KR20160086818A - Methods of determining response to therapy - Google Patents
Methods of determining response to therapy Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20160086818A KR20160086818A KR1020167009042A KR20167009042A KR20160086818A KR 20160086818 A KR20160086818 A KR 20160086818A KR 1020167009042 A KR1020167009042 A KR 1020167009042A KR 20167009042 A KR20167009042 A KR 20167009042A KR 20160086818 A KR20160086818 A KR 20160086818A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- mice
- erk
- ratio
- subject
- fmr1
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4415—Pyridoxine, i.e. Vitamin B6
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/40—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil
- A61K31/4015—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. piracetam, ethosuximide
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/68—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving proteins, peptides or amino acids
- G01N33/6893—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving proteins, peptides or amino acids related to diseases not provided for elsewhere
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2300/00—Mixtures or combinations of active ingredients, wherein at least one active ingredient is fully defined in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N2800/00—Detection or diagnosis of diseases
- G01N2800/52—Predicting or monitoring the response to treatment, e.g. for selection of therapy based on assay results in personalised medicine; Prognosis
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
- Steroid Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 일반적으로 취약 X 증후군 및 다른 인지 장애의 치료에서 메타독신 요법에 대한 반응의 결정 방법에 관한 것이다. 본 발명은 또한 메타독신 요법에 대해 반응할 개체를 확인하는 것에 관한 것이다.The present invention generally relates to methods for determining responses to meta-cognitive therapy in the treatment of Fragile X syndrome and other cognitive disorders. The present invention also relates to identifying individuals who will respond to meta-cognic therapy.
Description
관련 출원Related application
본원은 그 내용 전체가 각각 본원에 참고로 포함된, 2013년 9월 9일 출원된 미국 특허 가출원 USSN 61/875,384, 2013년 9월 26일 출원된 미국 특허 가출원 USSN 14/038258, 및 2014년 5월 9일 출원된 미국 특허 가출원 USSN 61/991,351을 기초로 한 우선권 및 이익을 주장한다.This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 61 / 875,384, filed September 9, 2013, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, U.S.Patent Application No. USSN 14/038258 filed September 26, 2013, Claims priority to and benefit from U.S. Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 61 / 991,351, filed on September 9th.
발명의 분야Field of invention
본 발명은 일반적으로 취약 X 증후군 및 다른 인지 장애의 치료를 위한 메타독신 요법(metadoxine therapy)에 대한 반응을 결정하는 방법에 관한 것이다. 본 발명은 또한 메타독신 요법에 반응성일 개체의 확인에 관한 것이다. The present invention generally relates to methods for determining the response to metadoxine therapy for the treatment of Fragile X syndrome and other cognitive disorders. The present invention also relates to the identification of individual responsive to meta-bangin therapy.
그 명칭이 암시하는 바와 같이 취약 X 증후군 (FXS)은 지도 위치 Xq 27.3에서 중기 염색체 내의 동위염색분체 갭 (isochromatid gap)으로서 발현되는 취약 부위와 연관된다. 취약 X 증후군은 X 염색체 상에 위치하는 취약 X 정신 지체 1 (FMR1) 유전자의 5'-비번역 영역의 돌연변이에 의해 야기되는 유전 질환이다. FXS를 일으키는 돌연변이는 취약 X 정신 지체 유전자 FMR1 내의 CGG 반복체와 연관된다. 대부분의 건강한 개체에서, CGG 반복체의 총수는 10 내지 40 미만이고, 평균 약 29이다. 취약 X 증후군에서, CGG 서열은 200 내지 1,000회 초과까지 반복된다. 대상체가 약 200개 초과의 CGG 반복체를 보유하면, 취약 X 유전자가 과메틸화되고, 이는 유전자를 침묵시킨다. 그 결과, 취약 X 정신 지체 단백질 (FMRP)은 생산되지 않거나 감소한 수준으로 생산되고, 대상체는 FXS의 소견을 보인다. As its name implies, Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) is associated with fragile sites expressed as isochromatid gaps in mid-range chromosomes at map location Xq 27.3. Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the 5'-untranslated region of the vulnerable X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene located on the X chromosome. Mutations that cause FXS are associated with CGG repeats within the vulnerable X mental retardation gene FMR1. In most healthy individuals, the total number of CGG repeats is less than 10 to 40, with an average of about 29. In Fragile X syndrome, the CGG sequence is repeated from 200 to more than 1,000 times. If the subject has more than about 200 CGG repeats, the fragile X gene is hypermethylated, which silences the gene. As a result, the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) is produced at an undifferentiated or reduced level, and the subject exhibits FXS findings.
FMR1 유전자의 전돌연변이 팽창 (premutation expansion) (55-200개의 CGG 반복체)은 일반적인 인구집단에서 빈번하여, 추정 유병률은 259명의 여성 중 1명 및 812명의 남성 중 1명이다. 전돌연변이 보유자는 대개 정상 IQ를 갖지만, 불안증과 같은 정서 문제는 흔하다. 보다 고령의 남성 전돌연변이 보유자 (50세 이상)는 진행성 활동 떨림 (intention tremor) 및 운동실조를 발병한다. 이들 운동 장애는 종종, 기억 상실, 불안증, 및 실행 기능 결핍, 은둔 또는 과민한 행동, 및 치매를 비롯한 진행성 인지 및 행동 문제를 동반한다. 상기 장애는 취약 X-염색체 연관 떨림/운동실조 증후군 (FXTAS)으로 지정되었다. FXTAS이 있는 대상체에서 자기 공명 영상화는 중간 소뇌 다리 및 인접한 소뇌 백색질에서 T2-가중 신호 강도의 증가를 보인다. The premutation expansion of the FMR1 gene (55-200 CGG repeats) is frequent in the general population, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 259 females and 1 in 812 males. All mutation holders usually have normal IQ, but emotional problems such as anxiety are common. Elderly older male mutants (aged 50 years or older) develop intestinal tremor and ataxia. These motor impairments are often accompanied by progressive cognitive and behavioral problems, including memory loss, anxiety, and impaired executive function, seclusion or irritability, and dementia. This disorder was designated as vulnerable X-chromosome associated tremor / ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). In subjects with FXTAS, magnetic resonance imaging shows an increase in T2-weighted signal intensity in the medial cerebellar bridge and adjacent cerebellar white matter.
FXS는 감소된 침투도를 갖는 X-연관 우성 장애로서 구분한다. 취약 X 돌연변이를 보유하는 경우 두 성별 모두 지적 장애를 보일 수 있고, 중증도는 가변적이다. FXS가 있는 아동 및 성인은 자폐-유사 특징 및 경향을 비롯한 다양한 정도의 지적 장애 또는 학습 장애와 행동 및 정서 문제를 갖는다. FXS가 있는 어린 아동은 종종 앉고 걷고 말하는 방법 학습과 같은 발달 이정표가 지연된다. 이환된 아동은 빈번한 짜증, 주의 집중 곤란, 빈번한 발작 (예를 들어, 측두엽 발작)을 일으킬 수 있고, 종종 매우 불안하고, 쉽게 당황하고, 감각 과다각성 장애, 위장 장애가 있을 수 있고, 언어 문제 및 이상한 행동, 예컨대 손 퍼덕이기 및 손 물어뜯기가 있을 수 있다. FXS distinguishes as an X-linked dominant disorder with reduced penetrance. If you have a fragile X mutation, both genders can show cognitive impairment and the severity is variable. Children and adults with FXS have varying degrees of intellectual or learning disabilities and behavioral and emotional problems, including autism-like characteristics and trends. Young children with FXS often delay developmental milestones such as learning how to sit, walk and speak. The affected child can cause frequent irritability, difficulty in attention, frequent seizures (eg, temporal lobe seizures), often very anxious, easily panic, sense hyperreach disorder, gastrointestinal disorder, language problems and strange There may be behavior, such as hand flapping and hand biting.
FXS는 대상체의 샘플 (예를 들어, 혈액 샘플, 구강 샘플)에 대해 수행한 확립된 유전자 시험에 의해 진단될 수 있다. 시험은 CGG 반복체의 수에 기반하여 대상체의 FMR1 유전자 내에 돌연변이 또는 전돌연변이가 존재하는지 여부를 결정한다. FXS can be diagnosed by an established genetic test performed on a sample of a subject (e.g., a blood sample, a mouth sample). The test determines whether there is a mutation or an entire mutation in the FMR1 gene of the subject based on the number of CGG repeats.
FXS가 있는 대상체는 또한 자폐증이 있을 수 있다. 자폐증으로 진단된 모든 아동의 약 5%에서는 FMR1 유전자 내에 돌연변이가 있고, 또한 취약 X 증후군 (FXS)이 있다. 자폐 범주성 장애 (ASD)는 FXS가 있는 남성의 약 30%와 여성의 약 20%에서 보이고, FXS 개체의 추가의 30%는 ASD 진단 없이 자폐 증상을 보인다. 지적 장애가 FXS의 전형적인 특징이지만, FXS가 있는 대상체는 종종 경증에서 수줍음, 눈 마주치기 어려움, 및 사회적 불안증부터 중증에서 손 퍼덕이기, 손 물어뜯기 및 집착 언어에 이르는 자폐 특징을 보인다. FXS가 있는 대상체는 자폐증과 연관된 다른 증상, 예컨대 주의력 결핍 및 과잉행동, 발작, 감각 자극에 대한 과민성, 강박 행동 및 변경된 위장 기능을 보인다. FMR1 돌연변이는 단일 단백질 (FMRP)의 발현을 방지하거나 크게 감소시킨다. FMRP 부재 하에서의 뇌 발달이 FXS의 주요 증상을 일으키는 것으로 생각된다. Subjects with FXS may also have autism. About 5% of all children diagnosed with autism have mutations in the FMR1 gene and also have Fragile X Syndrome (FXS). Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is seen in about 30% of men with FXS and in about 20% of women, and an additional 30% of FXS subjects show autism symptoms without ASD diagnosis. Although mental retardation is a typical feature of FXS, subjects with FXS often exhibit autism characteristics ranging from mild to shyness, difficulty with eye contact, and social anxiety to severe to hand fluttering, hand biting, and obsessive language. Subjects with FXS exhibit other symptoms associated with autism such as attention deficit and hyperactivity, seizures, hypersensitivity to sensory stimuli, compulsive behaviors, and altered gastrointestinal function. The FMR1 mutation prevents or greatly reduces the expression of a single protein (FMRP). Brain development in the absence of FMRP is thought to cause major symptoms of FXS.
핵심 증상에 추가로, FXS가 있는 아동은 종종 심각한 행동 장애, 예컨대 자극과민성, 공격 및 자해 행동이 있다. FXS이 있는 남성 (연령 8-24)의 최근 연구에서, 2개월의 관찰 기간 동안 자해 행동은 대상체의 79%에서 및 공격적 행동은 75%에서 보고되었다. In addition to the core symptoms, children with FXS often have severe behavioral disorders, such as irritability, aggression, and self-harm. In a recent study of men with FXS (ages 8-24), self-injurious behavior was reported in 79% of subjects and 75% of aggressive behaviors during a 2-month observation period.
FXS이 있는 인간에 대한 현재 이용가능한 치료 요법은 예를 들어, 행동 수정, 및 항우울제와 항정신병 약물을 포함한 일정 범위의 의약 (FXS 치료에 대해 FDA에서 승인받지 않은)을 사용한 치료를 포함한다. FXS 및 자폐증이 있는 개체에서 언어 및 사회화를 개선하기 위해 인지 행동 요법이 사용되어 왔다. 최근에, 비전형적 항정신병약인 리스페리돈을 사용하는 약물학적 치료가 자폐증이 있는 개체의 치료에서 비-약물학적 방안을 증대시키기 위해 일반적으로 사용되고 있다. 자폐 아동에서 리스페리돈의 무작위 위약-대조 시험은 이상 행동 척도 (Aberrant Behavior Checklist) 및 임상 총괄 평가 척도-개선 (Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement)의 자극과민성 하위척도에 대한 유의한 개선을 입증하였다 (McCracken, J.T., et al., N. Engl. J. Med. 347:314-321 (2002)). 그러나, 유해 사례는 체중 증가, 식욕 증가, 피로, 졸림, 어지러움, 및 침흘림을 포함한다. 사회적 고립 및 의사소통은 리스페리돈의 투여에 의해 개선되지 않았고, 추체외로 증상 및 운동 장애와 같은 유해한 부작용이 자폐 아동에서 리스페리돈 사용과 연관된 바 있었다.Currently available therapies for humans with FXS include, for example, behavior modification, and treatment with a range of medicines including antidepressants and antipsychotics (not approved by the FDA for FXS treatment). Cognitive behavior therapy has been used to improve language and socialization in individuals with FXS and autism. Recently, pharmacologic therapies using risperidone, an atypical antipsychotic drug, have been commonly used to increase non-pharmacologic options in the treatment of individuals with autism. Random placebo-controlled trials of risperidone in autistic children have demonstrated a significant improvement in the Aberrant Behavior Checklist and the Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement subscale (McCracken, JT , et al., N. Engl., J. Med., 347: 314-321 (2002)). However, adverse events include weight gain, increased appetite, fatigue, drowsiness, dizziness, and salivation. Social isolation and communication were not improved by the administration of risperidone, and adverse side effects such as extrapyramidal symptoms and movement disorders were associated with risperidone use in autistic children.
발명의 개요Summary of the Invention
본 발명은 대상체로부터 유래된 샘플 내의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양을 측정하고; 샘플 내의 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고; 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 비를 계산하고; 계산된 비를 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 측정된 계산된 비와 비교함으로써, 메타독신 치료를 받은 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체에서 메타독신 치료 요법의 유효성을 평가하는 방법을 제공한다. 대상체의 계산된 비가 공지의 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체에 대한 계산된 비와 유사한 경우, 치료는 효과적이다.The present invention comprises measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in a sample derived from a subject; Measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the sample; Calculating the ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein; And comparing the calculated ratio to the calculated ratio from the subject not suffering from the disease, provides a method for evaluating the effectiveness of meta-cognitive therapy in subjects with fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorders that have been treated with meta-cognition. Treatment is effective if the calculated ratio of the subject is similar to the calculated ratio for subjects not afflicted with the known disease.
본 발명에서 또한 대상체로부터 유래된 샘플 내의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양을 측정하고; 샘플 내의 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고; 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 비를 계산하고; 상기 대상체의 계산된 비를 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 측정된 계산된 비와 비교함으로써, 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체가 메타독신 치료 요법으로부터 이익을 얻게 될지 결정하는 방법이 제공된다. 상기 대상체의 계산된 비가 공지의 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체의 계산된 비보다 더 높은 경우, 대상체는 메타독신 치료 요법으로부터 이익을 얻게 될 것이다.In the present invention, the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in the sample derived from the subject is also measured; Measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the sample; Calculating the ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein; There is provided a method of determining whether a subject with Fragile X syndrome or other cognitive impairment will benefit from meta-cognitive therapy by comparing the calculated ratio of the subject to a calculated ratio measured from a subject not suffering from the disease. If the calculated ratio of the subject is higher than the calculated ratio of the subject not suffering from a known disease, the subject will benefit from meta-cognitive therapy.
또한, 본 발명에서 제1 기간에서 대상체로부터의 제1 샘플에서 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양을 측정하고; 제1 기간에서 제1 샘플에서 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고; 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 제1 비를 계산하고; 제2 기간에서 대상체로부터의 제2 샘플에서 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양을 측정하고; 제2 기간에서 제2 샘플에서 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고; 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 제2 비를 계산하고, 제1 비 대 제2 비를 비교함으로써, 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체에서 메타독신 치료 요법을 모니터링하는 방법이 제공된다. 제2 비가 제1 비보다 낮은 경우, 치료는 효과적이다.Further, in the present invention, the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in the first sample from the subject in the first period is measured; Measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the first sample in the first period; Calculating a first ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein; Measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in the second sample from the subject in the second period; Measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the second sample in the second period; Meta-cognitive therapy therapy is monitored in subjects with fragile X syndrome or other cognitive impairment by calculating a second ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein, and comparing the first versus second ratio Is provided. When the second ratio is lower than the first ratio, the treatment is effective.
일부 측면에서, 측정 단계는 면역 검정을 포함한다. 일부 실시양태에서, 샘플은 전체 혈액 또는 그의 분획이다. 일부 실시양태에서, 샘플은 말초 혈액 단핵 세포 (PBMC)이다. 일부 실시양태에서, PMBC는 림프구 또는 단핵구이다. In some aspects, the measuring step comprises an immunoassay. In some embodiments, the sample is whole blood or a fraction thereof. In some embodiments, the sample is peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). In some embodiments, the PMBC is a lymphocyte or monocyte.
달리 규정되지 않으면, 본원에서 사용되는 모든 기술 및 학술 용어는 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야의 통상의 기술자에 의해 통상적으로 이해되는 바와 동일한 의미를 갖는다. 본원에서 설명된 것과 유사하거나 동등한 방법 및 물질이 본 발명의 실시에 사용될 수 있지만, 적합한 방법 및 물질을 아래에 설명한다. 본원에 언급된 모든 간행물, 특허 출원, 특허, 및 다른 인용문은 명시적으로 그 전체가 참조로 포함된다. 충돌이 있는 경우에, 정의를 포함한 본 명세서가 우선할 것이다. 또한, 본원에 설명되는 물질, 방법 및 실시예는 단지 예시적이고, 제한하는 것으로 의도되지 않는다. Unless otherwise specified, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Although methods and materials similar or equivalent to those described herein can be used in the practice of the present invention, suitable methods and materials are described below. All publications, patent applications, patents, and other citations referred to herein are expressly incorporated by reference in their entirety. In the event of a conflict, the present specification, including definitions, will control. In addition, the materials, methods, and embodiments described herein are illustrative only and not intended to be limiting.
본 발명의 다른 특징 및 이점은 다음 상세한 설명 및 청구항으로부터 명확해지고 그에 의해 포괄될 것이다. Other features and advantages of the invention will be apparent from and elucidated with reference to the following detailed description and claims.
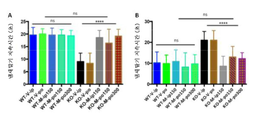
도 1은 환경적 공포 조건화 (contextual fear conditioning)에 대한 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (knockout) (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 비히클 (V) 또는 메타독신 (M) (100, 150, 또는 200 mg/kg)의 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 (ip) 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 구체적으로, 패널 A는 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg의 메타독신의 효과를 보여준다. 패널 B는 비히클 또는 100 mg/kg의 메타독신의 효과를 보여준다. 패널 C는 비히클 또는 200 mg/kg의 메타독신의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± 평균의 표준 오차 (sem)이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, NS = 유의하지 않음.
도 2는 사회적 접근 행동에 대한 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. *p<0.05 및 ****p<0.0001.
도 3은 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 Y형 미로 (Y-maze) 자발 변경 (패널 A), Y형 미로 보상된 변경 (패널 B) 또는 Y형 미로 수조 미로 공간 변별 (패널 C)에 대한 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, NS = 유의하지 않음.
도 4는 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 T형 미로 (T-maze) 보상된 변경에 대한 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ****p<0.0001.
도 5는 N = 10마리 야생형 (WT) 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 2개월령 마우스의 군에서 연속 주로 (successive alley) 과제에서 행동에 대한 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 보여준다. 장치의 연속 주로는 마우스를 탐구하기 위해 진행적으로 보다 불안유발성 환경을 제공하였다. 따라서, 주로 아래로의 운동은 불안증을 평가하였다. 추가로, 전체 활동 수준을 또한 이 장치 내에서 정량할 수 있다.
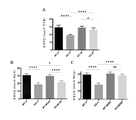
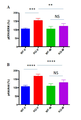
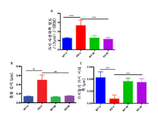
도 6은 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 ERK (ERK 활성을 표시함) (패널 A) 및 Akt (Akt 활성을 표시함) (패널 B)의 인산화의 전체 뇌 수준에 대한 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 5마리 마우스/군이다. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, NS = 유의하지 않음.
도 7은 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 6개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ****p<0.0001 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 8은 한차례 냄새맡기 (sniffing bout)의 수 또는 냄새맡기의 지속시간에 의해 측정할 때, 6개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 사회적 접근 (패널 A 및 C) 및 사회적 기억 (패널 B 및 D) 행동에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 9는 6개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 ERK (패널 A) 및 Akt (패널 B)의 인산화의 전체 뇌 수준에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 10은 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 7일 동안 1일 1회 150 mg/kg의 메타독신 (M) ip, 또는 비히클 (V) 또는 150 및 300 mg/kg의 메타독신의 경구 투여 (po)의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. 구체적으로, 패널 A는 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 야생형 마우스에서 비히클을 사용한 ip 및 경구 치료를 보여준다. 패널 B는 야생형 마우스에서 메타독신을 사용한 ip 및 경구 치료를 보여준다. 패널 C는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 메타독신을 사용한 ip 및 경구 치료를 보여준다. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 11은 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 사회적 접근 (패널 A) 및 사회적 기억 (패널 B)에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 또는 300 mg/kg의 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 또는 경구 투여 (po)의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
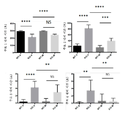
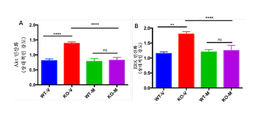
도 12는 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 및 야생형 (WT) 마우스에서 유동 세포측정법을 사용하여 측정할 때 림프구 바이오마커 (biomarker)에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 또는 300 mg/kg의 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 또는 경구 투여 (po)의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 바이오마커는 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 야생형 마우스에서 pAkt (패널 A) 및 pERK (패널 B)이다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
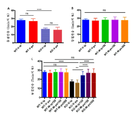
도 13은 2개월령 야생형 (WT) 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 마우스의 뇌 영역에서 pERK 수준에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip의 효과를 보여준다. 분석된 영역은 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 야생형 마우스에서 해마 (패널 A), 전전두 (pre-frontal) 피질 (패널 B), 및 선조체 (패널 C)이었다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 14는 2개월령 야생형 (WT) 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 마우스의 뇌 영역에서 pAkt 수준에 대한 7일 동안 비히클 (V) 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신 (M)의 1일 1회 ip 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 분석된 영역은 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 야생형 마우스에서 해마 (패널 A), 전전두 피질 (패널 B), 및 선조체 (패널 C)이었다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 10마리 마우스/군이다. ****p<0.0001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
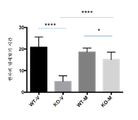
도 15는 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스로부터 뉴런 (neuron) 해마 배양액에서 사상위족 (filopodia) 밀도 (패널 A), 길이 (패널 B), 및 폭 (패널 C)에 대한 시험관 내 비히클 (V) 또는 300 μΜ 메타독신 (M)을 사용한 5시간 치료의 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이다 (야생형, N = 20개의 뉴런, 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스, N = 20개 뉴런). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, 및 ns = 유의하지 않음.
도 16은 Fmr1 낙아웃 (KO) 또는 야생형 (WT) 마우스로부터 400 μM 해마 절편 (slice)에서 기초 드 노보 (de novo) 단백질 합성에 대한 비히클 (V) 또는 300 μΜ 메타독신 (M)을 사용한 시험관 내 치료 효과를 보여준다. 제시된 데이터는 평균 ± sem이고, N = 6개 절편/군이다. *p<0.001 및 ****p<0.0001. Figure 1 shows the effect of vehicle (V) or metadoxine (M) (100, 150, or 200 mg) on 2 month old Fmr1 knockout (KO) or wild type (WT) mice for contextual fear conditioning / kg) once a day for seven days. Specifically, panel A shows the effect of vehicle or metadocin at 150 mg / kg. Panel B shows the effect of vehicle or 100 mg / kg metadoxine. Panel C shows the effect of vehicle or 200 mg / kg metadoxine. The data presented are mean ± standard error (sem) and N = 10 mice / group. * p <0.05, **** p <0.0001, NS = not significant.
Figure 2 shows the effect of intraperitoneal administration once daily for 7 days of vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) in 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (WT) Lt; / RTI > The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. * p < 0.05 and **** p < 0.0001.
FIG. 3 is a graph showing the results of a Y-maze spontaneous change (panel A), a Y-type maze-compensated change (panel B), or a Y-shaped maze aquarium space in a 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxin (M) for the differentiation (Panel C). The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. *** p <0.001, **** p <0.0001, NS = not significant.
Figure 4 shows vehicle (V) for a T-maze compensated change in a 2-month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (WT) Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > intraperitoneal < / RTI > The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. **** p <0.0001.
Figure 5 shows the effect of vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) on behavior in the successive alley task in a group of N = 10 wild-type (WT) or Fmr1 null out (KO) It shows the effect of treatment once a day on 7 days. The continuum of the device has progressively provided a more anxious environment for exploring the mouse. Thus, mainly downward movements evaluated anxiety. In addition, the overall activity level can also be quantified within this device.
FIG. 6 is a graph showing the total brain level of phosphorylation of ERK (indicating ERK activity) (panel A) and Akt (indicating Akt activity) (panel B) in 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxin (M) once daily for 7 days. The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 5 mice / group. ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001, **** p <0.0001, NS = not significant.
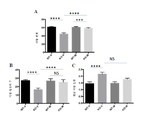
Figure 7 shows the effect of ip administration of vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) once daily for 7 days in 6 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (WT) mice for environmental fear conditioning Lt; / RTI > The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. **** p <0.0001 and ns = not significant.
Figure 8 shows that the social approach (panels A and C) and social memory (FT) in 6-month old Fmr1 dropout (KO) or wild-type (WT) mice, as measured by the number of sniffing bouts or duration of odor- (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) ip for 7 days on the behavior (Panel B and D). The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. * p <0.05, **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 9 shows vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg < RTI ID = 0.0 > meta < / RTI > for 7 days for the entire brain level of ERK (Panel A) and Akt (Panel B) phosphorylation in 6 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wildtype It shows the effect of single dose ip administration of single (M). The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 10 is a graph showing the effect of 150 mg / kg of metadoxine (M) ip, or vehicle (V) once daily for 7 days for environmental fear conditioning in 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type And 300 mg / kg of metadoxine (po). The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. Specifically, Panel A shows ip and oral treatment with vehicles in Fmr1 fallout and wild type mice. Panel B shows ip and oral treatment with metadoxine in wild-type mice. Panel C shows ip and oral treatment with metadoxine in Fmr1 null mice. ** p <0.01, **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 11 shows vehicle (V) for 7 days for social access (Panel A) and social memory (Panel B) in 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (WT) (M) once daily ip or oral administration (po). The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. ** p <0.01, **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 12 shows vehicle (V) for lymphocyte biomarker for 7 days or 150 or 300 mg / kg for 7 days when measured using flow cytometry in 2 month old Fmr1 null out (KO) and wild type (WT) The effect of ip or oral administration (po) once a day on metadoxin (M) is shown. The biomarkers presented are Fmr1 dropout and pAkt (panel A) and pERK (panel B) in wild type mice. The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 13 shows the effect of ip (once daily for vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) ip for 7 days on the pERK level in the brain area of 2-month old wild-type (WT) and Fmr1 null out Lt; / RTI > The analyzed regions were hippocampus (Panel A), pre-frontal cortex (Panel B), and striatum (Panel C) in Fmr1 fallout or wild type mice. The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 14 shows the effect of ip administration of vehicle (V) or 150 mg / kg metadoxine (M) once daily for 7 days on pAkt levels in the brain regions of 2-month old wild type (WT) and Fmr1 null out Show effects. The analyzed regions were hippocampus (Panel A), prefrontal cortex (Panel B), and striatum (Panel C) in Fmr1 fallout or wild type mice. The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 10 mice / group. **** p <0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 15 is a plot of the filopodia density (panel A), length (panel B), and width (panel C) in neuron hippocampal cultures from Fmr1 null out (KO) or wildtype (WT) 5 hours treatment with vehicle (V) or 300 [mu] M metadoxin (M). The data presented are mean ± sem (wild type, N = 20 neurons, and Fmr1 null out mice, N = 20 neurons). ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001, and ns = not significant.
Figure 16 shows the results of a test using a vehicle (V) or 300 μM metadoxine (M) for de novo protein synthesis based on 400 μM hippocampal slice from Fmr1 null out (KO) or wild type (WT) It shows my treatment effect. The data presented are mean ± sem, and N = 6 intercepts / group. * p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.
발명의 상세한 설명DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
본 발명은 취약 X 증후군 (FXS) 및 다른 인지 장애가 있는 개체의 메타독신 요법에 대한 반응과 연관된 바이오마커의 확인에 관한 것이다. 구체적으로, 메타독신 치료는 대상체 샘플 내의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 정상 비에 보다 근접하게 되돌리는 것으로 밝혀졌다. 정상 비는 정상 (즉, 질환에 걸리지 않은) 대상체에서 발견된 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 의미한다. 또한, 상기 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 비의 변경이 혈액에서 검출될 수 있음이 예상치 않게 밝혀졌다.The present invention relates to the identification of biomarkers associated with responses to Meta-cognitive therapy of individuals with Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) and other cognitive disorders. Specifically, meta-cognition therapy has been found to bring the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein in the subject sample closer to normal ratios. Normal ratio means the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein found in normal (i.e., not diseased) subjects. It has also unexpectedly been found that alterations in the phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein ratios can be detected in the blood.
따라서, 본 발명은 대상체 샘플에서 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 결정함으로써 FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애에 대한 메타독신 치료를 받고 있는 대상체를 모니터링하는 방법을 제공한다. 비는 대조군 비, 예컨대 인지 장애에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 얻은 비와 비교된다. 정상 대조군 비와 유사한 대상체의 비는 치료가 효능이 있음을 나타낸다.Thus, the present invention provides a method for monitoring a subject undergoing metacortar treatment for FXS or other cognitive impairment by determining the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein in a subject sample. The ratio is compared to the ratio obtained from the control ratios, e. The ratio of subjects similar to the normal control ratios indicates that the treatment is efficacious.
추가로, 본 발명은 대상체 샘플에서 인산화된 ERK 또는 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 결정함으로써 메타독신 치료로부터 이익을 얻게 될 인지 장애가 있는 대상체를 선택하는 방법을 제공한다. 비는 대조군 비, 예컨대 인지 장애에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 얻은 비와 비교된다. 정상 대조군 비보다 큰 대상체의 비는 대상체가 메타독신 치료로부터 이익을 얻을 수 있음을 나타낸다. 반면에, 정상 대조군 비보다 큰 비를 갖지 않는 대상체는 메타독신 치료로부터 이익이 얻어지지 않을 수 있다.In addition, the present invention provides a method for selecting a subject with cognitive impairment that will benefit from meta-cognitive therapy by determining the ratio of phosphorylated ERK or Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein in a subject sample. The ratio is compared to the ratio obtained from the control ratios, e. The ratio of subjects greater than the normal control ratio indicates that the subject can benefit from meta-cognitive therapy. On the other hand, subjects who do not have a greater ratio than the normal control ratio may not benefit from meta-cognitive therapy.
비의 계산은 본원에서 일방향으로 설명되지만, 통상의 기술자에게 자명한 바와 같이 그 역을 계산하는 것을 포함하는 것이 이해되어야 한다. 또한, 본원에서 설명되는 비의 계산은 유용한 상대적인 수를 제공할 때 유용한 반면, 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질과 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 수준 사이의, 및 시험 대상체와 대조군 대상체 사이의 절대적인 차이의 계산도 사용될 수 있고, 본 발명을 실시하는데 효과적으로 사용될 것이다.The calculation of the ratio is described herein as one way, but it should be understood that it includes calculating the inverse as would be apparent to one of ordinary skill in the art. Also, the calculation of the ratios described herein is useful when providing a useful relative number, while the calculation of the absolute difference between the phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein and the total ERK and Akt protein levels, as well as between the test and control subjects, And may be used effectively to practice the present invention.
정의Justice
"정확도"는 측정된 또는 계산된 양 (시험 보고된 값)의 그의 실제 (또는 진정한) 값에 대한 일치도를 의미한다. 임상 정확도는 진정한 성과 (진정한 양성 (TP) 또는 진정한 음성 (TN)) 대 오분류된 성과 (거짓 양성 (FP) 또는 거짓 음성 (FN))의 비율에 관한 것이고, 양성 예측 값 (PPV) 또는 음성 예측 값 (NPV), 또는 다른 척도 중에서 가능성, 승산비 (odds ratio)로 언급될 수 있다."Accuracy" means the degree of agreement with the actual (or true) value of the measured or calculated amount (the reported value of the test). Clinical accuracy is related to the ratio of true performance (true positive (TP) or true negative (TN)) to misclassified performance (false positive (FP) or false negative (FN)), positive predictive value (PPV) Prediction value (NPV), or probability, odds ratio, among other measures.
본 발명의 문맥에서 "바이오마커"는 비제한적으로, 단백질, 핵산, 및 대사산물, 이들의 다형성, 돌연변이, 변이체, 변형, 서브유닛, 단편, 단백질-리간드 복합체, 및 분해 생성물, 단백질-리간드 복합체, 요소, 관련 대사산물, 및 다른 분석물 또는 샘플-유래 척도를 포함한다. 바이오마커는 또한 돌연변이된 단백질 또는 돌연변이된 핵산을 포함할 수 있다. 바이오마커는 또한 건강 상태의 비-혈액 매개 인자 또는 비-분석물 생리학적 마커, 예컨대 본원에서 규정되는 "임상 파라미터", 및 또한 본원에서 규정되는 "전통적인 실험 위험 인자"를 포함한다. 바이오마커는 또한 수학적으로 생성된 임의의 계산된 지수 (index) 또는 일시적 경향 및 차이를 비롯한 임의의 하나 이상의 상기 측정의 조합을 포함한다. 이용가능한 경우에, 본원에서 달리 설명하지 않으면, 유전자 생성물인 바이오마커는 국제 인간 게놈 기구 명명 위원회 (Human Genome Organization Naming Committee) (HGNC)에 의해 할당되고 미국 국립 생물공학 정보센터 (US National Center for Biotechnology Information) (NCBI)의 웹 사이트에 본 출원의 출원일에 게시된 공식적인 문자 약어 또는 유전자 기호를 기초로 하여 확인된다."Biomarkers" in the context of the present invention include, but are not limited to, proteins, nucleic acids, and metabolites, polymorphisms, mutations, variants, modifications, subunits, fragments, protein- ligand complexes and degradation products, protein- , Urea, related metabolites, and other analytes or sample-derived scales. The biomarker may also comprise a mutated protein or a mutated nucleic acid. Biomarkers also include non-blood or non-analyte physiological markers of health, such as the "clinical parameters" as defined herein, and also the "traditional laboratory risk factors" The biomarker also includes any one or more of the above measurement combinations, including any computed index or temporal trend and difference mathematically generated. Where available, biomarkers that are gene products, unless otherwise specified herein, are assigned by the International Genome Organization Naming Committee (HGNC) and are provided by the US National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website on the basis of official letter abbreviations or genetic symbols posted at the filing date of the present application.
"임상 지표"는 세포 또는 유기체의 집단의 생리학적 상태를 평가할 때 단독으로 또는 다른 데이터와 함께 사용되는 임의의 생리학적 데이터이다. 이 용어는 전-임상 지표를 포함한다. "Clinical indicator" is any physiological data used alone or in conjunction with other data in assessing the physiological state of a population of cells or organisms. This term includes pre-clinical indicators.
"임상 파라미터"는 대상체 건강 상태에 대한 모든 비-샘플 또는 비-분석물 바이오마커 또는 다른 특징, 예컨대, 비제한적으로, 연령 (Age), 민족성 (RACE), 성별 (Sex), 또는 가족력 (FamHX)을 포함한다."Clinical parameters" include all non-sample or non-analyte biomarkers or other characteristics of a subject's health status, such as, but not limited to, Age, Ethnicity (RACE), Sex, ).
"FN"은 거짓 음성이고, 질환 상태 시험에서 질환 대상체를 비-질환 또는 정상으로서 부정확하게 분류하는 것을 의미한다. "FN" is a false negative, meaning that the disease entity is incorrectly classified as non-disease or normal in the disease state test.
"FP"는 거짓 양성이고, 질환 상태 시험에서 정상 대상체를 질환이 있는 것으로 부정확하게 분류하는 것을 의미한다. "FP" is a false positive, meaning that the disease state test incorrectly classifies a normal subject as having a disease.
"공식", "알고리즘" 또는 "모델"은 하나 이상의 연속형 또는 범주형 입력 (이하 "파라미터"로 부름)을 통해, 때때로 "지수" 또는 "지수 값"으로 언급되는 출력 값을 계산하는 임의의 수학식, 알고리즘, 분석 또는 프로그램된 (programmed) 과정, 또는 통계학적 기술이다. "공식"의 비제한적인 예는 합계, 비, 및 회귀 연산자 (operator), 예컨대 계수 또는 지수 (exponent), 바이오마커 값 전환 및 표준화 (비제한적으로, 임상 파라미터, 예컨대 성별, 연령, 또는 민족성을 기초로 한 표준화 방식 포함), 규칙 및 지침, 통계학적 분류 모델, 및 선조 집단 (historical population)에 대해 훈련된 신경 네트워크를 포함한다. 패널 및 조합의 구축에서, 특히 관심을 끄는 것은 구조적 및 공동작용의 (synactic) 통계학적 분류 알고리즘, 및 패턴 인지 특징을 이용하는 위험 지수 구축 방법, 예를 들어 확립된 기술, 예컨대 상호 상관관계 (cross-correlation), 주성분 분석 (PCA), 요인 변환 (factor rotation), 로지스틱 회귀 (LogReg), 선형 판별 분석 (LDA), 고유유전자 (Eigengene) 선형 판별 분석 (ELDA), 지지 벡터 머신 (Support Vector Machine) (SVM), 랜덤 포레스트 (Random Forest) (RF), 반복적 분할 트리 (Recursive Partitioning Tree) (RPART), 및 다른 관련 결정 트리 (decision tree) 분류 기술, 특히 수축 중심 (Shrunken Centroid) (SC), StepAIC, Kth-최근린법 (Kth-Nearest Neighbor), 부스팅 (Boosting), 결정 트리, 신경 네트워크 (Neural Network), 베이즈 네트워크 (Bayesian Networks), 지지 벡터 머신, 및 히든 마르코프 (Hidden Markov) 모델이다. 통상의 기술자에게 잘 알려진 콕스 (Cox), 웨이불 (Weibull), 카플란-마이어 (Kaplan-Meier) 및 그린우드 (Greenwood) 모델을 포함하는 다른 기술이 생존 및 time to 사건 위험 분석에 사용될 수 있다. 많은 이들 기술은 선택 기술, 예컨대 전진 (forward) 선택, 후진 (backwards) 선택, 또는 단계식 선택, 제시된 크기의 모든 잠재적인 패널의 완전한 목록, 유전적 알고리즘과 유용하게 조합되거나, 또는 이들은 그 자체의 기술 내에 바이오마커 선택 방법을 포함할 수 있다. 이들은 추가의 바이오마커와 모델 개선 사이의 균형 유지 (tradeoff)를 정량하기 위해, 및 과적응 (overfit)의 최소화를 돕기 위해 정보 기준, 예컨대 아카이케 정보 기준 (Akaike's Information Criterion) (AIC) 또는 베이즈 정보 기준 (Bayes Information Criterion) (BIC)과 연계될 수 있다. 생성되는 예측 모델은 다른 연구에서 검증되거나, 또는 부츠트랩 (Bootstrap), 리브-원-아웃 (Leave-One-Out) (LOO) 및 10-배 교차-검증 (10-배 CV)과 같은 기술을 사용하여 이들이 본래 훈련된 연구에서 교차-검증될 수 있다. 다양한 단계에서, 거짓 발견율은 관련 기술분야에 공지된 기술에 따른 값 순열 (value permutation)에 의해 추정할 수 있다. "보건 경제적 유용성 함수"는 진단적 또는 치료적 개입의 치료 기준 내로의 도입 전 및 후 둘 모두에 이상적인 적용가능한 환자 집단에서 다양한 임상 성과의 예상된 확률의 조합으로부터 유래되는 식이다. 이것은 상기 개입의 정확도, 타당성 및 성능 특징의 추정치, 및 실제 보건 시스템 비용 (서비스, 물품, 장비 및 약물 등)으로부터 및/또는 각각의 성과를 유도하는 질 보정 수명 (QALY) 당 추정된 허용되는 값으로부터 유도될 수 있는 각각의 성과와 연관된 비용 및/또는 값 측정 (유용성)을 포함한다. 모든 예측된 성과에 걸쳐, 각각의 성과의 예상된 유용성을 곱한 성과에 대해 예측된 집단 크기의 곱의 총합은 제시된 치료 기준의 총 보건 경제적 유용성이다. (i) 개입이 존재하는 상태의 치료 기준에 대해 계산된 총 보건 경제적 유용성 대 (ii) 개입이 없는 상태의 치료 기준에 대한 총 보건 경제적 유용성 사이의 차이는 개입의 보건 경제적 비용 또는 값에 대한 전체 척도를 제시한다. 이것은 단위 개입 당 비용에 도달하고 상기 결정을 시장 지위, 가격 책정, 및 보건 시스템 허용도의 추정으로서 유도하기 위해 분석되는 전체 환자군 사이에서 (또는 단지 개입군 사이에서) 나뉠 수 있다. 상기 보건 경제적 유용성 함수는 개입의 비용-유효성을 비교하기 위해 통상적으로 사용되지만, 또한 보건 시스템이 기꺼이 지불할 수 있는 QALY 당 허용되는 값, 또는 새로운 개입을 필요로 하는 허용되는 비용-효과적인 임상 성능 특징을 추정하기 위해 변환될 수 있다.&Quot; Formulas, "" Algorithms, "or " models" refer to any arbitrary number of terms that are sometimes referred to as "exponent" or "exponent values", through one or more contiguous or categorical inputs An equation, an algorithm, an analysis or a programmed process, or a statistical technique. Non-limiting examples of "formulas " include sum, ratio, and regression operators such as coefficients or exponents, biomarker value conversion and standardization (including but not limited to clinical parameters such as sex, age, Based standardized methods), rules and guidelines, statistical classification models, and neural networks trained for the historical population. Particularly interesting in the construction of panels and combinations is the use of structured and synergistic statistical classification algorithms and risk index construction methods using pattern recognition features such as established techniques such as cross- correlation, PCA, factor rotation, LogReg, linear discriminant analysis (LDA), Eigenengine linear discriminant analysis (ELDA), Support Vector Machine SVM), Random Forest (RF), Recursive Partitioning Tree (RPART), and other related decision tree classification techniques, in particular Shrunken Centroid (SC), StepAIC, Kth-Nearest Neighbor, Boosting, Decision Tree, Neural Network, Bayesian Networks, Support Vector Machine, and Hidden Markov Model. Other techniques, including the well-known Cox, Weibull, Kaplan-Meier and Greenwood models known to the ordinary artisan, can be used for survival and time to event risk analysis. Many of these techniques may be usefully combined with selection techniques, such as forward selection, backwards selection, or stepwise selection, a complete listing of all potential panels of the presented size, genetic algorithms, A biomarker selection method within the technology. They may use information criteria, such as Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) or Bayesian < (R) >, to quantify the tradeoff between additional biomarkers and model improvement and to help minimize overfitting, May be associated with the Bayes Information Criterion (BIC). The resulting predictive model may be validated in other studies or may be applied to techniques such as Bootstrap, Leave-One-Out (LOO) and 10-fold cross-validation (10-fold CV) They can be cross-validated in their original trained studies. At various stages, the false discovery rate can be estimated by value permutation according to techniques known in the relevant art. A "health economic utility function" is an expression derived from a combination of expected probabilities of various clinical outcomes in the applicable patient population, which is ideal both before and after the introduction of the diagnostic or therapeutic intervention into the treatment standard. This is an estimate of the accuracy, validity and performance characteristics of the intervention, and the estimated acceptable value per quality-of-life (QALY) leading to actual health system costs (such as services, goods, equipment and drugs) and / (Usefulness) associated with each performance that can be derived from the cost and / or value measurements. Over all predicted outcomes, the sum of the product of the predicted population sizes for performance multiplied by the expected utility of each performance is the total health and economic utility of the proposed treatment standard. The difference between (i) the total health and economic utility calculated for a treatment standard in the presence of an intervention versus (ii) the total health and economic availability for a treatment standard without intervention is the total The scale is presented. This can be divided between the entire patient population (or only between intervention groups) that is analyzed to reach a cost per unit of intervention and derive the decision as an estimate of market position, pricing, and health system tolerance. The health economic usability function is typically used to compare the cost-effectiveness of an intervention, but it is also an acceptable value per QALY that the health care system is willing to pay, or an acceptable cost that requires new intervention. Lt; / RTI >
각각의 성과 (질환 분류 진단 시험에서 TP, FP, TN, 또는 FN일 수 있음)는 상이한 비용이 소요되기 때문에, 본 발명의 진단적 (또는 예후) 개입을 위해, 보건 경제적 유용성 함수는 임상 상황 및 개별 성과 비용 및 값을 기초로 하여 특이성보다 민감성을, 또는 NPV보다 PPV를 우선적으로 선호할 수 있고, 따라서 보다 직접적인 임상적 또는 분석적 성능 척도와 상이할 수 있는 보건 경제적 성능 및 값의 또 다른 척도를 제공한다. 이러한 상이한 측정치 및 상대적인 균형 유지는 일반적으로 오류율 0 (0의 예측된 대상체 성과 착오분류 또는 FP 및 FN로 알려짐)의 완전한 시험의 경우에만 수렴될 것이고, 모든 성능 척도는 상이한 정도이지만 불완전한 상태보다 더 유리할 것이다.For the diagnostic (or prognostic) intervention of the present invention, each economic outcome (which may be TP, FP, TN, or FN in a disease classification diagnostic test) is at a different cost, Another measure of health economic performance and value that may be more sensitive than specificity, or preferentially PPV over NPV, based on individual performance costs and values, and therefore may differ from a more direct clinical or analytical performance measure to provide. These different measures and relative equilibrium maintenance will generally converge only in the case of a complete test of error rate 0 (predicted objectivity and error classification of zero or FP and FN), and all performance measures are different but more favorable than imperfect conditions will be.
"측정하는" 또는 "측정" 또는 별법으로 "검출하는" 또는 "검출"은 임상 또는 대상체-유래 샘플 내의 제시된 물질의 정성적 또는 정량적 농도 수준의 유도를 포함하는 상기 물질의 존재, 부재, 수량 또는 양 (유효량일 수 있음)의 평가 또는 대상체의 비-분석물 임상 파라미터의 값 또는 분류에 대한 평가를 의미한다.&Quot; Measuring "or" measuring ", or alternatively, "detecting" or "detecting" refers to the presence, absence, quantity, or amount of a substance, including induction of a qualitative or quantitative concentration level of a given substance in a clinical or object- Means an evaluation of the amount (which may be an effective amount) or an evaluation of the value or classification of a non-analyte clinical parameter of the subject.
"음성 예측 값" 또는 "NPV"는 TN/(TN+FN) 또는 모든 음성 시험 결과의 진정한 음성 분율에 의해 계산한다. 이것은 또한 시험이 의도되는 집단의 질환 유병률 및 사전검사 확률에 의해 본질적으로 영향받는다. 예를 들어, 시험, 예를 들어, 임상 진단 시험의 특이성, 민감성, 및 양성 및 음성 예측 값을 논의하고 있는 문헌 [O'Marcaigh A S, Jacobson R M, "Estimating The Predictive Value Of A Diagnostic Test, How To Prevent Misleading Or Confusing Results," Clin. Ped. 1993, 32(8): 485-491]을 참고한다. 종종, 연속 진단 시험 측정을 이용하는 이진 (binary) 질환 상태 분류 방식에 대해, 민감성 및 특이성은 문헌 [Pepe et al., "Limitations of the Odds Ratio in Gauging the Performance of a Diagnostic, Prognostic, or Screening Marker," Am. J. Epidemiol 2004, 159 (9): 882-890]에 따른 수신기 작동 특성 (ROC) 곡선에 의해 요약되고, 곡선하 면적 (AUC) 또는 단지 단일 값으로 시험 (또는 검정) 차단점 (cut point)의 전체 범위에 걸친 시험, 검정, 또는 방법의 민감성 및 특이성의 제시를 허용하는 지표인 c-통계학에 의해 요약된다. 또한, 예를 들어, 문헌 [Shultz, "Clinical Interpretation Of Laboratory Procedures," chapter 14 in Teitz, Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry, Burtis and Ashwood (eds.), 4th edition 1996, W.B. Saunders Company, pages 192-199]; 및 [Zweig et al., "ROC Curve Analysis: An Example Showing The Relationships Among Serum Lipid And Apolipoprotein Concentrations In Identifying Subjects With Coronory Artery Disease," Clin. Chem., 1992, 38(8): 1425-1428]을 참고한다. 가능성 함수, 승산비, 정보 이론, 예측 값, 교정 (calibration) (적합도 (goodness-of-fit) 포함), 및 재분류 측정을 이용하는 다른 방식은 문헌 [Cook, "Use and Misuse of the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve in Risk Prediction," Circulation 2007, 115: 928-935]에 따라 요약된다. 마지막으로, 시험에 의해 규정되는 대상체 코호트 (cohort) 내의 위험 비 및 절대적 및 상대적 위험 비는 임상 정확도 및 유용성의 추가의 척도이다. 참조 한계, 식별 한계, 및 위험 역치를 비롯하여 비정상 또는 질환 값을 규정하기 위해 다수의 방법이 빈번하게 사용된다.The "negative predictive value" or "NPV" is calculated by the true speech fraction of TN / (TN + FN) or all the speech test results. It is also essentially influenced by the disease prevalence and pre-test probability of the population for which the trial is intended. For example, a test, for example, O'Marcaigh AS, Jacobson RM, "Estimating The Predictive Value Of A Diagnostic Test, How To ", discussing the specificity, sensitivity, Prevent Misleading Or Confusing Results, "Clin. Ped. 1993, 32 (8): 485-491). Often, for binary disease status classification schemes that use continuous diagnostic test measurements, sensitivity and specificity can be determined by the method described in Pepe et al., &Quot; Limits of the Odds Ratio in Performance of a Diagnostic, Prognostic, or Screening Marker, "Am. (Or black) cut point with an area under the curve (AUC) or only a single value, summarized by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves according to J. Epidemiol 2004, 159 (9): 882-890. Statistics, which is an index that allows the presentation of tests, assays, or the sensitivity and specificity of the method over its entire range. Also, for example, literature [Shultz, "Clinical Interpretation Of Laboratory Procedures," chapter 14 in Teitz, Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry, Burtis and Ashwood (eds.), 4 th edition 1996, WB Saunders Company, pages 192-199] ; And Zweig et al., "ROC Curve Analysis: An Example Showing The Relationships Among Serum Lipid And Apolipoprotein Concentrations In Identifying Subjects With Coronary Artery Disease," Clin. Chem., 1992, 38 (8): 1425-1428. Other ways of using probability functions, multiplication ratios, information theory, predictive values, calibration (including goodness-of-fit), and reclassification measurements are described in Cook, "Use and Misuse of Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve in Risk Prediction, "Circulation 2007, 115: 928-935. Finally, the hazard ratio and absolute and relative risk ratios within the subject cohort defined by the test are additional measures of clinical accuracy and usefulness. A number of methods are frequently used to define abnormal or diseased values, including reference limits, discrimination limits, and risk thresholds.
"분석 정확도"는 측정 과정 자체의 재현가능성 및 예측가능성을 의미하고, 변동 계수와 같은 측정치, 및 상이한 시간, 사용자, 장치 및/또는 시약을 사용한, 동일한 샘플 또는 대조군의 일치 및 교정의 시험에 의해 요약될 수 있다. 새로운 바이오마커의 평가시에 이들 및 다른 고려사항은 또한 문헌 [Vasan, 2006]에 요약되어 있다."Analytical accuracy" means the reproducibility and predictability of the measurement process itself, and can be determined by measuring the same as the coefficient of variation, and testing the matching and calibration of the same sample or control using different times, users, devices and / Can be summarized. These and other considerations in the evaluation of new biomarkers are also summarized in the literature [Vasan, 2006].
"성능"은 특히 임상 및 분석 정확도, 다른 분석 및 공정 특징, 예컨대 사용 특징 (예를 들어, 안정성, 사용 용이성), 보건 경제적 가치, 및 시험 성분의 상대적인 비용을 포함하는, 진단 또는 예후 시험의 전체적인 유용성 및 질에 관련되는 용어이다. 임의의 이들 인자는 우수한 성능, 따라서 시험의 유용성의 원천일 수 있고, 적절한 "성능 계측", 예컨대 관련되는 AUC, 결과 획득 시간, 유효 기간 등에 의해 측정될 수 있다."Performance" refers to the overall performance of a diagnostic or prognostic test, including, in particular, clinical and analytical accuracy, other analytical and process characteristics such as the use characteristics (e.g., stability, ease of use), health economic value, It is a term related to usability and quality. Any of these factors may be a source of good performance, and thus usefulness of the test, and may be measured by appropriate "performance measures ", such as the associated AUC, result acquisition time,
"양성 예측 값" 또는 "PPV"는 TP/(TP+FP) 또는 모든 양성 시험 결과의 진정한 양성 분율에 의해 계산된다. 이것은 시험이 의도되는 집단의 질환 유병률 및 사전검사 확률에 의해 본질적으로 영향받는다.The "positive predictive value" or "PPV" is calculated by the true positive fraction of TP / (TP + FP) or all positive test results. This is essentially influenced by the disease prevalence and pre-test probability of the population for which the trial is intended.
본 발명의 문맥에서 "위험"은 치료에 대한 반응처럼 사건이 특정 기간에 걸쳐 발생할 확률에 관한 것이고, 대상체의 "절대적" 위험 또는 "상대적" 위험을 의미할 수 있다. 절대적 위험은 관련 시간 코호트에 대해 측정 후 실제 관찰을 참고로 하여, 또는 관련 시간 동안 경과가 관찰된 통계학상 유효한 과거 (historical) 코호트로부터 발생한 지수 값을 참고로 하여 측정될 수 있다. 상대적인 위험은 저위험 코호트의 절대적 위험 또는 임상 위험 인자 평가 방법에 따라 상이할 수 있는 평균 집단 위험과 비교한 대상체의 절대적 위험의 비를 의미한다. 제시된 시험 결과에 대한 양성 사건 대 음성 사건의 비율인 승산비가 또한 전환하지 않은 상태로 통상적으로 사용된다 (승산비는 식 p/(1-p)에 따르고, 여기서 p는 사건의 확률이고, (1-p)는 사건이 발생하지 않을 확률임).In the context of the present invention, "risk" refers to the probability that an event will occur over a certain period of time, such as a response to treatment, and may mean an "absolute" or "relative" risk of the subject. The absolute risk can be measured with reference to the actual observation after the measurement for the relevant time cohort, or by reference to the exponent value resulting from a statistically valid historical cohort whose progress has been observed for the relevant time period. Relative risk refers to the absolute risk of a low-risk cohort or the ratio of the absolute risk of an object compared to the mean group risk, which may vary depending on the method of assessing the clinical risk factors. The multiplication ratio, which is the ratio of positive to negative events for the proposed test results, is also commonly used without conversion (the multiplication ratio follows the formula p / (1-p), where p is the probability of the event and -p) is the probability that an event will not occur.
본 발명의 문맥에서 "위험 평가" 또는 "위험의 평가"는 사건 또는 질환 상태가 발생할 수 있는 확률, 승산, 또는 가능성, 한 질환 상태로부터 사건 또는 전환의 발생 비율을 예측하는 것을 포함한다. 위험 평가는 또한 이전에 측정된 집단에 대한 절대적인 또는 상대적인 측면에서 미래의 임상 파라미터, 전통적인 실험 위험 인자 값, 또는 FXS의 다른 지수의 예측을 포함할 수 있다. 본 발명의 방법은 치료에 대한 반응의 연속형 또는 범주형 측정을 수행하고, 이에 따라 반응자 또는 비-반응자로서 규정된 대상체 범주의 위험 스펙트럼의 진단 및 규정을 위해 사용될 수 있다. 범주형 시나리오에서, 본 발명은 반응에 대한 더 높은 위험에서 정상 및 다른 대상 코호트 사이를 식별하기 위해 사용될 수 있다.In the context of the present invention, "risk assessment" or "assessment of risk" includes predicting the probability, multiplication, or likelihood that an event or disease condition may occur, The risk assessment may also include the prediction of future clinical parameters, traditional laboratory risk factor values, or other indices of FXS, either in absolute or relative terms relative to previously measured populations. The methods of the present invention can be used for performing continuous or categorical measurements of response to treatment and thus for diagnosing and defining a risk spectrum of a subject category defined as a respondent or non-respondent. In a categorical scenario, the present invention can be used to identify between normal and other target cohorts at a higher risk for response.
본 발명의 문맥에서 "샘플"은 대상체로부터 단리된 생물학적 샘플이고, 예를 들어, 비제한적으로 전체 혈액, 혈청, 혈장, 뇌척수액 (CSF), 뇌 세포, 또는 임의의 다른 분비물, 배설물, 또는 다른 체액을 포함할 수 있다. "샘플"은 단일 세포 또는 다수 세포 또는 세포의 단편을 포함할 수 있다. 샘플은 또한 조직 샘플이다. 샘플은 뇌 세포 또는 림프구이거나 이를 함유한다. 바람직하게는, 샘플은 말초 혈액 단핵 세포, 예컨대 림프구 또는 단핵구이다. In the context of the present invention, a "sample" is a biological sample isolated from a subject, including but not limited to whole blood, serum, plasma, CSF, brain cells, or any other secretion, . ≪ / RTI > A "sample" may include a single cell or a plurality of cells or a fragment of a cell. The sample is also a tissue sample. The sample is or contains a brain cell or a lymphocyte. Preferably, the sample is a peripheral blood mononuclear cell, such as a lymphocyte or monocyte.
"민감성"은 TP/(TP+FN) 또는 질환 대상체의 진정한 양성 분율에 의해 계산된다."Sensitivity" is calculated by TP / (TP + FN) or by the true positive fraction of the disease subject.
"특이성"은 TN/(TN+FP) 또는 비-질환 또는 정상 대상체의 진정한 음성 분율에 의해 계산된다. "Specificity" is calculated by the true negative fraction of TN / (TN + FP) or non-disease or normal subject.
"통계학상 유의한"은 변경이 단지 우연히 발생할 것으로 예상될 수 있는 것 ("거짓 양성"일 수 있음)보다 더 큼을 의미한다. 통계학적 유의성은 관련 기술분야에 공지된 임의의 방법에 의해 결정할 수 있다. 통상적으로 사용되는 유의성 척도는 데이터 점이 단지 우연의 결과임을 가정하면서, 적어도 제시된 데이터 점만큼 극단적인 결과를 얻을 확률을 나타내는 p-값을 포함한다. 결과는 0.05 이하의 p-값에서 매우 유의한 것으로 간주된다. 바람직하게는, p-값은 0.04, 0.03, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.001 또는 그 미만이다. A "statistically significant" means greater than a change can only be expected to happen by chance (which may be "false positives"). Statistical significance can be determined by any method known in the art. A commonly used significance measure includes a p-value indicating the probability of obtaining an extreme result by at least a given data point, assuming that the data point is only a coincidence result. The results are considered to be highly significant at p-values less than 0.05. Preferably, the p-value is 0.04, 0.03, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.001 or less.
본 발명의 문맥에서 "대상체"는 바람직하게는 포유동물이다. 포유동물은 인간, 비-인간 영장류, 마우스, 래트, 개, 고양이, 말, 또는 소일 수 있고, 이들 예로 제한되지 않는다. 인간 이외의 다른 포유동물은 FXS의 동물 모델을 나타내는 대상체로서 유용하게 사용될 수 있다. 대상체는 남성 또는 여성일 수 있다. 대상체는 FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애가 존재하고 있거나 또는 존재할 것으로 의심된다. "Subject" in the context of the present invention is preferably a mammal. The mammal may be a human, a non-human primate, a mouse, a rat, a dog, a cat, a horse, or a pet, and is not limited to these examples. Other mammals other than humans may be usefully used as subjects to represent animal models of FXS. The subject may be male or female. The subject is suspected of, or is present, FXS or other cognitive disorders.
"TN"은 진정한 음성이고, 질환 상태 시험에서 비-질환 또는 정상 대상체를 정확하게 분류하는 것을 의미한다."TN" is true speech, meaning to correctly classify non-diseases or normal subjects in disease state testing.
"TP"는 진정한 양성이고, 질환 상태 시험에서 질환 대상체를 정확하게 분류하는 것을 의미한다. "TP" is true positive, meaning accurate classification of a disease subject in a disease state test.
"전통적인 실험 위험 인자"는 대상체 샘플로부터 단리되거나 유래되고 현재 임상 실험실에서 평가되고 전통적인 전반적 위험 평가 알고리즘에서 사용되는 바이오마커에 대응한다. 취약 X에 대한 다른 전통적인 실험 위험 인자는 관련 기술 분야의 통상의 기술자에게 알려져 있다."Traditional experimental risk factors" correspond to biomarkers isolated or derived from a sample of the subject and currently being evaluated in clinical laboratories and used in conventional overall risk assessment algorithms. Other traditional experimental risk factors for fragile X are known to those of ordinary skill in the relevant art.
본 발명의 방법The method of the present invention
본원에 개시된 방법은 FXS 및 다른 인지 장애에 대한 메타독신 치료 및/또는 요법을 받고 있는 대상체 및 FXS 및 다른 인지 장애를 진단받은 대상체에게 사용된다.The methods disclosed herein are used for subjects undergoing meta-cognitive therapy and / or therapy for FXS and other cognitive disorders, and subjects diagnosed with FXS and other cognitive disorders.
본 발명의 방법은 대상체에서 FXS 및 다른 인지 장애의 치료를 모니터링하고 메타독신 치료로부터 이익을 얻게 될 대상체를 선택하기 위해 유용하다. The methods of the present invention are useful for monitoring treatment of FXS and other cognitive disorders in a subject and for selecting subjects to benefit from metacortin therapy.
일반적으로, FXS의 징후 및 증상은 다음과 같은 5개의 범주에 해당한다: 지능및 학습; 신체적, 사회적 및 정서적, 말하기 및 언어 및 통상적으로 취약 X와 연관되거나 취약 X와 특징을 공유하는 지각 장애. 예를 들어, FXS가 존재하는 개체는 손상된 지적 기능, 사회적 불안증, 언어 장애 및 특성 감각에 대한 민감성을 갖는다.In general, the signs and symptoms of FXS fall into the following five categories: intelligence and learning; Physical, social and emotional, speech and language, and perceptual disorders commonly associated with fragile X or sharing features with fragile X. For example, individuals in which FXS exists have susceptibility to impaired intellectual function, social anxiety, speech disturbances, and personality traits.
인지 장애는 정신 작용의 기능장애/손상이 중심 증상을 구성하는 일군의 장애를 포함한다. 인지 장애는 신경유전적 인지 장애 또는 행동 인지 장애를 포함한다.Cognitive disorders include a group of disorders in which dysfunction / impairment of mental function constitutes a central symptom. Cognitive disorders include neurogenetic cognitive disorders or behavioral cognitive disorders.
인지 장애는 발달 장애, 주의력 결핍 과잉행동 장애 (ADHD), 자폐 범주성 장애, 알츠하이머 (Alzheimer) 질환, 정신분열증 및 뇌혈관 질환을 포함한다. Cognitive disorders include developmental disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorders, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and cerebrovascular disease.
자폐 범주성 장애 및 자폐 증상은 취약 X 증후군이 있는 개체와 일반적으로 연관된다. 자폐증의 징후 또는 증상은 유의한 언어 지연, 사회적 및 의사소통 문제, 및 이상한 행동 및 관심을 포함한다. 자폐 장애가 있는 많은 사람은 또한 지적 장애를 갖고 있다. Autism spectrum disorders and autism symptoms are generally associated with individuals with fragile X syndrome. Signs or symptoms of autism include significant language delay, social and communication problems, and strange behaviors and concerns. Many people with autism disorders also have intellectual disabilities.
대상체 샘플 내의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비의 결정은 FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애의 치료 과정의 모니터링을 허용한다. 상기 방법에서, 생물학적 샘플은 치료를 받고 있는 대상체로부터 제공된다. 요구될 경우, 생물학적 샘플은 치료 전, 동안 또는 후의 다양한 시점에서 대상체로부터 얻는다. 이어서, 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 계산한 후, 대조군 값과 비교한다. 대조군 값은 그의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비가 알려져 있거나 지수 값인 대조군 개체 또는 집단이다. 참조 샘플 또는 지수 값은 발병하지 않은 (예를 들어, FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애가 이환되지 않은) 하나 이상의 개체로부터 얻거나 유도될 수 있다. 별법으로, 참조 샘플 또는 지수 값은 치료 전에 대상체로부터 얻거나 유도될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 샘플은 치료의 진행을 모니터링하기 위해 초기 치료를 받지 않은 대상체로부터 후속 치료 후에 수집될 수 있다. 참조 샘플 또는 지수 값은 초기 치료 후에 대상체로부터 얻거나 유도될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 샘플은 치료의 진행을 모니터링하기 위해 초기 치료 및 FXS에 대한 후속 치료를 받은 대상체로부터 수집될 수 있다.Determination of the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein in a subject sample allows monitoring of the course of treatment of FXS or other cognitive disorders. In the method, the biological sample is provided from a subject undergoing treatment. If desired, biological samples are obtained from the subject at various times before, during, or after treatment. The ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein is then calculated and compared to the control value. Control values are control individuals or populations whose ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein is known or indexed. A reference sample or index value may be derived or derived from one or more individuals that are not onset (e. G., Without FXS or other cognitive impairment). Alternatively, the reference sample or index value may be obtained or derived from the subject prior to treatment. For example, a sample may be collected after a subsequent treatment from an untreated subject to monitor the progress of the treatment. The reference sample or index value may be obtained or derived from the subject after the initial treatment. For example, a sample may be collected from an initial therapy and a subject receiving subsequent therapy for FXS to monitor the progress of the treatment.
또 다른 실시양태에서, 참조 값은 지수 값 또는 기준선 값이다. 지수 값 또는 기준선 값은 FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애를 앓고 있지 않은 개체로부터의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비의 복합 표본이다.In another embodiment, the reference value is an exponent value or a baseline value. The exponent value or baseline value is a composite sample of the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein from individuals not suffering from FXS or other cognitive impairment.
치료의 유효성은 시간에 걸쳐 대상체로부터 얻은 샘플 내의 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 결정하고 비들을 비교함으로써 모니터링될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 제1 샘플은 대상체가 치료 받기 전에 얻고, 하나 이상의 후속적인 샘플은 대상체의 치료 후 또는 치료 동안 채취할 수 있다.The effectiveness of treatment can be monitored by determining the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein in the sample over time and comparing the ratios. For example, the first sample may be obtained before the subject is treated, and one or more subsequent samples may be taken after or during treatment of the subject.
"효능 있는"은 치료가 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 FXS 또는 다른 인지 장애가 없는 대상체로부터의 대응하는 비와 유사하게 만드는 것을 의미한다. 효능은 FXS의 진단, 확인, 또는 치료를 위한 임의의 공지의 방법과 함께 결정될 수 있다. "Efficacy" means that the treatment makes the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein to total ERK and Akt protein similar to the corresponding ratio from subjects without FXS or other cognitive impairment. Efficacy may be determined with any known method for diagnosis, identification, or treatment of FXS.
인산화된 ERK 및 Akt와 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질은 관련 기술분야에 공지된 임의의 방법, 예컨대 면역 검정에 의해 결정할 수 있다. The phosphorylated ERK and Akt and total ERK and Akt protein may be determined by any method known in the art, e.g., immunoassays.
본 발명의 성능 및 정확도 척도The performance and accuracy measures of the present invention
본 발명의 성능 및 따라서 절대적 및 상대적 임상 유용성은 상기한 많은 방법으로 평가할 수 있다. 진단, 예측, 또는 예후 시험, 검정, 또는 방법의 정확도는 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 대 총 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 비를 기초로 하여 메타독신 치료에 반응성인 대상체와 그렇지 않은 대상체를 구별하는 시험, 검정, 또는 방법의 능력에 관련된다. 정상과 비정상 사이의 비의 차이는 바람직하게는 통계학상 유의하다.The performance and thus the absolute and relative clinical utility of the present invention can be evaluated in a number of ways as described above. The accuracy of a diagnostic, prognostic, or prognostic test, assay, or method is based on the ratio of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein versus total ERK and Akt protein, and tests to distinguish between subjects that are responsive to meta- , Or the ability of the method. The difference in the ratio between normal and abnormal is preferably statistically significant.
따라서, 대상체의 상태를 평가하기 위해 제시된 의료 시험, 검정, 또는 방법의 정확도 및 유용성을 평가할 때, 항상 민감성 및 특이성을 모두 고려하고, 민감성 및 특이성은 차단점의 범위에 걸쳐 유의하게 상이할 수 있기 때문에 민감성 및 특이성이 어떠한 차단점에서 보고되는지 유의하여야 한다. 모든 잠재적인 차단점 값을 포함하는 통계학, 예컨대 AUC의 사용은 본 발명을 사용하는 대부분의 범주성 위험 척도에 대해 바람직한 반면, 연속 위험 척도의 경우, 관찰된 결과 또는 다른 최적 표준 (gold standard)에 대한 적합도 및 교정의 통계학이 바람직하다.Therefore, when assessing the accuracy and usefulness of the proposed medical tests, tests, or methods for assessing the condition of a subject, always consider sensitivity and specificity, and sensitivity and specificity may be significantly different across the range of the interception point It should be noted that sensitivity and specificity are reported at any interception point. The use of statistical, including AUC, including all potential cut-off point values is desirable for most categorical risk measures using the present invention, while for continuous risk measures, the observed results or other gold standard Statistics of fit and calibration are desirable.
상기 통계학을 사용하여, "진단 정확도의 허용되는 정도"는 본원에서 AUC (시험 또는 검정에 대한 ROC 곡선 하 면적)가 적어도 0.60, 바람직하게는 적어도 0.65, 보다 바람직하게는 적어도 0.70, 바람직하게는 적어도 0.75, 보다 바람직하게는 적어도 0.80, 가장 바람직하게는 적어도 0.85인 시험 또는 검정으로 규정된다.Using the above statistics, the "acceptable degree of diagnostic accuracy" is defined herein as an AUC (area under the ROC curve for test or assay) of at least 0.60, preferably at least 0.65, more preferably at least 0.70, 0.75, more preferably at least 0.80, and most preferably at least 0.85.
"매우 높은 정도의 진단 정확도"는 AUC (시험 또는 검정에 대한 ROC 곡선 하 면적)가 적어도 0.80, 바람직하게는 적어도 0.85, 보다 바람직하게는 적어도 0.875, 바람직하게는 적어도 0.90, 보다 바람직하게는 적어도 0.925, 가장 바람직하게는 적어도 0.95인 시험 또는 검정을 의미한다.A "very high degree of diagnostic accuracy" means that the AUC (area under the ROC curve for test or assay) is at least 0.80, preferably at least 0.85, more preferably at least 0.875, preferably at least 0.90, more preferably at least 0.925 , And most preferably at least 0.95.
임의의 시험의 예측 값은 시험의 민감성 및 특이성, 및 시험되는 집단 내의 병태의 유병률에 따라 결정된다. 상기 개념은 베이즈 정리 (Bayes' theorem)를 기초로 하여, 스크리닝되는 병태가 개체 또는 집단에 존재할 가능성 (사전검사 확률)이 클수록, 양성 시험의 유효성이 크고 결과가 진정한 양성일 가능성이 더 큼을 제시한다. 따라서, 병태가 존재할 가능성이 낮은 임의의 집단에서 시험을 사용할 때의 문제는 양성 결과가 제한된 값을 갖는다 (즉, 거짓 양성일 가능성이 크다)는 것이다. 이와 유사하게, 위험이 매우 높은 집단에서, 음성 시험 결과는 거짓 음성일 가능성이 더 높다.The predictive value of any test is determined by the sensitivity and specificity of the test, and the prevalence of the condition within the population being tested. Based on Bayes' theorem, the concept suggests that the greater the likelihood that the screened condition exists in an individual or group (the pre-test probability), the greater the likelihood that the test will be more effective and the outcome will be genuine . Thus, the problem with using a test in any population with a low likelihood of a condition is that the positive outcome has a limited value (ie, it is likely to be false positives). Similarly, in very high risk groups, the results of the negative test are more likely to be false negative.
그 결과, ROC 및 AUC는 낮은 질환 유병률 (매년 1% 미만의 발생률 (발생 정도), 또는 특정 시간대에 걸쳐 10% 미만의 누적 유병률을 보이는 집단으로 규정되는)의 시험 집단에서 시험의 임상 유용성에 대해 오도할 수 있다. 별법으로, 본 개시내용의 다른 곳에서 규정되는 절대적 위험 및 상대적 위험 비는 임상 유용성 정도를 결정하기 위해 사용될 수 있다. 시험되는 대상체의 집단은 또한 시험 측정값에 의해 사분위수 (quartile)로 분류되고, 여기서 상위 사분위수 (집단의 25%)는 치료 비반응성에 대해 가장 높은 상대적인 위험을 갖는 대상체의 군을 포함하고, 하위 사분위수는 치료 비반응성에 대해 가장 낮은 상대적인 위험을 갖는 대상체의 군을 포함한다. 일반적으로, 낮은 유병률 집단에서 상위 사분위수로부터 하위 사분위수까지 2.5배 초과의 상대적인 위험을 갖는 시험 또는 검정으로부터 유래된 값은 "높은 정도의 진단 정확도"로 간주되고, 각각의 사분위수에 대해 5 내지 7배의 상대적인 위험을 갖는 것은 "매우 높은 정도의 진단 정확도"로 간주된다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 각각의 사분위수에 대해 단지 1.2 내지 2.5배의 상대적인 위험을 갖는 시험 또는 검정으로부터 유래된 값은 임상적으로 유용하고 질환에 대한 위험 인자로서 널리 사용되고; 이것은 총 콜레스테롤 및 미래 사건의 예측에 대한 많은 염증 바이오마커의 경우에도 그러하다. 종종 상기 더 낮은 진단 정확도 시험은 상기 언급된 전반적 위험 평가 지수를 사용하여 수행하는 바와 같이 치료적 개입을 위해 의미있는 임상 역치를 유도하기 위해 추가의 파라미터와 조합되어야 한다.As a result, the ROC and AUC are related to the clinical usefulness of the test in a test population of low disease prevalence (incidence less than 1% per year (incidence), or cumulative prevalence of less than 10% over a certain period of time) It can be misleading. Alternatively, the absolute risk and relative risk ratio specified elsewhere in this disclosure may be used to determine the degree of clinical utility. The population of subjects being tested is also classified as quartiles by test measures, where the upper quartiles (25% of the population) comprise the group of subjects with the highest relative risk for treatment non-responsiveness, The lower quartiles include the group of subjects with the lowest relative risk for treatment non-responsiveness. In general, values derived from tests or tests that have a relative risk greater than 2.5 times from the upper quartile to the lower quartile in the low prevalence group are considered "high degree of diagnostic accuracy" Having a seven-fold relative risk is considered to be "a very high degree of diagnostic accuracy." Nevertheless, values derived from tests or tests that have a relative risk of only 1.2 to 2.5 times for each quartile are clinically useful and widely used as risk factors for disease; This is also the case for many cholesterol and many inflammatory biomarkers for predicting future events. Often, the lower diagnostic accuracy test should be combined with additional parameters to derive a meaningful clinical threshold for therapeutic intervention, as is done using the above-mentioned overall risk rating index.
보건 경제적 유용성 함수는 각각의 임상 및 경제적 가치의 실제 척도를 기초로 하여 잠재적인 범주적 시험 성과에 가중치를 주는 것으로 이루어진, 제시된 시험의 성능 및 임상적 가치를 측정하는 또 다른 수단이다. 보건 경제적 유용성 함수는 정확한 분류의 이익 및 시험된 대상체의 오류 분류의 비용에 대해 경제적 가치를 특이적으로 할당하기 때문에, 보건 경제적 성능은 정확도에 밀접하게 관련된다. 성능 척도로서, 시험의 표적 가치를 초과하는 시험당 보건 경제적 가치 (시험 비용 차감 전)의 증가를 유도하는 성능 수준을 달성하기 위해 시험을 필요로 하는 것은 이상한 것이 아니다.The health economic utility function is another means of measuring the performance and clinical value of the proposed test, which is based on weighting the potential categorical test performance based on the actual scale of each clinical and economic value. The health economic performance is closely related to the accuracy because the health economic usability function specifically assigns economic value to the benefit of the correct classification and the cost of the error classification of the tested object. As a performance measure, it is not uncommon to require testing to achieve a performance level that leads to an increase in the health economic value per test (before test cost reduction) exceeding the target value of the test.
임상 알고리즘의 구축Construction of clinical algorithm
임의의 공식을 사용하여 결과를 본 발명의 실행에 유용한 지수로 조합할 수 있다. 상기 나타낸 바와 같이, 비제한적으로, 상기 지수는 다양한 다른 지표 중에서 메타독신에 반응할 확률, 가능성, 절대적 또는 상대적 기회를 나타낼 수 있다. 이것은 특정 기간 또는 시간대, 또는 잔여 생애 위험에 대한 것이거나, 또는 간단히 또 다른 참조 대상체 집단에 상대적인 지수로서 제공될 수 있다.Any formula may be used to combine the results into an index useful for the practice of the present invention. As indicated above, and without limitation, the index may represent probability, likelihood, absolute or relative opportunity to respond to metadoxine among various other indicators. This may be for a particular time period or time zone, or for residual lifetime risk, or simply as an exponent relative to another set of reference objects.
다양한 바람직한 공식이 본원에서 설명되지만, 본원에서 및 상기 정의에서 언급된 것 이외의 여러 다른 모델 및 공식 종류가 통상의 기술자에게 잘 공지되어 있다. 사용되는 실제 모델 종류 또는 공식은 훈련 집단에서 그의 결과의 성능 및 정확도 특징을 기초로 하여 잠재적인 모델의 분야로부터 그 자체가 선택될 수 있다. 바람직한 공식은 광범한 클래스의 통계학상 분류 알고리즘, 및 특히 식별 분석의 사용을 포함한다. 식별 분석의 목표는 이전에 확인된 세트의 속성으로부터 클래스 구성원 수를 예측하는 것이다. 선형 식별 분석 (LDA)의 경우에, 일부 기준에 의해 군 중에서 분리를 최대화하는 속성의 선형 조합이 확인된다. 속성은 상이한 역치 (ELDA) 또는 다변량 분산 분석 (MANOVA)을 기초로 한 스테핑 (stepping) 알고리즘을 사용하는 고유유전자 기반 방식을 통해 LDA에 대해 확인될 수 있다. 호텔링-롤리 (Hotelling-Lawley) 통계학을 기초로 하여 분리가 이루어지지 않는 확률을 최소화하는 전진, 후진, 및 단계적 알고리즘을 수행할 수 있다.While various preferred formulas are described herein, various other models and formulation types are well known to those of ordinary skill in the art and other than those mentioned herein. The actual model type or formula used may itself be selected from the field of potential models based on the performance and accuracy characteristics of the results in the training population. The preferred formulas include the use of a broad class of statistical classification algorithms, and in particular identification analysis. The goal of the identification analysis is to predict the number of class members from the previously identified set of attributes. In the case of linear discriminant analysis (LDA), a linear combination of attributes that maximize separation in the group is identified by some criterion. Attributes can be identified for LDA through a unique gene based approach using a stepping algorithm based on different threshold values (ELDA) or multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA). Based on the Hotelling-Lawley statistics, it is possible to perform forward, backward, and step-by-step algorithms that minimize the probability of non-separation.
고유유전자-기반 선형 식별 분석 (ELDA)은 문헌 [Shen et al. (2006)]에 의해 개발된 속성 선택 기술이다. 공식은 가장 중요한 고유벡터 (eigenvector)와 연관된 속성을 확인하기 위해 변형된 고유 분석을 이용하여 다변량 프레임워크에서 속성 (예를 들어 바이오마커)을 선택한다. "중요한"은 일부의 역치에 대해 분류가 시도되는 샘플 사이에서 차이의 대부분의 변화를 설명하는 고유벡터로서 규정된다.Dedicated gene-based linear discriminant analysis (ELDA) is described in Shen et al. (2006)]. The formula selects attributes (eg, biomarkers) in the multivariate framework using modified eigenvalue analysis to identify attributes associated with the most important eigenvectors. "Important" is defined as an eigenvector describing most of the variation of the differences between the samples to be classified for some thresholds.
지지 벡터 머신 (SVM)은 2개의 클래스를 분리하는 초평면 (hyperplane)을 발견하기 위해 시도하는 분류 방식이다. 상기 초평면은 지지 벡터, 초평면으로부터 정확히 경계간 (margin) 거리인 데이터 점을 포함한다. 분리 초평면이 데이터의 현재 차원에 존재하지 않는 가능한 사건에서, 차원수 (dimensionality)는 원래의 변수의 비-선형 함수를 취하여 데이터를 보다 큰 차원으로 투사함으로써 크게 팽창된다 (Venables and Ripley, 2002). 요구되지는 않지만, SVM에 대한 속성의 여과는 종종 예측을 개선한다. 속성 (예를 들어, 바이오마커)은 최적의 단변량 속성을 선택하기 위해 비-파라미터 크루스칼-월리스 (Kruskal-Wallis) (KW) 시험을 사용하여 지지 벡터 머신에 대해 확인될 수 있다. 랜덤 포레스트 (RF, Breiman, 2001) 또는 반복적 분할 (RPART, Breiman et al. 1984)이 또한 별개로 또는 가장 중요한 바이오마커 조합을 확인하기 위해 조합하여 사용될 수 있다. KW 및 RF는 둘 모두 많은 속성이 전체로부터 선택될 것을 필요로 한다. RPART는 이용가능한 바이오마커의 하위세트를 사용하여 단일 분류 트리를 생성한다.A support vector machine (SVM) is a classification scheme that attempts to find a hyperplane that separates two classes. The hyperplane includes a support vector, a data point that is exactly a margin distance from the hyperplane. In possible events where the separating hyperplane is not present in the current dimension of the data, the dimensionality is greatly expanded by taking the nonlinear function of the original variable and projecting the data to a larger dimension (Venables and Ripley, 2002). Although not required, filtering of attributes to SVMs often improves prediction. Attributes (e.g., biomarkers) can be verified against the support vector machine using a non-parameter Kruskal-Wallis (KW) test to select the optimal univariate attribute. Random forests (RF, Breiman, 2001) or iterative partitions (RPART, Breiman et al. 1984) can also be used in combination to identify distinct or most important biomarker combinations. Both KW and RF require that many attributes be selected from the whole. RPART generates a single classification tree using a subset of available biomarkers.
ERK 및/또는 Akt 측정의 개별 인산화의 결과를 예측 공식에 적용하기 전에 보다 가치있는 정보 형태로 미리 처리하기 위해 다른 공식이 사용될 수 있다. 특히, 통상적인 수학적 전환, 예컨대 대수 또는 로지스틱 함수를 사용하여 집단의 평균 값에 관하여 정규 분포 또는 다른 분포 위치 등으로서 바이오마커의 표준화 결과는 모두 통상의 기술자에게 잘 공지되어 있다. 임상 파라미터, 예컨대 연령, 성별, 인종, 또는 성을 기초로 한 표준화의 세트가 특히 관심을 끌고, 여기서 특정 공식이 클래스 내의 대상체에 대해서만 사용되거나 또는 입력으로서 임상 파라미터를 연속적으로 조합한다. 다른 경우에, 분석물-기반 바이오마커는 후에 공식에 제시되는 계산된 변수로 조합될 수 있다. Other formulas can be used to pre-process the results of individual phosphorylation of ERK and / or Akt measurements into more valuable information forms before applying them to the predictive formula. In particular, standard mathematical conversions, such as normal distribution or other distribution locations with respect to the mean value of a population using logarithmic or logistic functions, are well known to those of ordinary skill in the art of standardizing biomarkers. A set of standardizations based on clinical parameters, such as age, gender, race, or gender, is of particular interest, wherein a particular formula is used only for a subject within a class or continuously combines clinical parameters as input. In other cases, the analyte-based biomarker may later be combined with the calculated variables presented in the formula.
잠재적으로 정규화되는 1명의 대상체의 개별 파라미터 값에 추가로, 모든 대상체, 또는 대상체의 임의의 알려진 클래스에 대한 전체 예측 공식은 문헌 [D'Agostino et al., (2001) JAMA 286:180-187]에 개관된 기술, 또는 다른 유사한 표준화 및 재교정 기술에 따라 집단의 예상된 유병률 및 평균 바이오마커 파라미터 값에 대한 조정을 기초로 하여 그 자체가 재교정되거나 다른 방식으로 조정될 수 있다. 상기 역학적 (epidemiological) 조정 통계학은 기기 판독가능하거나 다른 방식을 판독가능한, 모델에 제시된 과거 데이터의 등록을 통해, 또는 때때로 저장된 샘플 또는 언급 대상의 상기 파라미터의 이전 연구 및 통계학에 대한 후향 질의 (retrospective query)를 통해 연속적으로, 포착, 확인, 개선 및 업데이트될 수 있다. 공식 재교정 또는 다른 조정의 대상일 수 있는 추가의 예는 승산비의 제한에 대해 문헌 [Pepe, M. S. et al., 2004]; ROC 곡선에 관해 문헌 [Cook, N. R., 2007]에 의해 연구에서 사용된 통계학을 포함한다. 마지막으로, 분류기 (classifier) 공식의 수치 결과는 절대적 위험을 교정하고 분류기 또는 위험 공식의 다양한 수치 결과에 대한 신뢰 구간을 제공하기 위해 그 자체가 그 기준에 의해 실제 임상 집단 및 연구 결과 및 관찰된 종점으로 처리 후에 변환될 수 있다. 이것의 예는 실제 임상 연구를 사용하여 유도되고 제노믹 헬쓰, 인크. (Genomic Health, Inc., 미국 캘리포니아주 레드우드 시티)의 온코타입 (Oncotype) Dx 제품에서 재발 점수 공식의 출력에 대해 선택되는, 절대적 위험 및 이 위험에 대한 신뢰 구간의 제시이다. 추가의 변형은 분류기의 출력 또는 위험 공식을 기초로 하고 그의 임상 파라미터, 예컨대 연령 또는 성별에 의해 규정되고 선택되는 연구의 보다 작은 하위-집단을 조정하는 것이다.In addition to the individual parameter values of one potentially normalized object, the overall predictive formula for all objects, or for any known class of objects, can be found in D'Agostino et al. (2001) JAMA 286: 180-187 , Or other similar standardization and re-calibration techniques, may be recalibrated or otherwise adjusted itself based on adjustments to the expected prevalence and average biomarker parameter values of the population. The epidemiological adjustment statistic may be stored either in a machine-readable or otherwise readable manner, through the registration of historical data presented in the model, or in a retrospective query Captured, verified, improved, and updated over the network. A further example, which may be the subject of formal recalibration or other adjustments, is Pepe, M. S. et al., 2004; Includes the statistics used in the study by Cook, N. R., 2007 on ROC curves. Finally, the numerical results of classifier formulas can be used to correct absolute risks and to establish confidence intervals for the various numerical results of classifiers or risk formulations, Lt; / RTI > Examples of this are derived using actual clinical studies and are described in Genomics Health, Inc. And the confidence interval for this risk, chosen for the output of the recall score formula in the Oncotype Dx product of Genomic Health, Inc. (Redwood City, CA, USA). A further variant is to adjust the smaller sub-populations of studies defined and selected by their clinical parameters, such as age or gender, based on the output of the classifier or risk formula.
실시예Example
실시예Example 1: 일반적인 방법 1: general method
본원에 기재된 실시예는 아래 일반적으로 설명하는 시약 및 방법을 사용하여 수행하였다. The examples described herein were carried out using the reagents and methods generally described below.
실험 동물Experimental animal
Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 (KO2) 마우스 (The Dutch-Belgium Fragile X Consortium, 1994)를 초기에 잭슨 래보래토리 (Jackson Laboratory)로부터 입수하고, 야생형 (WT) 한배자손을 C57BL/6J 배경에서 생성하고, 8세대 초과 동안 C57BL/6J 배경에 대해 반복적으로 역교배하였다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스를 동일한 유전자형의 군으로, 12h 명암 사이클을 갖는 온도 및 습도 제어실 내에 수용하였다 (오전 7시부터 오후 7시까지 조명; 시험은 조명기 동안 수행하였다). 사료 및 물을 자유롭게 (ad libitum) 이용가능하도록 하면서 수용실 내에서 실내 온도 및 습도를 연속적으로 기록하였다. 행동 실험 동안 2 또는 6개월령의 건강한 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 그들의 야생형 한배자손 (N = 10마리 마우스/치료군)에 대해 시험을 수행하였다. 마우스를 시판 플라스틱 케이지 내에 수용하고, 영국 동물에 관한 과학적 실험 법안 (UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986)의 요건에 따라 실험을 수행하였다. 유전자형 및 약물 치료에 대해 모르는 실험자가 모든 실험을 수행하였다. 임의의 실험을 수행하기 전에 동물에게 1주의 최소 적응 기간을 허용하였다. 적응 기간 동안 예방 또는 치료적 처치를 투여하지 않았다. Fmr1 null mouse (KO2) mice (The Dutch-Belgium Fragile X Consortium, 1994) were initially obtained from Jackson Laboratory and wild-type (WT) clones were generated in the C57BL / 6J background, Repeated crosses over C57BL / 6J background for generation excess. Fmr1 null mice were housed in a temperature and humidity control room with the same genotype group and a 12 h contrast cycle (illumination from 7 am to 7 pm; the test was performed during the fixture). Room temperature and humidity were continuously recorded in the storage room, allowing feed and water to be freely available (ad libitum). During the behavioral tests, tests were performed on healthy Fmr1 calf mice at 2 or 6 months of age and their wild-type offspring (N = 10 mice / treatment group). The mice were housed in commercial plastic cages and experiments were conducted according to the requirements of the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures Act, 1986). All the experiments were performed by the experimenter who did not know about genotype and drug treatment. Animals were allowed a minimum acclimatization period of one week prior to performing any experiment. No prophylactic or therapeutic treatment was given during the adaptation period.
약물drug
연구 1 (실시예 2)을 위해, 메타독신을 염수에 용해시키고, 7일 동안 1일 1회 100, 150, 또는 200 mg/kg의 용량으로 복강내 투여하였다. 연구 2 (실시예 3, 생체내 시험)를 위해, 메타독신을 염수에 용해시키고, 7일 동안 1일 1회 150 mg/kg/일의 복강내 용량 또는 150 또는 300 mg/kg/일 (0.1 ml의 부피)의 경구 용량으로 투여하였다. 연구 2 (시험관 내 시험)를 위해, 메타독신을 5시간 동안 300 μΜ의 농도로 투여하였다. 모든 경우에, 염수를 비히클 (대조군)로서 사용하였다. For Study 1 (Example 2), metadoxine was dissolved in saline and administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 100, 150, or 200 mg / kg once daily for 7 days. For study 2 (Example 3, in vivo testing), metadoxin was dissolved in saline and administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 150 mg / kg / day once daily for 7 days or at a dose of 150 or 300 mg / kg / day (0.1 ml < / RTI > volume). For Study 2 (in vitro study), metadoxine was administered at a concentration of 300 μM for 5 hours. In all cases, saline was used as vehicle (control).
행동 시험Behavior test
사회적 상호작용 및 사회적 인지 기억: 마우스는 접근하기, 따라다니기, 냄새맡기, 몸단장하기, 공격적 만남, 성적 상호작용, 육아 행동, 보금자리 짓기 (nesting), 및 한 무리 (group huddle)로의 수면을 비롯한, 쉽게 점수 매겨지는 사회적 행동에 참여하는 사회적 종이다. 마우스에서 사회적 접근은 새로운 마우스를 향한 냄새맡기 지속시간에 의해 평가하였다. Social Interaction and Social Cognitive Memory : The mouse has a variety of functions, including approaching, following, smelling, grooming, aggressive encounters, sexual interactions, parenting behaviors, nesting, and sleeping in a group huddle , A social species that participates in social behaviors that are easily scored. The social approach in mice was assessed by the duration of the smell to the new mouse.
마우스를 바닥에 신선한 나뭇조각을 깔아놓은, 성체의 가정용 케이지과 동일한 크기의 시험 무대/케이지 (40x23x12 cm 케이지, 마우스를 쉽게 보도록 퍼스펙스 (Perspex) 덮개가 있는)에 넣었다. 배경 마우스 냄새는 시험에 앞서 일부 비-실험 마우스를 장치 내에 넣음으로써 생성하였다. 마우스를 시험 10-15 min 전에 실험실로 옮겼다. 시험 대상체 및 준성체 (juvenile)를 시험 케이지 내에 동시에 넣었다. 시험한 마우스에 의한 자극 준성체를 향한 냄새맡기 및 가까이 따라다니기 (꼬리로부터 <2 cm)로서 정의된 사회적 조사의 총 지속시간 및 한차례 조사의 수를 3 min 동안 평가하였다. 30 min 후에, 동일한 자극 준성체를 사용하여 시험을 반복하였다. 수집한 데이터 파라미터는 습득 및 인식을 위한 한차례 냄새맡기의 총 지속시간 및 총수였다. 시험 2/시험 1+2로서 정의한 사회적 기억 비를 유도하였다. 따라서, 기억 없음 (예를 들어 20/(20+20)) =0.5이고, 기억 (예를 들어 10/(20+10)) =<0.5이다. The mouse was placed in a test stage / cage (40x23x12 cm cage, with a Perspex cover for easy viewing of the mouse) that was the same size as the adult household cage, with a fresh piece of wood on the floor. The background mouse smell was generated by placing some non-experimental mice in the apparatus prior to testing. The mice were transferred to the laboratory 10-15 min before the test. The test subject and juvenile were simultaneously placed in the test cage. The total duration of the social survey defined as sniffing and closely following (2 cm from the tail) and the number of one-time surveys for the stimulus subspecies by the tested mice were evaluated for 3 min. After 30 min, the test was repeated using the same stimulus generators. The collected data parameters were the total duration and the total number of odors taken for learning and recognition. The social memory ratio defined as Test 2 / Test 1 + 2 was derived. Therefore, no memory (for example, 20 / (20 + 20)) = 0.5, and memory (for example, 10 / (20 + 10)) = 0.5.
Y형 미로 변경: 2개의 과제를 실행하였다. 제1 과제는 아암 (arm) 입장 사이에 자발 변경의 비학습 평가이었다. 제2 과제는 공간 참조 기억 과제이고, 여기서 동물은 2개의 아암 중 어느 것에 사료 보상의 미끼가 있는지 학습하였다. 훈련 시작 전날에, 마우스가 5 min 동안 미로를 자유롭게 탐색하도록 하였다. 이어서, 이들을 2개의 시험으로 실험하였고, 하나는 사료가 좌측 아암에 놓이는 것이고, 다른 하나는 사료가 우측 아암에 배치되는 것이다. 상기 절차는 아암 중 하나에 대한 선호의 발생을 방지하였다. Y-type maze change : Two tasks were carried out. The first challenge was the non-learning assessment of voluntary changes between arm positions. The second task is a spatial reference memory task where the animal learned which of the two arms had bait of rewarding feed. On the day before training began, the mice were allowed to freely navigate the maze for 5 min. They then experimented with two tests, one for the feed on the left arm and the other for the feed on the right arm. This procedure prevented the occurrence of preference for one of the arms.
Y형 미로 수조 미로: 투명한 퍼스펙스 Y형 미로를 20℃에서 2 cm 물로 채웠다. 이것은 마우스가 하나의 아암의 먼 단부에서 출구 튜브로 헤엄친 후 미로를 떠나도록 동기화하였다. 미로를 눈에 잘 띄는 시각적 단서로 둘러싸인 방의 중간에 놓았다. Y-type maze water tank Maze : A transparent Perspex Y-type maze was filled with 2 cm of water at 20 ° C. This synchronized the mouse to swing from the far end of one arm to the exit tube and then leave the maze. I put the maze in the middle of the room surrounded by visible visual clues.
보상된 T형 미로 변경: T형의 상승되거나 닫힌 장치 (수평으로 놓인)를 사용하였다. 마우스를 T자형의 기부에 놓고, 줄기의 다른 단부에 인접하는 목표 아암 중 하나를 선택하도록 허용하였다. 2회의 시험을 연달아 수행하였다: 제2 시험에서는 마우스가 이전에 방문하지 않은 아암을 선택하도록 요구하였고, 이것은 제1 선택의 기억을 반영한다 (자발 변경). 동물을 굶기고 변경한 경우에 원하는 사료로 보상함으로써 상기 경향을 강화시켰다. 구체적으로, T형 미로에서 4일의 적응 기간 후에, 보상으로서 달콤한 농축 우유를 받기 위해 마우스가 아암 선택을 변경하도록 훈련시켰다. Compensated T-type maze changes : T-shaped raised or closed devices (lying horizontally) were used. The mouse was placed on the T-shaped base and allowed to select one of the target arms adjacent to the other end of the stem. Two trials were performed consecutively: in the second test the mice were asked to select a previously unarmed arm, reflecting the memory of the first choice (spontaneous change). This tendency was enhanced by compensating for the desired feed when the animal was starved and changed. Specifically, after an adaptation period of 4 days in the T-type maze, mice were trained to change arm selection to receive sweetened concentrated milk as compensation.
연속 주로: 장치는 도색한 목재로 제조한 4개의 연속적인, 직선으로 배열된, 점증적인 불안유발성 주로로 이루어졌다 (각각의 이어지는 주로는 선행 주로보다 더 밝은 색상으로 도색하고/하거나 벽이 더 낮고/낮거나 더 좁았다). 각각의 구역 또는 주로는 길이가 25 cm이었다. 주로 1은 25 cm 높이 벽을 갖고, 폭은 8.5 cm이고, 흑색으로 도색하였다. 0.5 cm 계단이 주로 2로 이어지고, 이것은 폭은 다시 8.5 cm이지만, 1.3 cm 높이 벽을 갖고 회색이었다. 1.0 cm 계단이 주로 3으로 이루어지고, 이것은 폭이 3.5 cm이고 0.8 cm 높이 벽을 갖고 백색이었다. 0.4 cm 계단이 주로 4로 이어지고, 이것은 또한 백색이지만, 폭이 1.2 cm 이고 0.2 cm 높이 벽을 가졌다. 주로 1의 후면이 50 cm 높이로 서있도록 고정함으로써 장치를 상승시켰다. 마우스가 추락하는 경우를 위해 아암 3 및 4 아래에 패딩 (padding)을 제공하였다. 각각의 마우스를 벽을 대면하는 주로 1의 닫힌 단부에 놓았다. 1) 전체 시험 길이 (5 min) + 각각의 아암에 들어가는 대기시간 (latency), 및 2) 주로 1에서 보낸 시간 동안 타이머 (timer)를 시작하였다. 마우스가 4개의 모든 발을 다음 주로에 놓을 때, 주로에 들어간 것으로 간주하였다. 각각의 주로에서 보낸 총 시간 (4개의 모든 발)을 기록하였다. Continuous Main : The device consisted of four consecutive, straight-line, incremental anxiety-provoking principals made of painted wood (each succeeding main being painted in a lighter color than the preceding one and / Low / low or narrow). Each zone or main body was 25 cm in length. Mainly 1 had a 25 cm height wall, 8.5 cm wide, and painted black. The 0.5 cm steps lead mainly to 2, which was 8.5 cm in width, but gray with a 1.3 cm height wall. The 1.0 cm step consists mainly of 3, which was 3.5 cm wide and had a 0.8 cm height wall and was white. The 0.4 cm step leads mainly to 4, which is also white, but with a width of 1.2 cm and a height of 0.2 cm. The device was elevated mainly by fixing the rear side of the 1 so that it stands at a height of 50 cm. Padding was provided beneath arms 3 and 4 for the case of a mouse crash. Each mouse was placed on the closed end of the wall facing one. 1) Total test length (5 min) + latency into each arm, and 2) a timer was started during the time spent in the main one. When the mice placed all four feet on the next week, they were considered to be in the main. The total time spent in each state (all four feet) was recorded.
환경적 공포 조건화: 공포 조건화 실험에서, 마우스를 새로운 환경 (어두운 방)에 넣고, 힌트와 전기 충격 (electric footshock) (0.2 mA, 1초 (연구 1) 또는 0.7 mA, 0.5 sec (연구 2))을 짝을 지어 인가하였다. 후속적으로, 원래 훈련 환경에서 시험할 때, 마우스는 동결반응 (freezing) (Blanchard, 1969) 또는 환경적 공포 조건화로 불리는 자연 방어 반응을 보였다. 동결반응 시간은 마우스가 호흡을 제외한 불가동 행동으로 보낸 시간으로서 정의하였다. 데이터를 시험 기간의 백분율로서 표현하였다. 훈련 기간의 24시간 후에, 마우스를 5 min 동안 훈련실에서 충격 제시 없이 시험하고, 동결반응 행동에 대해 관찰하였다. Environmental fear conditioning : In a fear conditioning experiment, mice were placed in a new environment (dark room), hints and electric footshock (0.2 mA, 1 second (Study 1) or 0.7 mA, 0.5 sec (Study 2) Were paired with each other. Subsequently, when tested in the original training environment, the mice showed a natural defense reaction, called freezing (Blanchard, 1969) or environmental fear conditioning. The freezing time was defined as the time spent by the mouse for inactivity, excluding respiration. The data was expressed as a percentage of the test duration. Twenty-four hours after the training period, the mice were tested in the training room for 5 min without impact presentation and observed for freezing behavior.
통계학: 다변량 분산 분석을 이용하여 데이터를 가로질러 군 차이를 평가하였다. 반복 측정치 ANOVA를 행동 데이터에 대해 수행하였다. 각각의 ANOVA에서 통계학상 유의한 효과는 뉴먼-클스 (Newman-Keuls) 검정 (연구 1) 또는 터키 (Tukey) 검정 (연구 2)를 이용하여 사후 (post hoc) 비교에 따랐다. 0.05 미만의 p 값을 유의한 것으로 간주하였다. Statistics: Multivariate ANOVA was used to evaluate group differences across the data. Repeat measurements ANOVA were performed on behavioral data. A statistically significant effect on each ANOVA was followed by a post hoc comparison using the Newman-Keuls test (Study 1) or the Turkish (Tukey) Test (Study 2). A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
생화학적 시험Biochemical test
인산화된 ERK 및 Akt: Ras-Mek-ERK 및 PI3K-Akt-mToR 신호전달 경로는 시냅스 가소성 (synaptic plasticity)의 변화의 근거가 되는 유전자 전사의 활동 의존적 변경을 매개하는데 관여한다 (Klann and Dever, 2004). 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 발현은 이전에 문헌 (Lopez Verrilli et al., 2009)에 설명된 바와 같이 웨스턴 블롯 (western blot) 분석에 의해 측정하였다. 사용된 항체는 Akt (1/1000) 및 키나제 (ERK)1/2 (1/2000)에 대한 항-포스포특이적 항체 (셀 시그널링 테크놀로지 (Cell Signaling Technology, 미국 매사추세츠주 댄버)이었다. 포스포-ERK에 대한 항체는 포스포-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204)에서 인산화를 검출하는 반면, 포스포-Akt에 대한 항체는 포스포-Akt (Thr308)에서 인산화를 검출한다. 총 Akt 및 ERK1/2 단백질 함량과 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt는, 멤브레인을 항포스포-Akt (1/1000) 및 항포스포-ERK 항체 (1/2000) (셀 시그널링 테크놀로지, 미국 매사추세츠주 댄버)로 블로팅함으로써 평가하였다. Akt 또는 ERK 인산화를 동일한 샘플에서 단백질 함량으로 정규화하고, 기초 수준을 100%로서 간주하여 기초 조건에 관한 변화 %로서 표현하였다. 단백질 부하는 멤브레인을 벗겨내고 β-액틴 항체 (1/1000) (시그마-알드리치 (Sigma-Aldrich), 미국 미주리주 세인트루이스)로 재-블로팅함으로써 평가하였다. 혈액 림프구 내에서 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질 발현을 유동 세포측정법에 의해 측정하였다. 림프구 바이오마커 결정을 위해, 488 nm로 조정한 여기 레이저를 갖는 FACStar 플러스 (벡톤 디킨슨 (Becton Dickinson))을 사용하였고, FITC (GST)로부터 초록 형광을 515-545 nm 대역 (bandpass) 필터를 통해 수집하였다. 평균 FITC 형광 강도를 참조 세포의 형광에 관하여 계산하였다. 평균 세포 형광 강도 (MFI)는 세포당 결합된 Ab 분자의 평균 수에 정비례한다. The phosphorylated ERK and Akt : Ras-Mek-ERK and PI3K-Akt-mToR signaling pathways are involved in mediating activity-dependent changes in gene transcription that are the basis for changes in synaptic plasticity (Klann and Dever, 2004 ). The phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein expression was measured by western blot analysis as previously described in Lopez Verrilli et al., 2009. The antibodies used were anti-phospho-specific antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Danber, Mass., USA) for Akt (1/1000) and kinase (ERK) 1/2 (1/2000) Antibodies to ERK1 / ERK detect phosphorylation in phospho-ERK1 / 2 (Thr202 / Tyr204) whereas antibodies against phosphoAkt detect phosphorylation in phospho-Akt (Thr308) 2 protein content and phosphorylated ERK and Akt were measured by blotting the membrane with anti-phospho-Akt (1/1000) and anti-phospho-ERK antibody (1/2000) (Cell Signaling Technology, Danbury, Mass. Akt or ERK phosphorylation was normalized to the protein content in the same sample and expressed as% change relative to basal conditions, assuming basal level as 100%. Protein loading was done by peeling the membrane and incubating with < RTI ID = (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo. The phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein expression in blood lymphocytes was measured by flow cytometry. For lymphocyte biomarker determination, a FACStar Plus with excitation laser adjusted to 488 nm (< RTI ID = 0.0 > (Becton Dickinson), and green fluorescence from FITC (GST) was collected via a 515-545 nm bandpass filter. Average FITC fluorescence intensities were calculated for the fluorescence of reference cells, The intensity (MFI) is directly proportional to the average number of Ab molecules bound per cell.
뉴런 형태학: 재태 17.5의 배아일 (E17.5)의 야생형 및 Fmr1 KO 태아 마우스로부터 해마 세포 배양액을 제조하였다. 마우스를 경추 탈골로 치사시키고, 분리시킨 해마 세포를 15 mm 다중웰 용기 (팔콘 프리마리아 (Falcon Primaria)) 내에 플레이팅하였다. 시험관 내에서 5d 후에, 약물 치료 후 가지돌기 형태형성을 쉽게 모니터링하기 위해 초록 형광 단백질 (GFP)로 형질감염시켰다 ([Ethell and Yamaguchi, 1999]; [Ethell et al., 2001], [Henkemeyer et al., 2003]). 가지 돌기는 시험관 내에서 약 16일 (DIV)에 형성되었다. 배양액을 시험관 내 제17일에 메타독신으로 300 μΜ 농도에서 5 hr 동안 처리하였다. Neuronal morphology : Hippocampal cell cultures were prepared from wild-type and Fmr1 KO fetal mice of embryonic day (E17.5) of gestation 17.5. The mice were sacrificed by cervical disassembly and the isolated hippocampal cells were plated in 15 mm multiwell containers (Falcon Primaria). (Ethel and Yamaguchi, 1999); [Ethell et al., 2001], [Henkemeyer et al., 1999], and then transfected with green fluorescent protein (GFP) ., 2003]). The dendrites were formed in the test tube for about 16 days (DIV). The culture was treated with metadoxine at 300 μM for 5 hr on day 17 in vitro.
GFP 형질감염된 뉴런의 사상위족 밀도는 스택형 (stacked) 자이스 (Zeiss) 공초점 생성된 영상 (40x 대물렌즈, 20x0.2 ㎛의 스택)의 숄 (Sholl) 분석을 수행함으로써 정량하였다. 메타몰프 (Metamorph) 소프트웨어를 사용하여, 동일한 간격의 동심원 (20 ㎛마다)을 각각의 뉴런의 세포 몸체의 둘레에 그리고, 후속적으로 원마다 사상위족의 양을 계수하였다. 계수의 평균을 짝이없는 양측 스튜던트 (unpaired two-tailed Student) T-검정을 이용하여 비교하였다. The supernatant densities of GFP transfected neurons were quantified by performing a Sholl analysis of stacked Zeiss confocal generated images (40x objective, 20x0.2 mu m stack). Using the Metamorph software, concentric circles of equal spacing (every 20 탆) were counted around the cell body of each neuron and subsequently in a circle for each circle. The mean of the coefficients was compared using unpaired two-tailed Student's T-test.
GFP 형질감염된 뉴런의 가시 (spine) 성숙도는 메타몰프 소프트웨어 (몰레큘라 디바이시즈 (Molecular Devices), 미국 캘리포니아주 서니베일)를 사용하여 분석하였다. 가시 형태측정 분석을 위해 뉴런마다 70-100 ㎛의 2개의 말단 가지돌기 절편을 선택하였다. 각각의 가시에 대해, 길이 및 폭을 측정하였다. 길이는 기부로부터 돌출부의 끝까지 거리로서 정의한 반면; 폭은 가시의 장축에 수직인 최대 거리로서 정의하였다. 측정치를 짝이없는 양측 스튜던트 T-검정을 이용하여 비교하고, 다중 비교를 위해 ANOVA 교정하였다. The spine maturation of GFP transfected neurons was analyzed using Metamorph software (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Two tip truncated sections of 70-100 ㎛ were selected per neuron for visual form analysis. For each visual, length and width were measured. The length is defined as the distance from the base to the end of the protrusion; The width was defined as the maximum distance perpendicular to the long axis of the spine. Measurements were compared using unpaired two-tailed Student T-test and ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons.
드 노보 해마 단백질 합성: 횡단 해마 절편 (400 ㎛)를 6주령 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 WT 마우스로부터 수득하였다. 단백질 합성 검정은 비-방사성 형광-활성화 세포 분류-기반 검정, 표면 감지 번역 (surface sensing of translation (SUnSET)) 방법을 사용하여 이전에 설명된 바와 같이 수행하였고, 상기 방법은 개별 포유동물 세포에서 및 불균질 세포 집단에서 전반적 단백질 합성의 모니터링 및 정량을 허용한다 (Hoeffer, 2011). 본 연구에 사용된 메타독신의 농도는 300 μΜ이었다. De novo hippocampus protein synthesis : Transverse hippocampal slices (400 쨉 m) were obtained from 6 week old Fmr1 dropout and WT mice. Protein synthesis assays were performed as previously described using non-radioactive fluorescence-activated cell sort-based screening, surface sensing of translation (SUNSET) methods, which were performed in individual mammalian cells and Allowing monitoring and quantification of overall protein synthesis in heterogeneous cell populations (Hoeffer, 2011). The concentration of metadoxine used in this study was 300 μM.
실시예Example
2: 취약 X 증후군의 2: Fragile X syndrome
Fmr1Fmr1
낙아웃Out
마우스 모델 (연구 Mouse Model (Research
1)에서1) in
학습 및 기억 결핍 및 생화학적 이상에 대한 For learning and memory deficits and biochemical abnormalities
메타독신Metathe
(100 대 (100
행동 분석Behavior analysis
환경적 공포 조건화: 초기 실험은 N = 10마리 WT 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 7일 동안 1일 1회 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신의 복강내 투여의 효과를 시험하였다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 시험 기간 동안 동결반응 감소로 반영되는 바와 같이 환경적 공포 조건화 패러다임에서 학습의 결핍을 보였다 (도 1의 패널 A (p<0.0001)). 메타독신 투여는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 학습 결핍 효과를 역전시켰고, 여기서 상기 역전은 부분적이고, 따라서 메타독신-치료 동물은 메타독신-치료 WT 동물과 상이하였다 (p<0.05). 상기 실험의 반복은 N = 10마리 WT 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 7일 동안 1일 1회의 비히클, 100 또는 200 mg/kg 메타독신의 복강내 투여의 용량-의존 효과를 조사하였다 (도 1의 패널 B 및 C). 본 실험에서, 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클-치료 WT 마우스에 비해 학습 결핍을 보였고 (p<0.0001), 이것은 제1 실험을 반복한다. 100 mg/kg 메타독신은 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 결핍의 역전을 일으켰지만 (P<0.05), 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 메타독신-치료 야생형 마우스와 상이하기 때문에 (p<0.0001) 이것은 부분적인 역전이었다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 보이는 학습 결핍은 200 mg/kg i.p. 메타독신을 사용한 치료 후에 완전히 역전되었다 (치료된 Fmr1 마우스는 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스와 상이하였지만 (P<0.0001), 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다). 메타독신 치료는 두 실험에서 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다 (도 1의 패널 A-C). Environmental Fear Conditioning : Initial experiments tested the effect of intraperitoneal administration of vehicle or 150 mg / kg metadoxine once daily for 7 days on environmental panic conditioning in the group of N = 10 WT and Fmr1 null out mice Respectively. Vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice showed a lack of learning in the environmental fear conditioning paradigm as reflected by reduced freeze response during the test (Panel A (p < 0.0001) in Figure 1). Metadoxine administration reversed the learning deficit effect in Fmr1 null out mice, where the inversion was partial, and therefore the metadocin-treated animals differed from metadoxin-treated WT animals (p < 0.05). Repetition of the experiment demonstrated dose-dependent effects of intraperitoneal administration of vehicle, 100 or 200 mg / kg metadoxine once daily for 7 days for environmental panic conditioning in the group of N = 10 WT and Fmr1 null out mice (Panels B and C in Fig. 1). In this experiment, vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice showed learning deficit (p < 0.0001) as compared to vehicle-treated WT mice, which repeats the first experiment. 100 mg / kg metadoxine caused a reversal of deficiency in Fmr1 knockout mice (P <0.05), but because metadoxin-treated Fmr1 fallout mice were different from metadoxin-treated wild type mice (p <0.0001) It was a reversal. The learning deficit seen in Fmr1 null mice was completely reversed after treatment with 200 mg / kg ip metadoxin (treated Fmr1 mice were different from vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice (P < 0.0001), metadoxin-treated WT It did not differ from the mouse). Metadokine treatment was ineffective for WT mice in both experiments (panel AC of FIG. 1).
사회적 접근: 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 한차례 냄새맡기에 의해 표시되는 바와 같이 더 적은 사회적 접근을 보여주었다 (도 2 (p<0.0001)). 7일 동안 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용한 1일 1회 복강내 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 사회적 접근을 증가시켰다 (비히클 치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 p<0.0001). 메타독신으로 치료한 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신 치료 WT 마우스와 상이하였지만 (p<0.05), WT 마우스의 효과에 접근하는 경향이 있었다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Social Approach : Vehicle-Treated Fmr1 dropout mice showed less social access as shown by once smelling (Figure 2 (p <0.0001)). One-day intraperitoneal treatment with 150 mg / kg metadoxine for 7 days increased social access in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.0001 compared to vehicle treated Fmr1 null mice). Fmr1 null mice treated with metadoxine were different from metadoxin treated WT mice (p <0.05) but tended to approach the effect of WT mice. Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice.
Y형 미로 자발 변경: N = 10마리 WT 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 자발 변경에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신의 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 도 3의 패널 A에 제시한다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클 치료 WT 마우스보다 더 적은 자발 변경을 보였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 비히클 치료에 비해 자발 변경을 증가시켰지만 (p<0.0001), 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스에 비해 결핍을 보였다 (p<0.01). 따라서, 메타독신은 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 보이는 결핍의 부분적 역전을 일으켰다. Y-type maze spontaneous change : N = 10 mice WT or Fmr1 The effects of the vehicle for spontaneous changes in the group of null mice or the once-a-day treatment of 7 days of 150 mg / kg meta- do. Vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice showed less spontaneous changes than vehicle treated WT mice (p < 0.0001). Metadoxin treatment increased spontaneous changes in Fmr1 null mice compared to vehicle treatment (p <0.0001), but metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice were deficient compared to metadoxin-treated WT mice (p <0.01). Thus, metadoxin caused a partial reversal of the deficiency seen in Fmr1 knockout mice.
Y형 미로 참조 기억 과제: N = 10마리 WT 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 보상된 참조 기억 학습에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용한 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 도 3의 패널 B에 제시한다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클-치료 WT 마우스보다 더 적은 적절한 아암 입장을 보였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신 치료는 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 상기 결핍을 감소시켰고 (p<0.0001), 따라서, 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Y-type maze memory task : The effect of 7 days of once-daily treatment with vehicle or 150 mg / kg meta-cognition on compensated reference memory learning in the group of N = 10 WT or Fmr1 null out mice is shown in Figure 3 In Panel B. Vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice showed less than adequate arm entry (p < 0.0001) than vehicle-treated WT mice. Metathexone treatment reduced the deficit (p < 0.0001) compared to vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice, and therefore, metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice did not differ from metadoxin-treated WT mice. Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice.
Y형 미로 수조 미로 좌측 우측 변별: N = 10마리 WT 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 혐오로 동기화된 공간 변별 학습에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용하는 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 도 3의 패널 C에 제시한다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클-치료 WT 마우스보다 더 많은 수의 부정확한 아암 입장을 보였다. 상기 결핍은 메타독신을 사용한 치료에 의해 감소하였다. Y-shaped labyrinth maze Left-hand side discrimination : N = 10 WT or Fmr1 mice in a group of naïve mice with aversion to synchronized spatial discrimination learning or once daily treatment with 7 days of 150 mg / kg meta- The effect of which is shown in Panel C of FIG. Vehicle-Treated Fmr1 knockout mice showed more inaccurate arm entries than vehicle-treated WT mice. The deficiency was reduced by treatment with metadoxine.
T형 미로 보상된 변경 과제: N = 10마리 WT 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 보상된 변경 작업 기억에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용한 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 도 4에 제시한다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클-치료 WT 마우스보다 정확한 아암에 도달하는데 더 긴 대기시간을 보였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 비히클 치료에 비해 상기 결핍을 감소시켰고 (p<0.0001), 여기서 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 WT 마우스보다 더 느리게 반응하였으므로 (p<0.0001) 상기 역전은 부분적이었다. The modified task assigned to the T-type maze : N = 10 WT or Fmr1 The effect of once-daily treatment with 7 days of vehicle or 150 mg / kg meta-cognition on compensated change working memory in the group of null mice 4. Vehicle-treated Fmr1 knockout mice showed longer waiting times to reach the correct arm than vehicle-treated WT mice (p < 0.0001). Metadocin treatment reduced this deficit in Fmr1 knockout mice compared to vehicle treatment (p < 0.0001), since the metadoxine-treated Fmr1 knockout mice responded more slowly (p < 0.0001) than WT mice .
연속 주로: N = 10마리 WT 또는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 연속 주로 과제에서 행동에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용한 7일의 1일 1회 치료의 효과를 도 5에 도시하고, 아래에 추가로 설명한다. Continuous mainly: N = shown in Figure 5 to 10 WT or Fmr1 camel vehicle or 150 mg / kg meth 1 il effects of one treatment of 7 days with a single person for action in a continuous mainly assignment from the group of-out mice, This is explained further below.
연속 주로 시험은 불안증 (주로 1에 들어가는 대기시간) 및 과잉행동 (주로 2 내지 4)을 효과적으로 측정하였다. 주로 1에서부터 연속 주로 2, 3, 및 4를 통한 진행은 벽이 점증적으로 더 낮고 더 좁고 보다 노출된 열린 아암을 갖는 점증적으로 밝게 도색한 환경에의 노출과 연관되었다. 열린 아암 상에서 소모한 시간 및 열린 아암 내로의 입장 불안증을 지시하고; 이와 반대로, 보다 열린 아암 내에서 소모한 시간의 증가는 과잉행동을 반영하였다. 이들 요인은 과잉행동과 함께 불안증-유사 행동의 범위를 포괄하는 민감한 시험을 허용하였다. Continuous primary testing effectively measured anxiety (latency primarily to 1) and hyperactivity (mainly 2 to 4). Progression from predominantly 1 to continuous 2, 3, and 4 was associated with exposure to an incrementally brightly colored environment with increasingly lower, narrower and more exposed open arms. Indicating time spent on the open arm and anxiety in the open arm; Conversely, the increase in time consumed in the more open arms reflected hyperactivity. These factors allowed sensitive testing to encompass a range of anxiety-like behaviors with hyperactivity.
주로 1: Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 WT 마우스보다 더 많은 불안증을 보였다 (p<0.001). 메타독신으로 처리된 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 비히클 치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 불안증의 완화를 보였고 (p<0.001), 따라서 완전한 정상화가 일어났다. 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스 사이에 차이가 존재하지 않았다. 또한, 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Mainly 1 : Fmr1 knockout mice showed more anxiety than WT mice (p <0.001). Fmr1 null mice treated with metadoxine showed anxiety relief (p <0.001) as compared to vehicle treated Fmr1 null mice, thus complete normalization occurred. There was no difference between the meta-cognate-treated Fmr1 fallout mouse and the meta-cx-treated WT mice. In addition, metathexone treatment was ineffective for WT mice.
주로 2: WT 마우스는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 주로 2에서 더 적은 활동을 보였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 과잉행동을 감소시켰지만 (p<0.001), 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 WT 마우스가 상이하였으므로 (p<0.001) 상기 과잉행동 역전은 부분적이었다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Mainly 2 : WT mice showed mainly less activity in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.0001). Treatment with metadoxine reduced hyperactivity in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.001), but the hyperactivity reversal was partial because metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice and WT mice were different (p <0.001). Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice.
주로 3: Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 WT 마우스에 비해 과잉행동을 보였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스와 상이하지 않았으므로, 상기 과잉행동은 메타독신에 의해 역전되지 않았다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Mainly 3 : Fmr1 null mice showed hyperactivity (p <0.0001) compared to WT mice. Since the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null out mice did not differ from the vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice, the hyperactivity was not reversed by metadoxin. Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice.
주로 4: Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 WT 마우스에 비해 과잉행동을 보였다 (p<0.01). 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스보다 더 적은 활동을 보였으므로 (p<0.01), 메타독신 치료는 상기 과잉행동을 역전시켰다. 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았으므로, 상기 효과는 정상화를 반영하였다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Mainly 4 : Fmr1 null out mice showed hyperactivity compared to WT mice (p <0.01). Metadoxin - treated Fmr1 knockout mice exhibited less activity than vehicle - treated Fmr1 knockout mice (p <0.01), so metathexone therapy reversed this hyperactivity. Since the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 knockout mice did not differ from the metadoxin-treated WT mice, the effects reflected normalization. Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice.
종합하면, 이론에 매이기를 바라지 않지만, 연속 주로 시험은 WT 마우스에 비해 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 불안증 및 과잉행동이 증가하였음을 보여주었다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 영향을 미치지 않으면서 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 상기 불안증 및 과잉행동을 감소시켰다. Taken together, we do not want to be bound by theory, but the sequential test showed that Fmr1 null mice outgrew anxiety and hyperactivity compared to WT mice. Metathexone treatment reduced the anxiety and hyperactivity in Fmr1 null mice without affecting WT mice.
생화학적 분석Biochemical analysis
ERK 및 Akt의 인산화: 뇌 내의 ERK 또는 Akt의 전체 뇌 인산화에 대한, N = 5마리 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 WT 마우스에서 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용하는 7일의 1일 1회 복강내 치료의 효과를 도 6에 제시한다. 인산화 수준은 인산화된 ERK 대 총 ERK의 비로서 평가하였다. 상기 비의 증가는 ERK의 활성화를 지시하였다. ERK의 인산화는 비히클 대조군보다 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 증가하였다 (p<0.001) - 상기 효과는 취약 X 증후군이 있는 인간 대상체에서 보이는 ERK의 이상 활성화를 복제하였다 (Wang et al., 2012). 상기 효과는 메타독신 치료에 의해 감소하였고 (p<0.01), 따라서, 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스에 비해 차이가 없었다. 메타독신은 WT 마우스에서 ERK의 인산화 또는 임의의 마우스에서 총 ERK 수준에 대해 효과가 없었다. 인산화된 Akt 대 총 AKT의 비는 비히클-치료 WT 마우스보다 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 또한 증가하였다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 인산화된 Akt의 상대적인 수준을 감소시켰고 (p<0.01), 따라서, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 대조군과 상이하지 않았다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해, 또는 임의의 마우스의 총 Akt 수준에 대해 효과가 없었다. Phosphorylation of ERK and Akt : N = 5 Fmr1 null out for ERK or Akt whole brain phosphorylation in the brain or intraperitoneal treatment once daily for 7 days using vehicle or 150 mg / kg metadoxine in WT mice Is shown in Fig. Phosphorylation levels were assessed as the ratio of phosphorylated ERK to total ERK. The increase in the ratio indicated the activation of ERK. ERK phosphorylation was increased in vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice (p < 0.001) than in vehicle controls - this effect replicated abnormal activation of ERK seen in human subjects with Fragile X syndrome (Wang et al., 2012) . The effect was reduced by meta-coxin treatment (p < 0.01) and was therefore not different from metadoxin-treated WT mice. Metadoxin was not effective on ERK phosphorylation in WT mice or on total ERK levels in any mouse. The ratio of phosphorylated Akt to total AKT also increased (p < 0.0001) in vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice out of vehicle-treated WT mice. Treatment with metadoxine reduced the relative levels of phosphorylated Akt in Fmr1 null mice (p < 0.01), and thus Fmr1 null mice did not differ from the control group. Metatocortical therapies were ineffective for WT mice, or for the total Akt level of any mouse.
실시예Example 3: 3: Fmr1Fmr1 낙아웃Out 취약 X 마우스 모델에서 In the vulnerable X mouse model 메타독신의Metamorphic 평가 (연구 2) Evaluation (Study 2)
6개월령6 months Fmr1Fmr1 낙아웃Out 마우스에서 From the mouse 메타독신의Metamorphic 행동 효과 Behavioral effect
환경적 공포 조건화: 초기 실험은 N = 10마리의 6개월령 WT 및 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 군에서 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 7일 동안 1일 1회 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신의 복강내 투여의 효과를 시험하였다. 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 (KO-V)는 시험 기간 동안 동결반응의 감소 (도 7 (p <0.0001))로 반영되는 바와 같이 비히클-치료 WT 마우스 (WT-V)에 비교할 때 환경적 공포 조건화 패러다임에서 학습의 결핍을 보였다. 메타독신 투여는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 학습 결핍 효과를 역전시켰다 (p<0.0001 KO-M-150 대 KO-V). 이것은 완전한 역전이었고, 따라서, 메타독신-치료 KO 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다. Environmental Fear Conditioning : Initial experiments were performed in groups of N = 10 6-month-old WT and Fmr1 null mice with intraperitoneal administration of vehicle or 150 mg / kg metadoxine once daily for 7 days for environmental panic conditioning The effect was tested. Vehicle-treated Fmr1 dropout mice (KO-V) were significantly more effective than vehicle-treated WT mice (WT-V) as reflected by a decrease in freezing response during the test period (Figure 7 The conditioning paradigm showed a lack of learning. Metadoxin administration reversed the learning deficit effect in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.0001 KO-M-150 vs. KO-V). This was a complete reversal and, therefore, the metadoxin-treated KO mice did not differ from the metadoxin-treated WT mice.
사회적 접근 및 사회적 기억: 사회적 접근 데이터 (초기 시험 1)을 도 8의 패널 A (한차례 냄새맡기의 수) 및 패널 C (냄새맡기의 지속 시간)에 제시한다. 사회적 기억 데이터 (시험 2, 시험 1의 24시간 후)를 도 8의 패널 B (한차례 냄새맡기의 수) 및 패널 D (냄새맡기의 지속 시간)에 제시한다. 이들 결과를 아래에서 추가로 논의한다. Social Approach and Social Memory : Social access data (initial test 1) are presented in Panel A (number of odor entrapment) and Panel C (duration of stench) in Figure 8. Social memory data (test 2, 24 hours after test 1) are presented in panel B (number of odor-taking) and panel D (duration of odor-taking) These results are discussed further below.
시험 1 동안, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 WT 마우스에 비해 한차례 냄새맡기의 수의 증가 (p<0.0001) (도 8의 패널 A 참조) 및 냄새맡기의 지속시간의 감소 (p<0.0001) (도 8의 패널 C 참조)를 보여주었다. 이들 사회적 상호작용 결핍은 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 다른 연구자들이 보고한 것과 일치한다 (Thomas et al., 2011). 한차례 냄새맡기의 수 및 냄새맡기의 지속시간 둘 모두에 대해, 메타독신을 사용하는 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 이상의 역전을 일으켰고 (각각에 대해 p<0.0001 KO-M-150 대 KO-V), 따라서, 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 한차례 냄새맡기의 수 측정치에 대해 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다. 냄새맡기의 지속시간 측정치에 대해 구제가 보이지만, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신 치료 후에 WT 마우스에 비해 상이하게 남았기 때문에 (p<0.05) 상기 효과는 부분적이었다. 메타독신은 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. 이들 데이터는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 비정상 사회적 접근 행동이 메타독신에 의해 구제되었음을 보여준다. During test 1, the Fmr1 dropout mouse showed a decrease in the number of odorants (p < 0.0001) (see panel A in Figure 8) and a decrease in the duration of deodorization (p < 0.0001) See panel C). These social interaction deficits are consistent with those reported by other researchers in Fmr1 null mice (Thomas et al., 2011). For both the number of odorants and the duration of odor entrapment, treatment with metadoxine resulted in overturning in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.0001 KO-M-150 vs. KO-V for each) Thus, the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice did not differ from the metadoxin-treated WT mice in terms of the number of odorant counts. Remedies were observed for the duration of the smell, but the effect was partial because Fmr1 null mice remained different than WT mice after meta-cognition treatment (p < 0.05). Metadokinesin had no effect on WT mice. These data demonstrate that abnormal social access behaviors in Fmr1 null mice were rescued by meta-cognition.
시험 2 동안, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 야생형 마우스에 비해 한차례 냄새맡기의 수의 증가 및 냄새맡기의 지속시간의 증가를 보여주었다 (각각의 측정치에 대해 p<0.0001, 각각 도 8의 패널 B 및 D). 이것은 적응의 실패, 및 따라서 사회적 기억 결핍을 반영하였다. 메타독신 치료는 이들 차이를 감소시켰다 (KO-M-150 대 KO-V에 대해 p<0.0001). 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스 사이에 차이가 남았기 때문에 (p<0.05), 한차례 냄새맡기의 수에 대한 역전은 부분적이었다. 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스 사이에서 차이가 관찰되지 않았으므로, 냄새맡기 지속시간에 대한 메타독신에 의한 역전은 완전하였다. 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. 이들 데이터는 메타독신이 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 사회적 기억 손상을 감소시켰음을 보여준다. 상기 사회적 기억 결핍의 감소는 사회적 기억 비의 계산 (실시예 1에 설명된)에 의해 아래에 예시된다:During trial 2, Fmr1 null out mice exhibited an increase in the number of odorants and an increase in the duration of deodorization (compared to wild-type mice (p <0.0001 for each measurement, panels B and D, respectively, of Figure 8) . This reflected the failure of adaptation, and therefore, social memory deficits. Meta-cognitive therapy reduced these differences (p <0.0001 for KO-M-150 vs. KO-V). Because there was a difference between the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice and the metadoxin-treated WT mice (p < 0.05), the reversal to the number of odorants was partial. Since no differences were observed between the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice and the metadoxin-treated WT mice, the inversion by metadokines for the odor duration was complete. Metatocarcinoma treatment had no effect on WT mice. These data show that meta-cognition reduced social memory impairment in Fmr1 null mice. The reduction in social memory deficits is illustrated by the calculation of the social memory ratio (described in Example 1) below:
사회적 기억 비는 한차례 냄새맡기의 지속시간으로서 정의하였다: 시험 2/시험 1+2. 따라서, 기억 없음의 예는 (예를 들어 20/(20+20)) =0.5인 한편, 기억의 예는 (예를 들어 10/(20+10)) =<0.5이었다. The social memory ratio was defined as the duration of odor-taking once: Test 2 / Test 1 + 2. Thus, an example of no memory (for example, 20 / (20 + 20)) = 0.5 while an example of memory (for example, 10 / (20 + 10)) = 0.5.
계산된 사회적 기억 비는 다음과 같았다:The calculated social memory ratios were as follows:
WT-V 시험 2/시험 1 + 시험 2: 12.4 / 12.4 + 26.8 = 0.3, <0.5 기억 WT-V Test 2 / Test 1 + Test 2: 12.4 / 12.4 + 26.8 = 0.3, <0.5
KO-V 시험 2/시험 1 + 시험 2: 325 / 325 + 24.1 = 0.9, 기억 없음KO-V Test 2 / Test 1 + Test 2: 325/325 + 24.1 = 0.9, No memory
WT-M 시험 2/시험 1 + 시험 2: 12.5 / 38.5 + 12.5 = 0.2, <0.5 기억 WT-M test 2 / test 1 + test 2: 12.5 / 38.5 + 12.5 = 0.2, <0.5
KO-M 시험 2/시험 1 + 시험 2: 12.7 / 28.4 + 12.7 = 0.3, <0.5 기억 KO-M Test 2 / Test 1 + Test 2: 12.7 / 28.4 + 12.7 = 0.3, <0.5
6개월령6 months Fmr1Fmr1 낙아웃Out 마우스에서 From the mouse 메타독신의Metamorphic 생화학적 효과 Biochemical effect
상기 설명된 행동 시험 이후 뇌 내의 전체 뇌 pERK (도 9의 패널 A) 및 pAkt (도 9의 패널 B)에 대한, N = 10마리 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 WT 마우스에서 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg 메타독신을 사용한 7일의 1일 1회 ip 치료의 효과를 도 9에 제시한다. 구체적으로, 도 9의 패널 A는 pAkt의 뇌 수준을 보여주고, 이것은 선행 실험에서 보이는 바와 같이 WT 마우스보다 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 증가하였다 (P<0.0001). 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 뇌 pAkt의 상기 증가를 역전시켰고 (KO-M-150 대 KO-V에 대해 p<0.0001), 따라서, 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다. 도 9의 패널 B는 pERK의 뇌 수준을 보여주고, 이것은 선행 실험에서 보이는 바와 같이 WT 마우스에 비해 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 증가하였다 (KO-M-150 대 KO-V에 대해 p<0.0001). 상기 증가는 메타독신 치료에 의해 역전되었고 (p<0.0001), 따라서, 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았다. N = 10 mice Fmr1 dropout or mice in the WT mice or 150 mg / kg metadoxine for the entire brain pERK (panel A of FIG. 9) and pAkt (panel B of FIG. 9) The effect of ip treatment once a day on the used 7 days is shown in Fig. Specifically, Panel A of FIG. 9 shows the brain levels of pAkt, which increased in Fmr1 null mice out of WT mice (P < 0.0001) as shown in the preceding experiments. Treatment with metadoxine reversed this increase in brain pAkt (p <0.0001 for KO-M-150 vs. KO-V), and therefore the metadoxine-treated Fmr1 null mice responded with meta- Did not do it. Panel B of FIG. 9 shows the brain levels of pERK, which increased in Fmr1 null mice as compared to WT mice (p <0.0001 for KO-M-150 vs. KO-V), as seen in previous experiments. The increase was reversed by meta-cognate treatment (p < 0.0001), and therefore the metadocyte-treated Fmr1 null out mice did not differ from the metadoxin-treated WT mice.
2개월령2 months 마우스의 행동에 대한 About the behavior of the mouse 복강내Abdominal cavity 또는 경구 투여 후의 Or after oral administration 메타독신의Metamorphic 효과 effect
도 10은 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 WT 마우스에서 환경적 공포 조건화에 대한 7일 동안 150 mg/kg ip, 또는 150 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 용량으로 1일 1회 메타독신의 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 구체적으로, 도 10의 패널 A는 비히클을 사용한 ip 및 경구 치료 후에 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 WT 마우스로부터 환경적 공포 조건화 데이터를 보여준다. 비히클의 투여 경로에 관한 차이는 없었다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 ip 및 경구 경로를 통한 비히클 치료 후에 WT 마우스에 비해 동결반응 행동의 감소를 보여주었다 (각각의 경우에 p<0.0001). 도 10의 패널 B는 WT 마우스에서 두 투여 경로를 통한 메타독신 치료의 효과를 보여준다. 효과는 보이지 않았다. 도 10의 패널 C는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 ip 150 mg/kg 및 경구 150 및 300 mg/kg의 메타독신 치료가 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 보이는 동결반응 행동의 감소를 역전시켰음을 보여준다 (KO-M-ip, KO-M-po 150, 및 KO-M-po 300 대 KO-V-ip 및 KO-V po에 대해 각각 p<0.01, p<0.0001, 및 p<0.0001). 150 mg po 메타독신을 사용한 투여의 효과는 300 mg/kg po 메타독신의 투여의 효과와 상이하지 않았다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 150 및 300 mg/kg 경구 메타독신의 효과는 150 mg/kg ip 메타독신의 효과와 상이하지 않았다. 각각의 경우에, 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았으므로 역전은 완전하였다. Figure 10 shows the effect of metadoxine administration once daily at a dose of 150 mg / kg ip, or 150 and 300 mg / kg orally for 7 days for environmental fear conditioning in 2 month old Fmr1 fallout and WT mice . Specifically, panel A of FIG. 10 shows environmental fear conditioning data from Fmr1 dropouts and WT mice after ip with vehicle and oral treatment. There was no difference in the route of administration of the vehicle. Fmr1 null out mice showed a decrease in freezing behavior (p <0.0001 in each case) compared to WT mice after vehicle treatment with ip and oral route. Panel B of FIG. 10 shows the effect of metazohalcine treatment over two routes of administration in WT mice. The effect was not seen. Panel C of Figure 10 shows that metadoxin treatment with
도 11은 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 WT 마우스에서 사회적 접근 및 사회적 기억에 대한 7일 동안 150 mg/kg ip 또는 150 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 용량으로 1일 1회 메타독신의 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 구체적으로, 도 11의 패널 A는 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 WT 마우스에서 사회적 접근 행동에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg ip 또는 150 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 메타독신의 효과를 보여준다. 비히클을 사용한 ip 또는 경구 치료 후에, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 냄새맡기 행동의 지속시간은 WT 마우스에 비해 감소하였다 (각각 p<0.0001). 임의의 용량의 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. 그러나, 150 mg/kg ip, 150 mg/kg, 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 메타독신 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 보이는 사회적 접근 결핍을 역전시켰다 (KO-M-po 150 및 KO-M-po 300 대 KO-V po에 대해 각각 p<0.0001). 경구 메타독신의 효과는 150 및 300 mg/kg 사이에서 용량 의존적이 아니었다. 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았으므로, 상기 역전은 완전하였다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 150 mg/kg ip 메타독신의 효과는 150 mg/kg 경구 또는 300 mg/kg 경구 메타독신의 효과와 상이하지 않았다. 도 11의 패널 B는 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 WT 마우스에서 사회적 기억에 대한 비히클 또는 150 mg/kg ip 또는 150 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 메타독신의 효과를 보여준다. 비히클을 사용한 ip 또는 경구 치료 후에, Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 냄새맡기 행동의 지속시간은 WT 마우스에 비해 증가하였다 (각각에 대해 p<0.0001). 임의의 용량의 메타독신 치료는 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. 그러나, 150 mg/kg ip, 150 mg/kg 경구, 및 300 mg/kg 경구의 메타독신 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 보이는 사회적 접근 결핍을 역전시켰다 (KO-M-ip 150, KO-M-po 150, 및 KO-M-po 300 대 KO-V-ip 및 KO-V po에 대해 각각 p<0.0001, p<0.05, 및 p<0.01). 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스는 메타독신-치료 WT 마우스와 상이하지 않았으므로, 상기 역전은 완전하였다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 150 mg/kg ip 메타독신의 효과는 150 mg/kg 경구 또는 300 mg/kg 경구 메타독신의 효과와 상이하지 않았다. 또한, 150 mg/kg 및 300 mg/kg 사이에서 경구 메타독신 치료의 효과에 대한 용량 의존성은 없었다. FIG. 11 shows the effect of metadoxine administration once daily at doses of 150 mg / kg ip or 150 and 300 mg / kg for 7 days for social access and social memory in Fmr1 fallout and WT mice. Specifically, panel A of FIG. 11 shows the effect of 150 mg / kg ip or 150 and 300 mg / kg oral metadoxine on social access behavior in Fmr1 null out or WT mice. After ip or oral treatment with vehicle, the duration of stinking behavior in Fmr1 knockout mice was reduced compared to WT mice (p <0.0001, respectively). An arbitrary dose of metacortice treatment was ineffective for WT mice. However, methadone therapy at 150 mg / kg ip, 150 mg / kg, and 300 mg / kg orally reversed the social access deficit seen in Fmr1 null mice (KO-M-
2개월령2 months 마우스에서 From the mouse 복강내Abdominal cavity 또는 경구 투여 이후 생화학적 Or biochemical after oral administration 마커에On the marker 대한 메타독신의 효과 Effects of Meta-Single Cow
말초 림프구: 도 12는 2개월령 Fmr1 낙아웃 및 WT 마우스에서 유동 세포측정법에 의해 결정할 때, 림프구 pAkt (도 12의 패널 A) 및 pERK (도 12의 패널 B)에 대한 7일 동안 150 mg/kg ip 또는 150 mg/kg 및 300 mg/kg 경구 용량의 1일 1회 메타독신의 투여의 효과를 보여준다. 구체적으로, 도 12의 패널 A는 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 동등한 비히클 치료를 받은 WT 마우스에 비해 림프구 Akt의 인산화 증가를 보였음을 보여준다 (ip 및 경구 투여 모두에 대해 p<0.0001). 7일 동안 150 mg/kg ip 또는 150 mg/kg 또는 300 mg/kg의 경구 용량으로 1일 1회 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 과다활성화된 Akt를 정상화하였고, 따라서, pAkt 수준은 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 동일한 치료를 받은 WT 마우스 사이에서 상이하지 않았다. 도 12의 패널 B는 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스가 동등한 비히클 치료를 받은 WT 마우스에 비해 림프구 ERK의 인산화 증가를 보였음을 보여준다 (ip 및 경구 투여 모두에 대해 p<0.0001). 7일 동안 150 mg/kg ip, 또는 150 mg/kg 또는 300 mg/kg의 경구 용량의 1일 1회 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 과다활성화된 ERK를 정상화시켰고, 따라서, pERK 수준은 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 및 동일한 치료를 받은 WT 마우스 사이에서 상이하지 않았다. Peripheral lymphocyte : Figure 12 shows the effect of 150 mg / kg for 7 days on lymphocyte pAkt (panel A in Figure 12) and pERK (panel B in Figure 12), when determined by flow cytometry in 2 month old Fmr1 null out and WT mice ip or doses of 150 mg / kg and 300 mg / kg oral doses of metadoxine once daily. Specifically, panel A of FIG. 12 shows that vehicle-treated Fmr1 null out mice showed increased phosphorylation of lymphocyte Akt (p < 0.0001 for both ip and oral administration) compared to WT mice that received equivalent vehicle treatment. Treatment with metadoxine once daily at an oral dose of 150 mg / kg ip or 150 mg / kg or 300 mg / kg for 7 days normalized the hyperactively activated Akt and thus the pAkt levels were metadoxin-treated Fmr1 Lt; / RTI > mice did not differ between the null mice and the same treated WT mice. Panel B of Figure 12 shows that vehicle-treated Fmr1 null out mice showed increased phosphorylation of lymphocyte ERK (p < 0.0001 for both ip and oral administration) compared to WT mice that received equivalent vehicle treatment. Treatment with metadoxine once daily at a dose of 150 mg / kg ip, or 150 mg / kg or 300 mg / kg for 7 days, normalized the hyperactive ERK and therefore the pERK levels were meta- Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > Fmr1 < / RTI > null mice and the same treated WT mice.
뇌 영역: 도 13은 해마, 전전두 피질, 및 선조체에서 pERK 수준에 대한 7일 동안 150 mg/kg 메타독신의 투여의 효과를 보여준다. pERK 수준은 3개의 모든 뇌 영역에서 WT 마우스에 비해 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 증가하였다 (모든 경우에 p<0.0001). pERK 수준은 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 감소하였다 (모든 경우에 p<0.0001). 해마 및 선조체에서 KO-M 및 WT-M 군 사이에서 차이는 없었고, 이것은 ERK의 활성화의 완전한 역전을 보여준다. 전전두 피질에서 효과는 부분적이고, KO-V 및 KO-M 군은 상이하게 남았다 (p<0.05). 메타독신은 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. Brain area : Figure 13 shows the effect of administration of 150 mg / kg metadoxine for 7 days on pERK levels in hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and striatum. pERK levels were increased in Fmr1 null mice out of all three brain regions compared to WT mice (p <0.0001 in all cases). pERK levels were reduced in the metadoxin-treated Fmr1 null mice (p <0.0001 in all cases) compared to the vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice. There was no difference between the KO-M and WT-M groups in hippocampus and striatum, indicating complete reversal of activation of ERK. The effect was partial in the prefrontal cortex, and the KO-V and KO-M groups remained different (p <0.05). Metadokinesin had no effect on WT mice.
도 14는 해마, 전전두 피질 및 선조체에서 pAkt 수준에 대한 7일 동안 150 mg/kg 메타독신의 투여의 효과를 보여준다. pAkt 수준은 3개의 모든 뇌 영역에서 WT 마우스에 비해 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 증가하였다 (모든 경우에 p<0.0001). pAkt 수준은 3개의 모든 뇌 영역에서 비히클-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에 비해 메타독신-치료 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 감소하였다 (모든 경우에 p<0.0001). 모든 경우에, KO-M 및 WT-M 군 사이에 차이는 없었고, 이것은 Akt의 활성화의 완전한 역전을 보여준다. 메타독신은 WT 마우스에 대해 효과가 없었다. 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt의 뇌 및 혈액 수준 상승의 감소는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스의 개선된 행동 성과와 상호관련되고, 이것은 인산화 수준이 메타독신 치료 반응의 바이오마커임을 제안한다. Figure 14 shows the effect of administration of 150 mg / kg metadoxine for 7 days on pAkt levels in hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and striatum. pAkt levels were increased in Fmr1 null mice out of WT mice in all three brain regions (p <0.0001 in all cases). pAkt levels were reduced in meta-cognate-treated Fmr1 null mice (in all cases p <0.0001) compared to vehicle-treated Fmr1 null mice in all three brain regions. In all cases, there was no difference between KO-M and WT-M groups, indicating complete reversal of activation of Akt. Metadokinesin had no effect on WT mice. Reduced brain and blood level elevations of phosphorylated ERK and Akt are correlated with improved behavioral performance of Fmr1 null mice, suggesting that phosphorylation levels are biomarkers of meta-cognitive therapy response.
시험관 내에서 In vitro Fmr1Fmr1 낙아웃Out 마우스로부터 일차 해마 뉴런 내의 From the mouse into the first hippocampal neuron 가지돌기Bifurcation 사상위족 밀도 및 Threshold Density and 성숙화에On maturity 대한 About 메타독신의Metamorphic 효과 effect
도 15 (패널 A-C)는 300 μM 메타독신을 사용하는 5시간 동안 치료의 효과를 보여준다. 가지돌기를 각각 몸체로부터 거리에 기반하여 (근위부에서 원위부로, 좌측에서 우측으로) 10 ㎛의 10개 절편으로 나누었다. 가시 밀도는 절편 3에서 WT 마우스로부터 뉴런에 비해 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스로부터 뉴런에서 증가하였다. 구체적으로, 도 15의 패널 A는 뉴런 사상위족의 밀도를 보여준다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스로부터 일차 해마 뉴런은 사상위족 밀도의 증가를 보여주었다 (p<0.001). 300 μΜ 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스에서 뉴런 사상위족 밀도의 이상 증가를 감소시켰다 (p<0.001). Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스로부터 뉴런은 보다 길고 (도 15의 패널 B (p<0.01)) 보다 좁은 (도 15의 패널 C (p<0.01)) 미성숙의 특징을 갖는 사상위족을 보여주었다. 메타독신을 사용한 치료는 상기 사상위족 길이의 증가를 역전시키고 (도 15의 패널 B (p<0.01)), 폭의 감소를 역전시켰다 (도 15의 패널 C (p<0.001)). 15 (Panel A-C) shows the effect of treatment for 5 hours using 300 μM metadoxine. The dendrites were divided into 10 sections of 10 ㎛ each based on distance from the body (from proximal to distal, from left to right). Visible density increased in neurons from Fmr1 null mice out of WT mice compared to neurons in section 3. Specifically, panel A of FIG. 15 shows the density of the neuron threshold. Primary hippocampal neurons from the Fmr1 knockout mice showed an increase in supratentorial densities (p <0.001). Treatment with 300 μM metadoxine reduced the abnormal increase in neuronal somatosensory density in Fmr1 null mice (p <0.001). Neurons from the Fmr1 knockout mice showed a mysterious stomach with a longer immature characteristic (Panel C (p < 0.01) in Figure 15) than in the longer (Panel B (p < 0.01) Treatment with metadoxine reversed the increase in the sagittal length (Panel B in Figure 15 (p < 0.01)) and reversed the decrease in width (Panel C (p < 0.001) in Figure 15).
시험관 내에서 In vitro Fmr1Fmr1 낙아웃Out 마우스에서 드 Mouse de 노보Novo 해마 단백질 합성에 대한 For hippocampal protein synthesis 메타독신의Metamorphic 효과 effect
도 16은 Fmr1 낙아웃 또는 WT 마우스로부터 400 ㎛ 해마 절편에서 기초 드 노보 단백질 합성에 대한 비히클 또는 300 μΜ 메타독신을 사용한 치료의 효과를 보여준다. 단백질 합성은 비히클-치료 WT 대조 해마보다 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스로부터 비히클-치료 해마에서 더 높았다 (p<0.0001). 메타독신 치료는 Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스 해마에서 단백질 합성 속도를 감소시켰다. Fmr1 낙아웃 마우스로부터 해마는 WT 마우스로부터 메타독신-치료 해마보다 더 높은 단백질 합성 속도를 보유하였으므로 (p<0.001), 상기 효과는 부분적이었다. Figure 16 shows the effect of treatment with vehicle or 300 [mu] M metadoxine for baseline de novo protein synthesis in 400 [mu] m hippocampal slices from Fmr1 null out or WT mice. Protein synthesis was higher in vehicle-treated hippocampus from Fmr1 null mice than in vehicle-treated WT control hippocampus (p <0.0001). Metadokine therapy reduced the rate of protein synthesis in Fmr1 null mouse hippocampus. Since hippocampus from Fmr1 null mice had a higher rate of protein synthesis from WT mice than the metadoxin-treated hippocampus (p <0.001), the effect was partial.
<표 1> <Table 1>
Claims (8)
b) 샘플 내의 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고;
c) 단계 a)에서 결정된 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 단계 b)에서 결정된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양의 비를 계산하고;
d) 단계 c)의 계산된 비를 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 측정된 계산된 비와 비교하는 것
을 포함하고, 여기서 단계 c)의 계산된 비가 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체의 계산된 비와 유사할 경우는 치료가 효과적임을 나타내는 것인, 메타독신 치료를 받은 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체에서 메타독신 치료 요법의 유효성을 평가하는 방법.a) measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in a sample derived from a subject suffering from metazohalcine-treated Fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorders;
b) measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the sample;
c) calculating the ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein determined in step a) to the amount of ERK and Akt protein determined in step b);
d) comparing the calculated ratio of step c) to the calculated ratio from an unaffected subject
Wherein the calculated ratio of step c) is similar to the calculated ratio of the subject not suffering from a disease, wherein the meta-cognitive therapy is administered to a subject having a fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorder, A method of assessing the efficacy of a bipolar therapy.
b) 샘플 내의 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고;
c) 단계 a)에서 결정된 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 단계 b)에서 결정된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양의 비를 계산하고;
d) 단계 c)의 계산된 비를 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체로부터 측정된 계산된 비와 비교하는 것
을 포함하고, 단계 c)의 계산된 비가 질환에 걸리지 않은 대상체의 계산된 비보다 더 높은 경우는 대상체가 메타독신 치료 요법으로부터 이익을 얻게 될 것임을 나타내는 것인, 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체가 메타독신 치료 요법으로부터 이익이 얻어질 것인지 여부를 결정하는 방법.a) measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in a sample derived from a subject having Fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorders;
b) measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the sample;
c) calculating the ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein determined in step a) to the amount of ERK and Akt protein determined in step b);
d) comparing the calculated ratio of step c) to the calculated ratio from an unaffected subject
And wherein the calculated ratio of step c) is higher than the calculated ratio of the subject not suffering from the disease indicates that the subject will benefit from the meta-cognitive therapy therapy, wherein the subject has a fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorder A method of determining whether or not a benefit will be gained from meta-cognitive therapy.
b) 제1 기간에서 제1 샘플에서 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고;
c) 단계 a)에서 결정된 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 단계 b)에서 결정된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 제1 비를 계산하고;
d) 제2 기간에서 대상체로부터의 제2 샘플에서 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양을 측정하고;
e) 제2 기간에서 제2 샘플에서 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량을 측정하고;
f) 제2 비를 생성하기 위해 단계 d)에서 결정된 인산화된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 양 대 단계 e)에서 결정된 ERK 및 Akt 단백질의 총량의 제2 비를 계산하고,
g) 제1 비 대 제2 비를 비교하는 것
을 포함하는, 취약 X 증후군 또는 다른 인지 장애가 있는 대상체에서 메타독신 치료 요법을 모니터링하는 방법.a) measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in the first sample from the subject in the first period;
b) measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the first sample in the first period;
c) calculating a first ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein determined in step a) to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein determined in step b);
d) measuring the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein in the second sample from the subject in the second period;
e) measuring the total amount of ERK and Akt protein in the second sample in the second period;
f) calculating a second ratio of the amount of phosphorylated ERK and Akt protein determined in step d) to the total amount of ERK and Akt protein determined in step e) to produce a second ratio,
g) comparing the first ratio to the second ratio
Wherein the meta-cognitive therapy is monitored in a subject having a Fragile X syndrome or other cognitive disorder.
8. The method of claim 7, wherein the PMBC is a lymphocyte or mononuclear cell.
Applications Claiming Priority (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201361875384P | 2013-09-09 | 2013-09-09 | |
| US61/875,384 | 2013-09-09 | ||
| US14/038,258 | 2013-09-26 | ||
| US14/038,258 US20150073023A1 (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2013-09-26 | Method Of Treating Fragile X Syndrome And Related Disorders |
| US201461991351P | 2014-05-09 | 2014-05-09 | |
| US61/991,351 | 2014-05-09 | ||
| PCT/US2014/054816 WO2015035402A1 (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2014-09-09 | Methods of determining response to therapy |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160086818A true KR20160086818A (en) | 2016-07-20 |
Family
ID=52629036
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020167009042A KR20160086818A (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2014-09-09 | Methods of determining response to therapy |
| KR1020167009040A KR20160078956A (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2014-09-09 | Methods of treating fragile x syndrome and related disorders |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020167009040A KR20160078956A (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2014-09-09 | Methods of treating fragile x syndrome and related disorders |
Country Status (12)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (2) | EP3044589A1 (en) |
| JP (2) | JP2016530536A (en) |
| KR (2) | KR20160086818A (en) |
| CN (2) | CN105517546A (en) |
| AU (2) | AU2014315026A1 (en) |
| CA (2) | CA2923421A1 (en) |
| EA (2) | EA201690557A1 (en) |
| IL (2) | IL244343A0 (en) |
| MX (2) | MX2016003002A (en) |
| SG (2) | SG11201601830PA (en) |
| TW (2) | TW201605443A (en) |
| WO (2) | WO2015033224A2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015014835A1 (en) * | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-05 | Basf Se | Luminescent diazabenzimidazole carbene metal complexes |
| US20150073023A1 (en) | 2013-09-09 | 2015-03-12 | Alcobra Ltd. | Method Of Treating Fragile X Syndrome And Related Disorders |
| CN108538365A (en) * | 2017-03-24 | 2018-09-14 | 华东师范大学 | A kind of self-closing disease sociability assessment system based on data analysis technique |
| WO2019197632A1 (en) * | 2018-04-13 | 2019-10-17 | Healx Limited | Treatment of fragile x syndrome |
| KR20190121569A (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2019-10-28 | 건국대학교 글로컬산학협력단 | Pharmaceutical Composition for Improving Fragile X Syndrome Comprising Agmatine or its derivatives |
| US10813899B2 (en) * | 2018-06-07 | 2020-10-27 | Ovid Therapeutics Inc. | Use of (s)-3-amino-4-(difluoromethylenyl) cyclopent-1-ene-l-carboxylic acid and related compounds, (1s,3S)-3-amino-4-(difluoromethylidene) cyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid and vigabatrin in the treatment of developmental disorders |
| US20230024384A1 (en) * | 2020-01-08 | 2023-01-26 | Neuroventi | Composition comprising lisuride compound for treating fragile x syndrome or related developmental disorders |
| KR102398219B1 (en) * | 2020-02-07 | 2022-05-17 | 주식회사 뉴로벤티 | Composition comprising rilmenidine compound for treating fragile x syndrome and related developmental disorders |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT1131856B (en) | 1980-06-30 | 1986-06-25 | Baldacci Lab Spa | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION FOR THE TREATMENT OF ALCOHOLIC INTOXICATIONS |
| US20020155170A1 (en) * | 2000-11-30 | 2002-10-24 | Walsh William John | Nutrient supplements and methods for treating autism and for preventing the onset of autism |
| IL187159A0 (en) | 2007-07-03 | 2009-02-11 | Gur Megiddo | Use of metadoxine in relief of alcohol intoxication |
| EA023758B1 (en) * | 2009-06-25 | 2016-07-29 | Алкобра Лтд. | Use of metadoxine for treating attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd/add) |
-
2014
- 2014-09-05 TW TW103130856A patent/TW201605443A/en unknown
- 2014-09-05 TW TW103130859A patent/TW201606304A/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 WO PCT/IB2014/002398 patent/WO2015033224A2/en active Application Filing
- 2014-09-09 CN CN201480049671.5A patent/CN105517546A/en active Pending
- 2014-09-09 SG SG11201601830PA patent/SG11201601830PA/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 EA EA201690557A patent/EA201690557A1/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 AU AU2014315026A patent/AU2014315026A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-09-09 JP JP2016540930A patent/JP2016530536A/en active Pending
- 2014-09-09 MX MX2016003002A patent/MX2016003002A/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 KR KR1020167009042A patent/KR20160086818A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2014-09-09 CA CA2923421A patent/CA2923421A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-09-09 EA EA201690559A patent/EA201690559A1/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 EP EP14776939.2A patent/EP3044589A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-09-09 CA CA2922901A patent/CA2922901A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-09-09 KR KR1020167009040A patent/KR20160078956A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2014-09-09 EP EP14830858.8A patent/EP3043792A2/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-09-09 JP JP2016539645A patent/JP2016530291A/en active Pending
- 2014-09-09 MX MX2016003006A patent/MX2016003006A/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 WO PCT/US2014/054816 patent/WO2015035402A1/en active Application Filing
- 2014-09-09 SG SG11201601605YA patent/SG11201601605YA/en unknown
- 2014-09-09 CN CN201480060722.4A patent/CN105917225A/en active Pending
- 2014-09-09 AU AU2014316779A patent/AU2014316779A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2016
- 2016-02-29 IL IL244343A patent/IL244343A0/en unknown
- 2016-03-06 IL IL244453A patent/IL244453A0/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MX2016003006A (en) | 2016-06-10 |
| TW201605443A (en) | 2016-02-16 |
| JP2016530291A (en) | 2016-09-29 |
| CN105517546A (en) | 2016-04-20 |
| MX2016003002A (en) | 2016-09-08 |
| IL244343A0 (en) | 2016-04-21 |
| EA201690557A1 (en) | 2016-07-29 |
| AU2014315026A1 (en) | 2016-03-24 |
| CN105917225A (en) | 2016-08-31 |
| AU2014316779A1 (en) | 2016-03-17 |
| SG11201601830PA (en) | 2016-04-28 |
| KR20160078956A (en) | 2016-07-05 |
| WO2015033224A3 (en) | 2015-07-02 |
| EA201690559A1 (en) | 2016-08-31 |
| JP2016530536A (en) | 2016-09-29 |
| CA2923421A1 (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| EP3044589A1 (en) | 2016-07-20 |
| TW201606304A (en) | 2016-02-16 |
| EP3043792A2 (en) | 2016-07-20 |
| CA2922901A1 (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| IL244453A0 (en) | 2016-04-21 |
| WO2015033224A2 (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| WO2015035402A1 (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| SG11201601605YA (en) | 2016-04-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Stessman et al. | Targeted sequencing identifies 91 neurodevelopmental-disorder risk genes with autism and developmental-disability biases | |
| Antonarakis et al. | Down syndrome | |
| KR20160086818A (en) | Methods of determining response to therapy | |
| Fromer et al. | Gene expression elucidates functional impact of polygenic risk for schizophrenia | |
| Taubes et al. | Experimental and real-world evidence supporting the computational repurposing of bumetanide for APOE4-related Alzheimer’s disease | |
| Korvatska et al. | R47H variant of TREM2 associated with Alzheimer disease in a large late-onset family: clinical, genetic, and neuropathological study | |
| Lucariello et al. | Whole exome sequencing of Rett syndrome-like patients reveals the mutational diversity of the clinical phenotype | |
| Haberman et al. | Prominent hippocampal CA3 gene expression profile in neurocognitive aging | |
| Ozkul et al. | A heritable profile of six miRNAs in autistic patients and mouse models | |
| Tuzovic et al. | A human de novo mutation in MYH10 phenocopies the loss of function mutation in mice | |
| Hu et al. | Mutations in PTRH2 cause novel infantile‐onset multisystem disease with intellectual disability, microcephaly, progressive ataxia, and muscle weakness | |
| Fusar-Poli et al. | Peripheral BDNF levels in psychiatric patients with and without a history of suicide attempt: A systematic review and meta-analysis | |
| Montgomery et al. | Maternal serotonin levels are associated with cognitive ability and core symptoms in autism spectrum disorder | |
| Reiling et al. | The association of mitochondrial content with prevalent and incident type 2 diabetes | |
| Stradomska et al. | Serum very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) levels as predictive biomarkers of diseases severity and probability of survival in peroxisomal disorders | |
| Kamath et al. | A molecular census of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease | |
| Brase et al. | A landscape of the genetic and cellular heterogeneity in Alzheimer disease | |
| Corvin et al. | The cognitive genetics of neuropsychiatric disorders | |
| Latvala et al. | Genetic origins of the association between verbal ability and alcohol dependence symptoms in young adulthood | |
| US9851355B2 (en) | Methods of determining response to therapy | |
| Sokol et al. | The genetics of autism | |
| Zhuang et al. | Mega-analysis of gene expression in mouse models of Alzheimer’s Disease | |
| Kaare et al. | Depression-Associated Negr1 Gene-Deficiency Induces Alterations in the Monoaminergic Neurotransmission Enhancing Time-Dependent Sensitization to Amphetamine in Male Mice | |
| JP2023506637A (en) | Use of Synaptotagmin-7 in Diagnosis and Treatment of Bipolar Disorder | |
| Runge et al. | Disruption of the transcription factor NEUROD2 causes an autism syndrome via cell-autonomous defects in cortical projection neurons |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WITN | Application deemed withdrawn, e.g. because no request for examination was filed or no examination fee was paid |