KR20170026496A - Thermally stable meltblown web comprising multilayer fibers - Google Patents
Thermally stable meltblown web comprising multilayer fibers Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170026496A KR20170026496A KR1020177001928A KR20177001928A KR20170026496A KR 20170026496 A KR20170026496 A KR 20170026496A KR 1020177001928 A KR1020177001928 A KR 1020177001928A KR 20177001928 A KR20177001928 A KR 20177001928A KR 20170026496 A KR20170026496 A KR 20170026496A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- polymer
- fibers
- melt blown
- layer
- fibrous web
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/56—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving in association with fibre formation, e.g. immediately following extrusion of staple fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/098—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching
- D01D5/0985—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching by means of a flowing gas (e.g. melt-blowing)
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/28—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like while mixing different spinning solutions or melts during the spinning operation; Spinnerette packs therefor
- D01D5/30—Conjugate filaments; Spinnerette packs therefor
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01F—CHEMICAL FEATURES IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF CARBON FILAMENTS
- D01F8/00—Conjugated, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, artificial filaments or the like; Manufacture thereof
- D01F8/04—Conjugated, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, artificial filaments or the like; Manufacture thereof from synthetic polymers
- D01F8/14—Conjugated, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, artificial filaments or the like; Manufacture thereof from synthetic polymers with at least one polyester as constituent
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/42—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece
- D04H1/4391—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece characterised by the shape of the fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/42—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece
- D04H1/4391—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece characterised by the shape of the fibres
- D04H1/43918—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece characterised by the shape of the fibres nonlinear fibres, e.g. crimped or coiled fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/541—Composite fibres, e.g. sheath-core, sea-island or side-by-side; Mixed fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/541—Composite fibres, e.g. sheath-core, sea-island or side-by-side; Mixed fibres
- D04H1/5412—Composite fibres, e.g. sheath-core, sea-island or side-by-side; Mixed fibres sheath-core
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/541—Composite fibres, e.g. sheath-core, sea-island or side-by-side; Mixed fibres
- D04H1/5414—Composite fibres, e.g. sheath-core, sea-island or side-by-side; Mixed fibres side-by-side
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/559—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving the fibres being within layered webs
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2331/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products
- D10B2331/04—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products polyesters, e.g. polyethylene terephthalate [PET]
Abstract
복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹으로서, 여기에서 용융취입 다층 섬유의 적어도 일부는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 느리게 결정화하는 제1 중합체를 포함하는 1개 이상의 제1 층, 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 빠르게 결정화하는 제2 중합체를 포함하는 1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함한다.A thermostable meltblown fiber web comprising a plurality of the melt-blown multilayered fiber, in which at least the meltblown multi-layer fiber portion is at least one first layer comprising a first polymer to crystallize slowly, having more than about 200 ℃ T m It includes, and a second layer at least one of a second polymer having a fast crystallization at least about 200 ℃ T m respectively.
Description
용융취입은 열가소성 중합체성 섬유의 부직 섬유질 웹을 형성하기 위한 공정이다. 전형적인 용융취입 공정에서, 하나 이상의 용융 중합체 스트림(stream)은 다이 오리피스를 통해 압출되고, 고속 공기("취입" 공기)의 수렴 스트림에 의해 감쇠되어(attenuate) 섬유를 형성하며, 이는 수집되어 용융취입 부직 섬유질 웹을 형성한다. 용융취입 부직 섬유질 웹은 특히 방음재 및 단열재, 여과 매체, 외과용 드레이프(surgical drape), 및 와이프(wipe)를 비롯한 다양한 응용에 사용된다.Melt blowing is a process for forming a nonwoven fibrous web of thermoplastic polymeric fibers. In a typical meltblowing process, one or more molten polymer streams are extruded through a die orifice and attenuated by a converging stream of high velocity air ("blown" air) to form fibers, To form a nonwoven fibrous web. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION [0002] Melt blown nonwoven fibrous webs are used in a variety of applications including, in particular, soundproofing materials and insulation, filtration media, surgical drapes, and wipes.
일반적인 개요로, 본 명세서는 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 개시하며, 여기에서 적어도 선택된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 느리게 결정화하는 중합체인 제1 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제1 층, 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체인 제2 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함한다. 이러한 측면 및 다른 측면이 하기의 상세한 설명으로부터 명백해질 것이다. 그러나, 어떠한 경우에도, 최초 출원된 바와 같은 출원의 청구범위에 제시되든, 절차 중 보정되거나 달리 제시되는 청구범위에 제시되든 간에, 상기 일반적인 개요가 청구가능한 발명의 요지를 제한하는 것으로 해석되어서는 안 된다.As a general overview, the present disclosure discloses a thermally stable meltblown fibrous web comprising a plurality of the melt-blown multilayered fiber, melt-blown multilayer fiber least selected herein is a polymer which crystallize slowly, having more than about 200 ℃ T m first It includes a polymer of one or more first layers, and at least one second layer consisting of a polymer of a second polymer which crystallized rapidly with about 200 or more m ℃ T consisting, respectively. These and other aspects will become apparent from the following detailed description. However, in no event shall the general summary be construed as limiting the gist of the claimed invention, whether presented in the claims of the application as originally filed, or in the claims as amended or otherwise set forth in the proceedings do.
도 1은 예시적인 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹 부분의 개략 측단면도이다.
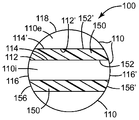
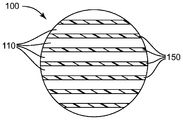
도 2는 예시적인 용융취입 다층 섬유의 단면도이다.
도 3은 예시적인 용융취입 다층 섬유의 또다른 단면도이다.
도 4는 예시적인 용융취입 다층 섬유의 또다른 단면도이다.1 is a schematic side cross-sectional view of an exemplary heat-stable melt blown fibrous web portion.
2 is a cross-sectional view of an exemplary melt blown multilayer fiber.
3 is another cross-sectional view of an exemplary melt blown multilayer fiber.
4 is another cross-sectional view of an exemplary melt blown multilayer fiber.
달리 표시되지 않는한, 본 명세서 내의 모든 수치들 및 도면들은 크기조정되지 않았으며 본 발명의 상이한 실시양태들을 예시할 목적으로 선택된 것이다. 특히 다양한 구성요소들의 치수들은 단지 예시적인 형태로 표시된 것이며, 다양한 구성요소들의 치수들 간의 관계는, 그리 표시되지 않는한, 도면들로부터 추론되어서는 안된다. 다양한 도면에서 유사한 도면 번호는 유사한 요소를 나타낸다. 일부 요소는 다수로 존재할 수 있으며; 그러한 경우에 오직 하나 이상의 대표적인 요소가 도면 번호에 의해 지정될 수 있지만, 그러한 도면 번호는 그러한 요소 모두에 적용된다는 것이 이해될 것이다(일부 경우에서, 설명의 목적으로 표시(예를 들어, ')가 다수의 균등한 요소를 구별하는 편의를 위해 사용될 수 있다). "상단", "하단", "상부", "하부", "아래", "위", "전방", "후방", "외향", "내향", "상방" 및 "하방", 및 "제1" 및 "제2"와 같은 용어가 본 개시 내용에 사용될 수 있지만, 이들 용어는 달리 언급되지 않는다면 그들의 상대적 의미로만 사용됨을 이해하여야 한다. 특히, 균등한 다수의 구성요소에 대해, "제1" 및 "제2"의 지정은, 본 명세서에서 언급된 바와 같이, 설명의 순서에 적용될 수 있다(이는 구성요소들 중 하나가 첫번째로 설명되도록 선택되는지에 관해서는 무관함).Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers and figures in the specification are not to scale and are selected for the purpose of illustrating different embodiments of the invention. In particular, the dimensions of the various components are shown in exemplary form only, and the relationship between the dimensions of the various components should not be deduced from the drawings unless so indicated. Like numbers refer to like elements in the various figures. Some elements may exist in multiple; It will be appreciated that in such a case, only one or more representative elements may be designated by the drawing numbers, but such numbers apply to all such elements (in some cases, for purposes of illustration only, Can be used for convenience in distinguishing a number of equal elements). The terms "top", "bottom", "upper", "lower", "lower", "above", "forward", "rearward", "outward", "inward", " Quot; first "and" second "may be used in this disclosure, they should be understood to be used only in their relative sense unless otherwise stated. In particular, for an equal number of components, the designations of "first" and "second" can be applied to the order of description, as mentioned herein (which means that one of the components is described first As long as it is chosen to be the best.
특성 또는 속성에 대한 수식어로서 본 명세서에 사용되는 바와 같이, 용어 "대체로"는, 달리 구체적으로 정의되지 않는 한, 그 특성 또는 속성이 절대적인 정밀도 또는 완벽한 일치를 요구함이 없이(예를 들어, 정량화가능한 특성에 대해 +/- 20% 이내) 당업자에 의해 용이하게 인식가능할 것이라는 것을 의미한다. 용어 "실질적으로"는, 달리 구체적으로 정의되지 않는 한, 절대적인 정밀도 또는 완벽한 일치를 요구함이 없이 높은 정도의 근사(예를 들어, 정량화가능한 특성에 대해 +/- 10% 이내)를 의미한다. 동일한, 같은, 균일한, 일정한, 엄밀하게 등과 같은 용어는, 절대적인 정밀도 또는 완벽한 일치를 요구하기보다는 특정 환경에 적용가능한 통상의 공차 또는 측정 오차 내에 있는 것으로 이해된다. 본 명세서에 사용되는 바와 같이, "실질적으로 없는", "실질적으로 부재하는" 등과 같은 용어는, 예를 들어 통상적인 세정 절차에 처해지는 대규모 생산 장비를 사용하는 경우에 일어날 수 있는 바와 같이, 일부 극히 낮은, 예컨대 0.1% 이하의 양의 재료가 존재하는 것을 배제하지 않는다는 것을 당업자는 알 것이다.The term "substantially ", as used herein as a modifier for a characteristic or attribute, means that, unless otherwise specifically defined, that characteristic or attribute may be used without requiring absolute precision or perfect agreement (e.g., ≪ / RTI > within +/- 20% of the property). The term "substantially" means a high degree of approximation (e.g., within +/- 10% of a quantifiable characteristic) without requiring absolute precision or perfect agreement unless otherwise specifically defined. It is understood that terms such as the same, equal, uniform, constant, strict, etc. are within the ordinary tolerances or measurement errors applicable to the particular environment, rather than requiring absolute precision or perfect agreement. As used herein, terms such as "substantially free "," substantially absent ", and the like are intended to encompass all or part of the entirety of a part of the apparatus, such as may occur, for example, It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the present invention does not exclude the presence of an extremely low amount of material, e.g., less than 0.1%.
용어 설명Term Description
열안정성 웹은 본 명세서의 실시예에서 설명된 바와 같이 시험된 경우, 10% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 웹을 의미한다.A thermally stable web, when tested as described in the examples herein, refers to a web exhibiting less than 10% heat shrinkage.
용융취입 섬유/웹은 용융취입에 의해 제조된 섬유/웹을 의미한다.Melt blown fibers / web refers to fibers / webs produced by melt blown.
용융취입은 용융된 섬유-형성 재료를 다이의 복수의 오리피스를 통하여 압출하여 용융된 필라멘트를 제공함을 의미한다. 필라멘트는 본질적으로 오리피스에서 배출 직후, 이 필라멘트를 (용융취입) 섬유로 감쇠시키기 위하여 가스(예를 들어 공기)의 고속 스트림과 접촉되고, 그 후 수집되며, 이는 본 명세서에서 아래에서 상세하게 설명되는 바와 같다.Melt blowing means that the molten fiber-forming material is extruded through a plurality of orifices of the die to provide a molten filament. The filaments are contacted with a high velocity stream of gas (e. G., Air) to attenuate the filaments into (melt blown) fibers immediately after discharge from the orifices and then collected, Same as.
"필라멘트"는 한 세트의 오리피스로부터 압출되는 열가소성 재료의 용융된 스트림을 의미하며; 섬유는 고형화된 필라멘트를 의미한다. 웹은 수집된 섬유 덩어리(mass)를 의미하며, 이들 중 적어도 일부는 그 웹이 통상의 롤-투-롤(roll-to-roll) 장치로 취급되기에 충분한 기계 강도를 갖기에 충분한 정도로 서로 결합되어져 있다."Filament" means a molten stream of thermoplastic material extruded from a set of orifices; Fiber refers to a solidified filament. The web refers to the collected fiber masses, at least some of which are bonded to each other to a degree sufficient to have sufficient mechanical strength to allow the web to be treated as a conventional roll-to- .
Tm은 반결정성 중합체의 결정성 용융점을 의미하며, 본 명세서의 실시예에서 설명된 바와 같이 측정된다.T m means the crystalline melting point of the semi-crystalline polymer and is measured as described in the examples herein.
반결정성 중합체에 적용된 바와 같은 용어 '빠르게 결정화하는' 및 '느리게 결정화하는'은, 본 명세서에서 이하에 상세하게 정의 및 설명된다.The terms " fast crystallizing " and " slow crystallizing " as applied to semi-crystalline polymers are defined and described in detail herein below.
중합체는 약 10,000 이상의 수평균 분자량을 갖는 거대분자로 제조된 재료를 의미한다. 중합체라는 용어는 설명의 편의를 위해 사용되며, 특히 공중합체를 포괄하고, 달리 표시되지 않는 한, (예를 들어, 여러 목적을 위해 열가소성 중합체 중에 종종 존재하는 것과 같은) 비-중합체성 첨가제의 존재 또한 허용한다.Polymers refer to materials made from macromolecules having a number average molecular weight of at least about 10,000. The term polymer is used for convenience of description and includes, in particular, the presence of a non-polymeric additive (including, for example, often present in thermoplastic polymers for various purposes) Also allow.
비-중합체성은 10000 미만의 수평균 분자량을 가짐을 의미한다.Non-polymeric nature means having a number average molecular weight of less than 10,000.
외측은, 다층 섬유의 방사상으로 최외측 부분을 제공하는 층, 표면 또는 가장자리를 의미한다.The outside refers to the layer, surface or edge that provides the radially outermost portion of the multi-layered fiber.
발명의 상세한 설명DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
본 명세서는 도 1의 예시적인 실시양태에 나타낸 바와 같은, 열안정성 용융취입 부직 섬유질 웹(1)을 개시한다. 상기 웹은 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유(100)를 포함한다. 다층은 섬유가 2개 이상의 층; 특히 제1 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제1 층(110) 및 제2 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제2 층(150)을 가짐을 의미한다. 다층은 1개 이상의 제1 층(110), 및 1개 이상의 제2 층(150) 각각이 외측 가장자리 및/또는 주요 외측 표면을 포함함을 추가로 의미한다. 따라서 용어 다층 섬유의 정의는 특히, 코어 층이 외측 가장자리 또는 주요 외측 표면을 포함하지 않는(예를 들어 산발적인 통계적 발생 및 결함 제외) 소위 외피-코어(sheath-core) 섬유는 배제한다.The present disclosure discloses a heat stable melt blown nonwoven
예시적인 2-층 다층 섬유(100)의 (실질적으로 상기 다층 섬유의 장축을 따라 배열된 방향을 따라 본) 단면도를 도 2에 나타낸다. 섬유(100)는 제1 중합체 층(110)을 포함하며, 이는 주요 외측 표면(118) 및 외측 가장자리(116)를 포함하고(본 유형의 실시양태에서는, 주요 외측 표면으로 명명되는 층 부분(110) 및 외측 가장자리로 명명되는 부분 사이의 명확한 구분 선이 없을 수 있음), 주요 내측 표면(112)을 추가로 포함한다. 섬유(100)는 제2 중합체 층(150)을 추가로 포함하며, 이는 주요 내측 표면(152) 및 외측 가장자리(156)를 포함하고, 본 실시양태에서는 주요 외측 표면(158)을 추가로 포함한다. 제2 중합체 층(150)의 주요 내측 표면(152), 및 제1 중합체 층(110)의 주요 내측 표면(112)은 내측 계면(114)에서 서로 직접 접촉한다.A cross-sectional view of the exemplary two-ply multi-layered fiber 100 (viewed along the direction substantially along the long axis of the multi-ply fibers) is shown in Fig. The
또 하나의 예시적인 다층 섬유(100)(이 경우, 5층 섬유)를 도 3에, 또다시 단면도로 나타낸다. 도 3의 예시적인 5층 섬유(100)는 교번하는 제1 및 제2 층을 포함하여, 총 3개의 제1 중합체 층(110) 및 2개의 제2 중합체 층(150)을 갖는다. 제1 층(110)은 각각, 계면(114)에서 제2 중합체 층(150)의 주요 내측 표면(152)과 직접 접촉하는 1개 이상의 주요 내측 표면(112)을 포함한다(2개의 그러한 계면, 및 층(110 및 150)의 주요 내측 표면이 도 3에 (114 및 114', 112 및 112', 및 152 및 152')로서 표시된다). 이러한 일반 유형의 다층 섬유(예를 들어, 3개 이상의 제1 층(110) 및 2개 이상의 제2 층(150))에서, 1개 이상의 제1 층(110)은 내측 제1 층(도 3에서 110i로 명명됨)일 것이며, 이는 그러한 제1 층이 2개의 제2 층(150) 사이에 끼워진 것을 의미한다. 1개 이상의 다른 제1 층(110)은 외측 제1 층(도 3에서 110e로 명명됨)일 수 있으며, 이는 계면(114)에서 제2 층(150)의 주요 내측 표면(152)과 직접 접촉하는 주요 내측 표면(112)을 포함하고, 주요 외측 표면(118)인 또다른 주요 표면을 포함한다. 의미상, 다층 섬유의 제1 층(110)은 외측 가장자리(116)(2개의 그러한 가장자리 116 및 116'를 도 3에 나타냄), 주요 외측 표면(118), 또는 이들 모두를 나타낼 것이다. (상기 나타낸 바와 같이) 예를 들어 수개의 층을 갖는 다층 섬유의 경우, 주요 외측 표면으로 명명된 제1 층의 부분 및 외측 가장자리로 명명된 부분 사이의 명확한 구분 선은 없을 수 있지만, 더 많은 층이 존재시, 외측 가장자리는 (예를 들어, 외측 제1 층의) 주요 외측 표면과 더욱 쉽게 구분될 수 있다. 또다시, 의미상 다층 섬유의 제2 층(150)은 외측 가장자리(156)(2개의 그러한 가장자리 156 및 156'를 도 3에 나타냄)를 나타낼 것이다.Another exemplary multilayered fiber 100 (in this case, five-ply fibers) is shown in Fig. 3 and again in cross-section. The exemplary five-
또 하나의 예시적인 다층 섬유(100)(이 경우, 15-층 섬유)가 도 4에, 또다시 단면도로서 표시된다. 도 4의 예시적인 15-층 섬유(100)는 8개(6개의 내부 및 2개의 외부)의 제1 중합체 층(110) 및 7개의 제2 중합체 층(150)을 포함한다. 더욱 일반적인 측면에서, 다층 섬유는 n개 이상의 제1 층 및 n-1개 이상의 제2 층을 포함할 수 있고, 상기 제2 층 중 n-2개 이상은 한 쌍의 제1 층들 사이에 개별적으로 끼워져 있으며, 여기에서 n은 3 내지 51의 수이다. (본 명세서에서 사용된 바와 같이, 개별적으로 끼워진다는 것은 특정 제1 층들의 특정 쌍 사이에 다른 제2 층이 없음을 의미한다.)Another exemplary multilayer fiber 100 (in this case 15-layer fiber) is shown in Fig. 4 and again in cross-section. The exemplary 15-
상기 설명으로부터, 본 명세서에서 정의된 것과 같은 다층 섬유가 제1 및 제2 층(110 및 150) 사이에 1개 이상, 및 종종 수개 이상(예를 들어, 5개, 10개 이상)의 내부 계면(114)을 나타내며, 이 내부 계면(들)은 예정된 및 본질적으로 연속된 방식으로 다층 섬유의 장축을 따라 실질적으로 연장됨을 이해할 것이다. 즉, 본 명세서에서 정의된 바와 같은 다층 섬유에서, 제1 및 제2 층 및 그 사이의 계면은 본질적으로 연속성이며, 연속된 방식으로 본질적으로 다층 섬유의 전체 길이를 따라 연장된다(현실의 용융취입 공정에 의해 제조된 임의의 섬유에 통계적으로 존재하는 것으로 이해되는 바와 같은, 그러한 산발적 변이, 중단 등은 제외된다). 따라서, 본 명세서에 개시된 바와 같은 다층 섬유는 의미상 중합체의 블렌드를 포함하는 단일층 섬유와 구분된다(여기에서, 2개의 중합체 상은, 하나의 중합체 상이 다른 하나의 중합체 상 중에 분산되어, 예를 들어, 섬(island), 구체, 덩굴손 형태(tendril) 등으로 다소 랜덤 방식으로 분포된다). 당업자는, 블렌드된-중합체 섬유가 섬유의 장축을 따라 어느 정도 연장되는 하나의 중합체 상을 가끔 나타낼 수 있다 하더라도, 그러한 불안정하며 비예측적 경우들을 본 명세서에 개시된 바와 같은 예정된 다층 섬유와 동일시할 수 없음을 이해할 것이다.It should be understood from the above description that multilayer fibers such as those defined herein may be used in combination with one or more, and often several, or more (e.g., five, ten or more) internal interfaces between the first and
많은 실시양태에서, 제1 및 제2 층 사이의 계면(114)은 평균적으로, 대체로 또는 심지어는 실질적으로 (도 2 내지 도 4의 묘사에서와 같이) 평면일 수 있다. 그러나 도 2 내지 도 4의 묘사는 이상적인 것이며, 실제 각종 층에서, 표면 및 계면은 모든 위치에서 엄격히 반드시 평면이어야 하거나, 섬유(100)는 외측 형태가 반드시 완전하게 둥글 필요는 없음에 주목하여야 한다. 또한, 2개의 제1 층(110) 및 그 사이에 끼워진 1개의 제2 층(150)을 갖는 일반 유형의 다층 섬유는 도면에서 나타내지 않았지만, 본 명세서의 개시는 그러한 구조를 포괄하는 것으로 이해된다. 유사하게, 짝수개의 제2 층을 갖는 다층 섬유 또는 제1층과 동일하거나 그 이상의 수의 제2 층을 갖는 다층 섬유를 이들 도면에 나타내지 않았지만, 그러한 방식은 본 명세서의 개시에 의해 포괄된다.In many embodiments, the
적어도 일부의 실시양태에서, 제1 층(들)(110) 및 제2 층(들)(150)은 각각 단일성분 층이다. 단일성분 층이라 함은 층의 두께, 폭 및 길이에 걸쳐 본질적으로 동일한 조성을 갖는 층이다; 조성이 섬유의 두께, 폭 및 길이에 걸쳐 실질적으로 균일한 한(당업자가 임의의 실제 제조 공정에서 존재할 것으로 이해할 그러한 산발적 통계적 변이는 제외), 단일성분 층은 첨가제 등을 포함할 수 있다. 일부 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 제1 층(110)만의 중합체성 구성성분이며, 제2 중합체는 제2 층(150)만의 중합체성 구성성분이다.In at least some embodiments, the first layer (s) 110 and the second layer (s) 150 are each a single component layer. A single component layer is a layer having essentially the same composition over the thickness, width and length of the layer; The single-component layer may include additives, etc., as long as the composition is substantially uniform across the thickness, width, and length of the fibers (except for such sporadic statistical variations that those skilled in the art will understand exist in any actual manufacturing process). In some embodiments, the first polymer is a polymeric component of only the
(대표적인 섬유를 샘플링하여, 예를 들어 광학 현미경에 의해 측정한) 용융취입 다층 섬유의 평균 직경은 임의의 바람직한 범위 내일 수 있다. 용융취입은 (예를 들어, 용융된 필라멘트의 직경을 감소시키는 고속 "취입" 공기의 경향 때문에) 소위 (평균 직경이 10마이크로미터(μm) 이하인 섬유를 의미하는) 마이크로섬유의 형성에 특히 적합함이 이해될 것이다. 따라서, 각종 실시양태에서, 용융취입 다층 섬유의 평균 직경은 약 30μm, 20μm, 15μm, 10μm, 5μm, 2μm, 또는 1μm 미만일 수 있다. 추가의 실시양태에서, 용융취입 다층 섬유의 평균 직경은 약 0.5μm, 1μm, 2μm, 또는 5μm 이상일 수 있다The average diameter of the meltblown multilayer fibers (as measured by, for example, optical microscopy, by sampling representative fibers) may be within any desired range. Melt blowing is particularly suitable for the formation of so-called microfibers (meaning fibers with an average diameter of less than 10 micrometers (μm)) due to the tendency of high-speed "blown" air to reduce the diameter of the melted filaments Will be understood. Thus, in various embodiments, the melt-blown multilayer fibers may have an average diameter of less than about 30 占 퐉, 20 占 퐉, 15 占 퐉, 10 占 퐉, 5 占 퐉, 2 占 퐉, or 1 占 퐉. In a further embodiment, the melt-blown multilayer fibers may have an average diameter of about 0.5 [mu] m, 1 [mu] m, 2 [mu] m,
다층 섬유(100)는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 제1 중합체를 포함하는 1개 이상의 제1 층(110), 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 제2 중합체를 포함하는 1개 이상의 제2 층(150)으로 구성된다. 이는, 제1 중합체 및 제2 중합체 모두가 적어도 일부 조건 하에서 (약 200℃ 이상의) 결정 용융점 Tm을 나타낼 수 있어야만 함을 의미한다. 즉, 그러한 중합체는 (예를 들어, 충분히 느린 냉각 조건 하에서) 상당한 수의 결정성 도메인을 형성할 수 있어야만 하며; 용어 제1 중합체 및 제2 중합체는, 예를 들어 매우 느리게 냉각되어서 잘 규정된 결정성 용융점을 나타낼 수 없을지라도 상당한 결정성 도메인들을 형성하지 않을 본질적으로 무정형인 중합체는 포괄하지 않는다. 각종 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 약 210℃, 220℃, 230℃, 240℃, 250℃ 또는 260℃ 이상의 Tm을 나타낼 수 있다. 각종 실시양태에서, 제2 중합체는 약 210℃, 220℃, 230℃, 240℃, 250℃ 또는 260℃의 이상의 Tm을 나타낼 수 있다.
제1 중합체 및 제2 중합체는, 제1 중합체가 느리게 결정화하는 중합체이고 제2 중합체는 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체라는 점에서 상이하다. 간략하게는, 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체는, 통상의 용융취입 공정에서 사용된 비교적 신속한 냉각 조건 하에서 충분히 빠른 속도로 결정화 영역을 형성하여, 고형화된 용융취입 섬유가 중합체가 더욱 느린 냉각 공정 처리된 경우 나타낼 수 있는 값과 대체로 유사한 결정화도를 나타내도록 하는 중합체를 의미한다. 대조적으로, 느리게 결정화하는 중합체는, 통상의 용융취입 공정에서 사용된 냉각 조건 하에서 충분히 느린 속도로 결정화 영역을 형성하여, 고형화된 용융취입 섬유가 중합체가 더욱 느린 냉각 공정 처리된 경우 나타낼 수 있는 값보다 현저히 낮은 결정화도를 나타내도록 하는 중합체를 의미한다.The first and second polymers are different in that the first polymer is a slow crystallizing polymer and the second polymer is a fast crystallizing polymer. Briefly, a rapidly crystallizing polymer forms a crystallization zone at a sufficiently rapid rate under relatively rapid cooling conditions used in conventional meltblowing processes, so that the solidified meltblown fibers can be displayed when the polymer is subjected to a slower cooling process ≪ RTI ID = 0.0 > and / or < / RTI > In contrast, the slowly crystallizing polymer forms a crystallization zone at a sufficiently slow rate under the cooling conditions used in a conventional melt-blowing process so that the solidified melt-blown fibers have a value that is less than a value that can be exhibited when the polymer is subjected to a slower cooling process Quot; means a polymer that exhibits a significantly lower degree of crystallinity.
중합체는 하기 방식에 따라 느리게 결정화하는 특성 및 빠르게 결정화하는 특성으로 스크리닝될 수 있다. 중합체 샘플은 샘플에서 임의의 기존 열 이력을 없애도록, Tm 이상으로 먼저 제1 가열 단계 처리될 수 있다. 따라서 그에 부가된 표준 열 이력을 갖는 이 샘플은 이후 느린 냉각 처리될 수 있다(이 목적을 위하여, 분 당 10℃의 냉각 속도를 취할 수 있다). 이 샘플을 Tm 보다 충분히 낮게(예를 들어, 실온으로) 냉각시킨다. 샘플은 이 후 Tm 이상으로 제2 가열 단계(예를 들어, 분 당 10℃로) 처리된다. 용융 및 냉각 결정화의 열은 이후 제2 가열 단계로부터 수득된 데이타로부터 계산되고, 결정화도의 정도(% 결정화도)를 그로부터 계산한다. (상기 측정 및 계산은 임의의 적당한 시차 주사 열량계(DSC)를 이용하여, 예를 들어 그 전체가 본 명세서에 참고문헌으로 포함된 "문제 해결 도구로서의 DSC: 열가소성 수지의 결정화도 %의 측정(DSC as Problem Solving Tool: Measurement of Percent Crystallinity of Thermoplastics)", 퍼킨-엘머(Perkin-Elmer)(2000)에 개괄된 방법을 이용하여 수행될 수 있다.)The polymer can be screened with slow crystallizing properties and fast crystallizing properties according to the following manner. The polymer sample may first be subjected to a first heating step above T m to remove any existing thermal history in the sample. This sample with a standard thermal history added to it can then be subjected to a slow cooling process (for this purpose, a cooling rate of 10 ° C per minute may be taken). The sample is cooled to a temperature sufficiently lower than T m (e.g., to room temperature). The sample is then processed in a second heating step (e.g., at 10 [deg.] C per minute) above T m . The heat of the melting and cooling crystallization is then calculated from the data obtained from the second heating step and the degree of crystallinity (% crystallinity) is calculated therefrom. (These measurements and calculations may be made using any suitable differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), for example, DSC as a "troubleshooting tool ", which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety: measurement of percent crystallinity of thermoplastic resin Problem Solving Tool: Measurement of Percent Crystallinity of Thermoplastics ", Perkin-Elmer (2000)).
중합체의 또 다른 샘플을 중합체에서 임의의 기존 열 이력을 없애도록, Tm 이상으로 유사하게 제1 가열 단계 처리할 수 있다. 따라서 그에 부가된 표준 열 이력을 갖는 이 샘플은 이후 빠른 냉각 처리될 수 있다(이 목적을 위하여, 분 당 200℃의 냉각 속도를 취할 수 있다). 제2 가열 단계를 이후 수행하고, 상기 논의된 것과 유사한 방식으로 신속하게 냉각된 샘플에 대해 계산된 결정화도의 정도를 계산할 수 있다.Another sample of the polymer can be similarly treated in a first heating step above T m to eliminate any existing thermal history in the polymer. This sample with a standard thermal history added to it can then be subjected to a rapid cooling process (for this purpose, a cooling rate of 200 ° C per minute can be taken). The second heating step is then carried out and the degree of crystallinity calculated for the rapidly cooled sample can be calculated in a manner analogous to that discussed above.
신속하게 냉각된 샘플 및 느리게 냉각된 샘플에 대한 결정화도 정도는 이후 비교될 수 있다. 신속하게 냉각된 조건 대 느리게 냉각된 조건 하에서 약 20% 이상의 결정화도 정도에서의 차이는 느리게 결정화하는 중합체를 나타낸다. 특정 실시예에서, 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트)(PET)는 본 명세서에서 규정된 바와 같은 원형의(prototypical) 느리게 결정화하는 중합체이다. PET는 결정성 도메인을 형성할 수 있고, 종종 용융물로부터 느리게 냉각된 후 약 250 내지 260℃ 범위의 잘 규정된 Tm 및 예를 들어 30% 또는 40% 이상의 범위에서 결정화도 정도를 나타낼 수 있다. 그러나, 상기 기재된 바와 같이 용융물로부터 신속하게 냉각된 경우, PET는 30% 미만 (종종 현저히 미만)의 범위에서 결정화도 정도를 나타낼 수 있다.The degree of crystallinity for a rapidly cooled sample and a slowly cooled sample can then be compared. The difference in degree of crystallinity between about 20% or more under rapidly cooled conditions versus slowly cooled conditions represents a slowly crystallizing polymer. In certain embodiments, poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET) is a prototypical slowly crystallizing polymer as defined herein. PET can form a crystalline domain and can often exhibit a degree of crystallinity in the range of well defined T m in the range of about 250 to 260 ° C and in the range of, for example, 30% or 40% or more after being slowly cooled from the melt. However, when rapidly cooled from the melt as described above, PET can exhibit degrees of crystallinity in the range of less than 30% (often significantly less).
대조적으로, 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트)는 원형의 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체로, 이는 신속하게 냉각되거나 느리게 냉각된 여부에 관계없이 (예를 들어 서로 약 10% 이내의) 유사한 정도의 결정화도를 전형적으로 나타낼 것이다.In contrast, poly (butylene terephthalate) is a circular, rapidly crystallizing polymer, which typically exhibits a similar degree of crystallinity (e.g., within about 10% of each other) whether rapidly cooled or slowly cooled will be.
상기 기재된 바와 같은 DSC 스크리닝은 잠재적으로 유용한 제1 및 제2 중합체를 확인하는데 유용할 수 있다. 그러나, 본 명세서에서 사용된 목적을 위하여, 제1 중합체 또는 제2 중합체로서 반결정성 중합체를 확인하는 가장 편리한 방법은 (200℃가 넘는 식별가능한 Tm이라는 최초 기준을 만족시킨다는 가정 하에) 평가될 중합체의 단일성분의(다층이 아닌) 용융취입 섬유로 이루어지는 용융취입 웹을 제조하는 것이다. 이는 그 특정 재료의 용융취입에 대한 통상의 범위 내에 있는 용융취입 공정 조건(이에 제한되지는 않지만, 압출기 온도, 다이 및 취입 공기, 체적비 및 취입 공기의 선형 속도, 다이에서 수집기까지의 거리 등이 포함되며, 이는 당업자에 의해 잘 이해될 것이다)을 이용하여 수행되어야 한다. (소정 중합체에 대한 통상의 용융취입 조건의 예는 본 명세서의 실시예에서 발견된다.)DSC screening as described above may be useful in identifying potentially useful first and second polymers. However, for the purposes used herein, the first polymer or the most convenient method is the polymer to be evaluated (under the assumption that meet the first criteria of possible T m identification of over 200 ℃) to determine the semi-crystalline polymer as a second polymer (Not multi-layer) melt blown fibers of a single component. Including but not limited to extruder temperature, die and blowing air, volume ratio and linear velocity of blowing air, distance from die to collector, etc., which are within the usual range for melt blowing of that particular material Which will be well understood by those skilled in the art). (Examples of typical melt blowing conditions for a given polymer are found in the examples herein.)
그러한 방식으로 제조된 단일성분 시험 웹은 이후 본 명세서의 실시예에 개시된 바와 같은 열 수축률 시험으로 처리될 수 있다. 단일성분 용융취입 웹으로서 10% 미만의 열 수축률을 나타내는 중합체는 (다시 말해서, 다른 하나가 본 명세서에서 개시된 기준을 충족시키는 한) 본 명세서에서 정의된 바와 같이 제2 중합체이다. 각종 실시양태에서, 제2 중합체는 8%, 6%, 4% 또는 2% 미만의 열 수축률을 나타낼 수 있다. 용융취입 단일중합체 웹으로서 10% 초과의 열 수축률을 나타내는 중합체는 (다시 말해서, 다른 하나가 본 명세서에서 개시된 기준을 충족시키는 한) 본 명세서에서 정의된 바와 같이 제1 중합체이다. 각종 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 약 20%, 30%, 40% 또는 심지어는 50% 초과의 열 수축률을 나타낼 수 있다.A single component test web produced in such a manner can then be treated with a heat shrinkage test as described in the examples herein. A polymer that exhibits a heat shrinkage of less than 10% as a single component melt blown web is a second polymer as defined herein (i.e., so long as the other meets the criteria set forth herein). In various embodiments, the second polymer may exhibit a heat shrinkage of less than 8%, 6%, 4% or 2%. A polymer that exhibits a heat shrinkage of greater than 10% as a melt blown homopolymer web (i. E., As long as the other meets the criteria set forth herein) is a first polymer as defined herein. In various embodiments, the first polymer may exhibit a heat shrinkage of greater than about 20%, 30%, 40% or even 50%.
적합한 제1 중합체는 예를 들어 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트), 폴리(에틸렌 나프탈레이트), 폴리(트라이메틸렌 테레프탈레이트)와 같은 폴리에스테르 및 200℃ 초과의 Tm을 나타낼 수 있는 적어도 일부의 폴리 락트산(예를 들어, 비교적 높은 함량의 D-락타이드를 갖는 것들)으로부터 선택될 수 있다. 이러한 제1 중합체의 임의의 바람직한 조합이 사용될 수 있다. 적합한 제2 중합체는 예를 들어 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트)와 같은 폴리에스테르, 폴리메틸펜텐과 같은 폴리올레핀, 및 신디오택틱 폴리스티렌과 같은 기타 중합체, 및 이들의 임의의 바람직한 조합으로부터 선택될 수 있다.Suitable first polymers such as poly (ethylene terephthalate), poly (ethylene naphthalate), poly (trimethylene terephthalate) and at least some of the polylactic acid, which may indicate a T m of the same polyester and 200 ℃ excess ( For example, those having a relatively high content of D-lactide). Any desired combination of such first polymers may be used. Suitable second polymers may be selected from, for example, polyesters such as poly (butylene terephthalate), polyolefins such as polymethylpentene, and other polymers such as syndiotactic polystyrene, and any desired combination thereof.
제1 중합체 및 제2 중합체는, 웹의 용융취입 섬유 중 제1 중합체와 제2 중합체의 총 중량을 기준으로 계산하여 약 95:5 내지 약 45:55(제1:제2)의 중량비로 존재할 수 있으며, 이는 다층 섬유에 추가로 존재하는 단일성분 용융취입 섬유 내에 존재할 수 있는 어느 하나의 유형의 임의의 중합체는 포함하지만, 스테이플 섬유 내에 존재할 수 있는 임의의 제1 또는 제2 중합체는 포함하지 않는다. 각종 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체 대 제2 중합체의 중량비는 약 50:50, 60:40, 70:30, 75:25, 80:20, 85:15 또는 90:10 이상일 수 있다. 추가의 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체 대 제2 중합체의 중량비는 약 90:10, 85:15, 80:20, 75:25, 70:30, 60:40 또는 50:50 이하일 수 있다.The first polymer and the second polymer are present in a weight ratio of about 95: 5 to about 45:55 (first: second), based on the total weight of the first polymer and the second polymer in the meltblown fibers of the web Which does not include any first or second polymer that may be present in the staple fiber, including but not limited to any polymer of any type that may be present in the single component melt blown fibers present in the multi-layer fibers . In various embodiments, the weight ratio of the first polymer to the second polymer can be about 50:50, 60:40, 70:30, 75:25, 80:20, 85:15, or 90:10 or more. In a further embodiment, the weight ratio of the first polymer to the second polymer may be about 90:10, 85:15, 80:20, 75:25, 70:30, 60:40 or 50:50 or less.
하기에 상세하게 기재되는 바와 같이, 본 명세서에서 개시된 방식은, 제1 중합체 단독 사용으로 가능한 성능을 뛰어넘는 현저한 장점을 달성하는 한편, 비교적 적은 양(중량%)의 제2 중합체의 이용을 가능하게 한다. 그러한 방식은 예를 들어, 제2층(150)의 적어도 일부의 두께(즉, 도 3에 나타낸 바와 같은, 주표면(152 및 152') 사이의 평균 거리)를 제1층(110)의 적어도 일부의 두께(즉, 이 또한 도 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 주표면(112 및 112') 사이의 평균 거리) 미만으로 만듬으로써 다층 섬유에서 달성될 수 있다. 그러한 방식으로, 사용된 제1 중합체의 전체 양에 대하여 사용된 제2 중합체의 전체 양을 최소화하면서, 1개 이상의 제2 층이 제공될 수 있다. 따라서 각종 실시양태에서, 제1 층(들)(110) 대 제2 층(들)(150)의 두께의 비는 약 1.2:1, 1.5:1, 2:1, 3:1 또는 4:1일 수 있다. (그러한 계산에서, 아치형 주 표면을 갖는 외측 층(예를 들어, 도 3의 (110e))의 두께는 외측 층으로서 동일한 단면적을 갖는 직사각형 영역의 두께로 간주될 수 있다.)As described in detail below, the approach disclosed herein achieves significant advantages over possible performance with the use of the first polymer alone, while enabling the use of a relatively small amount (wt.%) Of the second polymer do. Such a scheme may be used, for example, to provide at least a portion of the
빠르게 결정화하는 제2 중합체의 1개 이상의 제2 층의 포함은 느리게 결정화하는 제1 중합체의 결정화를, 용융취입에서 만연하는 바와 같은 비교적 신속한 냉각 조건 하에서도, 아마도 현저히 가속화할 수 있음이 발견되었다. 이는 현저히 증가된 결정화도를 갖는 제1 중합체를 포함하는 고형화된 생성물을 제공할 수 있고, 그 결과 예를 들어 제1 중합체의 단일성분 섬유로 이루어지는 경우 가능한 것보다 훨씬 더 낮은 열 수축율을 나타내는 용융취입 웹을 제공할 수 있다. 유리하게는, 상기 나타낸 바와 같이 제2 중합체 대 제1 중합체의 전체 중량비가 비교적 낮은 수준으로 유지될 수 있도록, 이는 예를 들어 제2 중합체의 더 적은 층 및/또는 얇은 층을 이용하면서도 달성될 수 있다. 그러한 제2 중합체는 종종 제1 중합체보다 더욱 현저히 비싸기 때문에 이는 현저한 이익을 제공할 수 있다.It has been found that the inclusion of one or more second layers of a rapidly crystallizing second polymer can significantly accelerate the crystallization of the slowly polymerizing first polymer, even under relatively rapid cooling conditions as prevailing in melt blowing. This can provide a solidified product comprising a first polymer having a significantly increased degree of crystallinity and as a result can provide a melt blown web exhibiting a much lower heat shrinkage than is possible, Can be provided. Advantageously, this can be achieved, for example, by using fewer and / or thinner layers of the second polymer, so that the total weight ratio of the second polymer to the first polymer, as indicated above, can be maintained at a relatively low level have. Such a second polymer is often much more expensive than the first polymer, which can provide a significant benefit.
또한, 본 명세서에 기재된 바와 같이 1개 이상의 층 형태의 1개 이상의 제2 중합체의 포함은, 제2 중합체가 예를 들어 중합체 블렌드 형태로, 제1 중합체와 물리적으로 밀접하게 혼합된(예를 들어, 용융 블렌드된) 경우보다 제1 중합체의 결정화를 더 양호하게 가속화할 수 있는 것으로 나타난다는 것이 발견되었다. 이는 놀라운 결과이다. 제2 중합체의 가속 효과가 제1 중합체와 제2 중합체의 계면에서 제1 중합체를 위한 핵화 자리를 제공하는 제2 중합체의 (신속히 결정화되는) 표면을 통하여 유도될 수 있음을 당업자는 예측할 수 있을 것이다. 따라서, (예를 들어 덩굴손 형태 또는 구체에서 가능하게는 거대분자 절편에 이르기까지의 범위의) 수많은 무리(parcel)의 형태로 제1 중합체 중에 제2 중합체의 분산이 예측될 수 있는, 제2 중합체를 제1 중합체와 블렌드로서 혼합하는 것은, 제1 중합체 중에 제2 중합체의 현저히 더욱 높은 표면적을 달성하고, 이에 따라 본 명세서에서 개시된 것과 같은 층 형태로 제2 중합체를 포함하는 것에 비해, 제1 중합체의 결정화를 가속시키는 데에 더욱 효과적일 것이라는 것이 예측될 것이다. 그러나, 본 명세서에 제시된 실시예들은 제2 중합체 대 제1 중합체의 중량비가 유사하거나 또는 더욱 낮은 경우, 본 명세서에서 개시된 바와 같은 다층의 용융취입 섬유가 블렌드된-중합체 용융취입 단일층 섬유보다 더욱 낮은 열 수축률을 보이는 것으로 나타남을 보여준다. 따라서 이는 예측가능하지 않은 유리한 결과이다.Also, inclusion of one or more second polymers in the form of one or more layers, as described herein, means that the second polymer is in the form of, for example, a polymer blend and is physically intimately mixed with the first polymer , ≪ / RTI > melt-blended), the crystallization of the first polymer can be accelerated better. This is an amazing result. It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the acceleration effect of the second polymer can be induced through the (rapidly crystallizing) surface of the second polymer that provides nucleation sites for the first polymer at the interface of the first and second polymers . Thus, a second polymer, which can be expected to have a dispersion of the second polymer in the first polymer in the form of a number of parcels (e.g., in the form of a tangle or sphere, possibly up to the macromolecular slice) With the first polymer as a blend achieves a significantly higher surface area of the second polymer in the first polymer and thus comprises a second polymer in the form of a layer as disclosed herein, Will be more effective in accelerating the crystallization of < / RTI > However, the embodiments presented herein are particularly advantageous when the weight ratio of the second polymer to the first polymer is similar or lower, such that the multi-layer melt blown fibers as disclosed herein are lower than the blended-polymer melt blown single layer fibers Heat shrinkage rate. This is therefore an unpredictable beneficial result.
일부 실시양태에서, 웹(1)은 도 1의 예시적인 실시양태에 나타낸 바와 같이, 선택적인 스테이플 섬유(200)를 추가적으로 포함할 수 있다. 웹(1)에서, 스테이플 섬유(200)는 용융취입 섬유의 네트워크 전체에 걸쳐 분포되고, 그 안에서 섞인다. 각종 실시양태에서, 스테이플 섬유(200)는 웹의 섬유질 재료(예를 들어, 용융취입 섬유와 스테이플 섬유의 합)의 총 중량의 약 5중량%, 10중량%, 20중량%, 30중량% 또는 40중량% 이상을 구성할 수 있다. 추가의 실시양태에서, 스테이플 섬유(200)는 웹의 섬유질 재료의 총 중량의 약 60중량%, 50중량%, 40중량%, 30중량% 또는 20중량% 이하를 구성할 수 있다.In some embodiments, the
그의 특정 제조 공정 또는 조성에 관계없이, 스테이플 섬유는 전형적으로 특정의 예정된 또는 식별가능한 길이로 기계 절단되고 고형화된 형태로 부직 웹에 첨가된다. 스테이플 섬유의 길이는 종종 용융취입 섬유의 길이보다 훨씬 적고; 각종 실시양태에서, 약 1cm 내지 8cm 또는 약 2.5cm 내지 6cm일 수 있다. 스테이플 섬유의 평균 섬유 직경은 종종 평균 약 15μm 초과이고, 각종 실시양태에서, 20μm, 30μm, 40μm 또는 50μm 초과일 수 있다. 이에 따라, 많은 실시양태에서 스테이플 섬유의 평균 섬유 직경은 용융취입 다층 섬유의 평균 직경의 약 2배, 4배 또는 8배 이상일 수 있다.Regardless of its particular manufacturing process or composition, staple fibers are typically added to the nonwoven web in a machine cut and solidified form to a predetermined or identifiable length. The length of the staple fibers is often much less than the length of the meltblown fibers; In various embodiments, from about 1 cm to about 8 cm, or from about 2.5 cm to about 6 cm. The average fiber diameter of the staple fibers is often on the average greater than about 15 microns, and in various embodiments may be greater than 20 microns, 30 microns, 40 microns, or 50 microns. Thus, in many embodiments, the average fiber diameter of the staple fibers may be about 2, 4, or 8 times the average diameter of the melt-entrained multilayer fibers.
일부 실시양태에서, 스테이플 섬유는 합성 중합체성 재료를 포함할 수 있다. 일부 실시양태에서, 스테이플 섬유는 (예를 들어, 대나무, 면, 울, 황마, 아가베, 사이잘, 코코넛, 대두, 대마 등으로부터 유래된 섬유에서 선택된) 천연 섬유를 포함할 수 있다. 바람직한 경우, 스테이플 섬유의 적어도 일부 조성은 이들이 (용융취입된 웹을 포함하는 성형품을 형성하는데 사용될 수 있는 것과 같은) 성형 공정 동안 서로에 대해 및/또는 용융취입 섬유에 대해 용융결합될 수 있도록 선택될 수 있다. 대안적으로, 이들은 성형 공정 동안 서로에 대해 또는 용융취입 섬유에 대해 결합되지 않도록 하는 특성(예를 들어, 용융점)을 갖는 재료로 제조될 수 있다.In some embodiments, the staple fibers may comprise a synthetic polymeric material. In some embodiments, the staple fibers may comprise natural fibers (selected from fibers derived from, for example, bamboo, cotton, wool, jute, agave, sisal, coconut, soybean, hemp, etc.). If desired, at least some of the composition of the staple fibers may be selected such that they can be melt bonded to each other and / or melt blown fibers during a molding process (such as may be used to form a molded article comprising a meltblown web) . Alternatively, they may be made of a material having properties (e.g., melting points) that prevent it from bonding to each other or to the melt blown fibers during the molding process.
적합한 스테이플 섬유는 예를 들어 임의의 적합한 폴리에스테르 및 그의 공중합체, 폴리올레핀 예컨대 폴리에틸렌, 폴리프로필렌 및 그의 공중합체, 폴리아미드 또는 이들의 임의의 조합으로부터 제조될 수 있다. 스테이플 섬유는 예를 들어, 하우저(Hauser)의 미국특허 제4,118,531호에 기재된 섬유처럼 크림핑된(crimped) 섬유일 수 있다. 크림핑된 섬유는 그 길이를 따라 연속적인 물결 형태(wavy), 말린 형태(curly) 또는 톱날 형태(jagged)의 프로파일을 가질 수 있다. 스테이플 섬유는 예를 들어 cm당 약 10개 내지 30개의 크림프를 포함하는 크림핑된 섬유를 포함할 수 있다. 스테이플 섬유는 단일성분 섬유 또는 다중성분 섬유일 수 있다.Suitable staple fibers may be prepared from, for example, any suitable polyester and its copolymers, polyolefins such as polyethylene, polypropylene and its copolymers, polyamides, or any combination thereof. The staple fibers can be, for example, crimped fibers as described in U.S. Patent No. 4,118,531 to Hauser. The crimped fiber can have a continuous wavy, curly or jagged profile along its length. The staple fibers may comprise, for example, crimped fibers comprising from about 10 to 30 crimps per cm. The staple fiber can be a single component fiber or a multicomponent fiber.
각종 목적에 요구됨에 따라, 각종 다른 성분들이 웹(1) 중에, 특히 용융취입 다층 섬유(100) 중에 존재할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 임의의 바람직한 유형의 미립자 첨가제가 웹(1) 중에 존재할 수 있다. 특히, 웹(1)이 여과 목적으로 사용된 경우, 임의의 적합한 흡수제, 촉매 반응성, 화학 반응성 등의 미립자 첨가제가 존재할 수 있다. 용융취입 다층 섬유(100)는 특히, 그 안에 존재하는 임의의 적합한 보조성분을 가질 수 있다. 그러한 구성성분은 예를 들어 수득된 바와 같은 상기 설명된 제1 중합체 및/또는 제2 중합체 내에 존재할 수 있으며, 예를 들어, 가공 첨가제, 산화방지제, UV 안정화제, 내화성 첨가제 등을 포함할 수 있다. 일부 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 하나 이상의 비-중합체성 핵제(예를 들어, 용융 첨가제)를 포함할 수 있고, 이는 예를 들어 각종 스테아레이트, 카르복실산 염, 질소-함유 헤테로방향족 화합물 등으로부터 선택될 수 있다. 그러나, 특정 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 약 5중량%, 2중량%, 1중량% 또는 0.5중량% 미만의 임의의 비-중합체성 핵제를 포함한다. 특정 실시양태에서, 제1 중합체는 임의의 비-중합체성 핵제가 실질적으로 없다.As required for various purposes, various other components may be present in the
일부 추가의 실시양태에서, 웹(1)은 적어도 일부 양의 중합체성 핵제를, 다층 섬유의 별개의 층 형태로 또는 제1 또는 제2 중합체 등과 (예를 들어 용융 첨가제로서) 블렌드되어 첨가되는지의 여부에 관계없이, 포함할 수 있다. 그러한 재료는 예를 들어 폴리에스테르-설포네이트 염, 폴리프로필렌, 폴리에틸렌과 같은 소정의 폴리올레핀 및 이들의 공중합체 및 블렌드를 포함할 수 있다. 그러나 일부 그러한 재료는 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 나타낼 수 있으며, 따라서 본 명세서에 개시된 바와 같이 제2 중합체로 간주될 수 없다는 것이 이해될 것이다. 그러나, 그러한 재료는 그럼에도 불구하고, 그들이 결과로서 생성되는 웹의 예를 들어 열 수축률에 허용될 수 없는 영향을 미치는 양으로 존재하지 않는 한, 이익을 제공한다. 따라서, 각종 실시양태에서, 다층 섬유(100)는 약 5중량%, 2중량%, 1중량% 또는 0.5중량% 이하의 임의의 중합체성 핵제를 포함할 수 있다. 특정 실시양태에서, 다층 섬유(100)는 임의의 중합체성 핵제가 실질적으로 없다.In some further embodiments, the
일부 실시양태에서, 용융취입 섬유질 웹에서 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 나타내는 중합체성 재료의 양을 최소화하는 것이 유리할 수 있다. (이러한 문맥에서, 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 나타내는 중합체성 재료라는 용어는 구체적으로 중합체성 재료의 단일 중합체 사슬만을 포함할 뿐 아니라, 공중합체 내에 존재할 수 있는 그러한 재료의 임의의 중합체 절편을 포함한다.) 따라서, 각종 실시양태에서, 200℃ 미만의 Tm 을 갖는 임의의 중합체성 재료는 (예를 들어, 스테이플 섬유를 포함하여) 웹의 총 섬유질 재료를 기준으로 약 20중량%, 10중량%, 5중량%, 2중량%, 1중량% 또는 0.5중량% 미만으로 존재한다. 추가의 실시양태에서, 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 갖는 중합체성 재료가 실질적으로 없다. 일부 실시양태에서, 특히 웹의 용융취입 섬유에서, 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 나타내는 중합체성 재료의 양을 최소화하는 것이 도움이 될 수 있다. 따라서, 각종 실시양태에서, 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 갖는 임의의 중합체성 재료는 (임의의 다층이 아닌 용융취입 섬유를 포함하여) 웹의 용융취입 섬유 내에 약 20중량%, 10중량%, 5중량%, 2중량%, 1중량% 또는 0.5중량% 미만으로 존재한다. 추가의 실시양태에서, 웹의 용융취입 섬유는 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 갖는 중합체성 재료가 실질적으로 없다.In some embodiments, it may be advantageous to minimize the amount of polymeric material having a T m of less than 200 ℃ meltblown fibers in the web. (And in this context, the term polymeric material exhibiting a T m of less than 200 ℃ not only specifically comprise only a single polymer chain of the polymeric material, including any polymer segment of such materials that may be present in the copolymer .) Thus, in various embodiments, any polymeric material having a T m of less than 200 ℃ (e.g., including staple fibers) of about 20% by weight, based on the total fibrous material in the web, 10 weight percent , 5 wt%, 2 wt%, 1 wt%, or less than 0.5 wt%. In a further embodiment, meltblown fibrous web is a polymeric material having less than 200 ℃ T m substantially free. In some embodiments, in particular in the meltblown fibers of the web, it may be beneficial to minimize the amount of polymeric material having a T m of less than 200 ℃. Thus, in various embodiments, any polymeric material having a T m of less than 200 ℃ (including the meltblown fibers non-random multi-layer) of about 20% by weight in the melt blown fibers of the web, 10 weight%, 5 By weight, 2% by weight, 1% by weight or less than 0.5% by weight. In a further embodiment, the meltblown fibers of the web is a polymeric material having a T m of less than 200 ℃ substantially free.
각종 실시양태에서, 본 명세서에서 개시된 바와 같은 웹(1)은 약 10%, 8%, 6%, 4%, 2% 또는 1% 미만의 (본 명세서의 실시예에 개시된 바와 같이 측정된) 열 수축을 나타낼 수 있다. 본 명세서에서 논의된 바와 같이, 그러한 특성은 소정의 응용분야에서 현저한 장점을 제공할 수 있다.In various embodiments, the
나타낸 바와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 부직 웹은 상기 정의된 것과 같은 용융취입 섬유를 사용한다. 당업자는 용융취입 공정 및 그러한 공정에 의해 형성된 용융취입 섬유 및 용융취입 부직 웹이, 예를 들어 용융방사와 같은 공정들 및 그 결과의 생성물 예컨대 용융방사 섬유 및 용융방사(예를 들어 스펀본딩된) 부직 웹과 구별됨을 이해할 것이다. 용어 '용융방사' 및 '용융방사된'은 한 세트의 오리피스들로부터 용융 필라멘트를 압출하고 이 필라멘트를 냉각 및 고형화하여 섬유를 형성함으로써 섬유를 형성하는 것을 지칭하는 기술용어로, 이때 필라멘트는 필라멘트를 냉각시키는 것을 돕기 위해 (이동 공기의 스트림을 포함할 수 있는) 공기 공간(air space)으로 통과된다. 냉각된 필라멘트는, 이후 필라멘트를 (예를 들어 배향 및 증진된 물성을 유도하도록) 적어도 부분적으로 연신시키기 위하여 연신 단위로 통과된다. 따라서 용융취입은 압출 오리피스에 매우 근접하게(예를 들어, 1cm 내) 위치된 공기-취입(air-blowing) 개구들(예를 들어 에어나이프(air knife))에 의해 도입된 수렴하는 고속 공기 스트림 내로 용융된 필라멘트를 압출하는 것을 포함한다는 점에서, 용융방사는 용융 취입과 구별될 수 있다. 따라서, 당업자는 용융취입과 용융방사가 결과로서 생성되는 섬유와 웹에 (섬유/웹이 유사한 조성이라 하더라도) 상이한 특징(예를 들어, 분자 배향 및 결과의 물성에서의 특징)을 부여함을 이해할 것이며, 따라서 용융취입 섬유와 용융방사 섬유가 서로 용이하게 구별될 수 있음을 인식할 것이다.As shown, the nonwoven web disclosed herein employs melt blown fibers as defined above. Those skilled in the art will recognize that meltblowing processes and the meltblown fibers and meltblown nonwoven webs formed by such processes can be used to produce processes such as melt spinning and the resulting products such as meltblown fibers and melt spinning (e. G., Spunbonded) You will understand that it is distinct from the non-woven web. The term " melt spinning " and " melt spinning " are technical terms used to refer to forming fibers by extruding molten filaments from a set of orifices and cooling and solidifying the filaments to form fibers, (Which may include a stream of moving air) to aid in cooling the air. The cooled filaments are then passed in a stretch unit to at least partially stretch the filaments (e.g., to induce orientation and enhanced physical properties). Thus, the melt blowing may be accomplished by a converging high velocity air stream introduced by air-blowing openings (e.g., air knife) positioned very close to (e.g., within 1 cm) the extrusion orifice The melt spinning can be distinguished from the melt spinning in that it involves extruding the molten filament into the melt. Thus, those skilled in the art will understand that melt blowing and melt spinning impart different characteristics (e.g., characteristics in molecular orientation and resultant physical properties) to the resulting web and the web (even if the fiber / web is similar in composition) , So that it will be appreciated that melt-blown fibers and melt-spun fibers can easily be distinguished from each other.
따라서, 본 명세서에 개시된 용융취입 섬유는 그로부터 용융된 다층 필라멘트를 방출할 수 있는 용융취입 다이, 본질적으로 용융된 다층 필라멘트가 용융취입 다이의 오리피스에서 나오는 직후 필라멘트를 용융취입 섬유로 감쇠시키기 위하여 고속 "취입" 공기를 용융된 필라멘트 상에 충돌시키는 장치, 용융취입 섬유의 수집을 위한 수집기 및 용융취입에서 관례적으로 사용되는 바와 같은 각종 다른 장비(예를 들어, 압출기, 온도 제어 장비, 등)를 이용하여 생산될 수 있다.Thus, the melt blown fibers disclosed herein include a meltblown die capable of releasing molten multi-layered filaments therefrom, a high-speed "hot melt " die to attenuate the filament into meltblown fibers immediately after the essentially molten multi-layer filaments exit the orifice of the meltblown die. (E.g., extruders, temperature control equipment, etc.) as conventionally used in meltblowing and collecting for the collection of meltblown fibers, as well as for blowing air on the melted filaments .
그러한 장치는 예를 들어 문헌[van Wente, "Superfine Thermoplastic Fibers", Industrial Engineering Chemistry, Vol. 48, pages 1342 et sec (1956)] 또는 문헌 [Report No. 4364 of the Naval Research Laboratories, published May 25, 1954 entitled "Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fiber" by van Wente, A. Boone, C. D., and Fluharty, E. L.]에서 교시된 일반적인 유형의 것일 수 있다. 그러한 장치는 다층의 용융취입 섬유를 생산하는 특정 목적을 위해 변경될 수 있고, 예를 들어 제1 및 제2 유동스트림이 이후 다중 오리피스에 분산되는 단일한, 적층된 유동스트림으로 조합되는 피드블록(feedblock) 내로 용융 중합체의 제1 및 제2 유동스트림을 각각 공급하는 제1 및 제2 압출기를 포함할 수 있다. 다층의 용융취입 섬유를 생산하기 위하여 사용될 수 있는 방법 및 장치는 예를 들어 조셉(Joseph)의 미국특허 제5,207,790호 및 제5,232,770호에서 추가로 상세히 논의되어 있다. 이러한 방식으로 제조된 다층 섬유는 예를 들어 2개의 용융 중합체가 단일 압출기에서 단일 블렌드된 유동스트림으로 조합되고, 그 후 일반 오리피스를 통하여 압출된 블렌드된-중합체 단일층 섬유와 구분된다는 것이 명백할 것이다. 이러한 방식으로 제조된 다층 섬유는, 제1 용융 중합체 스트림이 제1의 내측 오리피스로부터 압출되고, 제2 용융 중합체 스트림이 내측 오리피스를 고리모양으로 둘러싸는 제2 오리피스를 통하여 압출되는, 외피-코어 섬유와 구분된다는 것이 추가적으로 명백할 것이다.Such devices are described, for example, in van Wente, "Superfine Thermoplastic Fibers ", Industrial Engineering Chemistry , Vol. 48, pages 1342 et sec (1956)] or in the report [Report No. 1]. 4364 of the Naval Research Laboratories, May 25, 1954 entitled "Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fiber" by van Wente, A. Boone, CD, and Fluharty, EL. Such a device may be modified for a particular purpose to produce a multi-layer melt blown fiber, for example, a feed block (e.g., a feed block), wherein the first and second flow streams are then combined into a single, the first and second extruders supplying the first and second flow streams of the molten polymer into the feedblock, respectively. Methods and apparatus that can be used to produce multilayer melt blown fibers are discussed in further detail in, for example, US Patent Nos. 5,207,790 and 5,232,770 to Joseph. It will be apparent that the multi-layer fibers produced in this manner are, for example, separated from the blended-polymer monolayer fibers extruded through a common orifice, and then the two molten polymers are combined into a single blended flow stream in a single extruder . The multi-layer fibers produced in this manner are formed by extruding a first molten polymer stream from a first inner orifice and a second molten polymer stream being extruded through a second orifice annularly enclosing an inner orifice, It is additionally clear that it is different from
일부 실시양태에서, 용융취입 다층 섬유는 편평한 표면(예를 들어, 다공성 수집 벨트 또는 네팅(netting))상에 또는 단일 수집 드럼의 표면 상에 수집될 수 있다. 다른 실시양태에서, 용융취입 다층 섬유는 수렴하는 수집 표면 사이, 예를 들어 제1 및 제2 수집 드럼 사이의 갭 내에서 수집될 수 있다. 그러한 방식은, 용융취입 섬유(100)가 적어도 대체로 또는 실질적으로 "C"-형태의 단면 구조로 웹(1) 중에 존재하도록 제공할 수 있다. (본 명세서에 그 전체가 참고문헌으로서 포함된, 올슨(Olson)의 미국특허 제7,476,632호에 상세히 설명된) 그러한 방식은 증가된 로프트(loft) 및/또는 기타 유리한 특성을 제공할 수 있다.In some embodiments, melt blown multi-layer fibers can be collected on a flat surface (e.g., a porous collection belt or netting) or on the surface of a single collection drum. In another embodiment, meltblown multi-layer fibers can be collected between the converging collection surfaces, e.g., within the gaps between the first and second collection drums. Such a method may provide that the melt blown
적어도 일부 실시양태에서, 스테이플 섬유는 상기 나타낸 바와 같이 용융취입 웹 내로 선택적으로 포함될 수 있다. 이는 예를 들어 스테이플 섬유의 공기매개(airborne) 스트림을 감쇠된 필라멘트/섬유의 공기매개 스트림 내로 주입함으로써 수행될 수 있다. (용융된 필라멘트가 다이 오리피스로부터 수집기로의 그의 이동 동안 고형화되어 섬유를 형성하는 공정은 통계적 공정일 것이므로, 용어 필라멘트 및 섬유는 공정의 이 단계에서는 다소 서로 바꾸어 사용가능하다.) 이는 다층의 용융취입 섬유 및 스테이플 섬유의 섞인 에어스트림을 형성할 수 있으며, 이 에어스트림은 섞인 다층의 용융취입 섬유 및 스테이플 섬유를 섬유 덩어리로서 수집하기 위하여 수집기 상에 충돌될 수 있다. 스테이플 섬유를 예를 들어 용융취입 섬유의 스트림으로 주입하기 위한 장치 및 공정은 안가지밴드(Angadjivand)의 미국특허 제7,989,371호 및 하우저의 미국특허 제4,118,531호에 추가로 상세히 기재되어 있다.In at least some embodiments, the staple fibers may optionally be incorporated into the meltblown web as indicated above. This can be done, for example, by injecting an airborne stream of staple fibers into an air-mediated stream of attenuated filaments / fibers. (The process of solidifying the molten filament during its movement from the die orifice to the collector to form the fiber will be a statistical process, so the filaments and fibers can be used interchangeably somewhat at this stage of the process.) This is because the multi- Fibers and staple fibers, which air stream can be impinged on the collector to collect mixed multi-layer melt blown fibers and staple fibers as a fiber agglomerate. Apparatus and processes for injecting staple fibers into a stream of melt blown fibers, for example, are described in further detail in U.S. Patent Nos. 7,989,371 to Angadjivand and U.S. Patent No. 4,118,531 to Hauser.
일부 실시양태에서, 적어도 일부 스테이플 섬유는 앞서 나타낸 바와 같이 섬유를 결합시키는 것으로서 작용할 수 있다. 대안적으로, 또는 이에 대한 보조로서, 용융취입 섬유의 적어도 일부는 (예를 들어, 수집 방식 등에 따라) 결합, 예를 들어 서로 용융-결합될 수 있다. 바람직한 경우, 임의의 적합한 후-결합(post-bonding) 공정이 사용될 수 있다(예를 들어, 캘린더링 조작을 통한 지점-결합 등).In some embodiments, at least some of the staple fibers can act as binding fibers as indicated above. Alternatively, or as an aid to this, at least some of the melt-blown fibers may be bonded (e.g., depending on the collection manner, etc.), for example, melt-bonded to each other. If desired, any suitable post-bonding process may be used (e.g., point-to-bond through calendering operations, etc.).
본 명세서에 기재된 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 단열 용품 및 방음 용품, 제조된 액체 및 기체 필터 등과 같은 용품 내로 (예를 들어, 임의의 적합한 두께, 치수 등의 웹, 시트, 스크림(scrim), 직물 등으로서) 포함될 수 있다. 임의의 적합한 사용이 구체화되지만, 용융취입 웹의 열 수축률에 대한 저항성은 그러한 용품이 비교적 고온 환경에서의 사용에 특히 적합하도록 만들 수 있다. 그러한 용품은 광범위한 각종 응용분야, 예를 들어 차량 또는 건축 구성요소, 개인 보호 장비 또는 의류 등에서의 방음 및/또는 단열에서의 용도를 찾을 수 있다. 그러한 용융취입 웹은 단열 용품 및/또는 고온 방음 용품에서 특히 유용할 수 있으며, 일부 용도(예를 들어 자동차 후드라이너(hoodliner))에서 그러한 용품은 두가지 기능을 수행할 수 있음에 유의한다. 용융취입 섬유질 웹(1)은 임의의 바람직한 추가 층(예를 들어, 스크림, 페이싱(facing) 등)과 조합될 수 있으며, 이는 특정 용품을 형성하는데 유리할 수 있다. 웹(1)은 임의의 그러한 추가 층과 함께 가공(예를 들어, 성형, 절단 등)되어 특정 구조의 용품을 형성할 수 있다.The meltblown fibrous webs described herein can be incorporated into articles such as thermal insulation and soundproofing articles, manufactured liquid and gas filters and the like (e.g., as webs, sheets, scrims, fabrics, etc., ). While any suitable use may be embodied, the resistance to heat shrinkage of the meltblown web may make such articles particularly suitable for use in relatively hot environments. Such articles find use in a wide variety of applications, for example in soundproofing and / or insulation in vehicles or building components, personal protective equipment or clothing. It should be noted that such meltblown webs may be particularly useful in adiabatic and / or high temperature soundproofing articles, and that such articles may perform two functions in some applications (e.g., automotive hoodliners). The melt blown
예시적인 실시양태들의 목록List of exemplary embodiments
실시양태 1은 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹으로서, 여기에서 적어도 선택된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 느리게 결정화하는 중합체인 제1 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제1 층, 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체인 제2 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하고, 상기 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 45:55 내지 약 95:05의 상기 제1 중합체 대 상기 제2 중합체의 평균 중량비를 나타내고, 상기 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 약 10% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.
실시양태 2는, 실시양태 1에 있어서, 상기 제1 중합체는 약 240℃ 이상의 Tm을 나타내고, 상기 제2 중합체는 약 240℃ 이상의 Tm을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiments 2, in the
실시양태 3은, 실시양태 1 또는 실시양태 2에 있어서, 상기 용융취입 섬유는 약 60:40 내지 약 90:10의 제1 중합체 대 제2 중합체의 평균 중량비를 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 3 is the heat stable melt blown fibrous web of
실시양태 4는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 3 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 용융취입 섬유는 약 70:30 내지 약 80:20의 제1 중합체 대 제2 중합체의 평균 중량비를 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 4 is a process according to
실시양태 5는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 4 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 제1 중합체는 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트), 폴리(에틸렌 나프탈레이트), 폴리(락트산), 폴리(트라이메틸렌 테레프탈레이트) 및 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 폴리에스테르인 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 5 is a process of any one of
실시양태 6은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 4 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 제1 중합체는 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트)인 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 6 Embodiment 6 is the heat stable melt blown fibrous web according to any one of
실시양태 7은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 6 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 제1 중합체는 비-중합체성 핵제가 실질적으로 없는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 7 is a heat stable melt blown fibrous web as in any of
실시양태 8은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 7 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 제2 중합체는 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트), 폴리메틸펜텐, 및 신디오택틱 폴리스티렌으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 8 is a process of any one of
실시양태 9는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 8 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 적어도 선택된 다층 섬유는 그 사이에 제2 층이 개별적으로 끼워진(sandwiched) 제1 층들의 쌍을 하나 이상 각각 포함하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 9 is a process according to any one of
실시양태 10은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 8 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 적어도 선택된 다층 섬유는 3개 이상의 제1 층 및 2개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하고, 여기에서 각 제2 층은 한 쌍의 제1 층들 사이에 개별적으로 끼워져 있는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 10 is a combination according to any of
실시양태 11은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 8 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 적어도 선택된 다층 섬유는 5개 이상의 제1 층 및 4개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하고, 여기에서 각 제2 층은 한 쌍의 제1 층들 사이에 개별적으로 끼워져 있는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 11 Embodiment 11 is according to any of
실시양태 12는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 8 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 적어도 선택된 다층 섬유는 n개 이상의 제1 층 및 n-1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하고, 상기 제2 층 중 n-2개 이상은 제1 층들 사이에 개별적으로 끼워져 있으며, 여기에서 n은 7 내지 51의 수인 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 12 is a process as set forth in any of
실시양태 13은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 12 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 제1 층은 단일성분 층이고, 상기 제2 층은 단일성분 층인 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 13 is a heat stable melt blown fibrous web according to any one of
실시양태 14는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 13 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 복수 개의 상기 용융취입 섬유는 종합적으로 약 10μm 미만의 평균 섬유 직경을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 14 is a heat stable melt blown fibrous web as in any of
실시양태 15는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 14 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 웹은 스테이플 섬유를 추가로 포함하며, 상기 스테이플 섬유는 상기 웹의 섬유질 재료의 총 중량의 약 5중량% 내지 약 50중량%를 구성하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 15 is Embodiment 15 wherein, in any of
실시양태 16은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 15 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 웹은 약 6% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 16 is the heat stable melt blown fibrous web of any one of
실시양태 17은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 15 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 웹은 약 2% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 17 is the heat stable melt blown fibrous web of any one of
실시양태 18은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 17 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 웹의 용융취입 섬유는 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 나타내는 임의의 중합체성 재료를 약 5중량% 이하로 포함하는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 18,
실시양태 19는, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 17 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 웹의 용융취입 섬유는 200℃ 미만의 Tm을 갖는 임의의 중합체성 재료가 실질적으로 없는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 19,
실시양태 20은, 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 19 중 어느 하나의 열 안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 포함하는 용품으로서, 상기 용품은 단열 용품, 방음 용품, 유체 여과 용품 또는 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 용품이다.Embodiment 20 is an article comprising a heat stable melt blown fibrous web of any one of
실시양태 21은, 실시양태 20에 있어서, 상기 용품은 약 5% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 방음 용품인 용품이다.Embodiment 21 is the article of embodiment 20 wherein the article is a soundproof article that exhibits less than about 5% heat shrinkage.
실시양태 22는, 용융된 다층 유동스트림(flowstream)을 용융취입 다이의 오리피스를 통하여 압출하여, 용융된 다층 필라멘트를 형성하는 단계;Embodiment 22 comprises the steps of extruding a molten multi-layer flowstream through an orifice of a meltblowing die to form a molten multi-layer filament;
상기 용융된 다층 필라멘트를 고속 가스 스트림을 이용하여 감쇠시켜, 다층 용융취입 섬유를 형성하는 단계; 및,Damping said molten multi-layer filaments using a high velocity gas stream to form multi-layer melt blown fibers; And
상기 다층 용융취입 섬유를 섬유 덩어리로서 수집하는 단계를 포함하는 방법으로서,Collecting the multi-layer melt blown fibers as a fiber agglomerate,
여기에서 상기 섬유 유동스트림의 수집된 덩어리 중 적어도 선택된 다층 용융취입 섬유는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 느리게 결정화하는 중합체인 용융된 제1 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제1 층 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체인 용융된 제2 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하는 방법이다.At least selected multi-layered melt of the collected lump of the fiber flow stream where the blown fibers are at least about 200 ℃ T m a slow crystallizing polymer is melt the at least one or more first layers and about 200 ℃ consisting of one polymer having T lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > m , < / RTI >
실시양태 23은, 실시양태 22에 있어서, 상기 감쇠된 다층 필라멘트는 다층 용융취입 섬유의 공기매개 스트림을 형성하고, 상기 방법은 스테이플 섬유의 공기매개 스트림을 상기 다층 섬유의 공기매개 스트림 내로 주입하는 단계 및 상기 섞인(intermingled) 다층 용융취입 섬유 및 스테이플 섬유를 섬유 덩어리로서 수집하는 단계를 추가로 포함하는 방법이다.Embodiment 23 is Embodiment 23 wherein, in embodiment 22, the attenuated multilayer filaments form an air-entrained stream of multilayer meltblown fibers, the method comprising injecting an air-borne stream of staple fibers into the air- And collecting the intermixed multilayer melt blown fibers and staple fibers as a fiber agglomerate.
실시양태 24는, 실시양태 22 또는 실시양태 23에 있어서, 상기 방법은 상기 섬유 덩어리 중 섬유의 적어도 일부를 서로 결합시켜, 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 형성하는 단계를 추가로 포함하는 방법이다.Embodiment 24 is the method of embodiment 22 or embodiment 23, wherein the method further comprises bonding at least a portion of the fibers in the fiber agglomerate together to form a heat-stable melt blown fibrous web.
실시양태 25는, 실시양태 22 내지 실시양태 24 중 어느 한 방법에 의해 제조된 실시양태 1 내지 실시양태 19 중 어느 하나의 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹이다.Embodiment 25 is a heat stable melt blown fibrous web of any one of
실시양태 26은, 실시양태 22 내지 실시양태 24 중 어느 한 방법에 의해 제조된 실시양태 20 또는 실시양태 21의 용품이다.Embodiment 26 is the article of Embodiment 20 or Embodiment 21 produced by any one of Embodiment < RTI ID = 0.0 > 22 < / RTI >
실시예Example
시험 방법Test Methods
열 수축률Heat shrinkage
용융취입 웹의 열 수축률은 3개의 10cmX10cm 샘플을 이용하여 수득될 수 있다. 각 시편의 치수는 전형적으로, 기계 방향 (MD) 및 가로 방향 (CD) 모두에서 180℃에서 15분 동안 피셔 사이언티픽 아이소템프 오븐 (Fisher Scientific Isotemp Oven) (또는 그 등가물)에 위치시킨 전 후에 측정한다. 각 샘플에 대한 수축률은 MD와 CD에서 하기 등식에 의해 계산된다:The heat shrinkage of the melt blown web can be obtained using three 10 cm x 10 cm samples. The dimensions of each specimen are typically measured before and after placement in a Fisher Scientific Isotemp Oven (or equivalent) at 180 ° C for 15 minutes in both machine direction (MD) and transverse direction (CD) do. The shrinkage percentage for each sample is calculated by the following equation in MD and CD:
여기서, L0은 초기 시편 길이이고 L은 최종 시편 길이이다. 수축률의 평균 값을 계산 및 보고한다.Where L 0 is the initial specimen length and L is the final specimen length. Calculate and report the mean value of shrinkage.
TT mm (결정성 용융점)(Crystalline melting point)
중합체 샘플의 Tm은 티에이 인스트루먼츠(TA Instruments) Q2000 조절된 시차 주사 열량계(MDSC) 또는 등가물을 이용하여 수득될 수 있다. 시편을 칭량하고 양립성 알루미늄 팬 내에 부하하였다. 제1 가열을 적용하여 샘플을 샘플의 추정된 Tm 초과의 온도로 가열하고; 이후, 샘플을 충분히 느린 속도로 냉각시켜(예를 들어, 분당 10℃) 결정화가 일어나도록 한다. 이들 초기 가열/냉각 단계 후, 제2 가열을 예를 들어 분 당 10℃의 가열 속도로 적용하고 열 흐름을 관찰한다. 결정성 용융점 Tm을 제2 가열 데이타로부터 잘 규정된 1차 용융 피크(그러한 피크가 존재하는 경우)의 정점으로서 수득될 수 있으며, 이는 당업자에 의해 잘 이해될 것이다.T m of the polymer samples can be obtained by using a tieyi Instruments (TA Instruments) The differential scanning calorimetry (MDSC), or equivalent control Q2000. The specimens were weighed and loaded into a compatible aluminum pan. Heating the sample by applying a first heated to a temperature greater than the estimated T m of the sample and; Thereafter, the sample is cooled at a sufficiently slow rate (e.g., 10 [deg.] C per minute) to cause crystallization to occur. After these initial heating / cooling steps, the second heating is applied, for example, at a heating rate of 10 [deg.] C per minute and the heat flow is observed. The crystalline melting point T m can be obtained from the second heating data as a peak of a well defined primary melting peak (if such a peak exists), which will be well understood by those skilled in the art.
용융취입 웹의 제조 장치 및 방법Apparatus and method for manufacturing melt blown web
용융취입 웹을, 문헌[Wente, Van A., "Superfine Thermoplastic Fibers" in Industrial Engineering Chemistry, Vol. 48, pages 1342 et seq (1956)] 및 문헌[Report No. 4364 of the Naval Research Laboratories, published May 25, 1954 entitled "Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fibers" by Wente, Van. A. Boone, C. D., and Fluharty, E. L.]에 기재된 것과 유사한 장치 및 공정을 이용하여 제조하였다. 이 장치는 중합체 용융 흐름을 제어하고 그를 5:1의 길이 대 직경 비를 갖는 원형의 매끄러운 표면의 오리피스를 갖는 용융취입 다이에 분포시키기 위하여 기어 펌프가 장치된 압출기를 이용하였다. 오리피스는 cm 당 10개의 오리피스들의 간격으로 다이 페이스에 선형 방식으로 배열되었다. 용융 필라멘트가 본질적으로 용융취입 다이의 오리피스들에서 배출된 직후 그 용융 필라멘트에 수렴하는 방식으로 고속 "취입" 공기를 충돌시키기 위하여, 공기-공급 장치(에어 나이프)가 다이 페이스(die face)에 제공된다.A melt blown web was prepared according to Wente, Van A., "Superfine Thermoplastic Fibers" in Industrial Engineering Chemistry , Vol. 48, pages 1342 et seq (1956); 4364 of the Naval Research Laboratories, published May 25, 1954 entitled "Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fibers" by Wente, Van. A. Boone, CD, and Fluharty, EL. The apparatus utilized an extruder equipped with a gear pump to control the polymer melt flow and distribute it to a melt blowing die having a circular smooth surface orifice with a length to diameter ratio of 5: 1. The orifices were arranged in a linear fashion on the die face at intervals of 10 orifices per cm. The air-feeding device (air knife) is provided on the die face in order to collide the high-speed "blown" air in such a way that the molten filament converges to the melt filament immediately after it is essentially discharged from the orifices of the melt- do.
실시예의 다층 섬유의 경우, 장치를 (미국특허 제5,207,970호의 실시예 1에 개시된 것과 대체로 유사한 방식으로) 2개의 압출기를 포함하도록 변경시키고, 각 압출기는 각 압출기의 산출물이 독립적으로 제어될 수 있도록 기어 펌프를 갖고, 각 압출기는 용융된 압출 산출물을 키숄름(Chisholm)의 미국특허 제3,480,502호 및 슈렝크(Shrenk)의 미국특허 제3,487,505호에 기재된 것과 유사한 분할 피드블록으로 공급하도록 구성된다. 분할 피드블록은 다층 용융 중합체 스트림이 대체로 상기 기재된 바와 같이 용융취입 다이로 전달되도록 구성된다.In the case of the multilayer fibers of the Examples, the apparatus was modified to include two extruders (in a manner analogous to that disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,207,970), each extruder having a gear Pump, and each extruder is configured to feed the molten extruded product to a split feed block similar to that described in US Pat. No. 3,480,502 to Chisholm and US Pat. No. 3,487,505 to Shrenk. The split feed block is configured such that the multilayer molten polymer stream is delivered to the melt blowing die generally as described above.
대표 실시예Representative Embodiment
실시예Example 1 One
복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 상기 기재된 장치 및 일반 방법을 이용하여, 하기 기재된 바에 따라 작동시켜 제조하였다. 제1 중합체는 미국 뉴저지주 리빙스톤 소재의 난야 플라스틱스 코포레이션, 아메리카(Nan Ya Plastics Corporation, America)로부터 상표명 N211 하에 수득된 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트)(PET; 0.54 고유 점도)수지였다. 제2 중합체는 미국 메사추세츠주 피츠필드 소재의 사빅 이노베이티브 플라스틱스(SABIC Innovative Plastics)로부터 상표명 발록스(Valox)-195-1001 하에 수득된 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트)(PBT)였다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of melt blown multi-layer fibers was prepared using the apparatus described above and the general method, operating as described below. The first polymer was a poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET; 0.54 intrinsic viscosity) resin obtained under the tradename N211 from Nan Ya Plastics Corporation, America, Livingstone, NJ. The second polymer was poly (butylene terephthalate) (PBT) obtained under the tradename Valox -195-1001 from SABIC Innovative Plastics, Pittsfield, MA.
제1 및 제2 압출기는 각각 PET 및 PBT 용융 스트림을 피드블록으로 전달하였다. 75:25 PET:PBT 중량비의 중합체 용융물이 피드블록으로 전달되고, 용융취입 다이에서 0.175 ㎏/hr/cm 다이 폭의 총 중합체 처리 속도가 유지되도록 기어 펌프를 조절하였다. 다이를 약 305℃로 유지시켰고, 피드블록을 약 305℃로 유지시켰으며; (각 압출기 배럴(barrel)의 방출 말단에 가까이에서의) 압출기 용융 온도를 제1 압출기와 제2 압출기에서 각각 약 305℃ 및 270℃로 유지시켰다. 취입 공기 공급 장치의 에어 나이프 간극 폭은 약 0.76mm였고; 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 400℃의 설정점에서 그리고 압력은 균일한 웹을 생산하기에 적합하게 유지되었다. 용융 스트림은 피드블록에서 배출시 교번하는 방식으로 5개 층의 용융 스트림으로 나오며, 제1, 제3 및 제5 층은 PET이고, 제2 및 제4 층은 PBT였다.The first and second extruders delivered the PET and PBT melt streams, respectively, to the feed block. The gear pump was adjusted so that a 75:25 PET: PBT weight ratio polymer melt was delivered to the feed block and a total polymer throughput rate of 0.175 kg / hr / cm die was maintained in the meltblowing die. The die was maintained at about 305 占 폚 and the feed block was maintained at about 305 占 폚; The extruder melt temperature (close to the discharge end of each extruder barrel) was maintained at about 305 ° C and 270 ° C in the first extruder and the second extruder, respectively. The air knife gap width of the blown air supply was about 0.76 mm; The temperature of the high-velocity inlet air was maintained at a set point of about 400 ° C and the pressure was suitable for producing a uniform web. The molten stream emerged as a five-layer molten stream in alternating fashion upon discharge from the feed block, the first, third and fifth layers were PET, and the second and fourth layers were PBT.
이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 38cm의 DCD(다이에서 수집기까지의 거리)로 통기성 벨트 상에서 수집되었다. 이에 따라 형성된 섬유 덩어리는 자가-지지 부직 웹으로서 제공되기에 충분한 기계적 건전성을 나타내는 것으로 발견되었으며; 부수적인 결합 조작은 수행되지 않았다. 용융취입 다층 섬유는 5개의 교번하는 층을 포함하였다(3개의 PET의 제1 층 및 2개의 PBT의 제2층). 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 10μm 미만의 평균 직경을 나타내었으며; 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 약 130 g/㎡의 기본 중량(basis weight)을 가졌다.The melt blown multilayer fibers thus formed were collected on a breathable belt with a DCD of about 38 cm (distance from the die to the collector). The fiber agglomerates thus formed were found to exhibit sufficient mechanical integrity to be provided as self-supporting nonwoven webs; Ancillary join operations were not performed. The meltblown multilayer fiber comprised five alternating layers (the first layer of three PETs and the second layer of two PBTs). The melt blown multi-layer fibers exhibited an average diameter of less than about 10 占 퐉; The melt blown fibrous web had a basis weight of about 130 g / m < 2 >.
실시예Example 2 2
중합체 용융물의 50:50 PET:PBT 중량비가 전달되도록 기어 펌프를 조절한 것을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 1과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다. 다이 및 피드블록을 모두 약 280℃로 유지하였고; 제1 및 제2 압출기의 용융 온도는 각각 약 280℃ 및 270℃였다. 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 390℃의 설정점으로 유지하였다. 이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 30.5cm의 DCD(다이에서 수집기까지의 거리)로 수집되었다. 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 10μm 미만의 평균 직경을 나타내었고; 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 약 130g/㎡의 기본 중량을 가졌다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of melt blown multilayer fibers was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 1, except that the gear pump was adjusted to deliver a 50:50 PET: PBT weight ratio of polymer melt. The die and feed block were both maintained at about 280 ° C; The melting temperatures of the first and second extruders were about 280 ° C and 270 ° C, respectively. The temperature of the fast blown air was maintained at a set point of about 390 ° C. The melt blown multilayer fibers thus formed were collected at a DCD of about 30.5 cm (distance from the die to the collector). The melt blown multi-layer fibers exhibited an average diameter of less than about 10 占 퐉; The melt blown fibrous web had a basis weight of about 130 g / m < 2 >.
실시예Example 3 3
제2 중합체가 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트)보다는 폴리메틸펜텐(PMP; 미국 뉴욕주 라이 브룩 소재의 미쓰이 케미칼스(Mitsui Chemicals)로부터 상표명 TPX 하에 수득)인 것을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 대체로 실시예 1과 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다. 제1 중합체:제2 중합체(PET:PMP) 중량비는 약 75:25이고, 총 중합체 처리 속도인 0.14 ㎏/hr/cm 다이 폭을 용융취입 다이에서 유지시켰다.Except that the second polymer is polymethylpentene (PMP; obtained under the tradename TPX from Mitsui Chemicals, Liebruck, NY) rather than poly (butylene terephthalate), a plurality of melt- Lt; / RTI > was prepared in a manner analogous to Example 1, generally. The first polymer: second polymer (PET: PMP) weight ratio was about 75:25 and the total polymer throughput rate of 0.14 kg / hr / cm die width was maintained in the meltblowing die.
다이 및 피드블록을 모두 약 300℃로 유지하였고; 제1 및 제2 압출기의 용융 온도는 각각 약 285℃ 및 300℃였다. 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 400℃의 설정점으로 유지되었다. 이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 15cm의 DCD(다이에서 수집기까지의 거리)로 수집되었다. 용융취입 다층 섬유는 5개의 교번하는 층들을 포함하였다(3개의 PET의 제1 층 및 2개의 PMP의 제 2층). 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 10μm 미만의 평균 직경을 나타내었으며; 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 약 90g/㎡의 기본 중량을 가졌다.The die and feed block were both maintained at about 300 ° C; The melting temperatures of the first and second extruders were about 285 ° C and 300 ° C, respectively. The temperature of the high-speed blowing air was maintained at a set point of about 400 ° C. The melt blown multilayer fibers thus formed were collected at a DCD of about 15 cm (distance from the die to the collector). The meltblown multilayer fiber comprised five alternating layers (the first layer of three PETs and the second layer of two PMPs). The melt blown multi-layer fibers exhibited an average diameter of less than about 10 占 퐉; The melt blown fibrous web had a basis weight of about 90 g / m < 2 >.
실시예Example 4 4
제1:제2(PET:PMP) 중량비가 약 90:10이었음을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of melt blown multilayer fibers was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3, except that the first: second (PET: PMP) weight ratio was about 90:10.
실시예Example 5 5
제1:제2(PET:PMP) 중량비가 약 80:20이었음을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of meltblown multilayer fibers was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3, except that the first: second (PET: PMP) weight ratio was about 80:20.
실시예Example 6 6
제1:제2(PET:PMP) 중량비가 약 70:30이었음을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of melt blown multilayer fibers was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3, except that the first: second (PET: PMP) weight ratio was about 70:30.
실시예Example 7 7
제1:제2(PET:PMP) 중량비가 약 60:40이었음을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다.A melt blown fibrous web comprising a plurality of melt blown multilayer fibers was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3, except that the first: second (PET: PMP) weight ratio was about 60:40.
실시예 4 내지 7의 웹은 약 90g/㎡ 의 기본 중량을 나타내었고, 약 10μm 미만의 평균 직경을 갖는 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하였다.The webs of Examples 4 to 7 were about 90 g / m2 And contained meltblown multilayer fibers having an average diameter of less than about 10 [mu] m.
실시예Example 8 8
다층 섬유가 17개의 교번하는 층(8개의 PET의 제1 층 및 9개의 PMP의 제2 층)을 포함하도록 분할 피드블록이 구성된 것을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다. PET:PMP 중량비는 약 75:25로 유지되었다. 다이 및 피드블록을 모두 약 300℃로 유지하였고; 제1 및 제2 압출기의 용융 온도는 각각 약 285℃ 및 300℃였다. 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 400℃의 설정점으로 유지되었다. 이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 15cm의 DCD(다이에서 수집기까지의 거리)로 수집되었다.Meltblown fibers comprising a plurality of meltblown multilayer fibers, except that the split feedblock is constructed such that the multilayer fibers comprise 17 alternating layers (the first layer of 8 PETs and the second layer of 9 PMPs) The web was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3. The PET: PMP weight ratio was maintained at about 75:25. The die and feed block were both maintained at about 300 ° C; The melting temperatures of the first and second extruders were about 285 ° C and 300 ° C, respectively. The temperature of the high-speed blowing air was maintained at a set point of about 400 ° C. The melt blown multilayer fibers thus formed were collected at a DCD of about 15 cm (distance from the die to the collector).
실시예Example 9 9
다층 섬유가 2개의 교번하는 층(1개의 PET의 제1 층 및 1개의 PMP의 제2 층)을 포함하도록 분할 피드블록이 구성된 것을 제외하고는, 복수의 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하는 용융취입 섬유질 웹을 실시예 3과 대체로 유사한 방식으로 제조하였다. PET:PMP 중량비는 약 75:25로 유지되었다. 다이 및 피드블록을 모두 약 300℃로 유지하였고; 제1 및 제2 압출기의 용융 온도는 각각 약 285℃ 및 300℃였다. 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 400℃의 설정점으로 유지되었다. 이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 15cm의 DCD(다이에서 수집기까지의 거리)로 수집되었다.Meltblown fibers comprising a plurality of meltblown multilayer fibers, except that the split feedblock is constructed such that the multilayer fibers comprise two alternating layers (the first layer of one PET and the second layer of one PMP) The web was prepared in a substantially similar manner to Example 3. The PET: PMP weight ratio was maintained at about 75:25. The die and feed block were both maintained at about 300 ° C; The melting temperatures of the first and second extruders were about 285 ° C and 300 ° C, respectively. The temperature of the high-speed blowing air was maintained at a set point of about 400 ° C. The melt blown multilayer fibers thus formed were collected at a DCD of about 15 cm (distance from the die to the collector).
실시예 4 내지 실시예 9의 웹은 약 90g/㎡ 범위의 기본 중량을 나타내었고, 약 10μm 미만의 평균 직경을 갖는 용융취입 다층 섬유를 포함하였다.The webs of Examples 4 to 9 contained about 90 g / m2 Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > 10 < / RTI > m in diameter.
비교예Comparative Example
비교예 1Comparative Example 1
분할 피드블록이 사용되지 않았고, 용융취입 섬유가 모두 제1 중합체, 특히 미국 뉴저지주 리빙스톤 소재의 난야 플라스틱스 코포레이션, 아메리카로부터 상표명 N211 하에 수득된 폴리(에틸렌 테레프탈레이트)(PET; 0.54 고유 점도)수지로 이루어지는 완전히 단일층 섬유였다는 것을 제외하고는, 용융취입 부직 웹을 실시예 1과 대체로 유사한 공정 조건을 이용하여 제조하였다.No split feed block was used and the meltblown fibers were all comprised of a first polymer, particularly a poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET; 0.54 intrinsic viscosity) resin obtained under the tradename N211 from Nanya Plastics Corporation of Livingston, Meltblown nonwoven web was prepared using substantially similar process conditions as in Example 1, except that the meltblown nonwoven web was a completely monolayer fabric made from the meltblown nonwoven web.
PET 중합체 용융물이 약 0.175 ㎏/hr/cm 다이 폭의 처리 속도로 전달되도록 압출기 기어 펌프를 조절하였다. 다이를 약 305℃로 유지시키고, 피드블록을 약 305℃로 유지시키고; 압출기 용융 온도는 약 305℃로 유지시켰다. 취입 공기 공급 장치의 에어 나이프 간극 폭은 약 0.76mm였고; 고속 취입 공기의 온도는 약 400℃의 설정점에서 그리고 압력은 균일한 웹을 생산하기에 적합하게 유지되었다. 이에 따라 형성된 용융취입 단일층 섬유는 약 38cm의 DCD로 수집되었다.The extruder gear pump was adjusted so that the PET polymer melt was delivered at a throughput rate of about 0.175 kg / hr / cm die. Keeping the die at about 305 캜 and keeping the feed block at about 305 캜; The extruder melt temperature was maintained at about 305 占 폚. The air knife gap width of the blown air supply was about 0.76 mm; The temperature of the high-velocity inlet air was maintained at a set point of about 400 ° C and the pressure was suitable for producing a uniform web. The melt blown monolayer fibers thus formed were collected with a DCD of about 38 cm.
비교예 2Comparative Example 2
모든 섬유가 제2 중합체, 특히 미국 메사추세츠주 피츠필드 소재의 사빅 이노베이티브 플라스틱스로부터 상표명 발록스(Valox)-195-1001 하에 수득된 폴리(부틸렌 테레프탈레이트)(PBT)로 이루어지는 단일층 섬유인 용융취입 부직 웹으로부터 수축률 데이타를 수득하였다. 공정 조건은 수득되지 않았지만, 이는 통상의 (단일층 섬유) 용융취입 장치 및 공정 조건이 사용된 것으로 여겨졌다. 또한, 이러한 재료에 대해 보고된 열 수축 측정은 상기 기재된 절차와 약간 상이한 열 수축 시험을 이용하여 수득되었다(첸 등의 PCT 특허출원 제PCT/CN2014/080901호, 사건 일람 번호 75424WO003, 용융취입 블렌드된-중합체 섬유를 포함하는 열안정성 부직 웹(THERMALLY STABLE NONWOVEN WEB COMPRISING MELTBLOWN BLENDED-POLYMER FIBERS)이라는 제목). 예를 들어, 샘플을 180℃에서 15분에서 유지하기보다는 170℃에서 15분 동안 유지시켰다. 따라서, 비교예 2의 수축률 숫자는 다른 데이타에 정확하게 필적하지 않을 수 있다; 그러나 비교예 2는 본 명세서에 개시된 일반적인 경향을 예시하는데 여전히 유용하다.All fibers are single layer fibers consisting of a second polymer, especially poly (butylene terephthalate) (PBT) obtained under the trade name Valox -195-1001 from SABIC Innovative Plastics, Fitzpatrick, MA Shrinkage data were obtained from the meltblown nonwoven web. No process conditions were obtained, but it was considered that conventional (single layer fiber) melt blown apparatus and process conditions were used. The heat shrinkage measurements reported for these materials were also obtained using heat shrinkage tests slightly different from those described above (see Chen et al., PCT Patent Application No. PCT / CN2014 / 080901, Case Number 75424WO003, melt blown THERMALLY STABLE NONWOVEN WEB COMPRISING MELTBLOWN BLENDED-POLYMER FIBERS WITH POLYMER FIBERS. For example, the sample was held at 170 占 폚 for 15 minutes rather than held at 180 占 폚 for 15 minutes. Thus, the shrinkage number of Comparative Example 2 may not exactly match other data; However, Comparative Example 2 is still useful for illustrating the general trends disclosed herein.
각종 실시예 및 비교예에 대한 열 수축은 표 1에 보고된다.Heat shrinkage for various examples and comparative examples is reported in Table 1.
[표 1][Table 1]
기타 Other 실시예Example
전술한 실시예들은 이용가능한 기록에 따라 제공되었으며, 단지 명확한 이해를 위해 제공되었고; 그로부터 불필요한 제한으로 이해되어서는 안 된다. 실시예들에 기술된 시험과 시험 결과는 예측적이기보다는 예시적인 것으로 의도되고, 시험 절차의 변화가 상이한 결과를 산출할 것으로 예상될 수 있다. 실시예들의 모든 정량적 값들은 사용된 절차에 수반된 일반적으로 알려진 허용오차의 측면에서 근사치로 이해된다.The above-described embodiments have been provided in accordance with available records, and have been provided merely for clarity of understanding; It should not be understood as an unnecessary limitation therefrom. The tests and test results described in the embodiments are intended to be illustrative rather than predictive, and variations of the test procedure may be expected to produce different results. All quantitative values of the embodiments are approximated in terms of generally known tolerances involved in the procedure used.
본 명세서에 개시된 예시적인 특정 요소, 구조, 특징, 상세 사항, 구성 등이 다수의 실시양태에서 변형 및/또는 조합될 수 있음이 당업자에게 명백할 것이다. 이러한 모든 변형 및 조합은 단지 예시적인 실례로서의 역할을 하도록 선택된 대표적인 설계가 아닌 고안된 발명의 범위 내에 있는 것으로 본 발명자에 의해 고려된다. 따라서, 본 발명의 범주는 본 명세서에 기재된 예시적인 특정 구성으로 한정되는 것이 아니라, 오히려 적어도 청구범위의 표현에 의해 기술되는 구성 및 이들 구성의 등가물로 확장된다. 본 명세서에서 대안으로 분명하게 언급된 임의의 요소는 원하는 대로 임의의 조합을 통해 청구항에 명시적으로 포함되거나 청구항에서 배제될 수 있다. 본 명세서에서 개방형(open-ended) 언어로(예를 들어, 포함한다(comprise) 및 이의 파생어) 언급된 임의의 요소 또는 요소의 조합은 폐쇄형(closed-ended) 언어(예를 들어, 이루어지다(consist) 및 이의 파생어) 및 부분적으로 폐쇄형 언어(예를 들어, 본질적으로 이루어지다 및 이의 파생어)로 추가적으로 언급되는 것으로 간주된다. 다양한 이론 및 가능한 메커니즘이 본 명세서에서 논의되었을 수 있지만, 어떠한 경우에도 그러한 논의는 청구가능한 본 발명의 요지를 제한하지 않는다. 서면으로 된 본 명세서와 본 명세서에 참고로 포함되는 임의의 문헌의 개시 내용 간에 임의의 상충 또는 모순이 있는 경우에는, 서면으로 된 본 명세서가 우선할 것이다.It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that the specific elements, structures, features, details, configurations, etc. disclosed in this specification may be modified and / or combined in numerous embodiments. It is contemplated by the inventor that all such modifications and combinations are within the scope of the inventive concept, not the exemplary design chosen to serve as an illustrative example only. Accordingly, the scope of the invention is not to be limited to the specific illustrative embodiments described herein, but rather extends to the arrangements described by the following claims and equivalents thereof. Any element that is explicitly referred to herein as an alternative may be expressly included in the claims or excluded from the claims in any combination as desired. Any element or combination of elements referred to herein in an open-ended language (e.g., comprise and derivations thereof) is defined as a closed-ended language (e.g., (such as consist and its derivatives) and a partially closed language (e.g., consisting essentially of and derivatives thereof). While various theories and possible mechanisms may be discussed herein, in any case such discussion does not limit the gist of the claimed invention. In the event of any conflicts or contradictions between the written specification of the present disclosure and the disclosure of any of the documents incorporated herein by reference, the written description herein shall prevail.
Claims (24)
상기 용융취입 다층 섬유는 약 45:55 내지 약 95:05의 상기 제1 중합체 대 상기 제2 중합체의 평균 중량비를 나타내고, 상기 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹은 약 10% 미만의 열 수축을 나타내는 열안정성 용융취입 섬유질 웹.A thermostable meltblown fiber web comprising a plurality of the melt-blown multilayered fiber, where at least selected meltblown multilayer fiber is at least one first layer consisting of the first polymer is a polymer which slowly crystallized with at least about 200 ℃ T m in include, and at least one second layer consisting of a polymer of a second polymer which crystallized rapidly with about 200 or more ℃ T m respectively, and
Said meltblown multi-layer fibers representing an average weight ratio of said first polymer to said second polymer of from about 45:55 to about 95: 05, said thermally stable melt blown fibrous web having a thermal stability Melt blown fibrous web.
상기 용융된 다층 필라멘트를 고속 가스 스트림을 이용하여 감쇠시켜(attenuate), 다층 용융취입 섬유를 형성하는 단계; 및,
상기 다층 용융취입 섬유를 섬유 덩어리(mass)로서 수집하는 단계를 포함하는 방법으로서,
여기에서 상기 섬유 유동스트림의 수집된 덩어리 중 적어도 선택된 다층 용융취입 섬유는 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 느리게 결정화하는 중합체인 용융된 제1 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제1 층 및 약 200℃ 이상의 Tm을 갖는 빠르게 결정화하는 중합체인 용융된 제2 중합체로 구성된 1개 이상의 제2 층을 각각 포함하는 방법.Extruding a molten multi-layer flow stream through an orifice of the melt blowing die to form a molten multi-layer filament;
Attenuating the melted multilayer filaments using a high velocity gas stream to form multilayer melt blown fibers; And
Collecting the multi-layer melt blown fibers as a fiber mass,
At least selected multi-layered melt of the collected lump of the fiber flow stream where the blown fibers are at least about 200 ℃ T m a slow crystallizing polymer is melt the at least one or more first layers and about 200 ℃ consisting of one polymer having T It comprises the at least one second layer consisting of a polymer, the molten second polymer to crystallize rapidly with m, respectively.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201462017864P | 2014-06-27 | 2014-06-27 | |
| US62/017,864 | 2014-06-27 | ||
| PCT/US2015/035334 WO2015199998A1 (en) | 2014-06-27 | 2015-06-11 | Thermally stable meltblown web comprising multilayer fibers |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170026496A true KR20170026496A (en) | 2017-03-08 |
Family
ID=54938667
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020177001928A KR20170026496A (en) | 2014-06-27 | 2015-06-11 | Thermally stable meltblown web comprising multilayer fibers |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20170191197A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3161198A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6592017B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20170026496A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106460270B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015199998A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018025209A1 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2018-02-08 | Fitesa Germany Gmbh | System and process for preparing polylactic acid nonwoven fabrics |
| US11441251B2 (en) | 2016-08-16 | 2022-09-13 | Fitesa Germany Gmbh | Nonwoven fabrics comprising polylactic acid having improved strength and toughness |
| EP3682048A4 (en) * | 2017-09-15 | 2021-09-01 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Non-woven fibrous web and methods thereof |
| MX2022003697A (en) * | 2019-09-25 | 2022-04-26 | Bast Fibre Tech Inc | Bast fiber, fabrics made therewith, and related method of manufacture. |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS57167418A (en) * | 1981-04-03 | 1982-10-15 | Kuraray Co Ltd | Heat bonding composite spun fiber |
| JP2538602B2 (en) * | 1987-08-03 | 1996-09-25 | 旭化成工業株式会社 | Fiber for spunbond nonwovens |
| JP2599847B2 (en) * | 1991-08-13 | 1997-04-16 | 株式会社クラレ | Polyethylene terephthalate type melt blown nonwoven fabric and its manufacturing method |
| US5232770A (en) * | 1991-09-30 | 1993-08-03 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | High temperature stable nonwoven webs based on multi-layer blown microfibers |
| US5190812A (en) * | 1991-09-30 | 1993-03-02 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Film materials based on multi-layer blown microfibers |
| AT400840B (en) * | 1994-01-21 | 1996-03-25 | Melcher Gerhard Dr | METHOD FOR PRODUCING A PRIMARY INORGANIC FOAMED MATERIAL, AND A METHOD OR MOLD PRODUCED BY THIS PROCESS |
| US5439741A (en) * | 1994-08-03 | 1995-08-08 | Hoechst Celanese Corporation | Heterofilament composite yarn |
| WO1996026232A1 (en) * | 1995-02-22 | 1996-08-29 | The University Of Tennessee Research Corporation | Dimensionally stable fibers and non-woven webs |
| US5665235A (en) * | 1995-05-09 | 1997-09-09 | Pall Corporation | Supported fibrous web assembly |
| JP3458924B2 (en) * | 1995-10-19 | 2003-10-20 | 東洋紡績株式会社 | Nonwoven fabric and method for producing the same |
| US5773375A (en) * | 1996-05-29 | 1998-06-30 | Swan; Michael D. | Thermally stable acoustical insulation |
| DE69738870D1 (en) * | 1996-09-06 | 2008-09-11 | Chisso Corp | NONWOVEN COMPOSITE WELDING AND ASSOCIATED METHOD OF MANUFACTURING |
| US6007914A (en) * | 1997-12-01 | 1999-12-28 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Fibers of polydiorganosiloxane polyurea copolymers |
| US20050039836A1 (en) * | 1999-09-03 | 2005-02-24 | Dugan Jeffrey S. | Multi-component fibers, fiber-containing materials made from multi-component fibers and methods of making the fiber-containing materials |
| JP2002124238A (en) * | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-26 | Tonen Tapyrus Co Ltd | Heat-resistant separator |
| US20030207639A1 (en) * | 2002-05-02 | 2003-11-06 | Tingdong Lin | Nonwoven web with improved adhesion and reduced dust formation |
| US20060035555A1 (en) * | 2004-06-22 | 2006-02-16 | Vasanthakumar Narayanan | Durable and fire resistant nonwoven composite fabric based military combat uniform garment |
| JP2007105163A (en) * | 2005-10-12 | 2007-04-26 | Toyobo Co Ltd | Disposable pocket heater |
| US8802002B2 (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2014-08-12 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Dimensionally stable bonded nonwoven fibrous webs |
| ES2644455T3 (en) * | 2007-08-17 | 2017-11-29 | Fiberweb, Llc | Non-woven fabric with adhesive surface from a single polymer system |
| JP5744925B2 (en) * | 2011-02-15 | 2015-07-08 | 三井化学株式会社 | Nonwoven laminate |
-
2015
- 2015-06-11 US US15/323,614 patent/US20170191197A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2015-06-11 CN CN201580033212.2A patent/CN106460270B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2015-06-11 KR KR1020177001928A patent/KR20170026496A/en unknown
- 2015-06-11 WO PCT/US2015/035334 patent/WO2015199998A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-06-11 JP JP2016574434A patent/JP6592017B2/en active Active
- 2015-06-11 EP EP15811945.3A patent/EP3161198A4/en not_active Withdrawn
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3161198A4 (en) | 2018-03-07 |
| JP2017519916A (en) | 2017-07-20 |
| CN106460270A (en) | 2017-02-22 |
| EP3161198A1 (en) | 2017-05-03 |
| US20170191197A1 (en) | 2017-07-06 |
| WO2015199998A1 (en) | 2015-12-30 |
| JP6592017B2 (en) | 2019-10-16 |
| CN106460270B (en) | 2019-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2102401B1 (en) | Method for making dimensionally stable bonded nonwoven fibrous webs | |
| US20200216979A1 (en) | Multi-die melt blowing system for forming co-mingled structures and method thereof | |
| WO2015080913A1 (en) | Dimensionally-stable melt blown nonwoven fibrous structures, and methods and apparatus for making same | |
| KR20170026496A (en) | Thermally stable meltblown web comprising multilayer fibers | |
| US20160341119A1 (en) | Melt blown fiber forming process and method of making fibrous structures | |
| KR100713760B1 (en) | Meltblown Web | |
| JP7377809B2 (en) | Multicomponent fibers and their polymer compositions | |
| EP3161200B1 (en) | Thermally stable nonwoven web comprising meltblown blended-polymer fibers | |
| EP3775336B1 (en) | Bicomponent fiber and polymer composition thereof | |
| US7470748B2 (en) | Polymeric fibers and fabrics | |
| US20060234588A1 (en) | Improved abrasion resistance of nonwovens | |
| JP7425729B2 (en) | Fibers with odor control ingredients | |
| EP2096198A1 (en) | Polyolefin fibres loaded with polar, rigid and incompatible polymers | |
| JP2022519058A (en) | Multi-layer sheet structure |