WO2008080015A2 - Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor - Google Patents
Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2008080015A2 WO2008080015A2 PCT/US2007/088443 US2007088443W WO2008080015A2 WO 2008080015 A2 WO2008080015 A2 WO 2008080015A2 US 2007088443 W US2007088443 W US 2007088443W WO 2008080015 A2 WO2008080015 A2 WO 2008080015A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- fluoro
- lower alkyl
- group
- optionally substituted
- alkyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *C(C=C1C(*)=C=NC1C#C)=CN Chemical compound *C(C=C1C(*)=C=NC1C#C)=CN 0.000 description 6
- PFLHBLWEOGXXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)O Chemical compound CC(C)(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)O PFLHBLWEOGXXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KELCKSADPTZELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(c1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1)=C Chemical compound CC(c1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1)=C KELCKSADPTZELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KKBBAMKDHPJKNN-UHFFFAOYSA-O COC(C(C1OC)C=CCC1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl)C1=CNC2[NH2+]CCC=C12 Chemical compound COC(C(C1OC)C=CCC1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl)C1=CNC2[NH2+]CCC=C12 KKBBAMKDHPJKNN-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- URAYGQFDPRWONO-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC1C(OCC(CC2)=CC=C2Cl)=CCCC1C(c1c[nH]c2ncccc12)O Chemical compound COC1C(OCC(CC2)=CC=C2Cl)=CCCC1C(c1c[nH]c2ncccc12)O URAYGQFDPRWONO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZLONKEPPEMKOBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(c(C(C1c2cccnc2NC1)=O)ccc1)c1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl Chemical compound COc(c(C(C1c2cccnc2NC1)=O)ccc1)c1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl ZLONKEPPEMKOBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DDEFOLHFKVPOFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(c(O)c1)cc(C=O)c1F Chemical compound COc(c(O)c1)cc(C=O)c1F DDEFOLHFKVPOFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OLVWVOPLCFKINL-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(cc(C=O)c(F)c1)c1OCc1ccccc1 Chemical compound COc(cc(C=O)c(F)c1)c1OCc1ccccc1 OLVWVOPLCFKINL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- POAQFNBBHXYUGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(cc1)cc2c1[nH]c(COC(CC(C(Cc1c[nH]c(NC3)c1C=C3Cl)=C1)F)=C1OC)n2 Chemical compound COc(cc1)cc2c1[nH]c(COC(CC(C(Cc1c[nH]c(NC3)c1C=C3Cl)=C1)F)=C1OC)n2 POAQFNBBHXYUGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODKNZJFSEWIFGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N C[n]1ncc(-c2cc(c(Cc(cc(c(O)c3)F)c3F)c[nH]3)c3nc2)c1 Chemical compound C[n]1ncc(-c2cc(c(Cc(cc(c(O)c3)F)c3F)c[nH]3)c3nc2)c1 ODKNZJFSEWIFGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DJCJHFFRHKGOCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1 Chemical compound Cc1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1 DJCJHFFRHKGOCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KQNBRMUBPRGXSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Clc1ccc(CBr)cc1 Chemical compound Clc1ccc(CBr)cc1 KQNBRMUBPRGXSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WVCOPKJNWQZTKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fc(cc1OCc2nc(cccc3)c3[nH]2)c(Cc2c[nH]c(nc3)c2cc3Br)cc1F Chemical compound Fc(cc1OCc2nc(cccc3)c3[nH]2)c(Cc2c[nH]c(nc3)c2cc3Br)cc1F WVCOPKJNWQZTKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BALBNSFYMXBWNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fc1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1 Chemical compound Fc1cnc2[nH]ccc2c1 BALBNSFYMXBWNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MRZOCAOAMHULLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(c1c[nH]c2ncccc12)c(cccc1OCc(cc2)ccc2Cl)c1OCC(F)F Chemical compound O=C(c1c[nH]c2ncccc12)c(cccc1OCc(cc2)ccc2Cl)c1OCC(F)F MRZOCAOAMHULLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GWUMAKZIHXGJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=Cc(c(Cl)c1)cc(F)c1F Chemical compound O=Cc(c(Cl)c1)cc(F)c1F GWUMAKZIHXGJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RFQNYXIOWVNCHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=Cc(cc1)cc(F)c1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl Chemical compound O=Cc(cc1)cc(F)c1OCc(cc1)ccc1Cl RFQNYXIOWVNCHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OKRYOCRQJQCQEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oc1cc(Cl)c(C=O)cc1F Chemical compound Oc1cc(Cl)c(C=O)cc1F OKRYOCRQJQCQEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSBHJTCAPWOIIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oc1ccc(C=O)cc1F Chemical compound Oc1ccc(C=O)cc1F QSBHJTCAPWOIIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D471/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00
- C07D471/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D471/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/04—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system for ulcers, gastritis or reflux esophagitis, e.g. antacids, inhibitors of acid secretion, mucosal protectants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/02—Nasal agents, e.g. decongestants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/06—Antiasthmatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/08—Bronchodilators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/12—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of the kidneys
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
- A61P17/04—Antipruritics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/02—Drugs for skeletal disorders for joint disorders, e.g. arthritis, arthrosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/08—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/08—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease
- A61P19/10—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease for osteoporosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/12—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for electrolyte homeostasis
- A61P3/14—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for electrolyte homeostasis for calcium homeostasis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- A61P35/02—Antineoplastic agents specific for leukemia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- A61P35/04—Antineoplastic agents specific for metastasis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/04—Immunostimulants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/06—Immunosuppressants, e.g. drugs for graft rejection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/08—Antiallergic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/48—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the pancreatic hormones
- A61P5/50—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the pancreatic hormones for increasing or potentiating the activity of insulin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/04—Inotropic agents, i.e. stimulants of cardiac contraction; Drugs for heart failure
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
Definitions
- the present invention relates to kinases and compounds which modulate kinases, and uses therefor.
- Particular embodiments contemplate disease indications which arc amenable to treatment by modulation of kinase activity by the compounds of the present invention.
- Receptor protein kinases regulate key signal transduction cascades that control or are involved in the control of a plethora of physiological functions including cellular growth and proliferation, cell differentiation, cellular development, cell division, cell adhesion, stress response, short-range contact-mediated axonal guidance, transcription regulation, aberrant mitogenesis, angiogenesis, abnormal endothelial cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions during vascular development, inflammation, lymphohematopoietic stem cell activity, protective immunity against specific bacteria, allergic asthma, aberrant tissue-specific responses to the activation of the JNK signal transduction pathway, cell transformation, memory, apoptosis, competitive activity-dependent synapse modification at the neuromuscular synapse, immunological mediation of disease, and calcium regulation.
- Specific disease states associated with aberrant regulation of protein kinases include, for example without limitation, acrocephalo-syndactyly type I, acute myeloid leukemia, AIDS-induced non-Hodgkm's lymphoma, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, atopic dermatitis, autoimmune diseases, bacterial infection, bladder cancer, cancer of the breast, cancer of the central nervous system, cancer ot the colon, cancer of the endometrium, cancer of the fallopian tube, cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, cancer of the ovary, heart failure, chronic myeloid leukemia, colon carcinoma, colorectal cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Crouzon Syndrome, diabetes, diabetic nephropathy, emphysema, endometriosis, epidermoid cancer f ⁇ brotic disorders, gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST ), glomerulonephritis,
- Compounds are contemplated that are active on protein kinases in general, including, but not limited to, AbI, Aktl , Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHK 1 , c-Raf-1 , Csk, EGFR, EphAl , EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl , FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Flt l , Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Frk, Fyn, Gsk3 ⁇ , Gsk3 ⁇ , HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl , Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl , Ink2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1 , MAP2
- Atty, Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 compounds are active on protein kinases including, but not limited to. Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA, and/or TrkB, including any mutations thereof.
- compounds are of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV as described below.
- Also contemplated in accordance with the present invention are methods for the use of the above-described compounds in treating diseases and conditions associated with regulation of the activity of the above-described kinases.
- the use of compounds for therapeutic methods involving modulation of protein kinases is provided, as well as compounds that can be used for therapeutic methods involving modulation of protein kinases.
- compounds have the structure according to the following Formula I:
- Q has a structure selected from the group consisting of
- Z 2 is N or CR 12 ;
- Z 4 is N or CR 14 ;
- Z 5 is N or CR 15 ;
- Z 6 is N or CR 16 ;
- L 2 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR 1 V %-NR 25 -(CR 10 R 1 '),,->
- Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 p and q are independently 0, 1 , or 2 provided, however, that at least one of p and q is 0, s is 1 or 2,
- A is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, and -S(O) 2 -,
- R a and R b at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of lndrogen, fjuoro, -OH, -NH;, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkvlammo, di-alkylammo, and -NR 8 R 9 , wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, or di-alkylammo arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N
- R a and R b combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo,
- R 1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -C(O)R 7 , -C(S)R 7 , -S(O) 2 R 7 , -C(O)NHR 7 , -C(S)NHR 7 , and -S(O) 2 NHR 7 , wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -NR 8 R 9 , wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower
- R 7 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxv, lower alkylthio, mono-alkyla ⁇ nno, di-alkylammo, and -NR 8 R 9 , provided however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to the N of -C(O)NHIf, -C(S)NHR' or -S(O) 2 NHR 7 is fluoro, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH;, lower
- L at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -(alk) d -X-(alk) b - -(alk) a -NR 25 -(alk) b -, -(alk),-C(X)-(alk) b -, -(alk) a -S(O)-(alk) b -, -(alk) a -S(O) 2 -(alk) b -, -(alk) ⁇ -OC(X)-(alk) b -, -(alk) a -C(X)O-(alk) b -, -(alk) a -C(X)NR 25 -(alk) b -, -(alk) a -S(O) 2 NR 25 -(alk) b -, -(alk) a -NR 25 C(X)-(alk)
- R " at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionall ⁇ substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroarvl
- R ft at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of h>drogcn provided, bowe ⁇ er, that hydrogen is not bound to any of S(O) S(O) 2 , C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted low er alkyl, optionally substituted low er alkenyl provided, however, that when R " ' is optionally substituted lower alkenyl, no alkene carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O) 2 , C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, provided, however, that when R 2 ⁇ is optionally substituted lower alkynyl, no alkyne carbon thereof is bound to N
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl and -OR 15 , each of R 11 and R 13 are independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303
- R 32 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl. and -OR 18 , and
- R 1 * is hydrogen or optionally substituted lower alkyl; provided, however, that the compound is not 3- ⁇ 3-[2-(tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-ethoxyJ-bcnzyl ⁇ - 5-thiophen-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine, which has the structure
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ia:
- Fo ⁇ nula Ia all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, L 2 , Z 2 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 15 , R 17 and R 31 are as defined for Formula I.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkyl thio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R 15 Att
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen
- R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl
- R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl
- the alkyl chain of R " , R" or R 22 when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ib:
- a 1 is -O-, -CR 40 R 41 -, -C(O)- or -NR 48 -;
- Z 12 is N or CR 52 ;
- Z 16 is N or CR 56 ;
- R 40 and R 41 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo; or R 40 and R ' combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alky], lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamm
- U is selected from the group consisting of -NR 48 -, -S-, -O-, -NR 48 CII(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, -OCH(R 49 )-, -C(O)NR 48 -, -S(O) 2 NR 48 -, -CH(R 4 ' J )NR 48 -, -CH(R 49 )O-, -CH(R 49 )S-, -NR 48 C(O)-, and -NR 48 S(O) 2 -;
- R 53 and R 53 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro;
- R 52 and R 56 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy,
- R 49 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl;
- Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalkyl;
- R TO is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, aryl, heteroaryl, and NR 50 R.”, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and wherein aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R 23 ;
- R 50 is hydrogen or lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 ,
- R 21 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 . -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , ⁇ tty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
- R 58 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR 58 , -SR 58 , -NR 48 R 58 , -C(O)OR 58 , -C(O)NR 48 R 58 , or -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 58 is fluoro, and wherein heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, lower alkyl,
- is -CR 40 R '11 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -.
- A is -CR 4 V- Or -C(O)-, preferably Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303
- L 1 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- A is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -, and L, is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ic;
- R 23 , R 39 , Cy, and t are as defined in Formula Ib;
- Z 22 is N or CR 62 ;
- Z 26 is N or CR hh ; r is O, 1 , or 2; and
- R 62 , R 63 , R 65 and R 66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- A is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, and R 62 , R 64 , R 65 and R 66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Id: Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- Formula Id all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, s, Z 2 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 15 , R ⁇ , and R 32 are as defined for Formula I.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R 15 is selected from
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 3 - or -C(O)-
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino.
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- Z 2 is N or CR 12
- Z 6 is N or CR l fi
- R 12 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and -NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and -NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the follow mg sub-generic structure Formula Ie
- Formula Ie all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, s, Z 2 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 15 , and R 12 are as defined for Formula I.
- R 4 and R 6 arc hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- Z 2 is N or CR 12
- Z 6 is N or CR 16
- R 12 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and -NR 21 R' 2 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl
- R 32 is optionally substituted lower alkyl or -OR 18 , where R 18 is as defined for Formula Atty. Dkt No 039363-3303
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula If
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or CR 15 , Zh is N or CR 16 , and R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or CR 15 , Z 6 is N or CR 16 , R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O- -CR d R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- CR 5 , Z 6 is N or CR 16
- R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fhioro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R *1 is hydrogen or lower alkyl
- R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl
- the alkyl chain of R 5 , R 21 or R 22 when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower al
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ig:
- Z 14 is N or CR 54 ;
- R 54 and R 55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain oflower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CII 2 -, and R 54 and R 55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, Atty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303 preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)- more preferably -CH 2 -
- L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ih:
- Formula Ih all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R' 0 , R" and R 33 are as defined for Formula I, and r is 0, 1 , or 2.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or CR 15 , Z 6 is N or CR 16 , and R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycl
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or CR 15 , Z 6 is N or CR 16 , R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cyclo
- Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHj, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino,
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 2 is N or CR 12 , Z 4 is N or CR 14 , Z 5 is N or CR 15 , Z 6 is N or CR 16 , R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R 10 and R 1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro.
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 5 , R 21 or R 22 , when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
- compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ii:
- R 23 , R 39 , Cy and t are as defined for Formula Ib;
- Z 24 is N or CR 64 ;
- Z 25 is N or CR 65 ;
- R M and R 6S are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303 alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- A] is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 2 , R 4 , R 5 and R 6 * are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- Formula II all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein: t is 0, 1 , 2, or 3;
- L 4 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR l0 R ⁇ ) p -NR 25 -(CR I0 R n ) q -,
- R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO 2 , -CR a R b R 26 , and -LR 26 ;
- R is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl
- A, Z 2 , Z 6 , R d , R b , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 10 , R 1 ', R 15 , R 17 , R 25 , R 26 , p, q, X and L are as defined for
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen and R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH. -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 .
- R 48 , R 57 , and R 58 are as defined for Formula Tb.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- R a , R b , and R 1 are as defined for Formula I.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -, R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -Oil, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio,
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH,, -C(O)NII 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituent
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -0-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro
- R 15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, R ftl is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CR a R b - ( -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, R 17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally Atty. Dkt.
- R and R 6 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 2 ", -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 5 , R 21 or R 22 , when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH,
- both ofZ 2 and Z 6 are N, also one of Z 2 or Z $ is N and the other of Z 2 or Zg is CR 12 or CR 16 , preferably Z 2 is CR 17 and Z 6 is CR 16 .
- each R 60 is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents
- the compound is selected from the group consisting of: Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- compounds of Formula II have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ha:
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 3 , -C(O)OII, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR", -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 ,
- R 101 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 3 NR 48 R 57 .
- lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , C(O)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 4 V 7 , cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R 101 , or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 ,
- R 6 '' is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of
- Aj is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -, and R 53 and R 55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -
- L 3 is -NR 43 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- R 40 , R 41 , R 4S and R 49 arc as defined for Formula Ib.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, Ai is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl,
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -, and R 53 and R 55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted Atty, Dkt No.: 039363-3303 lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl,
- A is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH 2 -, and L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R*)-.
- R 48 and R 49 are as defined for Formula Ib.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 .
- -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R 100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -SR 58 ,
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R' 7 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NII 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR", -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of
- R 10 ⁇ is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN 1 -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more Atty. Dkt.
- R l ⁇ l is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 -, C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or
- A is -CH 2 -;
- L 3 is -OCH(R 1 ')-;
- R I O ⁇ is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 4S R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 ;
- Z 12 is CR 52 ;
- Z 16 is CR 5
- both of Z 12 and Z ]6 are N, also one of Z n or Zi 6 is N and the other of Z n or Zi 6 is CR 52 or CR 55 , preferably Z n is CR 52 and Z 16 is CR 56 .
- R 52 and R 56 are as defined for Formula Ib.
- compounds of Formula II have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula lib:
- and t are as defined for Formula Ib; R 100 , R 101 are as defined for Formula Ha; R 63 , R 65 , Z 22 and Z 2 ⁇ are as defined for Formula Ic; and R 70 and R 61 are independently hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NII 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R", -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 37 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consist
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OII, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, ⁇ uoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 4 '- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- A is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 22 is CR 52 , and Z 26 is CR 66 .
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is, 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, A, is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- R 61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R 61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, Ai is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, Z 22 is CR 62 , and Z 26 is CR 66 .
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 37 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NTl 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 5S , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 ;
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 -;
- R 101 is selected from the group consisting of -
- Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 43 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 5i ; Z 22 is CR ⁇ 2 ; and Z 25 is CR 66 .
- both of Z 22 and Z 26 are N, also one of Z 22 or Z 26 is N and the other OfZ 22 or Z 25 is CR 62 or CR 66 , preferably
- Z,- is CR M and Z 66
- compounds have the structure according to the following Formula HI:
- A, Z 4 , Z 5 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , and R 6 are as defined for Formula I; L. 4 is as defined for Formula II; R 80 is C 1 ⁇ J alkyl or C 3 _ 5 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci. 3 alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C 3 ⁇ 5 cycloalkyl; and R 81 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, C 2 .
- R 81 is optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- R 4 and R h are hydrogen and R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 3 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substitu
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen and R 5 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-. preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- R a , R b are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CRV-, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R S1 is optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- R S1 is optionally substituted heteroary
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 37 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, hcterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or
- 039363-3303 group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- R a , R b , and R 1 are as defined for Formula I.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 1 S and R lh are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro
- R 5 is selected from the
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -. or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroary
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroary
- At most two OfZ 4 , Z ⁇ , or Z 5 are N, also at most one of Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 is N, preferably Z 4 is CR 14 , Z ; is CR 15 and Z 6 is CR 16 .
- R ' is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, CY 4 alkyl, fluoro substituted C 2 - 4 alkyl, and -(CH 2 CH 2 O)JR 71 , wherein aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R", -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R", -C(
- cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as a substituent of R 8 ', or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 58 , -SR SS , -NR 48 R 58 , -NR 4S C(O)R 58 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 58 , -S(O)R 58 , -S(O) 2 R 58 , -C(O)R 58 , -C(O)OR 58 , -C(O)NR 48 R 58 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 53 , halogen, lower alkyl, fluor
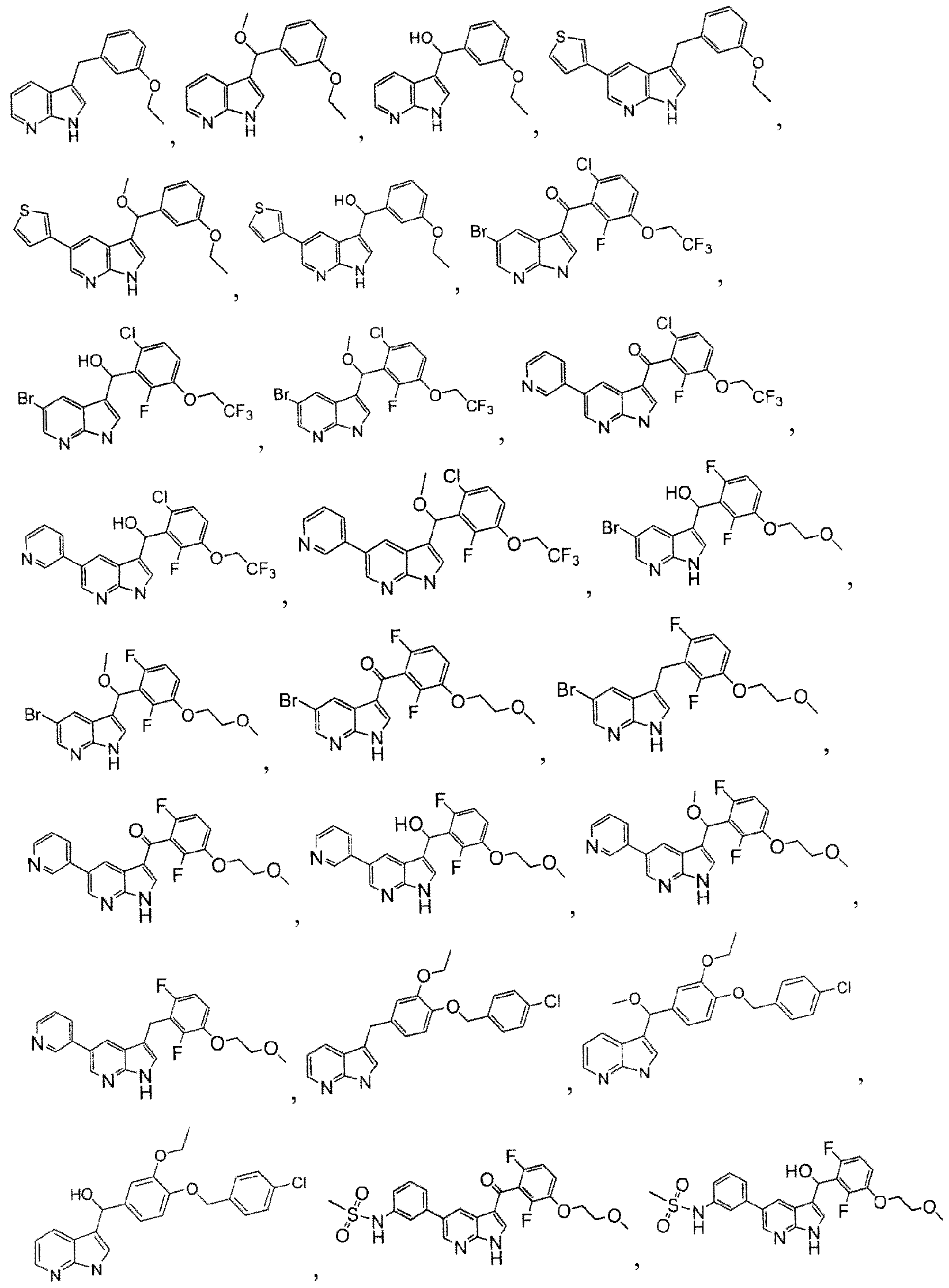
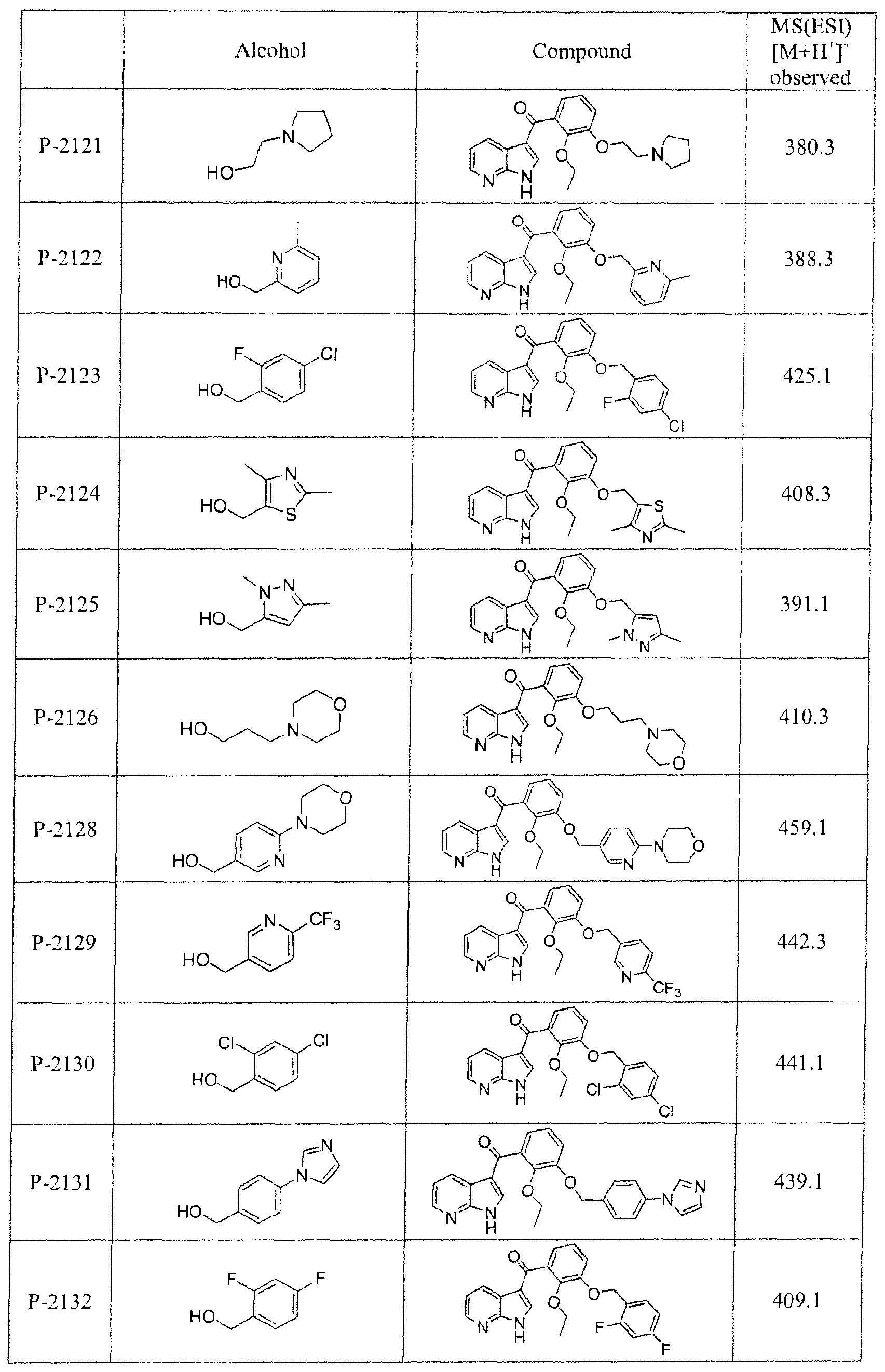
- the compound is selected from the group consisting of: r3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
- compounds of Formula III have the structuie according to the following sub-gene ⁇ c structure Formula Ilia
- Z 14 and Zi 5 are as defined for Formula Ig;
- Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalk>'l;
- L 3a is selected from the group consisting of -NR 48 -, -S-, -O-, -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-,
- R is Ci j alkyl or C 3 ⁇ 5 cycloalkyl, wherein C M alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C 3- , cycloalkyl; and Ai, Zi 6 , R 48 , R 4 , and t are as defined for Formula Ib.
- Cy is heteroaryl
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R", -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoride, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalky
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and R 54 and R 35 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- L 3 is -NR 48 ClI(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- Cy is heteroaryl, ⁇ , is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-.
- Cy is heteroaryl
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-
- R 54 and R 55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- Cy is heteroaryl
- Lj is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- Cy is heteroaryl
- A is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-
- L 3 is -NR 48 CH(R 49 )-, -SCH(R 49 )-, or -OCH(R 49 )-, preferably -OCH(R 49 )-.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 37 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 4 R 37 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OII, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the
- aryl, or heteroaryl as R 100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 58 , -SR 58 , -NHR 58 , -NR 48 R 58 , -NR 48 C(O)R 58 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 58 , -S(O) 2 R 58 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 58 , -C(O)R 58 , -C(O)NR 48 R 58 , halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino;
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-; and R
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NII 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- -NR 48 R 57 -NR 4H C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 43 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 37 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 .
- R 101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 1 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 -, C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , T/US2007/088443
- -S(O) 2 NR R " halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 38 halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- Ai is -C(O)-;
- L 3 is -OCH(R 41 *)-;
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 .
- -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 37 fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
- R 101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 -, C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from
- 5 , or Zi 6 are N and the other of Z 14 , Z 15 , or Z 16 is CR 54 , CR 55 or CR 56 , also one OfZ 14 , Z 15 , or Zi f i is N and the others of Z 14 , Z 15 , or Z 16 are CR 54 , CR 55 or CR 56 , preferably Z 14 is CR 54 , Z 13 is CR 55 and Z )6 is CR 55 .
- compounds of Formula III have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula HIb:
- A, Z 4 , Z 5 , Z 6 , R 4 , R 5 , R h , R 10 , R" and R 33 are as defined for Formula I;
- R 80 is as defined for Formula 111; and
- Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 r is O, 1, or 2.
- R.” is optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- R 4 and R 5 are hydrogen and R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR", -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 37 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -0-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -0-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R 33 is optionally substituted
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 1 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR r , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 1 R", -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R", -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the
- R 4 and R" are hydrogen, ⁇ is -0-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of tluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- R 10 and R 1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl,-CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 3 , R 21 or R 22 , when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkyl
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 1S and R 1 " are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R !0 and
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 10 and R 11 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 ,
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -0-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 10 and R 1 ' are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl
- R 5 is selected from the Atty. Dkt.
- 039363-3303 group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R " is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 5 , R 21 or R 22 , when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH.
- R a , R b , and R 1 are as defined for Formula I.
- two OfZ 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 are N and the other of Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 is CR 14 , CR 15 or CR 16 , also one of Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 is N and the others of Z 4 , Z,, or Z 6 are CR 14 , CR 15 or CR 16 , preferably Z 4 is CR 14 , Z 5 is CR 15 and Z 5 is CR 16 .
- R 33 is aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocycloalkyl, wherein aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2
- NR 48 R 58 halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R 48 , R 57 and R 58 are as defined for Formula Ib.
- Z 4 is CR 14
- Z 5 is CR 15
- Z 6 is CR 10
- R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- compounds of Formula III have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula IHc: Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- Ai, Cy and t are as defined for Formula Ib; R lM and R 101 arc as defined for Formula Ha; R 80 is as defined for Formula Ilia; Z 26 and r are as defined for Formula Ic; and Z 24 and Z 25 are as defined for Formula Ii.
- Cy is heteroaryl
- R luo is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 51 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- Aj is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, and Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- R , R and R ' are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy,
- Cy is heteroaryl, A, is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- Cy is heteroaryl, A, is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, and R M , R 63 and R 66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consist
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR", -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of flu
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 45 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- A is -CH 2 - or -C(O)-;
- R 1Q0 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , tluoro, chloro.
- R 64 , R 65 and R 66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- Aj is -CH 2 - or -C(O)-;
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 3 R 58 ;
- Z 24 is CR 64 ;
- Z 25 is CR 65 ;
- Z 24 , Z 25 , or Z 26 are N and the other of Z 24 , Z 25 , or Z 26 is CR 64 , CR 65 or CR 66 .
- one of Z 24 , Z 25 , or Z 26 is
- Z 24 , Z 25 , or Z 26 are CR M , CR 65 or CR 66 , preferably Z 24 is CR M , Z 25 is CR" and Z 2 is CR 66 .
- compounds have the structure according to the following Formula IV:
- R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , and Z 6 are as defined for Formula I; and R 90 is C 2 ⁇ alkyl, fluoro substituted C M alkyl, or -(CH 2 CH 2 .OO;) m R 91 ; mm iiss 11 ,, 22.. o orr 33;; aanndd
- R 91 is C i _ 3 alkyl or fluoro substituted Cu alkyl, provided, however, the compound is not
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, pretcrably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 12 , R 14 , R 1 ' and R ltl are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluor
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R ⁇ -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 12 , R H , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain ot lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino and cycloalkykmino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- ot Atty.
- lower alkoxy is fluoro
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 5 , R 21 or R 2 , when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono
- R 4 and R 6 are hydrogen
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 1 - or -C(O)-
- R 12 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally
- two Of Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 are N and the others of Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 arc CR 12 , CR 14 , CR 15 or CR 16 , also one of Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 is N and the others of Z 2 , Z 4 , Z 5 , or Z 6 are CR 12 , CR 14 , CR 15 or CR 16 , preferably Z 2 is CR 12 , Z 4 is CR 14 , Z 3 is CR 15 and Z 6 is CR 16 .
- the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
- compounds of Formula IV have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Wa:
- a and R s are as defined for Formula I;
- R 90 is as defined for Formula IV;
- Z 32 is N or CR 72 ;
- Z 34 is N or CR 74 ;
- Z 35 is N or CR 75 ;
- Z 36 is N or CR 76 ;
- R 72 , R 74 , R 75 , and R 7fl are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CII 2 - or -C(O)-.
- A is -O-, -CR"R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, and R 72 , R 14 , R 75 and R' 6 are independently selected from the group consisting of Atty. Dkt.
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 2 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R 3 , R 21 or R 22 .
- R a , R b , and R 1 are as defined for Formula I.
- A is -O-, -CR a R b -, -NR 1 -. or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-
- R 72 , R 74 , R 75 and R 76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 22 , -OR 22 , -S(O) 1 R 22 , and NR 21 R 22 , wherein R 21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R 22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl,
- R a , R b , and R 1 are as defined for Formula I.
- two Of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 are N and the others of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 are CR 72 , CR 74 , CR 75 or CR 76 , also one of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 3 ⁇ , or Z i6 is N and the others of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 are CR 72 , CR 74 , CR 75 or CR 6 , preferably Z 2 is CR 72 , Z 4 is CR 74 , Z 5 is CR 75 and Z 6 is CR 76 .
- compounds have the structure according to the following Formula IVb: Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303
- R 100 is as defined for Formula Ha
- Zj 2 , Zj4, Z 15 , and X ⁇ b are as defined for Formula FVa; and R 90 is as defined for Formula IV.
- a 1 is -CR 40 R 41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-.
- A is -CR 4 V 1 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH 2 - or -C(O)-, and R 72 , R 74 , R 75 and R 76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
- R 00 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR", -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alk
- Ai is -CH 2 - or -C(O)-;
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R 57 , -S(O)R 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substitu
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl.
- heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 .
- Ai is -CH 2 - or -C(O)-;
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 ; and R 72 , R 74 , R 75 and R 76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl
- Aj is -CH 2 - or -C(O)-;
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -CN, -NO 2 , -C(O)OH, -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(O)NH 2 , -OR 57 , -SR 57 , -NR 48 R 57 , -NR 48 C(O)R 57 , -NR 48 S(O) 2 R", -S(O)R 37 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , -C(O)R 57 , -C(O)OR 57 , -C(O)NR 48 R 57 , -S(O) 2 NR 48 R 57 , halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substitute
- R 100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR S7 , -NR 48 R 57 , -OR 57 , -S(O) 2 R 57 , fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR 48 R 58 , -OR 58 and -S(O) 2 R 58 ; Z 32 is CR 72 ; Z 34 is CR 74 ; Z 3J is
- two OfZ 32 , Z 34 , Z 15 , or Z 36 are N and the others of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 are CR 72 , CR 74 , CR 75 or CR 76 , also one Of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 is N and the others of Z 32 , Z 34 , Z 35 , or Z 36 are CR 72 , CR ⁇ 4 , CR 75 or CR "6 , preferably Z 2 is CR 72 , Z 4 is CR 74 , Z 5 is CR 75 and Z 6 is CR 76 .
- compounds are excluded where N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, or S is bound to a carbon that is also bound to N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, or S except where the carbon forms a double bond with one of the heteroatoms, such as in an amide, carboxylic acid, and the like; or where N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, C(S), C(O), or S(O) n (n is 0-2) is bound to an alkene carbon of an alkenyl group or bound to an alkyne carbon of an alkynyl group; accordingly, in some embodiments compounds which include linkages such as the following are excluded from the compounds provided: -NR-CH 2 -NR-, -0-CII 2 -NR-, -S-CH 2 -NR-, -NR-CH 2 -O-, -0-CH 2 -O-, -S-
- a compound of Formula I includes compounds of Formulae Ia-Ii, and all sub-embodiments thereof
- Formula II includes compounds of Formulae Ha-IIb, and all sub-embodiments thereof
- Formula III includes compounds of Formulae IHa-IIIc, and all sub-embodiments thereof
- Formula IV includes compounds of Formulae IVa-IVb, and all sub-embodiments thereof, unless indicated otherwise.
- methods for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective Atty. Dkt. No : 039363-3303 amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV
- the terms "treat,” “therapy,” and like terms refer to the administration of matenal, e.g., one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, in an amount effective to prevent, alleviate, or ameliorate one or more symptoms of a disease or condition, i.e., indication, and/or to prolong the survival of the subject being treated
- protein kinase mediated disease or condition refers to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a protein kinase affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of the protein kinase alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition.
- a protein kinase mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which modulation provides a therapeutic benefit, e.g. wherein treatment with protein kinase inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition.
- the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with one or more other therapies for the disease or condition
- methods for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound of any one or more of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- Fms protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV
- Fms protein kinase mediated disease or condition refers to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a Fms protein kinase, including any mutations thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of Fms alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition
- a Fms mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which Fms inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e.g wherein treatment with Fms inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition.
- the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II
- kits for treating a Kit protein kinase mediated disease or condition m an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- the terms ''Kit mediated disease or condition,” "Kit protein kinase mediated disease or condition,” and the like refer to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a Kit protein kinase, including any Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 mutation thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and or in which modulation of Kit alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition
- a Kit mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which Kit inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment with Kit inhibitors, including compounds described herein, prov ides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition
- the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of
- TrkA mediated disease or condition refers to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a TrkA protein kinase, including any mutation thereof, affects the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/ or in which modulation of TrkA alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition
- TrkA mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which TrkA inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment w ith 1 rk ⁇ inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition
- the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one
- TrkB mediated disease or condition refers to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a TrkB protein kinase, including any mutation thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of TrkB alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition
- TrkB mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for w hich 1 rkB inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment with TrkB inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at nsk of the disease or condition
- the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC 50 of less than 500 urn, less than 100 nM, less than 50 tiM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted kinase activity assay,
- a compound of any of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC 50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, Akt2, Akt3.
- Kit LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl , Pyk2, ROCKl, ROCK2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof.
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC 50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Akt 1, Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Fyn, Gsk3 ⁇ , Gsk3 ⁇ , HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, J
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC 5U of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl.
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC 50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, MAP2K1, MAP4K4, MAPKAP kinase 2, Met, p38, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof.
- kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will an ICs 0 of less than 500 mn, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 iiM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA and TrkB, and any mutations thereof
- a compound of any of Fo ⁇ nula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC W of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to Fms, MAP4K4, TrkA, and/or TrkB
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV is an inhibitor of a Fms kinase and has an IC 50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted Fms kinase activity assay.
- a compound of Formula I Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will selectively inhibit Fms kinase relative to Kit kinase
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula TV is an inhibitor of a Fms kinase, a MAP4K4 kinase, a TrkA kinase, and/or a TrkB kinase and has an ICNo of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined m a generally accepted Fms kinase activity assay, MAP4K4 kinase activity assay, TrkA kinase activity assay, and/or TrkB kinase activity assay.
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Fo ⁇ nula III or Formula IV will selectively inhibit Fms kinase, MAP4K4 kinase, TrkA kinase, and' or TrkB
- a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Fo ⁇ nula W is an inhibitor of a Kit kinase and has an IC s o of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted Kit kinase activity assay
- a compound may selectively inhibit one kinase relative to one or more other kinases, where preferably inhibition is selective with respect to any of the other kinases whether a kinase discussed herein, or other kinases
- the compound may selectively inhibit the effects of a mutation of the kinase relative to the wild type kinase, for example B-Raf V600E relative to wild type B-Raf
- the compound may selectively inhibit Fms relative to Kit Selective inhibition of one kinase relative to another is such that the IC 50 for the one kinase may be at least about 2-fold, also 5-fold, also 10-fold, also 20-fold, also 50-fold, or at least about 100-fold less than the IC 50 for any of the other kinases as determined m a generally accepted kinase activity assay Atty. Dkt. No : 039363-3303
- a compound may selectively inhibit one or more kinases relative to one or more other kinases, where preferably inhibition is selective with respect to any of the other kinases, whether a kinase discussed herein, or other kinases.
- the compound may selectively inhibit Fms and one or more kinases relative to Kit, such as Fms and/or TrkA relative to Kit Selective inhibition of one kinase relative to another is such that the IC 50 for the one kinase may be at least about 2-fold, also 5-fold, also 10-fold, also 20-fold, also 50-fold, or at least about 100-fold less than the IC 50 for any of the other kinases as determined in a generally accepted kinase activity assay.
- compositions that include a therapeutically effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, excipient, and/or diluent, including combinations of any two or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- the composition can further include a plurality of different pharmacologically active compounds, which can include one or more compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV
- the composition can include one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV along with one or more compounds that arc therapeutically effective for the same disease indication.
- the composition includes one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV along with one or more compounds that are therapeutically effective for the same disease indication, whcrem the compounds have a synergistic effect on the disease indication.
- methods for modulating the activity of a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl , Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, ⁇ -Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms.
- a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl , Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, ⁇ -Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, Eph
- methods for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- methods are provided for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Akt 1, Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, ⁇ kt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl , c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl , EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Fyn, Gsk3 ⁇ , Gsk3 ⁇ , HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDPKl, Piml
- the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, MAP2K1, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, p38, PDGFRB, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Ret, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula FV.
- a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB
- the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, MAP2K1, M ⁇ P4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, p38, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
- the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA, and TrkB, and any mutations thereof, by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV,
- the invention provides a method of treating a cancer by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Atty. Dkt. No 039363-3303
- the one or more suitable anticancer therapies or medical procedures is selected lrom treatment with a chemotherapeutic agent (e g chemotherapeutic drug), radiation treatment (e g x-ray, ⁇ -ray, or electron, proton, neutron, or ⁇ particle beam), hyperthermia heating (e g microwave, ultrasound, radiofrequency ablation), Vaccine therapy (e g AFP gene hepatocellular carcinoma vaccine, AFP adenoviral vector vaccine, AG-858, allogeneic GM-CSF-secretion breast cancer vaccine, dendritic cell peptide vaccines), gene therapy (e g Ad5CMV-p53 vector, adenovector encoding M
- chemotherapeutic agent e g chemotherapeutic drug
- radiation treatment e g x-ray, ⁇ -ray, or electron, proton, neutron, or ⁇ particle beam
- hyperthermia heating e g microwave, ultrasound, radiofrequency ablation
- Vaccine therapy e g AFP
- the invention provides a method ot treating a cancer by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, in combination with one or more suitable chemotherapeutic agents
- the one or more suitable chemotherapeutic agents is selected from an alkylating agent, including, but not limited to, adozelesm, altretamme, bizelesm, busulfan, caiboplatm, carboquone, carmustme, chlorambucil, cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazme, estramustme, fotemustme, hepsulfam, lfosfamide, lmprosulfan, lrofulven, lomustme, mechlorethamme, melphalan, oxahplatin, piposulfan, semustine, streptozocin, temozolomide, thio
- an alkylating agent
- a kinase inhibitor including, but not limited to, erlotimb, gefitinib, flavopiridol, imatimb mesylate, lapatinib.
- the method of treating a cancer involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent selected from 5-fluorouracil, carboplatin. dacarbazme, gefitinib, oxaliplatm, paclitaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, vinblastine, bevacizumab, cetuximab, or erlotinib.
- a chemotherapeutic agent selected from 5-fluorouracil, carboplatin. dacarbazme, gefitinib, oxaliplatm, paclitaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, vinblastine, bevacizumab, cetuximab, or erlotinib.
- the invention provides a method of treating or prophylaxis of a disease or condition in a mammal, by administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, a prodrug of such compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of such compound or prodrug.
- the compound can be alone or can be part of a composition
- kits that include a composition as descnbed herein
- the composition is packaged, e g , in a vial, bottle, flask, which may be further packaged, e.g., within a box, envelope, or bag, the composition is approved by the U.
- the composition is approved for administration to a mammal, e.g., a human; the composition is approved for administration to a mammal, e g , a human, for a protein kinase mediated disease or condition; the invention kit includes written instructions for use and/ or other indication that the composition is suitable or approved for administration to a mammal, e.g., a human, for a protein kinase -mediated disease or condition, and the composition is packaged m unit dose or single dose form, e.g., single dose pills, capsules, or the like.
- the disease or condition is, for example without limitation, neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, cerebrovascular ischemia, multi-mfarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, dementia, senile chorea, and Huntmgton's disease; neoplastic diseases and associated complications, including, but not limited to, chemotherapy-mduced hypoxia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), prostate tumors, mast cell tumors (including, but not limited to, canine mast cell tumors), acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, melanoma, mastocytosis, gliomas, glioblastoma, Atty.
- neurologic diseases including, but not limited to, cerebrovascular ischemia, multi-mfarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer
- Dkt No 039363-3303 astrocytoma neuroblastoma, sarcomas (e g sai comas of neuroectodermal ongin, leiomyosarcoma), carcinomas (c g lung, breast, pancreatic colon, hepatocellular, renal, female genital tract, squamous cell, carcinoma m situ), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma, non-IIodgkm's lymphoma), MFN2 syndromes, neurofibiomatosis (including but not limited to, Schwann cell neoplasia), myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, cancers of the thyroid, liver, bone, skin, brain, central nervous system, pancieas, lung (e g small cell lung cancer, non small cell lung cancel), breast, colon, bladder, prostate, gastrointestinal tract, endometrium, fallopian tube, testes and o ⁇ ary,
- motor neuron diseases including, but not limited to, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy, intermediate spinal muscular atrophy, juvenile spinal muscular atrophy, spinal bulbar muscular atrophy, and adult spinal muscular atrophy
- inflammatory myopathies including, but not limited to, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis
- diseases of the neuromuscular junction including, but not limited to, myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, and congenital myasthenic syndrome
- myopathies due to endocrine abnormalities including, but not limited to, hyperthyroid myopathy and hypothyroid myopathy
- diseases of peripheral nerve including, but not limited to, Charcot-Ma ⁇ e
- the invention provides methods for treating a c-fms-mediated disease or condition in an animal subject (e g a mammal such as a human, other primates, sports animals, animals of commercial interest such as cattle, farm animals such as horses, or pets such as dogs and cats), e g , a disease or condition characterized by abnormal c-fms activity (e g kinase activity)
- Invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula II, F ormula III or Formula IV Ln
- the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic ob
- the invention provides methods for treating a c-fms-mediated disease or condition in an animal subject (e g a mammal such as a human, other primates, sports animals, animals of commercial interest such as cattle, farm animals such as horses, or pets such as dogs and cats), e g , a disease or condition characterized by abnormal c-fms activity (e g kinase activity)
- Invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I
- the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease, diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pam, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to tissues other than bone
- a mammal such as a human,
- invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, wherin the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis stroke, Abheimcr's disease. Parkinson's disease inflammatory pain, chronic pain, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to other tissues
- invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering trom or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain
- invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediatcd disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease
- invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosa (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthntis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and hpolysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mcdiated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Iype II diabetes. Paget's disease, diabetic nephropathy), multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pain, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to other tissues
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, chronic pam, and bone pain
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used m the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediatcd disease or condition selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pain, chronic pam, and bone pam
- compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV can be used m the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Kit-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasm associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel syndrome,
- the compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV with kinase activity IC 5C less than 10 ⁇ M as determined in a standard ass>ay described herein can be used to treat protein kinase mediated diseases and conditions related to the following protein kinases, for example without limitation Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
- CML chronic myeloid leukemia
- ALL acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- AML acute myelogenous leukemia
- ⁇ ktl related to gastric, prostate, colorectal ova ⁇ an, pancreatic and breast cancer, glioblastoma and leukemia, as w ell as schizophrenia and bipolar disorders, and also use in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs,
- Akt2 related to hyperglycemia due to penpheral insulin resistance and nonsuppressible hepatic glucose production accompanied by inadequate compensatory hyperinsulinemia, also related to pancreatic, ovarian and breast cancer,
- Akt3 related to melanoma, prostate and breast cancer
- ALK related to non-Hodgkin lymphomas such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- Alk5 related to pancreatic and biliary cancers, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- A-Raf related to neurologic diseases such as multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovanan), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma), neurofibromatosis, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, pam of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pam, chronic pam, cancer-related pam and migraine, and diseases associated with muscle regeneration or degeneration, including, but not limited to, ⁇ ascular restenosis, sarcopema, muscular dystrophies (including, but not limited to, Duchenne, Becker, Emery-Dreifuss, Limb-Girdle, Facioscapulohumer
- B-Raf or c-Raf-1 related to neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, as multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma) neurofibromatosis, acute myeloid leukemia, myelodvsplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, neuroendoc ⁇ ne tumors such as medullary thyroid cancer, carcinoid, small cell lung cancer and pheochromocytoma, pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pain, chronic pam, cancer-related pain, and migraine, cardiovascular diseases including, but not limited to, heart failure, ischemic stroke, cardiac
- Btk related to X-linked agammaglobulinemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Graves' disease, immune suppression in organ transplant, and drug sensitivity of B-hneage cells,
- Cdk2 related to prostate, breast, colorectal and ovanan cancer
- Cdk4 related to glioblastoma (e g glioblastoma multiforme), anaplastic astrocytoma, and breast cancer,
- Cdk5 related to Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Lewy body disease.
- Cdk6 related to glioblastoma multiforme, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL),
- CHKl related to DNA damage repair, sensitizes cells to chemotherapeutic agents
- Csk related to colon and pancreatic carcinomas, and autoimmune pathology such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus,
- EGFR related to breast, colorectal, bladder, prostate and non small cell lung cancer, squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck cancer, oral cavity and esophagus, and glioblastoma multiforme
- EphAl related to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, hepatoma and lung cancer, Eph ⁇ 2, related to aberrant short-range contact-mediated axonal guidance, bladder, breast, prostate, colon, skin, cervical, ova ⁇ an, pancreatic and lung cancers, and metastatic melanoma
- EphB2 related to angiogenesis disorder (e g ocular angiogenesis disease such as retinopathy), and cancer (e g glioblastoma, breast and liver cancer)
- EphB4 related to colorectal cancer (CRC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and tumours of the prostate, breast, endometrium, and bladder
- Erk2 related to aberrant proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development, and may be usctul in treating inflammation, for example inflammation associated with Lyme neuroborrehosis, and in treating cancers, such as gastric cancer,
- Fak related to colon and breast tumors, and is also related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma, ductal carcinoma in situ, prostate and hepatocellular carcinoma, and tumor metastases, and may also provide synergistic effects when used with other chemotherapeutic drugs, FGFRl , related to 8pl 1 myeloproliferative syndrome; FGFR2, related to Crouzon Syndrome, Jackson-Weiss Syndrome, Apert Syndrome, craniosynostosis, Pfeiffer Syndrome, acrocephalo syndactyly type V, and Beare-Stevenson Cutis Gyrata Syndrome;
- FGFR3 related to angiogenesis, wound healing, achondroplasia, Muenke craniosynostosis, Crouzon syndrome, acanthosis nigricans, thanatophoric dysplasia, bladder carcinomas, and multiple myeloma;
- FGFR4 related to cancer of the breast, lung, colon, medullary thyroid, pancreas, ovary, prostate, endometrium, and fallopian tube, head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and leiomyosarcoma;
- Fltl related to non-small cell lung carcinoma, prostate carcinoma, and colorectal cancer
- Flt3 related to acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, acute lymphoblastic leukemia,
- Fms related to immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, Atty Dkt No • 039363-3303 hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including but not limited to.
- inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, Atty Dkt No • 039363-3303 hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophag
- Frk related to acute myeloid leukemia and type 1 diabetes
- Fyn related to Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and prevention of metastases, e g in melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- GSK3 Gsk3 ⁇ and/or Gsk3 ⁇
- CNS disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetes type II, bipolar disorders, stroke, cancer, chronic inflammatory disease, leucopenia, schizophrenia, chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and traumatic head injury,
- HCK related to chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia
- Her2/Erbb2 related to prostate and breast cancer
- Her4/Erbb4 related to childhood medulloblastoma
- IGFlR related to prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma
- IKK beta related to leukemia of T-cells, necrosis, insulin resistance, and malignant neoplasms
- Irak4 related to bacterial infections, immunodeficiency syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, cardio hypertrophy, and kidney hypertension,
- Jak2 related to myeloproliferative disorders such as polycythaemia ⁇ era, myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, myeloid metaplasia and leukemias, including, but not limited to, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic neutrophilic leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, CMML, Philadelphia chromosome-negative CML, megakaryocyte leukemia, and acute erythroid leukemia, Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
- Jak3 related to X-lmked severe combined immunodeficiency, myeloproliferative disorders, transplant rejection and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis inflammatory bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis,
- Jnk Jnkl Jnk2, Jnk3
- metabolic diseases including, but not limited to, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and hepatic steatosis
- cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, ischemia (e g cerebrovascular ischemia, liver ischemia), reperfusion injury, cardiac hypertrophy
- renal diseases such as chronic renal failure
- neoplastic diseases and associated complications including, but not limited to, chemotherapy-mduced hypoxia, prostate tumors, myeloid leukemia and cancers of the liver bone, skin, brain, pancreas, lung breast, colon, prostate and ovary, transplant rejection, pam ot neuropathic or inflammatory origin including, but not limited to, acute and chronic pain, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including, but not limited to, age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, Sjo
- Kdr related to anti-angiogenesis for treating solid tumor growth (e g ovarian, lung, breast, prancreatic, prostate, colon, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, non small cell lung cancer, and epidermoid cancer), metastasis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic retinopathy and age related macular degeneration,
- Kit related to malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma, 2007/088443
- Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 neuroblastoma carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas ot neuroectodermal ongin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasia associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chionic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant re j ection, and hypereosmophiha,
- LCK related to acute lymphoblastic leukemia, T-cell lymphoma, lymphopenia, renal carcinoma, colon carcinoma, severe combined immunodeficiency, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel and type I diabetes
- MAP2K1 related to acute myeloid leukemia, breast, ovarian and liver cancer
- MAP2K2 related to cancer and inflammation
- MAP4K4 related to metabolic indications, including, but not limited to, re-sens>itizing fat and muscle cells to insulin, ameliorating the pathology in adipocytes, ameliorating the pathology in muscle cells, metabolic syndrome, and type II diabetes, a broad range of oncology indications, including, but not limited to, blocking the migration, invasion and metastasis in many different tumor types, and T-cell mediated autoimmune diseases, MAPKAPK2, cancer (e g prostate, breast), stroke, menengitis, and inflammatory disorders, Met, related to kidney, breast, bladder, non-small-cell lung, colorectal, and bladder cancers, and hepatocellular carcinoma,
- Mnkl related to conditions associated with heat shock, nut ⁇ ent dep ⁇ vation, oxidative or osmotic stress, and infection of mammalian cells (e g with viruses such as adenovirus (Ad) or influenza virus), and autoimmune diseases, MLKl, related to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson ' s disease, and inflammatory disorders, p38, related to acute coronary syndrome, stroke, atherosclerosis, and inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and Crohn's disease, PDGrR (PDGFR ⁇ , PDGFRB), related to idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia glioma, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, metastatic medulloblastoma, atherogenesis, and restenosis More particularly, PDGFRA related to idiopathic
- Piml related to cancers such as hematopoietic (e g acute myeloid and acute lymphoid leukemias) and prostate cancers and non-Hodgkm's lymphomas, Pim2, related to lymphomas, Pim3, related to hepatocellular carcinoma,
- cancers such as hematopoietic (e g acute myeloid and acute lymphoid leukemias) and prostate cancers and non-Hodgkm's lymphomas
- Pim2 related to lymphomas
- Pim3 related to hepatocellular carcinoma
- PKC alpha related to pituitary tumors and prefrontal cortical dysfunction such as distractibihty, impaired judgment, impulsivity, and thought disorder, also may be used to sensitize chemotherapy in breast, colon, and non small cell lung cancers
- PKC beta related to diabetic retinopathy
- PKC-theta related to insulin resistance
- F-cell lymphoma Plkl
- cancers e g lymphoma of the thyroid, non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, colorectal cancers leukemias and melanoma
- Pyk2 related to inflammation (e g osteoporosis, polycystic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthintis and inflammatory bowel disease), CNS disease (e g Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease), stroke and cancers (e g gliomas, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer), Ret, related to cancer of the thyroid, neuroblastoma, familial medu
- ROCK ROCK
- cancers e g o ⁇ a ⁇ an cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer
- ocular disease e g glaucoma
- cardiac hypertrophy improved renal perfusion, transplant rejection, and acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Ron related to cancer and inflammation
- Src related to cancer and osteoporosis
- Stk6 related to gastric bladder, breast, lung, CNS, ovarian, kidney, colon, prostate, pancreas, and cervical cancers, melanoma, leukemia, and neuroblastoma
- Syk related to lymphomas (e g mantle cell lymphoma)
- TEC related to sepsis, septic shock, inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel disease (EBD), and ulcerative colitis
- Tie2 related to cancer, arthritis (e g rheumatoid arthritis), and atherosclerosis, IYkA, related to pain (e g chronic pam, neuropathic pain), cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer), allergic disorders (e g asthma), arthritis, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and psoriasis,
- TrkB related to obesity, hyperphagia, developmental delays, cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, Wilms tumors, neuroblastoma pancreatic cancer), ⁇ anous neuropathies (e g stroke, multiple sclerosis, transverse myelitis, and encephalitis), and diabetes
- Zap70 related to AIDS, systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, atherosclerosis, rejection of transplanted organs or tissues, allograft rejection including, but not limited to, acute and chronic allograft rejection, graft versus host disease, rheumathoid arthritis, psoriasis, systemic sclerosis, atopic dermatitis, eczematous dermatitis, alopecia, and inflammation of the nasal mucus membrane, including all forms of rhinitis.
- Halogen refer to all halogens, that is, chloro (Cl), fluoro (F), bromo (Br), or iodo (I).
- Thiol refers to the group -SH.
- “Lower alkyl” alone or in combination means an alkane -derived radical containing from 1 to 6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) that includes a straight chain alkyl or branched alkyl.
- the straight chain or branched alkyl group is attached at any available point to produce a stable compound.
- a lower alkyl is a straight or branched alkyl group containing from 1-6, 1-4, or 1-2, carbon atoms, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, t-butyl, and the like.
- a “substituted lower alkyl” denotes lower alkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O)R 0 , -C(S)R 0 ,
- substitutions include subsets of these substitutions, such as are indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound.
- fluoro substituted lower alkyl denotes a lower alkyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, such as perfluoroalkyl, where preferably Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 the lower alkyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms.
- alkyl is an R group of a moiety such as -OR (e.g. alkoxy), -SR (e.g. thioalkyl), -NHR (e.g.
- substitution of the alkyl R group is such that substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substituents that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety.
- C2-6 alkyl denotes lower alkyl containing 2-6 carbon atoms.
- a "substituted C 2 . 6 alkyl” denotes optionally substituted lower alkyl containing 2-6 carbon atoms.
- a "substituted methyl” denotes methyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with 1 , 2, or 3 substituents, wherein the substituents are selected as per optionally substituted lower alkyl.
- C 1 . 3 alkylene refers to a divalent alkane-derived radical containing 1-3 carbon atoms, straight chain or branched, from which two hydrogen atoms are taken from the same carbon atom or from different carbon atoms.
- C) 3 alkylene includes methylene -CH 2 -, ethylene -CHaCH 2 -. propylene -CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 -, and isopropylene -CH(CH 3 )CH 2 - or -CH 2 CH(CH 3 )-.
- C 1-3 alkylene substituted with one or more substituents indicates C 1 . 3 alkylene that is independently substituted, with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents as indicated, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound.
- “Lower alkenyl” alone or in combination means a straight or branched hydrocarbon containing 2-6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) and at least one, preferably 1-3, more preferably 1-2, most preferably one, carbon to carbon double bond. Carbon to carbon double bonds may be either contained within a straight chain or branched portion. Examples of lower alkenyl groups include ethenyl, propenyl, isopropenyl, butenyl, and the like.
- a “substituted lower alkenyl” denotes lower alkenyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O
- fluoro substituted lower alkenyl denotes a lower alkenyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkenyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms.
- substitutions are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound
- substitution of alkenyl groups are such that -F, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -C(NH)-, -S(O)-, -S(O) 2 -, -O-, -S-, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), are not bound to an alkene carbon thereof.
- alkenyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)R, and the like
- substitution of the moiety is such that any -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, -S(O) 2 -, -O-, -S-, or N thereof (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkene carbon of the alkenyl substituent or R group.
- alkenyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)NHR, and the like
- substitution of the alkenyl R group is such that substitution of the alkenyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substitucnts that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkenyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety.
- An “alkenyl carbon” refers to any carbon within an alkenyl group, whether saturated or part of the carbon to carbon double bond.
- An “alkene carbon” refers to a carbon within an alkenyl group that is part of a carbon to carbon double bond.
- “Lower alkynyl” alone or in combination means a straight or branched hydrocarbon containing 2-6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) containing at least one, preferably one, carbon to carbon triple bond.
- alkynyl groups include ethynyl, propynyl, butynyl, and the like.
- a "substituted lower alkynyl” denotes lower alkynyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O)R 0 , -C(S)R
- substitutions include subsets of these substitutions, such as are indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound.
- "'fluoro substituted lower alkynyl” denotes a lower alkynyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkynyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms. While it is understood that substitutions 43
- Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, substitution of alkynyl groups arc such that -F, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -C(NH)-, -S(O)-, -S(O) 2 -, -O-, -S-, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkyne carbon thereof.
- alkynyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)R, and the like
- substitution of the moiety is such that any -C(O)-, -C(S)-,-S(O)-, -S(O) 2 -, -O-. -S-, or N thereof (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkyne carbon of the alkynyl substituent or R group.
- alkynyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)NHR, and the like
- substitution of the alkynyl R group is such that substitution of the alkynyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substituents that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkynyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety.
- alkynyl carbon refers to any carbon within an alkynyl group, whether saturated or part of the carbon to carbon triple bond.
- alkyne carbon refers to a carbon within an alkynyl group that is part of a carbon to carbon triple bond.
- Cycloalkyl refers to saturated or unsaturated, non-aromatic monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic carbon ring systems of 3-10, also 3-8, more preferably 3-6, ring members per ring, such as cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, adamantyl, and the like.
- a "substituted cycloalkyl” is a cycloalkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O)R
- Hetcrocycloalkyl refers to a saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic cycloalkyl group having from 5 to 10 atoms in which from 1 to 3 carbon atoms in the ring are replaced by heteroatoms of O, S or N, and are optionally fused with benzo or heteroaryl of 5-6 ring members. Heterocycloalkyl is also intended to include oxidized S or N, such as sulfinyl, sulfonyl and N-oxide of a tertiary ring nitrogen. Heterocycloalkyl is also intended to include compounds in which a ring carbon may be oxo substituted, i.e. the ring carbon is a carbonyl group, such as lactones and lactams. The point of attachment of the heterocycloalkyl ring is at a carbon or nitrogen atom such that a stable ring is US2007/088443
- heterocycloalkyl groups include, but are not limited to, morpholino, tetrahydrofuranyl, dihydropyridinyl, piperidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrrolidonyl, piperazinyl, dihydrobenzofuryl, and dihydroindolyl.
- a “substituted heterocycloalkyl” is a heterocycloalkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NlI 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NII 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O)R 0 , -C(
- Aryl alone or in combination refers to a monocyclic or bicyclic ring system containing aromatic hydrocarbons such as phenyl or naphthyl, which may be optionally fused with a cycloalkyl of preferably 5-7, more preferably 5-6, ring members.
- a “substituted aryl” is an aryl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0 , -OC(O)R 0 , -OC(S)R 0 , -C(O)R", -C(C
- Heteroaryl alone or in combination refers to a monocyclic aromatic ring structure containing 5 or 6 ring atoms, or a bicyclic aromatic group having 8 to 10 atoms, containing one or more, preferably 1-4, more preferably 1-3, even more preferably 1-2, heteroatoms independently selected from the group consisting of O, S, and N. Heteroaryl is also intended to include oxidized S or N, such as sulfmyl, sulfonyl and N-oxide of a tertiary ring nitrogen. A carbon or nitrogen atom is the point of attachment of the heteroaryl ring structure such that a stable compound is produced. Atty. Dkt No.: 039363-3303
- heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, pyridinyl, pyridazinyl pyrazinyl, quinaoxalyl, indolizinyl, benzo[b]thienyl, quinazolinyl, purinyl, indolyl, quinolinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, oxathiadiazolyl, isothiazolyl, tetrazolyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, furanyl, benzofuryl, and indolyl.
- “Nitrogen containing heteroaryl” refers to heteroaryl wherein any heteroaloms are N.
- Heteroarylene is a divalent heteroaryl.
- ⁇ "substituted heteroaryl” is a heteroaryl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR 0 , -SR 0
- each R 0 , R p , and R c are independently selected from the group consisting of R d , R e , R f , and R g , or R p and R c combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or a 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl, wherein the 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO 2 , -CN, -OH, -NII 2 , -OR U , -SR U , -NHR U , -NR U R U , -R ⁇ and -R y ;
- each R d is independently lower alkyl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -0R k , -SR ⁇ -0C(0)R k , -OC(S)R k , -C(O)R", -C(S)R L , -C(0)0R ⁇ -C(S)OR", -S(O)R k , -S(O) 2 R ⁇
- each R c is independently lower alkenyl, wherein lower alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 .
- each R* is independently lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkynyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NII 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -0R k , -SR k , -OC(O)R k , -OC(S)R", -C(O)R k , -C(S)R k , -C(O)OR", -C(S)OR k , -S(
- each R g is independently selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 7 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -0R k , -SR k , -OC(O)R", -OC(S)R
- R k , R' n , and R" at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of R h , R', and R', or R ra and R n combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or a 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl, wherein the 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally 88443
- each R h is independently lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHT 1 -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -0R r , ⁇ SR r , -OC(O)R r , -OC(S)R r , -C(0)R r , -C(S)R r , -C(O)OR r , -C(S)OR r , -C(S)OR r , -C(S)
- each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkenyl and lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkenyl or lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR', -SR', -OC(O)R', -OC(S)R', -C(O)R', -C(O)R', -C(S)R'
- each R 1 is independently selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, hcterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NII 2 , -C(S)NH 2 , -S(O) 2 NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(O)NH 2 , -NHC(S)NH 2 , -NHS(O) 2 NH 2 , -C(NH)NH 2 , -OR', -SR', -OC(O)R', -OC(S)
- each R r , R ⁇ and R 1 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, C 3 _ 6 alkenyl, C,_ 6 alkynyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of-R y , fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 .
- each R 11 is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, C M alkenyl, C 3 _ 6 alkynyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is Atty. Dkt.
- No.: 039363-3303 optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of-R y , fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the lower alkyl carbon bound to the O of -OR U , S of -SR U , or N of -NHR" is fluoro or -R y , and wherein Cj-6 alkenyl or C 3 .
- 6 alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -R*, fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the C M alkenyl or C 3 .
- 6 alkynyl carbon bound to the O of -OR U , S of -SR U , or N of -NHR" is fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, or -R y , and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
- each R" is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, lower alkenyl and lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -R y , fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, and wherein lower alkenyl or lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -R y , fluoro, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkyl
- each R y is selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino.
- all occurrences of optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 . 6 alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, or optionally substituted lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 consisting of fluoro, -NO 2 , -CN, -OR la , -SR la , -NR la R la , -OC(O)R la , -OC(S)R 1 ", -C(O)R 1 ".
- all occurrences of optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 _ 6 alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, or optionally substituted lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -CN, -OR la , -SR la , -NR la R la , -C(O)R la , -C(S)R ld , -C(O)OR 1 ", -C(O)NR 111 R 1 a , -C(S)NR l a R la , -S(O) 2 NR 13 R 13 , -NR la C(O)R Ia , -NR u C(S)R la , -NR la S(O) 2 R la , -S(O)R Ia , -S(O) 2 R la , cycloalkyl
- cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected lrom the group consisting of halogen, -CN, -OH, -NH 2 , lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino.
- Lower alkoxy' denotes the group -OR Z , where R ⁇ is lower alkyl
- Substituted lower alkoxy denotes lower alkoxy m which R z is lower alkyl substituted with one or more substituents as indicated herein, for example, m the descnption of compounds of Formula I Formula II, Formula III ⁇ r Formula IV, including descriptions of substituted cycloalkyl, cycloheteroalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound
- substitution of lower alkoxy is with 1 , 2, 3, 4, or 5 substituents, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents
- fluoro substituted lower alkoxy denotes lower alkoxy in which the lower alkyl is substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkoxy is substituted with 1 , 2 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1 , 2, or 3 fluoro
- Lower alkylthio denotes the group -SR aa , where R aa is lower alkyl
- Substituted lower alkylthio denotes lower alkylthio m which R aa is lower alkyl substituted with one or more substituents as indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, including descriptions of substituted cycloalkyl, cycloheteroalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound
- substitution of lower alkylthio is with 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 substituents, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents
- fluoro substituted lower alkylthio denotes lower alkylthio in which the lower alkyl is substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkylthio is substituted with 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also
- composition refers to a formulation suitable tor administration to an intended ammal subject for therapeutic purposes that contains at least one pharmaceutically active compound and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient
- pharmaceutically acceptable indicates that the indicated material does not have properties that would cause a reasonably prudent medical practitioner to avoid administration of the material to a patient, taking into consideration the disease or conditions to be treated and the respective route of administration For example, it is commonly required that such a material be essentially sterile, e g , tor mjectibles
- the term "therapeutically effective” or “effective amount” indicates that the materials or amount of material is effective to prevent, alleviate, or ameliorate one or more symptoms of a disease or medical condition, and/or to prolong the survival of the subject being treated
- the terms “synergistically effective” or “synergistic effect” indicate that two or more compounds that are therapeutically effective, when used in combination, provide improved therapeutic effects greater than the additive effect that would be expected based on the effect of each compound used by itself
- ligand and “modulator” are used equivalently to refer to a compound that changes (i e , increases or decreases) the activity of a target biornolecule, e g , an enzyme such as a kinase
- a ligand or modulator will be a small molecule, where "small molecule refers to a compound with a molecular weight of 1500 daltons or less, or preferably 1000 daltons or less, 800 daltons or less, or 600 daltons or less
- an "improved ligand” is one that possesses better pharmacological and/or pharmacokinetic properties than a reference compound, where “better” can be defined by one skilled in the relevant art for a particular biological system or therapeutic use
- the terms “greater affinity” and “selective” indicates that the compound binds more tightly than a reference compound, or than the same compound in a reference condition, i e , with a lower dissociation constant
- the greater affinity is at least 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 50, 100, 200, 400, 500, 1000, or 10,000-fold greater affinity
- enzymes can be assayed based on their ability to act upon a detectable substrate
- a compound or hgand can be assayed based on its ability to bind to a particular target molecule or molecules
- the term “modulating” or “modulate” refers to an effect of altering a biological activity especially a biological activity associated with a particular biomolecule such as a protein kinase
- a biological activity associated with a particular biomolecule such as a protein kinase
- an agonist or antagonist of a particular biomolecule modulates the activity of that biomolecule, e g , an enzyme by either increasing (e g agonist, activator), or decreasing (e g antagonist, inhibitor) the activity of the biomolecule, such as an enzyme
- Such activity is typically indicated in terms of an inhibitory concentration (IC 50 ) or excitation concentration (EC 50 ) of the compound for an inhibitor or activator, respectively, with respect to, for example an enzyme
- the term "contacting" means that the compound(s) are caused to be in sufficient proximity to a particular molecule, complex, cell, tissue, organism, or other specified material that potential binding interactions and/or chemical reaction between the compound and other specified material can occur
- isolated indicates that the sequence is separated from at least a portion of the ammo acid and/or nucleic acid sequences with which it would normally be associated
- the term "purified" indicates that the subject molecule constitutes a significantly greater proportion of the biomolecules in a composition than the proportion observed in a prior composition, e g , in a cell culture
- the greater proportion can be 2-fold, 5-fold, 10-fold, or more than 10-fold, with respect to the proportion found in the prior composition
- the present invention concerns compounds of Formula I, and all sub-generic formulae, compounds of Formula II and all sub-generic formulae, compounds of Formula III and all sub-generic formulae, and compounds of Formula IV and all sub-gene ⁇ c formulae that are modulators of protein kinases, for example without limitation, the compounds are modulators of at least one of the kinases selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, ⁇ kt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4 CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, BphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl , FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Frk, Fyn, Gsk3 ⁇ , Gsk3 ⁇ , HCK,
- Protein kinases play key roles m propagating biochemical signals in diverse biological pathways More than 500 kinases have been described, and specific kinases have been implicated in a wide range of diseases or conditions (i e , indications), including for example without limitation, cancer, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory disease, neurological disease, and other diseases As such, kinases represent important control points for small molecule therapeutic intervention
- diseases or conditions i e , indications
- kinases represent important control points for small molecule therapeutic intervention
- Description of specific target protein kinases contemplated by the present invention may be found, for example, in US Patent Application Serial number 1 1/473,347 (PCT publication WO2007002433) , the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety, m addition to the following
- A-Raf Target kinase
- A-Raf i e , v-raf murine sarcoma 3611 viral oncogene homolog 1
- A-Raf is a 67 6 kDa serine/threonine kinase encoded by chromosome XpI 1 4-pl 1 2 (symbol.
- the mature protein comprises RDD (i e , Ras binding domain) and phorbol-ester / DAG-type 7inc finger domain and is involved in the transduction of autogenic signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus
- A-Raf inhibitors may be useful in treating neurologic diseases including, but not limited to, multi-mfarct dementia, head injury, spmal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma), neurofibromatosis, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis; pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pam, chronic pam, cancer-related pain and migraine, and diseases associated with muscle regeneration or degeneration, including,
- B-Kaf Target kinase B-Raf (i e , ⁇ -raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog Bl) is a 84 4 kDa se ⁇ ne'threomne kinase encoded by chromosome 7q34 (symbol BRAF)
- the mature protein comprises RBD (i e , Ras binding domain), Cl (i e , protein kinase C conserved region 1) and STK (i e , serine/threonine kinase) domains
- Target kinase B-Raf is involved m the transduction of mitogenic signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus and may play a role in the postsynaptic responses of hippocampal neurons
- genes of the RAF family encode kinases that are regulated by Ras and mediate cellular responses to growth signals
- B-Raf kinase is a key component of the RAS-> Raf-> MEK->ERK/M AP kinase signaling pathway, which plays a fundamental role in the regulation of cell growth, division and proliferation, and, when constitutively actuated, causes tumo ⁇ genebis Among several isoforms of Raf kinase, the B-type, or B-Raf, is the strongest activator of the downstream MAP kinase signaling
- Niiho ⁇ et al report that in 43 individuals with cardio-facio cutaneous (CFC) syndrome, they identified two heterozygous KRAS mutations in three individuals and eight BRAF mutations in 16 Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 individuals, suggesting that dysregulation of the RAS-RAF-ERK pathway is a common molecular basis for the three related disorders (Nnho ⁇ et al , Nat Genet 2006, 38(3) 294-6)
- c-Raf-1 Target kinase c-Raf-1 (i e , v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 ) is a 73 0 kDa STK encoded by chromosome 3p25 (symbol RAFl)
- c-Raf-1 can be targeted to the mitochondria by BCL2 (i e , oncogene B-cell leukemia 2) which is a regulator of apoptotic cell death Active
- c-Raf-1 improves BCL2-mediated resistance to apoptosis, and c-Raf-1 phosphorylates BAD (i e , BCL2-bindmg protein)
- c-Raf-1 is implicated in carcinomas, including, but not limited to, colorectal, o ⁇ a ⁇ an, lung and renal cell carcinoma
- C-Raf-1 is also implicated as an important mediator of tumor angiogenesis (Hood, J D et
- B-Raf and/or C-Raf inhibitors may be useful in treating A-Raf-mediated, B-Raf-mediated or c-Raf-1 -mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma) neurofibromatosis, acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, neuroendocnne tumors such as medullary thyroid cancer, carcinoid, small cell lung cancer and pheochromocytoma, pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin,
- LFOPARD syndrome cardio-faciocutaneous syndrome (CFC)
- CFC cardio-faciocutaneous syndrome
- neural crest syndrome abnormalities causing cardiovascular, skeletal intestinal, skin, hair and endoc ⁇ ne diseases
- cell proliferative disorders which can be treated by the present invention include cancers, and mast cell proliferative disorders.
- c-kit has also been associated with a number of different types of cancers
- association between abnormalities in c-kit and disease are not rcstncted to cancer
- c-kit has been associated with malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasia associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis
- c-fms has been associated with immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosa (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and lipo lysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget' s disease, hyper
- TrkA 1 arget kinase TrkA (i e , neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 1) is a 140 kDa tyrosine kinase encoded by chromosome Iq21-q22 (symbol NTRKl) TrkA inhibitors may be useful in treating pam (e g chronic pam, neuropathic pain), cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, myeloid leukemia, pancreatic cancer), allergic disorders (e g asthma), arthritis, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and psoriasis
- pam e g chronic pam, neuropathic pain
- cancer e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, myeloid leukemia, pancreatic cancer
- allergic disorders e g asthma
- arthritis diabetic retinopathy
- LrkA is a plasma member receptor composed of an extracellular domain (responsible for high affinity binding to nerve growth factor, NGF), a transmembrane segment and an intracellular protein tyrosine kinase domain (responsible to transmit the NGF signal to initiate and coordinate neuronal responses) NGF binding induces TrkA clustering on the membrane and activates the kinase The kinase initiates a cascade of protein phosphorylation events through multiple pathways including SHC/Ras/MAPK, PI3K and PLCgI A TrkA kinase inhibitor would not prevent NGF'TrkA binding, but could prevent down-stream signal transduction
- Nerve Growth Factor is produced by a number of tissues and inflammatory cells during tissue injury and host immune response It initiates and maintains hypersensitivity to incoming stimulus (hyperalgesia) and the perception of non-noxious stimuli (allodynia) Through its high- affimty receptor TrkA, NGF increases the excitation state of sensory neurons leading to the central nervous system (peripheral sensitization), and increases transmitter release from the dorsal spinal cord (central sensitization) In clinical t ⁇ als, a single NGF subcutaneous injection generated local hyperalgesia persisting up to 7 weeks At doses above 0 1 microgram/kg, NGF caused muscle pain that varied from mild to moderate, primarily in the bulbar and truncal musculature Intravenous NGF produced earlier and more pronounced systemic effects (Petty et al, 1994, Ann Neurol 36 244-6) Conversely, TrkA kinase inhibitors could be used to treat diseases of enhanced states of nociception
- TrkB Target kinase TrkB (i e , neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2) is a 145 kDa tyrosine kinase encoded by chromosome 9q22 1 (symbol NTRK2) TrkB inhibitors may be useful in treating various cancers and their metastases (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, Wilms tumors, neuroblastoma, and pancreatic cancer), and various neuropathies (e g stroke, multiple sclerosis, trans ⁇ erse myelitis, and encephalitis)
- cancers and their metastases e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, Wilms tumors, neuroblastoma, and pancreatic cancer
- various neuropathies e g stroke, multiple sclerosis, trans ⁇ erse myelitis, and encephalitis
- paresthesia was developed at the site of subcutaneous injection (Couhe et al, 2000, Gastroenterology 119 41-50) Intrathecal infusion of BDNF in humans also induced paresthesia and warmth as side effects (Ochs et al, 2000, Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1 201-6) Chronic paresthesia is often a symptom of an underlying neurological disease or traumatic nerve damage Paresthesia can be caused by disorders affecting the central nervous system, such as stroke and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes), 007/088443
- Trkb kinase inhibitors could be used to treat certain patients with neuropathy
- BDNF is known to act at the synapses between primary sensory and spmal dorsal horn neurons to affect pam transmission during inflammation f he primary afferent is the only source of BDNF in the spmal cord, and it is up-regulated m the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by peripheral NGF a few days aftei inflammation, and is transported and released into the superficial dorsal horn in an activity-dependent manner TrkB expression in the dorsal horn also increases for a few days after inflammation
- TrkB inhibitors could be used to treat a sub-population of cancer patients with an activated TrkB pathway
- TrkB expression is correlated with perineural invasion, positive reti ope ⁇ toneal margin, and shorter latency to development of liver metastasis (Sclabas et al, 2005, Clin Cancer Res Vl 1 440-449)
- TrkB activates the PI3K pathway to suppress anoikis (apoptosis resulting from loss of cell-matrix interactions) which is one of the physiological barriers to metastasis TrkB kinase inhibition could break down resistance to anoikis of metastasizing tumors (Douma et al, 2004, Nature 430 1034-9) Therefore, TrkB inhibitors could have utility in a broad range of tumor types
- Target kinase MAP4K4 (i e , Mitogen-actn ated protein kinase kinase 4, aka Hematopoietic progenitor kinase/Germinal center kinase-hke Kinase) is a 130 kDa senne/threonine kinase encoded by chromosome 2ql 1 2-ql2 (symbol MAP4K4) and is also known as HGK It is a member of the human STE20/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase (MAP4K) family of serine/threonine kinases and is the human ortholog of mouse NIK (Nck-interacting kinase) The N- terminus of the mature HGK protein has a catalytic kinase domain that shares 47" o and 48% ammo acid sequence identity to
- HGK-induced JNK activation was inhibited by dominant-negative MAP2K4, MAP2K7, and TAKl mutants TNP-alpha also stimulated HGK kinase activity
- HGK was identified as a putative effect of Rap2 to activate JNK (Machida et al J Biol Chem 279 1571 1-15714, 2004) This link establishes HGK as a potential target for a range of metabolic indications, since the JNK pathway clearly antagonizes insulin signaling An HGK inhibitor could re-sensitize fat and muscle cells to insulin
- HGK is found to be broadly expressed in human tumor cells and can modulate cellular transformation, invasion, and adhesion (Wright et al MoI Cell Biol 23 2068-2082, 2003) Wright et al showed HGK to be highly expressed in most tumor cell lines relative to normal tissue
- An active role for this kinase in transformation was suggested by an inhibition of H-Ras(V12)-induced focus formation by expression of inactive, dominant-negative mutants of HGK in both fibroblast and epithelial cell lines
- Expression of an inactive mutant of HGK also inhibited the anchorage- independent growth of cells yet had no effect on proliferation in monolayer culture
- Expression of HGK mutants modulated integ ⁇ n receptor expression and had a striking effect on hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated epithelial cell invasion
- a small interfering RNA screen for modulators of tumor cell motility identifies MAP4K4 as a promigr
- Insulin-regulated glucose transporter GLUT4 is a key modulator of whole body glucose homeostasis, and its selective loss in adipose tissue or skeletal muscle causes insulin resistance and diabetes Using an RNA interference-based screen, Tang et al (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 208 7 - 2092, 2006) tound 4 negative regulators of msulin-responsive glucose transport in mouse adipocytes Pctkl, Pftkl, Ikbka (CHUK), and HGK HGK suppressed expression of adipogenic transcnption factors, C/EBPA, C/EBPB, and PPARG, and it suppressed surface expression of GLUT4 (SLC2A4), resulting in attenuated membrane hexose transport activity RNA interference-mediated depletion of HGK early in differentiation enhanced adipogenesis and triglyceride deposition, in fully differentiated adipocytes, loss of HGK upregulated
- JNK and ERK-I /2 phosphorylation as well as IRS- 1 sc ⁇ ne phosphorylation
- IRS- 1 sc ⁇ ne phosphorylation These results highlight the HGK/JNK'ERK 'IRS module in the negative regulation of insulin signaling to glucose transport in response to TNt- -alpha Depletion of HGK also prevented TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance on AKT and the AKT substrate 160 (AS 160), providing evidence that approp ⁇ ate insulin signaling inputs for glucose metabolism were rescued
- siRNA against HGK restored insulin action on glucose uptake to levels observed
- HGK inhibitors may be useful m treating metabolic indications, including, but not limited to, re-sensitizing fat and muscle cells to insulin, ameliorating the pathology in adipocytes, ameliorating the pathology in muscle cells, metabolic syndrome and type II diabetes, a broad range of oncology indications, including, but not limited to, blocking the migration, invasion and metastasis in many different tumor types, and T-cell mediated autoimmune diseases
- a number of different assays for kinase activity can be utilized for assaying for active modulators and/or determining specificity of a modulator for a particular kinase or group or kinases
- assays for kinase activity can be utilized for assaying for active modulators and/or determining specificity of a modulator for a particular kinase or group or kinases
- one of ordinary skill in the art will know of other assays that can be utilized and can modify an assay for a particular application
- numerous papers concerning kinases describe assays that can be used
- Additional alternative assays can employ binding determinations
- this sort of assay can be formatted either in a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) format, or using an ⁇ lphaScreen (amplified /ummescent proximity ⁇ omogeneous assay) format by varying the donor and acceptor reagents that are attached to streptavidin or the phosphor-specific antibody
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- ⁇ lphaScreen amplified /ummescent proximity ⁇ omogeneous assay
- sohents include polar and non-polar solvents known to those of skill in the art, including polar aprotic and polar protic solvents
- Polar solvents include, without limitation, protic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, t- butanol, n-butanol, acetic acid, formic acid or water, or aprotic solvents such as tetrahydrofuran (THF), acetonitnle, dioxane, methylene chloride, dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), acetone, N,N- dimethylformamide (DMF), N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA), ethyl acetate, 1,2-dimethoxyethane, 1,2- dichloroethane, chloroform, 1 ,2-dichloroethane, or pyridine
- Polar solvents include a mixture of water with any of the above, or a mixture of any two
- reducing agent includes, without limitation, a reducing agent such as catalytic reducing agents using hydrogen and transition metal catalysts such as palladium, platinum, rhodium, etc (e g Pt/acetic acid/H->), a mixture of t ⁇ fluoroacetic acid and t ⁇ ethylsilane, borane tetrahydrofuran complex, diborane, borane dimethylsulfide complex, and a combination of sodium borohyd ⁇ de and boron t ⁇ fluo ⁇ de, metals such as reduced iron, zinc powder, magnesium etc , metal hydrogen complex compounds such as alkali metal borohyd ⁇ des (for example, potassium borohyd ⁇ de, sodium borohyd ⁇ de, lithium borohyd ⁇ de, zinc borohyd ⁇ de, sodium tnacetoxyborohydride, etc ), aluminum lithium hydride, etc , metal hydrides such as sodium hydride, etc
- oxidizing agent includes, without limitation, an oxidizing agent such as Dess-Martin reagent TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpipe ⁇ dine-N- oxide), DDQ (2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-l ,4-bcnzoqumone), PDC (py ⁇ dimum dichromate), PCC (py ⁇ dinium chlorochromate), Pyridine SO3, Chromium t ⁇ oxide, p-mtroperbenzoic acid, magnesium monoperoxyphthalatc, sodium penodate, potassium pe ⁇ odate, hydrogen peroxide, urea peroxide, alkali metal bromates, cumene hydroperoxide, tert-butyl peroxide, peracids such as performic acid, peracetic acid, pert ⁇ fluoroacetic acid, perbenzoic acid, m-chloroperbenzoic acid, o- carboxyperbenzoic acid and the like,
- an oxidizing agent such as Dess-
- a nitrogen protecting group is a chemical group covalently bound to a nitrogen atom of a compound that is used to protect the nitrogen from reaction during a synthetic step
- the nitrogen protecting group may be added to a compound and removed in a subsequent step by methods known to those of skill in the art
- invention compounds may exist m a number of different forms or derivatives, all within the scope of the present invention
- Alternative forms or derivatives such as (a) Isomeis, Prodrugs, and Active Metabolites (b) Tautomers, Stereoisomers, Regioisomers, and Solvated Forms (c) Prodrugs and Metabolites (d) Pharmaceutically acceptable salts and (e) Polymorphic forms, are described, for example, in US Patent Application Se ⁇ al number 11 '473,347 (see also, PCI publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entnety
- the methods and compounds will typically be used in therapy for human subjects However, they may also be used to treat similar or identical indications in other animal subjects
- the terms "subject,” "animal subject,” and the like refer to human and non-human vertebrates, e g mammals, such as non-human primates, sports and commercial animals, e g , equmes, bovines, porcmes, ovines, rodents, and pets, e g , canines and felines
- a description of possible methods and routes of administration may be found, for example, in US Patent Application Se ⁇ al number 11/473,347 (see also, PCT publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety
- the mass spectrometry result indicated for a compound may have more than one value due to the isotope distribution of an atom in the molecule, such as a compound having a bromo or chloro substituent.
- Z 5 , Z 6 , R 15 and R 17 are as defined in paragraph [0008]
- L 4 , R 60 and R 61 are as defined in paragraph [0034]
- R 80 and R 81 are as defined in paragraph [0057]
- R > 9 w 0 is as defined in paragraph [0093]
- * indicates the attachment point to the carbonyl carbon is added an appropriate solvent (e.g. methanol) followed by an appropriate base (e.g. potassium hydroxide, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 sodium methoxide).
- an appropriate solvent e.g. methanol
- an appropriate base e.g. potassium hydroxide, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 sodium methoxide.
- the reaction is typically allowed to stir at room temperature overnight. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction, washing and filtering) affords a mixture of compounds of Formula Xc and Xd, which may be separated by silica gel chromatography
- a compound of Formula Xc or Xd in an appropriate solvent e.g. acetonitrile
- a reducing agent e.g. trifhioroacetic acid and triethylsilane.
- the reaction is allowed to stir at room temperature overnight. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction and silica gel column chromatography) affords compounds of Formula X.
- Compound of Formula Xl is synthesized by reacting a compound of Formula Xa (see Example 1) with a compound of Formula Xe (Y is as defined in Example 1), e.g. benzoyl chloride, in the presence of a Lewis acid (e.g. aluminum trichloride) in an inert solvent (e.g. dichloromethane) under an inert atmosphere (e.g. argon) at room temperature or with heating up to reflux for 1-18 hours.
- a Lewis acid e.g. aluminum trichloride
- an inert solvent e.g. dichloromethane
- an inert atmosphere e.g. argon
- Step 1 Preparation of5-bromo-l-triis ⁇ propylsilanyl-lli-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (2): [0253] To 5-bromo-7-a/aindole (1, 1.5 g, 7,6 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (20 mL) were added sodium hydride (60% in mineral oil, 0.27 g, 11.0 mmol) and trriisopropylsilyl chloride ( 2.6 mL, 12.0 mmol), under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate.
- sodium hydride 50% in mineral oil, 0.27 g, 11.0 mmol
- trriisopropylsilyl chloride 2.6 mL, 12.0 mmol
- Step 2 Preparation 5-chloro-l-triis ⁇ propykilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (3): [0254] To 5-bromo-l -triisopropylsilyl-7-azaindole (2, 1 ,60 g, 4.53 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (50.0 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0 C, was added terr-butyllithium (1.70 M in hexane, 6.12 mL). The reaction was stirred for 1 hour, followed by addition of hexachloroethane (1.29 g, 5.43 mmol).
- Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 1, substituting hexachloroethane with N-fluoro-N- (phenylsulfonyl) benzenesulfonamide in Step 2.
- MS(ESl) [M + ⁇ Cf 137.1.
- Example 5 Synthesis of l-triisopropylsHanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde 8. [0257] Compound 8 was synthesized in two steps from 7-azaindole 6 as described in Scheme 2.
- Step 2 Preparation ⁇ f 1 -triisopropylsilanyl- 1 H-pyrrolo [2 ,3-b] pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (8): [0259] To lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (7, 4.05 g, 27.71 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (30.0 mL) were added sodium hydride (60% in mineral oil, 1.5 g, 38 mmol) and trriisopropylsilyl chloride (8.0 mL, 38 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature.
- Step 1 Preparation of2-(l-trnsopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)-propan-2-ol (9): [0261] To 5-bromo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (2, 2.0 g, 5.66 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4) in tetrahydrofuran (20.0 rriL), cooled in a -78 0 C acetone/dry ice bath, under an atmosphere of nitrogen, was added tert-butyllithium (1.7 M in tetrahydrofuran, 7.3 mL, 12 mmol) dropwise.
- Step 1 Preparation of5-Methyl-l-triisopropyisilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (12): Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
- Step 1 Preparation of4-(4-chloroben ⁇ yloxy)-3-methoxyben ⁇ aldehyde (23): [0277] To 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (21, 600.0 mg, 3.94 mmol) and 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 1.20 g, 5.84 mmol) in acetonitrile (6 mL) was added potassium carbonate (0.390 g, 2.82 mmol). The reaction was microwaved on 300 watts, 120 0 C for 10 minutes. The reaction was extracted with ethyl acetate and water. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and the volatiles removed by evaporation. The desired compound was purified by recrystallization from hexanes to provide 23 (1.01 g, 93%). MS(tSI) [M-H"] " - 275.1.
- Step 3 Preparation of 3-(4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methoxyhenzyl)- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-bJ pyridine (P-1247):
- Steps 1-3 are identical to Steps 1-3 of Scheme 8.
- Step 1 Preparation o/3-chloro-4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-ben ⁇ aldehyde (31): [0297] To acetonitrile (15.0 mL) were added 3-chloro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (29, 0.6 g, 4 mmol), 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 1.2 g, 6 mmol), and potassium carbonate (0.9 g, 7 mmol). The reaction was heated to 150 0 C for 10 minutes in a CEM Discover microwave instrument. The reaction was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, and washed with brine. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (ethyl acetate: hexanes) (31, 0.85 g, 76%).
- Step 2 Preparation of3-[3-chloro-4 ⁇ (4-chloro-hcnzyloxy)-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine (32):
- Step 1 Preparation of3-[(4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine (34):
- Step 2 Preparation of 3-(4-ben ⁇ yloxy-3-methoxy-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (P-1613): [0303] The crude 3-[(4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]py ⁇ idine (34, 0.9g, 2.4 mmol) from step 1 and acetonitrile (50 mL) were mixed with trifluoroacetic acid (0.360 mL, 4.7 mmol) and triethylsilanc (0.746 mL, 4.7 mmol). The reaction was heated at 80 0 C and stirred overnight.
- Step 1- Synthesis of3-methoxy-4-[4 ⁇ (4-methyl-piperazin-l-ylmethyI)-hen ⁇ yloxy] ⁇ benzaldehyde (37): Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- Step 2 (4-Bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenoxy)-tert-hutyl-dimethyl-silane (42):
- Step 1 Synthesis of4-(4-chloro-ben ⁇ yhxy)-3- ⁇ uoro-ben ⁇ aldehyde (46):
- Step 2 (4-Benzy!oxy-2, 5-difluoro-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsilanyl- lH-pyrrolo[2, 3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (48):
- Step 3 Synthesis ⁇ f(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (P-1902):
- Step 4 Synthesis of3-(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-diflnoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1901): [0323] To (4-Bcnzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (P-1902, 500.0 mg, 1.37 mmol) in acetonitrile (25.0 mL) were added triethylsilane (2.00 mL, 0.0125 mol) and trifluoroacetic acid (1.00 mL, 0.0130 mol). The reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours.
- Step 1 Synthesis of3-(4-benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-benzyl)-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrr ⁇ la[2,3- b] pyridine (49):
- Step 2 Synthesis of2,5-difluoro-4-(l-trii$opropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3 ⁇ b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)- phenol (50): Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
- Step 3 3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyIoxv)-2,5- ⁇ fluoro-benzylJ-l-trus ⁇ pr ⁇ pyls ⁇ lanyI-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyndute (51)
- Step 4 Synthesis of 3-[4-(4-chloi o-benzvloxy)-2,5-d ⁇ fluoi o-benzvl]-lH-pvrrolo[2,3 bjpvri ⁇ ne
- Step 4a Preparation of3-(3-benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrr ⁇ lo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1852):
- Step 2 Preparation of(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl- ⁇ henyl)-methanol (57) [0340] To a solution of 3-benz ⁇ loxy-2-methyl-benzoic acid (56, 3 0 g, 0 012 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (100 mL), lithium aluminum hydride (25 mL, IM solution m tetrahydrofuran, 0 025 mol) was added dropwise at 0 0 C for 5 minutes The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature overnight under an atmosphere of nitrogen After sodium sulfate decahydrate (20 0 g, 0 062 mol) was added, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes A white solid was collected by filtration I he solid compound was further washed with a mixture of hexane and dichloromethane (9 1) and dried under high-vacuum (57, 2 8 g, 91%) Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
- Step 4 Preparation of(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (59) and 3-[(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lI1-pyrrolo[2, 3-bJpyridine (60): [0342] A mixture of lH-pyrrolo[2,3- ⁇ ]pyridine (6, 0.33 g, 2.8 mmol), 3-benzyloxy-2-methyl- benzaldehyde (58, 0.55 g, 2.4 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (0.39 g, 6.1 mmol) in methanol (40 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 17 hours.
- Step 5 a Preparation of (3-Benzyloxy-2 ⁇ methyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1848):
- Step 5b Preparation of 3-(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-benzyl)-]II-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1857): [0344] A mixture of 3-[(3-benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (60, 24 mg, 0.067 mmol), trifluoroacetic acid (1 mL, 13 mmol), and triethylsilane (2 mL, 12.5 mmol) in acetonitrile (10 mL) was refluxed for 4 hours. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate.
- Example 21 Synthesis of [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy) ⁇ 2-ethoxy-phenyI]-(lH-pyrroloI2,3-£]pyridin- 3-yI)-methanone P-1892 and 3-I3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrroIo[2,3- 6]pyridine P-1893
- reaction mixture was poured into ice water and extracted with ethyl acetate.
- the organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as an off-white solid (62, 2.3 gm, 46%).
- Step 2 Preparation of3-(4-chloro-henzyloxy)-2-hydr ⁇ xy-benzaldehyde (63): [0347] To magnesium (0.098 g, turnings, 4.0 mmol) in a mixture of anhydrous ether (20 mL) and benzene (20 mL) at 0 0 C, bromine (0,10 mL, 2.0 mmol) was added dropwise. When the reaction had started, stirring was commenced and the addition of bromine continued until complete. The ice bath Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 was removed and the reaction mixture was heated until the solution was almost colorless.
- Step 4 Preparation of [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrr ⁇ 1o[2,3-h]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (65) and 3- ⁇ [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl ⁇ -lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (66):
- Step 5a Preparation of[3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-J 892):
- Step 5b Preparation of3-[3-(4-chl ⁇ r ⁇ -bemyl ⁇ xy)-2-eth ⁇ xy-benzyl]-lH-pyrr ⁇ h[2,3-b] ⁇ yridine (P-1893):
Abstract
Compounds active on protein kinases are described, as well as methods of using such compounds to treat diseases and conditions associated with aberrant activity of protein kinases. Formula (II), all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein: t is 0, 1, 2, or 3; Z2 is N or CR12; Z6 is N or CR16; L4 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR10R11)P-NR25-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p-X-(CR10R11)q, -(CR10R11)p-C(X)-(CR10R11)q, -(CR10R11)p-S(O)-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p -S(O)2-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p-C(X)NR25-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p-S(O)2NR25-(CR10R11)q-,-(CR10R11)p-NR25C(X)-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p-NR25S(O)2-(CR10R11)q-, -(CR10R11)p-NR25-(CR10R11)q-, and -(CR10R11)p-NR25S(O)2NR25-(CR10R11)q-; p and q are independently 0, 1, or 2 provided, however, that at least one of p and q is O.
Description
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR KINASE MODULATION, AND INDICATIONS
THEREFOR
RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application claims priority to U.S. Provisional App. No. 60/877,052, entitled "Compounds and Methods for Kinase Modulation, and Indications Therefor", filed December 21 , 2006, and is related to U.S. Patent App. No. 11/473.347, entitled "Compounds and Methods for Kinase Modulation, and Indications Therefor", filed June 21 , 2006, which claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional App. No. 60/731,528, entitled "Compounds and Methods for Kinase Modulation, and Indications Therefor", filed October 28, 2005, and U.S. Provisional App. No. 60/692,960, entitled "Compounds and Methods for Kinase Modulation, and Indications Therefor", filed June 22, 2005, all of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties and for all purposes.
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0002] The present invention relates to kinases and compounds which modulate kinases, and uses therefor. Particular embodiments contemplate disease indications which arc amenable to treatment by modulation of kinase activity by the compounds of the present invention.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0003] The information provided herein is intended solely to assist the understanding of the reader. None of the information provided nor references cited is admitted to be prior art to the present invention. Each of the references cited herein is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
[0004] Receptor protein kinases regulate key signal transduction cascades that control or are involved in the control of a plethora of physiological functions including cellular growth and proliferation, cell differentiation, cellular development, cell division, cell adhesion, stress response, short-range contact-mediated axonal guidance, transcription regulation, aberrant mitogenesis, angiogenesis, abnormal endothelial cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions during vascular development, inflammation, lymphohematopoietic stem cell activity, protective immunity against specific bacteria, allergic asthma, aberrant tissue-specific responses to the activation of the JNK signal transduction pathway, cell transformation, memory, apoptosis, competitive activity-dependent synapse modification at the neuromuscular synapse, immunological mediation of disease, and calcium regulation.
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0005] Specific disease states associated with aberrant regulation of protein kinases include, for example without limitation, acrocephalo-syndactyly type I, acute myeloid leukemia, AIDS-induced non-Hodgkm's lymphoma, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, atopic dermatitis, autoimmune diseases, bacterial infection, bladder cancer, cancer of the breast, cancer of the central nervous system, cancer ot the colon, cancer of the endometrium, cancer of the fallopian tube, cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, cancer of the ovary, heart failure, chronic myeloid leukemia, colon carcinoma, colorectal cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Crouzon Syndrome, diabetes, diabetic nephropathy, emphysema, endometriosis, epidermoid cancer fϊbrotic disorders, gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST ), glomerulonephritis, Graves' disease, head injury, hepatocellular carcinoma, Hirschsprung's disease, human gliomas, immunodeficiency diseases, inflammatory disorders, ischemic stroke, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, leiomyosarcoma, leukemias, lupus nephritis, malignant melanoma, malignant nephrosclerosis, mastocytosis, mast cell rumors, melanoma of the colon, MEN2 syndromes, metabolic disorders, migraine, multiple sclerosis, myeloproliferative disorders, nephritis, neurodegenerative diseases, neurotraumatic diseases, non small cell lung cancer, organ transplant rejection, osteoporosis, pain, Parkinson's disease, Pfeiffer Syndrome, polycystic kidney disease, primary lymphoedema, prostate cancer, psoriasis, vascular restenosis, rheumatoid arthritis, dermal and tissue scarring, selective 1 -cell detect (STD), severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), small cell lung cancer, spinal cord injury, squamous cell carcinoma, systemic lupus crythematosis, testicular cancer, thrombotic microangiopathy syndromes, Wegener's granulomatosis, X-lmked agammaglobulinemia, viral infection, diabetic retinopathy, alopecia, erectile dysfunction, macular degeneration, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), myelodysplasia syndrome (MDS), neurofibromatosis, and tuberous sclerosis
[0006] T. his application is related to the following published patent applications WO 2004024895, US 20040142864, WO 2004078923, US 20050170431 , WO 2005028624, US 20050164300, and WO 2005062795, each of which are hereby incorporated by reference herein in their entireties including all specifications, figures, and tables, and for all purposes
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0007] Compounds are contemplated that are active on protein kinases in general, including, but not limited to, AbI, Aktl , Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHK 1 , c-Raf-1 , Csk, EGFR, EphAl , EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl , FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Flt l , Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Frk, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl , Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl , Ink2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1 , MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MΛPKΛPK2, Met. Mnkl , MLKl , p38, PDGFRA, PDGIHB, PDPKl Pirn 1 , Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl , Pyk2, Ret, ROCKl , ROCK2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, I EC, Fie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and/or Zap70, including any mutations of these kinases In some aspects, the
Atty, Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 compounds are active on protein kinases including, but not limited to. Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA, and/or TrkB, including any mutations thereof. In some aspects, compounds are of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV as described below.
[0008] Also contemplated in accordance with the present invention are methods for the use of the above-described compounds in treating diseases and conditions associated with regulation of the activity of the above-described kinases. Thus, the use of compounds for therapeutic methods involving modulation of protein kinases is provided, as well as compounds that can be used for therapeutic methods involving modulation of protein kinases.
[0009] In some embodiments, compounds have the structure according to the following Formula I:
Formula I
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein: Q has a structure selected from the group consisting of
in which ? indicates the attachment point of Q to A of Formula I;
Z2 is N or CR12; Z4 is N or CR14; Z5 is N or CR15; Z6 is N or CR16;
L2 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR1V %-NR25-(CR10R1 '),,->
-(CR10R11VX-(CR10R1 1),-, -(CR10R11VC(X)-(CR1V !)q-, -(CR10R1 1^-S(O)-(CR10R1 1V, -(CR1V)P-S(O)2-(CR1 V1)q-, -(CR10R1 I)p-C(X)NR25-(CR10R")L|-)
-(CR1V1)p-S(O)2NR25-(CR11)Ru)(,-, -(CR1V 1^-NR25C(X)-(CR10R1 ')q-, and
-(CR1V1VMrS(O)2-(CR 11OVn IK1V;
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 p and q are independently 0, 1 , or 2 provided, however, that at least one of p and q is 0, s is 1 or 2,
A is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, and -S(O)2-,
Ra and Rb at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of lndrogen, fjuoro, -OH, -NH;, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkvlammo, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, or di-alkylammo arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylainino is fluoro, or
Ra and Rb combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo,
R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -C(O)R7, -C(S)R7, -S(O)2R7, -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7, and -S(O)2NHR7, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, further provided that when R1 is lower alkyl, any substitution on the lower alkyl carbon bound to the N of -NR1- is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo,
R7 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxv, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylaπnno, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, provided however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to the N of -C(O)NHIf, -C(S)NHR' or -S(O)2NHR7 is fluoro, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH;, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylamino provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, each of R4, R5, R6, R12, R14, R15, and R16, are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower dlkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NOi, -CRaRbR26, and -LR26,
L at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -(alk)d-X-(alk)b- -(alk)a-NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk),-C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)η-OC(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)O-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)O-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-OC(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR23C(X)NR25-(alk)b-, and -(alk)a-NR2'S(O)2NR25-(alk)b-, a and b are independently O or 1 , alk at each occurrence is independently C) •) alkylene or C| 3 alkylcne substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NRSR9, wherein lower alkyl or the alkyl chdin(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, X at each occurrence is independently O or S,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
R" at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionall} substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroarvl, R ft at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of h>drogcn provided, bowe\er, that hydrogen is not bound to any of S(O) S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted low er alkyl, optionally substituted low er alkenyl provided, however, that when R"' is optionally substituted lower alkenyl, no alkene carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, provided, however, that when R2β is optionally substituted lower alkynyl, no alkyne carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl, R10 and R11 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di- alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, or any two of R10 and R" on the same or adjacent carbon atoms combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, and any others of R10 and R1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, and wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo, R8 and R9 combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy. fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, and fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl and -OR15, each of R11 and R13 are independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl,
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303
R32 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl. and -OR18, and
R1 * is hydrogen or optionally substituted lower alkyl; provided, however, that the compound is not 3-{3-[2-(tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-ethoxyJ-bcnzyl} - 5-thiophen-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine, which has the structure
4-(4-Methyl-piperazin-l-ylmethyl)-N-[4-(lH-pyrrolo[2.3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl)-phenyl]- benzamide, which has the structure
[0010] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ia:
Foπnula Ia all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, L2, Z2, Z6, R4, R5, R6, R15, R17 and R31 are as defined for Formula I.
[0011] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ia, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkyl thio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R15
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0012] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ia, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, Z2 is N or CR12, Z6 is N or CR16, R12 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR21R22. wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R", R" or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
[0013] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ib:
Formula Ib all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A1 is -O-, -CR40R41-, -C(O)- or -NR48-; Z12 is N or CR52; Z16 is N or CR56;
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
R40 and R41 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo; or R40 and R ' combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alky], lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylamino;
U is selected from the group consisting of -NR48-, -S-, -O-, -NR48CII(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, -OCH(R49)-, -C(O)NR48-, -S(O)2NR48-, -CH(R4'J)NR48-, -CH(R49)O-, -CH(R49)S-, -NR48C(O)-, and -NR48S(O)2-;
R53 and R53 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro; R52 and R56 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R49 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl;
Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalkyl; RTO is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, aryl, heteroaryl, and NR50R.", wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and wherein aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R23; R50 is hydrogen or lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino; R51 is aryl or heteroaryl, wherein aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R" ,
R21 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57. -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57,
Λtty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
-NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R23, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R5*, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; R57 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, or -S(O)2NR48R57 is fluoro, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R57 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino;
R58 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, or -S(O)2NR48R58 is fluoro, and wherein heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy; R48 at each occurrence is independently hydrogen or lower alkyl; and t is O, 1, 2, or 3.
[0014] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ib, Λ| is -CR40R'11- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-. In some embodiments, A, is -CR4V- Or -C(O)-, preferably
Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303
-CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and Rϊ3 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, L1 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and L, is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-.
[UU 15] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ic;
Formula Ic all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A], R23, R39, Cy, and t are as defined in Formula Ib;
Z22 is N or CR62;
Z26 is N or CRhh; r is O, 1 , or 2; and
R62, R63, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
[UOI 6] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ic, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R62, R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[OUI 7] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Id:
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Formula Id all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, s, Z2, Z6, R4, R5, R6, R15, Rπ, and R32 are as defined for Formula I.
[0018] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Id, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0019J In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Id, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH3- or -C(O)-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino. di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, Z2 is N or CR12, Z6 is N or CRl fi, R12 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and -NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R2' or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted
Atty. Dkt. No/ 039363-3303 lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylammo, further wherein R32 is optionally substituted lower alkyl or -OR18, where R18 is as defined for Formula I.
[0020] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the follow mg sub-generic structure Formula Ie
Formula Ie all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, s, Z2, Z6, R4, R5, R6, R15, and R12 are as defined for Formula I.
[0021] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ie, R4 and R6 arc hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0022] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ie, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, Z2 is N or CR12, Z6 is N or CR16, R12 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and -NR21R'2, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII2, lower alkoxy. fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, further wherein R32 is optionally substituted lower alkyl or -OR18, where R18 is as defined for Formula
Atty. Dkt No 039363-3303
[0023J In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula If
Formula If all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, L2, Z2, Z4, Z5, Z6, R4, R5, R6, and R3? are as defined for Formula I
[0024] In some embodiments of compounds ol Formula If, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Zh is N or CR16, and R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro
[0025] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula If, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Z6 is N or CR16, R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR21R", wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylammo
[0026] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula If, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O- -CRdRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
CR 5, Z6 is N or CR16, R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fhioro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR21R22, wherein R*1 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
[0027] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ig:
Formula Ig all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A,, L3, Z12, Z(6, R23, R39, Cy and t are as defined for Formula Ib;
R54 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain oflower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
[0028] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ig, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CII2-, and R54 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-,
Atty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303 preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)- more preferably -CH2-, and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-
[0029] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ih:
Formula Ih all salts, prodrugs, tautomers and isomers thereof, wherein A, Z2, Z4, Z5, Z6, R4, R5, R6, R'0, R" and R33 are as defined for Formula I, and r is 0, 1 , or 2.
[0030] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Di, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Z6 is N or CR16, and R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
[0031] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ih, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Z6 is N or CR16, R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R10 and R11 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR" 1R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R3, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHj, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino,
[0032] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ih, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z2 is N or CR12, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Z6 is N or CR16, R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R10 and R1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro. lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino.
[0033J In some embodiments, compounds of Formula I have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ii:
Formula Ii all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A), R23, R39, Cy and t are as defined for Formula Ib;
Z22, ^26, and r are as defined for Formula Ic;
Z24 is N or CR64;
Z25 is N or CR65;
RM and R6S are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower
Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303 alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
[0034] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ii, A] is -CR40R41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)- In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R 2, R 4, R 5 and R6* are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0035] In some embodiments, compounds have the structure according to the following Formula
II:
Formula II all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein: t is 0, 1 , 2, or 3;
L4 is selected from the group consisting of -(CRl0Rπ)p-NR25-(CRI0Rn)q-,
-(CR10R11VX-(CR10R11V, -(CRI0R")p-C(XHCR10Rπ)q-, -(CR10R1 1^-S(O)-(CR10R1 ')q-, -(CR10R1 VS(O)2-(CR1V)0 -(CR10R1 VC(X)NR25-(CRIOR 11V, -(CR10R1 VS(O)2NR2S-(CRI0RnV, -(CR10R1 ^p-NR25C(X)-(CR10R1 ')q-, -(CR10R11Jp-NR25S(O)2-(CR10R11V, -(CRloRπ)p-NR25C(X)NR25-(CR10R1 1)q-, and -(CR10R11)p-NR25S(O)2NR25-(CRI0R")q-;
R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO2, -CRaRbR26, and -LR26;
R is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl; and
A, Z2, Z6, Rd, Rb, R4, R5, R6, R10, R1 ', R15, R17, R25, R26, p, q, X and L are as defined for
[0036] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
[0037] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R4 and R6 are hydrogen and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH. -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57. -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R5", -S(O)2R5', -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)7NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR5", -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR4SR57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R5, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NFI2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR4SC(O)R5S, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. wherein R48, R57, and R58 are as defined for Formula Tb. In some embodiments, R4 and R6 are hydrogen and R5 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted hcteroaryl.
[0038] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0039] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -Oil, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0040] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH,, -C(O)NII2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R5, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R'7, and R5S are as defined for Formula Ib , A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CII2-, R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I,
[0041] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NII2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R12 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alky], fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di- alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. R", Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0042] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula II, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, Rftl is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CRaRb-( -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy. fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alky lamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R15 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy. and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R and R 6 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR2", -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0043] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula II, both ofZ2 and Z6 are N, also one of Z2 or Z$ is N and the other of Z2 or Zg is CR12 or CR16, preferably Z2 is CR17 and Z6 is CR16.
[0044] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula II, each R60 is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NH48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R60, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R57 and R58 are as defined for Formula Ib, Z2 is CR13, Z6 is CR16, and R12, R15, R16 and R17 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0045] In one embodiment of compounds of Formula II, the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-fluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2099),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethylJ-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2100),
2-[2,5-Difluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2101),
2-[3,5-Difluoro-4-(lH-p>τrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazolc (P-2102),
2-[5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiπ-3-ylmethy])-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2103),
2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2104),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-3,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2105),
2-[4-(5 -Chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl] - 1 -methyl - lH-benzoimidazole (P-2106),
2-[4-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymcthylJ-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2107),
2-{2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzo imidazole (P-2108),
2-{5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmcthylJ- phenoxymethyl} -lH-benzoimidazole (P-2109),
2-{l-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl)-5-fIuoro-2-methoxy-phenoxy]-ethyl}-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2110),
6-Chloro-2-[4-(5 -chloro- lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]- lH-benzoimidazolc (P-2111),
6-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2112),
2-[5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-6-methoxy-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2113),
2-[5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2114),
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-fluoro-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2115),
2-[2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2116),
2-{2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]-
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 phenoxymethyl} -lH-benzoimidazole (P-2117),
2-{4-[(5-Ch]oro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methoxy-methyl]-5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl } - 1 H-benzoimidazole (P-2168),
[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyτidm-3-yI)-methanoπe (P-2169),
2-[2,5-Difluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-lH-ρyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyπ-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2170),
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine-5- carbomtnle (P-2171),
5,6-Dichloro-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazoIe (P-2172),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyI]-lH- benzoimidazole-5 -sulfonic acid dimethylamide (P-2173),
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazo]-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-5- carboxylit acid methyl ester (P-2174),
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyπdine-5- carboxylic acid (P-2175),
2-{2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl]-phenoxymethyl}-
1 H-benzoimidazole (P-2176),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-l-ethyl- lH-benzoimidazole (P-2177),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxyinethyl]-5- tπfluoromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole (P-2178),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-5-fluoro- lH-benzoimidazole (P-2179),
2-{2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxy]-ethyl}-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2180),
2-[4-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yImethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lII- benzoimidazole (P-2181),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-pheπoxymethyl]-5- methoxy-1 H-benzo imidazole (P-2182),
5-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(5-methyl-lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]- lH-benzomudazole (P-2184),
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2,5-difluoro-bcnzyl]-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine-5-carbonitnle
(P-2185),
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 phenoxymcthyl]-lH-benzoimidazole (P-2186), and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof.
[0046] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula II have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Ha:
Formula Ha all salts, prodrugs, lautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO3, -C(O)OII, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR", -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R101;
R101 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)3NR48R57. halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR4V7, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R101, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR43C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-S(O)R53, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; and Ai, Z12, Z1,, L3, t, R48, R53, R53, R57, and R58 are as defined for Formula Ib.
[0047] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R6'' is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
[0048] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino.
[0049] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, Aj is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and R53 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and L3 is -NR43CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. R40, R41, R4S and R49 arc as defined for Formula Ib.
[0050] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, Ai is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-. In some embodiments, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is O, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is O, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and R53 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted
Atty, Dkt No.: 039363-3303 lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-, and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R*)-. R40, R4!. R48 and R49 are as defined for Formula Ib.
[0051] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57. -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2,
-SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR4bC(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-.
[0052] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R'7, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R10 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)7NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR55, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R38, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; Ai is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-; and R53 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0053] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lla, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NII2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR", -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R1IM or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R38, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-.
|0054] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lla, R10α is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, more preferably -CH2-; and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. R40, R41, R48 and R49 are as defined for Formula Ib.
[0055] hi some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN1 -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58. In some embodiments, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and Rlϋl is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
[0056] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, A, is -CH2-; L3 is -OCH(R1')-; RI Oϋ is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR4SR57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; Z12 is CR52; Z16 is CR5"; Rini is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R53, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and R52, R53, R55 and R56 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0057] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula Ha, both of Z12 and Z]6 are N, also one of Zn or Zi6 is N and the other of Zn or Zi6 is CR52 or CR55, preferably Zn is CR52 and Z16 is CR56. R52 and R56 are as defined for Formula Ib.
[0058] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula II have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula lib:
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303
Formula lib all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A| and t are as defined for Formula Ib; R100, R101 are as defined for Formula Ha; R63, R65, Z22 and Z2β are as defined for Formula Ic; and R70 and R61 are independently hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
[0059] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl.
|0060] In some embodiments of compounds of Foπnula lib, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NII2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R", -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R37, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. In some embodiments, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OII, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, βuoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0061] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, A1 is -CR40R4'- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z22 is CR52, and Z26 is CR66.
[0062] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is, 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl and t is 0, 1 , 2, 3 or 4, provided, however, that when t is 0, R61 is lower alkyl or fluoro substituted lower alkyl, Ai is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, Z22 is CR62, and Z26 is CR66.
[0063] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R37, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NTl48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR4V8, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2-; and R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
[0064] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R5S, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2-; R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR43R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R5i; Z22 is CR^2; and Z25 is CR66.
[0065] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula lib, both of Z22 and Z26 are N, also one of Z22 or Z26 is N and the other OfZ22 or Z25 is CR62 or CR66, preferably
Z,- is CRM and Z 66
-2,6s : is CR
[0066] In some embodiments, compounds have the structure according to the following Formula HI:
Formula III all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A, Z4, Z5, Z6, R4, R5, and R6, are as defined for Formula I; L.4 is as defined for Formula II; R80 is C1^J alkyl or C3_5 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci.3 alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C3^5 cycloalkyl; and R81 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, C2.4 alkyl, fluoro substituted C2_4 alkyl, and -(CH2CH2O)1nR71; m is 1, 2, or 3; and R71 is Cu alkyl or fluoro substituted C1^3 alkyl, provided, however, that the compound is not
[0067] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula 111, R81 is optionally substituted heteroaryl.
[0068] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and Rh are hydrogen and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)3R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fiuoro, -OH, -NH2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2. -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl. aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R5, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substiluents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58. -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R57, and R58 are as defined for Formula Ib. In some embodiments, R4 and R6 are hydrogen and R5 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
[0069] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-. preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0070] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRV-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and RS1 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula 1.
[0071] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR37, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, hcterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R5, or as subslituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR53, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R57, and R5S, A is -0-, -CRaR -, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the
Atty, Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0072] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R"4, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0073] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R1 S and Rlh are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R\ R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH3, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and R81 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
Atty, Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
[0074] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-. or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0075] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and R81 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0076] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula III, at most two OfZ4, Z<ι, or Z5 are N, also at most one of Z4, Z5, or Z6 is N, preferably Z4 is CR14, Z; is CR15 and Z6 is CR16.
[0077] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula III, R ' is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, CY4 alkyl, fluoro substituted C2-4 alkyl, and -(CH2CH2O)JR71, wherein aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R", -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R", -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2,
-SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl. and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as a substituent of R8', or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SRSS, -NR48R58, -NR4SC(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R53, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R57 and R58 are as defined for Formula Ib, Z4 is CR14, Z5 is CR15, Z6 is CR16, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0078] In one embodiment of compounds of Formula III, the compound is selected from the group consisting of: r3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2118), t3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2-difluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2119), f3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- melhanone (P-2120),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2-pyrrolidin-l-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2121),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)~methanone
(P-2122),
[3.(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phcnyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-mcthanone
(P-2123),
[3-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2124),
[3-(2,5-Dimethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2125),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2127). r2-Ethoxy-3-(6-moφholin-4-yl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2128),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2129),
[3-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2130). [2-Ethoxy-3-(4-imidazol-l-yl-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2131),
[3-(2,4-Difluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2132), {2-Ethoxy-3-[l-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
(P-2133),
[3 -( 1 ,5 -Dimethyl-1 H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyπdm-3 -yl)- methanone (P-2134),
[2-Ethoκ>-3-(l-pyπdin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyττolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)-methanone (P-2135),
[2-Ethoxy-3-((R)-l-pyndin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2136),
[2-rthoxy-3-(2,4,6-trifluoro-ben7yloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndm-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2137),
{3-[l-(2)4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-2-ethoxy-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)-raethanone
(P-2138),
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- mcthanone (P-2139),
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4-dimeth>l-thiazol-5- ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanone (P-2140),
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4,6-tπfluoro-benzyloxy)- phenyl] -methanone (P-2141).
(5-Chloro-lH-pyπOlo[2,3-b]pyndm-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(6-tufluoromethyl-pyπdm-3- ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanone (P-2142),
[3-(6-Diethylamino-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yI)- methanone (P-2143),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-pyrrohdin-l-yl-pyridin-3->lmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2144), and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof
[0079] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula III have the structuie according to the following sub-geneπc structure Formula Ilia
Formula Ilia all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein R100 and R101 are as defined tor Formula Ha,
Atty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
Z14 and Zi5 are as defined for Formula Ig;
Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalk>'l;
L3a is selected from the group consisting of -NR48-, -S-, -O-, -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-,
-NR48C(O)-, and -NR48S(O)2-; R is Ci j alkyl or C3^5 cycloalkyl, wherein CM alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C3-, cycloalkyl; and Ai, Zi 6, R48, R4 , and t are as defined for Formula Ib.
[0080] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, Cy is heteroaryl.
[0081] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R", -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. In some embodiments, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
[0082] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, A| is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and R54 and R35 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, L3 is -NR48ClI(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
10083] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, Cy is heteroaryl, Λ, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-. In some embodiments, Cy is heteroaryl, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and R54 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. In some embodiments, Cy is heteroaryl, Lj is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-. In some embodiments, Cy is heteroaryl, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-, and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-.
[0084] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR37, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR4 R37, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A , is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-.
[0085] hi some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OII, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl. aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-; and R54 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
|0086] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHa, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NII2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-NR48R57, -NR4HC(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy. fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R45)-, or -OCH(R49)-, preferably -OCH(R4')-.
[0087] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR43R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R37, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as Rltw or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -C(O)-; and L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R4*)-, preferably -OCH(R49)-.
[0088] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula Ilia, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58. In some embodiments, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58. -OR58 and -S(O)2R'8; and R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH1, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57,
T/US2007/088443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
-S(O)2NR R" , halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl. -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R38.
[0089] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHa, Ai is -C(O)-; L3 is -OCH(R41*)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57. -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R37, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl. -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; Z14 is CR54; Z15 is CR55; Z16 is CR56; R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and R54, R55 and R56 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0090] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula IHa, two OfZ)4, Z|5, or Zi6 are N and the other of Z14, Z15, or Z16 is CR54, CR55 or CR56, also one OfZ14, Z15, or Zifi is N and the others of Z14, Z15, or Z16 are CR54, CR55 or CR56, preferably Z14 is CR54, Z13 is CR55 and Z)6 is CR55.
[0091] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula III have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula HIb:
Formula IHb all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A, Z4, Z5, Z6, R4, R5, Rh, R10, R" and R33 are as defined for Formula I; R80 is as defined for Formula 111; and
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 r is O, 1, or 2.
[0092] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R." is optionally substituted heteroaryl.
[0093] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHb, R4 and R5 are hydrogen and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR", -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R37, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R5 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR5S, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R5S, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. In some embodiments, R4 and R6 are hydrogen and R5 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl,
[0094] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0095] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R33 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. R\ Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0096] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)1NH2, -C(O)NH2, -ORr, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)1R", -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R", -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R5 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48RW, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH3- or -C(O)-, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0097] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R4 and R" are hydrogen, Λ is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of tluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro. R10 and R1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl,-CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R3, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio. mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
Atty, Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0098] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R1S and R1" are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R!0 and R11 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and R33 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
10099] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R10 and R11 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0100] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHb, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -0-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R10 and R1 ' are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, R5 is selected from the
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R" is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH. -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, and R33 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0101] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula HIb, two OfZ4, Z5, or Z6 are N and the other of Z4, Z5, or Z6 is CR14, CR15 or CR16, also one of Z4, Z5, or Z6 is N and the others of Z4, Z,, or Z6 are CR14, CR15 or CR16, preferably Z4 is CR14, Z5 is CR15 and Z5 is CR16.
[0102] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula Mb, R33 is aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocycloalkyl, wherein aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as a substituent of R33, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR43S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)?NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino, wherein R48, R57 and R58 are as defined for Formula Ib. Z4 is CR14, Z5 is CR15, Z6 is CR10, and R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0103] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula III have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula IHc:
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Formula IIIc all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
Ai, Cy and t are as defined for Formula Ib; RlM and R101 arc as defined for Formula Ha; R80 is as defined for Formula Ilia; Z26 and r are as defined for Formula Ic; and Z24 and Z25 are as defined for Formula Ii.
[0104] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IIIc, Cy is heteroaryl.
[0105] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IIIc, Rluo is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR51, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR43S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR4SR58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. In some embodiments, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
[0106] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IIIc, Aj is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
R , R and R ' are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy,
[0107] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IIlc, Cy is heteroaryl, A, is -CR40R41 - or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, Cy is heteroaryl, A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and RM, R63 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0108] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula HIc, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHRS8, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR411S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; Aj is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-.
[0109] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula 11Ic, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR", -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NII2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NU48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)3R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; A, is -CR40R4'- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-; and R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
10110] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHc, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR45R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58. In some embodiments, A, is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R1Q0 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, tluoro, chloro. bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0111) In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IHc, Aj is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)3R58; Z24 is CR64; Z25 is CR65; Z26 CR66; and R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0112] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula IHc, two
Of Z24, Z25, or Z26 are N and the other of Z24, Z25, or Z26 is CR64, CR65 or CR66. one of Z24, Z25, or Z26 is
N and the others of Z24, Z25, or Z26 are CRM, CR65 or CR66, preferably Z24 is CRM, Z25 is CR" and Z2 is CR66.
[0113] In some embodiments, compounds have the structure according to the following Formula IV:
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein;
A, R4, R5, R6, Z2, Z4, Z5, and Z6 are as defined for Formula I; and R90 is C2^ alkyl, fluoro substituted CM alkyl, or -(CH2CH2.OO;)mR91; mm iiss 11 ,, 22.. o orr 33;; aanndd
R91 is Ci_3 alkyl or fluoro substituted Cu alkyl, provided, however, the compound is not
(0114] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IV, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, pretcrably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R12, R14, R1' and Rltl are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I
[0115] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IV, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaR\ -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R12, RH, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain ot lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino and cycloalkykmino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- ot
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 lower alkoxy is fluoro, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R 2, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. R\ Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0116] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IV, R4 and R6 are hydrogen, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH1- or -C(O)-, R12, R14, R15 and R16 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0117] Tn some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula IV, two Of Z2, Z4, Z5, or Z6 are N and the others of Z2, Z4, Z5, or Z6 arc CR12, CR14, CR15 or CR16, also one of Z2, Z4, Z5, or Z6 is N and the others of Z2, Z4, Z5, or Z6 are CR12, CR14, CR15 or CR16, preferably Z2 is CR12, Z4 is CR14, Z3 is CR15 and Z6 is CR16.
[0118] In one embodiment of compounds of Formula IV, the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2148), [2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2149), [2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2>2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2150),
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phcnyl]-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl]-methanone (P-2151),
3-[2,6-ϋichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifIuoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2>3-b]pyridme (P-2153),
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 methanone (P-2154),
5-Chloro-3-[2^chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2157), 3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-raethoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2158), [2-Chloro-6-nuoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2159),
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2160), and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof,
10119] In some embodiments, compounds of Formula IV have the structure according to the following sub-generic structure Formula Wa:
Formula IVa
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A and Rs are as defined for Formula I;
R90 is as defined for Formula IV;
Z32 is N or CR72;
Z34 is N or CR74;
Z35 is N or CR75;
Z36 is N or CR76; and
R72, R74, R75, and R7fl are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro.
[0120] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IVa, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CII2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A is -O-, -CR"Rb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R72, R14, R75 and R'6 are independently selected from the group consisting of
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[01211 In some embudiments of compounds of Formula IVa, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-, or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)2R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R3, R21 or R22. when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
(0122] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IVa, A is -O-, -CRaRb-, -NR1-. or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, R72, R74, R75 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, and R5 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR22, -OR22, -S(O)1R22, and NR21R22, wherein R21 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, and R22 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl, and wherein the alkyl chain of R5, R21 or R22, when lower alkyl, or the alkyl chain of lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro. -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di- alkylamino and cycloalkylamino. Ra, Rb, and R1 are as defined for Formula I.
[0123] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula IVa, two Of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 are N and the others of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 are CR72, CR74, CR75 or CR76, also one of Z32, Z34, Z3^, or Zi6 is N and the others of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 are CR72, CR74, CR75 or CR 6, preferably Z2 is CR72, Z4 is CR74, Z5 is CR75 and Z6 is CR76.
[U 124] In some embodiments, compounds have the structure according to the following Formula IVb:
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303
Formula IVb
all salts, prodrugs, tautoraers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A) is as defined for Formula Ib; R100 is as defined for Formula Ha;
Zj2 , Zj4, Z15, and X^b are as defined for Formula FVa; and R90 is as defined for Formula IV.
[0125] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula FVb, A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-. In some embodiments, A, is -CR4V1- or -C(O)-, preferably -CH2- or -C(O)-, and R72, R74, R75 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0126] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula FVb, R 00 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57,
-NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR", -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkyllhio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R10 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NH48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R53, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino. In some embodiments, Ai is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR5\ -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; and R72, R'4, R'5 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0127] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IVb, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl. heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58. In some embodiments, Ai is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and R72, R74, R75 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0128] In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IVb, Aj is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R", -S(O)R37, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NII2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino; Z32 is CR72; Z34 is CR74; Z35 is CR75; Z36 is CR'6; and R72, R74, R75 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0129J m some embodiments of compounds of Formula IVb, A, is -CH2- or -C(O)-; R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)ORS7, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; Z32 is CR72; Z34 is CR74; Z3J is CR75; Z36 is CR76; and R72, R74, R75 and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
[0130] In some embodiments of any of the above embodiments of compounds of Formula IVb, two OfZ32, Z34, Z15, or Z36 are N and the others of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 are CR72, CR74, CR75 or CR76, also one Of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 is N and the others of Z32, Z34, Z35, or Z36 are CR72, CR^4, CR75 or CR"6, preferably Z2 is CR72, Z4 is CR74, Z5 is CR75 and Z6 is CR76.
[0131] In some embodiments of the above compounds, compounds are excluded where N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, or S is bound to a carbon that is also bound to N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, or S except where the carbon forms a double bond with one of the heteroatoms, such as in an amide, carboxylic acid, and the like; or where N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), O, C(S), C(O), or S(O)n (n is 0-2) is bound to an alkene carbon of an alkenyl group or bound to an alkyne carbon of an alkynyl group; accordingly, in some embodiments compounds which include linkages such as the following are excluded from the compounds provided: -NR-CH2-NR-, -0-CII2-NR-, -S-CH2-NR-, -NR-CH2-O-, -0-CH2-O-, -S-CH2-O-, -NR-CH2-S-, -0-CH2-S-, -S-CH2-S-, -NR-CH=CH-, -CII=CH-NR-, -NR-C =C-, -C ≡€-NR-, -0-CH=CH-, -CH=CH-O-, -O-C Ξ£-, -C =£-0-, -S(OV2-CH=CH-, -CH=CH-S(OV2-, -S(OV2-C =€-, -C ≡€-S(OV2-, -C(O)-CH=CH-, -CH=CH-C(O)-, -C ^C-C(O)-, or -C(O)-C =€-, -C(S)-CH=CH-, -CH=CH-C(S)-, -C ≡€-C(S)-, or -C(S)-C -C-.
[0132] In reference to compounds herein, unless clearly indicated to the contrary, specification of a compound or group of compounds includes pharmaceutically acceptable salts of such compound(s), prodrug(s), and all stereoisomers thereof. In reference to compositions, kits, methods of use, etc. of compounds of Formula I, II, III, or IV described herein, it is understood that a compound of Formula I includes compounds of Formulae Ia-Ii, and all sub-embodiments thereof, Formula II includes compounds of Formulae Ha-IIb, and all sub-embodiments thereof, Formula III includes compounds of Formulae IHa-IIIc, and all sub-embodiments thereof, Formula IV includes compounds of Formulae IVa-IVb, and all sub-embodiments thereof, unless indicated otherwise.
[0133] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective
Atty. Dkt. No : 039363-3303 amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV The terms "treat," "therapy," and like terms refer to the administration of matenal, e.g., one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, in an amount effective to prevent, alleviate, or ameliorate one or more symptoms of a disease or condition, i.e., indication, and/or to prolong the survival of the subject being treated The term "protein kinase mediated disease or condition" refers to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a protein kinase affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of the protein kinase alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition. A protein kinase mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which modulation provides a therapeutic benefit, e.g. wherein treatment with protein kinase inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition. In one aspect, the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with one or more other therapies for the disease or condition
[0134] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound of any one or more of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
[0135] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a Fms protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV The terms "Fms protein kinase mediated disease or condition," "Fms mediated disease or condition," and the like refer to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a Fms protein kinase, including any mutations thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of Fms alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition A Fms mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which Fms inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e.g wherein treatment with Fms inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition. In one aspect, the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with one or more other therapies for the disease or condition.
[0136] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a Kit protein kinase mediated disease or condition m an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV. The terms ''Kit mediated disease or condition," "Kit protein kinase mediated disease or condition," and the like refer to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a Kit protein kinase, including any
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 mutation thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and or in which modulation of Kit alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition A Kit mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which Kit inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment with Kit inhibitors, including compounds described herein, prov ides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition In one aspect, the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination w ith one or more other therapies for the disease or condition
[0137] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a TrkA protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV The terms "TrkA mediated disease or condition," "TrkA protein kinase mediated disease or condition," and the like refer to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a TrkA protein kinase, including any mutation thereof, affects the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/ or in which modulation of TrkA alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition A TrkA mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for which TrkA inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment w ith 1 rkΛ inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at risk of the disease or condition In one aspect, the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with one or more other therapies for the disease or condition
[0138] In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a TrkB protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV The terms "TrkB mediated disease or condition," "TrkB protein kinase mediated disease or condition," and the like refer to a disease or condition in which the biological function of a TrkB protein kinase, including any mutation thereof, affects the development, course and/or symptoms of the disease or condition, and/or in which modulation of TrkB alters the development, course, and/or symptoms of the disease or condition A TrkB mediated disease or condition includes a disease or condition for w hich 1 rkB inhibition provides a therapeutic benefit, e g wherein treatment with TrkB inhibitors, including compounds described herein, provides a therapeutic benefit to the subject suffering from or at nsk of the disease or condition In one aspect, the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with one or more other therapies for the disease or condition
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
|01391 ϊn some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC50 of less than 500 urn, less than 100 nM, less than 50 tiM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted kinase activity assay, In some embodiments, a compound of any of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, Akt2, Akt3. ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Frk, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Hcr4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr. Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl , Pyk2, ROCKl, ROCK2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof.
[0140] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Akt 1, Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl , Pyk2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof.
[0141] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC5U of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl. Fltl, Flt3, FH4, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl , Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, MAP2K1, MAP4K4, MAPKAP kinase 2, Met, p38, PDGFRB, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Ret, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof,
[0142] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an IC50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, MAP2K1, MAP4K4, MAPKAP kinase 2, Met, p38, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, including any mutations thereof.
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0143] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will an ICs0 of less than 500 mn, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 iiM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to at least one kinase selected from the group consisting of Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA and TrkB, and any mutations thereof In some embodiments, a compound of any of Foπnula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will have an ICW of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM with respect to Fms, MAP4K4, TrkA, and/or TrkB
|0144] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV is an inhibitor of a Fms kinase and has an IC50 of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted Fms kinase activity assay In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV will selectively inhibit Fms kinase relative to Kit kinase
[0145] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula TV is an inhibitor of a Fms kinase, a MAP4K4 kinase, a TrkA kinase, and/or a TrkB kinase and has an ICNo of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined m a generally accepted Fms kinase activity assay, MAP4K4 kinase activity assay, TrkA kinase activity assay, and/or TrkB kinase activity assay In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Foπnula III or Formula IV will selectively inhibit Fms kinase, MAP4K4 kinase, TrkA kinase, and' or TrkB kinase relative to Kit kinase
[0146] In some embodiments, a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Foπnula W is an inhibitor of a Kit kinase and has an ICso of less than 500 nm, less than 100 nM, less than 50 nM, less than 20 nM, less than 10 nM, less than 5 nM, or less than 1 nM as determined in a generally accepted Kit kinase activity assay
[0147] Further to any of the above embodiments, a compound may selectively inhibit one kinase relative to one or more other kinases, where preferably inhibition is selective with respect to any of the other kinases whether a kinase discussed herein, or other kinases In some embodiments, the compound may selectively inhibit the effects of a mutation of the kinase relative to the wild type kinase, for example B-Raf V600E relative to wild type B-Raf In some embodiments, the compound may selectively inhibit Fms relative to Kit Selective inhibition of one kinase relative to another is such that the IC50 for the one kinase may be at least about 2-fold, also 5-fold, also 10-fold, also 20-fold, also 50-fold, or at least about 100-fold less than the IC50 for any of the other kinases as determined m a generally accepted kinase activity assay
Atty. Dkt. No : 039363-3303
[0148| Further to any of the above embodiments, a compound may selectively inhibit one or more kinases relative to one or more other kinases, where preferably inhibition is selective with respect to any of the other kinases, whether a kinase discussed herein, or other kinases. In some embodiments, the compound may selectively inhibit Fms and one or more kinases relative to Kit, such as Fms and/or TrkA relative to Kit Selective inhibition of one kinase relative to another is such that the IC50 for the one kinase may be at least about 2-fold, also 5-fold, also 10-fold, also 20-fold, also 50-fold, or at least about 100-fold less than the IC50 for any of the other kinases as determined in a generally accepted kinase activity assay.
[0149J In another aspect, compositions are provided that include a therapeutically effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, excipient, and/or diluent, including combinations of any two or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV. The composition can further include a plurality of different pharmacologically active compounds, which can include one or more compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV In another aspect, the composition can include one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV along with one or more compounds that arc therapeutically effective for the same disease indication. In one aspect, the composition includes one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV along with one or more compounds that are therapeutically effective for the same disease indication, whcrem the compounds have a synergistic effect on the disease indication.
[0150] In another aspect, methods are provided for modulating the activity of a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl , Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, Λ-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms. Frk, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl , Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, PM, Pyk2, ROCKl, ROCK2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, or Zap70 by contacting the protein kinase with an effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
[0151] In another aspect, methods are provided for treating a protein kinase mediated disease or condition in an animal subject, wherein the method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
(01521 In one aspect, methods are provided for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Akt 1, Akt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Fak, FGFRl, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, FHl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl, Pyk2, ROCKl, ROCK2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkΛ, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV
[0153] Ln one aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, Λkt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4, CDK5, CDK6, CHKl , c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl , EphA2, EphB2, EphB4, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK, Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, Itk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl, Pyk2, Ron, Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula PV.
[0154] In one aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, MAP2K1, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, p38, PDGFRB, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Ret, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula FV.
[0155] In one aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of AbI, A-Raf, B-Raf, Btk, c-Raf-1, EGFR, EphB2, Erk2, Fak, Fms, Irak4, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kit, MAP2K1, MΛP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, p38, Piml, PKC theta, Pyk2, Src, Stk6, TrkA, TrkB, Yes, and Zap70 by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV.
[0156] In one aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a disease or condition mediated by a protein kinase selected from the group consisting of Fms, Kit, MAP4K4, TrkA, and TrkB, and any mutations thereof, by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV,
[0157] In one aspect, the invention provides a method of treating a cancer by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II,
Atty. Dkt. No 039363-3303
Formula III or Formula IV, m combination with one or more other therapies or medical procedures effective in treating the cancer Other therapies or medical procedures include suitable anticancer therapy (e g drug therapy, vaccine therapy, gene therapy, photodynamic therapy) or medical procedure (e g surgery, radiation treatment, hyperthermia heating, bone marrow or stem cell transplant) In one aspect, the one or more suitable anticancer therapies or medical procedures is selected lrom treatment with a chemotherapeutic agent (e g chemotherapeutic drug), radiation treatment (e g x-ray, γ-ray, or electron, proton, neutron, or α particle beam), hyperthermia heating (e g microwave, ultrasound, radiofrequency ablation), Vaccine therapy (e g AFP gene hepatocellular carcinoma vaccine, AFP adenoviral vector vaccine, AG-858, allogeneic GM-CSF-secretion breast cancer vaccine, dendritic cell peptide vaccines), gene therapy (e g Ad5CMV-p53 vector, adenovector encoding MDA7, adenovirus 5-tumor necrosis factor alpha), photodynamic therapy (e g aminolevulinic acid, motexafin lutetium), surgery, and bone marrow and stem cell transplantation
(0158] In one aspect, the invention provides a method ot treating a cancer by administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition including one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, in combination with one or more suitable chemotherapeutic agents In one aspect, the one or more suitable chemotherapeutic agents is selected from an alkylating agent, including, but not limited to, adozelesm, altretamme, bizelesm, busulfan, caiboplatm, carboquone, carmustme, chlorambucil, cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazme, estramustme, fotemustme, hepsulfam, lfosfamide, lmprosulfan, lrofulven, lomustme, mechlorethamme, melphalan, oxahplatin, piposulfan, semustine, streptozocin, temozolomide, thiotepa, and treosulfan, an antibiotic, including, but not limited to, bleomycin, dactinomycm, daunorubicin, doxorubicin, epirubicin, ldarubicin, menogaπl, mitomycin, mitoxantrone, neocarzmostatin, pentostatin, and plicamycin, an antimetabolite, including, but not limited to, azacitidinc, capecitabme, cladπbine, clofarabme, cytarabine, decitabine, floxuπdine, fludarabine, 5-fluorouracil, ftorafur, gemcitabme, hydroxyurea, mercaptopurme, methotrexate, nelarabme, pemetrexed, raltitrexed, thioguamne, and tπmetrexate, an immunotherapy, including, but not limited to, alemtuzumab, bevacizumab, cetuximab, gahximab, gemtuzumab, pamtumumab, pertuzumab, πtuximab, tositumomab, trastu7umab, and 90 Y ibntumomab tiuxetan, a hormone or hormone antagonist, including, but not limited to, anastrozole, androgens, buserelm, diethylstilbestrol, exemestane, flutamide, fulvestrant, goserelm, idoxifene, letrozole, leuprolide, magestrol, raloxifene, tamoxifen, and toremifcne, a taxane, including, but not limited to, DJ-927, docetaxel, TPI 287, paclitaxel and DHA-paclitaxel, a retinoid, including, but not limited to, ahtretmoin, bexarotene, fenretinide, isotretinoin, and tretinoin; an alkaloid, including, but not limited to, etoposide, homoharπngtonine, temposide, vinblastine, vincristine, vindesinc, and vmorelbine, an antiangiogenic agent, including, but not limited to, AE-941 (GW786034, Neovastat), ABT-510, 2- methoxyestradiol, lenahdomide, and thalidomide, a topoisomerase inhibitor, including, but not limited to, amsacnne, edotecaπn, exatecan, innotecan (also active metabolite SN-38 (7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-
Atty. Dkt. No : 039363-3303 caπφtothecm)), rubitecan, topotecan, and 9-aminocaraptothecin; a kinase inhibitor, including, but not limited to, erlotimb, gefitinib, flavopiridol, imatimb mesylate, lapatinib. sorafenib, sunitinib malate, AEE-788, AG-013736, AMG 706, AMN107, BMS-354825, BMS-599626, UCN-Ol (7- hydroxystaurosporine), and vatalanib; a targeted signal transduction inhibitor including, but not limited to bortezomib, geldanamycin, and rapamycm, a biological response modifier, including, but not limited to, imiquimod, mterferon-α, and interleukin-2; and other chemotherapeutics, including, but not limited to, 3-AP (3-amino-2-carboxyaldehyde fhiosemicarba/one), ammoglutethimide, asparaginase, bryostatin-1, cilengitide, E7389, ixabepilone, procarbazine, suhndac, temsirolimus, tipifaraib. Preferably, the method of treating a cancer involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a composition of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent selected from 5-fluorouracil, carboplatin. dacarbazme, gefitinib, oxaliplatm, paclitaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, vinblastine, bevacizumab, cetuximab, or erlotinib.
10159] In another aspect, the invention provides a method of treating or prophylaxis of a disease or condition in a mammal, by administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of one or more compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, a prodrug of such compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of such compound or prodrug. The compound can be alone or can be part of a composition
[0160] In a related aspect, the invention provides kits that include a composition as descnbed herein In some embodiments, the composition is packaged, e g , in a vial, bottle, flask, which may be further packaged, e.g., within a box, envelope, or bag, the composition is approved by the U. S Food and Drug Administration or similar regulatory agency for administration to a mammal, e.g., a human; the composition is approved for administration to a mammal, e g , a human, for a protein kinase mediated disease or condition; the invention kit includes written instructions for use and/ or other indication that the composition is suitable or approved for administration to a mammal, e.g., a human, for a protein kinase -mediated disease or condition, and the composition is packaged m unit dose or single dose form, e.g., single dose pills, capsules, or the like.
[0161] In aspects involving treatment or prophylaxis of a disease or condition with the compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, the disease or condition is, for example without limitation, neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, cerebrovascular ischemia, multi-mfarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, dementia, senile chorea, and Huntmgton's disease; neoplastic diseases and associated complications, including, but not limited to, chemotherapy-mduced hypoxia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), prostate tumors, mast cell tumors (including, but not limited to, canine mast cell tumors), acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, melanoma, mastocytosis, gliomas, glioblastoma,
Atty. Dkt No 039363-3303 astrocytoma neuroblastoma, sarcomas (e g sai comas of neuroectodermal ongin, leiomyosarcoma), carcinomas (c g lung, breast, pancreatic colon, hepatocellular, renal, female genital tract, squamous cell, carcinoma m situ), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma, non-IIodgkm's lymphoma), MFN2 syndromes, neurofibiomatosis (including but not limited to, Schwann cell neoplasia), myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, cancers of the thyroid, liver, bone, skin, brain, central nervous system, pancieas, lung (e g small cell lung cancer, non small cell lung cancel), breast, colon, bladder, prostate, gastrointestinal tract, endometrium, fallopian tube, testes and o\ ary, and metastasis of tumors to other tissues, pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pain, chrome pain, bone pam, cancer-related pain and migraine, cardiovascular diseases, including, but not limited to, heart failure, ischemic stroke, cardiac hypertrophy, thiombosis (e g thrombotic microangiopathy syndromes), afherosdeiosis, reperfusion injury and ischemia (e g cerebrovascular ischemia, lrver ischemia), inflammation including, but not limited to, age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, Sjogren's Syndrome, Wegener's granulomatosis, psoriasis, scleroderma, chronic thyroiditis, Grave's disease, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, osteoarthritis, endometriosis, scarring (e g dermal, tissue), vascular restenosis, fibrotic disorders, hypereosinophiha, CNS inflammation, pancreatitis, nephritis, atopic dermatitis, and hepatitis, immunodeficiency diseases .including, but not limited to, severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), organ transplant rejection, and graft versus host disease, renal or prostatic diseases, including, but not limited to, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis, prostate hypeq^lasia, chronic renal failure, tubular necrosis, diabetes-associated renal complications, and hypertrophy, metabolic diseases, including, but not limited to, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, hepatic steatosis, insulin lesistance, hyperglycemia, hpolysis and obesity, infection, including, but not limited to, Helicobacter pylori, Hepatitis and Influenza viruses, fever, and sepsis, pulmonary diseases, including, but not limited to, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), asthma, allergy, bronchitis, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis, genetic developmental diseases, including, but not limited to, Noonan's syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, acrocephalosyndactyly type I, Pfeiffer's syndrome, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, Costello syndrome, (faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome), LEOPARD syndrome, cardio- faciocutaneous syndrome (CFC) and neural crest syndrome abnormalities causing cardiovascular, skeletal, intestinal, skin, hair and endocrine diseases, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone reformation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget's disease, hypercalcemia, and metastatis of cancer to bone, Grave's disease, Hirschsprung's disease, lymphoedema, selective T-cell defect (STD), X-hnked agammaglobulinemia, diabetic retinopathy, alopecia, erectile dysfunction, tuberous sclerosis, and diseases associated with muscle regeneration or degeneration, including, but not limited to, sarcopema, muscular dystrophics
Atty. Dkt. No 039363-3303
(including, but not limited to, Duchenne, Becker, Emcry-Dreifuss, Limb-Girdle, Facioscapulohumeral, Myotonic, Oculopharyngeal, Distal and Congenital Muscular Dystrophies), motor neuron diseases (including, but not limited to, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy, intermediate spinal muscular atrophy, juvenile spinal muscular atrophy, spinal bulbar muscular atrophy, and adult spinal muscular atrophy), inflammatory myopathies (including, but not limited to, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis), diseases of the neuromuscular junction (including, but not limited to, myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, and congenital myasthenic syndrome), myopathies due to endocrine abnormalities (including, but not limited to, hyperthyroid myopathy and hypothyroid myopathy) diseases of peripheral nerve (including, but not limited to, Charcot-Maπe-Tooth disease, Dejenne- Sottas disease, and Friedreich's ataxia), other myopathies (including, but not limited to, myotonia congenita, paramyotonia congenita, central core disease, nemahne myopathy, myotubular myopathy, and periodic paralysis), and metabolic diseases of muscle (including, but not limited to, phosphorylase deficiency, acid maltase deficiency, phosphofructokmase deficiency, debrancher enzyme deficiency, mitochondrial myopathy, carnitine deficiency, carnitine palmatyl transferase deficiency, phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency, phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency , lactate dehydrogenase deficiency, and myoadenylate deaminase deficiency).
[0162] In a further aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a c-fms-mediated disease or condition in an animal subject (e g a mammal such as a human, other primates, sports animals, animals of commercial interest such as cattle, farm animals such as horses, or pets such as dogs and cats), e g , a disease or condition characterized by abnormal c-fms activity (e g kinase activity) Invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula II, F ormula III or Formula IV Ln one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and hpolysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget's disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen-prosthetic or wcar-debns-mediated osteolysis, and metastasis of cancer to bone, kidney and genitourinary diseases, including, but not limited to, endometriosis, nephritis (e g glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, I upus nephritis), tubular necrosis, diabetes- associated renal complications (e g diabetic nephiopathy), and renal hypertrophy, disorders of the
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 central nervous system, including, but not limited to, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer s disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory and chronic pain, including, but not limited to, bone pain, and cancers, including, but not limited to, multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) chrome myeloid leukemia (CML), prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovanan cancer, melanoma, glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis of tumors to other tissues, and other chronic myeloproliferative diseases such as myelofibrosis In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulceratrve colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease, diabetic nephiopafhy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chrome pain, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to tissues other than bone In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain
[0163] In a further aspect, the invention provides methods for treating a c-fms-mediated disease or condition in an animal subject (e g a mammal such as a human, other primates, sports animals, animals of commercial interest such as cattle, farm animals such as horses, or pets such as dogs and cats), e g , a disease or condition characterized by abnormal c-fms activity (e g kinase activity) Invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease, diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pam, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to tissues other than bone In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pain, and bone pain In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease In one embodiment, the c-fms mediated disease is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pam, chionic pain, and bone pam
[0164] In a related aspect, invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at risk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, wherin the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis stroke, Abheimcr's disease. Parkinson's disease inflammatory pain, chronic pain, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to other tissues
[0165] In a related aspect, invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering trom or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain
[0166] In a related aspect, invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediatcd disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease
[0167] In a related aspect, invention methods involve administering to the subject suffering from or at nsk of a c-fms-mediated disease or condition an effective amount of compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, whenn the Fms-mediated disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pam, chronic pain, and bone pain
[0168] In a related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosa (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthntis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and hpolysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget's disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen-prosthetic or wear-debns- mediated osteolysis, and metastasis of cancer to bone, kidney and genitourinary diseases, including, but not limited to, endometriosis, nephntis (e g glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis), tubular necrosis, diabetes-associated renal complications (e g diabetic nephropathy), and renal hypertrophy, disorders of the central nervous system, including, but not limited to, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory and chronic pam, including, but not limited to, bone pain, and cancers, including, but not limited to, multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), prostate cancer, breast cancer,
Atty. Dkt No 039363-3303 ovarian cancer, melanoma, glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis of tumors to other tissues, and other chronic myeloproliferative diseases such as myelofibrosis
[0169] In a related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mcdiated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Iype II diabetes. Paget's disease, diabetic nephropathy), multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pain, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to other tissues
[0170] In a related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, chronic pam, and bone pain
[0171] In a related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used m the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediatcd disease or condition selected from the group consisting of multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease
[0172] In d related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Fms-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of inflammatory pain, chronic pam, and bone pam
[0173] In a related aspect, compounds of Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, can be used m the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a Kit-mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasm associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant rejection, and hypereosmophiha
[0174] The compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV with kinase activity IC5C less than 10 μM as determined in a standard ass>ay described herein can be used to treat protein kinase mediated diseases and conditions related to the following protein kinases, for example without limitation
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
AbI, related to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML),
Λktl, related to gastric, prostate, colorectal ovaπan, pancreatic and breast cancer, glioblastoma and leukemia, as w ell as schizophrenia and bipolar disorders, and also use in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs,
Akt2, related to hyperglycemia due to penpheral insulin resistance and nonsuppressible hepatic glucose production accompanied by inadequate compensatory hyperinsulinemia, also related to pancreatic, ovarian and breast cancer,
Akt3, related to melanoma, prostate and breast cancer,
ALK, related to non-Hodgkin lymphomas such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Alk5, related to pancreatic and biliary cancers, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
A-Raf, related to neurologic diseases such as multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovanan), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma), neurofibromatosis, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, pam of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pam, chronic pam, cancer-related pam and migraine, and diseases associated with muscle regeneration or degeneration, including, but not limited to, \ascular restenosis, sarcopema, muscular dystrophies (including, but not limited to, Duchenne, Becker, Emery-Dreifuss, Limb-Girdle, Facioscapulohumeral, Myotonic, Oculopharyngeal, Distal and Congenital Muscular Dystrophies), motor neuron diseases (including, but not limited to, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy, intermediate spinal muscular atrophy, juvenile spinal muscular atrophy, spinal bulbar muscular atrophy, and adult spinal muscular atrophy), inflammatory myopathies (including, but not limited to, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis), diseases of the neuromuscular junction (including, but not limited to, myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, and congenital myasthenic syndrome), myopathies due to endocrine abnormalities (including, but not limited to, hyperthyroid myopathy and hypothyroid myopathy) diseases of peripheral nerve (including, but not limited to, Charcot- Mane-Tooth disease, Dejeπne-Sottas disease, and Friedreich's ataxia), other myopathies (including, but not limited to, myotonia congenita, paramyotonia congenita, central core disease, nemahne myopathy, myotubular myopathy, and periodic paralysis), and metabolic diseases of muscle (including, but not limited to, phosphorylase deficiency acid maltase deficiency, phosphofructokmase deficiency, debrancher enzyme deficiency, mitochondrial myopathy, carnitine deficiency, carnitine palmatyl transferase deficiency, phosphoglycerate
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 kinase deficiency, phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency, lactate dehydrogenase deficiency, and myoaden\late deaminase deficiency)
B-Raf or c-Raf-1 , related to neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, as multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma) neurofibromatosis, acute myeloid leukemia, myelodvsplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, neuroendocπne tumors such as medullary thyroid cancer, carcinoid, small cell lung cancer and pheochromocytoma, pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pain, chronic pam, cancer-related pain, and migraine, cardiovascular diseases including, but not limited to, heart failure, ischemic stroke, cardiac hypertrophy, thrombosis (e g thrombotic microangiopathy syndromes), atherosclerosis, reperfusion injury, inflammation including, but not limited to, psoriasis, arthritis and autoimmune diseases and conditions, osteoarthritis, endometriosis, scarring, vascular restenosis, fibrotic disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), immunodeficiency diseases, including, but not limited to, organ transplant rejection, graft versus host disease, renal or prostatic diseases, including, but not limited to, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis, glomerulonephritis, prostate hyperplasia, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to obesity, infection, including, but not limited to, Helicobacter pylori Hepatitis and Influenza viruses, fever, and sepsis, pulmonary diseases including, but not limited to, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), genetic developmental diseases, including, but not limited to, Noonan's syndrome, Costello syndrome, (faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome), LEOPARD syndrome, cardio-faciocutaneous syndrome (CFC), and neural crest syndrome abnormalities causing cardiovascular skeletal, intestinal, skin, hair and endocrine diseases Brk, related to breast and colon cancer, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma,
Btk, related to X-linked agammaglobulinemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Graves' disease, immune suppression in organ transplant, and drug sensitivity of B-hneage cells,
Cdk2, related to prostate, breast, colorectal and ovanan cancer,
Cdk4, related to glioblastoma (e g glioblastoma multiforme), anaplastic astrocytoma, and breast cancer,
Cdk5, related to Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Lewy body disease.
Cdk6, related to glioblastoma multiforme, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL),
CHKl, related to DNA damage repair, sensitizes cells to chemotherapeutic agents,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Csk, related to colon and pancreatic carcinomas, and autoimmune pathology such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus,
EGFR, related to breast, colorectal, bladder, prostate and non small cell lung cancer, squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck cancer, oral cavity and esophagus, and glioblastoma multiforme,
EphAl , related to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, hepatoma and lung cancer, EphΛ2, related to aberrant short-range contact-mediated axonal guidance, bladder, breast, prostate, colon, skin, cervical, ovaπan, pancreatic and lung cancers, and metastatic melanoma, EphB2, related to angiogenesis disorder (e g ocular angiogenesis disease such as retinopathy), and cancer (e g glioblastoma, breast and liver cancer), EphB4, related to colorectal cancer (CRC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and tumours of the prostate, breast, endometrium, and bladder,
Erk2, related to aberrant proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development, and may be usctul in treating inflammation, for example inflammation associated with Lyme neuroborrehosis, and in treating cancers, such as gastric cancer,
Fak, related to colon and breast tumors, and is also related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma, ductal carcinoma in situ, prostate and hepatocellular carcinoma, and tumor metastases, and may also provide synergistic effects when used with other chemotherapeutic drugs, FGFRl , related to 8pl 1 myeloproliferative syndrome; FGFR2, related to Crouzon Syndrome, Jackson-Weiss Syndrome, Apert Syndrome, craniosynostosis, Pfeiffer Syndrome, acrocephalo syndactyly type V, and Beare-Stevenson Cutis Gyrata Syndrome;
FGFR3, related to angiogenesis, wound healing, achondroplasia, Muenke craniosynostosis, Crouzon syndrome, acanthosis nigricans, thanatophoric dysplasia, bladder carcinomas, and multiple myeloma;
FGFR4, related to cancer of the breast, lung, colon, medullary thyroid, pancreas, ovary, prostate, endometrium, and fallopian tube, head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and leiomyosarcoma;
Fltl , related to non-small cell lung carcinoma, prostate carcinoma, and colorectal cancer, Flt3, related to acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, acute lymphoblastic leukemia,
Flt4, related to primary lymphoedcma,
Fms, related to immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease,
Atty Dkt No • 039363-3303 hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including but not limited to. Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and hpolysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget' s disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen-prosthetic or wear-dcbπs-mediated osteolysis and metastasis of cancer to bone, kidney and genitourinary diseases, including, but not limited to, cndometπosis, nephritis (e g glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis), tubular necrosis, diabetes-associated renal complications (e g diabetic nephropathy), and renal hypertrophy, disorders of the central nervous system, including, but not limited to, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory and chronic pain, including, but not limited to, bone pain, and cancers, including, but not limited to, multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, melanoma, glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis of tumors to other tissues, and other chronic myeloproliferative diseases such as myelofibrosis,
Frk, related to acute myeloid leukemia and type 1 diabetes,
Fyn, related to Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and prevention of metastases, e g in melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma,
GSK3 (Gsk3α and/or Gsk3β), related to CNS disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetes type II, bipolar disorders, stroke, cancer, chronic inflammatory disease, leucopenia, schizophrenia, chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and traumatic head injury,
HCK, related to chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia,
Her2/Erbb2, related to prostate and breast cancer;
Her4/Erbb4, related to childhood medulloblastoma,
IGFlR, related to prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma,
IKK beta, related to leukemia of T-cells, necrosis, insulin resistance, and malignant neoplasms,
Irak4, related to bacterial infections, immunodeficiency syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, cardio hypertrophy, and kidney hypertension,
Itk, related to allergic asthma,
Jakl, related to Hepatitis C virus infection,
Jak2, related to myeloproliferative disorders such as polycythaemia \ era, myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, myeloid metaplasia and leukemias, including, but not limited to, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic neutrophilic leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, CMML, Philadelphia chromosome-negative CML, megakaryocyte leukemia, and acute erythroid leukemia,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Jak3, related to X-lmked severe combined immunodeficiency, myeloproliferative disorders, transplant rejection and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis inflammatory bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis,
Jnk (Jnkl Jnk2, Jnk3), related to metabolic diseases including, but not limited to, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, ischemia (e g cerebrovascular ischemia, liver ischemia), reperfusion injury, cardiac hypertrophy, renal diseases such as chronic renal failure, neoplastic diseases and associated complications, including, but not limited to, chemotherapy-mduced hypoxia, prostate tumors, myeloid leukemia and cancers of the liver bone, skin, brain, pancreas, lung breast, colon, prostate and ovary, transplant rejection, pam ot neuropathic or inflammatory origin including, but not limited to, acute and chronic pain, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including, but not limited to, age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, Sjogren's Syndrome, psonasis, scleroderma, chronic thyroiditis, Grave's disease, myasthenia gravis, and multiple sclerosis, and inflammation in other organs including, but not limited to, CNS inflammation, pancreatitis, nephritis, atopic dermatitis, and hepatitis, airway inflammatory diseases such as asthma, allergy, bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, neurologic diseases such as stroke, cerebrovascular ischemia, neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson s disease, Alzheimer's disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, dementia, senile chorea, head and spinal cord trauma, and Huntmgton's disease More particularly, Jnkl is related to type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity and hepatic steatosis, Jnk2 is related to atherosclerosis, and Jnk3 is related to inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosis, Sjogren's Syndrome, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, airway inflammatory diseases such as asthma, allergy, pulmonary fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and inflammation in other organs, such as CNS inflammation, pancreatitis, nephritis, and hepatitis, neurologic diseases such as stroke, cerebrovascular ischemia, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Huntmgton's disease, and neoplastic diseases such as prostate tumors and myeloid leukemia,
Kdr, related to anti-angiogenesis for treating solid tumor growth (e g ovarian, lung, breast, prancreatic, prostate, colon, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, non small cell lung cancer, and epidermoid cancer), metastasis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic retinopathy and age related macular degeneration,
Kit, related to malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma,
2007/088443
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas ot neuroectodermal ongin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasia associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chionic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant rejection, and hypereosmophiha,
LCK, related to acute lymphoblastic leukemia, T-cell lymphoma, lymphopenia, renal carcinoma, colon carcinoma, severe combined immunodeficiency, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel and type I diabetes
MAP2K1 , related to acute myeloid leukemia, breast, ovarian and liver cancer, MAP2K2, related to cancer and inflammation,
MAP4K4, related to metabolic indications, including, but not limited to, re-sens>itizing fat and muscle cells to insulin, ameliorating the pathology in adipocytes, ameliorating the pathology in muscle cells, metabolic syndrome, and type II diabetes, a broad range of oncology indications, including, but not limited to, blocking the migration, invasion and metastasis in many different tumor types, and T-cell mediated autoimmune diseases, MAPKAPK2, cancer (e g prostate, breast), stroke, menengitis, and inflammatory disorders, Met, related to kidney, breast, bladder, non-small-cell lung, colorectal, and bladder cancers, and hepatocellular carcinoma,
Mnkl , related to conditions associated with heat shock, nutπent depπvation, oxidative or osmotic stress, and infection of mammalian cells (e g with viruses such as adenovirus (Ad) or influenza virus), and autoimmune diseases, MLKl, related to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, and inflammatory disorders, p38, related to acute coronary syndrome, stroke, atherosclerosis, and inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and Crohn's disease, PDGrR (PDGFRΛ, PDGFRB), related to idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia glioma, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, metastatic medulloblastoma, atherogenesis, and restenosis More particularly, PDGFRA related to idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, glioma, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, metastatic medulloblastoma, atherogenesis, and restenosis, and PDGFRB related to idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, and metastatic medulloblastoma, PDPKl , related to cancer and diabetes,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Piml, related to cancers such as hematopoietic (e g acute myeloid and acute lymphoid leukemias) and prostate cancers and non-Hodgkm's lymphomas, Pim2, related to lymphomas, Pim3, related to hepatocellular carcinoma,
PKC alpha, related to pituitary tumors and prefrontal cortical dysfunction such as distractibihty, impaired judgment, impulsivity, and thought disorder, also may be used to sensitize chemotherapy in breast, colon, and non small cell lung cancers, PKC beta, related to diabetic retinopathy, PKC-theta, related to insulin resistance, F-cell lymphoma, Plkl, related to cancers (e g lymphoma of the thyroid, non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, colorectal cancers leukemias and melanoma), also useful as sensitizer in chemotherapy, Pyk2, related to inflammation (e g osteoporosis, polycystic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthintis and inflammatory bowel disease), CNS disease (e g Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease), stroke and cancers (e g gliomas, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer), Ret, related to cancer of the thyroid, neuroblastoma, familial medullary thyroid carcinoma (FM PC), multiple endocrine neoplasia type I1A and HB (MEN2A, MEN2B), and neurodegenerative disorders (e g Hirschsprung's disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis),
ROCK (ROCK-I , ROCK-2), related to cancers (e g o\aπan cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer), ocular disease (e g glaucoma), cardiac hypertrophy, improved renal perfusion, transplant rejection, and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ron, related to cancer and inflammation, Src, related to cancer and osteoporosis, Stk6, related to gastric bladder, breast, lung, CNS, ovarian, kidney, colon, prostate, pancreas, and cervical cancers, melanoma, leukemia, and neuroblastoma, Syk, related to lymphomas (e g mantle cell lymphoma), TEC, related to sepsis, septic shock, inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel disease (EBD), and ulcerative colitis,
Tie2 (TEK), related to cancer, arthritis (e g rheumatoid arthritis), and atherosclerosis, IYkA, related to pain (e g chronic pam, neuropathic pain), cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer), allergic disorders (e g asthma), arthritis, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and psoriasis,
TrkB, related to obesity, hyperphagia, developmental delays, cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, Wilms tumors, neuroblastoma pancreatic cancer), \ anous neuropathies (e g stroke, multiple sclerosis, transverse myelitis, and encephalitis), and diabetes
Yes, related to various cancers including, but not limited to, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and
US2007/088443
Atty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
Zap70, related to AIDS, systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, atherosclerosis, rejection of transplanted organs or tissues, allograft rejection including, but not limited to, acute and chronic allograft rejection, graft versus host disease, rheumathoid arthritis, psoriasis, systemic sclerosis, atopic dermatitis, eczematous dermatitis, alopecia, and inflammation of the nasal mucus membrane, including all forms of rhinitis.
[0175] Additional aspects and embodiments will be apparent from the following Detailed Description and from the claims.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0176] As used herein the following definitions apply unless clearly indicated otherwise:
[0177] "Halogen" refer to all halogens, that is, chloro (Cl), fluoro (F), bromo (Br), or iodo (I).
[0178] "Hydroxyl" or "hydroxy" refer to the group -OH.
[0179] "Thiol" refers to the group -SH.
[0180] "Lower alkyl" alone or in combination means an alkane -derived radical containing from 1 to 6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) that includes a straight chain alkyl or branched alkyl. The straight chain or branched alkyl group is attached at any available point to produce a stable compound. In many embodiments, a lower alkyl is a straight or branched alkyl group containing from 1-6, 1-4, or 1-2, carbon atoms, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, t-butyl, and the like. A "substituted lower alkyl" denotes lower alkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R0, -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R0, -S(O)2R0, -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0. -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NIIC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0, -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Re, -Rf, and -Rg. Furthermore, possible substitutions include subsets of these substitutions, such as are indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound. For example "fluoro substituted lower alkyl" denotes a lower alkyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, such as perfluoroalkyl, where preferably
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 the lower alkyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms. While it is understood that substitutions are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, when optionally substituted alkyl is an R group of a moiety such as -OR (e.g. alkoxy), -SR (e.g. thioalkyl), -NHR (e.g. alkylamino), -C(O)NHR, and the like, substitution of the alkyl R group is such that substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substituents that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety. "C2-6 alkyl" denotes lower alkyl containing 2-6 carbon atoms. A "substituted C2.6 alkyl" denotes optionally substituted lower alkyl containing 2-6 carbon atoms. A "substituted methyl" denotes methyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with 1 , 2, or 3 substituents, wherein the substituents are selected as per optionally substituted lower alkyl.
[0181] "C1.3 alkylene" refers to a divalent alkane-derived radical containing 1-3 carbon atoms, straight chain or branched, from which two hydrogen atoms are taken from the same carbon atom or from different carbon atoms. C) 3 alkylene includes methylene -CH2-, ethylene -CHaCH2-. propylene -CH2CH2CH2-, and isopropylene -CH(CH3)CH2- or -CH2CH(CH3)-. C1-3 alkylene substituted with one or more substituents indicates C1.3 alkylene that is independently substituted, with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents as indicated, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound.
[0182] "Lower alkenyl" alone or in combination means a straight or branched hydrocarbon containing 2-6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) and at least one, preferably 1-3, more preferably 1-2, most preferably one, carbon to carbon double bond. Carbon to carbon double bonds may be either contained within a straight chain or branched portion. Examples of lower alkenyl groups include ethenyl, propenyl, isopropenyl, butenyl, and the like. A "substituted lower alkenyl" denotes lower alkenyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R", -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R0, -S(O)2R0, -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0, -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Rf, and -Rg. Further, possible substitutions include subsets of these substitutions, such as are indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound. For example "fluoro substituted lower alkenyl" denotes a lower alkenyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkenyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms. While it is understood that substitutions are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, substitution of alkenyl groups are such that -F, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -C(NH)-, -S(O)-, -S(O)2-, -O-, -S-, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), are not bound to an alkene carbon thereof. Further, where alkenyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)R, and the like, substitution of the moiety is such that any -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, -S(O)2-, -O-, -S-, or N thereof (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkene carbon of the alkenyl substituent or R group. Further, where alkenyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)NHR, and the like, substitution of the alkenyl R group is such that substitution of the alkenyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substitucnts that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkenyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety. An "alkenyl carbon" refers to any carbon within an alkenyl group, whether saturated or part of the carbon to carbon double bond. An "alkene carbon" refers to a carbon within an alkenyl group that is part of a carbon to carbon double bond.
[0183] "Lower alkynyl" alone or in combination means a straight or branched hydrocarbon containing 2-6 carbon atoms (unless specifically defined) containing at least one, preferably one, carbon to carbon triple bond. Examples of alkynyl groups include ethynyl, propynyl, butynyl, and the like. A "substituted lower alkynyl" denotes lower alkynyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of -F, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R0, -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R", -S(O)2R0, -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R", -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NFIC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R", -NFIS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0, -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Re, and -RE. Further, possible substitutions include subsets of these substitutions, such as are indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound. For example "'fluoro substituted lower alkynyl" denotes a lower alkynyl group substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkynyl is substituted with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms. While it is understood that substitutions
43
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, substitution of alkynyl groups arc such that -F, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -C(NH)-, -S(O)-, -S(O)2-, -O-, -S-, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkyne carbon thereof. Further, where alkynyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)R, and the like, substitution of the moiety is such that any -C(O)-, -C(S)-,-S(O)-, -S(O)2-, -O-. -S-, or N thereof (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) are not bound to an alkyne carbon of the alkynyl substituent or R group. Further, where alkynyl is a substituent of another moiety or an R group of a moiety such as -OR, -NHR, -C(O)NHR, and the like, substitution of the alkynyl R group is such that substitution of the alkynyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) excludes substituents that would result in any O, S, or N of the substituent (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom) being bound to the alkynyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N of the moiety. An "alkynyl carbon" refers to any carbon within an alkynyl group, whether saturated or part of the carbon to carbon triple bond. An "alkyne carbon" refers to a carbon within an alkynyl group that is part of a carbon to carbon triple bond.
[0184] "Cycloalkyl" refers to saturated or unsaturated, non-aromatic monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic carbon ring systems of 3-10, also 3-8, more preferably 3-6, ring members per ring, such as cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, adamantyl, and the like. A "substituted cycloalkyl" is a cycloalkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R0, -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R0, -S(O)2R0, -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R", -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Re, -Rf, and -RE.
[Ol 85] "Hetcrocycloalkyl" refers to a saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic cycloalkyl group having from 5 to 10 atoms in which from 1 to 3 carbon atoms in the ring are replaced by heteroatoms of O, S or N, and are optionally fused with benzo or heteroaryl of 5-6 ring members. Heterocycloalkyl is also intended to include oxidized S or N, such as sulfinyl, sulfonyl and N-oxide of a tertiary ring nitrogen. Heterocycloalkyl is also intended to include compounds in which a ring carbon may be oxo substituted, i.e. the ring carbon is a carbonyl group, such as lactones and lactams. The point of attachment of the heterocycloalkyl ring is at a carbon or nitrogen atom such that a stable ring is
US2007/088443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 retained. Examples of heterocycloalkyl groups include, but are not limited to, morpholino, tetrahydrofuranyl, dihydropyridinyl, piperidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrrolidonyl, piperazinyl, dihydrobenzofuryl, and dihydroindolyl. A "substituted heterocycloalkyl" is a heterocycloalkyl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NlI2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NII2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R0, -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R0, -S(O)2R0. -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR", -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0. -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Re, -Rr, and -Re.
[0186] "Aryl" alone or in combination refers to a monocyclic or bicyclic ring system containing aromatic hydrocarbons such as phenyl or naphthyl, which may be optionally fused with a cycloalkyl of preferably 5-7, more preferably 5-6, ring members. "Arylene" is a divalent aryl, A "substituted aryl" is an aryl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R", -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR", -S(O)R0, -S(O)2R0, -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR0, -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NTl0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R0, -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NIIR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0, -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Re, -Rf, and -R8. A "substituted arylene" is a divalent substituted aryl.
[0187] "Heteroaryl" alone or in combination refers to a monocyclic aromatic ring structure containing 5 or 6 ring atoms, or a bicyclic aromatic group having 8 to 10 atoms, containing one or more, preferably 1-4, more preferably 1-3, even more preferably 1-2, heteroatoms independently selected from the group consisting of O, S, and N. Heteroaryl is also intended to include oxidized S or N, such as sulfmyl, sulfonyl and N-oxide of a tertiary ring nitrogen. A carbon or nitrogen atom is the point of attachment of the heteroaryl ring structure such that a stable compound is produced.
Atty. Dkt No.: 039363-3303
Examples of heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, pyridinyl, pyridazinyl pyrazinyl, quinaoxalyl, indolizinyl, benzo[b]thienyl, quinazolinyl, purinyl, indolyl, quinolinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, oxathiadiazolyl, isothiazolyl, tetrazolyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, furanyl, benzofuryl, and indolyl. "Nitrogen containing heteroaryl" refers to heteroaryl wherein any heteroaloms are N. "Heteroarylene" is a divalent heteroaryl. Λ "substituted heteroaryl" is a heteroaryl that is independently substituted, unless indicated otherwise, with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, wherein the substituents are selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR0, -SR0, -OC(O)R0, -OC(S)R0, -C(O)R0, -C(S)R0, -C(O)OR0, -C(S)OR0, -S(O)R", -S(O)2R", -C(O)NHR0, -C(S)NHR0, -C(O)NR0R0, -C(S)NR0R0, -S(O)2NHR", -S(O)2NR0R0, -C(NH)NHR0, -C(NH)NRPRC, -NHC(O)R0, -NHC(S)R0, -NR0C(O)R0, -NR0C(S)R0, -NHS(O)2R0, -NR0S(O)2R0, -NHC(O)NHR0, -NHC(S)NHR0, -NR0C(O)NH2, -NR0C(S)NH2, -NR0C(O)NHR0, -NR0C(S)NHR0, -NHC(O)NR0R0, -NHC(S)NR0R", -NR0C(O)NR0R0, -NR0C(S)NR0R0, -NHS(O)2NHR0, -NR0S(O)2NH2, -NR0S(O)2NHR0, -NHS(O)2NR0R0, -NR0S(O)2NR0R0, -NHR0, -NR0R0, -Rd, -Re, -Rf, and -Rg. "Substituted heteroarylene" is a divalent substituted heteroaryl.
[0188] The variables R0, Rp, Rc, Rd, Re, R1 and RB as used in the description of optional substituents for alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are defined as follows:
each R0, Rp, and Rc are independently selected from the group consisting of Rd, Re, Rf, and Rg, or Rp and Rc combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or a 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl, wherein the 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO2, -CN, -OH, -NII2, -ORU, -SRU, -NHRU, -NRURU, -R\ and -Ry;
each Rd is independently lower alkyl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -0Rk, -SR\ -0C(0)Rk, -OC(S)Rk, -C(O)R", -C(S)RL, -C(0)0R\ -C(S)OR", -S(O)Rk, -S(O)2R\ -C(O)NHR", -C(S)NHRk, -C(0)NRkRk, -C(S)NRfcRk, -S(O)2NHR",
-C(NH)NHRk, -C(NH)NRmRn, -NHC(O)R", -NHC(S)R", -NRkC(0)Rk, -NRkC(S)Rk, -NHS(0)2R\ -NRkS(0)2Rk, -NHC(0)NHRk, -NHC(S)NHR", -NRkC(0)NH2, -NRkC(S)NH2, -NR"C(0)NHRk, -NRkC(S)NHRk, -NHC(0)NRkRk. -NHC(S)NRkRk, -NRkC(0)NRkRk, -NRkC(S)NRkRk, -NHS(O)2NHR", -NRkS(O)2NH2, -NRkS(0)2NHRk, -NHS(0)2NRkRk, -NRkS(0)2NRkRk, -NHRk, -NRkRk, -R1, and -RJ;
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 each Rc is independently lower alkenyl, wherein lower alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2. -C(NH)NH2, -0Rk, -SRk, -OC(O)Rk, -OC(S)Rk, -C(O)Rk, -C(S)Rk, -C(O)OR", -C(S)ORk, -S(O)R\ -S(O)2Rk, -C(O)NHRk, -C(S)NHRk, -C(O)NRkRk, -C(S)NRkRk, -S(O)2NHRk, -S(O)2NRkRk, -C(NH)NHRk, -C(NH)NRmR", -NHC(O)R\ -NHC(S)Rk, -NRkC(O)Rk, -NRkC(S)Rk, -NHS(0)2Rk, -NRkS(O)2Rk, -NHC(O)NHR", -NHC(S)NHRk, -NRkC(0)NH2, -NRkC(S)NH;, -NRkC(O)NHR\ -NRkC (S)NIIR", -NHC(0)NRkRk, -NHC(S)NRkRk, -NRkC(O)NRkRk,
-NHS(O)2NHRk, -NRkS(0),NH2, -NRkS(O)2NHRk, -NHS(O)2NRkRk, -NRkS(0)2NRkR\ -NHRk, -NRkRk, -Rh, and -RJ;
each R* is independently lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkynyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NII2, -C(NH)NH2, -0Rk, -SRk, -OC(O)Rk, -OC(S)R", -C(O)Rk, -C(S)Rk, -C(O)OR", -C(S)ORk, -S(O)R\ -S(O)2R", -C(0)NHRk, -C(S)NHRk, -C(0)NRkRk, -C(S)NRkRk, -S(O)2NHR",
-C(NH)NHR", -C(NH)NR111R", -NHC(0)Rk, -NHC(S)R", -NRkC(0)Rk, -NRkC(S)R", -NHS(O)2R", -NRkS(O),Rk, -NHC(O)NHR", -NHC(S)NHRk, -NRkC(0)NH2, -NRkC(S)NH2, -NRkC(0)NHR", -NRkC(S)NHRk, -NHC(0)NRkRk, -NHC(S)NRkRk, -NRkC(0)NRkRk, -NRkC(S)NRkRk, -NHS(O)2NHR\ -NRkS(O)2NH2, -NRkS(0)2NHRk, -NHS(O)2NRkRk, -NR"S(0)2NRkRk, -NHR\ -NRkRk, -Rh, and -RJ;
each Rg is independently selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH7, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -0Rk, -SRk, -OC(O)R", -OC(S)Rk, -C(O)Rk, -C(S)Rk, -C(O)ORk, -C(S)OR\ -S(O)Rk, -S(O)2Rk, -C(0)NHRk, -C(S)NHRk, -C(0)NRkRk, -C(S)NRkRk, -S(O)2NHRk, -S(0)2NRkRk, -C(NH)NHRk, -C(NH)NR111R", -NHC(O)R", -NHC(S)R", -NRkC(0)Rk, -NRkC(S)Rk, -NHS(O)2R", -NRkS(0)2Rk, -NHC(0)NHRk, -NHC(S)NHRk, -NR"C(0)NH2) -NRkC(S)NH2, -NRkC(O)NHR", -NRkC(S)NHRk, -NHC(0)NRkRk, -NHC(S)NRkRk, -NR"C(0)NR"Rk, -NRkC(S)NRkRk, -NHS(0)2NHRk, -NRkS(O)2NH2, -NRkS(0)2NHRk, -NHS(0)2NRkRk, -NRkS(0)2NRkRk, -NHRk, -NRkRk, -Rh, -R1, and -R1;
wherein Rk, R'n, and R" at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of Rh, R', and R', or Rra and Rn combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or a 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl, wherein the 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally
88443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO2. -CN, -OH, -NII2, OR", -SR", -NHR11. -NRURU, -R\ and -Ry;
wherein each Rh is independently lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHT1 -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -0Rr, ~SRr, -OC(O)Rr, -OC(S)Rr, -C(0)Rr, -C(S)Rr, -C(O)ORr, -C(S)ORr, -S(O)Rr, -S(O)2Rr, -C(0)NHRr, -C(S)NHRr, -C(O)NR1R', -C(S)NRrRr, -S(0)2NHRr, -S(0)2NRrRr, -C(NH)NHR', -C(NH)NR8R1, -NHC(O)R1, -NHC(S)Rr, -NRrC(0)Rr, -NRrC(S)Rr, -NHS(O)2R', -NRrS(0)2Rr, -NHC(O)NHR', -NHC(S)NIIR', -NRrC(0)NH2, -NR'C(S)NH2, -NRrC(0)NHRr, -NR'C(S)NHRr, -NHC(0)NRrR', -NHC(S)NR'R', -NRrC(O)NRrRr, -NRrC(S)NRrRr, -NHS(O)2NHR', -NR'S(O)2NH2, -NR'S(0)2NHR', -NHS(O)2NR'Rr, -NRrS(0)2NR'Rr, -NHR', -NR1R', -R1, and -RJ;
wherein each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkenyl and lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkenyl or lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NH2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR', -SR', -OC(O)R', -OC(S)R', -C(O)R', -C(S)R', -C(O)OR', -C(S)OR', -S(O)R', -S(O)2R', -C(O)NHR', -C(S)NHR', -C(O)NR1R', -C(S)NR'Rr, -S(O)2NHR', -S(O)2NR1R', -C(NH)NHR', -C(NH)NRX -NHC(O)R'. -NHC(S)R', -NR1C(O)R', -NR'C(S)Rr, -NHS(O)2R', -NR'S(0)2R', -NHC(O)NHR', -NHC(S)NHR', -NRrC(0)NH2, -NR'C(S)NH2, -NR'C(0)NHRr, -NR'C(S)NHRr, -NHC(O)NR1R', -NHC(S)NR1R', -NR'C(0)NR'Rr, -NRrC(S)NR'Rr, -NHS(O)2NHR', -NR'S(O)2NH2, -NRrS(0)2NHR', -NHS(0)2NR'R', -NR1S(O)2NR1R', -NHR', -NR1R', and -RJ;
wherein each R1 is independently selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, hcterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2 or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(S)OH, -C(O)NII2, -C(S)NH2, -S(O)2NH2, -NHC(O)NH2, -NHC(S)NH2, -NHS(O)2NH2, -C(NH)NH2, -OR', -SR', -OC(O)R', -OC(S)Rr, -C(O)R', -C(S)R', -C(O)OR', -C(S)ORr, -S(O)R', -S(O)2R', -C(O)NHR', -C(S)NHR', -C(O)NR1R', -C(S)NR'Rr, -S(O)2NHR'. -S(O)2NR1R', -C(NH)NHR', -C(NH)NR4R1, -NIIC(O)R', -NHC(S)R', -NR'C(0)Rr, -NR'C(S)R', -NHS(O)2R', -NR'S(O)2Rr, -NHC(O)NHR', -NHC(S)NHR', -NR'C(O)NH2, -NR'C(S)NH2, -NR1C(O)NHR', -NR'C(S)NHRr, -NHC(O)NR1R', -NHC(S)NR1R', -NR^(O)NR1R'. -NR'C(S)NR'Rr, -NHS(O)2NHR', -NR'S(O)2NH2, -NR'S (O)2NHR', -NHS(0)2NR'R', -NR'S(0)2NR'Rr, -NHR', -NR'R', cycloalkylamino, and -Rx;
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 wherein each Rr, R\ and R1 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, C3_6 alkenyl, C,_6 alkynyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of-Ry, fluoro, -OH, -NH2. lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the lower alkyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N, of -ORr, -SRr, -C(O)ORr, -C(S)ORr, -C(0)NHRr, -C(S)NIW, -C(0)NRrRr, -C(S)NRV, -S(O)2NHRr, -S(O)2NRrRr, -C(NH)NHRr, -NRrC(O)Rr, -NRrC(S)Rr, -NRrS(O)2Rr, -NHC(0)NHRr, -NHC(S)NHRr, -NRrC(0)NH2, -NRrC(S)NH2, -NRrC(0)NHRr, -NRrC(S)NHRr, -NHC(O)NRrRr, -NΗC(S)NRrRr, -NRrC(0)NRrRr, -NRrC(S)NRrRr, -NHS(O)2NHRr, -NRrS(O)2NH2, -NRrS(O)2NHRr, -NHS(O)2NRrRr, -NRrS(O)2NRTlr, -NHRr, or -NRrRr is selected from the group consisting of fluoro and -R\ and wherein C3_6 alkenyl or C3_6 alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -Ry, fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the C3.6 alkenyl or C3.6 alkynyl carbon bound to any O, S, or N, of -0Rr, -SRr, -C(0)0Rr, -C(S)ORr, -C(0)NHRr, -C(S)NHRr, -C(0)NRrRr, -C(S)NRrRr, -S(O)2NIIRr, -S(O)2NR'Rr, -C(NH)NHR1, -NRrC(0)Rr, -NRrC(S)Rr, -NRrS(0)2Rr, -NIIC(0)NHRr, -NHC(S)NHRr, -NRrC(0)NH2, -NR1C(S)NH2, -NRrC(O)NHRr, -NRrC(S)NHRr, -NHC(0)NRrRr, -NHC(S)NRTf, -NRrC(0)NRrRr, -NRrC(S)NRrRr, -NHS(O)2NHRr, -NRrS(O)jNH2, -NRrS(0)2NHRr, -NHS(O)2NRTl', -NRrS(O)2NRrRr, -NHRr, or -NRrRr is selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and -Ry, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, or Rs and R1 combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or a 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl, wherein the 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl or 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO2, -CN, -OH, -NH2, ORU, -SRU, -NHRU, -NRURU, -R\ and -Ry;
wherein each R11 is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, CM alkenyl, C3_6 alkynyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of-Ry, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the lower alkyl carbon bound to the O of -ORU, S of -SRU, or N of -NHR" is fluoro or -Ry, and wherein Cj-6 alkenyl or C3.6 alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -R*, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the CM alkenyl or C3.6 alkynyl carbon bound to the O of -ORU, S of -SRU, or N of -NHR" is fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, or -Ry, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
wherein each R" is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, lower alkenyl and lower alkynyl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1 , 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -Ry, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, and wherein lower alkenyl or lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of -Ry, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
wherein each Ry is selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, -NO2, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino.
[0189] In some embodiments, all occurrences of optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted C2.6 alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, or optionally substituted lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 consisting of fluoro, -NO2, -CN, -ORla, -SRla, -NRlaRla, -OC(O)Rla, -OC(S)R1", -C(O)R1". -C(S)Rl a, -C(O)OR!a, -C(S)ORla, -C(0)NRl 3Rl a, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S (O)2NR13R1 \ -C(NH)NR13R1", -NRlaC(0)Rla, -NR13C(S)R13, -NR13S(O)2R13, -NRlaC(0)NRlaRla, -NRlaC(S)NRlaRla, -NRl aS(0)2NRlaRl a, -S(O)Rl a, -S(O)2R13, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl arc optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO2, -CN, -0Rla. -SRla, -NRl aRla, -OC(O)Rla, -OC(S)R13, -C(0)Rla, -C(S)R13, -C(O)OR13, -C(S)OR13, -C(0)NRlaRla, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S(0)3NRlaRla, -C(NH)NRlaRla, -NRIaC(O)Rla, -NRlaC(S)Rla, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -NRlaC(0)NRlaRIa, -NRlaC(S)NRlaRla, -NRlaS(0)2NRlaRla, -S(O)R13, -S(O)2Rla, -Rlb, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -Rlb, and all occurrences of optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted arylene, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted heteroarylene, or optionally substituted 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2, or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -NO2, -CN, -ORla, -SRla, -NRlaRla, -0C(0)Rla, -OC(S)Rla, -C(O)R13, -C(S)Rla, -C(O)ORla, -C(S)ORla, -C(0)NRlaRla, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S(O)2NR13R13, -C(NH)NRlaRu, -NRl aC(0)Rla, -NR13C(S)R13, -NRlaS(O)2Rl a, -NR13C(O)NR1 aRla, -NR13C(S)NR13R13, -NRlaS(0)2NRlaRla, -S(O)Rla, -S(O)2R13, -Rlb, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -Rlb, wherein Rla is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, provided, however, that hydrogen is not bound to any of C(S), C(O), S(O), or S(O)2 of -OC(O)Rla, -OC(S)R1', -C(O)R13, -C(S)Rla, -NRlaC(0)Rla, -NRuC(S)Rla, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -S(O)R13, or -S(O)2R1", -Rlb, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -Rlb, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR13, -SRl a, -NR18R1", -C(O)ORla, -C(S)OR13, -C(O)NRlaRla, -C(S)NR13R18, -S(O)2NR13R13, -C(NH)NRlaRla, -NRlaC(0)Rla, -NRlaC(S)Rla, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -NR13C(O)NR13R13, -NRlaC(S)NRl3Rla, or -NRl3S(O)3NRlaRla, is fluoro or -Rlb, and wherein -Rlb is selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heleroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino.
Atty Dkt. No.- 039363-3303
[0190] In some embodiments, all occurrences of optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted C2_6 alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, or optionally substituted lower alkynyl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -CN, -ORla, -SRla, -NRlaRla, -C(O)Rla, -C(S)Rld, -C(O)OR1", -C(O)NR111R1 a, -C(S)NRl aRla, -S(O)2NR13R13, -NRlaC(O)RIa, -NRuC(S)Rla, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -S(O)RIa, -S(O)2Rla, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, -ORl a, ~SRla, -NRlaRla, -C(O)Rla, -C(S)Rla, -C(O)ORla, -C(0)NRlaRla, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S(O),NRlaRu, -NRlaC(O)Rla, -NRlaC(S)Rld, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -S(O)Rla, -S(O)2Rla, -Rl b, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -Rlb, and all occurrences of optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted arylene, optionally substituted heteroaryl, optionally substituted heteroarylene, or optionally substituted 5 or 7 membered nitrogen containing heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2, or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, -OR1J, -SRla, -NRlaRla, -C(O)R1", -C(S)Rla, -C(O)ORla, -C(O)NR111R13, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S(O)2NR13R18, -NR111C(O)R1 \ -NRl aC(S)Rla, -NRlaS(O)2Rla, -S(O)Rl a, -S(O>Rla, -Rlb, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1 , 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -Rl b, wherein Rla is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, provided, however, that hydrogen is not bound to any of C(S), C(O), S(O), or S(O)2 Of -C(O)R13, -C(S)Rla, -NRl aC(0)Rl a, -NRl aC(S)Rla, -NR11S(O)2R1 \ -S(O)Rla, or -S(O)2Rla, -Rlb, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -Rlb, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -0Rl a, -SRla, -NRlaRla, -C(O)OR13, -C(0)NRlaRIϋ, -C(S)NRlaRla, -S(0)2NRlaRl a, -NRlaC(0)Rla, -NRlaC(S)Rla, or -NRlaS(O)2Rla, is fluoro or -Rlb, and wherein -Rl b is selected from the group consisting of cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl. wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more, also 1, 2 or 3 groups or substituents selected lrom the group consisting of halogen, -CN, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino.
US2007/088443
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0191] "Lower alkoxy'" denotes the group -ORZ, where R^ is lower alkyl "Substituted lower alkoxy" denotes lower alkoxy m which Rz is lower alkyl substituted with one or more substituents as indicated herein, for example, m the descnption of compounds of Formula I Formula II, Formula III υr Formula IV, including descriptions of substituted cycloalkyl, cycloheteroalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound Preferably, substitution of lower alkoxy is with 1 , 2, 3, 4, or 5 substituents, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents For example "fluoro substituted lower alkoxy" denotes lower alkoxy in which the lower alkyl is substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkoxy is substituted with 1 , 2 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1 , 2, or 3 fluoro atoms W hile it is understood that substitutions on alkoxy are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, substitution ot alkoxy is such that O, S, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl nng atom), are not bound to the alkyl carbon bound to the alkoxy O Further, where alkoxy is descnbed as a substituent of another moiety, the alkoxy oxygen is not bound to a carbon atom that is bound to an O, S, or N of the other moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl ring atom), or to an alkene or alkyne carbon of the other moiety
[0192] "Lower alkylthio" denotes the group -SRaa, where Raa is lower alkyl "Substituted lower alkylthio" denotes lower alkylthio m which Raa is lower alkyl substituted with one or more substituents as indicated herein, for example, in the description of compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III or Formula IV, including descriptions of substituted cycloalkyl, cycloheteroalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound Preferably, substitution of lower alkylthio is with 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 substituents, also 1, 2, or 3 substituents For example "fluoro substituted lower alkylthio" denotes lower alkylthio in which the lower alkyl is substituted with one or more fluoro atoms, where preferably the lower alkylthio is substituted with 1 , 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluoro atoms, also 1, 2, or 3 fluoro atoms While it is understood that substitutions on alkylthio are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, substitution of alkylthio is such that O, S, or N (except where N is a heteroaryl nng atom), are not bound to the alkyl carbon bound to the alkylthio S Further, where alkylthio is described as a substituent of another moiety, the alkylthio sulfur is not bound to a carbon atom that is bound to an O, S, or N of the other moiety (except where N is a heteroaryl nng atom), or to an alkene or alkyne carbon ol the other moiety
[0193J "Amino" or "amine" denotes the group -NFL "Mono-alkylammo" denotes the group -NHRbb where Rbb is lower alkyl '-Di-alkylamino" denotes the group -NRbbRc", where Rbb and Rcc are independently lower alkyl "Cycloalkylammo" denotes the group -NRddRee, where Rdd and R" combine with the nitrogen to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl, where the heterocyc Io alkyl may contain an additional heteroatom within the nng, such as O, N, or S, and may also be further substituted with lower alkyl Examples of 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl include, but are not limited to, pipeπdine, piperazme, 4-methylpiperazme, morphohne, and thiomorpholine While it is
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 understood that when mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, or cycloalkylamino are substituents on other moieties that are attached at any available atom to produce a stable compound, the nitrogen of mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo, or cycloalkylamino as substituents is not bound to a carbon atom that is bound to an O, S, or N of the other moiety
10194] As used herein, the term "composition" refers to a formulation suitable tor administration to an intended ammal subject for therapeutic purposes that contains at least one pharmaceutically active compound and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient
[0195] The term "pharmaceutically acceptable" indicates that the indicated material does not have properties that would cause a reasonably prudent medical practitioner to avoid administration of the material to a patient, taking into consideration the disease or conditions to be treated and the respective route of administration For example, it is commonly required that such a material be essentially sterile, e g , tor mjectibles
[0196] In the present context, the term "therapeutically effective" or "effective amount" indicates that the materials or amount of material is effective to prevent, alleviate, or ameliorate one or more symptoms of a disease or medical condition, and/or to prolong the survival of the subject being treated
[0197] In the present context, the terms "synergistically effective" or "synergistic effect" indicate that two or more compounds that are therapeutically effective, when used in combination, provide improved therapeutic effects greater than the additive effect that would be expected based on the effect of each compound used by itself
[0198] As used herein, the terms "ligand" and "modulator" are used equivalently to refer to a compound that changes (i e , increases or decreases) the activity of a target biornolecule, e g , an enzyme such as a kinase Generally a ligand or modulator will be a small molecule, where "small molecule refers to a compound with a molecular weight of 1500 daltons or less, or preferably 1000 daltons or less, 800 daltons or less, or 600 daltons or less Thus, an "improved ligand" is one that possesses better pharmacological and/or pharmacokinetic properties than a reference compound, where "better" can be defined by one skilled in the relevant art for a particular biological system or therapeutic use
[0199] hi the context of compounds binding to a target, the terms "greater affinity" and "selective" indicates that the compound binds more tightly than a reference compound, or than the same compound in a reference condition, i e , with a lower dissociation constant In some embodiments, the greater affinity is at least 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 50, 100, 200, 400, 500, 1000, or 10,000-fold greater affinity
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0200] As used herein in connection with compounds of the invention, the term 'synthesizing" and like terms means chemical synthesis from one or more precursor materials
[0201] By "assaying" is meant the creation of experimental conditions and the gathering of data regarding a particular result of the experimental conditions For example, enzymes can be assayed based on their ability to act upon a detectable substrate A compound or hgand can be assayed based on its ability to bind to a particular target molecule or molecules
[0202] As used herein, the term "modulating" or "modulate" refers to an effect of altering a biological activity especially a biological activity associated with a particular biomolecule such as a protein kinase For example, an agonist or antagonist of a particular biomolecule modulates the activity of that biomolecule, e g , an enzyme by either increasing (e g agonist, activator), or decreasing (e g antagonist, inhibitor) the activity of the biomolecule, such as an enzyme Such activity is typically indicated in terms of an inhibitory concentration (IC50) or excitation concentration (EC50) of the compound for an inhibitor or activator, respectively, with respect to, for example an enzyme
[0203] In the context of the use, testing, or screening of compounds that are or may be modulators, the term "contacting" means that the compound(s) are caused to be in sufficient proximity to a particular molecule, complex, cell, tissue, organism, or other specified material that potential binding interactions and/or chemical reaction between the compound and other specified material can occur
[0204] As used herein in connection with amino acid or nucleic acid sequence, the term "isolate" indicates that the sequence is separated from at least a portion of the ammo acid and/or nucleic acid sequences with which it would normally be associated
[0205] In connection with amino acid or nucleic sequences, the term "purified" indicates that the subject molecule constitutes a significantly greater proportion of the biomolecules in a composition than the proportion observed in a prior composition, e g , in a cell culture The greater proportion can be 2-fold, 5-fold, 10-fold, or more than 10-fold, with respect to the proportion found in the prior composition
[02061 The present invention concerns compounds of Formula I, and all sub-generic formulae, compounds of Formula II and all sub-generic formulae, compounds of Formula III and all sub-generic formulae, and compounds of Formula IV and all sub-geneπc formulae that are modulators of protein kinases, for example without limitation, the compounds are modulators of at least one of the kinases selected from the group consisting of AbI, Aktl, Λkt2, Akt3, ALK, Alk5, A-Raf, B-Raf, Brk, Btk, Cdk2, CDK4 CDK5, CDK6, CHKl, c-Raf-1, Csk, EGFR, EphAl, EphA2, EphB2, BphB4, Erk2, Fak, FGFRl , FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4, Fltl, Flt3, Flt4, Fms, Frk, Fyn, Gsk3α, Gsk3β, HCK,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Her2/Erbb2, Her4/Erbb4, IGFlR, IKK beta, Irak4, ltk, Jakl, Jak2, Jak3, Jnkl, Jnk2, Jnk3, Kdr, Kit, LCK, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAP4K4, MAPKAPK2, Met, Mnkl, MLKl, p38, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PDPKl, Piml, Pim2, Pim3, PKC alpha, PKC beta, PKC theta, Plkl, Pyk2, Ret, ROCKl, ROCK2, Ron. Src, Stk6, Syk, TEC, Tie2, TrkA. TrkB, Yes, and Zap70, and the use of such compounds m the treatment of diseases or conditions
II. Kinase targets and indications of the in\ ention
[0207] Protein kinases play key roles m propagating biochemical signals in diverse biological pathways More than 500 kinases have been described, and specific kinases have been implicated in a wide range of diseases or conditions (i e , indications), including for example without limitation, cancer, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory disease, neurological disease, and other diseases As such, kinases represent important control points for small molecule therapeutic intervention Description of specific target protein kinases contemplated by the present invention may be found, for example, in US Patent Application Serial number 1 1/473,347 (PCT publication WO2007002433) , the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety, m addition to the following
Exemplary Diseases Associated with Raf kinases.
[0208] A-Raf: Target kinase A-Raf (i e , v-raf murine sarcoma 3611 viral oncogene homolog 1 ) is a 67 6 kDa serine/threonine kinase encoded by chromosome XpI 1 4-pl 1 2 (symbol. ARAF) The mature protein comprises RDD (i e , Ras binding domain) and phorbol-ester/DAG-type 7inc finger domain and is involved in the transduction of autogenic signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus A-Raf inhibitors may be useful in treating neurologic diseases including, but not limited to, multi-mfarct dementia, head injury, spmal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma), neurofibromatosis, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis; pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including, but not limited to, acute pam, chronic pam, cancer-related pain and migraine, and diseases associated with muscle regeneration or degeneration, including, but not limited to, vascular restenosis, sarcopenia, muscular dystrophies (including, but not limited to, Duchenne, Becker, Emery-Dreifuss, Limb-Girdle, Facioscapulohumeral, Myotonic, Oculopharyngeal, Distal and Congenital Muscular Dystrophies), motor neuron diseases (including, but not limited to, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy, intermediate spmal muscular atrophy, juvenile spmal muscular atrophy, spmal bulbar muscular atrophy and adult spmal muscular atrophy), inflammatory myopathies (including, but not limited to, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis), diseases of the neuromuscular junction (including, but not limited to, myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, and congenital myasthenic syndrome), myopathies due to endocrine
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 abnormalities (including, but not limited to, hyperthyroid myopathy and hypothyroid myopathy) diseases ot peπpheral nerve (including, but not limited to, Charcot-Maπe Tooth disease, Dejenne- Sottas disease, and Friedreich's ataxia), other myopathies (including, but not limited to myotonia congenita, paramyotonia congenita central core disease, nemahne myopathy myotubular myopathy, and periodic paralysis), and metabolic diseases of muscle (including, but not limited to phosphorylase deficiency, acid maltase deficiency, phosphofructokmase deficiency, debrancher enzyme deficiency, mitochondrial myopathy, carnitine deficiency, carnitine palmatyl transferase deficiency, phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency, phosphoglycerate inutase deficiency, lactate dehydrogenase deficiency, and myoadenylate deaminase deficiency)
10209] B-Kaf: Target kinase B-Raf (i e , \-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog Bl) is a 84 4 kDa seπne'threomne kinase encoded by chromosome 7q34 (symbol BRAF) The mature protein comprises RBD (i e , Ras binding domain), Cl (i e , protein kinase C conserved region 1) and STK (i e , serine/threonine kinase) domains
[0210] Target kinase B-Raf is involved m the transduction of mitogenic signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus and may play a role in the postsynaptic responses of hippocampal neurons As such, genes of the RAF family encode kinases that are regulated by Ras and mediate cellular responses to growth signals Indeed, B-Raf kinase is a key component of the RAS-> Raf-> MEK->ERK/M AP kinase signaling pathway, which plays a fundamental role in the regulation of cell growth, division and proliferation, and, when constitutively actuated, causes tumoπgenebis Among several isoforms of Raf kinase, the B-type, or B-Raf, is the strongest activator of the downstream MAP kinase signaling
[0211] 1 he BRAF gene is frequently mutated in a vanety of human tumors, especially in malignant melanoma and colon carcinoma The most common reported mutation was a missense thymine (T) to adenine (A) transversion at nucleotide 1796 (T1796A, amino acid change in the B-Raf protein is Val<600> to Glu<600> ) observed in 80% of malignant melanoma tumors Functional analysis reveals that this transversion is the only detected mutation that causes constitutive activation of B-Raf kinase activity, independent of RAS activation, by converting B-Raf into a dominant transforming protein Based on precedents, human tumors develop resistance to kinase inhibitors by mutating a specific ammo acid in the catalytic domain as the "gatekeeper" (Balak, et al , CIm Cancer Res 2006, 12 6494-501) Mutation of Thr-529 in BRAF to He is thus anticipated as a mechanism of resistance to BRAF inhibitors, and this can be envisioned as a transition in codon 529 from ACC to ATC
[0212] Niihoπ et al , report that in 43 individuals with cardio-facio cutaneous (CFC) syndrome, they identified two heterozygous KRAS mutations in three individuals and eight BRAF mutations in 16
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 individuals, suggesting that dysregulation of the RAS-RAF-ERK pathway is a common molecular basis for the three related disorders (Nnhoπ et al , Nat Genet 2006, 38(3) 294-6)
[0213] c-Raf-1: Target kinase c-Raf-1 (i e , v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 ) is a 73 0 kDa STK encoded by chromosome 3p25 (symbol RAFl) c-Raf-1 can be targeted to the mitochondria by BCL2 (i e , oncogene B-cell leukemia 2) which is a regulator of apoptotic cell death Active c-Raf-1 improves BCL2-mediated resistance to apoptosis, and c-Raf-1 phosphorylates BAD (i e , BCL2-bindmg protein) c-Raf-1 is implicated in carcinomas, including, but not limited to, colorectal, o\aπan, lung and renal cell carcinoma C-Raf-1 is also implicated as an important mediator of tumor angiogenesis (Hood, J D et al , 2002, Science 296, 2404) C-Raf-1 inhibitors may also be useful for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and mvelodysplastic syndromes (Crump, Curr Pharm Des 2002, 8(25) 2243-8) Raf-1 activators may be useful as treatment for neuroendocnne tumors, such as medullary thyroid cancer, carcinoid, small cell lung cancer and pheochromocytoma (Kunmmalaiyaan et al , Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17(2) 139-42)
[0214] B-Raf and/or C-Raf inhibitors may be useful in treating A-Raf-mediated, B-Raf-mediated or c-Raf-1 -mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of neurologic diseases, including, but not limited to, multi-infarct dementia, head injury, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, neoplastic diseases including, but not limited to, melanoma, glioma, sarcoma, carcinoma (e g colorectal, lung, breast, pancreatic, thyroid, renal, ovarian), lymphoma (e g histiocytic lymphoma) neurofibromatosis, acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, tumor angiogenesis, neuroendocnne tumors such as medullary thyroid cancer, carcinoid, small cell lung cancer and pheochromocytoma, pain of neuropathic or inflammatory origin, including but not limited to, acute pam, chrome pain, cancer-related pain, and migraine, cardiovascular diseases, including, but not limited to, heart failure, ischemic stroke, cardiac hypertrophy, thrombosis (e g thrombotic microangiopathy syndromes), atherosclerosis, and reperfusion injury, inflammation including, but not limited to, psoriasis, arthritis and autoimmune diseases and conditions, osteoarthritis, endometriosis, scarring, vascular restenosis, fibrotic disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), immunodeficiency diseases including, but not limited to, organ transplant rejection, graft versus host disease, renal or prostatic diseases, including, but not limited to, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis, glomerulonephritis, prostate hyperplasia, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, obesity, infection including, but not limited to, Helicobacter pylon Hepatitis and Influenza viruses, fever, and sepsis, pulmonary diseases, including, but not limited to, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), genetic developmental diseases, including, but not limited to, Noonan's syndrome, Costello syndrome, (faciocutaneoskeletal s>ndrome),
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
LFOPARD syndrome, cardio-faciocutaneous syndrome (CFC), and neural crest syndrome abnormalities causing cardiovascular, skeletal intestinal, skin, hair and endocπne diseases
Exemplary Diseases Associated with c-Kit.
[0215] The compounds described herein are useful for treating disorders related to c kit e g , diseases related to unregulated kinase signal transduction, including, but not limited to, cell proliferative disorders, fibrotic disorders and metabolic disorders, among others As described in more detail below and in Lipson et al , U S 20040002534 (U S application 10/600, 868, filed Tune 23, 2003) which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, cell proliferative disorders which can be treated by the present invention include cancers, and mast cell proliferative disorders.
10216] The presence of c-kit has also been associated with a number of different types of cancers In addition, the association between abnormalities in c-kit and disease are not rcstncted to cancer As such, c-kit has been associated with malignancies, including, but not limited to, mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasia associated with neurofibromatosis, acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, mastocytosis, melanoma, and canine mast cell tumors, and inflammatory diseases, including, but not limited to, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant rejection, and hypereosinophilia
Exemplary diseases associated with c-fins
[0217] lhe presence of c-fms has been associated with a number of different types of diseases As such, c-fms has been associated with immune disorders, including, but not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosa (SLE), and transplant rejection, inflammatory diseases including, but not limited to, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, and atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, including, but not limited to, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, obesity, and lipo lysis, disorders of bone structure, mineralization and bone formation and resorption, including, but not limited to, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget' s disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen- prosthetic or wear-debπs-mediated osteolysis, and metastasis of cancer to bone, kidney and genitourinary diseases, including, but not limited to, endometriosis, nephritis (e g glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis), tubular necrosis, diabetes-associated renal complications (e g
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 diabetic nephropathy), and renal hypertrophy, disorders of the central nervous system, including, but not limited to, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory and chronic pain, including, but not limited to, bone pam, and cancers, including, but not limited to, multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, melanoma, glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis of tumors to other tissues, and other chronic myeloproliferative diseases such as myelofibrosis
Exemplary diseases associated with TrkA and TrkB
[0218] TrkA: 1 arget kinase TrkA (i e , neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 1) is a 140 kDa tyrosine kinase encoded by chromosome Iq21-q22 (symbol NTRKl) TrkA inhibitors may be useful in treating pam (e g chronic pam, neuropathic pain), cancer (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, myeloid leukemia, pancreatic cancer), allergic disorders (e g asthma), arthritis, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and psoriasis
[0219] LrkA is a plasma member receptor composed of an extracellular domain (responsible for high affinity binding to nerve growth factor, NGF), a transmembrane segment and an intracellular protein tyrosine kinase domain (responsible to transmit the NGF signal to initiate and coordinate neuronal responses) NGF binding induces TrkA clustering on the membrane and activates the kinase The kinase initiates a cascade of protein phosphorylation events through multiple pathways including SHC/Ras/MAPK, PI3K and PLCgI A TrkA kinase inhibitor would not prevent NGF'TrkA binding, but could prevent down-stream signal transduction
[0220] Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) is produced by a number of tissues and inflammatory cells during tissue injury and host immune response It initiates and maintains hypersensitivity to incoming stimulus (hyperalgesia) and the perception of non-noxious stimuli (allodynia) Through its high- affimty receptor TrkA, NGF increases the excitation state of sensory neurons leading to the central nervous system (peripheral sensitization), and increases transmitter release from the dorsal spinal cord (central sensitization) In clinical tπals, a single NGF subcutaneous injection generated local hyperalgesia persisting up to 7 weeks At doses above 0 1 microgram/kg, NGF caused muscle pain that varied from mild to moderate, primarily in the bulbar and truncal musculature Intravenous NGF produced earlier and more pronounced systemic effects (Petty et al, 1994, Ann Neurol 36 244-6) Conversely, TrkA kinase inhibitors could be used to treat diseases of enhanced states of nociception
[0221] In Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-induced hind-paw inflammation, spinal nerve ligation and streptozoticin-mduced neuropathic pam models, a single intraperitoneal injection of anti- NGF reversed established tactile allodynia from day 3 to day 7 following treatment In the mouse CCI model, anti-NGF reversed tactile allodynia when administered 2 weeks after surgery Repeated
US2007/088443
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 administration of this antibody to CCI mice for 3 weeks produced a sustained reversal of tactile allodynia (Wild et al, 2007, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322 282-287)
[0222] Prostate tumors that have metastasized to bone frequently induce bone pam which can be difficult to fully control as it seems to be driven simultaneously by inflammatory, neuropathic, and tumorigenic mechanisms Anti-NGF produced a significant reduction in both early and late stage bone cancer pam— related behaviors This therapy did not influence tumor-mduced bone remodeling, osteoblast proliferation, osteoclastogenesis, tumor growth, or markers of sensory or sympathetic innervation in the skm or bone All nerve fibers that innervate the bone express TrkA and p75, and these are the receptors through which NGF sensitizes and/or activates nociceptors (Halvorson et al, 2005, Cancer Res 65 9426-35)
[0223| In patients with mild asthma due to exposure to cat allergen, NGF expression was strongly induced in epithelial cells, fibroblasts, blood vessels, and a few infiltrating cells TrkA mRNA and protein levels in bronchial biopsies were increased significantly after allergen exposure in infiltrating mast cells before the onset of symptoms (Kassel et al, 2001 , Clin Exp Allergy 31 1432-40)
[0224] The late phase reaction in asthma following allergen provocation is dominated by an influx of activated eosinophils into the bronchial lumen, which correlates with the release of eosinophilic products into the airways to increase disease severity The viability and activation of eosinophils from patients with mild asthma were significantly enhanced after NGF stimulation Addition of neutralizing anti-NGF antibodies ex vivo abrogated the effects (Nassentein et al, 2003, J Exp Med 198 455-467) TrkA kinase inhibitors could decrease this paracrine loop between the respiratory tract and infiltrating mast cells as well as endobronchial eosinophils, and thus be useful for the treatment ol asthma and other allergic disorders
[0225] TrkB: Target kinase TrkB (i e , neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2) is a 145 kDa tyrosine kinase encoded by chromosome 9q22 1 (symbol NTRK2) TrkB inhibitors may be useful in treating various cancers and their metastases (e g prostate cancer, lung cancer, Wilms tumors, neuroblastoma, and pancreatic cancer), and various neuropathies (e g stroke, multiple sclerosis, trans\erse myelitis, and encephalitis)
[0226] In clinical trials with recombinant BDNF, paresthesia was developed at the site of subcutaneous injection (Couhe et al, 2000, Gastroenterology 119 41-50) Intrathecal infusion of BDNF in humans also induced paresthesia and warmth as side effects (Ochs et al, 2000, Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1 201-6) Chronic paresthesia is often a symptom of an underlying neurological disease or traumatic nerve damage Paresthesia can be caused by disorders affecting the central nervous system, such as stroke and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes),
007/088443
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 multiple sclerosis, transverse myelitis, and encephalitis Since BDNt binds to TrkB specifically with high affinity these neuropath effects are mediated through TrkB signaling Thus Trkb kinase inhibitors could be used to treat certain patients with neuropathy
[0227] BDNF is known to act at the synapses between primary sensory and spmal dorsal horn neurons to affect pam transmission during inflammation f he primary afferent is the only source of BDNF in the spmal cord, and it is up-regulated m the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by peripheral NGF a few days aftei inflammation, and is transported and released into the superficial dorsal horn in an activity-dependent manner TrkB expression in the dorsal horn also increases for a few days after inflammation These findings suggest that BDNF may act during the restricted peπod in the early phase of inflammation Through TrkB, BDNF activates two distinct channels (1) transient receptor potential canonicals (TRPC3), which produces a slow response by opening ot a non-selective cation channel, and (2) Na+ channel, which mediates a rapid depolarization in the hippocampus These channels have been strongly associated with inflammatory pain Anti-BDNF significantly increased the withdrawal threshold m CFA-treatcd rats, a model of inflammatory pain Since the swelling at the site of CFA injection was not affected by antiserum, the residual component might be due to peripheral sensitization (Matayoshi et al, 2005, J Physiol 569 685-95)
[0228] In patients with neuroblastomas, co-expression of TrkB and BDNF, co-expression ot TrkB with N-Myc amplification, and expression of truncated TrkB are found to be associated with poorer clinical outcome (Nakagawara et al, 1994, MoI Cell Biol 14 759-767) Co-expression of TrkB with its hgand BDNF could generate a positive feedback loop through autocrine and paracrine loops Also TrkB truncations found in these tumors generate activated forms of the intracellular protcm tyrosine kinase The constitutively active TrkB signals through multiple pathways to promote cancer initiation, progression and metastasis These truncated TrkB kinases were also found in hepatocellular carcinoma (Yang et al, 2005, Cancer Res 65 219-225) Thus TrkB inhibitors could be used to treat a sub-population of cancer patients with an activated TrkB pathway
[0229] In patients with pancreatic cancer, TrkB expression is correlated with perineural invasion, positive reti opeπtoneal margin, and shorter latency to development of liver metastasis (Sclabas et al, 2005, Clin Cancer Res Vl 1 440-449) Mechanistically, TrkB activates the PI3K pathway to suppress anoikis (apoptosis resulting from loss of cell-matrix interactions) which is one of the physiological barriers to metastasis TrkB kinase inhibition could break down resistance to anoikis of metastasizing tumors (Douma et al, 2004, Nature 430 1034-9) Therefore, TrkB inhibitors could have utility in a broad range of tumor types
Exemplary diseases associated with MΛPK4K
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0230I MAF4K4: Target kinase MAP4K4 (i e , Mitogen-actn ated protein kinase kinase 4, aka Hematopoietic progenitor kinase/Germinal center kinase-hke Kinase) is a 130 kDa senne/threonine kinase encoded by chromosome 2ql 1 2-ql2 (symbol MAP4K4) and is also known as HGK It is a member of the human STE20/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase (MAP4K) family of serine/threonine kinases and is the human ortholog of mouse NIK (Nck-interacting kinase) The N- terminus of the mature HGK protein has a catalytic kinase domain that shares 47" o and 48% ammo acid sequence identity to the catalytic domain of Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPKl) and Germinal center kinase (GCK), respectively Yao et al (J Biol Chem 274 2118 2125, 1999) identified 2 HGK isoforms, one of which has no pioline-πch domains, and another, longer variant that contains such domains and appears to be expressed in brain only Northern blot analysis revealed expression of 3 HGK transcripts of approximately 4 6, 6 5, and 8 5 kb in heart, brain, skeletal muscle, pancreas, placenta, liver, lung, and kidney By Western blot analysis with a polyclonal antibody, Yao et al (J Biol Chem 274 2118-2125, 1999) found that the 130-kD protein is expressed in multiple cell lines
[0231] Expression of HGK in transfected cell lines resulted in strong JNK activation and, in turn, c- iun transcriptional activity (Yao et al J Biol Chem 274 2118-2125, 1999) HGK-induced JNK activation was inhibited by dominant-negative MAP2K4, MAP2K7, and TAKl mutants TNP-alpha also stimulated HGK kinase activity HGK was identified as a putative effect of Rap2 to activate JNK (Machida et al J Biol Chem 279 1571 1-15714, 2004) This link establishes HGK as a potential target for a range of metabolic indications, since the JNK pathway clearly antagonizes insulin signaling An HGK inhibitor could re-sensitize fat and muscle cells to insulin
[0232] HGK is found to be broadly expressed in human tumor cells and can modulate cellular transformation, invasion, and adhesion (Wright et al MoI Cell Biol 23 2068-2082, 2003) Wright et al showed HGK to be highly expressed in most tumor cell lines relative to normal tissue An active role for this kinase in transformation was suggested by an inhibition of H-Ras(V12)-induced focus formation by expression of inactive, dominant-negative mutants of HGK in both fibroblast and epithelial cell lines Expression of an inactive mutant of HGK also inhibited the anchorage- independent growth of cells yet had no effect on proliferation in monolayer culture Expression of HGK mutants modulated integπn receptor expression and had a striking effect on hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated epithelial cell invasion Together, these results suggest an important role for HGK in cell transformation and invasiveness More recently, a small interfering RNA screen for modulators of tumor cell motility identifies MAP4K4 as a promigratory kinase (Collins et al Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 3775-3780, 2006) Collins et al showed that the knockdown of the HGK transcnpt inhibited the migration of multiple carcinoma cell lines, indicating a broad role in cell motility, and potently suppressed the invasion of SKO V-3 cells in vitro The effect of HGK on cellular migration
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 was found to be mediated through JNK kinase, independent of API activation and downstream transcription Accordingly, small molecule inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase suppressed SKOV-3 cell migration, undersconng the potential therapeutic utility of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathw ay inhibition in cancer progression (Collins et al Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 3775-3780, 2006) These studies strongly support HGK as a target in a broad range of oncology indications In particular, an HGK inhibitor could have utility m blocking the migration, invasion and metastasis in many different tumor types
[0233] Activation of T-cells by antigens initiates a complex series of signal-transduction events that are critical for immune responses Mack et al (Immunol Lett 96, 129-145, 2005) developed a genetic screen to survey the functional roles of kinases in antigen mediated T-cell activation and identified 19 protein kinases that were previously implicated in T-cell signaling processes and 12 kinases that were not previously linked to T-cell activation, including HGK siRNA studies showed a role for HGK in antigen mediated T-cell responses in Jurkat and primary T-cells In addition, by analyzing multiple promoter elements using reporter assays, Mack ct al have shown that MAP4K4 is implicated in the activation of the TNF-alpha promoter Therefore, inhibition of HGK could have broad therapeutic utility for T-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases
[0234] Insulin-regulated glucose transporter GLUT4 is a key modulator of whole body glucose homeostasis, and its selective loss in adipose tissue or skeletal muscle causes insulin resistance and diabetes Using an RNA interference-based screen, Tang et al (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 2087- 2092, 2006) tound 4 negative regulators of msulin-responsive glucose transport in mouse adipocytes Pctkl, Pftkl, Ikbka (CHUK), and HGK HGK suppressed expression of adipogenic transcnption factors, C/EBPA, C/EBPB, and PPARG, and it suppressed surface expression of GLUT4 (SLC2A4), resulting in attenuated membrane hexose transport activity RNA interference-mediated depletion of HGK early in differentiation enhanced adipogenesis and triglyceride deposition, in fully differentiated adipocytes, loss of HGK upregulated GLUT4 expression Conversely, conditions that inhibited adipogenesis, such as TNF-alpha treatment or PPARG depletion, markedly upregulated HGK Tang ct al (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 2087-2092, 2006) concluded that MAP4K4-dependcnt signaling inhibited PPARG-responsive gene expression, adipogenesis, and insulin-stimulated glucose transport Furthermore, TNF-alpha signaling to down-regulate GLUT4 is impaired in the absence of HGK, indicating that HGK expression is required for optimal TNF-alpha action This study further supports HGK as a target m metabolic disease, and suggests a role for HGK inhibition in ameliorating the pathology in adipocytes
[0235] In a separate study (Bouzakπ and Zierath J Biol Chein 282 7783-7789, 2007), using small interfering RNA (siRNA) to suppress the expression of HGK protein 85% in primary human skeletal muscle cells, TNF-alpha-mduced insulin resistance on glucose uptake was completely prevented
7 088443
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
HGK silencing inhibited TNF-alpha-induced negative signaling inputs by preventing excessive JNK and ERK-I /2 phosphorylation, as well as IRS- 1 scπne phosphorylation These results highlight the HGK/JNK'ERK 'IRS module in the negative regulation of insulin signaling to glucose transport in response to TNt- -alpha Depletion of HGK also prevented TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance on AKT and the AKT substrate 160 (AS 160), providing evidence that appropπate insulin signaling inputs for glucose metabolism were rescued The authors suggested that strategies to inhibit HGK may be efficacious in the prevention of TNF-alpha-mduced inhibitory signals that cause skeletal muscle insulin resistance on glucose metabolism in humans Moreover, in myotubes from msuhn- resistant type II diabetic patients, siRNA against HGK restored insulin action on glucose uptake to levels observed in healthy subjects This study further supports HGK as a target in metabolic diseases such as type II diabetes, and suggests a role for HGK inhibition in ameliorating the pathology in muscle cells
[0236] HGK inhibitors may be useful m treating metabolic indications, including, but not limited to, re-sensitizing fat and muscle cells to insulin, ameliorating the pathology in adipocytes, ameliorating the pathology in muscle cells, metabolic syndrome and type II diabetes, a broad range of oncology indications, including, but not limited to, blocking the migration, invasion and metastasis in many different tumor types, and T-cell mediated autoimmune diseases
Kinase Activity Assays
[0237] A number of different assays for kinase activity can be utilized for assaying for active modulators and/or determining specificity of a modulator for a particular kinase or group or kinases In addition to the assay mentioned m the Examples below, one of ordinary skill in the art will know of other assays that can be utilized and can modify an assay for a particular application For example, numerous papers concerning kinases describe assays that can be used
[0238] Additional alternative assays can employ binding determinations For example, this sort of assay can be formatted either in a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) format, or using an ΛlphaScreen (amplified /ummescent proximity Λomogeneous assay) format by varying the donor and acceptor reagents that are attached to streptavidin or the phosphor-specific antibody
Organic Synthetic Techniques
[0239] The versatility of computer-based modulator design and identification lies in the diversity of structures screened by the computer programs The computer programs can search databases that contain very large numbers of molecules and can modify modulators already complexed with the enzyme with a wide variety of chemical functional groups A consequence of this chemical diversity is that a potential modulator of kinase function may take a chemical form that is not predictable A
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
\\ ide array of organic synthetic techniques exist m the art to facilitate constructing these potential modulators Many of these organic synthetic methods arc described in detail in standard reference sources utilized by those skilled in the art One example of such a reference is March, 1994 Advanced Organic Chemistry, Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure. New York, McGraw Hill Thus, the techniques useful to synthesize a potential modulator of kinase function identified by computer-based methods aie ieadily available to those skilled in the art of organic chemical synthesis
[0240] Regarding the synthetic examples described herein, sohents include polar and non-polar solvents known to those of skill in the art, including polar aprotic and polar protic solvents Polar solvents include, without limitation, protic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, t- butanol, n-butanol, acetic acid, formic acid or water, or aprotic solvents such as tetrahydrofuran (THF), acetonitnle, dioxane, methylene chloride, dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), acetone, N,N- dimethylformamide (DMF), N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA), ethyl acetate, 1,2-dimethoxyethane, 1,2- dichloroethane, chloroform, 1 ,2-dichloroethane, or pyridine Polar solvents include a mixture of water with any of the above, or a mixture of any two or more of the above Apolar solvents include, without limitation, toluene, benzene, chlorobenzene, xylenes and hexanes
[0241] Regarding the synthetic examples described herein, reducing agent includes, without limitation, a reducing agent such as catalytic reducing agents using hydrogen and transition metal catalysts such as palladium, platinum, rhodium, etc (e g Pt/acetic acid/H->), a mixture of tπfluoroacetic acid and tπethylsilane, borane tetrahydrofuran complex, diborane, borane dimethylsulfide complex, and a combination of sodium borohydπde and boron tπfluoπde, metals such as reduced iron, zinc powder, magnesium etc , metal hydrogen complex compounds such as alkali metal borohydπdes (for example, potassium borohydπde, sodium borohydπde, lithium borohydπde, zinc borohydπde, sodium tnacetoxyborohydride, etc ), aluminum lithium hydride, etc , metal hydrides such as sodium hydride, etc , organic tin compounds (tnphenyltin hydride, etc ), and metal salts such as nickel compounds, zinc compounds, tin compounds (for example tm(TI) chloride), and samarium lodide/pivahc acid/hexamethylphorphoπc tπamide
[0242] Regarding the synthetic examples described herein, oxidizing agent includes, without limitation, an oxidizing agent such as Dess-Martin reagent TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpipeπdine-N- oxide), DDQ (2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-l ,4-bcnzoqumone), PDC (pyπdimum dichromate), PCC (pyπdinium chlorochromate), Pyridine SO3, Chromium tπoxide, p-mtroperbenzoic acid, magnesium monoperoxyphthalatc, sodium penodate, potassium peπodate, hydrogen peroxide, urea peroxide, alkali metal bromates, cumene hydroperoxide, tert-butyl peroxide, peracids such as performic acid, peracetic acid, pertπfluoroacetic acid, perbenzoic acid, m-chloroperbenzoic acid, o- carboxyperbenzoic acid and the like, sodium metapenodate, bichromic acid bichromates such as
Att>. Dkt. No . 039363-3303 sodium bichromate, potassium bichromate, permanganic acid, permanganates such as potassium permanganate, sodium permanganate, and lead salts such as lead tetraacetate
[0243] Regarding the synthetic examples described herein, a nitrogen protecting group is a chemical group covalently bound to a nitrogen atom of a compound that is used to protect the nitrogen from reaction during a synthetic step The nitrogen protecting group may be added to a compound and removed in a subsequent step by methods known to those of skill in the art Nitrogen protecting groups include, without limitation, carbamates, amides, N-sulfon>l derivatives, groups of formula -C(O)OR, wherein R is, for example, methyl, ethyl, t-butyl, benzyl, phenylethyl, CH2=CHCH2-, and the like, groups of the formula -C(O)R', wherein R' is, for example, methyl, phenyl, tπfluoromethyl, and the like, groups of the formula -SOjR", wherein R" is, for example, tolyl, phenyl, tπfluoromethyl, 2,2,5,7,8-pentamethylchroman-6-yl, 2,3,6-tπmethyl-4-methoxyphenyl, and the like, and silanyl containing groups, such as 2-tπmethylsilylethoxymethyl, t-butyldimethylsilyl, tπisopropylsilyl, and the like Other suitable nitrogen protecting groups may be found in texts such as T W Gieene & P G M Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, 1991
Alternative Compound Forms or Derivatives
[0244] Compounds contemplated herein aie described with reference to both generic foπnulae and specific compounds In addition, invention compounds may exist m a number of different forms or derivatives, all within the scope of the present invention Alternative forms or derivatives, such as (a) Isomeis, Prodrugs, and Active Metabolites (b) Tautomers, Stereoisomers, Regioisomers, and Solvated Forms (c) Prodrugs and Metabolites (d) Pharmaceutically acceptable salts and (e) Polymorphic forms, are described, for example, in US Patent Application Seπal number 11 '473,347 (see also, PCI publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entnety
Administration
[0245] The methods and compounds will typically be used in therapy for human subjects However, they may also be used to treat similar or identical indications in other animal subjects In this context, the terms "subject," "animal subject," and the like refer to human and non-human vertebrates, e g mammals, such as non-human primates, sports and commercial animals, e g , equmes, bovines, porcmes, ovines, rodents, and pets, e g , canines and felines A description of possible methods and routes of administration may be found, for example, in US Patent Application Seπal number 11/473,347 (see also, PCT publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety
EXAMPLES
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303
[0246] Examples related to the present invention are described below. In most cases, alternative techniques can be used. The examples are intended to be illustrative and are not limiting or restrictive to the scope of the invention. In some examples, the mass spectrometry result indicated for a compound may have more than one value due to the isotope distribution of an atom in the molecule, such as a compound having a bromo or chloro substituent.
[0247] Unless specifically indicated otherwise, the Formula enumeration and R group enumeration used in the following examples is not related to such enumeration in other sections of this application. The reagents and solvents used in these examples can be readily substituted with appropriate alternatives as are known in the art and isolation of products is readily achieved by methods known in the art, including, but not limited to, extraction, crystallization, and chromatographic methods. In addition to the following Examples, exemplary methods which may be employed for synthesis of compounds of the present invention may be found in US Patent Application Serial number 11/473,347 (see also, PCT publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. The lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine core of compounds described in the examples may also be referred to as 7-azaindole in the examples.
Example 1. Synthesis of compounds of Formula X
Step I - Preparation of compounds of Formula Xc and Xd
[0248] To a compound of Formula Xa (R4, R5, and R6 are as defined in paragraph [0008]) and a compound of Formula Xb (Y is consistent with compounds of Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, e.g. Y is:
Z5, Z6, R15 and R17 are as defined in paragraph [0008], L4, R60 and R61 are as defined in paragraph [0034], R80 and R81 are as defined in paragraph [0057], and R > 9w0 is as defined in paragraph [0093], where * indicates the attachment point to the carbonyl carbon) is added an appropriate solvent (e.g. methanol) followed by an appropriate base (e.g. potassium hydroxide,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 sodium methoxide). The reaction is typically allowed to stir at room temperature overnight. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction, washing and filtering) affords a mixture of compounds of Formula Xc and Xd, which may be separated by silica gel chromatography if desired.
Step 2 - Preparation of compounds of Formula X
[0249] To a compound of Formula Xc or Xd in an appropriate solvent (e.g. acetonitrile) is added a reducing agent (e.g. trifhioroacetic acid and triethylsilane). Typically, the reaction is allowed to stir at room temperature overnight. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction and silica gel column chromatography) affords compounds of Formula X.
Example 2. Synthesis of compounds of Formula XI
Step 1 - Preparation of compounds of Formula XI
[0250] To a compound of Formula Xc (See Example 1) in an appropriate solvent (e.g. tetrahydrofuran) is added an oxidizing agent (e.g.Dess-Martin periodane, TEMPO, DDQ). Typically, the reaction is allowed to stir at room temperature for 20 minutes. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction and silica gel column chromatography) affords compounds of Formula XL
Example 3. Synthesis of Compounds of Formula XI
Step -I- Synthesis of compound υf Formula XI
[0251] Compound of Formula Xl is synthesized by reacting a compound of Formula Xa (see Example 1) with a compound of Formula Xe (Y is as defined in Example 1), e.g. benzoyl chloride, in the presence of a Lewis acid (e.g. aluminum trichloride) in an inert solvent (e.g. dichloromethane) under an inert atmosphere (e.g. argon) at room temperature or with heating up to reflux for 1-18 hours. The desired compound XI is isolated by extraction and silica gel column chromatography,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 Example 4: Synthesis of 5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 4,
[0252] Compound 4 was synthesized in three steps from 5-bromo-7-azaindole 1 as shown in Scheme 1.
Scheme 1
Step 1 - Preparation of5-bromo-l-triisυpropylsilanyl-lli-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (2): [0253] To 5-bromo-7-a/aindole (1, 1.5 g, 7,6 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (20 mL) were added sodium hydride (60% in mineral oil, 0.27 g, 11.0 mmol) and trriisopropylsilyl chloride ( 2.6 mL, 12.0 mmol), under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 10 % ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (2, 1.6 g, 59%). MS(ESI)[M+H+]+ = 352.3.
Step 2 - Preparation 5-chloro-l-triisυpropykilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (3): [0254] To 5-bromo-l -triisopropylsilyl-7-azaindole (2, 1 ,60 g, 4.53 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (50.0 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0C, was added terr-butyllithium (1.70 M in hexane, 6.12 mL). The reaction was stirred for 1 hour, followed by addition of hexachloroethane (1.29 g, 5.43 mmol). The reaction was stirred for 3 hours, poured into water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated to give the crude compound (3, 1.60 g). MS (ESI) [M+H"]+ = 309.3.
Step 3 - Preparation 5-chloro-LH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (4):
[0255] To 5-chloro-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (3, 1.40 g, 4.53 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (15 mL) was added feft-α-n-butylammonium fluoride (1.42 g, 5.43 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was concentrated and isolated by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (4, 0.40 g. 58% over 2 steps), MS(ESI)[M-H+]" = 153.1.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 1, substituting hexachloroethane with N-fluoro-N- (phenylsulfonyl) benzenesulfonamide in Step 2. MS(ESl) [M + ϊCf = 137.1.
Example 5: Synthesis of l-triisopropylsHanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde 8. [0257] Compound 8 was synthesized in two steps from 7-azaindole 6 as described in Scheme 2.
Scheme 2
Step 1 - Preparation of 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (7):
[0258] To lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 16.0 g, 135 mmol) in water (110 mL), were added hexamethylenetetramine (26.0 g, 185 mmol), and acetic acid (55.0 mL, 967 mmol). The reaction was refluxed for 12 hours. Water (329 mL) was added and the reaction was cooled to room temperature.
The reaction was filtrated and washed with water to give the compound (7, 15.0 g, 76%).
MS(ESI)[M+H+]+ = 147.
Step 2 - Preparation υf 1 -triisopropylsilanyl- 1 H-pyrrolo [2 ,3-b] pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (8): [0259] To lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (7, 4.05 g, 27.71 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (30.0 mL) were added sodium hydride (60% in mineral oil, 1.5 g, 38 mmol) and trriisopropylsilyl chloride (8.0 mL, 38 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 10 % ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (8, 3.0 g, 36%). MS(ESI)[M+H+f = 303.
Example 6: Synthesis of 5-isopropyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 11.
[0260] Compound 11 was synthesized in three steps from 5-bromo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 2 described in Scheme 3.
Scheme 3
Step 1 Preparation of2-(l-trnsopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)-propan-2-ol (9): [0261] To 5-bromo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (2, 2.0 g, 5.66 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4) in tetrahydrofuran (20.0 rriL), cooled in a -78 0C acetone/dry ice bath, under an atmosphere of nitrogen, was added tert-butyllithium (1.7 M in tetrahydrofuran, 7.3 mL, 12 mmol) dropwise. After 20 minutes, acetone (0,830 mL, 11 mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction. The reaction was stirred for 30 minutes at -78 0C and then allowed to reach room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 10 % ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (9, 1.30 g, 69%). MS(ESI)[M-rH+]+ = 333.
Step 2 - Preparation of 5-isopropenyl-lH-pyrrolo[2.3-b] pyridine (10):
[0262] To 2-(l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)-propan-2-ol (9, 0.500 g, 1.5 mmol) in acetonitrile (10.0 mL) were added triethylsilane (1.00 mL, 6.3 mmol) and trifluoroacetic acid (0.50 mL, 6.5 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was refluxed for 3 hours, then cooled down to room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50 % ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (10, 0.200 g, 84%). MS(HSI) [M+HT = 159.
Step 3- Preparation of5-isopropyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (11):
[0263] To 5-isopropenyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (10, 0.080 g, 0.501 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (5.0 mL) was added 20 % palladium hydroxide on carbon (5.0 mg). The reaction was stirred under hydrogen at 40 psi for 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated to give the compound (11 , 0.078 g, 96%). MS(ESI)[M+H+]+ = 161.
Example 7: Synthesis of 5-Methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 13.
[0264] Compound 13 was synthesized in two steps from 5-bromo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 2 described in Scheme 4.
Scheme 4
Step 1 - Preparation of5-Methyl-l-triisopropyisilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (12):
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0265] 1 o PdCL(dppf) (O 04 g, O 05 mmol) in toluene (10 0 mL) under an atmosphere of nitrogen were added 5-bromo-l-tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (2, 0 3 g, 0 8 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4, 1 0 mL in toluene) and methylmagnesium bromide (1 O M m tetrahydrofuran, 3 0 ml 3 0 mmol) The reaction was stirred 90 0C for 2 hours and then allowed to reach to room temperature The reaction was poured into citric acid (0 1 M in water) and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography clutmg with 50 % ethyl acetate m hexane to give the compound (12, 0 16 g, 60 0 %) MS(ESI)[M+H+f = 289 4
Step 2 - Preparation of5-Methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrιdιne (13)
[0266] To 5-Methyl-l-tπιsoproρylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndinc (12, 0 160 g, 0 55 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (3 0 mL) was added tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (0 145 g, 0 55 mmol) The reaction was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 3% methanol in dichloromethane to provide light yellow solid (13, 0 07 g, 95%)
2
[0267] 5-Methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine 14
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 4, substituting methylmagnesium bromide with ethylmagnesium bromide m Step 1
Example 8: Synthesis of 5-Methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 15 and related compounds.
[0268] Compound 15 was synthesized in one step from 5-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2 3-b]pyπdine 1 as described in Scheme 5
1 15
Step 1 - Preparation of 5-Methoxy-IH-pyrrolo[2,3 b] pyridine (15)
[0269] 1 o 5-bromo-7-azaindole (1, 500 0 mg, 2 53 mmol) in N,N-dimethylforrnamide (8 mL) were
007/088443
Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303 added copper(I) iodide (966 mg, 5.08 mmol) and sodium methoxide in methanol (3 M, 5 mL). The reaction was stirred overnight at 120 °C under an atmosphere of Argon. The reaction was poured into water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatograph eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give white solid (15, 140 mg, 28%). MS(ESI)[M+HT = 149.1. In an alternative method, 2.3 g (11.7 mmol) 5-bromo-7-azaindole (1, 2.3 g, 11.7 mmol) was dissolved in 75 mL N,N-dimethylfϋrmamide and 50 mL methanol (50 mL), adding sodium methoxide (32 g, 0.6 mol) and copper-(T) bromide (3.2 g, 22.4 mmol) at room temperature. The reaction was stirred for three hours at 100 0C under an atmosphere of argon. The mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and poured into a solution of ammonium chloride: ammonium hydroxide (4:1). The organic layer was extracted with ammonium chloride:ammonium hydroxide (4: 1), washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, fdtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% to 70% ethyl acetate in hcxanes to give a yellow solid (15, 0.27 g, 15.6%). MS(ESI) [M + H+J+ = 149.2.
[0270] 5-Ethoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme 16
was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 5, substituting methanol with ethanol and sodium methoxide with sodium ethoxide.
[0271] 5-(2-Methoxy-ethoxy)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 17
was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 5, substituting methanol with 2-mefhoxy-ethanol and sodium methoxide with sodium 2-methoxy-ethoxide (prepared from 2-mefhoxy-ethanol and sodium hydride). MS(ESI) [M + H+J+ = 193.3.
[0272| Diethyl-[2-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)-ethyl]-amine l8
was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 5, substituting methanol with 2-diethylamino-efhanol and sodium methoxide with sodium 2-diethylammo-ethoxide (prepared from 2 2-diethylamino -ethanol and sodium hydride). MS(ESI) [M + H']+ = 234.5.
I l l
Atty Dkt No : 039363-3303 Example 9: Synthesis of 5-P}ridm-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]p>ridine 20 and related compounds.
[0273] 5-Pyridm-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme 20 was synthesized m one step from 5-bromo-lH- pyrrolo[2 3-b]pyπdine 1 as desenbed in Scheme 6
Scheme 6
Step 1 - Preparation oj 5-Pyrιdm-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (20)
[0274] To 5-bromo-7-azaindole (1. 1 00 g, 5 08 mmol) in water (13 0 mL) and acetonitrile (36 mL) were added pyπdine-3 -boronic acid (19, 1 0 g, 8 1 mmol), potassium carbonate (1 79 g, 0 0130 mol) and Tetrakis(tnphenylphosphine)palladium(0) (50 0 mg, 0 043 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen The reaction mixture was heated to 170 °C overnight The reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer w as washed with brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated The residue was punfied with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 25% ethyl acetate in hexane to provide a light yellow solid (20, 820 mg, 82%) MS(ESI)[M+fT]+ = 196 1
[0275] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 6, either by substituting pyridine-3-boromc acid with an appropriate boronic acid or by substituting the 5-bromo- 7-azaindole with 5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-[l,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine and reacting with a suitable aryl or heteroaryl hahde (i e coupling with the boronic acid ester on the azaindole, and the hahde on the group to be coupled to the 5-position of the azaindole) The following compounds were prepared by this procedure
5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme,
5-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme,
5-Phenyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine,
5-(6-Methoxy-pyπdin-3-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3~b]pyπdine,
5-(2-Methoxy-pyπmidin-5-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme,
5-Pyπdin-4-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine,
4-(lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndin-5-yl)-benzenesulionamide,
3-(lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)-benzenesulfonamide,
5-Pyπmidin-5-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine,
5-(3-Methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine,
3-(lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-5-yl)-benzamide,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
5-(5-Methyl-lH-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine,
5-(l-Methyl-lH-imidazol-2-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine, and
S-Cl .S-Dimethyl-lH-imidazol^-yO-lH-pyiTolo^.S-blpyridine.
The following table indicates either 5-bromo-7-azaindolc or 5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-[ 1 ,3,2] dioxaborolan-2-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine starting material (column 1) and the appropriate reagent to be coupled to the 5 position of the azaindole (column 2) to afford the resulting compound (column 3), with the observed mass given in column 4,
Example 10: Synthesis of 3-(4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methoxybenzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine P-1247.
[0276] Compound P-1247 was synthesized in three steps from 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde 21 as shown in Scheme 7.
Scheme 7
Step 1 - Preparation of4-(4-chloroben∑yloxy)-3-methoxyben∑aldehyde (23): [0277] To 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (21, 600.0 mg, 3.94 mmol) and 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 1.20 g, 5.84 mmol) in acetonitrile (6 mL) was added potassium carbonate (0.390 g, 2.82 mmol). The reaction was microwaved on 300 watts, 120 0C for 10 minutes. The reaction was extracted with ethyl acetate and water. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and the volatiles removed by evaporation. The desired compound was purified by recrystallization from hexanes to provide 23 (1.01 g, 93%). MS(tSI) [M-H"]" - 275.1.
Step 2 - Preparation of3-((4-(4-chloroben∑yloxy)-3-methoxyphenyl)(methoxy)methyl)-lH- pyrrolo [2, 3-b] pyridine (24) ■
[0278] To lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 0.235 g, 1.99 mmol) and 4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3- methoxybenzaldehyde (23, 0.500 g, 1.81 mmol) was added 5 mL of methanol followed by the addition of solid potassium hydroxide (0.203 g, 3.61 mmol). The reaction was allowed to stir at ambient temperature for 18 days. The reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was separated and volatiles removed to give a solid which was suspended in hot ethyl acetate. The suspension was allowed to cool and the solid collected by vacuum filtration to provide 24 (548 mg, 74%). MS(ESI) [M+H+f = 409.4.
Step 3 — Preparation of 3-(4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methoxyhenzyl)- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-bJ pyridine (P-1247):
[0279] To 3-((4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methoxyphenyl)(methoxy)methyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (24, 0.548 g, 1.34 mmol) in acetonitrile (20 mL) was added trifluoroacetic acid (1.7 mL, 2.21 mmol) and triethylsilane (3.47 mL, 2.17 mmol). The reaction was stirred at 60 0C for 15 hours. The volatiles were removed and the desired compound was purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with a gradient from 0% to 60% ethyl acetate in hexanes to provide a white solid (P-1247, 505 mg, 99%). MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 379.4.
[0280] Additional compounds were prepared using the protocol of Scheme 7, Steps 2 and 3, replacing 4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methoxybenzaldehyde 23 with a suitable aldehyde (prepared as described in Example 15 or 33), and optionally replacing lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 6 with an appropriate substituted 7-azaindole (5-chloro-7-azaindole per Example 4 or 5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8) in Step 2. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
3-[3-Methoxy-4-(4-trifluoromcthyl-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1721),
3-[3-Trifluoromethyl-4-(4-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-1797),
3-{3-Methoxy-4-[4-(4-methyl-piperazin-l -ylmethyl)-benzyloxy]-benzyl}-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1821),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1844),
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
3-[4-(3-Fluoro-4-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy)-3-αiethoxy-beii2yl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1849),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1851),
2-[2-Methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole
(P-1870),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-5-methoxy-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1885),
3-[4-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1886),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1896))
2-[2-Fluoro-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole
(P-1899),
3 -(4-Benzyloxy-2,5 -difluoro-benzyl)- 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -bjpyridine (P-1901) ,
5-Chloro-3-[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-1970),
5-Chloro-3-[4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1972),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-1973),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenox>rmethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-1976),
2-[5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]- lH-benzoimidazole (P-1977),
2-[5-Fluoro-2-melhoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-1978),
3 - {4-[2-(2-Bromo-ethoxy)-ethoxy] -2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl } -5-chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 - b]pyridine (P-1984),
5-Chloro-3-[2,5-difluoro-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1986),
5-Chloro-3-[2-fluoro-5-mcthoxy-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-1990),
{3-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxy]-propyl}- diethyl-amine (P-2004),
5-Chloro-3-{2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzyl}-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (P-2002),
3-(4-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluorϋ-benzyl)-lH-pyrro]o[2,3-b]pyi-idine (P-2022),
3-{2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzyl}-5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (P-2025), and
Atty, Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
3-{2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-bcnzyl}-lH-pyrrolo[2.3-b]pyndine (P-2026).
The following table indicates the aldehyde (column 2) and the azaindole (column 3) used to afford the target compound (column 4). Column 1 indicates the compound number and column 5 the observed mass.
Example 11: Synthesis of (3-BenzyIoxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(5-pyridin-3-yl-lH-pyrroloI2,3- b]pyridiπ-3-yl)-methanone P-1467 and related compounds
[0281] Compound P-1467 was synthesized in four steps from 2,4-diiluorophenol 25 as shown in Scheme 8. Scheme 8
Step 1 - Preparation ofl-Benzyloxy-2,4-difluoro-benzene (26):
[0282] To 2,4-difluoro-phenol (25, 7.60 g, 0.0584 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (50.0 mL) were added benzyl bromide (8.0 mL, 0.067 mol) and potassium carbonate (9.00 g, 0.0651 mol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as white solid (26, 3.2O g, 25%).
Step 2 - Preparation of3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-benzaldehyde (27):
[0283] To l-Benzyloxy-2,4-difluoro-benzene (26, 3.00 g, 13.6 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (48 mL) under an atmosphere of nitrogen and cooled with dry ice/acetone was added n-butyllithium (1.60 M in hexane, 8.94 mL). After 20 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamide (1.46 mL, 0.0189 mol) was added to the reaction. After another 20 minutes, the flask was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. The
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 reaction mixture was poured into water, acidified to pH = 1 , and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was washed with brme, dried over sodium sulfate, concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography cluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as a yellow solid (27, 2 5g, 74%)
Step 3 - Preparation of(3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(5-pyndin-3-yl-lH-pytrolo[2,3-b]pvndm- 3-vlj-methanol (28)
[0284] 1 o 5-pyπdm-3-yl-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (20, 750 0 mg, 0 003842 mol, prepared as in Example 9) in methanol (20 0 mL) were added 3-benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-benzaldehyde (27, 1 12 g, 4 5 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (1 50 g, 0 0267 mol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight and then poured into water, acidified with IN HCl to pH around 2 and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was dπed over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (28 700 mg, 35%)
5Ve/? 4 — Preparation of (3-Benzyloxy-2, 6-dιfluoro-phenyl)-( 5-pyrιdιn-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2 3-bJpyndιn- 3-yl)-methanone (P-1467)
[0285] To (3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-( 5-pyndin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-yl)- methanol (28, 300 0 mg, 0 68 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10 0 mL) was added Dess-Martin peπodmane (344 mg, 0 81 mmol) The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes The reaction mixture was concentrated with silica and purified with silica gel column chromatography elutmg with 10% methanol in dichloromethane to give the compound (P-1467, 240 mg, 80%) MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 442 2
[0286] (5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2,6-difluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyll- mcthanone P-1453
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 8, substituting benzyl bromide writh l-Bromo-2- methoxy-ethane in Step 1 and 5-Pyπdin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine 20 with 5-Bromo-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme 1 in Step 3 MS (ESI) [M + IT]+ = 410 1, 412 1
[0287] [2,6-Difluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)- methanone P-1584
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 8, substituting benzyl bromide with l-Bromo-2- methoxy-ethane in Step 1 and 5-Pyridin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine 20 with 5-methoxy-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine (15, prepared as in Example 8) m Step 3 MS (ESl) [M + H+]* - 363 2
[0288] (3-Benzylo\y-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-mcthanone P-1597
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 8, substituting 5-ρyπdin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyπdine 20 with 5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (15, prepared as in Example 8) m Step 3 MS(ESI) [M + H+J+ = 395 2
[0289] (5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-(2,6-difluoro-3-methoxy-phenyl)-inethanone P-1386
was prepared following the protocol of Steps 2, 3 and 4 of Scheme 8, substituting 1 -benzyloxy-2,4- difluoro-benzene 26 with 2,4-difluoro-l -methoxy-benzene m Step 2 and 5-Pyπdin-3->l-lH- pyrrolo[2 3-b]pyndine 20 with 5-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 1 m Step 3 MS (ESI) [M + Hf]+ = 367 0, 369 0
[0290] (3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-methanone P-1802
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 8, substituting 5-pyπdin-3-yl-l H-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyπdme 20 with 7-azaindole 6 in Step 3 To a solution of (3-benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-
Atty. Dkt No : 039363-3303 pyrrolo[2,3-A]pyridin-3-yl)-rnethanone (P-1802, O 5 g, 1 37 mol) in methanol (70 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (30 mL) was added palladium on carbon (120 mg, 10% wt , 0.58 mol). The mixture was stirred under hydrogenation (60 psi) for six hours After removal of solvent, the residue was dried under vacuum, which provided (2,6-Difluoro-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2.3-b]pyπdine-3- yl)-methanone 89
[0291] Additional compounds were prepared following steps 3 and 4 of Scheme 8, replacing 3- benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-ben7aldehyde 27 with an appropriate aldehyde and/or pyridin-3-yl- I H- pyrrolo[2,3-bjpyπdine 20 with an appropriate azaindole in Step 3. The 5-chloro-7-azaindole was synthesized as described in Example 4. The 4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy benzaldehyde and 2- fluoro~5-methoxy-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzaldehyde used were synthesized as described in Example 15. The following compounds were made following this procedure.
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-{2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)- ethoxy]-phenyl}-methanone (P-2003),
(4-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2020), and
[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-phenyl]-(lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-mcthanone
(P-1698).
The following table indicates the aldehyde (column 2) and the azaindole (column 3) used to afford the target compound (column 4). Column 1 provides the compound number and column 5 the observed mass
Example 12: Synthesis of 3-(3-Ben2yloxy-2,6-difluoro-benzyl)-5-pyridin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine P-1455:
[0292] Compound P-1455 was synthesized in four steps from 2,4-difluorophenol 25 as shown in Scheme 8a.
Scheme 8a
[0293] Steps 1-3 are identical to Steps 1-3 of Scheme 8.
Step 4 - Preparation of3-(3-Benzy/oxy-2, 6-diβuoro-ben∑yl) -5-pyridin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (P-1455):
[0294] To (3-benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-( 5-pyridin-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (28, 580.0 mg, 1.3 mmol) in acetonitrile (29.0 mL) were added trifluoroacetic acid (1.9 mL, 0.025 mol) and triethylsilane (3.9 mL, 0.024 mol). The reaction was stirred at 80 0C for 1 hour. The reaction was poured into water, basificd with 1 M potassium carbonate to pH = 4, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give as a yellow solid (P-1455, 530 mg). MS(ESI) [M+Hfj' = 428.3.
[0295] 5-Bromo-3-[2,6-difluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine P-1454
Λtty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 8a by substituting benzyl bromide with l-bromo-2- methoxy-ethane in Step 1 and 5-pyridin-3-yl-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 20 with 5-Bromo-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 1 in Step 3. MS (ESI) [M + H+]4 = 410.1, 412.1.
Example 13: Synthesis of 3-[3-chIoro-4-(4-chIoro-benzyIoxy)-benzyI]-lH-pyrroIo[2,3-b]pyridine P-1449.
[0296] Compound P-1449 was synthesized in three steps from 3-chloro-4-hydroxy-bcnzaldehyde 29 as shown in Scheme 9.
Scheme 9
Step 1 Preparation o/3-chloro-4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-ben∑aldehyde (31): [0297] To acetonitrile (15.0 mL) were added 3-chloro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (29, 0.6 g, 4 mmol), 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 1.2 g, 6 mmol), and potassium carbonate (0.9 g, 7 mmol). The reaction was heated to 150 0C for 10 minutes in a CEM Discover microwave instrument. The reaction was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, and washed with brine. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (ethyl acetate: hexanes) (31, 0.85 g, 76%).
Step 2 - Preparation of3-[3-chloro-4~(4-chloro-hcnzyloxy)-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine (32):
[0298] lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 0.3 g, 2.8 mmol) was mixed with 3-chloro-4-(4-chloro- benzyloxy)-benzaldehyde (31, 0.8 g, 3 mmol), potassium hydroxide (0.9 g, 17 mmol) and methanol (90.0 mL). The reaction was heated to 50 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen for six days. After
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 neutralization with 6N hydrochloric acid the reaction was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, and washed with brine. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (ethyl acetate: hexanes) to give a yellow solid (32, 0.6 g, 41 %). MS(ESI) [M + H+]"= 413.2, 415.2 [M- YfJ = 411.1, 413.1.
Step 3 - Preparation υf 3-[3-chloro-4-(4-ch!oro-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-h] pyridine (P-1449):
[0299] 3-[3-Chloro-4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]p>τidine (32, 0.2 g, 0.6 mmol) was mixed with trifluoroacetic acid (0.226 mL, 3 mmol), triethylsilane (0.4 ml., 3 mmol) and acetonitrile (5 mL). The reaction was heated at 50 0C and stirred for two days. The reaction was concentrated. The residue was diluted with ethyl acetate and neutralized with 2M aqueous sodium hydroxide. The reaction was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, and washed with brine. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography (ethyl acetate: hcxancs) to give a yellow solid (P-1449, 0.0744 g, 33%). MS(ESI) [M + H"]+= 383.2, 385.2.
[0300] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 9, replacing 3-chloro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 29 with an appropriate aldehyde and optionally replacing 4-chlorobenzyl bromide 22 with an appropriate benzyl halide in Step 1 , and optionally replacing 1 H- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 6 with an appropriate azaindole (7-azaindole (5-chloro-7-azaindole per Example 4 or 5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8) in Step 2. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
3-[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1450),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1462), 3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1466), 3-[4-(4_Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-ethoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1470), 3-[2-Chloro-4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (P-1471), 3.[4-(4-Chloro-bcnzyloxy)-3-trifluoromethoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1487), 3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1531), 5-Chloro-3-[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1532), 3-[4-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1544), 3-[4-(2,4-Dichloro-bcnzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1568), 3-[3-Methoxy-4-(4-methoxy-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1569), 3-[3-Methoxy-4-(2,4,6-trifluoro-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridinc (P-1578), 3-[4-(2,6-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1579), and 3-[3- Chloro-4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl] - 1 H-pyrrolo [2 ,3 -b]pyridine (P-1616)
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
The following table indicates the aldehyde (Column 2), the benzyl halide (Column 3), and the azaindole (Column 4) used to afford the target compound (Column 5), Column 1 indicates the compound number and column 6 the observed mass.
Example 14: Synthesis of 3-(4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine P-1613.
[0301] Compound P-1613 was synthesized in two steps from 4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy- benzaldehyde 33 as shown in Scheme 10.
Scheme 10
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 1 - Preparation of3-[(4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine (34):
[0302] Methanol (125 mL) and potassium hydroxide (4.4 g, 79 mmol) were mixed with IH- pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 3.1 g, 26.6 mmol) and 4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-benzaldehyde (33, 12.9 g, 53.2 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 days. The resulting white solid was filtered and washed with water. Crude material was carried forward without further purification.
Step 2 - Preparation of 3-(4-ben∑yloxy-3-methoxy-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine (P-1613): [0303] The crude 3-[(4-benzyloxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidine (34, 0.9g, 2.4 mmol) from step 1 and acetonitrile (50 mL) were mixed with trifluoroacetic acid (0.360 mL, 4.7 mmol) and triethylsilanc (0.746 mL, 4.7 mmol). The reaction was heated at 80 0C and stirred overnight. The reaction was concentrated. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and saturated sodium bicarbonate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The desired compound was isolated by silica gel column chromatography to give the compound (P-1613, 0.454 g 54.8%). MS(ESI) [M + H+]+= 345.3.
Example 15: Synthesis of aldehyde reagents for coupling to 7-azaindoles
[0304] Aldehyde compounds for coupling to the 3 -position of a 7-azaindole are shown in the following Schemes. 3-Methoxy-4-[4-(4-methyl-piperazin-l -ylmethyl)-benzyloxy]-benzaldehyde 37 was prepared in one Step as shown in Scheme 11.
Scheme 11
Step 1- Synthesis of3-methoxy-4-[4~(4-methyl-piperazin-l-ylmethyI)-hen∑yloxy]~benzaldehyde (37):
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0305] To 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (21, 2.1 g, 0.014 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (40.0 ml.) were added 1 ,4-bis(bromomethyl)-benzene (35, 4.00 g, 0.0152 mυl) and potassium carbonate (5.0 g, 0.036 mol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. After 12 hours 1 -methyl-piperaκine (36, 3.8 mL, 0.034 mol) was added to the reaction. After 2 hours, the reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% methanol in dichloromethane to give the compound (37, 1.2 g, 25.0%). MS(ESI) [M+Hr]' = 355.3.
[0306] 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 39 was synthesized in one step from 2-fluoro- 4,5-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde 38 as shown in Scheme 12.
Scheme 12
Step 1 - Synthesis of2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (39):
[0307] To 2-fluoro-4,5-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde (38, 1.00 g, 5.43 mol) in dichloromethane (50.0 mL) was added aluminum trichloride (4.34 g, 32.6 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and washed with ethyl acetate and hexane to give a white solid (39, 0.7Og,
76.0%).
[0308] 2,5-Difluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldchyde 43 was synthesized in three steps from 2,5- difluorophenol 40 as shown in Scheme 13.
Scheme 13
Step 1 - Synthesis of 4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenol (41):
[0309] To 2,5-difluorophenol (40, 5.50 g, 0.0423 mol) in chloroform (1 10.0 mL), bromine (2.18 mL, 0.0423 mol) was added slowly. After 3 hours, the reaction was poured into a solution of sodium thiosulfate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (41, 6.20 g, 70.2%).
Step 2 - (4-Bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenoxy)-tert-hutyl-dimethyl-silane (42):
[0310] To 4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenol (41, 3.50 g, 0.0167 mol) in N.N-dimethylformamide (50.0 mL) were added tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (3.83 g, 0.0254 mol) and lH-imidazole (6.00 g, 0.0529 mol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight, then poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 4% to 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (42, 3.0 g, 55.4%).
Step 3 - 2,5-Difluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (43):
[0311] To (4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenoxy)-tert-butyl-dimethyl-silane (42, 3.00 g, 9.28 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (37.5 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0C, n-butyllithium (3.90 mL, 2.50 M in hexane) was added slowly. After 30 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamide (0.825 mL, 0.0106 mol) was added to the reaction. One hour later, the reaction was allowed to come to room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and 1 N HCl, then extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 10% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as an off-white solid (43, 0.86 g, 59.0%).
[0312] 4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-benzaldehyde 46 was synthesized in one step from 3- fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 44 as shown in Scheme 14.
Scheme 14
Step 1 - Synthesis of4-(4-chloro-ben∑yhxy)-3-βuoro-ben∑aldehyde (46):
[0313] To 3-fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (44, 0.800 g, 5.71 mmol) in N.N-dimethylformamide (50.0 mL) was added sodium hydride (260.0 mg, 60% in mineral oil, 6.50 mmol). After 15 minutes, 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 1.29 g, 6.28 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture. The reaction was stirred at 80 0C for 5 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 compound (46, 1.3 g, 86,0%).
[0314] Additional aldehydes were prepared using the protocol of Scheme 14, replacing either 4- chlorobenzyl bromide 22 with a suitable alkylating agent, and/or 3-fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 44 with a suitable aldehyde. The following table indicates the alkylating agent (column 1) and the starting aldehyde (column 2) used to afford the aldehyde (column 3) synthesized following this protocol.
Example 16: Synthesis of [4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone P-1897 and related compounds
[0315] Compound P-1897 was synthesized in two steps from 4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro- benzaldehyde 46 as shown in Scheme 15.
Step 1 - Synthesis of [4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3~fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin~3-yl)- methanol (P-1895):
[0316] To lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 100.0 mg, 0.85 mmol) in methanol (50.0 mL) were added 4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-benzaldehyde (46, 250.0 mg, 0.94 mmol, prepared as described in Example 15) and potassium hydroxide (LOOg, 17.82 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound (P-1895, 55 mg, 17.0%). MS(ESI) [M+lT]* = 383.3.
Step 2 - Synthesis of[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-1897):
[0317] To [4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (P-1895, 17.7 mg, 0.046 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10.0 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (23.5 mg, 0.056 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes. The reaction
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 was concentrated, then purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-1897, 6.4 mg, 36.3%). MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 381.3.
[0318] Additional compounds were prepared using the protocol of Scheme 15, replacing 4-4-(4- chloro-benzyloxy)-3-fluoro-bcnzaldehyde 46 with a suitable aldehyde (prepared as described in Examples 15 or 34), and optionally replacing lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 6 with an appropriate substituted 7-azaindole (5-chloro-7-azaindole per Example 4, 5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8, or 5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-7-azaindole per Example 35) in Step 1. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
[4-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-1845),
[4-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy)-3-methoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-1850),
[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-3-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-1900),
(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1903),
[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridm-3-yl)-methanone (P-1979),
[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-niethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone (P-1982),
[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2,5-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-1987),
{4-[2-(2-Bromo-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl}-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1988)(
(5-Chloro-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2,5-difluoro-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]- mcthanone (P-1989),
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]- methanone (P-1991),
2-[2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- bcnzoimidazole (P-2116),
2-{2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzoimidazolc (P-2117),
2-[2,5-Difluoro-4-(5-methanesuIfonyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymcthyl]- l H-benzoimidazole (P-2170),
3 -[4-( 1 H-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5 -mcthoxy-benzyl] - 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyridine-5 - carbonitrile (P-2171),
3-[4-(lH-Bcnzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-5-
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 carboxylic acid methyl ester (P-2174),
2-{2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl } -1 H-benzoimidazolc (P-2176),
2-[4-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lII- benzoimidazole (P-2181),
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2,5-difluoro-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme-5- carbonitrile (P-2185), and
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-lH-pyrrolo[2.3-b]pyπdm-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole (P-2186)
The following table indicates the aldehyde (column 2) and the azamdole (column 3) used to afford the target compound (column 4). Column 1 indicates the compound number and column 5 the observed mass.
Example 17: Synthesis of 3-(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-benzyI)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine P-1901
[0319] Compound P-1901 was synthesized in four steps from 4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenol 41 as shown in Scheme 16.
Scheme 16
Step 1 — Synthesis of J -Ben∑yluxy-4-bromo-2, 5-difluoro-benzene (47):
[03201 To 4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenol (41, 0.90 g, 0.0043 mol, prepared as described in Example 15, Scheme 13) in N,N-dimethylformamide (30.0 mL) were added sodium hydride (0.21 g, 60% in mineral oil, 0.0052 mol) and benzyl bromide (0.563 mL, 0.00474 mol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 5% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (47, 0.84 g, 65,0%).
Step 2 - (4-Benzy!oxy-2, 5-difluoro-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsilanyl- lH-pyrrolo[2, 3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (48):
[0321] To 1 -Benzyloxy-4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-benzene (47, 0.84 g, 2.80 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (15.0 mL) and ether (15.0 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0C, n-butyllithium (1.20 mL, 2.50 M in hexane) was added slowly. After 20 minutes, l-Triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde (8, 0.82 g, 0,0027 mol, prepared as described in Example 5) was added to the reaction. After 20 minutes, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature for 10 minutes, then poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to a white solid (48, 1.Og, 70.0%). MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 523.4.
Step 3 - Synthesis υf(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (P-1902):
[0322] To (4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanol (48, 1.00 g, 1.91 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (15.0 mL) was added tetrabutylammonium fluoride, trihydrate (0.63 g, 2.04 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was roto-cvaporated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as a white solid (P-1902, 0.59 g, 84.0%). MS(ESl) [M+HT = 367.4.
Step 4 - Synthesis of3-(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-diflnoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1901): [0323] To (4-Bcnzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (P-1902, 500.0 mg, 1.37 mmol) in acetonitrile (25.0 mL) were added triethylsilane (2.00 mL, 0.0125 mol) and trifluoroacetic acid (1.00 mL, 0.0130 mol). The reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours. The reaction was concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-1901, 60.0 mg, 94.1%). MS(ESI) [M+HT = 351.4.
[0324] 3 -[3 -Trifluoromethyl-4-(4-trifluoromethyl-benzyl oxy)-benzy I]- 1 H-pyrroIo [2,3 -b]pyridine
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
P-1797
was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 16, substituting 4-bromo-2,5-difluoro-phenol 41 with 4-bromo-2-trifjuoromethyl-phenol (prepared as described in Example 15, Scheme 13, Step 1. substituting 2,5-difluoro-phenol 40 with 2-trifluoromethyl-phenol) and benzyl bromide with 1- bromomethyl-4-trifluoromethyl-benzene in Step 1. MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 451.
Example 18: Synthesis of 3-[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2,5-difluoro-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridine P-1974
[0325] Compound P-1974 was synthesized in four steps from 3-(4-benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-bcnzyl)- lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine P-1901 as shown in Scheme 17.
Scheme 17
Step 1 - Synthesis of3-(4-benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-benzyl)-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrπla[2,3- b] pyridine (49):
[0326] To 3-(4-benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1901, 560.0 mg, 1.60 mmol, prepared as described in Example 17) in tetrahydrofuran (28.0 mL) was added sodium hydride (100.0 mg, 60% in mineral oil, 2.50 mmol). After 10 minutes, triisopropylsilyl chloride (0.500 mL, 2.36 mmol) was added to the reaction. After 4 hours, the reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hcxane to give the compound (49, 0.70 g, 86.1%).
Step 2 - Synthesis of2,5-difluoro-4-(l-trii$opropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3~b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)- phenol (50):
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0327] To 3-(4-Benzyloxy-2,5-difluoro-benzyl)-l-tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (49, 0 70 g, 0 0014 inol) in methanol (30 0 ml ) was added 50% palladium hydroxide on carbon (0 1 g) under an atmosphere of hydrogen I he reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight The reaction was filtered and concentrated to give a colorless oil (50, 0 47 g, 82 0%)
Step 3 - 3-[4-(4-Chloro-benzyIoxv)-2,5-ώfluoro-benzylJ-l-trusυprυpylsιlanyI-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyndute (51)
[0328] To 2,5-difluoro-4-(l-tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3 ylmethyl)-phenol (50, 120 0 mg, 0 29 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (15 0 mL) was added sodium hydride (18 0 mg, 60% in mineral oil, 0 45 mol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen After 10 minutes, 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 65 1 mg, 0 32 mol) was added to the reaction I he reaction was stirred at 40 0C overnight The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered The filtrate was concentrated to give the crude compound (51, 0 15 g) that was used directly in the next step
Step 4 - Synthesis of 3-[4-(4-chloi o-benzvloxy)-2,5-dιfluoi o-benzvl]-lH-pvrrolo[2,3 bjpvriώne
(P-1974)
[0329] To 3-[4-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2,5-difluoro-benzyl]-l -tπisopropylsilanyl-1 H-pynolo[2,3- bjpyridme (51, 0 150 g, 0 28 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10 0 mL) was added tctra-n-butylammonium fluoride (80 0 mg, 0 31 mmol) After 10 minutes, the reaction was concentrated and puπfied by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as a white solid (P-1974, 30 8 mg, 28 9%) MS(ESI) [M+lT]+= 385 3
[0330] 2-[2]5-Difluoro-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmcthyl)-phenoxymethyl] IH- benzoimidazole P-1975
was prepared using the protocol of Scheme 17, substituting 4-chlorobenzyl bromide 22 with 2- chloromethyl-lH-ben/Coimidarole m step 3 MS(ESI) [M+H1] = 391 3
Example 19: Synthesis of 3-(3-Benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-ft]pyridine P-1852, (3-Benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-phenyI)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-6]pyridin-3-jl)-methanone P- 1853 and related compounds
[0331] Compounds P-1852 and P-1853 were synthesized in four steps from 2-chloro 4- fluorophenol 52 and lH-pyrrolo[2,3 έjpyridine 6 as shown in Scheme 18
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Scheme 18
Step 1 - Preparation of l-Benzyloxy-2-chloro-4-fluoro-benzene (S3)
[0332] To a solution of 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol (52, 7 g, 0 05 mol) in tetrahydroftiran (100 mL) was added sodium hydπde (1 8 g, 95% dry powder, 0 071 mol) at room temperature o\er 15 minutes under an atmosphere of nitrogen The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes Benzyl bromide (10 g, 0 060 mol) was added slowly to the reaction mixture, then stirred at room temperature overnight The reaction mixture was poured into ice water, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with hydrochloπc acid (10%), water, brine, and dπed over magnesium sulfate After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound as a white solid (53, 7 6 g, 60%)
Step 2 - Preparation of 3-Benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-flιιoro benzaldehvde (54) [0333J To a solution of l-benzyloxy-2-chloro-4-fluoro-benzene (53, 5 8 g, 0 024 mol) in tetrahydroftiran (100 mL) was added 2 50 M of n-butylhthium (2 7 mL, 2 50 M in hexane, 0 029 mol) slowly at -78 0C over 15 minutes under nitrogen The reaction mixture was stirred at -78 0C for 30 minutes To the reaction mixture was then added N,N-dimethylformamide (4 2 mL, 0 054 mol) The reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and was continued at room temperature overnight l he reaction mixture was poured into ice water, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with hydrochloric acid (10%), water, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as a white solid (54, 2 1 g, 32%) MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 265 08
Step 3 Preparation of3-[(3-Benzyloxy-2-thloro~6-fluoro-phenyl)-methoxy~methyl] IH pyrrolo[2,3-
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 b J pyridine (P-1867) and (3-Btjnzy1oxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl) - methanol (P-1868):
[0334] A mixture of lH-pyrrolo[2,3-£>]pyridine (6, 0,5 g, 4 mmol), 3-benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro- benzaldehyde (54, 1.3 g, 4,9 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (0.99 g, 18 mmol) in methanol (30 mL) was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate and water. The organic layer was collected and washed with brine. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound P-1867 as a white solid (1.3 g, 70%. MS(ESI) [M+JT]+ = 397.16), and compound P-1868 as an off-white solid (0.2 g, 10, MS(ESI) [M+ff ] " = 383.14).
Step 4a - Preparation of3-(3-benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrυlo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1852):
[0335] A mixture of 3-[(3-benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- ftjpyridine (P-1867, 0.1 g, 0.2 mmol), trifluoroacetic acid (0.6 mL, 8 mmol), and triethylsilane (0.3 mL, 2 mmol) in acetonitrile (10 mL) was refluxed for 2 hours. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The solution was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with methanol in dichloromethane to provide compound as an off- white solid (P-1852, 62 mg, 70%). MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 367.16.
Step 4b Preparation of(3-benzyloxy-2-ch1oro-6-flιωro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl) - methanone (P-18S3):
[0336] To a solution of (3-benzyloxy-2-chloro-6-fluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (P-1868, 65 mg, 0.17 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (79 mg, 0.19 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The reaction was quenched with a saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with methanol in dichloromethane to provide the compound as a light yellow solid (P-1853, 32 mg, 50%). MS(ESI) [M+HT = 381.13.
[0337] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 18, optionally replacing 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 52 with 2,6-difluorophenol or 2,6-dichlorophenol, optionally replacing benzyl bromide with an appropriate substituted benzyl bromide, and optionally replacing lH-pyrrolo[2,3-£]pyridine 6 with an appropriate substituted lH-pyrτolo[2,3-/)]pyridine (5-chloro-7- azaindole per Example 4 or 5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8). The following compounds were made following this procedure:
3-[2,6-Dichloro-3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-/?]pyridine (P-1768),
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(4-chloro-benz>'loxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyiτolo[2,3- δ]pyridin-3-yl) methanone (P-1769),
(3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2)3- fc]pyridin-3-yl)-methaiione (P-1802), 3-(3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- Z)]pyridine (P-1803), 3-(3-Benzyloxy-2,6-difluoro-benzyl)-5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- £]pyridine (P-1804), 3-(3-BenzyIoxy-2,6-difluoro-benzyl)-5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- 6]pyridine (P-1824), (3-BenzyIoxy-2,6-difluoro-phenyl)-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- fr]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1825),
[2-ChIoro-3-(3-chloro-benzyIoxy)-6-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3- 5]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1869),
[2-Chloro-3-(4-ch]oro-benzyloxy)-6-fluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrro]o[2,3- />]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1874),
3-[2,6-Difluoro-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1993), and 3-[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2,6-difluoro-benzyI]-lH-pyτrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1992). The phenol, benzyl bromide and azaindole used in Steps 1, 2, and 3, respectively, are indicated in columns 2, 3, and 4 of the following table, respectively, to afford the target compound (column 5). The compound number is provided in column 1, and the observed mass is given in column 6.
Example 20: Synthesis of (3-Benzyloxy-2-methyI-phenyI)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-6]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone P-1848 and 3-(3-BenzyIoxy-2-methyI-benzyl)-lH-pyrroIo[2,3-6]pyridine P-1857
[0338] Compounds P-1848 and P-1857 were synthesized in five steps from compounds 55 and IH- pyrrolo[2,3-&]pyridine 6 as shown in Scheme 19,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Scheme 19
Step 1 - Preparation of 3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-benzoιc acid (56)
[0339] To a solution of 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-benzoic acid (55, 5 0 g, 0 033 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (100 mL) and N,N-dimethylformamide (50 niL), sodium hydride (4 4 g as 60% dispersion in mineral oil, 0 11 mol) was added slowly over 30 minutes and the reaction was stirred at 0 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature, then stirred at room temperature for 1 hour Benzyl bromide (9 0 mL, 0 076 mol) was added slowly into the reaction mixture, and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight I he reaction mixture was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with a solution of ammonium chloride and ammonium hydroxide (4 1), bπne, and dried over magnesium sulfate After removal of solvent, (he residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as a white solid (56, 5 8 g, 73%)
Step 2 Preparation of(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-ρhenyl)-methanol (57) [0340] To a solution of 3-benzγloxy-2-methyl-benzoic acid (56, 3 0 g, 0 012 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (100 mL), lithium aluminum hydride (25 mL, IM solution m tetrahydrofuran, 0 025 mol) was added dropwise at 0 0C for 5 minutes The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature overnight under an atmosphere of nitrogen After sodium sulfate decahydrate (20 0 g, 0 062 mol) was added, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes A white solid was collected by filtration I he solid compound was further washed with a mixture of hexane and dichloromethane (9 1) and dried under high-vacuum (57, 2 8 g, 91%)
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 3 Preparation of3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-benzaldehyde (58):
[0341] To a solution of (3-benzyloxy-2-mεthyl-phenyl)-methanol (57, 627 mg, 2,75 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (60 mL) was added Dcss-Martin penodinane (2,9 g, 6,87 mmol) at 0 °C. The resulting mixture was stirred at 0 0C for 50 minutes. The reaction mixture was quenched with a solution of saturated sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as a white solid (58, 0.55 g, 84%).
Step 4 - Preparation of(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (59) and 3-[(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lI1-pyrrolo[2, 3-bJpyridine (60): [0342] A mixture of lH-pyrrolo[2,3-έ]pyridine (6, 0.33 g, 2.8 mmol), 3-benzyloxy-2-methyl- benzaldehyde (58, 0.55 g, 2.4 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (0.39 g, 6.1 mmol) in methanol (40 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 17 hours. The reaction mixture was poured into water and then extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound 59 as an off-white solid (330 mg, 39%, MS(ESI) [M+H+f - 345.29, and compound 60 as a white solid (24 mg, 3%, MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ - 359.30).
Step 5 a - Preparation of (3-Benzyloxy-2~methyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1848):
[0343] To a solution of (3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-έι]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (59, 0.12g, 0.35 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (15 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (0.37 g, 0.89 mmol) at 0 0C . The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 0C for 50 minutes, then quenched with a saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was washed with a mixture of ethyl ether and hexanes (1 :1) to provide the compound as a yellow solid (P-1848, 108 mg, 90%). MS(ESI) [M+ϊTf = 343.22.
Step 5b Preparation of 3-(3-Benzyloxy-2-methyl-benzyl)-]II-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-1857): [0344] A mixture of 3-[(3-benzyloxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (60, 24 mg, 0.067 mmol), trifluoroacetic acid (1 mL, 13 mmol), and triethylsilane (2 mL, 12.5 mmol) in acetonitrile (10 mL) was refluxed for 4 hours. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The solution was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was washed with a mixture of ethyl ether and hexanes (1 : 1 ) to provide the compound as a yellow solid (P-1857, 17 mg, 75%), MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 329.24.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Example 21: Synthesis of [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)~2-ethoxy-phenyI]-(lH-pyrroloI2,3-£]pyridin- 3-yI)-methanone P-1892 and 3-I3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrroIo[2,3- 6]pyridine P-1893
[0345] Compounds P-1892 and P-1893 were synthesized in five steps from compounds 61, 22 and lH-pyrrolo[2,3-&]pyridine 6 as shown in Scheme 20,
Scheme 20
Step 1 - Preparation of2,3-Bis-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-benzaldehyde (62):
[0346] To a solution of 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (61, 2.0 g, 14.5 mmol) in tetrahydrofiiran (100 mL) was added sodium hydride (0.52 g, 13.0 mmol) at 0 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. To the reaction mixture was then added 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 2.7 g, 13.0 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen overnight. N, N-dimethylformamide (50 mL) was added into the reaction mixture and it was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was poured into ice water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as an off-white solid (62, 2.3 gm, 46%).
Step 2 - Preparation of3-(4-chloro-henzyloxy)-2-hydrυxy-benzaldehyde (63): [0347] To magnesium (0.098 g, turnings, 4.0 mmol) in a mixture of anhydrous ether (20 mL) and benzene (20 mL) at 0 0C, bromine (0,10 mL, 2.0 mmol) was added dropwise. When the reaction had started, stirring was commenced and the addition of bromine continued until complete. The ice bath
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 was removed and the reaction mixture was heated until the solution was almost colorless. After cooling down, the reaction mixture was slowly added to a solution of 2, 3-bis-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)- benzaldchyde (62, 0.78 g, 2.0 mmol) in benzene (60 mL) at room temperature while stirring vigorously. Upon completion of the addition, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight, then refluxed for 36 hours. After the reaction mixture was cooled down to room temperature, a solid was collected by filtration and washed with benzene, then boiled in hydrochloric acid (100 mL, 1.0 M) for 30 minutes. After cool down, the solution was extracted with dichloromcthane. The organic layer was washed with brine and dried over magnesium sulfate. An off-white solid was obtained after removal of the solvent (63, 0.32 mg, 60%). MS(ESI) [M-H+]" =261.25.
Step 3 — Preparation of3-(4-chloro-ben∑yloxy)-2-ethoxy-benzaldehyde (64):
[0348] To a mixture of 3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (63, 110 mg, 0.42 mmol), potassium carbonate (150 mg, 1.1 mmol) in acetonitrilc (8 mL) was added iodoethane (0.2 mL, 2.5 mmol) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at 98 0C for 18 hours. The reaction mixture was poured into a solution of saturated ammonium chloride and was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, a light yellow solid was obtained (64, 116 mg, 95%).
Step 4 — Preparation of [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrυ1o[2,3-h]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (65) and 3-{[3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl}-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (66):
[0349] A mixture of lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-6]pyridine (6, 26 mg, 0.22 mmol), 3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2- ethoxy-benzaldehyde (64, 54 mg, 0.19 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (30 mg, 0.4.6 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 4 days. The reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound 65 as an off-white solid (20 mg, 26%, MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 409.32) and compound 66 as an off-white solid (44 mg, 56%, MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 423.33.
Step 5a - Preparation of[3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-J 892):
[0350] To a solution of [3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol (65, 20 mg, 0.05 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (8 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (52 mg, 0.12 mmol) at 0 0C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 0C for 50 minutes. The reaction was quenched with a saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 was washed with a mixture of ethyl ether and hexanes (1 : 1) to provide the compound as a yellow solid (P-1892, 15 mg, 75%). MS(ESI) [M+ITf = 407.38.
Step 5b - Preparation of3-[3-(4-chlυrυ-bemylυxy)-2-ethυxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrυh[2,3-b]ρyridine (P-1893):
[0351] Λ mixture of 3-{[3-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-methoxy-methyl} -lH- pyrrolo[2,3-&]pyridine (66. 44 mg, 0.1 mmol), trifluoroacetic acid (1 mL, 13 mmol), and triethylsilane (2 mL, 12.5 mmol) in acelonitrile (10 mL) was refluxed for 4 hours. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The solution was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was washed with a mixture of ethyl ether and hexanes (1 : 1) to provide the compound as a yellow solid (P-1893, 40 mg, 98%). MS(ESI) [M+lTf - 393.39.
[0352] [3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-methoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-1891), [3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone (P-2076), [3-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-l H- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2016), and 3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)- phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2, 3-6]pyπdin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2118)
were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 20, substituting iodoethane with iodomethane in Step 3 to provide P-1891, or substituting iodoethane with 2-iodo-l ,l ,l -trifluoroethane in Step 3 to provide P-2076, or substituting iodoethane with 2-iodo-l-fluoroethane in Step 3 to provide P-2118, or substituting 4-chlorobenzyl bromide 22 with 4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyl bromide in Step 1 and 7- azaindole 6 with 5-methoxy-7-azaindole in Step 4 to provide P-2016. MS(ESl) [M+H+J+ - 393.4 (P-1891), 461.08 (P-2076), 455.2 (P-2016), and 425.17 (P-2118).
Example 22: Synthesis of 3-Iodo-l-triisopropyIsilanyI-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiπe 68
[0353] 3-Iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3«b]pyridine 68 was synthesized in one step from 3-Iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 67 as shown in Scheme 21.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Scheme 21
68
Step 1 - Preparation of3-Iodo-l-trHsopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (68): [0354] 3-Iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 67 (2.00 g, 8.20 mmol) was dissolved in N,N- dimethylformamide (50 mL). Sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 390 mg, 9.8 mmol) was added. After 20 minutes, triisopropylsilyl chloride (1.74 mL, 8.20 mmol) was added dropwise. After 1.5 hours, the reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine. The organic portions were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification by silica gel chromatography, 0-25% gradient ethyl acetate/ hexane gave compound 68 as a white solid (3.224 g, 98.2%). 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound.
Example 23: Synthesis of l-(tert-ButyI-dimethyI-siIanyI)-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 69
[0355] l-(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyl)-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiπe 69 was synthesized in one step from 3-Iodo-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 67 as shown in Scheme 22.
Scheme 22
69
Step 1 - Preparation ofl-(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyl)-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (69): |0356] 3-Iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 67 (1.11 g, 4.6 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (120 mL). Sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 0.13 g, 5.5 mmol) was added, followed by tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (0.85 g, 5.5 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic portion was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the compound as a white solid (69, 100 mg, 15%).
Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303
Example 24: Synthesis of [5-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyridin-2-yl]-(lII-pyrrolo[2,3- bJpyridin-3-yl)-methanone P-2024
[0357J [5-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyridin-2-yl]-(lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone P-2024 was synthesized in six steps from Kojic acid 70 and 3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl- lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 68 as shown in Scheme 23.
Scheme 23
Step 1 - Preparation of5-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxymethyl-pyran-4-one (71): [0358] Kojic acid (70, 5.00 g, 35.2 mmol) and 4-chlorobenzyl bromide (22, 7.95 g, 38.7 mmol) were suspended in methanol (40 mL) in an 80 mL sealed tube. Sodium hydroxide in water (12 M, 2.93 mL) was added. The reaction was heated at 80 0C overnight. The resulting suspension was concentrated. Water was added and the mixture was filtered and washed with water to provide a brown solid. Washing with minimal methanol on the filter removed the brown color. A white solid (71, 7.58 g, 80%) was isolated. 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound.
Step 2 — Preparation of 5-(4-ch1υrυ-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxymelhyl- 1 H-pyridin-4-one (72) ■ [0359] 5-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxymethyl-pyran-4-onc (71, 8.00 g, 3.00 mmol) was suspended in ammonium hydroxide (200 mL) in an 80 mL sealed tube. The reaction was heated at 90
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
0C overnight Upon cooling, the reaction was lowered to pi I 10 with 6N HCl to provide a beige solid that was collected by filtration (72, 7 8 g, 98%)
Step 3 Preparation of [5-(4-chloro-henz\lox\)-4-methory-pχndιn-2-vl] -methanol (73) [0360] 5-(4-Chloro-benz} loxy)-2-hydroxymcthyl-l H-pyπdin-4-one (72, 1 06 g, 3 99 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (8 5 rnL) and N,N-dimethylformamide (46 rnL) frimethylsilyldiazomethane in hexane (2 00 M, 3 99 rnL) was added The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight, then additional trimethylsilyldiazomethane in hexane (2 00 M, 3 99 mL) was added The reaction w as stirred at room temperature for 2 days The mixture was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, methanol dichloromethane to provide the compound (73, ^98 mg, 72 %)
282 4
Step 4 — Preparation of5-(4-cMoro-benzylo\y)-4-methυxy-pyrιdιne-2-caihaldehyde (74) [0361] [5-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyπdin-2-yl]-methanol (73, 480 mg, 1 7 mmol) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (26 mL) and Dess-Martin penodinane (909 mg, 2 1 mmol) was added The reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature for 2 hours The reaction was concentrated under high vacuum and then poured into a solution OfNaHCO3 and Na2S2Oi The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate The organic portions were dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered 1 he filtrate was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, ethyl acetate hexanes, to provide the desired compound as a white powder (74, 343 mg, 72 %)
Step 5 - Preparation of [5-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyndιn-2-yl] -(I -trιιsopropylsdanyl-1 H- pyrroh[2 3-h]pyrιdιn-3-yl)-methanol (75)
[0362] 3-Iodo-l-tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine (68, 180 mg, 0 450 mmol, prepared as described in Example 22) was dissolved m tetrahydrofuran (2 5 ml ) and the reaction was cooled to -20 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen Isopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydrofuran (2 00 M, 0 243 ml ) was added The reaction was stirred for 1 hour, during which the temperature rose to 0 0C The reaction was cooled to -20 0C and 5-(4-chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyπdme-2-carbaldehyde (74, 80 0 mg, 0 288 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (0 75 mL) was added The reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred overnight The reaction was quenched with methanol and adsorbed onto silica, then purified by silica gel chromatography, methanol dichloromethane, to provide the desired compound (75, 94 mg, 59%) 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound MS(ESI) [M+H+]+= 552 4, 554 4, 555 4
Step 6- Preparation of [5-(4-chlof o-ben∑ylo\y)~4-methoxy-pyrιdιn-2-γl] -(I H-pyrrolo[2,3 bjpyndin- 3-yl)-methanone (P-2024)
[U363] [5 (4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-4-methoxy-pyndm-2-yl]-(l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyπdm-3-yl)-methanol (75, 60 0 mg, 0 11 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (2 00 mL)
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Dess-Martin periodinane (55.3 mg, 0.13 mraol) was added to the reaction and it was stirred at room temperature overnight. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and saturated sodium bicarbonate. The organic portions were dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and the filtrate was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography. methanol:dichloromethane, to provide the desired compound (P-2024, 10.7 mg, 25%). 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound. MS(ESI) [M+H+f = 394.1 , 396.1.
Example 25: Synthesis of 3-4-[l-(4-chIoro-phenyI)-ethoxy]-3-methoxy-benzyI-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine P-2000
[0364] 3-4-[l -(4-Chloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-3-methoxy-benzyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine P-2000 was synthesized in three steps from vanillin 21, 4-chlorophenylmethylcarbinol 76, and l-(tert-butyl- dimethyl-silanyl)-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 69, as shown in Scheme 24.
Scheme 24
Step 1 - Preparation of4-[l-(4-chloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-3-methoxy-ben∑aldehyde (77): [0365] 4-Chlorophenylmefhylcarbinol (76, 0.668 mL, 6.57 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (60.0 mL) at 0 °C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (21, 1.00 g, 6.57 mmol) and triphenylphosphiπe (2.07 g, 7.89 mmol) were added to the reaction, followed by diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (1.55 mL, 7.89 mmol) over 10 minutes. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours. The mixture was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, ethyl acetate:hexanes, to provide the desired compound, (77, 1.14 g, 60 %). 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound.
Any. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 2 - Preparation of ' [ 1 -(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyl)-lII -pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyridin-3-ylJ -4-[ l-(4- chloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-3-methoxy-phenyl-methanol (78):
[03661 l-(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyl)-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]p)τidine (69, 647.0 mg5 1.81 mmol, prepared as described in Example 23) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (10.0 niL) at -20 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. Isopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydroruran (2,0 M. 0.98 mL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was stirred for 1 hour, during which the temperature rose to 0 °C. The reaction was cooled to -20 0C and 4-[l -(4-chloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-3-methoxy-benzaldehyde (77, 420 mg. 1.4 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (3.00 mL) was added. The reaction was stirred for 2 hours during which time the temperature rose to 10 0C. The reaction was quenched with methanol and adsorbed onto silica, then purified by silica gel chromatography, ethyl acetate:hexanes, to provide the desired compound, (78, 463 mg, 61%). 1H-NMR was consistent with the desired compound.
Step 2 - Preparation υf3-4-[l-(4-chlnm-phenyl)-ethoxy]-3-rnethoxy-benzyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridine (P-2000):
[0367] [l-(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyl)-lH -pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl]-4-[l -(4-chloro-phenyl)- ethoxy]-3-methoxy-phenyl-methanol (78, 0.200 g, 0.382 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (5.00 mL). Trifluoroacetic acid (0 138 mL) was added and the reaction was stirred for five minutes. Triethylsilane (0.285 mL) was added and the reaction was heated at 80 0C for 2 hours. The reaction was concentrated, then redissolved in ethyl acetate and adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, ethyl acetate:hexanes, to provide the desired compound (P-2000, 57 mg, 38 %). 1H- NMR was consistent with the desired compound. MS(ESI): [M^H+J+= 393.3, 395.3.
Example 26: Synthesis of 5-I4-(2-methoxyethoxy)-phenyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 81
[0368] 5-[4-(2-Methoxyethoxy)-phenyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 81 was synthesized in two steps from 4-bromophenol 79 as shown in Scheme 25.
Scheme 25
Step 1 - Preparation J-Bromo-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzene (80):
[0369] To a solution of 4-bromophenol (79, 5.0 g, 28.9 mmol) in dimethylformamide (15 mL) were added potassium carbonate (4.40 g, 31.8 mmol) and 1 -bromo-2-mcthoxyethane (5.00 g, 36,0 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction mixture was stirred at ambient temperature overnight and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was slurried in ethyl acetate (50 mL) and
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 filtered The filtrate w as washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, dried over magnesium sulfate and filtered Silica gel column chromatography (0-10% ethyl acetate in hexanes) ga\e the desired compound as a colorless oil (80, 3 2 g, 48%)
Step 2 - Preparation of 5-[4-(2-Metho\y-etho\y)-phenyl] -1 H-pyrmlo[2 3 b] pyridine (81) [0370] To a solution of 5-(4,4,5.5,-tetramethyl-[l ,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)-lH-pyrrolol[2,3- b]pyπdme (1 1 g, 4 3 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (40 mL) was added 1 -bromo-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)- benzene (80, 1 50 g, 6 49 mmol) and tetrdkis(tπphenylphosphme)palladium (0) (0 25 g, 0 21 mmol) The reaction mixture was stirred with potassium carbonate solution (10 mL, 1 0 M) and warmed to reflux overnight The biphasic reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate (50 mL) and saturated sodium carbonate solution (20 mL) The organic layer was separated, w ashed w ith brine, dried over magnesium sulfate and punfied by silica gel column chromatography (50-100% ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the desired compound as a colorless solid (81, 782 mg, 67%) MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 267 4
Example 27: Synthesis of 5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin- 3-ylmethyl)-phenol 87.
[0371] 5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l-tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenol 87 was synthesized in five steps from 2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 39 and benzyl bromide as shown in Scheme 26
Scheme 26
Step I Preparation of 4-Benzyloxy-2-fluo> o-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (83)
[0372] 2-Fluorυ-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-bcnzaldehyde (39, 1 62 %, 9 52 mmol, prepared as described in Scheme 12 of Example 15) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (50 ml ) and sodium hydride
Atty, Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
(60% dispersion in mineral oil, 530 mg, 13 mmol) was added. After 20 minutes, benzyl bromide (1.5 niL, 12 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture The reaction was stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen for 5.5 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 0-50 % ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound as a white solid, consistent with the desired structure by 1H-NMR (83, 2.0 g, 81 %).
Step 2 - Preparation υf(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsi!anyl-lH~ pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (84):
[0373] 3-Iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (68, 620 mg, 1.5 mmol, prepared as described in Example 22) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (15 mL) at -20 °C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. Isopropylmagnesium chloride (2.0 M in tetrahydrofuran, 840 μL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was stirred for 1.5 hours, during which the temperature rose to 5 0C. The reaction was cooled to -20 °C. 4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (83, 250 mg, 0.9606 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (5.0 mL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was stirred for 2.5 hours during which time the temperature rose to 5 °C. The reaction was poured into water. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 2-25 % ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound as a white solid (84, 501 mg, 63 %). MS (ESI) [IvH H+J+ = 535.4.
Step 3 - Preparation of3-(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (85): [0374] (4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin- 3-yl)-methanol (84, 1.49 g, 2.79 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (50 mL) and trifluoroacetic Acid (1.1 mL) was added. The reaction was stirred for 5 minutes. Triethylsilane (2.2 mL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was heated at 80 0C for 6 hours. The reaction was concentrated and the crude material was dissolved into ethyl acetate and washed with 1 N HCl, saturated sodium bicarbonate, and brine. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. The solid obtained was used in the next reaction without further purification (85, 833 mg, 83%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 363.4.
Step 4 - Preparation υf3-(4-Benzyloxy-2-flnoro-5-methoxy-benzyl)-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH- μyrro!o[2,3-h]pyridine (86):
[0375] 3-(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (85, 0.877 g, 2.42 mmol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (30 mL). Sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 140 mg, 3.6 mmol) was added at room temperature. After 20 minutes, triisopropylsilyl chloride (513 μL, 2.42 mmol) was added dropwise. The reaction was stirred for four hours. The
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic portion was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was adsorbed onto silica gel and purified by silica gel chromatography using 20-80% ethyl acetate/ hexane. The resulting material was purified a second time with 5-30% gradient ethyl acetate/ hexane to provide the desired compound (86, 831 mg, 66%), MS (ESI) [M+HT = 519.4.
Step 5 - Preparation of5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l-triisopropyhilanyl~lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- ylιnethyl)-phenol (87):
[0376] 3-(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl)-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (86, 0.831 g, 1.60 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (40 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (40 mL), 10% Palladium on carbon (3.41 g) was added. The reaction was shaken at 50 psi for 1 hour. The reaction was filtered through Celite and washed with methanol. The organic portion was passed through celite several times until a clear solution was obtained. The organic portion was concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired compound as an off-white solid (87, 587 mg, 86%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 429.5.
Example 28: Synthesis of 3-[2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(pyridin-4-yImethoxy)-benzyI]-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b) pyridine P-2040 and related compounds.
[0377] Compound P-2040 was synthesized in one step from 5-fruoro-2-methoxy-4-(l- triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenol 87 and pyridin-4-yl-methanol 88 as shown in Scheme 27.
Scheme 27
87
Step 1 - Preparation of3-[2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrro!o[2,3- b] pyridine (P-2040):
[0378] 5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l-triiisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-ylmethyl)- phenol (87, 10 mg, 0.024 mmol, prepared as described in Example 27) was combined with pyridin-4- yl-methanol (88, 3.2mg, 0.029 mmol) in a 4 mL vial and dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (200μl). Triphenylphosphine (7.7 mg) was added and the solution was shaken until homogenous. The mixture
Atty. Dkt No/ 039363-3303 was cooled to below 0 0C in a liquid nitrogen bath and dnsopropyl azodicarboxylate solution (50μl of 20mg/50μl in THF) was added The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature After 2 hours, the solvent was removed under reduced atmosphere The crude material was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (300μl) and potassium fluoride (10 mg, 0 l δmmol) was added l he mixture was heated gently and allow ed to react overnight at room temperature The vial was centnfuged and the DMSO solution was puπfied by reverse phase HPLC using a YMC-Pack ODS-A C-18 column (50mm x 10mm ID), and eluting with water with 0 1% TFA and a gradient of 15%-80% acetonitrile with 0 1% TFA over 8 minutes and a flow rate of 6 mL/minute to provide the compound (P-2040, 4 4 mg, 50%) MS (ESI) [M+HT - 364 3
[0379] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 27, replacing pyridin-4-yl -methanol 88 with an appropriate alcohol The following compounds were made following this procedure
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(2-morpholm-4-yl-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine
(P-2037),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2038),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(6-methyl-pyπdin-2-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme
(P-2039),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(pyπdin-2-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme (P-2041),
3-[2-Fluoro-4-(2-fluoro-4-tπfluoromethyl-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrτolo[2,3- b]pyridine (P-2042),
3-[4-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-1973),
3-[4-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme
(P-2043),
3-[4-(2,5-Dimethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyπdme (P-2044),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(3-morpholin-4-yl-propoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-2045), l-{2-[5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxy]-ethyl} -pyrrolidm-
2-one (P-2046),
3-[2-Fluoro-4-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2047),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(3-methyl-pyπdin-4-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (P-2048),
3-[2-Fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(6-tπfluoromethyl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridme (P-2049), 3-[4-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme (P-20S0),
7 088443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
3-[2-Fluoro-4-(4-imidazol-l-yl-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl]-l H-pyrroloL2,3-b]ρyridine
(P-2051),
3-[4-(2,4.Difluorϋ-ben7>'loxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2052),
3-{2-Fluoro-4-[l -(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-5-methoxy-benzyl}-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme
(P-2053),
3-[4-(3-Cyclopentyl-propoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2054),
3-[4-(l ,5-Dimethyl-lH-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridine (P-2055), and
3-[4-(2-Cyclopentyl-ethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (P-2056) The following table indicates the alcohol (column 2) used in Scheme 78 to provide the compounds (column 4). Column 1 provides the compound number and column 4 the observed mass.
Example 29: Synthesis of [2,6-difluoro-3-(pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3- blpyridin-3-yl)-methanone P-2058 and related compounds.
[0380] Compound P-2058 was synthesized in 1 step from (2,6-Difluoro-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-mefhanone 89 and Pyridin-3-yl-methanol 90 as shown in Scheme 28.
Scheme 28
89
P-2058
Step 1 - Preparation of[2, 6-Diβuoro-3-(pyridιn-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone (P-2058):
[0381] In a 4mL vial, (2,6-Difluoro-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-yl)- methanone (89, 10 mg, 0.037 mmol, prepared as described in Example 11) was combined with pyridin-3-yl-methanol (90, 4.9 mg 0.044 mmol). The solids were dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (200μl) and triphenylphosphine (11.5 mg, 0.044 mmol) was added. Once the solution was homogenous, the mixture was cooled to below 0 "C in liquid nitrogen bath and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate solution (50μl of 20mg/50μl THF) was added. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and the reaction was continued for 2 hours. The solvents were removed under reduced atmosphere. The resultant residue was diluted with 200μl DMSO and the mixture purified by reverse phase HPLC using a YMC-Pack ODS-A C-18 column (50mm x 1 Omm ID), and eluting with water with 0.1 % TFA and a gradient of 15%-80% acetonitrile with 0.1% TFA over 8 minutes and a flow rate of 6 mL/minute to provide P-2058 (5.9 mg, 44 %). MS (ESI) [M+H+]τ = 365.9.
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0382] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 28, replacing pyπdin-3-yl-methanol 90 with an appropriate alcohol and optionally replacing (2 6-difluoro-3- hydroxy-phenyl)-(l H-pyττolo[2,3-b]pyπdme-3-yI)-methanone 89 with (2,6-difluoro-3-h>droxy- phenyl)-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme-3-yl)-methanone (prepared as described in Example 11, 3 and 4 of Scheme 8, replacing pyridm-3-yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine 20 with 5-chloro-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme 4 (see Example 4) in Step 3) The following compounds were made following this procedure
[2,6-Difluoro-3 -( 1 -methyl- 1 H-imidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3 -yl)- methanone (P-2033),
[2,6-Difluoro-3-(6-moφholin-4-yl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3- yl)-methanone (P-2034),
{2,6-Difluoro-3-[4-(5-methyl-[l ,2,4]oxadiazoI-3-yl)-benzyloxy]-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridm-3-yl)-methanone (P-2035),
[3-(6-Diethylamino-pyπdm-3-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)- methanone (P-2036),
[3-(2-Chloro-4-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2,6-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-yl)- methanone (P-2057),
[2,6-Difluoro-3-(6-methyl-pyπdm-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2!3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2059),
[2,6-Difluoro-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2060),
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2,6-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-yl)- methanonc (P-2061),
[3-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)- methanone (P-2062),
[3-(2,5-Dimethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluoro-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone (P-2063),
[2,6-Difluoro-3-(3-morpholin-4-yl-propoxy)-phenyl]-( lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2064),
(5-Chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)-[3-(2,4-dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluoro- phenyl] -methanone (P-2162),
(5 -Chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridm-3-yl)-[2, 6-difluoro-3 -(6-lπfluoromethyl-pyπdin-3 - ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanone (P-2163),
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-[3-(2,5-dimethyl-oxazol-4-ylmethoxy)-2,6-difluoro- phcnylj-methanone (P-2164), and
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]p>τidm-3-yl)-[2,6-difluoro-3-(l-πiethyl-lH-imidazol-2-ylmethoxy)- phenylj-melhanone (P2165)
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303
The following table indicates the alcohol (column 2) used to afford the compound (column 3). P-2162, P-2163, P-2164 and P-2165 were made starting with (2,6-difluoro-3-hydroxy- phenyl)-(5-chloro-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3-yl)-methanone (not shown in table). Column 1 provides the compound number and column 4 the observed mass.
Example 30: Synthesis of 4-chIoro-7-azaindole 92
[0383] 4-chloro-7-azaindole 92 was synthesized in two steps from 7-azaindole according to the
88443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 protocol of Scheme 29.
Scheme 29
Step -1 ~ Synthesis of IH-Py rrolo[ 2,3 -b] pyridine 7-oxιde (91)
[0384] lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme
91 was synthesized by reacting
6 with an oxidizing agent (e g m-CPBA) m a non-reactive solvent (e g dimethoxyethane) as described by Schneller, S W ; Luo, Jiann-Kuan. J Org, Chem. 1980, 45 4045-4048 The compound was isolated by filtration of the resultmg solid that forms upon standing at 5 0C for typically 1 -3 h.
Step - 2 - Synthesis of 4~chloro-7-azaιndole (92)
10385] 4-chloro-7-azamdole 92 was synthesized by reacting lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 7-oxide 91 with a chlorinating agent (e g POCl3) neat as described by Schneller, S W , Luo, Jiann-Kuan J Org. Chem 1980, 45-4045-4048. The resulting solution after heating for 3-5 h at elevated temperatures (100-150 0C) was neutralized with a base (e g. NH4OH) until a solid precipitated. The solid was isolated by filtration.
Example 31: Synthesis of [3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2- (2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH- pyrro lo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanonc P-2086 and 3-[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)- 2-(2- fluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrr olo[2,3-b] pyridine P-2085
[0386] Compounds P-2086 and P-2085 were synthesized in three steps from compounds 93 and lH-pyrrolo[2,3-έ>]pyπdine 6 as shown in Scheme 30
88443
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Scheme 30
Step 1 - Preparation of3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-henzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-cthoxy)-benzaldehyde (94): [0387] To a solution of 3-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (93, yyyyl40 mg, 0.5 mmol, prepared by protocol of Example 21, Steps 1 and 2 of Scheme 20, using 4-chloro-2- fluoro-benzyl bromide in place of 4-chloro-benzyl bromide in Step 1 ) in tetrahydrofuran (8 mL) was added dropwise a mixture of 2-fluoro-ethanol (64 mg, 1.0 mmol), triphenylphosphine (180 mg, 0.7 mmol), and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (120 mg, 0.6 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (5 ml) at 0 0C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 0C for 10 minutes and then at 40 0C for 3 days. The reaction mixture was dissolved in water and ethyl acetate. The organic layers were collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexanes to provide the compound as a white solid (94, 88 mg, 54%). MS (ESI) [M+H'T -327.12.
Step 2 - Preparation of[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2- (2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrro lo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (95) and 3-{[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy) -2-(2-fluυrυ-ethoxy)- phenyl] -methox y-methyl} -IH-pyrrolo [2 ,3-b] pyridine (96):
[0388] A solution of 3-(4-chloro-2-fhjoro-benzyloxy)-2-( 2-fluoro-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde (94, 88 mg, 0.27 mmol), lH-pyrrolo[2,3-ό]pyridine (6, 38 mg, 0.32 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (45 mg, 0.81 mol) in methanol (5 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound 95 as a white solid (67 mg, 56%), MS(ESl) [M+H+f = 445.13 and compound 96 as a white solid (36 mg, 29%). MS(ESI) [M+HT = 459.15.
Step 3a - Preparation υf[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2- (2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrro Io [2, 3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2086) :
[0389] To a solution of [3-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2- (2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH- pyrrolo[2,3-£>]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (95, 60 mg, 0.1 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (69 mg, 0.16 mmol) at 0 0C. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The reaction was quenched with a saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexanes to provide the compound as a white solid (P-2086, 15 mg, 20%). MS(ESI) [M+H1 ] 1 = 441.06.
Step 3b - Preparation of 3-[ 3-(4-Chloro-2-βιιoro-benzyloxy)- 2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrr olo[2, 3-b] pyridine (P-2085):
[0390] A mixture of 3-{[3-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy) -2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-methoxy- methyl} -lH-pyrrolo[2,3-έ>]pyridine (96, 36 mg, 0.078 mmol) , triethylsilane (0.5 mL, 3 mmol), and trifluoroacetic acid (0.2 mL, 2 mmol) in acetonitrile (20 mL) was stirred at 80 0C for 2 hours. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The solution was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexanes to provide the compound as a yellow solid (P-2085, 24 mg, 71 %). MS(ESI) [M+HT = 429.15.
[0391] 3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2-difluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2! 3-i]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2075)
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 30, substituting 2-fluoro-ethanol with 2,2-difluoro- ethanol and substituting 3-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 93 with 3-(4- chloro-benzyloxy)-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (63 of Example 21) in Step 1 to provide P-2075. MS(ESI) [M+HT = 443.1.
[0392] [3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-ben2yloxy)-2-(2,2-difluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2119), [3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-cyclopropylmcthoxy-
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 phenyl]-(l II-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2120), and [3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)~ 2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2139)
were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 30, substituting 2-fluoro-ethanol with 2,2-difluoro- ethanol in Step 1 to provide P-2119 (MS(ESI) [M+HT = 461.15), or substituting 2-fluoro-ethanol with cyclopropyl-methanol in Step 1 to provide P-2120 (MS(ESI) [M+H+]' = 451.18), or substituting 2-fluoro-ethanol with 2,2,2-trifluoro-ethanol in Step 1 to provide P2139 (MS(ESI) [M+lT]' = 479.11).
Example 32: Synthesis of [3-(2-chloro-4-methanesulfonyl-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone P-2094
[0393] Compound P-2094 was synthesized in four steps from compounds 68 and 97 as shown in Scheme 31.
Scheme 31
Step 1 Preparation of(3-Benzyhxy-2-ethoxy-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrroIo[2,3- b] pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (98):
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[0394] To a solution of 3-iodo-l -tnιsopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-&]pyπdme (68, 1 306 g, 3.26 mmol, prepared as described in Example 22) in tetrahydrofuran (42 rtiL) at -20 0C under nitrogen was added isopropylmagnesium chloride (1 70 mL, 2 0 M solution in tetrahydrofuran, 3 40 mmol) The reaction mixture was stirred at -20 0C for 1.5 hours. It was allowed to warm to 5 0C and then kept at 5 0C for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was then cooled down to -20 0C. To this solution was slowly added a solution of 2-ethoxy-3-benzyloxybenzaldehyde (97, 0.698 g, 2.72 mmol, prepared by protocol of Example 21 , Steps 1-3 of Scheme 20, using benzyl bromide in place of 4-chloro-benzyl bromide in Step 1) in tetrahydrofuran (42 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at -20 0C for 2 5 hrs, and was allowed to warm to 5 0C for 2 5 hours. The reaction mixture was poured into iced water, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with saturated ammonium chloride and brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as light-yellow oil (98, 200 mg, 13 9%).
Step 2 - Preparation of(2-ethoxy-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(l-trusopropyhilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridιn- 3-yl)-methanone (99)
[0395| To a solution of (3-benzyloxy-2-ethoxy-phenyl)-(l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyπdm-3-yl)-methanol (98,195 mg, 0.37 mmol) in a mixture of methanol (20 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) was added palladium on carbon (50 mg, 10% wt., 0.2 mmol). The mixture was stirred under hydrogenation for seventeen hours After removal of solvent, the residue was washed with a mixture of ethyl ether and hexanes to provide the compound as a white solid (99, 63 mg, 95%). MS(ESI) [M+LT]+ = 439.37.
Step 3 — Preparation of [3-(2-Chloro-4-mcthanesιdfonyl-henzyloxy)~2-ethoxy-phenyl] ~(1 - triisopropyhιlanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridιn-3-yl)-methanone (100):
[0396] To a solution of (2-ethoxy-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(l -triisopropyhilanyl-1 H-pyπolo[2,3- fc]pyπdm-3-yl)-mcthanonc (99, 40 mg, 0.064 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (15 mL) was added sodium hydride (3.32 mg, 0.083 mmol) at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 40 minutes, thenl -bromomethyl-2-chloro-4-methanesulfonyl- benzene (21 72 mg, 0.077 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture It was stirred at room temperature overnight. The mixture was then poured into water and was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected and washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of the solvent, a crude compound as light yellow oil was obtained (100, 84 mg)
Step 4 - Preparation of[3-(2-Chloro-4-methanesulfυnyl-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH- pyrrolo[2, 3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2094)
[0397| To a solution of (2-ethoxy-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(l -tπisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (100, 84 mg, 0.054 mmol) in methanol (10 mL) was added potassium hydroxide (6 N solution) until pH of the solution turned to over 10 Potassiun fluoride (30 mg, 0 5
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 mmol) was then added to the reaction mixture and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 6 hours. The reaction mixture was then poured into saturated sodium carbonate and was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected and washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of the solvent, the residue was purified by preparative HPLC to provide as a white solid (P-2094, 5 mg, 19%). MS(ESI) [M+HY = 485.17.
Example 33: Synthesis of 4-(3-diethylamino-propoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 102
[0398] 4-(3-Diethylamino-propoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 102 was synthesized in one step from 2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-rnethoxy-benzaldehyde 39 as shown in Scheme 32.
Scheme 32
Step 1 Synthesis of4-(3-diethylamino-propoxyJ-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (102): [0399] To 2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (39, 1.20 g, 7.05 mmol, prepared as described in Scheme 12 of Example 15) in tetrahydrofuran (60.0 mL) were added triphenylphosphine (1.93 g, 7.35 mmol) and 3-(diethylamino)-propan-l-ol, (0.96 g, 7.30 mmol). The reaction was cooled to 0 0C, followed by slow addition of diethyl azodicarboxylate (1.28 g, 7.35 mmol). The reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 10% methanol in dichloromethane to give a colorless oil (102, 0.90 g, 45.0%).
Example 34: Synthesis of 4-(lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-5-chloro-2-fluoro-benzaldehyde 106
|0400] 4-(lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-5-chloro-2-fluoro-benzaldehyde 106 was synthesized in three steps from 2-chloro-5-fluoro-phenol 103 as shown in Scheme 33.
Scheme 33
Step 1 — Preparation of4-bromo-2-chloro-5-fluorυ-phenυl (104):
[0401] To 2-chloro-5-fluoro-phenol (103, 6.20 g, 0.0423 mol) in chloroform (110.0 mL) bromine (2.18 mL, 0.0423 mol) was added slowly. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The reaction was poured into a solution of sodium thiosulfate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the desired compound as a colorless oil (104, 4.5O g, 47.2%).
Step 2 - Preparation of5-chloro-2-fluoro-4-hydrυxy-benzaldehyde (105): [0402] To 4-bromo-2-chloro-5-fluoro-phenol (104, 2.25 g, 9.98 mmol) in tetrahydronfuran (50 mL), cooled to -78 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen, was added n-butyllithium (2.50 M in hexane, 4.21 mL) and l ,2-bis-(chloro-dimethyl-silanyl)-ethane (1.08 g, 5.01 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The reaction was cooled to -78 0C, followed by adding tert- butyllithium (1.70 M in hexane, 12.4 mL). After 30 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamide (0.97 mL, 0.0125 mol) was added to the reaction. After 30 minutes, the reaction was warmed to room temperature for 10 minutes. 5N HCl (20 mL) was added to the reaction. After 30 minutes, the reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the desired compound (105, 0.50 g, 28.7). 1H NMR consistent with structure.
Step 3 Preparation of4-(lH-benzoimidazυl-2-ylmethoxy)-5-chloro-2-fluoro-benzaldehyde (107): [0403] To 5-chloro-2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (105, 0.500 g, 2.86 mmol) in N,N- dimethylformamide (30.0 mL, 0.387 mol) was added sodium hydride (130.0 mg, 3.25 mmol, 60% in mineral oil). After 20 minutes, 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzo imidazole (106, 436.0 mg, 2.62 mmol) was added to the reaction. The reaction was stirred at 30 °C for 15 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (107, 0.35 g, 43.9%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]~ = 305.1.
Example 35: Synthesis of 5-(l-methyl-lII-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyridiπe 109.
[0404] 5-(l-Methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 109 was synthesized in 1 step from 5-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 1 as shown in Scheme 34.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Scheme 34
Step 1 - Preparation of5-(l~Methyl-lH~pyra∑ol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (109): [0405] To 5-bromo-7-azaindole (1, 1.04 g, 5,28 mmol) in 1.00 M potassium carbonate in water (15.8 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (50.0 mL) were added 1 -methyl -4-(4,4,5, 5 -tetramethyl- [l,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)-lH-pyrazole (108, 1.65 g, 7.92 mmol), Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)- palladium(O) (0.305 mg, 0.26 mmol) and tetra-n-butylammonium iodide (0.20 g, 0.53 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 70 0C overnight. The reaction mixture was poured into water and the organic layer was washed with brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated. The residue was purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 25% ethyl acetate in hexane to provide a light yellow solid (109, 670 mg, 64.0%). MS(ESI)[M+H+]+ = 199.4.
Example 36: Synthesis of [2,6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l-methyl-lH- pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yll-methanone P-2151.
[0406] [2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl]-mcthanone P-2151 was synthesized in five steps as shown in Scheme 35.
Step 1 - Preparation oftert-butyl-(2,4-dichloro-phenoxy)-dimethyl-silane (113):
[0407] To 2,4-dichloro-phenol, (112, 4.80 g, 0.0294 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (100.0 mL) were added lH-imidazole (5.21 g, 0.0766 mol) and tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (5.33 g, 0.0353
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 mol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 15% to 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (113, 7, 1 O g, 87.0%).
Step 2 - Preparation of2,6-dichloro-3-hydroxy-benza!dehyde (114): [0408] To tert-butyl-(2,4-dichloro-phenoxy)-dimethyl-silane (113, 4.00 g, 0.0144 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (50.0 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0C, n-butyllithium (2.50 M in hexane, 6.06 mL) was added slowly. After 30 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamide (1.34 mL, 0.0173 mol) was added to the reaction. After 1 hour, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. IN HCl (40 mL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a yellow solid (114, 2.0 g, 72.6%).
Step 3 — Preparation of2, 6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)~benzaldehyde (115): [0409] To 2,6-dichloro-3-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (114, 2.06 g, 0.0108 mol) in N-methylpyrrolidinone (25.0 mL) were added cesium carbonate (7.02 g, 0.0215 mol) and trifluoro- methanesulfonic acid 2,2,2 -trifluoro-ethyl ester (2.50 g, 0.0108 mol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 90 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 15% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (115, 1.00 g, 34.0%).
Step 4 - Preparation of [2,6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl] -[5-(l-methyl-l H-pyrazol-4- yl)- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-bJ pyridin-3-yl] -methanol (116):
[0410] To 5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (109, 100.0 mg, 0.51 mmol, prepared as described in Example 35) in methanol (30 mL) were added 2,6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2- trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde (115, 154 mg, 0.56 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (596.0 mg, 10.62 mmol) under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 2% to 25% methanol in dichloromethane to give the desired compound (116, 0.1 8 g, 75.7%).
Step 5 - Preparation of [2, 6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l -methyl- 1 H-pyrazol-4- yl)-lH-pyrrolo [2, 3-b] pyridin-3-yl] -methanone (P-2151):
[0411] To [2,6-dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyra/ol-4-yl)-lH-
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methanol (116, 100,0 mg, 0.21 mmol) in dichloromethane (10.0 mL), Dess-Martin periodinane (108 mg, 0.26 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was poured into aqueous potassium carbonate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography cluting with 20% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-2151, 19.4 mg, 19.5%). MS (ESI) [M+H'f = 469.1.
[0412] 2,6-Difluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 117
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 35, steps 1 and 2, substituting 2,4-dichloro-phenol with 3,5-difluoro-phenol in step 1.
Example 37: Synthesis of 2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-|2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzaldehyde 121.
[0413] 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzaldehyde 121 was synthesized in 4 steps as shown in Scheme 36.
Scheme 36
Step 1- Preparation of 2-chlυro-4,5-diflιιoro-benzoic acid methyl ester (119): [0414] To 2-chloro-4,5-difluoro-bcnzoic acid (118, 14.0 g, 0.0727 mol) in methanol (100 mL) was added sulfuric acid (concentrated, 98%, 2.00 mL, 0.0375 mol). The reaction was stirred at 60 0C for 48 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (119, 13.0 g, 86,6%).
Step 2 - Preparation of(2-chloro-4,5-diβuυro-phenyl)-rnethanol (120): [0415] To 2-chloro-4,5-difluoro-benzoic acid methyl ester (119, 5.70 g, 0,0276 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (120,0 mL), 1.00 M of lithium tetrahydroaluminate in tetrahydrofuran (30.0 mL) was added slowly under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours, followed by adding sodium sulfate decahydrate. After 30 minutes, the reaction mixture was
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 filtered, concentrated and purified with silica gel column chromatography eluting with 8% methanol in dichloromethane to give a white solid (120, 4.20 g, 85.2%),
Step 3 - Preparation of2-chloro-4,5-difluoro-benzaldehyde (UO):
[0416] To (2-chloro-4,5-difluoro-phenyl)-methanol (120, 2.40 g, 0.0134 mol) in dichloromethane (40.0 πiL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (6.84 g, 0.0161 mol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was poured into aqueous potassium carbonate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (110, 1.7 g, 71 ,6%).
Step 4 - Preparation of 2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy] -benzaldehyde (121): [0417] To 2-chloro-4,5-difluoro-benzaldehyde (110, 0.40 g, 0.0023 mol) in N,N- dimethylformamide (10.0 mL), 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)-ethanol (0.327 g, 2.72 mmol) and cesium carbonate (0.886 g, 2.72 mmol) were added. The reaction was stirred at 90 °C overnight. The reaction was poured into water, acidified to pH around 5, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (121, 0.15 g, 24.0%).
Example 38: Synthesis of 2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 111.
[0418] 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde 111 was synthesized in one step from 2-chloro- 4,5-difluoro-benzaldehyde 110 as shown in Scheme 37.
Scheme 37
Step 1 - Preparation of2-chhro-5-fluoro-4-hydroxy-henzaldehyde (111):
[0419] To 2-chloro-4,5-diiluoro-benzaldehyde (110, 0.40 g, 2.30 mmol, prepared as described in Example 37) in N,N-dimethylformamide (10.0 mL) were added 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)-ethanol, (0.327 g, 2.72 mmol) and cesium carbonate (0.886 g, 2.72 mmol). The reaction was stirred at 90 0C overnight. The reaction was poured into water, acidified to pH around 5, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 hexane to give a white solid (111, 0.24 g, 61.0%). MS (ESI) [M-IFp = 173.1.
Example 39: Synthesis of 2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde 123.
10420] 2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde 123 was synthesized in 2 steps from 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 52 as shown in Scheme 38.
Step 1 — Preparation of 2-chloro-4-fluoro- 1 -(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzene (122); 10421] To 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol (52, 2.40 niL, 0.0213 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (30.0 mL), 1 -bromo-2-methoxy-ethane (2.00 mL, 0.0213 mol) and potassium carbonate (3.00 g, 0.0217 mol) were added under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at 80 0C for 2 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (122, 1.50 g, 34.4%).
Step 2 - Preparation of2-chhro-6-fluaro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde (123): [0422] To 2-chloro-4-fluoro-l-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzene (122, 1.50 g, 7.33 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (44,0 mL), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at -78 0C, n-butyllithium (2.50 M in hexane, 3.08 mL) was added slowly. After 15 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamidc (0.681 mL, 8.80 mmol) was added to the reaction. After 30 minutes, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 30% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a light yellow solid (123, 1.2O g, 70.4%).
Example 40: Synthesis of 2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde 125.
[0423] 2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde 125 was synthesized in 2 steps from 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 52 as shown in Scheme 39.
Scheme 39
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 1 - Preparation of2-chϊoro~4-fluoro-l-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-henzene (124): [0424] To 2-chloro-4-fluorophenol (52, 1.58 g, 0.0108 mol) in N-methylpyrrolidinone (25.0 mL), cesium carbonate (7.02 g, 0.0215 mol) and trilluoro-methanesulfonic acid 2,2,2-trifluoro-ethyl ester (2.50 g, 0.0108 mol) were added under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 90 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 15% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (124, 2.10 g, 85.3%).
Step 2 — Preparation of2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-triflnυro-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde (125): [0425] To 2-chloro-4-fluoro-l -(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzene (124, 2.1O g, 9.19 mmol), under an atmosphere of nitrogen at at -78 0C, n-butyllithium (2.50 M in hexane, 3.86 mL) was added slowly. After 60 minutes, N,N-dimethylformamide (0.782 mL, 0.0101 mol) was added to the reaction. After 30 minutes, the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the desired compound (125, 450 mg, 19
Example 41: Synthesis of 5-chIoro-3-2-chIoro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-benzyI- lH-pyrroIo[2,3-b]pyridine P-2155.
[0426] 5-Chloro-3-2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-ben7yl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine P-2155 was synthesized in 2 steps from 5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 4 as shown in Scheme 40.
LScheme 40
Step 1 - Preparation of2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-phenyl-(5-chloro-lH- pyrrolo[2, 3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (126):
[0427] To 5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (4, 74.1 mg, 0.49 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4) in methanol (30.0 mL), 2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]- benzaldehyde (121, 150.0 mg, 0.54 mmol, prepared as described in Example 37) and potassium hydroxide (574.0 mg, 10.23 mmol) were added under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the desired compound (126, 0.11 g, 52.7%).
Step 2 — Preparation of 5-chloro-3-2-chloro-5~fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy] -benzyl- III- pyrrolo[2, 3-b] pyridine (P-2155):
[0428] To 2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-cthoxy]-phenyl-(5-chloro-lH-p>τrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (126, 65.0 mg, 0.15 mmol) in acetonitrile (10.0 mL), triethylsilane (1 ,00 mL, 6.26 mmol) and trifluoroacetic acid (0.50 mL, 6.50 mmol) were added. The reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours. The reaction was poured into aqueous potassium carbonate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and washed with ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-2155, 21.3 mg, 34.0%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 413.2.
[0429] Additional compounds were prepared using the protocol of Scheme 40, substituting 2- chloro-5-fluoro-4-[2-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-cthoxy]-benzaldehyde 121 with a suitable aldehyde (prepared as described in Examples 15, 36, 39, or 40), and optionally replacing 5-chloro-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 4 with an appropriate substituted 7-azaindole (5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8, 5-(l -methyl- lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-7-azaindole per Example 35) in Step 1. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
5-Chloro-3-[2-chloro-5-fluoro-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-
2156),
2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-fluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2099),
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2100),
2-[2,5-Difluoro-4-(5-melhoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2101),
2-[3,5-Difluoro-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole
(P-2102),
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-3,5-difluoro-phcnoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2105),
2-[4-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2107),
2-{2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(1 -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethy 1 } - 1 H-benzo imidazole (P-2108),
2-{5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl } -1 H-benzoimidazole (P-2109),
5-Chloro-3-[2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]- lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine
(P-2157),
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]- l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2158),
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-bcnzyl]-5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2146),
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-5-methoxy-lH-pyττolo[2,3-b]pyridinc
(P-2147),
2-[5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2114),
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (P-2148))
3-[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridine (P-2152), and
3-[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndine
(P-2153).
The following table indicates the aldehyde (column 2) and the azaindole (column 3) used to afford the target compound (column 4). Column 1 indicates the compound number and column 5 the observed mass.
Example 42: Synthesis of I2-chIoro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyI]-(5-chloro-lH- pyrrolol2,3-b]pyridin-3-yI)-methanone P-2159.
10430] [2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone P-2159 was synthesized in 2 steps from 5-Chloro-lH-pyriOlo[2,3-b]pyridine 4 as shown in Scheme 41.
Scheme 41
Step 1 --■ Preparation of[2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-ntethoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chlυro-lII-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (127):
[0431] To 5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyridine (4, 270.0 mg, 1.77 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4) in methanol (15.0 mL), 2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde (123. 474.0 mg, 2.04 mmol, prepared as described in Example 39) and potassium hydroxide (1.20 g, 0.0214 mol) were added under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 40% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a colorless oil (127, 0,26 g, 38.1 %). MS (ESI) [M-H+]' = 383.1.
Step 2 ■- Preparation of[2-chloro-6-fluow-3-(2-nιethoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pvrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone (P-2159):
[0432] To [2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanol (127, 210.0 mg, 0.5.45 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (20.0 mL) was added Dess-Martin periodinane (277 mg, 0,65 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The reaction was poured into aqueous potassium carbonate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate. The filtrate was concentrated and purified silica gel column chromatography eluting with 50% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-2159, 88.1 mg, 42.2%). MS (ESI) [M-H+]' = 381.1.
[0433] Additional compounds were prepared using the protocol of Scheme 41 , optionally substituting 2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzaldehyde 123 with a suitable aldehyde (prepared as described in Examples 36, 39 or 40), and/or optionally replacing 5-chloro-lH- pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridine 4 with an appropriate substituted 7-azaindole (5-methoxy-7-azaindole per Example 8, 5-(l -methyl-lII-pyrazol-4-yl)-7-azaindole per Example 35) in Step 1. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2160),
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl]-methanone (P-2145),
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- yl)-methanone (P-2149),
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2150),
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2)2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl]-methanone (P-2151), and
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2!2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2154).
The following table indicates the aldehyde (column 2) and the azaindole (column 3) used to afford the target compound (column 4). Column 1 indicates the compound number and column 5 the observed mass.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Example 43: Synthesis of 2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-ylmcthyl]-phenol P-2161.
[0434] 2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]-phenol P-2161 was synthesized in 1 step from 2-[4-(5-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5- difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-l ll-benzoimidazole P-2107 as shown in Scheme 42.
Scheme 42
Step 1 ~ Preparation of2,5-difluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-h]ρyridin-3- ylmethyl] -phenol (P-2161):
|0435] To 2-[4-(5-bromo-lH-pyτrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole (P-2107, 25.0 mg, 0.053 mmol, prepared as described in Example 41) in acetonitrile (4.00 mL) and IM potassium carbonate in water (2.00 mL), l -methyl-4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl- [l ,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)-l H-pyrazolc (13.3 mg, 0.064 mmol) and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)- palladium(O) (10.0 mg, 8.65E-3 mmol) were added. The reaction was heated to 160 0C for 20 minutes in a CHM Discover microwave instrument. The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give a white solid (P-2161, 5.4 mg, 29.8%). MS (ESI) [M+HT = 341.2.
Example 44: Synthesis of (5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b|pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cycIopropyImethoxy-3- (2,4,6-trifluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyll-methanone P-2141.
[0436] (5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4,6-trifluoro- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-methanone P-2141 was synthesized in 7 steps as shown in Scheme 43.
Step 1 - Preparation of2,3-bis-henzylυxy-benzaldehyde (128):
[0437] To a solution of 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (61, 25 g, 0.18 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (150 mL) tctrahydrofuran (250 mL), sodium hydride (7.24 g, 0.18 mol) was added at 0 °C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. To the reaction mixture was then added benzyl bromide (54 mL, 0.45 mol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen for 3 hours, then cooled down to 0 0C. Sodium hydride (8 g, 0.2 mol) was added to the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was poured into ice water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl
Atty. Dkt, No,: 039363-3303 acetate in hexane to provide the compound as an off-white solid (128, 46.2 gm, 80%).
Step 2 — Preparation of 3-benzyloxy-2-hydroxy-benza!de.hyde (129):
[0438] To magnesium (2.9 g, turnings, 0.12 mol) in a mixture of anhydrous ether (85 mL) and benzene (85 mL) at 0 0C, bromine (3.4 mL, 0.066mol) was added dropwise. When the reaction had started, stirring was commenced and the addition of bromine continued until complete. The ice bath was removed and the reaction mixture was heated until the solution was almost colorless. After cooling down, the reaction mixture was slowly added to a solution of 2,3-bis-benzyloxy-benzaldehyde (128, 20 g, 0.063mol) in benzene (415 mL) at room temperature while stirring vigorously. Upon completion of the addition, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight, and then re fluxed for 36 hours. After the reaction mixture was cooled down to room temperature, a solid was collected by filtration and washed with benzene, then boiled in hydrochloric acid (100 mL, 1.0 M) for 30 minutes. After cool down, the solution was extracted with dichloro methane. The organic layer was washed with brine and dried over magnesium sulfate. A light tan solid was obtained after removal of the solvent (129, 12.5 g, 87%).
Step 3 Preparation of3~benzyloxy~2~cydopropylmethoxy~benzaldehyde (130): [0439] To a mixture of 3-benzyloxy-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (129, 1.0 g, 4.38 mmol) and cesium carbonate (2.14 g, 6.57 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (50 mL), cyclopropylmethyl bromide (1.77 g, 13.1 mmol) was added at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at 40 0C for 3 days. The reaction mixture was poured into a solution of saturated ammonium chloride and was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, a viscous liquid was obtained (130, 1.21 g, 98%).
Step 4 - Preparation of[3-benzyloxy-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (131):
[0440] A mixture of 5-chloro-lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-6]pyridine (4, 0.68 g, 4.46 mmol, prepared as described in Example 4), 3-benzyloxy-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-benzaldehyde (130, 1.2 g, 4.25 mmol), and potassium hydroxide (0.68 g, 1 1 mmol) in methanol (50 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 4 days. The reaction mixture was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide compound as a white solid (131, 0.99g, 54%). MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 435.21.
Step 5 - Preparation of[3-benzyloxy-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrroIo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanυne (132):
[0441] To a solution of [3-benzyloxy-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phcnyl]-(5-chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (131, 0.99g, 2.28 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (120 mL), Dess-Martin
Atty. Dkt. Ko.: 039363-3303 periodinane (2.4 g, 5.69 mmol) was added at O 0C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 0C for 50 minutes. The reaction was quenched with a saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was dried over vacuum to provide the compound as a yellow solid (132, 0.92 g, 93%).
Step 6- Preparation of(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-(2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-hydroxy- phenylj-methanone (133):
[0442] A mixture of [3-benzyloxy-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-metbanone (132, 0.92 g, 2.13 mmol) and palladium on carbon (100 mg, 10%, 0.5 mmol) in methanol (60 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (60 mL) was stirred under an atmosphere of hydrogen overnight. After filtering off of catalyst and removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as a white solid (133, 236 mg, 32%).
Step 7- Preparation of(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4, 6- trifluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-methanone (P-2141):
[0443] To a solution of (5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-(2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3- hydroxy-phenyl)-methanone (133, 50 mg, 0.15 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (3.0 mL), a mixture of (2,4,6-trifluoro-phenyl)-methanol (47.3 mg, 0.29 mmol), triphenylphosphine (53.6 mg, 0.20 mmol), and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (35.4 mg, 0.18 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (2.0 mL) was added at 0 0C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 65 °C overnight. The reaction mixture wras poured into ice water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was collected, washed with brine, and dried over magnesium sulfate. After removal of solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane to provide the compound as a white solid (P-2141, 19.3 mg, 27%). MS(ESI) [M+H"]+ = 487.22.
[0444] [(5-Chloro-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(6-trifluoromethyl- pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanone (P-2142) and (5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2- cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4-dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanone (P-2140)
were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 43, substituting (2,4,6-trifluoro-phenyl)-methanol with (6-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3-yl)-rnethanol in Step 7 to provide P-2142 (MS(ESI) [M+H1] ' = 502.23), or substituting (2,4,6-trifluoro-phenyl)-methanol with (2,4-dimethyl-thiazol-5-yl)-methanol in Step 7 to provide P-2140. (MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 468.19).
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Example 45: Synthesis of [2-ethoxy-3-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-blpyridin-3- yl)-methanoπe P-2127 and related compounds.
[0445] t2-Ethoxy-3-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methaπone P-2127 was synthesized in one step from (2-ethoxy-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2.3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone 99 as shown in Scheme 44.
Scheme 44
Step 1 — Preparation [2-ethoxy-3-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2127):
[0446] In a 4 mL vial, (2-ethoxy-3-hydroxy-phenyl)-(l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin- 3-yl)-methanone (99, 10 mg, 0.022 mmol, isolated after step 2 of Scheme 31 , Example 32) was combined with (2-fluoro-phenyl)-methanol (134, 3.5 mg 0.027 mmol). The solids were dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (200μl) and triphenylphosphine (7.0 mg, 0.022 mmol) was added. Once the solution was homogeneous, the mixture was cooled to below 0 0C in a liquid nitrogen bath and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate solution (20mg in 100μl tetrahydrofuran) was added. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and the reaction was continued for 2 hours. The solvents were removed under reduced atmosphere. The resultant residue was diluted with 200μl dimethyl sulfoxide and potassium fluoride (10 mg) was added. The solution was allowed to react overnight to remove the TiPS group. The supernatant was purified by reverse phase HPLC using a Phenomcnex C-18 column (50mm x 10mm ID), and eluting with water with 0.1 % trifluoroacetic acid and a gradient of 20%-100% acetonitrile with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid over 16 minutes and a flow rate of 6 mL/minute to provide P-2127 (1.2 mg, 14 %). MS(ESI) [M+H*]+ = 391.1.
[0447] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 44, replacing (2- fluoro-phcnyl)-methanol 134 with an appropriate alcohol. The following compounds were made following this procedure:
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2-pyrrolidin-l -yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2121),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2122),
Atty. Dkt No.: 039363-3303
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-mcthanone
(P-2123),
[3-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2124),
[3 -(2,5-Dimethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl] -( 1 I I-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyndin-3 -yl)- methanone (P-2125),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(3-morpholin-4-yl-propoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2126),
[2 -Ethoxy-3 ~(6-morpholin-4-yl ~pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyπdm-3 -yl)- methanone (P-2128),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-tnfluoromethyl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrTolo[2.3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2129),
[3-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2130),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(4-imidazol-l -yl-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2131),
[3-(2,4-Difluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2132),
{2-Ethoxy-3-[l -(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-mcthanone
(P-2133),
[3-(l ,5-Dimethyl-lH-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2134),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(l-pyridin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]p>τidin-3-yl)-mcthanone
(P-2135),
[2-Ethoxy-3-((R)-l -p>τidin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolor2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2136),
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2,4,6-trifluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone
(P-2137),
{3-[l-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-2-ethoxy-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2>3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanonc (P-2138),
[3-(6-Diethylamino-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2143), and
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-pyrrolidm-l-yl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone (P-2144),
The following table indicates the alcohol used in Column 2 to provide the compounds shown by structure in Column 3 Column 1 provides the compound number and Column 4 the mass spectrometry result.
Atty Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Example 46: Synthesis of 2-I5-chIoro-4-(5-chIoro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2- methoxy-phenoxyπiethyI]-lH-benzoimidazolc P-2104.
[0448] 2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyI]- lH-benzoimidazole P-2104 was synthesized in four steps from 2-chloro-4,5-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde 135 as shown in Scheme 45.
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Step I - Preparation of2-chloro 4 hydroxy -5 methoxy benzaldehyde (136)
[0449] 2-Chloro-4,5-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde (135, 2 OO g, O 00997 mol), dichloromethane (73 44 mL) and aluminum trichloride (2 50 g, 0 0187 mol) were combined under an atmosphere of nitrogen The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight The reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and washed with 5% ethyl acetate in hexane to provide an off-white solid (136, 757 mg, 41%) MS (ESI) [M-H+] = 185 0, 187 0
Step 2 - Preparation of 4-(lH-benzounιda∑ol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-chloro-5-methoxy benzaldehyde (137) [0450] 2-Chloro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (136, 2 30 g, 0 0123 mol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (89 5 mL, 1 16 mol) and sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 541 mg, 0 0135 mol) was added After 20 minutes, 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole (106, 2 05 g, 0 0123 mol) was added to the reaction The reaction was stirred at 80 °C overnight The reaction was concentrated in vacuo to an oil Ethyl acetate was added and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and puπfied b> silica gel column chromatography e luting with 30-70% ethyl acetate in hexane over 30 minutes to provide a white solid (137, 1 79 g, 46%) MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 317 1, 319 1
Step 3 - Preparation of [4-(lH-benzounidazol-2-ylmethoyy)-2-thloro-5-methoxy-phenvl]-(5-chloro- IH-pyrrυlυ[2, 3-b]pvndιn-3-yl)-methano! (138)
[0451] 5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme (4, 783 9 mg, 0 005138 mol, prepared as described in Example 4) and 4-(lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-chloro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (137, 1 79 g, 0 00565 mol) were combined in methanol (100 mL, 2 mol) and potassium hydroxide (2 88 g, 0 0514 mol) was added The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight The reaction was adsorbed onto silica and puπfied by silica gel column chromatography, elutmg with 1-15% methanol
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 dichloromethane to provide the desired compound as a yellow oil, which was redissolved in 200 mL of 25% ethyl acetate: hexanes and concentrated to provide a yellow solid (138, 1 .2 g, 50%). MS(EST) [M+HT = 469.1. 471.1.
Step 4 - Preparation of2-[5-chhro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiri-3-ylrnethyl)-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-ben∑oimidazole (P-2104):
[0452] [4-(l H-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (138, 1.25 g, 0.00266 mol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (100 mL, 2 mol) and trifluoroacetic acid (5.65 mL, 0.0734 mol) and triethylsilane (11.3 mL, 0.0708 mol) were added. The reaction was heated at 70 °C for 2.5 hours The reaction was concentrated and ethyl acetate and 1 M aqueous potassium carbonate were added. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was adsorbed onto silica and purified with silica gel column chromatography, eluting with 0-8% methanol: dichloromethane to provide the desired compound as a solid, which was washed with a minimum of ethyl acetate and hexanes and filtered. The collected solid was dried to provide P-2104 (232 mg, 19%). MS(ESI) [M+H+] " = 453.1, 455.1.
[0453] 2-[5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole P-2103
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 45, replacing 5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 4 with lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine in Step 3. MS(ESI) [M+H+f = 419.2, 421.2.
Example 47: Synthesis of 3-[2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-beπzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine P-2166
[0454] 3-[2-Chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine P-2166 was synthesized in three steps from 2-chloro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 136 as shown in Scheme 46.
Scheme 46
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 1 - Preparation of2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (140): [0455] 2-Chloro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (136, 0.548 g, 2.94 mmol, prepared as described in Example 46, Scheme 45, step 1) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (40 mL) and sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 0.200 g, 5.00 mmol) was added. After 20 minutes, 1- bromomethyl-4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzene (139, 685 μL, 5.00 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture. The reaction was stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen for 5.5 hours. The reaction was concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The reaction was resuspended in water/saturated sodium bicarbonate and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography, eluting with 5-35 % ethyl acetate in hexane give a white solid (140, 0.942 g, 97 %), consistent with the desired compound by 1H-NMR.
Step 2 - Preparation of [2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(l- triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (141):
[0456] 3-iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (68, 582.0 mg, 1.45 mmol, prepared as described in Example 22) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (10.0 mL) at -20 0C under an atmosphere of nitrogen, lsopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydrofuran (2.0 M, 0.79 mL) was added to the reaction. The reaction was stirred for 1 hour, during which the temperature rose to 0 0C. The reaction was cooled to -20 0C and 2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy- benzaldehyde (140, 200 mg, 0.61 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (7.0 mL) was added. The reaction was stirred for 1.5 hours during which time the temperature rose to 0 0C. The reaction was quenched with methanol and adsorbed onto silica, then purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with 0-20% ethyl acetate: hexanes, to provide the desired compound (141, 318 mg, 87%). MS (ESI): [M+H+] + = 603.3, 605.3.
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 3 - Preparation of3-4-[l-(4-chIoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]~3-methoxy-benzyl-lH-pyrroϊo[2,3- h] pyridine (P-2166):
[0457] [2-Chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (141. 0.160 g, 0.27 mmol) was dissolvewd in acetonitrile (10.0 mL). Trifluoroacetic acid (0.150 mL) and triethylsilane (0.250 mL) were added and the reaction was heated at 80 0C for 1.5 hours. The reaction was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with 20-65% ethyl acetaterhexanes, to provide the desired compound (P-2166, 83.4 mg, 74 %). MS (ESI): [M+HT = 431.2, 433.2.
[0458] 5-Chloro-3 -[2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy) -5 -methoxy-benzyl] - 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 - b]pyridme P-2167
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 46, replacing 3-iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 68 with 5-chloro-3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (prepared as described in Example 49) in Step 2 and eluting with 30-95% ethyl acetate in hexanes in Step 3. MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 465.1 , 467.1.
Example 48: Synthesis of 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2- methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-l-mettayl-lH-benziinidazole P-2106
[0459] 2-[4-(5 -Chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3-b]pyridin-3 -ylmethyl)-5 -fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl] - 1 -methyl- lH-benzimidazole P-2106 was synthesized in four steps from 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5- methoxy-benzaldehyde 39 as shown in Scheme 47.
Scheme 47
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Step 1 ~ Preparation of4-(lH-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (142): |0460] 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (39, 0.290 g, 1.7 rnmol, prepared as described in Scheme 12 of Example 15) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylfoπnamide (20 mL, 200 mmol). Sodium hydride (60% dispersion in oil, 0.852 g, 2.13 mmol) was added to the solution and after the mixture was stirred for 20 minutes at room temperature, 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole (106, 0.28 g, 1.7 mmol) was added to the reaction. The obtained mixture was heated to 80 0C and stirred overnight. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction was poured into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (40 to 100%) in hexane to give the desired coompound (142, 0.233 g, 45%).
Step 2- Preparation of 2-βuoro-5-methoxy-4-(l -methyl- lII-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-benzaldehyde (143):
[0461] 4-(lH-Benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (142) (0.600 g, 2,0 mmol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (15 mL, 190 mmol). After the addition of sodium hydride (60% dispersion in oil, 0.072 g, 3.0 mmol) the reaction was stirred for 15 minutes at room temperature. Methyl iodide (140 μL, 2.2 mmol) was added dropwise to the mixture. The reaction was stirred overnight at room temperature under an atmosphere of nitrogen. The solvent was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and the organic portion was washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel flash chromatography with a gradient of ethyl acetate in hexanes gave the desired compound as a white powder (143, 0.345 g, 55%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]+= 315.2.
Step 3 - Preparation ( 5 -Chloro-1-triisυprυpylsilanyl- IH- pyrrol o[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-fluυ ro-5- methoxy-4-( 1 -methyl- 1 H-benzυimida∑ol-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanol (145): [0462] 5-Chloro-3-iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (144, 0.235g, 0.541 mmol, prepared as described in Example 49) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (5 mL, 60 mmol). The
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 solution was cooled to -25 0C. After the addition of 2 M of isopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydrofuran (400 μL) the reaction was wanned to -10 0C with stirring. The reaction was cooled to -30 0C and 2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(l -methyl- lH-bcnzimidazol-2-ylmcthoxy)-benzaldchydc (143, 0.170 g, 0.541 mmol) in 4 mL of tetrahydrofuran was added at once to the mixture. The reaction warmed to -10 0C and then evaporated to dryness. Ethyl acetate was added and the organic portion was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel flash chromatography with a gradient of ethyl acetate (5 to 80%) in hexanes gave the desired compound 145.
Step 4 — Preparation 2-[4-(5-Chlυrυ-lH-pyrrυlυ[2,3-h]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluυrυ-2-methυxy - phenoxymethyl] -J -methyl- IH-benzimidazole (P-2106):
[0463] (5-Chloro-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-fluo ro-5-methoxy-4-(l - methyl-lH-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanol (145) (0.140 g, 0.225 mmol) was suspended in acetonitrile (5 mL, 100 mmol). Triethylsilane (1 .0 mL, 6.3 mmol) was added followed by trifluoroacetic acid (0.500 mL, 6.4 mmol). After the reaction was stirred at 60-80 0C for 1.5 hours the solvent was evaporated to dryness. Ethyl acetate was added and the organic portion was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel flash chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (20 to 100%) in hexanes gave the desired compound as a white powder (P-2106, 0.034g, 34%). MS (ESI) [M+HT= 451.2.
[0464] 2-(l-Chloro-ethyl)-lH-benzoimidazole 147 was prepared in one step from 1-(1H- benzoimidazol-2-yl)-ethanol 146 as shown in Scheme 48.
Scheme 48
146 147
Step I - Preparation of 2-(l-Chloro-ethyl)-l H-benzimidazole (147): [0465] l-(lH-Benzimidazol-2-yl)-ethanol (146) (1.00 g, 6.16 mmol) was suspended in dichloromethane (50 mL, 800 mmol), Thionyl chloride (4.00 mL, 54.8 mmol) was added dropwise and the reaction was stirred at room temperature and then heated to 60 0C for 6 hours. After cooling to room temperature the reaction was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. The obtained solid was washed with ethyl acetate. The powder was suspended in ethyl acetate and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and brine. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. The obtained off-white solid was used without further purification
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
(147, 0.864 g, 76%). MS (ESI) [NMT]+ = 181.2.
[0466] 2-l-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-iluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxy]- ethyl-lH-benzimidazole P-2110
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 47, replacing 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzimidazole 106 with 2-(l-chloro-ethyl)-lH-benzimidazole 147. MS(ESI) [M+H+]+ = 451.2, 453.2.
[0467] S-Chloro^-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole 148 and 2-Chloromethyl~5-methoxy-lH- benzoimidazole 149
= 197.2) were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 48 replacing l-(lH-benzimidazol-2-yl)-ethanol 146 with (5-chloro-lH-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-methanol and (5-methoxy-lH-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-methanol, respectively.
Example 49: Synthesis of 5-chloro-3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 144
[0468] 5-Chloro-3-iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 144 was synthesized in one step from 5-Chloro-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 150 as shown in Scheme 49.
Scheme 49
Step 1 - Preparation of5-Chloro-3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (144): [0469] 5-Chloro-3-iodo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (150, 31.2 g, 0.1 12 mol) was dissolved in N- methylpyrrolidinone (800 mL) and NaH (60% dispersion, 4.93 g, 0.123 mol) was added at room temperature. The resulting mixture was stirred for 30 minutes. To this mixture was then added triisopropylsilylchloride (24.0 mL, 0.1 12 mol) and the resulting mixture was stirred for 2 hours. The reaction was quenched with water and extracted with ethyl acetate three times, washed by brine, dried, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was subjected to silica gel Hash chromatography
Atty. Dkt, No.: 039363-3303
(eluted by heptane to 5% ethyl acetate/heptane) to afford the desired compound (43 g, 88 %) as a pale-yellow solid.
Example 50: Synthesis of 6-chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- ylmethyl) -phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzimidazole P-2112
[0470] 6-chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl) -phenoxymethyl]- lH-benzimidazole P-2112 was synthesized in four steps from 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy- benzaldehyde 39 as shown in Scheme 50.
Scheme 50
Step 1 - Preparation of4-(6-chloro-lH-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-flιwro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde
(151):
[0471] 4-(6-Chloro-lH-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (151) was prepared using the same protocol as described in Scheme 47 substituting 2-chloromethyl-lH- benzoimidazole 106 with 5-Chloro-2-chloromethyl-H-benzoimidazole 148 (prepared as described in
Example 48) in Step 1. Purification through silica gel column chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (10 to 100%) in hcxanc gave the desired compound 151,
Step 2 - Preparation of 6-chloro-2-(5-βuoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl)-benzimidazole- 1 - carboxylic acid ten-butyl ester (152):
[0472] To a solution of 4-(5-chloro-l H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy- benzaldehyde (151) (0.330 g, 0,98 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml ) at room temperature was added N,N-diisopropylethylamine (0.40 mL, 2.3 mmol) followed by the addition of 4- dimethylaminopyridine (0.01 g, 0.1 mmol) polymer bound. To the stirring mixture a solution of di- tert-butyldicarbonate (0.24 g, 1.1 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (5 mL) was added. After the reaction
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The resulting solid was dissolved in ethyl acetate and the organic portion was washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated to dryness. The desired compound 152 was used without further purification.
Step 3 -- Preparation υf(5-Chlυro-2-{5-fluoro-4-[hydroxy-(l- triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bj ] pyridin- 3 -yl) -methyl) '-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl}-benzimidazole- 1 -carboxylic acid tert-hutyl ester (153):
[0473] 3-Iodo-l -triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (68, 0.200 g, 0.5 mmol, prepared as described in Example 22) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (3 mL, 40 mmol). After the reaction reached the temperature of -20 °C, a solution of 2M of isopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydrofuran (300 μL) was added dropwise. The resulted mixture was stirred to -5 °C. After cooling the reaction to -20 0C, a solution of 6-chloro-2-(5-fluoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl)-benzoimidazole-l -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (152, 0.2 g, 0.46 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (4 mL) was added at once to the mixture. The reaction warmed to -5 0C and was then evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added. The organic portion was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel flash chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (5 to 80%) in hexanes gave the desired compound (153, 0.142 g, 44%). MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 709.4.
Step 4 - Preparation of6-Chloro-2-[5-fluυrυ-2-methυxy-4-(l H-pyrroIo[2,3-h]pyridin-3-ylmethyl) - phenoxy methyl]- 1 H-benzimidazole (P-2112):
10474] 6-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl) - phenoxymethy I]-I H-benzimidazole (P-2112) was prepared using the same protocol as described in Scheme 47, step 4, substituting (5-chloro-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2- fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(l -methyl- 111-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-methanol 145 with (5- chloro-2- {5 -fluoro-4-[hydro xy-( l- triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-2- methoxy-phenoxymethyl}-benzoimidazole-l-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 153. Purification with silica gel flash chromatography eluting with a gradient of methanol (2 to 25%) in dichloromefhane gave the desired compound (P-2112, 0.052 g, 59%). MS (ESI) [M+H1] ' = 437.1, 439.1.
[0475] Additional compounds were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 50, substituting 5-chloro-2-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole 148 with the appropriate benzoimidazole in Step 1 , and 3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2)3-b]pyridine 68 with the appropriate substituted 7-azaindole in Step 3. Compound P-1976 (see Example 10) was prepared by this procedure and isolated with silica gel flash chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (60 to 100%) in hexanes followed by additional washes with acetonitrile over the final solid. Compound P-2113 was
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 further purified with silica gel flash chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (20 to 100%) in hexanes. The following compounds were also made following this procedure:
5-Chloro-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl] - 1 H-benzimidazole (P-2111 ) ,
2-[5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmcthyl)-phenoxymethyl]-5- mcthoxy-1 H-benzimidazole (P-2113),
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-fluoro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-
1 H-benzimidazole (P-2115)
The following table indicates the benzoimidazole used in Column 2 and the 7-azaindole used in Column 3 to provide the compounds shown by structure in Column 4. Column 1 provides the compound number and Column 5 the mass spectrometry result.
Example 51: Synthesis of N-phenyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-amine 158 and related compounds
[0476] N-phcnyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-amine 158 was synthesized in five steps from IH- pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyridine 6 as shown in Scheme 51.
Atty, Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 Scheme 51
Ste/7 i - Preparation of 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-N-oxide (154):
[0477] To lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (6, 3.0 g, 25.3mmol) dissolved in 175 mL of diethyl ether was added m-CPBA (1.5 equiv) in portions over 30 minutes with vigorous stirring. The solution turned yellow, and precipitates formed. After two hours the solid was collected, washed with 2 x 50 mL of ether, and recrystallized from acetone: ether. Yield was approximately 125% due to contaminating acid. This crude material was carried through to the next step.
Step 2 - (6-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-l-yl)(phenyl)methanone (155):
[0478] lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-N-oxide (154, 500 mg, 3.72mmol) was dissolved in 40 mL of dry benzene. In a separate dry flask, benzoyl bromide (2.5 equiv) and 1,1, 1 ,3,3, 3-hexamethyldisilazane (1.0 equiv) were combined in 20 mL of dry benzene, The bromide solution was added in 5 mL aliquots over 30 minutes to the reaction flask, The reaction was stirred at ambient temperature for two hours. It was then washed with 3 x 30 mL NaHCOj (aq,, satd.) and 1 x 30 mL brine. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate and evaporated, The crude material was taken directly to the next step without further purification.
Step 3 — Preparation of 6-bromo-lH-pyrrolo [2, 3-b] pyridine (156):
[0479] (6-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-l -yl)(phenyl)methanone 155 was dissolved in 20 mL of dioxane and 20 mL of 2M KOH (aq). This was stirred at ambient temperature until analysis indicated all of the starting material had been consumed (2 to 4 hours). The reaction was diluted with 50 mL of ethyl acetate and washed with 2 x 25 mL OfNaHCO3 (aq. satd.) and 25 mL of brine. The organic layer was dried with sodium sulfate, evaporated and purified by column chromatography. Combined steps 2 and 3 gave approximately 65% overall yield.
Step 4 - Preparation of6-hromo~l-(triisopropy!silyl)~-JH-pyrro!o[2,3-h]pyridine (157): [0480] 6-bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (156, 275 mg, 1.39mmol) was dissolved in 4 mL of dry dioxane. DIEA (3 equiv) and TIPS-OTf (2.5 equiv) were added and the reaction was stirred at 50 "C overnight. The reaction was then diluted with 20 mL of ethyl acetate and washed 2 times with 10 mL NaHCθ3 (aq., 5%) and once with 10 mL brine. The organic fraction was dried over MgSO4,
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 evaporated and diluted with 5.5 niL of dry toluene (~ 10 mg bromide per 0.2 mL of solution) to use directly in the next reaction step.
Step 5- Preparation ofN-pheny!-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-amine (158):
[0481] A 1 dram vial was charged with aniline (2 -3 equiv), and 0.200 mL of the 157 stock solution of bromide in toluene was added. A catalyst stock solution containing 3 mmol Pd(OAc)2, 3 mmol biphenyl-2-yl-di-tert-butyl-phosphane and 15 mL of toluene was prepared and 0.050 mL of the catalyst solution was added to the reaction. An excess of NaOtBu was added as a solid to the reaction. The vial was placed in an 80 0C oven for 60 minutes (shaken several times over the hour). After cooling, the reaction was neutralized with 0.100 mL of TFA. After 30 minutes the sample was evaporated and resolvated in 0.300 mL of DMSO. The desired compound was isolated by preparative HPLC/MS. MS(ESI) PVH-IT]+ = 210.4.
[0482] The following compounds were prepared following the protocol of scheme 51 , substituting aniline with a suitable amine is Step 5:
Cyclohexyl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (159), Benzyl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (160), Cyclopropylmethyl-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (161), (3-Methoxy-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (162), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-amine (163), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]p>τidin-6-yl)-(2-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-amine (164), Cyclohexylmethyl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (165), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(4-trifluoromethoxy-benzyl)-amine (166), (lH-PyrroloP^-bJpyridin-ό-y^^S-trifluoromcthoxy-bcnzyO-aminc (167), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(2-trifluoromethoxy-benzyl)-amine (168), Pyridin-2-ylmethyl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (169), (4-Methanesulfonyl-benzyl)-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (170), (4-Methoxy-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (171), Ethyl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (172), (3 -Chloro-benzyl)-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (173), (4-Methyl-benzyl)-( 1 H-pyrro]o[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (174), (l-Methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (175), Pyridin-3 -ylmethyl-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine ( 176), [4-(Morpholine-4-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (177), (4-Methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (178), (2-Chloro-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (179), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(tetrahydro-pyran-4-yl)-amine (180),
Atty. Dkt, No,: 039363-3303
(4-Chloro-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (181), (3-Methyl-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (182), [3-(Moφholinc-4-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (183), (3-Methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidin-6-yl)-amine (184), Pyridin-3-yl-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (185), (2-Methoxy-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (186), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amine (187), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(4-trifIuoromethoxy-phenyl)-amiπe (188), (4-Methoxy-phenyl)-(lH-pyrτolo[2J3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (189), N,N-Dimethyl-Nl-(lH-pyπ-olo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-benzene-l ,4-diamine (190), (3-Methoxy-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (191), (4-Morpholin-4-yl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (192), (4-Piperidin-l -yl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (193), (HI-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(3-trifluoromethoxy-plienyl)-amine (194), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-p-tolyl-amine (195), (3-tert-Butyl-phenyl)-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (196), (3-Dimethylamino-benzyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (197), (3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (198), (lH-Pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-(4-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-ainine (199), N,N-Dimethyl-N'-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-benzene-l,3-diamine (200), (3-Chloro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amiπe (201), (4-Chloro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-aminc (202), (2-Chloro-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (203), (5 -Methyl-isoxazol-3 -yl)-( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (204) , (2-Mθφholin-4-yl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (205), and (2-Methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)-amine (206).
The following table indicates the amine (Column 2) that is substituted in place of the aniline in Step 5 to afford the compound (Column 3), Column 1 provides the compound number and Column 4 the observed mass.
Example 52: Synthesis of 5-methanesulfonyl-lH-pyrroloI2,3-b]pyridiπe 207
[0483] 5-Methanesulfonyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 207 was synthesized in one step from 5-bromo-7-azaindole 1 as shown in Scheme 52.
Scheme 52
[0484] I'o 5-bromo-7-azaindole (1, 1.00 g, 5.08 mmol) in dimethyl sulfoxide (15.0 mL) were added sodium methanesulfmate (0.622 g, 6.09 mmol), L-proline (0.117 g, 1.02 mmol), copper(I) iodide (0.200 g, 1.05 mmol), and sodium hydroxide (0.0406 g, 1 .02 mmol). The reaction was stirred at 120 0C overnight. The reaction was poured into aqueous ammonia, and extracted with ethyl acetate, The
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 organic layer w as dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with 20% to 100% ethyl acetate in hexane to give the desired compound as a white solid (207, 0 50 g, 50 2%) MS (ESI) [M-H+] = 195 1
Example 53: Synthesis of 3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-bcnz>l]- lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-5-carboxylk acid P-2175
[0485] 3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-p>rrolo[2,3- b]pyπdme-5-carboxylic acid P-2175 was synthesized in one step from 3-[4-(lII-benzoimidazol-2- yhnethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrτolo[2,3-b]p>ridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester P- 2174 as shown in Scheme 53
Scheme 53
[0486] To 3-[4-(lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methox>-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridine-5-cdrboxyhc acid methyl ester (P-2174, 0 030 g, 0 065 mmol, prepared as described in Example 16) in tetrahydrofuran (9 0 mL) were added water (3 0 mL) and lithium hydroxide (20 0 mg, 0 84 mmol) The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight The reaction was poured into water, and extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was discarded The aqueous layer was acidified with 5 N HCl to pH around 3, and then extracted with ethyl acetate The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered The filtrate was concentrated, and washed with ethyl acetate and hexane to give a white solid (P-2175, 21 3 mg, 73%) MS (ESI) [M+H+]+ = 447 0
Example 54: Synthesis of Sjό-Dichloro^-^-fS-chloro-lH-pyrroloβ^-blpyridin-S-ylmethy^-S- fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole P-2172
[0487] 5,6-Dichloro-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fIuoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole P-2172 was synthesized in 3 steps from 2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5- methoxy-benzaldehyde 38 as shown in Scheme "54 Scheme 54
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303
Step 1 - Preparation of4-(5, 6-dichlorυ-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy~ benzaldehyde (209):
[0488] 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (38, 0.364 g, 2.14 rnmol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (10.0 mL) and sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 100 mg, 2.50 mmol) was added. After 20 minutes, 5,ό-dichloro-2-chloromethyl~lH-benzoimidazole (208, 0.420 g, 1.78 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred at 80 0C overnight. The reaction was concentrated, then washed with ethyl acetate and saturated sodium bicabonate. The organic portions were dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and the filtrate was adsorbed onto silica. The mixture was purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with methanol/ dichloromethane, to provide the desired compound, consistent by 1H-NMR (209, 140 mg, 21%).
Step 2 — Preparation of 5, 6-dich!oro~2-4-[(5-ch!oro-lH-pyrrolo[2, 3-b] pyridin-3-yl)-methoxy-methyl] - 5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl-lH-benzoimidazυh (210):
[0489] 5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (4, 52.6 mg, 0.345 mmol) and 4-(5,6-dichloro-lH- benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy~benzaldehyde (209. 0.140 g, 0.379 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (7 mL) and potassium hydroxide (0.193 g, 3.45 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 72 hours. The reaction was adsorbed onto silica and purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with methanol/ dichloromethane to provide the desired compound, consistent by 1H-NMR and MS(ESI) [M+H+]+=535.1 (210, 60 mg, 33%).
Step 3 - Preparation of 5, 6-Dichloro-2-[4~(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro- 2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole (P-2172):
[0490] 5,6-Dichloro-2-4-[(5-chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidin-3-yl)-methoxy-methyl]-5-fluoro-2- methoxy-phenoxymethyl- 1 H-benzoimidazole (210, 0.041 g, 0.077 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (10 mL) and trifluoroacetic acid (0.3 mL, 4.0 mmol) and triethylsilane (0.6 mL, 4.0 mmol) were added. The reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours. The mixture was adsorbed onto silica gel
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 and purified by silica gel chromatography, eluting with methanol/dichloromethane, to provide the desired compound, consistent by 1H-KMR and MS(ESI): [M+HT = 505.0, 507.0 (P-2172, 8.1 mg, 21 %).
[0491] 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]- 5-trifluoromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole P-2178 and 2-[4-(5-chIoro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3- ylmethy^-S-fluoro^-mcthoxy-phcnoxymcthylJ-S-fluoro-lH-benzoimidazole P-2179 ,
were prepared following the protocol of Scheme 54, replacing 5,6-dichloro-2-chloromethyl-lH- benzoimidazole 208 with 2-chloromethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole or 2-chloromethyl-5- fluoro-lH-benzoimidazole, respectively, in Step 1. MS(ESI): [M+lT]+= 505.1 , 507.1 (P-2178) and 455.0, 456.5 (P-2179).
Example 55: Synthesis of 2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2- methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-l-methyl-lH-benzoimidazole P-2106
[0492] 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiπ-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]- 1-methyl-lH-benzoimidazolc P-2106 was synthesized in 4 steps from N-methyl-phenylenediamine 211 as shown in Scheme 55.
Scheme 55
Step 1 - Preparation of 2-chloromethyl- 1 -methyl- 1 H-benzoimidazole (212):
[0493] N-methyl-phenylenediamine (1 g, 8,2 mmol) and chloroacetic acid (0.9 g, 9.4 mol) were dissolved in 5 N aqueous hydrochloric acid (10 mL) and stirred at 55 0C overnight. The reaction
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 mixture was then diluted with water and basified with solid sodium bicarbonate to give a precipitate which was filtered, washed with water and dried to provide the desired compound (1.3 g, 87 %).
Step 2 - Preparation of 2-fluoro- 5-methoxy-4-( 1 -methyl- 1 H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmcthoxy)- benzaldehyde (213):
[0494] To a solution of 2-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (39, 3.0 g, 18 mmol) in N,N- dimethylacetamide (120 rnL) was added sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 0.8 g, 19 mmol) portion wise. After the addition was complete, the reaction was stirred for 30 minutes after which 2-chloromethyl-l -methyl- lH-benzoimidazole (212, 2.9 g, 16 mmol) was added and then heated at 80 0C overnight. The reaction mixture was then poured into water (1 L) with stirring and the precipitated solid was filtered, washed with water and dried to give the desired compound (213, 4.2 g, 84 % yield).
Step 3 - Preparation of(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-βuoro-5-methoxy-4-(l-methyl- 1 H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyi] -methanol (214a) and 2-{4-[(5-chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3- bJpyridin-3-yl)-methoxy-methyl]-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl}-l -methyl- IH-benzoimidazole (214b):
[0495] To a solution of 2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4-(l -methyl-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)- benzaldehyde (213, 4 g, 13 mmol) and 5-chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (4, 2 g, 13 mmol) in methanol (140 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (140 mL) was added potassium hydroxide (5 g, 89 mmol). The reaction was stirred for 5 days at room temperature. The solution was diluted with water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The layers were separated and the aqueous layer was back-extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and evaporated in vacuo to give crude compound as a yellow semi-solid which was used directly in the next step.
Step 4 - Preparation of2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl] -1 -methyl- lH-benzυimidazυle (P-2106) •
[0496] To a solution of above crude mixture of aldol compounds 214a and 214b (13 mmol, theoretical yield) in acetonitrile (300 mL) was added trifluoroacetic acid (5.7 mL, 77 mmol) and triethylsilane (54 mL, 339 mmol). The resulting mixture was stirred for 2 hours at reflux. The solvent was removed in vacuo and the residue taken up in ethyl acetate (1 L) and then washed with saturated aqueous potassium carbonate. The layers were separated and the aqueous layer was back-extracted with ethyl acetate (1 L). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and evaporated in vacuo to give a crude oily solid that was subjected to Boc protection (20 volumes of tetrahydrofuran, 2.0 equiv. of Boc-anhydride, 0.10 equiv of DMAP) followed by silica gel chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexanes). The isolated material was then deprotected using 20% trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane (10 volumes) and neutralized to the free base using saturated aqueous potassium carbonate. The dichloromethane was removed in vacuo and the resulting product
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 was filtered, washed with water and the solid was slurried with ethyl acetate, filtered, and dried to give P-2106 (1.3 g, 23% over 2 steps) MS(ESI): [M+H'J 1 = 451.2, 453.0.
[0497] 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]- 1 -ethyl- lH-benzoimidazole P-2177
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 55, steps 3 and 4, substituting 2-fluoro-5-methoxy-4- (1 -methyl- lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-benzaldehyde 213 with 4-(l-ethyl-lH-benzoimidazol-2- ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 216 (see Example 56) in step 3. MS(ESI): [M+H"]+ = 465.3, 467.1.
Example 56: Synthesis of 4-(l-ethyl-lH-bcnzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy- benzaldehyde 216
[0498] 4-(l-Ethyl-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 216 was synthesized in 1 step from 4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 215 as shown in Scheme 56.
Step 1 — Preparation of4-(l-Ethyl-lH-ben∑oirnidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-βuoro-5-methυxy-benzaldehyde (22):
[0499] To a solution of 4-( 111-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (215, 4,0 g, 13 mmol) in N,N-dimethylacetamide (80 mL) was added sodium hydride (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 0.65 g, 16 mmol) portion wise. After the addition was complete, the reaction was stirred for 30 minutes after which bromoethane (1.2 mL, 16 mmol) was added and then allowed to stir for several hours. The reaction mixture was then poured into water (1 L) with stirring and the precipitated solid was filtered, washed with water and dried to give the desired compound (216, 3.8 g, 87 % yield).
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Example 57: Synthesis of 2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yImcthyI)-5-fluoro-2- πiethoxy -pheiioxyinethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole-5 -sulfonic acid diethylamide P-2173
[050Oj 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymelhyl]- lH-benzoimidazole-5-sulfonic acid dimethylamide P-2173 was synthesized in 4 steps from 2-fluoro- 4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 39 as shown in Scheme 57.
Scheme 57
ftep / - Preparation oj 2-(5-fluoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl)-lH-benzoimidazole-5- sulfonic acid dimethylamide (218):
[0501] 2-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (39, 0.38 g, 2.2 mmol) was dissolved in N,N- dimethylformamide (30 mL) and sodium hydride 60% dispersion in mineral oil (120 mg) was added. After 20 minutes, 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazolc-5-sulfonic acid dimethylamide hydrochloride salt (217. 0.559 g, 1.80 mmol) was added to the mixture. The reaction was stirred at 60 °C overnight. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and the organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (20-100 %) in hexane to provide the desired compound (218, 0, 122 g, 17%).
Step 2 - Preparation υf5-dimethylsulfamoyl-2-(5-fluoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl)- benzimidazole-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (219):
[0502] 2-(5-Fluoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl)-l H-benzoimidazole-5 -sulfonic acid dimethylamide (218, 0.122 g, 0.299 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (5 mL). N,N- Diisopropylethylamine (0.10 mL, 0.60 mmol) and 4-dimethyl aminopyridine polymer bound (0.007 g. 0.06 mol) were added followed by di-tert-butyldicarbonate (0.072 g, 0.33 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated. The
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 resulting compound was used without further purification (219, 0.133 g, 87 %).
Step 3 - Preparation of2-4-[(5-chloro-I-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrnln[2, 3-h]pyridin-3-yl)-hydroxy- methylJ-S-fluoro-I-methoxy-phenoxymethyl-S-dimethylsulfamoyl-benzoimidazole-l-carhoxylic acid tert-butyl ester (220):
[0503] 5-Chloro-3-iodo-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (144, 0.17 g, 0.39 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (2 mL). The reaction was cooled to -20 0C. 2 M isopropylmagnesium chloride in tetrahydrofuran (0.2 mL) was added drop wise to the mixture. The reaction was stirred to -5 0C. 5-Dimefhylsulfamoyl-2-(5-fluoro-4-formyl-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl)-benzimidazole-l -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (219, 0.133 g, 0.262 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (3 mL) was added at once to the mixture at -20 0C. The reaction was stirred to -5 0C and concentrated. Ethyl acetate was added and washed with sodium bicarbonate saturated solution and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel column chromatography, eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (5-80%) in hexanes, gave the isolation of the desired compound (220, 0.083 g, 39%).
Step 4 - Preparation of2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]py idin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy - phenoxymethyl] -1 H-benzoimidazole-5-sulfonic acid dimethyϊamide (P-2173) [0504] 2-4-[(5-Chloro-l-triisopropylsilanyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-hydroxy-methyl]-5- fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl-5-dimethylsulfamoyl-benzoimidazole-l -carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (220, 0.083 g, 0.10 mmol) was combined with acetonitrile (4 mL). Triethylsilane (0.6 mL) was added followed by trifluoroacetic acid (0.3 mL). The reaction was stirred at 60 0C for one hour. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and washed with sodium bicarbonate saturated solution and brine. After the organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate the solvent was evaporated to dryness. Purification by trituration with a mixture of ethyl acetate in hexanes allowed obtaining the desired compound. The remaining material was further purified with silica gel column chromatography, eluting with a gradient of methanol (5-35%) in dichloromethane, to provide the desired compound (P-2173, 0.022 g, 41%). MS (ESI):[M+lT] + = 544.1 , [M-H+] • = 542.1.
[0505] 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]- 5-methoxy-l H-benzoimidazole P-2182
was prepared following the protocol of Scheme 57, replacing 2-chloromethyl-lH-benzoimidazole-5- sulfonic acid dimethylamide hydrochloride salt 217 with 2-Chloromethyl-5-mefhoxy-lH-
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 ben/oimida/ole 222 (see Example 58) in step 1 MS (ESI) [M+H+] + = 467 2
Example 58: Synthesis of 2-chloromethyl-5-methoxy-lH-benzoimidazole 222
[0506] 2-Chloromethyl-5-methoxy-lH-benzoimidazole 222 was synthesized in 1 step from (5- Methoxy-lH-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-methanol 221 as shown in Scheme 58
Scheme 58
Step 1 - Preparation oj 2-chloromethyl-5-methoxy-lH-benzoιmιdazole (222)
[0507] (5-Methoxy-lH-benzoimidazol~2-yl)-methanol (221, 0 5 g, 3 mmol) was combined with 30 mL dichloromethane Thionyl chloride (0 51 mL, 7 mmol) was added and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours The reaction was concentrated Fthyl acetate was added and washed with sodium bicarbonate saturated solution and brine The organic portion was dned over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered through Celite and evaporated to dryness The resulting desired compound was used without further purification MS (ESI) [TvH-H+] + = 197 2
Example 59: Synthesis of 2-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylπiethyl)-5-fIuoro-2- methoxy-phenoxy]-ethyl-lH-benzimidazole P-2180
[0508] 2-2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxy]- ethyl- lH-benzimidazole P-2180 was synthesized in 4 steps from 4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy- benzdldehyde 83 as shown in Scheme 59
Scheme 59
Step 1 - Preparation of(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phcnyl)-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- b] pyridin~3-vl)~methanol (223a) and 3-[(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methylJ-
5-chloro-lH-pyrrolϋ[2, 3-b] pyridine (223b)
[0509] 4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (83, 12.4 g, 48 mmol) was combined with
5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (4, 7.3 g, 48 mmol), methanol (500 mL) and potassium hydroxide
(22 g, 335 mmol). The reaction was stirred overnight at room temperature. The solution was diluted with water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated under reduced pressure to give the desired compounds 223a and 223b that were used without further purification.
Step 2 - Preparation of3-(4-benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl)-5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- bjpyridine (224)
[0510] (4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-(5-chIoro-llI-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanol 223a and 3-[(4-benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-methoxy-methyl]-5-chloro-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine 223b (48 mmol) were combined with acetonitrile (1.4 L), trifluoroacetic acid (21 mL, 288 mmol) and triethylsilane (31 mL, 192 mmol). The resulting mixture was stirred for two hours at reflux. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate (6 L) was added and the organic layer was washed with aqueous potassium carbonate saturated solution. The layers were separated and the aqueous layer was back-extracted with ethyl acetate (2 L). The combined organic portions were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated under reduced pressure to give the desired compound 224 which was used without further purification.
Step 3 — Preparation of4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-rnethoxy-phenol
(225)
[0511] 3-(4-Benzyloxy-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzy])-5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (224, 48 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (300 mL) and 20 % palladium on carbon (50% water wet, 2.3 g) was added. The mixture was stirred under an atmosphere of hydrogen at 50 psi in the presence of acetic acid (100 mL). The reaction mixture was filtered through Celite and evaporated to dryness to give the desired compound 225. MS (ESI) :[M+H+] + = 307.1.
Step 4 - Preparation of 2-2-[4-(5-Chioro-lH-pyrrolo[2, 3-b] pyridin-3-ylmethyi)-5-fluoro-2-meth oxy- phenoxy] -ethyl- 1 H-benzimidazole (P-2180)
[0512] 4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoI (225, 0.200 g, 0.652 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (5 mL). Triphenylphosphine (0.190 g, 0,72 mmol) and 2-(lH-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-ethanol (226, 0.110 g, 0.68 mmol) were added followed by diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (0.140 mL, 0.72 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The mixture was placed into water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic portion was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated. Purification with silica gel column
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 chromatography, eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (20-100%) in hexanes, gave the isolation of the desired compound (P-2180, 0.0189 g, 6%). MS (ESI):[M+HT = 451.0, [M-H"] " = 449,1
Example 60: Synthesis of 5-chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(5-methyl-lH-pyrrolo|2,3- bJpyridiπ-3-ylαiethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole P-2184
[0513J 5-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(5-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)- phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole P-2184 was synthesized in 2 steps from 4-(lII-Benzoimidazol- 2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 227 as shown in Scheme 60.
Scheme 60
Step 1 ~ Preparation of [4-(5-chloro-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5- methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (228a) and 5-chloro-2-{5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4- [methoxy-(5-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzoimidazole (228b):
[0514] 5-Methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine (13) was combined with methanol and potassium hydroxide. After the mixture was stirred for 45 minutes 4-(5-chloro-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)- 2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde (227, per step 1 of Example 57 substituting 2-chloromethyl-lH- benzoimidazole-5-sulfonic acid dimethylamide 217 with 5-chloro-2-chloromethyl-lH- bcnzoimidazole) was added and the reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and washed with sodium bicarbonate saturated solution and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel chromatography, eluting with a gradient of ethyl acetate (10-100%) in hexanes, gave the desired compounds 228a and 228b as a mixture.
Step 2 - Preparation of5-chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2~methoxy-4-(5 -methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrιdin-3- ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-ben∑oimidazole (P-2184):
[0515J t4-(5-chloro-lH-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5-methyl-lH- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanol (228a) and 5-chloro-2-{5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-[methoxy-(5- methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methyl]-phenoxymethyl} -lH-benzoimidazole (228b) were
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 dissolved in acetonitrile. Triethylsilane was added followed by trifluoroacetic acid. The reaction was stirred for one hour at 60 0C. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate was added and the organic layer was washed with sodium bicarbonate saturated solution and brine, then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. Purification with silica gel column chromatography, eluting with a gradient of methanol (2-25%) in dichloromethane, provided the desired compound P-2184. MS (ESi): [M+H 1J ' = 451.0, [M-Hf] ~ = 449.1.
Example 61: Synthesis of benzoimidazole compounds of Formula XXX
Step 1 - Preparation of compounds of Formula XXXh
[0516] A phenyldiamine compound of Foπnula XXXa (R is an optional substituent of benzoimidazole) and chloroacctic acid arc typically refluxed in 4N hydrochloric acid for one to several hours and then cooled and neutralized. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction, washing and filtering) affords a mixture containing compound of Foπnula XXXb, which may be isolated by silica gel chromatography if desired. Bloom and Day, J. Org. Chem. 1939, 14, 17.
Example 62: Synthesis of compounds of Formula XXX
XXXa XXXc xxx
Step 1 - Preparation of 2-Chloro-acetimidic acid ethyl ester
[0517] 2-Chloro-acetimidic acid ethyl ester may be prepared by dissolving chloroacetonitrile in an appropriated solvent (e.g. ether, THF) with ethanol and bubbling hydrogen chloride gas with cooling. The hydrogen chloride solution is stirred in a closed system for one to deveral hours and warmed to room temperauture. Isolation by conventional means (e.g. extraction, distillation, washing and filtering) affords a mixture containing compound of Formula XXXc, which may be isolated by silica gel chromatography if desired.
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
Step! - Preparation of compounds of Formula XXX
[0518] A phenyldiamine compound of Formula XXXa (sec Example 52) and 2-chloro-acetimidic acid ethyl ester XXXc arc typically stirred together in an appropπate solvent (e g ethanol) for one to se\eral hours at room temperature Isolation by conventional means (e g extraction, washing and filtering) affords a mixture containing compound of Formula X, which may be isolated by silica gel chromatography if desired Komoyira et al , Bioorg Med Chem 2004, 12, 2099
Example 63: Cell-based assays of c-fins kinase activity or c-kit kinase activity.
[0519] M-CSF dependent RAW264 7 cells were seeded on a 12 well plate, 2 5\105 cells/well and the cells were allowed to attach overnight at 37 0C, 5% CO2 The cells were then starved in serum- free medium overnight at 37 0C, 5% CO2 The cells were treated with compound for 1 hour m scrum- free media (1% DMSO final concentration), and then stimulated with 20 ng/ml M-CSF for 5 minutes After stimulation, the cells were lysed on ice, and the lysates were centπfuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 minute The amount of protein in the sample was quantitated sample buffer was added, and the samples were boiled at 95 0C for 10 minutes The samples w ere then centπfuged at 13 000 rpm for 1 minute The samples (15-20 μg/lane) were loaded and run on 4-12% tπs-glycine gel at 75V, and then transferred onto a PVDF membrane The membrane was blocked for 1 hour with 5% BbA in PBS '1% Tween-20 (PBST), or 5% milk, depending on the primary antibody used Then the blots were incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4 degrees with gentle shaking After incubation with the capture antibody, the membranes were washed 3 x 10 minutes with PBST, then incubated with detection antibody Goat Anti-Rdbbit-HRP for 1 hour, with gentle shaking l he membranes were washed again 3 x 10 minutes with PBST ECL Plus substrate was then added to the blots the image captured with chemilummescence camera, and the bands quantitated for pFMS and FMS levels
[0520] The Fms inhibitors may also be assessed using M-NFS-60 mouse myelogenous leukemia cell line (ATCC catalog #CRL-1838) This cell line proliferation is stimulated by M-CSF, which binds and activates the fms tyrosine kinase receptor Inhibitors of fms kinase activity reduce or eliminate the M-CSF stimulated kinase activity, resulting in reduced cell proliferation This inhibition is measured as a function of compound concentration to assess IC50 values M-NTS-60 cells were seeded at 5 x 104 cells per well of a 96 well cell culture plate in 50 μl of cell culture medium of RPMI 1640 (CellGro Mediatech catalog #10-040-CV) supplemented with 10 % FBS (HyClone catalog #SH30071 03) Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 1 mM and were serially diluted 1 3 for a total of eight points and added to the cells to final concentrations of 10 3 3, 1 1 , 0 37, 0 12, 0 041 , 0 014 and 0 0046 μM in 100 μl cell culture medium (final concentration 0 2% DMSO) Cells were also treated with staurospoπne as a positive control The cells were stimulated by adding 20 μl ot 372 ng/ml M-CSF to a final concentration of 62 ng/ml (R&D Systems catalog #216-MC) The cells were incubated at 37 1C, 5% CO2 for three days CellTiter-Glo Buffer (Promega Cell
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Viability Assay catalog #G7573) and substrate were equilibrated to room temperature, and enzyme/substrate Recombinant Firefly Luciferasc/Bectle Luciferin was reconstituted. The cell plates were equilibrated to room temperature for 30 minutes, then lysed by addition of an equivalent volume of the Celltiter-Glo Reagent. The plate was mixed for 2 minutes on a plate shaker to lyse the cells, then incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. The plates were read on a Victor Wallac II using Luminescence protocol modified to read 0.1s per well. The luminescence reading assesses the ATP content, which correlates directly with cell number such that the reading as a function of compound concentration was used to determine the IC50 value.
[0521] The c-Kit inhibitors were assessed using M-07e cell line (DSMZ catalog #ACC 104). The M-07e proliferation is stimulated by SCF (Stem Cell Factor), which binds and activates c-Kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Inhibitors of c-Kit kinase reduce or eliminate the SCF mediated kinase activation, resulting in reduced cell proliferation of SCF stimulated cells. This inhibition is measured by the effect of compound concentration on cell growth to assess IC50 values. M-07e cells were seeded at 5 x 104 cells per well of a 96 well cell culture plate in 50 μl of cell culture medium of Iscove's Medium I X (MOD, CcllGro Mediatech catalog #15-016-CV) supplemented with 10% FBS (HyClone catalog #SH30071.03). Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 0.1 mM and were serially diluted 1 :3 for a total of eight points and added to the cells to final concentrations of 1 , 0.33, 0.1 1, 0.037, 0.012, 0.0041, 0.0014 and 0.00046 μM in 100 μl cell culture medium (final concentration 0.2% DMSO). Cells were also treated with staurosporine as a positive control. Cells were stimulated by adding 20 μl of 600 ng/ml SCF to a final concentration of 100 ng/ml (Biosource International SCF kit ligand catalog #PHC2115) in cell culture medium. The cells were incubated at 37 0C, 5% CO2 for three days. CellTiter-Glo Buffer (Promega Cell Viability Assay catalog #G7573) and substrate were equilibrated to room temperature, and enzyme/substrate Recombinant Firefly Luciferase/Beetle Luciferin was reconstituted. The cell plates were equilibrated to room temperature for 30 minutes, then lysed by addition of an equivalent volume of the Celltiter-Glo Reagent. The plate was mixed for 2 minutes on a plate shaker to lyse the cells, then incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. The plates were read on a Victor Wallac II using Luminescence protocol modified to read 0.1s per well. The luminescence reading assesses the ATP content, which correlates directly with cell number such that the reading as a function of compound concentration is used to determine the IC5O value.
[0522] This cell based assay was also used to assess phosphorylation. Samples were prepared with compounds as described for the growth inhibition assay only M-07e cells were seeded at 2 x 10 cells per well m a 96 well filter plate. Cells were incubated for 1 hour at 37 0C with the compounds as described above, and then stimulated by adding SCF to a final concentration of 50 ng/ml and incubated for 10 minutes at 37 0C. The culture medium was removed by centrifugation and the cells were lysed by addition of 30 μl lysis buffer (25 mM Tris HCl pll 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA,
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
1 % Tπton XlOO, 5 mM NaF, 1 mM NaVanadate, 10 mM Beta-glycerophosphate, no FDTA (Boehπnger-Roche catatalog #1873580) and placed on ice for 30 minutes A 15 μl aliquot of the lvsate was taken and assayed according to Biosource Immunoassay Kit Human c-Kit [pY823] (Catalog # KHO0401) by diluting the aliquot with 85 μl dilution buffer in the assay plate, incubating for 2 hours at room temperature and washing the plate 4 times with wash buffer Detection antibody (100 μl) was added to the plate and samples incubated for 1 hour at room temperature, then washed 4 times with wash buffer HRP anti-rabbit antibody (100 μl) was added and samples incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature, then washed 4 times with wash buffer Stabilized chromogen (100 μl) was added and samples incubated for 15-25 minutes at room temperature, then washed 4 times with wash buffer Stop solution (100 μl) was added and the samples read on a Wallac Victor reader at 450 nm The absorbance w as plotted against the compound concentration and the IC50 concentration was determined
[0523] Additional cell based assays can be correlated to the Fms activity of compounds of the invention For example, the ability or osteoclast precursor cells (commercially available from Lonza) to differentiate into mature osteoclasts, due to stimulation by M-CSF and RANKL, in the presence of compounds, can be measured using a method analogous to that previously reported (Hudson et al , Journal of Urology, 1947, 58 89-92), where the amount of acid phosphatase in the supernatant (1 e TRAP5b excreted by mature osteoclasts) is proportional to the number of mature osteoclasts present In another example, the ability of M-CSF-dependent munne macrophage cells (BACl 2F5) to proliferate in the presence of compounds can be measured by cultunng cells as previously described (Morgan et al , Journal of Cellular Physiology, 1987, 130 420-427) and determining cell viability by analysis of ATP levels in the cell culture (Crouch et al , Journal of Immunological Methods, 1993, 160 81-8)
Example 64: Kinase Activity Assays
[0524] The effect of potential modulators of kinase activity of c-kit and other kinases can be measured in a variety of different assays known m the art, e g , biochemical assays, cell-based assays, and in vivo testing (e g model system testing) Such in vitro and/or in vivo assays and tests can be used in the present invention As an exemplary kinase assay, the kinase activity of c-kit or Fms is measured in AlphaScreemng (Packard BioSciencc) Assays for the activity of various kinases are described, for example, in US Patent Application Serial number 11/473,347 (see also PCT publication WO2007002433), the disclosure of which is hereby incorporated by reference
Exemplary c-kit biochemical assay
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
[0525] The c-kit (or kinase domain thereof) is an active kinase in AlphaScreen KN0 values are determined with respect to inhibition of c-Kit kinase activity, where inhibition of phosphorylation of a peptide substrate is measured as a function of compound concentration Compounds to be tested w ere dissolved in DMSO to a concentration of 20 mM These were diluted 30 μl into 120 μl of DMSO (4 mM) and 1 μl was added to an assay plate These were then serially diluted 1 3 (50 μl to 100 μl DMSO) for a total of 8 points Plates were prepared such that each kinase reaction is 20 μl m 1 x kinase buffer (50 mM HFPES, pH 7 2, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM MnCl,, 0 01 % NP-40, 0 2% BSA), 5% DMSO and 10 μ\l ATP Substrate was 100 nM biotm-(E4Y)3 (Open Source Biotech, Inc ) C-kit kinase was at 0 1 ng per sample After incubation of the kinase reaction for 1 hour at room temperature, 5 μl of donor beads (Streptavidin coated beads (Perkin Flmer Life Science) final concentration 1 μg/ml) in stop buller (5OmM EDTA m ix kinase buffer) was added, the sample was mixed and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature before adding 5 μl of acceptor beads (PY20 coated beads (Perkin Elmer Life Science) final concentration 1 μg/ml) in stop buffer The samples were incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and the signal per well was read on AlphaQucst reader Phosphorylated substrate results in binding of the PY20 antibody and association of the donor and acceptor beads such that signal correlates with kinase activity The signal vs compound concentration was used to determine the IC50
[0526] Compounds were also tested using a similar assay with a 10-fold higher AJ P concentration For these samples, compounds to be tested were dissolved m DMSO to a concentration of 20 mM 1 hese were diluted 30 μl into 120 μl of DMSO (4 mM) and 1 μl was added to an assay plate These were then serially diluted 1 3 (50 μl to 100 μl DMSO) for a total of 8 points Plates were prepared such that each kinase reaction is 20 μl in Ix kinase buffer (25 mM HEPES, pH 7 5, 2 mM MgCk, 2 mM MnCl2, 0 01 % Twecn-20, 1 mM DTT, and 0 001% BSA), 5% DMSO and 100 μM ATP Substrate was 30 nM biotin-(E4Y)10 (Upstate Biotech, Cat# 12-440) C-kit kinase was at 1 ng per sample After incubation of the kinase reaction for 1 hour at room temperature, 5 μl of donor beads (Streptavidin coated beads (Perkin Flmer Life Science) final concentration 10 μg/ml) in stop buffer (25 mM HEPES pH 7 5, 100 mM ED 1 A, 0 3% BSA) was added, the sample was mixed and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature before adding 5 μl of acceptor beads (PY20 coated beads (Perkin Elmer Life Science) final concentration 10 μg/ml) in stop buffer The samples were incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and the signal per well was read on AlphaQuest or Envision reader (Perkin Elmer Life Science) Phosphorylated substrate results in binding of the PY20 antibody and association of the donor and acceptor beads such that signal correlates w ith kinase activity The signal vs compound concentration was used to determine the IC5Q
[0527] The c-kit enzyme used in the above assay was cither optained from Cell Signaling Technology (Cat #7754) or was prepared as follows A plasmid encoding kit (DNA and encoded
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 protein sequences shown below) was engineered using common polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods Complementary DN A. cloned from various human tissues were purchased from Invitrogen, and these were used as substrates in the PCR reactions Specific custom synthetic oligonucleotide primers were designed to initiate the PCR product, and also to provide the appropπate restnction enzyme cleavage sites for ligation with the plasmids The entire sequence encoding the enzyme was made through a gene synthesis procedure, using custom synthetic oligonucleotides covering the entire coding sequence (Invitrogen, see below)
[0528] The plasmid used for ligation with the kinase-encodmg inserts was denvatrve of pET (Novagen) for expression using E coli The Kit kinase was engineered to include a Histidine tag for purification using metal affinity chromatography 1 he kinase-encoding plasmid was engineered as bicistromc mRNA to co-express a second protein that modifies the kinase protein during its expression in the host cell Protein tyrosine phosphatase IB (PTP), was co-expressed for dephosphorylation of the phospho-Tjrosines
[0529] For protein expression, the plasmid containing the Kit gene was transformed into E coli strains BL21 (DE3)RIL and transformants selected for growth on LB agar plates containing appropriate antibiotics Single colonies were grown overnight at 370C in 200ml TB (Terrific broth) media 16x1 L of fresh TB media in 2 8L flasks were inoculated with 10ml of overnight culture and grown with constant shaking at 370C Once cultures reached an absorbance of 1 0 at 600nm, IPTG was added and cultures were allowed to grow for a further 12 to 18hrs at temperatures ranging from 12-300C Cells were harvested by centπfugation and pellets frozen at 800C until ready for lysis
[0530] For protein Purification, frozen E coli cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer and lysed using standard mechanical methods Protein was purified via poly-Histidine tags using immobilized metal affinity purification IMAC The Kit kinase was purified using a 3 step purification process utilizing, IMAC, size exclusion chromatography and ion exchange chromatography The poly- Histidine tag was removed using Thrombin (Calbiochem)
[0531] Compounds were assayed using a similar assay to that described above, using in a final reaction volume of 25 μl c-Kit (h) (5-10 mU) in 8mM MOPS pH 7 0, 0 2 mM EDTA, 10 mM MnCL, 0 1 mg'ml poly (GIu, Tyr) 4 1 , 10 mM MgAcetate and γ- 13P-ATP (approximately 500 cpm/pmol), with appropriate concentrations ot compound Incubated for 40 minutes at room temperature and stopped by addition of 5 μl of 3% phosphonc acid Spotted 10 μl of each sample onto Filtermat A and washed 3x with 75 mM phosphoric acid, once with methanol, dried and measured on scintillation counter (performed at Upstate USA, Charlottesville, VA)
Kit
Atty.Dkt.No.: 039363-3303
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
P1332.N6 BI PTP KIT M552-K948-X COD
(Nucleic Acid SEQ ID NO:_ ) (Protein SEQ ID NO:_ )
taatacgactcactataggggaattgtgagcggataacaattcccctctagaaataattt tgtttaactttaagaaggagatataccatgggtcaccaccatcaccatcatatgtacgaa
M G H H H H H H M Y E gttcagtggaaagttgttgaagaaatcaacggtaacaactacgtttacatcgacccgacc
V Q W K V V E E I N G N N Y V Y I D P T cagctgccgtacgaccacaaatgggagttcccgcgtaaccgtctgtctttcggtaaaacc
Q L P Y D H K W E F P R N R L S F G K T ctgggtgcgggtgcgttcggtaaagttgttgaagcgaccgcgtacggtctgatcaaatct
L G A G A F G K V V E A T A Y G L I K S gacgcggcgatgaccgttgcggttaaaatgctgaaaccgtctgcgcacctgaccgaacgt
D A A M T V A V K M L K P S A H L T E R gaagcgctgatgtctgaactgaaagttctgtcttacctgggtaaccacatgaacatcgtt
E A L M S E L K V L S Y L G N H M N I V aacctgctgggtgcgtgcaccatcggtggtccgaccctggttatcaccgaatactgctgc
N L L G A C T I G G P T L V I T E Y C C tacggtgacctgctgaacttcctgcgtcgtaaacgtgactctttcatctgctctaaacag
Y G D L L N F L R R K R D S F I C S K Q gaagaccacgcggaagcggcgctgtacaaaaacctgctgcactctaaagaatcttcttgc
E D H A E A A L Y K N L L H S K E S S C tctgactctaccaacgaatacatggacatgaaaccgggtgtttcttacgttgttccgacc
S D S T N E Y M D M K P G V S Y V V P T aaagcggacaaacgtcgttctgttcgtatcggttcttacatcgaacgtgacgttaccccg
K A D K R R S V R I G S Y I E R D V T P gcgatcatggaagacgacgaactggcgctggacctggaagacctgctgtctttctcttac
A I M E D D E L A L D L E D L L S F S Y caggttgcgaaaggtatggcgttcctggcgtctaaaaactgcatccaccgtgacctggcg
Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303
Q V A K G M A F L A S K N C I H R D L A gcgcgtaacatcctgctgacccacggtcgtatcaccaaaatctgcgacttcggtctggcg
A R N I L L T H G R I T K I C D F G L A cgtgacatcaaaaacgactctaactacgttgttaaaggtaacgcgcgtctgccggttaaa
R D I K N D S N Y V V K G N A R L P V K tggatggcgccggaatctatcttcaactgcgtttacaccttcgaatctgacgtttggtct
W M A P E S I F N C V Y T F E S D V W S tacggtatcttcctgtgggaactgttctctctgggttcttctccgtacccgggtatgccg
Y G I F L W E L F S L G S S P Y P G M P gttgactctaaattctacaaaatgatcaaagaaggtttccgtatgctgtctccggaacac
V D S K F Y K M I K E G F R M L S P E H gcgccggcggaaatgtacgacatcatgaaaacctgctgggacgcggacccgctgaaacgt
A P A E M Y D I M K T C W D A D P L K R ccgaccttcaaacagatcgttcagctgatcgaaaaacagatctctgaatctaccaaccac
P T F K Q I V Q L I E K Q I S E S T N H atctactctaacctggcgaactgctctccgaaccgtcagaaatagtcgactgaaaaagga
I Y S N L A N C S P N R Q K - agagt
Additional biochemical and cell-based assays
[0532] In general, any protein kinase assay can be adapted for use with c-kit. For example, assays (e.g. biochemical and cell-based assays) as descnbed in Lipson et al , U.S. Patent Publ.20040002534 (incorporated herein by reference in its entirety) can be used in the present invention
In vivo model system testing
[0533] For in vivo testing, a suitable animal model system can be selected for use. For example, for multiple scerosis, the rodent experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is commently used This system is well-known, and is described, for example, in Steinman, 1996, Cell 85299-302 and Secor et al., 2000, J Exp. Med 5:813-821, which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties. Similarly, other model systems can be selected and used m assessing compounds of the present invention
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 Exemplary Fms biochemical assay
[0534] IC50 values were determined with respect to inhibition of Fms kinase activity, where inhibition of phosphorylation of a peptide substrate is measured as a function of compound concentration. Compounds to be tested, dissolved in DMSO (1 μL), were added to a white 384-wcll plate (Costar #3705). Working stocks of Fms kinase (Upstate Biotech, #14-551), biotin-(E4Y)10 substrate (Upstate Biotech, Cat# 12-440), and ATP (Sigma, Cat#A-3377) were prepared in 8 niM MOPS pH 7.4, 2 mM MgCl2 8 rnM MnCl2, 2 niM DTT, and 0.01% Tween-20. All components were added to the 384-well plate for a final concentration of 0.5 ng/well Fms, 30 nM biotin-(E4Y)io (Upstate Biotechnology) and 10 μM ATP in a volume of 20 μL. Each sample was at 5% DMSO. The plate was then incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature. Just before use, working stocks of donor and acceptor beads from the AlphaScreen PY20 Detection Kit (PerkinElmer, Cat#676601M) were prepared in 8 mM MOPS, pH 7.4, 100 mM EDTA, 0.3% BSA. To stop the reaction, the plate was uncovered in the dark and 5 μl of Donor Beads solution (Streptavidin beads) was added to each well. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes. Five microliters of Acceptor Beads solution (PY20 coated beads) were then added to each well. The final concentration of each bead was 20 μg/mL. The plates were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. Fluorescence signal was recorded on the Fusion Alpha reader or AlphaQuest reader. Phosphorylated substrate results in binding of the PY20 antibody and association of the donor and acceptor beads such that signal correlates with kinase activity. The signal vs. compound concentration was used to determine the IC50.
|0535] Compounds were also tested using a similar assay with a 10-fold higher ATP concentration. Compounds to be tested, dissolved in DMSO (1 μL), were added to a white 384-well plate (Costar #3705). Working stocks of Fms kinase (Upstate Biotech, #14-551), biotin-(E4Y)!0 substrate (Upstate Biotech, Cat# 12-440), and ATP (Sigma, Cat#A-3377) were prepared in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.01% BSA, and 0.01% Tween-20. All components were added to the 384-well plate for a final concentration of 0.5 ng/well Fms, 30 nM biotin-(E4Y)]0 (Upstate Biotechnology) and 100 μM ATP in a volume of 20 μL. Each sample was at 5% DMSO. The plate was then incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Just before use, working stocks of donor and acceptor beads from the AlphaScreen PY20 Detection Kit (PerkinElmer, Cat#676601M) were prepared in 25 mM IIEPES pH 7.5, 100 mM EDTA, 0.01 % BSA. To stop the reaction, the plate was uncovered in the dark and 5 μl of Donor Beads solution (Streptavidin beads) was added to each well. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes. Five microliters of Acceptor Beads solution (PY20 coated beads) were then added to each well. The final concentration of each bead was 10 μg/mL. The plates were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. Fluorescence signal was recorded on the AlphaQuest or Envision reader. Phosphorylated substrate results in
Atty. Dkt. No.; 039363-3303 binding of the PY20 antibody and association of the donor and acceptor beads such that signal correlates with kinase activity. The signal vs. compound concentration was used to determine the IC50,
[0536] Compounds were assayed using a similar assay to that described above, using in a final reaction volume of 25 μl: Fms (h) (5-10 mU) in 8mM MOPS pH 7.0, 0.2 mM EDTA, 250 mM
KKKSPGEYVNIEFG (SEQ ID NO:_ ), 10 mM MgAcetate and 7- 33P-ATP (approximately 500 cpm/pmol), with appropriate concentrations of compound. Samples were incubated for 40 minutes at room temperature and stopped by addition of 5 μl of 3% phosphoric acid, 10 μl of each sample is spotted onto a P30 filtermat and washed 3x with 75 mM phosphoric acid, once with methanol, dried and measured on scintillation counter (Upstate USA, Charlottesville, VA).
Exemplary TrkA biochemical assay
10537] Compounds were similarly assayed to determine IC50 values with respect to inhibition of TrkA kinase activity, where inhibition of phosphorylation of a peptide substrate was measured as a function of compound concentration. Compounds tested were dissolved in DMSO (1 μL) and added to a white 384-well plate (Costar #3705). Working stocks of TrkA kinase (Upstate Biotech, #14-571), biotin-(E4Y)i0 substrate (Upstate Biotech, Cat# 12-440), and ATP (Sigma, Cat#A-3377) were prepared in 25 mM Hepes pH 7.5, 10 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 0.01 % Tween-20. All components were added to the 384-well plate for a final concentration of 1 ng/well TrkA, 30 nM biotin-(E4Y)10 (Upstate Biotechnology) and 100 μM ATP in a volume of 20 μL. Each sample was at 5% DMSO. The plate was then incubated for 40 minutes at room temperature. Just before use, working stocks of donor and acceptor beads from the AlphaScreen PY20 Detection Kit (PerkinElmer, Cat#676601M) were prepared in 25 mM Hepes pH 7.5, 100 mM EDTA, 0.3% BSA. To stop the reaction, the plate was uncovered in the dark and 5 μl of Donor Beads solution (Streptavidin beads) was added to each well. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes. Five microliters of Acceptor Beads solution (PY20 coated beads) were then added to each well. The final concentration of each bead was 10 μg/mL. The plates were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. Fluorescence signal was recorded on the AlphaQuest or Envision reader. Phosphorylated substrate results in binding of the PY20 antibody and association of the donor and acceptor beads such that signal correlates with kinase activity. The signal vs. compound concentration was used to determine the IC50.
Exemplary HGK biochemical assay
|0538] The MΛP4K4 (or kinase domain thereof) is an active kinase in AlphaScreen. IC50 values are determined with respect to inhibition of MAP4K4 kinase activity, where inhibition of phosphorylation
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 of a peptide substrate is measured as a function of compound concentration. Compounds to be tested were dissolved in DMSO to a concentration of 20 mM. These were diluted 30 μl into 120 μl of DMSO (4 mM) and 1 μl was added to an assay plate. These were then serially diluted 1 :3 (50 μl to 100 μl DMSO) for a total of 8 points. Plates were prepared such that each kinase reaction is 20 μl in Ix kinase buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, ImM DTT, 0.01% Twccn-20), 5% DMSO and 10 μM ATP. Substrate was 10 nM biotin-ERM (T567/T564/T558, Cell Signaling, Inc., cat#1344). MAP4K4 kinase was at 0.5 ng per sample. After incubation of the kinase reaction for 40min at room temperature, 5 μl of donor beads and protein A acceptor beads (Perkin Elmer Life Science, cat# 67606017) at final concentration 1 μg/ml in stop buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.4,20OmM Nacl, 10OmM EDTA ,0.03% BSA) was added, along with Phospho-ERM Antibody (T567/T564/T558, Cell Signaling, Inc., cat#3141) at 1 :1000 dilution. The samples were incubated for 2 hours at room temperature and the signal per well was read on AlphaQuest reader. Phosphorylated substrate results in binding of the antibody which binds to protein A acceptor bead and association of the donor and acceptor beads is such that the signal correlates with kinase activity. The signal vs. compound concentration was used to determine the IC50.
[0539] Representative compounds screened by at least one of the methods described above, or as described in US Patent Application Serial number 11/473,347 (PCT publication WO2007002433), or by similar methods, having IC50 of less than 10 μM under the test conditions employed are shown in tables 2a (B-Raf), 2b (B-Raf V600E), 2c (B-Raf V600E/T529I), 2d (Btk), 2e (c-Raf-1), 2f (Fak), 2g (FGFRl), 2h (FItI), 2i (Fms), 2j (Jnkl), 2k (Kdr), 21 (Kit), 2m (Met), 2n (p38), 2o (Src), 2p (TrkA), and 2q (HGK).
Table 2a, Compounds with activity toward kinase B-Raf with ICso≤ 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
B-Raf P-1247, P-1453, P-1454, P-1455, P-1467, P-1532, P-1544, P-1568, P-] 569, P-1584, P-1597, P-1613, P-1616, P-1721, P-1768, P-1769, P-1802, P-1825, P-2100, P-2144, P-2145, P-2151 , P-2164, P-2165, P-2170, P-2173, P-2185, P-2186
Table 2b. Compounds with activity toward kinase B-Raf V600E with ICso£ 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
B-Raf P-1247, P-1449, P-1450, P-1453, P-1454, P-1455, P-1462, P-1466, P-1467, P-1470, V600E P-1471, P-1531 , P-1 532, P-1544, P-1568, P-1569, P-1578, P-1579, P-1584, P-1597, P-1613, P-1698, P-1721 , P-1768, P-1769, P-1797, P-1802, P-2100, P-2164, P-2165, P-2185, P-2186
Table 2c. Compounds with activity toward kinase B-Raf V600E/T529I with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
B-Raf P-2151, P-2152, P-2154, P-2156, P-2166
V600E/
T529I
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Table 2d. Compounds with activity toward kinase Btk with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Btk: P-2140, P-2143, P-2144, P-2145, P-2161, P-2162, P-2163, P-2164
Table 2e. Compounds with activity toward kinase c-Raf-1 with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed. c-Raf-1 : P-1247, P-1453, P-1454, P-1455, P-2107, P-2143, P-2155, P-2185
Table 2f. Compounds with activity toward kinase Fak with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Fak: P-1247, P-1449, P-1450, P-1453, P-1455, P-2181
Table 2g. Compounds with activity toward kinase FGFR with ICs0^ 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
FGFR: P-1249, P-1453, P-1454, P-1455, P-1467, P-1584, P-1597, P-2155, P-2157, P-2159, P-2160
Table 2h. Compounds with activity toward kinase Fltl with IC505 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Fltl: P-1247, P-1462, P-1467, P-1531, P-1532, P-1544, P-1569, P-1584, P-1597, P-1613,
P-2101, P-2107, P-2108, P-2109, P-2117, P-2145, P-2146, P-2149, P-2151 , P-2154,
P-2161 , P-2164, P-2165, P-2170, P-2185
Table 2i. Compounds with activity toward kinase Fms with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
2113, P-2114, P-2125,
Table 2j Compounds with activity toward kinase Jnkl with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Jnkl : P-1896. P-1897
Table 2k. Compounds with activity toward kinase Kdr with IC50 ≤ 10 μM under the test conditions employed. P-2145, P-2146, P-2156, P-2157, P-2166, P-2167,
Table 21. Compounds with activity toward kinase Kit with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Kit: P-1247, P-1449, P-1450. P-1453, P-1454, P-1455, P-1462, P-1466, P-1467, P-1470, P-1471, P-1531, P-1532, P-1544, P-1568, P-1569, P-1578, P-2100, P-2101, P-2105, P-2106, P-2107, P-2108, P-2109, P-21 10, P-21 11 , P-2112, P-21 14, P-2117, P-2120, P-2130, P-2137, P-2139, P-2140, P-2145, P-2146, P-2148, P-2149, P-2151 , P-2156, P-2157, P-2158, P-2159, P-2160, P-2161, P-2162, P-2163, P-2164, P-2165, P-2167, P-2172, P-2173, P-2174, P-2176, P-2178, P-2180, P-2184, P-2185
Table 2m. Compounds with activity toward kinase Met with IC51) < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Table 2n. Compounds with activity toward kinase p38 with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed. p38: P-2167
Table 2o. Compounds with activity toward kinase Src with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Src: P-1247, P-2108, P-2109, P-21 17, P-2145, P-2151
Table 2p. Compounds with activity toward kinase TrkA with IC50 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
TrkA: ] P-1844, P-1885, P-1976, P-1978, P-2038, P-2099, P-2100, P-2101 , P-2103, P-2104, P-2106, P-2107, P-2108, P-2109, P-2110, P-211 1 , P-21 12, P-2114, P-21 15, P-21 16, , P-21 17, P-2145, P-2146, P-2170, P-2171, P-2172, P-2173, P-2174, P-2175, P-2176, P-2178, P-2179, P-2180, P-2181, P-2182, P-2185, P-2186
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Tabic 2q, Compounds with activity toward kinase HGK with ICS0 < 10 μM under the test conditions employed.
Example 55: Efficacy of Compounds in Combination with Standard-of-Care Chemotherapeutic agents in four human cancer cell lines.
[0540] Compounds of the invention, such as compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, in combination with a standard chemotherapeutic agent, such as 5-fluorouracil, carboplatin, dacarbazine, gefitinib, oxaliplatin, paclitaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, or vinblastine, can be assessed for their effectiveness in killing human tumor cells. Human tumor cell lines, such as A- 375 (malignant melanoma), SK-MEL-2 (malignant melanoma, skin metastasis), COLO 205 (colorectal adenocarcinoma, ascites metastasis) or SW-620 (colorectal adenocarcinoma, lymph node metastasis) can be treated with a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, alone, or in combination with one of the above-mentioned chemotherapeutic agents.
[0541] Tumor cells are grown as a monolayer at 37 0C in a humidified atmosphere (5% CO2, 95% air). Cells are grown in a suitable culture medium, e.g. RPMl 1640 (Ref BE12-702F, Cambrex, Verviers, Belgium) containing 2 mM L-glutamine and supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Ref DE 14-80 IE, Cambrex). For experimental use, the tumor cells are detached from the culture flask by a 5-minute treatment with trypsin-versene (Ref 02-007E, Cambrex), diluted in Hanks' medium without calcium or magnesium (Ref BE10-543F, Cambrex). Trypsin treatment is neutralized by culture medium addition. The cells arc counted in a hemocytometer and their viability assessed by 0.25% trypan blue exclusion.
[0542] The cell lines are checked for mycoplasma contamination with the Mycotect assay kit (Ref 15672-017, Invitrogen, Cergy-Pontoise, France) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. The mycoplasma test is assayed from the culture supernatants of the cell lines and compared to negative and positive controls.
[0543] The tumor cells (10,000 per well) are plated in 96-well flat-bottom microtitration plates (Ref 055260, Nunc, Dutscher, Brumath, France) and incubated at 37 0C for 24 hours before treatment in 100 μl of drug-free culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS. In order to assess the IC50 of each compound to be used for each cell line, the tumor cells are incubated in a 200 μl final volume of RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS and containing either a compound of Formula I, Formula II,
Atty. Dkt. No - 039363-3303
Formula III, or Formula IV, or one of 5-fluorouracil, carboplatm, dacarbazine, gefitimb, oxahplatin, pachtaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, or vinblastine The compounds are tested in a suitable concentration range, such as 10 8 to 10 3 M for a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, 5-fluorouracil, dacarbazine or gefitimb, 10 9 to 104 M for carboplatm, oxahplatin, or temozolomide, 10 " to 10 6 M for pachtaxel or SN-38, and 10 1S to 10 10 M for vinblastine Compounds of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, are dissolved in DMSO and diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations 5-fluorouracil (50 mg/ml, Dakota Pharm, LePlessis Robmson, France), carboplatm (10 mg/ml, A.guettant, Lyon, France), and pachtaxel (6 mg/ml, Bristol-Myers Squibb SpA, Rueil Malmaison, France), are diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations Dacarbazine (Sigma, Saint Quentin Fallavier, France) and vinblastine (Lilly France S A , Saint Cloud, France) are dissolved in NaCl 0 9% and diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations Gefitimb is dissolved in a mixed solution of RPMI 1640 and DMSO and diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations (maximum final DMSO of 0 1% v/v) SN- 38 (LKT Laboratories, lnc , St Paul, Minnesota) is dissolved in DMSO and diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations (maximum final DMSO of 0 1 % v/v) Temozolomide (LKT Laboratories, lnc , St Paul, Minnesota) is dissolved in water for injection and diluted with culture medium to the desired concentrations Cells are incubated for 96 hours in the presence of test substances at 37 0C under 5% CO2 At the end of treatments, the cytotoxic activity is evaluated by an MTl assay
[0544] For the MTT assay, at the end of the cells treatment, 20 μl of a 5 mg/ml solution 0 22 μm filtered tetrazohum reagent (MTT, Ref M2128, Sigma) in Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS, Ref BF17-517Q, Cambrex), is added in each well Culture plates are incubated for 2 h at 37 0C The resulting supernatant is removed and formazan crystals dissolved with 200 μl of DMSO per well Absorbency (OD) is measured at 570 nm in each well using VICTOR1™ 1420 multilabeled counter (Wallac, PerkinElmer, Courtaboeuf, France).
[0545] The IC50 for each compound on each cell line is determined from the OD measurements of each sample The dose response inhibition of cell proliferation is expressed as
IC = (OD of drug exposed cells / OD of drug free wells) x 100
The mean of multiple measurements for each concentration is plotted vs the drug concentration The dose-response curves are plotted using XLF it 3 (IDBS, United Kingdom) The IC50 (drag concentration to obtain 50% inhibition of cell proliferation) determination values are calculated using the XLF it 3 from semi-log curves The IC50 value determined for each compound in each cell line is
Atty. Dkt. No. : 039363-3303 used to determine the concentration of a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, and of the standard chemotherapeutic to be used in combination.
[0546] The cells are treated with a combination of five concentrations of a compound of Formula I, Formula II, Formula III, or Formula IV, and five concentrations ot one of 5-fluorouracil, carboplatm, dacarbazine, gefitinib, oxaliplatm, paclitaxel, SN-38, temozolomide, or vinblastine, based on the IC^o results. The compounds and cells are treated per the IC50 determination described above and assayed by the MTT assay.
[0547] The results are assessed to determine whether the combination is synergistic or antagonistic. The compound interactions are calculated by multiple drug effect analysis and are perfoπned by the median equation principle according to the methodology described by Chou and Talalay (Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1984, 22: 27-55).
[0548] The combination index (CI) will be calculated by the Chou et al. equation (Adv En/yme Regul 1984, 22: 27-55 ; Encyclopaedia of human biology, Academic Press, 1991, 2 371-9: Synergism and Antagonism in Chemotherapy, Academic Press, 1991 , 61-102) which takes into account both the potency (D111 or IC50) and the shape of the dose-effect curve (the m value). The general equation for the CI of the two compounds is given by:
CI = (£>)l i (D)- i (jP)' (Z^ (£>,), (Dt)2 (Z)J1 (D.), where
(Dx) i and (Dx)2 in the denominators are the doses (or concentrations) for compound 1 and compound 2 alone which demonstrate x% of inhibition, whereas (D) j and (D)2 in the numerators are doses of both compounds (1 and 2) in combination that also inhibit x% (iso-effective). CI<1, =1, and >1 indicate synergism, additive effect and antagonism, respectively.
[0549] The (Dx)] and (Dx)2 can be calculated from the median-effect equation of Chou et al (J, Natl. Cancer Inst. 1994, 86 1517-24):
Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
D1n is the median-effect dose that is oblamed from the anti-log of x-intercept of the median-effect plot, x - log(D) versus y = log {/7(1 -/J}, or Dn, = 10 (> maL'rt) m, and m is the slope of the median-effect plot and /a is the fraction of cells affected by the treatment
Each CI will be calculated with CalcuSyn software (Biosoft, UK) from the mean affected fraction at each drug ratio concentration
[0550] Additional examples of certain methods contemplated by the present invention may be found in the following applications U S Patent Pub 1 No 2006/058339, App Ser No 11/154,287, U S Patent Publ No 2006/058340, App Ser No 11/154,988, U S Prov App No 60/682,076, filed May 17, 2005, U S Prov App No 60/682,058, filed May 17, 2005, U S Prov App No 60/682,063, filed May 17, 2005, U S Prov App No 60/682,051, filed May 17, 2005, U S Prov App No 60/682,042, filed May 17, 2005, U S Prov App No 60/692,750, filed June 22, 2005, and U S Prov App No 60/692,960, filed June 22, 2005, U S Pro\ App No 60/731,528, filed October 28, 2005, U S Patent App No 1 1/435,381 , filed May 16, 2006, and U S Patent App No 11/473,347, filed June 21, 2006, each of which are hereby incorporated by reference herein in their entireties including all specifications, figures, and tables, and for all purposes
[0551] All patents and other references cited in the specification are indicative oi the level of skill of those skilled in the art to which the invention pertains, and arc incorporated by reference in their entireties, including any tables and figures, to the same extent as if each reference had been incorporated by reference in its entirety individually
[0552] One skilled in the art would readily appreciate that the present invention is well adapted to obtain the ends and advantages mentioned, as well as those inherent therein The methods vaπances, and compositions described herein as presently representative of preferred embodiments are exemplary and are not intended as limitations on the scope of the invention Changes therein and other uses will occur to those skilled in the art which are encompassed within the spirit of the invention, are defined by the scope of the claims
[0553] It will be readily apparent to one skilled in the art that varying substitutions and modifications may be made to the invention disclosed herein without departing from the scope and spirit of the invention
Atty Dkt. No : 039363-3303
[0554] The invention illustratively descnbed herein suitably may be practiced in the absence ot any element or elements, limitation or limitations w hich is not specifically disclosed herein Thus, for example, in each instance herein any of the terms "comprising", "consisting essentially of and "consisting of may be replaced with either of the other two teπns Thus, for an embodiment of the in\ention using one of the teπns, the πrvention also includes another embodiment wherein one of these terms is replaced with another of these terms In each embodiment, the terms have their established meaning Thus, for example, one embodiment may encompass a method "comprising'" a series of steps, another embodiment would encompass a method "consisting essentially of the same steps and a third embodiment would encompass a method "consisting of the same steps The terms and expressions which have been employed are used as terms of description and not of limitation, and there is no intention that m the use of such terms and expressions of excluding any equivalents of the features shown and descnbed or portions thereof, but it is recognized that various modifications are possible within the scope of the invention claimed 1 hus, it should be understood that although the present invention has been specifically disclosed by preferred embodiments and optional features, modification and variation of the concepts herein disclosed may be resorted to by those skilled in the art, and that such modifications and variations are considered to be within the scope of this invention as defined by the appended claims
[0555] In addition, where features or aspects of the invention are described in terms of Markush groups or other grouping of alternatives, those skilled in the art will recognize that the invention is also thereby descnbed in terms of any individual member or subgroup of members of the Markush group or other group
[0556] Also, unless indicated to the contrary, where various numerical values are provided for embodiments, additional embodiments are described by taking any 2 different values as the endpoints of a range Such ranges are also within the scope of the descnbed invention
[0557] Thus, additional embodiments are within the scope of the invention and withm the following claims
Claims
1. A compound having the chemical structure of Formula II,
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein t is O, 1, 2, or 3, Z2 is N or CR12, Z6 is N or CR16, L4 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR10R1 ' VNR^-(CR10R1 V>
-(CR10R11VX-(CR10R1V, -(CR10R' 1^-C(X)-(CR10R11),-, -(CR10R11^-S(O)-(CR10R11V, -(CR10R11VS(O)2-(CR10R1 1V -(CR1V 1)p-C(X)NR25-(CR10R")q-,
-(CR10R11VS(O)2NR25-(CR10Ru)q-, -(CR10R11VNR25C(X)-(CR10R11V. -(CR10R11VNR25S(O)2-(CR10R11),,-, -(CRl0R11)p-NR2'C(X)NR25-(CR10R11)q-, and -(CR10R11)p-NR2SS(O)2NR25-(CR10R11)q-, p and q are independently 0, 1, or 2 provided, however, that at least one of p and q is 0;
R is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO2, -CR11R11R26, and -LR26,
R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl;
A is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -CRaRh-, -NR1-, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, and -S(O)2-;
Ra and Rb at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NR15R9, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, Atty. Dkt. No. 039363-3303 mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, or
Ra and Rb combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -C(O)R7, -C(S)R7, -S(O)2R7, -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7, and -S(O)2NHR7, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R^, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, further provided that when R1 is lower alkyl, any substitution on the lower alkyl carbon bound to the N of -NR1- is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R*, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to the N of -C(O)NHR", -C(S)NHR7 or -S(O)2NHR7 is fluoro, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group Atty Dkt No • 039363-3303 consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2. lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo, each of R , R5, R6, R1*, R13, and R16, are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO2, -CRaRbR26, and -LR26,
L at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -(alk)a-X-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)d-C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)d-S(O)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-OC(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)O-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2NR2S-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a -NR25S(O)2 -(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)O-(alk)h-, -(alk)a-OC(X)NR2S-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)NR95-(alk)b-, and -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2NR2'-(alk)b-, a and b are independently 0 or 1 , alk at each occurrence is independently C] 3 alkylene or Ci ^ alkylene substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, wherein lower alkyl or the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo or di-alkylammo are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, X at each occurrence is independently O or S; R25 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl, R26 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, provided, however, that hydrogen is not bound to any of S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, provided, however, that when R26 is optionally substituted lower alkenyl, no alkene carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, provided, however, that when R h is optionally substituted lower alkynyl, no alkyne carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl, Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
R10 and R11 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH,, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio mono-alky lammo di- alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, or any two of R10 and R1 1 on the same or adjacent carbon atoms combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, and any others of R10 and R11 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, and wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino,
R8 and R9 combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, and fluoro substituted lower alkylthio,
Rr IS selected from the group consisting of hydrogen halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl and -OR18, and
R18 is hydrogen or optionally substituted lower alkyl, provided, however, that the compound is
2. The compound of Claim 1, having the chemical structure of Formula Ha,
A1 is -O-, -CR4UR" '-, -C(O)- or -NR48-;
L3 is selected from the group consisting of -NR4 -, -S-, -O-, -NR48ClI(R4")-, -SCH(R4>, -OCH(R49)-, -C(O)NR48-, -S(O)2NR48-, -CH(R49)NR48-, -CH(R49)O-, -CH(R49)S-, -NR48C(O)-, and -NR48S(O)2-;
R40 and R41 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino; or
R40 and R41 combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic Atty Dkt No. 039363-3303 hctcrocycloalkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted low er alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, R61 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, or fluoro substituted lower alkyl,
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R'7 -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR'7, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR4V7, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R101,
R101 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R5", -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH7, -OR57, -SR5", -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R", cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein c>cloalk>l, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R101, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino,
R53 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of low er alkoxy is fluoro, R52 and R56 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R57 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, Atty Dkt No • 039363-3303 fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alk>lthio, mono- alkylammo, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR5", -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R3", or -S(O)2NR48R57 is fluoro, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R57 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR38, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)^NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino,
R58 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, or -S(O)2NR48R58 is fluoro, and wherein heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy,
R48 at each occurrence is independently hydrogen or lower alkyl;
R49 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and
t is O, 1, 2, or 3
3. The compound of Claim 2 wherein A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-
4. The compound of Claim 3 wherein L3 is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCII(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-
5. The compound of Claim 4 wherein R5λ and R5S are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy
6. The compound of Claim 5, wherein
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R5', halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R130 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -ORS8. -SR58, -NHR5S, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R53, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino.
7. The compound of Claim 6 wherein A| is -CH2-,
8. The compound of Claim 7 wherein L3 is -OCH(R49)-.
9. The compound of Claim 8 wherein:
Z12 is CR52;
Z16 is CR56;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl. fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and
R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2,
-S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
10. The compound of claim 9. wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-fluoro-phenoxymethyl]-l H- benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-l H- benzoimidazole,
2-[2.5-Difluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-l H- benzoimidazole, 2-[3,5-Difluoro-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimidazole, Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
2-[5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmcthyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[5-Chloro-4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-3,5-difluoro-phcnoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yliτiethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymetliyl]-l -methyl-
1 H-benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl)-2,5-difluoro-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2- {2,5-Difluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzoimidazole,
2- {5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-l H-pyrτolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzoimidazole,
2- { 1 -[4-(5-Chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3 -ylmethyl)-5 -fluoro-2-m ethoxy-phenoxy] -ethyl} - IH- benzoimidazole,
6-Chloro-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-
1 H-benzoimidazole,
6-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[5-Fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-6-methoxy-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[5-Chloro-2-fluoro-4-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimiddzole,
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-fluoro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-(5 -methoxy- 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndm-3 -ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl] - 1 H- ben7oimidazole,
2-{2-Chloro-5-fluoro-4-[5-(l-methyl-l H-pyra/ol-4-yl)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl]- phenoxymethyl}-lH-benzoimidazole,
2-{4-[(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-yl)-methoxy-methyl]-5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl } - 1 H-benzoimidazole,
[4-( 1 H-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-phenyl]-(5 -chloro- 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 - b]pyridm-3-yl)-methanone,
2-[2,5-Difluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-lH-pyiτolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-i-nethoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridme-5- Atty. Dkt No : 039363-3303 carbonitnle,
5,6-Dichloro-2-[4-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmcthyl)-5-fIuoro-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-benzoimida7ole,
2-[4-(5-Cliloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-bJpyπdm-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethylJ-lH- benzoimidazole-5-sulfonic acid dimethylamide,
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimida7ol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme-5- carboxylic acid methyl ester,
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-benzyl]-lH-pyπ-olo[2,3-b]pyτidine-5- carboxylic acid,
2-{2,5-DifIuoro-4-[5-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridm-3-ylmethyl]-phenoxymethyl}-
1 H-benzoimidazole, 2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmcthyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-l -ethyl- lH-benzoimida7ole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]ρyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-5- tπfluoromethyl- 1 H-benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-5-fIuoro-
1 H-benzoimidazole,
2-{2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-rπethoxy-phenoxyJ-cthyl}-lH- benzoimidazole,
244-(5-Bromo-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethyl]-lH- benzoimidazole,
2-[4-(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndm-3-ylmethyl)-5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenoxymethylJ-5- methoxy- 1 H-benzoimidazole,
5-Chloro-2-[5-fluoro-2-methoxy-4-(5-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-phenoxymethyl]-
1 H-bcnzoimidazole,
3-[4-(lH-Benzoimidazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2,5-difIuoro-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdme-5- cdrbonitπle,
2-[5-Fluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy- phenoxymethyl]-lH-ben7oimidazole, and all salts, prodrugs, tautomcrs, and isomers thereof Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
11. A compound having the chemical structure of Formula III,
Z4 is N or CR14;
Z5 is N or CR15;
Z6 is N or CR16;
L4 is selected from the group consisting of -(CR R")P-NR -(CR1 R )q->
-(CR10R1 VX-(CR10R1 V, -(CR10R1VC(XMCR10R1V, -(CR1V)P-S(O)-(CR10R11),,-, -(CR10R1 1VS(O)2-(CR10R1V -(CR10R1 VC(X)NR25-(CR'°R' V -(CR10R11)p-S(O)2NR25-(CR10R11)q-) -(CR10R11VNR25C(X)-(CR10R1V -(CR10R11VNR25S(O)2-(CR10R11V, -(CR10R1 ' VNR25C(X)NR2^(CR10R1 V and
-(CR'"R")P-NR/DS(O)2NR" -(CR'"Ru)q-, p and q are independently 0, 1, or 2 provided, however, that at least one of p and q is 0,
A is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -CRaRh-, -NR1-, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, and -S(O)2-;
Rd and Rb at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHi, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, or
R8 and Rb combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylamino; Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -C(O)R7, -C(S)R7, -S(O)2R7, -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7, and -S(O)2NHR7, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, further provided that when R1 is lower alkyl, any substitution on the lower alkyl carbon bound to the N of -NR1- is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R9, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to the N of -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7 or -S(O)2NHR" is fluoro, wherein the alkyl cham(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, each of R4, R5, R6, R14, RH, and R16, are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO2, -CRdRbR26, and -LR:e; Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
L at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -(alk)a-X-(alk)b-, -(alk),-NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk),-S(O)-(alk)b-, -(alk).-S(O),-(alk)b-. -(alk)a-OC(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk),-C(X)O-(alk)h-) -(alk)a-C(X)NR75-(alk)b-) -(aIk)a-S(O)2NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR2<;C(X)O-(alk)b-( -(alk)a-OC(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)NR2:ι-(alk)b-, and -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2NR2S-(alk)b-, a and b are independently 0 or 1 , alk at each occurrence is independently Cj i alkylene or Ci 3 alkylene substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R", wherein lower alkyl or the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylarmno or di-alkylammo are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, X at each occurrence is independently O or S, R25 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl, R26 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, provided, however, that hydrogen is not bound to any of S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of I , optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, provided, however, that when R26 is optionally substituted lower alkenyl, no alkene carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, provided, however, that when R26 is optionally substituted lower alkynyl, no alkyne carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl, R10 and R1 1 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted low er alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di- alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, or any two of R10 and R1 1 on the same or adjacent carbon atoms combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, and any others of R10 and R1 1 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally subslituted with one or more substituents selected from the group Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo, and wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2 lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio. fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo,
R8 and R9 combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, and fluoro substituted lower alkylthio,
R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl and -OR18, and
R18 is hydrogen or optionally substituted lower alkyl,
R80 is Ci 3 alkyl or C3 5 cycloalkyl, wherein C] 3 alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C3 5 cycloalkyl, and
R8' is selected from the group consisting ot optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted hcteroaryl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, C2 4 alkyl, fluoro substituted C2 4 alkyl, and -(CH2CH2O)1nR7', m is 1 , 2, or 3, and
R7' Is C] 3 alkyl or fluoro substituted C1 3 alkyl, provided, however, that the compound is not
12. The compound of Claim 11 having the chemical structure of Formula Ilia, all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein:
A) is -O-, -CR4UR4 '-, -C(O)- or -NR" -; Z14 is N or CR54;
Z15 is N or CR I5555;;
Z16 Is N Or CR1 ;
Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalkyl; Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
L3a is selected from the group consisting of -NR48-, -S-, -O-, -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, -OCII(R49)-, -C(O)NR*-, -S(O)2NR48-, -CH(R49)NR4\ -CH(R49)O-. -CH(R49)S-. -NR48C(O)-, and -NR18S(O)2-, Rω is C, 3 alkyl or C3 5 cycloalkyl, wherein C1 3 alky] is optionally substituted v» ith one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and C3 5 cycloalkyl, R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH1, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R5", -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48Rr, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted w ith one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocyclodlkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R101,
R!01 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR43R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R101, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino,
R54 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy. lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino or cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro, R56 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, R57 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
Ωuoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R", or -S(O)2NR48R57 is fluoro, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R57 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino;
R58 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, thai any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, or -S(O)2NR48R58 is fluoro, and wherein heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy;
R48 at each occurrence is independently hydrogen or lower alkyl;
R49 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl; and t is O, 1, 2, or 3.
13. The compound of Claim 12 wherein A1 is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-.
14. The compound of Claim 13 wherein LJa is -NR48CH(R49)-, -SCH(R49)-, or -OCH(R49)-.
15. The compound of Claim 14 wherein RS4 and R55 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
16. The compound of Claim 15, wherein:
Rlϋϋ is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)RS7, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH1 -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NHR58, -NR4SR5S, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino.
17. The compound of Claim 16, wherein A) is -C(O)-.
18. The compound of claim 17 wherein L3, is -OCH(R49)-.
19. The compound of claim 18 wherein: Z14 is CR54;
Z15 is CR55;
Z16 Js CR56;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and
R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2,
-S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
20. The compound of claim 11, wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
[3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2-difluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyi-idin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(2, 5 -Dimethyl -2H~pyrazol-3 -ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl] -( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyridin-3 -yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidiπ-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-moφholin-4-yl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[3 -(2,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl] -( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(4-imidazol-l-yl-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(2,4-Difluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
{2-Ethoxy-3-[l -(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-phenyl}-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(l ,5-Dimcthyl-lH-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(l-pyridin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyπOlo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-((R)-l -pyridin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2,4,6-trifluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
{3-[l-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-2-ethoxy-phenyl}-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyπ-olo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4-dimethyl-thiazol-5- ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanone,
(5-Ch]oro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4,6-trifluoro-benzyloxy)- phenyl] -methanone,
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(6-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3- ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanone,
[3-(6-Diethylammo-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-pyrrolidin-l-yl-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone, and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof. Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
21. A compound having the chemical structure of Formula IHc,
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein: A1 is -O-, -CR40R41-, -C(O)- or -NR48-;
64.
Z24 is N or CR
Z25 is N or CR65;
Z25 is N or CR66;
Cy is selected from the group consisting of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycloalkyl;
R80 is Cu alkyl or C3^5 cycloalkyl, wherein Ci-3 alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and Cv, cycloalkyl;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents R10 ;
R101 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R101, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, Atty. Dkt. No,: 039363-3303
-S(O)R5*, -S(O)2R'8, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino;
R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro; R57 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of iluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, or -S(O)2NR48R57 is fluoro, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R57 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR'8, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R'18, -S(O)2NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylamino,
R58 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to O, S, or N of -OR58, -SR58, -NR48R58, -C(O)OR58, -C(O)NR48R58, or -S(O)2NR48R58 is fluoro, and wherein heterocycloalkyl and heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen. -CN, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy; R48 at each occurrence is independently hydrogen or lower alkyl; R49 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, and fluoro substituted lower alkyl; r is O, 1 or 2; and t is O, 1 , 2, or 3, provided, however, that the compound is not Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
22. The compound of Claim 21 wherein A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-.
23. The compound of Claim 22 wherein R64, R65 and R66 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
24. The compound of claim 23 wherein: Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR", -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR4SR'7, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and hetcroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NII2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR5S, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R38, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkyl amino.
25. The compound of claim 24 wherein:
Z24 is CR64;
Z25 is CR65;
Z2, is CR66;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OII, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58; and
R101 is selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -C(O)NH2,
-S(O)2NH2-, C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
26. The compound of claim 21, wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
[3-(4-Chloro-benzyloxy)-2-(2-fluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone, [3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-(2,2-difluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lII-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-cyclopropylmethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone, Atty, Dkt No., 039363-3303
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2-pyrrolidin-l-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-methyl-pyridm-2-ylmethoxy)-phcnyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methaπone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(2,4-Dimethyl-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrro]o[2,3-bJpyridiii-3-yl)-methanoπe,
[3-(2.5-Dimethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-pheπyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3 -(2-fluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl] -( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3 -yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-morpholm-4-yl-pyπdin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(6-tnf]uoromethyl-pyπdin-3-ylmethoxy)-phenylJ-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone,
[3-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(4-imidazol-l -yl-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(2,4-Difluoro-ben7yloxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
{2-Ethoxy-3 -[ 1 -(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethoxy]-phenyl } -( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyπdm-3 -yl)-methanone,
[3-(l,5-Dimethyl-lH-pyrazol-3-ylmcthoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3 -( 1 -pyridin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyndin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-((R)-l -pyridm-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3-(2,4,6-tπfluoro-benzyloxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyπOlo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone,
{3-[ 1 -(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ethoxy] -2-ethoxy-phenyl } -( 1 H-pyrrolo [2,3 -b]pyridm-3-yl)-methanone,
[3-(4-Chloro-2-fluoro-ben7yloxy)-2-(2,2,2-tnfluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)- methanone,
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdm-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4-dimethyl-thiazol-5- ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanone,
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]ρyridin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(2,4,6-tπfluoro-benzyloxy)- phenyl] -methanone,
(5-Chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)-[2-cyclopropylmethoxy-3-(6-tπfluoromethyl-pyπdin-3- ylmethoxy)-phenyl] -methanone,
[3-(6-Diethylamino-pyridin-3-ylmethoxy)-2-ethoxy-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Ethoxy-3 -(6-pyrrolidin- 1 -yl-pyπdm-3 -ylmethoxy)-phenyl]-( 1 H-pyrrolo[2,3 -b]pyridin-3 -yl)- methanone, and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof. Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
27. Acompound having the chemical structure of Formula IV
all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof, wherein Z2 ih N or CRπ, Z4 is N or CR14, Z5 is N or CR15, Z6 is N or CR16, A is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -CR"Rb-, -NR1-, -C(O)-, -C(S)-, -S(O)-, and
-S(O)2-
Ra and R at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHn, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, or
R3 and Rb combine to form a 3-7 mcmbered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-dlkylamino, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo,
R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -C(O)R7, -C(S)R7, -S(O)2R7, -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7, and -S(O)2NHR7, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-dlkylammo, di-alkylamino, and -NR8R9, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NHi, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, further provided that when R1 is lower alkyl, any substitution on the lower alkyl carbon bound to the N of -NR!- is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, hetcrocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
R7 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and -NR8Rg, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl carbon bound to the N of -C(O)NHR7, -C(S)NHR7 or -S(O)2NHR7 is fluoro, wherein the alkyl chain(s) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NIL, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylamino is fluoro, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl arc optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino; each of R4, Rs, R6, R12, R14, R15, and R16, are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, -CN, -NO2, -CRaRbR26, and -LR26;
L at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of -(alk)a-X-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-OC(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)O-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-C(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-S(O)2NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)O-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-OC(X)NR25-(alk)b-, -(alk)a-NR25C(X)NR25-(alk)b-, and -(alk)a-NR25S(O)2NR25-(alk)b-; Atty Dkt No 039363-3303 a and b are independently 0 or 1 , alk at each occurrence is independently Ci 3 alkylene or Cj 3 alkylene substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylammo, and -NR8R9, wherein lower alkyl or the alkyl chain(s>) of lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino or di-alkylamino are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH7, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo and cycloalkylammo, provided, however, that any substitution of the alkyl chain carbon bound to O of alkoxy, S of thioalkyl or N of mono- or di-alkylammo is fluoro,
X at each occurrence is independently O or S,
R25 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl,
R26 at each occurrence is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, provided, however, that hydrogen is not bound to any of S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkyl, optionally substituted lower alkenyl, provided, however, that when R26 is optionally substituted lower alkenyl, no alkene carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted lower alkynyl, provided, however, that when R26 is optionally substituted lower alkynyl, no alkyne carbon thereof is bound to N, S, O, S(O), S(O)2, C(O) or C(S) of L, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted heterocycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl,
R10 and R11 at each occurrence are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di- alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, or any two of R10 and R1' on the same or adjacent carbon atoms combine to form a 3-7 membered monocyclic cycloalkyl or 5-7 membered monocyclic heterocycloalkyl, and any others of Rlϋ and Ru are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen fluoro, lower alkyl, and lower alkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted low er alkylthio, mono-alkylammo, di-alkylammo, and cycloalkylammo, and wherein the monocyclic cycloalkyl or monocyclic heterocycloalkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl lower alkoxy, fluoro Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303 substituted lower alkoxy, tower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino, and cycloalkylamino;
R8 and R9 combine with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a 5-7 membered heterocycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, and fluoro substituted lower alkylthio;
R17 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, optionally substituted lower alkyl and -OR18; and
R18 is hydrogen or optionally substituted lower alkyl;
R90 is C2-t alkyl, fluoro substituted C2.4 alkyl, or -(CH2CH2O)1nR91; m is 1, 2, or 3; and
R1" is C i_3 alkyl or fluoro substituted C1.3 alkyl, provided, however, the compound is not
Atty. Dkt. No.: 039363-3303
28. The compound of Claim 27 having the chemical structure of Formula IVb,
A1 is -O-, -CR40R41-, -C(O)- or -NR48-;
Z32 is N or CR72;
Z34 is N or CR74;
Z35 is N or CR75;
Z36 is N or CR76;
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O)2NH2, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R57, -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R57, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, C(O)OII, -C(O)NH2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl as R100, or as substituents of lower alkyl, are optionally substituted with one or more independent substituents Rι n ι;
R72, R74, R75, and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl and lower alkoxy, wherein the alkyl chain of lower alkyl or lower alkoxy is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, -OH, -NH2, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono-alkylamino, di-alkylamino and cycloalkylamino, provided, however, that any substitution on the alkyl carbon bound to the -O- of lower alkoxy is fluoro; R'n is C2-4 alkyl, fluoro substituted C1A alkyl, or -(CH2CH2O)111R91; m is 1 , 2, or 3; and R91 is Cj.3 alkyl or fluoro substituted Cu alkyl.
29. The compound of Claim 28 wherein A, is -CR40R41- or -C(O)-. Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
30. The compound of Claim 29 wherein R72, R74, R7S and R76 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, and fluoro substituted lower alkoxy.
31. The compound of claim 30 wherein*
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -C(O)OH, -S(O),NH,, -C(O)NII2, -OR57, -SR57, -NR48R57, -NR48C(O)R57, -NR48S(O)2R57, -S(O)R", -S(O)2R57, -C(O)R57, -C(O)OR57, -C(O)NR48R57, -S(O)2NR48R^, halogen, lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein lower alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro, lower alkoxy, fluoro substituted lower alkoxy, lower alkylthio, fluoro substituted lower alkylthio, mono- alkylamino, di-alkylammo, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, and wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl as R100 or as substituents of lower alkyl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of -OH, -NH2, -CN, -NO2, -S(O)2NII2, -C(O)NH2, -OR58, -SR5S, -NHR58, -NR48R58, -NR48C(O)R58, -NR48S(O)2R58, -S(O)2R58, -S(O)2NR48R58, -C(O)R58, -C(O)NR48R58, halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, and cycloalkylammo.
32. The compound of claim 31 wherein:
Z12 is CR72;
Z14 is CR74;
Z35 is CR75,
Z36 is CR76, and
R100 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, -CN, -C(O)OH, -C(O)OR57, -NR48R57, -OR57, -S(O)2R57, fluoro, chloro, bromo, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl, wherein cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl are optionally substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of halogen, lower alkyl, fluoro substituted lower alkyl, -NR48R58, -OR58 and -S(O)2R58.
33. The compound of claim 27, wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine, [2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-ρhenyl]-(5-methoxy-l H-pyrrolof2,3-b]p>τidin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2,2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)-methanone, [2,6-Dichloro-3-(2>2,2-tπfluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-[5-(l -methyl-lH-pyrazol-4-yl)-l H-pyrrolo[2,3- b]pyridm-3-yl]-methanone, Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
3-[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-tnfluoro-ethoxy)-benzyl]-5-mcthoxy-lH-ρyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine,
[2,6-Dichloro-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-methoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridiπ-3-yl)- methanone,
5-Chloro-3-[2-chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-ben7yl]-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyndiπe,
3-[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-benzyl]-l H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdine,
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(5-chloro-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyπdin-3-yl)- methanone,
[2-Chloro-6-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyτidin-3-yl)-methanone, and all salts, prodrugs, tautomers, and isomers thereof
34. A composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and a compound according to any of Claims 1-33
35. A method for treating a subject suffering from or at risk of a c-frns, c-kit, HGK, TrkA, and/or TrkB mediated disease or condition, comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound of any of Claims 1-33, or a composition of Claim 34
36. The method of Claim 35, wherein the disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma m situ, Schwann cell neoplasia associated with neurofibromatosis, Wilms tumor, acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, multiple myeloma, mastocytosis, melanoma, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, canme mast cell tumors, myelofibrosis, metastasis of cancer to bone or other tissues, hypertrophy, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant rejection, systemic lupus erythematosis, psoriasis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, atherosclerosis, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, hyperglycemia, obesity, lipolysis, hypereosmophiha, osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture, Paget's disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen-prosthetic or wear-debπs-mediated osteolysis, endometriosis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis, tubular necrosis, diabetic nephropathy, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, neuropathic pam, chronic pain and bone pam Atty Dkt No 039363-3303
37. A kit comprising a compound according to any of Claims 1-33 or a composition according to Claim 34
38. The kit of Claim 37, wherein the compound or composition is approved for a medical indication selected from the group consisting of mast cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, glioblastoma, astrocytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinomas of the female genital tract, sarcomas of neuroectodermal origin, colorectal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, Schwann cell neoplasm associated with neurofibromatosis, Wilms tumor, acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, multiple myeloma, mastocytosis, melanoma, breast cancer, ovaπan cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, canine mast cell tumors, myelofibrosis, metastasis of cancer to bone or other tissues, hypertrophy, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, allergic rhinitis, multiple sclerosis, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, transplant rejection, systemic lupus erythematosa, psoriasis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome (macrophage activation syndrome), multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, atherosclerosis, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, hyperglycemia, obesity, lipolysis, hypereosmophilia, osteoporosis, increased πsk of fracture, Paget's disease, hypercalcemia, infection-mediated osteolysis (e g osteomyelitis), pen-prosthetic or wear-debns- mediated osteolysis, endometriosis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, Lupus nephritis, tubular necrosis, diabetic nephropathy, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pam, neuropathic pam, chronic pam, and bone pain
39. A method for treating a subject suffering from or at πsk of a c-fms mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Kawasaki's Disease, hemophagocytic syndrome, multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, obesity, Paget's disease, osteomyelitis, peπ- prosthetic or wcar-debπs-mediated osteolysis, endometriosis, diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pam, bone pain, prostate cancer, melanoma, glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis of tumors to tissues other than bone, and myelofibrosis comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound of any of Formulae I, Ia, Ib, Ic, Id, Ie, If, Ig, Ih or Ii
40. The method of Claim 39, wherein the c-fms mediated disease or condition selected from the group consisting of inflammatory bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, Paget's disease, diabetic nephropathy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, inflammatory pain, chronic pam, bone pain, prostate cancer, and metastasis of tumors to tissues other than bone
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US87705206P | 2006-12-21 | 2006-12-21 | |
| US60/877,052 | 2006-12-21 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2008080015A2 true WO2008080015A2 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| WO2008080015A3 WO2008080015A3 (en) | 2008-10-02 |
Family
ID=39129228
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2007/088412 WO2008080001A2 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2007-12-20 | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| PCT/US2007/088443 WO2008080015A2 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2007-12-20 | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2007/088412 WO2008080001A2 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2007-12-20 | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
Country Status (12)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7872018B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2094701A2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2010514695A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101641351A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2007336811A1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0720695A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2673736A1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL199278A0 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2009006688A (en) |
| NO (1) | NO20092612L (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2009122670A (en) |
| WO (2) | WO2008080001A2 (en) |
Cited By (75)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011136319A1 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2011-11-03 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | Anticancer agent |
| WO2011143645A1 (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2011-11-17 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| WO2012137089A1 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo [2, 3 -d] pyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of tropomyosin- related kinases |
| JP2013511541A (en) * | 2009-11-18 | 2013-04-04 | プレキシコン インコーポレーテッド | Compounds and methods for kinase regulation and indications thereof |
| WO2013150416A1 (en) | 2012-04-06 | 2013-10-10 | Pfizer Inc. | Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 inhibitors |
| US8592448B2 (en) | 2008-11-20 | 2013-11-26 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-b]-pyridines and -pyrazines |
| JP2013543883A (en) * | 2010-11-29 | 2013-12-09 | アステックス、セラピューティックス、リミテッド | Substituted benzopyrazine derivatives as FGFR kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer diseases |
| WO2014053968A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2014053965A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2014053967A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| US8710043B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2014-04-29 | Amgen Inc. | TRPM8 antagonists and their use in treatments |
| US8778941B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2014-07-15 | Amgen Inc. | TRPM8 antagonists and their use in treatments |
| US8952009B2 (en) | 2012-08-06 | 2015-02-10 | Amgen Inc. | Chroman derivatives as TRPM8 inhibitors |
| WO2015092610A1 (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2015-06-25 | Pfizer Limited | N-acylpiperidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2015159175A1 (en) | 2014-04-15 | 2015-10-22 | Pfizer Inc. | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors containing both a 1h-pyrazole and a pyrimidine moiety |
| WO2015170218A1 (en) | 2014-05-07 | 2015-11-12 | Pfizer Inc. | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2016009296A1 (en) | 2014-07-16 | 2016-01-21 | Pfizer Inc. | N-acylpiperidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2016020784A1 (en) | 2014-08-05 | 2016-02-11 | Pfizer Inc. | N-acylpyrrolidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| AU2010343102B2 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2016-03-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II Raf kinase inhibitors |
| US9303029B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-05 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted quinoxalines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US9303030B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2016-04-05 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Compounds |
| US9309242B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-12 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US9309241B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-12 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Naphthyridine derivative compounds |
| US9439896B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-09-13 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinolines as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US9447098B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2016-09-20 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pteridines as FGFR inhibitors |
| US9464071B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2016-10-11 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pyrazolyl quinoxaline kinase inhibitors |
| US9493426B2 (en) | 2013-04-26 | 2016-11-15 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Quinazolinone derivatives useful as FGFR kinase modulators |
| WO2017011776A1 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2017-01-19 | Array Biopharma, Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US9758522B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2017-09-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| WO2017176744A1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2017-10-12 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| WO2017176751A1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2017-10-12 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Liquid formulations of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide |
| US9862688B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-01-09 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US9902714B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2018-02-27 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinoxaline derivatives useful as FGFR kinase modulators |
| WO2018071454A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Andrews Steven W | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| WO2018071447A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Andrews Steven W | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10000483B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2018-06-19 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Bone marrow on X chromosome kinase (BMX) inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US10017477B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-07-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| WO2018136661A1 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2018-07-26 | Andrews Steven W | SUBSTITUTED PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRAZINE COMPOUNDS AS RET KINASE INHIBITORS |
| WO2018136663A1 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2018-07-26 | Array Biopharma, Inc. | Ret inhibitors |
| US10045991B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2018-08-14 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| WO2018170381A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Andrews Steven W | Macrocyclic compounds as ros1 kinase inhibitors |
| US10087191B2 (en) | 2015-06-16 | 2018-10-02 | Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd. | Piperidine derivative and preparation method and pharmaceutical use thereof |
| US10085982B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2018-10-02 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combinations |
| US10112927B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2018-10-30 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10144730B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2018-12-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US10251889B2 (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2019-04-09 | Array BioPharm Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as Trk kinase inhibitors |
| WO2019075114A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Mark Reynolds | Formulations comprising 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazab icyclo[3.1.1]heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile |
| WO2019075108A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Metcalf Andrew T | Crystalline forms |
| US10281388B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-05-07 | Ducom Instruments Pvt. Ltd. | Tester to estimate co-efficient of friction and determine properties of a sample lubricant |
| WO2019143977A1 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| WO2019143994A1 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolyl[4,3-c]pyridinecompounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10478494B2 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2019-11-19 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | FGFR/PD-1 combination therapy for the treatment of cancer |
| US10550121B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2020-02-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| WO2020028258A1 (en) | 2018-07-31 | 2020-02-06 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Spray-dried dispersions and formulations of (s)-5-amino-3-(4-((5-fluoro-2-methoxybenzamido)methyl)phenyl)-1-(1,1,1-trifluoro propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrazole-4-carboxamide |
| WO2020055672A1 (en) | 2018-09-10 | 2020-03-19 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Fused heterocyclic compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| WO2020131674A1 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | 7-((3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)amino)quinoxaline derivatives as fgfr inhibitors for treating cancer |
| WO2020131627A1 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as inhibitors of fgfr tyrosine kinases |
| US10702527B2 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2020-07-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Combination therapy of transcription inhibitors and kinase inhibitors |
| US10724102B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2020-07-28 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Point mutations in TRK inhibitor-resistant cancer and methods relating to the same |
| US10736900B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2020-08-11 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combinations of an FGFR inhibitor and an IGF1R inhibitor |
| US10870651B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2020-12-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10898482B2 (en) | 2015-02-10 | 2021-01-26 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N'-1 methylethyl)-N-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine |
| US10906889B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-02-02 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Polycyclic inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US11040957B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-06-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Heteroaromatic compounds useful for the treatment of proliferative diseases |
| WO2021134004A1 (en) | 2019-12-27 | 2021-07-01 | Schrodinger, Inc. | Cyclic compounds and methods of using same |
| WO2021144360A1 (en) | 2020-01-17 | 2021-07-22 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Small molecule csf-1r inhibitors in therapeutic and cosmetic uses |
| US11091486B2 (en) | 2016-10-26 | 2021-08-17 | Array Biopharma, Inc | Process for the preparation of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines and salts thereof |
| US11142507B2 (en) | 2015-09-09 | 2021-10-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US11155555B2 (en) | 2015-09-23 | 2021-10-26 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Compounds |
| US11214571B2 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2022-01-04 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Process for the preparation of (S)-N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide and salts thereof |
| WO2022055963A1 (en) | 2020-09-10 | 2022-03-17 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Heterocyclic pericondensed cdc7 kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer |
| WO2022164789A1 (en) | 2021-01-26 | 2022-08-04 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Tricyclic compounds useful in the treatment of cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disoders |
| WO2022197898A1 (en) | 2021-03-18 | 2022-09-22 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Cyclic compounds and methods of using same |
| US11524963B2 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2022-12-13 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US11542247B2 (en) | 2015-09-23 | 2023-01-03 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Bi-heteroaryl substitute 1,4-benzodiazepines and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer |
Families Citing this family (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008063888A2 (en) | 2006-11-22 | 2008-05-29 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Compounds modulating c-fms and/or c-kit activity and uses therefor |
| BRPI0814423B1 (en) | 2007-07-17 | 2022-04-19 | Plexxikon, Inc | Kinase modulating compounds and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same |
| WO2009099982A1 (en) * | 2008-02-04 | 2009-08-13 | Osi Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2-aminopyridine kinase inhibitors |
| AR070317A1 (en) * | 2008-02-06 | 2010-03-31 | Osi Pharm Inc | FURO (3,2-C) PIRIDINE AND HAVING (3,2-C) PIRIDINES |
| US20110003859A1 (en) * | 2008-02-29 | 2011-01-06 | Array Biopharma Inc. | N- (6-aminopyridin-3-yl) -3- (sulfonamido) benzamide derivatives as b-raf inhibitors for the treatment of cancer |
| US20110003809A1 (en) * | 2008-02-29 | 2011-01-06 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Imidazo [4,5-b] pyridine derivatives used as raf inhibitors |
| CA2716951A1 (en) * | 2008-02-29 | 2009-09-11 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Raf inhibitor compounds and methods of use thereof |
| JP2011513331A (en) * | 2008-02-29 | 2011-04-28 | アレイ バイオファーマ、インコーポレイテッド | Pyrazole [3,4-b] pyridine RAF inhibitor |
| WO2009143018A2 (en) | 2008-05-19 | 2009-11-26 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| BR112012012156A2 (en) * | 2009-11-06 | 2015-09-08 | Plexxikon Inc | compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications for this |
| BR112012015745A2 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2016-05-17 | Plexxikon Inc | compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications thereof |
| TWI619713B (en) | 2010-04-21 | 2018-04-01 | 普雷辛肯公司 | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| JP2013526570A (en) | 2010-05-14 | 2013-06-24 | オーエスアイ・ファーマシューティカルズ,エルエルシー | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitor |
| BR112013020041B1 (en) | 2011-02-07 | 2021-11-23 | Plexxikon, Inc | COMPOUNDS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR THE MODULATION OF KINASES AND THEIR USE |
| WO2012158658A1 (en) | 2011-05-16 | 2012-11-22 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| BR112013029163A2 (en) | 2011-05-17 | 2017-01-31 | Plexxikon Inc | kinase modulation and indications thereof |
| MX353190B (en) * | 2012-01-30 | 2018-01-05 | F Hoffmann La Roche Ag Star | Isoquinoline and naphthyridine derivatives. |
| US9358235B2 (en) | 2012-03-19 | 2016-06-07 | Plexxikon Inc. | Kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| KR20150020228A (en) | 2012-05-31 | 2015-02-25 | 에프. 호프만-라 로슈 아게 | Aminoquinazoline and pyridopyrimidine derivatives |
| EP2892534B8 (en) | 2012-09-06 | 2021-09-15 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| CN105712992B (en) * | 2012-09-29 | 2018-10-26 | 上海科州药物研发有限公司 | Compound and its preparation method and application as cMet inhibitor |
| SG11201504754QA (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2015-07-30 | Plexxikon Inc | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| PL2970265T3 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2018-11-30 | Plexxikon Inc. | Heterocyclic compounds and uses thereof |
| US20140303121A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-10-09 | Plexxikon Inc. | Heterocyclic compounds and uses thereof |
| EP3004060B1 (en) | 2013-05-30 | 2019-11-27 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| WO2015134536A1 (en) | 2014-03-04 | 2015-09-11 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| WO2016030534A1 (en) | 2014-08-29 | 2016-03-03 | Tes Pharma S.R.L. | INHIBITORS OF α-AMINO-β-CARBOXYMUCONIC ACID SEMIALDEHYDE DECARBOXYLASE |
| ES2774177T3 (en) | 2014-09-15 | 2020-07-17 | Plexxikon Inc | Heterocyclic compounds and uses of these |
| US10160755B2 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2018-12-25 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| US11274108B2 (en) * | 2015-07-20 | 2022-03-15 | Genzyme Corporation | Colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) inhibitors |
| US10829484B2 (en) | 2015-07-28 | 2020-11-10 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| CA2999253C (en) | 2015-09-21 | 2021-10-26 | Plexxikon Inc. | Heterocyclic compounds and uses thereof |
| WO2017100201A1 (en) | 2015-12-07 | 2017-06-15 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| US10160747B2 (en) | 2016-03-16 | 2018-12-25 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| TW201815766A (en) | 2016-09-22 | 2018-05-01 | 美商普雷辛肯公司 | Compounds and methods for IDO and TDO modulation, and indications therefor |
| JP7193460B2 (en) | 2016-12-23 | 2022-12-20 | プレキシコン インコーポレーテッド | Compounds and methods for CDK8 modulation and indications thereof |
| ES2896502T3 (en) | 2017-03-20 | 2022-02-24 | Plexxikon Inc | Crystal forms of 4-(1-(1,1-di(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl)-6-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin acid -3- yl)benzoic that inhibit the bromodomain |
| WO2018226846A1 (en) | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-13 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation |
| CA3070505C (en) | 2017-07-25 | 2023-09-26 | Plexxikon Inc. | Formulations of a compound modulating kinases |
| CA3079029A1 (en) | 2017-10-13 | 2019-04-18 | Plexxikon Inc. | Solid forms of a compound for modulating kinases |
| TWI803530B (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2023-06-01 | 美商普雷辛肯公司 | Formulations of a compound modulating kinases |
| CA3094336A1 (en) | 2018-03-20 | 2019-09-26 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for ido and tdo modulation, and indications therefor |
| US20210253571A1 (en) * | 2018-07-19 | 2021-08-19 | Medshine Discovery Inc. | Azaindole derivative and use thereof as fgfr and c-met inhibitor |
| EP4089094A4 (en) | 2020-01-10 | 2023-08-02 | Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. | Tricyclic tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative, preparation method therefor and application thereof in medicine |
| CN115052877B (en) * | 2020-01-15 | 2023-08-22 | 无锡瓴方生物医药科技有限公司 | Crystal form of azaindole derivative and application thereof |
| US11691963B2 (en) | 2020-05-06 | 2023-07-04 | Ajax Therapeutics, Inc. | 6-heteroaryloxy benzimidazoles and azabenzimidazoles as JAK2 inhibitors |
| TW202227437A (en) * | 2020-11-17 | 2022-07-16 | 大陸商重慶復創醫藥研究有限公司 | Substituted pyrrolo [2, 3-b] pyridine and pyrazolo [3,4-b] pyridine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors |
| JP2024500919A (en) | 2020-12-23 | 2024-01-10 | ジェンザイム・コーポレーション | Deuterated colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) inhibitor |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2005062795A2 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-14 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Compounds and methods for development of ret modulators |
| WO2006009797A1 (en) * | 2004-06-17 | 2006-01-26 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Azaindoles modulating c-kit activity and uses therefor |
| WO2006015123A1 (en) * | 2004-07-27 | 2006-02-09 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| WO2006114180A1 (en) * | 2005-04-25 | 2006-11-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Novel aza- heterocycles serving as kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007002325A1 (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2007-01-04 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007013896A2 (en) * | 2005-05-17 | 2007-02-01 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrol (2,3-b) pyridine derivatives protein kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007106236A2 (en) * | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-20 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
Family Cites Families (107)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2234705A (en) | 1940-04-12 | 1941-03-11 | Eastman Kodak Co | Cellulose organic derivative composition containing esters of monoalkoxy benzoic acids |
| US2413258A (en) | 1942-07-07 | 1946-12-24 | United Gas Improvement Co | Polystyrene-type resins plasticized with high boiling fatty acid alkyl esters |
| DE2413258A1 (en) | 1974-03-20 | 1975-10-02 | Bayer Ag | Herbicidal N-(alkoxycarbonyl-phenyl)-N'-methyl-urea derivs - prepd by reacting alkoxycarbonyl-phenyl isocyanates with methylamines |
| GB1573212A (en) | 1976-04-15 | 1980-08-20 | Technicon Instr | Immunoassay for gentamicin |
| US4664504A (en) | 1983-01-20 | 1987-05-12 | Tokyo Shibaura Denki Kabushiki Kaisha | Image forming apparatus |
| US4568649A (en) | 1983-02-22 | 1986-02-04 | Immunex Corporation | Immediate ligand detection assay |
| US4626513A (en) | 1983-11-10 | 1986-12-02 | Massachusetts General Hospital | Method and apparatus for ligand detection |
| EP0154734B1 (en) | 1984-03-15 | 1990-08-29 | Immunex Corporation | Immediate ligand detection assay, a test kit and its formation |
| US5688655A (en) | 1988-02-10 | 1997-11-18 | Ict Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method of screening for protein inhibitors and activators |
| US5700637A (en) | 1988-05-03 | 1997-12-23 | Isis Innovation Limited | Apparatus and method for analyzing polynucleotide sequences and method of generating oligonucleotide arrays |
| US6054270A (en) | 1988-05-03 | 2000-04-25 | Oxford Gene Technology Limited | Analying polynucleotide sequences |
| US5658775A (en) | 1988-05-17 | 1997-08-19 | Sloan-Kettering Institute For Cancer Research | Double copy retroviral vector |
| EP0432216A1 (en) | 1988-09-01 | 1991-06-19 | Whitehead Institute For Biomedical Research | Recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges |
| US5703055A (en) | 1989-03-21 | 1997-12-30 | Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation | Generation of antibodies through lipid mediated DNA delivery |
| US5527681A (en) | 1989-06-07 | 1996-06-18 | Affymax Technologies N.V. | Immobilized molecular synthesis of systematically substituted compounds |
| US5143854A (en) | 1989-06-07 | 1992-09-01 | Affymax Technologies N.V. | Large scale photolithographic solid phase synthesis of polypeptides and receptor binding screening thereof |
| US5744101A (en) | 1989-06-07 | 1998-04-28 | Affymax Technologies N.V. | Photolabile nucleoside protecting groups |
| US5800992A (en) | 1989-06-07 | 1998-09-01 | Fodor; Stephen P.A. | Method of detecting nucleic acids |
| AU7906691A (en) | 1990-05-23 | 1991-12-10 | United States of America, as represented by the Secretary, U.S. Department of Commerce, The | Adeno-associated virus (aav)-based eucaryotic vectors |
| DE4022414A1 (en) | 1990-07-13 | 1992-01-16 | Bayer Ag | SUBSTITUTED PYRROLO-PYRIDINE |
| WO1993002556A1 (en) | 1991-07-26 | 1993-02-18 | University Of Rochester | Cancer therapy utilizing malignant cells |
| US5632957A (en) | 1993-11-01 | 1997-05-27 | Nanogen | Molecular biological diagnostic systems including electrodes |
| FR2687402B1 (en) | 1992-02-14 | 1995-06-30 | Lipha | NOVEL AZAINDOLES, METHODS OF PREPARATION AND MEDICAMENTS CONTAINING THEM. |
| JPH05236997A (en) | 1992-02-28 | 1993-09-17 | Hitachi Ltd | Chip for catching polynucleotide |
| NZ261593A (en) | 1993-03-01 | 1996-09-25 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | 3-piperazinylmethly-1h-indolopyridine derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions |
| US5700809A (en) | 1993-03-01 | 1997-12-23 | Merck Sharp & Dohme, Ltd. | Pyrrolo-pyridine derivatives |
| US5576319A (en) | 1993-03-01 | 1996-11-19 | Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd. | Pyrrolo-pyridine derivatives |
| AU686186B2 (en) | 1993-05-27 | 1998-02-05 | Aventisub Ii Inc. | Topologically segregated, encoded solid phase libraries |
| US5840485A (en) | 1993-05-27 | 1998-11-24 | Selectide Corporation | Topologically segregated, encoded solid phase libraries |
| US5631236A (en) | 1993-08-26 | 1997-05-20 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Gene therapy for solid tumors, using a DNA sequence encoding HSV-Tk or VZV-Tk |
| US5426039A (en) | 1993-09-08 | 1995-06-20 | Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. | Direct molecular cloning of primer extended DNA containing an alkane diol |
| US6045996A (en) | 1993-10-26 | 2000-04-04 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Hybridization assays on oligonucleotide arrays |
| US5965452A (en) | 1996-07-09 | 1999-10-12 | Nanogen, Inc. | Multiplexed active biologic array |
| US6468742B2 (en) | 1993-11-01 | 2002-10-22 | Nanogen, Inc. | Methods for determination of single nucleic acid polymorphisms using bioelectronic microchip |
| US5807522A (en) | 1994-06-17 | 1998-09-15 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Methods for fabricating microarrays of biological samples |
| US5763198A (en) | 1994-07-22 | 1998-06-09 | Sugen, Inc. | Screening assays for compounds |
| GB9416162D0 (en) | 1994-08-10 | 1994-09-28 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Therapeutic agents |
| GB9416189D0 (en) | 1994-08-10 | 1994-09-28 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Therapeutic agents |
| US5556752A (en) | 1994-10-24 | 1996-09-17 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Surface-bound, unimolecular, double-stranded DNA |
| US5830645A (en) | 1994-12-09 | 1998-11-03 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Comparative fluorescence hybridization to nucleic acid arrays |
| GB2298199A (en) | 1995-02-21 | 1996-08-28 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Synthesis of azaindoles |
| GB9503400D0 (en) | 1995-02-21 | 1995-04-12 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Therpeutic agents |
| US5959098A (en) | 1996-04-17 | 1999-09-28 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Substrate preparation process |
| US6117681A (en) | 1995-03-29 | 2000-09-12 | Bavarian Nordic Research Inst. A/S | Pseudotyped retroviral particles |
| GB2299581A (en) | 1995-04-07 | 1996-10-09 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | 3-(Tetrahydropyridin-1-yl-methyl)pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives as ligands for dopamine receptor subtypes |
| GB9507291D0 (en) | 1995-04-07 | 1995-05-31 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Therapeutic agents |
| US6110456A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2000-08-29 | Yale University | Oral delivery or adeno-associated viral vectors |
| US5856174A (en) | 1995-06-29 | 1999-01-05 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device |
| US5866411A (en) | 1995-09-08 | 1999-02-02 | Pedersen; Finn Skou | Retroviral vector, a replication system for said vector and avian or mammalian cells transfected with said vector |
| US5747276A (en) | 1995-09-15 | 1998-05-05 | The Scripps Research Institute | Screening methods for the identification of novel antibiotics |
| US5721118A (en) | 1995-10-31 | 1998-02-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California, San Diego | Mammalian artificial chromosomes and methods of using same |
| US6022963A (en) | 1995-12-15 | 2000-02-08 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Synthesis of oligonucleotide arrays using photocleavable protecting groups |
| US6013440A (en) | 1996-03-11 | 2000-01-11 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Nucleic acid affinity columns |
| US6025155A (en) | 1996-04-10 | 2000-02-15 | Chromos Molecular Systems, Inc. | Artificial chromosomes, uses thereof and methods for preparing artificial chromosomes |
| US5804585A (en) | 1996-04-15 | 1998-09-08 | Texas Biotechnology Corporation | Thieno-pyridine sulfonamides derivatives thereof and related compounds that modulate the activity of endothelin |
| US6294330B1 (en) | 1997-01-31 | 2001-09-25 | Odyssey Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Protein fragment complementation assays for the detection of biological or drug interactions |
| US6243980B1 (en) | 1997-03-07 | 2001-06-12 | Tropix, Inc. | Protease inhibitor assay |
| US5977131A (en) | 1997-04-09 | 1999-11-02 | Pfizer Inc. | Azaindole-ethylamine derivatives as nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding agents |
| US6096718A (en) | 1997-06-05 | 2000-08-01 | Gene Targeting Corp. | Tissue specific adenovirus vectors for breast cancer treatment |
| US6235769B1 (en) | 1997-07-03 | 2001-05-22 | Sugen, Inc. | Methods of preventing and treating neurological disorders with compounds that modulate the function of the C-RET receptor protein tyrosine kinase |
| US6826296B2 (en) | 1997-07-25 | 2004-11-30 | Affymetrix, Inc. | Method and system for providing a probe array chip design database |
| US6161776A (en) | 1997-08-12 | 2000-12-19 | Nibco Inc. | Multi-layered, porous mat turf irrigation apparatus and method |
| ES2260157T3 (en) | 1997-09-11 | 2006-11-01 | Bioventures, Inc., | METHOD TO BE HIGH DENSITY DEVICES. |
| US6178384B1 (en) | 1997-09-29 | 2001-01-23 | The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York | Method and apparatus for selecting a molecule based on conformational free energy |
| US6465178B2 (en) | 1997-09-30 | 2002-10-15 | Surmodics, Inc. | Target molecule attachment to surfaces |
| US6048695A (en) | 1998-05-04 | 2000-04-11 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Chemically modified nucleic acids and methods for coupling nucleic acids to solid support |
| EP1085846A2 (en) | 1998-06-08 | 2001-03-28 | Advanced Medicine, Inc. | Multibinding inhibitors of microsomal triglyceride transferase protein |
| US6113913A (en) | 1998-06-26 | 2000-09-05 | Genvec, Inc. | Recombinant adenovirus |
| US6277628B1 (en) | 1998-10-02 | 2001-08-21 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Linear microarrays |
| US6277489B1 (en) | 1998-12-04 | 2001-08-21 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses |
| US6221653B1 (en) | 1999-04-27 | 2001-04-24 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Method of performing array-based hybridization assays using thermal inkjet deposition of sample fluids |
| FR2793793B1 (en) | 1999-05-19 | 2004-02-27 | Adir | NOVEL SUBSTITUTED DIMERIC DERIVATIVES, PROCESS FOR PREPARING THEM AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING SAME |
| US6653151B2 (en) | 1999-07-30 | 2003-11-25 | Large Scale Proteomics Corporation | Dry deposition of materials for microarrays using matrix displacement |
| US20010008765A1 (en) | 1999-12-06 | 2001-07-19 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | DNA chip and reactive solid carrier |
| DE60029138T2 (en) | 1999-12-22 | 2007-06-06 | Sugen, Inc., San Francisco | Use of indolinone compounds for the production of pharmaceuticals for the modulation of the function c-kit protein tyrosine kinase |
| GB0114417D0 (en) | 2001-06-13 | 2001-08-08 | Boc Group Plc | Lubricating systems for regenerative vacuum pumps |
| EP1267111A1 (en) | 2001-06-15 | 2002-12-18 | Dsm N.V. | Pressurized fluid conduit |
| US6858860B2 (en) | 2001-07-24 | 2005-02-22 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Apparatus and method for measuring natural period of liquid |
| TW200403243A (en) | 2002-07-18 | 2004-03-01 | Wyeth Corp | 1-Heterocyclylalkyl-3-sulfonylazaindole or-azaindazole derivatives as 5-hydroxytryptamine-6 ligands |
| TWI329112B (en) | 2002-07-19 | 2010-08-21 | Bristol Myers Squibb Co | Novel inhibitors of kinases |
| US6878887B2 (en) | 2002-08-07 | 2005-04-12 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Anti-malfunction mechanism for variable output device |
| SE0202463D0 (en) | 2002-08-14 | 2002-08-14 | Astrazeneca Ab | Novel compounds |
| KR20120104412A (en) | 2002-09-06 | 2012-09-20 | 인설트 테라페틱스, 인코퍼레이티드 | Cyclodextrin-based polymers for delivering the therapeutic agents covalently bound thereto |
| AU2003272548A1 (en) | 2002-09-16 | 2004-04-30 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Crystal structure of pim-1 kinase |
| US7696225B2 (en) | 2003-01-06 | 2010-04-13 | Osi Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | (2-carboxamido)(3-Amino) thiophene compounds |
| SE0300120D0 (en) | 2003-01-17 | 2003-01-17 | Astrazeneca Ab | Novel compounds |
| SE0300119D0 (en) | 2003-01-17 | 2003-01-17 | Astrazeneca Ab | Novel compounds |
| US20050085463A1 (en) | 2003-01-23 | 2005-04-21 | Weiner David M. | Use of N-desmethylclozapine to treat human neuropsychiatric disease |
| MXPA05008441A (en) | 2003-02-14 | 2005-10-19 | Wyeth Corp | Heterocyclyl-3-sulfonylazaindole or -azaindazole derivatives as 5-hydroxytryptamine-6 ligands. |
| JP2007524374A (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2007-08-30 | プレキシコン,インコーポレーテッド | PYK2 crystal structure and use |
| US20050164300A1 (en) | 2003-09-15 | 2005-07-28 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Molecular scaffolds for kinase ligand development |
| DE10357510A1 (en) | 2003-12-09 | 2005-07-07 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | Heteroaryl-substituted benzenes |
| GB0330042D0 (en) | 2003-12-24 | 2004-01-28 | Pharmacia Italia Spa | Pyrrolo [2,3-b] pyridine derivatives active as kinase inhibitors process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions them |
| GB0330043D0 (en) | 2003-12-24 | 2004-01-28 | Pharmacia Italia Spa | Pyrrolo [2,3-b] pyridine derivatives active as kinase inhibitors process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions comprising them |
| GB0403635D0 (en) | 2004-02-18 | 2004-03-24 | Devgen Nv | Pyridinocarboxamides with improved activity as kinase inhibitors |
| GB0405055D0 (en) | 2004-03-05 | 2004-04-07 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | JNK inhibitors |
| KR101298967B1 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2013-09-02 | 버텍스 파마슈티칼스 인코포레이티드 | Azaindoles useful as inhibitors of JAK and other protein kinases |
| US7498342B2 (en) | 2004-06-17 | 2009-03-03 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Compounds modulating c-kit activity |
| WO2006004984A1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-12 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Azaindoles useful as inhibitors of protein kinases |
| AU2005269387A1 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2006-02-09 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7709645B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2010-05-04 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7626021B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2009-12-01 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| MX2007014619A (en) | 2005-05-20 | 2009-02-13 | Vertex Pharma | Pyrrolopyridines useful as inhibitors of protein kinase. |
| GB0516156D0 (en) | 2005-08-05 | 2005-09-14 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | JNK inhibitors |
| PE20121126A1 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2012-08-24 | Plexxikon Inc | PIRROLO [2,3-B] PYRIDINES COMPOUNDS AS KINASE MODULATORS |
| WO2008079909A1 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2008-07-03 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrolo [2,3-b] pyridines as kinase modulators |
| CL2008001540A1 (en) | 2007-05-29 | 2009-05-22 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals Inc | Compounds derived from pyrrolopyridines and pyrazolopyridines; pharmaceutical composition; and use in the treatment of cancer. |
-
2007
- 2007-12-20 BR BRPI0720695-0A2A patent/BRPI0720695A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-12-20 EP EP07871726A patent/EP2094701A2/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-12-20 JP JP2009543230A patent/JP2010514695A/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-12-20 CN CN200780051610A patent/CN101641351A/en active Pending
- 2007-12-20 AU AU2007336811A patent/AU2007336811A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-12-20 CA CA002673736A patent/CA2673736A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-12-20 RU RU2009122670/04A patent/RU2009122670A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-12-20 US US11/962,044 patent/US7872018B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-12-20 WO PCT/US2007/088412 patent/WO2008080001A2/en active Application Filing
- 2007-12-20 WO PCT/US2007/088443 patent/WO2008080015A2/en active Application Filing
- 2007-12-20 MX MX2009006688A patent/MX2009006688A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2009
- 2009-06-10 IL IL199278A patent/IL199278A0/en unknown
- 2009-07-10 NO NO20092612A patent/NO20092612L/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2005062795A2 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-14 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Compounds and methods for development of ret modulators |
| WO2006009797A1 (en) * | 2004-06-17 | 2006-01-26 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Azaindoles modulating c-kit activity and uses therefor |
| WO2006015123A1 (en) * | 2004-07-27 | 2006-02-09 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| WO2006114180A1 (en) * | 2005-04-25 | 2006-11-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Novel aza- heterocycles serving as kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007013896A2 (en) * | 2005-05-17 | 2007-02-01 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrol (2,3-b) pyridine derivatives protein kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007002325A1 (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2007-01-04 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrolo[2,3-b] pyridine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007002433A1 (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2007-01-04 | Plexxikon, Inc. | Pyrrolo [2, 3-b] pyridine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors |
| WO2007106236A2 (en) * | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-20 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
Cited By (133)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8592448B2 (en) | 2008-11-20 | 2013-11-26 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-b]-pyridines and -pyrazines |
| US10251889B2 (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2019-04-09 | Array BioPharm Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as Trk kinase inhibitors |
| US10758542B2 (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2020-09-01 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[l,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as Trk kinase inhibitors |
| JP2013511541A (en) * | 2009-11-18 | 2013-04-04 | プレキシコン インコーポレーテッド | Compounds and methods for kinase regulation and indications thereof |
| US9617267B2 (en) | 2009-11-18 | 2017-04-11 | Plexxikon Inc. | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
| AU2016201096B2 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2017-08-31 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type ii raf kinase inhibitors |
| US11826365B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2023-11-28 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II raf kinase inhibitors |
| AU2010343102B2 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2016-03-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II Raf kinase inhibitors |
| US9358231B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2016-06-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II RAF kinase inhibitors |
| US9464071B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2016-10-11 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pyrazolyl quinoxaline kinase inhibitors |
| US9156827B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2015-10-13 | The University Of Tokyo | Anticancer agent |
| US9850228B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2017-12-26 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pyrazolyl quinoxaline kinase inhibitors |
| US10519137B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2019-12-31 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pyrazolyl quinoxaline kinase inhibitors |
| WO2011136319A1 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2011-11-03 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | Anticancer agent |
| CN102971316A (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2013-03-13 | Osi药物有限责任公司 | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| JP2013526569A (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2013-06-24 | オーエスアイ・ファーマシューティカルズ,エルエルシー | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitor |
| WO2011143645A1 (en) * | 2010-05-14 | 2011-11-17 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| US8445510B2 (en) | 2010-05-14 | 2013-05-21 | OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Fused bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| JP2013543883A (en) * | 2010-11-29 | 2013-12-09 | アステックス、セラピューティックス、リミテッド | Substituted benzopyrazine derivatives as FGFR kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer diseases |
| US9856236B2 (en) | 2010-11-29 | 2018-01-02 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted quinoxalines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US9290478B2 (en) | 2010-11-29 | 2016-03-22 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted quinoxalines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| WO2012137089A1 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo [2, 3 -d] pyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of tropomyosin- related kinases |
| US9096527B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2015-08-04 | Amgen Inc. | TRPM8 antagonists and their use in treatments |
| US8778941B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2014-07-15 | Amgen Inc. | TRPM8 antagonists and their use in treatments |
| US8710043B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2014-04-29 | Amgen Inc. | TRPM8 antagonists and their use in treatments |
| US9309242B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-12 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US9309241B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-12 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Naphthyridine derivative compounds |
| US10045982B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2018-08-14 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US9439896B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-09-13 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinolines as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US9757364B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2017-09-12 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Naphthyridine derivative compounds |
| US9303029B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-04-05 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted quinoxalines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US10039759B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2018-08-07 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinolines as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US9527844B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2016-12-27 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Naphthyridine derivative compounds |
| US10052320B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2018-08-21 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Substituted quinoxalines as FGFR kinase inhibitors |
| US10144730B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2018-12-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US10981903B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2021-04-20 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| WO2013150416A1 (en) | 2012-04-06 | 2013-10-10 | Pfizer Inc. | Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 inhibitors |
| US10272087B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2019-04-30 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pteridines as FGFR inhibitors |
| US9737544B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2017-08-22 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Compounds |
| US9447098B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2016-09-20 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pteridines as FGFR inhibitors |
| US9303030B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2016-04-05 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Compounds |
| US8952009B2 (en) | 2012-08-06 | 2015-02-10 | Amgen Inc. | Chroman derivatives as TRPM8 inhibitors |
| WO2014053967A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2014053965A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2014053968A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | Pfizer Limited | Pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| US10787436B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2020-09-29 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10112927B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2018-10-30 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US9758522B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2017-09-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| US10000483B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2018-06-19 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Bone marrow on X chromosome kinase (BMX) inhibitors and uses thereof |
| USRE48175E1 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2020-08-25 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| US9493426B2 (en) | 2013-04-26 | 2016-11-15 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Quinazolinone derivatives useful as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US10906889B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-02-02 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Polycyclic inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US11040957B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-06-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Heteroaromatic compounds useful for the treatment of proliferative diseases |
| WO2015092610A1 (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2015-06-25 | Pfizer Limited | N-acylpiperidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| US10085982B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2018-10-02 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combinations |
| US9902714B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2018-02-27 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinoxaline derivatives useful as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US10716787B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2020-07-21 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combinations |
| US10421747B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2019-09-24 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Quinoxaline derivatives useful as FGFR kinase modulators |
| US11918576B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2024-03-05 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combination of an FGFR inhibitor and a CMET inhibitor |
| US10736900B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 | 2020-08-11 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Combinations of an FGFR inhibitor and an IGF1R inhibitor |
| WO2015159175A1 (en) | 2014-04-15 | 2015-10-22 | Pfizer Inc. | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors containing both a 1h-pyrazole and a pyrimidine moiety |
| US10017477B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-07-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US9862688B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-01-09 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| WO2015170218A1 (en) | 2014-05-07 | 2015-11-12 | Pfizer Inc. | Tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2016009296A1 (en) | 2014-07-16 | 2016-01-21 | Pfizer Inc. | N-acylpiperidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| WO2016020784A1 (en) | 2014-08-05 | 2016-02-11 | Pfizer Inc. | N-acylpyrrolidine ether tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitors |
| US10870651B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2020-12-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US11684620B2 (en) | 2015-02-10 | 2023-06-27 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N′-(1-methylethyl)-N-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine |
| US10898482B2 (en) | 2015-02-10 | 2021-01-26 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N'-1 methylethyl)-N-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxalin-6-yl]ethane-1,2-diamine |
| US11325910B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2022-05-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10550121B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2020-02-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10478494B2 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2019-11-19 | Astex Therapeutics Ltd | FGFR/PD-1 combination therapy for the treatment of cancer |
| US10702527B2 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2020-07-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Combination therapy of transcription inhibitors and kinase inhibitors |
| US10087191B2 (en) | 2015-06-16 | 2018-10-02 | Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd. | Piperidine derivative and preparation method and pharmaceutical use thereof |
| US10385060B2 (en) | 2015-06-16 | 2019-08-20 | Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd. | Piperidine derivative and preparation method and pharmaceutical use thereof |
| US10174028B2 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2019-01-08 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10023570B2 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2018-07-17 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10138243B2 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2018-11-27 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| WO2017011776A1 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2017-01-19 | Array Biopharma, Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10174027B2 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2019-01-08 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US11142507B2 (en) | 2015-09-09 | 2021-10-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US11542247B2 (en) | 2015-09-23 | 2023-01-03 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Bi-heteroaryl substitute 1,4-benzodiazepines and uses thereof for the treatment of cancer |
| US11155555B2 (en) | 2015-09-23 | 2021-10-26 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Compounds |
| US10907215B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2021-02-02 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Point mutations in TRK inhibitor-resistant cancer and methods relating to the same |
| US10724102B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2020-07-28 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Point mutations in TRK inhibitor-resistant cancer and methods relating to the same |
| US10281388B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-05-07 | Ducom Instruments Pvt. Ltd. | Tester to estimate co-efficient of friction and determine properties of a sample lubricant |
| US11191766B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2021-12-07 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| US10137127B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2018-11-27 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Liquid formulations of (S)-N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide |
| US10045991B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2018-08-14 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| US10668072B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2020-06-02 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Liquid formulations of (S)-N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide |
| US11484535B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2022-11-01 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Liquid formulations of (S)-N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide |
| WO2017176751A1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2017-10-12 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Liquid formulations of (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide |
| WO2017176744A1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2017-10-12 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| US10588908B2 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2020-03-17 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Methods of treating pediatric cancers |
| US11214571B2 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2022-01-04 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Process for the preparation of (S)-N-(5-((R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide and salts thereof |
| US10441581B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2019-10-15 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10881652B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2021-01-05 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10144734B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-12-04 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10137124B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-11-27 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10112942B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-10-30 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| WO2018071454A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Andrews Steven W | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| EP3753939A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2020-12-23 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10172845B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2019-01-08 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10172851B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2019-01-08 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US11648243B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2023-05-16 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| EP4144735A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2023-03-08 | Array Biopharma, Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10953005B1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2021-03-23 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| WO2018071447A1 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Andrews Steven W | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US10555944B2 (en) | 2016-10-10 | 2020-02-11 | Eli Lilly And Company | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-A]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US11091486B2 (en) | 2016-10-26 | 2021-08-17 | Array Biopharma, Inc | Process for the preparation of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines and salts thereof |
| WO2018136661A1 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2018-07-26 | Andrews Steven W | SUBSTITUTED PYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRAZINE COMPOUNDS AS RET KINASE INHIBITORS |
| WO2018136663A1 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2018-07-26 | Array Biopharma, Inc. | Ret inhibitors |
| US11168090B2 (en) | 2017-01-18 | 2021-11-09 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrazines as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US10688100B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2020-06-23 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Macrocylic compounds as ROS1 kinase inhibitors |
| US10966985B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2021-04-06 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Macrocyclic compounds as ROS1 kinase inhibitors |
| WO2018170381A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Andrews Steven W | Macrocyclic compounds as ros1 kinase inhibitors |
| WO2019075108A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Metcalf Andrew T | Crystalline forms |
| WO2019075114A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Mark Reynolds | Formulations comprising 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazab icyclo[3.1.1]heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile |
| WO2019143977A1 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| WO2019143994A1 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2019-07-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolyl[4,3-c]pyridinecompounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US11603374B2 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2023-03-14 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US11524963B2 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2022-12-13 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as RET kinase inhibitors |
| US11472802B2 (en) | 2018-01-18 | 2022-10-18 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolyl[4,3-c]pyridine compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| WO2020028258A1 (en) | 2018-07-31 | 2020-02-06 | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | Spray-dried dispersions and formulations of (s)-5-amino-3-(4-((5-fluoro-2-methoxybenzamido)methyl)phenyl)-1-(1,1,1-trifluoro propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrazole-4-carboxamide |
| WO2020055672A1 (en) | 2018-09-10 | 2020-03-19 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Fused heterocyclic compounds as ret kinase inhibitors |
| US11964988B2 (en) | 2018-09-10 | 2024-04-23 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Fused heterocyclic compounds as RET kinase inhibitors |
| WO2020131674A1 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | 7-((3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)amino)quinoxaline derivatives as fgfr inhibitors for treating cancer |
| WO2020131627A1 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Substituted pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine compounds as inhibitors of fgfr tyrosine kinases |
| WO2021134004A1 (en) | 2019-12-27 | 2021-07-01 | Schrodinger, Inc. | Cyclic compounds and methods of using same |
| WO2021144360A1 (en) | 2020-01-17 | 2021-07-22 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Small molecule csf-1r inhibitors in therapeutic and cosmetic uses |
| WO2022055963A1 (en) | 2020-09-10 | 2022-03-17 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Heterocyclic pericondensed cdc7 kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer |
| WO2022164789A1 (en) | 2021-01-26 | 2022-08-04 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Tricyclic compounds useful in the treatment of cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disoders |
| WO2022197898A1 (en) | 2021-03-18 | 2022-09-22 | Schrödinger, Inc. | Cyclic compounds and methods of using same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CA2673736A1 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| BRPI0720695A2 (en) | 2014-02-18 |
| MX2009006688A (en) | 2009-06-30 |
| WO2008080001A2 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| WO2008080001A3 (en) | 2009-01-08 |
| CN101641351A (en) | 2010-02-03 |
| IL199278A0 (en) | 2010-03-28 |
| US20080221148A1 (en) | 2008-09-11 |
| AU2007336811A1 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| JP2010514695A (en) | 2010-05-06 |
| US7872018B2 (en) | 2011-01-18 |
| NO20092612L (en) | 2009-07-17 |
| RU2009122670A (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| WO2008080015A3 (en) | 2008-10-02 |
| EP2094701A2 (en) | 2009-09-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7872018B2 (en) | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor | |
| US7863289B2 (en) | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor | |
| US8268858B2 (en) | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor | |
| US10426760B2 (en) | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor | |
| EP1893612B1 (en) | Pyrrolo [2, 3-b]pyridine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors | |
| CA2395593C (en) | Azaindoles | |
| CA2608733A1 (en) | Pyrrol (2,3-b) pyridine derivatives protein kinase inhibitors | |
| WO2010111527A1 (en) | Pyrazolo [ 3, 4 -b] pyridines as kinase inhibitors and their medical use | |
| EP2427433A1 (en) | Solid forms of sulfonamides and amino acids | |
| JP4871474B2 (en) | Azaindole | |
| NZ613786B2 (en) | Compounds and methods for kinase modulation, and indications therefor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 07855308 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 07855308 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |