RU2589819C1 - VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA - Google Patents
VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2589819C1 RU2589819C1 RU2015120081/15A RU2015120081A RU2589819C1 RU 2589819 C1 RU2589819 C1 RU 2589819C1 RU 2015120081/15 A RU2015120081/15 A RU 2015120081/15A RU 2015120081 A RU2015120081 A RU 2015120081A RU 2589819 C1 RU2589819 C1 RU 2589819C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- moraxella
- vaccine
- bacteria
- concentration
- bovoculi
- Prior art date
Links
Landscapes
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к области ветеринарной микробиологии и биотехнологии, в частности к производству и применению биологического препарата против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота. Вакцина предназначена для специфической профилактики инфекционного кератоконъюнктивит крупного рогатого скота, вызываемого бактериями Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi.The invention relates to the field of veterinary microbiology and biotechnology, in particular to the production and use of a biological preparation against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle. The vaccine is intended for specific prophylaxis of infectious cattle conjunctivitis caused by the bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi.
Инфекционный кератоконъюнктивит крупного рогатого скота (ИКК) - острое контагиозное заболевание, характеризующееся слезотечением, гиперемией сосудов конъюнктивы, светобоязнью, серозно-гнойным истечением, помутнением и изъязвлением роговицы, деформацией глазного яблока в виде кератоглобуса или кератоконуса, частичной или полной потерей зрения пораженного глаза животного. Болезнь распространена во всех странах мира и наносит скотоводческим хозяйствам значительный экономический ущерб вследствие снижения удоев молока до 50%, прироста массы тела на 31-37%, падежа, а также затрат на проведение ветеринарно-санитарных и лечебно-профилактических мероприятий. Нами установлено, что заболеваемость телят 2-6-месячного возраста в отдельных хозяйствах достигает до 85%, среди откормочного поголовья - 22% и среди дойного стада - в пределах 8-10%.Infectious keratoconjunctivitis of cattle (ICC) is an acute contagious disease characterized by lacrimation, conjunctival vascular hyperemia, photophobia, serous-purulent outflow, clouding and ulceration of the cornea, deformity of the eyeball in the form of keratogon or keratoglobus palatus, or keratogloidus. The disease is widespread in all countries of the world and causes significant economic damage to livestock farms due to a decrease in milk yield by 50%, an increase in body weight by 31-37%, mortality, as well as the costs of veterinary, sanitary and therapeutic measures. We found that the incidence of calves of 2-6 months of age in individual farms reaches 85%, among fattening livestock - 22% and among dairy herds - in the range of 8-10%.
Заболевание вызывается гемолитическими штаммами бактерий Moraxella bovis (Гаффаров Х.З., Валебная Л.В., Спиридонов Г.Н. Инфекционный кератоконъюнктивит крупного рогатого скота в регионе Среднего Поволжья и Предуралья / Матер. междунар. науч.-практ. конф.: Актуальные проблемы болезней молодняка в современных условиях. - Воронеж. - 2002. - С. 188-191; Карайченцев В.Н., Дунаев Г.В., Русинов А.Ф., Бабенко О.В. Изоляция Moraxella bovis от молодняка крупного рогатого скота при инфекционном кератоконъюнктивите / Ветеринария. - 1992. - №2. - С. 26-27; Русинов А.Ф. Инфекционный кератоконъюнктивит у крупного рогатого скота / Информ. бюлл. Укр. акад. аграр. наук. Ин-т эксперим. клинич. вет. медицины, 1995; Спиридонов Г.Н. Инфекционный кератоконьюнктивит крупного рогатого скота // Проблемы профилактики и борьбы с особо опасными, экзотическими и малоизученными инфекционными болезнями животных. - Труды межд. научн.-производ. конф., посвященной 50-летию ВНИИВВиМ. - том 2. - Покров. - 2008. - С. 195-197. Arora А.К. Studies on Moraxella bovis isolated from cattle affected with or convalescing from infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis / Vet. Arhiv. - 1989. - V. 50. - №l. - P. 17-23).The disease is caused by hemolytic strains of bacteria Moraxella bovis (Gaffarov Kh.Z., Valebnaya L.V., Spiridonov G.N. Infectious keratoconjunctivitis of cattle in the Middle Volga and Ural regions / Mater. International scientific-practical conference: Topical problems of young diseases in modern conditions - Voronezh. - 2002. - P. 188-191; Karaichentsev VN, Dunaev GV, Rusinov AF, Babenko OV Isolation of Moraxella bovis from young cattle cattle with infectious keratoconjunctivitis / Veterinary medicine. - 1992. - No. 2. - P. 26-27; Rusinov AF. Infectious keratococcus bovine conjunctivitis / Information Bulletin, Ukrainian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Institute of Experimental Clinical Veterinary Medicine, 1995; Spiridonov GN, Infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle // Problems of prevention and control of especially dangerous , exotic and poorly studied infectious diseases of animals. - Proceedings of the international scientific production conference dedicated to the 50th anniversary of VNIIVViM. - Volume 2. - Veil. - 2008. - P. 195-197. Arora A.K. Studies on Moraxella bovis isolated from cattle affected with or convalescing from infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis / Vet. Arhiv. - 1989. - V. 50. - No. l. - P. 17-23).
В последние годы установлено, что инфекционный кератоконъюнктивит крупного рогатого скота может быть вызван другими представителями рода Moraxella, в частности бактериями Moraxella bovoculi (Angelos J.A., Spinks P.Q., Ball L.M., George L.W. Moraxella bovoculi sp.nov., isolated from calves with infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis // Int J Syst Evol Microbiol - 2007 Apr; 57 (Pt 4):789-95; Galvão K.N., Angelos J.A., Ulcerative blepharitis and conjunctivitis in adult dairy cows and association with Moraxella bovoculi // Can Vet J. - 2010 Apr; 51(4):400-2; Angelos J.A., Lane V.M., Ball L.M., Hess J.F. Recombinant Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis. / Vet Res Commun. 2010 Mar; 34 (3); Angelos J.A., Ball L.M, Differentiation of Moraxella bovoculi sp. nov. from other coccoid moraxellae by the use of polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease analysis of amplified DNA // J Vet Diagn Invest - 2007 Sep; 19 (5):532-(4).In recent years, it has been established that infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle can be caused by other representatives of the genus Moraxella, in particular bacteria Moraxella bovoculi (Angelos JA, Spinks PQ, Ball LM, George LW Moraxella bovoculi sp.nov., Isolated from calves with infectious bovine keratoconjun // Int J Syst Evol Microbiol - 2007 Apr; 57 (Pt 4): 789-95; Galvão KN, Angelos JA, Ulcerative blepharitis and conjunctivitis in adult dairy cows and association with Moraxella bovoculi // Can Vet J. - 2010 Apr; 51 (4): 400-2; Angelos JA, Lane VM, Ball LM, Hess JF Recombinant Moraxella bovoculi cytotoxin-ISCOM matrix adjuvanted vaccine to prevent naturally occurring infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis. / Vet Res Commun. 2010 Mar; 34 (3); Angelos JA, Ball LM, Differentiation of Moraxella bovoculi sp. Nov.f rom other coccoid moraxellae by the use of polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease analysis of amplified DNA // J Vet Diagn Invest - 2007 Sep; 19 (5): 532- (4).
Инфекционный кератоконъюнктивит крупного рогатого скота, вызванный бактериями Moraxella bovoculi, мы наблюдали в хозяйствах Республики Татарстан (совхоз-техникум Чистопольского; ООО «Среднее Девятово», ООО «Хаерби» Лаишевского и СХПК «Енали» Апастовского районов), Республики Башкортостан (СПК-колхоз имени Калинина Дюртюлинского района), Ленинградской области (ООО «Яровое» Приозерского района), Челябинской области (ООО «Агрофирма «Калининское» Брединского района).Infectious keratoconjunctivitis of cattle caused by bacteria Moraxella bovoculi, we observed in the farms of the Republic of Tatarstan (Chistopolsky state farm technical school; Srednye Devyatovo LLC, Khaerby LLC Laishevsky and Yenali agricultural production complex of Apastovsky district), Republic of Bashkortostan named after SPK-Kolk Kalinin of the Dyurtyulinsky district), the Leningrad region (Yarovoye LLC of the Priozersky region), the Chelyabinsk region (Kalininsky Agrofirm LLC of the Bredinsky district).
В настоящее время основным методом борьбы с инфекционным кератоконъюнктивитом крупного рогатого скота является специфическая ее профилактика с использованием различных видов вакцинных препаратов (Hughes D. et. al. Experimenally induced Bovine Infectious Keratoconjunctivitis: Effectivcnes of Intramuscular Vaccination with Viable Moraxella bovis Culture. // Am, J. Vet. Res., 1971, 32 №6 - p.879-886; Pugh G.W. et al. Infections bovine keratoconjunctivitis in cattle vaccinated and medicated against Moraxella bovis befare parturition. // Am. J. Vet. Res., 1982, 43 №2 - p.320-325; Gwin R. Medicament and method for prodicing immunity the infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis.// Патент США №4539.201. от 3 сентября 1985). В Российской Федерации разработана и выпускается «Ассоциированная вакцина для специфической профилактики инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis и герпес-вируса типа 1» (патент RU №2264227, А61К 39/295, С12N 1/20, 7/00, А61Ρ 31/00, опуб. 20.11.05 г.). Недостатком данной вакцины является неполный ее антигенный состав, а именно отсутствие в ней антигена бактерий Moraxella bovoculi, одного из наиболее часто встречающихся возбудителей инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота, что делает ее малоэффективной в хозяйствах, где превалирует этот возбудитель.Currently, the main method of combating infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle is its specific prevention using various types of vaccines (Hughes D. et. Al. Experimenally induced Bovine Infectious Keratoconjunctivitis: Effectivcnes of Intramuscular Vaccination with Viable Moraxella bovis Culture. // Am, J. Vet. Res., 1971, 32 No. 6 - p. 799-886; Pugh GW et al. Infections bovine keratoconjunctivitis in cattle vaccinated and medicated against Moraxella bovis befare parturition. // Am. J. Vet. Res., 1982 43 No. 2 - p. 320-325; Gwin R. Medicament and method for prodicing immunity the infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis.// US Patent No. 4539.201. Of September 3, 1985). In the Russian Federation, an “Associated vaccine for the specific prophylaxis of infectious keratoconjunctivitis of cattle based on the antigens of bacteria Moraxella bovis and herpes virus type 1” has been developed and is being produced (patent RU No. 2264227, A61K 39/295, C12N 1/20, 7/00 A61Ρ 31/00, published on November 20, 2005). The disadvantage of this vaccine is its incomplete antigenic composition, namely the absence of the bacterial antigen Moraxella bovoculi, one of the most common pathogens of infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle, which makes it ineffective in farms where this pathogen prevails.
Технический результат, на достижение которого направлено изобретение, заключается в получении вакцины, обладающей повышенной антигенной и иммуногенной активностью, расширении спектра действия и защитного эффекта вакцины.The technical result to which the invention is directed is to obtain a vaccine having increased antigenic and immunogenic activity, expanding the spectrum of action and the protective effect of the vaccine.
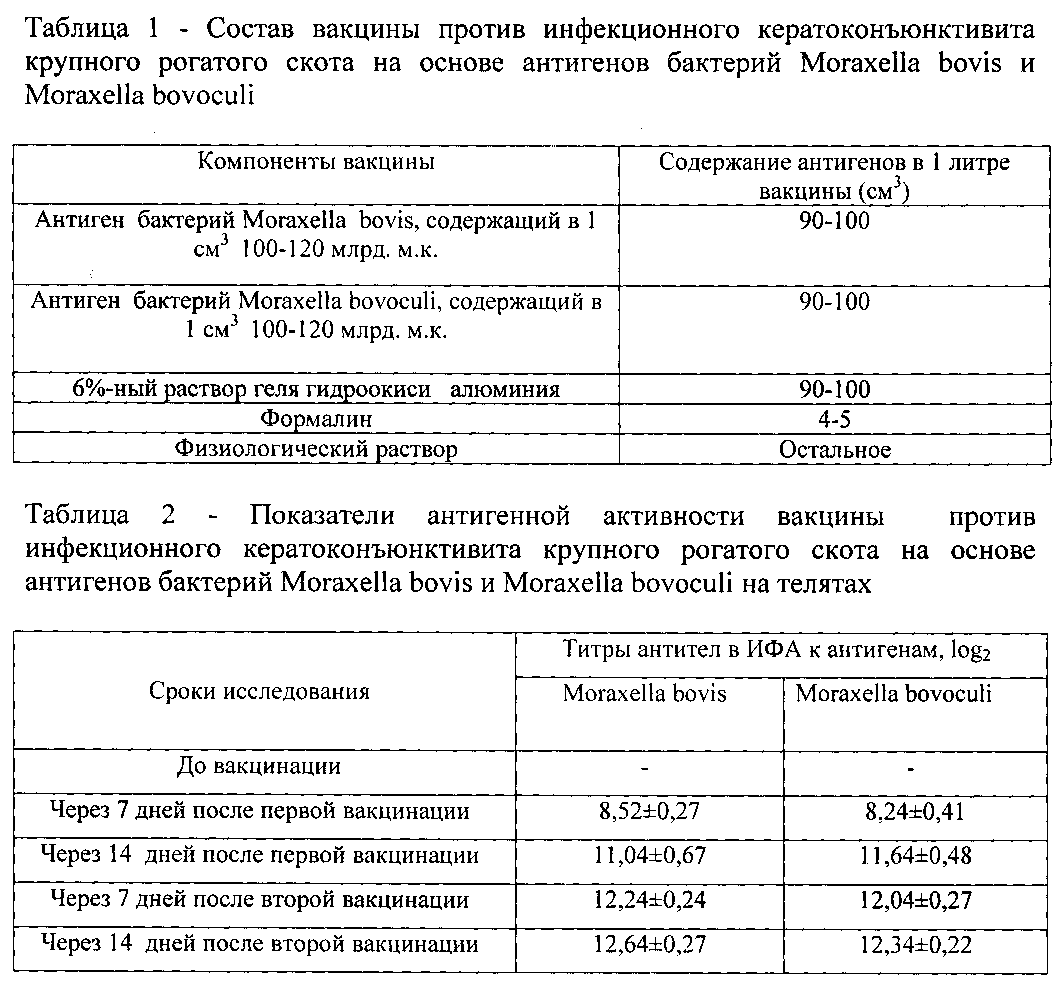
Это достигается тем, что вакцина против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi в качестве антигенов содержит инактивированные суспензии клеток штаммов бактерий Moraxella boyis «Г97-ВНИВИ» с концентрацией 100-120 млрд. м.к. на 1 см3 и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» с концентрацией 100-120 млрд. м.к. на 1 см3, взятые в равных соотношениях на физиологическом растворе, в качестве адъюванта - 6%-ный гель гидроокиси алюминия, в качестве инактиватора - формалин при следующем соотношении компонентов на 1 л. вакцины: суспензия клеток штамма бактерий Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» с концентрацией 100-120 млрд. м.к. в 1 см3, см3 - 90,0-100,0; суспензия клеток штамма бактерий Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» с концентрацией 100-120 млрд. м.к. в 1 см3, см3 - 90,0-100,0; гель гидроокиси алюминия, 6%-ный, см3 - 90,0-100,0; формалин, см3 - 4,0-5,0 и физиологический раствор, л. - до 1.This is achieved by the fact that the vaccine against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle based on the bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi contains inactivated cell suspensions of bacteria strains Moraxella boyis "G97-VNIVI" with a concentration of 100-120 billion mk. per 1 cm 3 and Moraxella bovoculi “CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT” with a concentration of 100-120 billion m. per 1 cm 3 , taken in equal proportions on physiological saline, as an adjuvant - 6% gel of aluminum hydroxide, as an inactivator - formalin in the following ratio of components per 1 liter. vaccines: cell suspension of the bacterial strain Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" with a concentration of 100-120 billion m. in 1 cm 3 , cm 3 - 90.0-100.0; cell suspension of the bacterial strain Moraxella bovoculi "CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT" with a concentration of 100-120 billion m. in 1 cm 3 , cm 3 - 90.0-100.0; gel of aluminum hydroxide, 6%, cm 3 - 90.0-100.0; formalin, cm 3 - 4.0-5.0 and physiological saline, l. - up to 1.
Для изготовления вакцины ассоциированной для специфической профилактики инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi используют запатентованные нами штаммы бактерий Moraxella bovis «Г97- ВНИВИ» (Патент РФ №2145353; опубл. 10.02.2000 г.) и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» (Патент РФ №2521651; опубл. 10.07.2014 г.), выделенные от больных инфекционным кератоконъюнктивитом телят.For the manufacture of a vaccine associated for specific prophylaxis of cattle infectious keratoconjunctivitis based on the antigens of the bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi, we used the strains of bacteria Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" (RF Patent No. 2145353; publ. 10.02.2000) and Morax that we patented "CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT" (RF Patent No. 2521651; publ. 07/10/2014), isolated from patients with infectious keratoconjunctivitis of calves.
Штамм бактерий Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» характеризуется следующими свойствами: это короткие толстые палочки длиной 1,5-2,0 и в диаметре 0,5-1,0 мкм с округленными концами, расположенные парами или в виде коротких цепочек, спор не образуют, неподвижные, окрашиваются грамотрицательно. На кровяном ΜΠΑ при рН 7,2-7,6 после 24 часовой инкубации при 37°С образуют колонии диаметром от 1 до 3 мм с зоной β-гемолиза шириной 0,5-2,0 мм. Колонии гладкие, круглые, блестящие, серовато-белые. На МПБ через 24-48 часовой инкубации при 37°С наблюдается помутнение бульона с образованием небольшого осадка. Штамм факультативный аэроб, не ферментирует сахаров, не восстанавливает нитраты в нитриты, не образует индол, разжижает желатину, т.е. обладает протеолитической активностью, пептонизирует лакмусовое молоко, дает положительную реакцию на оксидазу.The strain of bacteria Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" is characterized by the following properties: these are short thick sticks 1.5-2.0 in length and 0.5-1.0 μm in diameter with rounded ends, arranged in pairs or in the form of short chains, no spores form, motionless, stained gram-negative. On blood ΜΠΑ at pH 7.2-7.6, after 24-hour incubation at 37 ° C, colonies with a diameter of 1 to 3 mm with a β-hemolysis zone 0.5 to 2.0 mm wide are formed. The colonies are smooth, round, shiny, grayish-white. On the BCH, after a 24-48 hour incubation at 37 ° C, turbidity of the broth is observed with the formation of a small precipitate. The optional aerobic strain does not ferment sugars, does not restore nitrates to nitrites, does not form indole, liquefies gelatin, i.e. possesses proteolytic activity, peptones litmus milk, gives a positive reaction to oxidase.
Штамм бактерий Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» характеризуется следующими свойствами: бактерии представляют собой грамотрицательные диплококки с редко встречающимися кокками диметром 0,7-1,3 мкм, спор не образует. На кровяном ΜΠΑ формирует колонии белого цвета диаметром ≤1 мм, круглые, выпуклые, с ровными краями, зоной β-гемолиза. Факультативный аэроб, не ферментирует сахаров, не образует индол. Не разжижает желатину; дает положительную реакцию на оксидазу и отрицательную - на пробу с лакмусовым молоком. Штамм характеризуется полным набором антигенов, типичных для бактерий рода Moraxella.The bacterial strain Moraxella bovoculi "CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT" is characterized by the following properties: bacteria are gram-negative diplococci with rarely encountered cocci with a diameter of 0.7-1.3 microns, do not form a spore. On blood ΜΠΑ forms colonies of white color with a diameter of ≤1 mm, round, convex, with smooth edges, a zone of β-hemolysis. Optional aerob, does not ferment sugars, does not form indole. Does not thin gelatin; gives a positive reaction to oxidase and a negative reaction to a test with litmus milk. The strain is characterized by a complete set of antigens typical of bacteria of the genus Moraxella.
Штаммы бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi активно образуют эндотоксины, переходящие в анатоксины под действием тепла и формалина. Продуцируемый токсин обладает гемолитическим и некротическим действиями. LD50 для белых мышей составляет 5×108 микробных клеток. Инактивированные формалином культуры штаммов Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» при подкожном введении индуцируют у телят образование специфических антител в сыворотке крови в титрах 1:1280-1:5120, а также формирование специфического иммунитета.The bacterial strains of Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi actively form endotoxins, which transform into toxoids under the influence of heat and formalin. The produced toxin has hemolytic and necrotic effects. LD 50 for white mice is 5 × 10 8 microbial cells. Formalin inactivated cultures of Moraxella bovis strains “G97-VNIVI” and Moraxella bovoculi “СХ-Ч6 No.-DEPT”, when administered subcutaneously, induce the formation of specific antibodies in blood serum in titers 1: 1280-1: 5120, as well as the formation of specific immunity.
Входящие в состав вакцины антигены в эффективных количествах обеспечивают синергетический эффект, проявляемый в увеличении напряженности и длительности иммунитета.The antigens included in the vaccine in effective amounts provide a synergistic effect, manifested in an increase in tension and duration of immunity.
Пример 1. Получение матровых расплодок штаммов бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculiExample 1. Obtaining matrovodnogo seed strains of bacteria strains Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi
Для изготовления вакцины берут ампулы с лиофилизированными производственными штаммами Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП», которые растворяют в 0,5 см3 МПБ и переносят в чашки Петри с 10% кровяным ΜΠΑ. Выращивание проводят в течение 16-18 часов, затем культуры проверяют на соответствие морфологических, культуральных, ферментативных и вирулентных свойств. Если они соответствуют паспортным данным, то их используют для получения бактериальной массы, необходимой для изготовления ассоциированной вакцины.For the manufacture of the vaccine, take ampoules with lyophilized production strains of Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" and Moraxella bovoculi "CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT", which are dissolved in 0.5 cm 3 of MPB and transferred to Petri dishes with 10% blood ΜΠΑ. Cultivation is carried out for 16-18 hours, then the cultures are checked for compliance with morphological, cultural, enzymatic and virulent properties. If they correspond to the passport data, then they are used to obtain the bacterial mass necessary for the manufacture of the associated vaccine.
Штаммы хранят в лиофилизированном виде. Для этого суспензию суточных культур бактерий Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП» с концентрацией 50 млрд. м. к. в 1 см3 смешивают с защитной средой (снятое молоко с сахарозой 5%, желатиной 1,5%) в соотношении 1:1, расфасовывают в ампулы по 1 см3, высушивают методом сублимации, запаивают ампулы под вакуумом и хранят при температуре +2-8°С.The strains are stored in lyophilized form. For this, a suspension of daily cultures of bacteria Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" and Moraxella bovoculi "СХ-Ч6 No.-DEPT" with a concentration of 50 billion m 3 in 1 cm 3 is mixed with a protective medium (skim milk with sucrose 5%, gelatin 1.5%) in a ratio of 1: 1, packaged in ampoules of 1 cm 3 , dried by sublimation, sealed ampoules under vacuum and stored at a temperature of + 2-8 ° C.
Пример 2. Выращивание бактериальной массы каждого штамма бактерий Moraxella bovis в отдельности и ее инактивация.Example 2. Cultivation of the bacterial mass of each strain of bacteria Moraxella bovis separately and its inactivation.
Для получения биомассы культур Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi используют ΜΠΑ, содержащий 10% дефибринированной крови барана. С этой целью указанную среду в стерильных условиях разливают в 1,5 литровые матровые колбы по 250-300 см3, после застывания среды делают посев указанных штаммов путем внесения в каждый матрас по 5 см3 бактериальной суспензии, содержащей по 1 млрд. м. к. в 1 см3. Посевы выдерживают в термостате при температуре 37°С. Через 36-48 ч выросшие колонии культур Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi смывают 0,9%-ным раствором натрия хлорида, готовят суспензию с концентрацией 100-120 млрд. м.к. в 1 см3 по бактерийному или оптическому стандарту мутности ГИСК им. Тарасевича. Культуру проверяют на чистоту, морфологическую и серологическую типичность.To obtain the biomass of Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi cultures, ΜΠΑ containing 10% defibrinated sheep blood is used. For this purpose, the indicated medium is poured into sterile conditions into 1.5 liter mother flasks of 250-300 cm 3 , after solidification of the medium, the strains of these strains are seeded by adding 5 cm 3 of a bacterial suspension containing 1 billion m to each mattress in 1 cm 3 . Crops are kept in a thermostat at a temperature of 37 ° C. After 36-48 hours, the grown colonies of the cultures of Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi are washed off with 0.9% sodium chloride solution, a suspension is prepared with a concentration of 100-120 billion m. in 1 cm 3 according to the bacterial or optical standard turbidity GISK them. Tarasevich. The culture is checked for purity, morphological and serological typicality.
Инактивацию бактериальной взвеси осуществляют формалином. Для этого в микробную взвесь добавляют формалин с содержанием 37-38% активного формальдегида из расчета 0,5 см3 на 100 см3 суспензии. Перемешивают и ставят в термостат на 72 ч. Затем берут пробу на полноту инактивации, которую проводят путем посева инактивированных микробных взвесей на кровяной ΜΠΑ.Inactivation of bacterial suspensions is carried out with formalin. For this, formalin with a content of 37-38% active formaldehyde is added to the microbial suspension at the rate of 0.5 cm 3 per 100 cm 3 of suspension. Stirred and placed in a thermostat for 72 hours. Then take a sample for completeness of inactivation, which is carried out by plating inactivated microbial suspensions on the blood ΜΠΑ.
Пример 3. Приготовление вакцины против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis и герпес-вируса типа 1.Example 3. Preparation of a vaccine against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle based on the antigens of bacteria Moraxella bovis and herpes virus type 1.
Вакцину готовят из инактиврованных формалином производственных штаммов бактерий Moraxella bovis «Г97-ВНИВИ» и Moraxella bovoculi «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП».The vaccine is prepared from formalin inactivated production strains of bacteria Moraxella bovis "G97-VNIVI" and Moraxella bovoculi "CX-Ch6 No.-DEPT".
Берут физиологический раствор и к нему добавляют инактивированные суспензии бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovis из расчета 9-10 см3 каждого штамма на 100 см3 вакцинного препарата, а также 6%-ный гель гидроокиси алюминия из расчета 9-10 см3 и формалин 4-5 см3 на 100 см3 вакцины. Доводят рН вакцины до 7,2-7,4 и расфасовывают при тщательном периодическом перемешивании во флаконы, которые потом закрывают резиновыми пробками, обкатывают металлическими колпачками и этикетируют. В таблице 1 приведен состав вакцины.Saline is taken and inactivated suspensions of bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovis are added to it at a rate of 9-10 cm 3 of each strain per 100 cm 3 of vaccine preparation, as well as 6% aluminum hydroxide gel at a rate of 9-10 cm 3 and formalin 4 -5 cm 3 per 100 cm 3 of vaccine. The pH of the vaccine is adjusted to 7.2-7.4 and packaged with thorough periodic stirring into bottles, which are then closed with rubber stoppers, wrapped in metal caps and labeled. Table 1 shows the composition of the vaccine.
Пример 4. Контроль вакцины на стерильность, безвредность и на антигенную активность.Example 4. The control of the vaccine for sterility, safety and antigenic activity.
Для проверки на стерильность из 6 флаконов вакцины каждой серии делают посевы по 0,2 см3 на МПБ, ΜΠΑ, кровяной ΜΠΑ, МППБ под вазелиновым маслом и агар Сабуро по 2 пробирки на каждый флакон. Посевы со всеми средами выдерживают в термостате при 37°С, а с агаром Сабуро - при 20-22°С в течение 15 суток. Питательные среды должны оставаться стерильными.To test for sterility, from 6 bottles of vaccine of each series, cultures of 0.2 cm 3 are made on MPB, ΜΠΑ, blood ΜΠΑ, MPPB under paraffin oil and Saburo agar, 2 tubes per bottle. Crops with all media are kept in a thermostat at 37 ° C, and with Saburo agar - at 20-22 ° C for 15 days. Culture media should remain sterile.
Для проверки на безвредность отбирают 10 белых мышей живой массой 17-18 г и вводят им вакцину подкожно в дозе 0,5 см3. Вакцину считают безвредной, если мыши в течение 10 суток после введения вакцины остаются живыми и клинически здоровыми.To test for harmlessness, 10 white mice with a live weight of 17-18 g are selected and a vaccine is injected subcutaneously at a dose of 0.5 cm 3 . The vaccine is considered harmless if the mice remain alive and clinically healthy for 10 days after administration of the vaccine.
Антигенную активность вакцины контролируют на 3-х кроликах живой массой 2,0-2,5 кг, которым вводят препарат подкожно в дозе 2 см3 двукратно с интервалом 14 дней. Через 14 дней после последней вакцинации у кроликов из ушной вены берут кровь и исследуют сыворотку с целью установления уровня специфических антител к антигенам бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi. Титры антител к антигенам бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi должны быть в пределах 10,0-11,0 log2 в реакции ИФА.The antigenic activity of the vaccine is monitored on 3 rabbits with a live weight of 2.0-2.5 kg, to which the drug is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 2 cm 3 twice with an interval of 14 days. 14 days after the last vaccination, blood was taken from the ear vein in rabbits and the serum was examined to determine the level of specific antibodies to the antigens of the bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi. Antibody titers of the bacterial antigens Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi should be in the range of 10.0-11.0 log 2 in the ELISA.
Пример 5. Эффективность вакцины оценивают в неблагополучном хозяйстве по количеству заболевших инфекционным кератоконъюнктивитом крупного рогатого скота. Производственные испытания экспериментальных серий вакцины проведены в СХПК «Енали» Апастовского района; ООО «Хаерби» и ООО «Среднее Девятово» Лаишевского района, совхозе-техникуме Чистопольского района Республики Татарстан, СПК-колхозе им. Калинина и СПК-колхозе им. Кирова Дюртюлинского района Республики Башкортостан, неблагополучных по инфекционному кератоконъюнктивиту крупного рогатого скота, где заболеваемость телят до 6-месячного возраста составляла 30-56%, молодняка до 12-месячного возраста - 27-36% и молодняка старше года и взрослого поголовья 8-22%. Вакцину применяли с профилактической целью. При этом вакцинировали телят от 1 до 6-месячного возраста в дозе 2,5 см3, молодняка от 6 до 12 мес. в дозе 4 см3, молодняка старше года и взрослого поголовья в дозе 5 см3. Результаты испытаний вакцины в этих хозяйствах представлены в таблице 3. Из этой таблицы следует, что вакцина против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота обладает высокой иммуногенной активностью. Применение ее с профилактической целью в 6 стационарно неблагополучных хозяйствах позволило полностью искоренить заболевание в течение года в 4 хозяйствах, а в остальных двух снизить заболеваемость до 1-3%.Example 5. The effectiveness of the vaccine is evaluated in a dysfunctional farm by the number of cases of infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle. Production tests of experimental vaccine series were carried out in the Yenali agricultural production complex of the Apastovsky District; Khaerbi LLC and Srednyaya Devyatovo LLC, Laishevsky District, state farm technical school of the Chistopol District of the Republic of Tatarstan, SPK collective farm named after Kalinin and SEC collective farm. Of the Kirov of the Dyurtyulinsky district of the Republic of Bashkortostan, which are disadvantaged for infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle, where the incidence of calves up to 6 months of age was 30-56%, young animals up to 12 months old were 27-36% and young animals over one year old and an adult population were 8-22% . The vaccine was used for prophylactic purposes. In this case, calves from 1 to 6 months of age were vaccinated at a dose of 2.5 cm 3 , young animals from 6 to 12 months. at a dose of 4 cm 3 , young animals over one year old and adult livestock at a dose of 5 cm 3 . The results of the vaccine tests in these farms are presented in table 3. From this table it follows that the vaccine against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle has a high immunogenic activity. Its prophylactic use in 6 stationary dysfunctional farms made it possible to completely eradicate the disease during the year in 4 farms, and in the other two to reduce the incidence to 1-3%.
Таким образом, предлагаемая вакцина против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi обладает более широким спектром действия, повышенной антигенной и иммуногенной активностью, иммунитет у животных сохраняется в течение 12 мес. после вакцинации.Thus, the proposed vaccine against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle based on the antigens of bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi has a wider spectrum of action, increased antigenic and immunogenic activity, the immunity in animals persists for 12 months. after vaccination.
Пример 5. Общие сведения, биологические свойства, порядок применения вакцины против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота на основе антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculiExample 5. General information, biological properties, the order of use of the vaccine against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle based on the antigens of bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi
Общие сведенияGeneral information
Вакцина изготовлена из концентрированных антигенов бактерий Moraxella bovis (штамм «Г97-ВНИВИ») и Moraxella bovoculi (штамм «СХ-Ч6 №-ДЕП»), инактивированных формалином (0,5% к объему) с добавлением в качестве адъюванта гидроокиси алюминия (10% к объему).The vaccine is made from concentrated antigens of bacteria Moraxella bovis (strain "G97-VNIVI") and Moraxella bovoculi (strain "СХ-Ч6 No.-DEPT"), inactivated with formalin (0.5% by volume) with the addition of aluminum hydroxide as adjuvant (10 % by volume).
По внешнему виду вакцина представляет собой жидкость желтоватого цвета с белым осадком, легко разбивающимся при взбалтывании.In appearance, the vaccine is a yellowish liquid with a white precipitate that breaks easily when shaken.
Вакцина расфасована по 100 и 200 см3 в стеклянные флаконы соответствующей вместимости, укупоренные резиновыми пробками, укрепленными алюминиевыми колпачками.The vaccine is packaged in 100 and 200 cm 3 in glass bottles of the appropriate capacity, corked with rubber stoppers, reinforced with aluminum caps.
Флаконы с вакциной упакованы в картонные коробки с разделительными перегородками, обеспечивающими их целостность. В каждую коробку вложена инструкция по применению вакцины.Vaccine bottles are packed in cardboard boxes with dividing walls to ensure their integrity. Each box contains instructions for using the vaccine.
Срок годности вакцины 12 месяцев с даты выпуска при соблюдении условий хранения и транспортирования.The shelf life of the vaccine is 12 months from the date of release, subject to storage and transportation conditions.
Запрещено использовать вакцину по истечении срока годности.It is forbidden to use the vaccine after the expiration date.
Вакцину хранят и транспортируют в сухом темном месте при температуре от 2 до 8°С.The vaccine is stored and transported in a dry, dark place at a temperature of 2 to 8 ° C.
Вакцину следует хранить в местах, недоступных для детей.The vaccine should be stored out of the reach of children.
Вакцину во флаконах без этикеток с истекшим сроком годности, с нарушением целостностью и/или герметичности укупорки, с измененным цветом и/или консистенцией содержимого, с наличием посторонних примесей, а также остатки вакцины, не использованные в течение 4 часов после вскрытия флаконов, бракуют, обеззараживают путем кипячения в течение 30 минут или обрабатывают 2% раствором щелочи или 5% раствором хлорамина (1:1) в течение 30 минут и утилизируют.A vaccine in vials without labels with an expired shelf life, with a violation of the integrity and / or tightness of the cork, with a changed color and / or consistency of the contents, with the presence of impurities, as well as vaccine residues not used within 4 hours after opening the vials, are rejected, they are disinfected by boiling for 30 minutes or treated with a 2% alkali solution or 5% chloramine solution (1: 1) for 30 minutes and disposed of.
Утилизация обеззараженной вакцины не требует соблюдения специальных мер предосторожности.Disposal of a disinfected vaccine does not require special precautions.
Биологические свойстваBiological properties
Вакцина вызывает формирование иммунного ответа у крупного рогатого скота к возбудителям инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита - бактериям Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi через 14 суток после двукратного введения продолжительностью 12 месяцев.The vaccine causes the formation of an immune response in cattle to the causative agents of infectious keratoconjunctivitis - the bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi 14 days after a double administration of 12 months.
В 1 см3 вакцины содержится по 10 млрд. инактивированных микробных клеток бактерий Moraxella bovis и Moraxella bovoculi.In 1 cm 3 of the vaccine contains 10 billion inactivated microbial cells of bacteria Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi.
Вакцина безвредна, лечебными свойствами не обладает.The vaccine is harmless, does not possess medicinal properties.
Порядок применения вакциныVaccine Administration
Вакцина предназначена для профилактики инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота в угрожаемых и стационарно неблагополучных хозяйствах.The vaccine is intended for the prevention of infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle in threatened and permanently dysfunctional farms.
Запрещено вакцинировать клинически больных и/или ослабленных животных.It is forbidden to vaccinate clinically sick and / or weakened animals.
Вакцинации подлежит крупный рогатый скот, начиная с 30-35-дневного возраста и старше.Cattle are subject to vaccination, starting from 30-35 days of age and older.
Вакцину вводят подкожно в среднюю треть шеи, двукратно с интервалом 14-15 дней в дозах: телятам от 1 до 6 месяцев - 2,5 см3, молодняку в возрасте от 6 месяцев до года -4,0 см3, взрослым животным - 5,0 см3.The vaccine is administered subcutaneously in the middle third of the neck, twice with an interval of 14-15 days in doses: calves from 1 to 6 months - 2.5 cm 3 , young animals aged 6 months to a year - 4.0 cm 3 , adult animals - 5 , 0 cm 3 .
Перед применением вакцину подогревают на водяной бане до температуры 37-38°С, в процессе применения флаконы с вакциной периодически взбалтывают.Before use, the vaccine is heated in a water bath to a temperature of 37-38 ° C, during the application, the vaccine bottles are periodically shaken.
Вакцину вводят с соблюдением правил асептики и антисептики, для введения используют стерильные материалы и инструменты. Для каждого животного используют отдельную иглу. Место инъекции обрабатывают 70° спиртом.The vaccine is administered in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics, sterile materials and instruments are used for administration. A separate needle is used for each animal. The injection site is treated with 70 ° alcohol.
Симптомов проявления инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита или других патологических признаков при передозировке вакцины не установлено.Symptoms of the manifestation of infectious keratoconjunctivitis or other pathological signs with an overdose of the vaccine have not been established.
Следует избегать нарушений схемы проведения вакцинации, поскольку это может привести к снижению эффективности иммунопрофилактики инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита. В случае пропуска очередного введения вакцины необходимо провести иммунизацию как можно скорее.Violations of the vaccination schedule should be avoided, as this can lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of immunoprophylaxis of infectious keratoconjunctivitis. If the next vaccine is missed, immunization should be carried out as soon as possible.
При применении вакцины с настоящей инструкцией побочных явлений, как правило, не отмечается. У отдельных животных через сутки после вакцинации возможно незначительное повышение температуры и формирование припухлости в месте инъекции, самопроизвольно исчезающей через 3-5 суток.When using a vaccine with these instructions, side effects, as a rule, are not noted. In individual animals, a slight increase in temperature and the formation of swelling at the injection site, which spontaneously disappears after 3-5 days, is possible a day after vaccination.
Запрещается применение вакцины, ассоциированной против инфекционного кератоконъюнктивита крупного рогатого скота, совместно с другими иммунобиологическими препаратами, а также с антигельминтиками и инсектоакарицидами в течение 14 суток до и после очередной иммунизации.It is forbidden to use the vaccine associated with infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle, together with other immunobiological preparations, as well as with anthelmintics and insectoacaricides within 14 days before and after the next immunization.
Молоко и продукты от вакцинированных животных реализуют без ограничений независимо от сроков вакцинации.Milk and products from vaccinated animals are sold without restriction, regardless of the timing of vaccination.
Меры личной профилактикиPersonal Prevention
При работе с вакциной следует соблюдать общие правила личной гигиены и техники безопасности, предусмотренные при работе с лекарственными средствами ветеринарного назначения.When working with the vaccine, the general rules of personal hygiene and safety precautions provided for when working with veterinary medicines should be observed.
Все лица, участвующие в проведении вакцинации, должны быть одеты в спецодежду (резиновые сапоги, халат, брюки, головной убор, резиновые перчатки) и обеспечены очками закрытого типа. В местах работы должна быть аптечка первой доврачебной помощи.All persons involved in the vaccination should wear special clothing (rubber boots, a bathrobe, trousers, a hat, rubber gloves) and be provided with goggles. In places of work there should be a first aid kit.
В случае попадания вакцины на кожу и/или слизистые оболочки их рекомендуется немедленно промыть большим количеством чистой воды.If the vaccine gets on the skin and / or mucous membranes, it is recommended to immediately rinse with plenty of clean water.
При случайном введении вакцины человеку необходимо место укола обработать 70°-ным раствором этилового спирта и обратиться в медицинское учреждение.If the vaccine is accidentally administered to a person, the injection site should be treated with a 70 ° solution of ethyl alcohol and contact a medical institution.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2015120081/15A RU2589819C1 (en) | 2015-05-27 | 2015-05-27 | VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2015120081/15A RU2589819C1 (en) | 2015-05-27 | 2015-05-27 | VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2589819C1 true RU2589819C1 (en) | 2016-07-10 |
Family
ID=56371350
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2015120081/15A RU2589819C1 (en) | 2015-05-27 | 2015-05-27 | VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2589819C1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2699035C2 (en) * | 2017-05-22 | 2019-09-03 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Московская государственная академия ветеринарной медицины и биотехнологии - МВА имени К.И. Скрябина" (ФГБОУ ВО МГАВМиБ - МВА имени К.И. Скрябина) | Polyvalent cattle vaccine against anaerobic enterotoxemia and method of using it |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2145353C1 (en) * | 1998-09-15 | 2000-02-10 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский ветеринарный институт | Strain of bacterium moraxella bovis "g97-vnivi" used for preparing diagnostica and vaccines against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle |
| RU2240820C2 (en) * | 2000-07-10 | 2004-11-27 | Карайченцев Виктор Николаевич | Preparation for preventing infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle and method for preventing this disease |
| RU2004105105A (en) * | 2004-02-24 | 2005-08-10 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский ветеринарный институт (RU) | ASSOCIATED VACCINE FOR SPECIFIC PREVENTION OF INFECTIOUS KERATO-CONJUNCTIVITIS OF CATTLE BASED ON MORAXELLA BOVIS BACTERIA ANTIGENS AND TYPE I HERPESVIRUS |
-
2015
- 2015-05-27 RU RU2015120081/15A patent/RU2589819C1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2145353C1 (en) * | 1998-09-15 | 2000-02-10 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский ветеринарный институт | Strain of bacterium moraxella bovis "g97-vnivi" used for preparing diagnostica and vaccines against infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle |
| RU2240820C2 (en) * | 2000-07-10 | 2004-11-27 | Карайченцев Виктор Николаевич | Preparation for preventing infectious keratoconjunctivitis in cattle and method for preventing this disease |
| RU2004105105A (en) * | 2004-02-24 | 2005-08-10 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский ветеринарный институт (RU) | ASSOCIATED VACCINE FOR SPECIFIC PREVENTION OF INFECTIOUS KERATO-CONJUNCTIVITIS OF CATTLE BASED ON MORAXELLA BOVIS BACTERIA ANTIGENS AND TYPE I HERPESVIRUS |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| КАРАЙЧЕНЦЕВ В. Н. Профилактика инфекционного кератоконьюнктивита скота// Молочное и мясное скотоводство, 2005, N 7, с. 38. * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2699035C2 (en) * | 2017-05-22 | 2019-09-03 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Московская государственная академия ветеринарной медицины и биотехнологии - МВА имени К.И. Скрябина" (ФГБОУ ВО МГАВМиБ - МВА имени К.И. Скрябина) | Polyvalent cattle vaccine against anaerobic enterotoxemia and method of using it |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Stepanov et al. | Development of novel vaccines against anthrax in man | |
| RU2403063C1 (en) | Inactivated combined vaccine against viral diarrhea, rota-, corona-virus diseases and escherichiosis of cattle | |
| RU2428202C1 (en) | Associated vaccine against anaerobic enterotoxemia and colibacillosis diarrhea in calves | |
| CN107184985B (en) | Heat-resistant freeze-drying protective agent for newcastle disease live vaccine (Lasota strain) | |
| RU2589819C1 (en) | VACCINE AGAINST INFECTIOUS BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS BASED ON ANTIGENS OF Moraxella bovis and Moraxella bovoculi BACTERIA | |
| RU2020959C1 (en) | Vaccine for prevention and treatment of dermatophytoses in animals | |
| Woodward | Rickettsial vaccines with emphasis on epidemic typhus-initial report of an old vaccine trial | |
| Friis et al. | Isolation of Mycoplasma bovoculi from cases of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis | |
| RU2523389C1 (en) | Method of production of hyperimmune serum against anaerobic enterotoxaemia and colibacillosis diarrhoea in calves | |
| RU2696007C1 (en) | Associated with parainfluenza-3 vaccine, infectious rhinotracheitis, viral diarrhea, rota- and coronaviral infections of cattle inactivated emulsion | |
| US20220072116A1 (en) | Bacterial vaccine | |
| RU2650628C1 (en) | Method of obtaining vaccine associated with colibacillosis, streptococcosis and enterococcal infection of calves and piglets | |
| RU2263143C2 (en) | Strain of bacterium streptococcus pyogenes 289 used for preparing vaccine against streptococcosis in fur animal | |
| RU2457859C1 (en) | Cattle viral diarrhoeia vaccine | |
| RU2348425C2 (en) | Production method of combined streptococcosis and pseudomonosis vaccine for polar foxes and foxes | |
| RU2517733C1 (en) | Inactivated emulsion vaccine associated against adenoviral, herpes virus infection, parainfluenza-3 and viral diarrhea - mucosal disease of cattle | |
| RU2521651C1 (en) | STRAINS OF BACTERIA Moraxella bovoculi "SH-CH6 N-DEP" USED TO MANUFACTURE DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS AND VACCINES AGAINST INFECTIOUS KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS OF CATTLE | |
| RU2814593C1 (en) | Method of preventing escherichiosis in calves | |
| RU2456998C1 (en) | Polyspecific rota-, coronaviral gastroenteritis and pig colibacillosis diarrhea hyperimmune serum | |
| RU2395297C1 (en) | Inactivated combined vaccine against cattle infectious rhinotracheitis, virus diarrhoea and leptospirosis | |
| EA029938B1 (en) | Vaccine against strangles in horses | |
| RU2531054C1 (en) | Associated pseudomonosis and rabbit viral haemorrhagic disease vaccine | |
| RU2761379C1 (en) | Polyvalent inactivated vaccine against swine streptococcosis, method for its production and use | |
| Smith | The basis of immunity to anthrax | |
| RU2357755C2 (en) | Inactivated vaccine against porcine transmissible gastroenteritis (ptge) and porcine epidemic diarrhea (ped) from enteric virus of artificially infected colostrum-free pigs (ptge/ped vaccine) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20170528 |