WO2010023951A1 - セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラム - Google Patents
セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010023951A1 WO2010023951A1 PCT/JP2009/004239 JP2009004239W WO2010023951A1 WO 2010023951 A1 WO2010023951 A1 WO 2010023951A1 JP 2009004239 W JP2009004239 W JP 2009004239W WO 2010023951 A1 WO2010023951 A1 WO 2010023951A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- processing
- encryption
- decryption
- network protocol
- authentication
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/04—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks
- H04L63/0428—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
Definitions
- IP secure communication is common as a means for encrypting information flowing on a network.
- IPsec that performs encrypted communication is standardized as a standard function in RFC (Request For Comment).
- server In order to perform IP secure communication, it is necessary to execute encryption / decryption authentication processing, which is a high load processing, in real time. For this reason, in IP secure communication, special hardware that performs cryptographic authentication (hereinafter referred to as “server” or “router” or the like) is required to achieve high speed, or when realized with a weak machine such as an embedded device. It may implement
- the pre-processing of the second packet can not be performed unless the post-processing of the first packet is performed in advance.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining communication stack processing when HW encryption authentication is performed
- FIG. 1A shows normal communication stack processing
- FIG. 1B shows communication stack processing when HW encryption authentication is performed.
- the communication stack unit 11 executes layer processing 1 and layer processing 2 via the buffer 12 in response to a transmission instruction or reception interrupt.
- the HW preprocessing unit 22 acquires a request from the queue 24 (see (3)), and issues an HW processing request to the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 14 according to the acquired request (see (4)).
- the two processes are executed discontinuously, only the first half of the stack with high priority may be continuously executed at the time of packet burst reception, and the second half may not be executed indefinitely.
- the load on the CPU and the HW engine may be uneven, and as a result, the throughput of packet transmission may be reduced.
- the context of layer processing 2 is completed after the context of layer processing 1 ends. There is a gap in time to start and performance is reduced. Further, as shown in FIG. 3, the request for the next packet can not be transmitted until the HW post-processing unit 23 is activated by the delay process start instruction (see (5)). There is a problem that the utilization efficiency falls, the performance falls, and the queue overflows.
- a secure communication apparatus comprises communication means for transmitting and receiving communication packets, network protocol processing means for performing first half processing and second half processing of network protocol, encryption / decryption authentication processing means for performing encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing, and The processing result of the packet for which the encryption / decryption processing or the authentication processing has been completed is acquired from the decryption authentication processing means, and the latter half process of the network protocol of the packet and the first half process of the network protocol of the next packet are continuously performed. And an encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit that controls the network protocol processing unit.
- the present invention is a program for causing a computer to execute each step of the secure communication method.
- the present invention by realizing processing to the upper layer in the same context, it is possible to perform encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing in which load deviation of a CPU or HW engine is less likely to occur without overhead due to processing division. It is possible to realize high-speed encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing including network protocol processing in secure communication.
- a diagram for explaining communication stack processing when performing conventional HW encryption authentication A diagram showing a detailed configuration of a cryptographic authentication processing unit of a conventional secure communication device Timing chart showing operation timings of the encryption authentication processing unit and the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit of the conventional secure communication device
- Overall configuration diagram described at the protocol level to explain the basic idea of the present invention Diagram showing load leveling to explain the basic idea of the present invention
- Diagram showing a high-speed control method using load leveling to explain the basic concept of the present invention A diagram showing a configuration of a secure communication device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention
- a block diagram showing a configuration of a secure communication device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention Control sequence diagram for explaining the operation at the time of secure communication processing when the secure communication device according to the second embodiment functions as the receiving side Control sequence diagram for explaining the operation at the time of secure communication processing by the secure communication device according to the second embodiment
- Control sequence diagram for explaining the operation at the time of secure communication processing when the secure communication device according to the third embodiment of the present invention functions as a receiving side Control sequence diagram for explaining the operation at the time of secure communication processing by the secure communication device according to the third embodiment
- the secure communication device 100 is configured to include an IP secure protocol 110, a crypto manager (Crypto Manager) 120, and an HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130.
- the crypto manager 120 generates a request for initializing the HW engine by the processing below the IP layer, generates a request for HW initialization unit 121, acquires and stores the HW encryption / decryption authentication result, and processes above the IP layer And an HW post-processing result storage unit 122 to be delivered to the
- the crypto manager 120 performs network stack processing (stack first half processing) to be performed before pre-processing and post-processing by using load leveling described later and a high-speed control method using this load leveling.
- the two processes are continuously executed without being divided by the encryption / decryption authentication process (pre-processing, HW engine processing, and post-processing) with the network stack processing to be performed (stack second half processing).
- the crypto manager 120 processes the processing (for example, layer processing 1) of the IP secure protocol 110 or higher (for example, layer processing 1) and the processing for IP or lower layers (for example, layer processing 2).
- layer processing 1 the processing for example, layer processing 1
- IP or lower layers for example, layer processing 2.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 transmits a plaintext packet to be transmitted to the communication partner as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard), etc.
- AES Advanced Encryption Standard
- 3DES Triple Data Encryption Standard
- the encryption algorithm is used to encrypt the data, or the authentication information is added using an algorithm such as SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm-1), or both the encryption and the authentication information are added.
- the encrypted packet received from the communication partner is subjected to falsification check based on the added authentication information, or the encrypted packet is decrypted, or both falsification check and decryption are performed.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 outputs the encryption / decryption authentication result to the HW post-processing result storage unit 122 of the crypto manager 120 when the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing by the corresponding HW processing request is finished.
- the crypto manager 120 performs the first half of the stack process and the second half of the stack for the process (for example, layer process 1) of the IP secure protocol 110 or more (for example, layer process 1) and the process for the IP layer or less (for example, layer process 2).
- the processing is continuously executed without being divided by the encryption / decryption authentication processing (pre-processing, HW engine processing, post-processing).
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 performs the encryption / decryption authentication process by the HW according to the HW processing request from the request generation HW initialization unit 121 of the crypto manager 120, and the encryption / decryption authentication result is stored in the HW post-processing result storage unit 122 of the crypto manager 120.
- Output to The processing here corresponds to (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining load leveling
- FIG. 5A shows (1) the first half process, (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication process, and (3) second half process in FIG. 4 when no special control is performed.
- FIG. 5B shows the (1) first half process, (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication process, and (2) second half process of FIG. 4 when load balancing is performed.
- the numbers in "" indicate the arrival order of packets.
- the broken line arrow of the number 150 indicates the timing of the first half process of the network protocol
- the broken line arrow of the number 151 indicates a delay process start instruction based on the HW interrupt context.
- the request generation HW initialization unit 121 performs the first half process of high priority for the packets “1” to “4” in the (1) first half process, 1)-"4" requests are issued to the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 performs the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing of the request for the packet “1” among the issued packets “1” to “4” in the (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- the HW post-processing result storage unit 122 acquires and stores the HW encryption / decryption authentication result for the packet “1” in the second half process of the network protocol (3), and passes it to the process of the IP layer or more. Although illustration is omitted, after that, the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 sequentially performs the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing of the request for the packets “2” to “4” in the (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- the post-processing result storage unit 122 acquires and stores the HW encryption / decryption authentication result for the packets “2” to “4” in the second half processing (3). As shown in FIG.
- the request generation HW initialization unit 121 does not process the next packet “5” to “7” in the (1) first half process only after the processes so far for the packets “1” to “4” end. Request can be issued to the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130.
- the IP secure protocol 110 and the HW post-processing result storage unit 122 acquire and store the HW encryption / decryption authentication result of the packet “2” in the second half processing (3) and perform the second half processing (processing of IP layer or more) of the network protocol .
- the IP secure protocol 110 and the request generation HW initialization unit 121 perform the first half process (process below IP layer) of the network protocol of the packet “3” in the first half process (HWW) of the packet “3” It is issued to the encryption / decryption authentication engine 130.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 performs the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing of the request for the issued packet “3” in (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- the IP secure protocol 110 and the HW post-processing result storage unit 122 acquire and store the HW encryption / decryption authentication result of the packet “3” in the second half processing (3) and perform the second half processing (processing of IP layer or more) of the network protocol .
- the encryption / decryption authentication process is operated at the timing of the first half process of the network protocol, so HW / SW can not be processed in parallel for order maintenance.
- the present invention realizes parallel processing of HW / SW while maintaining the processing order by combining, dividing and rearranging.
- FIG. 6A illustrates the load leveling of FIG. 5B in more detail.
- the IP secure protocol 110 and the request generation HW initialization unit 121 perform “the first half process of the network protocol (process below IP layer)” for the packet “2” in the first half process.
- “encryption / decryption authentication first half processing (request generation and HW initialization)” is performed.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 130 performs the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing of the issued packet “2” request in the (2) HW encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- FIG. 6BC is a diagram for explaining the high speed control method.
- FIG. 6B shows a method A of a high-speed control method for performing high-speed control after load leveling
- FIG. 6C shows a method B of a high-speed control method obtained by further dividing the method A.
- This high-speed control method performs the first half processing and the second half processing in a series of contexts. That is, by combining the last half process (the process after layer 2) of the previous packet and the process (the process of layer 1) of the next packet, the process of the packet is performed without waiting time as a function time.
- Method B of FIG. 6C realizes parallel processing of HW / SW by rearranging the respective processing of method A, thereby achieving higher-speed control.
- the rearrangement of each process is as follows (i)-(iv).
- the second half processing of the above (iv) network protocol is continuously performed, whereby the delay processing start instruction based on the HW interrupt context number 151 is reduced. . That is, when there is a function call by the upper program, the above (i) to (iv) are continuously executed without any loss, so that the delay processing start instruction of the number 151 is not necessary.
- a delay processing start instruction of number 151 is issued in order to generate a HW interrupt and start the second half processing.
- the next packet may arrive before that. In such a case, method B of FIG.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a configuration of a secure communication device of the encryption information communication system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention based on the above basic idea.
- FIG. 8 is a timing chart showing operation timings of the encryption and authentication processing unit 230 and the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240.
- numbers (1) to (6) are symbols for explaining the flow of processing.
- the communication stack unit 210 instructs the encryption authentication processing unit 230 to perform processing in layer process 1 when receiving a transmission instruction or reception interrupt, and the encryption authentication processing unit 230 performs HW encryption / decryption authentication processing An HW processing request is issued to the unit 240.
- the cryptographic authentication processing unit 230 performs the following operation.
- the request control unit 231 places the request in the queue 233 (see (1)). If the request control unit 231 is not in the HW busy state, the request control unit 231 instructs the HW post-processing unit 232 to perform the HW preprocessing (see (2)).
- the HW pre / post processing unit 232 acquires the HW processing result from the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240 (see (3)) and executes the HW post processing.
- the HW pre-processing and post-processing unit 232 instructs the layer processing 2 to perform the second half processing (see (6)).
- the HW post-processing unit 232 acquires the request from the queue 233 (see (4)), and the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240 performs the HW processing request according to the acquired request. Issue (see (5)).
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240 performs the encryption / decryption authentication process by the HW in accordance with the HW processing request (see (5)) from the HW pre / post processing unit 232.
- the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240 generates an HW interrupt context when the encryption / decryption authentication processing by the corresponding HW processing request is completed (see FIG. 8), and instructs the delay processing start instruction based on the HW interrupt context to the HW pre / post processing unit 232 Output to (see (0)).
- the HW post-processing unit 232 acquires the HW processing result from the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240 (see (3)) and executes the HW post-processing. When the HW post-processing ends, the HW post-processing unit 232 instructs the layer processing 2 to perform the latter half processing.
- the communication stack unit 210 executes layer processing 2.
- the cryptographic processing unit 230 executes layer processing 1 and layer 2 in the same context without HW processing latency.
- the HW post-processing unit 232 of the encryption and authentication processing unit 230 performs HW process result acquisition (see (3)) and a second half process instruction (see (6)) when there is a processed request. If a request is accumulated in the queue 233, HW pre-processing (see (4) and (5)) is performed. Further, the HW post-processing unit 232 performs the same processing by looking at the queue 233 also at the time of a delay processing start instruction (see (0)) from the HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 240.
- secure communication apparatus 300 includes upper program 310, network protocol processing unit 320, communication unit 330, encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340, encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350, and encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360. Configured
- the upper program 310, the network protocol processor 320, and the encryption / decryption authentication process controller 340 are executed by the CPU.
- the upper program 310 is an application or another program that is actually trying to transmit and receive encrypted data.
- the network protocol processor 320 receives a command from the encryption / decryption authentication process controller 340 to process the lower layer of the network protocol of the encrypted packet for which the encryption authentication process is completed (a part of the IP protocol process, and the processes thereafter) And instructs the communication unit 330 to transmit the encrypted packet whose processing has been completed.
- the network protocol processor 320 receives the encrypted packet received by the communication unit 330, performs lower layer processing of the network protocol, and encrypts and decrypts the encrypted packet for which processing has been completed, together with the parameters necessary for the encryption / decryption authentication process.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 is requested to perform encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- the communication unit 330 performs transmission processing of an arbitrary packet according to an instruction of the network protocol processing unit 320. Also, the communication unit 330 receives data transmitted by the opposite secure communication device, and transfers the data to the network protocol processing unit 320. Specifically, a network device capable of IP communication such as a wired LAN or a wireless LAN is desirable.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 instructs the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 to encrypt the plaintext / encrypted data stored in the encryption / decryption authentication request based on the encryption / decryption authentication instruction from the network protocol processing unit 320. Perform decryption authentication processing.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 encrypts / decrypts the encryption / decryption authentication process of the encryption / decryption authentication request stored earlier.
- the authentication processing unit 350 is requested, and the encryption / decryption authentication request requested by the network protocol processing unit 320 is stored in the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 stores the encryption / decryption authentication request in the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360 and ends the processing.
- encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 completes encryption / decryption authentication of encryption / decryption authentication request that has already been processed. The process is performed first, and then an encryption / decryption authentication processing request for the encryption / decryption authentication request newly received is issued to the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350.
- the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360 sets a priority for each packet in which the first half process of the network protocol is completed, and stores it as an encryption / decryption authentication request together with parameters necessary for the encryption / decryption process or authentication process.
- the decryption authentication request is delivered to the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 in order of priority.
- the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360 is a queue structure for taking in / out the encryption / decryption authentication request.
- the TOS field is information of 8 bits in length included in the IP header, and the upper 3 bits are IP presence indicating priority.
- the secure communication device 300 functions as a receiver of encrypted packets.
- step S103 the network protocol processor 320 reconstructs the received plaintext data as a plaintext packet for each maximum transmission unit, and performs upper layer processing (such as TCP protocol processing or part of IP protocol processing) of the network protocol.
- upper layer processing such as TCP protocol processing or part of IP protocol processing
- step S105 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 determines whether the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is in process. If the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is in process, the process ends.
- step S106 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 determines whether the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 has already completed the encryption / decryption authentication processing or not.
- step S107 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 causes the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 to execute encryption / decryption authentication completion processing of the encryption / decryption authentication request for which encryption / decryption authentication processing has already been completed.
- the processes from step S105 to step S107 executed by the CPU correspond to, for example, the HW second half process of the (ii) first packet “1” in FIG. 6B.
- step S108 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 determines whether the encryption / decryption authentication request is stored in the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360 or not.
- step S110 the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 starts encryption / decryption authentication processing based on an instruction of the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340.
- the encryption / decryption authentication process is executed asynchronously and does not wait for the completion of the process.
- step S111 if there is the encryption / decryption authentication request for which the encryption / decryption authentication completion processing has been performed in step S107, the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 instructs the network protocol processing unit 320 to perform network protocol second half processing (upper layer processing).
- the upper layer process is instructed to be performed in the same CPU context.
- step S112 the network protocol processor 320 performs lower layer processing of the network protocol, and instructs the communication module 330 to transmit the encrypted packet whose processing has been completed.
- the processes of step S111 and step S112 executed by the CPU correspond to, for example, the processes of layer 2 and thereafter of the (iv) first packet “1” in FIG. 6B.
- step S113 the communication unit 330 transmits the encrypted packet received from the network protocol processing unit 320 to the opposite secure communication device (the opposite secure communication device).
- the first half processing and the second half processing are performed with a series of CPU contexts.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 executes processing of layer 2 and subsequent layers without returning the function only by notifying the request (in other words, in the same CPU context), and then returns the function.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 is executed in one sequence by not returning the function halfway. Therefore, when processing the received packet in the network protocol, the processing up to the upper layer can be realized in the same context without any division of the processing by the encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- step S201 the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 instructs the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 to start the software delay interrupt processing to start the processing of step S202 and subsequent steps.
- step S202 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 determines whether the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is in process. If the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is in process, the process ends.
- step S203 the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 determines whether the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 has already completed the encryption / decryption authentication processing or not.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 sets up the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 in step S206. Specifically, the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 performs encryption / decryption authentication processing using encryption / decryption data stored in the encryption / decryption authentication request and parameters necessary for the encryption / decryption authentication processing. It instructs the part 350.
- step S207 the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 starts encryption / decryption authentication processing based on an instruction of the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340.
- the encryption / decryption authentication process is executed asynchronously and does not wait for the completion of the process.
- step S208 if there is the encryption / decryption authentication request for which the encryption / decryption authentication processing processing has been performed in step S207, the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 instructs the network protocol processor 320 to perform the network protocol second half processing (upper layer processing).
- the network protocol second half processing (upper layer processing)
- step S209 the network protocol processing unit 320 performs lower layer processing of the network protocol, and instructs the communication unit 330 to transmit the encrypted packet whose processing has been completed.
- step S210 the communication unit 330 transmits the encrypted packet received from the network protocol processing unit 320 to the opposite secure communication device (the opposite secure communication device).
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 of the secure communication device 300 causes the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 to complete encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing 1
- the network protocol processor 320 is controlled to acquire the processing result of the previous packet, and to continuously execute the second half of the network protocol of the first packet and the first half of the network protocol of the next packet.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 when the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 is requested by the network protocol processing unit 320 to perform encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing of the next packet after the first half processing of the network protocol, the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 The processing result of the immediately preceding packet for which the decryption processing or the authentication processing is completed is acquired from the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350, and the network protocol processing unit 320 processes the second half processing of the network protocol of the immediately preceding packet. Control.
- the processing up to the upper layer can be realized in the same context without any division of the processing by the encryption / decryption authentication processing.
- the network protocol second half processing of the immediately preceding packet is performed as a network protocol.
- the encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing of the next packet is requested to the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 by the same CPU context.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 processes the immediately preceding packet whose processing has been completed by the completion hardware interrupt context from the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 or the software delay interrupt context.
- the encryption / decryption authentication second half process of acquiring the result from the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is performed, and there is a next packet in which the first half process of the network protocol is completed, the next CPU encryption / decryption process or authentication process
- the first half process of the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 is requested to control the network protocol processing unit 320 to process the second half of the network protocol processing of the immediately preceding packet.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 can be operated at the earlier timing of the first half processing of the network protocol or the completion hardware interrupt (or software delayed interrupt), so that high speed encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing can be performed. Can be implemented.
- the encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 340 performs each processing as (i) the first half of the network protocol of the next packet, (ii) the second half of encryption / decryption authentication of the immediately preceding packet, iii) rearrange processing of next packet encryption / decryption authentication first half processing and (iv) previous packet network protocol second half processing to parallel process network protocol processor 320 and encryption / decryption authentication processor 350 Therefore, parallel processing of HW / SW can be realized while maintaining the processing order by combining, dividing and rearranging.
- a packet for which the first half process of the network protocol has been completed is set with priority for each packet, and is stored as an encryption / decryption authentication request together with parameters necessary for encryption / decryption processing or authentication processing. Since the encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit 360 for transferring requests to the encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 350 in the order of priority is provided, for example, speeding up of transmission / reception packets which must be processed with high priority like AV streaming Can be
- the third embodiment describes another operation example of the secure communication device.
- the hardware configuration of the secure communication device according to the third embodiment of the present invention is the same as the secure communication device 300 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 12 is a control sequence diagram for explaining the operation at the time of secure communication processing when the secure communication device 300 functions as a receiving side.
- the same step numbers are given to steps performing the same processing as the flow shown in FIG. 10, and the description will be omitted.
- step S301 in order to process the encrypted packet received from the opposite secure communication device, the communication unit 330 instructs the start of software delay interrupt processing for performing the processing of step S302 and subsequent steps.
- step S302 the network protocol processor 320 performs lower layer processing (layer processing of part of the IP protocol processing and lower) of the network protocol on the received encrypted packet.
- step S104 to step S111 is the same as the corresponding processing in FIG.
- step S303 the network protocol processor 320 performs upper layer processing (such as TCP protocol processing and part of IP protocol processing) of the network protocol, and stores the plaintext packet whose processing has been completed in the reception buffer of the upper program 310.
- upper layer processing such as TCP protocol processing and part of IP protocol processing
- step S202 to step S208 is the same as the corresponding processing in FIG.
- step S401 the network protocol processor 320 performs upper layer processing (such as TCP protocol processing and part of IP protocol processing) of the network protocol, and stores the plaintext packet whose processing has been completed in the reception buffer of the upper program 310.
- upper layer processing such as TCP protocol processing and part of IP protocol processing
- the same effect as that of the second embodiment, that is, when the received packet is subjected to the network protocol processing, in the same context without division of processing by the encryption / decryption authentication processing Processing up to upper layers can be realized, and high-speed secure reception processing can be realized even between devices such as routers and gateways that require special acceleration, and terminals that have only weak resources such as embedded devices. can do.
- the above description is an illustration of a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and the scope of the present invention is not limited to this.
- the encryption information communication system which performs encryption communication by the IPsec protocol via the IPv6 network
- it may be the IPv network, and if the upper version including the function of the IPv6 network is formulated, this is also possible. It is included.
- Each functional block such as the network protocol processor 320 and the encryption / decryption authentication controller 340 is typically implemented as an LSI which is an integrated circuit. These may be individually made into one chip, or may be made into one chip so as to include some or all. It may be called IC, system LSI, super LSI or ultra LSI depending on the degree of integration.
- the method of circuit integration is not limited to LSI's, and implementation using dedicated circuitry or general purpose processors is also possible.
- a programmable field programmable gate array FPGA
- a reconfigurable processor that can reconfigure connection and setting of circuit cells in the LSI may be used.
- secure communication device and secure communication method are used in the present embodiment, this is for convenience of explanation, and may be an encrypted information communication device, an encrypted information communication system, a security association method, etc. Of course.
- the respective units constituting the secure communication apparatus for example, the type of the network protocol processing unit, the number thereof, the connection method and the like may be used.
- the secure communication method described above is also realized by a program for causing the secure communication method to function.
- This program is stored in a computer readable recording medium.
- the secure communication device, the secure communication method, and the program according to the present invention have an effect that high-speed IP secure communication processing can be performed by software processing or hardware processing, and the secure communication device and the secure communication device It is useful for communication methods etc.
- IP secure protocol 100, 200, 300 secure communication device 110 IP secure protocol 120 crypto manager 130 HW encryption / decryption authentication engine 210 communication stack unit 220 buffer 230 encryption authentication processing unit 231 request control unit 232 HW pre / post processing unit 233 queue 240 HW encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 310 upper program 320 network protocol processing unit 330 communication unit 340 encryption / decryption authentication processing control unit 350 encryption / decryption authentication processing unit 360 encryption / decryption authentication request storage unit
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
- Communication Control (AREA)
Abstract
ネットワークスタック処理を含む高速暗復号認証処理を行うことができるセキュア通信装置。このセキュア通信装置300の暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350から、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うようにネットワークプロトコル処理部320を制御する。
Description
本発明は、セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラムに関する。
ネットワーク上を流れる情報を暗号化するための手段としてIPセキュア通信が一般的である。IPv6においては暗号化通信を行うIPsecが標準機能としてRFC(Request For Comment)において規格化されている。
IPセキュア通信を行うには高負荷処理である暗復号認証処理をリアルタイムに実行する必要がある。このため、IPセキュア通信では、サーバやルータ等のように特別に高速化が求められる場合や、組み込み機器のように非力なマシンで実現する場合、暗号認証処理を行う特別なハードウェア(以後、HWエンジンと呼ぶ)を用いて実現することがある(例えば、特許文献1参照)。なお、以後ハードウェアのことをHWと略記する場合がある。
通常、HWエンジンが暗復号認証処理を行うためには、ソフトウェアによるHWエンジンへのセットアップなどの事前処理と、HWエンジンから演算結果などを取得する事後処理が必要である。したがって、あらかじめ1つめのパケットの事後処理を済まさなければ、2つめのパケットの事前処理を行えないことが一般的である。
特許文献2には、暗復号認証エンジン内に、暗復号ユニットと複数の認証ユニットとを搭載し、それらのユニットをパイプライン処理で動作させることで、1つめのパケットに対する、暗復号ユニットもしくは認証ユニットのどちらか一方における処理が完了した時点で、2つめに対するパケットの事前処理を行えるようにする方法が提案されている。
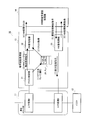
図1は、HW暗号認証を行う場合の通信スタック処理を説明する図であり、図1Aは通常の通信スタック処理を示し、図1BはHW暗号認証を行う場合の通信スタック処理を示す。
図1において、セキュア通信装置10は、レイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2を実行する通信スタック部11と、受信/送信情報を一時的に格納するバッファ12と、HWエンジンにHW処理リクエストを発行して暗号認証処理を実行する暗号認証処理部13とを備えて構成される。
図1Aに示すように、通常の通信スタック処理では、通信スタック部11は、送信指示又は受信割込みによりバッファ12を介してレイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2を実行する。
図1Bに示すように、HW暗号認証を行う場合には、通信スタック部11は、送信指示又は受信割込みを受けると、レイヤ処理1で暗号認証処理部13に処理を指示し、暗号認証処理部13は後述するHW暗復号認証処理部14(図2参照)にHW処理リクエストを発行する。HW暗復号認証処理部14(図2参照)は、このHW処理リクエストを受け取り、HWによる暗復号認証処理を行って暗号認証処理完了の遅延処理を、暗号認証処理部13を介して通信スタック部11に返す。通信スタック部11は、暗号認証処理部13による暗号認証処理結果を受け取り、バッファ12を介してレイヤ処理2を実行する。
通信スタック部11は、レイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2による送受信処理中、HW暗復号認証処理部14(図2参照)による暗復号認証処理を行う場合、前半処理と後半処理を非同期に処理する。通信スタック部11は、前半処理と後半処理とを非同期に処理することで、HW暗復号認証処理部14(図2参照)や図示しないネットワークデバイスの利用効率を高めることができる。
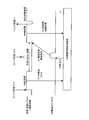
図2は、上記暗号認証処理部13の詳細な構成を示す図である。図3は、上記暗号認証処理部13及びHW暗復号認証処理部14の動作タイミングを示すタイミングチャートである。図2及び図3中、番号(1)-(7)は処理の流れを説明するための符号である。
図2において、セキュア通信装置10は、通信スタック部11と、暗号認証処理部13と、HWエンジンにより暗復号認証処理を実行するHW暗復号認証処理部14とを備えて構成される。また、暗号認証処理部13は、リクエスト制御部21、HW前処理部22、HW後処理部23、及びキュー24を備える。
リクエスト制御部21は、通信スタック部11のレイヤ処理1により暗号認証処理が指示されると、そのリクエストをキュー24に積む((1)参照)。リクエスト制御部21は、HWビジーでない場合にはHW前処理部22にHW前処理を指示する((2)参照)。
HW前処理部22は、キュー24からリクエストを取得し((3)参照)、取得したリクエストに従ってHW暗復号認証処理部14にHW処理リクエストを発行する((4)参照)。
HW暗復号認証処理部14は、暗号認証処理部13からのHW処理リクエストに従ってHWによる暗復号認証処理を行う。HW暗復号認証処理部14は、該当HW処理リクエストによる暗復号認証処理が終わると、HW割込み信号を発生し(図3参照)、このHW割込み信号に基づく遅延処理開始指示をHW後処理部23に出力する((5)参照)。
暗号認証処理部13は、HW暗復号認証処理部14からの遅延処理開始指示を受けてHW後処理を開始する。図3に示すように、レイヤ処理1から見て、HW前処理部22によるHW前処理が終了してHW後処理部23がHW後処理を起動するまでの時間は、HW後処理部23がHW後処理を行えない、利用できない時間となる。暗号認証処理部13は、HW暗復号認証処理部14からHW処理結果を取得して((6)参照)HW後処理を実行する。暗号認証処理部13は、HW後処理を終了すると、レイヤ処理2に後半処理を指示する。暗号認証処理部13は、レイヤ処理2を実行する。これにより、図3に示すように、キュー24から取得したリクエストによる暗号認証処理が終わり、同様にして次のHW前処理が実行される。
しかしながら、このような従来のHW暗号認証方法にあっては、通信スタック部11が、前半処理と後半処理とを非同期に処理することで、HW暗復号認証処理部14やネットワークデバイスの利用効率を高めることができるものの、事前処理の前に行うべきネットワークスタック処理(以下、スタック前半処理という)と、事後処理の後に行うべきネットワークスタック処理(以下、スタック後半処理という)とが、暗復号認証処理(事前処理、HWエンジン処理、及び事後処理)で分断されるため、2つの処理は不連続で実行される。
2つの処理が不連続で実行されると、パケットのバースト受信時に、優先度の高いスタック前半処理のみが連続実行されて後半処理がいつまでも実行されなくなってしまうことがある。このため、CPUやHWエンジンの負荷に偏りが生じ、結果的にパケット伝送のスループットが低下してしまう問題がある。
また、事後処理やスタック後半処理を実行するためのソフトウェア遅延割り込みを起床する必要があるので、余計なオーバーヘッドが発生するという問題もある。
例えば、図2及び図3に示すように、HWによるIPSec処理では、レイヤ処理1とレイヤ処理2のコンテキストが分断されているため、レイヤ処理1のコンテキストが終了してからレイヤ処理2のコンテキストが開始されるまで間が開き、パフォーマンスが低下してしまう。また、図3に示すように、遅延処理開始指示((5)参照)によってHW後処理部23が起動するまで次のパケットのリクエストを送信することができず、HW暗復号認証処理部14の利用効率が下がってパフォーマンスが低下したり、キューがあふれてしまう問題がある。
本発明は、上記に鑑みてなされたものであり、処理分断によるオーバーヘッドなしに、CPUやHWエンジンの負荷の偏りが起こりにくい暗復号処理又は認証処理を行うことができ、ネットワークスタック処理を含む高速暗復号認証処理を行うことができるセキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラムを提供することを目的とする。
本発明のセキュア通信装置は、通信パケットを送受信する通信手段と、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理及び後半処理を行うネットワークプロトコル処理手段と、暗復号処理又は認証処理を行う暗復号認証処理手段と、前記暗復号認証処理手段から、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了しているパケットの処理結果を取得し、前記パケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うように前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段を制御する暗復号認証処理制御手段と、を備える構成を採る。
本発明の暗号化情報通信方法は、通信パケットを送受信するステップと、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理及び後半処理を行うネットワークプロトコル処理ステップと、暗復号処理又は認証処理を行う暗復号認証処理ステップと、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了しているパケットの処理結果を取得し、前記パケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うように制御する制御ステップとを有する。
また他の観点から、本発明は、上記セキュア通信方法の各ステップをコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムである。
本発明によれば、同じコンテキストで上位レイヤまでの処理を実現することにより、処理分断によるオーバーヘッドなしに、CPUやHWエンジンの負荷の偏りが起こりにくい暗復号処理又は認証処理を行うことができ、セキュア通信における、ネットワークプロトコル処理も含めた暗復号処理又は認証処理の高速化を実現することができる。
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
(原理説明)
まず、本発明の基本的な考え方について説明する。
まず、本発明の基本的な考え方について説明する。
図4乃至図6は、本発明の基本的な考え方を説明する図であり、図4はプロトコルレベルで記述した全体構成を、図5は負荷の平準化を、図6は負荷の平準化を用いた高速制御方式をそれぞれ示す。
図4において、セキュア通信装置100は、IPセキュアプロトコル110、クリプトマネージャ(Crypto Manager)120、及びHW暗復号認証エンジン130を備えて構成される。
IPセキュアプロトコル110は、アプリケーション/ミドルソフトウェア(application/middle software)を実行するIP層以上の処理(例えばレイヤ処理1)と、ネットワークデバイスに接続されIP層以下の処理(例えばレイヤ処理2)とを有する。
クリプトマネージャ120は、上記IP層以下の処理によりHWエンジンを初期化するためのリクエストを生成するリクエスト生成HW初期化部121と、HW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、上記IP層以上の処理に渡すHW後処理結果格納部122とを備えている。クリプトマネージャ120は、後述する負荷の平準化と、この負荷の平準化を用いた高速制御方式を用いることにより、事前処理の前に行うべきネットワークスタック処理(スタック前半処理)と、事後処理の後に行うべきネットワークスタック処理(スタック後半処理)とを、暗復号認証処理(事前処理、HWエンジン処理、及び事後処理)で分断することなく、2つの処理を連続して実行する。すなわち、クリプトマネージャ120は、IPセキュアプロトコル110のIP層以上の処理(例えばレイヤ処理1)とIP層以下の処理(例えばレイヤ処理2)に対して、前記図2の従来例の暗号認証処理部13のように、HW前処理部22とHW後処理部23とを非同期で動作させる構成ではなく、2つの処理を連続して実行する。
HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、クリプトマネージャ120のリクエスト生成HW初期化部121からのHW処理リクエストに従って、通信相手に送信する平文パケットを、AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)、3DES(Triple Data Encryption Standard)等の暗号アルゴリズムで暗号化するか、SHA-1(Secure Hash Algorithm-1)等のアルゴリズムを用いて認証情報の付与をするか、暗号化と認証情報の付与の両方をおこなう。同様に、通信相手から受信した暗号パケットを、付与された認証情報を元に改ざんチェックをおこなうか、暗号化されたパケットを復号化するか、改ざんチェックと復号化の両方をおこなう。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、該当HW処理リクエストによるHW暗復号認証処理が終わると、暗復号認証結果をクリプトマネージャ120のHW後処理結果格納部122に出力する。
以下、上述のように構成されたセキュア通信装置100の動作について説明する。
図4中、番号(1)-(3)で示される矢印は処理の流れを示す。
図4に示すように、クリプトマネージャ120は、IPセキュアプロトコル110のIP層以上の処理(例えばレイヤ処理1)とIP層以下の処理(例えばレイヤ処理2)に対して、スタック前半処理とスタック後半処理とを、暗復号認証処理(事前処理、HWエンジン処理、事後処理)で分断することなく連続して実行する。
具体的には、IPセキュアプロトコル110は、IP層以下の処理がネットワークデバイスからの優先度の高い処理をクリプトマネージャ120のリクエスト生成HW初期化部121に渡す。リクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、IP層以下の処理から渡された優先度の高い要求を基に、HWエンジンを初期化するためのリクエストを生成する。ここまでの処理が、(1)ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理(以下、前半処理という)に相当する。
HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、クリプトマネージャ120のリクエスト生成HW初期化部121からのHW処理リクエストに従ってHWによる暗復号認証処理を行い、暗復号認証結果をクリプトマネージャ120のHW後処理結果格納部122に出力する。ここでの処理が、(2)HW暗復号認証処理に相当する。
HW後処理結果格納部122は、HW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、IPセキュアプロトコル110のIP層以上の処理に渡し、このIP層以上の処理はアプリケーション/ミドルソフトウェアの要求に基づくIP層以上の処理を実行する。ここまでの処理が、(3)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理(以下、後半処理という)に相当する。
図5は、負荷の平準化を説明する図であり、図5Aは特別な制御を行わない場合の図4の(1)前半処理、(2)HW暗復号認証処理、(3)後半処理を示し、図5Bは負荷の平準化を行った場合の図4の(1)前半処理、(2)HW暗復号認証処理、(3)の後半処理を示す。また図5中、「」内の数字は、パケットの到着順序を示す。また、番号150の破線矢印は、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理のタイミングを、番号151の破線矢印は、HW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示をそれぞれ示す。
まず、図5Aの特別な制御を行わない場合には、リクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理でパケット「1」-「4」について優先度の高い前半処理を行い、パケット「1」-「4」のリクエストをHW暗復号認証エンジン130に発行する。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、発行されたパケット「1」-「4」のリクエストのうちパケット「1」についてのリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を行う。HW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理でパケット「1」についてHW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、IP層以上の処理に渡す。図示は省略しているが、その後、HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、パケット「2」-「4」についてのリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を順次行い、HW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)後半処理でパケット「2」-「4」についてHW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納する。図5Aに示すように、パケット「1」-「4」についてここまでの処理が終了してはじめて、リクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理で次のパケット「5」-「7」のリクエストをHW暗復号認証エンジン130に発行することができる。
このように、図4の構成を採ったとしても図5Aのように特別な制御を行わない場合には、ビットレート低下や負荷上昇による再生品質低下が考えられる。
そこで、図4の構成に加え図5Bに示す負荷の平準化を行う。
図5Bの負荷の平準化では、まず、IPセキュアプロトコル110とリクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理でパケット「1」のネットワークプロトコルの前半処理(IP層以下の処理)を行い、パケット「1」のリクエストをHW暗復号認証エンジン130に発行する。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、発行されたパケット「1」のリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を行う。IPセキュアプロトコル110とHW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)後半処理でパケット「1」のHW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理(IP層以上の処理)を行う。次いで、IPセキュアプロトコル110とリクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理でパケット「2」のネットワークプロトコルの前半処理(IP層以下の処理)を行い、パケット「2」のリクエストをHW暗復号認証エンジン130に発行する。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、発行されたパケット「2」のリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を行う。IPセキュアプロトコル110とHW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)後半処理でパケット「2」のHW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理(IP層以上の処理)を行う。次いで、IPセキュアプロトコル110とリクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理でパケット「3」のネットワークプロトコルの前半処理(IP層以下の処理)を行い、パケット「3」のリクエストをHW暗復号認証エンジン130に発行する。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、発行されたパケット「3」についてのリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を行う。IPセキュアプロトコル110とHW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)後半処理でパケット「3」のHW暗復号認証結果を取得・格納し、ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理(IP層以上の処理)を行う。
このように、図5Bの負荷の平準化を行うと、図5Aの特別な制御を行わない場合に比べ、(1)前半処理でリクエストが滞留することがなくなるため、処理の均質化及びビットレート低下抑制を図ることができる。
しかし、上述した負荷の平準化では、番号150の破線矢印に示すようにネットワークプロトコルの前半処理のタイミングで暗復号認証処理を動作させるため、順序維持のためにHW/SWを並列処理できない。本発明は、合成・細分化・並び替えにより、処理順序を維持しつつ、HW/SWの並列処理を実現するものである。
図6Aは、図5Bの負荷の平準化をより詳細に説明する図である。
図6Aの負荷の平準化では、IPセキュアプロトコル110とリクエスト生成HW初期化部121は、(1)前半処理でパケット「2」について「ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理(IP層以下の処理)」を行うとともに、「暗復号認証前半処理(リクエスト生成とHW初期化)」を行う。HW暗復号認証エンジン130は、(2)HW暗復号認証処理で、発行されたパケット「2」のリクエストのHW暗復号認証処理を行う。IPセキュアプロトコル110とHW後処理結果格納部122は、(3)後半処理でパケット「2」について「暗復号認証後半処理(HW後処理と結果格納)」を行うとともに、「ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理(IP層以上の処理)」を行う。
図6BCは、本高速制御方式を説明する図である。図6Bは、負荷平準化後に高速制御を行うための高速制御方式の方式Aを、図6Cは、方式Aを更に細分化した高速制御方式の方式Bをそれぞれ示す。
本高速制御方式は、前半処理と後半処理を一連のコンテキストで行う。すなわち、直前のパケットの後半処理(レイヤ2以降の処理)と次のパケットの処理(レイヤ1の処理)とを合体させることで、関数の時間として待ち時間なしでパケットの処理を行う。
図6Bの高速制御方式の方式Aでは、1つ前のパケットの(3)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットの(1)ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理を合体した、(1)(3)前半処理/後半処理を実現する。図6Bの場合、(1)(3)前半処理/後半処理で1つ前のパケット「1」の(3)後半処理と次のパケット「2」の(1)前半処理を合体する。(2)HW暗復号認証処理はそのままである。このため、方式Aの(1)(3)前半処理/後半処理では、 図6Aの番号151の破線矢印に示すHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示よりも先に、図6Bの番号152の破線矢印に示すネットワークプロトコルの前半処理開始のタイミングで(1)(3)前半処理/後半処理を開始できることになる。このため、方式Aは、図6Bの番号152の破線矢印に示すネットワークプロトコルの前半処理開始のタイミングか、図6Aの番号151の破線矢印に示すHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示のうち、いずれか早い方で処理を開始することができ、処理時間を短縮することができる。ここで、(1)前半処理と(3)後半処理の優先度が異なる場合であっても処理が滞ることなくスムーズな処理を実現することができる。
図6Cの方式Bは、方式Aの各処理を並び替えることで、HW/SWの並行処理を実現し、より高速制御を図るものである。各処理の並び替えは以下(i)-(iv)の通りである。
(i)ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理
(ii)暗復号認証後半処理
(iii)暗復号認証前半処理
(iv)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理
上記各処理の並べ替えを具体的に説明すると、図6Cの場合、図6Bのパケット「1」とパケット「2」は以下の並べ替え処理となる。
(ii)暗復号認証後半処理
(iii)暗復号認証前半処理
(iv)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理
上記各処理の並べ替えを具体的に説明すると、図6Cの場合、図6Bのパケット「1」とパケット「2」は以下の並べ替え処理となる。
(i)2番目のパケット「2」の前半処理
(ii)1番目のパケット「1」のHW後半処理
(iii)2番目のパケット「2」のHW前半処理
(iv)1番目のパケット「1」のレイヤ2以降の処理
HW暗復号処理が終わってから実際に後半処理が開始されるまでには若干のロス(余分な処理)がある。なにか別の処理が入ってきたり、またカーネルの処理が含まれる。図6Cの方式Bは、各処理の並び替えにより1つのシーケンスで、上記(i)ネットワークプロトコル前半処理の直後に、上記(ii)暗復号認証後半処理を行う。続いて、上記上記(iii)暗復号認証前半処理の直後に、上記(iv)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理を連続して行うことで、番号151のHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示が削減される。すなわち、上位プログラムによる関数呼び出しがあると、上記(i)-(iv)をロスなしで連続で実行するので、番号151の遅延処理開始指示が必要なくなる。図6Aの負荷の平準化では、HW割り込みが発生して後半処理を開始するために、番号151の遅延処理開始指示が出される。しかし実際には、それよりも前に次のパケットが到着することも有りうる。このような場合、図6Cの方式Bでは、開始指示を待つ前に開始できるようになるので、その分速度改善につながる。パケットの送信指示が先かHW処理完了(割り込みHW割り込み)が先かの競争が行われ、早い方で処理を開始するものである。このように、各処理を並び替えることで、HW/SWの並行処理を実現することができる。
(ii)1番目のパケット「1」のHW後半処理
(iii)2番目のパケット「2」のHW前半処理
(iv)1番目のパケット「1」のレイヤ2以降の処理
HW暗復号処理が終わってから実際に後半処理が開始されるまでには若干のロス(余分な処理)がある。なにか別の処理が入ってきたり、またカーネルの処理が含まれる。図6Cの方式Bは、各処理の並び替えにより1つのシーケンスで、上記(i)ネットワークプロトコル前半処理の直後に、上記(ii)暗復号認証後半処理を行う。続いて、上記上記(iii)暗復号認証前半処理の直後に、上記(iv)ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理を連続して行うことで、番号151のHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示が削減される。すなわち、上位プログラムによる関数呼び出しがあると、上記(i)-(iv)をロスなしで連続で実行するので、番号151の遅延処理開始指示が必要なくなる。図6Aの負荷の平準化では、HW割り込みが発生して後半処理を開始するために、番号151の遅延処理開始指示が出される。しかし実際には、それよりも前に次のパケットが到着することも有りうる。このような場合、図6Cの方式Bでは、開始指示を待つ前に開始できるようになるので、その分速度改善につながる。パケットの送信指示が先かHW処理完了(割り込みHW割り込み)が先かの競争が行われ、早い方で処理を開始するものである。このように、各処理を並び替えることで、HW/SWの並行処理を実現することができる。
(実施の形態1)
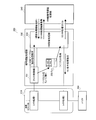
図7は、上記基本的な考え方に基づく本発明の実施の形態1に係る暗号化情報通信システムのセキュア通信装置の構成を示す図である。
図7は、上記基本的な考え方に基づく本発明の実施の形態1に係る暗号化情報通信システムのセキュア通信装置の構成を示す図である。
図7において、セキュア通信装置200は、レイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2を実行する通信スタック部210と、受信/送信情報を一時的に格納するバッファ220と、HWエンジンにHW処理リクエストを発行して暗号認証処理を実行する暗号認証処理部230と、HWエンジンにより暗復号認証処理を実行するHW暗復号認証処理部240とを備えて構成される。また、暗号認証処理部230は、リクエスト制御部231、HW前後処理部232、及びキュー233を備える。
HW前後処理部232は、図6Bの方式A又は図6Cの方式Bにより前半処理と後半処理を一連のコンテキストで行う。HW前後処理部232は、図6Cの方式Bを採用した場合、(i)ネットワークプロトコル前半処理、(ii)暗復号認証後半処理、(iii)暗復号認証前半処理、乃至(iv)ネットワークプロトコル後半処理を連続して行う。具体的には、HW前後処理部232は、取得したリクエストに従ってHW暗復号認証処理部240にHW処理リクエストを発行する((5)参照)一方で、HW暗復号認証処理部240からHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示を受け取り、さらに、HW暗復号認証処理部240からHW処理結果を取得して((6)参照)HW後処理を実行する。ここで、レイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2は、図6Bの各処理の並べ替え処理となる。例えば、(i)2番目のパケット「2」の前半処理、(ii)1番目のパケット「1」のHW後半処理、(iii)2番目のパケット「2」のHW前半処理、乃至(iv)1番目のパケット「1」のレイヤ2以降の処理である。
以下、上述のように構成されたセキュア通信装置200の動作について説明する。
図8は、上記暗号認証処理部230及びHW暗復号認証処理部240の動作タイミングを示すタイミングチャートである。図7及び図8中、番号(1)-(6)は処理の流れを説明するための符号である。
通信スタック部210は、通常の通信スタック処理では、送信指示又は受信割込みによりバッファ120を介してレイヤ処理1及びレイヤ処理2を実行する。レイヤ処理1は、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理であり、TCPプロトコル処理及びIPプロトコル処理の一部を含む優先度の高い上位レイヤ処理である。レイヤ処理2は、ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理であり、IPプロトコル処理の一部やそれ以下のレイヤ処理を含む下位レイヤ処理である。
通信スタック部210は、HW暗号認証を行う場合には、送信指示又は受信割込みを受けると、レイヤ処理1で暗号認証処理部230に処理を指示し、暗号認証処理部230はHW暗復号認証処理部240に対しHW処理リクエストを発行する。
HW暗復号認証処理部240は、このHW処理リクエストを受け取り、HWによる暗復号認証処理を行って暗号認証処理完了の遅延処理を、暗号認証処理部230を介して通信スタック部210に返す。通信スタック部210は、暗号認証処理部230による暗号認証処理結果を受け取り、バッファ220を介してレイヤ処理2を実行する。
具体的には、暗号認証処理部230は、以下の動作を行う。
リクエスト制御部231は、通信スタック部210のレイヤ処理1により暗号認証処理が指示されると、そのリクエストをキュー233に積む((1)参照)。リクエスト制御部231は、HWビジーでない場合にはHW前後処理部232にHW前処理を指示する((2)参照)。
HW前後処理部232は、処理済みのリクエストがあればHW暗復号認証処理部240からHW処理結果を取得して((3)参照)HW後処理を実行する。HW前後処理部232は、HW後処理を終了すると、レイヤ処理2に後半処理を指示する((6)参照)。
また、HW前後処理部232は、キュー233にリクエストが積まれていれば、キュー233からリクエストを取得し((4)参照)、取得したリクエストに従ってHW暗復号認証処理部240にHW処理リクエストを発行する((5)参照)。
HW暗復号認証処理部240は、HW前後処理部232からのHW処理リクエスト((5)参照)に従ってHWによる暗復号認証処理を行う。HW暗復号認証処理部240は、該当HW処理リクエストによる暗復号認証処理が終わると、HW割込みコンテキストを発生し(図8参照)、このHW割込みコンテキストに基づく遅延処理開始指示をHW前後処理部232に出力する((0)参照)。
図8の符号a.で示すように、HW前後処理部232は、HW暗復号認証処理部240からの遅延処理開始指示((0)参照)、又はレイヤ処理1からの指示のうち、いずれか早い方で処理を開始する。HW前後処理部232は、いずれかの指示によりHW前後処理をすぐに実行できるため、レイヤ処理1から見た場合、レイヤ処理1が利用できない時間はなくなる。
HW前後処理部232は、HW暗復号認証処理部240からHW処理結果を取得して((3)参照)HW後処理を実行する。HW前後処理部232は、HW後処理を終了すると、レイヤ処理2に後半処理を指示する。通信スタック部210は、レイヤ処理2を実行する。
図8の符号b.で示すように、暗号認証処理部230は、HW処理待ち時間なしに、レイヤ処理1とレイヤ2を同じコンテキストで実行する。
このように、暗号認証処理部230のHW前後処理部232は、処理済みのリクエストがある場合はHW処理結果取得((3)参照)と後半処理指示((6)参照)を行う。キュー233にリクエストが積まれていれば、HW前処理((4)(5)参照)を行う。また、HW前後処理部232は、HW暗復号認証処理部240からの遅延処理開始指示時((0)参照)も、キュー233を見て同様の処理を行う。
したがって、暗号認証処理部230は、レイヤ処理2以降をレイヤ処理1と同じシーケンスで実行できるので、利用できない時間が減り、パフォーマンスが向上する。従来例では、図3に示すようにHW前処理部22によるHW前処理が終了してHW後処理部23がHW後処理を起動するまでの時間は、HW後処理部23がHW後処理を行えない、利用できない時間となっていた。これに対して、暗号認証処理部230は、遅延処理開始依頼によってHW後処理部23(図2の従来例)を起動するよりも早くHW後処理、次のHW処理リクエストを実行することができ、HW暗復号認証処理部240の利用効率を高めることができる。
(実施の形態2)
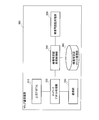
図9は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る暗号化情報通信システムのセキュア通信装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
図9は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る暗号化情報通信システムのセキュア通信装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
図9において、セキュア通信装置300は、上位プログラム310、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320、通信部330、暗復号認証処理制御部340、暗復号認証処理部350、及び暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360を備えて構成される。
上記上位プログラム310、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320及び暗復号認証処理制御部340は、CPUにより実行される。
セキュア通信装置300は、セキュア通信を行う相手側セキュア通信装置と、通信部330により接続され、セキュア通信装置間で通信可能になっている。
上位プログラム310は、実際に暗号化されたデータの送受信を行おうとしているアプリケーション、もしくは、その他のプログラムである。
ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、トランスポート層やネットワーク層などのネットワークプロトコル処理を行う。より具体的には、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、上位プログラム310の指示によって、任意のデータのネットワークプロトコルの上位レイヤ処理(TCPプロトコル処理やIPプロトコル処理の一部等)を行い、処理が完了した平文パケットを、暗復号認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして、暗復号認証処理制御部340に依頼して暗号認証処理を行う。
また、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、暗復号認証処理制御部340からの指示で、暗号認証処理が完了した暗号化パケットのネットワークプロトコルの下位レイヤ処理(IPプロトコル処理の一部やそれ以下の処理等)を行い、通信部330に処理が完了した暗号化パケットの送信処理を指示する。
また、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、通信部330で受信した暗号化パケットを受け取り、ネットワークプロトコルの下位レイヤ処理を行い、処理が完了した暗号化パケットを、暗復号認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして、暗復号認証処理制御部340に依頼して暗号認証処理を行う。
また、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、暗復号認証処理制御部340からの指示で、暗号認証処理が完了した平文パケットのネットワークプロトコルの上位レイヤ処理を行い、上位プログラム310の受信バッファに処理が完了した平文パケットを格納する。
通信部330は、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320の指示で任意のパケットの送信処理を行う。また、通信部330は、対向のセキュア通信装置が送信したデータを受信し、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320に転送する。具体的には、有線LANや無線LANなどの、IP通信が行えるネットワークデバイスが望ましい。
暗復号認証処理制御部340は、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320からの暗復号認証指示に基づき、暗復号認証リクエストに格納されている平文・暗号化データを、暗復号認証処理部350に指示して暗復号認証処理を行う。
また、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に暗復号認証リクエストが格納されている場合には、先に格納されている暗復号認証リクエストの暗復号認証処理を暗復号認証処理部350に依頼し、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320から依頼された暗復号認証リクエストについては暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に格納する。
また、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350が処理中の場合には、暗復号認証リクエストを暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に格納して処理を終了する。
特に、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350から、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うようにネットワークプロトコル処理部320を制御する。
また、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350において既に処理が完了した暗復号認証リクエストが存在する場合には、既に処理が完了している暗復号認証リクエストの暗復号認証完了処理を先に行い、次に新たに指示を受けた暗復号認証リクエストの暗復号認証処理要求を暗復号認証処理部350に対して行う。その後、暗復号認証完了処理を行った暗号データのネットワークプロトコル後半処理(上位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は下位レイヤ処理、下位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は上位レイヤ処理)を同じCPUコンテキストで行うよう、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320に指示し、ネットワークプロトコル後半処理が完了すると、暗復号認証処理制御部340の処理を終了する。処理の詳細については後述する。
暗復号認証処理部350は、暗復号認証処理制御部340の、暗復号認証開始指示によって暗復号認証処理を開始し、暗復号認証処理が完了した時点で暗復号認証処理制御部340に処理完了通知を行う。具体的には、ハードウェア割り込み処理にて起床されたソフトウェア割り込みによって処理完了通知をすることが望ましい。その後、暗復号認証処理制御部340の、暗復号認証完了処理指示によって、結果や付随データを取得するための完了処理を行う。
暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360は、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了したパケットを、パケット毎に優先度を設定し、暗復号処理又は認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして蓄積し、該暗復号認証リクエストを優先度順に前記暗復号認証処理部350に受け渡す。暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360は、暗復号認証リクエストを出し入れするためのキュー構造である。通常FIFO(First-In First-Out)で構成されるが、例えばパケットのTOS(Type of Service)フィールドや、送受信アドレス、送受信ポート、プロトコルなどの情報を元に、デキューする暗復号認証リクエストに優先度をつけるようにするなど、その他の構成であってもよい。なお、TOSフィールドは、IPヘッダに含まれる長さ8ビットの情報であり、上位3ビットが優先度を表示するIPプレシデンスである。
以下、上述のように構成されたセキュア通信装置300の動作について説明する。
まず、セキュア通信装置300が暗号化パケットの受信側として機能する場合について説明する。
図10は、セキュア通信装置300が受信側として機能する場合のセキュア通信処理時の動作を説明する制御シーケンス図である。図10において、上位プログラム310、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320及び暗復号認証処理制御部340は、CPUにより実行される。
ステップS101では、上位プログラム310は、ソケットを生成し、対向のセキュア通信装置のアドレス情報やポート番号をバインドする。
ステップS102では、上位プログラム310は、暗号化したい平文データを、ソケットを通してネットワークプロトコル処理部320に処理を依頼する。
ステップS103では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、受け取った平文データを最大送信単位ごとに平文パケットとして再構成し、ネットワークプロトコルの上位レイヤ処理(TCPプロトコル処理やIPプロトコル処理の一部等)を行う。
ステップS104では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、平文パケットを暗復号認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に格納し、暗復号認証処理制御部340に暗号認証処理を指示する。CPUにより実行されるここまでの処理が、例えば図6Bの(i)2番目のパケット「2」についてのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理に相当する。
ステップS105では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350が処理中でないかを判別する。暗復号認証処理部350が処理中であった場合は、処理を終了する。
ステップS106では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350において既に暗復号認証処理が終了している暗復号認証リクエストがないか否かを判別する。
ステップS107では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350において既に暗復号認証処理が終了している暗復号認証リクエストの暗復号認証完了処理を行う。CPUにより実行されるステップS105乃至ステップS107までの処理が、例えば図6Bの(ii)1番目のパケット「1」のHW後半処理に相当する。
ステップS108では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に暗復号認証リクエストが格納されているか否かを判別する。
暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に暗復号認証リクエストが存在する場合、ステップS109で暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350のセットアップを行う。具体的には、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証リクエストに格納されている平文・暗号化データと暗復号認証処理に必要なパラメータを用いて、暗復号認証処理を暗復号認証処理部350に指示する。CPUにより実行されるステップS108及びステップS109の処理が、例えば図6Bの(iii)2番目のパケット「2」のHW前半処理に相当する。
ステップS110では、暗復号認証処理部350は、暗復号認証処理制御部340の指示に基づき、暗復号認証処理を開始する。ここで、暗復号認証処理は非同期に実行され、処理の完了を待ち合わせることはしない。
ステップS111では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、上記ステップS107において暗復号認証完了処理を行った暗復号認証リクエストがあれば、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320に対して、ネットワークプロトコル後半処理(上位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は下位レイヤ処理、下位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は上位レイヤ処理)を同じCPUコンテキストで行うように指示する。
ステップS112では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、ネットワークプロトコルの下位レイヤ処理を行い、処理が完了した暗号化パケットを送信するように通信部330に指示する。CPUにより実行されるステップS111及びステップS112の処理が、例えば図6Bの(iv)1番目のパケット「1」のレイヤ2以降の処理に相当する。
ステップS113では、通信部330は、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320から受け取った暗号化パケットを対向のセキュア通信装置(相手側セキュア通信装置)に送信する。
このように、ステップS101からステップS112に至るまで、前半処理と後半処理を一連のCPUコンテキストで行う。直前のパケットの後半処理(レイヤ2以降の処理)と次のパケットの処理(レイヤ1の処理)をシームレスに連続させることで、関数の時間としては待ち時間なしでパケットの処理が行えることになる。すなわち、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、リクエストの通知だけで関数をリターンせずにレイヤ2以降の処理を実行して(換言すれば、同じCPUコンテキストにて)、その後に関数をリターンする。暗復号認証処理制御部340が、途中で関数をリターンしないことで1つのシーケンスで実行される。したがって、受信したパケットをネットワークプロトコル処理する際、暗復号認証処理による処理の分断なしに、同じコンテキストで上位レイヤまでの処理を実現することができる。
次に、セキュア通信装置300が、送信側の暗号化情報通信装置である場合を例に動作を説明する。この場合は、暗復号認証処理部350で暗復号認証処理が終了した際の動作に対応する。
図11は、セキュア通信装置300によるセキュア通信処理時の動作を説明する制御シーケンス図である。
ステップS201では、暗復号認証処理部350は、暗復号認証処理制御部340に対してステップS202以降の処理を開始するようソフトウェア遅延割り込み処理の開始を指示する。
ステップS202では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350が処理中でないかを判別する。暗復号認証処理部350が処理中であった場合は、処理を終了する。
ステップS203では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350において既に暗復号認証処理が終了している暗復号認証リクエストがないか否かを判別する。
ステップS204では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350において既に暗復号認証処理が終了している暗復号認証リクエストの暗復号認証完了処理を行う。
ステップS205では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に暗復号認証リクエストが格納されているか否かを判別する。
暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360に暗復号認証リクエストが存在する場合、ステップS206で暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350のセットアップを行う。具体的には、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証リクエストに格納されている平文・暗号化データと暗復号認証処理に必要なパラメータを用いて、暗復号認証処理を暗復号認証処理部350に指示する。
ステップS207では、暗復号認証処理部350は、暗復号認証処理制御部340の指示に基づき、暗復号認証処理を開始する。ここで、暗復号認証処理は非同期に実行され、処理の完了を待ち合わせることはしない。
ステップS208では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、上記ステップS207において暗復号認証完了処理を行った暗復号認証リクエストがあれば、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320に対して、ネットワークプロトコル後半処理(上位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は下位レイヤ処理、下位レイヤ処理から指示を受けている場合は上位レイヤ処理)を同じCPUコンテキストで行うように指示する。
ステップS209では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、ネットワークプロトコルの下位レイヤ処理を行い、処理が完了した暗号化パケットを送信するように通信部330に指示する。
ステップS210では、通信部330は、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320から受け取った暗号化パケットを対向のセキュア通信装置(相手側セキュア通信装置)に送信する。
以上詳細に説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、セキュア通信装置300の暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350から、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うようにネットワークプロトコル処理部320を制御する。例えば、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320から、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理を終えた次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を依頼された際、同じCPUコンテキストにより、直前に暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を暗復号認証処理部350から取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理をネットワークプロトコル処理部320が処理するように制御する。これにより、受信したパケットをネットワークプロトコル処理する際、暗復号認証処理による処理の分断なしに、同じコンテキストで上位レイヤまでの処理を実現することができる。その結果、処理分断によるオーバーヘッドなしに、CPUやHWエンジンの負荷の偏りが起こりにくい暗復号処理又は認証処理を行うことができる。したがって、ルータやゲートウェイなど、特別に高速化が求められる機器や、組み込み機器など非力なリソースしか持たない端末同士であっても、高速なセキュア送信処理を実現することができる。
また、本実施の形態では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、1つ前のパケットの処理結果を暗復号認証処理部350から取得した後、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理をネットワークプロトコル処理部320において処理する前に、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を暗復号認証処理部350に対して依頼する。この構成により、CPUコンテキストの切り替えを行うことなく、1つ目のパケット処理完了後に2つ目のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理の依頼を行うことができ、暗復号処理又は認証処理の高速化を図ることができる。また、暗復号認証処理部350が動作していない時間を最小にすることができ、暗復号処理又は認証処理の高速化や、暗復号認証処理手段の効率的な利用を図ることができる。
また、本実施の形態では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、暗復号認証処理部350からの完了ハードウェア割り込みコンテキスト、又は、ソフトウェア遅延割り込みコンテキストにより、処理が完了した1つ前のパケットの処理結果を暗復号認証処理部350から取得する暗復号認証後半処理を行い、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了した次のパケットがある場合は、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を暗復号認証処理部350に依頼する暗復号認証前半処理を行い、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理をネットワークプロトコル処理部320が処理するように制御する。この構成により、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理、完了ハードウェア割り込み(又はソフトウェア遅延割り込み)のうち、いずれか早いタイミングで暗復号認証処理制御部340を動作させることができ、暗復号処理又は認証処理の高速化を図ることができる。
また、本実施の形態では、暗復号認証処理制御部340は、各処理を、(i)次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理、(ii)1つ前のパケットの暗復号認証後半処理、(iii)次のパケットの暗復号認証前半処理、及び(iv)1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理、の順に並び替えてネットワークプロトコル処理部320と暗復号認証処理部350とを並列処理させるので、合成・細分化・並び替えにより、処理順序を維持しつつ、HW/SWの並行処理を実現することができる。
さらに、本実施の形態では、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了したパケットを、パケット毎に優先度を設定し、暗復号処理又は認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして蓄積し、暗復号認証リクエストを優先度順に暗復号認証処理部350に受け渡す暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部360を備えているので、例えばAVストリーミングのように、高い優先度で処理を行わなければならない送受信パケットの高速化を図ることができる。
(実施の形態3)
実施の形態3は、セキュア通信装置の別の動作例について説明する。
実施の形態3は、セキュア通信装置の別の動作例について説明する。
本発明の実施の形態3に係るセキュア通信装置のハード的構成は、図9に示すセキュア通信装置300と同一構成であるため説明を省略する。
図12は、セキュア通信装置300が受信側として機能する場合のセキュア通信処理時の動作を説明する制御シーケンス図である。図10に示すフローと同一処理を行うステップには同一ステップ番号を付して説明を省略する。
ステップS301では、通信部330は、対向のセキュア通信装置から受信した暗号化パケットを処理するため、ステップS302以降の処理を行うためのソフトウェア遅延割り込み処理の開始指示を行う。
ステップS302では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、受け取った暗号化パケットの、ネットワークプロトコルの下位レイヤ処理(IPプロトコル処理の一部とそれ以下のレイヤ処理)を行う。
ステップS104からステップS111までの処理は図10の対応する処理と同じである。
ステップS303では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、ネットワークプロトコルの上位レイヤ処理(TCPプロトコル処理やIPプロトコル処理の一部等)を行い、処理が完了した平文パケットを上位プログラム310の受信バッファに格納する。
次に、セキュア通信装置300が、送信側の暗号化情報通信装置である場合を例に動作を説明する。この場合は、暗復号認証処理部350で暗復号認証処理が終了した際の動作に対応する。
図13は、セキュア通信装置300によるセキュア通信処理時の動作を説明する制御シーケンス図である。図11に示すフローと同一処理を行うステップには同一ステップ番号を付して説明を省略する。
ステップS201では、暗復号認証処理部350は、暗復号認証処理制御部340に対してステップS202以降の処理を開始するようソフトウェア遅延割り込み処理の開始を指示する。
ステップS202からステップS208までの処理は図11の対応する処理と同じである。
ステップS401では、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320は、ネットワークプロトコルの上位レイヤ処理(TCPプロトコル処理やIPプロトコル処理の一部等)を行い、処理が完了した平文パケットを上位プログラム310の受信バッファに格納する。
このように、本実施の形態のセキュア通信装置によれば、実施の形態2と同様の効果、すなわち受信したパケットをネットワークプロトコル処理する際、暗復号認証処理による処理の分断なしに、同じコンテキストで上位レイヤまでの処理を実現することができ、ルータやゲートウェイなど、特別に高速化が求められる機器や、組み込み機器など非力なリソースしか持たない端末同士であっても、高速なセキュア受信処理を実現することができる。
以上の説明は本発明の好適な実施の形態の例証であり、本発明の範囲はこれに限定されることはない。例えば、IPv6ネットワークを介してIPsecプロトコルにより暗号化通信を行う暗号化情報通信システムに適用可能であるが、IPvネットワークであればよく、IPv6ネットワークの機能を含む上位バージョンが策定された場合はこれも包含するものである。
また、ネットワークプロトコル処理部320、暗復号認証処理制御部340等の各機能ブロックは典型的には集積回路であるLSIとして実現される。これらは個別に1チップ化されてもよいし、一部又は全てを含むように1チップ化されてもよい。集積度の違いにより、IC、システムLSI、スーパーLSI、ウルトラLSIと呼称されることもある。
また、集積回路化の手法はLSIに限るものではなく、専用回路又は汎用プロセッサで実現してもよい。LSI製造後に、プログラムすることが可能なFPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array)や、LSI内部の回路セルの接続や設定を再構成可能なリコンフィギュラブル・プロセッサを利用してもよい。
さらには、半導体技術の進歩又は派生する別技術によりLSIに置き換わる集積回路化の技術が登場すれば、当然、その技術を用いて機能ブロックの集積化を行ってもよい。バイオ技術の適応等が可能性としてありえる。
また、本実施の形態ではセキュア通信装置及びセキュア通信方法という名称を用いたが、これは説明の便宜上であり、暗号化情報通信装置、暗号化情報通信システム、セキュリティアソシエーション方法等であってもよいことは勿論である。
さらに、上記セキュア通信装置を構成する各部、例えばネットワークプロトコル処理部の種類、その数及び接続方法などはどのようなものでもよい。
以上説明したセキュア通信方法は、このセキュア通信方法を機能させるためのプログラムでも実現される。このプログラムはコンピュータで読み取り可能な記録媒体に格納されている。
2008年8月29日出願の特願2008-222554の日本出願に含まれる明細書、図面および要約書の開示内容は、すべて本願に援用される。
以上のように、本発明に係るセキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラムは、ソフトウェア処理、又は、ハードウェア処理によって高速なIPセキュア通信処理を行うことができる効果を有し、セキュア通信機器及びセキュア通信方法等に有用である。
100,200,300 セキュア通信装置
110 IPセキュアプロトコル
120 クリプトマネージャ
130 HW暗復号認証エンジン
210 通信スタック部
220 バッファ
230 暗号認証処理部
231 リクエスト制御部
232 HW前後処理部
233 キュー
240 HW暗復号認証処理部
310 上位プログラム
320 ネットワークプロトコル処理部
330 通信部
340 暗復号認証処理制御部
350 暗復号認証処理部
360 暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部
110 IPセキュアプロトコル
120 クリプトマネージャ
130 HW暗復号認証エンジン
210 通信スタック部
220 バッファ
230 暗号認証処理部
231 リクエスト制御部
232 HW前後処理部
233 キュー
240 HW暗復号認証処理部
310 上位プログラム
320 ネットワークプロトコル処理部
330 通信部
340 暗復号認証処理制御部
350 暗復号認証処理部
360 暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積部
Claims (14)
- 通信パケットを送受信する通信手段と、
ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理及び後半処理を行うネットワークプロトコル処理手段と、
暗復号処理又は認証処理を行う暗復号認証処理手段と、
前記暗復号認証処理手段から、暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了しているパケットの処理結果を取得し、前記パケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うように前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段を制御する暗復号認証処理制御手段と、
を備えるセキュア通信装置。 - 前記暗復号認証処理制御手段は、前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段から、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理を終えた次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を依頼された際、同じCPUコンテキストにより、直前に暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を前記暗復号認証処理手段から取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段が処理するように制御する請求項1記載のセキュア通信装置。
- 前記暗復号認証処理制御手段は、1つ前のパケットの処理結果を前記暗復号認証処理手段から取得した後、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段において処理する前に、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を前記暗復号認証処理手段に対して依頼する請求項1記載のセキュア通信装置。
- 前記暗復号認証処理制御手段は、前記暗復号認証処理手段からの完了ハードウェア割り込みコンテキスト、又は、ソフトウェア遅延割り込みコンテキストにより、処理が完了した1つ前のパケットの処理結果を前記暗復号認証処理手段から取得する暗復号認証後半処理を行い、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了した次のパケットがある場合は、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を前記暗復号認証処理手段に依頼する暗復号認証前半処理を行い、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段が処理するように制御する請求項1記載のセキュア通信装置。
- 前記暗復号認証処理制御手段は、前記各処理を、(i)次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理、(ii)1つ前のパケットの暗復号認証後半処理、(iii)次のパケットの暗復号認証前半処理、及び(iv)1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理、の順に並び替えて前記ネットワークプロトコル処理手段と前記暗復号認証処理手段とを並列処理させる請求項4記載のセキュア通信装置。
- ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了したパケットを、パケット毎に優先度を設定し、暗復号処理又は認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして蓄積し、該暗復号認証リクエストを優先度順に前記暗復号認証処理手段に受け渡す暗復号認証リクエスト蓄積手段をさらに備える請求項1記載のセキュア通信装置。
- 前記ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理は、IPプロトコル処理の一部やそれ以下のレイヤ処理を含む下位レイヤ処理であり、前記ネットワークプロトコルの後半処理は、TCPプロトコル処理及びIPプロトコル処理の一部を含む上位レイヤ処理である請求項1記載のセキュア通信装置。
- 通信パケットを送受信するステップと、
ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理及び後半処理を行うネットワークプロトコル処理ステップと、
暗復号処理又は認証処理を行う暗復号認証処理ステップと、
暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了しているパケットの処理結果を取得し、前記パケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理と次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理とを連続して行うように制御する制御ステップと
を有するセキュア通信方法。 - 前記制御ステップでは、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理を終えた次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を依頼された際、同じCPUコンテキストにより、直前に暗復号処理又は認証処理が完了している1つ前のパケットの処理結果を取得し、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理ステップにおいて処理する請求項8記載のセキュア通信方法。
- 前記制御ステップでは、1つ前のパケットの処理結果を取得した後、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理ステップにおいて処理する前に、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を前記暗復号認証処理ステップに対して依頼する請求項8記載のセキュア通信方法。
- 前記制御ステップでは、前記暗復号認証処理ステップからの完了ハードウェア割り込みコンテキスト、又は、ソフトウェア遅延割り込みコンテキストにより、処理が完了した1つ前のパケットの処理結果を前記暗復号認証処理ステップから取得する暗復号認証後半処理を行い、ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了した次のパケットがある場合は、同じCPUコンテキストにより、次のパケットの暗復号処理又は認証処理を前記暗復号認証処理手段に依頼する暗復号認証前半処理を行い、1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコル後半処理を前記ネットワークプロトコル処理ステップにおいて処理する請求項8記載のセキュア通信方法。
- 前記制御ステップでは、前記各処理を、(i)次のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの前半処理、(ii)1つ前のパケットの暗復号認証後半処理、(iii)次のパケットの暗復号認証前半処理、及び(iv)1つ前のパケットのネットワークプロトコルの後半処理、の順に並び替える請求項11記載のセキュア通信方法。
- ネットワークプロトコルの前半処理が完了したパケットを、パケット毎に優先度を設定し、暗復号処理又は認証処理に必要なパラメータとともに暗復号認証リクエストとして蓄積し、該暗復号認証リクエストを優先度順に前記暗復号認証処理ステップに受け渡すステップをさらに備える請求項8記載のセキュア通信方法。
- 請求項8記載のセキュア通信方法の各ステップをコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラム。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/060,791 US8719902B2 (en) | 2008-08-29 | 2009-08-28 | Secure communication device, secure communication method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008-222554 | 2008-08-29 | ||
| JP2008222554A JP5294761B2 (ja) | 2008-08-29 | 2008-08-29 | セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010023951A1 true WO2010023951A1 (ja) | 2010-03-04 |
Family
ID=41721132
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/004239 WO2010023951A1 (ja) | 2008-08-29 | 2009-08-28 | セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8719902B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5294761B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010023951A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9317689B2 (en) | 2012-06-15 | 2016-04-19 | Visa International Service Association | Method and apparatus for secure application execution |
| US9894143B1 (en) * | 2013-11-06 | 2018-02-13 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Pre-processing and processing pipeline for queue client |
| JP6399382B2 (ja) | 2014-01-08 | 2018-10-03 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 認証システム |
| CN112003689A (zh) * | 2020-08-31 | 2020-11-27 | 北京三未信安科技发展有限公司 | 一种ssl数据包的快速处理方法、系统和电子设备 |
| JP7355073B2 (ja) * | 2021-05-19 | 2023-10-03 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両制御装置、車両、車両制御方法及びプログラム |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002164924A (ja) * | 2000-11-29 | 2002-06-07 | Nec Access Technica Ltd | パケット処理装置 |
| JP2002217951A (ja) * | 2001-01-15 | 2002-08-02 | Sony Corp | 情報処理装置および方法、記録媒体、並びにプログラム |
| JP2002524891A (ja) * | 1998-06-19 | 2002-08-06 | アスアスホー コミュニケーションズ セキュリティ リミティド | フィルタコードを使用するipsecポリシー管理を実行するための方法および装置 |
| JP2008048042A (ja) * | 2006-08-11 | 2008-02-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 暗号装置、復号装置、暗号方法、および復号方法 |
| JP2008512950A (ja) * | 2004-09-10 | 2008-04-24 | カビウム・ネットワークス | パケットのキューイング、スケジューリングおよび順序づけ |
| JP2008310270A (ja) * | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-25 | Panasonic Corp | 暗号装置及び暗号操作方法 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4771458A (en) * | 1987-03-12 | 1988-09-13 | Zenith Electronics Corporation | Secure data packet transmission system and method |
| US6983366B1 (en) | 2000-02-14 | 2006-01-03 | Safenet, Inc. | Packet Processor |
| WO2003021447A1 (en) | 2001-08-31 | 2003-03-13 | Adaptec, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for partially reordering data packets |
| US7409558B2 (en) * | 2004-09-02 | 2008-08-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Low-latency data decryption interface |
| DK1794979T3 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2017-07-24 | Cavium Inc | Selective copying of data structure |
| JP2008270870A (ja) * | 2007-04-16 | 2008-11-06 | Sony Corp | 通信システム、通信装置及び通信方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
-
2008
- 2008-08-29 JP JP2008222554A patent/JP5294761B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2009
- 2009-08-28 US US13/060,791 patent/US8719902B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-08-28 WO PCT/JP2009/004239 patent/WO2010023951A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002524891A (ja) * | 1998-06-19 | 2002-08-06 | アスアスホー コミュニケーションズ セキュリティ リミティド | フィルタコードを使用するipsecポリシー管理を実行するための方法および装置 |
| JP2002164924A (ja) * | 2000-11-29 | 2002-06-07 | Nec Access Technica Ltd | パケット処理装置 |
| JP2002217951A (ja) * | 2001-01-15 | 2002-08-02 | Sony Corp | 情報処理装置および方法、記録媒体、並びにプログラム |
| JP2008512950A (ja) * | 2004-09-10 | 2008-04-24 | カビウム・ネットワークス | パケットのキューイング、スケジューリングおよび順序づけ |
| JP2008048042A (ja) * | 2006-08-11 | 2008-02-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 暗号装置、復号装置、暗号方法、および復号方法 |
| JP2008310270A (ja) * | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-25 | Panasonic Corp | 暗号装置及び暗号操作方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5294761B2 (ja) | 2013-09-18 |
| US8719902B2 (en) | 2014-05-06 |
| US20110162044A1 (en) | 2011-06-30 |
| JP2010057122A (ja) | 2010-03-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11966355B2 (en) | Network adapter with a common queue for both networking and data manipulation work requests | |
| US11171936B2 (en) | Method, device, and system for offloading algorithms | |
| US7266703B2 (en) | Single-pass cryptographic processor and method | |
| US7360076B2 (en) | Security association data cache and structure | |
| JP3990565B2 (ja) | セキュリティ通信パケット処理装置及びその方法 | |
| US9065701B2 (en) | Enhanced serialization mechanism | |
| EP1787212B1 (en) | Packet queuing, scheduling and ordering | |
| EP1192782B1 (en) | Classification engine in a cryptography acceleration chip | |
| EP1791060B1 (en) | Apparatus performing network processing functions | |
| JP2019528604A (ja) | 仮想マルチパスデータトランスポートのためのシステム及び方法 | |
| US20230421627A1 (en) | Technologies for accelerated http processing with hardware acceleration | |
| WO2010023951A1 (ja) | セキュア通信装置、セキュア通信方法及びプログラム | |
| WO2010032533A1 (ja) | ネットワークプロトコル処理システム、及びネットワークプロトコル処理方法 | |
| US11677727B2 (en) | Low-latency MACsec authentication | |
| US7603549B1 (en) | Network security protocol processor and method thereof | |
| JP4346962B2 (ja) | 暗号化通信制御装置 | |
| US8838999B1 (en) | Cut-through packet stream encryption/decryption | |
| CN116436864A (zh) | 一种基于quic协议的部分可靠多路径传输方法 | |
| US20060013397A1 (en) | Channel adapter managed trusted queue pairs | |
| JP2004328359A (ja) | パケット処理装置 | |
| JP2003069555A (ja) | 暗号装置および暗復号処理方法 | |
| JP2004180234A (ja) | 暗号パケット処理装置 | |
| WO2010023950A1 (ja) | 暗号処理装置、暗号処理方法及びプログラム | |
| KR102476159B1 (ko) | Nic로의 보안연결 설정기능 이양방법 및 이를 이용한 nic, 그리고 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체 | |
| Gao et al. | The Case for Transport-Level Encryption in Datacenter Networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09809606 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13060791 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 09809606 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |