US20080098789A1 - Draw Forming Method and Device - Google Patents
Draw Forming Method and Device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20080098789A1 US20080098789A1 US11/718,052 US71805205A US2008098789A1 US 20080098789 A1 US20080098789 A1 US 20080098789A1 US 71805205 A US71805205 A US 71805205A US 2008098789 A1 US2008098789 A1 US 2008098789A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- blank material
- holder means
- blank
- holder
- region
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 22
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 169
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 62
- 230000000452 restraining effect Effects 0.000 claims description 51
- 238000010008 shearing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 10
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D22/00—Shaping without cutting, by stamping, spinning, or deep-drawing
- B21D22/02—Stamping using rigid devices or tools
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D24/00—Special deep-drawing arrangements in, or in connection with, presses
- B21D24/04—Blank holders; Mounting means therefor
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a draw forming method and device for reducing deflection created in the center of a blank material when the blank material is subjected to plastic working using a press and a metal die unit.
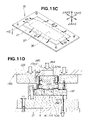
- Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open Publication No. H01-153820 proposes a draw forming method in which the periphery of a blank material is held by pressure from a blank holder, and the blank material is formed when subjected to plastic working using a metal die unit mounted on a press. This draw forming is described below with reference to FIGS. 13A through 13C hereof.
- the periphery of a blank material B is first pressed by an upper die holddown 303 of an upper die 302 and a lower die holddown 305 of a lower die 304 , and a section adjacent to the center of the blank material B is pressed by a pad 306 and a cushion 307 , as shown in FIG. 13A .
- a first draw (cylindrical section G 1 ) is formed with a punch 308 , as shown in FIG. 13B .
- a second draw (square base section G 2 ) is then formed with the cushion 307 , as shown in FIG. 13C .
- the first and second draws can thus be formed in a single step in the conventional draw forming method.
- the punch 308 is disposed on the underside of the drawing die 301
- the punch is sometimes disposed on the topside depending on the circumstances.
- the blank material B is set on the pad 306 to form draws, whereupon deflection is created in the center of the blank material B. Deflection tends to occur easily and in greater amounts particularly in cases in which the blank material is extremely thin, or in cases in which a thin blank material is hot-formed (including warm forming). As a result, there is concern that the forming dimensions will be markedly nonuniform.
- a draw forming method wherein a blank material set into a metal die unit is restrained by a blank holder and then drawn, the method comprising the steps of: setting the blank material into the metal die unit, the blank material having a stretching region and a restraint region set in the stated order outward and lined up with a drawing region that is subjected to pressure from an upper die and a lower die; restraining the restraint region of the blank material with first holder means of the blank holder; and applying tensile force to the drawing region and restraining the stretching region while second holder means of the blank holder displaces the stretching region in the shearing direction in relation to the restraint region.
- the restraint region of the blank material is restrained by the first holder means, and the stretching region of the blank material is then displaced in the shearing direction by the second holder means, whereupon tensile force is applied to the stretching region of the blank material and the drawing region in the middle, and the deflection formed in the drawing region is removed. It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in the middle of the blank material set into the metal die unit.
- a device for draw forming a blank material which device comprises: a metal die unit having an upper die and a lower die; a blank holder for restraining the blank material set in the metal die unit; and a press for applying pressure to the restrained blank material, wherein the blank holder comprises first holder means for restraining an outer peripheral section of the blank material at a first restraining position when the press is lowered; and second holder means disposed on the inside of the first holder means to restrain the inside section of the outer peripheral section of the blank material at a second restraining position when the press is further lowered.
- the press operates the first holder means, the outer peripheral section of the blank material is restrained by the first holder means, and the press is then lowered further.
- the second holder means positioned on the inside of the first holder means then stretches the middle of the blank material outward.
- the press is a double-action press
- the first restraining position is the position in which the first holder means protrudes past the second holder means and in which the blank material is held by the lowering of the double-action press
- the second restraining position is the position in which the double-action press is lowered further from the first restraining position
- the upper die is held to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means, and is disposed separate from an inner slider of the double-action press
- the first holder means and second holder means are fixed to an external slider positioned on the outside of the inner slider.
- first and second holder means are integrally fixed to the external slider of the double-action press, there is no movement between the external slider and the first and second holder means, and nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article can be reduced.
- FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a draw forming device according to a first embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 2 a flowchart showing the steps of a draw forming method according to the present invention
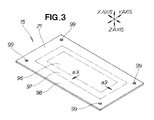
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the blank material used in the draw forming method of the invention.
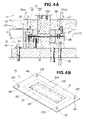
- FIGS. 4A and 4B are schematic views showing the manner in which the blank material is set on the metal die unit and restrained by first holder means in the draw forming method shown in FIG. 2 ;
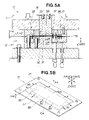
- FIGS. 5A and 5B are schematic views showing the manner in which the press is lowered to displace the stretching region of the blank material upward and to remove the deflection created in the central section of the blank material;
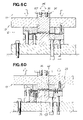
- FIGS. 6A through 6D are schematic views showing the manner in which a formed article is extracted after the formed article is obtained by drawing the central section of the blank material;
- FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the draw forming device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
- FIGS. 8A through 8D are schematic views showing an operation of the draw forming device according to the second embodiment, and also showing the manner in which the formed article is obtained by drawing after the blank is set on a metal die unit;
- FIGS. 9A and 9B are schematic views showing the manner in which the formed article is extracted
- FIG. 10 is a schematic view showing a modification of the draw forming device according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7 ;
- FIGS. 11A through 11D are schematic views showing the actions taken from the time the blank material is set until the time the blank material is drawn in the draw forming device in the modification;
- FIGS. 12A and 12B are schematic views showing the manner in which the formed article is extracted.
- FIGS. 13A through 13C are schematic cross-sectional views showing a conventional draw forming device.
- X indicates a horizontal axis in the longitudinal direction of a blank material 15
- Y indicates a horizontal axis orthogonal to X
- Z indicates a vertical axis orthogonal to both X and Y.
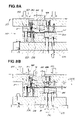
- a draw forming device 11 of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 is composed of a metal die unit 12 comprising an upper metal die unit 13 and a lower metal die unit 14 , and a blank holder 16 provided to the metal die unit 12 to apply pressure to the blank material 15 .
- the upper metal die unit 13 is mounted on a ram 18 of a press 17 .
- the lower metal die unit 14 is mounted on a bed 19 of the press 17 .
- the draw forming device 11 performs draw forming.
- the blank holder 16 includes first holder means 22 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 (restraint region 98 in FIG. 3 ) of the blank material 15 , and second holder means 23 disposed on the inside (in the direction of the arrows a 1 , a 1 ) of the first holder means 22 .
- An upper cushion mechanism 24 is mounted on the upper metal die unit 13
- a lower cushion mechanism 25 is mounted on the lower metal die unit 14 in order to operate the first and second holder means 22 , 23 .
- the first holder means 22 is composed of a first upper holddown member 27 connected to the upper cushion mechanism 24 , and a first lower holddown member 28 connected to the lower cushion mechanism 25 .
- H 1 indicates the position in which the first holder means 22 restrains the blank material.
- the second holder means 23 is composed of a second upper holddown member 31 connected to the upper cushion mechanism 24 , and a second lower holddown member 32 connected to the lower cushion mechanism 25 .
- the position in which the second holder means 23 restrains the blank material is indicated by H 2 .
- the restraining position H 2 is set deeper in the shearing direction (Z-axis direction) than the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 22 by a distance Hg.
- the upper metal die unit 13 will now be described in detail.
- the upper metal die unit 13 includes an upper base member 34 attached to the ram 18 .
- An upper die (die) 35 is attached to the center of the upper base member 34 by bolts 35 a.
- a holder placement part 36 is formed on the upper base member 34 .
- the upper metal die unit 13 includes the first upper holddown member 27 and the second upper holddown member 31 of the blank holder 16 .
- the upper cushion mechanism 24 has third cylinders 37 , 37 mounted on the upper base member 34 of the upper metal die unit 13 .
- a cushion base 41 is mounted on rods 38 , 38 of the third cylinders 37 , 37 , and is fitted over the holder placement part 36 and allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction.
- a stopper groove 44 is formed in the left side surface 43 of the cushion base 41 .
- a stopper shaft 45 that fits into the stopper groove 44 is mounted on the upper base member 34 .
- the operation of the third cylinders 37 , 37 causes the cushion base 41 to slide in the Z-axis direction irrespective of the movement of the ram 18 .
- the third cylinders 37 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders.
- the rods 38 are used in place of pins in this case.
- the first upper holddown member 27 has a holddown main body 51 .
- the holddown main body 51 has a pressure surface 54 formed on the underside, and a recessed hole 55 formed in the pressure surface 54 .
- the reference numeral 56 indicates a bolt for fastening the first upper holddown member 27 to the cushion base 41 .
- the second upper holddown member 31 has a holddown main body 58 that faces the second lower holddown member 32 .
- the holddown main body 58 has a pressure surface 61 formed on the underside.
- the pressure surface 61 is located deeper (upward) than the pressure surface 54 of the first upper holddown member 27 by a distance Hg.
- the upper die 35 has a die surface 67 formed at the bottom of an upper die main body 65 .
- the lower metal die unit 14 will now be described in detail.
- the lower metal die unit 14 includes a lower base member 72 provided to the bed 19 of the press 17 .
- the lower base member 72 includes a lower die 73 in the center of the base member.
- the lower metal die unit 14 includes the first lower holddown member 28 and second lower holddown member 32 of the blank holder 16 .
- the lower cushion mechanism 25 has first cylinders 75 , 75 and second cylinders 76 , 76 mounted on the lower base member 72 .
- Rods, 77 , 77 , 78 , 78 of the first and second cylinders 75 , 76 are all connected to the first and second lower holddown members 28 , 32 .
- First guide shafts 81 , 81 for guiding the first lower holddown member 28 and second guide shaft 82 for guiding the second lower holddown member 32 are mounted on the lower base member 72 .
- the first cylinders 75 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders.
- the rods 77 are used in place of pins in this case.
- the second cylinders 76 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders.
- the rods 78 are used in place of pins in this case.
- the first lower holddown member 28 faces the first upper holddown member 27 , and the rods 77 , 77 of the first cylinders 75 , 75 are connected to the underside of a holddown main body 83 .
- the holddown main body 83 has guide holes 84 , 84 into which the first guide shafts 81 , 81 are fitted, and these shafts are allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction.
- the top surface of the holddown main body 83 constitutes a pressure surface 85 .
- the blank material 15 is firmly held by the pressure surface 85 and the pressure surface 54 facing the pressure surface 85 .
- the blank is set on the first lower holddown member 28 at the position indicated by U 1 .
- the blank setting position U 1 and the pressure surface 85 are located higher than a die surface 92 of the lower die 73 by a distance H 3 .
- the second lower holddown member 32 faces the second upper holddown member 31 , and the rods 78 , 78 of the second cylinders 76 , 76 are connected to the underside of a holddown main body 86 .
- the holddown main body 86 has guide holes 87 , 87 into which the second guide shaft 82 are fitted, and these shafts are allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction.
- the top surface of the holddown main body 86 constitutes a pressure surface 88 .
- the blank material 15 is firmly held by the pressure surface 88 and the pressure surface 61 facing the pressure surface 88 . This is described in further detail hereinafter.
- the position of the pressure surface 88 is the same as that of the pressure surface 85 of the first lower holddown member 28 located on the outside of the pressure surface 88 , and is set to the blank setting position U 1 .
- the die surface 92 is formed on the top surface of a lower die main body 91 of the lower die 73 .
- the blank material 15 is formed into the desired shape by the die surface 92 of the lower die 73 and the die surface 67 of the upper die 35 .
- the second lower holddown member 32 is raised above the die surface 92 , whereby the blank material 15 can be formed into the desired shape as shown in FIG. 5A .
- the lower die 73 has four setting shafts 103 .
- the number of cylinders and guide shafts (including guide holes) in the blank holder 16 provided to the metal die unit 12 is arbitrary.
- FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of the draw forming method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- ST02 The blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit 12 , which is mounted on the press 17 in advance.
- the first holder means 22 is lowered, whereby the second holder means 23 displaces the stretching region 97 (see FIG. 3 ) of the blank material 15 relative to the restraint region 98 in the shearing direction, and restrains the stretching region 97 .
- This displacement causes tensile force to be applied to a drawing region 96 (see FIG. 3 ) of the blank material 15 .
- a drawing force is applied to the drawing region 96 (see FIG. 3 ), and the region is subjected to plastic working by the upper die 35 and the lower die 73 , whereby the blank material 15 is formed (see FIG. 6B ).
- FIG. 3 shows the first step of the forming method in ST01 shown in FIG. 2 .
- the blank material 15 is obtained in the first step.
- the blank material 15 is a plate member (material) including a stretching region 97 and a restraint region 98 disposed in the stated order outward from the drawing region 96 (in the direction of the arrows a 3 , a 3 ).
- four fitting holes 99 are formed in the restraint region 98 .
- the four aforementioned setting shafts 103 are fitted into the four fitting holes 99 .
- the restraint region 98 is the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 .
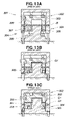
- FIGS. 4A and 4B show the second step of the draw forming method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of ST02 and ST03 shown in FIG. 2 .
- the blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit 12 in the second step shown in FIG. 4A .
- the metal die unit 12 is opened as shown in FIG. 1 , the four setting shafts 103 are fitted into the four fitting holes 99 of the blank material 15 shown in FIG. 3 , and the blank material 15 is set on the first lower holddown member 28 of the first holder means 22 and the second lower holddown member 32 of the second holder means 23 .
- the first holder means 22 of the blank holder 16 restrains the restraint region 98 in the second step.
- the press 17 is operated to lower the upper metal die unit 13 by a stroke S 1 as shown in FIG. 4A , the first upper holddown member 27 is pressed against the blank material 15 with a pressure Ph, and the blank material 15 is restrained by the first upper holddown member 27 and first lower holddown member 28 with a specific surface pressure.
- the closed restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 22 coincides with the blank setting position U 1 at this time.
- the pressure Ph is transmitted to the first upper holddown member 27 via the third cylinders 37 , 37 of the upper cushion mechanism 24 .
- the central section 104 of the blank material 15 is not supported, and deflection 105 occurs in the central section 104 as shown in FIG. 4B .
- the first holder means 22 restrains the restraint region 98 of the blank material 15 in which deflection 105 has occurred in the central section 104 .
- FIGS. 5A and 5B show the third step of the draw forming method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of ST04 shown in FIG. 2 .
- step S 3 the restraint region 98 of the blank material 15 is restrained, and the second holder means 23 of the blank holder 16 displaces the stretching region 97 in relation to the restraint region 98 in the shearing direction (the direction of the arrow a 4 , and the Z-axis direction).
- Tensile force is thereby applied to the drawing region 96 as shown by the arrow a 5 , and the drawing region is then restrained. In other words, tensile force is applied radially outward to the drawing region 96 in an amount proportional to the amount of displacement.
- the press 17 operates and lowers the first holder means 22 while still restraining the blank material 15 , and the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is pressed against the second lower holddown member 32 .
- the second lower holddown member 32 is stationary at this time.
- the first holder means 22 is then lowered by a distance H 4 from the blank setting position U 1 , and the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 22 is lowered by a distance H 4 .
- the stretching region 97 is displaced by a distance H 4 from the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 22 , and the second holder means 23 is stopped at the restraining position H 2 while the second lower holddown member 32 and the second upper holddown member 31 restrain the stretching region 97 .
- FIGS. 6A through 6D show the plastic working step in ST05 and the extraction of the formed article in ST06, shown in FIG. 2 .
- the upper metal die unit 13 is lowered to lower the first and second holder means 22 , 23 by a stroke S 3 , as shown in FIG. 6A .
- the upper metal die unit 13 is lowered against resistance from the first cylinders 75 , 75 and the second cylinders 76 , 76 , and the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 is pressed against the die surface 92 of the lower die 73 .
- the upper metal die unit 13 is lowered by a stroke S 3 , whereupon the first and second holder means 22 , 23 come into contact with the lower base member 72 and stop.
- the upper die 35 is then lowered and pressed against the blank material 15 , whereby the blank material is drawn into the desired shape, as shown in FIG. 6B .
- the upper base member 34 is lowered to apply a draw force Pm to the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 through the upper die 35 , and the drawing region 96 is plastically deformed by the lower die 73 , whereby the formed article 107 is obtained.
- the upper base member 34 is raised, whereby only the upper die 35 rises in the direction of the arrow a 6 , and the upper die 35 separates from the formed article 107 .
- the entire upper metal die unit 13 is then raised, whereby the formed article 107 is lifted and separated from the lower die 73 , as shown in FIG. 6D . Consequently, the first and second holder means 22 , 23 open, and the operator is therefore able to extract the formed article 107 .
- a blank material 15 is obtained in the first step of the draw forming method in the first embodiment, as described above.
- This blank material includes a stretching region 97 and a restraint region 98 disposed in the stated order outward from the drawing region 96 , as shown in FIG. 3 .
- the blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit 12 , and the restraint region 98 is restrained by the first holder means 22 of the blank holder 16 , as shown in FIG. 4A .
- the stretching region 97 is forcibly displaced in the shearing direction by the second holder means 23 of the blank holder 16 as shown in FIG. 5A , whereby tensile force is applied to the drawing region 96 .
- the tensile force does not result in deflection 105 in the drawing region 96 . It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 set on the metal die unit 12 .
- the draw forming device 11 shown in FIG. 1 includes the blank holder 16 , which comprises the first holder means 22 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the first restraining position H 1 , and the second holder means 23 for restraining the inner section of the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the second restraining position H 2 when the press 17 is lowered. Therefore, after the outer peripheral section 21 is restrained, the inner section of the outer peripheral section 21 is restrained by the second holder means 23 so as to be displaced.
- the central section 104 of the blank material 15 is thereupon stretched outward as shown by the arrow a 5 (see FIG. 5 ). As a result, deflection is reduced in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 , and drawing can be performed with minimal nonuniformities in the formed dimensions.
- a double-action press 217 is used as the press 17 shown in FIG. 1 .
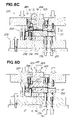
- a draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7 is composed of a metal die unit 212 comprising an upper metal die unit 213 and a lower metal die unit 214 , and a blank holder 216 provided to the metal die unit 212 to hold down the blank material 15 .
- the upper metal die unit 213 is mounted on the double-action press 217 .
- the lower metal die unit 214 is mounted on a bed 219 .
- the double-action press 217 includes an inner slider 245 for applying pressing force in order to form the blank material 15 , and an external slider 246 disposed on the outside of the inner slider 245 to hold down the blank material 15 .
- the external slider 246 is raised and lowered individually by hydraulic pressure, for example.
- the upper metal die unit 213 is composed of an upper base member 234 integrally mounted on the external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 , and an upper die 235 disposed inside an open section 247 formed in the center of the upper base member 234 .
- the lower metal die unit 214 is composed of a lower base member 272 mounted on the bed 219 , and a lower die 273 fixed in the center of the lower base member 272 .
- the blank holder 216 is composed of first holder means 222 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 shown in FIG. 3 , and second holder means 223 disposed on the inside of the first holder means 222 .
- the first holder means 222 includes a first upper holddown member 227 integrally fixed to the upper base member 234 by bolts 256 , and a first lower holddown member 228 that is mounted on the lower base member 272 by first cylinders 275 and is allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction.
- the first upper holddown member 227 has a holddown member main body 251 , which is formed into a rectangular shape large enough to come into contact with the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 .
- the holddown member main body 251 has a pressure surface 254 formed on the underside, and a recessed hole 255 formed so that the pressure surface 254 is open.
- the pressure surface 254 reaches the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 and holds down the upper surface of the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 .
- the restraining position H 1 is the position in which the first holder means 222 protrudes past the second holder means 223 ; i.e., where the first holder means is lowered to hold the blank material 15 .
- the first lower holddown member 228 has a holddown member main body 283 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that faces the holddown member main body 251 of the first upper holddown member 227 .
- the holddown member main body 283 has a pressure surface 285 formed on the topside to press on the underside of the blank material 15 .
- the pressure surface 285 is provided with four setting shafts 203 for setting the blank material 15 .
- the holddown member main body 283 also has guide holes 284 , 284 into which first guide shafts 281 , 281 are fitted and allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction by means of a collar 283 a.
- the first guide shafts 281 , 281 are mounted on the lower base member 272 .
- the first cylinders 275 , 275 are mounted on the lower base member 272 , and the distal ends of the rods of the first cylinders 275 , 275 are connected to the holddown member main body 283 , whereby the first lower holddown member 228 supports the underside of the blank material 15 .
- the first guide shafts 281 , 281 guide the first lower holddown member 228 vertically (in the Z-axis direction).
- the entire lengths of the first guide shafts 281 , 281 can be limited so as to not protrude from the pressure surface 285 of the first lower holddown member 228 , for example.
- the recessed hole 255 is optionally provided to the first upper holddown member 227 to allow the insertion and withdrawal of the first guide shafts 281 , 281 .
- the second holder means 223 includes a second upper holddown member 231 integrally fixed to the upper base member 234 by bolts (not shown), and a second lower holddown member 232 that is mounted on the lower base member 272 and is allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction by means of the lower base member 272 .
- the second upper holddown member 231 has a holddown member main body 258 formed into a rectangular shape corresponding to the size of the stretching region 97 , which is an extension of the inside of the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 shown in FIG. 3 .
- the underside of the holddown member main body 258 constitutes a pressure surface 261 for pressing on the stretching region 97 .
- the top of the holddown member main body 258 is provided with a hole 263 into which a guide post 262 is fitted, first elastic member mounting holes 265 into which elastic members 264 are fitted, and a mounting hole 269 for mounting a stopper member 268 .
- the pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown member 231 reaches the restraining position H 2 of the second holder means 223 and holds down the topside of the blank material 15 .
- the mounting shape of the guide post 262 and the hole 263 for fitting the guide post 262 constitute one example, and another possibility, for example, is to not form the hole 263 and to fasten the guide post 262 with bolts.
- the pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown member 231 is positioned above the pressure surface 254 of the first upper holddown member 227 at a distance Hg.
- the second lower holddown member 232 has a holddown member main body 286 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that faces the holddown member main body 258 of the second upper holddown member 231 , a pressure surface formed on the topside of the holddown member main body 286 , a guide hole 287 formed so as to open towards the bottom of the holddown member main body 286 , and a second guide shaft 282 that fits into the guide hole 287 by means of a collar 286 a.
- the second guide shaft 282 is mounted on the lower base member 272 .
- Second cylinders 276 , 276 are mounted on the lower base member 272 .
- the top ends of the rods of the second cylinders 276 , 276 are connected to the lower ends of the second lower holddown member 232 .
- first upper holddown member 227 and the first lower holddown member 228 are formed into rectangular shapes in this example. However, these shapes are arbitrary and can also be circular. The same applies to the second upper holddown member 231 and the second lower holddown member 232 .
- the upper die 235 has an upper die main body 236 , which has a die surface 237 on the underside.
- a supporting member 238 is provided in the central part of the upper die main body 236 .
- a guide hole 239 is formed in the supporting member 238 , and the guide post 262 is slidably fitted into the guide hole 239 by means of a collar 240 .
- Second elastic member mounting holes 241 are formed in the supporting member 238 .
- the other ends (upper ends) of the aforementioned elastic members 264 are fitted into the second elastic member mounting holes 241 .
- the supporting member 238 has a return-restricting section 242 .
- the return-restricting section 242 has a hole for receiving the stopper member 268 .
- the stopper member 268 is mounted using a bolt 243 in the mounting hole 269 formed in the second upper holddown member 231 .
- the topside of the upper die main body 82 constitutes a contact surface 94 that comes into contact with the underside of the inner slider 245 .
- the elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression springs that urge the upper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into standby mode.
- the return-restricting section 242 holds the die surface 237 at a position separated upward from the pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown member 231 by a distance M.
- the lower die 273 has a die surface 292 that faces the die surface 237 of the upper die 235 .
- the upper die 235 is supported to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means 223 , and is disposed so as to be separated from the inner slider 245 of the double action double-action press 217 .
- the first and second holder means 222 , 223 are fixed to the external slider 246 .
- FIGS. 8A through 8D The following is a description, made with reference to FIGS. 8A through 8D , of the operation whereby the blank material 15 shown in FIG. 3 is drawn by the draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7 .
- the blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit 212 .
- the metal die unit 212 is opened, the four setting shafts 203 (see FIG. 7 ) are fitted into the four fitting holes 99 (see FIG. 3 ) in the blank material 15 , and the blank material 15 is set on the first lower holddown member 228 and the second lower holddown member 232 .
- the external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is lowered, whereby the first upper holddown member 227 and the second upper holddown member 231 are lowered as shown in FIG. 8A .
- the first upper holddown member 227 reaches the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 , and the pressure surface 254 on the underside of the first upper holddown member 227 presses on the outer peripheral section 21 .
- Combining the outputs of the double-action press 217 and the first cylinders 275 allows the first holder means 222 (first upper holddown member 227 and first lower holddown member 228 ) to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 .
- the drawing region 96 of the central section 104 in the blank material 15 is not supported, and deflection 105 occurs in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 as described in FIG. 4B .
- the external slider 246 further lowers the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sa 1 against resistance from the output of the first cylinders 275 , whereupon a pressure surface 288 on the topside of the second lower holddown member 232 is raised by a stroke Sa 1 as a result, and the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is displaced upward from the outer peripheral section 21 by a distance H 4 (see FIG. 5B ) that corresponds to the stroke Sa 1 .
- the output of the second cylinders 276 at this time is greater than the output of the double-action press 217 , and the second cylinders 276 stop without being lowered.
- the second lower holddown member 232 displaces the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 while the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained.
- the drawing region 96 and the stretching region 97 are therefore stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as indicated by the arrows a 5 , and the deflection 105 (see FIG. 4B ) is removed from in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 .
- the blank material 15 is displaced, and the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is restrained by the pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown member 231 and the pressure surface 288 of the second lower holddown member 232 .
- the output of the double-action press 217 and the second cylinders 276 allows the second holder means 223 (the second upper holddown member 231 and the second lower holddown member 232 ) to restrain the blank material 15 at the restraining position H 2 of the second holder means 223 .
- the second upper holddown member 231 of the second holder means 223 does not move in the Z-axis direction independent of the external slider 246 , because the first and second holder means 222 , 223 are fixed to the external slider 246 . Therefore, nonuniformities are reduced in the dimensions of the formed article.
- the second holder means 223 is also lowered, and the entire drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 is deformed by the die surface 292 of the lower die 273 .
- the first lower holddown member 228 and the second lower holddown member 232 come into contact with the lower base member 272 and stop.
- the outer peripheral section 21 and stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 are restrained by the first holder means 222 and the second holder means 223 .
- the inner slider 245 is lowered based on information about the position of the external slider 246 , whereupon the underside of the inner slider 245 comes into contact with a contact surface 244 of the upper die 235 , the upper die 235 is lowered against the repulsive force of the elastic members 264 , and the upper die applies pressure to the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 .
- the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 is drawn into the desired shape by the die surface 237 of the upper die 235 and the die surface 292 of the lower die 273 , and the formed article 107 is obtained.
- FIGS. 9A and 9B show the operation of extracting the formed article 107 obtained by drawing.
- the inner slider 245 is raised in FIG. 9A , whereupon the repulsive force of the elastic members 264 raises the upper die 235 .
- the stopper member 268 comes into contact with the return-restricting section 242 , the upper die 235 reaches an upper limit, and the device goes into standby mode.
- the external slider 246 continues to apply pressure.
- the second lower holddown member 232 reaches an upper limit and stops at the stroke end of the second cylinders 276 , and the second holder means 223 opens.
- the formed article 107 separates from the die surface 292 of the lower die 273 in this step.
- the rods of the first cylinders 275 are raised further, and the first lower holddown member 228 stops at an upper limit at the stroke end of the first cylinders 275 .
- the first holder means 222 opens and the operator extracts the formed article 104 .
- pressing the “start button” on the operating panel of the double-action press 17 automatically executes the operation in FIGS. 7 through 9B , and the operator extracts the formed article 104 , whereby one formation cycle is completed.
- tensile force is applied to the central section 104 of the blank material 15 connected to the stretching region 97 .
- the tensile force is applied from the time the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained at the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 until the time the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is restrained at the restraining position H 2 of the second holder means 223 .
- the deflection in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 can be removed.
- the upper die 235 is supported by the elastic members 264 , is allowed to slide (in the Z-axis direction) in relation to the second holder means 223 , and is disposed separate from the inner slider 245 of the double-action press 217 .
- the upper die is therefore operated using the second holder means 223 as a reference. Accordingly, the upper die 235 can be positioned with greater accuracy.
- FIG. 10 shows a modified example of the draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7 .
- components identical to those in the draw forming device of the second embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed descriptions are omitted.
- the draw forming device 211 A of the modified example has a metal die unit 212 A comprising an upper metal die unit 213 A and a lower metal die unit 214 A, and also has a blank holder 216 A disposed on the metal die unit 212 A to restrain the blank material 15 .
- the upper metal die unit 213 A has an upper die 235 A disposed in an open section 247 formed in the upper base member 234 .
- the lower metal die unit 214 A has a lower die 273 mounted on a lower base member 272 A, which is mounted on a bed 219 .
- the lower base member 272 A is mounted on the bed 219 .
- a blank holder 216 A includes first holder means 222 , and second holder means 223 A disposed on the inside thereof.
- the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 is located farther out than the second holder means 223 A, and is the position in which the blank material 15 is held. The details are described hereinafter.
- the second holder means 223 A has a second lower holddown member 232 A fixed to the lower base member 272 A.
- the restraining position Hb 2 of the second holder means 223 A is the position in which the double-action press 17 is lowered past the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sb 1 .
- the blank material 15 is restrained at a position that is lower by a stroke Sb 1 than the restraining position H 1 of the first holder means 222 .
- the second lower holddown member 232 A has a holddown member main body 286 A formed into a rectangular shape facing the holddown member main body 258 of the second upper holddown member 231 .
- the holddown member main body 286 A has a pressure surface 288 on the topside.
- first upper holddown member 227 , first lower holddown member 228 , second upper holddown member 231 , and second lower holddown member 232 A are rectangular in this description, but the shapes of these components are arbitrary and may also be circular.
- the upper die 235 A has an upper die main body 236 A.
- the elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression springs that urge the upper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into standby mode.
- the upper die 235 A is supported to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means 223 A.
- the upper die 235 A is also disposed so as to be separated from the inner slider 245 of the double action double-action press 217 .
- the first holder means 222 and second holder means 223 A are fixed integrally to the external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 .
- the descending stroke Sb 1 of the first holder means 222 of the modified example which is necessary to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 , is greater than the descending stroke Sa 1 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7 . Therefore, the displaced depth H 5 of the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 , described later, is greater than the displaced depth in the second embodiment. In other words, the amount of displacement is greater, and the stretching region 97 and drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 are subjected to a tensile force that corresponds to the amount of displacement. Therefore, deflection in the central section of the blank material 15 is reduced.
- the blank material 15 is set in the opened metal die unit 212 A as shown in FIG. 10 , the blank material 15 is set on the first lower holddown member 228 and second lower holddown member 232 A as previously described.
- lowering the external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 causes the first upper holddown member 227 and the second upper holddown member 231 to be lowered, whereupon the first upper holddown member 227 reaches the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 , and the pressure surface 254 of the first upper holddown member 227 applies pressure to the outer peripheral section 21 .
- the output of the double-action press 217 and of the first cylinders 275 allows the first holder means 222 to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the restraining position H 1 .
- the blank material 15 is restrained at the external peripheral section 21 in the restraining position H 1 , and is not supported at the drawing region 96 in the central section 104 .
- Deflection 105 is formed in the central section 104 of the blank material 15 , as shown in FIG. 4B .
- the external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is then lowered as shown in FIG. 11B , whereupon the first holder means 222 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is lowered by a stroke Sb 1 against resistance from the output of the first cylinders 275 , and the first lower holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222 comes into contact with the lower base member 272 A and stops.
- the lowering of the first holder means 222 causes the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 to be displaced upward from the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 , which is restrained by the first holder means 222 .
- This displacement causes the stretching region 97 and the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 to be stretched outward.
- the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is then restrained by the second holder means 223 A.
- the second upper holddown member 231 and the second lower holddown member 232 A of the second holder means 223 A restrain the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 at the restraining position Hb 2 , which is set to the position in which the external slider 246 is lowered by a stroke Sb 1 .
- the external slider 246 continues to apply pressure, whereby the first holder means 222 and second holder means 223 A continue to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 and the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 .
- the inner slider 245 is lowered based on information about the position of the external slider 246 as shown in FIG. 11D , whereupon the underside of the inner slider 245 comes into contact with the contact surface 244 of the upper die 235 A, and the upper die 235 A is lowered against the repulsive force of the external slider 246 to apply pressure to the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 .
- the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 is drawn into the desired shape by the die surface 237 of the upper die 235 A, and the die surface 292 of the lower die 273 , and a formed article 107 A is obtained.
- the external slider 246 then continues to be raised as shown in FIG. 12B , whereupon the rods of the first cylinders 275 are raised as well, and the first upper holddown member 227 and first lower holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222 are raised while the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained. As a result, the blank material 15 moves upward away from the pressure surface 288 of the second lower holddown member 232 A. The first lower holddown member 228 reaches an upper limit and stops at the stroke end of the first cylinders 275 .
- the external slider 246 is then raised further, whereupon the first holder means 222 opens as shown in FIG. 10 , and the operator therefore extracts the formed article 107 A.
- pressing the “start button” on the operating panel of the double-action press 17 automatically executes the operation beginning with drawing the blank material 15 and ending with opening the metal die unit, and the operator extracts the formed article 107 A, whereby one formation cycle is completed.
- a draw forming device of a modified example was described above, but according to this draw forming device of the modified example, settings are selected so that there is an increase in the descending stroke Sb 1 of the first holder means 222 of the modified example necessary to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 .
- the displacement of the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is therefore proportionally greater, and the stretching region 97 and drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 are stretched farther.
- the deflection in the central section of the blank material 15 is therefore further reduced.
- the outer peripheral section of a blank material is restrained by first holder means, and the stretching region on the inside of the outer peripheral section is displaced and restrained in the shearing direction relative to the outer peripheral section.
- Tensile force is thereby applied to the drawing region in the middle of the blank material, and deflection in the drawing region is reduced.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Shaping Metal By Deep-Drawing, Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
A draw forming method for drawing a blank material (15). In this method, a restraint region (98) that is an outer peripheral section (21) of the blank material is held by a first holder means (22), and then a tension region (97) inside the outer peripheral section is displaced upward by a second holder means (23) relative to the restraint region. The displacement applies tensile force to a drawing region (96) that is the central section of the blank material.
Description
- The present invention relates to a draw forming method and device for reducing deflection created in the center of a blank material when the blank material is subjected to plastic working using a press and a metal die unit.
- Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open Publication No. H01-153820, for example, proposes a draw forming method in which the periphery of a blank material is held by pressure from a blank holder, and the blank material is formed when subjected to plastic working using a metal die unit mounted on a press. This draw forming is described below with reference to
FIGS. 13A through 13C hereof. - In a forming method that uses a conventional drawing die 301, the periphery of a blank material B is first pressed by an
upper die holddown 303 of anupper die 302 and alower die holddown 305 of alower die 304, and a section adjacent to the center of the blank material B is pressed by apad 306 and acushion 307, as shown inFIG. 13A . - Next, a first draw (cylindrical section G1) is formed with a
punch 308, as shown inFIG. 13B . - A second draw (square base section G2) is then formed with the
cushion 307, as shown inFIG. 13C . - The first and second draws can thus be formed in a single step in the conventional draw forming method.
- However, although an example is given in which the
punch 308 is disposed on the underside of thedrawing die 301, the punch is sometimes disposed on the topside depending on the circumstances. In cases in which the drawing die 301 is turned upside-down, the blank material B is set on thepad 306 to form draws, whereupon deflection is created in the center of the blank material B. Deflection tends to occur easily and in greater amounts particularly in cases in which the blank material is extremely thin, or in cases in which a thin blank material is hot-formed (including warm forming). As a result, there is concern that the forming dimensions will be markedly nonuniform. - In view of this, there is a need for a draw forming technique that reduces deflection in the center of the blank material set on the metal die unit, and that reduces nonuniformities in the forming dimensions.
- According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a draw forming method wherein a blank material set into a metal die unit is restrained by a blank holder and then drawn, the method comprising the steps of: setting the blank material into the metal die unit, the blank material having a stretching region and a restraint region set in the stated order outward and lined up with a drawing region that is subjected to pressure from an upper die and a lower die; restraining the restraint region of the blank material with first holder means of the blank holder; and applying tensile force to the drawing region and restraining the stretching region while second holder means of the blank holder displaces the stretching region in the shearing direction in relation to the restraint region.
- Thus, the restraint region of the blank material is restrained by the first holder means, and the stretching region of the blank material is then displaced in the shearing direction by the second holder means, whereupon tensile force is applied to the stretching region of the blank material and the drawing region in the middle, and the deflection formed in the drawing region is removed. It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in the middle of the blank material set into the metal die unit.
- According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a device for draw forming a blank material, which device comprises: a metal die unit having an upper die and a lower die; a blank holder for restraining the blank material set in the metal die unit; and a press for applying pressure to the restrained blank material, wherein the blank holder comprises first holder means for restraining an outer peripheral section of the blank material at a first restraining position when the press is lowered; and second holder means disposed on the inside of the first holder means to restrain the inside section of the outer peripheral section of the blank material at a second restraining position when the press is further lowered.
- In the thus-arranged device, the press operates the first holder means, the outer peripheral section of the blank material is restrained by the first holder means, and the press is then lowered further. The second holder means positioned on the inside of the first holder means then stretches the middle of the blank material outward. As a result, the deflection in the central section of the blank material is extremely small, and it is possible to reduce nonuniformities in the positional relationship between the central section and the upper and lower dies. It is therefore possible to reduce nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article when drawing is performed.
- Preferably, in the device of the present invention, the press is a double-action press; the first restraining position is the position in which the first holder means protrudes past the second holder means and in which the blank material is held by the lowering of the double-action press; the second restraining position is the position in which the double-action press is lowered further from the first restraining position; the upper die is held to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means, and is disposed separate from an inner slider of the double-action press; and the first holder means and second holder means are fixed to an external slider positioned on the outside of the inner slider. As a result, tensile force is applied to the inside of the outer peripheral section and to the central section of the blank material until the blank material reaches the second restraining position while the outer peripheral section is restrained at the first restraining position, and deflection in the central section of the blank material can be prevented from occurring.
- Furthermore, since the first and second holder means are integrally fixed to the external slider of the double-action press, there is no movement between the external slider and the first and second holder means, and nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article can be reduced.
-
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a draw forming device according to a first embodiment of the present invention; -
FIG. 2 a flowchart showing the steps of a draw forming method according to the present invention; -
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the blank material used in the draw forming method of the invention; -
FIGS. 4A and 4B are schematic views showing the manner in which the blank material is set on the metal die unit and restrained by first holder means in the draw forming method shown inFIG. 2 ; -
FIGS. 5A and 5B are schematic views showing the manner in which the press is lowered to displace the stretching region of the blank material upward and to remove the deflection created in the central section of the blank material; -
FIGS. 6A through 6D are schematic views showing the manner in which a formed article is extracted after the formed article is obtained by drawing the central section of the blank material; -
FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the draw forming device according to a second embodiment of the present invention; -
FIGS. 8A through 8D are schematic views showing an operation of the draw forming device according to the second embodiment, and also showing the manner in which the formed article is obtained by drawing after the blank is set on a metal die unit; -
FIGS. 9A and 9B are schematic views showing the manner in which the formed article is extracted; -
FIG. 10 is a schematic view showing a modification of the draw forming device according to the second embodiment shown inFIG. 7 ; -
FIGS. 11A through 11D are schematic views showing the actions taken from the time the blank material is set until the time the blank material is drawn in the draw forming device in the modification; -
FIGS. 12A and 12B are schematic views showing the manner in which the formed article is extracted; and -
FIGS. 13A through 13C are schematic cross-sectional views showing a conventional draw forming device. - Certain embodiments of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
- In
FIG. 1 , X indicates a horizontal axis in the longitudinal direction of ablank material 15, Y indicates a horizontal axis orthogonal to X, and Z indicates a vertical axis orthogonal to both X and Y. - A
draw forming device 11 of the first embodiment shown inFIG. 1 is composed of ametal die unit 12 comprising an uppermetal die unit 13 and a lowermetal die unit 14, and ablank holder 16 provided to themetal die unit 12 to apply pressure to theblank material 15. The uppermetal die unit 13 is mounted on aram 18 of apress 17. The lowermetal die unit 14 is mounted on abed 19 of thepress 17. Thedraw forming device 11 performs draw forming. - The
blank holder 16 includes first holder means 22 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 (restraint region 98 inFIG. 3 ) of theblank material 15, and second holder means 23 disposed on the inside (in the direction of the arrows a1, a1) of the first holder means 22. Anupper cushion mechanism 24 is mounted on the uppermetal die unit 13, and alower cushion mechanism 25 is mounted on the lowermetal die unit 14 in order to operate the first and second holder means 22, 23. - The first holder means 22 is composed of a first
upper holddown member 27 connected to theupper cushion mechanism 24, and a firstlower holddown member 28 connected to thelower cushion mechanism 25. H1 indicates the position in which the first holder means 22 restrains the blank material. - The second holder means 23 is composed of a second
upper holddown member 31 connected to theupper cushion mechanism 24, and a secondlower holddown member 32 connected to thelower cushion mechanism 25. - The position in which the second holder means 23 restrains the blank material is indicated by H2. The restraining position H2 is set deeper in the shearing direction (Z-axis direction) than the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 22 by a distance Hg.
- The upper metal die
unit 13 will now be described in detail. - The upper metal die
unit 13 includes anupper base member 34 attached to theram 18. An upper die (die) 35 is attached to the center of theupper base member 34 bybolts 35 a. Aholder placement part 36 is formed on theupper base member 34. In other words, the upper metal dieunit 13 includes the firstupper holddown member 27 and the secondupper holddown member 31 of theblank holder 16. - The
upper cushion mechanism 24 hasthird cylinders upper base member 34 of the upper metal dieunit 13. Acushion base 41 is mounted onrods third cylinders holder placement part 36 and allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. Astopper groove 44 is formed in theleft side surface 43 of thecushion base 41. Astopper shaft 45 that fits into thestopper groove 44 is mounted on theupper base member 34. The operation of thethird cylinders cushion base 41 to slide in the Z-axis direction irrespective of the movement of theram 18. - The
third cylinders 37 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders. Therods 38 are used in place of pins in this case. - The first
upper holddown member 27 has a holddownmain body 51. The holddownmain body 51 has apressure surface 54 formed on the underside, and a recessedhole 55 formed in thepressure surface 54. - The
reference numeral 56 indicates a bolt for fastening the firstupper holddown member 27 to thecushion base 41. - The second
upper holddown member 31 has a holddownmain body 58 that faces the secondlower holddown member 32. The holddownmain body 58 has apressure surface 61 formed on the underside. Thepressure surface 61 is located deeper (upward) than thepressure surface 54 of the firstupper holddown member 27 by a distance Hg. - The
upper die 35 has adie surface 67 formed at the bottom of an upper die main body 65. - The lower metal die
unit 14 will now be described in detail. - The lower metal die
unit 14 includes alower base member 72 provided to thebed 19 of thepress 17. Thelower base member 72 includes alower die 73 in the center of the base member. In other words, the lower metal dieunit 14 includes the firstlower holddown member 28 and secondlower holddown member 32 of theblank holder 16. - The
lower cushion mechanism 25 hasfirst cylinders second cylinders lower base member 72. Rods, 77, 77, 78, 78 of the first andsecond cylinders lower holddown members First guide shafts lower holddown member 28 andsecond guide shaft 82 for guiding the secondlower holddown member 32 are mounted on thelower base member 72. - The
first cylinders 75 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders. Therods 77 are used in place of pins in this case. - The
second cylinders 76 have a structure for storing fluid, for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the fluid-storing cylinders. Therods 78 are used in place of pins in this case. - The first
lower holddown member 28 faces the firstupper holddown member 27, and therods first cylinders main body 83. The holddownmain body 83 has guide holes 84, 84 into which thefirst guide shafts main body 83 constitutes apressure surface 85. Theblank material 15 is firmly held by thepressure surface 85 and thepressure surface 54 facing thepressure surface 85. - The blank is set on the first
lower holddown member 28 at the position indicated by U1. The blank setting position U1 and thepressure surface 85 are located higher than adie surface 92 of thelower die 73 by a distance H3. - The second
lower holddown member 32 faces the secondupper holddown member 31, and therods second cylinders main body 86. The holddownmain body 86 has guide holes 87, 87 into which thesecond guide shaft 82 are fitted, and these shafts are allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. The top surface of the holddownmain body 86 constitutes apressure surface 88. Theblank material 15 is firmly held by thepressure surface 88 and thepressure surface 61 facing thepressure surface 88. This is described in further detail hereinafter. - The position of the
pressure surface 88 is the same as that of thepressure surface 85 of the firstlower holddown member 28 located on the outside of thepressure surface 88, and is set to the blank setting position U1. - The
die surface 92 is formed on the top surface of a lower diemain body 91 of thelower die 73. Theblank material 15 is formed into the desired shape by thedie surface 92 of thelower die 73 and thedie surface 67 of theupper die 35. The secondlower holddown member 32 is raised above thedie surface 92, whereby theblank material 15 can be formed into the desired shape as shown inFIG. 5A . - The
lower die 73 has four settingshafts 103. - The number of cylinders and guide shafts (including guide holes) in the
blank holder 16 provided to the metal dieunit 12 is arbitrary. - The following is a description, made with reference to
FIG. 1 andFIGS. 2 through 6D , of the draw forming method performed using thedraw forming device 11. -
FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of the draw forming method according to the first embodiment of the present invention. - Step (hereinafter abbreviated as ST) 01: The
blank material 15 is obtained. - ST02: The
blank material 15 is set on the metal dieunit 12, which is mounted on thepress 17 in advance. - ST03: The metal die
unit 12 is operated, and the restraint region 98 (seeFIG. 3 ) of theblank material 15 is restrained by the first holder means 22 of theblank holder 16. - ST04: The first holder means 22 is lowered, whereby the second holder means 23 displaces the stretching region 97 (see
FIG. 3 ) of theblank material 15 relative to therestraint region 98 in the shearing direction, and restrains the stretchingregion 97. This displacement causes tensile force to be applied to a drawing region 96 (seeFIG. 3 ) of theblank material 15. - ST05: A drawing force is applied to the drawing region 96 (see
FIG. 3 ), and the region is subjected to plastic working by theupper die 35 and thelower die 73, whereby theblank material 15 is formed (seeFIG. 6B ). - ST06: A formed
article 107 is extracted (seeFIG. 6D ). - Details of ST01 through ST06 will now be described in detail.
-
FIG. 3 shows the first step of the forming method in ST01 shown inFIG. 2 . - The
blank material 15 is obtained in the first step. Specifically, theblank material 15 is a plate member (material) including astretching region 97 and arestraint region 98 disposed in the stated order outward from the drawing region 96 (in the direction of the arrows a3, a3). At the same time, fourfitting holes 99 are formed in therestraint region 98. The fouraforementioned setting shafts 103 are fitted into the four fitting holes 99. Therestraint region 98 is the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15. -
FIGS. 4A and 4B show the second step of the draw forming method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of ST02 and ST03 shown inFIG. 2 . - The
blank material 15 is set on the metal dieunit 12 in the second step shown inFIG. 4A . Specifically, the metal dieunit 12 is opened as shown inFIG. 1 , the four settingshafts 103 are fitted into the fourfitting holes 99 of theblank material 15 shown inFIG. 3 , and theblank material 15 is set on the firstlower holddown member 28 of the first holder means 22 and the secondlower holddown member 32 of the second holder means 23. - Next, the first holder means 22 of the
blank holder 16 restrains therestraint region 98 in the second step. Specifically, thepress 17 is operated to lower the upper metal dieunit 13 by a stroke S1 as shown inFIG. 4A , the firstupper holddown member 27 is pressed against theblank material 15 with a pressure Ph, and theblank material 15 is restrained by the firstupper holddown member 27 and firstlower holddown member 28 with a specific surface pressure. The closed restraining position H1 of the first holder means 22 coincides with the blank setting position U1 at this time. - The pressure Ph is transmitted to the first
upper holddown member 27 via thethird cylinders upper cushion mechanism 24. - When the
blank material 15 is set on theblank holder 16 provided to the metal dieunit 12, thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 is not supported, anddeflection 105 occurs in thecentral section 104 as shown inFIG. 4B . As a result, the first holder means 22 restrains therestraint region 98 of theblank material 15 in whichdeflection 105 has occurred in thecentral section 104. -
FIGS. 5A and 5B show the third step of the draw forming method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of ST04 shown inFIG. 2 . - In step S3, the
restraint region 98 of theblank material 15 is restrained, and the second holder means 23 of theblank holder 16 displaces the stretchingregion 97 in relation to therestraint region 98 in the shearing direction (the direction of the arrow a4, and the Z-axis direction). Tensile force is thereby applied to thedrawing region 96 as shown by the arrow a5, and the drawing region is then restrained. In other words, tensile force is applied radially outward to thedrawing region 96 in an amount proportional to the amount of displacement. - Specifically, the
press 17 operates and lowers the first holder means 22 while still restraining theblank material 15, and the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is pressed against the secondlower holddown member 32. The secondlower holddown member 32 is stationary at this time. The first holder means 22 is then lowered by a distance H4 from the blank setting position U1, and the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 22 is lowered by a distance H4. - In other words, the stretching
region 97 is displaced by a distance H4 from the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 22, and the second holder means 23 is stopped at the restraining position H2 while the secondlower holddown member 32 and the secondupper holddown member 31 restrain the stretchingregion 97. - Thus, tensile force is applied in the directions of the arrows a5 to the stretching
region 97 and drawingregion 96 shown inFIG. 5B . The drawingregion 96, which is set in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15, is therefore stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as shown by the arrows a5, and thecentral section 104 is free of deflection. It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in the central section 104 (drawing region 96) of theblank material 15 set on the metal dieunit 12. -
FIGS. 6A through 6D show the plastic working step in ST05 and the extraction of the formed article in ST06, shown inFIG. 2 . - After the second holder means 23 restrains the stretching
region 97 of theblank material 15 as described inFIG. 5A , the upper metal dieunit 13 is lowered to lower the first and second holder means 22, 23 by a stroke S3, as shown inFIG. 6A . At this time, the upper metal dieunit 13 is lowered against resistance from thefirst cylinders second cylinders drawing region 96 of theblank material 15 is pressed against thedie surface 92 of thelower die 73. The upper metal dieunit 13 is lowered by a stroke S3, whereupon the first and second holder means 22, 23 come into contact with thelower base member 72 and stop. - The
upper die 35 is then lowered and pressed against theblank material 15, whereby the blank material is drawn into the desired shape, as shown inFIG. 6B . Specifically, theupper base member 34 is lowered to apply a draw force Pm to thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15 through theupper die 35, and thedrawing region 96 is plastically deformed by thelower die 73, whereby the formedarticle 107 is obtained. - After drawing is complete, the
upper base member 34 is raised, whereby only theupper die 35 rises in the direction of the arrow a6, and theupper die 35 separates from the formedarticle 107. - The entire upper metal die
unit 13 is then raised, whereby the formedarticle 107 is lifted and separated from thelower die 73, as shown inFIG. 6D . Consequently, the first and second holder means 22, 23 open, and the operator is therefore able to extract the formedarticle 107. - The steps described above are automated by pressing a “start button” on the operating panel of the
press 17. - A
blank material 15 is obtained in the first step of the draw forming method in the first embodiment, as described above. This blank material includes a stretchingregion 97 and arestraint region 98 disposed in the stated order outward from the drawingregion 96, as shown inFIG. 3 . - In the second step, the
blank material 15 is set on the metal dieunit 12, and therestraint region 98 is restrained by the first holder means 22 of theblank holder 16, as shown inFIG. 4A . - In the third step, the stretching
region 97 is forcibly displaced in the shearing direction by the second holder means 23 of theblank holder 16 as shown inFIG. 5A , whereby tensile force is applied to thedrawing region 96. The tensile force does not result indeflection 105 in thedrawing region 96. It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 set on the metal dieunit 12. - The
draw forming device 11 shown inFIG. 1 includes theblank holder 16, which comprises the first holder means 22 for restraining the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 at the first restraining position H1, and the second holder means 23 for restraining the inner section of the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 at the second restraining position H2 when thepress 17 is lowered. Therefore, after the outerperipheral section 21 is restrained, the inner section of the outerperipheral section 21 is restrained by the second holder means 23 so as to be displaced. Thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 is thereupon stretched outward as shown by the arrow a5 (seeFIG. 5 ). As a result, deflection is reduced in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15, and drawing can be performed with minimal nonuniformities in the formed dimensions. - The draw forming device according to a second embodiment will now be described with reference to
FIG. 7 . In the draw forming device of the second embodiment, a double-action press 217 is used as thepress 17 shown inFIG. 1 . - A
draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown inFIG. 7 is composed of ametal die unit 212 comprising an upper metal dieunit 213 and a lowermetal die unit 214, and ablank holder 216 provided to themetal die unit 212 to hold down theblank material 15. The upper metal dieunit 213 is mounted on the double-action press 217. The lowermetal die unit 214 is mounted on abed 219. - The double-
action press 217 includes aninner slider 245 for applying pressing force in order to form theblank material 15, and anexternal slider 246 disposed on the outside of theinner slider 245 to hold down theblank material 15. Theexternal slider 246 is raised and lowered individually by hydraulic pressure, for example. - The upper metal die
unit 213 is composed of anupper base member 234 integrally mounted on theexternal slider 246 of the double-action press 217, and anupper die 235 disposed inside anopen section 247 formed in the center of theupper base member 234. - The lower
metal die unit 214 is composed of alower base member 272 mounted on thebed 219, and alower die 273 fixed in the center of thelower base member 272. - The
blank holder 216 is composed of first holder means 222 for restraining the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 shown inFIG. 3 , and second holder means 223 disposed on the inside of the first holder means 222. - The first holder means 222 includes a first
upper holddown member 227 integrally fixed to theupper base member 234 bybolts 256, and a firstlower holddown member 228 that is mounted on thelower base member 272 byfirst cylinders 275 and is allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. - The first
upper holddown member 227 has a holddown membermain body 251, which is formed into a rectangular shape large enough to come into contact with the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15. The holddown membermain body 251 has apressure surface 254 formed on the underside, and a recessedhole 255 formed so that thepressure surface 254 is open. Thepressure surface 254 reaches the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 and holds down the upper surface of the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15. The restraining position H1 is the position in which the first holder means 222 protrudes past the second holder means 223; i.e., where the first holder means is lowered to hold theblank material 15. - The first
lower holddown member 228 has a holddown membermain body 283 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that faces the holddown membermain body 251 of the firstupper holddown member 227. The holddown membermain body 283 has apressure surface 285 formed on the topside to press on the underside of theblank material 15. Thepressure surface 285 is provided with four settingshafts 203 for setting theblank material 15. The holddown membermain body 283 also has guide holes 284, 284 into whichfirst guide shafts collar 283 a. Thefirst guide shafts lower base member 272. Thefirst cylinders lower base member 272, and the distal ends of the rods of thefirst cylinders main body 283, whereby the firstlower holddown member 228 supports the underside of theblank material 15. - The
first guide shafts lower holddown member 228 vertically (in the Z-axis direction). The entire lengths of thefirst guide shafts pressure surface 285 of the firstlower holddown member 228, for example. - The recessed
hole 255 is optionally provided to the firstupper holddown member 227 to allow the insertion and withdrawal of thefirst guide shafts - The second holder means 223 includes a second
upper holddown member 231 integrally fixed to theupper base member 234 by bolts (not shown), and a secondlower holddown member 232 that is mounted on thelower base member 272 and is allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction by means of thelower base member 272. - The second
upper holddown member 231 has a holddown membermain body 258 formed into a rectangular shape corresponding to the size of the stretchingregion 97, which is an extension of the inside of the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 shown inFIG. 3 . The underside of the holddown membermain body 258 constitutes apressure surface 261 for pressing on the stretchingregion 97. - The top of the holddown member
main body 258 is provided with ahole 263 into which aguide post 262 is fitted, first elasticmember mounting holes 265 into whichelastic members 264 are fitted, and a mountinghole 269 for mounting astopper member 268. - The
pressure surface 261 of the secondupper holddown member 231 reaches the restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223 and holds down the topside of theblank material 15. - The mounting shape of the
guide post 262 and thehole 263 for fitting theguide post 262 constitute one example, and another possibility, for example, is to not form thehole 263 and to fasten theguide post 262 with bolts. - The
pressure surface 261 of the secondupper holddown member 231 is positioned above thepressure surface 254 of the firstupper holddown member 227 at a distance Hg. - The restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223 is the position in which the double-
action press 17 is lowered past the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sa1 (Sa1=Hg). - The second
lower holddown member 232 has a holddown membermain body 286 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that faces the holddown membermain body 258 of the secondupper holddown member 231, a pressure surface formed on the topside of the holddown membermain body 286, aguide hole 287 formed so as to open towards the bottom of the holddown membermain body 286, and asecond guide shaft 282 that fits into theguide hole 287 by means of acollar 286 a. - The
second guide shaft 282 is mounted on thelower base member 272.Second cylinders lower base member 272. The top ends of the rods of thesecond cylinders lower holddown member 232. - In the first holder means 22 (first
upper holddown member 227 and first lower holddown member 228) and the second holder means 223 (secondupper holddown member 231 and second lower holddown member 232), the firstupper holddown member 227 and the firstlower holddown member 228 are formed into rectangular shapes in this example. However, these shapes are arbitrary and can also be circular. The same applies to the secondupper holddown member 231 and the secondlower holddown member 232. - The
upper die 235 has an upper diemain body 236, which has adie surface 237 on the underside. A supportingmember 238 is provided in the central part of the upper diemain body 236. Aguide hole 239 is formed in the supportingmember 238, and theguide post 262 is slidably fitted into theguide hole 239 by means of acollar 240. - Second elastic
member mounting holes 241 are formed in the supportingmember 238. The other ends (upper ends) of the aforementionedelastic members 264 are fitted into the second elastic member mounting holes 241. The supportingmember 238 has a return-restrictingsection 242. The return-restrictingsection 242 has a hole for receiving thestopper member 268. Thestopper member 268 is mounted using abolt 243 in the mountinghole 269 formed in the secondupper holddown member 231. The topside of the upper diemain body 82 constitutes a contact surface 94 that comes into contact with the underside of theinner slider 245. - The
elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression springs that urge theupper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into standby mode. - With the aid of the
stopper member 268, the return-restrictingsection 242 holds thedie surface 237 at a position separated upward from thepressure surface 261 of the secondupper holddown member 231 by a distance M. - The
lower die 273 has adie surface 292 that faces thedie surface 237 of theupper die 235. - Thus, in the
draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment, theupper die 235 is supported to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means 223, and is disposed so as to be separated from theinner slider 245 of the double action double-action press 217. The first and second holder means 222, 223 are fixed to theexternal slider 246. - The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 8A through 8D , of the operation whereby theblank material 15 shown inFIG. 3 is drawn by thedraw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown inFIG. 7 . - First, the
blank material 15 is set on themetal die unit 212. Specifically, themetal die unit 212 is opened, the four setting shafts 203 (seeFIG. 7 ) are fitted into the four fitting holes 99 (seeFIG. 3 ) in theblank material 15, and theblank material 15 is set on the firstlower holddown member 228 and the secondlower holddown member 232. - The
external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is lowered, whereby the firstupper holddown member 227 and the secondupper holddown member 231 are lowered as shown inFIG. 8A . The firstupper holddown member 227 reaches the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15, and thepressure surface 254 on the underside of the firstupper holddown member 227 presses on the outerperipheral section 21. Combining the outputs of the double-action press 217 and thefirst cylinders 275 allows the first holder means 222 (firstupper holddown member 227 and first lower holddown member 228) to restrain the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 at the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222. - The drawing
region 96 of thecentral section 104 in theblank material 15 is not supported, anddeflection 105 occurs in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 as described inFIG. 4B . - Next, as shown in
FIG. 8B , theexternal slider 246 further lowers the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sa1 against resistance from the output of thefirst cylinders 275, whereupon apressure surface 288 on the topside of the secondlower holddown member 232 is raised by a stroke Sa1 as a result, and the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is displaced upward from the outerperipheral section 21 by a distance H4 (seeFIG. 5B ) that corresponds to the stroke Sa1. The output of thesecond cylinders 276 at this time is greater than the output of the double-action press 217, and thesecond cylinders 276 stop without being lowered. - Thus, the second
lower holddown member 232 displaces the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 while the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 is restrained. As was described inFIG. 5B , the drawingregion 96 and the stretchingregion 97 are therefore stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as indicated by the arrows a5, and the deflection 105 (seeFIG. 4B ) is removed from in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15. - Thus, the
blank material 15 is displaced, and the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is restrained by thepressure surface 261 of the secondupper holddown member 231 and thepressure surface 288 of the secondlower holddown member 232. At this time, the output of the double-action press 217 and thesecond cylinders 276 allows the second holder means 223 (the secondupper holddown member 231 and the second lower holddown member 232) to restrain theblank material 15 at the restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223. - The second
upper holddown member 231 of the second holder means 223 does not move in the Z-axis direction independent of theexternal slider 246, because the first and second holder means 222, 223 are fixed to theexternal slider 246. Therefore, nonuniformities are reduced in the dimensions of the formed article. - When the
external slider 246 is further lowered by a stroke S2 as shownFIG. 8C , the second holder means 223 is also lowered, and theentire drawing region 96 of theblank material 15 is deformed by thedie surface 292 of thelower die 273. The firstlower holddown member 228 and the secondlower holddown member 232 come into contact with thelower base member 272 and stop. The outerperipheral section 21 and stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 are restrained by the first holder means 222 and the second holder means 223. - In
FIG. 8D , theinner slider 245 is lowered based on information about the position of theexternal slider 246, whereupon the underside of theinner slider 245 comes into contact with acontact surface 244 of theupper die 235, theupper die 235 is lowered against the repulsive force of theelastic members 264, and the upper die applies pressure to thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15. As a result, the drawingregion 96 of theblank material 15 is drawn into the desired shape by thedie surface 237 of theupper die 235 and thedie surface 292 of thelower die 273, and the formedarticle 107 is obtained. -
FIGS. 9A and 9B show the operation of extracting the formedarticle 107 obtained by drawing. - The
inner slider 245 is raised inFIG. 9A , whereupon the repulsive force of theelastic members 264 raises theupper die 235. Thestopper member 268 comes into contact with the return-restrictingsection 242, theupper die 235 reaches an upper limit, and the device goes into standby mode. Theexternal slider 246 continues to apply pressure. - When the
external slider 246 begins to rise inFIG. 9B , the secondlower holddown member 232 reaches an upper limit and stops at the stroke end of thesecond cylinders 276, and the second holder means 223 opens. The formedarticle 107 separates from thedie surface 292 of thelower die 273 in this step. - The rods of the
first cylinders 275 are raised further, and the firstlower holddown member 228 stops at an upper limit at the stroke end of thefirst cylinders 275. When theexternal slider 246 is raised further, the first holder means 222 opens and the operator extracts the formedarticle 104. - In other words, pressing the “start button” on the operating panel of the double-
action press 17 automatically executes the operation inFIGS. 7 through 9B , and the operator extracts the formedarticle 104, whereby one formation cycle is completed. - In to the
draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment described above, tensile force is applied to thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 connected to the stretchingregion 97. The tensile force is applied from the time the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 is restrained at the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 until the time the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is restrained at the restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223. As a result, the deflection in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15 can be removed. - There is no independent movement between the
external slider 246 and the first and second holder means 222, 223, and nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article can be reduced because the first and second holder means 222, 223 are fixed to theexternal slider 246. - The
upper die 235 is supported by theelastic members 264, is allowed to slide (in the Z-axis direction) in relation to the second holder means 223, and is disposed separate from theinner slider 245 of the double-action press 217. The upper die is therefore operated using the second holder means 223 as a reference. Accordingly, theupper die 235 can be positioned with greater accuracy. -
FIG. 10 shows a modified example of thedraw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown inFIG. 7 . In the description of this drawing device in the modified example, components identical to those in the draw forming device of the second embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed descriptions are omitted. - The
draw forming device 211A of the modified example has ametal die unit 212A comprising an upper metal dieunit 213A and a lowermetal die unit 214A, and also has ablank holder 216A disposed on themetal die unit 212A to restrain theblank material 15. - The upper metal die
unit 213A has anupper die 235A disposed in anopen section 247 formed in theupper base member 234. - The lower
metal die unit 214A has alower die 273 mounted on alower base member 272A, which is mounted on abed 219. Thelower base member 272A is mounted on thebed 219. - A
blank holder 216A includes first holder means 222, and second holder means 223A disposed on the inside thereof. - The restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 is located farther out than the second holder means 223A, and is the position in which the
blank material 15 is held. The details are described hereinafter. - The second holder means 223A has a second
lower holddown member 232A fixed to thelower base member 272A. - The restraining position Hb2 of the second holder means 223A is the position in which the double-
action press 17 is lowered past the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sb1. In other words, theblank material 15 is restrained at a position that is lower by a stroke Sb1 than the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222. - The second
lower holddown member 232A has a holddown membermain body 286A formed into a rectangular shape facing the holddown membermain body 258 of the secondupper holddown member 231. The holddown membermain body 286A has apressure surface 288 on the topside. - The first
upper holddown member 227, firstlower holddown member 228, secondupper holddown member 231, and secondlower holddown member 232A are rectangular in this description, but the shapes of these components are arbitrary and may also be circular. - The
upper die 235A has an upper diemain body 236A. - The
elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression springs that urge theupper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into standby mode. - Thus, in the
draw forming device 211A of the modified example, theupper die 235A is supported to be capable of sliding in relation to the second holder means 223A. Theupper die 235A is also disposed so as to be separated from theinner slider 245 of the double action double-action press 217. The first holder means 222 and second holder means 223A are fixed integrally to theexternal slider 246 of the double-action press 217. - As is clear in
FIG. 10 , the descending stroke Sb1 of the first holder means 222 of the modified example, which is necessary to restrain the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15, is greater than the descending stroke Sa1 of the second embodiment shown inFIG. 7 . Therefore, the displaced depth H5 of the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15, described later, is greater than the displaced depth in the second embodiment. In other words, the amount of displacement is greater, and the stretchingregion 97 and drawingregion 96 of theblank material 15 are subjected to a tensile force that corresponds to the amount of displacement. Therefore, deflection in the central section of theblank material 15 is reduced. - The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 11A through 11C , of the operation of drawing the blank material with the draw forming device of the modified example. - First, when the
blank material 15 is set in the openedmetal die unit 212A as shown inFIG. 10 , theblank material 15 is set on the firstlower holddown member 228 and secondlower holddown member 232A as previously described. - In
FIG. 11A , lowering theexternal slider 246 of the double-action press 217 causes the firstupper holddown member 227 and the secondupper holddown member 231 to be lowered, whereupon the firstupper holddown member 227 reaches the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15, and thepressure surface 254 of the firstupper holddown member 227 applies pressure to the outerperipheral section 21. The output of the double-action press 217 and of thefirst cylinders 275 allows the first holder means 222 to restrain the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 at the restraining position H1. - The
blank material 15 is restrained at the externalperipheral section 21 in the restraining position H1, and is not supported at thedrawing region 96 in thecentral section 104.Deflection 105 is formed in thecentral section 104 of theblank material 15, as shown inFIG. 4B . - The
external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is then lowered as shown inFIG. 11B , whereupon the first holder means 222 for restraining the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 is lowered by a stroke Sb1 against resistance from the output of thefirst cylinders 275, and the firstlower holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222 comes into contact with thelower base member 272A and stops. - The lowering of the first holder means 222 causes the stretching
region 97 of theblank material 15 to be displaced upward from the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15, which is restrained by the first holder means 222. This displacement causes the stretchingregion 97 and thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15 to be stretched outward. The stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is then restrained by the second holder means 223A. - In other words, the second
upper holddown member 231 and the secondlower holddown member 232A of the second holder means 223A restrain the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 at the restraining position Hb2, which is set to the position in which theexternal slider 246 is lowered by a stroke Sb1. - There is no
deflection 105 in thecentral section 104 shown inFIG. 4B , because thedrawing region 96 and stretchingregion 97 are stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as indicated by the arrows a5. These regions are stretched in a process of plastic deformation of theblank material 15 by a displacement depth of H5 as shown inFIG. 11C , while the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 is restrained. It is therefore possible to reduce deflection in thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15 set in themetal die unit 212A. The displacement depth H5 is the depth of plastic working when the blank material is restrained at the restraining position Hb2 of the second holder means 223A. - Thus, there is an increase in the displacement depth H5 of the stretching
region 97 of theblank material 15 based on the lowering of the first holder means 222 in the modified example, and deflection in thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15 can be reduced proportionally. - The
external slider 246 continues to apply pressure, whereby the first holder means 222 and second holder means 223A continue to restrain the outerperipheral section 21 and the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15. - The
inner slider 245 is lowered based on information about the position of theexternal slider 246 as shown inFIG. 11D , whereupon the underside of theinner slider 245 comes into contact with thecontact surface 244 of theupper die 235A, and theupper die 235A is lowered against the repulsive force of theexternal slider 246 to apply pressure to thedrawing region 96 of theblank material 15. As a result, the drawingregion 96 of theblank material 15 is drawn into the desired shape by thedie surface 237 of theupper die 235A, and thedie surface 292 of thelower die 273, and a formedarticle 107A is obtained. - The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 12A and 12B , of the operation of extracting the formedarticle 107A in the draw forming device of the modified example. - When the
inner slider 245 is raised inFIG. 12A , theupper die 235A is raised against the repulsive force of theelastic members 264, and the return-restrictingsection 242 comes into contact with thestopper member 268, whereupon theupper die 235A reaches an upper limit and the device goes into standby mode. Theexternal slider 246 continues to apply pressure during this time. - The
external slider 246 then continues to be raised as shown inFIG. 12B , whereupon the rods of thefirst cylinders 275 are raised as well, and the firstupper holddown member 227 and firstlower holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222 are raised while the outerperipheral section 21 of theblank material 15 is restrained. As a result, theblank material 15 moves upward away from thepressure surface 288 of the secondlower holddown member 232A. The firstlower holddown member 228 reaches an upper limit and stops at the stroke end of thefirst cylinders 275. - The
external slider 246 is then raised further, whereupon the first holder means 222 opens as shown inFIG. 10 , and the operator therefore extracts the formedarticle 107A. - In other words, pressing the “start button” on the operating panel of the double-
action press 17 automatically executes the operation beginning with drawing theblank material 15 and ending with opening the metal die unit, and the operator extracts the formedarticle 107A, whereby one formation cycle is completed. - A draw forming device of a modified example was described above, but according to this draw forming device of the modified example, settings are selected so that there is an increase in the descending stroke Sb1 of the first holder means 222 of the modified example necessary to restrain the outer
peripheral section 21 of theblank material 15. The displacement of the stretchingregion 97 of theblank material 15 is therefore proportionally greater, and the stretchingregion 97 and drawingregion 96 of theblank material 15 are stretched farther. The deflection in the central section of theblank material 15 is therefore further reduced. - In the draw forming device of the present invention, the outer peripheral section of a blank material is restrained by first holder means, and the stretching region on the inside of the outer peripheral section is displaced and restrained in the shearing direction relative to the outer peripheral section. Tensile force is thereby applied to the drawing region in the middle of the blank material, and deflection in the drawing region is reduced. Thus, when the drawing region is drawn, formed articles having little nonuniformity in their dimensions are obtained, which articles are usable in various industries.
Claims (3)
1. A draw forming method wherein a blank material set into a metal die unit is restrained by a blank holder and then drawn, the method comprising the steps of:
setting the blank material into the metal die unit, the blank material having a stretching region and a restraint region set in the stated order outward and lined up with a drawing region subjected to pressure from an upper die and a lower die;
restraining the restraint region of the blank material with first holder means of the blank holder; and
applying tensile force to the drawing region and restraining the stretching region while second holder means of the blank holder displaces the stretching region in a shearing direction relative to the restraint region.
2. A device for draw forming a blank material, comprising:
a metal die unit comprised of an upper die and a lower die;
a blank holder for restraining the blank material set in the metal die unit; and
a press for applying pressure to the restrained blank material, wherein the blank holder comprises:
first holder means for restraining an outer peripheral section of the blank material at a first restraining position when the press is lowered; and
second holder means disposed inside the first holder means to restrain an inside section of the outer peripheral section of the blank material at a second restraining position when the press is further lowered.
3. The draw forming device of claim 2 , wherein:
the press comprises a double-action press;
the first restraining position is a position in which the first holder means protrudes past the second holder means and in which the blank material is held by the lowering of the double-action press;
the second restraining position is the position in which the double-action press is lowered further from the first restraining position;
the upper die is held to be capable of sliding relative to the second holder means and is disposed separate from an inner slider of the double-action press; and
the first holder means and second holder means are fixed to an external slider positioned outside the inner slider.
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004-339409 | 2004-11-24 | ||
| JP2004339409A JP2006142371A (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2004-11-24 | Drawing method and drawing apparatus |
| JP2005303306A JP2006255781A (en) | 2005-02-16 | 2005-10-18 | Drawing machine |
| JP2005-303306 | 2005-10-18 | ||
| PCT/JP2005/021176 WO2006057196A1 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2005-11-11 | Draw forming method and device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20080098789A1 true US20080098789A1 (en) | 2008-05-01 |
Family
ID=36497934
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/718,052 Abandoned US20080098789A1 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2005-11-11 | Draw Forming Method and Device |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20080098789A1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2586049C (en) |
| DE (1) | DE112005002868B4 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2006057196A1 (en) |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090241628A1 (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-01 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Draw Die and Method of Manufacturing Same |
| US20100050729A1 (en) * | 2008-09-01 | 2010-03-04 | Rahul Kulkarni | Die assembly for use in an apparatus for forming a workpiece |
| US20100064759A1 (en) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-03-18 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Method and device for press-hardening a metallic formed structure |
| US20100201031A1 (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2010-08-12 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Mold for press apparatus, and open-drawing method |
| US20100251799A1 (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2010-10-07 | Rexam Beverage Can Company | Tooling pod for double action can end press |
| CN102319799A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Side slide trimming die for inner supporting tube of shock absorber for automobile |
| CN102319798A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Compound stamping die for bended side-punching hole |
| CN102319801A (en) * | 2011-07-04 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Inner tapered wedge type bending die for elastic clamp |
| US20120090768A1 (en) * | 2009-04-14 | 2012-04-19 | Airbus Operations Gmbh | Apparatus and method for draping knitted fiber fabrics for curved profiled structural parts of fiber composite material |
| CN102847802A (en) * | 2012-09-12 | 2013-01-02 | 无锡红旗船厂有限公司 | Forming mould for pressing reinforcing ribs on high-strength sheet steel |
| US20130098132A1 (en) * | 2011-10-21 | 2013-04-25 | Bor-Tsuen Lin | Punch with groove structure, and micro-drawing device using the same |
| US20130213108A1 (en) * | 2012-02-20 | 2013-08-22 | Richard Paul KNERR | Method of making a stamped part |
| WO2013139731A1 (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2013-09-26 | Allgaier Werke Gmbh | Device and method for machining a workpiece consisting of metal, particularly for producing a cup-shaped component for the automobile industry, as well as such a workpiece |
| US8984927B2 (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2015-03-24 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Die for machine press |
| US20150107321A1 (en) * | 2013-10-21 | 2015-04-23 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Deep Draw Manufacturing Process |
| FR3018709A1 (en) * | 2014-03-20 | 2015-09-25 | Peugeot Citroen Automobiles Sa | TOOLING FOR BONDING FOR CONFORMING A BENT PIECE |
| US20160107280A1 (en) * | 2014-10-15 | 2016-04-21 | Fu Ding Electronical Technology (Jiashan) Co.,Ltd. | Press mechanism |
| US20160207093A1 (en) * | 2013-09-30 | 2016-07-21 | ALLGAIER WERK GmbH | Device for forming a sheet-metal workpiece |
| US9724745B2 (en) | 2009-08-26 | 2017-08-08 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Press forming method |
| US20180043421A1 (en) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-15 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Indexing self-aligning hardware tool |
| US20200197997A1 (en) * | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Dajun Zhou | Stretch forming die |
| US20230249239A1 (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2023-08-10 | Toyota Boshoku Kabushiki Kaisha | Workpiece production apparatus |
| CN119500885A (en) * | 2024-12-23 | 2025-02-25 | 中航西安飞机工业集团股份有限公司 | A double-action drawing die for large deep-cavity basin-shaped parts and an alternating drawing method |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101428482B (en) * | 2008-12-05 | 2010-09-08 | 北京康迪普瑞模具技术有限公司 | Method for manufacturing accurate special-shaped thin wall blank holder |
| DE102009053365A1 (en) * | 2009-11-14 | 2011-05-19 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Complex and pre-finished sheet metal shaped part i.e. motor vehicle body part, producing method, involves shaping surface section of blank and inhibiting continued flow of sheet metal material to edge-close section |
| DE102009053366A1 (en) * | 2009-11-14 | 2011-05-19 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Method for manufacturing profile component, particularly structure part for motor vehicle body, involves preparing output plate from sheet metal material |
| DE102013201613A1 (en) * | 2013-01-31 | 2014-07-31 | Thyssenkrupp System Engineering Gmbh | Method for producing component i.e. door inner panel, for vehicle door, involves pulling edge segment region from component section relative to base region of component section and parallel to main extension plane of component section |
| JP7155578B2 (en) * | 2018-03-30 | 2022-10-19 | マツダ株式会社 | Processing device and method |
| JP7403794B2 (en) * | 2019-11-07 | 2023-12-25 | 太陽工業株式会社 | Double acting press mold |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6830419B1 (en) * | 2000-11-20 | 2004-12-14 | Alfons Haar Inc. | Aerosol can ends |
| US7237423B1 (en) * | 2004-11-12 | 2007-07-03 | Miller Tool And Die Company Inc. | Apparatus for stretch forming blanks |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5376965A (en) * | 1976-12-20 | 1978-07-07 | Toyota Motor Co Ltd | Construction of swaging die |
| CH621271A5 (en) * | 1977-06-15 | 1981-01-30 | Aluminiumwerke Ag Rorschach | |
| JPS55103231A (en) * | 1979-02-01 | 1980-08-07 | Toyota Motor Corp | General purpose drawing die structure of double acting press |
| JPS59175428U (en) * | 1983-05-11 | 1984-11-22 | 日産自動車株式会社 | double action press type |
| JPH01153820U (en) * | 1988-04-08 | 1989-10-23 |
-
2005
- 2005-11-11 WO PCT/JP2005/021176 patent/WO2006057196A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2005-11-11 CA CA2586049A patent/CA2586049C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-11-11 US US11/718,052 patent/US20080098789A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2005-11-11 DE DE112005002868T patent/DE112005002868B4/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6830419B1 (en) * | 2000-11-20 | 2004-12-14 | Alfons Haar Inc. | Aerosol can ends |
| US7237423B1 (en) * | 2004-11-12 | 2007-07-03 | Miller Tool And Die Company Inc. | Apparatus for stretch forming blanks |
Cited By (40)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100201031A1 (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2010-08-12 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Mold for press apparatus, and open-drawing method |
| US8490455B2 (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2013-07-23 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Mold for press apparatus, and open-drawing method |
| US8490456B2 (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2013-07-23 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Draw die and method of manufacturing same |
| US20090241628A1 (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-01 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Draw Die and Method of Manufacturing Same |
| US20100050729A1 (en) * | 2008-09-01 | 2010-03-04 | Rahul Kulkarni | Die assembly for use in an apparatus for forming a workpiece |
| US20100064759A1 (en) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-03-18 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Method and device for press-hardening a metallic formed structure |
| US8839652B2 (en) * | 2008-09-18 | 2014-09-23 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Method and device for press-hardening a metallic formed structure |
| US20100251799A1 (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2010-10-07 | Rexam Beverage Can Company | Tooling pod for double action can end press |
| US9352379B2 (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2016-05-31 | Rexam Beverage Can Company | Tooling pod for double action can end press |
| WO2010118134A1 (en) * | 2009-04-07 | 2010-10-14 | Rexam Beverage Can Company | Tooling pod for double action can end press |
| US20120090768A1 (en) * | 2009-04-14 | 2012-04-19 | Airbus Operations Gmbh | Apparatus and method for draping knitted fiber fabrics for curved profiled structural parts of fiber composite material |
| US10668671B2 (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2020-06-02 | Airbus Operations Gmbh | Apparatus and method for draping knitted fiber fabrics for curved profiled structural parts of fiber composite material |
| US9724745B2 (en) | 2009-08-26 | 2017-08-08 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Press forming method |
| US8984927B2 (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2015-03-24 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Die for machine press |
| CN102319798A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Compound stamping die for bended side-punching hole |
| CN102319799A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Side slide trimming die for inner supporting tube of shock absorber for automobile |
| CN102319801A (en) * | 2011-07-04 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市中捷减震器有限公司 | Inner tapered wedge type bending die for elastic clamp |
| US20130098132A1 (en) * | 2011-10-21 | 2013-04-25 | Bor-Tsuen Lin | Punch with groove structure, and micro-drawing device using the same |
| US20130213108A1 (en) * | 2012-02-20 | 2013-08-22 | Richard Paul KNERR | Method of making a stamped part |
| US20140352390A1 (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2014-12-04 | Allgaier Werke Gmbh | Device and method for machining a workpiece consisting of metal, particularly for producing a cup-shaped component for the automobile industry, as well as such a workpiece |
| CN104136141A (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2014-11-05 | 奥盖尔沃克有限公司 | Device and method for machining a workpiece consisting of metal, particularly for producing a cup-shaped component for the automobile industry, as well as such a workpiece |
| WO2013139731A1 (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2013-09-26 | Allgaier Werke Gmbh | Device and method for machining a workpiece consisting of metal, particularly for producing a cup-shaped component for the automobile industry, as well as such a workpiece |
| US9289812B2 (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2016-03-22 | Allgaier Werke Gmbh | Device and method for machining a workpiece consisting of metal, particularly for producing a cup-shaped component for the automobile industry, as well as such a workpiece |
| CN104136141B (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2017-11-10 | 奥盖尔沃克有限公司 | For making device, apparatus and method and the workpiece manufactured whereby of slab deformation |
| RU2634830C2 (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2017-11-03 | Алльгайер Верке Гмбх | Device, plant and method of sheet metal workpiece forming, and part, produced according to this method |
| CN102847802A (en) * | 2012-09-12 | 2013-01-02 | 无锡红旗船厂有限公司 | Forming mould for pressing reinforcing ribs on high-strength sheet steel |
| US11833565B2 (en) * | 2013-09-30 | 2023-12-05 | Allgaier Werke Gmbh | Device for forming a sheet-metal workpiece |
| US20160207093A1 (en) * | 2013-09-30 | 2016-07-21 | ALLGAIER WERK GmbH | Device for forming a sheet-metal workpiece |
| US20150107321A1 (en) * | 2013-10-21 | 2015-04-23 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Deep Draw Manufacturing Process |
| US9044801B2 (en) * | 2013-10-21 | 2015-06-02 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Deep draw manufacturing process |
| FR3018709A1 (en) * | 2014-03-20 | 2015-09-25 | Peugeot Citroen Automobiles Sa | TOOLING FOR BONDING FOR CONFORMING A BENT PIECE |
| US20160107280A1 (en) * | 2014-10-15 | 2016-04-21 | Fu Ding Electronical Technology (Jiashan) Co.,Ltd. | Press mechanism |
| US10112276B2 (en) * | 2014-10-15 | 2018-10-30 | Fu Ding Electronical Technology (Jiashan) | Press mechanism |
| US20180043421A1 (en) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-15 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Indexing self-aligning hardware tool |
| US10471496B2 (en) * | 2016-08-12 | 2019-11-12 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Indexing self-aligning hardware tool |
| US20200197997A1 (en) * | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Dajun Zhou | Stretch forming die |
| US10933458B2 (en) * | 2018-12-19 | 2021-03-02 | Fca Us Llc | Stretch forming die |
| US20230249239A1 (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2023-08-10 | Toyota Boshoku Kabushiki Kaisha | Workpiece production apparatus |
| US12311425B2 (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2025-05-27 | Toyota Boshoku Kabushiki Kaisha | Workpiece production apparatus |
| CN119500885A (en) * | 2024-12-23 | 2025-02-25 | 中航西安飞机工业集团股份有限公司 | A double-action drawing die for large deep-cavity basin-shaped parts and an alternating drawing method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2006057196A1 (en) | 2006-06-01 |
| DE112005002868T5 (en) | 2007-10-31 |
| DE112005002868B4 (en) | 2010-07-01 |
| CA2586049A1 (en) | 2006-06-01 |
| CA2586049C (en) | 2011-03-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20080098789A1 (en) | Draw Forming Method and Device | |
| CN101767164A (en) | Method for producing thin-wall metal ring and progressive stamping die adopted by method | |
| JP2008142772A (en) | Total shearing die | |
| CN114653830B (en) | Stamping die and process with negative-angle flanging stamping part | |
| CA1079169A (en) | Blank and draw apparatus with gap control and method | |
| JP5938074B2 (en) | Drawing method and apparatus | |
| CN202192152U (en) | Switching mechanism for stamping die | |
| KR102512445B1 (en) | Multi-process unification press mold | |
| CN109092995A (en) | A kind of anti-deformation machined die | |
| JP3496457B2 (en) | Composite press mold | |
| CN210648102U (en) | Stamping die and stamping equipment | |
| CN107199281A (en) | A kind of computer buckle diel for being easy to position | |
| JP4598297B2 (en) | Press-type pressure intensifier and mold structure using the same | |
| CN212495144U (en) | Forging device with ejection mechanism | |
| JP4609188B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for correcting flange warpage of forged workpiece | |
| JPH06154865A (en) | Press die | |
| KR960011543B1 (en) | High precision blanking machine and method | |
| JP4347197B2 (en) | Molding method using servo press | |
| JP2006255781A (en) | Drawing machine | |
| JPS5865522A (en) | Deep-drawing device for board material | |
| CN217070435U (en) | Shaping die | |
| CN111421042A (en) | Bidirectional drawing forming method | |
| JP2007118017A (en) | Double-action press device and press method | |
| CN223684334U (en) | A stretching mold for an automotive crossbeam bracket | |
| CN219401936U (en) | Chain link joint punching device for improving flatness |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: HONDA MOTOR CO., LTD., JAPAN Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:HORI, YUICHI;KONNO, YUICHI;MONDA, TAKANORI;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:019220/0417 Effective date: 20061024 |
|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |