RU2578879C1 - Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting - Google Patents
Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2578879C1 RU2578879C1 RU2014135025/02A RU2014135025A RU2578879C1 RU 2578879 C1 RU2578879 C1 RU 2578879C1 RU 2014135025/02 A RU2014135025/02 A RU 2014135025/02A RU 2014135025 A RU2014135025 A RU 2014135025A RU 2578879 C1 RU2578879 C1 RU 2578879C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- titanium
- content
- remelting
- electrode
- δti
- Prior art date
Links
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к специальной электрометаллургии, конкретно к производству слитков нержавеющих титансодержащих марок стали методом ЭШП, и может быть использовано для получения титансодержащих высоколегированных коррозионно-стойких марок стали методом электрошлакового переплава.The invention relates to special electrometallurgy, specifically to the production of ingots of stainless titanium-containing steel grades by the ESR method, and can be used to produce titanium-containing highly alloyed corrosion-resistant steel grades by electroslag remelting.
Известен электрод для ЭШП титансодержащих коррозионно-стойких марок стали, содержащий титан в количестве, равном его содержанию в готовом металле, при переплаве которого, для сохранения нормированного содержания титана в готовом металле, переплав производится на флюсе, содержащем ТiO2, или в защитной атмосфере аргона или в процессе переплава производится раскисление флюса порошками раскислителей через дозатор. [1]A known electrode for ESR of titanium-containing corrosion-resistant steel grades containing titanium in an amount equal to its content in the finished metal, during remelting of which, to maintain the normalized titanium content in the finished metal, remelting is performed on a flux containing TiO 2 or in a protective argon atmosphere or during the remelting process, flux is deoxidized with deoxidizing powders through a dispenser. [one]
Недостатками расходуемого электрода являются необходимость дополнительного оборудования для переплава, неравномерное по высоте и сечению слитка и негарантированное содержание титана.The disadvantages of the consumable electrode are the need for additional equipment for remelting, uneven in height and cross-section of the ingot, and unwarranted titanium content.
В качестве прототипа принят расходуемый электрод для ЭШП коррозионно-стойких титансодержащих марок стали, содержащий в своем составе титан ближе к верхнему пределу или выше его на 0,15%, для переплава которого в качестве рабочего флюса используется флюс АНФ-6 с 1% титановой губки, и дополнительно в процессе переплава производится раскисление флюса порошком алюминия в количестве 0,5 кг/т. [2, 3]As a prototype, a consumable electrode for ESR of corrosion-resistant titanium-containing steel grades containing titanium 0.15% closer to the upper limit or higher is used for the remelting of which ANF-6 flux with 1% titanium sponge is used for remelting , and additionally, during the remelting process, flux is deoxidized with aluminum powder in an amount of 0.5 kg / t. [2, 3]
Недостатками применения данного электрода для ЭШП являются необходимость дополнительного оборудования при переплаве, опасность перехода алюминия в металл, что повышает хрупкость и снижает стойкость металла против коррозии, негарантированное и неравномерное содержание титана по высоте и сечению слитка, что не обеспечивает надежное качество металла.The disadvantages of using this electrode for ESR are the need for additional equipment during remelting, the danger of transition of aluminum to metal, which increases brittleness and reduces the resistance of metal to corrosion, unwarranted and uneven content of titanium in height and cross-section of the ingot, which does not ensure reliable metal quality.
Задачей изобретения является получение расходуемого электрода, обеспечивающего получение качественного металла с гарантированным содержанием титана и равномерным его распределением по объему слитка ЭШП.The objective of the invention is to obtain a consumable electrode that provides high-quality metal with a guaranteed titanium content and its uniform distribution over the volume of the ESR ingot.
Сущность изобретения состоит в том, что расходуемый электрод содержит титан выше требуемого в готовой стали на величину его угара при переплаве, определяемого по формулеThe essence of the invention lies in the fact that the consumable electrode contains titanium higher than that required in the finished steel by the value of its fume during remelting, determined by the formula
ΔTi=37Tiг+35·Tiг D2/(63+35D2),ΔTi = 37Ti g + 35 · Ti g D 2 / (63 + 35D 2 ),
где ΔTi - средний угар титана, %,where ΔTi is the average waste of titanium,%,
Tiг - содержание титана в готовом металле, %,Ti g - titanium content in the finished metal,%,
D - диаметр кристаллизатора, м,D is the diameter of the mold, m,
при этом соотношение содержания титана к алюминию должно быть в пределах 6,0-9,0.while the ratio of titanium to aluminum should be in the range of 6.0-9.0.
Известно, что в процессе переплава титан частично окисляется, переходя во флюс. Угар титана зависит от многих факторов.It is known that in the process of remelting, titanium partially oxidizes, passing into flux. Burnout of titanium depends on many factors.
В исследованиях, проведенных на Златоустовском электрометаллургическом заводе, рассмотрена зависимость угара титана от соотношения содержания титана и алюминия в электроде, от его содержания в готовом металле и от площади контакта жидкого флюса с газовой фазой (от площади зазора между кристаллизатором и расходуемым электродом) в процессе переплава.In studies conducted at the Zlatoust Electrometallurgical Plant, the dependence of titanium fume on the ratio of titanium and aluminum in the electrode, on its content in the finished metal, and on the area of contact of the liquid flux with the gas phase (on the area of the gap between the mold and the consumable electrode) during remelting is examined .
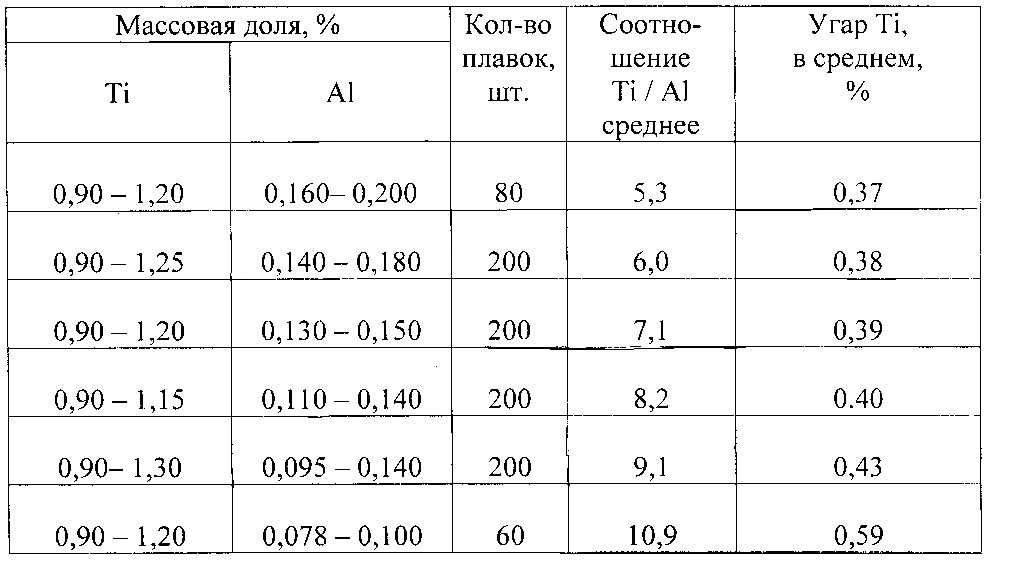
Получена зависимость угара титана от соотношения титана к алюминию в исходном металле (электроде) при одинаковом содержании титана в металле электрода. Опытные данные для электрода кр.445 мм при переплаве в кристаллизаторе кр.630 мм приведены в таблице 1.The dependence of titanium fume on the ratio of titanium to aluminum in the starting metal (electrode) is obtained for the same titanium content in the metal of the electrode. The experimental data for the electrode kr.445 mm during remelting in the crystallizer kr.630 mm are given in table 1.
При соотношении Ti/Аl в металле электрода более 9,0 угар титана значительно увеличивается.When the ratio Ti / Al in the metal of the electrode is more than 9.0, the carbon loss of titanium increases significantly.
При соотношении Ti/Аl менее 6,0 увеличивается расход алюминия, а угар титана уменьшается незначительно.When the ratio Ti / Al is less than 6.0, the consumption of aluminum increases, and the loss of titanium decreases slightly.
Соотношение Ti/Аl от 6,0 до 9,0 является оптимальнымThe ratio of Ti / Al from 6.0 to 9.0 is optimal
По результатам исследований, полученных при проведении опытных плавок ЭШП в кристаллизаторы различного профилеразмера, но с одинаковым коэффициентом заполнения кристаллизатора (отношение площади сечения электрода и кристаллизатора, таблица 2), на флюсе АНФ-6 и с соотношением титана к алюминию 6,0-9,0, получена эмпирическая формула зависимости угара титана от его содержания в готовом металле и от диаметра кристаллизатора.According to the results of studies obtained during the experimental melting of ESR into crystallizers of different profile sizes, but with the same fill factor of the mold (the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the electrode and mold, table 2), on flux ANF-6 and with a ratio of titanium to aluminum 6.0-9, 0, an empirical formula is obtained for the dependence of titanium fume on its content in the finished metal and on the diameter of the mold.
ΔTi=37Tiг+35·Tiг D2/(63+35D2),ΔTi = 37Ti g + 35 · Ti g D 2 / (63 + 35D 2 ),
где ΔTi - средний угар титана, %,where ΔTi is the average waste of titanium,%,
Tiг - содержание титана в готовом металле, %,Ti g - titanium content in the finished metal,%,
D - диаметр кристаллизатора, м.D is the diameter of the mold, m
Рассчитан средний угар титана при переплаве стали марки 08Х18Н10Т на электрошлаковой печи в кристаллизаторах кр.630, кр.500, кв.390 (ему соответствует круглый кристаллизатор кр.440 мм).The average burn-off of titanium was calculated during the remelting of steel grade 08X18H10T on an electroslag furnace in crystallizers kr.630, kr.500, kv.390 (it corresponds to a round mold kr.440 mm).
Опытные и расчетные данные по угару титана в процессе переплава стали марки 08Х18Н10Т-Ш приведены в таблице 3.The experimental and calculated data on the loss of titanium in the process of remelting steel grade 08X18H10T-Sh are shown in table 3.
Для расчета пределов содержания титана в исходном металле принимаем требования нижнего предела для металла ЭШП на 0,1% больше, а верхнего - на 0,1% меньше для гарантированного попадания в нормированные пределы, т.к. угар титана считался средний.To calculate the limits of the titanium content in the starting metal, we accept the requirements of the lower limit for the ESR metal by 0.1% more, and the upper one - 0.1% less for guaranteed falling into the normalized limits, since Titanium fume was considered average.
Результаты расчетов приведены в таблице 4.The calculation results are shown in table 4.
Расчетные данные хорошо согласуются с требованиями, полученными из практики работы на Златоустовском электрометаллургическом заводе.The calculated data are in good agreement with the requirements obtained from practice at the Zlatoust electrometallurgical plant.
При содержании титана в исходном металле (электроде) выше расчетного в слитках ЭШП оно будет выше верхнего предела его нормированного содержания.If the titanium content in the source metal (electrode) is higher than the calculated value in ESR ingots, it will be higher than the upper limit of its normalized content.
При содержании титана в исходном металле ниже расчетного в слитках ЭШП оно будет ниже нижнего предела его нормированного содержания.When the titanium content in the source metal is lower than the calculated in the ESR ingots, it will be below the lower limit of its normalized content.
По расчетным данным выплавлено по 10 плавок исходного металла каждой марки стали, которые были переплавлены на ЭШП. Содержание титана на всех плавках соответствует требованиям для готового металла и одинаково по высоте и сечению слитков (таблица 5).According to the calculated data, 10 melts of the initial metal of each steel grade were smelted, which were remelted for ESR. The titanium content on all melts meets the requirements for the finished metal and is equally high and the cross section of the ingots (table 5).
Использование предлагаемого расходуемого электрода для ЭШП позволяет получить качественный металл с гарантированным содержанием титана и с равномерным его распределением по объему слитка.Using the proposed consumable electrode for ESR allows you to get high-quality metal with a guaranteed titanium content and with its uniform distribution over the volume of the ingot.
Источники информацииInformation sources
1. А.Г. Глебов, Е.И. Мошкевич. Электрошлаковый переплав. - М.: Металлургия, стр. 246, 247.1. A.G. Glebov, E.I. Moshkevich. Electroslag remelting. - M.: Metallurgy, p. 246, 247.
2. С.А. Лейбензон, А.Ф. Трегубенко. Производство стали методом электрошлакового переплава. Металлургиздат, 1962, гл. 13.2. S.A. Leibenzon, A.F. Tregubenko. Steel production by electroslag remelting. Metallurgizdat, 1962, Ch. 13.
3. Сборник технологических инструкций по электрошлаковому и вакуумно-дуговому переплаву. Завод Днепроспецсталь.3. A collection of technological instructions for electroslag and vacuum-arc remelting. Dneprospetsstal plant.
Claims (1)
где ΔTi - средний угар титана, полученный при проведении плавок в кристаллизаторы различного профилеразмера с одинаковым коэффициентом заполнения, %;
Tiг - содержание титана в готовом металле, %;
D - диаметр кристаллизатора, м. A method for the production of titanium-containing corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting of a consumable electrode in a mold, characterized in that the consumable electrode is remelted with a ratio of titanium to aluminum in the range of 6.0-9.0, while the titanium content in the electrode exceeds the required titanium content in finished steel by the value of its fume during remelting, which is determined by the dependence: ΔTi = 37Ti g + 35 · Ti g D 2 / (63 + 35D 2 ),
where ΔTi is the average waste of titanium obtained by conducting melts into crystallizers of different profile sizes with the same fill factor,%;
Ti g - titanium content in the finished metal,%;
D is the diameter of the mold, m
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014135025/02A RU2578879C1 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2014-08-26 | Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014135025/02A RU2578879C1 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2014-08-26 | Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2578879C1 true RU2578879C1 (en) | 2016-03-27 |
| RU2014135025A RU2014135025A (en) | 2016-03-27 |
Family
ID=55638470
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014135025/02A RU2578879C1 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2014-08-26 | Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2578879C1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2774689C1 (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-06-21 | Публичное акционерное общество "Северсталь" (ПАО "Северсталь") | Method for producing a corrosion-resistant bimetallic ingot |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5311655A (en) * | 1990-10-05 | 1994-05-17 | Bohler Edelstahl Gmbh | Method of manufacturing titanium-aluminum base alloys |
| RU2423536C1 (en) * | 2009-12-28 | 2011-07-10 | Открытое Акционерное Общество "Златоустовский металлургический завод" | Procedure for melting hollow ingots of titan and boron containing grades of steel by method of esr (electro-slag re-melting) |
| RU2515411C1 (en) * | 2013-01-18 | 2014-05-10 | Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования "Национальный исследовательский технологический университет "МИСиС" | Method of titanium-based alloys production |
-
2014
- 2014-08-26 RU RU2014135025/02A patent/RU2578879C1/en active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5311655A (en) * | 1990-10-05 | 1994-05-17 | Bohler Edelstahl Gmbh | Method of manufacturing titanium-aluminum base alloys |
| RU2423536C1 (en) * | 2009-12-28 | 2011-07-10 | Открытое Акционерное Общество "Златоустовский металлургический завод" | Procedure for melting hollow ingots of titan and boron containing grades of steel by method of esr (electro-slag re-melting) |
| RU2515411C1 (en) * | 2013-01-18 | 2014-05-10 | Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования "Национальный исследовательский технологический университет "МИСиС" | Method of titanium-based alloys production |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2774689C1 (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-06-21 | Публичное акционерное общество "Северсталь" (ПАО "Северсталь") | Method for producing a corrosion-resistant bimetallic ingot |
| RU2774761C1 (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-06-22 | Публичное акционерное общество "Северсталь" (ПАО "Северсталь") | Method for obtaining a bimetallic ingot |
| RU2780082C1 (en) * | 2022-07-06 | 2022-09-19 | Публичное акционерное общество "Северсталь" (ПАО "Северсталь") | Method for producing bimetallic ingot with cladding layer from corrosion-resistant steel |
| RU2786101C1 (en) * | 2022-07-06 | 2022-12-16 | Публичное акционерное общество "Северсталь" (ПАО "Северсталь") | Method for production of bimetal ingot |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2014135025A (en) | 2016-03-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| MX2009003187A (en) | Method and apparatus for continuous producing of metallic titanium and titanium-based alloys. | |
| CN102912152B (en) | Vacuum arc remelting method for inhibiting macrosegregation of high-temperature alloy with high content of Nb | |
| UA93651C2 (en) | Electroslag system for refinement or producing of metal and method for refinement and method for producing of metal | |
| RU2423536C1 (en) | Procedure for melting hollow ingots of titan and boron containing grades of steel by method of esr (electro-slag re-melting) | |
| JP2017537224A5 (en) | ||
| Li et al. | Characteristics of nozzle clogging and evolution of oxide inclusion for Al-killed Ti-stabilized 18Cr stainless steel | |
| RU2578879C1 (en) | Method for production of titanium-corrosion-resistant steel by electroslag remelting | |
| CN108660320A (en) | A kind of low-aluminium high titanium-type high temperature alloy electroslag remelting process | |
| CN104195348A (en) | Low-silicon and low-impurity pre-melting slag for electro-slag remelting and preparing method and application thereof | |
| CN108559891A (en) | Aluminium, zinc, magnesium, the wrought aluminium alloy of scandium system and its manufacturing method | |
| RU2571021C1 (en) | Consumable electrode for steel "+t82-+" production | |
| RU2582406C1 (en) | Flux for electroslag melting of solid and hollow ingots from boron-containing steels | |
| RU2770807C1 (en) | Method for producing blanks from low-alloy copper-based alloys | |
| RU2796483C1 (en) | Method for smelting titanium- and boron-containing grade ingots by electroslag remelting method | |
| RU2382092C2 (en) | Remelting method of titanic sponge or powder and device for its implementation | |
| RU2721979C1 (en) | Method of producing consumable electrode for vacuum-arc remelting for precise alloying | |
| RU2792515C1 (en) | Method for smelting nickel-titanium alloys | |
| RU2778039C1 (en) | Method for modifying the structure of cast blanks from antifriction bronze for diffusion welding with steel (options) | |
| RU2399685C1 (en) | Procedure for production of hollow ingots of titanium containing grades of steel by method of electric slag re-melting (esr) | |
| JP4261602B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of high cleanliness steel | |
| Spiess et al. | Experimental Research on the Absorption of Fluorine in gamma-TiAl during Electroslag Remelting | |
| RU2630100C1 (en) | Method for steel deoxidation during electroslag remelting | |
| RU2026386C1 (en) | Method of preparing of ingot from stainless steel stabilized with titanium | |
| JP2022026393A (en) | Titanium-based ingot manufacturing method | |
| RU2635117C2 (en) | Method for refining magnesium and its alloys |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC43 | Official registration of the transfer of the exclusive right without contract for inventions |
Effective date: 20170116 |