RU2740009C1 - Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis - Google Patents
Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2740009C1 RU2740009C1 RU2019122697A RU2019122697A RU2740009C1 RU 2740009 C1 RU2740009 C1 RU 2740009C1 RU 2019122697 A RU2019122697 A RU 2019122697A RU 2019122697 A RU2019122697 A RU 2019122697A RU 2740009 C1 RU2740009 C1 RU 2740009C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- antigen
- concentration
- brucellosis
- interferon gamma
- stimulation index
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к медицине, в частности к инфекционным болезням и эпидемиологии, может быть использовано при проведении обследования людей перед профилактической вакцинацией и ревакцинацией против бруцеллеза и для установления факта сенсибилизации к бруцеллезному антигену.The invention relates to medicine, in particular to infectious diseases and epidemiology, can be used when examining people before preventive vaccination and revaccination against brucellosis and to establish the fact of sensitization to brucellosis antigen.
Согласно методическим указаниям МУК 3.1.7.3402-16 «Эпидемиологический надзор и лабораторная диагностика бруцеллеза» при обследовании населения перед профилактической вакцинацией целесообразно использовать пластинчатую реакцию агглютинации (Хеддельсона), реакцию непрямой гемагглютинации (РНГА) или иммуноферментный анализ (ИФА) и аллерготесты (кожно-аллергическая проба Бюрне, реакция лизиса лейкоцитов, определение экспрессии на базофилах рецепторов CD63 методом проточной цитометрии). Однако, в реальных условиях, руководители животноводческих предприятий и мясокомбинатов чаще выбирают только серологический метод исследования, как более экономичный (реакции агглютинации Райта и/или Хеддельсона) и исключают проведение ИФА и аллергологических реакций.According to the methodological guidelines MUK 3.1.7.3402-16 "Epidemiological surveillance and laboratory diagnostics of brucellosis", when examining the population before prophylactic vaccination, it is advisable to use a lamellar agglutination reaction (Heddelson's), an indirect hemagglutination reaction (RNGA) or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and allergy tests (allergy tests) Burne's test, leukocyte lysis reaction, determination of expression on basophils of CD63 receptors by flow cytometry). However, in real conditions, managers of livestock enterprises and meat processing plants often choose only the serological method of research, as it is more economical (Wright and / or Heddelson agglutination reactions) and exclude ELISA and allergic reactions.
Недостатком способов оценки поствакцинального иммунитета с использованием серологических реакций, включая ИФА, является возможность получения недостоверной информации из-за наличия блокирующих антител, а также наличия перекрестно реагирующих антител к микроорганизмам, имеющим общие антигенные детерминанты с бруцеллами, которые обусловливают ложноположительные серологические реакции на бруцеллез [Состояние и перспективы лабораторной диагностики бруцеллеза / Г.И. Лямкин [и др.] // Клиническая лабораторная диагностика. - 2002. - №12. - с. 46-49].The disadvantage of methods for assessing post-vaccination immunity using serological reactions, including ELISA, is the possibility of obtaining inaccurate information due to the presence of blocking antibodies, as well as the presence of cross-reacting antibodies to microorganisms that have common antigenic determinants with Brucella, which cause false-positive serological reactions to brucellosis [Status and prospects for laboratory diagnostics of brucellosis / G.I. Lyamkin [et al.] // Clinical laboratory diagnostics. - 2002. - No. 12. - from. 46-49].
Судить о напряженности поствакцинального иммунитета по результатам пробы Бюрне, также является невозможным, т.к. она имеет ряд недостатков. Во-первых, это инвазивная процедура, во-вторых, у лиц, высоко сенсибилизированных к бруцеллезному антигену, возможно развитие нежелательных реакций. Также известен риск возникновения ложноположительного результата при наличии аллергии и других иммунопатологических состояний. Учет реакции осуществляется через 24-48-72 часа, требуя наблюдение пациента в течение 72 часов [Инструкция по применению аллергена бруцеллезного жидкого (бруцеллина), раствор для внутрикожного введения: №01-11/198-06: утверждена Главным государственным санитарный врачом РФ Г.Г. Онищенко 22.11.06. - М, 2006].It is also impossible to judge the intensity of post-vaccination immunity based on the results of the Burne test, because it has several disadvantages. Firstly, this is an invasive procedure, and secondly, in persons highly sensitized to the brucellosis antigen, adverse reactions may develop. The risk of a false positive result in the presence of allergies and other immunopathological conditions is also known. The reaction is recorded after 24-48-72 hours, requiring observation of the patient within 72 hours [Instructions for the use of liquid brucellosis allergen (brucellin), solution for intradermal administration: No. 01-11 / 198-06: approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation G .G. Onishchenko 22.11.06. - M, 2006].
Известен метод оценки аллергической перестройки организма in vitro реакция лейкоцитолиза, но она имеет ряд ограничений, включая низкую специфичность, в результате чего не получил широкого применения в практике.There is a known method for assessing the allergic rearrangement of the organism in vitro, the reaction of leukocytolysis, but it has a number of limitations, including low specificity, as a result of which it has not received wide application in practice.
Известен новый метод аллергодиагностики - определение экспрессии на базофилах рецепторов CD63 методом проточной цитофлуориметрии [Новый подход к аллергодиагностике бруцеллеза / Пономаренко Д.Г. [и др.]. // Инфекция и иммунитет 2013. - Т. 3. - №1. - С. 89-92]. Определение аллергической перестройки организма проводят в условиях in vitro с помощью наборов для постановки тестов активации базофилов, который может применяться для определения аллергической реакции немедленного типа и гиперчувствительности к предполагаемым антигенам.A new method of allergy diagnostics is known - determination of expression on basophils of CD63 receptors by flow cytometry [A new approach to allergy diagnostics of brucellosis / Ponomarenko D.G. [and etc.]. // Infection and Immunity 2013. - T. 3. - №1. - S. 89-92]. Determination of the allergic rearrangement of the body is carried out in vitro using kits for setting up tests of activation of basophils, which can be used to determine an immediate type of allergic reaction and hypersensitivity to putative antigens.
Метод определения экспрессии на базофилах рецепторов CD63 методом проточной цитофлуориметрии является наиболее близким по технической сущности решением к заявленному изобретению по совокупности признаков. Способ включает инкубацию цельной гепаринизированной крови с бруцеллезным жидким аллергеном (бруцеллином) и моноклональными антителами против маркера дегрануляции базофилов - CD63. Далее определяют методом проточной цитофлуориометрии количество активированных базофилов, которое у вакцинированных против бруцеллеза находится в пределах от 5,1% до 19%. [Пат. 2574207, Российская Федерация, МПК. Способ дифференциации поствакцинного и инфекционного бруцеллезного процессов по степени повышенной чувствительности организма к бруцеллам в условиях in vitro [Электронный ресурс] / Пономаренко Д.Г. [и др.]; заявитель и патентообладатель: Федеральное казенное учреждение здравоохранения Ставропольский научно-исследовательский противочумный институт Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека. Режим доступа: https://findpatent.ru/patent/257/2574207.html].The method for determining the expression on basophils of CD63 receptors by flow cytometry is the closest solution in technical essence to the claimed invention in terms of a set of features. The method includes incubation of whole heparinized blood with brucellosis liquid allergen (brucellin) and monoclonal antibodies against the marker of basophil degranulation - CD63. Next, the amount of activated basophils is determined by the method of flow cytometry, which in those vaccinated against brucellosis ranges from 5.1% to 19%. [Pat. 2574207, Russian Federation, IPC. Method of differentiation of post-vaccine and infectious brucellosis processes according to the degree of increased sensitivity of the organism to brucella in vitro [Electronic resource] / Ponomarenko D.G. [and etc.]; applicant and patentee: Federal State Healthcare Institution Stavropol Research Anti-Plague Institute of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare. Access mode: https://findpatent.ru/patent/257/2574207.html].
К недостаткам прототипа относится:The disadvantages of the prototype include:
- ограничение по клеточному составу лейкоцитов, для оценки сенсибилизации используют базофилы, они составляют всего 0,5-1,0% от всех лейкоцитов и принимают активное участие преимущественно в развитии аллергических реакций немедленного типа;- restriction on the cellular composition of leukocytes, basophils are used to assess sensitization, they make up only 0.5-1.0% of all leukocytes and take an active part mainly in the development of immediate allergic reactions;
- в качестве специфического антигена применятся аллерген бруцеллезный жидкий - бруцеллин; содержащий белок от 3,8 до 5,4 мкг/мл в отличие от заявляемого способа, где в качестве специфического индуктора применяется инактивированный водорастворимый бруцеллезный антиген, полученный из вакцинного штамма Brucella abortus 19 ВА в конечном разведении по белку 50 мкг/мл, что позволяет получить более выраженный иммунный ответ в условиях in vitro;- liquid brucellosis allergen - brucellin is used as a specific antigen; containing protein from 3.8 to 5.4 μg / ml, in contrast to the proposed method, where an inactivated water-soluble brucellosis antigen obtained from the vaccine strain Brucella abortus 19 BA in a final protein dilution of 50 μg / ml is used as a specific inducer, which allows get a more pronounced immune response in vitro;
- для учета активированных бруцеллином базофилов, требуется проточный цитофлуометр и дорогостоящие реактивы, включающие специфические моноклональные антитела против маркера дегрануляции базофилов - CD63, что ограничивает применение этого метода.- to account for basophils activated by brucellin, a flow cytometer and expensive reagents are required, including specific monoclonal antibodies against the marker of basophil degranulation, CD63, which limits the use of this method.
Задачей изобретения является создание способа оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза, основанного на модифицированной реакции бласттрансформации лимфоцитов (мРБТЛ) с бруцеллезным антигеном (Brucella abortus 19 ВА) и определении концентрации спонтанного и антиген индуцированного гамма-интерферона (ИФН-γ) в культуральном супернатанте с помощью ИФА с последующим расчетом индекса стимуляции.The objective of the invention is to create a method for assessing post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis based on a modified reaction of lymphocyte blast transformation (mRBTL) with a brucella antigen (Brucella abortus 19 VA) and determining the concentration of spontaneous and antigen-induced interferon gamma (IFN-γ) in culture supernatant with the subsequent calculation of the stimulation index.
Поставленная задача решается благодаря тому, что в заявляемом способе оценивается клеточно-опосредованная реакция в ответ на специфический бруцеллезный антиген в условиях in vitro. Предусмотрены следующие отличия: проводится мРБТЛ с бруцеллезным антигеном Brucella abortus 19 ВА и определение концентрации спонтанного и антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ в культуральном супернатанте методом ИФА с последующим расчетом индекса стимуляции.The problem is solved due to the fact that the inventive method evaluates the cell-mediated response in response to a specific brucellosis antigen in vitro. The following differences are provided: mRBTL with brucellosis antigen Brucella abortus 19 VA and determination of the concentration of spontaneous and antigen-induced IFN-γ in the culture supernatant by ELISA with subsequent calculation of the stimulation index.
Кроме того предложенный способ отличается тем, что в качестве индуктора применяется инактивированный водорастворимый бруцеллезный антиген в конечном разведении по белку 50 мкг/мл, полученный из вакцинного штамма Brucella abortus 19 ВА, а определение концентрации спонтанного и антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ в культуральном супернатанте проводится спектрофотометрически при длине волны 450 нм, при этом уровень специфического клеточного ответа оценивается по индексу стимуляции с учетом концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ в культуральном супернатанте.In addition, the proposed method is characterized in that an inactivated water-soluble brucellosis antigen is used as an inducer in a final dilution of 50 μg / ml in protein, obtained from the vaccine strain Brucella abortus 19 VA, and the concentration of spontaneous and antigen-induced IFN-γ in the culture supernatant is determined spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450 nm, while the level of specific cellular response is assessed by the stimulation index, taking into account the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ in the culture supernatant.
Техническое решение позволяет усовершенствовать оценку поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза in vitro при помощи доступных лабораторных методов, оборудования и реактивов, не требующих высоких финансовых и трудозатрат, в том числе за счет применения готовых наборов тест-систем для определения ИФН-γ в супернатанте.The technical solution makes it possible to improve the assessment of post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis in vitro using available laboratory methods, equipment and reagents that do not require high financial and labor costs, including through the use of ready-made sets of test systems for determining IFN-γ in the supernatant.
Техническая сущность предлагаемого технического решения состоит в том, что с помощью мРБТЛ с бруцеллезным антигеном (Brucella abortus 19 ВА) и определения концентрации спонтанного и антиген-индуцированного ИФН-γ в культуральном супернатанте при помощи ИФА проводят оценку состояния специфического клеточного иммунного ответа in vitro по индексу стимуляции с учетом концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ.The technical essence of the proposed technical solution lies in the fact that using mRBTL with brucellosis antigen (Brucella abortus 19 VA) and determining the concentration of spontaneous and antigen-induced IFN-γ in the culture supernatant using ELISA, the state of the specific cellular immune response in vitro is assessed by the index stimulation taking into account the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ.
Описанное выше техническое решение «Способ оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза» осуществляется следующим образом. Сначала забирают кровь обследуемого пациента в вакуумную пробирку с зеленой крышкой (Li-гепарин/Na-гепарин). Гепаринизированную таким образом кровь в качестве контрольного образца в количестве 0,025 мл инкубируют в течение 72 часов во влажной камере термостата или СО2-инкубатора в стерильных условиях, в круглодонных иммунологических планшетах в 0,145 мл полной ростовой среды (ПРС).The above-described technical solution "Method for assessing post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis" is carried out as follows. First, the blood of the examined patient is taken into a vacuum tube with a green cap (Li-heparin / Na-heparin). Heparinized blood in this way as a control sample in an amount of 0.025 ml is incubated for 72 hours in a humid chamber of a thermostat or a CO 2 incubator under sterile conditions, in round-bottom immunological plates in 0.145 ml of complete growth medium (ORS).
Опытный образец крови в количестве 0,025 мл также культивируют в 0,145 мл ПРС, содержащей инактивированный водорастворимый специфический бруцеллезный антиген, полученный из вакцинного штамма Brucella abortus 19 ВА в конечном разведении 50 мкг/мл, в течение 72 часов.A test blood sample in the amount of 0.025 ml is also cultured in 0.145 ml of ORS containing inactivated water-soluble specific brucellosis antigen obtained from the vaccine strain Brucella abortus 19 BA at a final dilution of 50 μg / ml for 72 hours.
Из полученных контрольного и опытного образцов крови отбирают культуральные супернатанты (надосадок) и используют их для определения концентрации ИФН-γ с помощью набора реагентов тест-системы ИФА «гамма-Интерферон-ИФА-БЕСТ» (АО «Вектор-Бест», Новосибирск) в соответствии с инструкцией производителя. Учет результатов проводят спектрофотометрически при длине волны 450 нм с настройкой прибора «по воздуху».From the obtained control and experimental blood samples, culture supernatants (supernatant) are taken and used to determine the concentration of IFN-γ using a set of reagents of the ELISA test system "Interferon-IFA-BEST" (JSC "Vector-Best", Novosibirsk) in according to the manufacturer's instructions. The results are taken into account spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450 nm with the device set up "by air".
По значению индекса стимуляции (ИС) и концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ (пг/мл) судят о специфическом клеточном ответе на бруцеллезный антиген. Индекс стимуляции рассчитывается по формуле:By the value of the stimulation index (IS) and the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ (pg / ml), one can judge the specific cellular response to brucellosis antigen. The stimulation index is calculated by the formula:
ИС=Оп/К, гдеIS = Op / K, where
Оп - значение опытного образца в пг/мл (антиген индуцированная продукция ИФН-γ);Op is the value of the test sample in pg / ml (antigen-induced production of IFN-γ);
К - значение контроля в пг/мл (спонтанная продукции ИФН-γ).К - value of control in pg / ml (spontaneous production of IFN-γ).
Для реализации способа используют:To implement the method, use:
1. ПРС: среда 199, содержащая 10% эмбриональной телячьей сыворотки, L-глютамин (2 mM), HEPES (10 mM), гентамицина сульфат 50 мкг/мл.1. ORS: medium 199 containing 10% fetal calf serum, L-glutamine (2 mM), HEPES (10 mM), gentamicin sulfate 50 μg / ml.
2. Контрольный образец крови (0,025 мл).2. Control blood sample (0.025 ml).
3. Опытный образец крови (0,025 мл).3. Experimental blood sample (0.025 ml).
4. Инактивированный водорастворимый бруцеллезный антиген Brucella abortus 19 ВА.4. Inactivated water-soluble brucellosis antigen Brucella abortus 19 VA.
5. Раствор хлорида натрия 0,9% для разведения антигена.5. Sodium chloride solution 0.9% for antigen dilution.
6. Набор реагентов для иммуноферментного определения концентрации γ-интерферона в сыворотке, плазме крови, культуральном супернатанте (γ-Интерферон-ИФА-БЕСТ, Новосибирск).6. A set of reagents for the enzyme immunoassay for the determination of the concentration of γ-interferon in serum, blood plasma, culture supernatant (γ-Interferon-ELISA-BEST, Novosibirsk).
7. Принцип анализа: «Sandwich» - вариант твердофазного трехстадийного ИФА на планшетах.7. Principle of analysis: "Sandwich" is a variant of solid-phase three-stage ELISA on plates.
8. Учет результатов: спектрофотометрия на длине волны 450 нм.8. Accounting of results: spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 450 nm.
Статистическую обработку полученных результатов проводили с использованием программы Microsoft Excel 2010. Для интервальной оценки медианы значений применяли статистическую программу «Довинт v. 1.0». Достоверность различий в двух независимых выборках оценивалась с помощью критерия Манна-Уитни (U), при сравнении более двух независимых выборок - критерия Краскела-Уоллиса (Н). Критический уровень значимости при проверке статистических гипотез принимался равным 0,05.Statistical processing of the results was carried out using Microsoft Excel 2010. For interval estimation of the median values, the statistical program “Dovint v. 1.0 ". The significance of differences in two independent samples was assessed using the Mann-Whitney test (U), when comparing more than two independent samples - the Kruskal-Wallis test (H). The critical level of significance when testing statistical hypotheses was taken equal to 0.05.
Техническим результатом изобретения является усовершенствование оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза за счет создания информативного, экономичного и широкодоступного способа для практического здравоохранения in vitro с помощью мРБТЛ с бруцеллезным антигеном (Brucella abortus 19 ВА) и ИФА для определения концентрации спонтанного и антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ в культуральном супернатанте с последующим расчетом индекса стимуляции.The technical result of the invention is to improve the assessment of post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis by creating an informative, economical and widely available method for practical health care in vitro using mRBTL with brucellosis antigen (Brucella abortus 19 VA) and ELISA to determine the concentration of spontaneous and antigen-induced IFN-γ in the culture supernatant with subsequent calculation of the stimulation index.
Изобретение иллюстрируется следующими примерами. Пример 1. Обследование лиц, ранее невакцинированных от бруцеллеза, заявленным способом (перед вакцинацией)The invention is illustrated by the following examples. Example 1. Examination of persons previously unvaccinated against brucellosis by the claimed method (before vaccination)
Нами было проведено изучение предложенного способа у 34 лиц в возрасте от 23 до 59 лет, не имевших в анамнезе вакцинации от бруцеллеза. Всем обследуемым были проведены реакции агглютинации Райта и Хеддельсона, а также ИФА с определением противобруцеллезных антител классов IgM, IgG, IgA.We have studied the proposed method in 34 persons aged 23 to 59 years, who had no history of vaccination against brucellosis. All the subjects underwent Wright and Heddelson agglutination reactions, as well as ELISA with the determination of anti-brucellosis antibodies of the IgM, IgG, IgA classes.
Затем был оценен уровень спонтанной продукции ИФН-γ и уровень антиген индуцированной продукции ИФН-γ бруцеллезным антигеном (Brucella abortus 19 ВА) и рассчитан индекс стимуляции.Then the level of spontaneous production of IFN-γ and the level of antigen-induced production of IFN-γ by brucellosis antigen (Brucella abortus 19 VA) were assessed and the stimulation index was calculated.
В группе людей, не имевших в анамнезе вакцинации от бруцеллеза, при серологическом исследовании в реакциях Хеддельсона, Райта и ИФА не регистрировалось противобруцеллезных антител. Результаты исследования по продукции спонтанного и антиген индуцированнного ИФН-γ представлены в таблице 1.In the group of people who did not have a history of vaccination against brucellosis, anti-brucellosis antibodies were not recorded in the reactions of Heddelson, Wright and ELISA during serological examination. The results of the study on the production of spontaneous and antigen-induced IFN-γ are presented in Table 1.
В результате эксперимента было установлено достоверно значимое увеличение уровня антиген индуцированной продукции ИФН-γ (Н=81,7; р<0,05) и значения индекса стимуляции в группе вакцинированных лиц от бруцеллеза по сравнению с невакцинированными (Н=63,2; р<0,05).As a result of the experiment, a significantly significant increase in the level of antigen-induced production of IFN-γ (H = 81.7; p <0.05) and the value of the stimulation index in the group of vaccinated persons against brucellosis compared with unvaccinated persons (H = 63.2; p <0.05).
Уровень спонтанной продукции ИФН-γ в группах вакцинированных и невакцинированных от бруцеллеза лиц достоверно не различался (р>0,05).The level of spontaneous production of IFN-γ in the groups of persons vaccinated and unvaccinated against brucellosis did not differ significantly (p> 0.05).
Установлено, что у людей, не имевших в анамнезе вакцинации от бруцеллеза, медиана значений антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ равна 15,6 пг/мл, при этом с 99,9%-ной вероятностью находится в пределах 12,2-23,3 пг/мл. Медиана значений индекса стимуляции равна 1,0 и с 99,9%-ной вероятностью находится в пределах 1,0-1,3.It was found that in people who did not have a history of vaccination against brucellosis, the median of antigen-induced IFN-γ values is 15.6 pg / ml, while with a 99.9% probability it is in the range of 12.2-23.3 pg / ml. The median values of the stimulation index is 1.0 and with 99.9% probability is in the range of 1.0-1.3.
Результат считается отрицательным в пределах значений верхней границы доверительного интервала 99,9% антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ до 23,3 пг/мл (возможно округление до 23,0) и ИС - до 1,3. При таких значениях вышеуказанных показателей - показана вакцинация.The result is considered negative within the values of the upper limit of the confidence interval of 99.9% antigen-induced IFN-γ up to 23.3 pg / ml (rounding up to 23.0 is possible) and IS - up to 1.3. With such values of the above indicators, vaccination is indicated.
Пример 2. Способ оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза у ранее привитых лицExample 2. A method for assessing post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis in previously vaccinated individuals
Для изучения предложенного способа было обследовано 70 работников мясокомбината в возрасте от 23 до 59 лет, у которых документально был подтвержден факт вакцинации от бруцеллеза (13 месяцев назад) живой бруцеллезной вакциной Brucella abortus 19 ВА.To study the proposed method, 70 workers of the meat-packing plant were examined at the age of 23 to 59 years, in whom the fact of vaccination against brucellosis (13 months ago) with live brucellosis vaccine Brucella abortus 19 VA was documented.
Значения концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ и индекса стимуляции, в группе лиц, ранее вакцинированных от бруцеллеза, были вариабельными (табл. 2). Подавляющее большинство (81,4%) обследуемых лиц имело высокие и очень высокие значения концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ и ИС, что свидетельствует о наличии выраженной сенсибилизации к бруцеллезному антигену.The values of the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ and the stimulation index in the group of persons previously vaccinated against brucellosis were variable (Table 2). The vast majority (81.4%) of the examined individuals had high and very high values of the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ and IS, which indicates the presence of pronounced sensitization to brucellosis antigen.
За норму были приняты результаты исследования невакцинированных лиц: антиген индуцированный ИФН-γ Ме=15,6 пг/мл; ДИ 99,9% [12,2-23,3] пг/мл и ИС - Ме=1,0; ДИ 99,9% [1,0-1,3]. На основании этого, лица, имеющие сочетание значений антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ и ИС до 2-х норм Me [ДИ 99,9%] - допускаются к ревакцинации от бруцеллеза. При этом медиана значения антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ будет равна 31,2 пг/мл, верхняя граница доверительного интервала 99,9% - 46,6 пг/мл (возможно округление до 47,0 пг/мл), при этом медиана значения ИС равна 2,0 и с учетом верхней границы доверительного интервала 99,9% - 2,6. При таких значениях уровень антигенной индукции расценивается, как низкий, а поствакцинальный иммунитет - как недостаточно протективный. Таким образом, критериями допуска к ревакцинации является сочетание значений антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ до 47,0 пг/мл и ИС до 2,6.The results of the study of unvaccinated individuals were taken as the norm: antigen induced by IFN-γ Me = 15.6 pg / ml; CI 99.9% [12.2-23.3] pg / ml and IS - Me = 1.0; CI 99.9% [1.0-1.3]. On this basis, persons with a combination of values of antigen-induced IFN-γ and IS up to 2 norms of Me [CI 99.9%] are allowed for revaccination against brucellosis. In this case, the median value of the antigen-induced IFN-γ will be 31.2 pg / ml, the upper limit of the confidence interval of 99.9% - 46.6 pg / ml (rounding up to 47.0 pg / ml is possible), while the median of the IC value equal to 2.0 and, taking into account the upper limit of the confidence interval of 99.9%, 2.6. With such values, the level of antigenic induction is regarded as low, and post-vaccination immunity is regarded as insufficiently protective. Thus, the criteria for admission to revaccination is a combination of values of antigen-induced IFN-γ up to 47.0 pg / ml and IP up to 2.6.
Далее, в таблице 2 показано применение полученных критериев допуска к ревакцинации. Все рекомендованные к ревакцинации лица (согласно графику ревакцинации от бруцеллеза на мясокомбинате), были распределены по группам в зависимости от полученных значений концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ.Further, Table 2 shows the application of the obtained admission criteria for revaccination. All persons recommended for revaccination (according to the schedule of revaccination against brucellosis at a meat processing plant) were divided into groups depending on the obtained values of the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ.
Не допускаются к ревакцинации от бруцеллеза лица, имеющие сочетание значений антиген-индуцированного ИФН-γ выше 47,0 пг/мл и ИС выше 2,6 в связи с риском развития осложнений. Таким образом, на основании результатов обследования и полученного распределения, только 13 из 70 человек рекомендуется ревакцинация от бруцеллеза.Persons with a combination of antigen-induced IFN-γ values above 47.0 pg / ml and an IP of above 2.6 are not allowed for revaccination against brucellosis due to the risk of complications. Thus, based on the results of the examination and the obtained distribution, only 13 out of 70 people are recommended to revaccine against brucellosis.
Пример 3. Результаты серологического тестирования у лиц, ранее вакцинированных от бруцеллезаExample 3. Results of serological testing in persons previously vaccinated against brucellosis
Сыворотки обследуемых нами ранее 70 работников мясокомбината в возрасте от 23 до 59 лет, у которых документально был подтвержден факт вакцинации от бруцеллеза (13 месяцев назад) живой бруцеллезной вакциной Brucella abortus 19 ВА были поставлены в серологических реакциях агглютинации (Хеддельсона, Райта) и ИФА. В таблицах 3, 4, 5 представлены результаты.Sera of 70 workers of the meat-packing plant examined by us earlier, aged from 23 to 59 years, in whom the fact of vaccination against brucellosis (13 months ago) with live brucellosis vaccine Brucella abortus 19 VA was documented were delivered in serological agglutination tests (Heddelson, Wright) and ELISA. Tables 3, 4, 5 show the results.
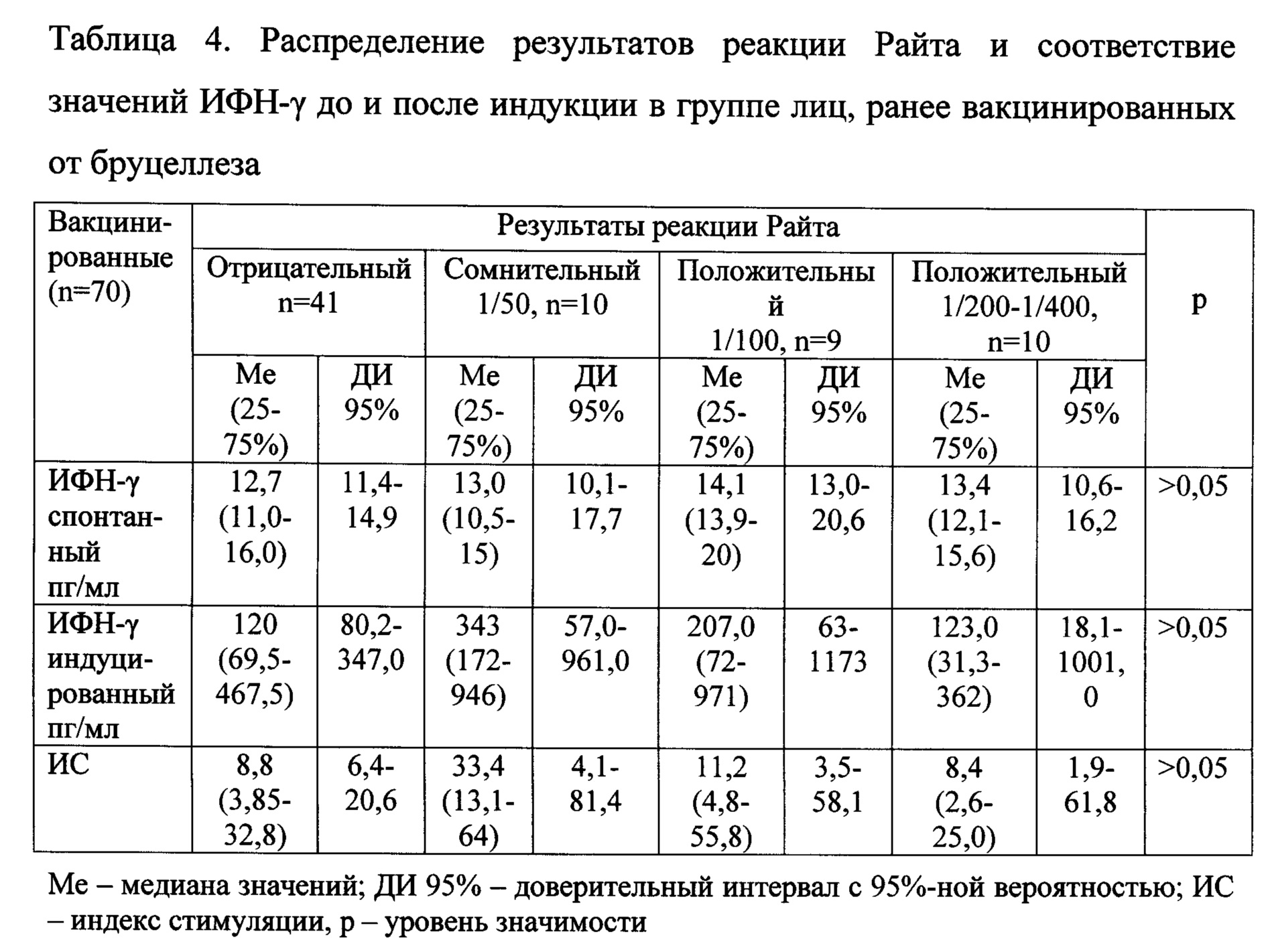
В группе лиц, ранее вакцинированных от бруцеллеза, были получены как отрицательные, так и положительные результаты серологических тестов: в реакциях Хеддельсона, Райта и ИФА (таблицы 3, 4, 5).In the group of persons previously vaccinated against brucellosis, both negative and positive results of serological tests were obtained: in the reactions of Heddelson, Wright and ELISA (tables 3, 4, 5).
В реакции Хеддельсона были получены следующие результаты: отрицательные - в 34 случаях (48,6%); сомнительные - в 9 случаях (12,8%); положительные/резко положительные - в 27 случаях (38,6%).The following results were obtained in the Heddelson reaction: negative - in 34 cases (48.6%); doubtful - in 9 cases (12.8%); positive / sharply positive - in 27 cases (38.6%).
При отрицательном результате в реакции Хеддельсона с 95%-ной вероятностью уровень антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ находился в пределах 76,0-424,0 пг/мл и индекс стимуляции ИФН-γ - в пределах 5,6-34,5.With a negative result in the Heddelson reaction with a 95% probability, the level of antigen-induced IFN-γ was in the range of 76.0-424.0 pg / ml and the stimulation index of IFN-γ was in the range of 5.6-34.5.
На фоне отрицательных и сомнительных результатов реакции Хеддельсона, что составило 61,4% (43 человека) от всех результатов данной реакции, отмечался выраженный антиген индуцированный клеточный иммунный ответ без статистически достоверной разницы в данных группах (U=1,7; р>0,05). При этом у 48,6% (34) пациентов при отрицательных результатах в реакции Хеддельсона был получен клеточный иммунный ответ. Достоверных различий в группах с отрицательным, сомнительным, положительным и резко положительными результатами по индуцированному ИФН-γ (Н=1,7; р>0,05) и по значению индекса стимуляции не было обнаружено (Н=0,7; р>0,05).Against the background of negative and doubtful results of the Heddelson test, which amounted to 61.4% (43 people) of all the results of this reaction, a pronounced antigen-induced cellular immune response was noted without a statistically significant difference in these groups (U = 1.7; p> 0, 05). Moreover, in 48.6% (34) patients with negative results in the Heddelson reaction, a cellular immune response was obtained. There were no significant differences in the groups with negative, doubtful, positive and sharply positive results for the induced IFN-γ (H = 1.7; p> 0.05) and the value of the stimulation index were not found (H = 0.7; p> 0 , 05).
Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о том, что для оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза серологическое исследование в пластинчатой реакции агглютинации Хеддельсона является недостаточным, и уровень специфического клеточного ответа достоверно не различается в группах с разными результатами реакции Хеддельсона.The results obtained indicate that serological research in the Heddelson lamellar agglutination test is insufficient to assess post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis, and the level of specific cellular response does not significantly differ in groups with different results of the Heddelson test.
В реакции агглютинации Райта были получены следующие результаты: отрицательные - в 41 случае (58,6%); сомнительные (титр антител 1/50)- в 10 случаях (14,3%); положительные (титр 1/100) - в 9 случаях (12,8%); положительные (титр 1/200-1/400) - в 10 случаях (14,3%). Достоверных различий по спонтанной, антиген индуцированной продукции ИФН-γ (Н=6,1; р>0,05) и индексам стимуляции в группах в зависимости от результатов реакции Райта не было получено (Н=1,6; р>0,05).The following results were obtained in the Wright agglutination reaction: negative - in 41 cases (58.6%); doubtful (antibody titer 1/50) - in 10 cases (14.3%); positive (titer 1/100) - in 9 cases (12.8%); positive (titer 1 / 200-1 / 400) - in 10 cases (14.3%). There were no significant differences in spontaneous, antigen-induced IFN-γ production (H = 6.1; p> 0.05) and stimulation indices in groups depending on the results of the Wright reaction (H = 1.6; p> 0.05 ).
При отрицательном результате в реакции Райта с 95%-ной вероятностью значение концентрации антиген индуцированного ИФН-γ находилось в пределах 80,2-347,0 пг/мл и индекс стимуляции ИФН-γ - в пределах 6,4-20,6. Таким образом, у пациентов данной группы отмечался только клеточный иммунный ответ на бруцеллезный антиген с медианой значения ИС - 8,8 пг/мл. Это свидетельствует о том, что для оценки поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза серологическое исследование в реакции агглютинации Райта является недостаточным.With a negative result in the Wright reaction with a 95% probability, the concentration of antigen-induced IFN-γ was in the range of 80.2-347.0 pg / ml and the stimulation index of IFN-γ was in the range of 6.4-20.6. Thus, in patients of this group, only a cellular immune response to brucellosis antigen with a median IS value of 8.8 pg / ml was noted. This indicates that the serological study in the Wright agglutination test is insufficient to assess post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis.
По результатам ИФА у ранее вакцинированных от бруцеллеза лиц (у 60 из 70 человек) выявлялись противобруцеллезные антитела (коэффициент позитивности более 1,0) либо одного класса, либо в сочетании. Антитела к бруцеллам всех трех классов (IgG+IgA+IgM) были выявлены у 5 человек. Антитела двух классов (IgG+IgA) - у 46 человек; только IgG - у 5; только IgA - у 4-х человек. При выявлении антител к бруцеллам в ИФА (особенно IgM) при наличии факторов риска заражения бруцеллезом необходима консультация инфекциониста для исключения инфицирования возбудителем бруцеллеза.According to the results of ELISA in persons previously vaccinated against brucellosis (60 out of 70 people), anti-brucellosis antibodies (positivity coefficient more than 1.0) were detected either of one class or in combination. Antibodies to brucella of all three classes (IgG + IgA + IgM) were detected in 5 people. Antibodies of two classes (IgG + IgA) - in 46 people; only IgG - in 5; only IgA - in 4 people. When detecting antibodies to brucella in ELISA (especially IgM) in the presence of risk factors for infection with brucellosis, it is necessary to consult an infectious disease specialist to exclude infection with the pathogen of brucellosis.
Независимо от результатов ИФА (положительный, отрицательный) были получены высокие значения индекса стимуляции (табл. 5). В случаях отсутствия антител к бруцеллезным антигенам в ИФА (Ig М, G, А) у лиц, ранее вакцинированных от бруцеллеза, были получены высокие значения ИС (Me ИС: 17,3; 9,3; 7,1 соответственно). Вышеизложенные данные свидетельствует о том, что применение ИФА с определением противобруцеллезных антител трех классов, также является недостаточным для оценки поствакцинального иммунитета.Regardless of the results of ELISA (positive, negative), high values of the stimulation index were obtained (Table 5). In the absence of antibodies to brucellosis antigens in ELISA (Ig M, G, A) in individuals previously vaccinated against brucellosis, high IS values were obtained (Me IS: 17.3; 9.3; 7.1, respectively). The above data indicate that the use of ELISA with the determination of anti-brucellosis antibodies of three classes is also insufficient for assessing post-vaccination immunity.
В примерах демонстрируется, что величина антиген индуцированной продукции ИФН-γ используется как показатель напряженности специфического клеточного иммунного ответа в группах невакцинированных и вакцинированных ранее от бруцеллеза лиц.The examples demonstrate that the value of antigen-induced production of IFN-γ is used as an indicator of the intensity of the specific cellular immune response in groups of unvaccinated and previously vaccinated against brucellosis.
Таким образом, разработанный способ позволяет усовершенствовать оценку поствакцинального иммунитета против бруцеллеза. По силе специфического клеточного ответа можно судить об уровне сенсибилизации организма к бруцеллезному антигену, предотвращая поствакцинальные осложнения. В связи с чем, способ может применяться перед вакцинацией и ревакцинацией от бруцеллеза и для установления факта сенсибилизации к бруцеллезному антигену в качестве аллерготеста in vitro.Thus, the developed method makes it possible to improve the assessment of post-vaccination immunity against brucellosis. By the strength of a specific cellular response, one can judge the level of body sensitization to the brucellosis antigen, preventing post-vaccination complications. In this connection, the method can be used before vaccination and revaccination against brucellosis and to establish the fact of sensitization to brucellosis antigen as an in vitro allergy test.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2019122697A RU2740009C1 (en) | 2019-07-15 | 2019-07-15 | Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2019122697A RU2740009C1 (en) | 2019-07-15 | 2019-07-15 | Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2740009C1 true RU2740009C1 (en) | 2020-12-30 |
Family
ID=74106506
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2019122697A RU2740009C1 (en) | 2019-07-15 | 2019-07-15 | Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2740009C1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115267204A (en) * | 2022-08-02 | 2022-11-01 | 中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所 | Method and kit for evaluating immunity of flocks to brucellosis vaccine |
| RU2785906C1 (en) * | 2022-01-12 | 2022-12-14 | Федеральное казённое учреждение здравоохранения "Ставропольский научно-исследовательский противочумный институт" Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека | Method for immunological diagnosis of brucellosis |
| CN115508561A (en) * | 2022-08-02 | 2022-12-23 | 中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所 | Method and kit for evaluating whether cattle are immunized with brucellosis vaccine |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20070224257A1 (en) * | 2006-03-21 | 2007-09-27 | The Secretary Of State For Environment, Foods & Rural Affairs | Brucellosis dna vaccine |
| RU2419096C2 (en) * | 2009-07-16 | 2011-05-20 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Федеральный центр токсикологической и радиационной безопасности животных" (ФГУ "ФЦТРБ-ВНИВИ") | Method of evaluating immunogenecity of anti-bricellosis vaccine strains |
| RU2574207C1 (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2016-02-10 | Федеральное казённое учреждение здравоохранения Ставропольский научно-исследовательский противочумный институт Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека | Method for differentiating in vitro postvaccinal and infectious brucellosis according to degree of body hypersensitivity to brucella |
-
2019
- 2019-07-15 RU RU2019122697A patent/RU2740009C1/en active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20070224257A1 (en) * | 2006-03-21 | 2007-09-27 | The Secretary Of State For Environment, Foods & Rural Affairs | Brucellosis dna vaccine |
| RU2419096C2 (en) * | 2009-07-16 | 2011-05-20 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Федеральный центр токсикологической и радиационной безопасности животных" (ФГУ "ФЦТРБ-ВНИВИ") | Method of evaluating immunogenecity of anti-bricellosis vaccine strains |
| RU2574207C1 (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2016-02-10 | Федеральное казённое учреждение здравоохранения Ставропольский научно-исследовательский противочумный институт Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека | Method for differentiating in vitro postvaccinal and infectious brucellosis according to degree of body hypersensitivity to brucella |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| A. N. KULICHENK et al. Use of antigen-specific cell tests in vitro to assess the formation of post-vaccination anti-plague immunity // Infection and Immunity, 2017, Vol. 7, N2, pp. 203-208. * |
| D.G. PONAMORENKO A new approach to a comprehensive assessment of the immuno-biological reactivity of the contingent subject to vaccination (revaccination) against brucellosis // EPIDEMIOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES. TOPICAL ISSUES, 2015, N3, pp. 28-31 . * |
| КУЛИЧЕНК0 A.Н. и др. Использование антигенспецифических клеточных тестов in vitro для оценки формирования поствакцинального противочумного иммунитета // Инфекция и иммунитет, 2017, Т.7, N2, с.203-208. ПОНАМОРЕНКО Д.Г. Новый подход к комплексной оценке иммуно-биологической реактивности контингента, подлежащего вакцинации (ревакцинации) против бруцеллеза // ЭПИДЕМИОЛОГИЯ И ИНФЕКЦИОННЫЕ БОЛЕЗНИ. АКТУАЛЬНЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ, 2015, N3, стр.28-31.. * |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2785906C1 (en) * | 2022-01-12 | 2022-12-14 | Федеральное казённое учреждение здравоохранения "Ставропольский научно-исследовательский противочумный институт" Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека | Method for immunological diagnosis of brucellosis |
| CN115267204A (en) * | 2022-08-02 | 2022-11-01 | 中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所 | Method and kit for evaluating immunity of flocks to brucellosis vaccine |
| CN115508561A (en) * | 2022-08-02 | 2022-12-23 | 中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所 | Method and kit for evaluating whether cattle are immunized with brucellosis vaccine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Stagno et al. | Comparative serial virologic and serologic studies of symptomatic and subclinical congenitally and natally acquired cytomegalovirus infections | |
| Taylor-Robinson et al. | A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production | |
| Zoschke et al. | Lymphoproliferative responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease | |
| Animut et al. | Febrile illnesses of different etiology among outpatients in four health centers in Northwestern Ethiopia | |
| Nielsen | Diagnosis of brucellosis by serology | |
| Errera et al. | Real-time polymerase chain reaction and intraocular antibody production for the diagnosis of viral versus toxoplasmic infectious posterior uveitis | |
| Narang et al. | Influenza vaccine-induced antibody responses are not impaired by frailty in the community-dwelling elderly with natural influenza exposure | |
| RU2740009C1 (en) | Method for assessing postvaccinal immunity against brucellosis | |
| Wieden et al. | Detection of coccidioidal antibodies by 33-kDa spherule antigen, Coccidioides EIA, and standard serologic tests in sera from patients evaluated for coccidioidomycosis | |
| Lappin et al. | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii-specific antibodies and antigens in the aqueous humor of cats | |
| Murphy et al. | THE PERSISTENCE OF COMPLEMENT‐FIXING ANTIBODIES TO Q–FEVER (COXIELLA BURNETI) AFTER INFECTION | |
| Barbuddhe et al. | Immunodetection of bacteria causing brucellosis | |
| Rahamathulla | Seroprevalence of human brucellosis in Wadi Al Dawaser region of Saudi Arabia | |
| Bergmann et al. | Comparison of four commercially available point-of-care tests to detect antibodies against canine distemper virus in dogs | |
| CN106939035A (en) | A kind of mycobacterium tuberculosis T cell antigen epitope polypeptide and its application | |
| JP2010525831A (en) | Assays for detecting mycobacterial infections | |
| Abdullahi et al. | Leucocytes and Th-associated cytokine profile of HIV-leishmaniasis Co-infected persons attending abuja teaching hospital, Nigeria | |
| RU2447445C1 (en) | Method for evaluating clinical effectiveness and dynamics of destructive changes in pulmonary tissue accompanying pulmonary tuberculosis | |
| Krakauer | Levels of interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor in serum from humans vaccinated with live, attenuated Francisella tularensis | |
| Holliman et al. | The post-natal serodiagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis | |
| RU2785906C1 (en) | Method for immunological diagnosis of brucellosis | |
| Russell et al. | Evaluation of the card test for diagnosis of human brucellosis | |
| RU2289138C2 (en) | Method for allergodiagnostics by the values of chemiluminescent phosphorescence of neutrophils | |
| US20180335432A1 (en) | System and Method of Detecting Bacterial Infections | |
| Sakakibara et al. | Concentrations of immunoglobulin G antibodies against pertussis toxin does not decrease over a long period of time in Japan |