP5753966B2 (ja) | 2010-08-05 | 2010-08-05 | 顔画像登録装置および方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012017589A1 true WO2012017589A1 (ja) | 2012-02-09 |
Family
ID=45559115
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/003146 Ceased WO2012017589A1 (ja) | 2010-08-05 | 2011-06-03 | 顔画像登録装置および方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9092660B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5753966B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN103080975A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2012017589A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103313018A (zh) * | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-18 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | 登记确定装置及其控制方法、以及电子装置 |
Families Citing this family (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120118383A (ko) * | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이미지 보정 장치 및 이를 이용하는 이미지 처리 장치와 그 방법들 |
| JP5923723B2 (ja) | 2011-06-02 | 2016-05-25 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 人物属性推定システム、人物属性推定装置、及び人物属性推定方法 |
| WO2013114862A1 (ja) | 2012-01-30 | 2013-08-08 | パナソニック株式会社 | 最適カメラ設定装置及び最適カメラ設定方法 |
| JP2014139734A (ja) * | 2013-01-21 | 2014-07-31 | Sony Corp | 情報処理装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| JP5506989B1 (ja) | 2013-07-11 | 2014-05-28 | パナソニック株式会社 | 追跡支援装置、追跡支援システムおよび追跡支援方法 |
| JP6410450B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-31 | 2018-10-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | オブジェクト識別装置、オブジェクト識別方法及びプログラム |
| US9275309B2 (en) * | 2014-08-01 | 2016-03-01 | TCL Research America Inc. | System and method for rapid face recognition |
| JP2017033547A (ja) | 2015-08-05 | 2017-02-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置及びその制御方法及びプログラム |
| JP6775343B2 (ja) | 2015-09-11 | 2020-10-28 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置及びその制御方法及びプログラム |
| EP3142040A1 (en) * | 2015-09-11 | 2017-03-15 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Information processing apparatus, method of controlling the same, and program |
| WO2017064838A1 (ja) | 2015-10-14 | 2017-04-20 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 顔検出装置およびこれを備えた顔検出システムならびに顔検出方法 |
| US10769255B2 (en) * | 2015-11-11 | 2020-09-08 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Methods and apparatuses for adaptively updating enrollment database for user authentication |
| US10497014B2 (en) * | 2016-04-22 | 2019-12-03 | Inreality Limited | Retail store digital shelf for recommending products utilizing facial recognition in a peer to peer network |
| JP6725381B2 (ja) | 2016-09-20 | 2020-07-15 | 株式会社東芝 | 画像照合装置および画像照合方法 |
| US10621419B2 (en) * | 2016-12-06 | 2020-04-14 | Robert William Kocher | Method and system for increasing biometric acceptance rates and reducing false accept rates and false rates |
| JP7299543B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-30 | 2023-06-28 | キヤノンマーケティングジャパン株式会社 | 情報処理システム、情報処理方法、プログラム |
| JP7104291B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-30 | 2022-07-21 | キヤノンマーケティングジャパン株式会社 | 情報処理システム、情報処理方法、プログラム |
| JP6921694B2 (ja) | 2017-09-21 | 2021-08-18 | 株式会社東芝 | 監視システム |
| WO2020050119A1 (ja) | 2018-09-06 | 2020-03-12 | Necソリューションイノベータ株式会社 | マスター顔画像の登録装置、登録方法、プログラム、および記録媒体 |
| US11289100B2 (en) * | 2018-10-08 | 2022-03-29 | Google Llc | Selective enrollment with an automated assistant |
| US11238294B2 (en) | 2018-10-08 | 2022-02-01 | Google Llc | Enrollment with an automated assistant |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11232459A (ja) * | 1998-02-17 | 1999-08-27 | Nec Corp | 個人認証用の認証対象原情報登録方法および個人認証装置 |
| JPH11312250A (ja) * | 1998-04-28 | 1999-11-09 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 個体認識装置 |
| JP2003099780A (ja) * | 2001-09-21 | 2003-04-04 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | アクセスコントロールシステム |
| JP2004086625A (ja) | 2002-08-27 | 2004-03-18 | Hitoshi Hongo | 顧客情報管理装置 |
| WO2006077764A1 (ja) * | 2005-01-21 | 2006-07-27 | Nec Corporation | 閾値決定装置、方法及びプログラム並びに本人認証システム |
| WO2008120576A1 (ja) * | 2007-03-29 | 2008-10-09 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | 辞書データの登録装置及び辞書データの登録方法 |
| JP2008257327A (ja) * | 2007-04-02 | 2008-10-23 | Omron Corp | 照合装置 |
| JP2009003898A (ja) * | 2007-06-25 | 2009-01-08 | Omron Corp | 監視システムおよび方法、情報処理装置、並びにプログラム |
| JP2010117852A (ja) * | 2008-11-12 | 2010-05-27 | Sankyo Co Ltd | 店舗用システム |
| JP2010175950A (ja) | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-12 | Alpine Electronics Inc | 車載用表示装置を用いたデータ通信方法およびデータ通信システム |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6173068B1 (en) * | 1996-07-29 | 2001-01-09 | Mikos, Ltd. | Method and apparatus for recognizing and classifying individuals based on minutiae |
| US5978494A (en) * | 1998-03-04 | 1999-11-02 | Sensar, Inc. | Method of selecting the best enroll image for personal identification |
| JP2003346149A (ja) * | 2002-05-24 | 2003-12-05 | Omron Corp | 顔照合装置および生体情報照合装置 |
| KR100442834B1 (ko) * | 2002-07-19 | 2004-08-02 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 얼굴/유사얼굴 영상으로 학습된 패턴 분류기를 이용한얼굴 검출 방법 및 시스템 |
| KR100831187B1 (ko) * | 2003-08-29 | 2008-05-21 | 닛본 덴끼 가부시끼가이샤 | 웨이팅 정보를 이용하는 객체 자세 추정/조합 시스템 |
| US6993166B2 (en) * | 2003-12-16 | 2006-01-31 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for enrollment and authentication of biometric images |
| EP1566788A3 (en) * | 2004-01-23 | 2017-11-22 | Sony United Kingdom Limited | Display |
| US7492943B2 (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2009-02-17 | George Mason Intellectual Properties, Inc. | Open set recognition using transduction |
| FR2884007A1 (fr) * | 2005-03-29 | 2006-10-06 | France Telecom | Procede d'identification de visages a partir d'images de visage, dispositif et programme d'ordinateur correspondants |
| KR100695155B1 (ko) * | 2005-06-18 | 2007-03-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 가리어진 얼굴 검출장치 및 방법과 이를 이용한 부정거래자식별장치 및 방법 |
| US7580563B1 (en) * | 2005-09-02 | 2009-08-25 | Adobe Systems Incorporated | Detection of objects in an image using color analysis |
| JP2007094633A (ja) * | 2005-09-28 | 2007-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | 顔検出装置ならびにプログラム |
| JP2007213378A (ja) * | 2006-02-10 | 2007-08-23 | Fujifilm Corp | 特定表情顔検出方法、撮像制御方法および装置並びにプログラム |
| JP2009163555A (ja) * | 2008-01-08 | 2009-07-23 | Omron Corp | 顔照合装置 |
| WO2009134482A2 (en) * | 2008-01-31 | 2009-11-05 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Illinois | Recognition via high-dimensional data classification |
| JP4636190B2 (ja) * | 2009-03-13 | 2011-02-23 | オムロン株式会社 | 顔照合装置、電子機器、顔照合装置の制御方法、および顔照合装置制御プログラム |
| US8194938B2 (en) * | 2009-06-02 | 2012-06-05 | George Mason Intellectual Properties, Inc. | Face authentication using recognition-by-parts, boosting, and transduction |
| IL199657A0 (en) * | 2009-07-02 | 2011-08-01 | Carmel Haifa University Economic Corp Ltd | Face representation systems for privacy aware applications and methods useful in conjunction therewith |
| US8498454B2 (en) * | 2009-07-14 | 2013-07-30 | General Electric Company | Optimal subspaces for face recognition |
| US8649612B1 (en) * | 2010-01-06 | 2014-02-11 | Apple Inc. | Parallelizing cascaded face detection |
| US8401250B2 (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2013-03-19 | MindTree Limited | Detecting objects of interest in still images |
| JP5669082B2 (ja) * | 2010-04-19 | 2015-02-12 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 照合装置 |
-
2010
- 2010-08-05 JP JP2010175950A patent/JP5753966B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-06-03 CN CN2011800386177A patent/CN103080975A/zh active Pending
- 2011-06-03 US US13/813,793 patent/US9092660B2/en active Active
- 2011-06-03 WO PCT/JP2011/003146 patent/WO2012017589A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11232459A (ja) * | 1998-02-17 | 1999-08-27 | Nec Corp | 個人認証用の認証対象原情報登録方法および個人認証装置 |
| JPH11312250A (ja) * | 1998-04-28 | 1999-11-09 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 個体認識装置 |
| JP2003099780A (ja) * | 2001-09-21 | 2003-04-04 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | アクセスコントロールシステム |
| JP2004086625A (ja) | 2002-08-27 | 2004-03-18 | Hitoshi Hongo | 顧客情報管理装置 |
| WO2006077764A1 (ja) * | 2005-01-21 | 2006-07-27 | Nec Corporation | 閾値決定装置、方法及びプログラム並びに本人認証システム |
| WO2008120576A1 (ja) * | 2007-03-29 | 2008-10-09 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | 辞書データの登録装置及び辞書データの登録方法 |
| JP2008257327A (ja) * | 2007-04-02 | 2008-10-23 | Omron Corp | 照合装置 |
| JP2009003898A (ja) * | 2007-06-25 | 2009-01-08 | Omron Corp | 監視システムおよび方法、情報処理装置、並びにプログラム |
| JP2010117852A (ja) * | 2008-11-12 | 2010-05-27 | Sankyo Co Ltd | 店舗用システム |
| JP2010175950A (ja) | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-12 | Alpine Electronics Inc | 車載用表示装置を用いたデータ通信方法およびデータ通信システム |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103313018A (zh) * | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-18 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | 登记确定装置及其控制方法、以及电子装置 |
| CN103313018B (zh) * | 2012-03-15 | 2016-12-28 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | 登记确定装置及其控制方法、以及电子装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103080975A (zh) | 2013-05-01 |
| JP5753966B2 (ja) | 2015-07-22 |
| US9092660B2 (en) | 2015-07-28 |
| JP2012037995A (ja) | 2012-02-23 |
| US20130129160A1 (en) | 2013-05-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5753966B2 (ja) | 顔画像登録装置および方法 | |
| US20200175263A1 (en) | Biometric identification and verification | |
| AU2015215826B2 (en) | A machine-learning system to optimise the performance of a biometric system | |
| JP4991317B2 (ja) | 顔特徴点検出装置及びその方法 | |
| JP6026119B2 (ja) | 生体情報処理装置 | |
| US11748864B2 (en) | Person verification device and method and non-transitory computer readable media | |
| CN107992807B (zh) | 一种基于cnn模型的人脸识别方法及装置 | |
| EP2657908A1 (en) | Image authentication apparatus, image processing system, control program for image authentication apparatus, computer-readable recording medium, and image authentication method | |
| CN104657705A (zh) | 图像识别装置及面向图像识别装置的数据登录方法 | |
| KR20060097074A (ko) | 객체의 모양모델 생성장치 및 방법과 이를 이용한 객체의특징점 자동탐색장치 및 방법 | |
| JP2016157420A (ja) | 画像テンプレートマスキング | |
| CN111860196A (zh) | 手部作业动作评分装置、方法及计算机可读存储介质 | |
| WO2021079442A1 (ja) | 推定プログラム、推定方法、情報処理装置、再学習プログラムおよび再学習方法 | |
| CN103150546A (zh) | 视频人脸识别方法和装置 | |
| Wang et al. | Modeling and predicting face recognition system performance based on analysis of similarity scores | |
| US11403875B2 (en) | Processing method of learning face recognition by artificial intelligence module | |
| CN112836629A (zh) | 一种图像分类方法 | |
| JP5557189B2 (ja) | 位置推定装置、位置推定方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2010231254A (ja) | 画像解析装置、画像解析方法およびプログラム | |
| CN117727084A (zh) | 一种基于大数据的人脸识别系统及其方法 | |
| JP4594176B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置及び入退室管理システム | |
| WO2022190655A1 (ja) | 画像解析システム及び機械学習モデルの更新方法 | |
| CN112949361B (zh) | 指纹识别方法及装置 | |
| JP7374632B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2011086202A (ja) | 照合装置、照合方法および照合プログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201180038617.7 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11814229 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13813793 Country of ref document: US Ref document number: 2011814229 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |