KR20200057144A - Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof - Google Patents
Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20200057144A KR20200057144A KR1020180140876A KR20180140876A KR20200057144A KR 20200057144 A KR20200057144 A KR 20200057144A KR 1020180140876 A KR1020180140876 A KR 1020180140876A KR 20180140876 A KR20180140876 A KR 20180140876A KR 20200057144 A KR20200057144 A KR 20200057144A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- pdrn
- acid
- hyaluronic acid
- complex
- polydeoxyribonucleotide
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/72—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic macromolecular compounds
- A61K8/73—Polysaccharides
- A61K8/735—Mucopolysaccharides, e.g. hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/549—Sugars, nucleosides, nucleotides or nucleic acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/69—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit
- A61K47/6953—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit the form being a fibre, a textile, a slab or a sheet
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/02—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K8/0204—Specific forms not provided for by any of groups A61K8/0208 - A61K8/14
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/02—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K8/0208—Tissues; Wipes; Patches
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/60—Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K8/606—Nucleosides; Nucleotides; Nucleic acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/0012—Galenical forms characterised by the site of application
- A61K9/0053—Mouth and digestive tract, i.e. intraoral and peroral administration
- A61K9/006—Oral mucosa, e.g. mucoadhesive forms, sublingual droplets; Buccal patches or films; Buccal sprays
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L15/00—Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads
- A61L15/16—Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads for physiological fluids such as urine or blood, e.g. sanitary towels, tampons
- A61L15/22—Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads for physiological fluids such as urine or blood, e.g. sanitary towels, tampons containing macromolecular materials
- A61L15/28—Polysaccharides or their derivatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L15/00—Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads
- A61L15/16—Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads for physiological fluids such as urine or blood, e.g. sanitary towels, tampons
- A61L15/42—Use of materials characterised by their function or physical properties
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
- A61P17/02—Drugs for dermatological disorders for treating wounds, ulcers, burns, scars, keloids, or the like
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q19/00—Preparations for care of the skin
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08B—POLYSACCHARIDES; DERIVATIVES THEREOF
- C08B37/00—Preparation of polysaccharides not provided for in groups C08B1/00 - C08B35/00; Derivatives thereof
- C08B37/006—Heteroglycans, i.e. polysaccharides having more than one sugar residue in the main chain in either alternating or less regular sequence; Gellans; Succinoglycans; Arabinogalactans; Tragacanth or gum tragacanth or traganth from Astragalus; Gum Karaya from Sterculia urens; Gum Ghatti from Anogeissus latifolia; Derivatives thereof
- C08B37/0063—Glycosaminoglycans or mucopolysaccharides, e.g. keratan sulfate; Derivatives thereof, e.g. fucoidan
- C08B37/0072—Hyaluronic acid, i.e. HA or hyaluronan; Derivatives thereof, e.g. crosslinked hyaluronic acid (hylan) or hyaluronates
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2800/00—Properties of cosmetic compositions or active ingredients thereof or formulation aids used therein and process related aspects
- A61K2800/40—Chemical, physico-chemical or functional or structural properties of particular ingredients
- A61K2800/57—Compounds covalently linked to a(n inert) carrier molecule, e.g. conjugates, pro-fragrances
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/20—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices containing or releasing organic materials
- A61L2300/23—Carbohydrates
- A61L2300/236—Glycosaminoglycans, e.g. heparin, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/20—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices containing or releasing organic materials
- A61L2300/258—Genetic materials, DNA, RNA, genes, vectors, e.g. plasmids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/60—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a special physical form
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/80—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a special chemical form
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2430/00—Materials or treatment for tissue regeneration
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Birds (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Cosmetics (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 히알루론산(Hyaluronic Acid, Sodium Hyaluronate; HA)-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(Polydeoxyribonucleotide; PDRN) 복합체 및 이의 제조방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는 수분 보유력과 항노화 기능이 우수한 히알루론산과 피부 재생 능력이 뛰어난 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드가 결합되어 기능성과 안정성이 증대된 히알루론산(Hyaluronic Acid, Sodium Hyaluronate; HA)-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(Polydeoxyribonucleotide; PDRN) 복합체 및 이의 제조방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronic Acid, Sodium Hyaluronate; HA) -polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex and a method for manufacturing the same, and more specifically, hyaluronic acid and skin excellent in water retention and anti-aging function Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronic Acid, Sodium Hyaluronate; HA) -polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex having an improved regeneration ability and enhanced functionality and stability by combining polydeoxyribonucleotides, and a method for preparing the same.
히알루론산(Hyaluronic Acid, HA)은 진피 층에 존재하는 뮤코 다당류로서 N-아세 글루코사민(N-acetyl glucosamine)과 D-글루쿠론산(D-Glucuronic acid)이 β-1, 4 글루코시드 결합으로 구성된 이당류들이 히알루론산염 사슬을 형성하기 위해 β-1, 3 글루코시드 결합으로 연결되어 있는 생체 고분자 물질이다. Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronic Acid, HA) is a polysaccharide present in the dermis layer myuko N- acetyl glucosamine (N-acetyl glucosamine) and D- glucuronic acid (D -Glucuronic acid) is composed of β-1, 4-glucoside bond Bisaccharides are biopolymers that are linked by β-1 and 3 glucoside bonds to form hyaluronic acid chains.
히알루론산은 백색의 분말이지만, 물에 녹으면 투명의 액체가 되고, 분자 내에 많은 수산기(-OH)로 인해 높은 수분 보유력을 지니며, 분자량이 0.5∼3.0MDa 정도로 매우 크기 때문에 높은 점탄성을 나타낸다.Hyaluronic acid is a white powder, but when dissolved in water, it becomes a transparent liquid, has high water retention due to many hydroxyl groups (-OH) in the molecule, and exhibits high viscoelasticity because its molecular weight is very high, such as 0.5 to 3.0MDa.
또한, 히알루론산은 인체의 결합조직, 상피 및 신경조직 등에 고루 분포되어 있으며 다양한 생리 활성을 지닌 생체 적합성 재료로서 피부 재생과 보습, 탄력 유지 및 주름 개선에 대한 효과가 입증됨에 따라, 최근 이를 함유하는 항 노화 관련 화장품, 식품, 의약품, 의료기기용 필러 등에 대한 수요가 급격히 증가하고 있다. In addition, hyaluronic acid is evenly distributed in the connective tissue, epithelium and nerve tissues of the human body, and is a biocompatible material with various physiological activities.It has recently been proven to have effects on skin regeneration and moisturizing, maintaining elasticity, and improving wrinkles. The demand for anti-aging cosmetics, food, pharmaceuticals, and fillers for medical devices is rapidly increasing.
그러나 히알루론산은 열, 감마선, 빛 등에 매우 약하기 때문에, 제형화하여 활용 시 물성이 쉽게 변하여 안전성이 떨어지는 문제점이 있다.However, since hyaluronic acid is very weak to heat, gamma rays, light, etc., there is a problem in that the properties are easily changed when formulated and used, resulting in poor safety.
한편, Polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN)은 인체의 태반에 극미량 존재하는 핵산 기반의 생리물질로서, 조직 재생에 관련된 자극을 야기함으로써 상처 치유 작용이 뛰어난 것으로 알려져 있다. 최근 연어, 송어 정자에서 추출한 PDRN이 인간 태반 PDRN과 같이 조직 재생 효능이 있다는 것이 밝혀졌으며, 이러한 기능들을 활용하여 피부 이식 후 재생, 족부 궤양, 욕창, 화상, 인대 재생, 각막 재생 등 다양한 인체조직의 재생 목적으로 사용이 확대되고 있다. On the other hand, Polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) is a nucleic acid-based physiological substance that is present in a very small amount in the human placenta, and is known to have excellent wound healing action by causing stimulation related to tissue regeneration. It has recently been discovered that PDRN extracted from salmon and trout sperm has tissue regeneration effects like human placental PDRN, and utilizes these functions to regenerate skin after transplantation, foot ulcers, bedsores, burns, ligament regeneration, and corneal regeneration. Its use is expanding for regeneration purposes.
한국등록특허 제1722181호는 PDRN(Polydeoxyribonucleotide)을 포함하는 화장품 조성물을 개시하였고, 한국공개특허 제2017-0060599호는 0.1 % 내지 200 %의 가교도를 갖는 히알루론산 유도체 및 전체 조성물에 대해 0.1 내지 50 중량%의 DNA 분획물을 포함하는 히알루론산 주사용 조성물을 개시하였으나, 히알루론산(HA) 또는 히알루론산 유도체는 여전히 열, 감마선, 빛 등에 의한 안전성이 낮은 문제점이 있었다.Korean Registered Patent No. 172181 discloses a cosmetic composition comprising polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN), and Korean Patent Publication No. 2017-0060599 discloses a hyaluronic acid derivative having a crosslinking degree of 0.1% to 200% and 0.1 to 50% by weight of the total composition % Hyaluronic acid injection composition containing a DNA fraction, but hyaluronic acid (HA) or a hyaluronic acid derivative still had a problem of low safety due to heat, gamma rays, light, and the like.
이에, 본 발명자들은 상기 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 노력한 결과, 히알루론산(HA)에 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)를 도입시킬 경우, 기존 히알루론산 대비 안정성 및 기능성이 증대된 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체를 제조할 수 있다는 것을 확인하고, 본 발명을 완성하게 되었다.Accordingly, the present inventors have tried to solve the above problems, and when introducing polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) into hyaluronic acid (HA), hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribo has improved stability and functionality compared to conventional hyaluronic acid. It was confirmed that the nucleotide complex can be prepared, and the present invention was completed.
본 발명의 목적은 피부 보습능 및 피부/조직 재생능이 우수한 화합물 및 이의 제조방법을 제공하는데 있다.An object of the present invention is to provide a compound having excellent skin moisturizing ability and skin / tissue regeneration ability and a method for manufacturing the same.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 피부 보습능 및 피부/조직 재생능이 우수한 화합물을 포함하는 필름을 제공하는데 있다. Another object of the present invention is to provide a film comprising a compound having excellent skin moisturizing ability and skin / tissue regeneration ability.
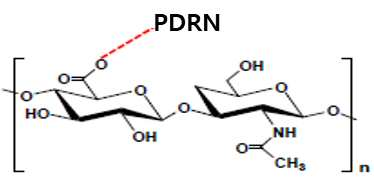
상기 목적을 달성하기 위하여, 본 발명은 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 제공한다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
본 발명은 또한, (a) 히알루론산 수용액에 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)를 첨가하고, 혼합하는 단계; 및 (b) 혼합액에 산을 적가하여 히알루론산 및 리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드를 해리시키는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체의 제조방법을 제공한다.The present invention also, (a) adding polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) to the hyaluronic acid aqueous solution, and mixing; And (b) provides a method for producing a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex represented by the following formula (1), characterized in that it comprises the step of dissociating hyaluronic acid and lideoxyribonucleotide by adding acid to the mixture.
본 발명에 있어서, 상기 산은 염산, 초산, 인산, 황산, 질산, 구연산, 젖산, α,β-디클로로말레익산, 말레익산 및 비타민 C로 구성된 군으로부터 선택되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In the present invention, the acid is characterized in that it is selected from the group consisting of hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, lactic acid, α, β-dichloromaleic acid, maleic acid and vitamin C.
본 발명에 있어서, 상기 혼합액의 pH가 3~4가 되도록 산을 적가하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In the present invention, the acid is added dropwise so that the pH of the mixed solution is 3-4.
본 발명은 또한, 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 필름을 제공한다.The present invention also provides a film comprising a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
본 발명에 따라 제조된 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체는 히알루론산에서 기인한 수분 보유력 및 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드에서 기인한 피부 재생을 통한 상처 치유능이 뛰어나 화장품이나 의약 외품 등의 피부 외용제로 이용할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 특히 필름 형태의 경우 화장품용 패치 또는 구강 내 부착 필름 등으로의 활용이 가능하다.The hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex prepared according to the present invention is excellent in water retention due to hyaluronic acid and wound healing through skin regeneration caused by polydeoxyribonucleotide, so it can be used as an external preparation for skin such as cosmetics or quasi-drugs. In addition, it can be used as a cosmetic patch or an intraoral attachment film, especially in the case of a film.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 히알루론산(HA)과 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)의 이온결합에 의한 복합체 생성을 나타낸 반응도이다.
도 2는 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 및 분자량에 따른 히알루론산(HA)의 해리도(pKa)를 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 3은 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체의 pH에 따른 점도 변화를 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 4는 HA-PDRN 혼합물(physical mixture)과 HA-PDRN 복합체(pH adjustment)의 FT-IR 그래프이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 제조된 HA-PDRN 복합체의 Hyaluronidase에 대한 안정성 측정 결과 그래프이다.1 is a reaction diagram showing the formation of a complex by ion bonding of hyaluronic acid (HA) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a graph showing the dissociation degree (pKa) of hyaluronic acid (HA) according to polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) and molecular weight.
Figure 3 is a graph showing the viscosity change according to the pH of the hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex.
4 is a FT-IR graph of the HA-PDRN mixture (physical mixture) and HA-PDRN complex (pH adjustment).
Figure 5 is a graph of the stability measurement results for Hyaluronidase of the HA-PDRN complex prepared according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명에서는 pH 조절을 통하여 히알루론산(HA)과 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)를 동시에 해리시킬 경우, 화학반응 촉매나 유독한 유기용매 사용없이 기존 히알루론산 대비 안정성 및 기능성이 증대된 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체를 제조할 수 있다는 것을 확인하고자 하였다. In the present invention, when dissociating hyaluronic acid (HA) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) at the same time through pH adjustment, hyaluronic acid has increased stability and functionality compared to conventional hyaluronic acid without using a chemical reaction catalyst or a toxic organic solvent- It was intended to confirm that a polydeoxyribonucleotide complex can be prepared.
본 발명에서는 히알루론산(HA) 수용액에 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)을 혼합하고, pH 조절을 통하여 해리시켰다. 그 결과, 해리된 분자들이 이온결합되어 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체가 생성되며, 생성된 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체는 효소에 대한 안정성이 증대된 것을 확인하였다. In the present invention, polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) was mixed with a hyaluronic acid (HA) aqueous solution and dissociated through pH adjustment. As a result, it was confirmed that the dissociated molecules were ion-bonded to form a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex, and the resulting hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex had increased stability to the enzyme.
따라서, 본 발명은 일 관점에서, 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체에 관한 것이다.Therefore, in one aspect, the present invention relates to a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by Chemical Formula 1 below.
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
본 발명에 있어서, 상기 히알루론산(HA)은 N-아세틸-D-글루코사민과 D-글루쿠론산으로 이루어진 반복 단위가 선형으로 연결되어 있는 생체 고분자 물질로서, 본 발명에서 히알루론산은 히알루론산 자체, 이의 염 또는 이들의 조합을 모두 포함하는 의미로 사용된다. 상기 히알루론산의 염은 예를 들어 히알루론산 나트륨, 히알루론산 칼륨, 히알루론산 칼슘, 히알루론산 마그네슘, 히알루론산 아연, 히알루론산 코발트 등의 무기염과, 히알루론산 테트라부틸암모늄 등의 유기염이 모두 포함되는 것이나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 본 발명에서는, 히알루론 산 자체, 또는 이의 염을 단독으로, 또는 히알루론산 자체, 또는 이의 염을 2종 이상 조합하여 사용할 수 있다. 본 발명에서, 상기 히알루론산의 분자량은 10~3,000kDa일 수 있으며, 1200~2300kDa인 것이 바람직하다.In the present invention, the hyaluronic acid (HA) is a biopolymer material in which a repeating unit composed of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid is linearly connected. In the present invention, hyaluronic acid is hyaluronic acid itself, It is used in the sense including all of salts or combinations thereof. The salt of hyaluronic acid includes, for example, inorganic salts such as sodium hyaluronate, potassium hyaluronate, calcium hyaluronate, magnesium hyaluronate, zinc hyaluronate, cobalt hyaluronate, and organic salts such as tetrabutylammonium hyaluronate It is, but is not limited to. In the present invention, hyaluronic acid itself or a salt thereof can be used alone or in combination of two or more types of hyaluronic acid itself or a salt thereof. In the present invention, the molecular weight of the hyaluronic acid may be 10 ~ 3,000kDa, preferably 1200 ~ 2300kDa.
상기 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(polydeoxyribonucleotide, 이하 'PDRN'이라 한다.)은 조직재생물질로 알려져 있는데, PDRN은 연어나 송어 정액으로부터 추출한 DNA로 제조된 것을 이용할 수 있으며, 분자량은 3~2,000kDa인 것을 사용하는 것이 바람직하다. 상기 PDRN은 5탄당(pentose)에 결합되는 퓨린(purines), 피리미딘(pyrimidines) 염기(base)에 따라 달라질 수 있다.The polydeoxyribonucleotide (hereinafter referred to as 'PDRN') is known as a tissue regeneration material. PDRN can be made of DNA extracted from salmon or trout semen, and has a molecular weight of 3 to 2,000 kDa. It is preferred to use. The PDRN may vary depending on the purines and pyrimidines base bound to pentose.
참고로, PDRN은 피부이식으로 인한 상처의 치료 및 조직수복에 사용하고 있지만, 마땅한 치료법이 없는 일부 조직재생이나 염증치료에도 의료진 판단에 따라 사용되고 있으며, 또한 피부재생 신호전달체인 A2 수용체를 자극해 각종 성장인자 분비촉진, VEGF(혈관내피세포증식인자)에 의한 모세혈관의 생성, 혈액순환 개선, 항 염증 작용 및 모세혈관 누출 방지 기능을 하는 성분으로 알려져 있다. For reference, PDRN is used for the treatment and tissue repair of wounds caused by skin transplantation, but it is also used at the discretion of medical staff for some tissue regeneration or inflammation treatment without proper treatment. It is known as a component that promotes secretion of growth factors, production of capillaries by VEGF (vascular endothelial cell growth factor), improvement of blood circulation, anti-inflammatory action and prevention of capillary leakage.
도 1과 같이, 상기 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체는 해리된 히알루론산 및 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드의 이온결합에 의하여 제조될 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 1, the hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex can be prepared by ion bonding of dissociated hyaluronic acid and polydeoxyribonucleotide.
따라서, 본 발명은 다른 관점에서, (a) 히알루론산 수용액에 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)를 첨가하고, 혼합하는 단계; 및 (b) 혼합액에 산을 적가하여 히알루론산 및 리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드를 해리시키는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체의 제조방법에 관한 것이다. Accordingly, the present invention, in another aspect, (a) adding a polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) to the aqueous hyaluronic acid solution, and mixing; And (b) relates to a method for producing a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex represented by
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
본 발명에 있어서, 상기 히알루론산 수용액은 0.2~5중량% 농도인 것이 바람직하며, 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)는 히알루론산 100중량부에 대하여 1~10중량부 첨가하는 것이 바람직하다. 상기 히알루론산 수용액의 농도가 0.2중량% 미만인 경우에는 히알루론산의 수분 보유력 효과가 미미하며, 일반적으로 히알루론산은 물을 용매로 할 경우 분자량 0.5MDa 이상의 경우 5중량%를 초과하여 용해되지 않는다. In the present invention, the hyaluronic acid aqueous solution is preferably 0.2 to 5% by weight concentration, polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) is preferably added 1 to 10 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of hyaluronic acid. When the concentration of the hyaluronic acid aqueous solution is less than 0.2% by weight, the water retention effect of hyaluronic acid is insignificant, and in general, when water is used as a solvent, hyaluronic acid does not dissolve in excess of 5% by weight when the molecular weight is 0.5MDa or more.
상기 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)의 첨가량이 히알루론산 100중량부에 대하여 1중량부 미만인 경우에는 PDRN의 도입 효과가 없는 문제가 있고, 10중량부를 초과할 경우에는 PDRN에 기인한 색상 유발의 문제가 있다.When the addition amount of the polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) is less than 1 part by weight based on 100 parts by weight of hyaluronic acid, there is a problem that there is no effect of introducing PDRN, and when it exceeds 10 parts by weight, a problem of color induction due to PDRN There is.
상기 히알루론산 및 리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 혼합액의 해리는 산을 적가하는 pH 조절에 의하여 수행될 수 있는데, 이때 사용되는 산은 염산, 초산, 인산, 황산, 질산, 구연산, 젖산, α,β-디클로로말레익산, 말레익산 및 비타민 C 등을 예시할 수 있다. Dissociation of the mixture of hyaluronic acid and radeoxyribonucleotide may be performed by adjusting the pH of the acid dropwise, wherein the acid used is hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, lactic acid, α, β-dichloromaleic acid , Maleic acid and vitamin C.
상기 산은 혼합액의 pH가 3~4가 되도록 적가하는 것을 특징으로 한다. 혼합액의 pH가 3~4가 되면 히알루론산 및 리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드가 해리된 후, 이온결합에 의하여 복합체를 형성하게 되는데, 이때 점도가 급격하게 변화된다. The acid is characterized in that the pH of the mixed solution is added dropwise to 3-4. When the pH of the mixed solution is 3 to 4, the hyaluronic acid and lideoxyribonucleotide are dissociated, and then a complex is formed by ion bonding. At this time, the viscosity is rapidly changed.
본 발명에 따른 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체의 제조방법은 어떠한 화학반응 촉매나 유독한 유기 용매 등의 사용 없이 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체를 제조할 수 있으므로, 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체 형성 후, 독성 케미칼 제거를 위한 공정없이, 화장품 또는 식품으로 제형화 할 수 있다.The method for preparing a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex according to the present invention can produce a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex without using any chemical reaction catalyst or toxic organic solvent, and thus, the hyaluronic acid-polyde After formation of the oxyribonucleotide complex, it can be formulated as a cosmetic or food without a process for removing toxic chemicals.
따라서, 본 발명은 또 다른 관점에서, 상기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 필름에 관한 것이다.Therefore, in another aspect, the present invention relates to a film comprising the hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by Chemical Formula 1 above.
상기 필름은 용매캐스팅 또는 자동도포기 캐스팅 방법으로 제조될 수 있으며, 본 발명자가 출원한 한국특허 출원번호 10-2017-0029094, 10-2017-0125213, 10-2018-0000182 및 10-2018-0027063에 보다 자세히 기재되어 있다. 즉 상기 특허에 기재된 히알루론산염 대신 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 이용하여 필름을 제조할 수 있다.The film may be prepared by a solvent casting or an automatic coating machine casting method, in Korean Patent Application Nos. 10-2017-0029094, 10-2017-0125213, 10-2018-0000182 and 10-2018-0027063 filed by the present inventors It is described in more detail. That is, a film may be prepared using a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex instead of the hyaluronic acid salt described in the patent.
본 발명에 따른 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 포함하는 필름은 히알루론산 필름에 비하여 안정화되고, PDRN의 피부 치료와 재생 기능이 추가되어 피부노화방지 기능 강화 및 부작용 발생을 최소화하는 장점이 있다.The film comprising the hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex according to the present invention is stabilized compared to the hyaluronic acid film, and the skin treatment and regeneration function of PDRN is added to strengthen the skin aging prevention function and minimize side effects. There are advantages.
따라서, 상기 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체를 포함하는 필름은 화장품용 마스크팩, 패치, 의료기기용 유착 방지제 등으로 활용 가능하다.Therefore, the film containing the hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex can be used as a cosmetic mask pack, patch, anti-adhesion agent for medical devices, and the like.
[실시예][Example]
이하, 실시예를 통하여 본 발명을 더욱 상세히 설명하고자 한다. 이들 실시예는 오로지 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 것으로, 본 발명의 범위가 이들 실시예에 의해 제한되는 것으로 해석되지 않는 것은 당 업계에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어서 자명할 것이다. Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail through examples. These examples are only for illustrating the present invention, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that the scope of the present invention is not to be construed as limited by these examples.
본 발명에서는 ㈜진우바이오의 히알루론산 나트륨 (Hi-Aqua)와 일본 마루하니치로사의 PDRN (DNA Extract)을 사용하였다.In the present invention, Jinwoo Bio's sodium hyaluronate (Hi-Aqua) and Maruhanichiro Corporation's PDRN (DNA Extract) were used.
실시예 1: HA와 PDRN의 해리도 측정Example 1: Measurement of dissociation of HA and PDRN
히알루론산(HA) (분자량: 10kDa, 0.8MDa, 1.2MDa, 2.3MDa)과 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) (분자량 0.1MDa)의 해리도를 측정하였다. The dissociation of hyaluronic acid (HA) (molecular weight: 10 kDa, 0.8 MDa, 1.2 MDa, 2.3 MDa) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) (molecular weight 0.1 MDa) was measured.
0.5% 분자량 별 HA 수용액과 PDRN 1% 수용액을 제조한 후 0.1N HCl을 사용하여 pH를 2.0까지 낮춘 시료에 0.1N NaOH를 천천히 적가하면서 pH 변화를 기록하여 해리도를 측정하고, 분자량에 따른 히알루론산(HA)와 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN)의 Potentiometric Curve를 도 2에 나타내었다. After preparing a 0.5% molecular weight HA solution and a 1% PDRN aqueous solution, 0.1N NaOH was slowly added dropwise to a sample whose pH was lowered to 2.0 using 0.1N HCl to record the pH change while measuring the dissociation degree, and the hyaluronic acid according to the molecular weight was measured. The potentiometric curves of (HA) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) are shown in FIG. 2.
도 2로부터, HA의 해리도(pKa)는 pH 2.5~4.0이고, PDRN의 해리도(pKa)는 pH 3.0~4.0인 것을 알 수 있었다. From FIG. 2, it was found that the degree of dissociation (pKa) of HA was pH 2.5-4.0, and the degree of dissociation (pKa) of PDRN was pH 3.0-4.0.
실시예 2: HA-PDRN 복합체 형성 확인 Example 2: Confirmation of HA-PDRN complex formation
0.5% HA (0.8MD과 1.2MDa) 200ml 수용액에 HA 중량 대비 10% 비율로 PDRN을 첨가하여 HA-PDRN mixture (혼합액)를 준비하였다. 혼합액을 천천히 교반하며 0.1N HCl를 일정량씩 적가하면서 pH와 점도 변화를 측정하여 HA-PDRN Complex 형성이 일어나는지를 확인하고, 그 결과를 도 3에 나타내었다. In a 200% aqueous solution of 0.5% HA (0.8MD and 1.2MDa), PDRN was added at a ratio of 10% by weight of HA to prepare a HA-PDRN mixture (mixture). The mixture was slowly stirred and 0.1N HCl was added dropwise at a predetermined amount to measure pH and viscosity changes to confirm whether HA-PDRN Complex formation occurred, and the results are shown in FIG. 3.
도 3으로부터, 0.8MDa의 HA의 경우 pH에 따른 점도 변화가 거의 없는 반면에 1.2MDa 및 2.3MDa의 경우 pH 3~4 사이에서 급격한 점도 변화가 생김을 알 수 있었으며 이 구간에서 HA-PDRN Complex가 효과적으로 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. From FIG. 3, it was found that while the HA of 0.8MDa had little change in viscosity depending on the pH, in the case of 1.2MDa and 2.3MDa, a rapid change in viscosity occurred between
한편, 히알루론산(HA)과 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 혼합물과 히알루론산(HA)-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체의 구조 변화를 확인하기 위하여 FT-IR을 측정하고, 그 결과를 도 4에 나타내었다. Meanwhile, FT-IR was measured to confirm the structural changes of the hyaluronic acid (HA) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) mixture and the hyaluronic acid (HA) -polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex. It is shown in FIG. 4.
도 4에 나타난 바와 같이, pH 조절에 의하여 형성된 히알루론산(HA)-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 복합체의 경우, 히알루론산(HA)과 폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(PDRN) 혼합물(physical mixture)과 비교해 볼 때, PDRN의 NH3 +와 HA의 COO-간의 이온 결합 형성에 따라 1,729, 1636 및 1555cm-1 근처에서 새로운 피크가 있음을 알 수 있었다. As shown in Figure 4, in the case of a hyaluronic acid (HA) -polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex formed by pH adjustment, the hyaluronic acid (HA) and polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) mixture (physical mixture) and By comparison, it was found that there are new peaks around 1,729, 1636 and 1555cm -1 depending on the formation of ionic bonds between NH 3 + of PDRN and COO - of HA.
실시예 3: HA-PDRN 복합체의 안정성 측정 Example 3: Measurement of stability of HA-PDRN complex
HA-PDRN 복합체의 효소에 대한 안정성은 다음의 방법에 의하여 측정하였다. 먼저 HA와 실시예 2에서 제조된 HA-PDRN 혼합물 및 HA-PDRN 복합체를 각각 0.1% 600㎕ 수용액으로 제조하고, phosphate buffer 용액 200㎕를 가한 후 이를 37℃에서 충분히 혼합하였다. The stability of the HA-PDRN complex for enzymes was measured by the following method. First, the HA and the HA-PDRN mixture prepared in Example 2 and the HA-PDRN complex were respectively prepared as a 0.1% 600 µl aqueous solution, 200 µl of a phosphate buffer solution was added, and then sufficiently mixed at 37 ° C.
다음으로, Hyaluronidase (1,000unit) 1㎖을 가하고, 1~6시간 동안 인큐베이션 시킨 후 최종적으로 200㎕의 Alkaline Borate 수용액을 가하고 5분간 끓여서 불활성화 시켰다. 다음으로 이를 얼음에 냉각시키고, 3㎖의 DMAB 용액을 적가 한 후 이를 30℃에서 30분간 인큐베이션 하였다. 최종적으로 효소에 대한 안정성은 UV Spectrometer를 사용하여 586nm에서의 흡광도를 측정하여 확인하고, 그 결과를 도 5에 나타내었다. Next, 1 ml of Hyaluronidase (1,000 units) was added, followed by incubation for 1 to 6 hours, and finally 200 μl of an Alkaline Borate aqueous solution was added and boiled for 5 minutes to inactivate. Next, it was cooled on ice, and 3 ml of DMAB solution was added dropwise, followed by incubation at 30 ° C for 30 minutes. Finally, the stability to the enzyme was confirmed by measuring the absorbance at 586 nm using a UV Spectrometer, and the results are shown in FIG. 5.
도 5에 도시된 바와 같이, HA-PDRN 복합체는 순수 HA와 HA-PDRN 혼합물에 비해 Hyaluronidase에 대한 안정성이 높다는 것을 알 수 있었다. As shown in Figure 5, it was found that the HA-PDRN complex has higher stability to Hyaluronidase than the pure HA and HA-PDRN mixture.
실시예 4: HA-PDRN 복합체 필름 제조Example 4: Preparation of HA-PDRN composite film
4-1: 용매 캐스팅을 이용한 필름 제조4-1: Film production using solvent casting
실시예 2에서 제조된 HA-PDRN 복합체를 20부피% 에탄올 수용액에 0.5~3.0중량% 농도로 용해시킨 후, 아크릴 몰드에 주입한 다음 항온항습 건조기 (상대 습도 50%, 온도 40℃)에서 6~24시간 건조하여 HA-PDRN 복합체 필름을 제조하였다.After the HA-PDRN complex prepared in Example 2 was dissolved in a 20% by volume aqueous ethanol solution at a concentration of 0.5 to 3.0% by weight, injected into an acrylic mold, and then in a constant temperature and humidity dryer (relative humidity 50%,
4-2: 자동도포기 캐스팅을 이용한 필름 제조4-2: Film production using automatic coating machine casting
실시예 2에서 제조된 HA-PDRN 복합체를 20부피% 에탄올 수용액에 0.5~3.0중량% 농도로 용해시킨 후, 자동 도포기 (COAD 411, 의왕기계, 한국)의 어플리케이터를 조절하여 0.025~5㎜ 두께의 필름을 캐스팅 후, 순환 건조기 (온도 30~60℃)에서 6~12시간 건조하여 HA-PDRN 복합체 필름을 제조하였다. After dissolving the HA-PDRN complex prepared in Example 2 in a concentration of 0.5 to 3.0% by weight in an aqueous 20% ethanol solution, the applicator of the automatic applicator (COAD 411, Uiwang Machinery, Korea) was adjusted to have a thickness of 0.025 to 5 mm. After casting the film, dried in a circulating dryer (temperature 30-60 ° C) for 6-12 hours to prepare a HA-PDRN composite film.
그 결과, 용매 캐스팅 또는 자동도포기 캐스팅 법으로 표면이 매우 균일한 HA-PDRN 복합체 필름을 제조할 수 있음을 확인할 수 있었다.As a result, it was confirmed that a HA-PDRN composite film having a very uniform surface can be prepared by solvent casting or automatic coating machine casting.
이상으로 본 발명 내용의 특정한 부분을 상세히 기술하였는 바, 당업계의 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어서 이러한 구체적 기술은 단지 바람직한 실시태양일 뿐이며, 이에 의해 본 발명의 범위가 제한되는 것이 아닌 점은 명백할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명의 실질적인 범위는 첨부된 청구항들과 그것들의 등가물에 의하여 정의된다고 할 것이다.Since the specific parts of the present invention have been described in detail above, it is obvious that for those skilled in the art, this specific technique is only a preferred embodiment, and the scope of the present invention is not limited thereby. something to do. Accordingly, the substantial scope of the present invention will be defined by the appended claims and their equivalents.
Claims (5)
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.
Hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by Formula 1 below.
[Formula 1]
In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
(b) 혼합액에 산을 적가하여 히알루론산 및 리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드를 해리시키는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 하기 화학식 1로 표현되는 히알루론산-폴리데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드 복합체의 제조방법.
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.
(a) adding polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) to the hyaluronic acid aqueous solution and mixing; And
(B) a method for producing a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex represented by the following Chemical Formula 1, comprising dissociating hyaluronic acid and lideoxyribonucleotide by adding acid to the mixed solution dropwise.
[Formula 1]
In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
The hyaluronic acid-polyide according to claim 2, wherein the acid is selected from the group consisting of hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, lactic acid, α, β-dichloromaleic acid, maleic acid and vitamin C. Method for preparing oxyribonucleotide complex.
The method for preparing a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide complex according to claim 2, wherein an acid is added dropwise so that the pH of the mixed solution becomes 3-4.
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서 PDRN은 분자량이 3,000~2,000,000Da이고, n은 20~7,000임.A film comprising a hyaluronic acid-polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) complex represented by Formula 1 below.
[Formula 1]
In Formula 1, PDRN has a molecular weight of 3,000 to 2,000,000 Da, and n is 20 to 7,000.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180140876A KR102132478B1 (en) | 2018-11-15 | 2018-11-15 | Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180140876A KR102132478B1 (en) | 2018-11-15 | 2018-11-15 | Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20200057144A true KR20200057144A (en) | 2020-05-26 |
| KR102132478B1 KR102132478B1 (en) | 2020-07-10 |
Family
ID=70915054
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180140876A KR102132478B1 (en) | 2018-11-15 | 2018-11-15 | Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102132478B1 (en) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010002244A (en) * | 1999-06-08 | 2001-01-15 | 페로 라우라 | Use of complexes among cationic liposomes and polydeoxyribonucleotides as medicaments |
| KR20140119513A (en) * | 2013-04-01 | 2014-10-10 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Composition for nucleic acid delivery containing hyaluronic acid |
| KR101710639B1 (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2017-03-08 | 주식회사 파마리서치프로덕트 | Filler composition comprising nucleic acid, chitosan and hyaluronic acid for tissue augmentation and process for producing the same |
| KR20170068857A (en) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-20 | 주식회사 한국비엔씨 | Method for Preparing of Composition for Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Regeneration Using Polydeoxyribonucleotide |
| WO2018008873A1 (en) * | 2016-07-06 | 2018-01-11 | 주식회사 리온메디코스 | Cosmetic composition containing polydeoxyribonucleotide (pdrn) |
| KR20180048520A (en) * | 2018-04-27 | 2018-05-10 | 주식회사 한국비엔씨 | Method for Preparing of Composition for Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Regeneration Using Polydeoxyribonucleotide |
| KR20180060537A (en) * | 2016-11-29 | 2018-06-07 | (주)웰빙해피팜 | Whitening functional cosmetic composition having skin-regeneration and moistureizing |
-
2018
- 2018-11-15 KR KR1020180140876A patent/KR102132478B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010002244A (en) * | 1999-06-08 | 2001-01-15 | 페로 라우라 | Use of complexes among cationic liposomes and polydeoxyribonucleotides as medicaments |
| KR20140119513A (en) * | 2013-04-01 | 2014-10-10 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Composition for nucleic acid delivery containing hyaluronic acid |
| KR20170068857A (en) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-20 | 주식회사 한국비엔씨 | Method for Preparing of Composition for Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Regeneration Using Polydeoxyribonucleotide |
| KR101710639B1 (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2017-03-08 | 주식회사 파마리서치프로덕트 | Filler composition comprising nucleic acid, chitosan and hyaluronic acid for tissue augmentation and process for producing the same |
| WO2018008873A1 (en) * | 2016-07-06 | 2018-01-11 | 주식회사 리온메디코스 | Cosmetic composition containing polydeoxyribonucleotide (pdrn) |
| KR20180060537A (en) * | 2016-11-29 | 2018-06-07 | (주)웰빙해피팜 | Whitening functional cosmetic composition having skin-regeneration and moistureizing |
| KR20180048520A (en) * | 2018-04-27 | 2018-05-10 | 주식회사 한국비엔씨 | Method for Preparing of Composition for Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Regeneration Using Polydeoxyribonucleotide |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102132478B1 (en) | 2020-07-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Yu et al. | Novel supramolecular self-healing silk fibroin-based hydrogel via host–guest interaction as wound dressing to enhance wound healing | |
| CN103415307B (en) | hyaluronic acid compositions | |
| JP5657545B2 (en) | Method for preparing an injectable hydrogel crosslinked in an injectable container | |
| US7521434B2 (en) | Cross-linked gels of hyaluronic acid with hydrophobic polymers and processes for making them | |
| EP2614090B2 (en) | Hybrid cooperative complexes of hyaluronic acid | |
| KR20060008906A (en) | Cross-linked polysaccharide composition | |
| JP2015537078A (en) | Glucose-responsive hydrogel comprising PBA grafted hyaluronic acid (HA) | |
| WO2015002091A1 (en) | Water-soluble hyaluronic acid gel and method for producing same | |
| CN109806182B (en) | Composition containing hyaluronic acid and amino acid and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN110124117B (en) | Injectable hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN101501075B (en) | Branched hyaluronic acid and method of manufacture | |
| EP2922581B1 (en) | Mucoadhesive compositions comprising hyaluronic acid and chitosan for topical application | |
| EP2222713B1 (en) | Mixed butyric-formic esters of acid polysaccharides, and their preparation and use as skin cosmetics | |
| Yang et al. | Injectable polylysine and dextran hydrogels with robust antibacterial and ROS-scavenging activity for wound healing | |
| CN111228296A (en) | Cross-linked hyaluronic acid ectoine isotonic wound flushing fluid | |
| KR102132478B1 (en) | Hyaluronic Acid-Polydeoxyribonucleotide Complex and Its Film and Preparation Method Thereof | |
| EP3331488A1 (en) | Improved hyaluronan and modified-hyaluronan in biomedical applications | |
| WO2019097427A1 (en) | Resorbable implantable devices based on crosslinked glycosaminoglycans, and process for the preparation thereof | |
| CN104225577A (en) | Double-treatment-course composite cell growth factor hydrogels as well as preparation methods and applications | |
| EP3416652B1 (en) | Injectable composition, method for preparing said composition, and use of said composition | |
| CN114350035B (en) | Hyaluronic acid crosslinking active material and application thereof | |
| CN114452436B (en) | Collagen-based injectable self-repairing hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114716578B (en) | Preparation method and application of soluble euglena polysaccharide | |
| CN113827501B (en) | Hyaluronic acid hydrogel mask with skin repair function and preparation method thereof | |
| KR102202188B1 (en) | Composition for improving the stability of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid and dermal filler comprising the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right |