WO2011122276A1 - 無線通信システム、移動局装置、基地局装置、ランダムアクセス方法および集積回路 - Google Patents
無線通信システム、移動局装置、基地局装置、ランダムアクセス方法および集積回路 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011122276A1 WO2011122276A1 PCT/JP2011/055483 JP2011055483W WO2011122276A1 WO 2011122276 A1 WO2011122276 A1 WO 2011122276A1 JP 2011055483 W JP2011055483 W JP 2011055483W WO 2011122276 A1 WO2011122276 A1 WO 2011122276A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- random access
- component carrier
- mobile station
- station apparatus
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/0001—Arrangements for dividing the transmission path
- H04L5/0003—Two-dimensional division
- H04L5/0005—Time-frequency
- H04L5/0007—Time-frequency the frequencies being orthogonal, e.g. OFDM(A) or DMT
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/0001—Arrangements for dividing the transmission path
- H04L5/0003—Two-dimensional division
- H04L5/0005—Time-frequency
- H04L5/0007—Time-frequency the frequencies being orthogonal, e.g. OFDM(A) or DMT
- H04L5/001—Time-frequency the frequencies being orthogonal, e.g. OFDM(A) or DMT the frequencies being arranged in component carriers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/003—Arrangements for allocating sub-channels of the transmission path
- H04L5/0053—Allocation of signalling, i.e. of overhead other than pilot signals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/0091—Signalling for the administration of the divided path, e.g. signalling of configuration information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/04—Wireless resource allocation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/20—Control channels or signalling for resource management
- H04W72/23—Control channels or signalling for resource management in the downlink direction of a wireless link, i.e. towards a terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/002—Transmission of channel access control information
- H04W74/006—Transmission of channel access control information in the downlink, i.e. towards the terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
- H04W74/0833—Random access procedures, e.g. with 4-step access
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/003—Arrangements for allocating sub-channels of the transmission path
- H04L5/0044—Allocation of payload; Allocation of data channels, e.g. PDSCH or PUSCH
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
- H04W74/0833—Random access procedures, e.g. with 4-step access
- H04W74/0838—Random access procedures, e.g. with 4-step access using contention-free random access [CFRA]
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a base station apparatus, a mobile station apparatus, and a radio communication system, and more particularly to a radio communication system, a mobile station apparatus, a base station apparatus, a random access method, and an integrated circuit in operation during random access.
- the W-CDMA system has been standardized as a third generation cellular mobile communication system, and services have been started sequentially.
- HSDPA with higher communication speed has also been standardized and the service has started.
- EUTRA Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access
- SC-FDMA Peak-to-Average Power Ratio
- PAPR peak-to-average power ratio
- Advanced-EUTRA is a further evolution of EUTRA.
- Advanced-EUTRA it is assumed that communication at a maximum transmission rate of 1 Gbps or more and uplink 500 Mbps or more is performed using a bandwidth up to a maximum of 100 MHz bandwidth in the uplink and downlink.
- Advanced-EUTRA is considering realizing a 100 MHz band by bundling a plurality of 20 MHz bands of EUTRA so that EUTRA mobile station devices can be accommodated.
- one band of 20 MHz or less of EUTRA is called a component carrier (Component Carrier: CC) (Non-patent Document 3).
- 3GPP TS (Technical Specification) 36.300, V8.70 (2009-03), Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN), Overall description Stage2 3GPP TS (Technical Specification) 36.321, V8.50 (2009-03), Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification 3GPP TR (Technical Specification) 36.814, V1.00 (2009-03), Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Radio Resource Control (RRC) Protocol specification
- the transmission timing to the base station apparatus differs for each uplink component carrier depending on the communication conditions and the connection status to the base station apparatus. In some cases, it is necessary to adjust transmission timing for each uplink component carrier.
- a wireless communication system a mobile station apparatus, a base station apparatus, a random access method, and a wireless communication system that enable efficient random access to an Advanced-EUTRA system.
- An object is to provide an integrated circuit.
- the radio communication system of the present invention is a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus, and the base station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus communicate via the component carrier.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information regarding random access, and component carrier setting information not including information regarding random access, and the mobile station An apparatus receives the allocation information and the setting information, and among a plurality of component carriers allocated from the base station apparatus, only a component carrier in which information on random access is included in the component carrier setting information run And executes a beam access procedure.
- the base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station apparatus, and the base station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus communicate with each other via the component carrier.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of security information to the mobile station apparatus, and the mobile station apparatus indicates from the security information when random access of a scheduling request becomes necessary. Random access is performed only when a random access procedure is executed on a component carrier for which the security function is set and a component carrier other than the component carrier to which the security function is assigned receives a random access instruction on the downlink control channel.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from a base station apparatus and communicates with the base station apparatus via the component carrier.
- the random access procedure is executed only on the component carrier in which information on random access is included in the component carrier setting information.
- the mobile station apparatus is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from a base station apparatus and communicates with the base station apparatus via the component carrier, wherein the base station apparatus
- a random access procedure is executed on the component carrier in which the security function indicated by the security information is set, and the security function is assigned.
- Component carriers other than the component carrier are characterized in that the random access procedure is executed only when a random access instruction is received on the downlink control channel.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from a base station apparatus and communicates with the base station apparatus via the component carrier.
- a random access procedure is executed on a component carrier to which the uplink control channel is allocated, and the uplink control channel In the component carriers other than the allocated component carrier, the random access procedure is executed only when the random access instruction is received on the downlink control channel.
- a mobile station apparatus is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from a base station apparatus and communicates with the base station apparatus via the component carrier.
- random access instruction information for another component carrier is received on a downlink control channel during execution of a random access procedure on a carrier, the random access instruction information is ignored or the random access procedure being executed is
- One of the processes is to stop and start the random access procedure with the component carrier indicated by the random access instruction information.
- the base station apparatus of the present invention is a base station apparatus that allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station apparatus and communicates with the mobile station apparatus via the component carrier, and includes component carrier allocation information. And component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access are notified to the mobile station apparatus.
- the base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station apparatus, and the base station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus communicate with each other via the component carrier.
- a random access method applied to a system wherein, in the base station apparatus, component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information on random access and component carrier setting information not including information on random access
- Co comprises at least the step of performing a random access procedure only on the component carriers included in the setting information of the port whereof carrier.
- the base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station apparatus, and the base station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus communicate with each other via the component carrier.
- a random access method applied to a system wherein the base station device notifies the mobile station device of security information to the mobile station device, and the mobile station device requires random access of a scheduling request.
- the security function indicated by the security information is set, the step of executing a random access procedure on the component carrier in which the security function is set, and the component carrier other than the component carrier to which the security function is assigned, Only when receiving the random access indication Le, characterized in that it comprises at least the step of performing a random access procedure.
- An integrated circuit according to the present invention is an integrated circuit that is mounted on a mobile station device to cause the mobile station device to perform a plurality of functions, and is a plurality of component carriers assigned by the base station device.
- the integrated circuit of the present invention is an integrated circuit that is mounted on a mobile station device to cause the mobile station device to perform a plurality of functions, and is a plurality of component carriers assigned by the base station device.
- a function of communicating with the base station device via the base station, component carrier assignment information from the base station device and component carrier setting information including information on random access, and component carrier setting information not including information on random access And a function of executing a random access procedure only in a component carrier in which information on random access is included in the component carrier setting information among a plurality of component carriers allocated from the base station device, Series of machines And wherein it is exerted on the mobile station apparatus.
- An integrated circuit according to the present invention is an integrated circuit that is mounted on a base station device to cause the base station device to perform a plurality of functions, and allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station device.
- the base station apparatus is caused to exhibit a series of functions of notifying the mobile station apparatus and the function.
- downlink pilot channel DPiCH Downlink Pilot Channel
- downlink synchronization channel DSCH Downlink Synchronization Channel
- downlink shared channel PDSCH Physical Downlink Shared Channel
- downlink control channel PDCCH Physical Downlink Control Channel
- a common control channel CCPCH Common Control Control Physical Channel
- the uplink pilot channel UPiCH Uplink Pilot Channel
- random access channel RACH Random Access Channel
- uplink shared channel PUSCH Physical Uplink Shared Channel
- uplink control channel PUCCH Physical Uplink Control Channel
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a channel configuration in EUTRA
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an uplink configuration in EUTRA.
- One block is composed of 12 subcarriers and 7 OFDM symbols. Then, one resource block is configured using two blocks.
- One random access channel RACH is prepared in one subframe, and a large number of mobile station devices such as mobile station devices 1-1 to 1-3 (hereinafter referred to as mobile station devices 1-1 to 1-3) are combined. Thus, the access from the mobile station apparatus 1 is also supported.
- the arrangement configuration (frequency position and time position) of the random access channel RACH is notified from the base station apparatus 3 to the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 as broadcast information.
- the random access channel RACH is arranged at a fixed period, and the random access channel RACH, the uplink shared channel PUSCH region, and the uplink control channel PUCCH region are divided as illustrated.
- One random access channel RACH is configured using six resource blocks.
- the purpose of use of the random access channel is to establish synchronization between the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 and the base station apparatus 3 in the uplink (from the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 to the base station apparatus). 3) to adjust the transmission timing to 3).
- the random access procedure includes two access procedures: Contention based Random Access (contention based random access) and Non-contention based Random Access (non-contention based random access) (Non-patent Document 1).
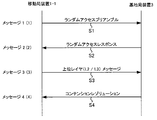
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a procedure of Contention based Random Access.
- the Contention based Random Access is a random access that may collide between the mobile station devices 1. This is performed, for example, when uplink data transmission occurs in the mobile station apparatus 1 while being connected to the apparatus 3 but in a state where uplink synchronization is lost.
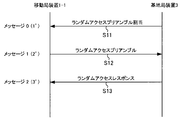
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the procedure of Non-contention based Random Access.
- Non-contention based Random Access is a random access in which no collision occurs between the mobile station apparatuses 1, and when the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1 are connected, the mobile station apparatus 1 and the base station apparatus 3 are quickly connected.
- the mobile station apparatus 1 starts random access when instructed by the base station apparatus 3 in a special case such as a handover for synchronization with the mobile station or when the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1 is not valid (non-patent) Reference 1).
- Non-contention based Random Access is instructed by an RRC (Radio Resource Control: Layer 3) layer message and control data of the downlink control channel PDCCH.
- RRC Radio Resource Control: Layer 3
- the random access preamble is composed of a preamble part and a CP (Cyclic prefix) part.
- the preamble portion uses a CAZAC (Constant-Amplitude-Zero-Auto-Correlation-Zone-Code) sequence which is a signal pattern representing information, and 64 types of sequences are prepared to express 6-bit information.
- CAZAC Constant-Amplitude-Zero-Auto-Correlation-Zone-Code
- the CAZAC sequence used for the random access preamble is roughly divided into a sequence used in the contention based random access (random sequence or random preamble) and a sequence used in the non-contention based random access. (Dedicated sequence or dedicated preamble).
- Information regarding the generation of the random access preamble is also notified from the base station apparatus 3 to the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 as broadcast information.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 transmits a random access preamble to the base station apparatus 3 (message 1: (1), step S1).
- the base station device 3 that has received the random access preamble transmits a response to the random access preamble (random access response) to the mobile station device 1-1 (message 2: (2), step S2).
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 transmits an upper layer (Layer2 / Layer3) message based on the scheduling information included in the random access response (message 3: (3), step S3).
- the base station apparatus 3 transmits a collision confirmation message to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 that has received the upper layer message of (3) (message 4: (4), step S4).
- the Contention based Random Access is also referred to as random preamble transmission.
- the base station device 3 notifies the mobile station device 1-1 of the preamble number (or sequence number) and the random access channel number to be used (message 0: (1) ′, step S11).
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 transmits the random access preamble of the designated preamble number to the designated random access channel RACH (message 1: (2) ', step S12).
- the base station device 3 that has received the random access preamble transmits a response to the random access preamble (random access response) to the mobile station device 1-1 (message 2: (3) ', step S13).
- Contention based Random Access is performed.
- Non-contention based Random Access is also referred to as dedicated preamble transmission.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects one random sequence from a random sequence group based on the downlink radio channel state (path loss) and the size of the message 3, and based on the selected random sequence A random access preamble is generated, and the random access preamble is transmitted using the random access channel RACH (message 1: (1)).
- the base station device 3 When the base station device 3 detects the random access preamble from the mobile station device 1-1, the base station device 3 calculates the amount of transmission timing shift between the mobile station device 1-1 and the base station device 3 from the random access preamble, and L2 / L3 message scheduling (uplink radio resource location, transmission format (message size), etc.), Temporary C-RNTI (Cell-Radio Network Temporary Identity) is assigned, An RA-RNTI indicating a response (random access response) addressed to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 that has transmitted the random access preamble of the random access channel RACH is arranged on the downlink control channel PDCCH, and transmission timing information is transmitted on the downlink shared channel PDSCH. Schedule Ring information, and transmits the the Temporary CRNTI and including the received preamble preamble number (sequence number) the random access response message (Message 2: (2)).
- L2 / L3 message scheduling uplink radio resource location, transmission format (message size), etc.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 When the mobile station apparatus 1-1 detects the presence of RA-RNTI in the downlink control channel PDCCH, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 confirms the content of the random access response message arranged in the downlink shared channel PDSCH and corresponds to the transmitted random access preamble. Message information is extracted, the transmission timing is adjusted, and C-RNTI (or TemporaryRNC-RNTI) or IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) is used in the scheduled radio resource and transmission format. The L2 / L3 message including information for identifying the mobile station device 1-1 is transmitted (message 3: (3)). When the transmission timing is adjusted, a timer in which the adjusted transmission timing is valid is started. When this timer expires, the transmission timing becomes invalid. While the transmission timing is valid, data transmission from the mobile station apparatus 1 is possible. When the transmission timing is invalid, uplink transmission can only transmit a random access preamble.
- C-RNTI or TemporaryRNC-RNTI
- IMSI International Mobile Subscriber Identity
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 continues to wait for a random access response message from the base station apparatus 3 for a certain period of time, and if it does not receive the random access response message including the preamble number of the transmitted random access preamble, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 again Send the access preamble.
- the base station apparatus 3 When the base station apparatus 3 receives the L2 / L3 message from the mobile station apparatus 1-1, the base station apparatus 3 uses the C-RNTI (or Temporary C-RNTI) or IMSI included in the received L2 / L3 message.
- C-RNTI or Temporary C-RNTI
- IMSI included in the received L2 / L3 message.
- a collision confirmation (contention resolution) message for determining whether or not a collision occurs between 1-1 and 1-3 is transmitted to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 (message 4: (4)).
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 does not detect the random access response message including the preamble number corresponding to the random access preamble transmitted within the predetermined period, fails to transmit the message 3, or for the predetermined period. If the identification information of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is not detected in the collision confirmation message, transmission is repeated from transmission of the random access preamble (message 1: (1)) (Non-patent Document 2). After the random access procedure is completed, control data for connection is further exchanged between the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- Advanced-EUTRA is a further evolution of EUTRA.
- Advanced-EUTRA it is assumed that communication at a maximum transmission rate of 1 Gbps or more and uplink 500 Mbps or more is performed using a bandwidth up to a maximum of 100 MHz bandwidth in the uplink and downlink.
- FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram of downlink component carriers in Advanced-EUTRA.
- FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram of uplink component carriers in Advanced-EUTRA.
- Advanced-EUTRA is considering realizing a 100 MHz band by bundling a plurality of 20 MHz bands of EUTRA so that the mobile station apparatus 1 of EUTRA can be accommodated.
- one band of 20 MHz or less of EUTRA is called a component carrier (Component Carrier: CC) (Non-patent Document 3).
- the base station apparatus 3 allocates one or more component carriers that meet the communication capability and communication conditions of the mobile station apparatus 1 from among a plurality of component carriers, and the mobile station apparatus 1 transmits and receives data using the allocated component carrier. Do.
- the mobile station device 1 When the mobile station device 1 communicates with the base station device 3 using a plurality of component carriers, depending on the communication conditions and the connection status to the base station device 3, the mobile station device 1 is connected to the base station device 3 for each uplink component carrier.
- the transmission timing may be different, and the transmission timing needs to be adjusted for each uplink component carrier.
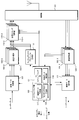
- FIG. 8 is a diagram showing a configuration of the mobile station apparatus 1 according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- the mobile station devices 1-1 to 1-3 include a radio unit 101, transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3 (hereinafter, the transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3 are also collectively referred to as a transmission processing unit 103), Reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3 (hereinafter, the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3 are also collectively referred to as a reception processing unit 105), a transmission data control unit 107, a scheduling unit 109, a control data extraction unit 111, A random access preamble generation unit 113 and transmission timing adjustment units 115-1 to 115-3 (hereinafter, the transmission timing adjustment units 115-1 to 115-3 are also collectively referred to as a transmission timing adjustment unit 115).
- the scheduling unit 109 includes a control data creation unit 117, a control data analysis unit 119, a UL scheduling unit 121, and a random access management unit 123.
- a control data creation unit 117 includes a control data creation unit 117, a control data analysis unit 119, a UL scheduling unit 121, and a random access management unit 123.
- a control data analysis unit 119 includes a control data analysis unit 119, a UL scheduling unit 121, and a random access management unit 123.
- User data and control data are input to the transmission data control unit 107.
- the transmission data control unit 107 assigns each data to each channel of each component carrier according to an instruction from the scheduling unit 109, encrypts the data, and transmits the data.
- the data is sent to the processing units 103-1 to 103-3.
- transmission processing sections 103-1 to 103-3 the signal from transmission data control section 107 is encoded and modulated.
- the modulated signal is subjected to DFT-IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) processing and CP is inserted.
- Transmission timing adjustment sections 115-1 to 115-3 adjust the data transmission timing from the transmission timing information passed from scheduling section 109, adjust the transmission timing, and then upconvert to a radio frequency by radio section 101. It is transmitted from the transmitting antenna.
- the random access preamble is transmitted without adjusting the transmission timing even when the transmission timing is set.
- the radio unit 101 down-converts the radio signal received from the antenna and passes it to the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3.
- the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3 perform FFT (Fast Fourier Transform (Fast Fourier Transform)) processing, decoding, demodulation processing, etc. on the signal passed from the wireless unit 101, and extract the demodulated data as control data To the unit 111. Further, downlink radio propagation path characteristics are measured, and the measurement result is passed to the scheduling unit 109.
- FFT Fast Fourier Transform
- the control data extraction unit 111 decrypts the input data and looks at C-RNTI (mobile station apparatus identification information) and downlink scheduling information arranged in the downlink control channel PDCCH of each component carrier, It is determined whether the data is destined for the own mobile station apparatus 1. If the data is destined for the own mobile station apparatus 1, the data of the downlink shared channel PDSCH demodulated by the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3 is used as the control data and the user. Divide into data. Then, the control data is passed to the scheduling unit 109, and the user data is passed to the upper layer. Also, uplink scheduling information included in the downlink control channel PDCCH is passed to the scheduling section 109.
- C-RNTI mobile station apparatus identification information
- PDCCH downlink control channel
- the random access response message is passed to the scheduling unit 109. In addition, it instructs the scheduling unit 109 to return a response to the received data.
- RA-RNTI Random Access-Radio Network Temporary Identity
- the scheduling unit 109 includes a UL scheduling unit 121, a control data analysis unit 119, a control data creation unit 117, and a random access management unit 123.
- the control data creation unit 117 creates control data
- the control data extraction unit 111 Create a response for the received downlink data.
- the control data analysis unit 119 analyzes the control data from the control data extraction unit 111, passes the scheduling information of the uplink data to the UL scheduling unit 121, and information on the random access broadcast from the base station apparatus 3 (random access channel).
- information related to security from the base station apparatus 3 is passed to the transmission data control unit 107, the control data extraction unit 111, the random access management unit 123, and the upper layer.
- the security-related information is used for data encryption (for example, encryption key information) and is set based on one component carrier. Since the physical information of the component carrier is also used for data encryption, information related to security is set on the basis of one component carrier.
- the data encryption is applied to all the component carriers assigned from the base station apparatus 3.
- the UL scheduling unit 121 controls the transmission data control unit 107 based on the scheduling information of uplink data. Further, the random access management unit 123 is instructed to perform random access based on the scheduling information from the upper layer.
- the random access management unit 123 manages information on random access and information on security for each component carrier.
- the random access management unit 123 determines a component carrier that transmits a random access preamble from information related to security. Then, the sequence to be used is randomly selected based on the downlink radio propagation path characteristic information and the transmission data size of the message 3 passed from the reception processing unit 105 using information on random access of the component carrier used for random access. The selected component carrier number and sequence number (preamble number) are notified to the random access preamble generation unit 113. Details of the random access will be described later.
- the transmission timing adjustment unit 115 corresponding to the component carrier that randomly accessed the transmission timing information. -1 to 115-3, and the assigned radio resource information is passed to the UL scheduling unit 121.
- the contention resolution message is confirmed, the random access is terminated.
- the component carrier number, sequence number (preamble number) and random access channel number to be used are extracted from the random access instruction information passed from the control data analysis unit 119, and the component carrier number and sequence number are extracted to the random access preamble generation unit 113. (Preamble number) is passed.
- the sequence selected by the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 is referred to as a random sequence (random preamble), and the sequence designated by the base station apparatus 3 is referred to as a dedicated sequence (dedicated preamble).
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access using the uplink component carrier corresponding to the downlink component carrier that has received the random access instruction information. If the sequence to be used is not specified, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a sequence from a random sequence.
- the random access preamble generation unit 113 creates a preamble part and a CP part from the information on the random access of the designated component carrier and the sequence number, and performs random access.
- a preamble is generated, a random access channel position to be used is selected from information regarding random access of a designated component carrier, and the generated random access preamble is assigned to the selected random access channel position.
- a preamble part and a CP part are created from the information on the random access of the specified component carrier and the sequence number to generate a random access preamble.
- the random access channel position to be used is selected from the information regarding the random access of the designated component carrier and the random access number.
- the generated random access preamble is assigned to the selected random access channel position in the designated component carrier.
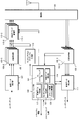
- FIG. 9 shows a configuration diagram of the base station apparatus 3 according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- the base station apparatus 3 includes a data control unit 201, transmission processing units 203-1 to 203-3 (hereinafter, the transmission processing units 203-1 to 203-3 are also collectively referred to as a transmission processing unit 203), a scheduling unit 205 ( Base station side scheduling unit), reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3 (hereinafter, the reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3 are also collectively referred to as reception processing unit 207), control data extraction unit 209, preamble detection Sections 211-1 to 211-3 (hereinafter, the preamble detection sections 211-1 to 211-3 are also collectively referred to as the preamble detection section 211) and the radio section 213.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215, a UL scheduling unit 217, a control data creation unit 219, and a random access management unit 221.
- the transmission processing unit 203, the reception processing unit 207, and the preamble detection unit 211 are each provided with three.
- the data control unit 201 maps control data to the downlink control channel PDCCH, the downlink synchronization channel DSCH, the downlink pilot channel DPiCH, the common control channel CCPCH, and the downlink shared channel PDSCH of each component carrier according to an instruction from the scheduling unit 205 Then, the transmission data for each of the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 is mapped to the downlink shared channel PDSCH. Further, the data control unit 201 encrypts transmission data for each of the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3.
- Transmission processing units 203-1 to 203-3 perform OFDM signal processing such as data modulation, serial / parallel conversion of input signals, IFFT conversion, CP insertion, filtering, and the like to generate OFDM signals.
- the radio unit 213 up-converts the OFDM-modulated data to a radio frequency and transmits it to the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- the radio unit 213 receives uplink data from the mobile station apparatus 1-1, down-converts it into a baseband signal, and converts the received data into reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3 and a preamble detection unit 211. -1 to 211-3.
- Reception processing sections 207-1 to 207-3 demodulate data by performing demodulation processing in consideration of transmission processing performed by mobile station apparatus 1-1 from uplink scheduling information from scheduling section 205. Also, the reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3 measure the radio channel characteristics from the uplink pilot channel UPiCH, and pass the result to the scheduling unit 205.
- the uplink communication scheme is assumed to be a single carrier scheme such as DFT-spreadspOFDM, but may be a multicarrier scheme such as the OFDM scheme.
- the control data extraction unit 209 decrypts the received data, confirms whether the received data is correct, and notifies the scheduling unit 205 of the confirmation result. If the received data is correct, the received data is separated into user data and control data.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215 that performs downlink scheduling, a UL scheduling unit 217 that performs uplink scheduling, a control data creation unit 219, and a random access management unit 221.
- the DL scheduling unit 215 is a mobile station apparatus.
- the UL scheduling unit 217 performs scheduling for mapping user data to each uplink channel from the uplink radio channel estimation result from the reception processing unit 207 and the radio resource allocation request from the mobile station apparatus 1-1. Then, the scheduling result is passed to the control data creation unit 219 and the reception processing unit 207.
- the uplink shared channel PUSCH is allocated, and the assigned uplink shared channel PUSCH and the preamble number (sequence number) are sent to the control data creation unit 219. Notice.
- the random access management unit 221 checks whether or not there is a dedicated sequence (dedicated preamble) when the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access. If there is a dedicated sequence, the random access management unit 221 selects and selects one dedicated sequence. The position of the random access channel RACH that can be used by the selected dedicated sequence is selected, the selected dedicated sequence number, the random access channel number, the selected dedicated sequence and the downlink component carrier information (component carrier number) corresponding to the random access channel, and The C-RNTI (mobile station device identification information) of the mobile station device 1 is passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- a dedicated sequence dedicated preamble
- the dedicated sequence number, random access channel number, and component carrier number are set to fixed values (for example, all 0 values) and passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- the random access channel number specified here is information indicating the position of the random access channel that can be selected by the mobile station apparatus 1, for example, information on the position of the random access channel RACH assigned at a fixed period (for example, every frame). It is.
- the control data creation unit 219 creates control data arranged on the downlink control channel PDCCH and control data arranged on the downlink shared channel PDSCH.
- Control message including scheduling information, ACK / NACK of uplink data, broadcast information message including information on random access such as information on random access channel position and information on sequence information and sequence group, setting information of component carrier to be used ( Initialization message including information on random access), security message including information on security, random access response message including preamble number, transmission timing information and scheduling information, contention resolution message, dedicated sequence number Control data such as a random access instruction message including the random access channel number and component carrier number To create.
- the control data creation unit 219 creates a security message from the security-related information passed from the upper layer, and passes the security-related information to the data control unit 201 and the control data extraction unit 209.
- the preamble detectors 211-1 to 211-3 calculate the transmission timing deviation amount from the detected random access preamble, and detect the component carrier that detected the random access preamble.
- the preamble number (sequence number) and the amount of transmission timing deviation are reported to the scheduling unit 205.
- a wireless communication system that uses the random access procedure described with reference to FIGS. 3 and 4 is assumed.
- a wireless communication system is assumed in which the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1 described in FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 communicate using a plurality of component carriers.
- the base station device 3 assigns one or more component carriers that meet the communication capability and communication conditions of the mobile station device 1 from among a plurality of component carriers, and the mobile station device 1 assigns the assigned component carrier. Send and receive data.
- the mobile station apparatus 1 communicates with the base station apparatus 3 using a plurality of component carriers, transmission to the base station apparatus 3 for each uplink component carrier depending on the communication conditions and the connection status to the base station apparatus 3
- the timing may be different, and the transmission timing needs to be adjusted for each uplink component carrier.
- the mobile station apparatus 1 connected to the base station apparatus 3 using a plurality of component carriers generates data to be transmitted in the uplink and performs random access for the purpose of a scheduling request (uplink transmission data).
- a scheduling request uplink transmission data
- the random access processing is performed only with the component carrier for which the security function is set, and the base station apparatus is used for the other component carriers.
- random access instruction from 3 random access instruction in the downlink control channel
- random access processing is performed.
- the component carrier set with the security function shown here may be an uplink component carrier set with the security function, or an uplink component carrier linked with the downlink component carrier set with the security function. But it ’s okay.
- the base station apparatus 3 can manage random access except for the component carrier for which the security function is set, useless random access does not occur.
- the mobile station apparatus 1 since the mobile station apparatus 1 also has random access determined by the mobile station apparatus 1 only for the component carrier to which the security function is set, the random access processing is not complicated.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs a cell search and searches for a communicable base station apparatus 3.
- One component carrier of the base station apparatus 3 is found, and broadcast information is acquired from this component carrier.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access for initial access to the base station apparatus 3 using information regarding random access included in the broadcast information.
- a random access response including transmission timing information is acquired from the base station apparatus 3, the transmission timing is set, and the message 3 is transmitted.
- the message 3 is transmitted including the contents indicating the initial access.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives various setting information from the base station apparatus 3 such as information related to security, component carrier to be used, and setting information for each component to be used (including information related to random access). Acquire and set the acquired information. Thereafter, user data is exchanged between the mobile station apparatus 1-1 and the base station apparatus 3 using a plurality of component carriers.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 enters a state in which uplink synchronization is lost (uplink transmission timing is not valid) if there is no data transmission within a certain period.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 executes random access as a scheduling request.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a component carrier in which a security function is set as a component carrier used for random access. Then, using the information regarding the random access of the component carrier for which the security function is set, one random sequence is selected, a random access preamble is generated, the random access preamble is transmitted to the base station apparatus 3, and the random access is performed. To do.
- uplink synchronization is in effect (transmission timing is valid)
- uplink radio resource uplink shared channel PUSCH
- the component with the security function set Similarly, it is possible to perform random access as a scheduling request using only the carrier.
- the mobile station device 1-1 is uplink-synchronized only when the random access instruction information is received from the base station device 3 through the downlink control channel PDCCH, or Regardless of uplink synchronization, random access is performed on the indicated component carrier. The random access is executed using a sequence specified by the random access instruction information. Similarly, even in the component carrier in which the security function is set, when random access instruction information is received from the base station apparatus 3, random access is performed.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 When the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 during the random access procedure process as a scheduling request, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 continues the random access process being executed and continues to the base station apparatus 3 The random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 is ignored or the currently executed random access processing is stopped, and random access is performed according to the random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3. Also, when random access instruction information on another component carrier is received during random access processing from the random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3, the first random access instruction is prioritized, and the subsequent random access instruction information is ignore. In this way, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 does not execute a plurality of random access processes at the same time, so that the random access processes are not complicated.
- the base station apparatus 3 When the base station apparatus 3 receives the random access preamble, the base station apparatus 3 calculates the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 from the random access preamble and notifies the transmission timing by a random access response. Then, after the random access process, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 notifies various setting information such as information relating to security and information relating to the component carrier to be used because of the initial access. Thereafter, user data is exchanged between the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- the base station device 3 transmits / receives data when downlink data for the mobile station device 1-1 is generated in a state where the uplink synchronization of the mobile station device 1-1 has been lost, or when an unused component carrier is used.
- a random access instruction is given to the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- random access instruction information including a component carrier number to be used, a sequence number to be used, and the like is notified to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 on the downlink control channel PDCCH.
- the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is calculated from the received random access preamble, and the transmission timing is notified by a random access response.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a configuration of the mobile station apparatus 1 according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 include a radio unit 101, transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3, reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3, a transmission data control unit 107, a scheduling unit 109, and control data.
- An extraction unit 111, a random access preamble generation unit 113, and transmission timing adjustment units 115-1 to 115-3 are included.
- the scheduling unit 109 includes a control data creation unit 117, a control data analysis unit 119, a UL scheduling unit 121, a random access management unit 123, and an uplink control channel management unit 125.
- the transmission processing unit 103 the reception processing unit 105, and the transmission timing adjustment unit 115 are each provided with three.
- the wireless unit 101, the transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3, the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3, the transmission data control unit 107, the control data extraction unit 111, the random access preamble generation unit 113, and the transmission timing adjustment The operations of the units 115-1 to 115-3 are the same as the operation of the mobile station apparatus 1 shown in FIG.
- the scheduling unit 109 includes an UL scheduling unit 121, a control data analysis unit 119, a control data creation unit 117, a random access management unit 123, and an uplink control channel management unit 125.
- the control data creation unit 117 creates control data. Then, the response of the downlink data received by the control data extraction unit 111 is created.
- the control data analysis unit 119 analyzes the data from the control data extraction unit 111, passes the scheduling information of the uplink data to the UL scheduling unit 121, and information on random access broadcast from the base station apparatus 3 (random access channel RACH Information, random access preamble generation information, random access information notified at the time of initial access, random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 and random access response message contents, the random access management unit 123 and the random access preamble. It passes to the generation unit 113. Also, the uplink control channel allocation information from the base station apparatus 3 is passed to the uplink control channel management unit 125, and the security-related information is passed to the random access management unit 123, the transmission data control unit 107, the control data extraction unit 111, and the upper layers. hand over.
- random access channel RACH Information random access preamble generation information
- random access information notified at the time of initial access random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 and random access response message contents
- the random access management unit 123 and the random access preamble It passes to the generation
- the security-related information is used for data encryption (for example, an encryption key) and is set based on one component carrier. Since the physical information of the component carrier is also used for data encryption, information related to security is set on the basis of one component carrier.
- the data encryption is applied to all the component carriers assigned from the base station apparatus 3.
- the UL scheduling unit 121 controls the transmission data control unit 107 based on the scheduling information of uplink data. Further, the random access management unit 123 is instructed to perform random access based on the scheduling information from the upper layer.
- the uplink control channel management unit 125 is used to transmit the radio resource of the uplink control channel PUCCH for downlink response transmission and the downlink radio channel information (CQI: Channel Quality Indicator) allocated from the base station apparatus 3.
- CQI Channel Quality Indicator
- the radio resource of the uplink control channel PUCCH and the radio resource of the uplink control channel for scheduling request transmission are managed. Then, when the period during which the uplink transmission timing is valid has passed, the radio resources of the allocated uplink control channel PUCCH are released. Also, the uplink control channel management unit 125 notifies the random access management unit 123 of information on the component carrier for which the uplink control channel PUCCH is set.
- the random access management unit 123 manages information regarding random access for each component carrier, information regarding security, and setting information of the uplink control channel.
- the random access management unit 123 determines a component carrier for transmitting a random access preamble from information on security and setting information on the uplink control channel PUCCH. Then, randomly select a sequence to be used in random access based on the information on the random access of the determined component carrier, the downlink radio propagation path characteristic information passed from the reception processing unit 105, and the transmission data size of the message 3,
- the random access preamble generation unit 113 is notified of the selected component carrier number and sequence number (preamble number). Details of the random access will be described later.
- the transmission timing adjustment unit 115 corresponding to the component carrier that randomly accessed the transmission timing information. -1 to 115-3, and the assigned radio resource information is passed to the UL scheduling unit 121.
- the contention resolution message is confirmed, the random access is terminated.
- the component carrier number, sequence number (preamble number) and random access channel number to be used are extracted from the random access instruction information passed from the control data analysis unit 119, and the component carrier number and sequence number are extracted to the random access preamble generation unit 113. (Preamble number) is passed.
- FIG. 11 shows a configuration diagram of the base station apparatus 3 according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- the base station apparatus 3 includes a data control unit 201, transmission processing units 203-1 to 203-3, a scheduling unit 205 (base station side scheduling unit), reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3, a control data extraction unit 209, It includes preamble detection units 211-1 to 211-3 and a radio unit 213.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215, a UL scheduling unit 217, a control data creation unit 219, a random access management unit 221, and an uplink control channel management unit 223.
- the transmission processing unit 203 since the present embodiment shows an example in which there are three component carriers, the transmission processing unit 203, the reception processing unit 207, and the preamble detection unit 211 are each provided with three.
- the operation is the same as that of the mobile station apparatus 1 shown in FIG.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215 that performs downlink scheduling, a UL scheduling unit 217 that performs uplink scheduling, a control data creation unit 219, a random access management unit 221, and an uplink control channel management unit 223.
- the DL scheduling section 215 downloads downlink radio propagation path information notified from the mobile station apparatus 1-1, data information of each user notified from the upper layer, and control data generated by the control data generation section 219. Scheduling is performed to map user data and control data to each channel of the link.
- the UL scheduling unit 217 performs scheduling for mapping user data to each uplink channel from the uplink radio channel estimation result from the reception processing unit 207 and the radio resource allocation request from the mobile station apparatus 1-1. Then, the scheduling result is passed to the control data creation unit 219 and the reception processing unit 207.
- the uplink shared channel PUSCH is allocated, and the assigned uplink shared channel PUSCH and the preamble number (sequence number) are sent to the control data creation unit 219. Notice.
- the random access management unit 221 checks whether or not there is a dedicated sequence (dedicated preamble) when the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access. If there is a dedicated sequence, the random access management unit 221 selects and selects one dedicated sequence. The position of the random access channel RACH that can be used by the selected dedicated sequence is selected, the selected dedicated sequence number, the random access channel number, the selected dedicated sequence and the downlink component carrier information (component carrier number) corresponding to the random access channel, and The C-RNTI (mobile station device identification information) of the mobile station device 1 is passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- a dedicated sequence dedicated preamble
- the dedicated sequence number, random access channel number, and component carrier number are set to fixed values (for example, all 0 values) and passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- the random access channel number specified here is information indicating the position of the random access channel that can be selected by the mobile station apparatus 1, for example, information on the position of the random access channel RACH assigned at a fixed period (for example, every frame). It is.
- the control data creation unit 219 creates control data arranged on the downlink control channel PDCCH and control data arranged on the downlink shared channel PDSCH.
- Control message including scheduling information, ACK / NACK of uplink data, broadcast information message including information on random access such as information on random access channel position and information on sequence information and sequence group, setting information of component carrier to be used ( Initialization message including information on random access), security message including information on security, random access response message including preamble number, transmission timing information and scheduling information, contention resolution message, dedicated sequence number Random access instruction message including random access channel number and component carrier number, uplink control Yaneru generates control data, such as the PUCCH allocation information laden control channel assignment message.
- the control data creation unit 219 creates a security message from the security-related information passed from the upper layer, and passes the security-related information to the data control unit 201 and the control data extraction unit 209.
- the uplink control channel management unit 223 manages the radio resources of the uplink control channel PUCCH, assigns the uplink control channel PUCCH to the mobile station apparatus 1-1, and passes the assignment information to the control data creation unit 219.
- Allocation of the uplink control channel PUCCH to each mobile station apparatus 1 is allocated to one component carrier in the same manner as the security information allocation.
- a scheduling request is randomly accessed only on a component carrier to which the uplink control channel PUCCH is allocated.
- the operation of the mobile station device 1-1 and the base station device 3 will be described.
- the mobile station device 1-1 performs a cell search and searches for a base station device 3 to be connected.
- One component carrier of the base station apparatus 3 is found, and broadcast information is acquired from this component carrier.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access for initial access to the base station apparatus 3 using information regarding random access included in the broadcast information.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 acquires random access response information including transmission timing information from the base station apparatus 3, sets uplink transmission timing, and transmits the message 3 to the base station apparatus 3.
- the message 3 is transmitted including the contents indicating the initial access.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives information from the base station apparatus 3 regarding security, uplink control channel PUCCH allocation information, component carrier to be used, and setting information for each component carrier to be used (related to random access). Information) and other setting information is acquired, and the acquired information is set. Thereafter, user data is exchanged between the mobile station apparatus 1-1 and the base station apparatus 3 using a plurality of component carriers.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 has no uplink shared channel PUSCH assigned from the base station apparatus 3, and uplink transmission data is newly generated while uplink synchronization is established (transmission timing is valid). If this is the case, random access is executed as a scheduling request. At this time, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a component carrier to which the uplink control channel PUCCH is assigned as a component carrier used for random access. Then, using the information on the random access of the component carrier to which the uplink control channel PUCCH is allocated, one random sequence is selected, a random access preamble is generated, and the random access preamble is transmitted to the base station apparatus 3 And execute a random access procedure.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 enters a state in which uplink synchronization is lost (the uplink transmission timing is not valid) if there is no data transmission within a certain period, and the uplink control assigned from the base station apparatus 3 Release radio resources of channel PUCCH.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 executes random access as a scheduling request.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a component carrier in which a security function is set as a component carrier used for random access. Then, using the information regarding the random access of the component carrier for which the security function is set, one random sequence is selected, a random access preamble is generated, the random access preamble is transmitted to the base station apparatus 3, and the random access is performed. Perform the procedure.
- the mobile station device 1-1 receives the random access instruction information from the base station device 3 on the downlink control channel PDCCH. Only when it is received, regardless of whether it is uplink-synchronized or not uplink-synchronized, random access is performed on the indicated component carrier. The random access is executed using a sequence specified by the random access instruction information. Similarly, in the component carrier to which the uplink control channel PUCCH is assigned, when random access instruction information is received from the base station apparatus 3, random access is performed.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 When the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 during the processing of the random access procedure as the scheduling request, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 continues the random access processing as the scheduling request and continues to the base station apparatus.
- the random access instruction information from 3 is ignored or the random access processing as the scheduling request is stopped, and random access is performed according to the random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3.
- the first random access instruction is prioritized, and the subsequent random access instruction information is ignore. In this way, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 does not execute a plurality of random access processes simultaneously.
- the base station apparatus 3 When the base station apparatus 3 receives the random access preamble, the base station apparatus 3 calculates the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 from the random access preamble and notifies the transmission timing by a random access response. Then, after the random access processing, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is the initial access, and thus notifies various setting information such as the allocation information of the uplink control channel for transmitting the CQI, information on the security, and information on the component carrier to be used. To do. Thereafter, user data is exchanged between the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- the base station device 3 transmits / receives data when downlink data for the mobile station device 1-1 is generated in a state where the uplink synchronization of the mobile station device 1-1 has been lost, or when an unused component carrier is used.
- a random access instruction is given to the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- random access instruction information including a component carrier number to be used, a sequence number to be used, and the like is notified to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 on the downlink control channel PDCCH.
- the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is calculated from the received random access preamble, and the transmission timing is notified by a random access response.
- the configuration of the mobile station apparatus 1 according to the embodiment of the present invention is the same as that in FIG.
- the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 include a radio unit 101, transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3, reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3, a transmission data control unit 107, a scheduling unit 109, and control data.
- An extraction unit 111, a random access preamble generation unit 113, and transmission timing adjustment units 115-1 to 115-3 are included.
- the scheduling unit 109 includes a control data creation unit 117, a control data analysis unit 119, a UL scheduling unit 121, and a random access management unit 123.
- the transmission processing unit 103 the reception processing unit 105, and the transmission timing adjustment unit 115 are each provided with three.
- the wireless unit 101, the transmission processing units 103-1 to 103-3, the reception processing units 105-1 to 105-3, the transmission data control unit 107, the control data extraction unit 111, the random access preamble generation unit 113, and the transmission timing adjustment The operations of the units 115-1 to 115-3 are the same as the operation of the mobile station apparatus 1 shown in FIG.
- the scheduling unit 109 includes a UL scheduling unit 121, a control data analysis unit 119, a control data creation unit 117, and a random access management unit 123.
- the control data creation unit 117 creates control data and creates a response of downlink data received by the control data extraction unit 111.
- the control data analysis unit 119 analyzes the data from the control data extraction unit 111, passes uplink data scheduling information to the UL scheduling unit 121, and receives information on random access from the base station apparatus 3 (arrangement of the random access channel RACH). Information, random access preamble generation information, etc.), random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 and random access response message contents are passed to the random access management unit 123 and random access preamble generation unit 113.
- the UL scheduling unit 121 controls the transmission data control unit 107 based on the scheduling information of uplink data. Further, the random access management unit 123 is instructed to perform random access based on the scheduling information from the upper layer.
- the random access management unit 123 manages information related to the random access of the acquired component carrier.
- the random access management unit 123 determines a component carrier for transmitting a random access preamble from among component carriers holding information on random access. Then, a sequence to be used is randomly selected based on the information on the random access of the determined component carrier, the downlink radio propagation path characteristic information passed from the reception processing unit 105, and the transmission data size of the message 3, and the random access
- the selected component carrier number and sequence number (preamble number) are notified to the preamble generation unit 113. Details of the random access will be described later.
- the transmission timing adjustment unit 115 corresponding to the component carrier that randomly accessed the transmission timing information. -1 to 115-3, and the assigned radio resource information is passed to the UL scheduling unit 121.
- the contention resolution message is confirmed, the random access is terminated.
- the component carrier number, sequence number (preamble number) and random access channel number to be used are extracted from the random access instruction information passed from the control data analysis unit 119, and the component carrier number and sequence number are extracted to the random access preamble generation unit 113. (Preamble number) is passed.
- the sequence selected by the mobile station apparatuses 1-1 to 1-3 is referred to as a random sequence (random preamble), and the sequence designated by the base station apparatus 3 is referred to as a dedicated sequence (dedicated preamble).
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access using the uplink component carrier corresponding to the downlink component carrier that has received the random access instruction information. If the sequence to be used is not specified, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a sequence from a random sequence.
- the configuration diagram of the base station apparatus 3 is the same as FIG.
- the base station apparatus 3 includes a data control unit 201, transmission processing units 203-1 to 203-3, a scheduling unit 205 (base station side scheduling unit), reception processing units 207-1 to 207-3, a control data extraction unit 209, It includes preamble detection units 211-1 to 211-3 and a radio unit 213.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215, a UL scheduling unit 217, a control data creation unit 219, and a random access management unit 221.
- the transmission processing unit 203, the reception processing unit 207, and the preamble detection unit 211 are each provided with three.
- the operation is the same as that of the mobile station apparatus 1 shown in FIG.
- the scheduling unit 205 includes a DL scheduling unit 215 that performs downlink scheduling, a UL scheduling unit 217 that performs uplink scheduling, a control data creation unit 219, and a random access management unit 221.
- the DL scheduling unit 215 downlinks the downlink radio propagation path information notified from the mobile station apparatus 1-1, the data information of each user notified from the higher layer, and the control data generated by the control data generation unit 219. Scheduling for mapping user data and control data to each of the channels, UL scheduling section 217 assigns uplink radio channel estimation results from reception processing section 207 and radio resource allocation from mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- Scheduling for mapping user data to each uplink channel from the request is performed, and the scheduling result is passed to the control data creation unit 219 and the reception processing unit 207. Further, when it is notified from the preamble detection unit 211 that the random access preamble has been detected, the uplink shared channel PUSCH is allocated, and the assigned uplink shared channel PUSCH and the preamble number (sequence number) are sent to the control data creation unit 219. Notice.
- the random access management unit 221 determines a component carrier that permits random access when a component carrier is allocated. Then, information regarding the random access of the permitted component carrier is passed to the control data creation unit 219. Further, the random access management unit 221 checks whether there is a dedicated sequence (dedicated preamble) when the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access, and if there is a dedicated sequence, selects one dedicated sequence. The position of the random access channel RACH that can be used by the selected dedicated sequence is selected, the selected dedicated sequence number, the random access channel number, and the information on the downlink component carrier corresponding to the selected dedicated sequence and the random access channel (component carrier number) ) And C-RNTI (mobile station apparatus identification information) of the mobile station apparatus 1 are passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- a dedicated sequence dedicated preamble
- the dedicated sequence number, random access channel number, and component carrier number are set to fixed values (for example, all 0 values) and passed to the control data creation unit 219.
- the random access channel number specified here is information indicating the position of the random access channel that can be selected by the mobile station apparatus 1, for example, information on the position of the random access channel RACH assigned at a fixed period (for example, every frame). It is.
- the control data creation unit 219 creates control data arranged on the downlink control channel PDCCH and control data arranged on the downlink PDSCH.
- Control message including scheduling information, ACK / NACK of uplink data, broadcast information message including information on random access such as information on random access channel position and information on sequence information and sequence group, setting information of component carrier to be used ( Initialization message including information on random access), security message including information on security, random access response message including preamble number, transmission timing information and scheduling information, contention resolution message, dedicated sequence number Control data such as a random access instruction message including the random access channel number and component carrier number To create.
- the base station apparatus 3 allocates a plurality of component carriers to the mobile station apparatus 1 and communicates with the mobile station apparatus 1, the base station apparatus 3 sets each component carrier setting information (for each component carrier) together with the component carrier allocation information.
- the mobile station apparatus 1 is notified of information determined for each component carrier such as information on the channel configuration of each physical channel to be set and information on random access).
- the mobile station apparatus 1 can acquire the setting information of each component carrier from the broadcast information, but when a plurality of component carriers are set, the base station apparatus 3 can start communication using a plurality of component carriers immediately. Is configured to individually notify component carrier setting information when component carriers are allocated. From this, for component carriers that do not require random access among the component carrier setting information at the time of notification of component carrier allocation information and each component carrier setting information, the component carrier setting information relates to the random access of the component carrier. Random access can be prohibited by not including information.
- the operation of the mobile station device 1-1 and the base station device 3 will be described.
- the mobile station device 1-1 performs a cell search, finds one component carrier of the base station device 3, and acquires broadcast information from this component carrier. Then, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 performs random access for initial access to the base station apparatus 3 using information regarding random access included in the broadcast information.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 acquires random access response information including transmission timing information from the base station apparatus 3, sets uplink transmission timing, and transmits the message 3 to the base station apparatus 3.
- the message 3 is transmitted including the contents indicating the initial access.
- the mobile station device 1-1 is notified of the component carrier to be used by the base station device 3 and the component carrier permitted to be random access.
- component setting information such as component carrier setting information excluding information related to the random access of the component carrier to be used and component carrier setting information including information related to the random access of the component carrier for which random access is permitted were acquired and acquired.
- component carrier setting information excluding information related to the random access of the component carrier to be used
- component carrier setting information including information related to the random access of the component carrier for which random access is permitted were acquired and acquired.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 has no uplink shared channel PUSCH assigned from the base station apparatus 3 and is in uplink synchronization (transmission timing is valid) or not in uplink synchronization (transmission)
- random access is executed as a scheduling request.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 selects a component carrier that is permitted random access as a component carrier used for random access.
- one random sequence is selected, a random access preamble is generated, the random access preamble is transmitted to the base station apparatus 3, and random access is performed. Perform the procedure.
- the component carrier to be used at random is selected.
- the component carrier to be used may be selected in consideration of the communication state of the component carrier.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 When the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives a random access instruction from the base station apparatus 3 through the downlink control channel PDCCH, if the component carrier indicated by the random access instruction is a component carrier permitted for random access, the mobile station The device 1-1 performs random access according to the content of the random access instruction. If the component carrier does not permit random access, random access is not performed even if there is a random access instruction.
- the mobile station apparatus 1-1 When the mobile station apparatus 1-1 receives random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3 during the processing of the random access procedure as the scheduling request, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 continues the random access processing as the scheduling request and continues to the base station apparatus.
- the random access instruction information from 3 is ignored or the random access processing as the scheduling request is stopped, and random access is performed according to the random access instruction information from the base station apparatus 3.
- the first random access instruction is prioritized, and the subsequent random access instruction information is ignore. In this way, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 does not execute a plurality of random access processes simultaneously.
- the base station apparatus 3 When the base station apparatus 3 receives the random access preamble, the base station apparatus 3 calculates the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 from the random access preamble and notifies the transmission timing by a random access response. Then, after the random access processing, the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is the initial access, so it notifies the component carrier that permits random access among the component carrier to be used and the component carrier to be used, and further uses the component carrier to be used. Various setting information such as component carrier setting information excluding information related to random access and component carrier setting information including information related to random access of a component carrier that permits random access is notified. Thereafter, user data is exchanged between the base station apparatus 3 and the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- the base station device 3 transmits / receives data when downlink data for the mobile station device 1-1 is generated in a state where the uplink synchronization of the mobile station device 1-1 has been lost, or when an unused component carrier is used.
- a random access instruction is given to the mobile station apparatus 1-1.
- random access instruction information including a component carrier number to be used, a sequence number to be used, and the like is notified to the mobile station apparatus 1-1 on the downlink control channel PDCCH.
- the transmission timing of the mobile station apparatus 1-1 is calculated from the received random access preamble, and the transmission timing is notified by a random access response.
- the random access processing of the mobile station device 1 does not become complicated.
- the component carrier that prohibits the random access by not reporting the information on the random access is notified, but the information on the random access of all the component carriers is notified, and the random access for each component carrier is separately performed. Information indicating whether to permit or not may be notified. By doing in this way, the base station apparatus 3 can freely set the mobile station apparatus 1 to permit or prohibit random access.
- the wireless communication system of the present invention is a wireless communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus, and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication, and the base station apparatus
- the mobile station device notifies the mobile station device of security information, and when the mobile station device needs random access of a scheduling request, the component carrier in which the security function indicated by the security information is set Random access preamble is transmitted by the component carrier other than the component carrier to which the security function is assigned, and the random access preamble is transmitted only when the random access instruction is received by the downlink control channel. That.
- the base station device notifies the mobile station device of security information, and the mobile station device performs random access of the scheduling request only with the component for which the security function indicated by the security information is set, and other components.
- the carrier performs random access according to the random access instruction, so that it is not possible to perform random access unless there is an instruction from the base station device other than the component carrier for which the security function is not set. Efficient random access can be executed.
- the radio communication system of the present invention is a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus, and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication.
- the station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information on random access and component carrier setting information not including information on random access, and the mobile station apparatus
- the allocation information and the setting information are received, and a random access preamble is transmitted only in a component carrier having setting information regarding random access among a plurality of component carriers allocated from the base station apparatus.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since random access is performed only on the component carrier to which information about access is notified, efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from the base station apparatus and performs random access even during communication with the base station apparatus.
- a random access preamble is transmitted by a component carrier in which the security function indicated by the security information is set, and the security function is assigned.
- a component carrier other than the component carrier transmits a random access preamble only when a random access instruction is received on a downlink control channel.
- the base station device notifies the mobile station device of security information, and the mobile station device performs random access of the scheduling request only with the component for which the security function indicated by the security information is set, and other components.
- the carrier performs random access according to the random access instruction, so that it is not possible to perform random access unless there is an instruction from the base station device other than the component carrier for which the security function is not set. Efficient random access can be executed.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from the base station apparatus and performs random access even during communication with the base station apparatus.
- a random access preamble is transmitted on a component carrier to which the uplink control channel is allocated, and the uplink control channel
- a random access preamble is transmitted only when a random access instruction is received on a downlink control channel.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of uplink control channel assignment, and the mobile station apparatus performs random access of the scheduling request only with the component for which the uplink control channel is set, and other component carriers. Then, by performing random access according to the random access instruction, it is impossible to perform random access unless there is an instruction from the base station apparatus other than the component carrier for which the uplink control channel is not set, so no useless random access occurs. Thus, efficient random access can be executed.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from the base station apparatus and performs random access even during communication with the base station apparatus.
- the random access preamble is transmitted only on the component carrier having the setting information regarding the random access.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since random access is performed only on the component carrier to which information about access is notified, efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- the mobile station apparatus of the present invention is a mobile station apparatus that is assigned a plurality of component carriers from the base station apparatus and performs random access even during communication with the base station apparatus.
- random access instruction information for another component carrier is received on the downlink control channel while the random access process is being performed on the component carrier, the random access instruction information is ignored or the random access process being performed is performed.
- One of the processes is to stop and transmit the random access preamble on the component carrier indicated by the random access instruction information.
- the mobile station apparatus when the mobile station apparatus receives random access instruction information for another component carrier on the downlink control channel during execution of random access processing with one component carrier, whether the random access instruction information is ignored Or by canceling the random access process being executed and transmitting the random access preamble on the component carrier indicated by the random access instruction information, thereby performing a plurality of random access processes simultaneously. Is not performed, and the load on the mobile station apparatus can be reduced.
- a base station apparatus of the present invention is a base station apparatus that allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus and receives a random access preamble from the mobile station apparatus during communication with the mobile station apparatus, Component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information on random access and component carrier setting information not including information on random access are notified to the mobile station apparatus.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of the component carrier setting information including information related to random access and the component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since the random access is performed only on the component carrier to which the information regarding the random access is notified from, the efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- the random access method of the present invention is applied to a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication.
- a method of notifying the mobile station apparatus of security information to the mobile station apparatus in the base station apparatus; and if the mobile station apparatus needs random access of a scheduling request, the security information The steps of transmitting a random access preamble on a component carrier to which the security function shown in FIG. 5 is set and the component carriers other than the component carrier to which the security function is assigned receive a random access instruction on the downlink control channel. Only when, characterized in that it comprises at least a step of transmitting a random access preamble.
- the base station device notifies the mobile station device of security information, and the mobile station device performs random access of the scheduling request only with the component carrier in which the security function indicated by the security information is set,
- the component carrier random access is performed by a random access instruction, so that a random access cannot be performed unless there is an instruction from the base station apparatus other than the component carrier for which the security function is not set. Therefore, useless random access does not occur.
- efficient random access can be executed.
- the random access method of the present invention is a radio communication method applied to a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication. And in the base station apparatus, notifying the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information on random access and component carrier setting information not including information on random access; The mobile station apparatus receives the allocation information and the setting information, and among the plurality of component carriers allocated from the base station apparatus, the random access is performed only on the component carrier having the setting information on random access. Characterized in that it comprises at least a step of transmitting a preamble.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since random access is performed only on the component carrier to which information about access is notified, efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- the integrated circuit of the present invention is an integrated circuit applied to a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication.
- a component carrier other than the component carrier to which the security function is assigned has means for transmitting a random access preamble only when a random access instruction is received on a downlink control channel.
- the base station device notifies the mobile station device of security information, and the mobile station device performs random access of the scheduling request only with the component for which the security function indicated by the security information is set, and other components.
- the carrier performs random access according to the random access instruction, so that it is not possible to perform random access unless there is an instruction from the base station device other than the component carrier for which the security function is not set. Efficient random access can be executed.
- the integrated circuit of the present invention is an integrated circuit applied to a radio communication system in which a base station device allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station device and the mobile station device performs random access during communication.
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since random access is performed only on the component carrier to which information about access is notified, efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- An integrated circuit according to the present invention is an integrated circuit applied to a radio communication system in which a base station apparatus allocates a plurality of component carriers to a mobile station apparatus and the mobile station apparatus performs random access during communication. And means for notifying the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including component carrier allocation information and information on random access and component carrier setting information not including information on random access. .
- the base station apparatus notifies the mobile station apparatus of component carrier setting information including information related to random access and component carrier setting information not including information related to random access. Since random access is performed only on the component carrier to which information about access is notified, efficient random access can be executed without causing unnecessary random access.
- the mobile station device 1-1 and the base station device 3 of the embodiment have been described using functional block diagrams, but the functions of the respective parts of the mobile station device 1-1 and the base station device 3 or these functions
- the mobile station apparatus 1 and the base station apparatus are recorded by recording a program for realizing a part of the functions in a computer-readable recording medium, causing the computer system to read and execute the program recorded in the recording medium.
- the control 3 may be performed.
- the “computer system” includes an OS and hardware such as peripheral devices.
- the “computer-readable recording medium” means a storage device such as a flexible disk, a magneto-optical disk, a portable medium such as a ROM and a CD-ROM, and a hard disk incorporated in a computer system.
- the “computer-readable recording medium” means that a program is dynamically held for a short time, like a communication line when a program is transmitted via a network such as the Internet or a communication line such as a telephone line. In this case, it is intended to include those that hold a program for a certain period of time, such as a volatile memory inside a computer system serving as a server or a client in that case.
- the program may be a program for realizing a part of the functions described above, and may be a program capable of realizing the functions described above in combination with a program already recorded in a computer system. .
- each functional block used in each of the above embodiments may be realized as an LSI that is typically an integrated circuit.
- Each functional block may be individually formed into chips, or a part or all of them may be integrated into a chip.
- the method of circuit integration is not limited to LSI, and may be realized by a dedicated circuit or a general-purpose processor.
- an integrated circuit based on the technology can also be used.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020127027559A KR101387181B1 (ko) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | 무선 통신 시스템, 이동국 장치, 기지국 장치, 랜덤 액세스 방법 및 집적 회로 |
| CN201180015466.3A CN102823315B (zh) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | 无线通信系统、移动站装置、基站装置、随机访问方法以及集成电路 |
| EP11762516.0A EP2555579B1 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | Wireless communication system, mobile station device, base station device, random access method and integrated circuit |
| US13/638,480 US8995371B2 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | Wireless communication system, mobile station apparatus, base station apparatus, random access method, and integrated circuit |
| US14/614,624 US9549418B2 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2015-02-05 | Wireless communication system, mobile station apparatus, base station apparatus, random access method and integrated circuit |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010074815A JP4945652B2 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2010-03-29 | 移動局装置、基地局装置、無線通信システム、ランダムアクセス方法及び集積回路 |
| JP2010-074815 | 2010-03-29 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/638,480 A-371-Of-International US8995371B2 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | Wireless communication system, mobile station apparatus, base station apparatus, random access method, and integrated circuit |
| US14/614,624 Division US9549418B2 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2015-02-05 | Wireless communication system, mobile station apparatus, base station apparatus, random access method and integrated circuit |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011122276A1 true WO2011122276A1 (ja) | 2011-10-06 |
Family
ID=44712001
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/055483 Ceased WO2011122276A1 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-09 | 無線通信システム、移動局装置、基地局装置、ランダムアクセス方法および集積回路 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US8995371B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2555579B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP4945652B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR101387181B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102823315B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI475916B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2011122276A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2640150A3 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2014-07-23 | Acer Incorporated | Apparatuses and methods for handling random access procedures |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014114001A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-07-31 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Method and apparatus for uplink resource allocation |
| BR112015020056A2 (pt) * | 2013-02-22 | 2017-07-18 | Huawei Tech Co Ltd | método de comunicação, equipamento de usuário, dispositivo de macronó de rede e dispositivo de microrrede |
| TW201434287A (zh) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-01 | Novatek Microelectronics Corp | 時脈內嵌資料的產生裝置及傳輸方法 |
| GB2515456B (en) * | 2013-04-05 | 2015-11-11 | Broadcom Corp | Resource Control |
| CN105229940B (zh) * | 2013-05-16 | 2018-09-25 | Lg电子株式会社 | 用于在无线通信系统中发送和接收信号的方法和设备 |
| EP2824986B1 (en) * | 2013-07-11 | 2023-03-22 | Fujitsu Limited | Buffer status reporting in small cell networks |
| US20150245252A1 (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2015-08-27 | Qualcomm Incorporated | High speed inter-radio access technology handover |
| EP3142403A4 (en) * | 2014-05-09 | 2017-05-03 | Fujitsu Limited | Wireless communication system, base station and terminal |
| WO2015191347A1 (en) * | 2014-06-13 | 2015-12-17 | Apple Inc. | Enhanced prach scheme for power savings, range improvement and improved detection |
| US9980292B2 (en) * | 2014-10-29 | 2018-05-22 | Mediatek Inc. | Contention based uplink orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) |
| JP6542899B2 (ja) * | 2015-01-26 | 2019-07-10 | 華為技術有限公司Huawei Technologies Co.,Ltd. | ランダムアクセス方法、端末、および基地局 |
| JP6626846B2 (ja) | 2015-01-28 | 2019-12-25 | 京セラ株式会社 | ユーザ端末、基地局、及び方法 |
| US10531512B2 (en) | 2015-04-01 | 2020-01-07 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for a tracking channel |
| US9973257B1 (en) * | 2015-08-19 | 2018-05-15 | Sprint Spectrum L.P. | RF slave repeater management |
| US10009856B2 (en) | 2016-02-08 | 2018-06-26 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Method and apparatus for transmitting PUCCH with a lower A-MPR |
| MX2019001052A (es) * | 2016-07-26 | 2019-09-23 | Sharp Kk | Aparato terminal, aparato de estacion base y metodo de comunicacion. |
| JP2019208085A (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2019-12-05 | シャープ株式会社 | 端末装置、基地局装置、通信方法、および、集積回路 |
| WO2018204922A1 (en) * | 2017-05-05 | 2018-11-08 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Transmitting sr prior to completing rach |
| CN109429351B (zh) * | 2017-09-05 | 2020-09-15 | 展讯通信(上海)有限公司 | Pucch资源释放方法及装置、存储介质、终端、基站 |
| US11019665B2 (en) * | 2018-10-30 | 2021-05-25 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Multiple Msg1 for PDCCH ordered RACH |
Family Cites Families (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6577618B2 (en) * | 1995-10-18 | 2003-06-10 | Telefonaktiebolaget L.M. Ericsson (Publ) | Packet control channel feedback support for contention and reservation based access |
| EP0993214B2 (en) * | 1998-10-05 | 2014-02-12 | Sony Deutschland GmbH | Random access channel prioritization scheme |
| US6937641B2 (en) * | 2001-02-28 | 2005-08-30 | Golden Bridge Technology, Inc. | Power-controlled random access |
| US7519041B2 (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2009-04-14 | Motorola, Inc. | Method for improving random access channel performance |
| WO2007078165A1 (en) * | 2006-01-05 | 2007-07-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Transmitting information in mobile communications system |
| US8345621B2 (en) * | 2006-08-08 | 2013-01-01 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method and apparatus for transmitting signals according to the segmented access |
| JP4867680B2 (ja) * | 2007-01-31 | 2012-02-01 | 日本電気株式会社 | 移動体無線通信システム、基地局、移動端末及びそれらに用いるランダムアクセス制御方法 |
| KR101486352B1 (ko) * | 2007-06-18 | 2015-01-26 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 통신 시스템의 단말에서의 상향링크 동기 상태 제어방법 |
| RU2446633C2 (ru) * | 2007-06-18 | 2012-03-27 | Нокиа Корпорейшн | Способ и устройство для обеспечения синхронизации |
| DK2661133T3 (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2016-09-19 | Huawei Tech Co Ltd | Time Control Adaptation in a radio communication system |
| CN101772984A (zh) * | 2007-08-09 | 2010-07-07 | 夏普株式会社 | 移动站装置、基站装置、通信系统、通信方法以及程序 |
| KR101274386B1 (ko) * | 2007-08-10 | 2013-06-17 | 후지쯔 가부시끼가이샤 | 무선 통신 시스템에서의 랜덤 액세스 방법 및 무선 통신 시스템, 무선 단말기 및 기지국 장치 |
| KR20090016431A (ko) * | 2007-08-10 | 2009-02-13 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 통신 시스템에서 채널품질 보고 수행 방법 |
| KR100925450B1 (ko) * | 2008-03-03 | 2009-11-06 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 상향링크 신호의 충돌 해결 방법 |
| MX2010012317A (es) * | 2008-06-19 | 2010-12-06 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Asignacion de recurso de señalizacion en una red de telecomunicaciones. |
| US8526374B2 (en) * | 2008-09-12 | 2013-09-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Physical random access channel (PRACH) transmission in multicarrier operation |
| US8130667B2 (en) * | 2008-09-19 | 2012-03-06 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Preamble group selection in random access of wireless networks |
| JP5145294B2 (ja) | 2008-09-22 | 2013-02-13 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | 移動端末装置、無線基地局装置及び移動通信システム |
| KR101151134B1 (ko) * | 2008-12-03 | 2012-06-01 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 넓은 셀 영역을 가지는 무선통신 시스템을 위한 계층적 임의 접속 방법 |
| CN101466153A (zh) | 2009-01-07 | 2009-06-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种无线通信系统中完成随机接入响应发送的方法及基站 |
| CN101478824B (zh) | 2009-02-02 | 2015-05-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种随机接入过程中标识下行分量载波的方法及基站 |
| US8406781B2 (en) * | 2009-02-02 | 2013-03-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Determination of user equipment antenna capability |
| CN101505538A (zh) | 2009-03-13 | 2009-08-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种多载波随机接入的方法和系统 |
| CN101540978B (zh) | 2009-04-27 | 2013-09-11 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 下行分量载波标识方法、同步下行分量载波上报方法与装置 |
| EP2532205A4 (en) * | 2010-02-03 | 2016-07-20 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | ADAPTATION OF CYCLICAL SHIFTS FOR DIRECT ACCESS PREAMBLE |
| CN103444110B (zh) * | 2011-03-25 | 2016-12-28 | 诺基亚通信公司 | 随机接入前导码配置 |
| EP3937551A3 (en) * | 2012-01-25 | 2022-02-09 | Comcast Cable Communications, LLC | Random access channel in multicarrier wireless communications with timing advance groups |
-
2010
- 2010-03-29 JP JP2010074815A patent/JP4945652B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-03-09 EP EP11762516.0A patent/EP2555579B1/en active Active
- 2011-03-09 KR KR1020127027559A patent/KR101387181B1/ko active Active
- 2011-03-09 US US13/638,480 patent/US8995371B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2011-03-09 WO PCT/JP2011/055483 patent/WO2011122276A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2011-03-09 CN CN201180015466.3A patent/CN102823315B/zh active Active
- 2011-03-22 TW TW100109765A patent/TWI475916B/zh active
-
2015
- 2015-02-05 US US14/614,624 patent/US9549418B2/en active Active
Non-Patent Citations (7)
| Title |
|---|
| "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN), Overall description Stage2", 3GPP TS (TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION) 36.300, V8.80, March 2009 (2009-03-01) |
| "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification", 3GPP TS (TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION) 36.321, V8.5.0, March 2009 (2009-03-01) |
| "Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Radio Resource Control (RRC) Protocol specification", 3GPP TR (TECHNICAL REPORT) 36.814, February 2009 (2009-02-01) |
| CATT: "Consideration on RACH in CA", 3GPP TSG RAN WG2 MEETING #69 R2-101058, 22 February 2010 (2010-02-22), XP050421372, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://ftp.3gpp.org/ftp/tsg_ran/WG2_RL2/TSGR2_69/docs/R2-101058.zip> [retrieved on 20110325] * |
| FUJITSU: "RACH for connected mode in carrier aggregation", 3GPP TSG-RAN WG2 MEETING #69 R2-101541, 22 February 2010 (2010-02-22), XP050421882, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://ftp.3gpp.org/ftp/tsg_ran/WG2_RL2/TSGR2_69/docs/R2-101541.zip> [retrieved on 20110325] * |
| LG ELECTRONICS INC.: "Multiple uplink carriers serving RACH", 3GPP TSG-RAN2 MEETING #68BIS R2-100335, 18 January 2010 (2010-01-18), XP050421034, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://ftp.3gpp.org/ftp/tsg_ran/WG2_RL2/TSGR268bis/docs/R2-100335.zip> [retrieved on 20110325] * |
| See also references of EP2555579A4 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2640150A3 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2014-07-23 | Acer Incorporated | Apparatuses and methods for handling random access procedures |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102823315B (zh) | 2016-09-14 |
| US20130136073A1 (en) | 2013-05-30 |
| US9549418B2 (en) | 2017-01-17 |
| KR101387181B1 (ko) | 2014-04-29 |
| TWI475916B (zh) | 2015-03-01 |
| CN102823315A (zh) | 2012-12-12 |
| TW201203910A (en) | 2012-01-16 |
| EP2555579A4 (en) | 2016-03-09 |
| EP2555579A1 (en) | 2013-02-06 |
| EP2555579B1 (en) | 2019-05-08 |
| US8995371B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 |
| KR20130018787A (ko) | 2013-02-25 |
| JP2011211321A (ja) | 2011-10-20 |
| JP4945652B2 (ja) | 2012-06-06 |
| US20150156800A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4945652B2 (ja) | 移動局装置、基地局装置、無線通信システム、ランダムアクセス方法及び集積回路 | |
| US10887925B2 (en) | Mobile station apparatus | |
| JP5322832B2 (ja) | 移動局装置、基地局装置、無線通信システムおよびランダムアクセス方法 | |
| CN103891376B (zh) | 无线通信系统、基站装置、移动站装置、无线通信方法以及集成电路 | |
| WO2013047219A1 (ja) | 無線通信システム、移動局装置、基地局装置、無線通信方法及び集積回路 | |
| WO2013105409A1 (ja) | 無線通信システム、移動局装置、基地局装置、無線通信方法及び集積回路 | |
| JP5756505B2 (ja) | 無線通信システム、移動局装置、ランダムアクセス方法及び集積回路 | |
| JP5385416B2 (ja) | 無線通信システム、移動局装置、ランダムアクセス方法及び集積回路 | |
| JP5771313B2 (ja) | 移動局装置、通信方法、および集積回路 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201180015466.3 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11762516 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 8996/CHENP/2012 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20127027559 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2011762516 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13638480 Country of ref document: US |