WO2011065480A1 - Nerve cell death inhibitor - Google Patents
Nerve cell death inhibitor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011065480A1 WO2011065480A1 PCT/JP2010/071127 JP2010071127W WO2011065480A1 WO 2011065480 A1 WO2011065480 A1 WO 2011065480A1 JP 2010071127 W JP2010071127 W JP 2010071127W WO 2011065480 A1 WO2011065480 A1 WO 2011065480A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- phosphatidic acid
- carbon atoms
- linear
- cell death
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/66—Phosphorus compounds
- A61K31/662—Phosphorus acids or esters thereof having P—C bonds, e.g. foscarnet, trichlorfon
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic System
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/28—Phosphorus compounds with one or more P—C bonds
- C07F9/38—Phosphonic acids RP(=O)(OH)2; Thiophosphonic acids, i.e. RP(=X)(XH)2 (X = S, Se)
- C07F9/40—Esters thereof
- C07F9/4003—Esters thereof the acid moiety containing a substituent or a structure which is considered as characteristic
- C07F9/4006—Esters of acyclic acids which can have further substituents on alkyl
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic System
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/547—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom
- C07F9/6564—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms
- C07F9/6571—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms having phosphorus and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07F9/657163—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms having phosphorus and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms the ring phosphorus atom being bound to at least one carbon atom
- C07F9/657181—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms having phosphorus and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms the ring phosphorus atom being bound to at least one carbon atom the ring phosphorus atom and, at least, one ring oxygen atom being part of a (thio)phosphonic acid derivative
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic System
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/547—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom
- C07F9/6564—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms
- C07F9/6571—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having phosphorus atoms, with or without nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium atoms, as ring hetero atoms having phosphorus and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07F9/6574—Esters of oxyacids of phosphorus
- C07F9/65742—Esters of oxyacids of phosphorus non-condensed with carbocyclic rings or heterocyclic rings or ring systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbcyclic phosphatidic acid as an active ingredient.
- Cerebral vascular disease includes some brain abnormalities caused by vascular pathological processes.
- Vascular pathological processes are considered to include any one or more of the following. There are changes due to occlusion of the lumen of blood vessels due to thrombus or embolism, rupture of blood vessels, change in permeability of blood vessel wall, increase in blood quality viscosity and the like.
- Cerebrovascular diseases typically present as seizures, which can be characterized as brain tissue death caused by lack of blood flow and insufficient oxygen to the brain. In the West, seizures are the main cause of death following heart disease and cancer. In Japan, the mortality rate of cerebrovascular disorders is decreasing, but the incidence is increasing, accounting for about 40% of the bedridden causes of the elderly.
- Seizures are ischemic or hemorrhagic.
- an ischemic stroke the blood supply to a part of the brain is reduced or stopped by a blood clot that occludes a blood vessel or by atherosclerosis. Reduced or stopped blood flow to the brain is known as cerebral ischemia. Cerebral ischemia can last from a few seconds to several minutes, and if the ischemia occurs for more than a few minutes, an infarction of the brain tissue occurs.
- cerebral ischemia can also result from circulatory and hypotensive disorders resulting from severe and prolonged heart failure or shock.
- Patent Document 1 a technique using lysophosphatidylethanolamine
- Patent Document 2 a glutamate receptor agonist
- Patent Document 3 a technique using lysophosphatidylethanolamine
- Patent Document 4 a glutamate receptor agonist
- Patent Document 5 preventive agent containing phosphatidylcholine and the like as an active ingredient
- Patent Document 6 pharmaceutical composition containing dilinoleoylphosphatidylethanolamine as an active ingredient
- Patent Document 6 Lysophosphatidic acid, lysophosphatidylinositol, etc.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a novel neuronal cell death inhibitor having an action of suppressing delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia.
- cyclic phosphatidic acid and its derivatives have neuronal differentiation induction, neuronal neurite outgrowth action, and suppress brain neuronal cell death.
- Cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidine The present inventors have found that acids and derivatives thereof suppress delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, and have completed the present invention.
- medical agent for suppressing the delayed neuronal cell death by transient cerebral ischemia containing cyclic phosphatidic acid, carb cyclic phosphatidic acid, or its salt is provided.
- the cyclic phosphatidic acid or the carbcyclic phosphatidic acid is a compound represented by the formula (1).
- R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms.
- An alkynyl group which may contain a cycloalkane ring or an aromatic ring, wherein X and Y each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, wherein X and Y are simultaneously —CH 2; (M is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation.)
- X and Y are —O—.
- X or Y is —CH 2 —.
- R is C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33 .
- the transient cerebral ischemia further comprising administering cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof to a patient with delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia.
- a method for inhibiting delayed neuronal cell death caused by is provided.
- the present invention further provides use of cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof for the manufacture of a medicament for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia. .
- a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia with few side effects comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid as an active ingredient.
- FIG. 1 shows the effects of 2 ccPA (carbacyclic phosphatidic acid) and cPA (cyclic phosphatidic acid) on hippocampal CAI region delayed neuronal death associated with transient cerebral ischemia treatment.
- FIG. 2 shows the results of observation of the hippocampal CAI region associated with transient cerebral ischemia treatment.
- FIG. 3 shows the effects of 2 ccPA (carbacyclic phosphatidic acid) and cPA (cyclic phosphatidic acid) on hippocampal CAI region delayed neuronal death associated with transient cerebral ischemia treatment.
- Delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia is a cause of hindering the therapeutic effect of diseases such as cerebral infarction.
- the mechanism is not yet clear, but it is thought that after transient cerebral ischemia, a neuronal cell death-determining mechanism works, which eventually proceeds irreversibly to a common pathway of apoptosis. .
- transient cerebral ischemia in the hippocampal CA1 region it is reported that the function of ubiquitin / proteasome is irreversibly decreased prior to delayed neuronal cell death, which causes neuronal cell death.
- caspase 3 and p53 are indispensable (Yonekura, I., Takai, K., Asai, A., Kawahara, N., Kirino, T. P53 potentiates hippocampal neuronal death caused by global ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 26: 1332-1340 (2006); and Asai, A., Tanahashi, N., Qui, J.-H., Saito, N., Chi , S., Kawahara, N., Tanaka, K., Kirino, T. Selective proteasomal dysfunction in the hippocampal CA1 rregion after transient forebrain ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 22: 705-710 (2002).
- oxidative stress due to free radical production from arachidonic acid metabolic system and nitric oxide synthase also promotes cell death (Love, S. Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol. 9: 119-131 (1999)).
- a free radical scavenger at the time of reperfusion may block or reduce the reperfusion injury by blocking the pathway to cell death.
- Generic name: edaravone This is a substance that suppresses peroxidation of cell membrane lipids by scavenging free radicals and exhibits a brain-protecting action, and its mechanism of action is completely different from cPA in this study.
- the agent of the present invention can be used for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, and contains cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof as an active ingredient.
- the cyclic phosphatidic acid or the carbcyclic phosphatidic acid is not particularly limited as long as it exhibits the effects of the present invention, but a cyclic phosphatidic acid represented by the following formula (I) can be preferably used.
- R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms.
- An alkynyl group which may contain a cycloalkane ring or an aromatic ring, wherein X and Y each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, wherein X and Y are simultaneously —CH 2;
- M is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation.
- specific examples of the linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include, for example, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, a butyl group, a pentyl group, and a hexyl group.
- linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include an allyl group, a butenyl group, an octenyl group, a decenyl group, a dodecadienyl group, a hexadecatrienyl group, and the like.
- linear or branched alkynyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include, for example, 8-decynyl group, 8-undecynyl group, 8-dodecynyl group, 8-tridecynyl group, and 8-tetradecynyl group.
- cycloalkane ring that can be contained in the alkyl group, alkenyl group, or alkynyl group
- a cyclopropane ring a cyclobutane ring, a cyclopentane ring, a cyclohexane ring, and a cyclooctane ring.
- the cycloalkane ring may contain one or more heteroatoms, and examples thereof include an oxirane ring, an oxetane ring, a tetrahydrofuran ring, and an N-methylprolysine ring.
- aromatic ring that can be contained in the alkyl group, alkenyl group, or alkynyl group include a benzene ring, a naphthalene ring, a pyridine ring, a furan ring, and a thiophene ring.
- substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by a cycloalkane ring
- substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by a cycloalkane ring
- specific examples in the case where the substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by a cycloalkane ring include a cyclopropylmethyl group, a cyclohexylethyl group, an 8,9-methanopentadecyl group, and the like.
- substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by an aromatic ring
- substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by an aromatic ring
- R is preferably a linear or branched alkyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched alkynyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms. It is a group. R is more preferably a linear or branched alkyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms. is there. R is particularly preferably a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms.
- X and Y in the compound represented by the general formula (1) each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, but X and Y are not simultaneously —CH 2 —. That is, there are the following three combinations of X and Y. (1) X is —O— and Y is —O—. (2) X is —CH 2 — and Y is —O—. (3) X is —O— and Y is —CH 2 —.
- M in the cyclic phosphatidic acid derivative represented by the formula (I) is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation.
- M is a counter cation.
- examples of the case where M is a counter cation include, for example, an alkali metal atom, an alkaline earth metal atom, and a substituted or unsubstituted ammonium group.
- examples of the alkali metal atom include lithium, sodium, and potassium
- examples of the alkaline earth metal atom include magnesium and calcium.
- the substituted ammonium group include a butyl ammonium group, a triethyl ammonium group, and a tetramethyl ammonium group.
- the compounds of formula (I) may have isomers such as positional isomers, geometric isomers, tautomers, or optical isomers depending on the type of substituent, but all possible Isomers and mixtures containing two or more of these isomers in any ratio are also within the scope of the present invention.
- the compound of formula (I) may exist in the form of an adduct (hydrate or solvate) with water or various solvents, and these adducts are also within the scope of the present invention. is there. Furthermore, any crystalline form of the compound of formula (I) and salts thereof is within the scope of the invention.
- compounds in which X and Y are —O— are, for example, JP-A-5-230088, JP-A-7-149772, JP-A-7-258278, It can be chemically synthesized according to the method described in Kaihei 9-25235.
- a compound in which X and Y are —O— causes phospholipase D to act on lyso-type phospholipid according to the method described in JP-A-2001-178589.
- the lyso-type phospholipid used here is not particularly limited as long as it is a lyso-type phospholipid capable of acting on phospholipase D.
- Many types of lyso-type phospholipids are known, those having different fatty acid species, and molecular species having an ether or vinyl ether bond are known, and these are available as commercial products.
- phospholipase D those derived from higher plants such as cabbage and peanuts, and those derived from microorganisms such as Streptomyces chromofuscus and Actinomadula sp. Are available as commercially available reagents .
- CPA is synthesized (Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 11-367032).
- the reaction between lyso-type phospholipid and phospholipase D is not particularly limited as long as the enzyme can exhibit its activity. For example, it is heated from room temperature in an acetic acid buffer solution (about pH 5 to 6) containing calcium chloride. (Preferably at about 37 ° C.) for about 1 to 5 hours.
- the produced cPA derivative can be purified by extraction, column chromatography, thin layer chromatography (TLC) or the like according to a conventional method.
- Cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid used as an active ingredient in the present invention can suppress delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia.
- the drug of the present invention can be used as a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia.
- the drug of the present invention comprises one or more pharmaceutically acceptable pharmaceutical additives and an active ingredient, cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid (preferably a compound represented by the formula (1)). It is preferably provided in the form of a pharmaceutical composition comprising.
- the drug of the present invention can be administered in various forms. Suitable administration forms include oral administration and parenteral administration (for example, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or intradermal injection, rectal administration, etc. Administration, transmucosal administration, etc.).
- Examples of the pharmaceutical composition suitable for oral administration include tablets, granules, capsules, powders, solutions, suspensions, syrups, etc.
- Examples of the pharmaceutical composition suitable for parenteral administration include , Injections, drops, suppositories, transdermal absorption agents, and the like, but the dosage form of the drug of the present invention is not limited thereto. Furthermore, it can be made into a sustained-release preparation by a known technique.
- the type of formulation additive used for the production of the drug of the present invention is not particularly limited, and can be appropriately selected by those skilled in the art.
- excipients, disintegrants or disintegration aids, binders, lubricants, coating agents, bases, solubilizers or solubilizers, dispersants, suspending agents, emulsifiers, buffers, antioxidants, antiseptics Agents, isotonic agents, pH adjusters, solubilizers, stabilizers, and the like can be used, and the specific components used for these purposes are well known to those skilled in the art.
- compositions for oral administration include, for example, excipients such as glucose, lactose, D-mannitol, starch, or crystalline cellulose; carboxymethylcellulose, starch, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, etc.
- Disintegrating agents or disintegrating aids include binders such as hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, or gelatin; lubricants such as magnesium stearate or talc; coatings such as hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, sucrose, polyethylene glycol, or titanium oxide
- Bases such as petrolatum, liquid paraffin, polyethylene glycol, gelatin, kaolin, glycerin, purified water, or hard fat can be used.
- Examples of pharmaceutical additives that can be used for the preparation of pharmaceutical preparations for injection or infusion include aqueous solutions such as distilled water for injection, physiological saline, propylene glycol, surfactants, etc. Agents or solubilizers; isotonic agents such as glucose, sodium chloride, D-mannitol, glycerin, etc .; use of pharmaceutical additives such as pH regulators such as inorganic acids, organic acids, inorganic bases or organic bases it can.
- the agent of the present invention can be administered to mammals such as humans.
- the dose of the drug of the present invention should be appropriately increased or decreased according to conditions such as the patient's age, sex, body weight, symptom, and route of administration.
- the amount of the active ingredient per adult day In the range of about 1 ⁇ g / kg to 1,000 mg / kg, preferably in the range of about 10 ⁇ g / kg to 100 mg / kg.
- the above dose of the drug may be administered once a day, or may be divided into several times (for example, about 2 to 4 times).
- Example 1 Method of Effect of cPA on Delayed Neuronal Cell Death After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Rat Hippocampus
- the method of cerebral ischemia and histological analysis is basically Kagitani, F., Uchida, S., Hotta, H, and Sato, A (2000) Effects fo nicotine on blood flow and delayed neuronal death fllowing internittent transient ischemia.
- rat hippocampus Jpn. J. Physiol. 50, 585-595, some modifications were made as described below.
- the animals were anesthetized with halothane (3.5% at the induction of anesthesia: 1.5% during surgery and ischemia).
- Antibiotics were administered (viccillin 50 mg / kg IM), and an osmotic pump for cyclic phosphatidic acid was implanted subcutaneously in the abdomen. Subsequently, tracheal intubation was performed and breathing was maintained using a ventilator (SN-480-7, Shinano, Tokyo). Rectal temperature and temporal muscle temperature were monitored, and both were maintained at about 37.5 ° C. using a heat pad and lamp (ATB-1100, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo). Bilateral vertebral arteries were permanently ligated and bilateral common carotid arteries were temporarily occluded for 8 minutes. Havante was cut immediately after the end of transient cerebral ischemia, and the ventilator was removed 15 minutes later.
- cPA18: 1 The structure of cPA18: 1 is as follows.
- a section of 3.3 mm behind Bregma was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and the left and right hippocampal CAI region pyramidal cells were observed histologically. Calculate the number of viable pyramidal cells per CAI unit length by measuring the number of viable pyramidal cells in the cone cells in the CAI region that show nuclear enrichment and the cell bodies are not atrophied and divide by the CAI length Further, the value of the CI group was set to 1, and the value of each group was represented relatively.
- Example 2 Effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus Using the same compounds (2ccPA16: 1 and cPA18: 1) as in Example 1, In a similar experimental system, the effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in the rat hippocampus was examined.
- FIG. 2 The result of histological observation of the pyramidal cells in the hippocampal CAI region is shown in FIG.
- a in A Vehicle administration group
- B in B cPA administration group
- CA1 range where the arrowhead is sandwiched
- hippocampus Bregma -3.3 mm
- FIG. 2A (Vehicle administration group) b and B (cPA administration group) b in FIG. 2 show the state of cells in the CA1 region.
- Small and darkly stained cells are cells that have aggregated the nucleus, that is, nerve cells that have undergone delayed cell death. Large round cells are living cells, and the nucleus is small in the center of the cell.
- a (Vehicle administration group) b the number of dead cells is large and almost no living neurons are found, whereas in B (cPA administration group) b, living cells are mainly used. Only a few cells are dead. It can be seen that the survival rate of neurons in the CA1 region is significantly increased by cPA treatment.
- c of A (vehicle administration group) and B (cPA administration group) of c show stained images of GFAP (glial-fibrillary acidic protein).
- GFAP is a protein constituting an intermediate filament localized in astroglia, and expression of GFAP is increased in neurological diseases such as brain injury and dementia, and is considered to be involved in the severity of cases.
- c of A (Vehicle administration group) there are some dark brown cells (anti-GFAP, DAB staining) around dead cells, but in c of B (cPA administration group) around the cells. The darkly stained sites were not found as much as A's c. That is, it is considered that the production of GFAP was suppressed by cPA administration.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Provided is a novel nerve cell death inhibitor which has an effect of inhibiting delayed nerve cell death caused by transient ischemia. Specifically provided is a drug for inhibiting delayed nerve cell death caused by transient ischemia, which contains cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof.
Description
本発明は、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸を有効成分とする一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤に関する。
The present invention relates to a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbcyclic phosphatidic acid as an active ingredient.
脳血管疾患には、血管の病的プロセスにより生じる何らかの脳の異常が含まれる。血管の病的プロセスには、次のいずれか1つまたは複数が含まれると考えられる。血栓または塞栓による血管内腔の閉塞、血管の破裂、血管壁の透過性の変化、血液質の粘度上昇などによる変化がある。
Cerebral vascular disease includes some brain abnormalities caused by vascular pathological processes. Vascular pathological processes are considered to include any one or more of the following. There are changes due to occlusion of the lumen of blood vessels due to thrombus or embolism, rupture of blood vessels, change in permeability of blood vessel wall, increase in blood quality viscosity and the like.
脳血管疾患は典型的には発作として現れる、発作は血流の欠如及び脳への不十分な酸素により生じる脳組織の死として特徴づけることができる。欧米においては、心疾患及び癌についで、発作が主な死因である。わが国においては、脳血管障害の死亡率は減少している一方、発症率は増加しており、高齢者の寝たきりの原因の約4割を占めている。
Cerebrovascular diseases typically present as seizures, which can be characterized as brain tissue death caused by lack of blood flow and insufficient oxygen to the brain. In the West, seizures are the main cause of death following heart disease and cancer. In Japan, the mortality rate of cerebrovascular disorders is decreasing, but the incidence is increasing, accounting for about 40% of the bedridden causes of the elderly.
発作は虚血性または出血性である。虚血性発作では、血管を閉塞する血餅により、またはアテローム硬化症により、脳の一部への血液供給が低下するか、止まる。脳への血流低下または停止が、脳虚血として知られている。脳虚血は数秒から数分持続する事があり、虚血が2,3分以上起こると脳組織の梗塞が生じる。更に、脳虚血は、重篤且つ長時間の心不全またはショックに由来する循環及び低血圧の障害からも起こりうる。
Seizures are ischemic or hemorrhagic. In an ischemic stroke, the blood supply to a part of the brain is reduced or stopped by a blood clot that occludes a blood vessel or by atherosclerosis. Reduced or stopped blood flow to the brain is known as cerebral ischemia. Cerebral ischemia can last from a few seconds to several minutes, and if the ischemia occurs for more than a few minutes, an infarction of the brain tissue occurs. In addition, cerebral ischemia can also result from circulatory and hypotensive disorders resulting from severe and prolonged heart failure or shock.
これまで、脳虚血疾患に対する治療薬は幾つか臨床の現場で使用されてきており多くの患者の救命に貢献してきているが、発作を発症してからの治療には充分な効果を発揮し得ていないのが現状である。また、下記の文献においては神経細胞死を引き起こす疾患の予防法並びに治療法として、リゾフォスファチジルエタノールアミンを用いる技術(特許文献1)、グルタメートレセプターアゴニスト(特許文献2)、ピリドキシン、ピリドキサミンなど(特許文献3)、ホスファチジルコリンなどを有効成分とする予防剤(特許文献4)、ドコサヘキサエン並びにその誘導体(特許文献5)、ジリノレオイルホスファチジルエタノールアミンを有効成分とする医薬組成物(特許文献6)、リゾホスファチジン酸、リゾホスファチジルイノシトールなど(特許文献7)が知られている。
Until now, some therapeutic agents for cerebral ischemic disease have been used in clinical practice and have contributed to the lifesaving of many patients, but they are effective enough for treatment after the onset of seizures. The current situation is that we have not obtained it. Further, in the following literature, as a method for preventing and treating a disease causing neuronal cell death, a technique using lysophosphatidylethanolamine (Patent Document 1), a glutamate receptor agonist (Patent Document 2), pyridoxine, pyridoxamine and the like ( Patent Document 3), preventive agent containing phosphatidylcholine and the like as an active ingredient (Patent Document 4), docosahexaene and derivatives thereof (Patent Document 5), pharmaceutical composition containing dilinoleoylphosphatidylethanolamine as an active ingredient (Patent Document 6), Lysophosphatidic acid, lysophosphatidylinositol, etc. (Patent Document 7) are known.
しかしながら、脳血管障害による一過性脳虚血による遅発性神経細胞死を原因とする病態に対して、現在までに充分な効果が認められる治療薬はなく、新たな薬剤の開発が求められている。即ち、本発明は、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制する作用を有する新規な神経細胞死抑制剤を提供することを解決すべき課題とする。
However, there is no therapeutic drug that has been shown to have a sufficient effect on the pathological condition caused by delayed neuronal death due to transient cerebral ischemia due to cerebrovascular disorder, and the development of a new drug is required. ing. That is, an object of the present invention is to provide a novel neuronal cell death inhibitor having an action of suppressing delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia.
本発明者は、すでに環状ホスファチジン酸及びその誘導体が神経細胞の分化誘導、神経細胞の神経突起伸長作用を有し、脳神経細胞死を抑制することを見いだしているが、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸及びその誘導体が、一過性脳虚血による遅発性神経細胞死を抑制することを見いだし、本発明を完成するに至った。
The present inventor has already found that cyclic phosphatidic acid and its derivatives have neuronal differentiation induction, neuronal neurite outgrowth action, and suppress brain neuronal cell death. Cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidine The present inventors have found that acids and derivatives thereof suppress delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, and have completed the present invention.
すなわち、本発明によれば、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩を含有する、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤が提供される。
好ましくは、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸は、式(1)で示される化合物である。
(式中、Rは、炭素数1~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキル基、炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基、又は炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキニル基であり、これらの基はシクロアルカン環又は芳香環を含んでいてもよい。X及びYはそれぞれ独立に、-O-又は-CH2-を示すが、X及びYが同時に-CH2-になることはない。Mは、水素原子又は対カチオンである。)
That is, according to this invention, the chemical | medical agent for suppressing the delayed neuronal cell death by transient cerebral ischemia containing cyclic phosphatidic acid, carb cyclic phosphatidic acid, or its salt is provided.
Preferably, the cyclic phosphatidic acid or the carbcyclic phosphatidic acid is a compound represented by the formula (1).
(In the formula, R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms. An alkynyl group, which may contain a cycloalkane ring or an aromatic ring, wherein X and Y each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, wherein X and Y are simultaneously —CH 2; (M is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation.)
好ましくは、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸は、式(1)で示される化合物である。
Preferably, the cyclic phosphatidic acid or the carbcyclic phosphatidic acid is a compound represented by the formula (1).
好ましくは、一般式(1)において、X及びYが-O-である。
好ましくは、一般式(1)において、X又はYが-CH2-である。
好ましくは、一般式(1)において、RがC15H29又はC17H33である。 Preferably, in the general formula (1), X and Y are —O—.
Preferably, in the general formula (1), X or Y is —CH 2 —.
Preferably, in the general formula (1), R is C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33 .
好ましくは、一般式(1)において、X又はYが-CH2-である。
好ましくは、一般式(1)において、RがC15H29又はC17H33である。 Preferably, in the general formula (1), X and Y are —O—.
Preferably, in the general formula (1), X or Y is —CH 2 —.
Preferably, in the general formula (1), R is C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33 .
本発明によればさらに、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩を、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を伴う患者に投与することを含む、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制する方法が提供される。
According to the present invention, the transient cerebral ischemia further comprising administering cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof to a patient with delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia. A method for inhibiting delayed neuronal cell death caused by is provided.
本発明によればさらに、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤の製造のための、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩の使用が提供される。
The present invention further provides use of cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof for the manufacture of a medicament for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia. .
本発明によれば、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸を有効成分として含有することを特徴とする、副作用の少ない一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤を提供できる。
According to the present invention, there is provided a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia with few side effects, comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid as an active ingredient. Can be provided.
以下、本発明について更に具体的に説明する。
本明細書中で以下に記載する実施例では、コントロール群を含むラット海馬CA1領域の錐体細胞に対して、一過性の脳虚血処理による遅発性神経細胞死が誘導されている実験系を用いた。この実験系において、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸は明らかに同領域の遅発性神経細胞死を抑制する働きがあることが示された。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically.
In the examples described hereinbelow, an experiment in which delayed neuronal cell death is induced by transient cerebral ischemia treatment on pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampal CA1 region including the control group. The system was used. In this experimental system, it was clearly shown that cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbcyclic phosphatidic acid has a function of suppressing delayed neuronal cell death in the same region.
本明細書中で以下に記載する実施例では、コントロール群を含むラット海馬CA1領域の錐体細胞に対して、一過性の脳虚血処理による遅発性神経細胞死が誘導されている実験系を用いた。この実験系において、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸は明らかに同領域の遅発性神経細胞死を抑制する働きがあることが示された。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically.
In the examples described hereinbelow, an experiment in which delayed neuronal cell death is induced by transient cerebral ischemia treatment on pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampal CA1 region including the control group. The system was used. In this experimental system, it was clearly shown that cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbcyclic phosphatidic acid has a function of suppressing delayed neuronal cell death in the same region.
一過性脳虚血によって、遅発性の神経細胞死が起こることが、脳梗塞などの疾患の治療効果を妨げる原因となっている。そのメカニズムは未だ明らかでないことも多いが、一過性脳虚血後に、神経細胞特有の細胞死決定機構が働いて、それが最終的にアポトーシス共通の経路に不可逆的に進行すると考えられている。その際に、海馬CA1領域で一過性脳虚血後、遅発性神経細胞死に先立って、ユビキチン/プロテアソームの機能が不可逆的に低下し、それが神経細胞死を引き起こすきっかけとなることが報告され、その際に、カスパーゼ3やp53が必要不可欠であることが明らかにされている(Yonekura,I., Takai,K., Asai,A., Kawahara,N., Kirino,T. p53 potentiates hippocampal neuronal death caused by global ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 26: 1332-1340 (2006);及びAsai,A., Tanahashi,N., Qui,J.-H., Saito,N., Chi,S., Kawahara,N., Tanaka,K., Kirino,T. Selective proteasomal dysfunction in the hippocampal CA1 rregion after transient forebrain ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 22: 705-710 (2002))。
遅 Delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia is a cause of hindering the therapeutic effect of diseases such as cerebral infarction. The mechanism is not yet clear, but it is thought that after transient cerebral ischemia, a neuronal cell death-determining mechanism works, which eventually proceeds irreversibly to a common pathway of apoptosis. . At that time, after transient cerebral ischemia in the hippocampal CA1 region, it is reported that the function of ubiquitin / proteasome is irreversibly decreased prior to delayed neuronal cell death, which causes neuronal cell death. At that time, it has been clarified that caspase 3 and p53 are indispensable (Yonekura, I., Takai, K., Asai, A., Kawahara, N., Kirino, T. P53 potentiates hippocampal neuronal death caused by global ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 26: 1332-1340 (2006); and Asai, A., Tanahashi, N., Qui, J.-H., Saito, N., Chi , S., Kawahara, N., Tanaka, K., Kirino, T. Selective proteasomal dysfunction in the hippocampal CA1 rregion after transient forebrain ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 22: 705-710 (2002).
また、虚血により、嫌気性代謝によるアシドーシスの進行によってNa+ の細胞内流入が起こり、Na+ 負荷のために細胞が膨張すること、その後に起こる再還流によってフリーラジカルの発生とCa2+ の流入が起こり、フリーラジカルによる細胞膜障害がさらなるCa2+ 増加を引き起こして、最終的には細胞膜破壊を起こして細胞死をきたすことも報告されている(橋本克次, 吉岡淳, 今橋憲一, 楠岡英雄 カルシムと再還流障害.呼吸と循環 49:43-49(2001))。また再還流後には、アラキドン酸代謝系や一酸化窒素合成酵素からのフリーラジカル産生による酸化ストレスも、細胞死を助長する(Love, S. Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol . 9: 119-131 (1999))。このことから、再還流時にフリーラジカルスカベンジャーを投与することにより、細胞死への経路を遮断して再還流障害を軽減あるいは阻止できる可能性が考えられ、この観点から開発された治療薬がラジカット(一般名:エダラボン)である。これは、フリーラジカル消去により、細胞膜脂質の過酸化を抑制して、脳保護作用を示す物質で、本研究によるcPAとは作用機序が全く異なる。
In addition, due to ischemia, the inflow of Na + occurs due to the progress of acidosis due to anaerobic metabolism, the cells expand due to Na + load, the generation of free radicals and the influx of Ca 2+ 起 こ り occur due to subsequent reperfusion, It has also been reported that cell membrane damage due to free radicals causes further Ca2 + increase and eventually cell membrane destruction resulting in cell death (Katsuji Hashimoto, Satoshi Yoshioka, Kenichi Sasahashi, Hideo Sasaoka and Calfim and reperfusion injury) Respiration and circulation 49: 43-49 (2001)). After reperfusion, oxidative stress due to free radical production from arachidonic acid metabolic system and nitric oxide synthase also promotes cell death (Love, S. Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol. 9: 119-131 (1999)). This suggests that administration of a free radical scavenger at the time of reperfusion may block or reduce the reperfusion injury by blocking the pathway to cell death. Generic name: edaravone). This is a substance that suppresses peroxidation of cell membrane lipids by scavenging free radicals and exhibits a brain-protecting action, and its mechanism of action is completely different from cPA in this study.
即ち、本発明の薬剤は、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するために使用することができ、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸又はその塩を有効成分として含む。環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸としては本発明の効果を示すものであれば特に限定されないが、好ましくは、下記式(I)で示される環状ホスファチジン酸を使用することができる。
That is, the agent of the present invention can be used for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia, and contains cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof as an active ingredient. The cyclic phosphatidic acid or the carbcyclic phosphatidic acid is not particularly limited as long as it exhibits the effects of the present invention, but a cyclic phosphatidic acid represented by the following formula (I) can be preferably used.
(式中、Rは、炭素数1~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキル基、炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基、又は炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキニル基であり、これらの基はシクロアルカン環又は芳香環を含んでいてもよい。X及びYはそれぞれ独立に、-O-又は-CH2-を示すが、X及びYが同時に-CH2-になることはない。Mは、水素原子又は対カチオンである。)
(In the formula, R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms. An alkynyl group, which may contain a cycloalkane ring or an aromatic ring, wherein X and Y each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, wherein X and Y are simultaneously —CH 2; (M is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation.)
式(I)において、置換基Rが示す炭素数1~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキル基の具体例としては、例えば、メチル基、エチル基、プロピル基、ブチル基、ペンチル基、ヘキシル基、ヘプチル基、オクチル基、ノニル基、デシル基、ウンデシル基、ドデシル基、トリデシル基、テトラデシル基、ペンタデシル基、ヘキサデシル基、ヘプタデシル基、オクタデシル基、ノナデシル基、エイコシル基などが挙げられる。
In the formula (I), specific examples of the linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include, for example, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, a butyl group, a pentyl group, and a hexyl group. , Heptyl, octyl, nonyl, decyl, undecyl, dodecyl, tridecyl, tetradecyl, pentadecyl, hexadecyl, heptadecyl, octadecyl, nonadecyl, eicosyl and the like.
置換基Rが示す炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基の具体例としては、例えば、アリル基、ブテニル基、オクテニル基、デセニル基、ドデカジエニル基、ヘキサデカトリエニル基などが挙げられ、より具体的には、8-デセニル基、8-ウンデセニル基、8-ドデセニル基、8-トリデセニル基、8-テトラデセニル基、8-ペンタデセニル基、8-ヘキサデセニル基、8-ヘプタデセニル基、8-オクタデセニル基、8-イコセニル基、8-ドコセニル基、ヘプタデカ-8,11-ジエニル基、ヘプタデカ-8,11,14-トリエニル基、ノナデカ-4,7,10,13-テトラエニル基、ノナデカ-4,7,10,13,16-ペンタエニル基、ヘニコサ-3,6,9,12,15,18-ヘキサエニル基などが挙げられる。
Specific examples of the linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include an allyl group, a butenyl group, an octenyl group, a decenyl group, a dodecadienyl group, a hexadecatrienyl group, and the like. More specifically, 8-decenyl group, 8-undecenyl group, 8-dodecenyl group, 8-tridecenyl group, 8-tetradecenyl group, 8-pentadecenyl group, 8-hexadecenyl group, 8-heptadecenyl group, 8- Octadecenyl group, 8-icosenyl group, 8-docosenyl group, heptadec-8,11-dienyl group, heptadec-8,11,14-trienyl group, nonadeca-4,7,10,13-tetraenyl group, nonadeca-4, 7,10,13,16-pentaenyl group, henicosa-3,6,9,12,15,18-hexaenyl group, etc. It is.
置換基Rが示す炭素数2~30の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキニル基の具体例としては、例えば、8-デシニル基、8-ウンデシニル基、8-ドデシニル基、8-トリデシニル基、8-テトラデシニル基、8-ペンタデシニル基、8-ヘキサデシニル基、8-ヘプタデシニル基、8-オクタデシニル基、8-イコシニル基、8-ドコシニル基、ヘプタデカ-8,11-ジイニル基などが挙げられる。
Specific examples of the linear or branched alkynyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms represented by the substituent R include, for example, 8-decynyl group, 8-undecynyl group, 8-dodecynyl group, 8-tridecynyl group, and 8-tetradecynyl group. Group, 8-pentadecynyl group, 8-hexadecynyl group, 8-heptadecynyl group, 8-octadecynyl group, 8-icosinyl group, 8-docosinyl group, heptadec-8,11-diynyl group and the like.
上記のアルキル基、アルケニル基又はアルキニル基に含有されうるシクロアルカン環の具体例としては、例えば、シクロプロパン環、シクロブタン環、シクロペンタン環、シクロヘキサン環、シクロオクタン環などが挙げられる。シクロアルカン環は、1個以上のヘテロ原子を含んでいてもよく、そのような例としては、例えば、オキシラン環、オキセタン環、テトラヒドロフラン環、N-メチルプロリジン環などが挙げられる。
Specific examples of the cycloalkane ring that can be contained in the alkyl group, alkenyl group, or alkynyl group include a cyclopropane ring, a cyclobutane ring, a cyclopentane ring, a cyclohexane ring, and a cyclooctane ring. The cycloalkane ring may contain one or more heteroatoms, and examples thereof include an oxirane ring, an oxetane ring, a tetrahydrofuran ring, and an N-methylprolysine ring.
上記のアルキル基、アルケニル基又はアルキニル基に含有されうる芳香環の具体例としては、例えば、ベンゼン環、ナフタレン環、ピリジン環、フラン環、チオフェン環などが挙げられる。
Specific examples of the aromatic ring that can be contained in the alkyl group, alkenyl group, or alkynyl group include a benzene ring, a naphthalene ring, a pyridine ring, a furan ring, and a thiophene ring.
従って、置換基Rがシクロアルカン環によって置換されたアルキル基である場合の具体例としては、例えば、シクロプロピルメチル基、シクロヘキシルエチル基、8,9-メタノペンタデシル基などが挙げられる。
Therefore, specific examples in the case where the substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by a cycloalkane ring include a cyclopropylmethyl group, a cyclohexylethyl group, an 8,9-methanopentadecyl group, and the like.
置換基Rが芳香環によって置換されたアルキル基である場合の具体例としては、ベンジル基、フェネチル基、p-ペンチルフェニルオクチル基などが挙げられる。
Specific examples when the substituent R is an alkyl group substituted by an aromatic ring include a benzyl group, a phenethyl group, a p-pentylphenyloctyl group, and the like.
Rは、好ましくは、炭素数9~17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキル基、炭素数9~17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基、又は炭素数9~17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキニル基である。Rは、さらに好ましくは、炭素数9、11、13、15又は17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルキル基、又は炭素数9、11、13、15又は17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基である。Rは、特に好ましくは、炭素数9、11、13、15又は17の直鎖状若しくは分岐状アルケニル基である。
R is preferably a linear or branched alkyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched alkynyl group having 9 to 17 carbon atoms. It is a group. R is more preferably a linear or branched alkyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms. is there. R is particularly preferably a linear or branched alkenyl group having 9, 11, 13, 15 or 17 carbon atoms.
一般式(1)で示される化合物中のX及びYはそれぞれ独立に、-O-又は-CH2-を示すが、X及びYが同時に-CH2-になることはない。即ち、X及びYの組み合わせは以下の3通りである。
(1)Xが-O-であり、Yが-O-である。
(2)Xが-CH2-であり、Yが-O-である。
(3)Xが-O-であり、Yが-CH2-である。 X and Y in the compound represented by the general formula (1) each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, but X and Y are not simultaneously —CH 2 —. That is, there are the following three combinations of X and Y.
(1) X is —O— and Y is —O—.
(2) X is —CH 2 — and Y is —O—.
(3) X is —O— and Y is —CH 2 —.
(1)Xが-O-であり、Yが-O-である。
(2)Xが-CH2-であり、Yが-O-である。
(3)Xが-O-であり、Yが-CH2-である。 X and Y in the compound represented by the general formula (1) each independently represent —O— or —CH 2 —, but X and Y are not simultaneously —CH 2 —. That is, there are the following three combinations of X and Y.
(1) X is —O— and Y is —O—.
(2) X is —CH 2 — and Y is —O—.
(3) X is —O— and Y is —CH 2 —.
式(I)で示される環状ホスファチジン酸誘導体中のMは、水素原子又は対カチオンである。Mが対カチオンである場合の例としては、例えば、アルカリ金属原子、アルカリ土類金属原子、置換若しくは無置換アンモニウム基が挙げられる。アルカリ金属原子としては、例えば、リチウム、ナトリウム、カリウムなどが挙げられ、アルカリ土類金属原子としては、例えば、マグネシウム、カルシウムなどが挙げられる。置換アンモニウム基としては、例えば、ブチルアンモニウム基、トリエチルアンモニウム基、テトラメチルアンモニウム基などが挙げられる。
M in the cyclic phosphatidic acid derivative represented by the formula (I) is a hydrogen atom or a counter cation. Examples of the case where M is a counter cation include, for example, an alkali metal atom, an alkaline earth metal atom, and a substituted or unsubstituted ammonium group. Examples of the alkali metal atom include lithium, sodium, and potassium, and examples of the alkaline earth metal atom include magnesium and calcium. Examples of the substituted ammonium group include a butyl ammonium group, a triethyl ammonium group, and a tetramethyl ammonium group.
式(I)の化合物はその置換基の種類に応じて、位置異性体、幾何異性体、互変異性体、又は光学異性体のような異性体が存在する場合があるが、全ての可能な異性体、並びに2種類以上の該異性体を任意の比率で含む混合物も本発明の範囲内のものである。
The compounds of formula (I) may have isomers such as positional isomers, geometric isomers, tautomers, or optical isomers depending on the type of substituent, but all possible Isomers and mixtures containing two or more of these isomers in any ratio are also within the scope of the present invention.
また、式(I)の化合物は、水あるいは各種溶媒との付加物(水和物又は溶媒和物)の形で存在することもあるが、これらの付加物も本発明の範囲内のものである。さらに、式(I)の化合物及びその塩の任意の結晶形も本発明の範囲内のものである。
The compound of formula (I) may exist in the form of an adduct (hydrate or solvate) with water or various solvents, and these adducts are also within the scope of the present invention. is there. Furthermore, any crystalline form of the compound of formula (I) and salts thereof is within the scope of the invention.
一般式(1)で示される化合物のうちX及びYが-O-である化合物は、例えば、特開平5-230088号公報、特開平7-149772号公報、特開平7-258278号公報、特開平9-25235号公報に記載の方法等に準じて化学的に合成することができる。
Among the compounds represented by the general formula (1), compounds in which X and Y are —O— are, for example, JP-A-5-230088, JP-A-7-149772, JP-A-7-258278, It can be chemically synthesized according to the method described in Kaihei 9-25235.
また、一般式(1)で示される化合物のうちX及びYが-O-である化合物は、特開2001-178489号公報に記載の方法に準じてリゾ型リン脂質にホスホリパーゼDを作用させることによって合成することもできる。ここで用いるリゾ型リン脂質は、ホスホリパーゼDを作用しうるリゾ型リン脂質であれば特に限定されない。リゾ型リン脂質は多くの種類が知られており、脂肪酸種が異なるもの、エーテル又はビニルエーテル結合をもった分子種などが知られており、これらは市販品として入手可能である。ホスホリパーゼDとしては、キャベツや落花生などの高等植物由来のものやStreptomyces chromofuscus, Actinomadula sp.などの微生物由来のものが市販試薬として入手可能であるが、Actinomadula sp. No.362由来の酵素によって極めて選択的にcPAが合成される(特開平11-367032号明細書)。リゾ型リン脂質とホスホリパーゼDとの反応は、酵素が活性を発現できる条件であれば特に限定されないが、例えば、塩化カルシウムを含有する酢酸緩衝液(pH5~6程度)中で室温から加温下(好ましくは37℃程度)で1から5時間程度反応させることにより行う。生成したcPA誘導体は、常法に準じて、抽出、カラムクロマトグラフィー、薄層クロマトグラフィー(TLC)などにより精製することができる。
Further, among the compounds represented by the general formula (1), a compound in which X and Y are —O— causes phospholipase D to act on lyso-type phospholipid according to the method described in JP-A-2001-178589. Can also be synthesized. The lyso-type phospholipid used here is not particularly limited as long as it is a lyso-type phospholipid capable of acting on phospholipase D. Many types of lyso-type phospholipids are known, those having different fatty acid species, and molecular species having an ether or vinyl ether bond are known, and these are available as commercial products. As phospholipase D, those derived from higher plants such as cabbage and peanuts, and those derived from microorganisms such as Streptomyces chromofuscus and Actinomadula sp. Are available as commercially available reagents . CPA is synthesized (Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 11-367032). The reaction between lyso-type phospholipid and phospholipase D is not particularly limited as long as the enzyme can exhibit its activity. For example, it is heated from room temperature in an acetic acid buffer solution (about pH 5 to 6) containing calcium chloride. (Preferably at about 37 ° C.) for about 1 to 5 hours. The produced cPA derivative can be purified by extraction, column chromatography, thin layer chromatography (TLC) or the like according to a conventional method.
また、一般式(1)で示される化合物のうちXが-CH2-であり、Yが-O-である化合物は、特開2004-010582号公報又は国際公開WO03/104246号公報に記載の方法により合成することができる。
Among the compounds represented by the general formula (1), a compound in which X is —CH 2 — and Y is —O— is described in JP-A No. 2004-010582 or WO 03/104246. It can be synthesized by the method.
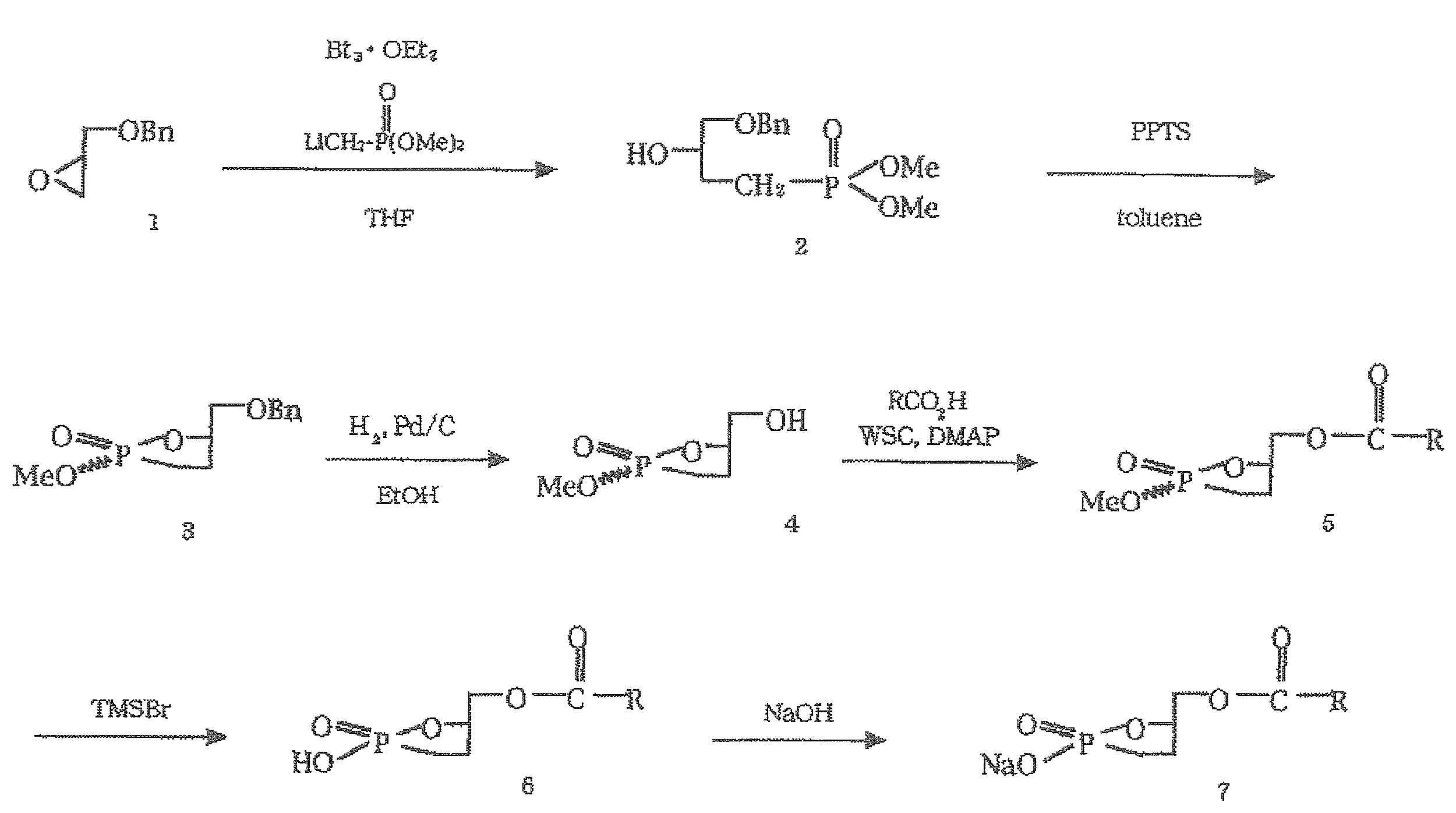
また、 一般式(1)で示される化合物のうちXが-O-であり、Yが-CH2-である化合物は、文献記載の方法(Kobayashi,S.,他,Tetrahedron Letters 34,4047-4050(1993);並びに「日本薬学会 第23回 反応と合成の進歩シンポジウム1997年11月17、18日(熊本市民会館)環状ホスファチジン酸およびカルバ体誘導体の合成と生理作用、要旨集ページ101-104」)に準じて合成することができ、また国際公開WO2002/094286号公報に記載の方法により合成することができる。具体的な合成経路の一例を以下に示す。
In addition, among the compounds represented by the general formula (1), a compound in which X is —O— and Y is —CH 2 — is prepared by a method described in the literature (Kobayashi, S., et al., Tetrahedron Letters 34, 4047- 4050 (1993); and "The Japan Pharmaceutical Association 23rd Symposium on Progress in Reactions and Synthesis, November 17 and 18, 1997 (Kumamoto Civic Center) Synthesis and Physiological Actions of Cyclic Phosphatidic Acid and Carba Derivatives, Abstracts Page 101- 104 ") and can be synthesized by the method described in International Publication No. WO2002 / 094286. An example of a specific synthesis route is shown below.
上記においては、先ず、市販の(R)-ベンジルグリシジルエーテル(1)をBF3・Et2Oで活性化させ、メチルホスホン酸ジメチルエステルにn-BuLiを作用させて得られるリチオ体を反応させることでアルコール(2)を得る。
得られたアルコールを、トルエン中で過剰のp-トルエンスルホン酸のピリジニウム塩を用いて80℃で反応させることにより、環化体(3)を得る。この環化体を、水素雰囲気下で20% Pd(OH)2-Cを用いて加水素分解し、脱ベンジル化を行う(4)。縮合剤として1-エチル-3-(3-ジメチルアミノプロピル)カルボジイミド塩酸塩を用いて、脂肪酸と反応させてカップリング体(5)を得る。次に、求核剤としてブロモトリメチルシランを用いて、メチル基だけを位置選択的に除去し、環状ホスホン酸(6)を得る。これをエーテルを用いて分液ロートに移しこみ、少量の0.02Nの水酸化ナトリウム水溶液を滴下して、分液操作を行い、ナトリウム塩(7)として目的化合物を抽出、精製する。 In the above, first, the commercially available (R) -benzyl glycidyl ether (1) is activated with BF 3 .Et 2 O, and the thio compound obtained by reacting n-BuLi with methylphosphonic acid dimethyl ester is reacted. To obtain alcohol (2).
The obtained alcohol is reacted at 80 ° C. with an excess of pyridinium salt of p-toluenesulfonic acid in toluene to obtain a cyclized product (3). This cyclized product is subjected to hydrogenolysis using 20% Pd (OH) 2 —C under hydrogen atmosphere to perform debenzylation (4). Using 1-ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride as a condensing agent, it is reacted with a fatty acid to obtain a coupled product (5). Next, using bromotrimethylsilane as a nucleophile, only the methyl group is regioselectively removed to obtain cyclic phosphonic acid (6). This is transferred to a separatory funnel using ether, and a small amount of 0.02N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is added dropwise to carry out a liquid separation operation to extract and purify the target compound as a sodium salt (7).
得られたアルコールを、トルエン中で過剰のp-トルエンスルホン酸のピリジニウム塩を用いて80℃で反応させることにより、環化体(3)を得る。この環化体を、水素雰囲気下で20% Pd(OH)2-Cを用いて加水素分解し、脱ベンジル化を行う(4)。縮合剤として1-エチル-3-(3-ジメチルアミノプロピル)カルボジイミド塩酸塩を用いて、脂肪酸と反応させてカップリング体(5)を得る。次に、求核剤としてブロモトリメチルシランを用いて、メチル基だけを位置選択的に除去し、環状ホスホン酸(6)を得る。これをエーテルを用いて分液ロートに移しこみ、少量の0.02Nの水酸化ナトリウム水溶液を滴下して、分液操作を行い、ナトリウム塩(7)として目的化合物を抽出、精製する。 In the above, first, the commercially available (R) -benzyl glycidyl ether (1) is activated with BF 3 .Et 2 O, and the thio compound obtained by reacting n-BuLi with methylphosphonic acid dimethyl ester is reacted. To obtain alcohol (2).
The obtained alcohol is reacted at 80 ° C. with an excess of pyridinium salt of p-toluenesulfonic acid in toluene to obtain a cyclized product (3). This cyclized product is subjected to hydrogenolysis using 20% Pd (OH) 2 —C under hydrogen atmosphere to perform debenzylation (4). Using 1-ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride as a condensing agent, it is reacted with a fatty acid to obtain a coupled product (5). Next, using bromotrimethylsilane as a nucleophile, only the methyl group is regioselectively removed to obtain cyclic phosphonic acid (6). This is transferred to a separatory funnel using ether, and a small amount of 0.02N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is added dropwise to carry out a liquid separation operation to extract and purify the target compound as a sodium salt (7).
本発明において有効成分として用いる環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸は、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制することができる。本発明の薬剤は、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤として使用することができる。
Cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid used as an active ingredient in the present invention can suppress delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia. The drug of the present invention can be used as a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia.
本発明の薬剤は、1又は2以上の製剤学的に許容される製剤用添加物と有効成分である環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸(好ましくは、式(1)で示される化合物)とを含む医薬組成物の形態で提供することが好ましい。
The drug of the present invention comprises one or more pharmaceutically acceptable pharmaceutical additives and an active ingredient, cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid (preferably a compound represented by the formula (1)). It is preferably provided in the form of a pharmaceutical composition comprising.
本発明の薬剤は、種々の形態で投与することができるが、好適な投与形態としては、経口投与でも非経口投与(例えば、静脈内、筋肉内、皮下又は皮内等への注射、直腸内投与、経粘膜投与など)でもよい。経口投与に適する医薬組成物としては、例えば、錠剤、顆粒剤、カプセル剤、散剤、溶液剤、懸濁剤、シロップ剤などを挙げることができ、非経口投与に適する医薬組成物としては、例えば、注射剤、点滴剤、坐剤、経皮吸収剤などを挙げることができるが、本発明の薬剤の剤形はこれらに限定されることはない。さらに、公知の技術によって持続性製剤とすることもできる。
The drug of the present invention can be administered in various forms. Suitable administration forms include oral administration and parenteral administration (for example, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or intradermal injection, rectal administration, etc. Administration, transmucosal administration, etc.). Examples of the pharmaceutical composition suitable for oral administration include tablets, granules, capsules, powders, solutions, suspensions, syrups, etc. Examples of the pharmaceutical composition suitable for parenteral administration include , Injections, drops, suppositories, transdermal absorption agents, and the like, but the dosage form of the drug of the present invention is not limited thereto. Furthermore, it can be made into a sustained-release preparation by a known technique.
本発明の薬剤の製造に用いられる製剤用添加物の種類は特に限定されず、当業者が適宜選択可能である。例えば、賦形剤、崩壊剤又は崩壊補助剤、結合剤、滑沢剤、コーティング剤、基剤、溶解剤又は溶解補助剤、分散剤、懸濁剤、乳化剤、緩衝剤、抗酸化剤、防腐剤、等張化剤、pH調節剤、溶解剤、安定化剤などを用いることができ、これらの目的で使用される個々の具体的成分は当業者に周知されている。
The type of formulation additive used for the production of the drug of the present invention is not particularly limited, and can be appropriately selected by those skilled in the art. For example, excipients, disintegrants or disintegration aids, binders, lubricants, coating agents, bases, solubilizers or solubilizers, dispersants, suspending agents, emulsifiers, buffers, antioxidants, antiseptics Agents, isotonic agents, pH adjusters, solubilizers, stabilizers, and the like can be used, and the specific components used for these purposes are well known to those skilled in the art.
経口投与用の製剤の調製に用いることができる製剤用添加物として、例えば、ブドウ糖、乳糖、D-マンニトール、デンプン、又は結晶セルロース等の賦形剤;カルボキシメチルセルロース、デンプン、又はカルボキシメチルセルロースカルシウム等の崩壊剤又は崩壊補助剤;ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース、ヒドロキシプロピルメチルセルロース、ポリビニルピロリドン、又はゼラチン等の結合剤;ステアリン酸マグネシウム又はタルク等の滑沢剤;ヒドロキシプロピルメチルセルロース、白糖、ポリエチレングリコール又は酸化チタン等のコーティング剤;ワセリン、流動パラフィン、ポリエチレングリコール、ゼラチン、カオリン、グリセリン、精製水、又はハードファット等の基剤を用いることができる。
Pharmaceutical additives that can be used in the preparation of formulations for oral administration include, for example, excipients such as glucose, lactose, D-mannitol, starch, or crystalline cellulose; carboxymethylcellulose, starch, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, etc. Disintegrating agents or disintegrating aids; binders such as hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, or gelatin; lubricants such as magnesium stearate or talc; coatings such as hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, sucrose, polyethylene glycol, or titanium oxide Agents: Bases such as petrolatum, liquid paraffin, polyethylene glycol, gelatin, kaolin, glycerin, purified water, or hard fat can be used.
注射あるいは点滴用の製剤の調製に用いることができる製剤用添加物としては、注射用蒸留水、生理食塩水、プロピレングリコール、界面活性剤等の水性あるいは用時溶解型注射剤を構成しうる溶解剤又は溶解補助剤;ブドウ糖、塩化ナトリウム、D-マンニトール、グリセリン,等の等張化剤;無機酸、有機酸、無機塩基又は有機塩基等のpH調節剤等の製剤用添加物を用いることができる。
Examples of pharmaceutical additives that can be used for the preparation of pharmaceutical preparations for injection or infusion include aqueous solutions such as distilled water for injection, physiological saline, propylene glycol, surfactants, etc. Agents or solubilizers; isotonic agents such as glucose, sodium chloride, D-mannitol, glycerin, etc .; use of pharmaceutical additives such as pH regulators such as inorganic acids, organic acids, inorganic bases or organic bases it can.
本発明の薬剤はヒトなどの哺乳動物に投与することができる。
本発明の薬剤の投与量は患者の年齢、性別、体重、症状、及び投与経路などの条件に応じて適宜増減されるべきであるが、一般的には、成人一日あたりの有効成分の量として1μg/kgから1,000mg/kg程度の範囲であり、好ましくは10μg/kgから100mg/kg程度の範囲である。上記投与量の薬剤は一日一回に投与してもよいし、数回(例えば、2~4回程度)に分けて投与してもよい。 The agent of the present invention can be administered to mammals such as humans.
The dose of the drug of the present invention should be appropriately increased or decreased according to conditions such as the patient's age, sex, body weight, symptom, and route of administration. Generally, the amount of the active ingredient per adult day In the range of about 1 μg / kg to 1,000 mg / kg, preferably in the range of about 10 μg / kg to 100 mg / kg. The above dose of the drug may be administered once a day, or may be divided into several times (for example, about 2 to 4 times).
本発明の薬剤の投与量は患者の年齢、性別、体重、症状、及び投与経路などの条件に応じて適宜増減されるべきであるが、一般的には、成人一日あたりの有効成分の量として1μg/kgから1,000mg/kg程度の範囲であり、好ましくは10μg/kgから100mg/kg程度の範囲である。上記投与量の薬剤は一日一回に投与してもよいし、数回(例えば、2~4回程度)に分けて投与してもよい。 The agent of the present invention can be administered to mammals such as humans.
The dose of the drug of the present invention should be appropriately increased or decreased according to conditions such as the patient's age, sex, body weight, symptom, and route of administration. Generally, the amount of the active ingredient per adult day In the range of about 1 μg / kg to 1,000 mg / kg, preferably in the range of about 10 μg / kg to 100 mg / kg. The above dose of the drug may be administered once a day, or may be divided into several times (for example, about 2 to 4 times).
以下の実施例により本発明を具体的に説明するが、本発明は実施例によって限定されることはない。
The present invention will be specifically described by the following examples, but the present invention is not limited to the examples.
実施例1:cPAがラット海馬における一過性脳虚血後の遅発性神経細胞死に及ぼす効果
方法
実験は、20匹の成熟雄ウィスター系ラット(体重280-370g)で行った。
脳虚血及び組織学的解析の方法は、基本的にKagitani,F., Uchida,S., Hotta,H, and Sato,A (2000) Effects fo nicotine on blood flow and delayed neuronal death fllowing internittent transient ischemia in rat hippocampus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 50, 585-595に従い、以下に述べるように一部改変した。動物をハロセン(麻酔の導入時3.5%:手術および虚血中1.5%)で麻酔した。抗生物質を投与(viccillin 50mg/kg 筋注)し、環状ホスファチジン酸投与用の浸透圧ポンプを腹部皮下へ埋め込んだ。続いて気管挿管し、呼吸を人工呼吸器(SN-480-7, Shinano, 東京)を用いて維持した。直腸温および側頭筋温をモニターし、ヒートパッドとランプ(ATB-1100, 日本光電工業、東京)を用いて両者とも約37.5℃に維持した。両側椎骨動脈を永久結紮し、両側総頚動脈を8分間一過性に閉塞した。一過性脳虚血終了直後にハロセンを切り、15分後に人工呼吸器をはずした。 Example 1 Method of Effect of cPA on Delayed Neuronal Cell Death After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Rat Hippocampus Experiments were performed on 20 adult male Wistar rats (weight 280-370 g).
The method of cerebral ischemia and histological analysis is basically Kagitani, F., Uchida, S., Hotta, H, and Sato, A (2000) Effects fo nicotine on blood flow and delayed neuronal death fllowing internittent transient ischemia. In rat hippocampus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 50, 585-595, some modifications were made as described below. The animals were anesthetized with halothane (3.5% at the induction of anesthesia: 1.5% during surgery and ischemia). Antibiotics were administered (viccillin 50 mg / kg IM), and an osmotic pump for cyclic phosphatidic acid was implanted subcutaneously in the abdomen. Subsequently, tracheal intubation was performed and breathing was maintained using a ventilator (SN-480-7, Shinano, Tokyo). Rectal temperature and temporal muscle temperature were monitored, and both were maintained at about 37.5 ° C. using a heat pad and lamp (ATB-1100, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo). Bilateral vertebral arteries were permanently ligated and bilateral common carotid arteries were temporarily occluded for 8 minutes. Halosene was cut immediately after the end of transient cerebral ischemia, and the ventilator was removed 15 minutes later.
方法
実験は、20匹の成熟雄ウィスター系ラット(体重280-370g)で行った。
脳虚血及び組織学的解析の方法は、基本的にKagitani,F., Uchida,S., Hotta,H, and Sato,A (2000) Effects fo nicotine on blood flow and delayed neuronal death fllowing internittent transient ischemia in rat hippocampus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 50, 585-595に従い、以下に述べるように一部改変した。動物をハロセン(麻酔の導入時3.5%:手術および虚血中1.5%)で麻酔した。抗生物質を投与(viccillin 50mg/kg 筋注)し、環状ホスファチジン酸投与用の浸透圧ポンプを腹部皮下へ埋め込んだ。続いて気管挿管し、呼吸を人工呼吸器(SN-480-7, Shinano, 東京)を用いて維持した。直腸温および側頭筋温をモニターし、ヒートパッドとランプ(ATB-1100, 日本光電工業、東京)を用いて両者とも約37.5℃に維持した。両側椎骨動脈を永久結紮し、両側総頚動脈を8分間一過性に閉塞した。一過性脳虚血終了直後にハロセンを切り、15分後に人工呼吸器をはずした。 Example 1 Method of Effect of cPA on Delayed Neuronal Cell Death After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Rat Hippocampus Experiments were performed on 20 adult male Wistar rats (weight 280-370 g).
The method of cerebral ischemia and histological analysis is basically Kagitani, F., Uchida, S., Hotta, H, and Sato, A (2000) Effects fo nicotine on blood flow and delayed neuronal death fllowing internittent transient ischemia. In rat hippocampus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 50, 585-595, some modifications were made as described below. The animals were anesthetized with halothane (3.5% at the induction of anesthesia: 1.5% during surgery and ischemia). Antibiotics were administered (viccillin 50 mg / kg IM), and an osmotic pump for cyclic phosphatidic acid was implanted subcutaneously in the abdomen. Subsequently, tracheal intubation was performed and breathing was maintained using a ventilator (SN-480-7, Shinano, Tokyo). Rectal temperature and temporal muscle temperature were monitored, and both were maintained at about 37.5 ° C. using a heat pad and lamp (ATB-1100, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo). Bilateral vertebral arteries were permanently ligated and bilateral common carotid arteries were temporarily occluded for 8 minutes. Halosene was cut immediately after the end of transient cerebral ischemia, and the ventilator was removed 15 minutes later.
ポンプ調製
5, 50μg/mL rac-2ccPA16:1/0.2%脂肪酸フリーのウシ血清アルブミン(BSA)-生理食塩水(0.9% NaCl)、500 μg/mL rac-2ccPA(16:1)/2% BSA-生理食塩水、50, 500μg/mL, 5mg/mL R-cPA18:1/0.2% BSA-生理食塩水を調整し、それぞれMini osmotic pump model 2000 (alzet, CA)に200μlずつ注入した。対照群として、0.2% BSA-生理食塩水、2% BSA-生理食塩水を注入したポンプを調整した。ポンプを虚血手術前に腹腔内に埋め込み、5日間継続皮下投与を行った。 Pump preparation 5, 50μg / mL rac-2ccPA16: 1 / 0.2% fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin (BSA) -saline (0.9% NaCl), 500 μg / mL rac-2ccPA (16: 1) / 2% BSA -Saline, 50, 500 μg / mL, 5 mg / mL R-cPA18: 1 / 0.2% BSA—Saline was prepared and 200 μl each was injected into a Mini osmotic pump model 2000 (alzet, CA). As a control group, a pump infused with 0.2% BSA-saline and 2% BSA-saline was prepared. The pump was implanted into the abdominal cavity before ischemic surgery and administered subcutaneously for 5 days.
5, 50μg/mL rac-2ccPA16:1/0.2%脂肪酸フリーのウシ血清アルブミン(BSA)-生理食塩水(0.9% NaCl)、500 μg/mL rac-2ccPA(16:1)/2% BSA-生理食塩水、50, 500μg/mL, 5mg/mL R-cPA18:1/0.2% BSA-生理食塩水を調整し、それぞれMini osmotic pump model 2000 (alzet, CA)に200μlずつ注入した。対照群として、0.2% BSA-生理食塩水、2% BSA-生理食塩水を注入したポンプを調整した。ポンプを虚血手術前に腹腔内に埋め込み、5日間継続皮下投与を行った。 Pump preparation 5, 50μg / mL rac-2ccPA16: 1 / 0.2% fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin (BSA) -saline (0.9% NaCl), 500 μg / mL rac-2ccPA (16: 1) / 2% BSA -Saline, 50, 500 μg / mL, 5 mg / mL R-cPA18: 1 / 0.2% BSA—Saline was prepared and 200 μl each was injected into a Mini osmotic pump model 2000 (alzet, CA). As a control group, a pump infused with 0.2% BSA-saline and 2% BSA-saline was prepared. The pump was implanted into the abdominal cavity before ischemic surgery and administered subcutaneously for 5 days.
実験群
C1群(比較例):0.2% BSA-生理食塩水(4匹)
C2群(比較例):2% BSA-生理食塩水(2匹)
2ccPA群(本発明):50μg/mL 2ccPA16:1(18μg/kg/5d)、(44 nmol/kg/5d)(4匹)
cPA群(本発明):500μg/mL cPA16:1(180μg/kg/5d)、(400 nmol/kg/5d)(4匹)
参考:2ccPA16:1 (分子量:410.22)、cPA18:1 (分子量:440.23) Experimental group C1 (comparative example): 0.2% BSA-saline (4 animals)
Group C2 (comparative example): 2% BSA-saline (2 animals)
2ccPA group (present invention): 50 μg / mL 2ccPA16: 1 (18 μg / kg / 5d), (44 nmol / kg / 5d) (4 animals)
cPA group (present invention): 500 μg / mL cPA16: 1 (180 μg / kg / 5d), (400 nmol / kg / 5d) (4 mice)
Reference: 2ccPA16: 1 (molecular weight: 410.22), cPA18: 1 (molecular weight: 440.23)
C1群(比較例):0.2% BSA-生理食塩水(4匹)
C2群(比較例):2% BSA-生理食塩水(2匹)
2ccPA群(本発明):50μg/mL 2ccPA16:1(18μg/kg/5d)、(44 nmol/kg/5d)(4匹)
cPA群(本発明):500μg/mL cPA16:1(180μg/kg/5d)、(400 nmol/kg/5d)(4匹)
参考:2ccPA16:1 (分子量:410.22)、cPA18:1 (分子量:440.23) Experimental group C1 (comparative example): 0.2% BSA-saline (4 animals)
Group C2 (comparative example): 2% BSA-saline (2 animals)
2ccPA group (present invention): 50 μg / mL 2ccPA16: 1 (18 μg / kg / 5d), (44 nmol / kg / 5d) (4 animals)
cPA group (present invention): 500 μg / mL cPA16: 1 (180 μg / kg / 5d), (400 nmol / kg / 5d) (4 mice)
Reference: 2ccPA16: 1 (molecular weight: 410.22), cPA18: 1 (molecular weight: 440.23)
光学顕微鏡観察
一過性脳虚血処理後5日目にラットをソムノペンチル深麻酔下で開胸し、ヘパリン含有生理食塩水、続いて10%ホルマリン溶液にて経心臓的還流固定を行った。2時間4度にて保存した後、脳を摘出した。海馬を含む部位を中心に厚さ3mmでスライスし、組織片はさらに4時間室温、10%ホルマリン溶液中にて浸漬固定した。ホルマリン固定の試料をパラフィンに包埋し、厚さ6μmのパラフィン切片を作成した。Bregmaより3.3mm後方の部分にあたる切片をヘマトキシリン・エオジン染色し、左右の海馬CAI領域の錐体細胞を組織学的に観察した。CAI領域の錐体細胞中、核濃縮を呈し、細胞体が萎縮していない生存錐体細胞数を測定し、CAIの長さで割ることでCAI単位長さ当たりの錐体細胞生存数を算出し、さらにCI群の値を1とし各群の値を相対的に表した。 Observation with Light Microscope On the fifth day after treatment with transient cerebral ischemia, the rat was thoracotomized under somnopentyl deep anesthesia, and transcardiac reflux fixation was performed with heparin-containing physiological saline followed by 10% formalin solution. After storage at 4 degrees for 2 hours, the brain was removed. The slice containing a hippocampus was sliced at a thickness of 3 mm, and the tissue pieces were immersed and fixed in a 10% formalin solution at room temperature for 4 hours. A formalin-fixed sample was embedded in paraffin to prepare a 6 μm-thick paraffin section. A section of 3.3 mm behind Bregma was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and the left and right hippocampal CAI region pyramidal cells were observed histologically. Calculate the number of viable pyramidal cells per CAI unit length by measuring the number of viable pyramidal cells in the cone cells in the CAI region that show nuclear enrichment and the cell bodies are not atrophied and divide by the CAI length Further, the value of the CI group was set to 1, and the value of each group was represented relatively.
一過性脳虚血処理後5日目にラットをソムノペンチル深麻酔下で開胸し、ヘパリン含有生理食塩水、続いて10%ホルマリン溶液にて経心臓的還流固定を行った。2時間4度にて保存した後、脳を摘出した。海馬を含む部位を中心に厚さ3mmでスライスし、組織片はさらに4時間室温、10%ホルマリン溶液中にて浸漬固定した。ホルマリン固定の試料をパラフィンに包埋し、厚さ6μmのパラフィン切片を作成した。Bregmaより3.3mm後方の部分にあたる切片をヘマトキシリン・エオジン染色し、左右の海馬CAI領域の錐体細胞を組織学的に観察した。CAI領域の錐体細胞中、核濃縮を呈し、細胞体が萎縮していない生存錐体細胞数を測定し、CAIの長さで割ることでCAI単位長さ当たりの錐体細胞生存数を算出し、さらにCI群の値を1とし各群の値を相対的に表した。 Observation with Light Microscope On the fifth day after treatment with transient cerebral ischemia, the rat was thoracotomized under somnopentyl deep anesthesia, and transcardiac reflux fixation was performed with heparin-containing physiological saline followed by 10% formalin solution. After storage at 4 degrees for 2 hours, the brain was removed. The slice containing a hippocampus was sliced at a thickness of 3 mm, and the tissue pieces were immersed and fixed in a 10% formalin solution at room temperature for 4 hours. A formalin-fixed sample was embedded in paraffin to prepare a 6 μm-thick paraffin section. A section of 3.3 mm behind Bregma was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and the left and right hippocampal CAI region pyramidal cells were observed histologically. Calculate the number of viable pyramidal cells per CAI unit length by measuring the number of viable pyramidal cells in the cone cells in the CAI region that show nuclear enrichment and the cell bodies are not atrophied and divide by the CAI length Further, the value of the CI group was set to 1, and the value of each group was represented relatively.
結果
C1群、C2群ラットの海馬CAI領域の錐体細胞に核濃縮及び細胞体の萎縮を起こしている細胞が観察され、一過性脳虚血処理による遅発性神経細胞死が誘導されていることが観察された。なお、BSAの濃度の違いによる錐体細胞生存率には差がみられなかった。各2ccPA群,cPA群ラットにおいても遅発性神経細胞死が観察されたが、2ccPA群においては、CAI単位長さ当たりの生存細胞の数はC1群よりも2倍多く顕著な遅発性神経細胞死抑制効果がみられた(図1)。 Results Cells with nuclear concentration and cell body atrophy were observed in the pyramidal cells of the hippocampal CAI region of C1 and C2 rats, and delayed neuronal cell death was induced by transient cerebral ischemia treatment. It was observed that There was no difference in the pyramidal cell viability due to the difference in BSA concentration. Delayed neuronal cell death was also observed in each of the 2ccPA group and cPA group rats, but in the 2ccPA group, the number of viable cells per CAI unit length was twice as large as that of the C1 group, and the markedly delayed neuron was observed. A cell death inhibitory effect was observed (FIG. 1).
C1群、C2群ラットの海馬CAI領域の錐体細胞に核濃縮及び細胞体の萎縮を起こしている細胞が観察され、一過性脳虚血処理による遅発性神経細胞死が誘導されていることが観察された。なお、BSAの濃度の違いによる錐体細胞生存率には差がみられなかった。各2ccPA群,cPA群ラットにおいても遅発性神経細胞死が観察されたが、2ccPA群においては、CAI単位長さ当たりの生存細胞の数はC1群よりも2倍多く顕著な遅発性神経細胞死抑制効果がみられた(図1)。 Results Cells with nuclear concentration and cell body atrophy were observed in the pyramidal cells of the hippocampal CAI region of C1 and C2 rats, and delayed neuronal cell death was induced by transient cerebral ischemia treatment. It was observed that There was no difference in the pyramidal cell viability due to the difference in BSA concentration. Delayed neuronal cell death was also observed in each of the 2ccPA group and cPA group rats, but in the 2ccPA group, the number of viable cells per CAI unit length was twice as large as that of the C1 group, and the markedly delayed neuron was observed. A cell death inhibitory effect was observed (FIG. 1).
実施例2:cPAがラット海馬における一過性脳虚血後の遅発性神経細胞死に及ぼす効果
実施例1と同様の化合物(2ccPA16:1、及びcPA18:1)を用いて、実施例1と同様の実験系で、cPAがラット海馬における一過性脳虚血後の遅発性神経細胞死に及ぼす効果を調べた。 Example 2: Effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus Using the same compounds (2ccPA16: 1 and cPA18: 1) as in Example 1, In a similar experimental system, the effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in the rat hippocampus was examined.
実施例1と同様の化合物(2ccPA16:1、及びcPA18:1)を用いて、実施例1と同様の実験系で、cPAがラット海馬における一過性脳虚血後の遅発性神経細胞死に及ぼす効果を調べた。 Example 2: Effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus Using the same compounds (2ccPA16: 1 and cPA18: 1) as in Example 1, In a similar experimental system, the effect of cPA on delayed neuronal cell death after transient cerebral ischemia in the rat hippocampus was examined.
海馬CAI領域の錐体細胞を組織学的に観察した結果を図2に示す。
図2のA(Vehicle投与群)のa、及びB(cPA投与群)のaは、海馬(Bregma -3.3mm)のCA1(矢頭が挟んでいる範囲)の領域を示す。 The result of histological observation of the pyramidal cells in the hippocampal CAI region is shown in FIG.
In FIG. 2, a in A (Vehicle administration group) and B in B (cPA administration group) indicate CA1 (range where the arrowhead is sandwiched) of the hippocampus (Bregma -3.3 mm).
図2のA(Vehicle投与群)のa、及びB(cPA投与群)のaは、海馬(Bregma -3.3mm)のCA1(矢頭が挟んでいる範囲)の領域を示す。 The result of histological observation of the pyramidal cells in the hippocampal CAI region is shown in FIG.
In FIG. 2, a in A (Vehicle administration group) and B in B (cPA administration group) indicate CA1 (range where the arrowhead is sandwiched) of the hippocampus (Bregma -3.3 mm).
図2のA(Vehicle投与群)のb、及びB(cPA投与群)のbは、CA1領域における細胞の状態を示す。小さく濃く染まっているのが核の凝集を起こした細胞、つまり遅発性細胞死を起こした神経細胞であり、大きな丸になっている細胞が生細胞であり、核は細胞の中心に小さく存在することがわかる。A(Vehicle投与群)のbでは、死細胞の数が多く、生存している神経細胞がほぼ見当たらないのに対し、B(cPA投与群)のbでは生きている細胞が主となっており、死んでいる細胞は僅かである。cPA処理により、CA1領域の神経細胞の生存率が大幅に上昇していることがわかる。
2A (Vehicle administration group) b and B (cPA administration group) b in FIG. 2 show the state of cells in the CA1 region. Small and darkly stained cells are cells that have aggregated the nucleus, that is, nerve cells that have undergone delayed cell death. Large round cells are living cells, and the nucleus is small in the center of the cell. I understand that In A (Vehicle administration group) b, the number of dead cells is large and almost no living neurons are found, whereas in B (cPA administration group) b, living cells are mainly used. Only a few cells are dead. It can be seen that the survival rate of neurons in the CA1 region is significantly increased by cPA treatment.
図2のA(Vehicle投与群)のc、及びB(cPA投与群)のcは、GFAP(glial-fibrillary acidic protein)の染色像を示す。GFAPはアストログリアに局在する中間径フィラメントを構成するタンパク質であり、GFAPの発現は、脳損傷、認知症などの神経疾患で増加、症例の重症度に関与すると考えられている。A(Vehicle投与群)のcでは、死細胞の周りにところどころ濃く茶色(anti-GFAP, DAB染色)に染色されている細胞がみられるが、B(cPA投与群)のcでは細胞の周りに濃く染色されている部位はAのcほど見当たらなかった。即ち、cPA投与により、GFAPの産生が抑制されたと考えられる。
In FIG. 2, c of A (vehicle administration group) and B (cPA administration group) of c show stained images of GFAP (glial-fibrillary acidic protein). GFAP is a protein constituting an intermediate filament localized in astroglia, and expression of GFAP is increased in neurological diseases such as brain injury and dementia, and is considered to be involved in the severity of cases. In c of A (Vehicle administration group), there are some dark brown cells (anti-GFAP, DAB staining) around dead cells, but in c of B (cPA administration group) around the cells. The darkly stained sites were not found as much as A's c. That is, it is considered that the production of GFAP was suppressed by cPA administration.
ラットの海馬CA1に存在する生細胞数の数を調べた結果を図3に示す。Control(虚血処理なし)のラットは、420個ほどの神経細胞を持つことが示された。一方、Vehicle(虚血処理後)のラットでは生神経細胞の数は平均48個と1割ほどに減少する。しかしながら、cPA、2ccPAで処理したラットの脳では生細胞の数が顕著に増えることが示された。特に、cPAは濃度依存的に、脳虚血後の遅発性神経細胞死を抑制することが分かり、18μg/kg/5日の投与で、平均253個の細胞が生き残り、6割の細胞が生存したまま残ることが分かった。虚血処理から比べても、5倍ほど生存率が上がったといえる。
The results of examining the number of viable cells present in the rat hippocampal CA1 are shown in FIG. Control (no ischemic) rats were shown to have as many as 420 neurons. On the other hand, in the vehicle (after ischemic treatment) rats, the average number of living neurons is 48, which is about 10%. However, it was shown that the number of living cells was significantly increased in the brains of rats treated with cPA and 2 ccPA. In particular, cPA was found to suppress delayed neuronal cell death after cerebral ischemia in a concentration-dependent manner, with an average of 253 cells surviving and 60% of cells remaining after administration at 18 μg / kg / 5 days. It turns out that it remains alive. Even after the ischemic treatment, it can be said that the survival rate has increased by about 5 times.
Claims (15)
- 環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩を含有する、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤。 An agent for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death caused by transient cerebral ischemia, comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof.
- 環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸が、式(1)で示される化合物である、請求項1に記載の薬剤。
- 一般式(1)において、X及びYが-O-である、請求項1又は2に記載の薬剤。 The drug according to claim 1 or 2, wherein in the general formula (1), X and Y are -O-.
- 一般式(1)において、X又はYが-CH2-である、請求項1又は2に記載の薬剤。 The drug according to claim 1 or 2, wherein in the general formula (1), X or Y is -CH 2- .
- 一般式(1)において、RがC15H29又はC17H33である、請求項1から4の何れか1項に記載の薬剤。 In the general formula (1), R is a C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33, the agent according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
- 環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩を、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を伴う患者に投与することを含む、一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制する方法。 Delayed neuronal cells due to transient cerebral ischemia, comprising administering cyclic phosphatidic acid or carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof to a patient with delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia How to control death.
- 環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸が、式(1)で示される化合物である、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 一般式(1)において、X及びYが-O-である、請求項6又は7に記載の方法。 The method according to claim 6 or 7, wherein in the general formula (1), X and Y are -O-.
- 一般式(1)において、X又はYが-CH2-である、請求項6又は7に記載の方法。 The method according to claim 6 or 7, wherein in the general formula (1), X or Y is -CH 2- .
- 一般式(1)において、RがC15H29又はC17H33である、請求項6から9の何れか1項に記載の方法。 In the general formula (1), R is a C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33, The method according to any one of claims 6 to 9.
- 一過性脳虚血による遅発性の神経細胞死を抑制するための薬剤の製造のための、環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸あるいはその塩の使用。 Use of cyclic phosphatidic acid, carbacyclic phosphatidic acid or a salt thereof for the manufacture of a drug for suppressing delayed neuronal cell death due to transient cerebral ischemia.
- 環状ホスファチジン酸又はカルバ環状ホスファチジン酸が、式(1)で示される化合物である、請求項11に記載の使用。
- 一般式(1)において、X及びYが-O-である、請求項11又は12に記載の使用。 The use according to claim 11 or 12, wherein in the general formula (1), X and Y are -O-.
- 一般式(1)において、X又はYが-CH2-である、請求項11又は12に記載の使用。 The use according to claim 11 or 12, wherein in the general formula (1), X or Y is -CH 2- .
- 一般式(1)において、RがC15H29又はC17H33である、請求項11から14の何れか1項に記載の使用。 In the general formula (1), R is a C 15 H 29 or C 17 H 33, Use according to any one of claims 11 14.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011543320A JP5747263B2 (en) | 2009-11-26 | 2010-11-26 | Neuronal death inhibitor |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009-268225 | 2009-11-26 | ||
| JP2009268225 | 2009-11-26 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011065480A1 true WO2011065480A1 (en) | 2011-06-03 |
Family
ID=44066584
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2010/071127 WO2011065480A1 (en) | 2009-11-26 | 2010-11-26 | Nerve cell death inhibitor |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5747263B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011065480A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013161978A1 (en) * | 2012-04-27 | 2013-10-31 | Sansho株式会社 | Hair growth agent |
| WO2014115885A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-07-31 | 国立大学法人お茶の水女子大学 | Therapeutic agent for demyelinating disease |
| US10385081B2 (en) | 2014-08-12 | 2019-08-20 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000009139A2 (en) * | 1998-08-10 | 2000-02-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods for promoting survival of myelin producing cells |
| JP2002308778A (en) * | 2001-04-13 | 2002-10-23 | Gencom Co | Nerve cell pro-survival agent containing cyclic phosphatidic acid derivative |
| JP2002308779A (en) * | 2001-04-13 | 2002-10-23 | Gencom Co | Agent for promoting propagation, differentiation and/or survival of glia cell, containing cyclic phosphatidic acid |
| JP2002540146A (en) * | 1999-03-25 | 2002-11-26 | イエダ リサーチ アンド デベロップメント カンパニー リミテッド | Pharmaceutical composition containing cyclic glycerophosphate and its analog for promoting neural cell differentiation |
-
2010
- 2010-11-26 JP JP2011543320A patent/JP5747263B2/en active Active
- 2010-11-26 WO PCT/JP2010/071127 patent/WO2011065480A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000009139A2 (en) * | 1998-08-10 | 2000-02-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods for promoting survival of myelin producing cells |
| JP2002540146A (en) * | 1999-03-25 | 2002-11-26 | イエダ リサーチ アンド デベロップメント カンパニー リミテッド | Pharmaceutical composition containing cyclic glycerophosphate and its analog for promoting neural cell differentiation |
| JP2002308778A (en) * | 2001-04-13 | 2002-10-23 | Gencom Co | Nerve cell pro-survival agent containing cyclic phosphatidic acid derivative |
| JP2002308779A (en) * | 2001-04-13 | 2002-10-23 | Gencom Co | Agent for promoting propagation, differentiation and/or survival of glia cell, containing cyclic phosphatidic acid |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| ABE, KOJI: "Therapeutic Potential of Neurotrophic Factors and Neural Stem Cells Against Ischemic Brain Injury", JOURNAL OF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM, vol. 20, 2000, pages 1393 - 1408 * |
| FUJIWARA, YUKO ET AL.: "Cyclic phosphatidic acid elicits neurotrophin-like actions in embryonic hippocampal neurons", JOURNAL OF NEUROCHEMISTRY, vol. 87, no. 5, 2003, pages 1272 - 1283 * |
| GOTOH, MARI ET AL.: "Effects of cyclic phosphatidic acid on delayed neuronal death following transient ischemia in rat hippocampal CA1", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY, vol. 649, no. 1-3, 2010, pages 206 - 209 * |
| HOTTA, HARUMI ET AL.: "Cyclic phosphatidic acid stimulates respiration without producing vasopressor or tachycardiac effects in rats", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY, vol. 543, no. 1-3, 2006, pages 27 - 31 * |
| SHIGENO, TAKU ET AL.: "Amelioration of Delayed Neuronal Death in the Hippocampus by Nerve Growth Factor", THE JOURNAL OF NEUROSCIENCE, vol. 11, no. 9, 1991, pages 2914 - 2919 * |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013161978A1 (en) * | 2012-04-27 | 2013-10-31 | Sansho株式会社 | Hair growth agent |
| JPWO2013161978A1 (en) * | 2012-04-27 | 2015-12-24 | Sansho株式会社 | Hair restorer |
| WO2014115885A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-07-31 | 国立大学法人お茶の水女子大学 | Therapeutic agent for demyelinating disease |
| US20150352132A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2015-12-10 | Ochanomizu University | Therapeutic agent for demyelinating disease |
| JP6007264B2 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2016-10-12 | 国立大学法人お茶の水女子大学 | Demyelinating disease treatment |
| US10413559B2 (en) | 2013-01-28 | 2019-09-17 | Ochanomizu University | Method for treating demyelinating disease |
| US10385081B2 (en) | 2014-08-12 | 2019-08-20 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
| EP3492479A3 (en) * | 2014-08-12 | 2019-10-02 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
| US10774100B2 (en) | 2014-08-12 | 2020-09-15 | Otsuka Checmial Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
| US10941169B2 (en) | 2014-08-12 | 2021-03-09 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
| US11168101B2 (en) | 2014-08-12 | 2021-11-09 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | Crystal of cyclic phosphonic acid sodium salt and method for manufacturing same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5747263B2 (en) | 2015-07-08 |
| JPWO2011065480A1 (en) | 2013-04-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU707779B2 (en) | Substituted liposaccharides useful in the treatment and prevention of endotoxemia | |
| JP2003528146A (en) | Treatment of cerebrovascular disease | |
| EP1402894B1 (en) | Cancerous metastasis inhibitors containing carbacyclic phosphatidic acid derivatives | |
| JP5747263B2 (en) | Neuronal death inhibitor | |
| EP2098237B1 (en) | Analgesic agent comprising cyclic phosphatidic acid derivative | |
| JP2002514185A (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating obsessive-compulsive disorder using NAALADase inhibitors | |
| JP2015515496A (en) | Pantothenic acid derivatives for the treatment of disorders of the nervous system | |
| EP0016310A1 (en) | Monophosphonate compounds, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them | |
| EP0201623B1 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of involutional brian syndromes and mental decay | |
| JP6007264B2 (en) | Demyelinating disease treatment | |
| RU2646457C2 (en) | Therapeutic agent for arthrose | |
| US9328128B2 (en) | Arylfluorophosphate inhibitors of intestinal apical membrane sodium/phosphate co-transport | |
| JP6864899B2 (en) | Injury remedy | |
| KR20060028630A (en) | Inositol polyphosphate derivatives and methods of using same | |
| EP3568138A1 (en) | Compositions and methods for the treatment of myelin related and inflammation related diseases or disorders | |
| KR900006132B1 (en) | Gem - dihalo - 1,8 -diamino - 4- aza - octane | |
| EP0149847A2 (en) | Therapeutic and preventive agent containing dolichol | |
| US4603126A (en) | Therapeutic and preventive agent containing dolichol | |
| JP2714678B2 (en) | Prevention and treatment of ischemic organ damage | |
| CN112218878A (en) | NTCP inhibitors | |
| CN116710105A (en) | Therapeutic agent for pulmonary fibrosis | |
| JP2009167137A (en) | Pharmaceutical comprising phenylalkanoic acid derivative | |
| KR20000048499A (en) | Inositol polyphosphate derivatives and methods of using same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10833326 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2011543320 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 10833326 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |