KR20110116019A - Battery electrolyte solutions containing aromatic phosphorus compounds - Google Patents
Battery electrolyte solutions containing aromatic phosphorus compounds Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20110116019A KR20110116019A KR1020117017106A KR20117017106A KR20110116019A KR 20110116019 A KR20110116019 A KR 20110116019A KR 1020117017106 A KR1020117017106 A KR 1020117017106A KR 20117017106 A KR20117017106 A KR 20117017106A KR 20110116019 A KR20110116019 A KR 20110116019A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- battery
- independently
- electrolyte
- formula
- battery electrolyte
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/056—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte characterised by the materials used as electrolytes, e.g. mixed inorganic/organic electrolytes
- H01M10/0564—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte characterised by the materials used as electrolytes, e.g. mixed inorganic/organic electrolytes the electrolyte being constituted of organic materials only
- H01M10/0566—Liquid materials
- H01M10/0567—Liquid materials characterised by the additives
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
- H01M10/4235—Safety or regulating additives or arrangements in electrodes, separators or electrolyte
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M6/00—Primary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M6/14—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M6/16—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte with organic electrolyte
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M6/00—Primary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M6/14—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M6/16—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte with organic electrolyte
- H01M6/162—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte with organic electrolyte characterised by the electrolyte
- H01M6/168—Cells with non-aqueous electrolyte with organic electrolyte characterised by the electrolyte by additives
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2300/00—Electrolytes
- H01M2300/0017—Non-aqueous electrolytes
- H01M2300/0025—Organic electrolyte
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/70—Energy storage systems for electromobility, e.g. batteries
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명의 전지 전해액은 0.01 내지 80 중량%의 방향족 인 화합물을 함유한다. 상기 방향족 인 화합물은, 상기 전해액에 증가된 열 안정성을 제공하여, 열 분해, 열 폭주 반응 및 연소 가능성을 낮추는 것을 돕는다. 상기 방향족 인 화합물은, 전지의 전기 특성에 대해 부정적인 영향을 거의 미치지 않으며, 몇몇 경우 실제로 전지 성능을 개선한다.The battery electrolyte of the present invention contains 0.01 to 80% by weight of aromatic phosphorus compounds. The aromatic phosphorus compounds provide increased thermal stability to the electrolyte, helping to reduce thermal decomposition, thermal runaway reactions, and the likelihood of combustion. Such aromatic phosphorus compounds have little negative effect on the electrical properties of the cell and in some cases actually improve the cell performance.
Description
본 발명은 2008년 12월 23일자로 출원된 미국 특허 가출원 제 61/140,579 호를 우선권으로 주장한다.The present invention claims priority to US Provisional Application No. 61 / 140,579, filed December 23, 2008.
본 발명은, 방향족 인 첨가제를 함유하는 비-수성 전해액에 관한 것이다.
The present invention relates to a non-aqueous electrolyte containing an aromatic phosphorus additive.
리튬 전지는 차량 및 많은 유형의 전자 장비용 1차 및 2차 전지로서 널리 사용된다. 이러한 전지는, 높은 에너지 및 출력 밀도를 갖는 경향이 있으며, 이러한 이유로 많은 용도에 선호된다. 리튬 전지 중의 전해액은 필요에 의해 비-수성 유형이다. 이러한 비-수성 전해액은 일반적으로, 유기 용매 또는 유기 용매들의 혼합물 중의 리튬 염의 고 유전체 함량 용액이다. 다양한 선형 및 환형 카보네이트가 통상적으로 사용되지만, 특정 에스터, 알킬 에터, 나이트릴, 설폰, 설폴란, 설톤 및 실록산도 용매로서 작용할 수 있다. 많은 경우, 상기 용매는 이러한 물질의 2종 이상을 함유할 수 있다. 중합체 겔 전해액도 공지되어 있다.Lithium batteries are widely used as primary and secondary batteries for vehicles and many types of electronic equipment. Such cells tend to have high energy and power densities and are therefore preferred for many applications. The electrolyte in a lithium battery is of non-aqueous type as needed. Such non-aqueous electrolytes are generally high dielectric content solutions of lithium salts in organic solvents or mixtures of organic solvents. Various linear and cyclic carbonates are commonly used, but certain esters, alkyl ethers, nitriles, sulfones, sulfolanes, sultones, and siloxanes can also act as solvents. In many cases, the solvent may contain two or more of these materials. Polymer gel electrolytes are also known.
이러한 전해액은 고농도의 유기 물질을 함유하기 때문에, 고온에 민감하다. 상기 전해액은 분해되거나, 발열성 폭주 반응에 관련되거나, 잘못된 조건에 노출되면 심지어 연소될 수 있다. 리튬 전지는, 과충전, 과방전, 단락(short circuit) 조건 및 기계적 또는 열적 오용으로 인해 발화되는 것으로 공지되어 있다. 연소 이외에 다른 문제, 예를 들어 전지 수명의 상당한 손실도 발생할 수 있다. 따라서, 전해액을 안정화시키는 것을 돕기 위해 리튬 전지의 전해액에 첨가제가 혼입되었다.Such electrolytes are sensitive to high temperatures because they contain high concentrations of organic materials. The electrolyte may decompose, be involved in exothermic runaway reactions, or even burn if exposed to the wrong conditions. Lithium batteries are known to ignite due to overcharge, overdischarge, short circuit conditions and mechanical or thermal misuse. In addition to combustion, other problems can occur, for example, significant losses in battery life. Therefore, additives have been incorporated into the electrolyte of the lithium battery to help stabilize the electrolyte.
전지 전해액을 위한 난연제 또는 "열 폭주 억제제"로서 다수의 인 화합물이 제안되었다. 상기 화합물은 다양한 포스핀 옥사이드(O:PR3), 포스피나이트(P(OR)R2), 포스포나이트(P(OR2)R), 포스파이트(P(OR)3), 포스피네이트(O:P(OR)R2), 포스포네이트(O:P(OR)2R), 포스페이트(O:P(OR)3) 및 포스파젠(-N=PR2-)n 화합물을 포함한다.Many phosphorus compounds have been proposed as flame retardants or "thermal runaway inhibitors" for battery electrolytes. The compounds include various phosphine oxides (O: PR 3 ), phosphinite (P (OR) R 2 ), phosphonite (P (OR 2 ) R), phosphite (P (OR) 3 ), phosphi Nate (O: P (OR) R 2 ), phosphonate (O: P (OR) 2 R), phosphate (O: P (OR) 3 ) and phosphazene (-N = PR 2- ) n compounds Include.
상기 인 화합물은 완전히 만족스럽지는 못했다. 이들 중 몇몇은, 효과적이기 위해서 매우 과량으로 첨가되어야 한다. 다른 화합물은 비-수성 용매, 리튬 염 또는 전해액 중의 다른 첨가제와 반응하거나, 애노드 또는 캐소드 물질과 반응한다. 또다른 화합물은, 전지 성능에 부정적인 영향을 미친다. 적당한 수준으로 우수한 안정성을 제공하고, 전해액 중의 다른 성분들 또는 애노드 또는 캐소드와 부정적으로 상호작용하지 않고, 전지 성능에 부정적인 영향을 거의 또는 전혀 미치지 않는, 비-수성 전지 전해액용 첨가제를 제공하는 것이 바람직할 것이다.
The phosphorus compound was not completely satisfactory. Some of these must be added in very excess in order to be effective. Other compounds react with other additives in non-aqueous solvents, lithium salts or electrolytes, or with anode or cathode materials. Another compound negatively affects cell performance. It is desirable to provide additives for non-aqueous cell electrolytes that provide good stability at an appropriate level, do not negatively interact with other components or anodes or cathodes in the electrolyte, and have little or no negative impact on cell performance. something to do.
하나의 양태에서, 본 발명은, 하나 이상의 리튬 염 및 비-수성 용매를 포함하는 전지 전해액이며, 이때 상기 리튬 염은 가용성이고, 상기 전지 전해액의 0.01 내지 80 중량%는 하나 이상의 하기 화학식 I의 방향족 인 화합물이다:In one embodiment, the invention is a battery electrolyte comprising at least one lithium salt and a non-aqueous solvent, wherein the lithium salt is soluble, and 0.01-80% by weight of the battery electrolyte is at least one aromatic of formula (I) Phosphorus compound is:
[화학식 I][Formula I]
상기 식에서,Where
A1은, 하나 이상의 방향족 고리를 함유하는 라디칼이고,A 1 is a radical containing one or more aromatic rings,
R은 각각 독립적으로, 1 내지 3개의 탄소 원자를 함유할 수 있고 상기 A1 기의 방향족 고리의 탄소 원자에 직접 결합되는 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이고, Each R is, independently, an alkylene divalent radical which may contain 1 to 3 carbon atoms and is directly bonded to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring of the A 1 group,
R1은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 할로겐, OH, 탄소수 12 이하의 하이드로카빌 기 또는 탄소수 12 이하의 알콕실 기이거나, 동일한 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 R1 기가 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성하고,R 1 is each independently hydrogen, halogen, OH, a hydrocarbyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or an alkoxyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or a ring structure in which two R 1 groups attached to the same phosphorus atom together contain a phosphorus atom Form the
x는 2 이상의 정수이다.x is an integer of 2 or more.
본 발명은 또한, 애노드, 캐소드, 상기 애노드와 상기 캐소드 사이에 배치된 분리막, 및 상기 애노드 및 상기 캐소드와 접촉하는 비-수성 전지 전해액을 포함하는 전지이며, 이때 상기 전지 전해액은 하나 이상의 리튬 염, 상기 리튬 염이 용해되는 비-수성 용매를 포함하며, 상기 전지 전해액의 약 0.01 내지 80 중량%는 하나 이상의 화학식 I의 방향족 인 화합물이다.The invention also relates to a battery comprising an anode, a cathode, a separator disposed between the anode and the cathode, and a non-aqueous battery electrolyte in contact with the anode and the cathode, wherein the battery electrolyte comprises at least one lithium salt, A non-aqueous solvent in which the lithium salt is dissolved, wherein about 0.01 to 80% by weight of the battery electrolyte is at least one aromatic phosphorus compound of formula (I).
본원에 기술된 바와 같은 방향족 인 화합물은, 전지 전해액에 우수한 열 안정화를 제공한다. 상기 전지 전해액은, 열 분해에 내성인 경향이 있으며, 열 폭주 반응에 덜 관여하고, 연소에 대해 내성이다. 놀랍게도, 상기 방향족 인 화합물은 때때로, 전지 용량 이용효율, 방전 속도 성능 및/또는 전지의 사이클 안정성을 실질적으로 증가시킨다.Aromatic phosphorus compounds as described herein provide excellent thermal stabilization for the cell electrolyte. The battery electrolyte tends to be resistant to thermal decomposition, is less involved in thermal runaway reactions, and is resistant to combustion. Surprisingly, the aromatic phosphorus compounds sometimes substantially increase cell capacity utilization, discharge rate performance and / or cycle stability of the cell.
특정 바람직한 실시양태에서, 상기 전지 전해액은 또한, (a) 하기 기술되는 바와 같은 하나 이상의 인-황 화합물, (b) 하나 이상의 지방족 탄소-탄소 이중 결합을 함유하는 하나 이상의 카보네이트 화합물, (c) 하나 이상의 설톤 화합물, 또는 (d) 전술된 화합물의 임의의 2종 이상의 혼합물을 함유한다. 이러한 바람직한 전해액을 함유하는 전지는, 특히 우수한 사이클 안정성을 갖는 경향이 있으며, 이러한 경우, 상기 전해액의 열 안정성은, 반복되는 사이클 후에도 매우 우수하게 유지되는 경향이 있다.
In certain preferred embodiments, the battery electrolyte further comprises (a) at least one phosphorus-sulfur compound as described below, (b) at least one carbonate compound containing at least one aliphatic carbon-carbon double bond, (c) one Or a sultone compound, or (d) a mixture of any two or more of the foregoing compounds. Batteries containing such a preferred electrolyte solution tend to have particularly excellent cycle stability, and in this case, the thermal stability of the electrolyte solution tends to be maintained very well even after repeated cycles.
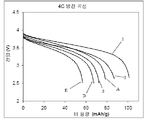
도 1은, 본 발명에 따른 2가지 전지와 3가지 비교 전지의 4C 방전 곡선의 그래프이다.
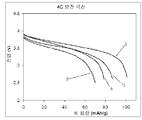
도 2는, 본 발명에 따른 3가지 전지와 3가지 비교 전지의 4C 방전 곡선의 그래프이다.
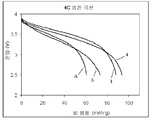
도 3은, 본 발명에 따른 2가지 전지와 2가지 비교 전지의 4C 방전 곡선의 그래프이다.
도 4는, 본 발명에 따른 3가지 전지와 하나의 비교 전지의 4C 방전 곡선의 그래프이다.1 is a graph of 4C discharge curves of two cells and three comparative cells according to the present invention.
2 is a graph of 4C discharge curves of three cells and three comparative cells according to the present invention.
3 is a graph of 4C discharge curves of two cells and two comparative cells according to the present invention.
4 is a graph of 4C discharge curves of three cells and one comparison battery according to the present invention.
화학식 I에서 R1 기는 각각 독립적으로 다를 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 탄소수 8 이하, 더욱 바람직하게는 탄소수 4 이하, 더더욱 바람직하게는 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실 기이다. 알콕실 R1 기는 선형 또는 분지형일 수 있으며, 치환기, 예컨대 할로겐(특히, 불소, 염소 또는 브롬) 또는 알콕실을 함유할 수 있다. 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 알콕실 R1 기는 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성할 수 있다. 이러한 고리 구조는 하기 화학식 II로 제시될 수 있다:The R 1 groups in formula (I) may each independently be different, preferably an alkoxyl group having 8 or less carbon atoms, more preferably 4 or less carbon atoms, even more preferably 1 to 3 carbon atoms. Alkoxyl R 1 groups may be linear or branched and may contain substituents such as halogen (especially fluorine, chlorine or bromine) or alkoxyl. Two alkoxyl R 1 groups attached to a phosphorus atom may together form a ring structure comprising a phosphorus atom. Such ring structures can be represented by the following formula (II):
[화학식 II]≪ RTI ID = 0.0 &
상기 식에서,Where
R2는, 에터 연결 기, 할로겐 또는 알콕실 기로 치환될 수 있는 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이다.R 2 is an alkylene divalent radical which may be substituted with an ether linking group, a halogen or an alkoxyl group.
화학식 I에서 특히 바람직한 R1 기는 메톡실, 에톡실, 아이소프로폭실 및 n-프로폭실이다.Particularly preferred R 1 groups in formula (I) are methoxyl, ethoxyl, isopropoxyl and n-propoxyl.
화학식 I에서 R 기는 각각, 바람직하게는 메틸렌(-CH2-), 에틸렌(-CH2-CH2-) 또는 아이소프로필렌(-CH2-CH(CH3)-)이고, 메틸렌이 가장 바람직하다. 화학식 I에서 R 기는 각각, 상기 A1 라디칼의 방향족 고리의 탄소 원자에 직접 결합된다.The R groups in formula (I) are each preferably methylene (-CH 2- ), ethylene (-CH 2 -CH 2- ) or isopropylene (-CH 2 -CH (CH 3 )-), with methylene being most preferred. . Each R group in formula (I) is bonded directly to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring of said A 1 radical.
화학식 I의 A1 라디칼은 하나 이상의 방향족 고리를 함유한다. 이는 2개 이상의 방향족 고리를 함유할 수 있다. 다수의 방향족 고리들 존재하는 경우, 이러한 고리들은 융합된 고리 구조로서 연결되거나(예컨대, 나프탈렌), 공유 결합으로 연결되거나(예컨대, 바이페닐 화합물), 하나 이상의 지방족 또는 지환족 기를 통해 연결되거나, 헤테로원자-함유 기(예컨대, 에터, 에스터, 아미노, 아미도, 카보네이트 또는 -SO2- 연결 기)를 통해 될 수 있다.The A 1 radical of formula (I) contains one or more aromatic rings. It may contain two or more aromatic rings. When multiple aromatic rings are present, these rings are linked as fused ring structures (e.g., naphthalene), covalently linked (e.g., biphenyl compounds), or linked via one or more aliphatic or alicyclic groups, or hetero Atom-containing groups (eg, ether, ester, amino, amido, carbonate, or —SO 2 — linking groups).
상기 A1 라디칼에 함유된 방향족 고리는, -R-P(O)-(R1)2 기에 더하여 치환기를 포함할 수 있으며, 다른 고리에 대한 임의의 연결 기를 포함할 수 있다. 이러한 치환기의 예는 할로겐, 하이드록실, 직쇄 또는 분지쇄 알킬(바람직하게는 4개 이하의 탄소 원자 함유), 알콕실(바람직하게는 4개 이하의 탄소 원자 함유), 또는 직쇄 또는 분지쇄 알켄일(바람직하게는 4개 이하의 탄소 원자 함유)을 포함한다.The aromatic ring contained in the A 1 radical may include a substituent in addition to the group —RP (O) — (R 1 ) 2 , and may include any linking group for another ring. Examples of such substituents are halogen, hydroxyl, straight or branched chain alkyl (preferably containing up to 4 carbon atoms), alkoxyl (preferably containing up to 4 carbon atoms), or straight or branched chain alkenyl (Preferably containing up to 4 carbon atoms).
바람직한 방향족 인 화합물은 하기 화학식 III의 구조를 갖는다:Preferred aromatic phosphorus compounds have the structure of formula III:
[화학식 III][Formula III]
상기 식에서,Where
R3은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 하이드록실, 할로겐, C1 -3 알킬, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,R 3 are each independently, hydrogen, hydroxyl, halogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, alkoxyl having 1-3 carbon atoms, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
R, R1 및 x는 상기 화학식 I에서 정의된 바와 같다.R, R 1 and x are as defined in formula (I) above.
R3은 가장 바람직하게는 수소 또는 C1 -3 알킬이다.R 3 is most preferably hydrogen or a C 1 -3 alkyl.
x의 값은 바람직하게는 2 내지 4이고, 더욱 바람직하게는 2 또는 3이다.The value of x is preferably 2 to 4, more preferably 2 or 3.
방향족 포스포네이트 화합물의 유용한 부류 중에는 하기 화학식 IV 또는 V의 화합물이 있다:Among useful classes of aromatic phosphonate compounds are compounds of formula IV or V
[화학식 IV][Formula IV]
[화학식 V][Formula V]
상기 식에서, 각각의 경우, R4는 각각 독립적으로, 탄소수 1 내지 8, 바람직하게는 탄소수 1 내지 4, 더욱 바람직하게는 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알킬이고, R3은 상기 화학식 III에서 정의된 바와 같다.In each case, R 4 is each independently alkyl having 1 to 8 carbon atoms, preferably 1 to 4 carbon atoms, more preferably 1 to 3 carbon atoms, and R 3 is as defined in Chemical Formula III. .
바람직하게, 화학식 IV 및 V에서 R4는 각각 독립적으로, 메틸, 에틸, 또는 아이소프로필이고, R3은 각각, 바람직하게는 수소 또는 C1 -3 알킬이다. 화학식 IV에서 포스포네이트 기들은, 이들 중 하나를 1번 위치로 잡을 경우, 벤젠 고리의 1,2,3-, 1,2,4- 또는 1,3,5- 위치에 있을 수 있다. 화학식 V에서 포스포네이트 기들은, 벤젠 고리에서 서로에 대해 오르쏘, 메타 또는 파라 위치에 있을 수 있다.Preferably, in formula IV and V R 4 are each independently a methyl, ethyl, or isopropyl, R 3 are each preferably a hydrogen or a C 1 -3 alkyl. The phosphonate groups in formula (IV) may be in the 1,2,3-, 1,2,4- or 1,3,5-position of the benzene ring when one of them is taken in position 1. The phosphonate groups in formula (V) may be in the ortho, meta or para position relative to each other in the benzene ring.
본 발명에 유용한 특정 방향족 인 화합물은 하기 화학식 VI 내지 XI의 구조를 포함한다.Particular aromatic phosphorus compounds useful in the present invention include structures of the following formulas VI-XI.
[화학식 VI][Formula VI]
[화학식 VII][Formula VII]
[화학식 VIII](VIII)
[화학식 IX](IX)
[화학식 X][Formula X]
[화학식 XI](XI)
상기 화학식 VI 및 X의 방향족 인 화합물이 특히 바람직하다.Particular preference is given to aromatic phosphorus compounds of the above formulas VI and X.
상기 방향족 인 화합물의 2종 이상의 혼합물이 사용될 수 있다. 특히 관심있는 혼합물은, 10 내지 95 중량%의 화학식 III의 방향족 인 화합물(이때, x 값은 3 이상, 바람직하게는 3 또는 4임)과, 5 내지 90 중량%의 화학식 III의 제 2 방향족 인 화합물(이때, x의 값은 2임)의 혼합물이다. 이러한 2가지 방향족 인 화합물의 중량 비는 바람직하게는 30:70 내지 70:30, 또는 40:60 내지 60:40(중량비)이다. 이러한 혼합물이 존재하면, 화학식 III의 화합물이 모두 x가 3 이상인 경우에 비해, 전지 전해질이 더욱 저장 안정성이 되게 할 수 있는 것으로 밝혀졌다.Mixtures of two or more of these aromatic phosphorus compounds may be used. Of particular interest are mixtures of from 10 to 95% by weight of an aromatic phosphorus compound of formula III, wherein the x value is at least 3, preferably 3 or 4, and from 5 to 90% by weight of second aromatic phosphorus of formula III Is a mixture of compounds, wherein the value of x is 2. The weight ratio of these two aromatic phosphorus compounds is preferably 30:70 to 70:30, or 40:60 to 60:40 (weight ratio). The presence of such a mixture has been found to make the battery electrolyte more storage stable compared to the case where all of the compounds of formula III have x equal to or greater than 3.
상기 방향족 인 화합물은 전지 전해액의 총 중량의 약 0.01 내지 80% 정도를 차지할 수 있다. 그러나, 본 발명의 이점은, 상기 방향족 인 화합물을 낮은 수준으로 첨가하는 경우에도 일반적으로 효과적이라는 것이다. 따라서, 상기 방향족 인 화합물은 바람직하게는, 전지 전해액의 총 중량의 15% 이하, 더욱 바람직하게는 10% 이하를 차지한다. 특히 바람직한 양은 전지 전해액의 총 중량의 5% 이하이다. 바람직한 하한 양은 전해액의 총 중량의 0.1% 이상이다.The aromatic phosphorus compound may account for about 0.01 to 80% of the total weight of the battery electrolyte. However, an advantage of the present invention is that it is generally effective even when the aromatic phosphorus compound is added at a low level. Therefore, the aromatic phosphorus compound preferably accounts for 15% or less, more preferably 10% or less of the total weight of the battery electrolyte. Particularly preferred amounts are up to 5% of the total weight of the battery electrolyte. The lower limit is preferably at least 0.1% of the total weight of the electrolyte.
상기 전지 전해액의 다른 주요 성분은 리튬 염 및 상기 리튬 염을 위한 비-수성 용매이다.Other major components of the battery electrolyte are lithium salts and non-aqueous solvents for the lithium salts.
상기 리튬 염은, 전지에 사용하기 적합한 임의의 것일 수 있으며, 예를 들어 무기 리튬 염, 예컨대 LiAsF6, LiPF6, LiB(C2O4)2, LiBF4, LiBF2C2O4, LiClO4, LiBrO4 및 LiIO4; 및 유기 리튬 염, 예컨대 LiB(C6H5)4, LiCH3SO3, LiN(SO2C2F5)2 및 LiCF3SO3이다. LiPF6, LiClO4, LiBF4, LiAsF6, LiCF3SO3 및 LiN(SO2CF3)2가 바람직한 유형이며, LiPF6이 특히 바람직한 리튬 염이다. The lithium salt may be any suitable for use in a battery, for example inorganic lithium salts such as LiAsF 6 , LiPF 6 , LiB (C 2 O 4 ) 2 , LiBF 4 , LiBF 2 C 2 O 4 , LiClO 4 , LiBrO 4 and LiIO 4 ; And organic lithium salts such as LiB (C 6 H 5 ) 4 , LiCH 3 SO 3 , LiN (SO 2 C 2 F 5 ) 2 and LiCF 3 SO 3 . LiPF 6 , LiClO 4 , LiBF 4 , LiAsF 6 , LiCF 3 SO 3 and LiN (SO 2 CF 3 ) 2 are the preferred types, and LiPF 6 is a particularly preferred lithium salt.
상기 리튬 염은 전해액의 0.5 mol/L 이상, 바람직하게는 0.75 mol/L 이상, 3 mol/L 이하, 더욱 바람직하게는 1.5 mol/L 이하의 농도로 적절히 존재한다.The lithium salt is suitably present at a concentration of at least 0.5 mol / L, preferably at least 0.75 mol / L, at most 3 mol / L, more preferably at most 1.5 mol / L of the electrolyte.
상기 비-수성 용매는, 예를 들어 하나 이상의 선형 알킬 카보네이트, 환형 카보네이트, 환형 에스터, 선형 에스터, 환형 에터, 알킬 에터, 나이트릴, 설폰, 설폴란, 실록산 및 설톤을 포함할 수 있다. 전술된 유형의 임의의 2종 이상의 혼합물이 사용될 수 있다. 환형 에스터, 선형 알킬 카보네이트 및 환형 카보네이트가 비-수성 용매의 바람직한 유형이다.The non-aqueous solvent may include, for example, one or more linear alkyl carbonates, cyclic carbonates, cyclic esters, linear esters, cyclic ethers, alkyl ethers, nitriles, sulfones, sulfolanes, siloxanes and sultones. Mixtures of any two or more of the aforementioned types can be used. Cyclic esters, linear alkyl carbonates and cyclic carbonates are the preferred types of non-aqueous solvents.
적합한 선형 알킬 카보네이트는 다이메틸 카보네이트, 다이에틸 카보네이트, 메틸 에틸 카보네이트 등을 포함한다. 적합한 환형 카보네이트는 에틸렌 카보네이트, 프로필렌 카보네이트, 부틸렌 카보네이트 등을 포함한다. 적합한 환형 에스터는, 예를 들어 γ-부티로락톤 및 γ-발레로락톤을 포함한다. 환형 에터는 테트라하이드로퓨란, 2-메틸테트라하이드로퓨란, 테트라하이드로피란 등을 포함한다. 알킬 에터는 다이메톡시에탄, 다이에톡시에탄 등을 포함한다. 나이트릴은 모노나이트릴, 예컨대 아세토나이트릴 및 프로피오나이트릴; 다이나이트릴, 예컨대 글루타로나이트릴; 및 이들의 유도체를 포함한다. 설폰은 대칭형 설폰, 예컨대 다이메틸 설폰, 다이에틸 설폰 등; 비대칭형 설폰, 예컨대 에틸 메틸 설폰, 프로필 메틸 설폰 등; 및 이들의 유도체를 포함한다. 설폴란은 테트라메틸렌 설폴란 등을 포함한다. Suitable linear alkyl carbonates include dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate, methyl ethyl carbonate and the like. Suitable cyclic carbonates include ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate, butylene carbonate and the like. Suitable cyclic esters include, for example, γ-butyrolactone and γ-valerolactone. Cyclic ethers include tetrahydrofuran, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, tetrahydropyran and the like. Alkyl ethers include dimethoxyethane, diethoxyethane and the like. Nitriles include mononitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Dynitrile such as glutaronitrile; And derivatives thereof. Sulfones are symmetrical sulfones such as dimethyl sulfone, diethyl sulfone and the like; Asymmetric sulfones such as ethyl methyl sulfone, propyl methyl sulfone and the like; And derivatives thereof. Sulfonanes include tetramethylene sulfolane and the like.
몇몇 바람직한 용매 혼합물은, 15:85 내지 40:60의 중량비의 환형 카보네이트/선형 알킬 카보네이트의 혼합물; 20:80 내지 60:40의 중량비의 환형 카보네이트/환형 에스터의 혼합물: (20 내지 48):(50 내지 78):(2 내지 20)의 중량비의 환형 카보네이트/환형 에스터/선형 알킬 카보네이트의 혼합물; 70:30 내지 98:2의 중량비의 환형 에스터/선형 알킬 카보네이트의 혼합물을 포함한다. Some preferred solvent mixtures include mixtures of cyclic carbonate / linear alkyl carbonates in a weight ratio of 15:85 to 40:60; Mixture of cyclic carbonate / cyclic ester in a weight ratio of 20:80 to 60:40: a mixture of cyclic carbonate / cyclic ester / linear alkyl carbonate in a weight ratio of (20 to 48) :( 50 to 78) :( 2 to 20); Mixtures of cyclic ester / linear alkyl carbonates in a weight ratio of 70:30 to 98: 2.
특히 관심있는 용매 혼합물은, 15:85 내지 40:60의 중량비의 에틸렌 카보네이트/프로필렌 카보네이트의 혼합물; 15:85 내지 40:60의 중량 비의 에틸렌 카보네이트/다이메틸 카보네이트의 혼합물; (20 내지 48):(50 내지 78):(2 내지 20)의 중량비의 에틸렌 카보네이트/프로필렌 카보네이트/다이메틸 카보네이트의 혼합물; 15:85 내지 40:60의 중량비의 프로필렌 카보네이트/다이메틸 카보네이트의 혼합물이다.Particularly interesting solvent mixtures include mixtures of ethylene carbonate / propylene carbonate in a weight ratio of 15:85 to 40:60; Mixtures of ethylene carbonate / dimethyl carbonate in a weight ratio of 15:85 to 40:60; A mixture of ethylene carbonate / propylene carbonate / dimethyl carbonate in a weight ratio of (20 to 48) :( 50 to 78) :( 2 to 20); Propylene carbonate / dimethyl carbonate in a weight ratio of 15:85 to 40:60.
상기 언급된 성분들에 더하여, 다양한 다른 첨가제가 상기 전지 전해액 중에 존재할 수 있다. 이러한 첨가제는, 예를 들어 흑연 전극의 표면에서 고체 전해질 계면의 형성을 촉진하는 첨가제; 다양한 캐소드 보호제; 리튬 염 안정화제; 리튬 침착 개선제; 이온성 용매화 개선제; 부식 억제제; 습윤제; 난연제; 및 점도 저하제를 포함할 수 있다. 이러한 유형의 많은 첨가제는 문헌[Zhang in "A review on electrolyte additives for lithium-ion batteries," J. Power Sources 162 (2006) 1379-1394]에 기술되어 있다.In addition to the components mentioned above, various other additives may be present in the battery electrolyte. Such additives include, for example, additives which promote the formation of a solid electrolyte interface at the surface of the graphite electrode; Various cathode protectants; Lithium salt stabilizers; Lithium deposition improvers; Ionic solvation improvers; Corrosion inhibitors; Wetting agents; Flame retardant; And viscosity reducing agents. Many additives of this type are described in Zhang in "A review on electrolyte additives for lithium-ion batteries," J. Power. Sources 162 (2006) 1379-1394.
고체 전해질 계면(SEI)의 형성을 촉진하는 제제는, 다양한 중합성 에틸렌형 불포화 화합물, 다양한 황 화합물 및 다른 물질을 포함한다. 적합한 캐소드 보호제는, N,N-다이에틸아미노트라이메틸실란 및 LiB(C2O4)2와 같은 물질을 포함한다. 리튬 염 안정화제는 LiF, 트리스(2,2,2-트라이플루오로에틸)포스파이트, 1-메틸-2-피롤리돈, 불화된 카바메이트 및 헥사메틸포스포아마이드를 포함한다. 리튬 침착 개선제의 예는 이산화 황, 폴리설파이드, 이산화 탄소; 계면활성제, 예컨대 테트라알킬암모늄 클로라이드; 퍼플루오로옥탄설포네이트의 리튬 및 테트라에틸암모늄 염; 다양한 퍼플루오로폴리에터 등을 포함한다. 크라운 에터가 적합한 이온성 용매화 개선제일 수 있으며, 다양한 보레이트, 붕소 및 보롤 화합물도 적합하다. LiB(C2O4)2 및 LiF2C2O4는 알루미늄 부식 억제제의 예이다. 사이클로헥산, 트라이알킬 포스페이트 및 특정 카복실산 에스터는 습윤제 및 점도 저하제로서 유용하다. LiB(C2O4)2와 같은 몇몇 물질은 전해액 중에서 다중 기능을 수행할 수 있다. Agents that promote the formation of a solid electrolyte interface (SEI) include various polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated compounds, various sulfur compounds, and other materials. Suitable cathode protectants include materials such as N, N-diethylaminotrimethylsilane and LiB (C 2 O 4 ) 2 . Lithium salt stabilizers include LiF, tris (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphite, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, fluorinated carbamate and hexamethylphosphoamide. Examples of lithium deposition improvers include sulfur dioxide, polysulfide, carbon dioxide; Surfactants such as tetraalkylammonium chloride; Lithium and tetraethylammonium salts of perfluorooctanesulfonate; Various perfluoropolyethers and the like. Crown ethers may be suitable ionic solvation improvers, and various borate, boron and borol compounds are also suitable. LiB (C 2 O 4 ) 2 and LiF 2 C 2 O 4 are examples of aluminum corrosion inhibitors. Cyclohexane, trialkyl phosphates and certain carboxylic acid esters are useful as wetting agents and viscosity reducing agents. Some materials, such as LiB (C 2 O 4 ) 2 , can perform multiple functions in the electrolyte.
다양한 다른 첨가제들이 함께 전지 전해액의 총 중량의 20% 이하, 바람직하게는 10% 이하를 차지할 수 있다.Various other additives may together comprise up to 20%, preferably up to 10%, of the total weight of the battery electrolyte.
화학식 III의 화합물을 함유하는 전해액은, 하기 화학식 XII에 대응하는 방향족 모노포스페이트 화합물을 함유할 수 있다:The electrolyte solution containing the compound of formula III may contain an aromatic monophosphate compound corresponding to formula XII:
[화학식 XII](XII)
상기 식에서, R3, R 및 R1은 각각 상기 화학식 I 및 III에서 정의된 바와 같다.Wherein R 3 , R and R 1 are as defined in Formulas I and III, respectively.
화학식 III의 화합물에서 x가 3 이상인 경우에는, 화학식 XII의 화합물이 존재하는 것이 바람직하다. 화학식 III의 화합물 대 화학식 XII의 화합물의 중량 비는 10:90 내지 95:5일 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 30:70 내지 70:30, 또는 40:60 내지 60:40이다. 화학식 III(여기서, x는 3 이상임)의 화합물과 함께, 화학식 XII의 화합물이 존재하면, 화학식 III의 화합물(여기서, x는 3 이상임)만 존재하는 경우에 비해 전지 전해액이 더욱 저장 안정성이 되는 것으로 밝혀졌다. 적합한 화학식 XII의 화합물의 예는 하기 화학식 XIII 내지 XVIII의 화합물이다.When x is 3 or more in the compound of formula III, it is preferred that a compound of formula XII is present. The weight ratio of the compound of formula III to the compound of formula XII may be 10:90 to 95: 5, preferably 30:70 to 70:30, or 40:60 to 60:40. When the compound of formula XII is present together with the compound of formula III (where x is 3 or more), the battery electrolyte is more storage stable than when only the compound of formula III (where x is 3 or more) is present. Turned out. Examples of suitable compounds of formula XII are compounds of formulas XIII to XVIII.
[화학식 XIII](XIII)
[화학식 XIV](XIV)
[화학식 XV](XV)
[화학식 XVI](XVI)
[화학식 XVII]Formula XVII]
[화학식 XVIII][Formula XVIII]
바람직한 전지 전해액은, (a) 하나 이상의 인-황 화합물, (b) 지방족 탄소-탄소 불포화기를 함유하는 하나 이상의 카보네이트, (c) 하나 이상의 설톤 화합물, 또는 (d) 전술된 성분의 임의의 2종 이상의 혼합물을 함유한다. 이러한 화합물이 하나 이상 존재하면, 이러한 전해액을 함유하는 전지의 사이클 안정성 및 사이클 후 상기 전해액의 열 안정성이 상당히 개선되는 것으로 밝혀졌다. 이러한 화합물들은 개별적으로 또는 전체적으로, 전지 전해액의 총 중량의 0.001 내지 20%를 차지할 수 있다. 전지 전해액의 총 중량을 기준으로, 바람직한 하한은 0.01 중량% 이상이고, 바람직한 상한 양은 10 중량% 이다.Preferred battery electrolytes include (a) one or more phosphorus-sulfur compounds, (b) one or more carbonates containing aliphatic carbon-carbon unsaturated groups, (c) one or more sultone compounds, or (d) any two of the aforementioned components It contains the above mixture. When one or more such compounds are present, it has been found that the cycle stability of the cells containing such electrolytes and the thermal stability of the electrolytes after cycles are significantly improved. These compounds, individually or in total, may account for 0.001 to 20% of the total weight of the battery electrolyte. Based on the total weight of the battery electrolyte, the lower limit is preferably 0.01% by weight or more, and the upper limit is preferably 10% by weight.
적합한 인-황 화합물은 국제 특허 출원 공개 제 WO 08/88487 호에 기술되어 있으며, 상기 특허의 개시내용을 본원에 참고로 인용한다. 이러한 인-황 화합물은 하기 화학식 XIX으로 제시된다:Suitable phosphorus-sulfur compounds are described in WO 08/88487, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. Such phosphorus-sulfur compounds are represented by the formula: XIX:
[화학식 XIX][Formula XIX]
상기 식에서, Where
X는 산소 또는 황이고,X is oxygen or sulfur,
T는 공유 결합, 산소 또는 황이되, 단 X 및 T 중 적어도 하나는 황이고, T is a covalent bond, oxygen or sulfur, provided that at least one of X and T is sulfur,
X'은 각각 독립적으로, 산소 또는 황이고, Each X 'is independently oxygen or sulfur,
m은 각각 독립적으로, X'이 산소인 경우에는 0 또는 1이고, X'이 황인 경우에는 0, 1 또는 2이고,each m is independently 0 or 1 when X 'is oxygen, 0, 1 or 2 when X' is sulfur,
n은 1 이상, 바람직하게는 2 이상이고,n is 1 or more, preferably 2 or more,
R5는 각각 독립적으로, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 하이드로카빌 기이거나, R5 기들이 함께, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 2가 유기 기를 형성하고,Each R 5 is, independently, an unsubstituted or inactively substituted hydrocarbyl group, or the R 5 groups together form an unsubstituted or inactively substituted divalent organic group,
A는 유기 연결 기이다.A is an organic linking group.
적합한 인-황 첨가제의 특정 유용한 유형은 하기 구조식 XX, XXI 및 XXII로 제시될 수 있다:Certain useful types of suitable phosphorus-sulfur additives can be represented by the following structural formulas XX, XXI and XXII:
[화학식 XX][Formula XX]
[화학식 XXI][Formula XXI]
[화학식 XXII][Formula XXII]
상기 식에서, R, X, T, A 및 n은 상기 화학식 XIX에서 기술된 바와 같으며, X 및 T 중 적어도 하나는 황이다. Wherein R, X, T, A and n are as described above in formula XIX, and at least one of X and T is sulfur.
화학식 XIX, XX, XXI 및 XXII에서 T는 바람직하게는 산소 또는 황이고, 가장 바람직하게는 황이다. X는 바람직하게는 황이고, n은 바람직하게는 2 이상이다. 화학식 XIX, XX, XXI 또는 XXII에서 R5 기는, 예를 들어 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 지방족, 지환족 또는 방향족 기일 수 있다. "비활성" 치환기는, 상기 첨가제의 SEI-형성 특성을 그다지 방해하지 않는 치환기이다. 상기 비활성 치환기는, 예를 들어 산소-함유 기, 예컨대 에터, 에스터, 카보닐 또는 옥시란 기 등일 수 있다. 비활성 치환기는 질소-함유 기, 예컨대 1급, 2급 또는 3급 아민 기, 이민 기, 아마이드 기 또는 나이트로 기일 수 있다. 상기 비활성 치환기는 다른 헤테로 원자, 예컨대 황, 인 등을 함유할 수 있다. T in the formulas XIX, XX, XXI and XXII is preferably oxygen or sulfur, most preferably sulfur. X is preferably sulfur and n is preferably 2 or more. The R 5 group in formula XIX, XX, XXI or XXII can be, for example, an unsubstituted or inertly substituted aliphatic, alicyclic or aromatic group. A "inactive" substituent is a substituent that does not interfere much with the SEI-forming properties of the additive. Such inert substituents can be, for example, oxygen-containing groups such as ether, ester, carbonyl or oxirane groups and the like. Inert substituents may be nitrogen-containing groups such as primary, secondary or tertiary amine groups, imine groups, amide groups or nitro groups. The inert substituents may contain other hetero atoms such as sulfur, phosphorus and the like.
본 발명의 목적을 위해, 하이드로카빌 기는, 수소 및 탄소 원자만 함유하는 기이다. 하이드로카빌 기는 지방족, 지환족, 방향족, 또는 이러한 유형의 2종 이상의 몇몇 조합일 수 있다. For the purposes of the present invention, hydrocarbyl groups are groups containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbyl groups may be aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, aromatic, or some combination of two or more of these types.
화학식 XIX, XX, XXI, 또는 XXII에서 R5 기는 바람직하게는, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 저급 알킬, 예컨대 메틸, 에틸, n-프로필, 아이소프로필, n-부틸, 아이소부틸, 2급-부틸, 3급-부틸 등이다. 다른 바람직한 실시양태에서는, 예를 들어 하기 화학식 XXIII으로 도시되는 바와 같이, 2개의 R5 기가 함께, 각각 -(X')m-P-(X')m-, -O-P-O-, -S-P-O- 또는 -S-P-S- 연결 기를 완성하는 2가 유기 라디칼을 형성한다. The R 5 group in formula XIX, XX, XXI, or XXII is preferably an unsubstituted or inertly substituted lower alkyl such as methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, secondary- Butyl, tert-butyl and the like. In another preferred embodiment, such as illustrated by the general formula XXIII for example, two R 5 groups together, and each - (X ') m -P- ( X') m -, -OPO-, -SPO- or To form a divalent organic radical which completes the -SPS- linking group.
특히 바람직한 인-황 첨가제는 하기 화학식 XXIII으로 제시되는 화합물이다:Particularly preferred phosphorus-sulfur additives are the compounds represented by the formula (XXIII):
[화학식 XXIII][Formula XXIII]
상기 식에서,Where
X, n 및 A는 상기 화학식 XIX(X는 바람직하게는 황임)에 대해 기술된 바와 같고,X, n and A are as described for Formula XIX (X is preferably sulfur),
R6은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 알킬 또는 비활성적으로 치환된 알킬이고,Each R 6 is independently hydrogen, alkyl or inactively substituted alkyl,
R7은 공유 결합 또는 2가 연결 기이다.R 7 is a covalent bond or a divalent linking group.
화학식 XXIII에서, R6 기는 바람직하게는 수소 또는 저급 알킬이고, 더욱 바람직하게는 수소이다. R7 기는 바람직하게는 직쇄 또는 분지쇄 하이드로카빌 기, -O- 또는 공유 결합이다. 더욱 바람직한 R7 기는, R6 2C 기에 직접 결합된 탄소 원자 또는 탄소 원자들 상의 동일 탄소상에서 이치환된 하이드로 카빌 기이다. R7 기는 가장 바람직하게는 다이알킬-치환된 메틸렌이며, R7 기가 (다이메틸)메틸렌인 경우에도 가장 바람직하다.In formula (XXIII), the R 6 group is preferably hydrogen or lower alkyl, more preferably hydrogen. The R 7 group is preferably a straight or branched chain hydrocarbyl group, —O— or a covalent bond. More preferred R 7 groups are hydrocarbyl groups disubstituted on the same carbon on carbon atoms or carbon atoms directly bonded to the R 6 2 C group. The R 7 group is most preferably dialkyl-substituted methylene, even most preferred when the R 7 group is (dimethyl) methylene.
특히 바람직한 유형의 인-황 첨가제는 하기 화학식 XXIV로 제시된다:Particularly preferred types of phosphorus-sulfur additives are represented by the formula XXIV:
[화학식 XXIV]Formula XXIV
상기 식에서, X, n 및 A는 상기 화학식 XIX에서 기술된 바와 같다.Wherein X, n and A are as described above in formula (XIX).
X는 바람직하게는 황이다.X is preferably sulfur.
화학식 XIX 내지 XXIV에서, A 기는 유기 연결 기이다. 이러한 유기 연결 기는 각종 다양한 가능한 구조를 가질 수 있다. 상기 유기 연결 기는 -T- 연결 기(화학식 XIX 내지 XXII에서) 또는 -S- 원자(화학식 XXIII 및 XXIV에서)에 공유 결합된다. 상기 -T- 또는 -S- 연결 기는, 유기 연결 기 A 상의 탄소 원자 또는 헤테로원자에 결합될 수 있지만, 바람직하게는 탄소 원자에 결합된다. 상기 탄소 원자는 바람직하게는 1급 또는 2급 탄소 원자(즉, 1개 또는 2개의 다른 탄소 원자에 결합됨)이지만, 덜 바람직하게는 3급 탄소 원자(즉, 3개의 다른 탄소 원자에 결합됨)이다.In the formulas XIX to XXIV, the A group is an organic linking group. Such organic linking groups may have a variety of possible structures. The organic linking group is covalently bonded to a -T- linking group (in formulas XIX to XXII) or an -S- atom (in formulas XXIII and XXIV). The -T- or -S- linking group may be bonded to a carbon atom or heteroatom on the organic linking group A, but is preferably bonded to a carbon atom. The carbon atom is preferably a primary or secondary carbon atom (ie bonded to one or two other carbon atoms), but less preferably a tertiary carbon atom (ie bonded to three other carbon atoms) )to be.
상기 유기 연결 기 A의 하나의 유형은, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 하이드로카빌 기이다. 상기 유기 연결 기 A는 임의의 개수의 탄소 원자를 함유할 수 있지만, 인 원자 당 분자량이 약 1000 Da을 초과하지 않는 것이 바람직하며, 더욱 바람직하게는 약 750 Da을 초과하지 않고, 특히 500 Da 미만이다. 상기 인-황 첨가제는 5 내지 50 중량% 이하의 황을 함유할 수 있다. 상기 유기 연결 기 A는 지방족(선형 또는 분지형), 지환족, 방향족, 또는 이들의 몇몇 조합일 수 있다. 상기 유기 연결 시 A의 원자가는 n과 동일하다.One type of such organic linking group A is an unsubstituted or inertly substituted hydrocarbyl group. The organic linking group A may contain any number of carbon atoms, but preferably a molecular weight per phosphorus atom does not exceed about 1000 Da, more preferably does not exceed about 750 Da, in particular less than 500 Da to be. The phosphorus-sulfur additive may contain 5 to 50 wt.% Sulfur. The organic linking group A may be aliphatic (linear or branched), alicyclic, aromatic, or some combination thereof. The valence of A in the organic connection is equal to n.
화학식 XIX 내지 XXIV에서 상기 연결 기 A의 하나의 바람직한 유형은, 벤질형 탄소 원자를 통해 (경우에 따라) -T- 또는 -S- 연결 기에 결합된다. 이러한 유형의 A 기를 함유하는 인-황 첨가제의 특정 예는 하기 화학식 XXV 내지 XXXIV의 화합물이다.One preferred type of the linking group A in the formulas XIX to XXIV is bonded to a -T- or -S- linking group (optionally) via a benzyl carbon atom. Particular examples of phosphorus-sulfur additives containing this type of A group are compounds of the formulas XXV to XXXIV.
[화학식 XXV][Formula XXV]
[화학식 XXVI]Formula XXVI
[화학식 XXVII]Formula XXVII
[화학식 XXVIII]Formula XXVIII
[화학식 XXIX][XXIX]
[화학식 XXX][Formula XXX]
[화학식 XXXI][Formula XXXI]
[화학식 XXXII][Formula XXXII]
[화학식 XXXIII][Formula XXXIII]
[화학식 XXXIV][Formula XXXIV]
또한, 상기 인-황 기의 경우, A 기의 방향족 고리에 직접 결합되는 것도 가능하다.In the case of the phosphorus-sulfur group, it is also possible to directly bond to the aromatic ring of the A group.
지방족 탄소-탄소 불포화기를 갖는 적합한 카보네이트 화합물은, 비닐리딘 카보네이트, 비닐 에틸 카보네이트, 알릴 에틸 카보네이트 등을 포함한다.Suitable carbonate compounds having aliphatic carbon-carbon unsaturated groups include vinylidine carbonate, vinyl ethyl carbonate, allyl ethyl carbonate, and the like.
설톤 화합물은, 하이드록실 설폰산의 환형 설포네이트 에스터이다. 이는, 하기 화학식 XXXV로 제시될 수 있다:The sultone compound is a cyclic sulfonate ester of hydroxyl sulfonic acid. This can be represented by the following formula XXXV:
[화학식 XXXV][Formula XXXV]
상기 식에서, R8은, 상기 고리 구조가 5 내지 7개의 원자를 함유하도록 하는 알킬렌 기이다.Wherein R 8 is an alkylene group such that the ring structure contains 5 to 7 atoms.
R8 기는 알킬 기로 치환될 수 있다. 적합한 설톤 화합물의 예는 1,3-프로판 설톤이다.R 8 groups may be substituted with alkyl groups. Examples of suitable sultone compounds are 1,3-propane sultone.
상기 전지 전해액은, 상기 리튬 염, 상기 방향족 인 화합물, 및 상기 비-수성 용매에 사용될 수 있는 임의의 다른 첨가제를 용해시키거나 분산시킴으로써 편리하게 제조된다. 일반적으로, 혼합 순서는 중요하지 않다. 생성 전지 전해액의 함수량은 가능한 한 낮아야 한다. 50 ppm 이하의 함수량이 바람직하며, 30 ppm 이하의 함수량이 더욱 바람직하다. 잔량의 물을 제거하기 위해, 상기 전해액을 형성하기 전에 이러한 다양한 성분을 개별적으로 건조하고/하거나, 배합된 전해액을 건조할 수 있다. 선택되는 건조 방법은, 상기 전해액의 다양한 성분을 열화시키거나 분해시키기 않아야 하며, 이들 성분 간의 바람직하지 않은 반응을 촉진하지 않아야 한다. 열 방법이 사용될 수 있으며, 제제(예컨대, 분자 체)를 건조하는 것도 사용될 수 있다.The battery electrolyte is conveniently prepared by dissolving or dispersing the lithium salt, the aromatic phosphorus compound, and any other additives that may be used in the non-aqueous solvent. In general, the mixing order is not important. The water content of the resulting cell electrolyte should be as low as possible. A water content of 50 ppm or less is preferable, and a water content of 30 ppm or less is more preferable. In order to remove the residual amount of water, these various components may be individually dried and / or the combined electrolyte may be dried before the electrolyte is formed. The drying method chosen should not degrade or decompose the various components of the electrolyte and should not promote undesirable reactions between these components. Thermal methods can be used, and drying agents (eg molecular sieves) can also be used.
본 발명의 전해액을 함유하는 전지는 임의의 유용한 구조일 수 있다. 전형적인 전지 구조는 애노드, 캐소드, 및 상기 애노드와 캐소드 사이에 배치된 분리막 및 전해액을 포함하여, 상기 애노드와 상기 캐소드 사이에서 전해액을 통해 이온이 이동할 수 있다. 이러한 어셈블리는 일반적으로 케이스 내에 포장된다. 전지의 형태는 제한되지 않는다. 상기 전지는, 나선형으로 감긴 시트 전극 및 분리막을 갖는 원통형일 수 있다. 상기 전지는, 펠릿 전극 및 분리막의 조합을 포함하는 인사이드-아웃(inside-out) 구조를 갖는 원통형일 수 있다. 상기 전지는, 중첩된 전극 및 분리막을 함유하는 판형일 수 있다.The battery containing the electrolyte solution of the present invention may be of any useful structure. Typical cell structures include an anode, a cathode, and a separator and electrolyte disposed between the anode and the cathode, through which ions can migrate through the electrolyte between the anode and the cathode. Such assemblies are generally packaged in a case. The form of the battery is not limited. The battery may be cylindrical having a spirally wound sheet electrode and a separator. The battery may be cylindrical having an inside-out structure including a combination of a pellet electrode and a separator. The battery may be a plate-type containing an overlapping electrode and a separator.
적합한 애노드 물질은, 예를 들어 탄소질 물질, 예컨대 천연 또는 인조 흑연, 탄소화된 피치, 탄소 섬유, 흑연화된 메조상 미소구체, 퍼니스 블랙, 아세틸렌 블랙 및 다양한 다른 흑연화된 물질을 포함한다. 상기 탄소질 물질은, 결합제(예를 들어 폴리(비닐리덴 플루오라이드), 폴리테트라플루오로에틸렌, 스타이렌-부타다이엔 공중합체, 아이소프렌 고무, 폴리(비닐 아세테이트), 폴리(에틸 메타크릴레이트), 폴리에틸렌 또는 나이트로셀룰로스)를 사용하여 함께 결합될 수 있다. 적합한 탄소질 애노드 및 이의 제조 방법은, 예를 들어 미국 특허 제 7,169,511 호에 기술되어 있다. Suitable anode materials include, for example, carbonaceous materials such as natural or artificial graphite, carbonized pitch, carbon fibers, graphitized mesophase microspheres, furnace black, acetylene black and various other graphitized materials. The carbonaceous material may be a binder (eg poly (vinylidene fluoride), polytetrafluoroethylene, styrene-butadiene copolymer, isoprene rubber, poly (vinyl acetate), poly (ethyl methacrylate) ), Polyethylene or nitrocellulose). Suitable carbonaceous anodes and methods for their preparation are described, for example, in US Pat. No. 7,169,511.
다른 적합한 애노드 물질은 리튬 금속, 리튬 합금 및 기타 리튬 화합물, 예컨대 리튬 티타네이트 애노드를 포함한다.Other suitable anode materials include lithium metals, lithium alloys and other lithium compounds such as lithium titanate anodes.
적합한 캐소드 물질은, 무기 화합물, 예컨대 전이 금속 옥사이드, 전이 금속/리튬 복합체 옥사이드, 리튬/전이금속 복합체 포스페이트, 전이금속 설파이드, 금속 옥사이드, 및 전이금속 실리케이트를 포함한다. 전이금속 옥사이드의 예는 MnO, V2O5, V6O13 및 TiO2를 포함한다. 전이금속/리튬 복합체 옥사이드는, 기본 조성이 대략 LiCoO2인 리튬/코발트 복합체 옥사이드; 기본 조성이 대략 LiNiO2인 리튬/니켈 복합체 옥사이드; 및 기본 조성이 대략 LiMn2O4 또는 LiMnO2인 리튬/망간 복합체 옥사이드를 포함한다. 이러한 경우에는 각각, 상기 코발트, 니켈 또는 망간의 일부가, 1종 또는 2종의 금속(예컨대, Al, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mg, Ga 또는 Zr)으로 대체될 수 있다. 리튬/전이금속 복합체 포스페이트는 리튬 철 포스페이트, 리튬 망간 포스페이트, 리튬 코발트 포스페이트, 리튬 철 망간 포스페이트 등을 포함한다. 유용한 금속 옥사이드의 예는 SnO2 및 SiO2를 포함한다. 유용한 금속 실리케이트의 예는 리튬 철 오르쏘실리케이트를 포함한다.Suitable cathode materials include inorganic compounds such as transition metal oxides, transition metal / lithium composite oxides, lithium / transition metal composite phosphates, transition metal sulfides, metal oxides, and transition metal silicates. Examples of transition metal oxides include MnO, V 2 O 5 , V 6 O 13 and TiO 2 . Transition metal / lithium composite oxides include lithium / cobalt composite oxides having a base composition of approximately LiCoO 2 ; Lithium / nickel composite oxide having a basic composition of approximately LiNiO 2 ; And lithium / manganese composite oxide having a base composition of approximately LiMn 2 O 4 or LiMnO 2 . In this case, a part of the cobalt, nickel or manganese may be replaced by one or two kinds of metals (for example, Al, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mg, Ga or Zr). Can be replaced. Lithium / transition metal composite phosphates include lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese phosphate, lithium cobalt phosphate, lithium iron manganese phosphate, and the like. Examples of useful metal oxides include SnO 2 and SiO 2 . Examples of useful metal silicates include lithium iron orthosilicates.
일반적으로, 상기 전극들은 각각 집전체와 전기적으로 접촉하거나, 집전체 상에 형성된다. 애노드에 적합한 집전체는, 금속 또는 금속 합금, 예컨대 구리, 구리 합금, 니켈, 니켈 합금, 스테인레스 강 등으로 제조된다. 캐소드에 적합한 집전체는, 알루미늄, 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 이들의 2종 이상의 합금 등으로 제조된 것들을 포함한다.In general, the electrodes are each in electrical contact with or are formed on the current collector. Suitable current collectors for the anode are made of metal or metal alloys such as copper, copper alloys, nickel, nickel alloys, stainless steel and the like. Current collectors suitable for the cathode include those made of aluminum, titanium, tantalum, two or more alloys thereof, and the like.
상기 분리막은, 상기 애노드와 상기 캐소드 사이에 개재되어, 상기 애노드와 상기 캐소드가 서로 접촉하여 단락이 되는 것을 방지한다. 상기 분리막은, 비전도성 물질로부터 편리하게 제조된다. 이는, 조작 조건 하에, 상기 전해액 또는 상기 전해액의 임의의 성분들과 반응성이 아니어야 하며, 이들에 가용성이어도 안된다. 중합체성 분리막이 일반적으로 적합하다. 상기 분리막을 형성하기에 적합한 중합체의 예는, 폴리에틸렌, 폴리프로필렌, 폴리부텐-1, 폴리-3-메틸펜텐, 에틸렌-프로필렌 공중합체, 폴리테트라플루오로에틸렌, 폴리스타이렌, 폴리메틸메타크릴레이트, 폴리다이메틸실록산, 폴리에터설폰 등이다. The separator is interposed between the anode and the cathode to prevent the anode and the cathode from contacting each other and causing a short circuit. The separator is conveniently manufactured from a nonconductive material. It must not be reactive with, or be soluble in, the electrolyte solution or any components of the electrolyte solution under operating conditions. Polymeric separators are generally suitable. Examples of suitable polymers for forming the separator include polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutene-1, poly-3-methylpentene, ethylene-propylene copolymers, polytetrafluoroethylene, polystyrene, polymethylmethacrylate, poly Dimethylsiloxane, polyethersulfone and the like.
상기 전해액은, 상기 분리막을 투과할 수 있어야 한다. 이러한 이유에서, 상기 분리막은 일반적으로 다공성이며, 다공성 시트, 부직물 또는 직물 형태 등이다. 상기 분리막의 다공도는 일반적으로, 20% 이상 90% 이하 정도이다. 바람직한 다공도는 30 내지 75%이다. 기공은 일반적으로, 이의 가장 큰 치수가 0.5 μm 이하, 바람직하게는 0.05 μm 이하이다. 상기 분리막은 전형적으로, 1 μm 이상의 두께이며, 50 μm 이하의 두께일 수 있다. 바람직한 두께는 5 내지 30 μm이다.The electrolyte solution should be able to pass through the separator. For this reason, the separator is generally porous, in the form of a porous sheet, nonwoven or woven fabric. The porosity of the separator is generally about 20% or more and about 90% or less. Preferred porosity is 30 to 75%. The pores generally have a largest dimension of 0.5 μm or less, preferably 0.05 μm or less. The separator is typically 1 μm or more in thickness, and may be 50 μm or less in thickness. Preferred thickness is between 5 and 30 μm.
상기 전지는 바람직하게는 2차 (재충전가능한) 리튬 전지이다. 이러한 전지에서, 방전 반응은, 애노드로부터의 리튬 이온의 용해 또는 탈리튬화(delithiation), 및 캐소드로의 리튬 이온의 동시 혼입을 포함한다. 반대로, 충전 반응은, 전해액으로부터 애노드로 리튬 이온이 혼입되는 것을 포함한다. 충전시, 리튬 이온은 애노드 쪽에서는 감소되고, 동시에 캐소드 물질 중의 리튬 이온은 전해액에 용해된다.The battery is preferably a secondary (rechargeable) lithium battery. In such cells, the discharge reaction involves dissolution or delithiation of lithium ions from the anode, and simultaneous incorporation of lithium ions into the cathode. In contrast, the charging reaction includes mixing lithium ions from the electrolyte solution to the anode. Upon charging, lithium ions are reduced on the anode side, while lithium ions in the cathode material dissolve in the electrolyte.
본 발명에 기술된 방향족 인 화합물이 존재하면, 열 분해 및 폭주 반응에 대해 전해액을 안정화시키고/시키거나 다르게는 전해액의 발화 능력을 감소시킴으로써 전지 안정성 및 전지 수명을 개선한다. 열 분해 및 폭주 반응은, (1) 전지에 대한 물리적 손상(이는 전지 구조물 내에 단락을 유발할 수 있음), (2) 전지의 열적 오용(이는 주로, 고온 조건 하에서 전지를 저장 및/또는 조작하는데서 기인함), 및 (3) 과충전 또는 전기 단락의 생성과 같은 전기 조건을 비롯한 몇몇 환경으로 인해 일어날 수 있다.The presence of the aromatic phosphorus compounds described in the present invention improves cell stability and battery life by stabilizing the electrolyte against thermal decomposition and runaway reactions and / or by reducing the fire ability of the electrolyte. Thermal decomposition and runaway reactions can result from (1) physical damage to the cell (which can cause short circuits within the cell structure), (2) thermal misuse of the cell (this is mainly due to storage and / or manipulation of the cell under high temperature conditions). And (3) some circumstances, including electrical conditions such as overcharging or the generation of electrical shorts.
과충전 환경은, 리튬이 덴드라이트 구조를 형성하도록 유발할 수 있다. 상기 덴드라이트 구조는 전해액을 통해 및 캐소드와 애노드 사이의 분리막을 통해 연장되어 단락을 유발할 수 있다. 이러한 단락은, 매우 짧은 시간에 걸쳐 전해액을 통해 매우 큰 전류가 흐르도록 하여, 전해액의 분해 또는 심지어 폭주 반응이 발생하도록 유발할 수 있는 열을 방출할 수 있다. 이러한 폭주 반응은 심지어, 난연제 또는 열 폭주 억제제의 부재 하에 전해액의 발화를 유발할 수 있다. 전해액이 발화되지 않더라도, 이러한 폭주 반응으로 인해 방출된 열은 전지 수명을 심하게 단축시킬 수 있다.An overcharged environment can cause lithium to form a dendrite structure. The dendrite structure may extend through the electrolyte and through the separator between the cathode and the anode to cause a short circuit. Such a short circuit can cause a very large current to flow through the electrolyte over a very short time, releasing heat that can cause decomposition or even runaway reaction of the electrolyte. This runaway reaction may even cause ignition of the electrolyte in the absence of a flame retardant or thermal runaway inhibitor. Even if the electrolyte is not ignited, the heat released due to this runaway reaction can severely shorten the battery life.
매우 놀랍게도, 상기 방향족 인 화합물이 존재하면, 부정적인 영향보다는, 전기 용량 활용효율, 방전 속도 성능 및/또는 사이클 안정성을 개선할 수 있는 것으로 밝혀졌다.Very surprisingly, it has been found that the presence of such aromatic phosphorus compounds can improve the capacity utilization efficiency, discharge rate performance and / or cycle stability, rather than negative effects.
사이클 안정성은, 고정된 횟수의 충전/방전 사이클 동안 주어진 충전/방전 속도로 전지를 작동시키고, 평가의 개시 및 종료시의 전지의 용량을 측정함으로써 평가될 수 있다. 전지가 계속 충전 및 방전되면, 용량은 떨어지는 경향이 있다. 예를 들어 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후, 전지의 용량은 흔히 시작 용량의 60 내지 70%로 떨어진다. 그러나, 전지 전해액이, 상기 방향족 인 화합물에 더하여, 전술된 하나 이상의 인-황 화합물; 탄소-탄소 불포화기를 함유하는 카보네이트; 및/또는 설톤 화합물을 함유하는 경우, 사이클 안정성은 상당히 우수해지고, 흔히 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후에 80% 이상의 용량이 보존되는 경향이 있다.Cycle stability can be assessed by operating the cell at a given charge / discharge rate for a fixed number of charge / discharge cycles and measuring the capacity of the cell at the start and end of the evaluation. If the battery continues to be charged and discharged, the capacity tends to drop. For example, after 100 1C charge / discharge cycles, the capacity of the cell often drops to 60-70% of the starting capacity. However, in addition to the aromatic phosphorus compound, the battery electrolyte may include at least one phosphorus-sulfur compound described above; Carbonates containing carbon-carbon unsaturated groups; And / or when containing sultone compounds, the cycle stability becomes quite good and often tends to preserve 80% or more capacity after 100 1C charge / discharge cycles.
본 발명의 전지는 산업적 용도, 예를 들어 전기 차량, 하이브리드 전기 차량, 플러그-인 하이브리드 전기 차량, 항공우주, 전동-자전거(e-bike) 등에 사용될 수 있다. 본 발명의 전지는 또한, 다수의 전기 및 전자 장치, 예를 들어 컴퓨터, 카메라, 비디오 카메라, 휴대폰, PDA, MP3 및 기타 음악 플레이어, 텔레비전, 인형, 비디오 게임 플레이어, 가전 제품, 전동 공구, 의료 장치, 예컨대 특히 심장 박동기 및 제세동기를 조작하는데 유용하다.The battery of the present invention can be used in industrial applications, for example electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, aerospace, e-bikes and the like. The batteries of the present invention also provide a number of electrical and electronic devices, such as computers, cameras, video cameras, mobile phones, PDAs, MP3 and other music players, televisions, dolls, video game players, home appliances, power tools, medical devices. For example, especially for manipulating cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators.
하기 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위해 제공되지만, 본 발명의 범주를 제한하는 것으로 의도되지 않는다. 달리 기재되지 않는 한, 모든 부 및 %는 중량에 대한 것이다.
The following examples are provided to illustrate the invention but are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. Unless otherwise stated, all parts and percentages are by weight.
[실시예][Example]
하기 실시예에서는 하기 방향족 인 화합물이 첨가제로서 평가된다.In the following examples, the following aromatic phosphorus compounds are evaluated as additives.
실시예Example 1 내지 5 및 비교 전지 A 내지 F 1 to 5 and Comparative Batteries A to F
50/50(부피비)의 에틸렌 카보네이트/다이에틸 카보네이트의 혼합물 중의 LiPF6의 1.0 M 용액으로 이루어진 대조구 전지 전해액을, LiCoO2 캐소드, 마이크로카본 마이크로비드(Mesocarbon Microbead; MCMB) 흑연 애노드 및 폴리올레핀 분리막을 갖는 2025 버튼 셀에 도입하였다. 상기 버튼 셀을 비교 전지 A로 지정하였다. 마코(Maccor) 4000 전지 시험기를 사용하고, 주위 온도에서 2회의 C/10 사이클 및 이어서 5회의 4C 사이클을 사용하여, 상기 비교 전지 A에 대해 5회의 4C 사이클 곡선을 생성하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을, 도 1 내지 4에서 각각 곡선 "A"로 지정하였다. A control cell electrolyte consisting of a 1.0 M solution of LiPF 6 in a 50/50 (volume ratio) mixture of ethylene carbonate / diethyl carbonate was prepared using LiCoO 2 cathode, Mesocarbon Microbead (MCMB) graphite anode and polyolefin separator. Introduced in 2025 button cells. The button cell was designated as Comparative Battery A. Five 4C cycle curves were generated for Comparative Cell A using a Maccor 4000 cell tester and using two C / 10 cycles followed by five 4C cycles at ambient temperature. Representative discharge curves from this test were designated as curves “A” in FIGS. 1 to 4, respectively.
전지 샘플 1을, 전해액이 5 중량%의 APC1을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는 상기와 같은 방식으로 제조하였다. 상기 전지 샘플 1을, 상기 비교 전지 A와 동일한 방식으로 시험하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을, 도 1 내지 3에서 각각 곡선 "1"로 제시하였다. Battery Sample 1 was prepared in the same manner as above except that the electrolyte solution contained 5% by weight of APC1. The battery sample 1 was tested in the same manner as the comparative battery A. Representative discharge curves from these tests are shown as curves "1" in FIGS.
전지 샘플 2를, 전해액이 APC1 대신 5 중량%의 APC2를 함유하는 것을 제외하고는 상기 전지 샘플 1과 같은 방식으로 제조하였다. 대표적인 방전 곡선을, 도 1 내지 3에서 각각 곡선 "2"로 제시하였다.
전지 샘플 3을, 전해액이 APC1 대신 5 중량%의 APC3을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는 상기 전지 샘플 1과 같은 방식으로 제조하였다. 대표적인 방전 곡선을, 도 2에서 곡선 "3"으로 제시하였다.
비교 전지 B 내지 F를, 전해액이 APC1 대신 5 중량%의 APC4, APC5, APC6, APC7 및 APC8을 각각 함유하는 것을 제외하고는 상기 전지 실시예 1에서와 같은 방식으로 제조하고 시험하였다. 이들의 대표적인 방전 곡선을, 도 1에서 곡선 B 및 C, 도 2에서 곡선 D 및 E, 및 도 3에서 곡선 F로 각각 제시하였다. Comparative Cells B to F were prepared and tested in the same manner as in Battery Example 1, except that the electrolyte contained 5% by weight of APC4, APC5, APC6, APC7 and APC8 instead of APC1, respectively. Their representative discharge curves are presented as curves B and C in FIG. 1, curves D and E in FIG. 2, and curve F in FIG. 3, respectively.
도 1 내지 4에서의 방전 곡선은, 산출된 충전 용량[전극 물질(이 경우, LiCoO2 캐소드)의 총량으로 표준화됨; 소위 "비 용량(specific capacity)"]에 대한, 전지를 드레인(drain)시킬 때 전지에 의해 생성되는 전압의 변화를 도시한 것이다. 목적하는 성능은, 셀이 특정 전압 윈도우(이 경우, 2.5 내지 4.2 V) 내에서 드레인되는 동안, 상기 전지가 가능한 한 많은 비 용량을 산출하는 것이다. 도 1 내지 3에서, 곡선 A는, 비교 전지 A(이는, APC 첨가제가 없는 대조구 전해액을 함유함)에 의해 생성된 전압이 약 75 내지 80 mAh/g의 비 용량이 산출된 후에 2.5 V로 떨어짐을 보여준다.The discharge curves in FIGS. 1 to 4 are normalized to the calculated charge capacity (the total amount of electrode material (in this case LiCoO 2 cathode); The so-called "specific capacity"] illustrates the change in voltage produced by a cell when the cell is drained. The desired performance is for the battery to yield as much specific capacity as possible while the cell is drained within a specific voltage window (2.5 to 4.2 V in this case). In Figures 1-3, curve A drops to 2.5 V after the voltage produced by comparative cell A (which contains a control electrolyte without APC additive) is calculated for a specific capacity of about 75 to 80 mAh / g. Shows.
전지 실시예 1은, 5 중량%의 APC1의 존재에도 불구하고, 이러한 방전 시험에서 더 우수한 성능을 나타낸다. 4C 방전 속도에서는, 상기 전압 윈도우 내에서 상기 전지에 의해 100 mAh/g 초과의 비 용량이 산출되었다.Battery Example 1 shows better performance in this discharge test despite the presence of 5% by weight of APC1. At 4C discharge rate, a specific capacity of more than 100 mAh / g was calculated by the battery within the voltage window.
또한, 전지 실시예 2도, 전지 실시예 1만큼은 아니지만, 이러한 방전 시험에서 대조구보다 우수한 성능을 나타냈다. 도 1 내지 3에서, 곡선 2는, 전지 샘플 2가 명시된 전압 윈도우 내에서 85 내지 90 mAh/g의 비 용량을 산출함으로 보여준다. 상기 전지 실시예 1과 함께, 상기 방향족 인 화합물의 존재는, 이러한 방전 시험에서 대조구(비교 전지 A)에 비해 전지 성능을 개선시킨다.In addition, Battery Example 2 also exhibited better performance than that of the control in this discharge test, although not as much as Battery Example 1. 1 to 3,
전지 실시예 3은, 이러한 방전 시험에서 비교 샘플 A에 비해 단지 약간 불량한 성능을 나타냈다. 전지 실시예 3은, 상기 전압 윈도우 내에서 72 내지 75 mAh/g의 비 용량을 산출하였다.Battery Example 3 showed only slightly poor performance in comparison with Comparative Sample A in this discharge test. Battery Example 3 calculated a specific capacity of 72 to 75 mAh / g within the voltage window.
전지 실시예 3은, 이러한 시험에서 각각의 비교 전지 B 내지 F보다 더 나은 성능을 나타냈다. 비교 전지 B, C 및 E의 경우, 상기 방전 시험에서의 성능은 상기 전지 실시예 3보다 더 불량했고, 비교 전지 F의 경우에는 이러한 성능이 상기 전지 실시예 3에 근접했지만 여전히 열등하였다.Battery Example 3 showed better performance than each of Comparative Cells B through F in this test. For Comparative Cells B, C and E, the performance in the discharge test was worse than that of Battery Example 3, and for Comparative Battery F this performance was close to Battery Example 3 but still inferior.
다양한 실시예 및 비교 샘플은, 전지 전해액 중의 인계 첨가제의 존재가 예측하지 못한 방식으로 전지의 전기 특성에 어떻게 영향을 미칠 수 있는지를 보여준다. 일반적으로, 인-함유 화합물의 첨가는 어느 정도 부정적인 영향을 미치지만, 이러한 영향의 규모는 상당히 다를 수 있다(예를 들어, 비교 전지 B, C 및 D의 성능을 비교 전지 D 및 F 및 전지 실시예 1의 성능과 비교하면). 그러나, 본 발명에 따른 방향족 인 화합물의 존재는, 전지 실시예 1 및 2에서와 같이 유리한 영향을 미치거나, 대부분의 경우 비 용량에 단지 약간의 부정적인 영향만을 미칠 수 있다(전지 실시예 3에서와 같이). 또한, 다양한 인-함유 화합물 간의 약간의 구조적 차이는 종종, 방전 곡선에 매우 상당한 영향을 미친다(전지 실시예 2의 결과를 전지 실시예 3의 결과와 비교하고, 비교 전지 E의 결과를 비교 전지 F의 결과와 비교함으로써 알 수 있음).Various examples and comparative samples show how the presence of phosphorus-based additives in the cell electrolyte can affect the electrical properties of the cell in an unexpected manner. In general, the addition of phosphorus-containing compounds has some negative effects, but the magnitude of these effects can vary considerably (eg, comparing the performance of Comparative Cells B, C, and D to Comparative Cells D and F and Cell Implementations). Compared to the performance of Example 1). However, the presence of the aromatic phosphorus compounds according to the invention can have a beneficial effect as in cell examples 1 and 2 or in most cases only a slight negative effect on specific capacity (as in cell example 3 and together). In addition, slight structural differences between the various phosphorus-containing compounds often have a very significant effect on the discharge curve (compare the results of Battery Example 2 with those of Battery Example 3, and compare the results of Comparative Cell E with Comparative Cell F By comparison with the results of).
전지 실시예 1을 다시 제조하였다. 다시 제조된 전지 샘플 1에 대해, 이번에는 2회의 C/10 사이클 및 이어서 C/2, 1C, 2C 및 4C로 각각 5회의 사이클을 사용하는 것을 제외하고는 상기와 같이 4C 방전 곡선을 결정하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을 도 4에 곡선 "1"로서 제시하였다.Battery Example 1 was prepared again. For Cell Sample 1, which was prepared again, the 4C discharge curve was determined as above except this time using two C / 10 cycles followed by five cycles of C / 2, 1C, 2C and 4C, respectively. Representative discharge curves from this test are presented as curve “1” in FIG. 4.
전지 실시예 4는, 단지 1 중량%의 APC1이 존재한다는 것을 제외하고는 전지 실시예 1과 동일하였다. 전지 실시예 4를, 다시 제조된 전지 실시예 1과 동일한 방식으로 시험하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을 도 4에 곡선 "4"로서 제시하였다.Battery Example 4 was identical to Battery Example 1 except that only 1% by weight of APC1 was present. Battery Example 4 was tested in the same manner as Battery Example 1, which was prepared again. Representative discharge curves from this test are shown in FIG. 4 as curve “4”.
전지 실시예 5는, 10 중량%의 APC1이 존재한다는 것을 제외하고는 전지 실시예 1과 동일하였다. 전지 실시예 5를, 다시 제조된 전지 실시예 1 및 전지 실시예 4와 동일한 방식으로 시험하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을 도 4에 곡선 "5"로서 제시하였다.Battery Example 5 was identical to Battery Example 1 except that 10% by weight of APC1 was present. Battery Example 5 was tested in the same manner as Battery Example 1 and Battery Example 4 which were prepared again. Representative discharge curves from this test are presented as curve “5” in FIG. 4.
비교를 위해, 비교 샘플 A(인-함유 첨가제가 없는 대조구)를 다시 제조하여, 상기와 같은 방식으로 평가하였다. 이러한 시험으로부터의 대표적인 방전 곡선을 도 4에 곡선 "A"로서 제시하였다.For comparison, Comparative Sample A (control without phosphorus-containing additive) was prepared again and evaluated in the same manner as above. Representative discharge curves from this test are presented as curve “A” in FIG. 4.
도 4에서 알 수 있는 바와 같이, 전지 실시예 1, 4 및 5는 각각, 인-함유 첨가제가 존재함에도 불구하고, 상기 방전 시험에서 비교 샘플 A보다 훨씬 우수한 성능을 가졌다.As can be seen in FIG. 4, Battery Examples 1, 4 and 5, respectively, had much better performance than Comparative Sample A in the discharge test, despite the presence of phosphorus-containing additives.
비교 샘플 A 및 전지 실시예 1의 전해액의 열 안정성을, 충전된 LiCoO2 캐소드 물질의 존재 하에 시차 주사 열량계(DSC)를 사용하여 시험하였다. 비교 샘플 A의 전해액은, 약 220℃에서 시작되는 큰 발열을 나타냈으며, 이는, 과량의 열 분해가 이 온도에서 시작됨을 나타낸다. 전지 실시예 1의 전해액은, 약 250℃의 온도에 도달할 때까지 아무런 발열을 나타내지 않았으며, 대조구에 의해 방출되는 것보다 훨씬 적은 양의 열을 방출하였다. 따라서, 5% 부하량으로 APC1을 첨가하면, 열 분해의 개시 온도를 증가시킬 뿐만 아니라, 열 분해시 열 방출 속도를 감소시킨다.
Thermal stability of the electrolyte solution of Comparative Sample A and Battery Example 1 was tested using a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) in the presence of a charged LiCoO 2 cathode material. The electrolyte of Comparative Sample A exhibited a large exotherm starting at about 220 ° C., indicating that excess thermal decomposition started at this temperature. The electrolyte solution of Battery Example 1 showed no exotherm until reaching a temperature of about 250 ° C., and released much less heat than that emitted by the control. Thus, adding APC1 at a 5% loading not only increases the onset temperature of pyrolysis but also reduces the rate of heat release during pyrolysis.
실시예Example 6 내지 9 6 to 9
전지 실시예 1을 다시 제조하여, 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클로 처리하였다. 이 전지의 비 용량을 각각의 사이클마다 측정하였다. 100회의 충전/방전 사이클이 끝날 무렵에, 전지 실시예 1의 비 용량은 출발 용량의 약 58%로 떨어졌다.Battery Example 1 was prepared again and subjected to 100 1C charge / discharge cycles. The specific capacity of this battery was measured at each cycle. At the end of 100 charge / discharge cycles, the specific capacity of Battery Example 1 dropped to about 58% of the starting capacity.
전지 실시예 6을, 이 경우 전지 전해액이 0.2 중량%의 화학식 XXVI의 인-황 화합물을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 전지 실시예 1과 동일한 방식으로 제조하고 시험하였다. 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후, 이 전지는 이의 출발 용량의 약 75%를 유지하였다. 따라서, 이러한 인-황 화합물을 단지 소량 첨가해도, 용량 보유율에 상당한 이점을 제공하는 것으로 보인다.Battery Example 6 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Battery Example 1, except that the battery electrolyte contained 0.2% by weight of the phosphorus-sulfur compound of Formula XXVI. After 100 1C charge / discharge cycles, the cell maintained about 75% of its starting capacity. Thus, even small additions of such phosphorus-sulfur compounds appear to provide a significant advantage in capacity retention.
전지 실시예 7을, 이 경우 전지 전해액이 0.2 중량%의 화학식 XXXIV의 인-황 화합물을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 전지 실시예 1과 동일한 방식으로 제조하고 시험하였다. 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후, 이 전지는 이의 출발 용량의 약 81%를 유지하였다. 역시, 이러한 인-황 화합물도 용량 보유율에 상당한 이점을 제공하는 것으로 보인다.Battery Example 7 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Battery Example 1, except that the battery electrolyte contained 0.2% by weight of the phosphorus-sulfur compound of Formula XXXIV. After 100 1C charge / discharge cycles, the cell maintained about 81% of its starting capacity. Again, these phosphorus-sulfur compounds also appear to offer significant advantages in capacity retention.
전지 실시예 8을, 이 경우 전지 전해액이 2.0 중량%의 비닐리덴 카보네이트를 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 전지 실시예 1과 동일한 방식으로 제조하고 시험하였다. 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후, 이 전지는 이의 출발 용량의 약 78%를 유지하였다. Battery Example 8 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Battery Example 1 above, except that the battery electrolyte contained 2.0% by weight of vinylidene carbonate. After 100 1C charge / discharge cycles, the cell maintained about 78% of its starting capacity.
전지 실시예 9를, 이 경우 전지 전해액이 2.0 중량%의 1,3-프로판 설톤을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 전지 실시예 1과 동일한 방식으로 제조하고 시험하였다. 100회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클 후, 이 전지는 이의 출발 용량의 약 76%를 유지하였다. Battery Example 9 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Battery Example 1, except that in this case the battery electrolyte contained 2.0% by weight of 1,3-propane sultone. After 100 1C charge / discharge cycles, the cell maintained about 76% of its starting capacity.
다시 제조된 전지 실시예 1 및 6의 샘플로, 200회의 1C 충전/방전 사이클을 수행하였다. 각각의 전해액의 열 안정성을 전술된 바와 같이 평가하였다. 전지 실시예 1로부터의 전해액은, 약 235 내지 260℃의 온도 범위에서 발열을 나타내었으며, 전지 실시예 6은 약 280℃에서 발열을 나타내었다. 이러한 데이터는, 상기 방향족 포스페이트 화합물에 더하여 상기 인-황 화합물이 존재하면, 사이클 후에 전해액의 열 안정성이 증가됨을 보여준다. 최적화된 전극 구조 또는 용량 밸런스를 선택함으로써 전체 전지 성능을 최적화하려는 시도 없이도, 이러한 결과가 수득되었다.
With the samples of the battery examples 1 and 6 again prepared, 200 1C charge / discharge cycles were performed. The thermal stability of each electrolyte was evaluated as described above. The electrolyte solution from Battery Example 1 exhibited exotherm at a temperature range of about 235 to 260 ° C., and Battery Example 6 exhibited exotherm at about 280 ° C. These data show that the presence of the phosphorus-sulfur compound in addition to the aromatic phosphate compound increases the thermal stability of the electrolyte after a cycle. These results were obtained without attempting to optimize the overall cell performance by selecting an optimized electrode structure or capacity balance.
실시예Example 10 내지 12 10 to 12
전지(실시예 10)를, 전해액이 6 중량%의 APC1을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는 상기 전지 실시예 1에 대해 기술된 것과 동일하게 제조하고, 포메이션(formation) 사이클로 처리하였다. 이어서, 이 전지를 1C 속도로 4.2 V까지 정전류식으로 충전하고, 이어서 전류가 C/10로 떨어지는 동안 4.2 V로 정전위식으로 방전하였다. 상기 전지를, 아르곤 대기 하에서 단락을 유발하지 않는 방식으로 해체하였다. 전극을 다이에틸카보네이트 용매로 세척하여 잔류 염 및 전해액을 제거하고, 진공 하에 건조하였다. 아르곤 하에, 대략 동일한 중량의 전극 및 회수된 전해액을 DSC 팬 상에 적재하고, 밀봉하였다. 이 샘플을 DSC로 처리하였다. 실시예 1과 유사하게, 이 물질들은 약 250℃까지 발열을 나타내지 않았으며, 주요 발열 피크는 약 290℃에서 나타났다.The cell (Example 10) was prepared in the same manner as described for Battery Example 1 above except that the electrolyte contained 6% by weight of APC1 and was treated in a formation cycle. The cell was then charged with a constant current to 4.2 V at 1 C rate, and then discharged to a potential of 4.2 V while the current dropped to C / 10. The cell was dismantled in a manner that did not cause a short circuit under an argon atmosphere. The electrode was washed with diethylcarbonate solvent to remove residual salts and electrolyte and dried under vacuum. Under argon, approximately equal weights of electrode and recovered electrolyte were loaded onto the DSC pan and sealed. This sample was treated with DSC. Similar to Example 1, these materials showed no exotherm up to about 250 ° C., with a major exothermic peak at about 290 ° C.
전지 실시예 11을, 전지 전해액이 단지 3%의 APC1 및 3%의 하기 구조식의 화합물을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 실시예 10과 동일하게 제조하고 시험하였다.Battery Example 11 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Example 10, except that the battery electrolyte contained only 3% of APC1 and 3% of the following structural formula.
DSC 시험에서, 이 물질은 약 240℃에서 적당한 발열을 나타내었으며, 300℃에 근접해서는 더 날카로운 발열을 나타냈다.In the DSC test, this material showed a moderate exotherm at about 240 ° C., and a sharper exotherm near 300 ° C.
전지 실시예 12를, 전지 전해액이 단지 3%의 APC1 및 3%의 하기 구조식의 화합물을 함유하는 것을 제외하고는, 상기 실시예 10과 동일하게 제조하고 시험하였다.Battery Example 12 was prepared and tested in the same manner as in Example 10, except that the battery electrolyte contained only 3% of APC1 and 3% of the following structural formula.
DSC 시험에서, 이 물질은 약 240℃에서 적당한 발열을 나타내었으며, 상기 실시예 11과 유사하게, 300℃에 근접해서는 더 날카로운 발열을 나타냈다.In the DSC test, this material showed a moderate exotherm at about 240 ° C., similar to Example 11 above, a sharper exotherm near 300 ° C.
실시예 10 내지 12는 모두, 속도 성능 시험에서 매우 유사한 성능을 나타냈다.Examples 10-12 all showed very similar performance in the speed performance test.
전해액 10 내지 12을 위한 새로운 전지 전해액을 밀봉된 병 내에서 실온으로 9주 동안 저장하였다. 실시예 10의 전해액은 저장 동안 매우 흐려졌지만, 실시예 11 및 12의 전해액은 투명한 채로 남아 있었다. 방향족 인 화합물의 혼합물이 존재하면, 전해액의 저장 안정성을 개선하는 것으로 보인다. Fresh cell electrolytes for electrolytes 10-12 were stored for 9 weeks at room temperature in sealed bottles. The electrolyte of Example 10 became very cloudy during storage, but the electrolytes of Examples 11 and 12 remained transparent. The presence of a mixture of aromatic phosphorus compounds appears to improve the storage stability of the electrolyte.
Claims (22)
상기 전지 전해액의 0.01 내지 80 중량%가, 하나 이상의 하기 화학식 I의 방향족 인 화합물인, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 I]
상기 식에서,
A1은, 하나 이상의 방향족 고리를 함유하는 라디칼이고,
R은 각각 독립적으로, 1 내지 3개의 탄소 원자를 함유할 수 있고 상기 A1 기의 방향족 고리의 탄소 원자에 직접 결합되는 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이고,
R1은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 할로겐, OH, 탄소수 12 이하의 하이드로카빌 기 또는 탄소수 12 이하의 알콕실 기이거나, 동일한 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 R1 기가 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성하고,
x는 2 이상의 정수이다.A battery electrolyte comprising at least one lithium salt and a non-aqueous solvent in which the lithium salt is dissolved,
A battery electrolyte wherein 0.01 to 80% by weight of the battery electrolyte is at least one aromatic phosphorus compound of formula I:
(I)
Where
A 1 is a radical containing one or more aromatic rings,
Each R is, independently, an alkylene divalent radical which may contain 1 to 3 carbon atoms and is directly bonded to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring of the A 1 group,
R 1 is each independently hydrogen, halogen, OH, a hydrocarbyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or an alkoxyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or a ring structure in which two R 1 groups attached to the same phosphorus atom together contain a phosphorus atom Form the
x is an integer of 2 or more.
R1이 각각, 탄소수 1 내지 4의 알콕실 기인, 전지 전해액.The method of claim 1,
The battery electrolyte solution, in which R 1 is each an alkoxyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms.
R이 각각, 메틸렌, 에틸렌 또는 아이소프로필렌인, 전지 전해액. The method according to claim 1 or 2,
The battery electrolyte wherein R is methylene, ethylene or isopropylene, respectively.
상기 방향족 인 화합물이 하기 화학식 III의 구조를 갖는, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 III]
상기 식에서,
R3은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, C1 -3 알킬, 하이드록실, 할로겐, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,
R은 각각 독립적으로, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이고,
R1은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 할로겐, OH, 탄소수 12 이하의 하이드로카빌 또는 탄소수 12 이하의 알콕실 기이거나, 동일한 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 R1 기가 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성하고,
x는 2 이상의 정수이다.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
A battery electrolyte in which the aromatic phosphorus compound has a structure of Formula III:
[Formula III]
Where
R 3 are each independently, hydrogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, halogen, C 1 -C 3 alkenyl, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
Each R is independently an alkylene divalent radical having 1 to 3 carbon atoms,
Each R 1 is independently hydrogen, halogen, OH, a hydrocarbyl having 12 or less carbon atoms, or an alkoxyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or two R 1 groups attached to the same phosphorus atom together form a ring structure containing a phosphorus atom Forming,
x is an integer of 2 or more.
상기 방향족 인 화합물이 하기 화학식 IV의 구조를 갖는, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 IV]
상기 식에서,
R3은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, C1 -3 알킬, 하이드록실, 할로겐, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,
R4는 각각 독립적으로, 탄소수 1 내지 8의 알킬 또는 알킬렌이다.The method of claim 4, wherein
A battery electrolyte in which the aromatic phosphorus compound has a structure of Formula IV:
[Formula IV]
Where
R 3 are each independently, hydrogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, halogen, C 1 -C 3 alkenyl, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
R 4 's are each independently alkyl or alkylene having 1 to 8 carbon atoms.
R4가 각각 독립적으로, 메틸, 에틸 또는 아이소프로필이고,
R3이 각각 독립적으로, 수소 또는 C1 -3 알킬인, 전지 전해액.The method of claim 5, wherein
Each R 4 is independently methyl, ethyl or isopropyl,
Are each independently R 3, hydrogen or a C 1 -3 alkyl, battery electrolyte.
상기 방향족 인 화합물이 하기 화학식 V의 구조를 갖는, 전지 전해액:
상기 식에서,
R3은 독립적으로, 수소, C1 -3 알킬, 하이드록실, 할로겐, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,
R4는 각각 독립적으로, 탄소수 1 내지 8의 알킬이다.The method of claim 4, wherein
A battery electrolyte in which the aromatic phosphorus compound has a structure of Formula V:
Where
R 3 is independently, hydrogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, halogen, C 1 -C 3 alkenyl, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
R 4 's are each independently alkyl having 1 to 8 carbons.
R4가 각각 독립적으로, 메틸, 에틸 또는 아이소프로필이고,
R3이 각각 독립적으로, 수소 또는 C1 -3 알킬인, 전지 전해액.The method of claim 7, wherein
Each R 4 is independently methyl, ethyl or isopropyl,
Are each independently R 3, hydrogen or a C 1 -3 alkyl, battery electrolyte.
상기 방향족 인 화합물이 하기 화학식 VI의 구조를 갖는, 전지 전해액.
[화학식 VI]
The method of claim 1,
A battery electrolyte, wherein the aromatic phosphorus compound has a structure of the following formula (VI).
(VI)
상기 방향족 인 화합물이 하기 화학식 X의 구조를 갖는, 전지 전해액.
[화학식 X]
The method of claim 1,
A battery electrolyte wherein the aromatic phosphorus compound has a structure of the following general formula (X).
[Formula X]
하기 화학식 III의 방향족 인 화합물을 2개 이상 함유하는, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 III]
상기 식에서,
R3은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, C1 -3 알킬, 하이드록실, 할로겐, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,
R은 각각 독립적으로, 1 내지 3개의 탄소 원자를 함유하고 상기 A1 기의 방향족 고리의 탄소 원자에 직접 결합되는 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이고,
R1은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 할로겐, OH, 탄소수 12 이하의 하이드로카빌 또는 탄소수 12 이하의 알콕실 기이거나, 동일한 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 R1 기가 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성하고,
상기 방향족 인 화합물 중 적어도 하나는, x가 3 이상이고,
상기 방향족 인 화합물 중 적어도 나머지 하나는, x가 2이다.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
A battery electrolyte containing two or more aromatic phosphorus compounds of formula III:
[Formula III]
Where
R 3 are each independently, hydrogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, halogen, C 1 -C 3 alkenyl, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
Each R is independently an alkylene divalent radical containing 1 to 3 carbon atoms and directly bonded to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring of said A 1 group,
Each R 1 is independently hydrogen, halogen, OH, a hydrocarbyl having 12 or less carbon atoms, or an alkoxyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or two R 1 groups attached to the same phosphorus atom together form a ring structure containing a phosphorus atom Forming,
At least one of the aromatic phosphorus compounds, x is 3 or more,
At least one of the aromatic phosphorus compounds has x 2.
상기 용매가, 선형 알킬 카보네이트, 환형 카보네이트, 에스터, 알킬 에터, 나이트릴, 설폰, 설폴란, 실록산 및 설톤으로부터 선택되는 물질 하나 이상을 포함하는, 전지 전해액.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 11,
Wherein said solvent comprises at least one material selected from linear alkyl carbonates, cyclic carbonates, esters, alkyl ethers, nitriles, sulfones, sulfolanes, siloxanes and sultones.
상기 용매가, 하나 이상의 선형 알킬 카보네이트, 하나 이상의 환형 카보네이트, 또는 이들의 혼합물을 포함하는, 전지 전해액.The method of claim 12,
A battery electrolyte, wherein the solvent comprises one or more linear alkyl carbonates, one or more cyclic carbonates, or mixtures thereof.
상기 리튬 염이, LiPF6, LiClO4, LiBF4, LiAsF6, LiCF3SO3 및 Li[(CF3SO3)2N] 중 하나 이상인, 전지 전해액.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 13,
The lithium electrolyte is at least one of LiPF 6 , LiClO 4 , LiBF 4 , LiAsF 6 , LiCF 3 SO 3 and Li [(CF 3 SO 3 ) 2 N].
고체 전해질 계면 형성 촉진제, 캐소드 보호제, 리튬 염 안정화제, 리튬 침착 개선제, 이온성 용매화 개선제, 부식 억제제, 습윤제 및 점도 감소제로부터 선택되는 다른 첨가제 하나 이상을 추가로 포함하는, 전지 전해액.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 14,
A battery electrolyte further comprising at least one other additive selected from solid electrolyte interfacial promoters, cathode protectors, lithium salt stabilizers, lithium deposition improvers, ionic solvation improvers, corrosion inhibitors, wetting agents and viscosity reducing agents.
하나 이상의 하기 화학식 XII의 화합물을 추가로 포함하는, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 XII]
상기 식에서,
R3은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, C1 -3 알킬, 하이드록실, 할로겐, 탄소수 1 내지 3의 알콕실, 또는 C2 -3 알킬렌이고,
R은, 1 내지 3개의 탄소 원자를 함유하고 상기 A1 기의 방향족 고리의 탄소 원자에 직접 결합되는 알킬렌 2가 라디칼이고,
R1은 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 할로겐, OH, 탄소수 12 이하의 하이드로카빌 또는 탄소수 12 이하의 알콕실 기이거나, 동일한 인 원자에 부착된 2개의 R1 기가 함께, 인 원자를 포함하는 고리 구조를 형성한다.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 15,
A battery electrolyte further comprising at least one compound of formula (XII):
[Formula XII]
Where
R 3 are each independently, hydrogen, C 1 -3 alkyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, halogen, C 1 -C 3 alkenyl, or C 2 -3 alkylene,
R is an alkylene divalent radical containing 1 to 3 carbon atoms and directly bonded to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring of said A 1 group,
Each R 1 is independently hydrogen, halogen, OH, a hydrocarbyl having 12 or less carbon atoms, or an alkoxyl group having 12 or less carbon atoms, or two R 1 groups attached to the same phosphorus atom together form a ring structure containing a phosphorus atom Form.
하나 이상의 하기 화학식 XIX의 인-황 화합물을 추가로 포함하는, 전지 전해액:
[화학식 XIX]
상기 식에서,
X는 산소 또는 황이고, T는 공유 결합, 산소 또는 황이되, 단 X 및 T 중 적어도 하나는 황이고,
X'은 각각 독립적으로 산소 또는 황이고,
m은 각각 독립적으로, X'이 산소인 경우에는 0 또는 1이고, X'이 황인 경우에는 0, 1 또는 2이고,
n은 1 이상이고, 바람직하게는 2 이상이고,
R5는 각각 독립적으로, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 하이드로카빌 기이거나, R5 기들이 함께, 비치환되거나 비활성적으로 치환된 2가 유기 기를 형성하고,
A는 유기 연결 기이다.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 16,
A battery electrolyte further comprising at least one phosphorus-sulfur compound of formula XIX:
[Formula XIX]
Where
X is oxygen or sulfur, T is a covalent bond, oxygen or sulfur, provided that at least one of X and T is sulfur,
Each X 'is independently oxygen or sulfur,
each m is independently 0 or 1 when X 'is oxygen, 0, 1 or 2 when X' is sulfur,
n is 1 or more, preferably 2 or more,
Each R 5 is, independently, an unsubstituted or inactively substituted hydrocarbyl group, or the R 5 groups together form an unsubstituted or inactively substituted divalent organic group,
A is an organic linking group.
지방족 탄소-탄소 불포화기를 갖는 카보네이트 화합물 하나 이상을 추가로 포함하는, 전지 전해액.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 17,
A battery electrolyte further comprising at least one carbonate compound having an aliphatic carbon-carbon unsaturated group.
하나 이상의 설톤 화합물을 추가로 포함하는, 전지 전해액.The method according to any one of claims 1 to 17,
A battery electrolyte further comprising at least one sultone compound.
상기 전지가 2차 전지인, 전지.The method of claim 20,
A battery, wherein said battery is a secondary battery.
상기 전지가 리튬 이온 전지, 리튬 황 전지, 리튬 금속 전지 또는 리튬 폴리머 전지인, 전지. 22. The method according to claim 20 or 21,
The battery, wherein the battery is a lithium ion battery, a lithium sulfur battery, a lithium metal battery or a lithium polymer battery.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14057908P | 2008-12-23 | 2008-12-23 | |
| US61/140,579 | 2008-12-23 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20110116019A true KR20110116019A (en) | 2011-10-24 |
Family
ID=41571396
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020117017106A KR20110116019A (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2009-11-16 | Battery electrolyte solutions containing aromatic phosphorus compounds |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8574773B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2382683B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5555716B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20110116019A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102265447B (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2748315A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2010074838A1 (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101444992B1 (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2014-09-26 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Non aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery comprising the same |
| WO2023085733A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| KR20230069829A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| KR20230069828A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| KR20230069831A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| WO2023085737A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolytic solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery containing same |
| WO2023085731A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| WO2023085734A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| KR20230069830A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5748193B2 (en) * | 2009-09-29 | 2015-07-15 | Necエナジーデバイス株式会社 | Secondary battery |
| EP2609646A1 (en) | 2010-08-24 | 2013-07-03 | Basf Se | Electrolyte materials for use in electrochemical cells |
| US9472813B2 (en) * | 2010-12-15 | 2016-10-18 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Battery electrolyte solution containing certain ester-based solvents, and batteries containing such an electrolyte solution |
| US9601806B2 (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2017-03-21 | Uchicago Argonne, Llc | Redox shuttle additives for lithium-ion batteries |
| CN105514483A (en) * | 2014-05-26 | 2016-04-20 | 宁德时代新能源科技股份有限公司 | Lithium ion battery and electrolyte thereof |
| WO2016031316A1 (en) * | 2014-08-25 | 2016-03-03 | 宇部興産株式会社 | Non-aqueous liquid electrolyte, electricity storage device using same, and phosphorus compound used therein |
| US10308587B2 (en) * | 2015-02-03 | 2019-06-04 | Blue Current, Inc. | Functionalized fluoropolymers and electrolyte compositions |
| WO2016160703A1 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2016-10-06 | Harrup Mason K | All-inorganic solvents for electrolytes |
| US10547083B2 (en) | 2015-06-22 | 2020-01-28 | Wildcat Discovery Technologies, Inc. | Electrolyte formulations for lithium ion batteries |
| US9887434B2 (en) | 2015-06-22 | 2018-02-06 | Wildcat Discovery Technologies, Inc | Electrolyte formulations for lithium ion batteries |
| US20160372790A1 (en) * | 2015-06-22 | 2016-12-22 | Johnson Controls Technology Company | Electrolyte formulations for lithium ion batteries |
| JP6538500B2 (en) * | 2015-09-16 | 2019-07-03 | 株式会社東芝 | Non-aqueous electrolyte battery, battery pack, and car |
| JP6941765B2 (en) * | 2015-09-28 | 2021-09-29 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Electrolytic capacitor |
| US10707531B1 (en) | 2016-09-27 | 2020-07-07 | New Dominion Enterprises Inc. | All-inorganic solvents for electrolytes |
| CN111900471B (en) * | 2020-05-15 | 2021-08-27 | 浙江锂威能源科技有限公司 | High-voltage electrolyte and lithium ion battery containing same |
| CN117154214B (en) * | 2023-10-30 | 2024-07-16 | 宁德时代新能源科技股份有限公司 | Electrolyte, secondary battery and electricity utilization device |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5830600A (en) | 1996-05-24 | 1998-11-03 | Sri International | Nonflammable/self-extinguishing electrolytes for batteries |
| JP3687283B2 (en) * | 1997-07-10 | 2005-08-24 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Solvent for lithium ion secondary battery |
| US6096447A (en) | 1997-11-05 | 2000-08-01 | Wilson Greatbatch Ltd. | Phosphonate additives for nonaqueous electrolyte in alkali metal electrochemical cells |
| US6210840B1 (en) | 1997-12-02 | 2001-04-03 | Denso Corporation | Flame-retardant electrolytic solution and nonaqueous secondary battery containing the same |
| EP1116315A4 (en) | 1998-08-28 | 2002-08-07 | Invensys Energy Systems Nz Ltd | Battery charge measurement and discharge reserve time prediction technique and apparatus |
| JP2001028272A (en) * | 1999-07-15 | 2001-01-30 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Electrolytic solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery using the same |
| US6924061B1 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2005-08-02 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of Army | Nonflammable non-aqueous electrolyte and non-aqueous electrolyte cells comprising the same |
| JP2002280061A (en) | 2001-03-15 | 2002-09-27 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Nonaqueous electrolyte and lithium secondary battery using the same |
| US6746794B2 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2004-06-08 | Tech Drive, Inc | Thermal runaway inhibitors |
| CN100334771C (en) * | 2002-10-22 | 2007-08-29 | 三菱化学株式会社 | Nonaqueous electrolytic solution and nonaqueous electrolytic solution secondary battery using it |
| KR100553775B1 (en) * | 2003-09-05 | 2006-02-20 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Organic electrolytic solution and lithium sulfur battery comprising the same |
| WO2005099023A1 (en) | 2004-04-07 | 2005-10-20 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery |
| US7638243B2 (en) | 2006-03-22 | 2009-12-29 | Novolyte Technologies Inc. | Stabilized nonaqueous electrolytes for rechargeable batteries |
| JP5315593B2 (en) * | 2006-04-27 | 2013-10-16 | 三菱化学株式会社 | Non-aqueous electrolyte and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery using the same |
| JP4396675B2 (en) * | 2006-06-16 | 2010-01-13 | ソニー株式会社 | Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery |
| JP2008021534A (en) * | 2006-07-13 | 2008-01-31 | Sony Corp | Nonaqueous electrolyte composition and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery |
| JP2008053211A (en) * | 2006-07-24 | 2008-03-06 | Bridgestone Corp | Nonaqueous electrolytic solution for battery, and nonaqueous electrolytic solution battery equipped with it |
| JP2008130528A (en) * | 2006-11-27 | 2008-06-05 | Sony Corp | Nonaqueous electrolyte composition and nonaqueous secondary battery |
| EP2125946A2 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2009-12-02 | Dow Global Technologies Inc. | Phosphorus-sulfur fr additives and polymer systems containing same |
| CN101304101A (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2008-11-12 | 东莞市杉杉电池材料有限公司 | Cylinder type lithium ion battery electrolytic solution and preparation method thereof |
-
2009
- 2009-11-16 CN CN200980152041.XA patent/CN102265447B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-11-16 EP EP09768266.0A patent/EP2382683B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2009-11-16 JP JP2011543523A patent/JP5555716B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-11-16 CA CA2748315A patent/CA2748315A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-11-16 WO PCT/US2009/064622 patent/WO2010074838A1/en active Application Filing
- 2009-11-16 KR KR1020117017106A patent/KR20110116019A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2009-11-16 US US13/132,374 patent/US8574773B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101444992B1 (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2014-09-26 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Non aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery comprising the same |
| WO2023085733A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| KR20230069829A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| KR20230069828A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| KR20230069831A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| WO2023085737A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolytic solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery containing same |
| WO2023085731A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| WO2023085734A1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| KR20230069830A (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2023-05-19 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Nonaqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising the same |
| US11973191B1 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2024-04-30 | Lg Energy Solution, Ltd. | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| US11978859B2 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2024-05-07 | Lg Energy Solution, Ltd. | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
| US11978858B2 (en) | 2021-11-12 | 2024-05-07 | Lg Energy Solution, Ltd. | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102265447B (en) | 2015-05-06 |
| US8574773B2 (en) | 2013-11-05 |
| US20110250503A1 (en) | 2011-10-13 |
| CA2748315A1 (en) | 2010-07-01 |
| EP2382683B1 (en) | 2013-12-25 |
| EP2382683A1 (en) | 2011-11-02 |
| WO2010074838A1 (en) | 2010-07-01 |
| CN102265447A (en) | 2011-11-30 |
| JP5555716B2 (en) | 2014-07-23 |
| JP2012513666A (en) | 2012-06-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5555716B2 (en) | Battery electrolyte solution containing aromatic phosphorus compound | |
| CN108428940B (en) | Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery including the same | |
| JP5886870B2 (en) | Electrolyte solution containing a predetermined ester-based solvent and battery containing the electrolyte solution | |
| CN102201596B (en) | Nonaqueous electrolyte solution and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery | |
| JP4001580B2 (en) | Organic electrolyte and lithium battery using the same | |
| JP4521525B2 (en) | Non-flammable non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion battery using the same | |
| JP5525057B2 (en) | Battery electrolyte solution containing phosphorus-sulfur compound | |
| JP7045240B2 (en) | Additives for non-aqueous electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolytes and power storage devices | |
| US20130230781A1 (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium secondary battery using the same | |
| WO2021166771A1 (en) | Electrolytic solution for secondary cell containing cyclic phosphoric acid ester | |
| JP5811361B2 (en) | Secondary battery | |
| CN110970662B (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion battery | |
| JP5093992B2 (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery provided with the same | |
| CN110970664A (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion battery | |
| JPWO2019187545A1 (en) | Additives for non-aqueous electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolytes and power storage devices | |
| CN110970652A (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion battery | |
| CN110970663A (en) | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion battery | |
| CN106165184A (en) | Alkylbenzoic acid ester derivant as lithium-base battery group additive agent electrolyte | |
| WO2012174704A1 (en) | Battery electrolyte solutions containing aromatic phosphite compounds | |
| CN114447434A (en) | Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery comprising same | |
| KR20230044082A (en) | Electrolyte additive compound for lithium secondary battery, electrolyte for lithium secondary battery containing the same, lithium secondary battery | |
| WO2018164130A1 (en) | Additive for non-aqueous electrolyte, non-aqueous electrolyte, and power storage device | |
| KR102503055B1 (en) | Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery including the same | |
| CN110970658B (en) | Lithium ion battery | |
| KR102017740B1 (en) | Efficient Electrolyte to Improve the Surface Stability of Graphite Anodes and lithium ion rechargeable battery including thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right |