JP7473060B2 - Gaming Machines - Google Patents
Gaming Machines Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7473060B2 JP7473060B2 JP2023096609A JP2023096609A JP7473060B2 JP 7473060 B2 JP7473060 B2 JP 7473060B2 JP 2023096609 A JP2023096609 A JP 2023096609A JP 2023096609 A JP2023096609 A JP 2023096609A JP 7473060 B2 JP7473060 B2 JP 7473060B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- game
- information
- ball
- mode
- balls
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 1801
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 1782
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 577
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 574
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 232
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 215
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 56
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 395
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 314
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 240
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 227
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 187
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 176
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 134
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 102
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 87
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 80
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 78
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 77
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 75
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 75
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 53
- 230000004397 blinking Effects 0.000 description 50
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 28
- FFBHFFJDDLITSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl N-[2-hydroxy-4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]carbamate Chemical compound OC1=C(NC(=O)OCC2=CC=CC=C2)C=CC(=C1)N1CCOCC1=O FFBHFFJDDLITSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 27
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 27
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 22
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 22
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 18
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 15
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002788 crimping Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008450 motivation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000002250 progressing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 208000019901 Anxiety disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000036506 anxiety Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001962 electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011017 operating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011120 plywood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000011179 visual inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
本発明は、遊技機に関するものである。 The present invention relates to gaming machines.
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている(例えば、特許文献1)。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
本発明は、上述の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の形態として実現することが可能である。 The present invention has been made to solve at least some of the above problems, and can be realized in the following forms:
[形態]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検出する複数の所定検出手段と、
前記複数の所定検出手段と電気的に接続され、遊技に対する遊技価値を付与するための処理を実行する遊技価値付与手段と、
前記遊技価値付与手段と電気的に接続され、前記遊技価値付与手段からの信号であって付与すべき賞球数に関する賞球付与信号に基づいて、前記遊技価値としての賞球を払い出すための払出処理を実行する払出手段と、
前記遊技価値付与手段と各種信号を送信可能な信号線によって電気的に接続され、前記払出処理とは別の異なる処理であって前記賞球付与信号に基づくことのない所定の遊技に関する所定の数値情報の出力に関する特定処理を少なくとも実行する処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記遊技価値付与手段は、
前記遊技に対する遊技価値を付与するための処理に用いられる情報であって、前記所定検出手段の検出に対して参照される参照用情報を記憶する第1参照用情報記憶手段と、
本遊技機への電力の所定の供給が開始された後であって少なくとも遊技を進行させるために定期的に繰り返される所定の遊技処理の実行を開始する前に、前記第1参照用情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記参照用情報に対応した参照用情報信号を前記処理実行手段に対して送信する第1送信手段と、
前記所定検出手段による検出に基づいて取得された情報である入球情報に基づく所定情報信号を前記処理実行手段に対して送信する第2送信手段と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技価値付与手段から送信された前記参照用情報信号に対応した参照用情報を記憶する第2参照用情報記憶手段と、
前記第2送信手段から送信された前記所定情報信号と、前記第2参照用情報記憶手段に記憶された前記参照用情報とに基づいて前記特定処理を実行する実行手段と、
前記実行手段による前記特定処理の処理結果に関する情報である処理結果情報を記憶する処理結果情報記憶手段と、
を備え、
本遊技機は、
本遊技機の前方から視認可能であり、所定の抽選処理の結果を告知する処理の1単位である遊技回毎に実行される遊技回演出を表示する演出用表示手段と、
前記処理結果情報を前記演出用表示手段に出力する手段と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、前記遊技価値付与手段の前記第1参照用情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記参照用情報を書き換え不能に構成されており、
前記遊技価値付与手段は、前記処理結果情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記処理結果情報を直接的に変更不能であり、
遊技機前面体が開放されて所定状態が発生した場合に、前記遊技価値付与手段から前記遊技機前面体の開放に対応する開放情報が送信され、前記処理実行手段において前記開放情報に対応した情報が記憶され、
前記複数の所定検出手段は、遊技球を検出したことに基づいて付与する遊技価値が異なる所定検出手段を少なくとも含んでおり、
前記実行手段は、前記遊技価値が異なる前記所定検出手段に基づいた前記所定情報信号と、前記第2参照用情報記憶手段に記憶された前記参照用情報とに基づいて前記特定処理を実行する手段を備え、
前記特定処理の終了後の所定タイミングで前記所定情報信号に基づいて記憶された情報が消去される構成である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[form]
A plurality of predetermined detection means for detecting game balls that have passed through a predetermined area;
a game value providing means electrically connected to the plurality of predetermined detection means and configured to execute a process for providing a game value for a game;
a payout means electrically connected to the game value providing means, and executing a payout process for paying out prize balls as the game value based on a prize ball providing signal from the game value providing means, the prize ball providing signal being related to the number of prize balls to be provided;
a process execution means that is electrically connected to the game value providing means by a signal line capable of transmitting various signals, and that executes at least a specific process related to the output of predetermined numerical information related to a predetermined game, which is a process different from the payout process and is not based on the prize ball providing signal ;
A gaming machine comprising:
The game value providing means includes:
a first reference information storage means for storing reference information used in a process for providing a game value to the game, the reference information being referenced in response to detection by the predetermined detection means;
a first transmitting means for transmitting a reference information signal corresponding to the reference information stored in the first reference information storage means to the process executing means after a predetermined supply of power to the gaming machine is started and before the execution of a predetermined game process that is periodically repeated at least to progress a game is started;
a second transmitting means for transmitting a predetermined information signal based on the ball-entering information, which is information acquired based on the detection by the predetermined detecting means, to the processing executing means;
Equipped with
The process execution means includes:
a second reference information storage means for storing reference information corresponding to the reference information signal transmitted from the game value providing means;
an execution means for executing the specific process based on the predetermined information signal transmitted from the second transmission means and the reference information stored in the second reference information storage means;
a processing result information storage means for storing processing result information which is information regarding a processing result of the specific processing performed by the execution means;
Equipped with
This gaming machine is
a presentation display means for displaying a presentation to be executed for each game round, which is one unit of a process for notifying the result of a predetermined lottery process, and which is visible from the front of the gaming machine;
A means for outputting the processing result information to the performance display means;
Equipped with
The processing execution means is configured to make the reference information stored in the first reference information storage means of the game value providing means non-rewritable,
the game value providing means cannot directly change the processing result information stored in the processing result information storage means;
When a front body of the gaming machine is opened and a predetermined state occurs, opening information corresponding to the opening of the front body of the gaming machine is transmitted from the gaming value providing means, and information corresponding to the opening information is stored in the processing execution means;
The plurality of predetermined detection means include at least a predetermined detection means which provides different game values based on the detection of a game ball,
The execution means includes a means for executing the specific process based on the predetermined information signal based on the predetermined detection means having different game values and the reference information stored in the second reference information storage means;
The information stored based on the predetermined information signal is erased at a predetermined timing after the specific process is completed.
A gaming machine characterized by:
上記形態によれば、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 The above-mentioned form can increase the enjoyment of the game.
本発明にかかる遊技機の実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら以下の順序で説明する。
A.第1実施形態:
B.他の構成への適用:
C.上記各実施形態等から抽出される発明群について:
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS An embodiment of a gaming machine according to the present invention will be described in the following order with reference to the drawings.
A. First embodiment:
B. Application to other configurations:
C. Regarding the inventions extracted from the above embodiments:
A.第1実施形態:
A1.遊技機の構造:
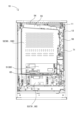
図1は、第1実施形態におけるパチンコ遊技機(以下、「パチンコ機」ともいう)の斜視図である。パチンコ機10は、略矩形に組み合わされた木製の外枠11を備えている。パチンコ機10を遊技ホールに設置する際には、この外枠11が遊技ホールの島設備に固定される。また、パチンコ機10は、外枠11に回動可能に支持されたパチンコ機本体12を備えている。パチンコ機本体12は、内枠13と、内枠13の前面に配置された前扉枠14とを備えている。内枠13は、外枠11に対して金属製のヒンジ15によって回動可能に支持されている。前扉枠14は、内枠13に対して金属製のヒンジ16によって回動可能に支持されている。内枠13の背面には、主制御装置、音声発光制御装置、表示制御装置など、パチンコ機本体12を制御する制御機器が配置されている。これら制御機器の詳細については後述する。さらに、パチンコ機10には、シリンダ錠17が設けられている。シリンダ錠17は、内枠13を外枠11に対して開放不能に施錠する機能と、前扉枠14を内枠13に対して開放不能に施錠する機能とを有する。各施錠は、シリンダ錠17に対して専用の鍵を用いた所定の操作が行われることによって解錠される。
A. First embodiment:
A1. Structure of the gaming machine:
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a pachinko game machine (hereinafter, also referred to as a "pachinko machine") in the first embodiment. The
前扉枠14の略中央部には、開口された窓部18が形成されている。前扉枠14の窓部18の周囲には、パチンコ機10を装飾するための樹脂部品や電飾部品が設けられている。電飾部品は、LEDなどの各種ランプからなる発光手段によって構成されている。発光手段は、パチンコ機10によって行われる各遊技回、大当たり当選時、リーチ発生時などに点灯又は点滅することによって、演出効果を高める役割を果たす。また、前扉枠14の裏側には、2枚の板ガラスからなるガラスユニット19が配置されており、開口された窓部18がガラスユニット19によって封じられている。内枠13には、後述する遊技盤が着脱可能に取り付けられており、パチンコ機10の遊技者は、パチンコ機10の正面からガラスユニット19を介して遊技盤を視認することができる。遊技盤の詳細については後述する。
An
前扉枠14には、遊技球を貯留するための上皿20と下皿21とが設けられている。上皿20は、上面が開放した箱状に形成されており、図示しない貸出機から貸し出された貸出球やパチンコ機本体12から排出された賞球などの遊技球を貯留する。上皿20に貯留された遊技球は、パチンコ機本体12が備える遊技球発射機構に供給される。遊技球発射機構は、遊技者による操作ハンドル25の操作によって駆動し、上皿20から供給された遊技球を遊技盤の前面に発射する。下皿21は、上皿20の下方に配置されており、上面が開放した箱状に形成されている。下皿21は、上皿20で貯留しきれなかった遊技球を貯留する。下皿21の底面には、下皿21に貯留された遊技球を排出するための排出口22が形成されている。排出口22の下方にはレバー23が設けられており、遊技者がレバー23を操作することによって、排出口22の閉状態と開状態とを切り替えることが可能である。遊技者がレバー23を操作して排出口22を開状態にすると、排出口22から遊技球が落下し、遊技球は下皿21から外部に排出される。
The
上皿20の周縁部の前方には、操作受入手段としての演出操作ボタン24が設けられている。演出操作ボタン24は、パチンコ機10によって行われる遊技演出に対して、遊技者が入力操作を行うための操作部である。パチンコ機10によって用意された所定のタイミングで遊技者が演出操作ボタン24を操作することによって、当該操作が反映された遊技演出がパチンコ機10によって行われる。
A
さらに、前扉枠14の正面視右側には、遊技者が操作するための操作ハンドル25が設けられている。遊技者が操作ハンドル25を操作すると、当該操作に連動して、遊技球発射機構から遊技盤の前面に遊技球が発射される。操作ハンドル25の内部には、遊技球発射機構の駆動を許可するためのタッチセンサー25aと、遊技者による押下操作によって遊技球発射機構による遊技球の発射を停止させるウェイトボタン25bと、操作ハンドル25の回動操作量を電気抵抗の変化により検出する可変抵抗器25cとが設けられている。遊技者が操作ハンドル25を握ると、タッチセンサー25aがオンになり、遊技者が操作ハンドル25を右回りに回動操作すると、可変抵抗器25cの抵抗値が回動操作量に対応して変化し、可変抵抗器25cの抵抗値に対応した強さで遊技球発射機構から遊技盤の前面に遊技球が発射される。
Furthermore, an
次に、パチンコ機10の背面の構成について説明する。パチンコ機10の背面には、パチンコ機10の動作を制御するための制御機器が配置されている。
Next, the configuration of the back of the
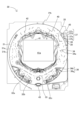
図2は、パチンコ機10の背面図である。図示するように、パチンコ機10は、第1制御ユニット51と、第2制御ユニット52と、第3制御ユニット53とを備えている。具体的には、これら機構部は内枠13の背面に設けられている。
Figure 2 is a rear view of the
第1制御ユニット51は、主制御装置60を備えている。主制御装置60は、遊技の主たる制御を司る機能と電源を監視する機能とを有する主制御基板を有している。主制御基板は、透明樹脂材料からなる基板ボックスに収容されている。この基板ボックスは、開閉の痕跡(開放の痕跡、開封の痕跡ともいう)が残るように構成されている。例えば、開閉可能な箇所に封印シールが貼付されており、基板ボックスを開放すると「開封」といった文字が現れるように構成されている。
The
第2制御ユニット52は、音声発光制御装置90と、表示制御装置100とを備えている。音声発光制御装置90は、主制御装置60から送信されたコマンドに基づいて、パチンコ機10の前面に設けられたスピーカーや各種ランプ等の発光手段の制御を行う。表示制御装置100は、音声発光制御装置90から送信されたコマンドに基づいて、図柄表示装置を制御する。図柄表示装置は、図柄や演出用の映像を表示する液晶ディスプレイを備えている。
The second control unit 52 includes an audio/light
第3制御ユニット53は、払出制御装置70と、発射制御装置80とを備えている。払出制御装置70は、賞球の払い出しを行うための払出制御を行う。発射制御装置80は、主制御装置60から遊技球の発射の指示が入力された場合に、遊技者による操作ハンドル25の回動操作量に応じた強さの遊技球の発射を行うように遊技球発射機構を制御する。その他、内枠13の背面には、遊技ホールの島設備から供給される遊技球が逐次補給されるタンク54、タンク54の下方に連結され遊技球が下流側に流れるように緩やかに傾斜した斜面を有するタンクレール55、タンクレール55の下流側に鉛直方向に連結されたケースレール56、ケースレール56から遊技球の供給を受け払出制御装置70からの指示により所定数の遊技球の払い出しを行う払出装置71など、パチンコ機10の動作に必要な複数の機器が設けられている。
The third control unit 53 includes a
次に、遊技盤について説明する。遊技盤は、内枠13の前面に着脱可能に取り付けられている。
Next, we will explain the game board. The game board is removably attached to the front of the
図3は、遊技盤30の正面図である。遊技盤30は、合板によって構成されており、その前面には遊技領域PAが形成されている。遊技盤30には、遊技領域PAの外縁の一部を区画するようにして内レール部31aと、外レール部31bとが取り付けられている。内レール部31aと外レール部31bとの間には、遊技球を誘導するための誘導レール31が形成されている。遊技球発射機構から発射された遊技球は、誘導レール31に誘導されて遊技領域PAの上部に放出され、その後、遊技領域PAを流下する。遊技領域PAには、遊技盤30に対して略垂直に複数の釘42が植設されるとともに、風車等の各役物が配設されている。これら釘42や風車は、遊技領域PAを流下する遊技球の落下方向を分散、整理する。
Figure 3 is a front view of the
遊技盤30には、一般入賞口32、第1始動口33、第2始動口34、スルーゲート35、および、可変入賞装置36が設けられている。また、遊技盤30には、可変表示ユニット40及びメイン表示部45が設けられている。メイン表示部45は、特図ユニット37と、普図ユニット38と、ラウンド表示部39とを有している。
The
一般入賞口32は、遊技球が入球可能な入球口であり、遊技盤30上に複数設けられている。本実施形態では、一般入賞口32に遊技球が入球すると、10個の遊技球が賞球として払出装置71から払い出される。本実施形態では、一般入賞口32として、3つの一般入賞口32a、32b、32cが設けられている。以下では、一般入賞口32aを第1入賞口32a、一般入賞口32bを第2入賞口32b、一般入賞口32cを第3入賞口32cとも呼ぶ。
The general winning
第1始動口33は、遊技球が入球可能な入球口である。第1始動口33は、遊技盤30の中央下方に設けられている。本実施形態では、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球すると、3個の遊技球が賞球として払い出されるとともに、後述する大当たり抽選が実行される。
The
第2始動口34は、遊技球が入球可能な入球口であり、遊技盤30の右側に設けられている。本実施形態では、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球すると、3個の遊技球が賞球として払い出されるとともに、後述する大当たり抽選が実行される。また、第2始動口34には、普通電動役物としての電動役物34aが設けられている。
The
スルーゲート35は、縦方向に貫通した貫通孔を備えている。スルーゲート35は、電動役物34aを開放状態とするための抽選を実行するための契機となるスルーゲートである。具体的には、遊技球がスルーゲート35を通過すると、主制御装置60は、当該通過を契機として内部抽選(電動役物開放抽選)を行なう。内部抽選の結果、電役開放に当選すると、電動役物34aは、所定の態様で開放状態となる電役開放状態へと移行する。スルーゲート35は、遊技球の流下方向に対して第2始動口34よりも上流側に配置されているため、スルーゲート35を通過した遊技球は、通過後に遊技領域PAを流下して第2始動口34へ入球することが可能となっている。なお、本実施形態では、スルーゲート35を遊技球が通過しても、賞球の払い出しは実行されない。
The through
可変入賞装置36は、遊技盤30の背面側へと通じる大入賞口36aと、当該大入賞口36aを開閉する開閉扉36bとを備えている。開閉扉36bは、通常は遊技球が大入賞口36aに入球できない閉鎖状態となっている。第1始動口33又は第2始動口34に遊技球が入球すると、主制御装置60は、大当たり抽選(内部抽選)を実行する。大当たり抽選の結果、大当たり又は小当たりに当選すると、パチンコ機10は、開閉実行モードに移行する。開閉実行モードとは、可変入賞装置36の開閉扉36bの開閉処理を実行するモードである。具体的には、可変入賞装置36の開閉扉36bは、開閉実行モードに移行すると、遊技球が入球できない閉鎖状態から遊技球が入球可能な開放状態に遷移するとともに、所定の条件が満たされた後に、再び、閉鎖状態に遷移する。本実施形態では、可変入賞装置36の大入賞口36aに遊技球が入球すると、払出装置71によって15個の遊技球が賞球として払い出される。
The
また、遊技盤30の最下部にはアウト口43が設けられており、各種入球口に入球しなかった遊技球は、アウト口43を通って遊技領域PAから排出される。
In addition, an
なお、本実施形態では、第1始動口33、第2始動口34、第1入賞口32a、第2入賞口32b、第3入賞口32c、大入賞口36a及びアウト口43に入球した遊技球は、遊技盤30の背面に設けられた排出通路に合流するように構成されており、当該排出通路には、遊技球を検知する排出通路検知センサーが設けられている。後述するように、本実施形態では、排出通路検知センサーによって遊技球を検知することによって、遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数を把握することが可能となっている。
In this embodiment, the game balls that enter the
特図ユニット37は、第1図柄表示部37aと、第2図柄表示部37bとを備えている。第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37bは、それぞれ、複数のセグメント発光部が所定の態様で配列されたセグメント表示器によって構成されている。
The
第1図柄表示部37aは第1の図柄を表示するための表示部である。第1の図柄とは、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球を契機とした大当たり抽選に基づいて変動表示または停止表示される図柄をいう。第1図柄表示部37aは、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球を契機とした大当たり抽選が行われると、セグメント表示器に、抽選結果に対応した表示を行なわせるまでの表示態様として、第1の図柄の変動表示又は所定の表示を行なわせる。抽選が終了した際には、第1図柄表示部37aは、セグメント表示器に、抽選結果に対応した第1の図柄の停止表示を行なわせる。以下、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球を契機として大当たり抽選が実行される遊技回を第1始動口用遊技回とも呼ぶ。
The first
第2図柄表示部37bは第2の図柄を表示するための表示部である。第2の図柄とは、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を契機とした大当たり抽選に基づいて変動表示または停止表示される図柄をいう。第2図柄表示部37bは、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を契機とした大当たり抽選が行われると、セグメント表示器に、抽選結果に対応した表示を行なわせるまでの表示態様として、第2の図柄の変動表示又は所定の表示を行なわせる。抽選が終了した際には、第2図柄表示部37bは、セグメント表示器に、抽選結果に対応した第2の図柄の停止表示を行なわせる。以下、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を契機として大当たり抽選が実行される遊技回を第2始動口用遊技回とも呼ぶ。
The second
ここで、第1図柄表示部37aに表示される第1の図柄、または、第2図柄表示部37bに表示される第2の図柄の変動表示が開始されてから停止表示されるまでの時間を変動時間とも呼ぶ。具体的には、第1図柄表示部37aに表示される第1の図柄の変動表示が開始されてから停止表示されるまでの時間を第1の変動時間とも呼び、第2図柄表示部37bに表示される第2の図柄の変動表示が開始されてから停止表示されるまでの時間を第2の変動時間とも呼ぶ。
Here, the time from when the first pattern displayed on the first
特図ユニット37は、さらに、第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37bに隣接した位置に、LEDランプからなる第1保留表示部37cおよび第2保留表示部37dを備えている。
The
第1保留表示部37cは、点灯させるLEDランプの色や組み合わせによって、第1始動口33の保留個数を表示する。本実施形態では、第1始動口33に入球した遊技球は、最大4個まで保留される。
The first
第2保留表示部37dは、点灯させるLEDランプの色や組み合わせによって、第2始動口34の保留個数を表示する。本実施形態では、第2始動口34に入球した遊技球は、最大4個まで保留される。
The second
普図ユニット38は、複数のLEDランプが所定の態様で配列された発光表示部によって構成されている。普図ユニット38は、スルーゲート35の通過を契機とした電動役物開放抽選が行われると、発光表示器の表示態様として点灯表示、点滅表示又は所定の態様の表示をさせる。電動役物開放抽選が終了した際には、普図ユニット38は、抽選結果に対応した所定の態様の表示を行う。
The
ラウンド表示部39は、複数のLEDランプが所定の態様で配列された発光表示部によって構成されており、開閉実行モードにおいて発生するラウンド遊技の回数の表示、又は、それに対応した表示をする。ラウンド遊技とは、予め定められた上限継続時間が経過すること、又は、予め定められた上限個数の遊技球が可変入賞装置36に入球することのいずれか一方の条件が満たされるまで、開閉扉36bの開放状態を継続する遊技のことである。ラウンド遊技の回数は、その移行の契機となった大当たり当選の種類に応じて異なる。ラウンド表示部39は、開閉実行モードが開始される場合にラウンド遊技の回数の表示を開始し、開閉実行モードが終了した場合に終了する。
The
なお、特図ユニット37、普図ユニット38、及びラウンド表示部39は、セグメント表示器やLEDランプによる発光表示器によって構成されることに限定されず、例えば、液晶表示装置、有機EL表示装置、CRT又はドットマトリックス表示器など、抽選中及び抽選結果を示すことが可能な種々の表示装置によって構成されてもよい。
The
可変表示ユニット40は、遊技領域PAの略中央に配置されている。可変表示ユニット40は、図柄表示装置41を備える。図柄表示装置41は、液晶ディスプレイを備えている。図柄表示装置41は、表示制御装置100によって表示内容が制御される。なお、可変表示ユニット40が備える表示装置の構成は、図柄表示装置41に限定されず、例えば、プラズマディスプレイ装置、有機EL表示装置又はCRTなど、種々の表示装置によって構成されてもよい。
The
図柄表示装置41は、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づいて第1図柄表示部37aが変動表示又は所定の表示をする場合に、それに合わせて図柄の変動表示又は所定の表示を行う。また、図柄表示装置41は、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に基づいて第2図柄表示部37bが変動表示又は所定の表示をする場合に、それに合わせて図柄の変動表示又は所定の表示を行う。図柄表示装置41は、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を契機とした図柄の変動表示又は所定の表示をすることに限らず、大当たり当選となった場合に移行する開閉実行モード中の演出表示なども行なう。以下、図柄表示装置41の詳細について説明する。
When the first
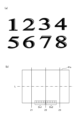
図4は、図柄表示装置41において変動表示される図柄及び表示面41aを示す説明図である。図4(a)は、図柄表示装置41において変動表示される図柄を示す説明図である。図4(a)に示すように、図柄表示装置41には、数字の1~8を示す図柄が変動表示される。なお、変動表示される図柄として、数字の1~8を示す各図柄に、キャラクターなどの絵柄が付された図柄を採用してもよい。
Figure 4 is an explanatory diagram showing the patterns and
図4(b)は、図柄表示装置41の表示面41aを示す説明図である。図示するように、表示面41aには、左、中、右の3つの図柄列Z1、Z2、Z3が表示される。各図柄列Z1~Z3には、図4(a)に示した数字1~8の図柄が、数字の昇順又は降順に配列されるとともに、各図柄列が周期性をもって上から下へ又は下から上へとスクロールする変動表示が行われる。図4(b)に示すように、スクロールによる変動表示の後、各図柄列毎に1個の図柄が、有効ラインL上に停止した状態で表示される。具体的には、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34へ遊技球が入賞すると、各図柄列Z1~Z3の図柄が周期性をもって所定の向きにスクロールする変動表示が開始される。そして、スクロールする各図柄が、図柄列Z1、図柄列Z3、図柄列Z2の順に、変動表示から待機表示に切り替わり、最終的に各図柄列Z1~Z3に所定の図柄が停止表示した状態となる。図柄の変動表示が終了して停止表示した状態となる場合、主制御装置60による大当たり抽選の結果が大当たり当選であった場合には、予め定められた所定の図柄の組み合わせが有効ラインL上に形成される。例えば、同一の図柄の組み合わせが有効ラインL上に形成される。なお、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示の態様は、上述の態様に限定されることなく、図柄列の数、有効ラインの数、図柄列における図柄の変動表示の方向、各図柄列の図柄数など、図柄の変動表示の態様は種々の態様を採用可能である。
Figure 4(b) is an explanatory diagram showing the
ここで、遊技回とは、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34のいずれかの入賞に基づいて取得された特別情報についての大当たり抽選の抽選結果を、遊技者に告知する処理の1単位である。換言すれば、パチンコ機10は、1遊技回毎に、1つの特別情報についての1つの大当たり抽選の抽選結果を遊技者に告知する。本実施形態のパチンコ機10は、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34のいずれかの入賞に基づいて特別情報を取得すると、1遊技回毎に、第1結果表示部37a又は第2結果表示部37bのいずれか一方において、セグメント表示器を変動表示させた後に、当該取得した特別情報の抽選結果に対応した表示となるようにセグメント表示器を停止表示させる。また、本実施形態のパチンコ機10は、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34のいずれかの入賞に基づいて特別情報を取得すると、1遊技回毎に、図柄表示装置41において、所定の図柄列を変動表示させた後に、当該取得した特別情報の抽選結果に対応した表示となるように図柄列を停止表示させる。また、1回の遊技回に要する時間を単位遊技時間とも呼ぶ。単位遊技時間は、変動表示が開始されてから所定の抽選結果が停止表示されるまでの時間である変動時間と、所定の抽選結果が停止表示されている時間である停止時間とによって構成されている。
Here, a play round is one unit of processing for notifying a player of the results of a jackpot lottery for special information acquired based on winning at either the
さらに、図4(b)に示すように、図柄表示装置41の表示面41aには、第1保留表示領域Ds1と、第2保留表示領域Ds2とが表示される。第1保留表示領域Ds1には、第1始動口33への入賞に基づく保留個数が表示される。第2保留表示領域Ds2には、第2始動口34への入賞に基づく保留個数が表示される。なお、本実施形態では、上述したように、第1始動口33及び第2始動口34に入賞した遊技球の保留個数は、それぞれ最大4つまでである。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 4(b), a first pending display area Ds1 and a second pending display area Ds2 are displayed on the
A2.遊技機の電気的構成:
次に、パチンコ機10の電気的構成について説明する。本説明においては、パチンコ機10の電気的構成をブロック図を用いて説明する。
A2. Electrical configuration of the gaming machine:
Next, a description will be given of the electrical configuration of the
図5は、第1実施形態のパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。パチンコ機10は、主に、主制御装置60を中心に構成されるとともに、音声発光制御装置90と、表示制御装置100とを備えている。
Figure 5 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
主制御装置60は、遊技の主たる制御を司る主制御基板61を備えている。主制御基板61は、複数の機能を有する素子によって構成されるMPU62を備えている。MPU62は、各種制御プログラムを実行するCPU62xと、各種制御プログラムや固定値データを記録したROM63と、ROM63内に記録されているプログラムをCPU62xが実行する際に各種データ等を一時的に記憶するためのメモリであるRAM64と、入出力ポート62aとを備えている。MPU62は、さらに、遊技履歴管理チップ300と、検査用端子65とを備えている。
The
遊技履歴管理チップ300は、始動口や入賞口、ゲート(以下ではこれらをまとめて「入球口」とも呼ぶ)への遊技球の入球情報に基づいて、後述する各種の遊技履歴情報を算出する。検査用端子65は、遊技履歴管理チップ300に記憶された遊技履歴情報を後述する検査機に送信するための端子である。遊技履歴管理チップ300及び検査用端子65の詳細については後述する。
The game
MPU62は、その他、割込回路、タイマー回路、データ入出力回路、乱数発生器としてのカウンタ回路を備えている。なお、MPU62が有する機能の一部を、別の素子が備えていてもよい。
The
MPU62の入力側には、払出制御装置70と、電源装置85に設けられた停電監視回路86とが接続されている。主制御基板61は、停電監視回路86を介して、電源装置85から直流安定24Vの電源の供給を受ける。電源装置85は、外部電源としての商用電源に接続されており、商用電源から供給される外部電力を、主制御装置60や払出制御装置70等が必要な動作電力に変換して、各装置に電力を供給する。また、本実施形態では、電源装置85は、コンデンサ87を備えており、停電が発生した場合や電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合には、所定期間、各装置への電力供給を継続する。
The input side of the
また、MPU62の入力側には、各入球口に設けられた入球検知センサーが接続されている。具体的には、大入賞口36aに入球した遊技球を検知する大入賞口検知センサー44aと、第1始動口33に入球した遊技球を検知する第1始動口検知センサー44bと、第2始動口34に入球した遊技球を検知する第2始動口検知センサー44cと、第1入賞口32aに入球した遊技球を検知する第1入賞口検知センサー44dと、第2入賞口32bに入球した遊技球を検知する第2入賞口検知センサー44eと、第3入賞口32cに入球した遊技球を検知する第3入賞口検知センサー44fと、スルーゲート35を通過した遊技球を検知するスルーゲート検知センサー44gと、上述した排出通路を通過した遊技球を検知する排出通路検知センサー44hとが接続されている。MPU62は、これらの検知センサーからの信号に基づいて、遊技領域PAを流下する遊技球が始動口や入賞口に入球したか否かの判定や、遊技球がスルーゲートや排出通路を通過したか否かの判定を行う。さらに、MPU62は、第1始動口33、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に基づいて大当たり抽選を実行する。
Also, the input side of the
MPU62の出力側には、可変入賞装置36の開閉扉36bを開閉動作させる可変入賞駆動部36cと、第2始動口34の電動役物34aを開閉動作させる電動役物駆動部34bと、メイン表示部45とが接続されている。主制御基板61には各種ドライバ回路が設けられており、MPU62は、当該ドライバ回路を通じて各種駆動部の駆動制御を実行する。
The output side of the
具体的には、MPU62は、開閉実行モードにおいては、開閉扉36bが開閉されるように可変入賞駆動部36cの駆動制御を実行する。また、電動役物開放抽選の結果、電役開放に当選した場合には、MPU62は、電動役物34aが開放されるように電動役物駆動部44bの駆動制御を実行する。さらに、各遊技回においては、MPU62は、メイン表示部45における第1図柄表示部37a又は第2図柄表示部37bの表示制御を実行するとともに、開閉実行モードにおいては、メイン表示部45におけるラウンド表示部39の表示制御を実行する。
Specifically, in the opening and closing execution mode, the
また、MPU62の送信側には、払出制御装置70と、音声発光制御装置90とが接続されている。払出制御装置70には、例えば、主制御装置60から入球判定結果に基づいて賞球コマンドが送信される。主制御装置60が賞球コマンドを送信する際には、主制御基板61のMPU62は、ROM63のコマンド情報記憶エリアを参照する。具体的には、一般入賞口32への遊技球の入球を特定した場合には10個の遊技球の払い出しに対応した賞球コマンドが主制御装置60から送信され、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球を特定した場合には3個の遊技球の払い出しに対応した賞球コマンドが主制御装置60から送信され、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を特定した場合には1個の遊技球の払い出しに対応した賞球コマンドが主制御装置60から送信される。払出制御装置70は、主制御装置60から受信した賞球コマンドに基づいて、払出装置71を制御して賞球の払出を行う。
The
払出制御装置70には、発射制御装置80が接続されている。発射制御装置80は、遊技球発射機構81の発射制御を行う。遊技球発射機構81は、所定の発射条件が整っている場合に駆動される。また、発射制御装置80には、操作ハンドル25が接続されている。上述のように、操作ハンドル25は、タッチセンサー25aと、ウェイトボタン25bと、可変抵抗器25cとを備える。遊技者が操作ハンドル25を握ることによって、タッチセンサー25aがオンになり、遊技者が操作ハンドル25を回動操作すると、可変抵抗器25cの抵抗値が回動操作量に対応して変化し、可変抵抗器25cの抵抗値に対応した強さで遊技球発射機構から遊技盤の前面に遊技球が発射される。
The
音声発光制御装置90は、主制御装置60から送信された各種コマンドを受信し、受信した各種コマンドに対応した処理を実行する。具体的には、音声発光制御装置90は、主制御装置60から受信した各種コマンドに基づいて、前扉枠14に配置されたLEDなどの発光手段からなる各種ランプ47の駆動制御や、スピーカー46の駆動制御を行うとともに、表示制御装置100の制御を行う。また、音声発光制御装置90には、演出操作ボタン24が接続されており、所定のタイミングで遊技者によって演出操作ボタン24が操作された場合には、当該操作を反映した遊技演出を行うように各種ランプ47、スピーカー46、表示制御装置100等の制御を行う。
The audio and light
表示制御装置100は、音声発光制御装置90から受信した各種コマンドに基づいて、図柄表示装置41の表示制御を実行する。具体的には、表示制御装置100は、音声発光制御装置90から受信した各種コマンドに基づいて、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動時間及び最終的に停止表示させる図柄の組み合わせの種類を把握するとともに、リーチの発生の有無、リーチ演出の内容、及び、第1液晶用図柄や第2液晶用図柄が変動表示をしている間に実行される演出の内容等を把握する。なお、本実施形態においては、第1液晶用図柄または第2液晶用図柄が停止表示している時間である停止時間は一定ある。従って、変動時間が決定されることによって、1遊技回に要する時間である単位遊技回時間は一意に決定される。以上、パチンコ機10の電気的構成について説明した。
The
図6は、大当たり抽選などに用いられる各種カウンタの内容を示す説明図である。各種カウンタは、RAM64の各種カウンタエリアに設けられており、MPU62が大当たり抽選、メイン表示部45の表示の設定、及び、図柄表示装置41の図柄表示の設定などを行う際に用いられる。具体的には、大当たり抽選には大当たり乱数カウンタC1が用いられる。大当たり種別を振り分ける際には大当たり種別カウンタC2が用いられる。図柄表示装置41に表示させる図柄列を外れ変動させる際にリーチを発生させるか否かのリーチ判定にはリーチ乱数カウンタC3が用いられる。
Figure 6 is an explanatory diagram showing the contents of various counters used for the jackpot lottery and the like. The various counters are provided in various counter areas of the
大当たり乱数カウンタC1の初期値設定には乱数初期値カウンタCINIが用いられる。また、メイン表示部45の第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37b、並びに図柄表示装置41における変動時間を決定する際には変動種別カウンタCSが用いられる。さらに、第2始動口34の電動役物34aを開放状態とするか否かの電動役物開放抽選には電動役物開放カウンタC4が用いられる。
The random number initial value counter CINI is used to set the initial value of the jackpot random number counter C1. In addition, the change type counter CS is used to determine the change time in the first and second
各カウンタC1~C3、CINI、CS、C4は、その更新の都度、カウンタ値に1が加算され、最大値に達した後に0に戻るループカウンタである。各カウンタは短時間の間隔で更新され、その更新値がRAM64の所定領域に設定された抽選カウンタ用バッファ64aに適宜記憶される。
Each of the counters C1 to C3, CINI, CS, and C4 is a loop counter that adds 1 to its counter value each time it is updated and returns to 0 after it reaches its maximum value. Each counter is updated at short intervals, and the updated value is appropriately stored in the
また、RAM64には保留情報記憶エリア64bと、判定処理実行エリア64cとが設けられている。保留情報記憶エリア64bには、第1保留エリアRaと第2保留エリアRbとが設けられている。本実施形態では、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球すると、入球のタイミングにおける大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3および変動種別カウンタCSの各値が保留情報記憶エリア64bの第1保留エリアRaに時系列的に記憶される。また、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球すると、入球のタイミングにおける大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3および変動種別カウンタCSの各値が保留情報記憶エリア64bの第2保留エリアRbに時系列的に記憶される。
The
大当たり乱数カウンタC1の詳細について説明する。大当たり乱数カウンタC1は、上述のように大当たり抽選に用いられる。大当たり乱数カウンタC1は、例えば、0~1199の範囲内で順に1ずつ加算され、最大値に達した後0に戻るように構成されている。また、大当たり乱数カウンタC1が1周すると、その時点の乱数初期値カウンタCINIの値が当該大当たり乱数カウンタC1の初期値として読み込まれる。なお、乱数初期値カウンタCINIは、大当たり乱数カウンタC1と同様のループカウンタである(値=0~1199)。 The details of the jackpot random number counter C1 will now be described. As described above, the jackpot random number counter C1 is used in the jackpot lottery. The jackpot random number counter C1 is configured to increment by one within the range of 0 to 1199, for example, and return to 0 after reaching a maximum value. When the jackpot random number counter C1 goes through one cycle, the value of the random number initial value counter CINI at that time is read as the initial value of the jackpot random number counter C1. The random number initial value counter CINI is a loop counter similar to the jackpot random number counter C1 (value = 0 to 1199).
大当たり乱数カウンタC1は定期的に更新され、その更新値は、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球した場合には、当該入球のタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第1保留エリアRaに記憶され、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球した場合には、当該入球のタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第2保留エリアRbに記憶される。
The jackpot random number counter C1 is updated periodically, and when a game ball enters the
第1保留エリアRaに記憶された大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値は、判定処理実行エリア64cの実行エリアAEに移動し、ROM63の当否テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている当否テーブルと照合され、大当たりとなるか否かが判定される。また、第2保留エリアRbに記憶された大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値は、判定処理実行エリア64cの実行エリアAEに移動し、ROM63の当否テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている当否テーブルと照合され、大当たりとなるか否かが判定される。
The value of the jackpot random number counter C1 stored in the first holding area Ra is moved to the execution area AE of the judgment process execution area 64c, where it is compared with the hit/miss table stored in the hit/miss table storage area of the
本実施形態のパチンコ機10においては、第1保留エリアRaまたは第2保留エリアRbに記憶された大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値は、第1始動口33または第2始動口34に遊技球が入球することによって取得された順番に判定処理実行エリア64cの実行エリアAEに移動する。そして、実行エリアAEに移動した大当たり乱数カウンタC1は、ROM63の当否テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている当否テーブルと照合され、大当たりとなるか否かが判定される。
In the
次に、大当たり種別カウンタC2の詳細について説明する。大当たり種別カウンタC2は、大当たり種別を判定する際に用いられる。大当たり種別カウンタC2は、0~39の範囲内で順に1ずつ加算され、最大値に達した後0に戻るように構成されている。 Next, the details of the jackpot type counter C2 will be described. The jackpot type counter C2 is used when determining the type of jackpot. The jackpot type counter C2 is configured to increment by one within the range of 0 to 39, and to return to 0 after reaching the maximum value.
大当たり種別カウンタC2は定期的に更新され、その更新値は、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球した場合には当該入球のタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第1保留エリアRaに記憶され、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球した場合には当該入球のタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第2保留エリアRbに記憶される。
The jackpot type counter C2 is updated periodically, and the updated value is stored in the first reserved area Ra of the reserved
上述したように、MPU62は、判定処理実行エリア64cに記憶されている大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値を用いて大当たり抽選を行なうとともに、大当たり抽選の結果が大当たりである場合には、判定処理実行エリア64cに記憶されている大当たり種別カウンタC2の値を用いて大当たり種別を判定する。さらに、MPU62は、これらの大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値及び大当たり種別カウンタC2の値を用いて、第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37bに停止表示させるセグメント表示器の表示態様を決定する。その決定に際しては、ROM63の停止結果テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている停止結果テーブルが参照される。
As described above, the
次に、リーチ乱数カウンタC3の詳細について説明する。リーチ乱数カウンタC3は、大当たり抽選の結果が大当たりではない場合においてリーチが発生するか否かを判定する際に用いられる。リーチ乱数カウンタC3は、例えば0~238の範囲内で順に1ずつ加算され、最大値に達した後0に戻るように構成されている。 Next, the reach random number counter C3 will be described in detail. The reach random number counter C3 is used to determine whether or not a reach will occur when the result of the jackpot lottery is not a jackpot. The reach random number counter C3 is configured to increment by 1 in sequence within a range of, for example, 0 to 238, and to return to 0 after reaching a maximum value.
リーチ乱数カウンタC3は定期的に更新され、その更新値は、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球したタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第1保留エリアRaに記憶され、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球したタイミングで保留情報記憶エリア64bの第2保留エリアRbに記憶される。第1保留エリアRaに記憶されたリーチ乱数カウンタC3の値は、判定処理実行エリア64cに移動した後、ROM63のリーチ判定用テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されているリーチ判定用テーブルと照合され、リーチが発生するか否かが判定される。第2保留エリアRbに記憶されたリーチ乱数カウンタC3の値は、判定処理実行エリア64cに移動した後、ROM63のリーチ判定用テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されているリーチ判定用テーブルと照合され、リーチが発生するか否かが判定される。ただし、大当たり抽選の結果が大当たりとなり、開閉実行モードに移行する場合には、MPU62は、リーチ乱数カウンタC3の値に関係なくリーチ発生が決定される。
The reach random number counter C3 is periodically updated, and the updated value is stored in the first holding area Ra of the holding
リーチとは、図柄表示装置41の表示画面に表示される複数の図柄列のうち一部の図柄列について、大当たりに対応した図柄の組み合わせが成立する可能性がある図柄の一部の組み合わせが停止表示され、その状態で残りの図柄列において図柄の変動表示を行う表示状態のことを言う。なお、本実施形態のパチンコ機10において大当たりに対応した図柄の組み合わせとは、所定の有効ラインにおける同一の図柄の組み合わせのことをいう。具体例としては、図4(b)の表示面41aのメイン表示領域MAにおいて、最初に図柄列Z1において図柄が停止表示され、次に図柄列Z3においてZ1と同じ図柄が停止表示されることでリーチラインが形成され、当該リーチラインが形成されている状況化において図柄列Z2において図柄の変動表示が行われることでリーチとなる。そして、大当たりが発生する場合には、リーチラインを形成している図柄と同一の図柄が図柄列Z2に停止表示される。
The term "reach" refers to a display state in which some combinations of symbols that may result in a combination of symbols corresponding to a jackpot are displayed as stopped in some of the multiple symbol rows displayed on the display screen of the
また、リーチには、リーチラインが形成された状態で、残りの図柄列において図柄の変動表示を行うとともに、その背景画面において所定のキャラクターなどを動画として表示することによりリーチ演出を行うものや、リーチラインが形成された図柄の組み合わせを縮小表示させる又は非表示とした上で、表示面41aの略全体において所定のキャラクターなどを動画として表示することによりリーチ演出を行うものが含まれる。また、リーチ演出が行われている場合又はリーチ表示の前に所定のキャラクターといった所定画像を用いた予告表示を行うか否かの決定を、リーチ乱数カウンタC3やその他のカウンタを用いて行うようにしてもよい。
The reach also includes a reach effect in which, when a reach line is formed, the remaining symbol rows are displayed in a varying manner while a predetermined character or the like is displayed as a moving image in the background screen, and a reach effect is performed by reducing or hiding the symbol combination on which the reach line is formed and then displaying a predetermined character or the like as a moving image on substantially the
次に、変動種別カウンタCSの詳細について説明する。変動種別カウンタCSは、第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37bにおける変動時間と、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動時間とを、MPU62において決定する際に用いられる。変動種別カウンタCSは、例えば0~198の範囲内で順に1ずつ加算され、最大値に達した後0に戻るように構成されている。
Next, the details of the change type counter CS will be explained. The change type counter CS is used when the
変動種別カウンタCSは、後述する通常処理が1回実行される毎に1回更新され、当該通常処理内の残余時間内でも繰り返し更新される。そして、第1図柄表示部37a又は第2図柄表示部37bにおける変動表示の開始時及び図柄表示装置41による図柄の変動開始時における変動パターンの決定に際して変動種別カウンタCSのバッファ値が取得される。第1図柄表示部37a及び第2図柄表示部37bにおける変動時間の決定に際しては、ROM63の変動時間テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている変動時間テーブルが用いられる。
The change type counter CS is updated once each time the normal processing described below is executed, and is repeatedly updated during the remaining time in the normal processing. The buffer value of the change type counter CS is acquired when the change display in the first
次に、電動役物開放カウンタC4の詳細について説明する。電動役物開放カウンタC4は、例えば、0~465の範囲内で順に1ずつ加算され、最大値に達した後0に戻る構成である。電動役物開放カウンタC4は定期的に更新され、スルーゲート35に遊技球が入球したタイミングでRAM64の電役保留エリア64dに記憶される。そして、所定のタイミングで、電役保留エリア64dに記憶されている電動役物開放カウンタC4の値が電動役物用実行エリア64eに移動した後、電動役物用実行エリア64eにおいて電動役物開放カウンタC4の値を用いて電動役物34aを開放状態に制御するか否かの抽選が行われる。例えば、C4=0,1であれば、電動役物34aを開放状態に制御し、C4=2~465であれば、電動役物34aを閉鎖状態に維持する。
Next, the details of the electric role opening counter C4 will be described. The electric role opening counter C4 is configured to be incremented by one in sequence within the range of, for example, 0 to 465, and to return to 0 after reaching the maximum value. The electric role opening counter C4 is periodically updated, and is stored in the electric role holding area 64d of the
なお、取得された大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値、大当たり種別カウンタC2の値、リーチ乱数カウンタC3の値、電動役物開放カウンタC4の値および変動種別カウンタCSの値の少なくとも一つが本発明における特別情報に相当する。また、第1保留エリアRaおよび第2保留エリアRbに記憶された大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値、大当たり種別カウンタC2の値、リーチ乱数カウンタC3の値および変動種別カウンタCSの値の少なくとも一つを保留情報とも呼ぶ。 In addition, at least one of the acquired values of the jackpot random number counter C1, the jackpot type counter C2, the reach random number counter C3, the electric role opening counter C4, and the variable type counter CS corresponds to special information in the present invention. In addition, at least one of the values of the jackpot random number counter C1, the jackpot type counter C2, the reach random number counter C3, and the variable type counter CS stored in the first holding area Ra and the second holding area Rb is also called reserved information.
次に、当否テーブルについて説明する。当否テーブルは、大当たり乱数カウンタC1に基づいて大当たり抽選を行う際に、当該大当たり乱数カウンタC1と照合するためのテーブルデータである。パチンコ機10には、大当たり抽選の抽選モードとして、低確率モードと高確率モードとが設定されており、低確率モード時における大当たり抽選の際には低確率モード用の当否テーブルが参照され、高確率モード時における大当たり抽選の際には高確率モード用の当否テーブルが参照される。
Next, the hit/miss table will be explained. The hit/miss table is table data for checking against the jackpot random number counter C1 when a jackpot lottery is held based on the jackpot random number counter C1. The
図7は、当否テーブルの内容を示す説明図である。図7(a)は低確率モード用の当否テーブル(低確率モード用)を示し、図7(b)は高確率モード用の当否テーブルを示している。 Figure 7 is an explanatory diagram showing the contents of the win/lose table. Figure 7(a) shows the win/lose table for the low probability mode (for the low probability mode), and Figure 7(b) shows the win/lose table for the high probability mode.
図7(a)に示すように、低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、大当たりとなる大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値として、0~4の5個の値が設定されている。そして、0~1199の値のうち、0~4の5個の値以外の値(5~1199)が外れである。一方、図7(b)に示すように、高確率モード用の当否テーブルには、大当たりとなる大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値として、0~15の16個の値が設定されている。そして、0~1199の値のうち、0~15の16個の値以外の値が外れである。このように、高確率モードは、低確率モードに比べて、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率が高くなっている。 As shown in FIG. 7(a), the hit/miss table for the low probability mode has five values, 0 to 4, set as the value of the jackpot random number counter C1 that will result in a jackpot. Of the values from 0 to 1199, any value other than the five values from 0 to 4 (5 to 1199) is a miss. On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 7(b), the hit/miss table for the high probability mode has 16 values, 0 to 15, set as the value of the jackpot random number counter C1 that will result in a jackpot. Of the values from 0 to 1199, any value other than the 16 values from 0 to 15 is a miss. In this way, the high probability mode has a higher probability of winning a jackpot in the jackpot lottery than the low probability mode.
また、本実施形態では、低確率モード用の当否テーブルに大当たりとして設定されている大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値群は、高確率モード用の当否テーブルに大当たりとして設定されている大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値群に含まれている。ただし、大当たり抽選の結果、低確率モードよりも高確率モードの方が大当たりとなる確率が高くなるのであれば、大当たりとして設定されている乱数の数及び値は任意である。 In addition, in this embodiment, the value group of the jackpot random number counter C1 set as a jackpot in the hit/miss table for the low probability mode is included in the value group of the jackpot random number counter C1 set as a jackpot in the hit/miss table for the high probability mode. However, as long as the result of the jackpot lottery shows a higher probability of winning a jackpot in the high probability mode than in the low probability mode, the number and value of the random numbers set as a jackpot are arbitrary.
なお、本実施形態における当否テーブルにおいては採用していないが、大当たり抽選の結果として「小当たり」を設けてもよい。 Although not adopted in the win/lose table in this embodiment, a "small win" may be provided as a result of the big win lottery.
「小当たり」とは、可変入賞装置36の開閉が実行される開閉実行モードへの移行契機とはなるが、抽選モードおよびサポートモードの両方について、移行契機とならない当否結果である。これに対して、「外れ」は、開閉実行モードの移行契機とはならず、さらに、抽選モードおよびサポートモードについても移行契機とならない当否結果である。
A "small win" is a result that triggers a transition to the opening and closing execution mode in which the opening and closing of the variable winning
次に、大当たり種別について説明する。パチンコ機10には、複数種類の大当たりを設定することができる。具体的には、例えば、以下の3つの態様又はモードに差異を設けることにより、複数種類の大当たりを設定することができる。
(1)開閉実行モードにおける可変入賞装置36の開閉扉36bの開閉回数(ラウンド数)
(2)開閉実行モードにおける可変入賞装置36の開閉制御の態様
(3)開閉実行モード終了後の大当たり抽選の抽選モード(低確率モード又は高確率モード)
Next, the types of jackpots will be described. A plurality of types of jackpots can be set in the
(1) The number of times (number of rounds) the opening and closing
(2) Aspects of the opening and closing control of the variable winning
上記の(2)開閉実行モードにおける可変入賞装置36の開閉制御の態様として、開閉実行モードが開始されてから終了するまでの間における可変入賞装置36への遊技球の入球(入賞)の発生頻度が相対的に高低となるように高頻度入賞モードと低頻度入賞モードとを設定することができる。例えば、高頻度入賞モードでは、開閉実行モードにおける開閉扉36bの1回の開放は30秒が経過するまで又は開閉扉36bへの遊技球の入球個数が10個となるまで継続するように設定することができる。一方、低頻度入賞モードでは、開閉実行モードにおける開閉扉36bの1回の開放が1.6秒が経過するまで又は開閉扉36bへの入球個数が10個となるまで継続するよう設定することができる。
As a mode of the opening and closing control of the variable winning
開閉扉36bの1回の開放に対する開放限度時間、及び1回の開放に対する開放限度個数は、開閉実行モードが開始されてから終了するまでの間における可変入賞装置36への入球の発生頻度が、高頻度入賞モードの方が低頻度入賞モードよりも高くなるのであれば、開閉扉36bの開放態様は任意である。具体的には、高頻度入賞モードの方が低頻度入賞モードよりも、1回の開放に対する開放限度時間が長い又は1回の開放に対する開放限度個数が多く設定されていればよい。高頻度入賞モードと低頻度入賞モードとの差異を明確にする上では、低頻度入賞モードの開閉実行モードでは、実質的に可変入賞装置36への入賞が発生しない構成としてもよい。
The opening time limit for one opening of the opening/
なお、本実施形態においては、開閉実行モードとして複数種類の入賞モードは設けておらず、開閉実行モード中は、上述した高頻度入賞モードとなる。すなわち、開閉実行モードにおける開閉扉36bの1回の開放は、30秒が経過するまで又は開閉扉36bへの遊技球の入球個数が10個となるまで継続するように設定される。
In this embodiment, the opening and closing execution mode does not have multiple types of winning modes, and during the opening and closing execution mode, the above-mentioned high frequency winning mode is set. In other words, one opening of the opening and closing
本実施形態では、大当たり抽選の結果、大当たりとなった場合には、大当たり種別カウンタC2を用いて、大当たり種別を振り分ける。大当たり種別カウンタC2の値に対応する大当たり種別の振り分けは、ROM63の振分テーブル記憶エリアに振分テーブルとして記憶されている。
In this embodiment, if a jackpot is selected as a result of the jackpot lottery, the jackpot type counter C2 is used to assign a jackpot type. The jackpot type assignment corresponding to the value of the jackpot type counter C2 is stored as an assignment table in the assignment table storage area of the
図8は、振分テーブルの内容を示す説明図である。図8(a)は第1始動口用の振分テーブルを示し、図8(b)は第2始動口用の振分テーブルを示している。第1始動口用の振分テーブルは、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づく大当たり抽選の際に参照され、第2始動口用の振分テーブルは、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に基づく大当たり抽選の際に参照される。
Figure 8 is an explanatory diagram showing the contents of the distribution table. Figure 8(a) shows the distribution table for the first start port, and Figure 8(b) shows the distribution table for the second start port. The distribution table for the first start port is referenced when a jackpot lottery is drawn based on a game ball entering the
図8(a)の第1始動口用の振分テーブルに示すように、本実施形態のパチンコ機10では、第1始動口33に基づく大当たり種別として、16R確変大当たり、8R確変大当たり、16R通常大当たり、8R通常大当たりが設定されている。
As shown in the distribution table for the first starting hole in FIG. 8(a), in the
16R確変大当たり及び8R確変大当たりは、開閉実行モードにおける可変入賞装置36の開閉制御の態様が高頻度入賞モードであり、開閉実行モードの終了後の当否抽選モードが高確率モードであり、開閉実行モードの終了後のサポートモードが高頻度サポートモードとなる大当たりである。
The 16R probability variable jackpot and 8R probability variable jackpot are jackpots in which the opening and closing control of the variable winning
16R通常大当たり及び8R通常大当たりは、開閉実行モードにおける可変入賞装置36の開閉制御の態様が高頻度入賞モードであり、開閉実行モードの終了後の当否抽選モードが低確率モードであり、開閉実行モードの終了後のサポートモードが高頻度サポートモードとなる大当たりである。
The 16R normal jackpot and 8R normal jackpot are jackpots in which the opening and closing control of the variable winning
第1始動口用の振分テーブルでは、「0~39」の大当たり種別カウンタC2の値のうち、「0~13」が16R確変大当たりに対応しており、「14~27」が8R通常大当たりに対応しており、「28~33」が16R通常大当たりに対応しており、「34~39」が8R通常大当たりに対応している。 In the distribution table for the first starting port, of the jackpot type counter C2 values of "0-39", "0-13" corresponds to a 16R special jackpot, "14-27" corresponds to an 8R regular jackpot, "28-33" corresponds to a 16R regular jackpot, and "34-39" corresponds to an 8R regular jackpot.
上記のように、本実施形態のパチンコ機10では、大当たりの種別として、4種類の大当たりが設定されている。したがって、大当たりの態様が多様化する。この4種類の大当たりを比較した場合、遊技者にとっての有利度合は、16R確変大当たりが最も高く、8R確変大当たりが次に高く、次に16R通常大当たり、最後に8R通常大当たりと続く。このように遊技者にとって有利度の異なる複数種類の大当たりが設定されていることにより、遊技の単調化が抑えられ、遊技への注目度を高めることが可能となる。
As described above, in the
図8(b)の第2始動口用の振分テーブルに示すように、本実施形態のパチンコ機10では、第2始動口34に基づく大当たり種別として、16R確変大当たり、8R通常大当たりが設定されている。第2始動口用の振分テーブルでは、「0~39」の大当たり種別カウンタC2の値のうち、「0~27」が16R確変大当たりに対応しており、「28~39」が8R通常大当たりに対応している。
As shown in the distribution table for the second starting port in FIG. 8(b), in the
このように、本実施形態のパチンコ機10では、大当たりとなった場合の大当たり種別の振分態様は、第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づいて大当たりとなった場合と、第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に基づいて大当たりとなった場合とで異なっているとともに、遊技者にとっての有利性に明確な差異が設けられている。
In this way, in the
上述のように、MPU62は、実行エリアAEに記憶されている大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値を用いて大当たり抽選を行なうとともに、実行エリアAEに記憶されている大当たり種別カウンタC2の値を用いて大当たり種別を判定するが、さらに、MPU62は、これらの大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値及び大当たり種別カウンタC2の値を用いて、第1結果表示部37a及び第2結果表示部37bに停止表示させるセグメント表示器の表示態様を決定する。その決定に際しては、ROM63の停止結果テーブル記憶エリアに記憶されている停止結果テーブルが参照される。
As described above, the
パチンコ機10には、上記の(3)開閉実行モード終了後の第2始動口34の電動役物34aのサポートモードの態様として、遊技領域PAに対して遊技球の発射が同様の態様で継続されている状況で比較した場合に、第2始動口34の電動役物34aが単位時間当たりに開放状態となる頻度が相対的に高低となるように、高頻度サポートモードと低頻度サポートモードとを設定することができる。
In the
具体的には、本実施形態におけるパチンコ機10は、高頻度サポートモードと低頻度サポートモードとでは、電動役物開放カウンタC4を用いた電動役物開放抽選における電役開放当選となる確率が異なる。高頻度サポートモードでは低頻度サポートモードよりも、電動役物開放抽選における電役開放当選となる確率を高くする。また、高頻度サポートモードでは低頻度サポートモードよりも、電役開放当選となった際に電動役物34aの1回の開放時間が長く設定されている。
Specifically, in the
なお、本実施形態においては採用していないが、高頻度サポートモードで電役開放当選となり電動役物34aの開放状態が複数回発生する場合において、1回の開放状態が終了してから次の開放状態が開始されるまでの閉鎖時間は、1回の開放時間よりも短く設定されてもよい。さらに、高頻度サポートモードでは低頻度サポートモードよりも、1回の電動役物開放抽選が行われてから次の電動役物開放抽選が行われるまでに確保される時間が相対的に短く設定されてもよい。 Although not adopted in this embodiment, in the case where an electric role opening win occurs in the high frequency support mode and the electric role opening state of the electric role 34a occurs multiple times, the closing time from the end of one opening state to the start of the next opening state may be set to be shorter than the opening time of one time. Furthermore, in the high frequency support mode, the time secured from the one electric role opening lottery to the next electric role opening lottery may be set to be relatively shorter than in the low frequency support mode.
上記のように高頻度サポートモードでは、低頻度サポートモードよりも第2始動口34への遊技球の入球が発生する確率が高くなる。すなわち、高頻度サポートモードは、特別情報の取得条件の成立を補助する補助遊技状態として機能する。
As described above, in the high-frequency support mode, the probability of a game ball entering the
図9は、電動役物開放抽選を実行する際に用いられる当否テーブル(電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブル)の内容を示す説明図である。 Figure 9 is an explanatory diagram showing the contents of the win/lose table (win/lose table for the lottery to open electric reels) used when executing the lottery to open electric reels.
図9(a)は、低頻度サポートモード時に用いられる電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブル(低頻度サポートモード用)を示している。図9(a)に示すように、電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブル(低頻度サポートモード用)には、電役開放当選となる電動役物開放カウンタC4の値として0、1の2個の値が設定されている。外れとなる電動役物開放カウンタC4の値として2~465の464個の値が設定されている。すなわち、低頻度サポートモード時に遊技球がスルーゲート35を通過し電動役物開放抽選が実行された場合には、1/233の確率で電役開放当選となる。本実施形態のパチンコ機10においては、低頻度サポートモード時に電役開放当選となった場合には、電動役物34aが1回開放し、その開放時間は1.4秒である。
Figure 9 (a) shows a winning/losing table for the electric role opening lottery (for low-frequency support mode) used in the low-frequency support mode. As shown in Figure 9 (a), the winning/losing table for the electric role opening lottery (for low-frequency support mode) has two values, 0 and 1, set as the value of the electric role opening counter C4 that will result in a winning electric role opening. 464 values, from 2 to 465, are set as the value of the electric role opening counter C4 that will result in a losing electric role opening. In other words, when the game ball passes through the through
図9(b)は、高頻度サポートモード時に用いられる電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブル(高頻度サポートモード用)を示している。図9(b)に示すように、電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブル(高頻度サポートモード用)には、電役開放当選となる電動役物開放カウンタC4の値として0~461の462個の値が設定されている。外れとなる電動役物開放カウンタC4の値として462~465の4個の値が設定されている。すなわち、高頻度サポートモード時に遊技球がスルーゲート35を通過し電動役物開放抽選が実行された場合には、231/233の確率で電役開放当選となる。本実施形態のパチンコ機10においては、高頻度サポートモード時に電役開放当選となった場合には、電動役物34aが1回開放し、その開放時間は1.6秒である。
Figure 9 (b) shows a winning/losing table for the electric role opening lottery (for high-frequency support mode) used in the high-frequency support mode. As shown in Figure 9 (b), the winning/losing table for the electric role opening lottery (for high-frequency support mode) has 462 values from 0 to 461 set as the value of the electric role opening counter C4 that will result in winning the electric role opening. Four values from 462 to 465 are set as the value of the electric role opening counter C4 that will result in losing. In other words, when the game ball passes through the through
このように、電動役物開放抽選用当否テーブルによって、高頻度サポートモードが低頻度サポートモードよりも第2始動口34への遊技球の入球が発生する確率が高くなるように設定されている。
In this way, the winning/losing table for the electric device opening lottery is set so that the high frequency support mode has a higher probability of the game ball entering the
図10は、第1実施形態のパチンコ機10が備える主制御装置60の構成及び検査機320の構成を詳細に示すブロック図である。以下では、MPU62、CPU62x、ROM63及びRAM64を、それぞれ主側MPU62、主側CPU62x、主側ROM63及び主側RAM64とも呼ぶ。
Figure 10 is a block diagram showing in detail the configuration of the
主側MPU62の主側ROM63には、賞球数データ記憶エリアと、演算実行条件記憶エリアとが設けられている。
The
賞球数データ記憶エリアには、各入球口に遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数データ)が記憶されている。本実施形態では、賞球数データ記憶エリアには、以下の賞球数データが記憶されている。
・第1始動口33に遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(第1始動口賞球数P1):3
・第2始動口34に遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(第2始動口賞球数P2):3
・第1入賞口32aに遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(第1入賞口賞球数PN1):10
・第2入賞口32bに遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(第2入賞口賞球数PN2):10
・第3入賞口32cに遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(第3入賞口賞球数PN3):10
・大入賞口36aに遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(大入賞口賞球数PS):15
The prize ball number data storage area stores the number of game balls (prize ball number data) that are paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters each ball entrance. In this embodiment, the prize ball number data storage area stores the following prize ball number data.
Number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the first starting hole 33 (number of first starting hole prize balls P 1 ): 3
The number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the second starting hole 34 (number of second starting hole prize balls P2 ): 3
Number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the first winning
Number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the second winning
Number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the third winning
Number of game balls paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters the
主側MPU62は、主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを参照することによって、遊技球が各入球口に入球した場合に賞球として払い出す遊技球の個数を決定する。
The
さらに、本実施形態では、この主側ROM63に記憶された賞球数データは、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた後に実行される初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される。これにより、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、本パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを把握することが可能となる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the prize ball count data stored in the
演算実行条件記憶エリアには、遊技履歴管理チップ300が遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を開始する条件である演算実行条件が記憶されている。本実施形態では、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数が500個に達することが演算実行条件として記憶されている。この主側ROM63に記憶された演算実行条件は、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた後に実行される初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される。これにより、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、本パチンコ機10に設定されている演算実行条件を把握することが可能となる。
The calculation execution condition memory area stores a calculation execution condition that is a condition for the game
遊技履歴管理チップ300は、各入球口への遊技球の入球情報に基づいて各種の遊技履歴情報を算出するとともに、算出した遊技履歴情報を記憶する半導体チップである。遊技履歴管理チップ300は、CPU62xから各入球口への遊技球の入球情報を取得するバッファ302と、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を記憶するレジスタ304と、主側ROM63から取得した賞球数データを記憶する賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306と、主側ROM63から取得した演算実行条件を記憶する演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307と、遊技履歴管理チップ300の全体の制御を司るとともに、演算実行条件の成立を契機として各入球口への遊技球の入球個数と各入球口に設定された賞球数とに基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出するCPU308と、算出された遊技履歴情報を記憶する演算結果記憶用メモリ309とを備えている。
The game
検査用端子65は、検査機320とパチンコ機10とを接続するための端子である。本実施形態では、検査用端子65を介して演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶された遊技履歴情報が検査機320に送信される。
The
検査機320は、各種制御プログラムを実行するCPU321と、各種制御プログラムや固定値データ等を記録したROM324と、各種データを一時的に記憶するためのメモリであるRAM326と、遊技履歴管理チップ300から受信した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示部328と、パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続するための接続ケーブル329とを備えている。
The
図11は、遊技履歴管理チップ300及び検査機320における処理の内容を模式的に示す説明図である。
Figure 11 is an explanatory diagram that shows a schematic of the processing performed by the game
バッファ302は、主側MPU62のCPU62xとレジスタ304との間に設けられており、各入球口における入球情報をCPU62xから取得する。具体的には、バッファ302には、各入球口に対応した複数のビットが設けられており、CPU62xは、遊技球が入球したと判定した入球口に対応したビットをON(「1」)にする。例えば、CPU62xは、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球したと判定すると、バッファ302の第1始動口33に対応したビットをON(「1」)にする。
The
また、バッファ302には、遊技球が各入球口に入球した際の遊技モードやパチンコ機10の状態(以下では、遊技状態とも呼ぶ)を把握するためのビットも設けられている。本実施形態では、通常モード中(高確率モード中でもなく、高頻度サポートモード中でもなく、開閉実行モード中でもないモード)であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、高確率モード中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、高頻度サポートモード中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、開閉実行モード中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、第1保留個数が上限値である期間中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、第2保留個数が上限値である期間中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、前扉枠14が開放中であるか否かを判定するためのビットと、パチンコ機10に故障等のトラブルが発生しているエラー中であるか否かを判定するためのビットとが設けられている。例えば、CPU62xは、第1始動口33に遊技球が入球したタイミングにおいて通常モード中であると判定すると、バッファ302の通常モード中であるか否かを判定するためのビットをON(「1」)にする。
The
レジスタ304は、各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数を記憶する。具体的には、レジスタ304は、各入球口に対応した複数のカウンタによって構成されており、バッファ302のビットに入球情報があると判定した場合(すなわち、ビットがONになっている場合)には、入球情報があると判定されたビットに対応したカウンタの値に1が加算される。なお、本実施形態では、レジスタ304は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のレジスタによって構成されている。
本実施形態では、レジスタ304は、各入球口に対応した各カウンタによって、下記の値を記憶している。
・大入賞口36aに入球した遊技球の個数=大入賞口入球個数NS
・第1始動口33に入球した遊技球の個数=第1始動口入球個数N1
・第2始動口34に入球した遊技球の個数=第2始動口入球個数N2
・第1入賞口32aに入球した遊技球の個数=第1入賞口入球個数NN1
・第2入賞口32bに入球した遊技球の個数=第2入賞口入球個数NN2
・第3入賞口32cに入球した遊技球の個数=第3入賞口入球個数NN3
・スルーゲート35を通過した遊技球の個数=スルーゲート通過個数NG
・排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数=排出通路通過個数NOUT
なお、上述したように、排出通路通過個数NOUTは、遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数と一致する。
In this embodiment, the
Number of game balls entering the
Number of game balls entering the
Number of game balls entering the
Number of game balls entering the first winning
Number of game balls entering the second winning
Number of game balls entering the third winning
Number of game balls that have passed through the through
Number of game balls passing through the discharge passage = Number of balls passing through the discharge passage N OUT
As described above, the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage coincides with the number of game balls shot onto the
さらに、本実施形態では、レジスタ304は、遊技状態毎に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数を記憶する。
・通常モード中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
・高確率モード中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
・高頻度サポートモード中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
・開閉実行モード中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
・通常モード中かつ第1保留個数が上限値である期間中に第1始動口33に入球した遊技球の個数
・通常モード中かつ第2保留個数が上限値である期間中に第2始動口34に入球した遊技球の個数
・前扉枠14が開放中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
・エラー中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the
The number of game balls that entered each entry port during normal mode; The number of game balls that entered each entry port during high probability mode; The number of game balls that entered each entry port during high frequency support mode; The number of game balls that entered each entry port during open/close execution mode; The number of game balls that entered the
例えば、バッファ302の第1始動口33に対応したビットに入球情報がある(ビットがONになっている)と判定し、かつ、通常モード中であるか否かを判定するビットに情報がある(ビットがONになっている)と判定した場合には、第1始動口33に入球した遊技球の入球個数を記憶するカウンタである第1始動口入球個数カウンタの値に1が加算されるとともに、通常モード中に第1始動口33に入球した遊技球の入球個数を記憶するカウンタである通常モード中の第1始動口入球個数カウンタの値に1が加算される。
For example, if it is determined that there is ball entry information in the bit corresponding to the
賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306は、パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを記憶するためのメモリである。本実施形態では、パチンコ機10の電源が投入されると、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データが遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信され、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される。したがって、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される賞球数データの内容は、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データの内容と同一となる。
The prize ball number
演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307は、パチンコ機10に設定されている演算実行条件を記憶するためのメモリである。演算実行条件は、上述したように、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を開始する条件である。本実施形態のパチンコ機10においては、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数が500個に達する毎に遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を開始するように設定されている。パチンコ機10の電源が投入されると、主側ROM63に記憶されている演算実行条件がCPU62xによって遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信され、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶される。したがって、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶される演算実行条件の内容は、主側ROM63に記憶されている演算実行条件の内容と同一となる。なお、演算実行条件として、排出通路以外を通過または入球した遊技球の個数が基準として記憶されていてもよく、また500個以外の個数が基準として記憶されていてもよい。
The calculation execution
CPU308は、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶されている演算実行条件が成立したか否かを判定するとともに、演算実行条件が成立したと判定した場合には、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データと、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数とに基づいて、各種の遊技履歴情報を算出する。本実施形態では、CPU308は、レジスタ304に記憶された排出通路通過個数NOUTの値が500個に達する毎に、遊技履歴情報として下記の値を算出する。
The
・役物比率
=役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数(役物賞球数)/賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数(総賞球数)
=(N2×P2+NS×PS)/(NN1×PN1+NN2×PN2+NN3×PN3+N1×P1+N2×P2+NS×PS)
・連続役物比率
=連続役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数(連続役物賞球数)/賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数(総賞球数)
=(NS×PS)/(NN1×PN1+NN2×PN2+NN3×PN3+N1×P1+N2×P2+NS×PS)
・出玉率(トータル)
=賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数(総賞球数)/遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
=(NN1×PN1+NN2×PN2+NN3×PN3+N1×P1+N2×P2+NS×PS)/NOUT
・Ratio of prize balls to be paid out as prize balls by the operation of the prize balls (number of prize balls) / total number of prize balls paid out as prize balls (total number of prize balls)
= ( N2 x P2 + NS x Ps ) / ( NN1 x PN1 + NN2 x PN2 + NN3 x PN3 + N1 x P1 + N2 x P2 + NS x Ps )
・Continuous feature ratio = Number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of continuous features (number of consecutive feature prize balls) / Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls (total number of prize balls)
= ( NS x Ps ) / ( NN1 x PN1 + NN2 x PN2 + NN3 x PN3 + N1 x P1 + N2 x P2 + NS x Ps )
・Payout rate (total)
=Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls (total number of prize balls)/number of game balls shot onto the
なお、上記の値の算出根拠は以下の通りである。
・役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数(役物賞球数)
=普通電動役物としての電動役物34a及び特別電動役物としての可変入賞装置36が作動することによって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=第2始動口34及び大入賞口36aへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=N2×P2+NS×PS
・連続役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数(連続役物賞球数)
=特別電動役物としての可変入賞装置36が作動することによって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=大入賞口36aへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=NS×PS
・第1~第3入賞口32a~32cへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=NN1×PN1+NN2×PN2+NN3×PN3
・賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数(総賞球数)
=第1~第3入賞口32a~32c、第1始動口33、第2始動口34及び大入賞口36aへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
=NN1×PN1+NN2×PN2+NN3×PN3+N1×P1+N2×P2+NS×PS
The above values are calculated based on the following criteria.
The number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of the device (number of prize balls)
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of the electric device 34a as a normal electric device and the variable winning
The number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of consecutive roles (number of consecutive role prize balls)
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of the variable winning
The number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on the game balls entering the first to third winning
- Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls (total number of prize balls)
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on the game balls entering the first to third winning
さらに、本実施形態では、遊技状態毎にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に基づいて、下記の遊技履歴情報を算出する。 Furthermore, in this embodiment, the following game history information is calculated based on the number of game balls that enter each ball entry port counted for each game state.
・払出比率(通常モード中)
=通常モード中に第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数/通常モード中に第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数+通常モード中に第1~第3入賞口32a~32cへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数
・出玉率(通常モード中)
=通常モード中に賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数/通常モード中に遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
・出玉率(高頻度サポートモード中)
=高頻度サポートモード中に賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数/高頻度サポートモード中に遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
・BY(通常モード中)
=通常モード中に第1~第3入賞口32a~32cへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数+通常モード中かつ第1保留個数が上限値である期間中に第1始動口33への遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数+通常モード中かつ第2保留個数が上限値である期間中に第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数/通常モード中に遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
・BYMIN(通常モード中)
=通常モード中に第1~第3入賞口32a~32cへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数/通常モード中に遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
・前扉枠開放中入球率
=前扉枠14が開放中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数/遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
・エラー中入球率
=エラー中に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数/遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数
なお、上記の遊技履歴情報は一例であり、これら以外の遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。
・Payout ratio (in normal mode)
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on game balls entering the
= Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls during normal mode / Number of game balls shot onto the
= Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls during the high frequency support mode / Number of game balls shot onto the
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on game balls entering the first to third winning
= Number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on game balls entering the first to third winning
CPU308は、上記の各種の遊技履歴情報を算出すると、算出した各種の遊技履歴情報を演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶させるとともに、レジスタ304の各カウンタの値を「0」にリセットする。なお、以下では、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される毎に算出された各種の遊技履歴情報をまとめて「短期遊技履歴情報群」とも呼ぶ。
After the
演算結果記憶用メモリ309は、CPU308によって算出された遊技履歴情報を記憶するメモリであり、本実施形態では、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリによって構成されている。演算結果記憶用メモリ309には、短期遊技履歴情報群が書き込まれた順番に関する情報も記憶されており、CPU308は、算出した短期遊技履歴情報群を書き込むための空きエリアがない場合には、算出した短期遊技履歴情報群を、書き込まれた順番が最も古い短期遊技履歴情報群が記憶されているエリアに記憶させる。すなわち、演算結果記憶用メモリ309は、最も古い短期遊技履歴情報群から順番に上書きされるように構成(ファーストイン・ファーストアウト方式)されており、常に直近の短期遊技履歴情報群が記憶されている状態となる。
The calculation
本実施形態では、演算結果記憶用メモリ309は、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される毎に算出された短期遊技履歴情報群を、1200個分記憶することが可能な容量を有している。例えば、1日に遊技球が連続して10時間発射される場合には、1日に60000個の遊技球が発射されることになるので、1日に120個の短期遊技履歴情報群が演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されることになる。したがって、演算結果記憶用メモリ309は、直近の10日間分の短期遊技履歴情報群を記憶することが可能となる。
In this embodiment, the calculation
検査機320は、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、遊技履歴情報の送信を要求する送信要求コマンドを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、検査用端子65を介して演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶された遊技履歴情報を検査機320に送信する。これにより、検査機320は、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を取得するとともに、取得した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
When the
このように、本実施形態では、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数が500個に達する毎に、すなわち、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される毎に、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報が算出されて演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶される。そして、算出された遊技履歴情報が検査機320の表示部328に表示されることになる。
In this manner, in this embodiment, every time the number of game balls that have passed through the discharge passage reaches 500, i.e., every
A3.遊技機において実行される各種処理の詳細:
次に、MPU62(本実施形態では、CPU62x)にて実行される各処理を説明する。かかるMPU62の処理としては大別して、電源投入に伴い起動されるメイン処理と、定期的に(本実施形態では4msec周期で)起動されるタイマ割込み処理とがある。
A3. Details of various processes executed in the gaming machine:
Next, a description will be given of each process executed by the MPU 62 (
先ず、図12のフローチャートを参照しながらメイン処理を説明する。 First, we will explain the main process with reference to the flowchart in Figure 12.
図12は、主側MPU62にて実行されるメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。ステップS10101では、初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、電源投入に伴う各制御装置の初期設定や、RAM64に記憶保持されたデータの有効性の判定などを実行する。さらに、本実施形態では、初期設定処理において、演算用データを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する処理を実行する。具体的には、主側ROM63に記憶されている演算用データ(賞球数データ及び演算実行条件)を遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。後述するように、当該演算用データを受信した遊技履歴管理チップ300は、賞球数データ及び演算実行条件を賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306及び演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307にそれぞれ記憶し、記憶が完了したことを示す設定完了コマンドを主側MPU62に送信する。ステップS10101を実行した後、ステップS10102に進む。
Figure 12 is a flowchart showing the main processing executed by the
ステップS10102では、設定完了コマンドを受信しているか否かを判定する。ステップS10102において、設定完了コマンドを受信していると判定した場合には(S10102:YES)、ステップS10103に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可するために割込み許可の設定を行う。一方、ステップS10102において、設定完了コマンドを受信していないと判定した場合には(S10102:NO)、再びステップS10102の処理を実行する。すなわち、設定完了コマンドを受信するまでは、ステップS10103に進まず、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可するための割込み許可の設定を行なわない。 In step S10102, it is determined whether or not a setting completion command has been received. If it is determined in step S10102 that a setting completion command has been received (S10102: YES), the process proceeds to step S10103, where interrupt permission is set to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10102 that a setting completion command has not been received (S10102: NO), the process of step S10102 is executed again. In other words, until the setting completion command is received, the process does not proceed to step S10103, and interrupt permission is not set to allow timer interrupt processing to occur.
ステップS10103を実行した後、ステップS10104~ステップS10107の残余処理に進む。つまり、主側MPU62は後述するようにタイマ割込み処理を定期的に実行する構成であるが、1のタイマ割込み処理と次のタイマ割込み処理との間に残余時間が生じることとなる。この残余時間は各タイマ割込み処理の処理完了時間に応じて変動することとなるが、かかる不規則な時間を利用してステップS10104~ステップS10107の残余処理を繰り返し実行する。この点、ステップS10104~ステップS10107の残余処理は、非定期的に実行される非定期処理であると言える。
After executing step S10103, the process proceeds to the remaining processing of steps S10104 to S10107. In other words, the
残余処理では、まずステップS10104では、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止するために割込み禁止の設定を行う。続くステップS10105では、乱数初期値カウンタCINIの更新を行う乱数初期値更新処理を実行するとともに、ステップS10106では、変動種別カウンタCSの更新を行う変動用カウンタ更新処理を実行する。これらの更新処理では、主側RAM64の対応するカウンタから現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報を1加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに上書きする処理を実行する。この場合、カウンタ値が最大値に達した際それぞれ「0」にクリアする。その後、ステップS10107にて、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止している状態から許可する状態へ切り換える割込み許可の設定を行う。ステップS10107の処理を実行した後は、ステップS10104に戻り、ステップS10104~ステップS10107の処理を繰り返す。
In the remaining process, first, in step S10104, interrupt prohibition is set to prohibit the occurrence of timer interrupt processing. In the following step S10105, random number initial value update processing is executed to update the random number initial value counter CINI, and in step S10106, fluctuation counter update processing is executed to update the fluctuation type counter CS. In these update processing, the current numerical information is read from the corresponding counter in the
次に、主側MPU62(本実施形態では、CPU62x)にて実行されるタイマ割込み処理について説明する。
Next, we will explain the timer interrupt processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
図13は、主側MPU62において実行されるタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。当該タイマ割込み処理は、特定の周期(本実施形態では4msec周期)で起動される。
Figure 13 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt process executed by the
タイマ割込み処理では、まずステップS10201にて抽選用乱数更新処理を実行する。抽選用乱数更新処理では、大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3及び電動役物開放カウンタC4の更新を実行する。具体的には、大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3及び電動役物開放カウンタC4から現状の数値情報を順次読み出し、それら読み出した数値情報をそれぞれ1加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに上書きする処理を実行する。この場合、カウンタ値が最大値に達した際それぞれ「0」にクリアする。その後、ステップS10202に進む。 In the timer interrupt process, first, in step S10201, a lottery random number update process is executed. In the lottery random number update process, the jackpot random number counter C1, the jackpot type counter C2, the reach random number counter C3, and the electric role release counter C4 are updated. Specifically, the current numerical information is read out sequentially from the jackpot random number counter C1, the jackpot type counter C2, the reach random number counter C3, and the electric role release counter C4, and the read numerical information is added by 1 to each counter, and then the counter from which it was read is overwritten. In this case, when the counter value reaches its maximum value, it is cleared to "0". Then, proceed to step S10202.
ステップS10202では、乱数初期値更新処理において乱数初期値カウンタCINIの更新を実行するとともに、ステップS10203に進み、変動種別カウンタ更新処理において変動種別カウンタCSの更新を実行する。その後、ステップS10204に進む。 In step S10202, the random number initial value counter CINI is updated in the random number initial value update process, and the process proceeds to step S10203, where the fluctuation type counter CS is updated in the fluctuation type counter update process. Then, the process proceeds to step S10204.
ステップS10204では、ポート出力処理を実行する。ポート出力処理では、前回のタイマ割込み処理において出力情報の設定が行われている場合に、その出力情報に対応した出力を各種駆動部36c,34bに行うための処理を実行する。例えば、大入賞口36aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には可変入賞駆動部36cへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。また、第2始動口34の電動役物34aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には電動役物駆動部34bへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。その後、ステップS10205に進む。
In step S10204, port output processing is executed. In the port output processing, when output information has been set in the previous timer interrupt processing, processing is executed to output corresponding to the output information to the
ステップS10205では、読み込み処理を実行する。読み込み処理では、入球信号以外の信号の読み込みを実行し、その読み込んだ情報を今後の処理にて利用するために記憶する。その後、ステップS10206に進む。 In step S10205, a read process is executed. In the read process, signals other than the ball-entering signal are read, and the read information is stored for use in future processes. Then, the process proceeds to step S10206.
ステップS10206では、各入球検知センサー44a~44hから受信している信号を読み込むとともに、その読み込んだ情報に対応した処理を行うための入球検知処理を実行する。当該入球検知処理の処理内容は、後に詳細に説明する。その後、ステップS10207に進む。
In step S10206, the signals received from each of the
ステップS10207では、入球検知情報を遊技履歴管理チップ300のバッファ302のビットに出力する。具体的には、ステップS10206の入球検知処理において遊技球が入球したと判定した入球口に対応したビットをON(「1」)にするとともに、パチンコ機10の遊技状態に対応したビットをON(「1」)にする。その後、ステップS10208に進む。
In step S10207, the ball entry detection information is output to a bit in the
ステップS10208では、主側RAM64に設けられている所定のタイマカウンタの数値情報をまとめて更新するためのタイマ更新処理を実行する。その後、ステップS10209に進み、賞球コマンドの出力設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS10210に進む。
In step S10208, a timer update process is executed to collectively update the numerical information of a predetermined timer counter provided in the
ステップS10210では、第1始動口33及び第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に伴う始動口用の入球処理を実行する。始動口用の入球処理では、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34に遊技球が入球したと判定されたことに基づいて大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2及びリーチ乱数カウンタC3の値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の保留情報記憶エリア64bに記憶する。ステップS10210を実行した後、ステップS10211に進む。
In step S10210, a ball entry process for the start port is executed in response to the entry of the game ball into the
ステップS10211では、スルーゲート35への遊技球の入球(通過)に伴うスルーゲート用の入球処理を実行する。スルーゲート用の入球処理では、スルーゲート35に遊技球が入球(通過)したと判定されたことに基づいて変動種別カウンタCSの値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の電役保留エリア64dに記憶する。ステップS10211を実行した後、ステップS10212に進む。
In step S10211, a ball entry process for the through gate is executed in response to the entry (passage) of a game ball into the through
ステップS10212では、各遊技回における遊技を制御するための遊技回制御処理を実行する。遊技回制御処理では、大当たり抽選や、第1図柄表示部37a,第2図柄表示部37bの表示制御などを行う。ステップS10212を実行した後、ステップS10213に進む。
In step S10212, a game round control process is executed to control the game in each game round. In the game round control process, a jackpot lottery is performed, and display control of the first and second
ステップS10213では、遊技状態を移行させるための遊技状態移行処理を実行する。遊技状態移行処理では、遊技状態を開閉実行モード、高確率モード、高頻度サポートモードなどへ移行させる処理を実行する。ステップS10213を実行した後、ステップS10214に進む。 In step S10213, a game state transition process is executed to transition the game state. In the game state transition process, a process is executed to transition the game state to an open/close execution mode, a high probability mode, a high frequency support mode, or the like. After executing step S10213, the process proceeds to step S10214.
ステップS10214では、電動役物34aを制御するための電役サポート用処理を実行する。電役サポート用処理では、電動役物34aを開放状態とするか否かの判定(電動役物開放抽選)を行なうとともに、開放状態とすると判定した場合には電動役物34aを駆動制御する。ステップS10214を実行した後、ステップS10215に進む。 In step S10214, an electric role support process is executed to control the electric role 34a. In the electric role support process, a determination is made as to whether or not the electric role 34a is to be opened (electric role opening lottery), and if it is determined that the electric role 34a is to be opened, the electric role 34a is driven and controlled. After executing step S10214, the process proceeds to step S10215.
ステップS10215では、遊技球発射制御処理を実行する。遊技球発射制御処理では、遊技者によって操作ハンドル25が操作された際に遊技球を遊技領域PAに発射するための処理を実行する。ステップS10215を実行した後、ステップS10216に進む。
In step S10215, a game ball launch control process is executed. In the game ball launch control process, a process is executed to launch a game ball into the game area PA when the player operates the
ステップS10216では、今回のタイマ割込み処理にて実行された各種処理の処理結果に応じた外部信号の出力の開始及び終了を制御するように外部情報設定処理を実行する。ステップS10216を実行した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。 In step S10216, an external information setting process is executed to control the start and end of the output of an external signal according to the results of the various processes executed in this timer interrupt process. After executing step S10216, this timer interrupt process is terminated.
次に、タイマ割込み処理(図13)のステップS10206にて実行される入球検知処理について説明する。 Next, we will explain the ball entry detection process executed in step S10206 of the timer interrupt process (Figure 13).
入球検知処理では、入球検知センサー44a~44hにおける検知結果を確認する処理を実行するが、当該確認に際しては主側MPU62の入出力ポート62aのうちの入力ポート62bが確認される。ここで、入球検知処理の説明に先立ち、図14を参照しながら、主側MPU62に設けられた入力ポート62bの構成について説明する。
The ball entry detection process involves a process to check the detection results of the ball
図14は、主側MPU62に設けられた入力ポート62bの構成について説明する説明図である。入力ポート62bは、8種類の信号を同時に扱うことができるように8ビットのパラレルインターフェースとして構成されている。そして、各信号の電圧に応じて「0」又は「1」の情報が格納されるエリアが、各端子に1対1で対応させて設けられている。つまり、当該エリアとして、第0ビットD0~第7ビットD7を備えている。
Figure 14 is an explanatory diagram explaining the configuration of the
また、入力ポート62bには8種類を超える信号が入力されることとなるが、同時に入力される対象を8種類に制限するために、入力ポート62bへの入力対象となる信号群はドライバICによる切換制御を通じて切り換えられる。入球検知処理では、入力ポート62bへの入力対象となる信号群が各入球検知センサー44a~44hに設定される。
In addition, more than eight types of signals are input to input
かかる設定がなされた状況では、第0ビットD0は大入賞口検知センサー44aからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第1ビットD1は第1始動口検知センサー44bからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第2ビットD2は第2始動口検知センサー44cからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第3ビットD3は第1入賞口検知センサー44dからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第4ビットD4は第2入賞口検知センサー44eからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第5ビットD5は第3入賞口検知センサー44fからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第6ビットD6はスルーゲート検知センサー44gからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納され、第7ビットD7は排出通路検知センサー44hからの入球信号に対応した情報が格納される。
In a situation where such a setting has been made, the 0th bit D0 stores information corresponding to the ball entry signal from the large prize entry opening
この場合に、上記各入球検知センサー44a~44hは、遊技球の通過を検知していない場合には入球信号として非検知中であることを示すHIレベル信号を出力し、遊技球の通過を検知している場合には入球信号として検知中であることを示すLOWレベル信号を出力する。但し、主制御基板151には反転回路が設けられており、入力ポート62bに上記各検知信号が入力される前に信号の状態が反転される。そして、入力ポート62bでは当該反転回路を通じてLOWレベル信号を受信している場合に該当するビットに「0」の情報(データ0又は無し情報)を格納し、反転回路を通じてHIレベル信号を受信している場合に該当するビットに「1」の情報(データ1又は有り情報)を格納する。
In this case, when the ball
つまり、入球検知センサー44a~44hにおいて遊技球の通過が検知されていない状況では該当するビットに非検知中を示す情報に対応した「0」の情報が格納され、遊技球の通過が検知されている状況では該当するビットに検知中を示す情報に対応した「1」の情報が格納される。
In other words, when the ball
なお、各入球検知センサー44a~44hは、遊技球の通過を検知していない間は入球信号としてLOWレベル信号を出力するとともに遊技球の通過を検知している間は入球信号としてHIレベル信号を出力する構成としてもよい。この場合、上記反転回路を不具備とすればよい。
Each ball
図15は、主側MPU62にて実行される入球検知処理を説明する説明図である。図15(a)は、主側MPU62にて実行される入球検知処理を示すフローチャートである。図15(b)は、入球検知処理において利用される入球判定エリアを模式的に示す説明図である。入球検知処理では、図15(a)のフローチャートに示すように、まずステップS10301にて、上記第0~第7ビットD0~D7に現状格納されている情報を、主側MPU62のレジスタにおける第1入球判定エリアWA1に移行させる処理を実行する。当該第1入球判定エリアWA1は、図15(b-1)に示すように8ビットから構成されており、上記第0~第7ビットD0~D7に格納されている情報の全てを格納することが可能なデータ容量となっている。この場合、第0~第7ビットD0~D7における格納元のビットと、第1入球判定エリアWA1における格納先のビットとは1対1で対応させて予め定められており、例えば第0ビットD0の情報は常に第1入球判定エリアWA1における所定のビットに格納される。
Figure 15 is an explanatory diagram explaining the ball entry detection process executed by the
続くステップS10302では、入球検知用のウェイト処理を実行する。当該ウェイト処理では、予め定められたウェイト時間が経過するまで主側MPU62において何ら処理を実行することなく待機する。本パチンコ機10では、当該ウェイト時間として10μsecが設定されているが、定期的なタイマ割込み処理の実行を阻害することなく、さらに当該ウェイト処理に設定したことによる後述する作用効果を十分に奏することができるのであれば、具体的なウェイト時間は任意であるが、2μsec~500μsecの範囲であることが好ましく、より好ましくは10μsec~100μsecの範囲である。
In the next step S10302, a wait process for ball entry detection is executed. In this wait process, the
ちなみに、一のステップの処理を実行するには少なくとも1.2μsecを要する。したがって、ステップS10302の処理が設定されていなくても、ステップS10301とステップS10303との間には1.2μsecの強制的なウェイト時間が発生することとなる。この点、ステップS10302では、処理を実行する上で最低限要する時間だけでなく、それに対して追加のウェイト時間をステップS10301の処理とステップS10303の処理との間に設定していることとなる。 By the way, it takes at least 1.2 μsec to execute the processing of one step. Therefore, even if the processing of step S10302 is not set, a compulsory wait time of 1.2 μsec occurs between steps S10301 and S10303. In this regard, in step S10302, not only is the minimum time required to execute the processing set, but an additional wait time is set between the processing of steps S10301 and S10303.
続くステップS10303では、上記第0~第7ビットD0~D7に現状格納されている情報を、主側MPU62のレジスタにおける第2入球判定エリアWA2に移行させる処理を実行する。ちなみに、入力ポート62bにおける情報の更新はステップS10301が完了してからステップS10303が開始されるまでの時間よりも短い間隔で行われているため、ステップS10303にて第0~第7ビットD0~D7から移行される情報は、ステップS10301の場合と異なるものとなり得る。
In the following step S10303, a process is executed to transfer the information currently stored in the 0th to 7th bits D0 to D7 to the second ball entry determination area WA2 in the register of the
第2入球判定エリアWA2は、第1入球判定エリアWA1と同様に、図15(b-2)に示すように8ビットから構成されており、上記第0~第7ビットD0~D7に格納されている情報の全てを格納することが可能なデータ容量となっている。この場合、第0~第7ビットD0~D7における格納元のビットと、第2入球判定エリアWA2における格納先のビットとは1対1で対応させて予め定められており、さらに格納元のビットと格納先のビットとの関係は、第1入球判定エリアWA1の場合と同一となっている。 The second entry judgment area WA2, like the first entry judgment area WA1, is composed of 8 bits as shown in FIG. 15(b-2), and has a data capacity that can store all of the information stored in the 0th to 7th bits D0 to D7. In this case, the storage source bits in the 0th to 7th bits D0 to D7 and the storage destination bits in the second entry judgment area WA2 are predetermined in a one-to-one correspondence, and the relationship between the storage source bits and the storage destination bits is the same as in the case of the first entry judgment area WA1.
その後、ステップS10304にて、入球判定処理を実行した後に、本入球検知処理を終了する。当該入球判定処理について、図16のフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Then, in step S10304, the goal determination process is executed, and the goal detection process ends. The goal determination process is explained with reference to the flowchart in FIG. 16.
図16は、主側MPU62にて実行される入球判定処理を示すフローチャートである。入球判定処理では、先ずステップS10401にて、主側RAM64に設けられた入球判定カウンタに8をセットする。なお、入球判定カウンタの数値情報は、8個の各入球口のビットに対応している。具体的には、本実施形態では、入球判定カウンタの数値情報の「8」は大入賞口36aの第0ビットD0、「7」は第1始動口33の第1ビットD1、「6」は第2始動口34の第2ビットD2、「5」は第1入賞口32aの第3ビットD3、「4」は第2入賞口32bの第4ビットD4、「3」は第3入賞口32cの第5ビットD5、「2」はスルーゲート35の第6ビットD6、「1」は排出通路の第7ビットD7に、それぞれ対応している。続くステップS10402では、第1入球判定エリアWA1及び第2入球判定エリアWA2における現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報に対応したビットの各情報を把握する。この場合に把握される各情報は、入力ポート62bにおける同一のビットから読み出された情報である。
Figure 16 is a flowchart showing the ball entry determination process executed by the
続くステップS10403では、ステップS10402にて把握した各情報のAND処理を実行し、そのAND処理結果をレジスタに記憶するとともに、ステップS10404にて、第1演算後エリアWA3及び第2演算後エリアWA4のうち、前回のタイマ割込み処理の処理回における入球検知処理にてAND処理の結果の情報が格納された側とは異なる側の対応するビットに上記AND処理結果を格納する。第1演算後エリアWA3及び第2演算後エリアWA4は、図15(b-3)及び図15(b-4)に示すように8ビットから構成されており、第1入球判定エリアWA1の各ビットと第2入球判定エリアWA2の各ビットとのAND処理結果の各情報を全て格納することが可能なデータ容量となっている。この場合、AND処理の対象となった第1入球判定エリアWA1及び第2入球判定エリアWA2のビットの順番と、第1演算後エリアWA3及び第2演算後エリアWA4における各ビットの順番とは一義的に定められている。 In the next step S10403, the AND process is performed on each piece of information grasped in step S10402, and the AND process result is stored in a register. In step S10404, the AND process result is stored in the corresponding bit of the first post-operation area WA3 and the second post-operation area WA4 on the side different from the side where the information of the AND process result was stored in the ball entry detection process in the previous timer interrupt process. The first post-operation area WA3 and the second post-operation area WA4 are composed of 8 bits as shown in Figures 15 (b-3) and 15 (b-4), and have a data capacity that can store all the information of the AND process result between each bit of the first entry ball determination area WA1 and each bit of the second entry ball determination area WA2. In this case, the order of the bits of the first entry ball determination area WA1 and the second entry ball determination area WA2 that were the subject of the AND process and the order of each bit in the first post-operation area WA3 and the second post-operation area WA4 are uniquely determined.
その後、ステップS10405にて、第1演算後エリアWA3及び第2演算後エリアWA4のうち、前回のタイマ割込み処理の処理回における入球判定処理にてAND処理の結果の情報が格納された側であって、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報に対応したビットの情報を読み出す。そして、ステップS10406にて、その読み出した情報を「0」と「1」との間で反転させるための反転処理を実行する。 Then, in step S10405, the information of the bit corresponding to the current numerical information of the goal determination counter is read from either the first post-calculation area WA3 or the second post-calculation area WA4, which is the side in which the information of the result of the AND process in the goal determination process in the previous timer interrupt process was stored. Then, in step S10406, an inversion process is performed to invert the read information between "0" and "1".
その後、ステップS10407にて、ステップS10403におけるAND処理結果の情報と、ステップS10406における反転処理結果の情報とのAND処理を実行し、続くステップS10408にて、そのAND処理の結果が入球検知開始情報に対応した「1」であるか否かを判定する。ステップS10408にてAND処理結果が「1」であると判定した場合には、ステップS10409以降の処理に進む。 Then, in step S10407, an AND process is performed between the information resulting from the AND process in step S10403 and the information resulting from the inversion process in step S10406, and in the following step S10408, it is determined whether the result of the AND process is "1", which corresponds to the ball entry detection start information. If it is determined in step S10408 that the result of the AND process is "1", the process proceeds to step S10409 and subsequent steps.
ステップS10409では、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報が第1始動口33及び第2始動口34のいずれかに対応したビットを示す情報であるか否かを判定する。第1始動口33及び第2始動口34のいずれかに対応している場合には、ステップS10410にて、主側RAM64に設けられた始動口入球フラグに「1」をセットし、ステップS10411にて、主側RAM64に設けられた3個賞球カウンタの数値情報を1加算する。
In step S10409, it is determined whether the numerical information of the current ball entry determination counter is information indicating a bit corresponding to either the
始動口入球フラグは、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34への遊技球の入球を主側MPU62にて特定するとともに、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に対応した処理であって賞球の実行以外の処理を実行すべき状態であることを主側MPU62にて特定するためのフラグである。ちなみに、第1始動口33と第2始動口34とのそれぞれに入球検知センサー44b,44cが設けられているため、第1始動口33への入球と第2始動口34への入球とがタイマ割込み処理の1処理回の範囲内で同時に把握されることがある。したがって、これに対応すべく、始動入球フラグは、始動口33,34の数に対応させて設けられており、具体的には2個設けられている。また、3個賞球カウンタは、3個の賞球の実行を指示する3個賞球コマンドを出力すべき回数を主側MPU62において特定するためのカウンタである。
The start hole entry flag is a flag for the
ステップS10409にて否定判定をした場合には、ステップS10412にて、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報が大入賞口36a(可変入賞装置36)に対応したビットを示す情報であるか否かを判定する。可変入賞装置36に対応している場合には、ステップS10413にて、主側RAM64に設けられた大入賞口入球フラグに「1」をセットし、ステップS10414にて、主側RAM64に設けられた15個賞球カウンタの数値情報を1加算する。
If a negative judgment is made in step S10409, in step S10412, it is judged whether the numerical information of the current ball entry judgment counter is information indicating a bit corresponding to the
大入賞口入球フラグは、可変入賞装置36への遊技球の入球を主側MPU62にて特定するとともに、可変入賞装置36への遊技球の入球に対応した処理であって賞球の実行以外の処理を実行すべき状態であることを主側MPU62にて特定するためのフラグである。また、15個賞球カウンタは、15個の賞球の実行を指示する15個賞球コマンドを出力すべき回数を主側MPU62にて特定するためのカウンタである。
The large prize entry ball flag is a flag that allows the
ステップS10412にて否定判定をした場合には、ステップS10415にて、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報がスルーゲート35に対応したビットを示す情報であるか否かを判定する。スルーゲート35に対応している場合には、ステップS10416にて、主側RAM64に設けられたスルー通過フラグに「1」をセットする。
If a negative judgment is made in step S10412, in step S10415, it is judged whether the numerical information of the current ball entry judgment counter is information indicating a bit corresponding to the through
スルー通過フラグは、遊技球がスルーゲート35を通過したことを主側MPU62にて特定するとともに、スルーゲート35への遊技球の入球に対応した処理を実行すべき状態であることを主側MPU62にて特定するためのフラグである。
The through pass flag is a flag that allows the
ステップS10415にて否定判定をした場合には、ステップS10417にて、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報が第1入賞口32a、第2入賞口32b及び第3入賞口32cのいずれかに対応したビットを示す情報であるか否かを判定する。第1入賞口32a、第2入賞口32b及び第3入賞口32cのいずれかに対応している場合には、ステップS10418にて、主側RAM64に設けられた一般入賞口入球フラグに「1」をセットし、ステップS10419にて、主側RAM64に設けられた3個賞球カウンタの数値情報を1加算する。
If a negative judgment is made in step S10415, in step S10417, it is judged whether the numerical information of the current winning ball judgment counter is information indicating a bit corresponding to any one of the first winning
一般入賞口入球フラグは、第1入賞口32a、第2入賞口32b又は第3入賞口32cへの遊技球の入球を主側MPU62にて特定するためのフラグである。ちなみに、第1入賞口32a、第2入賞口32b及び第3入賞口32cのそれぞれに入球検知センサー44d,44e,44fが設けられているため、第1入賞口32aへの入球と第2入賞口32bへの入球と第3入賞口への入球とがタイマ割込み処理の1処理回の範囲内で同時に把握されることがある。したがって、これに対応すべく、一般入賞口入球フラグは、一般入賞口32a,32b,32cの数に対応させて設けられており、具体的には3個設けられている。また、10個賞球カウンタは、10個の賞球の実行を指示する3個賞球コマンドを出力すべき回数を主側MPU62において特定するためのカウンタである。
The general winning hole ball entry flag is a flag for the
ステップS10417にて否定判定をした場合には、今回の入球が排出通路に対応していることを意味するため、ステップSAD20にて、主側RAM64に設けられた排出通路通過フラグに「1」をセットする。排出通路通過フラグは、遊技球が排出通路を通過したことを主側MPU62にて特定するためのフラグである。
If a negative judgment is made in step S10417, this means that the ball entry this time corresponds to the discharge passage, so in step SAD20, the discharge passage passing flag provided in the
ステップS10408にて否定判定をした場合、又はステップS10411、ステップS10414、ステップS10416、ステップS10419、ステップS10420のいずれかの処理を実行した後は、ステップS10421に進む。ステップS10421では、入球判定カウンタを1減算し、その後、ステップS10422にて入球判定カウンタが「0」であるか否かを判定する。 If a negative determination is made in step S10408, or after any of steps S10411, S10414, S10416, S10419, and S10420 has been executed, the process proceeds to step S10421. In step S10421, the goal determination counter is decremented by 1, and then in step S10422, it is determined whether the goal determination counter is "0".
入球判定カウンタが「0」でない場合には、ステップS10421にて更新した入球判定カウンタの数値情報に応じたビットについて、ステップS10402~ステップS10420の処理を実行する。かかるステップS10402~ステップS10420の処理を、ステップS10401にてセットした数値情報分実行した場合には、ステップS10422にて肯定判定をすることとなり、本入球判定処理を終了する。 If the goal counter is not "0", steps S10402 to S10420 are executed for the bit corresponding to the numerical information of the goal counter updated in step S10421. If steps S10402 to S10420 have been executed for the number of pieces of numerical information set in step S10401, a positive judgment is made in step S10422, and this goal determination process ends.
次に、上記入球検知処理(図15)が実行されることにより、一般入賞口32、可変入賞装置36、第1始動口33、第2始動口34、スルーゲート35、及び排出通路への入球の有無が検知される様子について図17を参照しながら説明する。
Next, with reference to Figure 17, we will explain how the ball entry detection process (Figure 15) is executed to detect whether or not a ball has entered the
図17は、入球の有無が検知される様子を説明する説明図である。まず、図17(A)を参照しながら、入球検知センサー44a~44hにおける検知結果(以下、入球情報ともいう)を監視するタイミングを説明する。図17(A)は各入球情報を監視するタイミングを説明するためのタイミングチャートである。
Figure 17 is an explanatory diagram that explains how the presence or absence of a goal is detected. First, with reference to Figure 17 (A), the timing for monitoring the detection results (hereinafter also referred to as goal information) of
図17(A)に示すように、T1(具体的には4msec)周期でタイマ割込み処理(図13)が起動される構成において、入球情報を監視する処理はタイマ割込み処理の各処理回で2回(ステップS10301,ステップS10303)行われる。各1組の入球情報を監視する処理はタイミングが前後するように実行されるが、先側の入球情報を監視する処理(ステップS10301)はタイマ割込み処理が起動されたタイミングに対してT2の時間が経過したタイミングで実行される。 As shown in Figure 17 (A), in a configuration in which the timer interrupt process (Figure 13) is started at a cycle of T1 (specifically, 4 msec), the process of monitoring the scoring information is carried out twice (steps S10301 and S10303) during each processing of the timer interrupt process. The process of monitoring each set of scoring information is carried out at different times, but the process of monitoring the scoring information on the front side (step S10301) is carried out when a time period of T2 has elapsed from the timing at which the timer interrupt process was started.
この場合に、タイマ割込み処理において入球検知処理が実行されるタイミングは遊技回制御処理及び電役サポート用処理といった処理時間が変動し易い処理よりも先に実行され、さらにタイマ割込み処理において入球検知処理よりも先に実行される処理は処理時間が比較的変動しにくい処理となっている。したがって、各処理回のタイマ割込み処理において先側の入球情報を監視する処理が開始されるまでの期間はT2で同一、略同一又は同様となる。よって、タイマ割込み処理の各処理回に含まれる1組の入球情報を監視する処理のうち、先側の入球情報を監視する処理は定期的に実行されることとなる。 In this case, the timing at which the ball entry detection process is executed in the timer interrupt process is before processes whose processing times are likely to fluctuate, such as the game round control process and the electric support process, and furthermore, the processes executed in the timer interrupt process before the ball entry detection process are processes whose processing times are relatively less likely to fluctuate. Therefore, the period until the process of monitoring the ball entry information on the leading side is started in the timer interrupt process for each processing round is the same, approximately the same, or similar at T2. Therefore, of the processes that monitor a set of ball entry information included in each processing round of the timer interrupt process, the process of monitoring the ball entry information on the leading side is executed periodically.
また、各1組の入球情報を監視する処理のうち、先側の入球情報を監視する処理(ステップS10301)と後側の入球情報を監視する処理(ステップS10303)との間では、入球検知用のウェイト処理(ステップS10302)が実行されるが、かかるウェイト処理では何ら処理を実行することなく一定のウェイト時間T3が経過するまで待機するだけである。したがって、タイマ割込み処理の各処理回に含まれる1組の入球情報を監視する処理のうち、後側の入球情報を監視する処理は定期的に実行されることとなる。 In addition, among the processes for monitoring each set of scoring information, a wait process for detecting scoring (step S10302) is executed between the process for monitoring the scoring information on the front side (step S10301) and the process for monitoring the scoring information on the back side (step S10303). However, this wait process does not execute any processing and simply waits until a certain wait time T3 has elapsed. Therefore, among the processes for monitoring a set of scoring information included in each processing round of the timer interrupt process, the process for monitoring the scoring information on the back side is executed periodically.
次に、図17(B)を参照しながら、入球判定が行われる場合に実行される演算の内容を説明する。図17(B)は入球判定が行われる場合に実行される演算の内容を説明するための説明図である。なお、実際には1ビット単位で各種演算が行われるが、以下の説明では1バイト単位で演算の内容を説明する。但し、以下に説明するような1バイト単位での演算が実際に行われる構成としてもよい。 Next, with reference to FIG. 17(B), the content of the calculation performed when a goal determination is made will be described. FIG. 17(B) is an explanatory diagram for explaining the content of the calculation performed when a goal determination is made. Note that, in practice, various calculations are performed in units of one bit, but in the following explanation, the content of the calculation is explained in units of one byte. However, a configuration in which calculations are actually performed in units of one byte as described below may also be used.
図17(B)の場合では、先ずn回目のタイマ割込み処理における先側の入球情報を監視する処理にて、図17(B1)に示すように、第1入球判定エリアWA1に「00100000」がセットされている。この場合、各入球検知センサー44a~44hのうち第3入賞口検知センサー44fの入球情報が遊技球を検知している旨の情報(以下、入球有り情報ともいう)となっており、他のセンサーの入球情報は遊技球を検知していない旨の情報(以下、入球無し情報ともいう)となっている。
In the case of FIG. 17(B), first, in the process of monitoring the ball entry information from the first side in the nth timer interrupt process, as shown in FIG. 17(B1), "00100000" is set in the first ball entry determination area WA1. In this case, the ball entry information from the third winning
また、当該n回目のタイマ割込み処理における後側の入球情報を監視する処理では、図17(B2)に示すように、第2入球判定エリアWA2に「10100000」がセットされている。この場合、各入球検知センサー44a~44hのうち排出通路検知センサー44h及び第3入賞口検知センサー44fのそれぞれが入球有り情報となっており、他のセンサーは入球無し情報となっている。
In addition, in the process of monitoring the subsequent ball entry information in the nth timer interrupt process, as shown in FIG. 17 (B2), "10100000" is set in the second ball entry determination area WA2. In this case, among the ball
上記のように第1入球判定エリアWA1及び第2入球判定エリアWA2の情報のセットが行われた場合、そのAND処理結果は、図17(B3)に示すように「00100000」となり、当該情報がn回目の処理回のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果として第1演算後エリアWA3にセットされる。なお、n-1回目のタイマ割込み処理にて入球情報の監視結果が第1演算後エリアWA3にセットされている場合にはn回目のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果は第2演算後エリアWA4にセットされる。また、n-1回目における入球情報の監視結果とn回目における入球情報の監視結果とを利用して入球判定処理が実行されるが、この処理の演算の内容はここでは省略する。 When the information of the first scoring judgment area WA1 and the second scoring judgment area WA2 is set as described above, the result of the AND process becomes "00100000" as shown in FIG. 17 (B3), and this information is set in the first post-calculation area WA3 as the result of monitoring the scoring information in the timer interrupt process of the nth processing round. Note that if the result of monitoring the scoring information in the n-1th timer interrupt process is set in the first post-calculation area WA3, the result of monitoring the scoring information in the nth timer interrupt process is set in the second post-calculation area WA4. Also, the scoring judgment process is executed using the result of monitoring the scoring information in the n-1th time and the result of monitoring the scoring information in the nth time, but the details of the calculations in this process are omitted here.
次にn+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における先側の入球情報を監視する処理にて、図17(B4)に示すように、第1入球判定エリアWA1に「10100110」がセットされている。この場合、各入球検知センサー44a~44hのうち排出通路検知センサー44h、第3入賞口検知センサー44f、第2始動口検知センサー44c及び第1始動口検知センサー44bのそれぞれが入球有り情報となっており他のセンサーは入球無し情報となっている。
Next, in the process of monitoring the ball entry information from the front side in the n+1th timer interrupt process, as shown in FIG. 17 (B4), "10100110" is set in the first ball entry judgment area WA1. In this case, among the ball
また、当該n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における後側の入球情報を監視する処理にて、図17(B5)に示すように、第2入球判定エリアWA2に「10100010」がセットされている。この場合、各入球検知センサー44a~44hのうち排出通路検知センサー44h、第3入賞口検知センサー44f及び第1始動口検知センサー44bのそれぞれが入球有り情報となっており、他のセンサーは入球無し情報となっている。
In addition, in the process of monitoring the subsequent ball entry information in the n+1th timer interrupt process, as shown in FIG. 17 (B5), "10100010" is set in the second ball entry determination area WA2. In this case, among the ball
上記のように第1入球判定エリアWA1及び第2入球判定エリアWA2の情報のセットが行われた場合、そのAND処理結果は、図17(B6)に示すように「10100010」となり、当該情報がn+1回目の処理回のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果として第2演算後エリアWA4にセットされる。 When the information in the first scoring judgment area WA1 and the second scoring judgment area WA2 is set as described above, the result of the AND process becomes "10100010" as shown in FIG. 17 (B6), and this information is set in the second post-calculation area WA4 as the result of monitoring the scoring information in the timer interrupt process of the n+1th processing round.
その後、当該n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における入球判定処理(図16)にて、先ずn回目のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果が第1演算後エリアWA3から読み出されるとともにその読み出された監視結果の情報に対して反転処理が実行される。そうすると、図17(B7)に示すように、「11011111」となる。そして、当該反転処理の結果の情報に、n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果をAND処理する。これにより、図17(B8)に示すように、「10000010」となる。この場合、当該入球判定処理では、排出通路検知センサー44hにて遊技球の入球が検知されたと判定するとともに、第1始動口検知センサー44bにて遊技球の入球が検知されたと判定する。
After that, in the ball entry determination process (FIG. 16) in the n+1th timer interrupt process, the result of the monitoring of the ball entry information in the nth timer interrupt process is first read from the first post-calculation area WA3, and an inversion process is performed on the information of the monitoring result that was read. This results in "11011111" as shown in FIG. 17 (B7). Then, the result of the inversion process is ANDed with the result of the monitoring of the ball entry information in the n+1th timer interrupt process. This results in "10000010" as shown in FIG. 17 (B8). In this case, the ball entry determination process determines that the discharge
また、図17(B4)に示すように、n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における先側の入球情報を監視する処理にて第2始動口検知センサー44cが入球有り情報となっているが、これは電気的なノイズにより発生したものである。この場合に、入球無し情報から入球有り情報への切り換えを確認したとしても即座に入球発生と特定するのではなく、入球有り情報が複数回に亘って確認された場合に入球発生と特定する構成である。したがって、図17(B5)に示すように、n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における後側の入球情報を監視する処理では第2始動口検知センサー44cが入球無し情報となっており、電気的なノイズの発生を遊技球の入球と取り扱わないようになっている。
Also, as shown in FIG. 17 (B4), in the process of monitoring the ball-entering information on the front side in the n+1th timer interrupt process, the second start
また、第3入賞口検知センサー44fではn回目のタイマ割込み処理における1組の入球情報を監視する処理及びn+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における1組の入球情報を監視する処理のそれぞれにて入球有り情報となっているが、これは既に入球の発生が把握された遊技球を継続して検知している状態を示している。この場合に、n回目のタイマ割込み処理における入球情報の監視結果が「0」であることを条件に入球の発生を特定しているため、1個の遊技球の入球を複数個の入球として扱ってしまわない。
In addition, the third winning
上記のように入球検知処理が実行されることにより、各入球検知センサー44a~44hにおける検知結果の監視が実行されることともに、遊技球の付与に対応した入球が発生している場合には、その入球箇所に応じて、3個賞球カウンタ、10個賞球カウンタ及び15個賞球カウンタへの加算処理が実行される。これらカウンタのいずれかが「1」以上となっている場合には、タイマ割込み処理(図13)における賞球コマンドの出力設定処理(ステップS10209)にて賞球コマンドの設定が行われ、その設定された賞球コマンドが払出制御装置70に送信される。この場合、賞球コマンドの出力設定はタイマ割込み処理の1処理回において1回のみ行われる。したがって、例えば15個賞球カウンタが「2」以上となっていたとしても、1処理回では15個賞球コマンドが1回のみ送信される。但し、これに限定されることはなく、1処理回において所定の複数(例えば2個又は3個)の賞球コマンドが送信される構成としてもよい。
By executing the ball entry detection process as described above, the detection results of each ball
また、3個賞球カウンタ、10個賞球カウンタ及び15個賞球カウンタのそれぞれが「1」以上となっている場合も考えられるが、この場合、賞球個数の多い賞球コマンドの出力が優先される。つまり、15個賞球コマンドの出力が10個賞球コマンドの出力や3個賞球コマンドの出力よりも優先され、10個賞球コマンドの出力が3個賞球コマンドの出力よりも優先される。 It is also possible that the 3 prize ball counter, 10 prize ball counter, and 15 prize ball counter are all equal to or greater than "1." In this case, the output of the prize ball command with the greater number of prize balls is prioritized. In other words, the output of the 15 prize ball command is prioritized over the output of the 10 prize ball command and the output of the 3 prize ball command, and the output of the 10 prize ball command is prioritized over the output of the 3 prize ball command.
15個賞球カウンタが「1」以上の場合に15個賞球コマンドが出力対象として設定された場合に、当該15個賞球カウンタは1減算される。また、10個賞球カウンタが「1」以上の場合に10個賞球コマンドが出力対象として設定された場合に、当該10個賞球カウンタは1減算される。また、3個賞球カウンタが「1」以上の場合に3個賞球コマンドが出力対象として設定された場合に、当該3個賞球カウンタは1減算される。 When the 15 prize ball counter is "1" or greater and a 15 prize ball command is set as the output target, the 15 prize ball counter is decremented by 1. Also, when the 10 prize ball counter is "1" or greater and a 10 prize ball command is set as the output target, the 10 prize ball counter is decremented by 1. Also, when the 3 prize ball counter is "1" or greater and a 3 prize ball command is set as the output target, the 3 prize ball counter is decremented by 1.
次に、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308が実行する処理について説明する。本実施形態では、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、パチンコ機10の電源投入に伴い下記のメイン処理を実行する。
Next, we will explain the processing executed by the
図18は、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 18 is a flowchart showing the main processing executed by the
ステップS10501では、賞球数データ及び演算実行条件を含む演算用データを受信しているか否かを判定する。ステップS10501において、演算用データを受信していると判定した場合には(S10501:YES)、ステップS10502に進む。一方、ステップS10501において、演算用データを受信していないと判定した場合には(S10501:NO)、再びこのステップS10501の処理を実行する。すなわち、演算用データを受信するまでは、次のステップS10502の処理に進まずに無限ループを継続する。 In step S10501, it is determined whether or not calculation data including prize ball count data and calculation execution conditions has been received. If it is determined in step S10501 that calculation data has been received (S10501: YES), the process proceeds to step S10502. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10501 that calculation data has not been received (S10501: NO), the process of step S10501 is executed again. In other words, until calculation data is received, the process continues in an infinite loop without proceeding to the next step S10502.
ステップS10502では、受信した賞球数データを賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶させる。その後、ステップS10503に進み、受信した演算実行条件を演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶させる。その後、ステップS10504に進む。
In step S10502, the received prize ball count data is stored in prize ball count
ステップS10504では、賞球数データの賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306への記憶が完了し、かつ、演算実行条件の演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307への記憶が完了したことを意味する設定完了コマンドを主側CPU62xに送信する。その後、ステップS10505に進む。
In step S10504, a setting completion command is sent to the
ステップS10505では、バッファ302のビットに主側CPU62xから受信した入球情報がある(ビットに「1」が格納されている)か否かを判定する。ステップS10505において、バッファ302のビットに主側CPU62xから受信した入球情報があると判定した場合には(S10505:YES)、ステップS10506に進み、バッファ302のビットに対応したレジスタのカウンタに1を加算する。具体的には、例えば、バッファ302の第1始動口入球情報に対応したビットが「1」であり、通常モード中に対応したビットが「1」である場合には、レジスタ304の大入賞口入球個数NSに対応したカウンタに1を加算するとともに、通常モード中の大入賞口入球個数に対応したカウンタに1を加算する。その後、ステップS10507に進む。一方、ステップS10505において、バッファ302のビットに主側CPU62xから受信した入球情報がないと判定した場合には(S10505:NO)、ステップS10506を実行することなく、ステップS10507に進む。
In step S10505, it is determined whether or not the bit of the
ステップS10507では、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶された演算実行条件が成立したか否かを判定する。本実施形態では、レジスタ304に記憶された排出通路通過個数NOUTの値が500であるか否か、すなわち、遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数が500個に達したか否かを判定する。ステップS10507において、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶された演算実行条件が成立したと判定した場合には(S10507:YES)、ステップS10508に進む。
In step S10507, it is determined whether or not the calculation execution condition stored in the calculation execution
ステップS10508では、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データと、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数とに基づいて、各種の遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算処理を実行する。その後、ステップS10509に進み、算出した各種の遊技履歴情報を演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶させる。その後、ステップS10510に進み、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を0にクリアする。その後、ステップS10511に進む。
In step S10508, calculation processing is performed to calculate various game history information based on the prize ball number data stored in prize ball number
一方、ステップS10507において、演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶された演算実行条件が成立していないと判定した場合には(S10507:NO)、ステップS10508からステップS10510を実行することなく、ステップS10511に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10507 that the calculation execution conditions stored in the calculation execution
ステップS10511では、検査機320から遊技履歴情報の送信要求コマンドを受信しているか否かを判定し、送信要求コマンドを受信していると判定した場合には(S10511:YES)、ステップS10512に進み、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を検査機320に対して送信する。検査機320は、受信した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。ステップS10512を実行した後、ステップS10505に戻り、ステップS10505以下の処理を繰り返す。一方、ステップS10511において、検査機320から遊技履歴情報の送信要求コマンドを受信していないと判定した場合には(S10511:NO)、ステップS10512の処理を実行することなく、ステップS10505に戻り、ステップS10505以下の処理を繰り返す。
In step S10511, it is determined whether or not a transmission request command for game history information has been received from the
以上説明したように、本実施形態によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、実行された遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報である遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。仮に、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていると、算出された遊技履歴情報が、想定された値とは異なる不自然な値になる場合がある。したがって、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、パチンコ機10に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the game
さらに、本実施形態によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、算出した遊技履歴情報を不揮発的に記憶する演算結果記憶用メモリ309を備える。遊技履歴情報は、実行された遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該遊技履歴情報はパチンコ機10毎に異なるとともに、パチンコ機10の固有の情報である。すなわち、遊技履歴情報は、パチンコ機10の特性が反映された情報である。本実施形態によれば、当該パチンコ機10の特性が反映された情報である遊技履歴情報をパチンコ機10本体の筐体内部に格納された遊技履歴管理チップ300の演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該パチンコ機10の特性を検査する場合には、当該パチンコ機10本体自身から遊技履歴情報を取得することによって、当該パチンコ機10の特性を検査することができる。パチンコ機10は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによってパチンコ機10の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、パチンコ機10は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来のパチンコ機10では、当該パチンコ機10の特性に関する情報を保持することができない。本実施形態のパチンコ機10は、パチンコ機10の特性が反映された情報である遊技履歴情報をパチンコ機10本体の筐体内部に格納された遊技履歴管理チップ300の演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶するので、パチンコ機10がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該パチンコ機10本体から遊技履歴情報を取得することができる。すなわち、本実施形態のパチンコ機10は、当該パチンコ機10がいかなる状態(遊技ホールに設置されている状態や流通状態)に置かれても、パチンコ機10と遊技履歴情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該パチンコ機10の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the game
さらに、本実施形態では、遊技履歴管理チップ300及び主側CPU62xは、共に主側MPU62に搭載されており、これらは同一の電源によって動作するように構成されている。したがって、例えば、当該パチンコ機10が遊技ホールに設置されている場合であって、ホールコンピュータによってパチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を算出していた場合に、当該ホールコンピュータの電源系統に不具合が生じた場合や、当該ホールコンピュータの処理に不具合が生じた場合であっても、パチンコ機10に電源が供給されている状況であれば、遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。仮に、主側CPU62xと遊技履歴管理チップ300とが異なる電源によって動作している場合、遊技履歴管理チップ300の電源供給に不具合があった場合に、パチンコ機10によって遊技が実行されているにも関わらず遊技履歴情報を算出できないといった不具合が生じる。これに対して、本実施形態によれば、主側CPU62xと遊技履歴管理チップ300とが同一の電源によって動作しているので、遊技が実行可能な状況であれば必ず遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。よって、遊技履歴情報の信頼性を向上させることができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the game
さらに、本実施形態によれば、開閉の痕跡(開放の痕跡、開封の痕跡ともいう)が残る空間である基板ボックスの内部に、演算結果記憶用メモリ309を格納している。したがって、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、基板ボックスを開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されている遊技履歴情報が演算結果記憶用メモリ309への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを基板ボックスの痕跡から把握することが可能となる。したがって、遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。パチンコ機10は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る基板ボックスの内部に演算結果記憶用メモリ309を格納するので、パチンコ機10が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、遊技履歴情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、遊技履歴情報を用いてパチンコ機10の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、本実施形態によれば、パチンコ機10の遊技に関する特性を反映した遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正にパチンコ機10を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the calculation
さらに、本実施形態によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを取得するので、払い出した賞球に関するパチンコ機10の特性を算出することができる。さらに、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)毎に異なる賞球数データが設定されていても、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、パチンコ機10の種類毎に設定された賞球数データを用いて正しい遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。仮に、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていると、算出された遊技履歴情報が、想定された値とは異なる不自然な値になる場合がある。したがって、パチンコ機10の検査者は、正しい遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、パチンコ機10に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the game
さらに、本実施形態によれば、主側CPU62xは、主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを含む信号を遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信するので、遊技履歴管理チップ300が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアにアクセスすることができない構成や、遊技履歴管理チップ300が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データの記憶位置(メモリアドレス)を把握することができない構成であっても、遊技履歴管理チップ300が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを取得することが可能となる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the
さらに、本実施形態によれば、主側CPU62xのメイン処理において、設定完了コマンドを受信するまでは、タイマ割込み処理の割り込みが許可されず、タイマ割込み処理に含まれる遊技球発射制御処理が実行されない構成となっている。すなわち、賞球数データの賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306への記憶が完了するまでは遊技球が発射されないので、遊技履歴管理チップ300による遊技履歴情報の算出対象から遊技球が漏れてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, in the main processing of the
さらに、本実施形態によれば、排出通路検知センサー44hによって500個の遊技球が検知されるまでの期間毎の遊技履歴情報を算出して記憶するので、各パチンコ機10によって500個の遊技球が検知されるまでの時間にバラつきがあったとしても、その時間のバラつきに影響しない遊技履歴情報を算出、記憶することができる。すなわち、遊技球が発射される頻度に高低差がある場合であっても、その影響を受けにくい精度の高い遊技履歴情報を算出、記憶することができる。また、各入球口への入球情報をそのまま記憶する構成と比較して、必要な記憶容量を低減することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, game history information for each period until 500 game balls are detected by the discharge
パチンコ機10の種類(機種)が異なると、遊技の特性も異なるため、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行する最適な条件も異なることになる。このため、演算実行条件は、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)毎に異なる条件が記憶されている。本実施形態によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶されている演算実行条件を取得するので、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)毎に設定された演算実行条件が成立した場合に遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行することができる。
Differing types (models) of
さらに、本実施形態によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308が遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行した後に、レジスタ304に記憶されている各入球口への遊技球の入球個数(カウンタ値)を消去するので、再びレジスタ304に遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を記憶することが可能となる。したがって、レジスタ304に必要な記憶容量を低減することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, after the
さらに、本実施形態によれば、パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報が検査機320に送信されるので、検査機320は、当該パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、パチンコ機10の検査者は、検査機320に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the game history information of the
A4.第1実施形態の他の態様:
<態様1>
上記第1実施形態では、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶された演算実行条件として、排出通路検知センサー44hに検知された遊技球が500個に達することが設定されていたが、演算実行条件として、演算を実行する時間的間隔が設定されている構成としてもよい。例えば、演算を実行する時間的間隔として1時間が設定されており、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、1時間が経過する毎に遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。パチンコ機10の検査者は、1時間毎に算出された詳細な遊技履歴情報を確認することができ、パチンコ機10に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
A4. Other aspects of the first embodiment:
<
In the first embodiment, the calculation execution condition stored in the calculation execution condition storage area of the
なお、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)が異なると、遊技の特性も異なるため、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行する最適な条件(時間的間隔)も異なることになる。このため、演算実行条件は、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)毎に異なる条件が記憶されている。したがって、この態様1においても、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶されている演算実行条件を取得するので、パチンコ機10の種類(機種)毎に設定された演算実行条件が成立した場合に演算を実行することができる。
Note that different types (models) of
また、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、演算が実行されてからの経過時間を計測するとともに、遊技者によって遊技が行なわれているか否かを判定し、遊技が行なわれていないと判定している期間は、経過時間の計測を中断する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、バッファ302のビットに入球情報がない状態が所定時間(例えば3分)経過した場合に、遊技が行なわれていないと判定して経過時間の計測を中断し、バッファ302のビットに入球情報が確認された場合に、遊技が再開されたと判定して経過時間の計測を再開する構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、実際に遊技が行なわれている期間のみを対象として遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。
The
なお、経過時間の計測は、タイマカウンタを用いる構成としてもよく、RTC(Real‐Time Clock)を設けてRTCの日時情報を用いる構成としてもよい。また、所定の時刻毎に遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。 The measurement of elapsed time may be configured to use a timer counter, or may be configured to provide an RTC (Real-Time Clock) and use the RTC's date and time information. Also, the game history information may be calculated at each predetermined time.
<態様2>
上記第1実施形態では、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶された演算実行条件として、排出通路検知センサー44hに検知された遊技球が500個に達することが設定されていたが、演算実行条件として、電源の遮断の発生が検知されたことが設定されている構成としてもよい。具体的には、停電監視回路86は、電源の遮断の発生を検知すると、電源遮断が発生したことを示す信号を遊技履歴管理チップ300に出力する。当該信号を受信した遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、電源の遮断が発生したと判定し、遊技履歴情報を算出する。そして、この構成ではレジスタ304は揮発性のメモリによって構成されており、入球個数情報が消去されることになる。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10への電源の供給が開始されてから電源の遮断が発生するまでの期間中において検知された遊技球の個数に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。すなわち、遊技ホールの営業が開始してから終了するまでの期間毎に遊技履歴情報が算出されるので、遊技ホールの営業日毎に遊技履歴情報が算出されることになる。したがって、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技ホールの営業日を跨いで遊技履歴情報の特性に変化があったか否かを容易に把握することができるので、パチンコ機10に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
<
In the first embodiment, the calculation execution condition stored in the calculation execution condition storage area of the
さらに、電源の遮断が発生した後においても遊技履歴管理チップ300に対して電源を供給するコンデンサ87を備える構成とすれば、CPU308による遊技履歴情報の算出及び遊技履歴情報の演算結果記憶用メモリ309への記憶を確実に完了させることができる。
Furthermore, if the chip is configured to include a
<態様3>
上記第1実施形態において、主側CPU62xが演算結果記憶用メモリ309にアクセス可能な構成とし、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、遊技履歴情報がパチンコ機10の図柄表示装置41に表示されるので、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置(検査機320等)を用いることなく、当該パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。なお、主側CPU62xは、演算結果記憶用メモリ309にアクセスは可能であるが、データの変更等は不可能な構成とすることが好ましい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報が、ノイズやプログラムのバグ等によって破壊されたり、内容が書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。
<
In the first embodiment, the
<態様4>
上記第1実施形態において、主側CPU62xが演算結果記憶用メモリ309にアクセス可能な構成とし、演算結果記憶用メモリ309に記憶されている遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを報知するためのLEDランプをパチンコ機10の前面(例えば、メイン表示部45の所定の箇所)に備える構成としてもよい。例えば、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値(例えば、役物比率、連続役物比率、払出比率(通常モード中))が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合にLEDランプを発光させる構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、パチンコ機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなったパチンコ機10を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、パチンコ機10に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。特に、第1始動口33や一般入賞口(第1~第3入賞口32a~32c)の近傍の釘に不正が施されていると、上述した払出比率(通常モード中)がパチンコ機の設計時に想定された所定の範囲(例えば、0.60~0.70)から外れることになる。したがって、払出比率(通常モード中)が所定の範囲(例えば、0.60~0.70)に含まれなくなった場合にLEDランプを発光させる構成とすることによって、第1始動口33や一般入賞口(第1~第3入賞口32a~32c)の近傍の釘に不正が施されていないかを適切に判断することができる。
<
In the first embodiment, the
さらに、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値(例えば、役物比率、連続役物比率、払出比率(通常モード中))の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じてLEDランプの発光態様(色)を決定する構成としてもよい。例えば、役物比率が所定の範囲(0.70以下)に含まれている場合には第1LEDランプは青色に発光し、役物比率が0.71~0.80の場合には第1LEDランプは紫色に発光し、役物比率が0.81~1.00の場合には第1LEDランプは赤色に発光する構成としてもよい。連続役物比率が所定の範囲(0.60以下)に含まれている場合には第2LEDランプは青色に発光し、連続役物比率が0.61~0.70の場合には第2LEDランプは紫色に発光し、連続役物比率が0.71~1.00の場合には第2LEDランプは赤色に発光する構成としてもよい。また、払出比率(通常モード中)が所定の範囲(0.60~0.70)に含まれている場合には第3LEDランプは青色に発光し、払出比率(通常モード中)が0.71~0.80の場合には第3LEDランプは紫色に発光し、払出比率(通常モード中)が0.81~1.00の場合には第3LEDランプは赤色に発光する構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。なお、主側CPU62xは、演算結果記憶用メモリ309にアクセスは可能であるが、データの変更等は不可能な構成とすることが好ましい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報が、ノイズやプログラムのバグ等によって破壊されたり、内容が書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, the light emission mode (color) of the LED lamp may be determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value (e.g., reel ratio, consecutive reel ratio, payout ratio (in normal mode)) included in the game history information from a predetermined range. For example, the first LED lamp may be configured to emit blue light when the reel ratio is within a predetermined range (0.70 or less), to emit purple light when the reel ratio is 0.71 to 0.80, and to emit red light when the reel ratio is 0.81 to 1.00. The second LED lamp may be configured to emit blue light when the consecutive reel ratio is within a predetermined range (0.60 or less), to emit purple light when the consecutive reel ratio is 0.61 to 0.70, and to emit red light when the consecutive reel ratio is 0.71 to 1.00. Also, the third LED lamp may be configured to emit blue light when the payout ratio (in normal mode) is within a predetermined range (0.60 to 0.70), emit purple light when the payout ratio (in normal mode) is 0.71 to 0.80, and emit red light when the payout ratio (in normal mode) is 0.81 to 1.00. With this configuration, the inspector of the
<態様5>
上記第1実施形態では、主側ROM63に記憶されている演算用データ(賞球数データ及び演算実行条件)は主側MPU62(CPU62x)が実行する初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される構成としたが、遊技履歴管理チップ300が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリア及び演算実行条件記憶エリアにアクセス可能な構成とし、パチンコ機10の電源投入直後に遊技履歴管理チップ300が当該主側ROM63にアクセスして演算用データ(賞球数データ及び演算実行条件)を取得し、取得した演算用データを賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306及び演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307に記憶させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、主側MPU62の処理負荷を低減することができる。
<
In the first embodiment, the calculation data (number of prize balls data and calculation execution conditions) stored in the
<態様6>
上記第1実施形態では、遊技履歴管理チップ300が役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としたが、レジスタに記憶された500個毎の入球個数をそのまま記憶し、検査機320が遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300の処理負荷を低減することができる。以下、態様6の詳細について、上記第1実施形態との相違点を中心に説明する。
<Aspect 6>
In the first embodiment, the game
図19は、第1実施形態の態様6のパチンコ機10が備える主制御装置60の構成及び検査機320の構成を詳細に示すブロック図である。
Figure 19 is a block diagram showing in detail the configuration of the
主側MPU62の主側ROM63には、賞球数データ記憶エリアと、記憶実行条件記憶エリアとが設けられている。
The
賞球数データ記憶エリアには、上記第1実施形態と同様に、各入球口に遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数データ)が記憶されている。また、上記第1実施形態と同様に、この主側ROM63に記憶された賞球数データは、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた後に実行される初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される。これにより、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、本パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを把握することが可能となる。
As in the first embodiment, the prize ball number data storage area stores the number of game balls (prize ball number data) that are paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters each ball entrance. As in the first embodiment, the prize ball number data stored in the
記憶実行条件記憶エリアには、遊技履歴管理チップ300が後述する記憶処理を実行する条件である記憶実行条件が記憶されている。この態様6では、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数が500個に達することが記憶実行条件として記憶されている。この主側ROM63に記憶された記憶実行条件は、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた後に実行される初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される。これにより、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、本パチンコ機10に設定されている記憶実行条件を把握することが可能となる。
The memory execution condition memory area stores memory execution conditions that are conditions under which the game
遊技履歴管理チップ300は、CPU62xから各入球口への遊技球の入球情報を取得するバッファ302と、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を記憶するレジスタ304と、主側ROM63から取得した賞球数データを記憶する賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306と、主側ROM63から取得した記憶実行条件を記憶する記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ307aと、遊技履歴管理チップ300の全体の制御を司るCPU308と、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を順次記憶する入球個数記憶用メモリ309aとを備えている。上述した記憶処理は、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶させる処理である。
The game
検査用端子65は、検査機320とパチンコ機10とを接続するための端子である。この態様6では、検査用端子65を介して入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶された入球個数情報及び賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データが検査機320に送信される。
The
検査機320は、各種制御プログラムを実行するCPU321と、各種制御プログラムや固定値データ等を記録したROM324と、各種データを一時的に記憶するためのメモリであるRAM326と、各種情報を表示する表示部328と、パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続するための接続ケーブル329とを備えている。
The
この態様6では、検査機320は、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、入球個数情報及び賞球数データの送信を要求する送信要求コマンドを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、検査用端子65を介して入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶された入球個数情報と、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データとを検査機320に送信する。そして、検査機320は、受信した入球個数情報と賞球数データとに基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
In this aspect 6, when the
図20は、第1実施形態の態様6の遊技履歴管理チップ300及び検査機320における処理の内容を模式的に示す説明図である。
Figure 20 is an explanatory diagram that shows a schematic diagram of the processing performed by the game
バッファ302及びレジスタ304における処理の内容は、上述した第1実施形態と同じであるため、説明を省略する。
The processing contents in the
賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306は、パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを記憶するためのメモリである。この態様6では、パチンコ機10の電源が投入されると、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データが遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信され、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される。したがって、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される賞球数データの内容は、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データの内容と同一となる。
The prize ball number
記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ307aは、パチンコ機10に設定されている記憶実行条件を記憶するためのメモリである。パチンコ機10の電源が投入されると、主側ROM63に記憶されている記憶実行条件がCPU62xによって遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信され、記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ307aに記憶される。したがって、記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ307aに記憶される記憶実行条件の内容は、主側ROM63に記憶されている記憶実行条件の内容と同一となる。
The memory for storing
CPU308は、記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ307aに記憶されている記憶実行条件が成立したか否かを判定するとともに、記憶実行条件が成立したと判定した場合には、レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶させるとともに、レジスタ304の各カウンタの値を「0」にリセットする。この態様6では、CPU308は、レジスタ304に記憶された排出通路通過個数NOUTの値が500個に達する毎に、当該レジスタ304に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶させる。なお、以下では、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される間にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を「短期入球個数情報群」とも呼ぶ。
The
入球個数記憶用メモリ309aは、レジスタ304に記憶された入球個数に関する情報(短期入球個数情報群)を順次記憶するメモリであり、本実施形態では、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリによって構成されている。入球個数記憶用メモリ309aには、短期入球個数情報群が書き込まれた順番に関する情報も記憶されており、CPU308は、短期入球個数情報群を書き込むための空きエリアがない場合には、短期入球個数情報群を、書き込まれた順番が最も古い短期入球個数情報群が記憶されているエリアに記憶させる。すなわち、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aは、最も古い短期入球個数情報群から順番に上書きされるように構成(ファーストイン・ファーストアウト方式)されており、常に直近の短期入球個数情報群が記憶されている状態となる。
The memory for storing the number of entering
この態様6では、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aは、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される間にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報である短期入球個数情報群を、1200個分記憶することが可能な容量を有している。例えば、1日に遊技球が連続して10時間発射される場合には、1日に60000個の遊技球が発射されることになるので、1日に120個の短期入球個数情報群が入球個数記憶用メモリ309aに記憶されることになる。したがって、入球個数記憶用メモリ309aは、直近の10日間分の短期入球個数情報群を記憶することが可能となる。
In this aspect 6, the memory for storing the number of entering
検査機320は、上述したように、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、送信要求コマンドを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、検査用端子65を介して短期入球個数情報群及び賞球数データを検査機320に送信する。そして、検査機320は、短期入球個数情報群及び賞球数データに基づいて、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
As described above, when the
具体的には、この態様6では、検査機320は、上記の第1実施形態のCPU308と同様に、1つの短期入球個数情報群に対して1つの短期遊技履歴情報群を算出することが可能であるとともに、複数の短期入球個数情報群のそれぞれに記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を加算し、当該加算した入球個数を用いて長期間における遊技履歴情報(長期遊技履歴情報群)を算出することが可能である。すなわち、この態様6の検査機320は、500個の遊技球が発射された短期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた短期遊技履歴情報群だけでなく、例えば、600000個(約10日分)の遊技球が発射された長期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた長期遊技履歴情報群を算出することが可能である。
Specifically, in this aspect 6, the
なお、この態様6において、以下の構成を採用してもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment 6, the following configuration may be adopted.
検査機320は、受信した短期入球個数情報群を表示部328に表示可能な構成としてもよい。また、検査機320は、レジスタ304に記憶されている各カウンタ値を受信するとともに、受信した各カウンタ値を表示部328に表示可能な構成としてもよい。
The
また、遊技履歴管理チップ300が賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶されている賞球数データを検査機320に送信する構成に代えて、主側CPU62xが主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データを検査機320に対して送信する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306を省略することができ、遊技履歴管理チップ300の製造コストを低減することができる。
In addition, instead of the configuration in which the game
また、主側ROM63の記憶実行条件記憶エリアに記憶された記憶実行条件として、記憶処理を実行する時間的間隔が設定されている構成としてもよい。例えば、記憶処理を実行する時間的間隔として1時間が設定されており、遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、1時間が経過する毎に記憶処理を実行する構成としてもよい。
In addition, the time interval for executing the storage process may be set as the storage execution condition stored in the storage execution condition storage area of the
また、主側ROM63の記憶実行条件記憶エリアに記憶された記憶実行条件として、電源の遮断の発生が検知されたことが設定されている構成としてもよい。具体的には、停電監視回路86は、電源の遮断の発生を検知すると、電源遮断が発生したことを示す信号を遊技履歴管理チップ300に出力する構成とし、当該信号を受信した遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、電源の遮断が発生したと判定し、記憶処理を実行する構成としてもよい。
The storage execution condition stored in the storage execution condition storage area of the
また、態様6では、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を検査機320のCPU321が実行する構成としたが、当該演算の一部又は全部を遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308が実行し、当該演算の結果である遊技履歴情報を検査機320に送信する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in aspect 6, the calculation for calculating the gaming history information is performed by the
<態様7>
上記第1実施形態では、遊技履歴管理チップ300が役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としたが、バッファにおける入球情報をそのまま記憶し、当該入球情報に基づいて検査機320が遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300の処理負荷を低減することができる。以下、態様7の詳細について、上記第1実施形態との相違点を中心に説明する。
<Aspect 7>
In the first embodiment, the gaming
図21は、第1実施形態の態様7のパチンコ機10が備える主制御装置60の構成及び検査機320の構成を詳細に示すブロック図である。
Figure 21 is a block diagram showing in detail the configuration of the
この態様7では、主側MPU62には、年月日情報及び時刻情報を遊技履歴管理チップ300に対して出力するRTC96(RTC:Real‐Time Clock)が設けられている。RTC96は、バックアップ電源を備えており、パチンコ機10の電源遮断時においても年月日情報及び時刻情報を更新することができる。
In this embodiment 7, the
主側MPU62の主側ROM63には、賞球数データ記憶エリアが設けられている。なお、この態様7では、演算開始条件記憶エリアは設けられていない。
The
賞球数データ記憶エリアには、上記第1実施形態と同様に、各入球口に遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数データ)が記憶されている。また、上記第1実施形態と同様に、この主側ROM63に記憶された賞球数データは、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた後に実行される初期設定処理において遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信される。これにより、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、本パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを把握することが可能となる。
As in the first embodiment, the prize ball number data storage area stores the number of game balls (prize ball number data) that are paid out as prize balls when a game ball enters each ball entrance. As in the first embodiment, the prize ball number data stored in the
遊技履歴管理チップ300は、CPU62xから各入球口への遊技球の入球情報を取得するバッファ302と、主側ROM63から取得した賞球数データを記憶する賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306と、遊技履歴管理チップ300の全体の制御を司るCPU308と、バッファ302に記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球情報等を順次記憶する入球情報記憶用メモリ309bとを備えている。
The game
検査用端子65は、検査機320とパチンコ機10とを接続するための端子である。この態様7では、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続されると、入球情報記憶用メモリ309bに記憶された入球情報等及び賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データが検査機320に送信される。
The
検査機320は、各種制御プログラムを実行するCPU321と、各種制御プログラムや固定値データ等を記録したROM324と、各種データを一時的に記憶するためのメモリであるRAM326と、各種情報を表示する表示部328と、パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続するための接続ケーブル329とを備えている。
The
この態様7では、検査機320は、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、入球情報等及び賞球数データの送信を要求する送信要求コマンドを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、検査用端子65を介して入球情報記憶用メモリ309bに記憶された入球情報等と、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データとを検査機320に送信する。そして、検査機320は、受信した入球情報等と賞球数データとに基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
In this aspect 7, when the
図22は、第1実施形態の態様7の遊技履歴管理チップ300及び検査機320における処理の概要を模式的に示す説明図である。
Figure 22 is an explanatory diagram that shows a schematic overview of the processing in the game
バッファ302における処理の内容は、上述した第1実施形態と同じであるため、説明を省略する。
The processing content in
入球情報記憶用メモリ309bは、バッファ302に記憶された入球情報及び遊技球が入球した際の遊技状態に関する情報を順次記憶するメモリであり、本実施形態では、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリによって構成されている。さらに、本実施形態では、入球情報及び遊技状態に関する情報が記憶される際に、遊技球が各入球口に入球した日時情報が付加されて記憶される。また、入球情報記憶用メモリ309bには、入球情報等が書き込まれた順番に関する情報も記憶されており、CPU308は、入球情報等を書き込むための空きエリアがない場合には、入球情報等を、書き込まれた順番が最も古い入球情報等が記憶されているエリアに記憶させる。すなわち、入球情報記憶用メモリ309bは、最も古い入球情報等から順番に上書きされるように構成(ファーストイン・ファーストアウト方式)されており、常に直近の入球情報等が記憶されている状態となる。
The memory for storing
賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306は、パチンコ機10に設定されている賞球数データを記憶するためのメモリである。この態様7では、パチンコ機10の電源が投入されると、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データが遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信され、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される。したがって、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される賞球数データの内容は、主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データの内容と同一となる。さらに、この態様7では、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続されると、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶される賞球数データが当該検査機320に送信される。
The prize ball number
検査機320は、上述したように、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、入球情報等及び賞球数データの送信を要求する送信要求コマンドを遊技履歴管理チップ300に送信する。遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308は、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、検査用端子65を介して入球情報記憶用メモリ309bに記憶された入球情報、遊技状態に関する情報及び日時情報と、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶された賞球数データとを検査機320に送信する。そして、検査機320は、受信したこれらの情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
As described above, when the
具体的には、この態様7の検査機320は、500個の遊技球が発射された短期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた遊技履歴情報(短期遊技履歴情報群)を算出することだけでなく、例えば、600000個(約10日分)の遊技球が発射された長期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた遊技履歴情報(長期遊技履歴情報群)を算出することが可能である。すなわち、任意の期間における遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能である。
Specifically, the
さらに、この態様7では、入球情報等に日時情報(年月日情報及び時刻情報)が付加されているので、検査機320は、受信した入球情報等に付加されている日時情報の範囲内において、遊技履歴情報の算出対象となる日時の範囲を指定して遊技履歴情報を算出することも可能である。したがって、パチンコ機10の検査者は、日時の範囲を指定した遊技履歴情報に基づいて詳細な検査をすることができる。
Furthermore, in this aspect 7, since date and time information (year, month, day and time information) is added to the winning ball information, etc., the
なお、この態様7において、以下の構成を採用してもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment 7, the following configuration may be adopted.
検査機320は、受信した入球情報等を表示部328に表示可能な構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、各入球検知センサーによって遊技球が検知された日時についても把握することが可能となる。
The
また、遊技履歴管理チップ300が賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306に記憶されている賞球数データを検査機320に送信する構成に代えて、主側CPU62xが主側ROM63に記憶されている賞球数データを検査機320に対して送信する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306を省略することができ、遊技履歴管理チップ300の製造コストを低減することができる。
In addition, instead of the configuration in which the game
また、態様7では、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を検査機320のCPU321が実行する構成としたが、当該演算の一部又は全部を遊技履歴管理チップ300のCPU308が実行し、当該演算の結果である遊技履歴情報を検査機320に送信する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in aspect 7, the calculation for calculating the gaming history information is performed by the
<態様8>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様では、主側ROM63に演算実行条件又は記憶実行条件が記憶されており、遊技履歴管理チップ300がこれらの条件を主側ROM63から取得する構成としたが、遊技履歴管理チップ300がこれらの条件を不揮発性のメモリに当初から記憶している構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、不適切な演算実行条件又は記憶実行条件が主側ROM63に記憶されてしまっており、遊技履歴情報又は入球個数情報を適切に記憶できないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。例えば、演算実行条件又は記憶実行条件として極端に短い期間(例えば、排出通路通過個数NOUT=5)が記憶されてしまっており、演算結果記憶用メモリ309又は入球個数記憶用メモリ309aには極端に短い期間分(例えば、1時間分程度)の遊技履歴情報又は入球個数情報しか記憶されないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。
<Aspect 8>
In the first embodiment and the other aspects, the calculation execution conditions or the storage execution conditions are stored in the
<態様9>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様では、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を記憶する機能や、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出する機能、算出した遊技履歴情報を記憶する機能を遊技履歴管理チップ300が備える構成としたが、主側CPU62x(遊技履歴管理チップ300を除いた主側MPU62)がこれらの機能の一部を備える構成としてもよい。また、遊技履歴管理チップ300を設けず、主側CPU62x(遊技履歴管理チップ300を除いた主側MPU62)がこれらの機能の全部を備える構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、別途に遊技履歴管理チップ300を設ける必要がないため、製造コストの低減を図ることができる。ただし、遊技履歴管理チップ300を設ける構成によれば、主側CPU62xの処理負荷を低減することができる。
<Aspect 9>
In the first embodiment and the other aspects, the game
<態様10>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、遊技履歴管理チップ300以外の機能部(例えば、検査機320や主側CPU62x)が備える機能の一部又は全部を遊技履歴管理チップ300が備える構成としてもよく、遊技履歴管理チップ300が備える機能の一部又は全部を遊技履歴管理チップ300以外の機能部が備える構成としてもよい。例えば、検査機320が備える機能の一部を遊技履歴管理チップ300が備える構成とすれば、検査機320の処理負荷や製造コストをさらに低減することができ、遊技履歴管理チップ300が備える機能の一部を検査機320が備える構成とすれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300の処理負荷や製造コストをさらに低減することができる。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects described above, the gaming
<態様11>
上記第1実施形態では、遊技履歴管理チップ300が役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としたが、遊技履歴管理チップ300を設けず、主側CPU62xが遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。以下、態様11の詳細について、上記第1実施形態との相違点を中心に説明する。
<
In the first embodiment, the game
図23は、第1実施形態の態様11におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。この態様11では、遊技履歴管理チップ300が設けられていない点と、主側RAM64に入球個数記憶エリアと演算結果記憶エリアが設けられている点が、上記第1実施形態(図5)と異なっている。
Figure 23 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
主側CPU62xは、入出力ポート62aから受信した遊技球の入球情報に基づいて、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアに記憶されている各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を更新する。そして、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶されている演算実行条件が成立した場合には、主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データと、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアに記憶されている各入球口における遊技球の入球個数とに基づいて演算を実行して遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該遊技履歴情報を主側RAM64の演算結果記憶エリアに記憶させる。以下、具体的に説明する。
Based on the game ball entry information received from the input/
図24は、第1実施形態の態様11の主側MPU62における処理の概要を模式的に示す説明図である。主側CPU62xは、主側ROM63の演算実行条件記憶エリアに記憶されている演算実行条件が成立したか否かを判定するとともに、演算実行条件が成立したと判定した場合には、主側CPU62xのキャッシュに記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアに記憶させる。この態様11では、主側CPU62xは、主側CPU62xのキャッシュに記憶された排出通路通過個数NOUTの値が500個に達する毎に、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアに記憶させる。なお、上述したように、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される間にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報を「短期入球個数情報群」とも呼ぶ。
24 is an explanatory diagram showing a schematic overview of the processing in the
主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアは、入球個数に関する情報(短期入球個数情報群)を順次記憶するエリアである。主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアには、短期入球個数情報群が書き込まれた順番に関する情報も記憶されており、主側CPU62xは、短期入球個数情報群を書き込むための空きエリアがない場合には、新たに書き込み対象となった短期入球個数情報群を、書き込まれた順番が最も古い短期入球個数情報群が記憶されているエリアに記憶させる。すなわち、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアは、最も古い短期入球個数情報群から順番に上書きされるように構成(ファーストイン・ファーストアウト方式)されており、常に直近の短期入球個数情報群が記憶されている状態となる。
The number of scoring balls storage area of the
この態様11では、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアは、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される間にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報である短期入球個数情報群を、1200個分記憶することが可能な容量を有している。例えば、1日に遊技球が連続して10時間発射される場合には、1日に60000個の遊技球が発射されることになるので、1日に120個の短期入球個数情報群が主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアに記憶されることになる。したがって、主側RAM64の入球個数記憶エリアは、直近の10日間分の短期入球個数情報群を記憶することが可能となる。
In this
そして、主側CPU62xは、演算実行条件が成立する毎に、新たに記憶された1つの短期入球個数情報群に対して1つの短期遊技履歴情報群を新たに算出する。さらに、主側CPU62xは、演算実行条件が成立する毎に、新たに記憶された短期入球個数情報群を含む複数の短期入球個数情報群のそれぞれに記憶された各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を加算し、当該加算した入球個数を用いて長期間における遊技履歴情報(長期遊技履歴情報群)を算出する。すなわち、この態様11の主側CPU62xは、500個の遊技球が発射された短期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた短期遊技履歴情報群だけでなく、例えば、600000個(約10日分)の遊技球が発射された長期間における各入球口への入球個数に基づいた長期遊技履歴情報群を算出することが可能である。そして、算出したこれらの遊技履歴情報を主側RAM64の演算結果記憶エリアに記憶させる。
Then, the
主側RAM64の演算結果記憶エリアは、短期遊技履歴情報群を順次記憶するエリアと、長期遊技履歴情報群を記憶するエリアとによって構成されている。短期遊技履歴情報群を順次記憶するエリアには、短期遊技履歴情報群が書き込まれた順番に関する情報も記憶されており、主側CPU62xは、短期遊技履歴情報群を書き込むための空きエリアがない場合には、新たに算出された短期遊技履歴情報群を、書き込まれた順番が最も古い短期遊技履歴情報群が記憶されているエリアに記憶させる。すなわち、主側RAM64の短期遊技履歴情報群を順次記憶するエリアは、最も古い短期遊技履歴情報群から順番に上書きされるように構成(ファーストイン・ファーストアウト方式)されており、常に直近の短期遊技履歴情報群が記憶されている状態となる。長期遊技履歴情報群を記憶するエリアには、演算実行条件が成立する毎に新たに算出された長期遊技履歴情報群が上書きされる。すなわち、長期遊技履歴情報群を記憶するエリアには、最新の短期入球個数情報群を含む複数の短期入球個数情報群に基づいて算出された最新の長期遊技履歴情報群が記憶されることになる。
The calculation result storage area of the
検査機320は、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、送信要求コマンドを主側CPU62xに送信する。主側CPU62xは、検査機320から送信要求コマンドを受信すると、主側RAM64に記憶された遊技履歴情報を検査機320に送信する。そして、検査機320は、受信した遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
When the
また、この態様11では、遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させるための所定の操作が実行されると、主側RAM64に記憶された遊技履歴情報が入出力ポート62xを介して音声発光制御装置90に出力され、図柄表示装置41に表示される。
In addition, in this
また、この態様11では、パチンコ機10への電源の供給が断たれても、コンデンサ87から供給されるバックアップ電源によって、主側RAM64に記憶された短期入球個数情報群及び遊技履歴情報が数日間保持されるように構成されている。
In addition, in this
このような構成によれば、単一の処理部である主側CPU62xが、大当たり抽選処理等の遊技を進行するための処理と、遊技履歴情報を算出、記憶する処理とを実行するので、遊技履歴情報を算出、記憶するための専用の遊技履歴管理チップ300を設ける必要がなく、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減させることができる。
With this configuration, the
さらに、500個の遊技球が遊技盤30に発射される間にカウントされた各入球口への遊技球の入球個数に関する情報である短期入球個数情報群を主側RAM64に記憶するように構成されているので、遊技球の入球情報をそのままの形式で記憶する構成(例えば、図22の入球情報記憶用メモリ309bに記憶されている入球情報の形式で記憶する構成)と比較して、主側RAM64に必要なメモリ容量を大幅に低減しつつ、直近の短期遊技履歴情報群及び長期遊技履歴情報群を算出することが可能となる。
Furthermore, the
なお、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴情報として短期遊技履歴情報群及び長期遊技履歴情報群の両方を算出する構成に限らず、これらの一方のみを算出する構成としてもよい。
The
<態様12>
図25は、第1実施形態の態様12におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。上述した態様11(図23)との違いは、主側MPU62に、書き換え可能であるとともに電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリであるフラッシュメモリ64xが設けられている点である。このフラッシュメモリ64xには、上述した態様11における短期入球個数情報群を記憶するための入球個数記憶エリアと、上述した態様11における短期遊技履歴情報群及び長期遊技履歴情報群を記憶するための演算結果記憶エリアとが設けられている。
<
Fig. 25 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
この態様12の主側CPU62xは、演算実行条件が成立する毎に、短期入球個数情報群及び算出した遊技履歴情報をフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶するように構成されている。
The
このような構成によれば、遊技履歴管理チップ300を備える構成と比較して、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減することができる。さらに、パチンコ機10への電源の供給が長期間にわたって断たれても、短期入球個数情報群及び遊技履歴情報が保持されるので、当該パチンコ機10がいかなる状態(例えば、長期間にわたってパチンコ機10に電源が供給されない流通状態等)に置かれても、パチンコ機10と遊技履歴情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該パチンコ機10の特性を管理、検査することができる。
This configuration allows the manufacturing costs of the
また、主側RAM64に短期入球個数情報群及び遊技履歴情報を記憶させるためのエリアを設けなくてもよいため、主側RAM64の記憶容量を抑えることができ、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減することができる。
In addition, since there is no need to provide an area in the
<態様13>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、主制御装置60は、遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである遊技モードと、遊技履歴情報を検査機320に出力するモードである検査モードとを切り替えて実行可能な構成としてもよい。遊技進行処理は、入球検知センサー44a~44hによって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて実行される処理であり、大当たり抽選処理や、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等が含まれる。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects, the
そして、検査モードでは、遊技球が入球検知センサー44a~44hによって検出される領域を通過した場合であっても、遊技進行処理を実行しない構成としてもよい。
In the inspection mode, the game progress process may not be executed even if the game ball passes through the area detected by the ball
具体的には、例えば、検査モードに移行すると、主制御装置60において検査モードであるか否かを判定するための検査モードフラグがONになる。そして、主制御装置60は、検査モードフラグがONであるか否かを判定し、検査モードフラグがONであると判定した場合には、通常の遊技進行処理を実行する処理フローには進まず、検査モード用の処理フローに進む。この結果、主制御装置60は、入球検知センサー44a~44hから遊技球が検知されたことを示す信号を受信した場合であっても、当該信号を受信したことに基づく処理(例えば、大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値を取得する処理や、賞球の払出処理、音声発光制御装置90にコマンドを送信する処理等)を実行しないように構成されている。
Specifically, for example, when the inspection mode is entered, the inspection mode flag for determining whether or not the
このような構成によれば、遊技進行処理と並行して実行することが好ましくない処理や、遊技進行処理と並行して実行した場合に不具合が生じやすい処理等を検査モードにおいて実行することができる。また、このような構成によれば、検査モードにおいては遊技進行処理を実行しないので、検査モードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムを開発する際に、遊技進行処理が並行して実行された場合における対策を考慮しなくてもよいため、検査モードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムの開発効率を大幅に向上させることができる。 With this configuration, it is possible to execute in the inspection mode processes that are undesirable to execute in parallel with game progress processing, or processes that are likely to cause malfunctions when executed in parallel with game progress processing. Furthermore, with this configuration, game progress processing is not executed in the inspection mode, so when developing a program for processing to be executed in the inspection mode, there is no need to consider measures to take in the event that game progress processing is executed in parallel, which can significantly improve the efficiency of developing programs for processing to be executed in the inspection mode.
また、遊技履歴情報は、遊技球が検知されて遊技進行処理が実行されると内容が変化する情報である。したがって、仮に、遊技進行処理と並行して遊技履歴情報を出力する処理を実行する構成を採用すると、パチンコ機10の検査者が遊技履歴情報によって当該パチンコ機10の特性を検査している間に遊技進行処理が実行されて当該遊技履歴情報の内容が随時変化してしまい、円滑に検査を実施することが困難になってしまう場合がある。これに対して、この態様13の構成によれば、遊技球が所定の領域を通過した場合であっても遊技進行処理を実行しない検査モードにおいて遊技履歴情報を出力するので、遊技履歴情報を出力している間に当該遊技履歴情報の内容が変化してしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の検査者は円滑に検査を実施することができる。
The game history information is information whose contents change when a game ball is detected and game progress processing is executed. Therefore, if a configuration is adopted in which a process for outputting game history information is executed in parallel with game progress processing, the game progress processing may be executed while an inspector of the
なお、検査モードにおいて遊技履歴情報を出力する態様は、遊技履歴情報を検査機320に出力して表示させる態様に限らず、他の様態であってもよい。例えば、遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に出力して表示させる構成としてもよい。
The manner in which the game history information is output in the inspection mode is not limited to the manner in which the game history information is output to the
また、検査モードにおいて出力する情報は、遊技履歴情報に限らず、他の情報であってもよい。例えば、遊技球の入球情報や入球個数情報等のように、入球検知センサー44a~44hによって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく他の情報であってもよい。
In addition, the information output in the inspection mode is not limited to game history information, and may be other information. For example, it may be other information based on the detection of game balls by the ball
<態様14>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様のうち、主制御装置60が遊技モードと検査モードとを切り替えて実行可能な構成において、遊技モードの遊技進行処理の実行中に、遊技モードから検査モードに移行させるための所定の操作(以下では「モード切替操作」とも呼ぶ)が検査者によって実行された場合には、実行中の遊技進行処理が予め定められた処理段階まで完了したタイミングで、遊技モードから検査モードに移行する構成としてもよい。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects described above, in a configuration in which the
具体的には、例えば、遊技モードの遊技進行処理の実行中に、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するというモード切替操作が実行された場合には、実行中の各遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理や、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)毎に予め定められた処理段階まで処理を完了させる。そして、予め定められた処理段階まで遊技進行処理が完了すると、当該処理段階の後の処理は実行されずに待機状態となる。そして、実行中の各遊技進行処理の全てが予め定められた処理段階まで処理が完了したタイミングで、遊技モードから検査モードに移行する。
Specifically, for example, when a mode switching operation is performed by pressing the power button while pressing the mode switching button during execution of game progress processing in game mode, the processing is completed up to a predetermined processing stage for each game progress processing being executed (jackpot lottery processing, electric role release lottery processing, prize ball payout processing, variable display processing of patterns on the
このような構成によれば、実行中の遊技進行処理が予め定められた処理段階まで処理が完了したか否かに関わらずにモード切替操作が実行された直後のタイミングで遊技モードから検査モードに移行する構成と比較して、検査モードに移行する際の処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 This configuration makes it possible to reduce the occurrence of processing errors when switching to the inspection mode, compared to a configuration in which the game mode is switched to the inspection mode immediately after a mode switching operation is performed, regardless of whether the ongoing game progress processing has been completed up to a predetermined processing stage.
例えば、仮に、実行中の遊技進行処理が予め定められた処理段階まで処理が完了したか否かに関わらずにモード切替操作が実行された直後のタイミングで遊技モードから検査モードに移行する構成を採用した場合において、遊技モードにおいて遊技進行処理としてのメイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、モード切替操作が実行された場合には、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示の途中で検査モードに移行することになり、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となる。これに対して、この態様14の構成によれば、例えば、遊技モードにおいて図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、モード切替操作が実行された場合には、図柄の変動表示処理が終了して図柄が停止したという処理段階まで処理が完了したタイミングで検査モードに移行することになる。したがって、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となるといった処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。
For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the game mode is switched to the inspection mode immediately after a mode switching operation is performed, regardless of whether the game progress processing being performed has been completed up to a predetermined processing stage, if a mode switching operation is performed during the period in which the pattern change display processing is being performed in the
なお、検査モードから遊技モードに移行(復帰)した際には、検査モードに移行する前において実行予定であった残りの処理段階の遊技進行処理を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、期待していた遊技進行処理が不完全な状態で終了するといった不快感を遊技者に与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 When the game mode is switched (returned) from the inspection mode, the game progress processing of the remaining processing stages that were scheduled to be executed before the game mode was switched to the inspection mode may be executed. With such a configuration, it is possible to prevent the player from feeling uncomfortable when the game progress processing that he or she was expecting ends in an incomplete state.
また、遊技モードにおける遊技進行処理の実行中に、モード切替操作が実行された場合には、実行中の各遊技進行処理の全ての処理が完了したタイミングで、遊技モードから検査モードに移行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技進行処理を再開させる場合における処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In addition, if a mode switching operation is performed while game progress processing is being executed in the game mode, the game mode may be switched to the inspection mode at the timing when all of the game progress processing being executed is completed. With such a configuration, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of processing errors when restarting the game progress processing.
また、遊技モードにおける遊技進行処理の実行中に、モード切替操作が実行された場合には、遊技実行処理を中断させるとともに、中断させた遊技進行処理の再開を可能とする情報を主側RAM64に記憶し、当該記憶が完了したタイミングで、遊技モードから検査モードに移行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10は、遊技モードから検査モードに速やかに移行するので、短期間で多くのパチンコ機10を検査することが可能となる。
In addition, when a mode switching operation is performed during execution of game progress processing in the game mode, the game execution processing is interrupted, and information that enables resumption of the interrupted game progress processing is stored in the
また、遊技モードから検査モードに移行させるためのモード切替操作は、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作に限らず、他の態様であってもよい。例えば、モード切替ボタンを押下するという単独の操作であってもよい。また、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合に、モード切替操作が実行された場合と同様の処理を実行する構成としてもよい。
The mode switching operation for transitioning from the game mode to the inspection mode is not limited to the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the mode switching button, and may be in other forms. For example, it may be a single operation of pressing the mode switching button. Furthermore, when the
<態様15>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様のうち、主制御装置60が遊技モードと検査モードとを切り替えて実行可能な構成において、検査モード中に、当該検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過したという自動復帰条件が成立した場合には、検査モードから遊技モードに移行させるための所定の操作(例えば、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作)が実行されていない場合であっても、検査モードから遊技モードに移行する構成としてもよい。
<
Among the above first embodiment and other aspects, in a configuration in which the
このような構成によれば、検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過した場合には、検査モードから遊技モードに移行させるための所定の操作が実行されていない場合であっても、検査モードから遊技モードに移行するように構成されているので、所定の操作の実行がされずに遊技モードに復帰しないことを確実に抑制することができる。例えば、パチンコ機10の検査者が検査モードにおいて出力される遊技履歴情報によって当該パチンコ機10の特性を検査した後、所定の操作の実行を失念してしまった場合であっても、検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過すれば遊技モードに復帰するので、パチンコ機10が遊技進行処理を実行可能な遊技モードに復帰せずに遊技者が当該パチンコ機10で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。
According to this configuration, if 10 minutes have passed since the transition to the inspection mode, the inspection mode is configured to transition to the game mode even if the specified operation for transitioning from the inspection mode to the game mode has not been performed, so it is possible to reliably prevent a situation in which the specified operation is not performed and the game mode is not returned to. For example, even if an inspector of the
なお、自動復帰条件は、検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過したという条件に限らず、他の態様であってもよい。例えば、検査モードに移行した時点から5分が経過したという条件であってもよく、検査用端子65から検査機320が取り外された時点から10分が経過したという条件であってもよい。
The automatic recovery condition is not limited to 10 minutes having passed since the mode was changed to the inspection mode, and may be other conditions. For example, the automatic recovery condition may be 5 minutes having passed since the mode was changed to the inspection mode, or 10 minutes having passed since the
また、検査モードから遊技モードに移行させるための所定の操作は、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作に限らず、他の態様であってもよい。例えば、モード切替ボタンを押下するという単独の操作であってもよい。 The predetermined operation for switching from the inspection mode to the game mode is not limited to the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the mode switching button, and may be in other forms. For example, it may be a single operation of pressing the mode switching button.
<態様16>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、主側RAM64を初期化するためのRAMクリアボタンを主制御装置60に設け、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作(以下では「消去用操作」とも呼ぶ)が実行された場合に、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報を消去する(初期化する)構成としてもよい。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects described above, a RAM clear button for initializing the
さらに、主制御装置60が遊技モードと検査モードとを切り替えて実行可能な構成としてもよい。そして、検査モードに移行後であって遊技モードに移行する前の状態、例えば、検査モード中の状態や、検査モードに移行後にそのまま電源がOFFになった状態では、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという消去用操作が実行された場合であっても、主側RAM64に記憶された情報を消去しない構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, the
このような構成によれば、検査モードに移行後であって遊技モードに移行する前の状態では、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報を消去するための消去用操作が実行された場合であっても、主側RAM64に記憶された情報を消去しないので、検査モードに移行後であって遊技モードに移行する前の状態において、遊技モードに移行させようとして誤って消去用操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
With this configuration, even if an erase operation is performed to erase information stored in the
例えば、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報を消去するための消去用操作が、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作であり、遊技モードと検査モードとの間でモードを移行させるための操作が、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作である構成においては、検査モードから遊技モードに移行させようとしてモード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤ってRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまう虞がある。しかしながら、この態様16の構成によれば、検査モードに移行後であって遊技モードに移行する前の状態では、誤ってRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという消去用操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
For example, in a configuration in which the erasing operation for erasing information stored in the
より具体的には、例えば、遊技モードから検査モードに移行する際に、遊技モードにおいて実行していた遊技進行処理を一時的に停止させるとともに、当該停止させた遊技進行処理を検査モードへの復帰後に再開させるための情報を主側RAM64に記憶させる構成を採用した場合において、検査モードから遊技モードに復帰させようとしてモード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤ってRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合には、遊技進行処理を再開するための情報が消去されてしまい、検査モードへの復帰後に遊技進行処理を再開させることができなくなり、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまう虞がある。これに対して、この態様16の構成によれば、検査モードに移行後であって遊技モードに移行する前の状態において、遊技モードに移行させようとして誤ってRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合であっても、主側RAM64に記憶された情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができるので、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。
More specifically, for example, when switching from the game mode to the inspection mode, if a configuration is adopted in which the game progress processing being executed in the game mode is temporarily stopped and information for resuming the stopped game progress processing after returning to the inspection mode is stored in the
なお、主側RAM64に遊技履歴情報を記憶する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報を記憶するための専用のメモリを別途設けなくてもよいため、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減することができる。
The game history information may be stored in the
また、消去用操作が実行された場合には、パチンコ機10の状態(電源のオン、オフの状態や、遊技モードか検査モードかといった状態)に関わらず、主側RAM64に記憶された遊技履歴情報は消去されず、主側RAM64に記憶された遊技履歴情報以外の情報(遊技進行処理を再開するために記憶されている情報等)のみが消去される(初期化される)構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、所定の規定範囲から逸脱した遊技履歴情報が意図的に消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, when an erasure operation is executed, the game history information stored in the
なお、消去用操作は、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作に限らず、他の態様であってもよい。例えば、RAMクリアボタンを押下するという単独の操作であってもよい。 The erase operation is not limited to the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the RAM clear button, and may be in other forms. For example, it may be a single operation of pressing the RAM clear button.
<態様17>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様のうち、主制御装置60が遊技モードと検査モードとを切り替えて実行可能な構成において、主制御装置60が遊技モードから検査モードに移行する際には、検査モードに移行して遊技進行処理が一時的に停止することを示すコマンドである遊技停止コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に対して送信するとともに、実行中であった遊技進行処理を検査モードにおいて一時的に停止させる構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示を実行中に検査モードに移行した場合には、メイン表示部45における表示を消灯させ、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動時間のカウントを停止する。また、主制御装置60が検査モードから遊技モードに移行する際には、遊技モードに移行して遊技進行処理が再開することを示すコマンドである遊技再開コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に対して送信する構成としてもよい。
<
In the first embodiment and the other aspects described above, in a configuration in which the
そして、音声発光制御装置90は、遊技停止コマンドを受信した場合には、実行中の演出を一時的に停止させ、その後、遊技再開コマンドを受信した場合には、一時的に停止させていた演出を再開させる構成とする。このような構成によれば、主制御装置60が遊技モードと検査モードとの間で移行する場合であっても、主制御装置60が実行する遊技進行処理(例えば、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理)と、音声発光制御装置90が制御する演出(例えば、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示処理)とを同期させることが可能となり、遊技モードへの移行後に遊技者が違和感を感じてしまうことを抑制することができる。
The audio and light emitting
なお、音声発光制御装置90は、遊技停止コマンドを受信した場合であっても、実行中の演出を停止させない構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示中に遊技停止コマンドを受信した場合には、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示の制御を継続したまま、図柄の変動表示のレイヤーの上に別の画像(例えば、黒色の画像)のレイヤーを表示させる構成とする。ただし、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示の制御は継続しているため、黒色の画像のレイヤーの下では、図柄の変動表示が継続している。そして、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動時間が経過した場合には、黒色の画像のレイヤーの下で図柄の変動表示は終了するが、図柄は停止せずに小さく揺れている態様となる。
The audio and light
そして、遊技再開コマンドを主制御装置60から受信した場合には、図柄の変動表示のレイヤーよりも上に表示されていた黒色の画像のレイヤーを取り除き、再び、図柄のレイヤーを表示させる。このとき、主制御装置60は、検査モードから遊技モードに移行(復帰)し、停止していた遊技進行処理(メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示)を再開する。
When a game resume command is received from the
そして、主制御装置60は、変動時間のカウントを停止していたメイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示を再開し、残りの変動時間が経過した場合、すなわち、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動を停止させるタイミングになった場合には、音声発光制御装置90に対して図柄停止コマンドを送信する。当該図柄停止コマンドを受信した音声発光制御装置90は、表示制御装置100に対して図柄停止コマンドを送信し、表示制御装置100は、図柄表示装置41において小さく揺れた態様で表示されていた図柄を完全に停止させる。
Then, the
このような構成によれば、主制御装置60が検査モード中には、メイン表示部45における表示は消灯し、図柄表示装置41における表示は黒色の画像となる。そして、主制御装置60が検査モードから遊技モードに移行すると、変動時間のカウントを停止していたメイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示が再開され、図柄表示装置41における図柄は変動表示している態様又は小さく揺れている表示態様となる。そして、メイン表示部45における図柄が停止するタイミングで図柄表示装置41における図柄も停止することになる。すなわち、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示と図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示とを同期させることが可能となる。また、遊技停止コマンドを受信した場合であっても実行中の演出の制御を停止させないので、実行中の演出の制御を一時的に停止させることによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。不具合としては、例えば、一時的に演出の制御を停止させた状態から演出の制御を再開すると、複数の演出を実行していた場合において当該複数の演出のタイミングにずれが生じたり、図柄表示装置41に表示される動画とスピーカー46から出力される音声とにずれが生じたりすること等が挙げられる。
According to this configuration, when the
なお、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動を停止させるタイミングになった場合であっても主制御装置60が音声発光制御装置90に対して図柄停止コマンドを送信しない構成を採用した場合には、図柄表示装置41における図柄の変動表示は、小さく揺れている態様が継続することになり、その後に主制御装置60から送信される変動コマンドや、保留情報が記憶されていない場合に送信される待機コマンドを受信することによって図柄表示装置41における図柄が停止することになる。
In addition, if the
<態様18>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、所定時刻になったことを契機として当該パチンコ機10に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、午後11時10分になったことを契機として遊技モードから検査モードに移行するとともに、当該パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技ホールの閉店後である午後11時10分頃に、各パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報が図柄表示装置41に表示された状態となるので、パチンコ機10の検査者は、各パチンコ機10を遊技モードから検査モードに移行させる手間をかけることなく、遊技ホールの閉店後に、速やかに多くのパチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を検査、確認することが可能となる。
<
In the first embodiment and the other aspects, the game history information stored in the
また、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信したことを契機として当該パチンコ機10に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、例えば、遊技ホールに設置された全てのパチンコ機10を一斉に検査モードに移行させるとともに、各パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報をそれぞれの図柄表示装置41に表示させることができるので、パチンコ機10の検査者は、各パチンコ機10を遊技モードから検査モードに移行させる手間をかけることなく、速やかに多くのパチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を検査、確認することが可能となる。
Also, the game history information stored in the
<態様19>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、遊技履歴情報を常に図柄表示装置41に表示する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技者や検査者は常に遊技履歴情報を確認することができるので、遊技履歴情報が所定の範囲から逸脱している等の異変が生じた場合に、早急に当該異変に気付くことが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を早急に確保することが可能となる。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects, the game history information may be configured to be always displayed on the
<態様20>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、7つの発光ダイオードによって構成された7セグメント表示器をパチンコ機10の背面に設け、当該7セグメント表示器に当該パチンコ機10に記憶されている遊技履歴情報に関連した情報を表示する構成としてもよい。例えば、主制御装置60が上述した遊技モードから検査モードに移行した際に、当該パチンコ機10に記憶されている役物比率や払出比率(通常モード時)等が所定の範囲内であるか否かを7セグメント表示器に表示させる構成としてもよい。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects described above, a seven-segment display composed of seven light-emitting diodes may be provided on the back of the
より具体的には、例えば、主制御装置60が遊技モードから検査モードに移行すると、役物比率に関する表示を行なうことを示す「1」が7セグメント表示器に表示された後、当該役物比率が所定の範囲内である場合(具体的には、役物比率が0.700以下の場合)には、OKを意味する「O」が7セグメント表示器に表示され、一方、当該役物比率が所定の範囲内ではない場合には、エラーを示す「E」が7セグメント表示器に表示される構成としてもよい。役物比率に関する表示を行なった後、連続役物比率に関する表示を行なうことを示す「2」が7セグメント表示器に表示され、当該連続役物比率が所定の範囲内である場合(具体的には、連続役物比率が0.600以下の場合)には、OKを意味する「O」が7セグメント表示器に表示され、一方、当該連続役物比率が所定の範囲内ではない場合には、エラーを示す「E」が7セグメント表示器に表示される構成としてもよい。連続役物比率に関する表示を行なった後、払出比率(通常モード時)に関する表示を行なうことを示す「2」が7セグメント表示器に表示され、当該払出比率(通常モード時)が所定の範囲内である場合(具体的には、払出比率(通常モード時)が0.60から0.70の範囲内である場合)には、OKを意味する「O」が7セグメント表示器に表示され、一方、当該払出比率(通常モード時)が所定の範囲内ではない場合には、エラーを示す「E」が7セグメント表示器に表示される構成としてもよい。
More specifically, for example, when the
このような構成によれば、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を簡易的に速やかに検査することが可能となる。また、7セグメント表示器は消費電力が少ないため、パチンコ機10の電源がオフの状態であっても、パチンコ機10の内部に設けられたコンデンサやバッテリー等による少ない電力のみで遊技履歴情報を検査することが可能となる。
This configuration makes it possible to easily and quickly check game history information such as the ratio of game devices. In addition, because the seven-segment display consumes little power, it is possible to check game history information using only a small amount of power from a capacitor, battery, etc. installed inside the
また、パチンコ機10に記憶されている遊技履歴情報に関連した情報を7セグメント表示器に常に表示させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技モードから検査モードに切り替えることなく、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を簡易的に速やかに検査することが可能となる。また、検査モードを有さないパチンコ機10においても、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を簡易的に速やかに検査することが可能となる。さらに、当該7セグメント表示器がパチンコ機10の背面に設けられている構成とすれば、当該7セグメント表示器が遊技者の視界に入らないので、遊技者が当該7セグメント表示器の表示が気になってしまい、遊技に集中できなくなってしまうことを抑制することができる。一方、パチンコ機10の検査者が当該パチンコ機10の遊技履歴情報を検査する場合には、ヒンジ15によって支持されているパチンコ機本体12を手前に回動させ、パチンコ機本体12の背面に設けられた7セグメント表示器の表示を確認すればよいため、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を簡易的に速やかに検査することが可能となる。なお、7セグメント表示器の代わりに、7つ以外の個数の発光ダイオードによって構成されたセグメント表示器など、遊技履歴情報を認識可能な態様で表示可能な他の表示器を採用してもよい。
In addition, the seven-segment display may be configured to always display information related to the game history information stored in the
<態様21>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、音声発光制御装置90が遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、主制御装置60の主側CPU62xが初期設定処理において主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを含む信号を音声発光制御装置90に送信する構成とし、音声発光制御装置90は、取得した賞球数データと、主制御装置60から送信される遊技球の入球情報とに基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該算出した遊技履歴情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる構成としてもよい。
<
In the first embodiment and the other aspects, the sound and light emitting
このような構成によれば、音声発光制御装置90が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアにアクセスすることができない構成や、音声発光制御装置90が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データの記憶位置(メモリアドレス)を把握することができない構成であっても、音声発光制御装置90が主側ROM63の賞球数データ記憶エリアに記憶されている賞球数データを取得することが可能となり、遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。また、主制御装置60の代わりに音声発光制御装置90が遊技履歴情報を算出するので、主制御装置60の処理負荷を大幅に低減させることができる。
With this configuration, even if the audio and light emitting
<態様22>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様は、遊技モードから検査モードに移行可能なパチンコ機10に限らず、遊技モードから他のモードに移行可能な遊技機に対しても適用することができる。例えば、高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグの状態、記憶されている保留情報の内容等、遊技に関する処理の状態を表示可能な遊技状態表示モードを備える遊技機に対しても適用することができる。
<
The first embodiment and the other aspects described above can be applied not only to the
<態様23>
図26は、第1実施形態の態様23におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。この態様23では、遊技履歴管理チップ300は設けられておらず、上述した遊技履歴情報を主側CPU62xが算出するように構成されている。また、主側RAM64は、2つのエリア(第1エリア及び第2エリア)に区分されており、主側RAM64の第1エリアは、遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するためのプログラム等を展開する領域として用いられ、主側RAM64の第2エリアは、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための処理(以下、遊技履歴用処理ともいう。)を実行するためのプログラム等を展開する領域として用いられる。そして、主側CPU62xは、遊技の進行に関する処理(遊技履歴用処理以外の処理)の実行時には、情報の書き込みを主側RAM64の第1エリアに対してのみ実行し、遊技履歴用処理の実行時には、情報の書き込みを主側RAM64の第2エリアに対してのみ実行する。
<
26 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
また、主側RAM64の第1エリアは、後述する8ビットの入球検知情報記憶エリア、スタック領域等としても用いられる。また、主側RAM64の第2エリアは、後述する8ビットのバッファエリア、賞球集計用バッファ、演算用バッファ、演算結果用バッファ、スタック領域等としても用いられる。これらの詳細については後述する。
The first area of the
また、入出力ポート62aには、遊技履歴情報表示部45zが接続されている。遊技履歴情報表示部45zは、4つの7セグメント表示器によって構成されており、パチンコ機10の背面に設けられている。後述するように、主側CPU62xによって算出された遊技履歴情報は、この遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示される。
The input/
図27は、第1実施形態の態様23の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。なお、本態様においても、タイマ割込み処理は、上記第1実施形態と同様に、4msec周期で起動される。上述した第1実施形態のタイマ割込み処理(図13)との違いは、ステップS10606に示した入球検知処理の内容が異なっている点と、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための遊技履歴用処理が本タイマ割込み処理の最後の処理(ステップS10616)として追加されている点と、遊技履歴管理チップに入球検知情報を出力する処理である入球検知情報出力処理(図13におけるステップS10207の処理)が省略されている点であり、その他の処理については、上述した第1実施形態のタイマ割込み処理(図13)において説明した処理と同じである。以下では、図27に示したステップS10606の入球検知処理と、ステップS10616に示した遊技履歴用処理について説明する。
Figure 27 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
図28は、第1実施形態の態様23の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する入球検知処理を示すフローチャートである。この態様23の入球検知処理では、前回(1回前)のタイマ割込み処理において入力ポート62bのビットに情報が無し(「0」)と判定され、今回のタイマ割り込み処理において入力ポート62bのビットに情報が有り(「1」)と判定され、かつ、当該タイマ割込み処理においてその後再び当該ビットに情報が有り(「1」)と判定された場合に、当該ビットに対応する入球口に遊技球が入球したと判定する。以下、入球検知処理の一例について説明する。
Figure 28 is a flowchart showing the ball entry detection process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS10701では、上述した入力ポート62bの上記第0~第7ビットD0~D7(図14)に現状格納されている情報(以下、入球判定用情報とも呼ぶ)を読み込み、ステップS10702として、読み込んだ入球判定用情報を8ビットのバッファである第1バッファに格納する。すなわち、第1バッファは、今回のタイマ割込み処理において入力ポート62bの各ビットから読み込んだ入球判定用情報を格納するためのバッファである。なお、後述する第2バッファは、前回のタイマ割込み処理において入力ポート62bの各ビットから読み込んだ入球判定用情報を格納する8ビットのバッファである。また、本態様では、第1バッファ及び第2バッファは、主側RAM64の第1エリアに設けられている。ステップS10702を実行した後、ステップS10703に進む。
In step S10701, the information currently stored in the 0th to 7th bits D0 to D7 (FIG. 14) of the
ステップS10703では、主側RAM64に設けられた入球判定カウンタに8をセットする。その後、10704に進む。なお、入球判定カウンタの数値情報は、上述した第1実施形態の入球判定処理(図16)にて用いられた入球判定カウンタ(ステップS10401)と同様に、8個の各入球口のビットに対応している。具体的には、本態様では、入球判定カウンタの数値情報の「8」は大入賞口36aの第0ビットD0、「7」は第1始動口33の第1ビットD1、「6」は第2始動口34の第2ビットD2、「5」は第1入賞口32aの第3ビットD3、「4」は第2入賞口32bの第4ビットD4、「3」は第3入賞口32cの第5ビットD5、「2」はスルーゲート35の第6ビットD6、「1」は排出通路の第7ビットD7に、それぞれ対応している。
In step S10703, the ball entry determination counter provided in the
ステップS10704では、第2バッファにおける入球判定カウンタの数値情報に対応したビットに入球判定用情報があるか否か、すなわち当該ビットに格納されている入球判定用情報が「1」であるか否かを判定する。ステップS10704において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」ではないと判定した場合には(S10704:NO)、ステップS10705に進む。一方、ステップS10704において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」であると判定した場合には(S10704:YES)、後述するステップS10705からステップS10709までの処理を実行せずに、ステップS10710に進む。 In step S10704, it is determined whether or not there is scoring determination information in the bit corresponding to the numerical information of the scoring determination counter in the second buffer, i.e., whether or not the scoring determination information stored in that bit is "1". If it is determined in step S10704 that the scoring determination information is not "1" (S10704: NO), the process proceeds to step S10705. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10704 that the scoring determination information is "1" (S10704: YES), the process proceeds to step S10710 without executing the processes from step S10705 to step S10709 described below.
ステップS10705では、第1バッファにおける入球判定カウンタの数値情報に対応したビットに入球判定用情報があるか否か、すなわち当該ビットに格納されている入球判定用情報が「1」であるか否かを判定する。ステップS10705において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」であると判定した場合には(S10705:YES)、ステップS10706に進む。一方、ステップS10705において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」ではないと判定した場合には(S10705:NO)、後述するステップS10706からステップS10709までの処理を実行せずに、ステップS10710に進む。 In step S10705, it is determined whether or not there is scoring determination information in the bit corresponding to the numerical information of the scoring determination counter in the first buffer, i.e., whether or not the scoring determination information stored in that bit is "1". In step S10705, if it is determined that the scoring determination information is "1" (S10705: YES), the process proceeds to step S10706. On the other hand, in step S10705, if it is determined that the scoring determination information is not "1" (S10705: NO), the process proceeds to step S10710 without executing the processes from step S10706 to step S10709 described below.
ステップS10706では、現状の入力ポート62bにおける入球判定カウンタの数値情報に対応したビットに入球判定用情報あるか否か、すなわち当該ビットに格納されている入球判定用情報がが「1」であるか否かを判定する。ステップS10706において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」であると判定した場合には(S10706:YES)、ステップS10707に進む。一方、ステップS10706において、当該入球判定用情報が「1」ではないと判定した場合には(S10706:NO)、後述するステップS10707からステップS10709までの処理を実行せずに、ステップS10710に進む。
In step S10706, it is determined whether or not there is scoring determination information in the bit corresponding to the numerical information of the scoring determination counter in the
ステップS10707では、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報がどの種別の入球口に対応したビットを示す情報であるのかを判定し、当該ビットに対応する入球口に遊技球が入球したことを示す入球フラグをONにする。具体的には、例えば、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報が大入賞口36aに対応したビットを示す情報であると判定した場合には、大入賞口36aに遊技球が入球したことを示す大入賞口入球フラグをONにする。また、例えば、現状の入球判定カウンタの数値情報が第2始動口34に対応したビットを示す情報であると判定した場合には、第2始動口34に遊技球が入球したことを示す第2始動口入球フラグをONにする。ステップS10707を実行した後、ステップS10708に進む。
In step S10707, it is determined which type of ball entry port the current numerical information of the ball entry judgment counter indicates the bit corresponding to, and a ball entry flag indicating that the game ball has entered the ball entry port corresponding to the bit is turned ON. Specifically, for example, if it is determined that the current numerical information of the ball entry judgment counter indicates the bit corresponding to the large
ステップS10708では、ステップS10707において入球フラグがONにされた、すなわち、遊技球が入球したと判定された入球口に対応した賞球カウンタの数値情報を1加算する。具体的には、例えば、大入賞口入球フラグがONにされた場合には15個賞球カウンタを1加算し、第2始動口入球フラグがONにされた場合には3個賞球カウンタを1加算する。ステップS10708を実行した後、ステップS10709に進む。 In step S10708, the numerical information of the prize ball counter corresponding to the ball entry port where the ball entry flag was set to ON in step S10707, i.e., where it was determined that a game ball has entered, is incremented by 1. Specifically, for example, if the large prize entry port ball entry flag is set to ON, the 15 prize ball counter is incremented by 1, and if the second start port ball entry flag is set to ON, the 3 prize ball counter is incremented by 1. After executing step S10708, proceed to step S10709.
ステップS10709では、入球判定カウンタを1減算し、その後、ステップS10710において、入球判定カウンタが「0」であるか否かを判定する。 In step S10709, the goal determination counter is decremented by 1, and then in step S10710, it is determined whether the goal determination counter is "0".
ステップS10710において、入球判定カウンタが「0」ではないと判定した場合には(S10710:NO)、ステップS10709において更新した入球判定カウンタの数値情報に応じたビットについて、ステップS10704~ステップS10708の処理を実行する。かかるステップS10704~ステップS10708の処理を、ステップS10703においてセットした数値情報分実行した場合には、入球判定カウンタが「0」となり、ステップS10710において肯定判定(S10710:YES)をすることとなり、ステップS10711に進む。 If it is determined in step S10710 that the goal counter is not "0" (S10710: NO), the process executes steps S10704 to S10708 for the bit corresponding to the numerical information of the goal counter updated in step S10709. If the process executes steps S10704 to S10708 for the numerical information set in step S10703, the goal counter becomes "0", a positive determination is made in step S10710 (S10710: YES), and the process proceeds to step S10711.
ステップS10711では、第1バッファに格納されている8ビットの入球判定用情報を第2バッファに格納(コピー)する。これにより、今回のタイマ割込み処理において入力ポート62bから取得された入球判定用情報が次回のタイマ割込み処理における入球検知処理において参照されることになる。ステップS10711を実行した後、ステップS10712に進む。
In step S10711, the 8-bit information for scoring a ball stored in the first buffer is stored (copied) in the second buffer. As a result, the information for scoring a ball obtained from
ステップS10712では、今回のタイマ割込み処理の入球検知処理において遊技球の入球が検知されたことを示す入球検知情報を、8ビットの情報を記憶可能な入球検知情報記憶エリアに記憶する。具体的には、入球検知情報記憶エリアは、上記の8個の入球口のそれぞれに対応する各ビット毎に、入球フラグがONになっている場合には「1」を、入球フラグがOFFになっている場合には「0」を入球検知情報として記憶する。例えば、今回のタイマ割込み処理において入球検知処理を実行した結果、大入賞口入球フラグ及び第2始動口入球フラグがONであり、他の入球口に対応する入球フラグがOFFである場合には、入球検知情報記憶エリアには、「00000101」という8ビットの入球検知情報が記憶される。この入球検知情報記憶エリアに記憶された8ビットの入球検知情報は、後述する遊技履歴処理において参照される。ステップS10712を実行した後、本入球検知処理を終了する。 In step S10712, the ball entry detection information indicating that a game ball has been detected in the ball entry detection process of the current timer interrupt process is stored in a ball entry detection information storage area capable of storing 8-bit information. Specifically, the ball entry detection information storage area stores, for each bit corresponding to each of the above-mentioned eight ball entry ports, "1" if the ball entry flag is ON, and "0" if the ball entry flag is OFF, as ball entry detection information. For example, as a result of executing the ball entry detection process in the current timer interrupt process, if the big prize entry port ball entry flag and the second start port ball entry flag are ON and the ball entry flags corresponding to the other ball entry ports are OFF, the ball entry detection information storage area stores 8-bit ball entry detection information of "00000101". The 8-bit ball entry detection information stored in this ball entry detection information storage area is referenced in the game history process described later. After executing step S10712, this ball entry detection process is terminated.
図29は、第1実施形態の態様23の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する遊技履歴用処理を示すフローチャートである。この遊技履歴用処理では、役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出し、これらを遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させるための処理を実行する。具体的には、役物比率を算出し、算出した役物比率を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに5秒間表示させる。その後、連続役物比率を算出し、算出した連続役物比率を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに5秒間表示させる。その後、再び役物比率を算出し、算出した役物比率を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに5秒間表示させる。このように、役物比率、連続役物比率を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに交互に表示させる。以下、具体的な処理の一例について説明する。
Figure 29 is a flowchart showing the game history processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS10801では、主側CPU62x内のレジスタに格納されている情報(以下、レジスタ情報ともいう)を主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に退避させる退避処理を実行する。この態様23では、タイマ割込み処理(図27)において、遊技履歴用処理(図27のステップS10616)が実行される前には、遊技履歴用処理以外の処理である遊技の進行に関する処理(図27のステップS10601~10615の処理)が実行されているため、当該退避処理では、遊技の進行に関するレジスタ情報が主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に退避されることになる。具体的には、主側CPU62xにおけるスタックポインタの値(第1エリアのスタック領域の最上段を示すアドレス値)を主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域の底に退避させる(Pushする)。そして、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに、主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域の最上段を示すアドレス値を設定する。その後、主側CPU62xに設定されたスタックポインタに示されたスタック領域(主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域の最上段)に、主側CPU62x内のレジスタに格納されているレジスタ情報を順次退避させる(Pushする)。この退避処理を実行することにより、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタには、主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域のアドレス値が設定されるので、主側CPU62xは、以下に説明する遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する処理を、主側RAM64の第2エリアを利用して実行することが可能となる。ステップS10801を実行した後、ステップS10802に進む。
In step S10801, a save process is executed to save information stored in the register in the
ステップS10802では、主側RAM64の第2エリアに格納されている異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。異常フラグは、後述する賞球集計値が異常な値である場合にONにされるフラグである。ステップS10802において、異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(S10802:YES)、ステップS10803に進み、賞球集計値を0クリアする。その後、ステップS10804に進み、異常フラグをOFFにする。その後、ステップS10805に進む。一方、ステップS10802において、異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(S10802:NO)、ステップS10803及びステップS10804の処理を実行することなく、ステップS10805に進む。
In step S10802, it is determined whether the abnormal flag stored in the second area of the
ステップS10805では、入球検知情報記憶エリア及びバッファエリアの対応するビット毎にOR処理を実行し、各OR処理の結果(論理和)をバッファエリアの対応するビットに記憶(上書き)する。この処理の詳細については後述する。なお、バッファエリアは、入球検知情報記憶エリアと同じ8ビットの情報を記憶可能な領域であり、主側RAM64の第2エリアに設けられている。ステップS10805を実行した後、ステップS10806に進む。
In step S10805, an OR operation is performed for each corresponding bit in the ball entry detection information storage area and the buffer area, and the result of each OR operation (logical sum) is stored (overwritten) in the corresponding bit in the buffer area. Details of this process will be described later. The buffer area is an area capable of storing the same 8 bits of information as the ball entry detection information storage area, and is provided in the second area of the
ステップS10806では、バッファエリアの8個のビットのうちの少なくとも1個のビットに入球検知情報が有るか否か(1個以上のビットに「1」が格納されているか否か)を判定する。ステップS10806において、バッファエリアの少なくとも1個のビットに入球検知情報が有ると判定した場合には(S10806:YES)、ステップS10807に進む。 In step S10806, it is determined whether or not there is ball-entry detection information in at least one of the eight bits in the buffer area (whether or not one or more bits store a "1"). If it is determined in step S10806 that there is ball-entry detection information in at least one bit in the buffer area (S10806: YES), the process proceeds to step S10807.
ステップS10807では、バッファエリアの8個のビットのうち、後述する賞球集計処理の対象とするビットを設定する対象設定処理を実行する。本態様では、1回の対象設定処理では、賞球集計処理の対象として連続する2個のビットを設定する。また、後述するように、次回または次回以降のタイマ割込み処理において対象設定処理が実行された場合には、前回の対象設定処理において設定した2個のビットの隣に位置する2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の対象として設定する。このように、賞球集計処理の対象の2個のビットを順次隣にシフトしていく。なお、8個のビットのうち最後の2個のビットが賞球集計処理の対象として設定された後は、次に実行される対象設定処理において、先頭の2個のビットを賞球集計処理の対象として再び設定する。このように、本態様では、バッファエリアの8個のビットの中から賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する2個のビットの順序が予め定められている。ステップS10807を実行した後、ステップS10808に進み、設定されたビットに対応した賞球集計処理を実行する。ここで、ステップS10805からステップS10808までの処理の具体的な一例について、図30を用いて説明する。 In step S10807, a target setting process is executed to set the bits to be the target of the prize ball counting process, which will be described later, among the eight bits in the buffer area. In this embodiment, in one target setting process, two consecutive bits are set as the target of the prize ball counting process. Also, as described later, when the target setting process is executed in the next or subsequent timer interruption process, two consecutive bits located next to the two bits set in the previous target setting process are set as the target of the prize ball counting process. In this way, the two bits to be the target of the prize ball counting process are shifted sequentially to the neighboring bits. Note that after the last two bits of the eight bits are set as the target of the prize ball counting process, the first two bits are set again as the target of the prize ball counting process in the next target setting process. In this way, in this embodiment, the order of the two bits to be set as the target of the prize ball counting process from the eight bits in the buffer area is predetermined. After executing step S10807, the process proceeds to step S10808, and the prize ball counting process corresponding to the set bits is executed. Here, a specific example of the processing from step S10805 to step S10808 is described using FIG. 30.
図30は、第1実施形態の態様23の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する具体的な処理の一例を示す説明図である。上述したように、入球検知情報記憶エリアは、主側RAM64の第1エリアに設けられた8ビットの記憶領域であり、各ビットは、各入球口に対応している。具体的には、本態様では、入球検知情報記憶エリアの第0ビットD0は大入賞口36a、第1ビットD1は第1始動口33、第2ビットD2は第2始動口34、第3ビットD3は第1入賞口32a、第4ビットD4は第2入賞口32b、第5ビットD5は第3入賞口32c、第6ビットD6はスルーゲート35、第7ビットD7は排出通路にそれぞれ対応している。
Figure 30 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of a specific process executed by the main MPU 62 (
バッファエリアは、主側RAM64の第2エリアに設けられた8ビットの記憶領域であり、各ビットは、各入球口に対応している。具体的には、本態様では、バッファエリアの第0ビットD0は大入賞口36a、第1ビットD1は第1始動口33、第2ビットD2は第2始動口34、第3ビットD3は第1入賞口32a、第4ビットD4は第2入賞口32b、第5ビットD5は第3入賞口32c、第6ビットD6はスルーゲート35、第7ビットD7は排出通路にそれぞれ対応している。すなわち、バッファエリアの各ビットは、入球検知情報記憶エリアの各ビットにそれぞれ対応している。
The buffer area is an 8-bit memory area provided in the second area of the
上述した入球検知処理(図28)において、大入賞口36a等の入球口に遊技球が入球したと判定されると、入球検知情報記憶エリアの8個のビットのうち、遊技球が入球したと判定された入球口に対応したビットがON(「1」)にされる。
In the ball entry detection process described above (Figure 28), when it is determined that a game ball has entered an entry port such as the large
図30(A1)には、n回目のタイマ割込み処理が実行された場合における処理の一例が示されている。このn回目のタイマ割込み処理では、入球検知処理において、第2始動口34及び第1入賞口32aに遊技球が入球したと判定されており、入球検知情報記憶エリアの8個のビットの値は、「00001100」となっている。また、OR処理を実行する前のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、「00000000」となっている。したがって、OR処理を実行した後のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、「00001100」となる。これにより、タイマ割込み処理が実行される毎に更新される入球検知情報記憶エリアにおける入球検知情報が、後述する賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定されて当該処理が実行されるまでバッファエリアに保持されることになる。
Figure 30 (A1) shows an example of processing when the nth timer interrupt processing is executed. In this nth timer interrupt processing, the ball entry detection processing determines that game balls have entered the
n回目のタイマ割込み処理では、OR処理が実行された後のバッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7のうち、第0ビットD0と第1ビットD1の2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。 In the nth timer interrupt process, of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area after the OR process is performed, the two consecutive bits D0 and D1 are set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process.
賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第0ビットD0(大入賞口36aに対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数及び連続役物賞球数に「15」を加算する。一方、第0ビットD0が「0」である場合には、当該加算を行わない。なお、本態様では、賞球集計用バッファはリングバッファとして構成されており、直近の所定期間に払い出された賞球数が記憶されるように構成されている。また、連続役物賞球数は、連続役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数であり、大入賞口36aへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数を意味する。
In the prize ball tallying process, if the 0th bit D0 (the bit corresponding to the
さらに、賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第1ビットD1(第1始動口33に対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数に「3」を加算する。一方、第1ビットD1が「0」ある場合には、当該加算を行わない。 Furthermore, in the prize ball tallying process, if the first bit D1 (the bit corresponding to the first starting hole 33) set as the processing target of the prize ball tallying process is "1", "3" is added to the total number of prize balls stored in the prize ball tallying buffer. On the other hand, if the first bit D1 is "0", this addition is not performed.
この図30(A1)に示した例では、第0ビットD0は「0」であり、第1ビットD1も「0」であるため、上述した加算は行わない。 In the example shown in Figure 30 (A1), the 0th bit D0 is "0" and the 1st bit D1 is also "0", so the above-mentioned addition is not performed.
賞球集計処理が実行された後は、バッファエリアの賞球集計処理の対象として設定された2個のビット(第0ビットD0及び第1ビットD1)は0にクリアされる。 After the prize ball counting process has been executed, the two bits (the 0th bit D0 and the 1st bit D1) set as targets for the prize ball counting process in the buffer area are cleared to 0.
図30(A2)には、n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理が実行された場合における処理の一例が示されている。このn+1回目のタイマ割込み処理では、入球検知処理において、第2入賞口32bに遊技球が入球したと判定されており、入球検知情報記憶エリアの8個のビットの値は、「00010000」となっている。また、OR処理を実行する前のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、上述したn回目のタイマ割込み処理における賞球集計処理後のバッファエリアと同じ「00001100」となっている。したがって、OR処理を実行した後のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、「00011100」となる。
Figure 30 (A2) shows an example of processing when the n+1th timer interrupt processing is executed. In this n+1th timer interrupt processing, the ball entry detection processing determines that a game ball has entered the second winning
n+1回目のタイマ割込み処理では、OR処理が実行された後のバッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7のうち、第2ビットD2と第3ビットD3の2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。 In the n+1th timer interrupt process, of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area after the OR process is performed, two consecutive bits, the second bit D2 and the third bit D3, are set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process.
賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第2ビットD2(第2始動口34に対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数及び役物賞球数に「3」を加算する。一方、第2ビットD2が「0」である場合には、当該加算を行わない。なお、役物賞球数は、役物作動によって賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数であり、第2始動口34及び大入賞口36aへの遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数を意味する。
In the prize ball tallying process, if the second bit D2 (the bit corresponding to the second start port 34) set as the processing target of the prize ball tallying process is "1", "3" is added to the total number of prize balls and the number of special prize balls stored in the prize ball tallying buffer. On the other hand, if the second bit D2 is "0", the addition is not performed. The number of special prize balls is the number of game balls paid out as prize balls by the operation of the special device, and means the number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on the entry of game balls into the
さらに、賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第3ビットD3(第1入賞口32aに対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数に「10」を加算する。一方、第3ビットD3が「0」ある場合には、当該加算を行なわない。
Furthermore, in the prize ball tallying process, if the third bit D3 (the bit corresponding to the first winning
この図30(A2)に示した例では、第2ビットD2は「1」であるため、総賞球数及び役物賞球数に「3」を加算する。また、第3ビットD3は「1」であるため、総賞球数に「10」を加算する。 In the example shown in FIG. 30 (A2), the second bit D2 is "1", so "3" is added to the total number of winning balls and the number of special winning balls. Also, the third bit D3 is "1", so "10" is added to the total number of winning balls.
賞球集計処理が実行された後は、バッファエリアの賞球集計処理の対象として設定された2個のビット(第2ビットD2及び第3ビットD3)は0にクリアされる。 After the prize ball counting process is executed, the two bits (second bit D2 and third bit D3) set as targets for the prize ball counting process in the buffer area are cleared to 0.
図30(A3)には、n+2回目のタイマ割込み処理が実行された場合における処理の一例が示されている。このn+2回目のタイマ割込み処理では、入球検知処理において、スルーゲート35に遊技球が入球(通過)したと判定されており、入球検知情報記憶エリアの8個のビットの値は、「01000000」となっている。また、OR処理を実行する前のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、上述したn+1回目のタイマ割込み処理における賞球集計処理後のバッファエリアと同じ「00010000」となっている。したがって、OR処理を実行した後のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、「01010000」となる。
Figure 30 (A3) shows an example of processing when the n+2th timer interrupt processing is executed. In this n+2th timer interrupt processing, the ball entry detection processing determines that a game ball has entered (passed through) the through
n+2回目のタイマ割込み処理では、OR処理が実行された後のバッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7のうち、第4ビットD4と第5ビットD5の2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。 In the n+2th timer interrupt process, of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area after the OR process is performed, two consecutive bits, the fourth bit D4 and the fifth bit D5, are set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process.
賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第4ビットD4(第2入賞口32bに対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数に「10」を加算する。一方、第4ビットD4が「0」である場合には、当該加算を行なわない。
In the prize ball tallying process, if the fourth bit D4 (the bit corresponding to the
さらに、賞球集計処理では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された第5ビットD5(第3入賞口32cに対応するビット)が「1」である場合には、賞球集計用バッファに記憶されている総賞球数に「10」を加算する。一方、第5ビットD5が「0」ある場合には、当該加算を行なわない。
Furthermore, in the prize ball tallying process, if the fifth bit D5 (the bit corresponding to the third winning
この図30(A3)に示した例では、第4ビットD4は「1」であるため、総賞球数に「10」を加算する。また、第5ビットD5は「0」であるため、上述した加算を行なわない。 In the example shown in FIG. 30 (A3), the fourth bit D4 is "1", so "10" is added to the total number of winning balls. Also, the fifth bit D5 is "0", so the above-mentioned addition is not performed.
賞球集計処理が実行された後は、バッファエリアの賞球集計処理の対象として設定された2個のビット(第4ビットD4及び第5ビットD5)は0にクリアされる。 After the prize ball counting process has been executed, the two bits (fourth bit D4 and fifth bit D5) set as targets for the prize ball counting process in the buffer area are cleared to 0.
図30(A4)には、n+3回目のタイマ割込み処理が実行された場合における処理の一例が示されている。このn+3回目のタイマ割込み処理では、入球検知処理において、大入賞口36aに遊技球が入球したと判定されており、入球検知情報記憶エリアの8個のビットの値は、「00100001」となっている。また、OR処理を実行する前のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、上述したn+2回目のタイマ割込み処理における賞球集計処理後のバッファエリアと同じ「01000000」となっている。したがって、OR処理を実行した後のバッファエリアの8個のビットの値は、「01100001」となる。
Figure 30 (A4) shows an example of processing when the n+3th timer interrupt processing is executed. In this n+3th timer interrupt processing, the ball entry detection processing determines that a game ball has entered the
n+3回目のタイマ割込み処理では、OR処理が実行された後のバッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7のうち、第6ビットD6と第7ビットD7の2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。 In the n+3 timer interrupt process, of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area after the OR process is performed, two consecutive bits, the sixth bit D6 and the seventh bit D7, are set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process.
ただし、本態様では、第6ビットD6はスルーゲート35に対応しており、第7ビットD7は排出通路に対応している。そして、スルーゲート35及び排出通路には賞球は設定されていない。したがって、本態様では、第6ビットD6及び第7ビットD7が賞球集計処理の対象として設定された場合には、賞球集計処理において総賞球数等への加算を行なわない。その後、バッファエリアの賞球集計処理の対象として設定された2個のビット(第6ビットD6及び第7ビットD7)は0にクリアされる。
However, in this embodiment, the sixth bit D6 corresponds to the through
その後、n+4回目のタイマ割込み処理では、再び第0ビットD0及び第1ビットD1を賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。以降、同様の処理を繰り返し実行する。ただし、後述するように、バッファエリアのビットに入球検知情報が1つも無い(全てのビットが「0」である)場合には、対象設定処理(ステップS10807)及び賞球集計処理(ステップS10808)は実行されない。また、本態様では、バッファエリアのビットに入球検知情報が1つも無い(全てのビットが「0」である)状態から、再び、バッファエリアの少なくとも1個のビットに入球検知情報が有る状態となり、対象設定処理が実行された場合には、前回の対象設定処理において賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された2個のビットを記憶しており、当該2個のビットの隣に位置する連続する2個のビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。なお、前回の対象設定処理において賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定された2個のビットが第6ビットD6及び第7ビットD7である場合には、第0ビットD0及び第1ビットD1の2個の連続するビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する。 After that, in the n+4th timer interrupt process, the 0th bit D0 and the 1st bit D1 are again set as the processing target of the prize ball counting process. Thereafter, the same process is repeatedly executed. However, as described below, if there is no ball entry detection information in the bits of the buffer area (all bits are "0"), the target setting process (step S10807) and the prize ball counting process (step S10808) are not executed. Also, in this embodiment, from a state in which there is no ball entry detection information in the bits of the buffer area (all bits are "0"), a state in which there is ball entry detection information in at least one bit of the buffer area again occurs, and when the target setting process is executed, the two bits set as the processing target of the prize ball counting process in the previous target setting process are stored, and the two consecutive bits located next to the two bits are set as the processing target of the prize ball counting process. In addition, if the two bits set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process in the previous target setting process are the sixth bit D6 and the seventh bit D7, the two consecutive bits, the zeroth bit D0 and the first bit D1, are set as the processing targets for the prize ball counting process.
以上説明したように、本態様では、1回のタイマ割込み処理においてバッファエリアの8個のビットのうち2個のビットを賞球集計処理の対象として設定するので、バッファエリアの少なくとも1個のビットに入球検知情報が有る場合には、タイマ割込み処理が4回実行されることによって、バッファエリアの8個のビットの全てに対して賞球集計処理が実行されることになる。 As described above, in this embodiment, two of the eight bits in the buffer area are set as the target for the prize ball tallying process in one timer interrupt process, so if there is ball entry detection information in at least one bit in the buffer area, the timer interrupt process is executed four times, and the prize ball tallying process is executed for all eight bits in the buffer area.
図29の説明に戻る。ステップS10808の賞球集計処理を実行した後、ステップS10809に進む。 Return to the explanation of Figure 29. After executing the prize ball tallying process in step S10808, proceed to step S10809.
ステップS10809では、演算結果表示制御処理を実行する。具体的には、後述する演算結果用バッファに保存されている値(算出した遊技履歴情報である役物比率又は連続役物比率)を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させる制御を実行する。ステップS10809を実行した後、ステップS10810に進む。
In step S10809, a calculation result display control process is executed. Specifically, control is executed to display the value (the combination ratio or continuous combination ratio, which is the calculated game history information) stored in the calculation result buffer described later on the game history
ステップS10810では、遊技履歴情報を算出する演算処理の実行タイミングであるか否かを判定する。具体的には、パチンコ機10の電源投入から所定時間(本態様では30分)が経過した場合、または、演算処理の前回の実行から5秒が経過した場合に、演算処理を実行するタイミングであると判定する。ステップS10810において、演算処理を実行するタイミングであると判定した場合には(S10810:YES)、ステップS10811に進む。一方、ステップS10810において、演算処理を実行するタイミングではないと判定した場合には(S10810:NO)、後述するステップS10811及びステップS10812の処理を実行せずに、ステップS10813に進む。
In step S10810, it is determined whether it is time to execute a calculation process to calculate game history information. Specifically, it is determined that it is time to execute the calculation process when a predetermined time (30 minutes in this embodiment) has passed since the
ステップS10811では、演算処理(後述するタスク1及びタスク2)において算出する遊技履歴情報の種別を設定する。本態様では、演算対象の遊技履歴情報の種別として、役物比率及び連続役物比率を交互に設定する。その後、ステップS10812に進み、後述するタスク処理(ステップS10814)において実行する次回のタスクとして、タスク1を指定する。ステップS10812を実行した後、ステップS10813に進む。
In step S10811, the type of game history information to be calculated in the calculation process (
ステップS10813では、上述した退避処理において主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に退避されていたレジスタ情報を、主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させる処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xに設定されたスタックポインタに示されたスタック領域(主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域の最上段)から、順次、退避されていたレジスタ情報を、主側CPU62x内のレジスタに復帰させる(Popする)。その後、第2エリアのスタック領域の底に退避されていたスタックポインタの値(第1エリアのスタック領域の最上段を示すアドレス値)を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに復帰させる(Popする)。この復帰処理を実行することにより、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタには、主側RAM64の第1エリアのスタック領域のアドレス値が設定されるので、主側CPU62xは、再び、主側RAM64の第1エリアを利用して遊技の進行に関する処理を実行することが可能となる。その後、本遊技履歴用処理を終了する。
In step S10813, a process is executed to restore the register information saved in the stack area of the second area of the
ステップS10806の説明に戻る。ステップS10806において、バッファエリアのビットに入球検知情報が1つも無い(全てのビットが「0」である)と判定した場合には(S10806:NO)、ステップS10814に進む。 Returning to the explanation of step S10806, if it is determined in step S10806 that there is no ball-entry detection information in the bits of the buffer area (all bits are "0") (S10806: NO), proceed to step S10814.
ステップS10814では、下記の3つのタスクのうち、指定されているいずれか1つのタスクを実行する。タスクが指定されていない場合には、タスク3を実行する。すなわち、1回のタイマ割込み処理において3つのタスクを順次実行するのではなく、1回のタイマ割込み処理では3つのタスクのうちの指定されたいずれか1つのタスクのみを実行する。
In step S10814, one of the following three tasks is executed as specified. If no task is specified,
[タスク1]
演算対象として設定された遊技履歴情報を算出するために必要となる被除数及び除数を演算用バッファに保存する。具体的には、例えば、役物比率を算出するように設定されている場合には、被除数として役物賞球数を、除数として総賞球数を演算用バッファに保存する。また、例えば、連続役物比率を算出するように設定されている場合には、被除数として連続役物賞球数を、除数として総賞球数を演算用バッファに保存する。その後、次回以降のタイマ割込み処理においてステップS10806の処理に進んだ場合に実行する次回タスクとしてタスク2を指定する。
[Task 1]
The dividend and divisor required to calculate the game history information set as the calculation target are stored in the calculation buffer. Specifically, for example, when it is set to calculate the ratio of the accessory, the number of accessory prize balls is stored as the dividend, and the total number of prize balls is stored as the divisor in the calculation buffer. Also, for example, when it is set to calculate the ratio of consecutive accessory, the number of consecutive accessory prize balls is stored as the dividend, and the total number of prize balls is stored as the divisor in the calculation buffer. After that,
[タスク2]
演算用バッファに保存されている被除数を除数で割る演算を実行し、当該演算結果(商)を演算結果用バッファに保存する。その後、次回以降のタイマ割込み処理においてステップS10806の処理に進んだ場合に実行する次回タスクとしてタスク3を指定する。
[Task 2]
The calculation is performed to divide the dividend stored in the calculation buffer by the divisor, and the calculation result (quotient) is stored in the calculation result buffer. After that,
[タスク3]
賞球集計値(役物賞球数、連続役物賞球数、総賞球数)が有効であるか否かを判定し、有効ではないと判定した場合には異常フラグをONにし、その後、次回以降のタイマ割込み処理においてステップS10806の処理に進んだ場合に実行する次回タスクとしてタスク3を指定する。一方、賞球集計値が有効であると判定した場合には、異常フラグはONにせず、次回タスクとしてタスク3を指定する。ここで、賞球集計値が有効ではない場合とは、役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合や、連続役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合、連続役物賞球数が役物賞球数を超えている場合など、賞球集計値に矛盾が生じている場合である。
[Task 3]
It is determined whether the prize ball tally values (number of accessory prize balls, number of consecutive accessory prize balls, total number of prize balls) are valid, and if it is determined that they are not valid, the abnormal flag is turned ON, and then
上述した3つのタスクのうちの指定されたタスクを実行した後、上述したステップS10809に進み、演算結果用バッファに保存されている値(役物比率又は連続役物比率)を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させる処理を実行する。本態様では、遊技履歴情報表示部45zを構成する1つ目の7セグメント表示器に遊技履歴情報の種別を示す情報を表示し、残りの3つの7セグメント表示器に遊技履歴情報の値を表示する。
After executing a specified task out of the three tasks described above, the process proceeds to step S10809 described above, and the value (role ratio or continuous role ratio) stored in the calculation result buffer is displayed on the game history
以上説明した本態様のパチンコ機10では、タイマ割込み処理に含まれる遊技の進行に関する処理(遊技履歴用処理以外の処理)は、次のタイマ割込み処理が開始されるまでの時間(本態様では4msec)よりも短い時間で終了するようにプログラムされているが、当該遊技の進行に関する処理が終了するまでに要する時間は、遊技の進行の状況に応じて変化する。一方、遊技履歴用処理は、遊技の進行には関係のない処理であるため、1回のタイマ割込み処理において、遊技履歴用処理を実行するための時間よりも、遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するための時間を優先して確保することが好ましい。また、遊技履歴用処理に含まれる各種処理(例えば、各ビットに対する賞球集計処理や演算処理等)を1回のタイマ割込み処理において連続的に実行して完結させる構成としなくても、遊技の進行には影響がない。したがって、本態様では、遊技の進行に関する処理の実行時間が遊技の進行の状況に応じて最大となった場合であっても、1回のタイマ割込み処理の実行時間(遊技の進行に関する処理の実行時間+遊技履歴用処理の実行時間)が次のタイマ割込み処理が開始されるまでの時間よりも短い時間となるように、遊技履歴用処理に含まれる各種処理を複数の処理に分割し、1回のタイマ割込み処理では当該分割された処理を実行し、タイマ割込み処理を複数回実行することによって各種処理が完結する構成とした。この結果、本態様によれば、1回のタイマ割込み処理における遊技の進行に関する処理の実行に要する時間を確保しつつ、遊技履歴用処理を実行することが可能となる。
In the
具体的には、本態様によれば、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行においては、遊技履歴情報を算出する処理である演算処理を構成する2つのタスク(タスク1及びタスク2)のうちの一のタスクを実行可能であり、タイマ割込み処理を2回実行することによって、演算処理を構成する2つのタスクの全てを実行するので、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行において2つのタスクの両方を実行する構成に比べて、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、タイマ割込み処理の実行を開始する間隔(以下では、割込み間隔ともいう)である4msecよりも長くなってしまい、タイマ割込み処理を4msecの間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。
Specifically, according to this embodiment, in one execution of the timer interrupt process, one of the two tasks (
また、本態様によれば、実行する順序が定められた一連の処理を複数のタスクに分割し、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行においては、複数のタスクのうちの一のタスクを実行した後、当該一のタスクの次に実行するタスクを指定するので、タイマ割込み処理に組み込んだ場合に当該タイマ割込み処理の実行に要する時間がタイマ割込み処理の割込み間隔よりも長くなってしまうような一連の処理であっても、タイマ割込み処理に組み込んで実行することができる。具体的には、本態様によれば、遊技履歴情報を算出する演算処理をタイマ割込み処理に組み込んだ場合に当該タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が4msecよりも長くなってしまうような構成の遊技機においても、4msecの間隔で実行されるタイマ割込み処理に当該演算処理を組み込んで実行することができる。また、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算処理は、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行において全てのタスクを実行しなくても遊技の進行に影響はないため、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間を、当該タイマ割込み処理に含まれる他の処理の実行時間に割り振ることができ、遊技機の設計の自由度を向上させることができる。 In addition, according to this aspect, a series of processes with a set execution order is divided into multiple tasks, and in one execution of the timer interrupt process, one of the multiple tasks is executed, and then the task to be executed next to the one task is specified. Therefore, even if a series of processes is incorporated into the timer interrupt process and the time required for the execution of the timer interrupt process is longer than the interrupt interval of the timer interrupt process when incorporated into the timer interrupt process, the series of processes can be incorporated into the timer interrupt process and executed. Specifically, according to this aspect, even in a gaming machine configured such that the time required for one execution of the timer interrupt process is longer than 4 msec when the arithmetic process for calculating the game history information is incorporated into the timer interrupt process executed at intervals of 4 msec, the arithmetic process can be incorporated and executed. Furthermore, since the arithmetic process for calculating the game history information does not affect the progress of the game even if all tasks are not executed in one execution of the timer interrupt process, the time required for one execution of the timer interrupt process can be allocated to the execution time of other processes included in the timer interrupt process, and the degree of freedom in designing the gaming machine can be improved.
また、本態様によれば、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行においては、バッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7の中から2個のビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定し、当該設定した処理対象のビットに対して賞球集計処理を実行可能であり、タイマ割込み処理を複数回実行することによって、バッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7の全てに対して賞球集計処理を実行する。したがって、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行において8個のビットD0~D7の全てに対して賞球集計処理を実行する構成に比べて、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、タイマ割込み処理の実行に要する時間が、タイマ割込み処理の実行を開始する間隔である4msecよりも長くなってしまい、タイマ割込み処理を4msecの間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, in one execution of the timer interrupt process, two bits out of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area are set as the processing target of the prize ball tallying process, and the prize ball tallying process can be executed for the set processing target bits. By executing the timer interrupt process multiple times, the prize ball tallying process is executed for all eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area. Therefore, the time required for one execution of the timer interrupt process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the prize ball tallying process is executed for all eight bits D0 to D7 in one execution of the timer interrupt process. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for execution of the timer interrupt process from becoming longer than 4 msec, which is the interval for starting the execution of the timer interrupt process, and making it impossible to execute the timer interrupt process at 4 msec intervals.
また、本態様によれば、バッファエリアの8個のビットD0~D7の中から2個のビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する際に、予め定められた順序で設定するので、賞球集計処理の処理対象をいずれのビットに設定するかの判定処理を実行する必要がなく、処理を簡易化することができ、この結果、処理速度を向上させることができる。さらに、判定処理を実行するために必要なプログラムやパラメータなどの情報を記憶するための記憶容量を削減することができる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, when two bits out of the eight bits D0 to D7 in the buffer area are set as the processing target for the prize ball counting process, they are set in a predetermined order, so there is no need to perform a determination process to determine which bit to set as the processing target for the prize ball counting process, which simplifies the process and, as a result, improves the processing speed. Furthermore, the memory capacity required to store information such as programs and parameters required to execute the determination process can be reduced.
また、本態様によれば、主側CPU62xは、1つの入球口に2個の遊技球が連続して入球して検知される最短の間隔(本態様では18msec程度)よりも短い時間でタイマ割込み処理を4回実行することができるので、当該最短の間隔よりも短い時間で8個の処理対象候補(バッファエリアのビットD0~D7)の全てに対して賞球集計処理(図29のステップS10808)を実行することができる。したがって、同一の入球口に2個の遊技球が連続して入球した場合であっても、最初の1個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知されることに基づいて更新された入球検知情報が処理対象として設定されて賞球集計処理が実行され、さらにその後に残りの他の入球口に対応した入球検知情報が処理対象として設定されて賞球集計処理が実行されたとしても、次の2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知されるよりも先にこれら全ての入球検知情報に対して賞球集計処理を終了することができる。すなわち、2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知されることに基づいて更新された入球検知情報が処理対象として設定されて賞球集計処理が実行された時点においては、既に、1個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知されることに基づいて更新された入球検知情報に対する賞球集計処理は終了していることになる。この構成による効果を以下に説明する。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the
本態様のように、入球検知情報として、遊技球の入球の有無を示す「0」または「1」の2値の情報を採用した構成において、仮に、ある入球口への2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知されるまでに、当該入球口への1個目の遊技球の入球に基づいて「0」から「1」に更新された入球検知情報に対して賞球集計処理が実行されない場合には、当該2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知された時点ではまだ当該入球口に対応する入球検知情報が「1」のままとなっており、当該2個目の遊技球の入球を記録することができない。すなわち、当該入球口には2個の遊技球が連続して入球した状況であるにも関わらず、当該入球口に対応した入球検知情報は、当該入球口に1個の遊技球しか入球していない状況と区別することができず、賞球集計処理においては1個の遊技球が当該入球口に入球した状況として扱われてしまう。この結果、賞球集計処理において正確な賞球数を記録することができない場合がある。 In a configuration in which binary information of "0" or "1" indicating whether or not a game ball has entered is used as the ball entry detection information as in this embodiment, if the prize ball counting process is not performed on the ball entry detection information updated from "0" to "1" based on the entry of the first game ball into a ball entry port by the time the entry of the second game ball into the ball entry port is detected at the ball entry port, the ball entry detection information corresponding to the ball entry port is still "1" at the time the entry of the second game ball is detected at the ball entry port, and the entry of the second game ball cannot be recorded. In other words, even though two game balls have entered the ball entry port in succession, the ball entry detection information corresponding to the ball entry port cannot be distinguished from a situation in which only one game ball has entered the ball entry port, and the prize ball counting process treats the situation as one game ball entering the ball entry port. As a result, the prize ball counting process may not be able to record the exact number of prize balls.
これに対して、本態様によれば、当該2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球口において検知された時点において既に当該入球口への1個目の遊技球の入球によって更新された入球検知情報に対して賞球集計処理が実行され、当該入球検知情報が「0」になっているため、当該2個目の遊技球の入球を記録することが可能となる。この結果、賞球集計処理において正確な賞球数を記録することが可能となる。これにより、賞球集計処理における正確性を担保しつつ、入球検知情報として、遊技球の入球の有無を示す「0」または「1」の2値の情報を採用することが可能となり、入球検知情報を記憶するための記憶容量を小さくすることができるとともに、賞球集計処理の処理速度を向上させることができる。 In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the prize ball tallying process is executed on the ball entry detection information that has already been updated by the entry of the first game ball into the ball entry port at the time the entry of the second game ball is detected at the ball entry port, and since the ball entry detection information is set to "0", it is possible to record the entry of the second game ball. As a result, it is possible to record an accurate number of prize balls in the prize ball tallying process. This makes it possible to adopt binary information of "0" or "1" indicating whether or not a game ball has entered as the ball entry detection information while ensuring accuracy in the prize ball tallying process, thereby reducing the memory capacity for storing the ball entry detection information and improving the processing speed of the prize ball tallying process.
また、本態様によれば、遊技履歴用処理(図29)は、主側CPU62x内のレジスタが保持する情報であって遊技の進行に関する処理の実行のための情報を主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に書き込む退避処理(図29のステップS10801)を含むので、主側CPU62xが遊技履歴用処理の開始時に、主側CPU62x内のレジスタが遊技履歴用処理の開始直前に実行していた遊技の進行に関する処理の実行のための情報を保持している場合には、当該情報を主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に書き込むことによって一時的に移動(退避)させることができる。よって、主側CPU62x内のレジスタに保持されていた遊技の進行に関する処理の実行のための情報を消去し、主側CPU62xによる遊技履歴用処理の実行時には、主側CPU62x内のレジスタに遊技履歴用処理の実行のための情報を保持させることができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the game history process (FIG. 29) includes a save process (step S10801 in FIG. 29) in which information held in the register in the
また、本態様によれば、遊技履歴用処理(図29)は、退避処理において主側RAM64の第2エリアのスタック領域に書き込まれた情報を主側CPU62xのレジスタに保持させる復帰処理(図29のステップS10813)を含むので、遊技履歴用処理を終了する際に、遊技の進行に関する処理の実行のための情報を主側CPU62xのレジスタに再び保持させ、遊技履歴用処理の開始以前に実行していた遊技の進行に関する処理を、遊技履歴用処理の開始直前の状態から再び実行することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the game history processing (Figure 29) includes a return process (step S10813 in Figure 29) that causes the information written in the stack region of the second area of the
また、本態様によれば、退避処理と復帰処理は遊技履歴用処理に含まれるので、遊技履歴用処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを削除しても遊技履歴用処理以外の遊技の進行に関する処理が問題なく実行される遊技機を提供することができる。すなわち、遊技履歴用処理以外の遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するためのプログラムを改変せずに、遊技履歴用処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを容易に削除することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、遊技履歴用処理を実行させないように当該遊技機を改良する場合や、当該遊技機に基づいて遊技履歴用処理を実行しない新たな遊技機を開発する場合において、設計変更を最小限にすることが可能となる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, since the save process and the return process are included in the game history process, it is possible to provide a gaming machine in which processes related to the progress of the game other than the game history process are executed without any problems even if only the program for executing the game history process is deleted. In other words, it is possible to easily delete only the program for executing the game history process without modifying the program for executing processes related to the progress of the game other than the game history process. As a result, it is possible to minimize design changes, for example, when improving the gaming machine so that it does not execute the game history process, or when developing a new gaming machine based on the gaming machine that does not execute the game history process.
また、本態様によれば、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴用処理における情報の書き込みを、主側RAM64の第2エリアに対してのみ実行するので、主側RAM64の第1エリアに書き込まれている情報が、遊技履歴用処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、遊技の進行に関する処理が主側RAM64の第1エリアを用いて実行される構成において、当該遊技の進行に関する処理に対して遊技履歴用処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the
また、本態様によれば、主側CPU62xは、遊技の進行に関する処理における情報の書き込みを、主側RAM64の第1エリアに対してのみ実行するので、主側RAM64の第2エリアに書き込まれている情報が、遊技の進行に関する処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、遊技履歴用処理が主側RAM64の第2エリアを用いて実行される構成において、当該遊技履歴用処理に対して遊技の進行に関する処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the
また、本態様によれば、入球検知情報を記憶可能な8ビットのバッファエリアを備えるので、タイマ割込み処理が実行される毎に更新される入球検知情報記憶エリアにおける入球検知情報を、賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定されて当該処理が実行されるまで保持することができる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, an 8-bit buffer area capable of storing ball entry detection information is provided, so that the ball entry detection information in the ball entry detection information storage area, which is updated each time the timer interrupt process is executed, can be set as the processing target for the prize ball counting process and held until the process is executed.
また、本態様によれば、図29に示すように、1回のタイマ割込み処理において賞球集計処理(ステップS10808)を実行する場合には演算処理(ステップS10814のタスク1及びタスク2)を実行しない。すなわち、1回のタイマ割込み処理においては賞球集計処理と演算処理の両方の処理を実行することはないので、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、タイマ割込み処理の割込み間隔よりも長くなってしまい、タイマ割込み処理を当該割込み間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。さらに、本態様によれば、遊技球の入球状況と処理負荷とが相関する賞球集計処理を、遊技球の入球状況と処理負荷とが相関しない演算処理よりも優先して実行するので、賞球集計処理の実行の間隔が大きくなることを抑制し、その結果として当該賞球集計処理の処理結果である賞球集計値が遊技球の入球状況を正確に反映することができなくなってしまうことを抑制することができる。具体的には、例えば、バッファエリアのあるビットに対して賞球集計処理が実行されるよりも前に次の遊技球が当該ビットに対応する入球口に入球してしまい、2個の遊技球の入球を1個の遊技球の入球として扱ってしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 29, when the prize ball counting process (step S10808) is executed in one timer interruption process, the calculation process (
また、本態様によれば、図29に示すように、賞球集計処理(ステップS10808)を実行しない場合であって、演算処理の実行のタイミングであると判定した場合(ステップS10810:YES)に演算処理(ステップS10814のタスク1及びタスク2)を実行するので、1回のタイマ割込み処理において賞球集計処理も演算処理も実行せずに、当該状況において、賞球集計処理及び演算処理の代わりに、これらの処理とは独立した他の処理(本態様では賞球集計値の有効性を判定する処理(ステップS10814のタスク3))を実行することが可能となる。さらに、本態様では、1回のタイマ割込み処理において賞球集計処理または演算処理のいずれかを実行した場合に当該タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が割込み間隔よりも短くなるように構成されているので、賞球集計処理も演算処理も実行しない状況において、賞球集計処理及び演算処理よりも処理時間の短い処理を実行することによって、当該タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が割込み間隔よりも長くなってしまうことを確実に抑制することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 29, when the prize ball tallying process (step S10808) is not executed and it is determined that it is time to execute the calculation process (step S10810: YES), the calculation process (
また、本態様によれば、役物比率及び連続役物比率の2個の種別の遊技履歴情報を算出可能であるにも関わらず、1回のタイマ割込み処理における演算処理においては、役物比率または連続役物比率のいずれか一方の算出についての処理を実行するので、1回のタイマ割込み処理における演算処理において2個の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理を実行する構成と比較して、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、割込み間隔よりも長くなってしまい、タイマ割込み処理を所定の割込み間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。また、算出した遊技履歴情報を一時的に記憶するための主側RAM64の記憶容量を削減することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, although it is possible to calculate two types of game history information, the role ratio and the continuous role ratio, in the calculation process in one timer interrupt process, the calculation process is performed for calculating either the role ratio or the continuous role ratio, so the time required for one execution of the timer interrupt process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the calculation process in one timer interrupt process is performed for calculating two types of game history information. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for one execution of the timer interrupt process from becoming longer than the interrupt interval, making it impossible to execute the timer interrupt process at a specified interrupt interval. In addition, the storage capacity of the
また、本態様によれば、入球検知処理において、各入球口に対応したビットの入球判定用情報が「0」→「1」→「1」となった場合に、当該ビットに対応した入球口に遊技球が入球したと判定するので、上述した第1実施形態と同様に、電気的なノイズによる誤検知の発生を抑制することができる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, in the ball entry detection process, when the ball entry determination information for a bit corresponding to each ball entry port changes from "0" to "1" to "1", it is determined that a game ball has entered the ball entry port corresponding to that bit, so that, as in the first embodiment described above, the occurrence of erroneous detection due to electrical noise can be suppressed.
<態様24>
上記態様23では、遊技履歴情報として、役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出する構成としたが、算出する遊技履歴情報はこれらに限られず、第1実施形態に示した種々の遊技履歴情報を算出する構成とすることができる。例えば、第1実施形態に示した出球率や、払出比率等を算出する構成としてもよい。この場合には、上述した賞球集計処理(図29のステップS10808)と同様にして、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数)も集計する構成とすればよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
<態様25>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)では、ステップS10802において異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には、賞球集計値をクリアし(ステップS10803)、異常フラグをOFFにする(ステップS10804)構成としたが、所定期間内に異常フラグが所定回数ONになった場合には、異常が発生していることを示す情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示する構成としてもよい。
<
In the game history processing of the above-mentioned mode 23 (Figure 29), if it is determined in step S10802 that the abnormality flag is ON, the prize ball tally value is cleared (step S10803) and the abnormality flag is turned OFF (step S10804). However, if the abnormality flag is turned ON a predetermined number of times within a predetermined period, information indicating that an abnormality has occurred may be displayed on the game history
<態様26>
上記態様23では、遊技履歴情報を算出する処理である演算処理を複数のタスクに分割して実行する構成としたが、複数のタスクに分割する処理の種別は当該演算処理に限らず、種々の処理を複数のタスクに分割して実行する構成とすることができる。例えば、実行する演出の内容を音声発光制御装置90の音光側MPU92が設定する構成において、当該演出の内容を設定する処理を複数のタスクに分割して実行する構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 26>
In the above-mentioned
<態様27>
上記態様23では、賞球集計処理の処理対象として、バッファエリアの8個のビットのうち、2個ずつのビットを処理対象として設定する構成としたが、処理対象とするビットの個数は2個に限らず、他の個数であってもよい。例えば、1回のタイマ割込み処理において5個のビットを処理対象として設定する構成としてもよい。また、1回のタイマ割込み処理において、8個のビットの全てを処理対象として設定する構成としてもよい。また、8個のビットのうちの所定のビット(例えば、賞球が設定されている第0ビットD0~第5ビットD5の6個のビット)のみを処理対象として設定可能であり、1回のタイマ割込み処理においては2個のビットを処理対象として設定する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
<態様28>
上記態様23では、遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するための記憶領域として主側RAM64の第1エリアが割り当てられ、遊技履歴用処理を実行するための記憶領域として主側RAM64の第2エリアが割り当てられている構成としたが、主側RAM64の第2エリアが、遊技履歴用処理以外の他の処理を実行するための記憶領域として割り当てられている構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
また、主側RAM64が3つ以上のエリアに区分されている構成としてもよい。そして、例えば、主側RAM64の3つ目のエリアである第3エリアが、遊技履歴情報を外部に出力するための処理を実行するための記憶領域として割り当てられている構成としてもよい。
The
<態様29>
上記態様23では、遊技履歴用処理に退避処理及び復帰処理が含まれる構成としたが、遊技履歴用処理以外の他の処理が退避処理及び復帰処理を含む構成としてもよい。例えば、遊技機の設計変更時には削除することが予定されている処理が退避処理及び復帰処理を含んでいる構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 29>
In the above-mentioned
<態様30>
上記態様23では、遊技履歴用処理がタイマ割込み処理(図27)に組み込まれている構成としたが、遊技履歴用処理がメイン処理(図12)に組み込まれている構成としてもよい。また、上記態様23では、タイマ割込み処理(図27)に、遊技の進行に関する処理とは異なる処理として遊技履歴用処理が組み込まれている構成としたが、遊技の進行に関する処理とは異なる処理として、遊技履歴用処理以外の他の処理がタイマ割込み処理に組み込まれている構成としてもよい。例えば、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータに対して遊技の状況に関する情報を所定のタイミングで送信する送信処理が、遊技の進行に関する処理とは異なる処理として、タイマ割込み処理に組み込まれている構成としてもよい。また、遊技の進行に関する処理とは異なる種々の処理が、メイン処理に組み込まれている構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
<態様31>
上記態様23では、遊技履歴管理チップ300を備えない構成とした上で、主側CPU62xが遊技履歴用処理(図29)を実行して遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としたが、遊技履歴管理チップ300を備える構成とした上で、主側CPU62xが遊技履歴用処理(図29)を実行して遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報を2系統で算出することができるので、1系統に不具合が生じても、遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。また、2系統から算出された遊技履歴情報を比較し、これらの値が一致しているか否かを報知(表示)する構成とすれば、算出された遊技履歴情報の信頼性、正確性を確認することが可能となる。
<
In the above-mentioned
また、遊技履歴管理チップ300が、上記態様23において説明した遊技履歴用処理(図29)を実行して遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としてもよい。
The gaming
<態様32>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)のステップS10805では、主側RAM64の第1エリアに設けられている入球検知情報記憶エリア(図30)の各ビットに格納されている情報をOR処理において読み出す構成としたが、この構成に代えて、当該入球検知情報記憶エリアに対応した8ビットの記憶エリア(以下、第2入球検知情報記憶エリアとも呼ぶ)を主側RAM64の第2エリアに設ける構成とした上で、主側RAM64の第1エリアに設けられている入球検知情報記憶エリアの各ビットに格納されている情報を、主側RAM64の第2エリアに設けられている第2入球検知情報記憶エリアに複製(コピー)し、当該複製された各ビットの情報を、ステップS10805のOR処理において読み出す構成としてもよい。
<
In step S10805 of the game history processing (Figure 29) of the above-mentioned
また、入球検知情報記憶エリアが主側RAM64の第2エリアに設けられている構成としてもよい。
The ball entry detection information storage area may also be configured to be provided in the second area of the
<態様33>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)のステップS10814では、遊技履歴情報を算出する演算処理(タスク1またはタスク2)を実行しない場合には、タスク3に含まれる賞球集計値の有効性を判定する処理を常に実行する構成としたが、賞球集計値の有効性を判定する処理は、遊技履歴情報が新たに算出される毎に1回のみ実行する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、タスク3において賞球集計値の有効性を判定した後に、判定済みであることを示す判定済みフラグをONにし、次にタスク3を実行する際に、当該判定済みフラグがONである場合には、当該賞球集計値の有効性を判定する処理を実行しない構成とする。そして、再び実行されたタスク1において、当該判定済みフラグをOFFにする構成とすればよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる賞球集計値の有効性を判定して当該遊技履歴情報の有効性を担保しつつ、1回の遊技履歴用処理が完了するまでに要する処理時間をさらに短縮することが可能となる。
<
In step S10814 of the game history processing (FIG. 29) of the above-mentioned
<態様34>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)のステップS10810では、パチンコ機10の電源投入から所定時間(例えば30分)が経過した場合、または、演算処理の前回の実行から5秒が経過した場合に、演算処理を実行するタイミングであると判定し、遊技履歴情報を算出する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、電源投入から所定時間の経過を待たずに、電源投入直後に1回目の演算処理を実行するタイミングであると判定し、その後、演算処理の前回の実行から5秒が経過する毎に、演算処理を実行するタイミングであると判定する構成としてもよい。この構成において、賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達するまでは、算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させる際に点滅表示とし、総賞球数が60000個に達した後は、算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させる際に点灯表示とする構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、表示されている遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる賞球集計値として十分な量の統計データが蓄積されているか否かを容易に把握することが可能となる。なお、総賞球数に代えて、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数)の集計値を基準として、点滅表示から点灯表示に切り替える構成としてもよい。
<
In step S10810 of the game history processing (FIG. 29) of the above-mentioned
<態様35>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)のステップS10807では、賞球集計処理の複数の処理対象候補は、バッファエリアの8個のビットとして予め固定されている構成としたが、バッファエリアの8個のビットを4個ずつの2つのグループに分け、賞球集計処理の複数の処理対象の候補として、2つのグループのうちの一のグループを選択し、選択したグループに属する4個のビットの中から2個のビットを賞球集計処理の処理対象として設定する構成としてもよい。ただし、上記態様23のように、賞球集計処理の複数の処理対象候補がバッファエリアの8個のビットとして予め固定されている構成とした方が、2つのグループのうちの一のグループを選択する処理を実行する必要がなく、処理を簡易化することができ、この結果、処理速度を向上させることができる。さらに、2つのグループのうちの一のグループを選択するために必要なプログラムやパラメータなどの情報を記憶するための記憶容量を削減することができる。
<
In step S10807 of the game history processing (FIG. 29) of the above-mentioned
<態様36>
上記態様23の遊技履歴用処理(図29)において、次のタイマ割込み処理が開始されるまでの残時間に基づいて、今回のタイマ割込み処理における遊技履歴用処理において実行するタスク(各種処理)の数や種別を決定する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、次のタイマ割込み処理が開始されるまでの残時間を有効に活用してタスクを実行することが可能となる。
<
In the game history process of the above-mentioned aspect 23 (FIG. 29), the number and type of tasks (various processes) to be executed in the game history process in the current timer interrupt process may be determined based on the remaining time until the next timer interrupt process is started. With such a configuration, it is possible to execute the tasks by effectively utilizing the remaining time until the next timer interrupt process is started.
<態様37>
図31は、第1実施形態の態様37におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。この態様37では、遊技履歴管理チップ300は設けられておらず、上述した遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための処理(遊技履歴用処理)を主側CPU62xが実行するように構成されている。また、主側RAM64は、上述した態様23(図26)と同様に、2つのエリア(第1エリア及び第2エリア)に区分されており、主側RAM64の第1エリアは、遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するためのプログラムや各種フラグ(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等)等を記憶する領域として用いられ、主側RAM64の第2エリアは、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための処理(遊技履歴用処理)を実行するためのプログラムや各種の数値情報(上述した賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)等を記憶する領域として用いられる。そして、主側CPU62xは、上述した態様23(図26)と同様に、遊技の進行に関する処理(遊技履歴用処理以外の処理)の実行時には、情報の書き込みを主側RAM64の第1エリアに対してのみ実行し、遊技履歴用処理の実行時には、情報の書き込みを主側RAM64の第2エリアに対してのみ実行する。
<
31 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
さらに、本態様のパチンコ機10の主側MPU62には、図31に示すように、書き換え可能であるとともに電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリであるフラッシュメモリ64xが設けられている。本態様では、フラッシュメモリ64xとして、NAND型のフラッシュメモリが用いられているが、NOR型のフラッシュメモリを用いてもよい。本態様の主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴用処理において、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている各種の数値情報を所定のタイミングでフラッシュメモリ64xに書き込む処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、主側CPU62xは、賞球集計値における総賞球数が500個に達する毎に、各種の賞球集計値等をフラッシュメモリ64xに書き込む処理を実行する。すなわち、フラッシュメモリ64xには、遊技の実行に基づいて取得された各種の数値情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)が記憶される。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 31, the
このように、本態様の構成によれば、遊技の実行に基づいて取得された各種の数値情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)がフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されるので、パチンコ機10への電源の供給が長期間にわたって断たれた場合であっても、これらの各種の数値情報を保持することができる。例えば、流通過程において長期間にわたってパチンコ機10に電源が供給されない場合であっても、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている各種の数値情報に基づいて、当該パチンコ機10において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。
In this way, according to the configuration of this embodiment, various numerical information (game history information such as prize ball tally, number of balls entered, and role ratio) obtained based on the execution of the game is stored in the
<態様38>
上記態様37において、押下可能なフラッシュメモリクリアボタンをパチンコ機10の背面に設け、当該フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)継続して押下された場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等)が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the
具体的には、例えば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行可能な消去処理用ICチップを設けるとともに、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下されている期間中は当該消去処理用ICチップの入力端子にHiレベル信号が入力される構成とする。そして、消去処理用ICチップは、当該入力端子に入力されているHiレベル信号が10秒間継続したことに基づいて、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する構成とする。このような構成によれば、主側CPU62xの処理によってフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する構成と比較して、主側CPU62xの遊技の実行に関する処理や主側RAM64の動作に与える影響を抑制しつつ、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去することができる。
Specifically, for example, an IC chip for erasure processing capable of executing an erasure process for erasing information stored in the
さらに、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンは、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されている構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンは、開封の痕跡が残る封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部に格納されており、当該封印シールを剥がして基板ボックスを開けなければ押下することができない構成としてもよい。 Furthermore, the flash memory clear button may be configured to be stored inside a space that leaves evidence of opening. Specifically, for example, the flash memory clear button may be stored inside a board box to which a seal sticker that leaves evidence of opening has been affixed, and the button cannot be pressed unless the seal sticker is peeled off and the board box is opened.
本態様の構成によれば、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けてフラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作する必要があり、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスが開かれてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。
According to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不正な改造(例えば、釘の不正な改変)が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(例えば、役物比率等)に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。パチンコ機10によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該パチンコ機10に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。
If the
しかしながら、本態様の構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けてフラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、不正な者がフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、パチンコ機10に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
However, according to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the
なお、パチンコ機10は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのあるパチンコ機10(いわゆる中古のパチンコ機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「正当な者」ともいう)のみが、基板ボックスの開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。具体的には、例えば、正当な者としての当該パチンコ機10の製造者のみが新たな封印シールを貼ることが可能な流通体制を構築することによって、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。
Incidentally,
なお、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンの操作に基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としては、上記の構成に限らず、他の様々な構成を採用することができる。例えば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に所定回数(例えば5回)押下された場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としてもよい。また、例えば、消去処理用ICチップを設けない構成とし、主側CPU62xがフラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを監視し、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)継続して押下された場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するための消去プログラムを実行して当該情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
The configuration for erasing information stored in the
また、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンは、封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部に格納されている構成に限らず、開放の痕跡(開封の痕跡、開閉の痕跡ともいう)が残る空間の内部に格納されている構成とすれば、他の構成であってもよい。例えば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンは、蓋部材によって覆われた空間の内部に収納されており、当該蓋部材の少なくとも一部を破壊して当該空間を開放しなければ当該フラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作することができない構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作するには蓋部材を破壊して当該空間を開放しなければならないため、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下された場合には、フラッシュメモリが収納されている空間が開放された痕跡として、破壊された蓋部材が残ることになる。また、例えば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンを、複数のケース体(例えば箱状のケース体と当該箱状のケース体の開放部分を封じることが可能な蓋状のケース体)が結合部(カシメ部)によって結合されることによって構成された基板ボックスの内部に収納する構成とし、当該基板ボックスを構成する複数のケース体を分離させる際には結合部(カシメ部)の所定部位の破壊を要する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作するには、結合部(カシメ部)の所定部位を破壊して複数のケース体を分離させて当該基板ボックスを開放しなければならないため、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下された場合には、基盤ボックスが開放された痕跡として、所定部位が破壊された結合部(カシメ部)が残ることになる。さらに、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンを、上述した結合部(カシメ部)によって結合された基板ボックスの内部に収納する構成とした上で、引き剥がしの際に粘着層が接着対象に残ることによって剥がされたことの痕跡を残す封印シールを複数のケース体間の境界を跨ぐようにして貼り付ける構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下された場合には、所定部位が破壊された結合部(カシメ部)という基板ボックスの開放の痕跡に加えて、封印シールが剥がされた又はケース体間の境界において封印シールが切断されたといった基板ボックスの開放の痕跡が残ることになる。 The flash memory clear button is not limited to being stored inside a board box to which a seal is affixed, and may be stored in a space that leaves traces of opening (also called traces of opening and closing). For example, the flash memory clear button may be stored inside a space covered by a lid member, and the flash memory clear button cannot be operated unless at least a part of the lid member is destroyed to open the space. According to such a configuration, the lid member must be destroyed to open the space in order to operate the flash memory clear button, so when the flash memory clear button is pressed, the destroyed lid member remains as a trace of the space in which the flash memory is stored being opened. Also, for example, the flash memory clear button may be stored inside a board box formed by joining multiple case bodies (for example, a box-shaped case body and a lid-shaped case body that can seal the open part of the box-shaped case body) with a joining part (crimping part), and a predetermined part of the joining part (crimping part) must be destroyed when separating the multiple case bodies that make up the board box. According to this configuration, in order to operate the flash memory clear button, a specific portion of the joint (crimping portion) must be destroyed to separate the multiple case bodies and open the board box, so when the flash memory clear button is pressed, the joint (crimping portion) with the specific portion destroyed remains as a trace of the board box being opened. Furthermore, the flash memory clear button may be configured to be stored inside the board box joined by the above-mentioned joint (crimping portion), and a seal seal that leaves a trace of its removal by leaving an adhesive layer on the bonded object when peeled off may be attached across the boundary between the multiple case bodies. According to this configuration, when the flash memory clear button is pressed, in addition to the trace of the board box being opened, which is the joint (crimping portion) with the specific portion destroyed, a seal seal that has been peeled off or cut at the boundary between the case bodies will remain.
<態様39>
上記態様37において、主側MPU62に設けられた検査用端子65に、各種の遊技履歴情報が正常な範囲内であるか否かを検査するための上述した検査機320(図10)が接続され、当該検査機320から所定の信号(例えば消去命令コマンド)を受信した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等)が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、上述した態様38と同様に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行可能な消去処理用ICチップを設けるとともに、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320から消去命令コマンドが送信された場合には、消去処理用ICチップの入力端子に当該消去命令コマンドが入力される構成とする。そして、消去処理用ICチップは、当該入力端子から消去命令コマンドを受信したことに基づいて、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する。
Specifically, for example, as in the above-mentioned
本態様の構成によれば、消去処理用ICチップは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320から消去命令コマンドを受信したことに基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するので、検査機320を有する者が、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去することができる。すなわち、検査機320を有さない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。
According to the configuration of this aspect, the erasure process IC chip erases the information stored in the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不正な改造(例えば、釘の不正な改変)が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(例えば、役物比率等)に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。パチンコ機10によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(検査者)は、例えば、検査機320を検査用端子65に接続し、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を検査機320によって確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該パチンコ機10に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(不正な者)が存在する可能性がある。
If the
しかしながら、本態様の構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続可能な検査機320が必要となる。そして、当該検査機320を有することができる者を制限すれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができ、ひいては、パチンコ機10に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
However, according to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the
なお、パチンコ機10は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのあるパチンコ機10(いわゆる中古のパチンコ機10)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者(例えば、当該パチンコ機10の製造者)と上述した検査者のみが検査機320を有することが可能な流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。
Note that
さらに、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される際には、当該消去に先立って、当該フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に送信される構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, when information stored in the
具体的には、例えば、上述した消去処理用ICチップは、当該入力端子から消去命令コマンドを受信したことに基づいて、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報の送信を開始することを示す送信開始コマンドを検査機320に送信する。送信開始コマンドを受信した検査機320は、情報の受信が可能な受信可能モードに移行し、受信可能モードであることを示す受信可能コマンドを消去処理用ICチップに送信する。受信可能コマンドを受信した消去処理用ICチップは、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報の送信を開始する。そして、当該情報の送信が完了した場合には、消去処理用ICチップは、送信完了コマンドを検査機320に送信する。送信完了コマンドを受信した検査機320は、受信した情報にデータの欠損等のエラーがないかを確認し、エラーがなければ受信完了コマンドを消去処理用ICチップに送信する。消去処理用ICチップは、受信完了コマンドを受信したことに基づいて、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する。
Specifically, for example, the above-mentioned IC chip for erasure processing transmits a transmission start command to the
このような構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が、検査機320を有する者の意思に反した誤った操作によって消去されてしまった場合であっても、フラッシュメモリ64xから消去されてしまった情報が検査機320に残ることになるので、当該情報を当該検査機320によって確認することができる。
With this configuration, even if the information stored in the
なお、検査機320から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としては、上記の構成に限らず、他の様々な構成を採用することができる。例えば、消去処理用ICチップを設けない構成とし、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320から消去命令コマンドを受信したか否かを主側CPU62xが監視し、当該消去命令コマンドを受信した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するための消去プログラムを実行して当該情報を消去する構成としてもよい。また、主側CPU62xは、検査機320から消去命令コマンドを受信した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を検査機320に送信した上で、当該情報を消去するための消去プログラムを実行してフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
The configuration in which the information stored in the
なお、本態様では、各種の遊技履歴情報が正常な範囲内であるか否かを検査するための検査機320を用いてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する構成としたが、検査機320を用いる構成に限らず、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するための専用の端末を用いて当該情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
In this embodiment, the information stored in the
<態様40>
上記態様37において、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されたフラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)継続して押下され、かつ、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320から所定の信号(例えば消去命令コマンド)を受信した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等)が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、上述した態様38と同様に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行可能な消去処理用ICチップを設けるとともに、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが押下されている期間中は当該消去処理用ICチップの入力端子にHiレベル信号が入力される構成とする。そして、消去処理用ICチップは、当該入力端子に入力されているHiレベル信号が10秒間継続したことに基づいて、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行可能な消去処理実行待機モードに移行する。消去処理用ICチップは、この消去処理実行待機モードにおいて検査機320から消去命令コマンドを受信すると、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する。
Specifically, for example, as in the above-mentioned
本態様の構成によれば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンは、開放の痕跡が残る基板ボックスの内部に格納されているので、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けてフラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作することになり、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになる。さらに、消去処理用ICチップは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するので、検査機320を有する者が、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去することができる。したがって、パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスが開かれてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となるとともに、検査機320を有さない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。
According to the configuration of this aspect, since the flash memory clear button is stored inside the board box that leaves traces of opening, in order to erase the information stored in the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不正な改造(例えば、釘の不正な改変)が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(例えば、役物比率等)に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。パチンコ機10によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(検査者)は、例えば、検査機320を検査用端子65に接続し、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を検査機320によって確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該パチンコ機10に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(不正な者)が存在する可能性がある。
If the
しかしながら、本態様の構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続可能な検査機320が必要となる。そして、当該検査機320を有することができる者を制限すれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。さらに、仮に不正な者が検査機320を有してしまった場合であっても、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けてフラッシュメモリクリアボタンを操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができるとともに、パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができる。この結果、パチンコ機10に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生をさらに抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
However, according to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the
なお、パチンコ機10は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのあるパチンコ機10(いわゆる中古のパチンコ機10)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者(例えば、当該パチンコ機10の製造者)と上述した検査者のみが検査機320を有することが可能であるとともに、正当な者のみが基板ボックスの開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。
Incidentally,
なお、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定の操作を受け付け、かつ、検査機320から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としては、上記の構成に限らず、他の様々な構成を採用することができる。例えば、フラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に所定回数(例えば5回)押下された場合に、消去処理用ICチップが上述した消去処理実行待機モードに移行する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、検査機320から消去命令コマンドを受信した場合に、消去処理用ICチップが上述した消去処理実行待機モードに移行し、当該消去処理実行待機モードにおいてフラッシュメモリクリアボタンが所定時間(例えば10秒)継続して押下されると、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、消去処理用ICチップを設けない構成とし、主側CPU62xが当該消去処理用ICチップと同等の機能を実行してフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
The configuration in which the information stored in the
また、上記の態様39と同様に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が消去される際には、当該消去に先立って、当該フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に送信される構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が、検査機320を有する者の意思に反した誤った操作によって消去されてしまった場合であっても、フラッシュメモリ64xから消去されてしまった情報が検査機320に残ることになるので、当該情報を当該検査機320によって確認することができる。
Furthermore, similar to the above-mentioned
<態様41>
上記態様37において、認証情報(例えば暗証番号)の入力操作を受け付ける操作パネルと、入力された認証情報を表示する表示器とをパチンコ機10の背面に設け、操作パネルによって入力された認証情報と当該パチンコ機10に個別に設定されている認証情報とが一致した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等)が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、上述した態様38と同様に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行可能な消去処理用ICチップを設けるとともに、操作パネルを介して入力された認証情報が、消去処理用ICチップの入力端子に入力される構成とする。そして、消去処理用ICチップは、操作パネルから入力された認証情報が、当該消去処理用ICチップのROMに格納されている認証情報と一致しているか否かを判定し、一致していると判定した場合に、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理を実行する。
Specifically, for example, as in the above-mentioned
本態様の構成によれば、消去処理用ICチップは、受付手段が受け付けた認証情報と当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報とが一致したことに基づいてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するので、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報を有する者(例えば、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている暗証番号を知っている者)が、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去することができる。すなわち、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報を有しない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。
According to the configuration of this aspect, the IC chip for erasure process erases the information stored in the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不正な改造(例えば、釘の不正な改変)が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(例えば、役物比率等)に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。パチンコ機10によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(検査者)は、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該パチンコ機10に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(不正な者)が存在する可能性がある。
If the
しかしながら、本態様の構成によれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報を有していることが必要となる。そして、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報を有することができる者を制限すれば、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができ、ひいては、パチンコ機10に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
However, according to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the
なお、パチンコ機10は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのあるパチンコ機10(いわゆる中古のパチンコ機10)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者(例えば、当該パチンコ機10の製造者)のみが、当該パチンコ機10に設定されている認証情報を有することが可能な流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。
Incidentally,
なお、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するために入力される認証情報は、暗証番号に限らず、種々の認証情報を採用することができる。例えば、認証情報として、複数の文字列の組合せである認証文字(パスワード、パスフレーズ)や、特定のパターンのバーコード、所定の規則に従って生成されたパスワード(例えば、ワンタイムパスワード)、特定の人物の生体認証情報(指紋、虹彩、静脈パターン等)等を採用することができる。
The authentication information input to erase information stored in the
<態様42>
上記態様37において、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行された場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等を含む遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)は消去され、第2エリアに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)は消去されない構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた直後に、主側CPU62xは、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを判定し、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であると判定した場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報を消去し、第2エリアに記憶されている情報は消去しない構成とする。
Specifically, for example, immediately after the power of the
このような構成によれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)を残しつつ、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)を消去することが可能となる。具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や、遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したいが、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は消去したくないといった要望がある。本態様の構成によれば、RAMクリアボタンを操作することによって、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報を消去して当該パチンコ機10の制御の初期化を実行することが可能となる。
According to this configuration, it is possible to erase the information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64 (information used to control the execution of the game) while leaving the information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64 (information acquired based on the executed game). Specifically, for example, when a malfunction occurs in the control of the execution of the game or when the business hours of the game parlor are opened or closed, there is a desire to erase the information used to control the execution of the game and initialize the control of the gaming machine, but not to erase the information acquired based on the executed game. According to the configuration of this aspect, by operating the RAM clear button, it is possible to erase the information used to control the execution of the game while leaving the information acquired based on the executed game, and initialize the control of the
さらに、上述したRAMクリアボタンに加えて、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するための第2RAMクリアボタンをパチンコ機10の背面側に設け、パチンコ機10の電源がONである状態中に第2RAMクリアボタンを所定時間(例えば10秒)押下するという操作が実行された場合には、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, in addition to the above-mentioned RAM clear button, a second RAM clear button for erasing information stored in the second area of the
具体的には、例えば、主側CPU62xは、第2RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを監視しており、第2RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続したと判定した場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去する構成とする。
Specifically, for example, the
このような構成によれば、RAMクリアボタンを操作することによっては消去することのできない主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)を、第2クリアボタンを操作することによって消去することができる。 With this configuration, information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64 (information acquired based on the executed game) that cannot be erased by operating the RAM clear button can be erased by operating the second clear button.
さらに、第2RAMクリアボタンは、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されている構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、第2RAMクリアボタンは、開封の痕跡が残る封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部に格納されており、当該封印シールを剥がして基板ボックスを開けなければ押下することができない構成としてもよい。 Furthermore, the second RAM clear button may be configured to be stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening. Specifically, for example, the second RAM clear button may be stored inside a board box to which a seal sticker that leaves traces of opening has been affixed, and the button cannot be pressed unless the seal sticker is peeled off to open the board box.
本態様の構成によれば、パチンコ機10の主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けて第2RAMクリアボタンを操作する必要があり、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスが開かれて主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。
According to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the second area of the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不正な改造(例えば、釘の不正な改変)が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該パチンコ機10の主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(例えば、役物比率等)に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。パチンコ機10によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(検査者)は、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報や主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該パチンコ機10に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(不正な者)が存在する可能性がある。
If the
しかしながら、本態様の構成によれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスを開けて第2RAMクリアボタンを操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、不正な者が主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、パチンコ機10に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、パチンコ機10に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
However, according to the configuration of this aspect, in order to erase the information stored in the second area of the
なお、パチンコ機10は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのあるパチンコ機10(いわゆる中古のパチンコ機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該パチンコ機10の主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、パチンコ機10の主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者(正当な者)のみが、基板ボックスの開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。具体的には、例えば、正当な者としての当該パチンコ機10の製造者のみが新たな封印シールを貼ることが可能な流通体制を構築することによって、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、パチンコ機10の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。
Note that
なお、開放の痕跡(開封の痕跡、開閉の痕跡ともいう)が残る空間の構成としては、上記態様38において説明した種々の構成を採用することができる。
The space that leaves traces of opening (also called traces of opening and closing) can be configured in any of the various ways described in
<態様43>
上記態様37において、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になった場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報は消去され、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報は消去されない構成とし、一方、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態がそのまま所定時間(例えば10秒)継続した場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報は消去されず、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた直後に、主側CPU62xは、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを判定し、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であると判定した場合には、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続するか否かを監視する。そして、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になったと判定した場合には、主側CPU62xは、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報は消去し、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報は消去しない。一方、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続したと判定した場合には、主側CPU62xは、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報は消去せず、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去する。
Specifically, for example, immediately after the power supply of the
このような構成によれば、RAMクリアボタンに対して異なる操作を実行することによって、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することが可能となる。すなわち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択するための他の操作部(例えばボタン等)を設けなくても、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することができるので、パチンコ機10の構造の簡易化を図ることができる。
With this configuration, by performing different operations on the RAM clear button, it is possible to select the information to be erased from the information stored in the
具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したい場合には、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作を実行するとともに所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態とし、一方、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報)を消去して当該遊技機を新たに流通させたい場合には、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作を実行するとともに当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態がそのまま所定時間(例えば10秒)継続するようにすればよい。このように、RAMクリアボタンに対して異なる操作を実行することによって、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することが可能となる。
Specifically, for example, when a malfunction occurs in the control of game execution or when the business hours of the game parlor are opened or closed, if it is desired to erase the information used to control the execution of the game (the information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64) and initialize the control of the game machine, the operation of turning on the power of the
なお、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報の消去処理の実行中は、上述した遊技履歴用処理を実行することができないため、遊技球の各入球口への入球個数や賞球集計値等に誤差が生じる可能性がある。したがって、当該消去処理が終了までは遊技の実行を開始させない構成(例えば、遊技球の発射を抑止する構成)とすれば、当該誤差の発生を抑制することができる。
Note that while the process of deleting the information stored in the second area of the
また、本態様において、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になった場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報を消去し、さらに、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効であるか否かを判定し、有効であると判定した場合には当該情報を消去せず、有効ではないと判定した場合には当該情報を消去する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効ではない状態のまま遊技が開始されてしまうことを抑制することができる。なお、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効ではない場合とは、例えば、役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合や、連続役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合、連続役物賞球数が役物賞球数を超えている場合など、賞球集計値に矛盾が生じている場合等である。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the operation of turning on the power of the
<態様44>
上記態様37において、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になった場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報は消去され、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報は消去されない構成とし、一方、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態がそのまま所定時間(例えば10秒)継続した場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報が消去されるだけでなく、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報も消去される構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 44>
In the above-mentioned
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた直後に、主側CPU62xは、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを判定し、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であると判定した場合には、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報を消去する。さらに、主側CPU62xは、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続するか否かを監視し、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になったと判定した場合には、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報は消去しない。一方、当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続したと判定した場合には、主側CPU62xは、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報も消去する。
Specifically, for example, immediately after the power supply of the
このような構成によれば、上述した態様43と同様に、RAMクリアボタンに対して異なる操作を実行することによって、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することが可能となる。さらに、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作を実行するとともに当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態がそのまま所定時間(例えば10秒)継続させることによって、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報と第2エリアに記憶されている情報の両方を消去することが可能となる。
According to this configuration, similar to the above-mentioned
なお、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報の消去処理の実行中は、上述した遊技履歴用処理を実行することができないため、遊技球の各入球口への入球個数や賞球集計値等に誤差が生じる可能性がある。したがって、当該消去処理が終了までは遊技の実行を開始させない構成(例えば、遊技球の発射を抑止する構成)とすれば、当該誤差の発生を抑制することができる。
Note that while the process of deleting the information stored in the second area of the
<態様45>
上記態様37において、パチンコ機10の電源がONである状態中に、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを所定時間(例えば10秒)押下するという操作が実行された場合には、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が消去される構成としてもよい。
<
In the
具体的には、例えば、主側CPU62xは、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であるか否かを監視しており、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続したと判定した場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去する構成とする。
Specifically, for example, the
このような構成によれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するための操作部(例えばボタン等)を別途設けることなく、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去することが可能となる。なお、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報の消去処理の実行中は、上述した遊技履歴用処理を一時的に実行することができなくなるため、遊技球の各入球口への入球個数や賞球集計値等に誤差が生じる可能性がある。したがって、当該消去処理の実行の開始から終了までの期間において遊技の実行を一時的に停止させる構成(例えば、遊技球の発射を一時的に抑止する構成)とすれば、当該誤差の発生を抑制することができる。
With this configuration, it is possible to erase the information stored in the second area of the
<態様46>
上記各態様において、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)が消去される際には必ず主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等の遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)が消去される構成としてもよい。すなわち、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するための所定の操作が実行された場合や、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するための所定の信号を他の装置(例えば検査機320)から受信した場合には、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するだけでなく、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報も必ず消去する構成としてもよい。
<
In each of the above aspects, when information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64 (information acquired based on the executed game, such as the prize ball tally, the number of balls entered, and the game history information, such as the ratio of special features) is erased, information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64 (information used to control the execution of the game, such as the high probability mode flag and the high frequency support mode flag) may be erased. In other words, when a predetermined operation for erasing information stored in the second area of the
このような構成によれば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されずにそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。具体的には、例えば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、当該パチンコ機10において実行された遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる情報であるため、当該担保となる情報が消去された場合には、当該パチンコ機10における遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(例えば、遊技状態を示す高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグに関する情報)を消去して当該パチンコ機10の遊技状態を初期化することが好ましい。本態様の構成によれば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報)を消去する際には遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)を消去するので、遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる情報が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されないことによって当該パチンコ機10の遊技状態がそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。
This configuration makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which information used to control the execution of a game (information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64) is not erased and is maintained as is even though information acquired based on an executed game (information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64) is erased. Specifically, for example, since the information acquired based on an executed game is information that serves as a guarantee for determining the fairness of a game executed in the
また、例えば、仮に、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されずにそのまま維持される構成とした場合には、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されたにも関わらず、当該パチンコ機10において高確率モードや高頻度サポートモードがそのまま維持される場合がある。この場合において当該パチンコ機10において遊技を実行すると、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報が統計データとして十分な量ではない状態において高確率モードや高頻度サポートモードで遊技が開始されるため、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報が偏った値として算出されてしまう可能性が高くなる。したがって、本態様のように、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)が消去される際には必ず主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等の遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)が消去される構成とすることによって、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報が偏った値として算出されてしまうことを抑制することが可能となる。
In addition, for example, if the information acquired based on the executed game (the information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64) is erased but the information used to control the execution of the game (the information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64) is maintained as is, the high probability mode or high frequency support mode may be maintained as is in the
なお、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去するための操作としては、種々の操作態様を採用することができる。例えば、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら当該パチンコ機10の電源をONにするとともに当該RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態をそのまま所定時間(例えば10秒)継続させる操作や、パチンコ機10の背面側に別途設けられた第2RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら当該パチンコ機10の電源をONにする操作、RAMクリアボタン及び第2RAMクリアボタンの両方を押下しながら当該パチンコ機10の電源をONにする操作等を採用することができる。
In addition, various operation modes can be used as the operation for erasing the information stored in the second area of the
さらに、例えば、RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにするという操作が実行され、かつ、所定時間(例えば10秒)以内に当該RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態になった場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等を含む遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)は消去され、第2エリアに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)は消去されない構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, for example, when an operation is performed in which the power of the
このような構成によれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)を残しつつ、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)を消去することが可能となる。具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や、遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したいが、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は消去したくないといった要望がある。本態様の構成によれば、RAMクリアボタンを操作することによって、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報を消去して当該パチンコ機10の制御の初期化を実行することが可能となる。
According to this configuration, it is possible to erase the information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64 (information used to control the execution of the game) while leaving the information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64 (information acquired based on the executed game). Specifically, for example, when a malfunction occurs in the control of the execution of the game or when the business hours of the game parlor are opened or closed, there is a desire to erase the information used to control the execution of the game and initialize the control of the gaming machine, but not to erase the information acquired based on the executed game. According to the configuration of this aspect, by operating the RAM clear button, it is possible to erase the information used to control the execution of the game while leaving the information acquired based on the executed game, and initialize the control of the
図32は、本態様の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行するメイン処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。主側CPU62xは、電源の投入に伴ってこのメイン処理を実行する。
Figure 32 is a flowchart showing an example of the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS10901では、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態であるか否かを判定する。ステップS10901において、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS10901:NO)、後述するステップS10902に進む。一方、ステップS10901において、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態であると判定した場合には(ステップS10901:YES)、ステップS10903に進み、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が継続しているか否かを判定する。 In step S10901, it is determined whether or not the RAM clear button is pressed. If it is determined in step S10901 that the RAM clear button is not pressed (step S10901: NO), the process proceeds to step S10902, which will be described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10901 that the RAM clear button is pressed (step S10901: YES), the process proceeds to step S10903, where it is determined whether or not the RAM clear button remains pressed.
ステップS10903において、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が継続していないと判定した場合、すなわち、RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態となったと判定した場合には(ステップS10903:NO)、ステップS10904に進み、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報を消去し、当該第1エリアの初期設定処理を実行する。その後、後述するステップS10908に進む。一方、ステップS10903において、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が継続していると判定した場合には(ステップS10903:YES)、ステップS10905に進み、RAMクリアボタンの押下状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続しているか否かを判定する。
If it is determined in step S10903 that the RAM clear button is not continuing to be pressed, i.e., if it is determined that the RAM clear button is no longer pressed (step S10903: NO), the process proceeds to step S10904, where the information stored in the first area of the
ステップS10905において、RAMクリアボタンの押下状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続していないと判定した場合には(ステップS10905:NO)、ステップS10903に戻り、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態が継続しているか否かを判定する。一方、ステップS10905において、RAMクリアボタンの押下状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続していると判定した場合には(ステップS10905:YES)、ステップS10906に進む。すなわち、RAMクリアボタンの押下状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続しなかった場合には上述したステップS10904に進み、RAMクリアボタンの押下状態が所定時間(例えば10秒)継続した場合には後述するステップS10906に進むことになる。 If it is determined in step S10905 that the RAM clear button has not been pressed for a predetermined time (e.g., 10 seconds) (step S10905: NO), the process returns to step S10903, where it is determined whether the RAM clear button is still pressed. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10905 that the RAM clear button has been pressed for a predetermined time (e.g., 10 seconds) (step S10905: YES), the process proceeds to step S10906. That is, if the RAM clear button has not been pressed for a predetermined time (e.g., 10 seconds), the process proceeds to step S10904 described above, and if the RAM clear button has been pressed for a predetermined time (e.g., 10 seconds), the process proceeds to step S10906 described below.
ステップS10906では、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報を消去し、当該第1エリアの初期設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS10907に進み、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去し、当該第2エリアの初期設定処理を実行する。その後、後述するステップS10908に進む。
In step S10906, the information stored in the first area of the
一方、ステップS10901において、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS10901:NO)、ステップS10902に進み、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効であるか否かを判定する。具体的には、例えば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報である賞球集計値(役物賞球数、連続役物賞球数、総賞球数)が有効であるか否かを判定する。ここで、賞球集計値が有効ではない場合とは、役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合や、連続役物賞球数が総賞球数を超えている場合、連続役物賞球数が役物賞球数を超えている場合など、賞球集計値に矛盾が生じている場合である。ステップS10902において、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS10902:NO)、上述したステップS10906及びステップS10907に進み、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報及び第2エリアに記憶されている情報を消去する。その後、ステップS10908に進む。一方、ステップS10902において、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報が有効であると判定した場合には(ステップS10902:YES)、そのままステップS10908に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S10901 that the RAM clear button is not pressed (step S10901: NO), the process proceeds to step S10902, where it is determined whether or not the information stored in the second area of the
ステップS10908では、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可するために割込み許可の設定を行う。ステップS10908を実行した後、ステップS10909~ステップS10912の残余処理に進む。このステップS10909~ステップS10912の残余処理は、上述した図12におけるステップS10104~ステップS10107の残余処理と同じ処理であるため、説明を省略する。 In step S10908, interrupt permission is set to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. After step S10908 is executed, the process proceeds to the remaining processing of steps S10909 to S10912. The remaining processing of steps S10909 to S10912 is the same as the remaining processing of steps S10104 to S10107 in FIG. 12 described above, and therefore will not be described here.
以上説明した処理フローによれば、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)を消去する処理(ステップS10906の処理)を実行する際には、必ず主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等の遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)を消去する処理(ステップS10907の処理)を実行することになる。 According to the processing flow described above, when executing the process of deleting the information stored in the second area of the main RAM 64 (information acquired based on the executed game, such as the prize ball tally, ball number information, and game history information such as the ratio of game devices) (step S10906), a process of deleting the information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64 (information used to control the execution of the game, such as the high probability mode flag and high frequency support mode flag) (step S10907) is always executed.
<態様47>
上記各態様において、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報等の実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)が消去される際には必ず主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等の遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)が消去される構成としてもよい。すなわち、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するための操作が実行された場合や、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するための所定の信号を他の装置(例えば検査機320)から受信した場合には、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報を消去するだけでなく、主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報も必ず消去する構成としてもよい。
<
In each of the above aspects, when information stored in the
このような構成によれば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報)が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されずにそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。具体的には、例えば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、当該パチンコ機10において実行された遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる情報であるため、当該担保となる情報が消去された場合には、当該パチンコ機10における遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(例えば、遊技状態を示す高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグに関する情報)を消去して当該パチンコ機10の遊技状態を初期化することが好ましい。本構成によれば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報)を消去する際には遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)を消去するので、遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる情報が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報)が消去されないことによって当該パチンコ機10の遊技状態がそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。
This configuration makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which information used to control the execution of a game (information stored in the first area of the main RAM 64) is not erased and is maintained as is even though information acquired based on an executed game (information stored in the
さらに、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報(実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)が消去される際には、必ず主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている情報(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等の遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報)に加えて、主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている情報(実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報)も消去される構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, when the information stored in the
<態様48>
上記の一部の態様では、主側RAM64は、2つのエリア(第1エリア及び第2エリア)に区分されており、主側RAM64の第1エリアは、遊技の進行に関する処理を実行するためのプログラムや各種フラグ(高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグ等)等を記憶する領域として用いられ、主側RAM64の第2エリアは、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための処理(遊技履歴用処理)を実行するためのプログラムや各種の数値情報(上述した賞球集計値や、入球個数情報、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)等を記憶する領域として用いられる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、主側RAM64の第1エリアの機能を担うRAM(遊技進行処理に用いられるRAM)と、主側RAM64の第2エリアの機能を担うRAM(遊技履歴用処理に用いられるRAM)とを別々に備える構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 48>
In some of the above-mentioned embodiments, the
<態様49>
上記の各態様のうち、フラッシュメモリ64xを備える態様において、当該フラッシュメモリ64xは、開放の痕跡が残る空間(例えば、封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、当該フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうとするためには、当該パチンコ機10の基盤ボックスを開けることになり、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、パチンコ機10の基板ボックスに開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該パチンコ機10の基板ボックスが開かれてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報に不正な改変が施された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。したがって、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報に施された不正な改変の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。
<Aspect 49>
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in the aspect having the
なお、開放の痕跡(開封の痕跡、開閉の痕跡ともいう)が残る空間の構成としては、上記態様38において説明した種々の構成を採用することができる。
The space that leaves traces of opening (also called traces of opening and closing) can be configured in the various ways described in
<態様50>
図33は、態様50におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成の一部を模式的に示す説明図である。本態様の主側MPU62には、入出力ポート62aと主側CPU62xとの間に、入球検知用IC62cが設けられている。
<Aspect 50>
33 is an explanatory diagram showing a schematic diagram of a part of the electrical configuration of the
入球検知用IC62cは、入出力ポート62aを介して各入球検知センサー44a~44hと電気的に接続されており、各入球検知センサー44a~44hから受信した信号に基づいて各入球口への遊技球の入球の有無を判定し、当該判定の結果を示す情報(各入球口への遊技球の入球の有無に関する情報である入球情報)を主側CPU62x及び検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に出力する。以下、具体的に説明する。
The ball
各入球口への遊技球の入球を検知する各入球検知センサー44a~44hは、入力ポート62bに設けられた8個の入力ビットである第0ビットD0~第7ビットD7に電気的に接続されており、当該8個の入力ビットD0~D7は、入球検知用IC62cに設けられた8個の入力ビットR0~R7にそれぞれ電気的に接続されている。本態様では、入球検知用IC62cに設けられた8個の入力ビットR0~R7のそれぞれには、常時Loレベルの信号が入力されており、入球口への遊技球の入球が入球検知センサーによって検知されると、8個の入力ビットR0~R7のうち当該入球検知センサーに対応した入力ビットに入力されている信号がLoレベルからHiレベルに立ち上がるように構成されている。
Each ball
入球検知用IC62cは、各入球検知センサー44a~44hから出力された信号に基づいて、各入球口への遊技球の入球の有無を判定する。本態様では、入球検知用IC62cは、8個の入球検知センサー44a~44hにそれぞれ対応する8個の入力ビットR0~R7を監視しており、各入力ビットに入力されている信号におけるLoレベルからHiレベルへの立ち上がりエッジを検出した場合に、当該入力ビットに対応した入球口に遊技球が入球したと判定する。ただし、立ち上がりエッジを検出したがHiレベルの状態が所定期間継続しない場合、及び、立ち上がりエッジを検出したが当該立ち上がりエッジが直近の立ち下がりエッジから所定の間隔以下で発生した立ち上がりエッジであった場合には、当該検出した立ち上がりエッジはノイズである可能性が高いため、当該入力ビットに対応した入球口には遊技球が入球していないと判定する。なお、遊技球が各入球口に入球したか否かの判定方法としては種々の方法を採用することが可能であり、例えば、上述した入球判定処理(図16、図17)と同様の方法を採用してもよい。
The ball
入球検知用IC62cは、所定期間毎に各入球口における遊技球の入球の有無を判定し、当該判定の結果を示す情報である入球情報を、シリアル伝送方式の通信によって、主側CPU62xに出力し、また、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に出力する。本態様では、8個の入球検知センサー44a~44hが設けられているため、入球検知用IC62cは、8個の各入球口における遊技球の入球の有無を示す入球情報(8ビット分の入球情報)を所定期間毎(4ms毎)に出力する。具体的には、入球検知用IC62cは、常時Loレベルの信号を出力しており、入球の有無を判定した所定期間毎(4ms毎)に、スタートビットとして50μsのHiレベル信号を出力し、その後、8個の各入球口における遊技球の入球の有無に対応した50μsのHiレベルの信号(入球有り)又はLoレベルの信号(入球無し)を8ビット分出力し、最後にストップビットとして50μsのLoレベルの信号を出力する。
The ball
入球検知用IC62cから入球情報を受信した主側CPU62xは、当該受信した各入球口の入球情報に基づいて、上述した大当たり抽選や、賞球の払出し等の遊技の進行に関する処理を実行する。また、主側CPU62xは、上述した遊技履歴用処理(図29)を実行し、出球率(トータル)や、役物比率、連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報の算出及び表示に関する処理も実行する。そして、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴情報の算出過程において用いた数値情報や、算出した遊技履歴情報をフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶させる。
The
次に、入球検知用IC62cから出力される入球情報を受信可能な検査機320を用いた検査について説明する。
Next, we will explain the inspection using an
本態様では、パチンコ機10の検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において遊技が実行されている最中、すなわち、遊技者又は検査者が当該パチンコ機10の操作ハンドル25を操作して遊技球を遊技盤30に発射させて通常通りに遊技を実行している最中に、検査機320を用いることによって、この検査中の期間において当該パチンコ機10において正当な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する。以下、具体的に説明する。
In this embodiment, while a game is being played on the
検査機320は、各入球口における遊技球の入球情報を入球検知用IC62cから受信するモードである入球情報受信モードと、パチンコ機10に設けられている入球口の種別や賞球数に関する情報である入球口情報を設定する入球口情報設定モードと、受信した入球情報及び設定された入球口情報に基づいて上述した各種の遊技履歴情報を算出する遊技履歴情報算出モードとを実行可能である。
The
検査者は、パチンコ機10において正当な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する際には、検査機320の接続ケーブル329を当該パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続し、当該検査機320の操作部327を操作して当該検査機320を上述した入球情報受信モードに移行させる。遊技者又は検査者は、検査対象のパチンコ機10の操作ハンドル25を操作して遊技球を遊技盤30に発射させ、遊技の実行を通常通りに継続する。
When an inspector inspects whether a legitimate game is being played on a
検査機320は、入球情報受信モードに移行すると、接続ケーブル329内の出力許可信号線329bにHiレベルの信号を出力する。出力許可信号線329bは、検査用端子65を介して入球検知用IC62cの出力許可判定用ビット62dに電気的に接続されている。入球検知用IC62cは、当該出力許可判定用ビット62dにHiレベルの信号が入力されているか否かを判定し、出力許可判定用ビット62dにHiレベルの信号が入力されていると判定している期間中に限り、検査用端子65を介して接続ケーブル329内の情報伝送用信号線329aに上述した入球情報をシリアル伝送方式の通信によって出力する。
When the
検査機320は、入球情報受信モードにおいて、所定期間毎に8個の入球口に対応した入球情報を受信し、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を計測(カウント)して記憶する。そして、検査機320は、計測(カウント)した各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を示す情報を表示部328に表示させる。すなわち、遊技者又は検査者が遊技を実行して各入球口に遊技球が入球する毎に、表示部328に表示されている各入球口に対応した入球個数を示す情報に1が加算される。この結果、検査機320の表示部328には、入球情報受信モードに移行した後に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数が表示されることになる。
In the ball entry information receiving mode, the
十分な検査期間(例えば、10時間程度等)が経過した後、検査者が検査機320の操作部327を操作して入球情報受信モードを終了させると、検査機320は、入球口情報設定モードに移行する。
After a sufficient inspection period (e.g., about 10 hours) has elapsed, the inspector operates the
検査機320は、入球口情報設定モードに移行すると、各入球口毎に、入球口の種別及び賞球数を検査者に入力させるための入力画面を表示部328に表示させる。本態様では、検査機320は、入球情報受信モードにおいて所定期間毎に8ビット分の入球情報を受信しているので、表示部328には、8個の入球口のそれぞれに対して入球口の種別及び賞球数を入力させるための入力画面が表示される。なお、入球口の種別とは、第1始動口33や第2始動口34、大入賞口36a、排出通路といった各入球検知センサー44a~44hが設けられている入球口の種別であり、賞球数とは、入球口に1個の遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数である。
When the
検査者は、操作部327を操作することによって、各入球口毎に、入球口情報(入球口の種別情報及び賞球数情報)を検査機320に入力する。具体的には、検査者は、入球検知用IC62cから出力される入球情報における何番目のビットがどの種別の入球口に対応しているのかといった情報(種別情報)や、どの種別の入球口に何個の賞球数を設定すればよいのかといった情報(賞球数情報)を、当該パチンコ機10の仕様書や説明書等によって把握し、当該把握した情報を検査機320に入力する。検査者が入球口情報の入力を完了すると、検査機320は、遊技履歴情報算出モードに移行する。
The inspector operates the
検査機320は、遊技履歴情報算出モードに移行すると、入球情報受信モードにおいて計測(カウント)した各入球口毎の遊技球の入球個数と、入球口情報設定モードにおいて設定された種別情報及び賞球数情報とに基づいて、上述した各種の遊技履歴情報を算出する。例えば、検査機320は、上述した出球率(トータル)、役物比率、連続役物比率を算出する。検査機320は、各種の遊技履歴情報の算出が完了すると、算出した各種の遊技履歴情報を表示部328に表示させる。
When the
検査者は、検査機320の表示部328に表示された各種の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、当該検査期間において正当な遊技が実行されていたか否かを確認することができる。
The inspector can check whether legitimate play was performed during the inspection period by checking the various game play history information displayed on the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して主側CPU62xを介さずに入球情報を出力するので、検査機320は、主側CPU62xによる影響を受けていない入球情報を受信することが可能となる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the ball
例えば、仮に、本態様の構成を採用せずに、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して主側CPU62xを介して入球情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該主側CPU62xに不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、検査機320に出力される入球情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。また、当該主側CPU62xの不具合や不正な改造の影響で、当該主側CPU62xが算出して表示している遊技履歴情報の信頼性が低いおそれもある。
For example, if the configuration of this embodiment were not adopted, and a configuration were adopted in which ball entry information is output via the
これに対して、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して主側CPU62xを介さずに入球情報を出力するので、主側CPU62xに不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、検査機320に出力される入球情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない入球情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。具体的には、検査機320は、主側CPU62xによる影響を受けていない入球情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、パチンコ機10の性能を検査する検査者は、主側CPU62xに不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている可能性があり、主側CPU62xが算出して表示している遊技履歴情報の信頼性が低い場合であっても、主側CPU62xによる影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を検査機320によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。
In contrast, according to this embodiment, the ball
また、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して、複数の入球口のそれぞれに対応した入球情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力するので、例えば、入球情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合と比較して、当該入球情報を検査機320に経由させる検査用端子65の構成を簡略化することができるとともに、当該入球情報を受信する検査機320の構成を簡略化することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the ball
具体的には、仮に、複数の入球口のそれぞれに対応した入球情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合には、検査用端子65は、当該複数の入球口の個数に対応した出力部(例えば、出力用のビット)を備える必要がある。同様に、検査機320は、当該複数の入球口の個数に対応した入力部(例えば、入力用のビット)を備える必要がある。また、パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数は、パチンコ機10の種別毎(機種毎)に異なるため、パチンコ機10の種別毎(機種毎)に異なる個数の入力部を備えた検査機320を用意する必要が生じる。
Specifically, if a configuration is adopted in which ball entry information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry ports is output by a parallel transmission method, the
これに対して、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して、複数の入球口のそれぞれに対応した入球情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、検査用端子65は、当該パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって入球情報を出力することのできる出力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよい。したがって、検査用端子65の構成を簡略化することができる。同様に、検査機320は、当該パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって出力された入球情報を入力することのできる入力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよいので、検査機320の構成を簡略化することができる。さらに、入球口の個数の異なるパチンコ機10に検査機320を接続した場合であっても、当該検査機320は、シリアル伝送方式によって複数の入球口のそれぞれに対応した入球情報を入力することができる。すなわち、検査機320を、入球口の個数の異なる他のパチンコ機10に対しても利用することが可能となる。この結果、検査機320の汎用性を高めることが可能となる。
In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the ball
また、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320からHiレベルの信号を受信している場合に限り当該検査機320に対して入球情報を出力するので、当該Hiレベルの信号を受信している場合以外において当該パチンコ機10の入球情報が外部に出力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、当該パチンコ機10の入球情報が悪意のある者に解析されて悪用されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the ball
<態様51>
上記態様50では、検査機320の入球口情報設定モードにおいて、入球口情報を検査者が操作部327を操作して検査機320に手入力する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、入球口情報を検査機320がパチンコ機10から受信して設定する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 50, in the entrance gate information setting mode of the
具体的には、例えば、検査機320は、入球口情報設定モードに移行すると、接続ケーブル329及び検査用端子65を介して、入球口情報の送信を要求する信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を入球検知用IC62cに送信する。当該信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を受信した入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65及び接続ケーブル329を介して当該パチンコ機10の入球口情報を検査機320に送信する。検査機320は、入球検知用IC62cから受信した入球口情報を各入球口毎に設定し、入球口情報設定モードを終了する。
Specifically, for example, when the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320に対して入球口情報(賞球数情報及び種別情報)を出力するので、検査機320に対して入球口情報(賞球数情報及び種別情報)を手入力する手間を省くことができるとともに、検査機320に対して誤った入球口情報(賞球数情報及び種別情報)が入力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、検査機320は、入球情報と正確な入球口情報(賞球数情報及び種別情報)とに基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the ball
なお、本態様では、入球検知用IC62cは、所定の信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を受信したことに基づいて、当該パチンコ機10の入球口情報を検査機320に送信する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、入球検知用IC62cは、検査機320の接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを契機として(すなわち、検査機320の接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続されたことを検知した場合に)、当該パチンコ機10の入球口情報を検査機320に送信する構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、検査機320は、接続ケーブル329が検査用端子65に接続された後に、当該入球口情報を必要とする処理を速やかに実行することが可能となる。
In this embodiment, the ball
また、本態様では、入球口情報を入球検知用IC62cが検査機320に送信する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、主側CPU62xが、主側ROM63に記憶されている入球口情報を読み出して検査機320に送信する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the ball
<態様52>
上記態様50では、入球検知用IC62cは、出力許可判定用ビット62dにHiレベルの信号が入力されていると判定している期間中に限り、検査用端子65を介して入球情報をシリアル伝送方式の通信によって出力する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、他の構成を採用してもよい。例えば、入球検知用IC62cは、出力許可判定用ビット62dに所定のパターンの信号が入力されていると判定している期間中に限り、検査用端子65を介して入球情報をシリアル伝送方式の通信によって出力する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、入球検知用IC62cは、出力許可判定用ビット62dに所定のパターンの信号が入力されたと判定した場合に、検査用端子65を介して入球情報をシリアル伝送方式の通信によって出力する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、検査用端子65に所定のスイッチを設け、所定の形状のケーブル端子が当該検査用端子65に接続されて当該所定のスイッチが押下された状態となっていると判定した場合に、入球検知用IC62cは、検査用端子65を介して入球情報をシリアル伝送方式の通信によって出力する構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 52>
In the above-mentioned aspect 50, the
<態様53>
上記態様50から態様52において、検査機320は、入球口情報設定モードにおいて入球口情報の設定が完了した後に入球情報受信モードに移行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、入球情報受信モードへの移行の時点において各入球口の種別が設定されるので、入球情報受信モード中において検査機320の表示部328に各入球口の種別及び入球個数を表示することが可能となる。
<Aspect 53>
In the above-mentioned aspects 50 to 52, the
この結果、検査者は、どの種別の入球口に遊技球が入球したのかを入球情報受信モード中においても把握することが可能となる。さらに、検査者は、表示部328に表示されている情報(各入球口の種別及び入球個数)と、目視で確認した実際に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数とが一致しているか否かを確認することによって、入球検知用IC62cから出力されている入球情報が真正なものであるか否かを確認することができる。
As a result, the inspector can ascertain which type of ball entry port the game ball entered even during the ball entry information receiving mode. Furthermore, the inspector can confirm whether the ball entry information output from the ball
<態様54>
上記態様50から態様53において、検査機320は、接続ケーブル329がパチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続されたことを契機として、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている遊技履歴情報を受信するモードである遊技履歴情報受信モードに移行し、その後、上述した入球口情報設定モード、入球情報受信モード及び遊技履歴情報算出モードに移行する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above aspects 50 to 53, the
具体的には、例えば、検査機320は、接続ケーブル329がパチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続されたことを検出すると、遊技履歴情報受信モードに移行する。検査機320は、遊技履歴情報受信モードに移行すると、接続ケーブル329及び検査用端子65を介して、遊技履歴情報の送信を要求する信号(遊技履歴情報送信要求コマンド)を主側CPU62xに送信する。当該信号(遊技履歴情報送信要求コマンド)を受信した主側CPU62xは、検査用端子65及び接続ケーブル329を介して、当該パチンコ機10のフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている遊技履歴情報を検査機320に送信する。検査機320は、主側CPU62xから受信した遊技履歴情報をRAM326に記憶すると、当該遊技履歴情報受信モードを終了し、入球口情報設定モードに移行する。
Specifically, for example, when the
検査機320は、入球口情報設定モードに移行すると、接続ケーブル329及び検査用端子65を介して、入球口情報の送信を要求する信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を主側CPU62xに送信する。当該信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を受信した主側CPU62xは、検査用端子65及び接続ケーブル329を介して、当該パチンコ機10の入球口情報を検査機320に送信する。検査機320は、主側CPU62xから受信した入球口情報を各入球口毎に設定すると、当該入球口情報設定モードを終了し、入球情報受信モードに移行する。
When the
検査機320は、入球情報受信モードに移行すると、所定期間毎に8個の入球口に対応した入球情報を受信し、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を計測(カウント)して記憶する。そして、検査機320は、計測(カウント)した各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を示す情報を表示部328に表示させる。すなわち、遊技者又は検査者が遊技を実行して各入球口に遊技球が入球する毎に、表示部328に表示されている各入球口に対応した入球個数を示す情報に1が加算される。この結果、検査機320の表示部328には、入球情報受信モードに移行した後に各入球口に入球した遊技球の個数が表示されることになる。
When the
十分な検査期間(例えば、10時間程度等)が経過した後、検査者が検査機320の操作部327を操作して入球情報受信モードを終了させると、検査機320は、遊技履歴情報算出モードに移行する。
After a sufficient inspection period has elapsed (e.g., about 10 hours), the inspector operates the
検査機320は、遊技履歴情報算出モードに移行すると、入球情報受信モードにおいて計測(カウント)した各入球口毎の遊技球の入球個数と、入球口情報設定モードにおいて設定された種別情報及び賞球数情報とに基づいて、上述した各種の遊技履歴情報を算出する。例えば、検査機320は、上述した出球率(トータル)、役物比率、連続役物比率を算出する。検査機320は、各種の遊技履歴情報の算出が完了すると、遊技履歴情報算出モードにおいて算出した各種の遊技履歴情報と、遊技履歴情報受信モードにおいて受信した各種の遊技履歴情報(フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されていた遊技履歴情報)とを表示部328に表示させる。すなわち、検査機320の表示部328には、当該検査機320の接続ケーブル329がパチンコ機10に接続されて入球情報受信モードにおいて入球情報を受信していた検査期間を対象とした遊技履歴情報と、当該パチンコ機10の主側CPU62xによって算出されてフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている過去の所定期間を対象とした遊技履歴情報とが表示される。
When the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、検査用端子65に接続された検査機320は、フラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている遊技履歴情報(以下、第1遊技履歴情報とも呼ぶ)を受信して表示することが可能となる。また、検査機320は、検査期間において受信した入球情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。具体的には、検査機320は、当該パチンコ機10の検査用端子65に接続されている所定の検査期間において受信した入球情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該遊技履歴情報(以下、第2遊技履歴情報とも呼ぶ)を表示することが可能となる。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10を検査する検査者は、パチンコ機10が備えるフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている第1遊技履歴情報と、検査機320が所定の検査期間において受信した入球情報に基づいた第2遊技履歴情報とを比較することが可能となる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the
ここで、仮に、パチンコ機10に不具合が発生したり、不正な改造(例えば釘の改変等)が施されたりしたこと等によって当該パチンコ機10における遊技の特性に変化が生じた場合には、パチンコ機10が備えるフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている第1遊技履歴情報(過去の所定期間における入球情報に基づいて主側CPU62xによって算出された遊技履歴情報)と、検査機320が所定の検査期間における入球情報に基づいて算出した第2遊技履歴情報とに差が生じることがある。したがって、パチンコ機10を検査する検査者は、2つの遊技履歴情報の差分に注目することによって、当該パチンコ機10において不具合や不正な改造(例えば、釘の改変)が発生していないかを検査することができる。
If a malfunction occurs in the
なお、検査機320は、上述した入球口情報設定モードにおいて入球口情報を受信して設定した後に、遊技履歴情報受信モードに移行して遊技履歴情報を受信する構成としてもよい。また、検査機320は、上述した遊技履歴情報算出モードにおいて当該検査期間における遊技履歴情報を算出した後に、遊技履歴情報受信モードに移行してフラッシュメモリ64xに記憶されている遊技履歴情報を受信する構成としてもよい。
The
<態様55>
上記態様50から態様54において、パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数は8個に限られず、9個以上であってもよく、7個以下であってもよい。そして、入球検知用IC62cは、入球口の個数に対応した入球情報を出力する構成とすればよい。例えば、パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数が7個以下の場合には、入球検知用IC62cは、シリアル伝送方式によって出力する8ビットのうちの前半のビットを用いて入球情報を出力する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、パチンコ機10が備える入球口の個数が9個以上の場合には、入球検知用IC62cは、シリアル伝送方式による8ビットの出力を複数回実行することによって9個以上の入球口に対応した入球情報を出力する構成としてもよい。また、入球検知用IC62cは、シリアル伝送方式によって16ビットや32ビット等の入球情報を一度に出力可能な構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspects 50 to 54, the number of ball entrances provided in the
<態様56>
上記態様23では、主側CPU62xが遊技履歴用処理をタイマ割込み処理に含まれる一処理として実行する構成(図23:ステップS10616)としたが、この構成に代えて、CPU62xが遊技履歴用処理をタイマ割込み処理では実行せず、上述したメイン処理の残余時間において実行する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
In the above-mentioned
図34は、態様56における主側CPU62xが実行するメイン処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。ステップS11001では、初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、電源投入に伴う各制御装置の初期設定や、RAM64に記憶保持されたデータの有効性の判定などを実行する。ステップS11001を実行した後、ステップS11002に進み、タイマ割込み処理(図13)の発生を許可するために割込み許可の設定を行う。
Figure 34 is a flow chart showing an example of main processing executed by the
ステップS11002を実行した後、ステップS11003~ステップS11007の残余処理に進む。すなわち、主側CPU62xは上述したようにタイマ割込み処理を定期的に実行する構成であるが、一のタイマ割込み処理と次のタイマ割込み処理との間に残余時間が生じることとなる。この残余時間は各タイマ割込み処理の処理完了時間に応じて変動することとなるが、この不規則な時間(残余時間)を利用してステップS11003~ステップS11007の処理(残余処理)を繰り返し実行する。
After executing step S11002, the process proceeds to the remaining processing of steps S11003 to S11007. That is, the
ステップS11003では、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止するために割込み禁止の設定を行う。その後、ステップS11004に進み、乱数初期値カウンタCINIの更新を行う乱数初期値更新処理を実行するとともに、ステップS11005に進み、変動種別カウンタCSの更新を行う変動用カウンタ更新処理を実行する。これらの更新処理では、主側RAM64の対応するカウンタから現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報を1加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに上書きする処理を実行する。この場合、カウンタ値が最大値に達した際それぞれ「0」にクリアする。その後、ステップS11006に進む。
In step S11003, interrupt prohibition is set to prohibit timer interrupt processing from occurring. Then, the process proceeds to step S11004, where a random number initial value update process is executed to update the random number initial value counter CINI, and to step S11005, where a fluctuation counter update process is executed to update the fluctuation type counter CS. In these update processes, the current numerical information is read from the corresponding counter in the
ステップS11006では、上述した遊技履歴用処理(図29)を実行する。遊技履歴用処理は、上述したように、順次実行することによって遊技履歴情報の算出が完了する複数のタスク(図29のステップS10814のタスク1及びタスク2)を含んでいる。そして、主側CPU62xは、残余処理に含まれる遊技履歴用処理の1回の実行では、複数のタスクのうちの一部のタスクを実行する。すなわち、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴用処理を複数回実行することによって、算出対象として設定された遊技履歴情報の算出を完了する。ステップS11006を実行した後、ステップS11007に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止している状態から許可する状態へ切り換える割込み許可の設定を行う。ステップS11007の処理を実行した後は、ステップS11003に戻り、ステップS11003~ステップS11007の処理を繰り返す。
In step S11006, the above-mentioned game history process (FIG. 29) is executed. As described above, the game history process includes a number of tasks (
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、メイン処理における残余時間(一のタイマ割込み処理の実行の終了後から次のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始までの期間)において遊技履歴用処理を含む残余処理を繰り返し実行するので、一のタイマ割込み処理の実行が終了していないにも関わらず遊技履歴用処理を含む残余処理の実行が開始されてしまうことを抑制することができる。すなわち、タイマ割込み処理の実行を優先しつつ、タイマ割込み処理が実行されていない期間において遊技履歴用処理を含む残余処理を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 As described above, according to this embodiment, the remaining processes including the game history process are repeatedly executed during the remaining time in the main process (the period from the end of execution of one timer interrupt process to the start of execution of the next timer interrupt process), so that it is possible to prevent the execution of the remaining processes including the game history process from starting even though the execution of one timer interrupt process has not ended. In other words, while giving priority to the execution of the timer interrupt process, it is possible to quickly calculate game history information by repeatedly executing the remaining processes including the game history process during the period when the timer interrupt process is not being executed.
また、仮に、本態様の構成を採用せずに、遊技履歴用処理をタイマ割込み処理に含めて実行する構成を採用した場合には、当該タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間が長くなってしまい、例えば、一のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始から所定時間(本態様では4msec)が経過し、次のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始のタイミングとなったにも関わらず未だ一のタイマ割込み処理の実行が終了しておらず、当該一のタイマ割込み処理の実行が終了するまで次のタイマ割込み処理の実行を開始することができなくなってしまう可能性がある。この場合には、次のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始が遅れてしまったことによって遊技の進行に不具合が発生するおそれがある。 Furthermore, if the configuration of this embodiment were not adopted, and a configuration in which the game history processing is included in the timer interrupt processing and executed was adopted, the time required from start to finish of one execution of the timer interrupt processing would be longer. For example, even though a predetermined time (4 msec in this embodiment) has passed since the start of execution of one timer interrupt processing and it is time to start execution of the next timer interrupt processing, the execution of the first timer interrupt processing has not yet finished, and it may not be possible to start execution of the next timer interrupt processing until the execution of the first timer interrupt processing has finished. In this case, there is a risk of a malfunction occurring in the progress of the game due to the delay in starting the execution of the next timer interrupt processing.
これに対して、本態様によれば、遊技履歴用処理を残余処理に含めて実行するので、遊技履歴用処理をタイマ割込み処理に含めて実行する構成と比較して、タイマ割込み処理の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間を短くすることができる。この結果、例えば、一のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始から所定時間(本態様では4msec)が経過し、次のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始のタイミングとなったにも関わらず未だ一のタイマ割込み処理の実行が終了していないといった事態の発生を抑制することができ、当該一のタイマ割込み処理の実行が終了するまで次のタイマ割込み処理の実行を開始することができないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。このように、本態様によれば、次のタイマ割込み処理の実行の開始が遅れてしまうことによる遊技の進行における不具合の発生を抑制しつつ、タイマ割込み処理が実行されていない期間において遊技履歴用処理を含む残余処理を繰り返し実行することによって効率的かつ速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the game history process is executed as part of the remaining process, so that the time required from start to end of one execution of the timer interrupt process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the game history process is executed as part of the timer interrupt process. As a result, for example, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which a predetermined time (4 msec in this embodiment) has passed since the start of execution of one timer interrupt process, and the timing for starting execution of the next timer interrupt process has arrived, but the execution of the first timer interrupt process has not yet ended, and it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which execution of the next timer interrupt process cannot be started until the execution of the first timer interrupt process ends. In this way, according to the present embodiment, it is possible to efficiently and quickly calculate game history information by repeatedly executing the remaining process including the game history process during the period in which the timer interrupt process is not being executed, while preventing the occurrence of problems in the progress of the game due to a delay in the start of execution of the next timer interrupt process.
さらに、本態様によれば、遊技履歴用処理は、順次実行することによって遊技履歴情報の算出が完了する複数のタスク(図29のステップS10814のタスク1及びタスク2)を含んでおり、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴用処理の1回の実行では、複数のタスクのうちの一部のタスクを実行するので、例えば、遊技履歴用処理の1回の実行において複数のタスクの全てを実行する構成と比較して、遊技履歴用処理の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間を短くすることができる。具体的には、例えば、遊技履歴用処理の実行中にタイマ割込み処理の実行開始の条件が成立した場合においても、実行中の遊技履歴用処理が短時間で終了するので、当該条件の成立からタイマ割込み処理の実行が開始されるまでの時間を短くすることができる。この結果、タイマ割込み処理の実行の開始が遅れてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制しつつ、残余処理を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the game history process includes a plurality of tasks (
さらに、本態様によれば、残余時間の長さは、タイマ割込み処理の開始から終了までに要した時間的な長さに応じて変化する。具体的には、例えば、一のタイマ割込み処理の長さが長くなると、当該一のタイマ割込み処理の終了後から次のタイマ割込み処理の開始までの残余時間は短くなり、一方、一のタイマ割込み処理の長さが短くなると、当該一のタイマ割込み処理の終了後から次のタイマ割込み処理の開始までの残余時間は長くなる。そして、残余時間が短い場合には、遊技履歴用処理の実行回数を少なくすることができ、一方、残余時間が長い場合には、遊技履歴用処理の実行回数を多くすることができる。すなわち、残余時間の長さに応じて遊技履歴用処理の実行回数を変更することができる。 Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the length of the remaining time changes depending on the length of time required from the start to the end of the timer interrupt process. Specifically, for example, if the length of one timer interrupt process is longer, the remaining time from the end of that timer interrupt process to the start of the next timer interrupt process is shorter, whereas if the length of one timer interrupt process is shorter, the remaining time from the end of that timer interrupt process to the start of the next timer interrupt process is longer. If the remaining time is short, the number of times the game history process is executed can be reduced, whereas if the remaining time is long, the number of times the game history process is executed can be increased. In other words, the number of times the game history process is executed can be changed depending on the length of the remaining time.
<態様57>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の各態様において、パチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率の異なる複数の設定を有する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、同じ低確率モードであっても、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率の異なる6段階の抽選設定(「抽選設定1」~「抽選設定6」)を有する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 57>
In the first embodiment and each of the above aspects, the
本態様のパチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、「抽選設定1」から「抽選設定6」までの6段階の抽選設定のそれぞれに対応した6種類の低確率モード用の当否テーブルを備えている。そして、主制御装置60は、設定されている抽選設定に対応した当否テーブルを参照して大当たり抽選を実行する。例えば、パチンコ機10が抽選設定1に設定されている状態であり、抽選モードが低確率モードである場合には、主制御装置60は、抽選設定1の低確率モード用の当否テーブルを参照して大当たり抽選を実行する。
The
本態様では、抽選設定1の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~4の5個の値が設定されている。また、抽選設定2の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~5の6個の値が設定されている。また、抽選設定3の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~6の7個の値が設定されている。また、抽選設定4の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~7の8個の値が設定されている。また、抽選設定5の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~8の9個の値が設定されている。また、抽選設定6の低確率モード用の当否テーブルには、0~1199の大当たり乱数カウンタC1の値のうち、大当たりに当選する値として、0~9の10個の値が設定されている。 In this embodiment, the hit/miss table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 1 has five values, 0 to 4, set as values that win the jackpot among the values of the jackpot random number counter C1 from 0 to 1199. The hit/miss table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 2 has six values, 0 to 5, set as values that win the jackpot among the values of the jackpot random number counter C1 from 0 to 1199. The hit/miss table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 3 has seven values, 0 to 6, set as values that win the jackpot among the values of the jackpot random number counter C1 from 0 to 1199. The hit/miss table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 4 has eight values, 0 to 7, set as values that win the jackpot among the values of the jackpot random number counter C1 from 0 to 1199. The hit/miss table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 5 has nine values, 0 to 8, set as values that win the jackpot among the values of the jackpot random number counter C1 from 0 to 1199. In addition, in the win/lose table for the low probability mode of lottery setting 6, 10 values from 0 to 9 are set as the winning values for the jackpot out of the jackpot random number counter C1 values from 0 to 1199.
すなわち、本態様では、「抽選設定」の後に続く数字が大きいほど、低確率モードにおける大当たり抽選の当選確率が高くなるように構成されている。 In other words, in this embodiment, the larger the number following "lottery setting", the higher the probability of winning the jackpot lottery in low probability mode.
なお、本態様では、6段階の抽選設定のうち、いずれに設定されていても、高確率モードにおいては同一の当否テーブルを参照して大当たり抽選を実行するように構成されている。すなわち、高確率モードにおいては、抽選設定に関わらず、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率は同じである。ただし、他の態様として、高確率モードにおいても、「抽選設定」の後に続く数字が大きいほど、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率が高くなるように構成されていてもよい。 In this embodiment, regardless of which of the six lottery settings is set, the same win/lose table is referenced in the high probability mode to execute the jackpot lottery. In other words, in the high probability mode, the probability of winning the jackpot in the jackpot lottery is the same regardless of the lottery setting. However, as another embodiment, the high probability mode may be configured such that the larger the number following the "lottery setting", the higher the probability of winning the jackpot in the jackpot lottery.
本態様では、6段階の抽選設定の変更は、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に実行可能であるように構成されている。以下、具体的に説明する。
In this embodiment, the six-stage lottery setting change is configured to be executable when the
本態様では、パチンコ機10の背面側に位置する主制御基板61には、設定変更用の鍵穴と、設定変更用ボタンとが設けられている。パチンコ機10を管理する管理者が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更する場合には、まず、パチンコ機10の電源がOFFの状態で当該鍵穴に設定変更用の鍵を挿入する。そして、挿入した鍵を設定変更側に回した状態(例えば時計回りに回した状態)で当該パチンコ機10の電源を投入すると、当該パチンコ機10は設定変更モードとして起動する。
In this embodiment, the
パチンコ機10が設定変更モードとして起動すると、上述した遊技履歴情報表示部45zに、現在の抽選設定を示す情報(以下、設定情報ともいう)が表示される。例えば、当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定が「抽選設定1」である場合には、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに「1」が表示される。そして、管理者が設定変更用ボタンを押下する度に、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が「1」→「2」→「3」→「4」→「5」→「6」→「1」→「2」...といった順序で切り替わる。
When the
遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報が管理者の所望の値となった状態で、管理者が設定変更用鍵を設定変更側から元の位置に回すと、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報に対応する抽選設定に変更される。具体的には、例えば、管理者が設定変更用ボタンを押下して遊技履歴情報表示部45zに「6」が表示されている状態で、設定変更用鍵を設定変更側から元の位置に回すと、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定が「抽選設定6」に変更される。
When the setting information displayed on the game history
このように、本態様によれば、パチンコ機10における抽選設定を変更することによって、大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率を変更することができる。この結果、同一のパチンコ機10であっても、大当たり抽選の結果、特別電動役物としての可変入賞装置36が作動することになる確率が変更されるので、遊技履歴情報として算出される上述した役物比率や連続役物比率の値は、変更された新たな抽選設定に対応した値に収束していくことになる。すなわち、パチンコ機10における抽選設定を変更することによって、当該パチンコ機10の役物比率や連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報が変化することになる。換言すれば、パチンコ機10における抽選設定を変更するといった簡易な方法によって、当該パチンコ機10の特性を変化させることができる。
In this manner, according to this embodiment, by changing the lottery settings in the
なお、以下に説明する各態様では、上述した遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる情報である各入球口への入球情報や入球個数情報、賞球集計値等を「遊技履歴基礎情報」ともいう。 In addition, in each aspect described below, the information that serves as the basis for calculating the above-mentioned game history information, such as ball entry information for each entry port, information on the number of balls that have entered, and the prize ball tally, is also referred to as "game history basic information."
<態様58>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、パチンコ機10における抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更の前に各種メモリ(主側RAM64やフラッシュメモリ64x等)に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去し、抽選設定が変更された後に各種メモリに記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 58>
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (a configuration in which the lottery settings for the jackpot lottery can be changed), when the lottery settings in the
このような構成とした理由について説明する。パチンコ機10における抽選設定(大当たり抽選において大当たりに当選する確率の設定)が変更されると、特別電動役物としての可変入賞装置36が作動することになる確率が変更されるので、遊技履歴情報として算出される上述した役物比率や連続役物比率の値は、変更された新たな抽選設定に対応した値に収束していくことになる。すなわち、抽選設定の変更の前後で、役物比率や連続役物比率の収束していくべき値が変化することになる。
The reason for this configuration will be explained below. When the lottery setting in the pachinko machine 10 (the setting of the probability of winning the jackpot in the jackpot lottery) is changed, the probability that the variable winning
仮に、抽選設定が変更された後においても、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去せずに、抽選設定の変更がされた後に取得された遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶する構成を採用すると、遊技履歴情報を算出する際に、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報の影響が含まれることになり、抽選設定の変更の後のパチンコ機10の本来の特性が遊技履歴情報に反映されるまでに時間を要する場合がある。
If a configuration were adopted in which the game history basic information stored before the lottery setting was changed is not erased even after the lottery setting is changed, and the game history basic information acquired after the lottery setting is changed is stored, the game history basic information stored before the lottery setting is changed will have an effect when calculating the game history information, and it may take some time for the original characteristics of the
そこで、本態様では、抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去し、抽選設定の変更の後に取得、記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成とする。 Therefore, in this embodiment, when the lottery settings are changed, the basic game history information stored before the lottery settings are changed is erased, and the game history information is calculated and displayed based on the basic game history information acquired and stored after the lottery settings are changed.
本態様によれば、役物比率や連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報が、変更後の抽選設定に対応した値に早く収束することになり、パチンコ機10の検査者は、当該パチンコ機10に現在設定されている抽選設定に対応した遊技履歴情報を早期に確認することが可能となる。
According to this embodiment, the game history information such as the ratio of the role and the ratio of consecutive roles quickly converges to a value corresponding to the changed lottery setting, and the inspector of the
<態様59>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後においても、抽選設定の変更の前に各種メモリに記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去せずに、抽選設定の変更がされた後に取得された遊技履歴基礎情報を各種メモリに追加して記憶し、抽選設定の変更の前後を問わず各種メモリに記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 59>
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (a configuration in which the lottery settings for the jackpot lottery can be changed), even after the lottery settings of the
本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更による影響も含めた遊技履歴情報を算出し、表示することが可能となる。したがって、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技ホールにおいて当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更が運用された結果として、抽選設定の変更による影響が含まれたトータルとしての遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲内に収まっているか否かを確認することができる。
According to this embodiment, it is possible to calculate and display game history information that includes the effects of changing the lottery settings of the
<態様60>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去し、今回の抽選設定の変更の後に取得された遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶し、当該記憶した遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (a configuration in which the lottery settings for the jackpot lottery can be changed), when the lottery settings of the
このような構成において、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が所定の量まで蓄積される前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す情報(以下、短期変更情報ともいう)を記録し、当該短期変更情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
In such a configuration, if the lottery settings of the
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が1000個に達する前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す短期変更情報を記録し、当該短期変更情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示する構成とする。また、例えば、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに短期変更情報を表示するためのLEDランプを設け、短期変更情報が記録された場合には当該LEDランプを発光させる構成としてもよい。
Specifically, for example, if the lottery setting of the
本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、短期変更情報が表示されているか否かを確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10において抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたか否かを確認することができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
According to this embodiment, an inspector of the
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10が検査者によって検査される前に、当該パチンコ機10の管理者が、当選確率の変更後に当該遊技機において遊技があまり実行されていない状況であるにも関わらず、再び抽選設定の変更を行なって、当該パチンコ機10に記憶されている遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。しかしながら、本態様によれば、抽選設定の変更後に当該パチンコ機10において遊技があまり実行されていない状況であるにも関わらず、再び抽選設定の変更が短期間で行なわれた場合には、上述した短期変更情報が記録され、表示されることになる。したがって、検査者は、短期変更情報を確認することによって、遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報の消去といった不正な意図によって抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかと認識することが可能となる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
Specifically, for example, before the
なお、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更されてから所定時間が経過する前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合に、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す情報(短期変更情報)を記録し、当該短期変更情報を表示する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更と変更の間に当該パチンコ機10において遊技が行なわれなかった場合であっても、抽選設定の変更と変更の間に所定時間が経過していれば短期変更情報が表示されない。したがって、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更と変更の間が比較的長期間となっているが当該変更と変更の間に当該パチンコ機10において遊技が行なわれなかったに過ぎない状況であるにも関わらず、不正な意図によって抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかといった検査者による誤認を抑制することができる。
In addition, if the lottery setting of the
<態様61>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を記憶・表示可能な構成としてもよい。そして、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、既に記憶されている直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去し、今回の抽選設定の変更の後に取得された遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (configuration capable of changing the lottery setting of the big win lottery), the basic game history information and the game history information for the most recent multiple periods with the past lottery setting changed as the boundary may be stored and displayed. When the lottery setting of the
このような構成において、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が所定の量まで蓄積される前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す情報(以下、短期変更情報ともいう)を記録し、当該短期変更情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
In such a configuration, if the lottery settings of the
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が1000個に達する前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す短期変更情報を記録し、当該短期変更情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示する構成とする。また、例えば、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに短期変更情報を表示するためのLEDランプを設け、短期変更情報が記録された場合には当該LEDランプを発光させる構成としてもよい。
Specifically, for example, if the lottery setting of the
以上説明した本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、当該パチンコ機10における過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報を確認することが可能となる。すなわち、検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において抽選設定が過去に変更されてきた過程において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。
According to the above-described embodiment, the inspector of the
さらに、本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、短期変更情報が表示されているか否かを確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10において抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたか否かを確認することができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, an inspector of the
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10が検査者によって検査される前に、当該パチンコ機10の管理者が、抽選設定の変更を短期間に繰り返し行なって、当該パチンコ機10の直近の複数の期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。しかしながら、本態様によれば、抽選設定の変更が短期間で繰り返し行なわれた場合には、上述した短期変更情報が記録され、表示されることになる。したがって、検査者は、短期変更情報を確認することによって、不正な意図によって抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかと認識することが可能となる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
Specifically, for example, before the
なお、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更されてから所定時間が経過する前に、再度パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合に、抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれたことを示す情報(短期変更情報)を記録し、当該短期変更情報を表示する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更と変更の間に当該パチンコ機10において遊技が行なわれなかった場合であっても、抽選設定の変更と変更の間に所定時間が経過していれば短期変更情報が表示されない。したがって、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更と変更の間が比較的長期間となっているが当該変更と変更の間に当該パチンコ機10において遊技が行なわれなかったに過ぎない状況であるにも関わらず、不正な意図によって抽選設定の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかといった検査者による誤認を抑制することができる。
In addition, if the lottery setting of the
<態様62>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後、遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な量まで蓄積されるまでは、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報が消去されずに保存(記憶)されている構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (a configuration in which the lottery settings for the jackpot lottery can be changed), after the lottery settings of the
さらに、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに点滅表示させる構成とし、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な量まで蓄積された後は、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, until the game history basic information acquired and stored after the lottery setting is changed is accumulated to a predetermined amount sufficient as statistical data, the game history information calculated based on the game history basic information stored before the lottery setting is changed may be displayed in a flashing manner on the game history
具体的には、例えば、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達するまでは、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報が消去されずに記憶されている構成とする。そして、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達するまでは、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに点滅表示させる構成とする。抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達した後は、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去し、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該算出した遊技履歴情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる構成とする。
Specifically, for example, the game history basic information stored before the lottery setting is changed is stored without being erased until the total number of prize balls in the prize ball tally value as the game history basic information acquired and stored after the lottery setting is changed reaches 60,000. Then, until the total number of prize balls in the prize ball tally value as the game history basic information acquired and stored after the lottery setting is changed reaches 60,000, the game history information calculated based on the game history basic information stored before the lottery setting is changed is displayed in a blinking manner on the game history
本態様によれば、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報が、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更を行なうことによって意図的に消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。例えば、仮に、抽選設定の変更の前に取得されて記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報が、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更が行なわれた直後に消去される構成を採用すると、パチンコ機10が検査者によって検査される前に、当該パチンコ機10の管理者が、抽選設定の変更を行なって、当該抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本態様によれば、抽選設定の変更の前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報は、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは消去されないので、パチンコ機の管理者による不正な意図による抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
According to this aspect, it is possible to prevent the basic game history information stored before the lottery setting is changed from being intentionally erased by changing the lottery setting of the
さらに、パチンコ機10の検査者は、遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示されている遊技履歴情報が点滅表示であるか点灯表示であるかを確認することによって、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積されているか否かを容易に把握することが可能となる。
Furthermore, by checking whether the game history information displayed on the game history
なお、抽選設定が変更される前に記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報の消去及び点滅表示から点灯表示への切り替えの条件としては、総賞球数の他にも種々の基準を採用することができる。例えば、排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数)の集計値を基準として採用してもよい。 In addition, various criteria other than the total number of winning balls can be used as the conditions for erasing the basic game history information stored before the lottery settings were changed and for switching from a flashing display to a lit display. For example, the total number of game balls that have passed through the discharge passage (the number of game balls that have been launched onto the game board 30) may be used as the criterion.
<態様63>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を記憶・表示可能な構成としてもよい。そして、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは、既に記憶されている直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去せず、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積された後に、既に記憶されている直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (configuration capable of changing the lottery setting of the big win lottery), the game history basic information and the game history information for the most recent multiple periods with the past lottery setting changed as a boundary may be stored and displayed. And, when the lottery setting of the
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された場合には、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達するまでは、既に記憶されている直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去せず、パチンコ機10の抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報としての賞球集計値における総賞球数が60000個に達した後に、既に記憶されている直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去する構成としてもよい。
Specifically, for example, when the lottery settings of the
本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、当該パチンコ機10における過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報を確認することが可能となる。すなわち、検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において抽選設定が過去に変更されてきた過程において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。
According to this embodiment, the inspector of the
さらに、本態様によれば、過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更が繰り返し行なわれることによって意図的に消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, it is possible to prevent the basic game history information and game history information for the most recent periods bounded by past changes in the lottery settings from being intentionally erased due to repeated changes in the lottery settings of the
例えば、仮に、過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が、パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更が行なわれた直後に消去される構成を採用すると、パチンコ機10が検査者によって検査される前に、当該パチンコ機10の管理者が、抽選設定の変更を繰り返し行なって、当該パチンコ機10の直近の複数の期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。
For example, if a configuration were adopted in which the basic game history information and game history information for the oldest of the most recent periods bounded by past lottery setting changes were erased immediately after the lottery settings of the
これに対して、本態様によれば、過去の抽選設定の変更を境界とした直近の複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報は、抽選設定が変更された後に取得されて記憶された遊技履歴基礎情報が統計データとして十分な所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは消去されないので、パチンコ機10の管理者による不正な意図による抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the basic game history information and the game history information for the oldest of the most recent periods bounded by past lottery setting changes are not erased until the basic game history information acquired and stored after the lottery setting is changed has accumulated to a predetermined amount sufficient as statistical data, thereby preventing the administrator of the
<態様64>
上記態様57(大当たり抽選の抽選設定を変更可能な構成)において、取得した遊技履歴基礎情報を、取得した時点におけるパチンコ機10の抽選設定毎に区別して記憶し、抽選設定毎に遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57 (a configuration in which the lottery settings for the jackpot lottery can be changed), the acquired basic game history information may be stored separately for each lottery setting of the
具体的には、例えば、遊技履歴基礎情報を各種メモリに記憶する際に、遊技履歴基礎情報を取得したタイミングにおける抽選設定を特定可能な情報を付加して記憶する。そして、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する際には、各抽選設定毎に遊技履歴基礎情報を抽出して、各抽選設定毎の遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。 Specifically, for example, when the game history basic information is stored in various memories, information capable of identifying the lottery setting at the time when the game history basic information was acquired is added and stored. Then, when calculating and displaying the game history information, the game history basic information may be extracted for each lottery setting, and the game history information for each lottery setting may be calculated and displayed.
また、他の具体的な構成として、各種メモリに抽選設定毎に対応した記憶エリアを設け、取得した遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶する際には、現在設定されている抽選設定に対応した記憶エリアに記憶する構成としてもよい。例えば、パチンコ機10が抽選設定1に設定されている場合には、取得した遊技履歴基礎情報を抽選設定1に対応した記憶エリアに記憶し、パチンコ機10が抽選設定2に設定されている場合には、取得した遊技履歴基礎情報を抽選設定2に対応した記憶エリアに記憶する。そして、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する際には、各記憶エリアに記憶されている遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて、各抽選設定毎の遊技履歴情報を算出・表示する構成としてもよい。
As another specific configuration, various memories may be provided with memory areas corresponding to each lottery setting, and the acquired basic game history information may be stored in the memory area corresponding to the currently set lottery setting. For example, when the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の検査者は、例えば、当該パチンコ機10が抽選設定1に設定されている状態において取得された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて算出された遊技履歴情報や、当該パチンコ機10が抽選設定2に設定されている状態において取得された遊技履歴基礎情報に基づいて算出された遊技履歴情報など、当該パチンコ機10の各抽選設定毎に算出された各遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。そして、検査者は、当該パチンコ機10の各抽選設定毎に算出された各遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲内に収まっているか否かを確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10において遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲内に収まっていない抽選設定が存在しないか否かを確認することが可能となる。
According to this configuration, an inspector of the
<態様65>
上記態様57では、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示させる構成としたが、遊技履歴情報表示部45zとは別に、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を表示する抽選設定表示部を当該パチンコ機10の背面側に設ける構成としてもよい。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 57, the lottery settings of the
<態様66>
上記各態様では、算出した遊技履歴情報そのものの数値を遊技履歴情報表示部45zに表示する構成としたが、遊技履歴情報そのものの数値は表示せずに、遊技履歴情報の数値が所定の範囲に収まっているか否かを示す情報を遊技履歴情報表示部45zやその他の表示部に表示する構成としてもよい。例えば、遊技履歴情報としての役物比率及び連続役物比率がそれぞれ所定の範囲に収まっているか否かを、発光させるLEDランプの色で表示する構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 66>
In each of the above-mentioned aspects, the calculated numerical value of the gaming history information itself is displayed on the gaming history
<態様67>
上記各態様において、パチンコ機10の背面に設けられた遊技履歴情報表示部45zは、4個の7セグメント表示器が横一列に隣接して配置されている構成としてもよい。なお、遊技履歴情報表示部45zは、遊技履歴情報を表示するだけでなく、抽選設定を変更する設定変更モード中においては遊技履歴情報の代わりに設定情報を表示するので、以下では単に「情報表示部45z」とも呼ぶ。
<Aspect 67>
In each of the above aspects, the game history
図35は、態様67における情報表示部45zの構成を示す説明図である。情報表示部45zは、4個の7セグメント表示器45z1~45z4が横一列に隣接して配置されて構成されている。各7セグメント表示器45z1~45z4は、それぞれ、7個のセグメント発光部A~Gと、小数点を示すDP発光部とを備えており、これらの発光部の発光の有無の組合せによって、「1」、「2」、「3」、「4」、「5」、「6」、「7」、「8」、「9」、「0」、「b」、「L.」、「6.」などの各種の数値や文字、記号等を表示することが可能である。本態様では、7個のセグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部は、赤色のLED(発光ダイオード)によって構成されている。
Figure 35 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of the
なお、以下では、左端に配置された7セグメント表示器45z1を左端7セグメント表示器45z1とも呼び、左端7セグメント表示器45z1の右側に隣接して配置された7セグメント表示器45z2を左中7セグメント表示器45z2とも呼び、左中7セグメント表示器45z2の右側に隣接して配置された7セグメント表示器45z3を右中7セグメント表示器45z3とも呼び、右中7セグメント表示器45z3の右側に隣接して配置され、かつ右端に配置された7セグメント表示器45z4を右端7セグメント表示器45z4とも呼ぶ。 In the following, the 7-segment display 45z1 located at the left end is also referred to as the left end 7-segment display 45z1, the 7-segment display 45z2 located adjacent to the right side of the left end 7-segment display 45z1 is also referred to as the left middle 7-segment display 45z2, the 7-segment display 45z3 located adjacent to the right side of the left middle 7-segment display 45z2 is also referred to as the right middle 7-segment display 45z3, and the 7-segment display 45z4 located adjacent to the right side of the right middle 7-segment display 45z3 and located at the right end is also referred to as the right end 7-segment display 45z4.
図35に示すように、左端7セグメント表示器45z1及び左中7セグメント表示器45z2は、遊技履歴情報を表示する際には、表示する遊技履歴情報の種別を識別するための情報である種別情報を表示するエリア(種別情報表示エリア)として利用される。また、右中7セグメント表示器45z3及び右端7セグメント表示器45z4は、種別情報表示エリアに表示されている種別に対応した遊技履歴情報の数値情報を表示するエリア(数値情報表示エリア)として利用される。以下、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報が表示されている具体例について説明する。
As shown in FIG. 35, when displaying game history information, the leftmost seven-segment display 45z1 and the left-center seven-segment display 45z2 are used as an area (type information display area) that displays type information, which is information for identifying the type of game history information to be displayed. In addition, the right-center seven-segment display 45z3 and the rightmost seven-segment display 45z4 are used as an area (numeric information display area) that displays numerical information of the game history information corresponding to the type displayed in the type information display area. Below, a specific example of game history information being displayed on the
図36は、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報が表示されている様子を示す説明図である。なお、図36では、点灯しているセグメント発光部及びDP発光部は黒で塗り潰された状態で表記されており、消灯しているセグメント発光部及びDP発光部は黒で塗り潰されておらず白抜きの状態で表記されている。図37以降の図面においても同様である。
Figure 36 is an explanatory diagram showing how game history information is displayed on the
本態様のパチンコ機10では、主制御装置60は、上述した抽選設定を変更する設定変更モード中以外の状態では、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報を常に表示させる。そして、本態様のパチンコ機10では、主制御装置60は、遊技履歴情報として、上述した出玉率(通常モード中)を算出し、算出した出球率(通常モード中)を情報表示部45zに表示させる。出球率(通常モード中)の定義は以下のとおりである。
・出玉率(通常モード中)
=通常モード中に賞球として払い出された遊技球の合計個数/通常モード中に遊技盤30に発射された遊技球の個数(=通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数))
なお、通常モード中とは、上述したように、高確率モード中でもなく、高頻度サポートモード中でもなく、大当たり当選に基づいた開閉実行モード中でもないモードをいう。また、以下では、出球率(通常モード中)を「ベース(通常モード中)」とも呼ぶ。
In the
・Ball payout rate (in normal mode)
= Total number of game balls paid out as prize balls during normal mode / Number of game balls shot onto the
As mentioned above, the normal mode refers to a mode that is not a high probability mode, not a high frequency support mode, and not a mode that is based on a big win. In the following, the ball output rate (in the normal mode) is also called the "base (in the normal mode)".
本態様のパチンコ機10では、主制御装置60は、計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達する毎に区間を分け、区間毎にベース(通常モード中)を算出する。そして、情報表示部45zは、算出対象となった区間の異なる2種類のベース(通常モード中)を交互に表示する。具体的には、本態様の情報表示部45zは、以下の2種類のベース(通常モード中)を表示する。
In the
・「bL」:計測中のベース(通常モード中)
現在計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達するまでの現在の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b6」:計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の1つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・"bL": Base being measured (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate calculated in the current section until the number of balls passing through the discharge passage currently being measured N OUT reaches 60,000 (in normal mode)
・"b6": Measured base (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section immediately preceding the section currently being measured in which the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT has reached 60,000.
本態様のパチンコ機10では、情報表示部45zは、「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」と「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」とを5秒毎に切り替えて交互に表示する。
In this embodiment of the
情報表示部45zが「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」を表示する際には、種別情報表示エリアに「bL.」を表示し、数値情報表示エリアに「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の数値を2桁で表示する。具体的には、種別情報表示エリアに「bL.」を表示する際には、左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部C、D、E、F、Gが発光した状態となり、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部D、E、F及びDP発光部が発光した状態となる。そして、数値情報表示エリアを構成する右中7セグメント表示器45z3及び右端7セグメント表示器45z4には、「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の数値情報が表示される。なお、本態様では、算出した「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の小数第三位の値を四捨五入して100倍した数値の整数部が数値情報表示エリアに表示される。図36に示した例では、情報表示部45zは、「bL.35」といった情報を表示しており、小数第三位の値を四捨五入した「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の値が「0.35」であることを意味する。また、小数第三位の値を四捨五入した「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の値が「1.00」以上である場合には、100倍した値が100以上となるので、この場合には、情報表示部45zは、「bL.99.」といった情報を表示する。
When the
情報表示部45zが「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」を表示する際には、種別情報表示エリアに「b6.」を表示し、数値情報表示エリアに「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」の数値を2桁で表示する。具体的には、種別情報表示エリアに「b6.」を表示する際には、左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部C、D、E、F、Gが発光した状態となり、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部A、C、D、E、F、G及びDP発光部が発光した状態となる。そして、数値情報表示エリアを構成する右中7セグメント表示器45z3及び右端7セグメント表示器45z4には、「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」の数値情報が表示される。なお、本態様では、算出した「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」の少数第三位の値を四捨五入して100倍した数値の整数部が数値情報表示エリアに表示される。図36に示した例では、情報表示部45zは、「b6.35」といった情報を表示しており、小数第三位の値を四捨五入した「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」の値が「0.35」であることを意味する。また、小数第三位の値を四捨五入した「計測済みのベース(通常モード中)」の値が「1.00」以上である場合には、100倍した値が100以上となるので、この場合には、情報表示部45zは、「b6.99.」といった情報を表示する。
When the
なお、本態様のパチンコ機10では、情報表示部45zが遊技履歴情報を表示する際には、数値情報表示エリアに表示すべき数値が1桁の値である場合であっても、右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「0」を表示して2桁で数値を表示する。例えば、小数第三位の値を四捨五入した「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」の値が「0.07」である場合には、100倍した値が7となるので、この場合には、情報表示部45zは、「bL.07」といった情報を表示する。
In addition, in the
ここで、本態様のパチンコ機10では、遊技履歴情報を表示する際には、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアには、「bL.」と「b6.」とが交互に表示され、これら2つの種別情報以外は表示されない。したがって、本態様のパチンコ機10では、遊技履歴情報を表示する際には、種別情報表示エリアを構成する左端7セグメント表示器45z1及び左中7セグメント表示器45z2のうち、以下の発光部は使用されない(発光しない)。
[遊技履歴情報の表示時に使用されない種別情報表示エリアの発光部]
・左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部A、B及びDP発光部
・左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部B
Here, in the
[Light-emitting portion of type information display area not used when displaying game history information]
Segment light emitting sections A, B and DP light emitting section of the leftmost 7-segment display 45z1 Segment light emitting section B of the center left 7-segment display 45z2
換言すれば、遊技履歴情報を表示する際には、種別情報表示エリアを構成する左端7セグメント表示器45z1及び左中7セグメント表示器45z2のうち、以下の発光部のみが使用される(発光する)。
[遊技履歴情報の表示時に使用される種別情報表示エリアの発光部]
・左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部C、D、E、F、G
・左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部A、C、D、E、F、G及びDP発光部
なお、参考として、図36に、遊技履歴情報の表示時に使用される種別情報表示エリアの発光部をクロスハッチングが施された態様で示した。
In other words, when displaying the game history information, only the following light-emitting portions of the leftmost 7-segment display 45z1 and the left center 7-segment display 45z2 that constitute the category information display area are used (illuminated).
[Light-emitting portion of type information display area used when displaying game history information]
Segment light emitting sections C, D, E, F, and G of the leftmost 7-segment display 45z1
- Segment light-emitting sections A, C, D, E, F, G and DP light-emitting section of left center 7-segment display 45z2.For reference, Figure 36 shows the light-emitting sections of the type information display area used when displaying game history information in a cross-hatched manner.
次に、上述した抽選設定を変更する設定変更モード中における情報表示部45zの表示態様について説明する。本態様では、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zは、現在の抽選設定を示す情報又は変更後の抽選設定を示す情報である設定情報を表示する。以下、具体的に説明する。
Next, the display mode of the
図37及び図38は、設定変更モード中において情報表示部45zに設定情報が表示されている様子を示す説明図である。この図37及び図38には、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに抽選設定を示す設定情報(数値情報)として「1」~「6」が表示されている様子が示されている。
Figures 37 and 38 are explanatory diagrams showing how setting information is displayed in the
上述したように、パチンコ機10が設定変更モードとして起動すると、情報表示部45zは、現在の抽選設定を示す数値情報を数値情報表示エリアに表示する。そして、管理者が設定変更用ボタンを押下すると、情報表示部45zは、変更後の抽選設定を示す数値情報を数値情報表示エリアに表示する。そして、管理者が設定変更用の鍵を設定変更側から元の位置に回すと、設定変更モードが終了し、情報表示部45zは、再び数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報を表示する。
As described above, when the
本態様では、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアには「--(2個のハイフン)」が表示され、数値情報表示エリアには「1」~「6」のいずれかの設定情報が表示される。設定変更モード中において種別情報表示エリアに表示される「--(2個のハイフン)」といった表示パターンは、遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示する際には表示されない表示パターンである。
In this embodiment, during the setting change mode, "-- (two hyphens)" is displayed in the type information display area of the
具体的には、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアを構成する左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部Gが発光し、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部Gが発光する。すなわち、本態様のパチンコ機10では、設定変更モード中においては、遊技履歴情報の表示時に使用される発光部のみが使用される。換言すれば、遊技履歴情報の表示時に使用されない発光部は、設定変更モード中においても使用されない。
Specifically, during the setting change mode, the segment light emitting section G of the leftmost seven-segment display 45z1 constituting the type information display area of the
また、本態様では、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアを構成する右中7セグメント表示器45z3及び右端7セグメント表示器45z4のうち、右中7セグメント表示器45z3は使用せず、右端7セグメント表示器45z4のみを使用して抽選設定を示す数値情報を表示する。すなわち、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアは、2桁の数値情報を表示することが可能であるが、設定変更モード中においては、1桁目の右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「0」を表示せずに消灯状態とし、2桁目の右端7セグメント表示器45z4のみに抽選設定を示す「1」~「6」のいずれかの数値情報を表示する。
In addition, in this embodiment, of the right center 7-segment display 45z3 and the rightmost 7-segment display 45z4 that constitute the numerical information display area of the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、種別情報表示エリアの表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の管理者に、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者が、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と抽選設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the display mode of the category information display area is clearly different when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the numerical information display area of the
さらに、本特徴によれば、遊技履歴情報を表示する際に使用されない種別情報表示エリアの発光部(左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部A、B、DP発光部、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部B)は、設定変更モード中においても使用されないので、種別情報表示エリアには、使用されない発光部(以下、不使用発光部)が存在することになる。したがって、例えば、種別情報表示エリアの不使用発光部に不具合が発生したとしても、種別情報表示エリアにおける表示態様には影響がない。この結果、種別情報表示エリアの発光部に不具合が発生した場合に表示態様に影響が生じてしまう可能性を低減することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the light-emitting parts in the type information display area that are not used when displaying game history information (segment light-emitting parts A, B and the DP light-emitting part of the leftmost seven-segment display 45z1, and segment light-emitting part B of the left-center seven-segment display 45z2) are not used even during the setting change mode, so that the type information display area has light-emitting parts that are not used (hereinafter, unused light-emitting parts). Therefore, for example, even if a malfunction occurs in an unused light-emitting part of the type information display area, the display mode in the type information display area is not affected. As a result, it is possible to reduce the possibility that the display mode will be affected if a malfunction occurs in a light-emitting part of the type information display area.
また、例えば、不使用発光部となる発光素子(LED)は発光する必要がないため、当該発光素子を発光させるために必要な部品を省略することができる。したがって、情報表示部45zのコストを低減することができる。
In addition, for example, since the light-emitting element (LED) that is the unused light-emitting portion does not need to emit light, the components required to make the light-emitting element emit light can be omitted. Therefore, the cost of the
さらに、本態様によれば、数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報に関する数値情報が表示されている場合と、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、表示されている数値の桁数が異なることになるので、仮に種別情報表示エリアの表示に不具合が発生していたとしても、管理者に対して、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報が遊技履歴情報であるのか、設定情報であるのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。すなわち、管理者は、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに2桁の数値が表示されている場合には当該数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値が遊技履歴情報であると判断し、数値情報表示エリアに1桁の数値が表示されている場合には当該数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値が設定情報であると判断することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the number of digits of the displayed numerical value differs when the numerical information display area displays numerical information related to game history information and when the numerical information display area displays numerical information related to lottery settings. Therefore, even if a malfunction occurs in the display of the type information display area, the administrator can clearly distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information displayed in the numerical information display area is game history information or setting information. In other words, when a two-digit number is displayed in the numerical information display area of the
<態様68>
上記態様67では、情報表示部45zは、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアに「--(2個のハイフン)」を点灯表示させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアに「--(2個のハイフン)」を点滅表示させる構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 68>
In the above-mentioned aspect 67, the
このような構成によれば、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、種別情報表示エリアの表示態様がさらに明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の管理者に、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかをさらに明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者が、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と抽選設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
With this configuration, the display mode of the category information display area becomes even more clearly different between when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the numerical information display area of the
さらに、本態様によれば、抽選設定に関する数値情報が数値情報表示エリアに表示されている設定変更モード中においては種別情報表示エリアにおける「--(2個のハイフン)」が点滅するので、パチンコ機10の管理者に対して、抽選設定の変更を慎重に行なうべき重要な状態であるといった注意を喚起することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, during the setting change mode in which the numerical information regarding the lottery setting is displayed in the numerical information display area, "-- (two hyphens)" flashes in the type information display area, alerting the administrator of the
<態様69>
上記態様67では、情報表示部45zは、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアに「--(2個のハイフン)」を点灯表示させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアには何も表示されない構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 69>
In the above-mentioned aspect 67, the
図39及び図40は、設定変更モード中において情報表示部45zに設定情報が表示されている様子を示す説明図である。この図39及び図40には、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに抽選設定を示す数値情報として「1」~「6」が表示されている様子が示されている。また、この図39に示すように、本態様では、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアを構成する左端7セグメント表示器45z1及び左中7セグメント表示器45z2の全てのセグメント発光部及びDP発光部を消灯させている。すなわち、上述したように、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアは、何も表示されていない状態となっている。
Figures 39 and 40 are explanatory diagrams showing the state in which setting information is displayed on the
このように、本態様によれば、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、種別情報表示エリアの表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の管理者に、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者が、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と抽選設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this way, according to this embodiment, the display mode of the category information display area is clearly different between when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the numerical information display area of the
さらに、本態様によれば、仮に種別情報表示エリアを構成する一部の発光部(セグメント発光部A~G等)が発光しないといった不具合が発生していたとしても、全ての発光部が発光しないといった重大な不具合が発生していない限りは、種別情報表示エリアの表示態様が、遊技履歴情報を表示している場合と抽選設定の設定情報を表示している場合とで異なることになる。したがって、本態様によれば、管理者に対して、仮に種別情報表示エリアを構成する一部の発光部(LED)が発光しない不具合が発生していたとしても、全ての発光部が発光しないといった重大な不具合が発生していない限りは、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報が遊技履歴情報であるのか、抽選設定の設定情報であるのかを区別して認識させることができる。すなわち、管理者は、種別情報表示エリアにおいて少なくとも一部の発光部が発光している場合には数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値が遊技履歴情報であると判断し、種別情報表示エリアを構成する全ての発光部が消灯している場合に限り数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値が抽選設定の設定情報であると判断することができる。 Furthermore, according to this aspect, even if a malfunction occurs in which some of the light-emitting parts (segment light-emitting parts A to G, etc.) constituting the category information display area do not emit light, the display mode of the category information display area will be different when displaying game history information and when displaying lottery setting information, as long as there is no serious malfunction in which all of the light-emitting parts do not emit light. Therefore, according to this aspect, even if a malfunction occurs in which some of the light-emitting parts (LEDs) constituting the category information display area do not emit light, as long as there is no serious malfunction in which all of the light-emitting parts do not emit light, the administrator can distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information displayed in the numerical information display area is game history information or lottery setting information. In other words, the administrator can determine that the numerical value displayed in the numerical information display area is game history information when at least some of the light-emitting parts in the category information display area are emitting light, and can determine that the numerical value displayed in the numerical information display area is lottery setting information only when all of the light-emitting parts constituting the category information display area are turned off.
<態様70>
上記態様67では、情報表示部45zは、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアに「--(2個のハイフン)」を点灯表示させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更モード中においては、種別情報表示エリアに、複数種類の表示パターンを短期間(例えば0.5秒毎)に切り替えて表示する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 67, the
図41は、設定変更モード中において情報表示部45zに設定情報が表示されている様子を示す説明図である。なお、この図41に示した例では、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに抽選設定を示す数値情報として「1」が表示されている様子が示されている。本態様のパチンコ機10では、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアには、下記の2種類の表示パターンが0.5秒毎に切り替えて交互に表示される。
Figure 41 is an explanatory diagram showing the state in which setting information is displayed in the
・種別情報表示エリアの表示パターンA:
左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部C、D、E、Gが点灯(発光)し、左中7セグメント表示器45z2の全ての発光部が消灯した表示パターン
・種別情報表示エリアの表示パターンB:
左端7セグメント表示器45z1の全ての発光部が消灯し、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部C、D、E、Gが点灯(発光)した表示パターン
Display pattern A of type information display area:
Display pattern in which the segment light emitting sections C, D, E, and G of the leftmost 7-segment display unit 45z1 are lit (illuminated), and all light emitting sections of the left center 7-segment display unit 45z2 are turned off. Display pattern B of the type information display area:
A display pattern in which all light-emitting parts of the leftmost 7-segment display 45z1 are turned off and the segment light-emitting parts C, D, E, and G of the left-center 7-segment display 45z2 are turned on (illuminated).
上述した表示パターンA及び表示パターンBは、遊技履歴情報を表示する際には種別情報表示エリアに表示されない表示パターンである。また、表示パターンA及び表示パターンBにおいては、遊技履歴情報の表示の際に使用される発光部のみが使用される。換言すれば、表示パターンA及び表示パターンBにおいては、遊技履歴情報の表示の際に使用されない発光部は使用されない。 The above-mentioned display pattern A and display pattern B are display patterns that are not displayed in the type information display area when displaying game history information. Furthermore, in display pattern A and display pattern B, only the light-emitting parts that are used when displaying game history information are used. In other words, in display pattern A and display pattern B, the light-emitting parts that are not used when displaying game history information are not used.
このように、本態様によれば、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、種別情報表示エリアの表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の管理者に、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアに遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、抽選設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、パチンコ機10の管理者が、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と抽選設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this way, according to this embodiment, the display mode of the category information display area is clearly different between when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the numerical information display area of the
さらに、本態様によれば、抽選設定に関する数値情報が数値情報表示エリアに表示されている設定変更モード中においては種別情報表示エリアにおける表示パターンが動的に変化することになるので、パチンコ機10の管理者に対して、抽選設定の変更を慎重に行なうべき重要な状態であるといった注意を喚起することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, during the setting change mode in which numerical information regarding the lottery setting is displayed in the numerical information display area, the display pattern in the type information display area changes dynamically, so that the administrator of the
さらに、本態様によれば、遊技履歴情報を表示する際に使用されない種別情報表示エリアの発光部(左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部A、B、DP発光部、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部B)は、設定変更モード中においても使用されないので、種別情報表示エリアには、使用されない発光部(以下、不使用発光部)が存在することになる。したがって、例えば、種別情報表示エリアの不使用発光部に不具合が発生したとしても、種別情報表示エリアにおける表示態様には影響がない。この結果、種別情報表示エリアの発光部に不具合が発生した場合に表示態様に影響が生じてしまう可能性を低減することができる。 Furthermore, according to this embodiment, the light-emitting parts in the type information display area that are not used when displaying game history information (segment light-emitting parts A, B and the DP light-emitting part of the leftmost seven-segment display 45z1, and segment light-emitting part B of the left-center seven-segment display 45z2) are not used even during the setting change mode, so that the type information display area has unused light-emitting parts (hereinafter, unused light-emitting parts). Therefore, for example, even if a malfunction occurs in an unused light-emitting part of the type information display area, the display mode in the type information display area is not affected. As a result, it is possible to reduce the possibility that the display mode will be affected if a malfunction occurs in a light-emitting part of the type information display area.
また、不使用発光部となる発光素子(LED)は発光する必要がないため、当該発光素子を発光させるために必要な部品を省略することができる。したがって、情報表示部45zのコストを低減することができる。
In addition, since the light-emitting elements (LEDs) that are unused light-emitting sections do not need to emit light, the components required to make the light-emitting elements emit light can be omitted. This allows the cost of the
なお、本態様では、設定変更モード中においては、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアには、2種類の表示パターンが交互に表示される構成としたが、3種類以上の表示パターンが順次切り替えて繰り返し表示される構成としてもよい。
In this embodiment, in the setting change mode, two types of display patterns are alternately displayed in the type information display area of the
<態様71>
上記各態様において、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が例えば6000個未満の場合には、種別情報表示エリアの「bL.」を点滅表示させ、6000個以上の場合には点灯表示させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、種別情報表示エリアにおける「bL.」の点滅表示を確認した者は、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が6000個未満であり、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値は、十分な量の統計データが蓄積されていない状態において算出された「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」であると認識することができる。
<
In each of the above aspects, if the "number of game balls passing through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, for example, "bL." in the type information display area may be displayed in a flashing manner, and if it is 6000 or more, the display may be lit up. With such a configuration, a person who sees the flashing display of "bL." in the type information display area can recognize that the "number of game balls passing through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, and that the value displayed in the numerical information display area is the "base during measurement (during normal mode)" calculated in a state in which a sufficient amount of statistical data has not been accumulated.
また、種別情報表示エリアの「bL.」を点灯表示とした上で、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が例えば6000個未満の場合には、数値情報表示エリアの数値を点滅表示させ、6000個以上の場合には点灯表示させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、数値情報表示エリアにおける数値の点滅表示を確認した者は、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が6000個未満であり、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値は、十分な量の統計データが蓄積されていない状態において算出された「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」であると認識することができる。 In addition, the "bL." in the category information display area may be displayed as a light, and if the "number of game balls that passed through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, the number in the numerical information display area may be displayed as a flashing number, and if it is 6000 or more, the number may be displayed as a light. With this configuration, a person who sees the flashing number in the numerical information display area can recognize that the "number of game balls that passed through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, and that the number displayed in the numerical information display area is the "base during measurement (during normal mode)" calculated when a sufficient amount of statistical data has not been accumulated.
また、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が例えば6000個未満の場合には、種別情報表示エリアの「bL.」及び数値情報表示エリアの数値を点滅表示させ、6000個以上の場合には点灯表示させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、種別情報表示エリアにおける「bL.」及び数値情報表示エリアの数値の点滅表示を確認した者は、計測中の「通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数)」が6000個未満であり、数値情報表示エリアに表示されている数値は、十分な量の統計データが蓄積されていない状態において算出された「計測中のベース(通常モード中)」であると認識することができる。 Also, if the "number of game balls that passed through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, for example, "bL." in the category information display area and the number in the numerical information display area may be displayed flashing, and if it is 6000 or more, they may be displayed lit up. With this configuration, a person who sees the flashing display of "bL." in the category information display area and the number in the numerical information display area can recognize that the "number of game balls that passed through the discharge passage during normal mode (number of outs during normal mode)" being measured is less than 6000, and that the number displayed in the numerical information display area is the "base during measurement (during normal mode)" calculated when a sufficient amount of statistical data has not been accumulated.
なお、点滅表示か点灯表示かを判定する基準としては種々の遊技履歴基礎情報を採用することができる。例えば、計測中の「排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(総アウト数)」を採用してもよい。 In addition, various basic game history information can be used as the criterion for determining whether to flash or light the display. For example, the "number of game balls that passed through the discharge passage (total number of outs)" during measurement may be used.
<態様72>
上記各態様では、設定変更モード中においては、数値情報表示エリアに抽選設定を示す数値情報を表示する際には、右中7セグメント表示器45z3を構成する全ての発光部を消灯させて使用せず、右端7セグメント表示器45z4のみを使用して1桁で当該抽選設定を示す数値情報を表示する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、右中7セグメント表示器45z3も使用して2桁で抽選設定を示す数値情報を表示する構成としてもよい。例えば、抽選設定を示す数値情報が1桁の情報しかない場合には、右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「0」を表示させる構成とすればよい。
<Aspect 72>
In each of the above aspects, during the setting change mode, when the numerical information indicating the lottery setting is displayed in the numerical information display area, all of the light-emitting parts constituting the right middle seven-segment display 45z3 are turned off and not used, and only the rightmost seven-segment display 45z4 is used to display the numerical information indicating the lottery setting in one digit, but instead of this configuration, the right middle seven-segment display 45z3 may also be used to display the numerical information indicating the lottery setting in two digits. For example, if the numerical information indicating the lottery setting is only one digit, the right middle seven-segment display 45z3 may be configured to display "0".
<態様73>
上記各態様において、抽選設定は1~6の6種類に限らず、抽選設定の種類は、5以下又は7以上の種類であってもよい。また、情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の個数は4個に限らず、3個以下でもよく、5個以上であってもよい。また、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアを構成する7セグメント表示器の個数は2個に限らず、1個でもよく、3個以上であってもよい。また、情報表示部45zの数値情報表示エリアを構成する7セグメント表示器の個数は2個に限らず、1個でもよく、3個以上であってもよい。また、情報表示部45zは、有機EL等のLED以外の発光素子によって構成されていてもよく、また、発光しない表示素子(表示要素)によって構成されていてもよい。例えば、情報表示部45zは、液晶や、電子ペーパーに用いられる電気泳動方式を採用した表示要素によって構成されていてもよい。
<Aspect 73>
In each of the above aspects, the number of lottery settings is not limited to six types, 1 to 6, and the number of lottery settings may be five or less or seven or more. The number of seven-segment displays constituting the
<態様74>
図42は、第1実施形態の態様74におけるパチンコ機10の電気的構成を示すブロック図である。この態様74では、遊技履歴管理チップ300は設けられておらず、上述した遊技履歴情報を主側CPU62xが算出するように構成されている。以下では、主制御装置60が備える各種の構成の詳細について説明し、その他の構成については、上述した第1実施形態及び各態様と同一の符号を付して、その詳細な説明は省略する。
<Aspect 74>
42 is a block diagram showing the electrical configuration of the
図42に示すように、主側ROM63は、プログラム記憶手段63aと、プログラム用データ記憶手段63bとを備えている。主側RAM64は、データ記憶手段64aと、スタック手段64bとを備えている。
As shown in FIG. 42, the
主側CPU62xは、レジスタセット62x1を含んで構成されており、主側ROM63のプログラム記憶手段63aに格納された複数種類のプログラムを組み合わせて実行することにより各種の処理を実施する。なお、各プログラムは、演算命令、転送命令、ローテイト命令、シフト命令、ジャンプ命令、コール命令、リターン命令など、予め予約されている複数の命令が組み合わされて構成されており、主側CPU62xは、プログラムに定義されている順番で複数の命令を順次実行する。
The
レジスタセット62x1は、Aレジスタ(アキュムレータレジスタ)、Fレジスタ(フラグレジスタ)、汎用レジスタ、スタックポインタ(SP)を含んでいる。なお、Aレジスタ、汎用レジスタは1バイト(8ビット)のサイズに形成され、スタックポインタ(SP)は2バイト(16ビット)のサイズに形成されている。また、レジスタセット62x1が、他のレジスタを含んでもよく、例えば、インデックスレジスタ、インタラプトレジスタ、リフレッシュレジスタ、プログラムカウンタなどのレジスタをさらに含んでいてもよい。 The register set 62x1 includes an A register (accumulator register), an F register (flag register), a general-purpose register, and a stack pointer (SP). The A register and the general-purpose register are formed to have a size of 1 byte (8 bits), and the stack pointer (SP) is formed to have a size of 2 bytes (16 bits). The register set 62x1 may also include other registers, such as an index register, an interrupt register, a refresh register, and a program counter.
Aレジスタは、演算命令の被演算対象となるデータ(値)および演算結果を格納する。 The A register stores the data (value) that is the subject of an arithmetic instruction and the result of the arithmetic operation.
Fレジスタは、演算命令の演算結果やロード命令などの特定命令の実行結果に応じて状態が自動的に変化する。 The state of the F register changes automatically depending on the results of calculations performed by arithmetic instructions or the results of execution of specific instructions such as load instructions.
汎用レジスタは、一般的なプログラムの変数と同様に使用されるものであり、具体的には、データ(値)を一時的に記憶したり、カウンタを構成したり、メモリのアドレスを指定したりするために使用される。 General-purpose registers are used in the same way as variables in general programs, specifically to temporarily store data (values), form counters, and specify memory addresses.
スタックポインタ(SP)は、主側RAM64に構成されたスタック手段64bが有する第1スタック領域64b1(後述する図44参照)および第2スタック領域64b2(後述する図44参照)にアクセスするためのスタックポインタ参照用アドレスを格納する。具体的には、スタックポインタ(SP)は、第1スタック領域64b1にアクセスする際に第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1を格納し、第2スタック領域64b2にアクセスする際に第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2を格納する。
The stack pointer (SP) stores a stack pointer reference address for accessing the first stack area 64b1 (see FIG. 44 described later) and the second stack area 64b2 (see FIG. 44 described later) of the stack means 64b configured in the
図43は、主側ROM63の構成を示す説明図である。上述したように、主側ROM63は、プログラム記憶手段63aと、プログラム用データ記憶手段63bとを備えている。
Figure 43 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of the
プログラム記憶手段63aは、第1プログラム63p1を記憶する第1プログラム制御領域63a1と、第1プログラム制御領域63a1と異なる領域であって、第2プログラム63p2を記憶する第2プログラム制御領域63a2とを有している。 The program storage means 63a has a first program control area 63a1 that stores a first program 63p1, and a second program control area 63a2 that is an area different from the first program control area 63a1 and stores a second program 63p2.
第1プログラム63p1は、遊技進行プログラム、記憶プログラム、変更プログラムを含んでいる。そして、主側CPU62xは、遊技進行プログラムを実行することにより遊技の進行を制御する遊技進行処理を実施し、記憶プログラムを実行することにより記憶処理を実施し、変更プログラムを実行することにより変更処理を実施する。遊技進行処理、記憶処理、変更処理の詳細については後述する。
The first program 63p1 includes a game progress program, a storage program, and a change program. The
第2プログラム63p2は、遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラム、退避プログラム、復帰プログラムを含んでいる。そして、主側CPU62xは、遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを実行することにより上述した遊技履歴情報を算出して表示する遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施し、退避プログラムを実行することにより退避処理を実施し、復帰プログラムを実行することにより復帰処理を実施する。遊技履歴情報算出表示処理、退避処理、復帰処理の詳細については後述する。
The second program 63p2 includes a game history information calculation and display program, a save program, and a return program. The
プログラム用データ記憶手段63bは、第1プログラム63p1を実行する際に必要な各種のデータを記憶する第1プログラムデータ領域63b1と、第1プログラムデータ領域63b1と異なる領域であって、第2プログラム63p2を実行する際に必要な各種のデータを記憶する第2プログラムデータ領域63b2とを有している。第1プログラムデータ領域63b1には、例えば、上述した大当たり抽選処理において使用する当否テーブルや振分テーブルなどのデータが格納され、第2プログラムデータ領域63b2には、例えば、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理において使用する各種の固定値データが格納されている。 The program data storage means 63b has a first program data area 63b1 that stores various data required when executing the first program 63p1, and a second program data area 63b2 that is an area different from the first program data area 63b1 and stores various data required when executing the second program 63p2. The first program data area 63b1 stores data such as a win/lose table and an allocation table used in the jackpot lottery process described above, and the second program data area 63b2 stores various fixed value data used in the game history information calculation and display process, for example.
以上のように、第1プログラム63p1を記憶する第1プログラム制御領域63a1および第1プログラム63p1を実行する際に必要なデータを格納する第1プログラムデータ領域63b1と、第2プログラム63p2を記憶する第2プログラム制御領域63a2および第2プログラム63p2を実行する際に必要なデータを格納する第2プログラムデータ領域63b2とが、それぞれ、主側ROM63の異なる領域に構成されている。
As described above, the first program control area 63a1 that stores the first program 63p1 and the first program data area 63b1 that stores data required to execute the first program 63p1, the second program control area 63a2 that stores the second program 63p2 and the second program data area 63b2 that stores data required to execute the second program 63p2 are each configured in different areas of the
図44は、主側RAM64の構成を示す説明図である。上述したように、主側RAM64は、データ記憶手段64aと、スタック手段64bとを備えている。
Figure 44 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of the
データ記憶手段64aは、データを更新可能な第1プログラム63p1に対応した第1データ記憶領域64a1と、第1データ記憶領域64a1と異なる領域であって、データを更新可能な第2プログラム63p2に対応した第2データ記憶領域64a2とを有している。なお、第1データ記憶領域64a1には、例えば、遊技進行処理において更新される各種のデータ(高確率モードフラグ等の各種フラグ)が記憶され、第2データ記憶領域64a2には、例えば、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理において更新される各種のデータが記憶される。 The data storage means 64a has a first data storage area 64a1 corresponding to a first program 63p1 capable of updating data, and a second data storage area 64a2, which is an area different from the first data storage area 64a1 and corresponds to a second program 63p2 capable of updating data. The first data storage area 64a1 stores, for example, various data (various flags such as a high probability mode flag) that are updated in the game progress process, and the second data storage area 64a2 stores, for example, various data that are updated in the game history information calculation and display process.
スタック手段64bは、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1によりアクセス可能な第1スタック領域64b1と、第1スタック領域64b1と異なる領域であって、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2によりアクセス可能な第2スタック領域64b2とを有している。第1スタック領域64b1は、第1プログラム63p1(遊技進行プログラム、記憶プログラム、変更プログラム)に対応し、第2スタック領域と64b2は、第2プログラム63p2(遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラム、退避プログラム、復帰プログラム)に対応している。 The stack means 64b has a first stack area 64b1 accessible by a first stack area reference address SP1 stored in a stack pointer (SP), and a second stack area 64b2 that is an area different from the first stack area 64b1 and accessible by a second stack area reference address SP2 stored in the stack pointer (SP). The first stack area 64b1 corresponds to the first program 63p1 (game progress program, storage program, change program), and the second stack area 64b2 corresponds to the second program 63p2 (game history information calculation and display program, save program, return program).
以上のように、第1プログラム63p1(遊技進行プログラム、記憶プログラム、変更プログラム)による処理によりデータを更新および参照可能な、第1スタック領域64b1および第1データ記憶領域64a1と、第2プログラム63p2(遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラム、退避プログラム、復帰プログラム)による処理によりデータを更新および参照可能な、第2スタック領域64b2および第2データ記憶領域64a2とが、それぞれ、主側RAM64の異なる領域に構成されている。なお、第1プログラム63p1による処理により、第2スタック領域64b2および第2データ記憶領域64a2のデータを更新することはできないがデータを参照可能に構成され、第2プログラム63p2による処理により、第1スタック領域64b1および第1データ記憶領域64a1のデータを更新することはできないがデータを参照可能に構成されている。
As described above, the first stack area 64b1 and the first data storage area 64a1, in which data can be updated and referenced by processing by the first program 63p1 (game progress program, storage program, change program), and the second stack area 64b2 and the second data storage area 64a2, in which data can be updated and referenced by processing by the second program 63p2 (game history information calculation and display program, save program, return program), are configured in different areas of the
図45は、主制御装置60のメモリマップの一例を示す模式図である。図45に示すように、本態様におけるメモリ空間には、主側ROM63に対応した内蔵ROM領域と、主側RAM64に対応した内蔵RAM領域とがこの順序で割り当てられている。そして、本態様では、内蔵ROM領域においては、第1プログラム制御領域63a1、第1プログラムデータ領域63b1、未使用領域、第2プログラム制御領域63a2、第2プログラムデータ領域63b2がこの順序で割り当てられており、内蔵RAM領域においては、第1データ記憶領域64a1、第1スタック領域64b1、第2データ記憶領域64a2、第2スタック領域64b2、未使用領域がこの順序で割り当てられている。
Figure 45 is a schematic diagram showing an example of a memory map of the
図46は、第1実施形態の態様74の主側CPU62xが実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。なお、本態様においても、タイマ割込み処理は、上記第1実施形態と同様に、4msec周期で実行される。
Figure 46 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt processing executed by the
なお、図46の紙面の左側に記載された各処理は、第1プログラム制御領域63a1に格納された第1プログラム63p1が主側CPU62xにより実行されることにより実施される処理であり、同図の紙面の右側に記載された各処理は、第2プログラム制御領域63a2に格納された第2プログラム63p2が主側CPU62xにより実行されることにより実施される処理である。
The processes shown on the left side of FIG. 46 are performed by the
ステップS11101では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる遊技進行プログラムを実行することによって、遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技進行処理では、上述した図27のステップS10601からステップS10615に示した処理群を実施する。ステップS11101の処理を実施した後、ステップS11102に進む。
In step S11101, the
ステップS11102では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる記憶プログラムを実行することによって記憶処理を実施する。記憶処理では、プッシュ命令(PUSH)により、複数のレジスタのうちAレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1によりアクセス可能な第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。このとき、AレジスタおよびFレジスタを転送対象として指定する特殊コードAFを利用した1回のプッシュ命令(PUSH AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。
In step S11102, the
ステップS11102を実行した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる退避プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11103からステップS11105に示す退避処理1、2、3を実施する。以下、具体的に説明する。
After executing step S11102, the
ステップS11103に示す退避処理1では、ロード命令(LD (W21),SP)により、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1を、第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW21で指定される領域に記憶する。このとき、ロード命令によりFレジスタのTZフラグの状態が変化することによって、Fフラグの値が変化することがある。ステップS11103の退避処理1を実施した後、ステップS11104に進む。
In the
ステップS11104に示す退避処理2では、ロード命令(LD SP,固定値)により、固定値である第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する。なお、このときスタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2は、例えば主側ROM63の第2プログラムデータ領域63b2に予め格納しておいた固定値である。本態様では、退避処理2を実施する時点においては第2スタック領域64b2にデータが記憶されていないため、退避処理2においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する固定値は、第2スタック領域64b2の底を示すアドレス値である。ステップS11104の退避処理2を実施した後、ステップS11105に進む。
In the
ステップS11105に示す退避処理3では、複数回のロード命令(LD (W22),レジスタ)により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW22で指定される領域に記憶する。なお、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタを転送対象として指定する特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶する構成としてもよい。ステップS11105の処理を実施した後、ステップS11106に進む。
In the
ステップS11106では、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを実行することによって遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施する。遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した図29のステップS10802からステップS10812に示す処理群を実施する。このとき、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理において、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタ、汎用レジスタの値が変化する。
In step S11106, the
ステップS11106の遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる復帰プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11107及びステップS11108に示す復帰処理1、2を実施する。以下、具体的に説明する。
After carrying out the game history information calculation and display process in step S11106, the
ステップS11107に示す復帰処理1では、複数回のロード命令(LD レジスタ,(W22))により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を、退避処理3(ステップS11105)により第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW22で指定される領域に記憶した値に設定する。なお、特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を退避処理3(ステップS11105)により第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶した値に設定する構成としてもよい。この復帰処理1では、退避処理1(ステップS11103)においてFレジスタの値が変化している場合には、遊技進行処理を終了した直後と異なる値がFレジスタに格納される。ステップS11107の処理を実施した後、ステップS11108に進む。
In the
ステップS11108に示す復帰処理2では、ロード命令(LD SP,(W21))により、退避処理1(ステップS11103)により第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW21で指定される領域に記憶した第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納し、主側CPU62xは第2プログラム63p2の実行を終了する。ステップS11108の処理を実施した後、ステップS11109に進む。
In the
ステップS11109では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる変更プログラムを実行することによって変更処理を実施する。変更処理では、ポップ命令(POP)により、復帰処理1(ステップS11107)により値が設定されたAレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタのうち、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、記憶処理(ステップS11102)により第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、特殊コードを利用した1回のポップ命令(POP AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を記憶処理(ステップS11102)によって第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、復帰処理1(ステップS11107)において、遊技進行処理を終了した直後と異なる値がFレジスタに格納された場合であっても、Fレジスタの値を遊技進行処理を終了した直後と同じ値に変更することができる。ステップS11109の処理を実施した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。
In step S11109, the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、退避処理3(図46のステップS11105)及び復帰処理1(図46のステップS11107)を実施するので、第2プログラム63p2から第1プログラム63p1へ復帰した際に、第1プログラム63p1において利用していたレジスタの値が変化してしまっていることによる不具合の発生を回避することができる。 As described above, according to this embodiment, save process 3 (step S11105 in FIG. 46) and restore process 1 (step S11107 in FIG. 46) are performed, so that when returning from the second program 63p2 to the first program 63p1, it is possible to avoid problems occurring due to the values of the registers used in the first program 63p1 having changed.
また、本態様によれば、退避処理3を実施する前(例えば、退避処理1(図46のステップS11103)においてロード命令が実行された場合)にFレジスタの状態が変化するおそれがあるが、退避処理1を実施する前に、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる記憶プログラムによる記憶処理(図46のステップS11102)においてAレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を記憶し、第2プログラム63p2による処理を終了した後に、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる変更プログラムによる変更処理(図46のステップS11109)においてAレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を記憶処理で記憶した値に変更する。したがって、例えば、退避処理1においてFレジスタの状態が変化しても、Fレジスタの状態が第1プログラム63p1による遊技進行処理(図46のステップS11101)の終了直後と同じ状態に復帰するので、第2プログラム63p2による処理から復帰した後に実施する処理に影響を及ぼすおそれがない。この結果、複数のプログラムを独立して構成することが可能となる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the state of the F register may change before the
また、本態様によれば、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理(図46のステップS11106)を実施するための遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを第2プログラム63p2に追加するだけで、遊技の進行を制御する遊技進行処理(図46のステップS11101)に影響を与えずに、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を追加することができる。したがって、遊技進行処理を実施するための遊技進行プログラムとは独立して遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを容易に作成することができる。 Furthermore, according to this embodiment, by simply adding a game history information calculation and display program for performing the game history information calculation and display process (step S11106 in FIG. 46) to the second program 63p2, the game history information calculation and display process can be added without affecting the game progress process (step S11101 in FIG. 46) that controls the progress of the game. Therefore, the game history information calculation and display program can be easily created independent of the game progress program for performing the game progress process.
また、本態様によれば、図45に示すように、第1プログラム63p1による処理が使用するメモリ空間と、第2プログラム63p2による処理が使用するメモリ空間とが互いに独立して配置されるので、両メモリ空間が物理的に互いに干渉するのを防止することができると共に、例えば一方の処理(メモリ空間)に対してなされた不正行為が他の処理(メモリ空間)にも影響を与えるのを防止することができる。 Furthermore, according to this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 45, the memory space used by the processing by the first program 63p1 and the memory space used by the processing by the second program 63p2 are arranged independently of each other, so that it is possible to prevent the two memory spaces from physically interfering with each other and, for example, to prevent fraudulent actions performed on one process (memory space) from affecting the other process (memory space).
また、本態様によれば、退避処理3(図46のステップS11105)において、1回のプッシュ命令(PUSH ALL)によって各レジスタの値の全てを第2スタック領域64b2に記憶する構成とするのではなく、ロード命令によって各レジスタの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶する構成とするので、利用していたレジスタのみを対象として第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶することが可能となる。したがって、退避処理3において各レジスタの値を記憶するために必要となる記憶容量を低減することができる。また、本態様によれば、各レジスタの値を第2スタック領域64b2に記憶する構成とするのではなく、各レジスタの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶する構成とするので、主側RAM64に占める第2スタック領域64b2の記憶容量を低減して、第2データ記憶領域64a2の記憶容量を拡大することが可能となる。
In addition, according to this aspect, in the save process 3 (step S11105 in FIG. 46), instead of storing all the values of each register in the second stack area 64b2 by a single push command (PUSH ALL), the values of each register are stored in the second data storage area 64a2 by a load command, so that only the registers that were being used can be stored in the second data storage area 64a2. Therefore, the storage capacity required to store the values of each register in the
また、例えば、プッシュ命令(PUSH)によってスタック領域に記憶させようとするデータの容量が、主側RAM64のスタック領域の記憶容量の上限値を超える場合には、当該スタック領域に記憶されている全データを消去するリセット処理が実施される構成である場合には、仮に退避処理3においてプッシュ命令(PUSH)によって各レジスタの値を第2スタック領域64b2に記憶させる構成とすると、当該リセット処理が実施されてしまうおそれがある。さらに、退避処理3において、1回のプッシュ命令(PUSH ALL)によって各レジスタの値の全てを第2スタック領域64b2に記憶する構成とすると、当該リセット処理が実施されてしまう可能性がさらに高くなってしまう。これに対して、本態様によれば、退避処理3においてプッシュ命令(PUSH ALL)を使用せず、ロード命令(LD)によって各レジスタの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶するので、スタック領域のリセット処理が実施されてしまうリスクを回避することができる。
In addition, for example, if the amount of data to be stored in the stack area by a push command (PUSH) exceeds the upper limit of the storage capacity of the stack area of the
<態様75>
上記態様74に示した構成において、図46に示したタイマ割込み処理の代わりに、以下に説明するタイマ割込み処理を実施してもよい。
<Aspect 75>
In the configuration shown in the above aspect 74, the timer interrupt process described below may be executed instead of the timer interrupt process shown in FIG.
図47は、第1実施形態の態様75の主側CPU62xが実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。図46に示したタイマ割込み処理に含まれる処理と同一の処理については同一のステップ番号を付している。図46に示したタイマ割込み処理との主な相違点は、図46のステップS11103に示す退避処理1が省略されている点と、図46のステップS11108に示す復帰処理2の内容が異なっている点である。以下、具体的に説明する。
Figure 47 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt processing executed by the
ステップS11101では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる遊技進行プログラムを実行することによって、遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技進行処理では、上述した図27のステップS10601からステップS10615に示した処理群を実施する。ステップS11101の処理を実施した後、ステップS11102に進む。
In step S11101, the
ステップS11102では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる記憶プログラムを実行することによって記憶処理を実施する。記憶処理では、プッシュ命令(PUSH)により、複数のレジスタのうちAレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1によりアクセス可能な第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。このとき、AレジスタおよびFレジスタを転送対象として指定する特殊コードAFを利用した1回のプッシュ命令(PUSH AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。
In step S11102, the
ステップS11102を実行した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる退避プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11104及びステップS11105に示す退避処理2、3を実施する。すなわち、本態様では、主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11103の退避処理1は実施しない。以下、具体的に説明する。
After executing step S11102, the
ステップS11104に示す退避処理2では、ロード命令(LD SP,固定値)により、固定値である第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する。なお、このときスタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2は、例えば主側ROM63の第2プログラムデータ領域63b2に予め格納しておいた固定値である。本態様では、退避処理2を実施する時点においては第2スタック領域64b2にデータが記憶されていないため、退避処理2においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する固定値は、第2スタック領域64b2の底を示すアドレス値である。ステップS11104の退避処理2を実施した後、ステップS11105に進む。
In the
ステップS11105に示す退避処理3では、複数回のロード命令(LD (W22),レジスタ)により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW22で指定される領域に記憶する。なお、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタを転送対象として指定する特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶する構成としてもよい。ステップS11105の処理を実施した後、ステップS11106に進む。
In the
ステップS11106では、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを実行することによって遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施する。遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した図29のステップS10802からステップS10812に示す処理群を実施する。このとき、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理において、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタ、汎用レジスタの値が変化する。
In step S11106, the
ステップS11106の遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる復帰プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11107及びステップS11108aに示す復帰処理1、復帰処理Aを実施する。すなわち、本態様では、主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11108の復帰処理2の代わりに、ステップS11108aに示す復帰処理Aを実施する。以下、具体的に説明する。
After carrying out the game history information calculation and display process of step S11106, the
ステップS11107に示す復帰処理1では、複数回のロード命令(LD レジスタ,(W22))により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を、退避処理3(ステップS11105)により第2データ記憶領域64a2のアドレスW22で指定される領域に記憶した値に設定する。なお、特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を退避処理3(ステップS11105)により第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶した値に設定する構成としてもよい。この復帰処理1では、退避処理1(ステップS11103)においてFレジスタの値が変化している場合には、遊技進行処理を終了した直後と異なる値がFレジスタに格納される。また、特別コードは利用せず、複数回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域64a2に記憶した値に設定する構成としてもよい。ステップS11107の処理を実施した後、ステップS11108aに進む。
In the
ステップS11108aに示す復帰処理Aでは、ロード命令(LD SP,固定値)により、固定値である第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する。このときスタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、例えば主側ROM63の第2プログラムデータ領域63b2に予め格納しておいた固定値である。以下、この固定値について説明する。
In the return process A shown in step S11108a, the load command (LD SP, fixed value) stores the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area, which is a fixed value, in the stack pointer (SP). At this time, the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) is a fixed value that has been stored in advance in, for example, the second program data area 63b2 of the
本態様では、遊技進行処理(ステップS11101)を構成する各処理(ステップS10601~ステップS10615の処理)の全てが終了した時点においては、第1スタック領域64b1に記憶されているデータが存在しないように構成されているため、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、第1スタック領域64b1の底を指定するアドレス値となっている。 In this embodiment, when all of the processes (steps S10601 to S10615) that make up the game progress process (step S11101) have been completed, there is no data stored in the first stack area 64b1, so the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) is an address value that specifies the bottom of the first stack area 64b1.
その後、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始すると、所定量のデータが第1スタック領域64b1に記憶される。この結果、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においては、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、第1スタック領域64b1の底から所定量だけ移動した位置を指定するアドレス値となっている。
Thereafter, when the
そして、記憶処理(ステップS11102)の実行及び第2プログラム63p2の実行の開始によって第1スタック領域64b1に記憶されるデータ量は毎回(毎タイマ割込み処理毎に)同じであるため、第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1の移動量も毎回同じとなる。したがって、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、毎回同じアドレス値となる。
And because the amount of data stored in the first stack area 64b1 by executing the storage process (step S11102) and starting execution of the second program 63p2 is the same every time (every timer interrupt process), the amount of movement of the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area is also the same every time. Therefore, the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) immediately after the
そして、本態様の復帰処理A(ステップS11108a)においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する固定値は、記憶処理(ステップS11102)を終了し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においてスタックポインタに毎回格納されているアドレス値と同じアドレス値に設定されている。この結果、上述した退避処理1(図46のステップS11103)を省略しても、本態様の復帰処理A(ステップS11108a)によって、スタックポインタ(SP)の値を、記憶処理(ステップS11102)を終了し第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)の値に復帰させることができる。 The fixed value stored in the stack pointer (SP) in the return process A (step S11108a) of this embodiment is set to the same address value as the address value stored in the stack pointer each time immediately after the storage process (step S11102) ends and execution of the second program 63p2 starts (timing TX1 shown in FIG. 47). As a result, even if the above-mentioned save process 1 (step S11103 in FIG. 46) is omitted, the return process A (step S11108a) of this embodiment can restore the value of the stack pointer (SP) to the value immediately after the storage process (step S11102) ends and execution of the second program 63p2 starts (timing TX1 shown in FIG. 47).
主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11108aの処理を終了して第2プログラム63p2の実行を終了し、第1プログラム63p1の実行を開始してステップS11109に進む。
The
ステップS11109では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラムに含まれる変更プログラムを実行することによって変更処理を実施する。変更処理では、ポップ命令(POP)により、復帰処理1(ステップS11107)により値が設定されたAレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタのうち、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、記憶処理(ステップS11102)により第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、特殊コードを利用した1回のポップ命令(POP AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を記憶処理(ステップS11102)によって第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、記憶処理(ステップS11102)が実施された後にFレジスタの値が変化しており、復帰処理1(ステップS11107)において、遊技進行処理を終了した直後と異なる値がFレジスタに格納された場合であっても、Fレジスタの値を遊技進行処理を終了した直後と同じ値に変更することができる。ステップS11109の処理を実施した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。
In step S11109, the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上述した態様74に示した効果に加えて、以下の効果を奏することができる。 As described above, this embodiment can achieve the following effects in addition to those described in embodiment 74 above.
本態様では、遊技進行処理(ステップS11101)を構成する各処理(ステップS10601~ステップS10615の処理)の全てが終了した時点においては、第1スタック領域64b1に記憶されているデータが存在しないように構成されているため、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、第1スタック領域64b1の底を指定するアドレス値となっている。このため、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、タイマ割込み処理が実施される毎に毎回同じアドレス値となる。したがって、本態様の復帰処理A(ステップS11108a)によってスタックポインタ(SP)に固定値を格納すればよいため、態様74に示した退避処理1を省略することができる。この結果、主側CPU62xの処理を簡略化することができるとともに、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1を退避させるために必要となる第2データ記憶領域64a2の記憶容量を低減することができる。
In this embodiment, when all of the processes (steps S10601 to S10615) constituting the game progress process (step S11101) are completed, the first stack area 64b1 is configured to have no data stored therein, so the first stack area reference address SP1 stored in the stack pointer (SP) is an address value that specifies the bottom of the first stack area 64b1. Therefore, the first stack area reference address SP1 stored in the stack pointer (SP) at the time immediately after the
<態様76>
図47に示したタイマ割込み処理の代わりに、以下に説明するタイマ割込み処理を実施してもよい。
<Aspect 76>
Instead of the timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. 47, the timer interrupt processing described below may be performed.
図48は、第1実施形態の態様76の主側CPU62xが実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。図47に示したタイマ割込み処理に含まれる処理と同一の処理については同一のステップ番号を付している。図47に示したタイマ割込み処理との主な相違点は、図47のステップS11105に示す退避処理3が省略されている点と、図47のステップS11107に示す復帰処理1が省略されている点と、図48のステップS11102及びステップS11108aに示す処理の後に、全てのレジスタの値を0に設定する処理が追加されている点である。以下、具体的に説明する。
Figure 48 is a flowchart showing timer interrupt processing executed by the
ステップS11101では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる遊技進行プログラムを実行することによって、遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技進行処理では、上述した図27のステップS10601からステップS10615に示した処理群を実施する。ステップS11101の処理を実施した後、ステップS11102に進む。
In step S11101, the
ステップS11102では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる記憶プログラムを実行することによって記憶処理を実施する。記憶処理では、プッシュ命令(PUSH)により、複数のレジスタのうちAレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1によりアクセス可能な第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。このとき、AレジスタおよびFレジスタを転送対象として指定する特殊コードAFを利用した1回のプッシュ命令(PUSH AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を第1スタック領域64b1に記憶する。ステップS11102の処理を実施した後、ステップS11102-2に進む。
In step S11102, the
ステップS11102-2では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラム63p1に含まれる第1クリアプログラムを実行することによって第1クリア処理を実施する。第1クリア処理では、複数回のロード命令(LD レジスタ,0)により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する。なお、特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する構成としてもよい。
In step S11102-2, the
ステップS11102-2を実行した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる退避プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11104に示す退避処理2を実施する。すなわち、本態様では、主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11103の退避処理1及びステップS11105の退避処理3は実施しない。以下、具体的に説明する。
After executing step S11102-2, the
ステップS11104に示す退避処理2では、ロード命令(LD SP,固定値)により、固定値である第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する。なお、このときスタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスSP2は、例えば主側ROM63の第2プログラムデータ領域63b2に予め格納しておいた固定値である。本態様では、退避処理2を実施する時点においては第2スタック領域64b2にデータが記憶されていないため、退避処理2においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する固定値は、第2スタック領域64b2の底を示すアドレス値である。ステップS11104の退避処理2を実施した後、ステップS11106に進む。すなわち、本態様では、主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11105の退避処理3は実施しない。
In the
ステップS11106では、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる遊技履歴情報算出表示プログラムを実行することによって遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施する。遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した遊技履歴情報を算出し、算出した遊技履歴情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための処理を実施する。具体的には、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理では、上述した図29のステップS10802からステップS10812に示す処理群を実施する。このとき、遊技履歴情報算出表示処理において、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタ、汎用レジスタの値が変化する。
In step S11106, the
ステップS11106の遊技履歴情報算出表示処理を実施した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる第2クリアプログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11107aに示す第2クリア処理を実施する。すなわち、本態様では、主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11107の復帰処理1は実施しない。
After performing the game history information calculation and display process of step S11106, the
ステップS11107aに示す第2クリア処理では、複数回のロード命令(LD レジスタ,0)により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する。なお、特別コードを利用した1回のロード命令により、Aレジスタ、Fレジスタおよび汎用レジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する構成としてもよい。 In the second clear process shown in step S11107a, the values of the A register, F register, and general-purpose registers are set to 0 by multiple load commands (LD register, 0). Note that a configuration may also be adopted in which the values of the A register, F register, and general-purpose registers are set to 0 by a single load command using a special code.
ステップS11107aの第2クリア処理を実施した後、主側CPU62xは、第2プログラム63p2に含まれる復帰プログラムを実行することによって、ステップS11108aに示す復帰処理Aを実施する。
After performing the second clear process in step S11107a, the
ステップS11108aに示す復帰処理Aでは、ロード命令(LD SP,固定値)により、固定値である第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1をスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する。このときスタックポインタ(SP)に格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、例えば主側ROM63の第2プログラムデータ領域63b2に予め格納しておいた固定値である。以下、この固定値について説明する。
In the return process A shown in step S11108a, the load command (LD SP, fixed value) stores the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area, which is a fixed value, in the stack pointer (SP). At this time, the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) is a fixed value that has been stored in advance in, for example, the second program data area 63b2 of the
本態様では、遊技進行処理(ステップS11101)を構成する各処理(ステップS10601~ステップS10615の処理)の全てが終了した時点においては、第1スタック領域64b1に記憶されているデータが存在しないように構成されているため、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、第1スタック領域64b1の底を指定するアドレス値となっている。 In this embodiment, when all of the processes (steps S10601 to S10615) that make up the game progress process (step S11101) have been completed, there is no data stored in the first stack area 64b1, so the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) is an address value that specifies the bottom of the first stack area 64b1.
その後、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)及び第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始すると、所定量のデータが第1スタック領域64b1に記憶される。この結果、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)及び第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においては、スタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、第1スタック領域64b1の底から所定量だけ移動した位置を指定するアドレス値となっている。
Then, when the
そして、記憶処理(ステップS11102)、第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)の実行及び第2プログラム63p2の実行の開始によって第1スタック領域64b1に記憶されるデータ量は毎回(毎タイマ割込み処理毎に)同じであるため、第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1の移動量も毎回同じとなる。したがって、主側CPU62xが記憶処理(ステップS11102)及び第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を実行し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスSP1は、毎回同じアドレス値となる。
The amount of data stored in the first stack area 64b1 by executing the storage process (step S11102), the first clear process (step S11102-2), and starting execution of the second program 63p2 is the same each time (for each timer interrupt process), so the amount of movement of the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area is also the same each time. Therefore, the address SP1 for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer (SP) immediately after the
そして、本態様の復帰処理A(ステップS11108a)においてスタックポインタ(SP)に格納する固定値は、記憶処理(ステップS11102)及び第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を終了し、第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)においてスタックポインタに毎回格納されているアドレス値と同じアドレス値に設定されている。この結果、上述した退避処理1(図46のステップS11103)を省略しても、本態様の復帰処理A(ステップS11108a)によって、スタックポインタ(SP)の値を、記憶処理(ステップS11102)及び第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を終了し第2プログラム63p2の実行を開始した直後の時点(図47に示すタイミングTX1)の値に復帰させることができる。 The fixed value stored in the stack pointer (SP) in the return process A (step S11108a) of this embodiment is set to the same address value as the address value stored in the stack pointer each time at the point immediately after the storage process (step S11102) and the first clear process (step S11102-2) are completed and the execution of the second program 63p2 is started (timing TX1 shown in FIG. 47). As a result, even if the above-mentioned save process 1 (step S11103 in FIG. 46) is omitted, the return process A (step S11108a) of this embodiment can restore the value of the stack pointer (SP) to the value immediately after the storage process (step S11102) and the first clear process (step S11102-2) are completed and the execution of the second program 63p2 is started (timing TX1 shown in FIG. 47).
主側CPU62xは、上述したステップS11108aの処理を終了して第2プログラム63p2の実行を終了し、第1プログラム63p1の実行を開始してステップS11109に進む。
The
ステップS11109では、主側CPU62xは、第1プログラムに含まれる変更プログラムを実行することによって変更処理を実施する。変更処理では、ポップ命令(POP)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を、記憶処理(ステップS11102)により第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、特殊コードを利用した1回のポップ命令(POP AF)により、AレジスタおよびFレジスタの値を記憶処理(ステップS11102)によって第1スタック領域64b1に記憶した値に変更する。このとき、記憶処理(ステップS11102)が実施された後にFレジスタの値が変化している場合であっても、Fレジスタの値を遊技進行処理を終了した直後と同じ値に変更することができる。ステップS11109の処理を実施した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。
In step S11109, the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上述した態様74及び態様75に示した効果に加えて、以下の効果を奏することができる。 As described above, this embodiment can achieve the following effects in addition to the effects described in the above-mentioned embodiments 74 and 75.
本態様によれば、第1プログラム63p1によって第1クリア処理(図48のステップS11102-2)を実施し、第2プログラム63p2によって第2クリア処理(図48のステップS11107a)を実施するので、上述した退避処理3(図47のステップS11105)及び復帰処理1(図47のステップS11107)を実施することなく、第2プログラム63p2の実行の開始直前の時点におけるレジスタの値と、第2プログラム63p2の実行の終了直後の時点におけるレジスタの値とを一致させることができる。したがって、第2プログラム63p2から第1プログラム63p1へ復帰した際に、第1プログラム63p1において利用していたレジスタの値が変化してしまっていることによる不具合の発生を回避することができる。そして、上述した退避処理3及び復帰処理1を省略することができるので、退避処理3及び復帰処理1において必要となる第2データ記憶領域64a2の記憶容量を低減することができる。
According to this aspect, the first clear process (step S11102-2 in FIG. 48) is performed by the first program 63p1, and the second clear process (step S11107a in FIG. 48) is performed by the second program 63p2. Therefore, without performing the above-mentioned save process 3 (step S11105 in FIG. 47) and restore process 1 (step S11107 in FIG. 47), the register value immediately before the start of execution of the second program 63p2 and the register value immediately after the end of execution of the second program 63p2 can be made to match. Therefore, when returning from the second program 63p2 to the first program 63p1, it is possible to avoid the occurrence of a problem caused by the value of the register used in the first program 63p1 having changed. And, since the above-mentioned save
また、本態様では、1回のタイマ割込み処理において、遊技進行処理(図48のステップS11101)に含まれる各種の処理が全て終了した後に第1クリア処理を実施し、当該第1クリア処理の後には遊技進行処理を実施しないので、第1クリア処理によってレジスタの値を0に設定することによって遊技進行処理に不具合が発生してしまうことを回避することができる。 In addition, in this embodiment, in one timer interrupt process, the first clear process is performed after all of the various processes included in the game progress process (step S11101 in FIG. 48) have been completed, and the game progress process is not performed after the first clear process, so it is possible to avoid a malfunction occurring in the game progress process by setting the register value to 0 by the first clear process.
<態様77>
上記態様74、態様75及び態様76のステップS11102の記憶処理において、特定レジスタ(Aレジスタ、Fレジスタ)の値を、ロード命令により第1データ記憶領域64a1に記憶する構成としてもよい。この場合には、ステップS11109の変更処理において、ロード命令により、特定レジスタ(Aレジスタ、Fレジスタ)の値を、記憶処理において第1データ記憶領域64a1に記憶した値に変更するようにするとよい。また、ステップS11102の記憶処理及びステップS11109の変更処理の対象となる特定レジスタをFレジスタのみとする構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 77>
In the storage process of step S11102 in the above aspects 74, 75, and 76, the values of the specific registers (A register, F register) may be stored in the first data storage area 64a1 by a load command. In this case, in the change process of step S11109, the values of the specific registers (A register, F register) may be changed to the values stored in the first data storage area 64a1 in the storage process by a load command. Also, the specific register that is the target of the storage process of step S11102 and the change process of step S11109 may be only the F register.
また、上記態様74において、第1プログラム63p1による遊技進行処理(図46のステップS11101)の実施を途中で中断し、ステップS11102の記憶処理からステップS11109の変更処理までを割り込んで実施した後に、中断していた遊技進行処理の実施を再開する構成としてもよい。 In addition, in the above aspect 74, the game progress processing by the first program 63p1 (step S11101 in FIG. 46) may be interrupted midway, and the process from the storage process in step S11102 to the change process in step S11109 may be interrupted and then the interrupted game progress processing may be resumed.
また、上記態様76において、遊技進行処理(ステップS11101)を実施した後であって記憶処理(ステップS11102)を実施する前に、第1クリア処理(ステップS11102-2)を実施する構成としてもよい。このような構成としても、上記態様76と同様の効果を奏することができる。 In addition, in the above aspect 76, the first clear process (step S11102-2) may be performed after the game progress process (step S11101) and before the storage process (step S11102) is performed. Even with such a configuration, the same effect as the above aspect 76 can be achieved.
<態様78>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、パチンコ機10を設定変更モードとして起動させる方法や設定変更モードにおける操作方法としては種々の態様を採用することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 78>
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode, various aspects can be adopted as a method of starting the
本態様では、パチンコ機10の背面側に位置する主制御基板61には、設定変更用の鍵穴と、上述したRAMクリアボタンとが設けられており、上述した設定変更用ボタンは設けられていない。パチンコ機10を管理する管理者が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更する場合には、まず、パチンコ機10の電源をOFFの状態とする。そして、パチンコ機10の内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態とし、設定変更用の鍵穴に設定変更用の鍵を挿入する。そして、挿入した鍵を設定変更側に回した状態(例えば時計回りに回した状態)とする。この状態において、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま当該パチンコ機10の電源を投入すると、当該パチンコ機10は設定変更モードとして起動する。
In this embodiment, the
すなわち、本態様のパチンコ機10は、電源の投入時に、以下の条件1~3の全てを満たしている場合に、設定変更モードとして起動する。
条件1:内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態であること
条件2:設定変更用の鍵穴が設定変更側に位置していること
条件3:RAMクリアボタンが押下されていること
なお、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、条件3は満たされているが条件1、2のいずれかが満たされていない場合には、パチンコ機10は、設定変更モードとしては起動せず、主側RAM64を初期化する処理を実行する。
That is, when the
Condition 1: The
パチンコ機10が設定変更モードとして起動すると、上述した情報表示部45zに、現在の抽選設定を示す情報(設定情報)が表示される。例えば、当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定が「抽選設定1」である場合には、情報表示部45zに「1」が表示される。そして、管理者がRAMクリアボタンを押下する度に、情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が「1」→「2」→「3」→「4」→「5」→「6」→「1」→「2」...といった順序で切り替わる。
When the
情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報が管理者の所望の値となった状態で、管理者が所定の入球口(例えばアウト口43)に遊技球を入球させて所定の入球検知センサー(例えば排出通路検知センサー44h)に遊技球を検知させると、情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報に対応する抽選設定への変更が確定する。具体的には、例えば、情報表示部45zに設定情報として「6」が表示されている状態で、排出通路検知センサー44hに遊技球を検知させると、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定が「抽選設定6」に変更される。そして、管理者が設定変更用の鍵を設定変更側から元の位置に回すと、パチンコ機10は設定変更モードを終了する。
When the setting information displayed on the
このように、本態様によれば、設定変更用ボタンを省略することができるので、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減することができる。
In this way, according to this embodiment, the setting change button can be omitted, thereby reducing the manufacturing costs of the
また、本態様によれば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更する際には、内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態にする必要があるので、例えば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更する権限を有しない者(以下、不正な者ともいう)が、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定を不正に変更しようとしたとしても、内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態とする手段を有しない限りは、抽選設定を変更することができない。したがって、パチンコ機10のセキュリティを向上させることができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, when changing the lottery settings of the
また、仮に、不正な者が内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態とすることができたとしても、内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態となると当該パチンコ機10のスピーカー46から警告音や警告用の音声(例えば、「扉が開いています」)が出力されるので、管理者は、不正な者が抽選設定の変更をしようとしている状況に容易に気付くことができる。したがって、不正な者による抽選設定の変更を抑制することができる。
Even if an unauthorized person were to open the
なお、本態様では、内枠13及び前扉枠14の両方が開放状態であることをパチンコ機10が設定変更モードとして起動する条件の1つとしたが、内枠13又は前扉枠14のいずれか一方が開放状態であることをパチンコ機10が設定変更モードとして起動する条件の1つとしてもよい。
In this embodiment, one of the conditions for the
また、本態様では、抽選設定の変更を確定させる条件として、排出通路検知センサー44hによる遊技球の検知を採用したが、この構成に限られず、他の入球検知センサーによる遊技球の検知を抽選設定の変更を確定させる条件として採用してもよい。例えば、抽選設定の変更を確定させる条件として、第1入賞口検知センサー44dによる遊技球の検知を採用してもよい。なお、第1入賞口検知センサー44dは、一般入賞口である第1入賞口32aへの遊技球の入球を検知するセンサーである。
In addition, in this embodiment, the detection of a game ball by the discharge
また、本態様では、設定変更モードにおいて管理者がRAMクリアボタンを押下する度に、情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が「1」→「2」→「3」→「4」→「5」→「6」→「1」→「2」...といった順序で切り替わる構成としたが、この構成に限られず、例えば、RAMクリアボタンとは別に設定変更用ボタンを設ける構成とし、管理者が当該設定変更用ボタンを押下する度に、情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が「1」→「2」→「3」→「4」→「5」→「6」→「1」→「2」...といった順序で切り替わる構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, each time the administrator presses the RAM clear button in the setting change mode, the setting information displayed on the
また、本態様では、設定変更用の鍵穴が設けられている構成としたが、設定変更用の鍵穴が設けられていない構成としてもよい。例えば、パチンコ機10は、電源の投入時に、上記の条件1及び条件3を満たしている場合に、設定変更モードとして起動させる構成としてもよい。また、例えば、パチンコ機10は、電源の投入時に、上記の条件1及び条件3を満たしている場合に、設定変更モードとして起動するか又は主側RAM64を初期化するRAMクリア処理を実行するかを管理者に選択させる選択モードを実行する構成としてもよい。そして、選択モードでは、RAMクリアボタンの押下によって、設定変更モードとして起動させるかRAMクリア処理を実行させるのかを選択させ、RAMクリアボタンを所定時間押下した状態とすることで選択を確定させる構成としてもよい。また、選択モードでは、所定の入球口(例えばアウト口43)に遊技球を入球させて所定の入球検知センサー(例えば排出通路検知センサー44h)に遊技球を検知させた場合のみ、設定変更モードとして起動させることが選択可能となる構成としてもよい。このような構成としても、管理者以外の者がパチンコ機10の抽選設定を不正に変更してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, a keyhole for changing the settings is provided, but a keyhole for changing the settings may not be provided. For example, the
<態様79>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、設定変更モード中には、当該設定変更モード中であることを報知する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 79>
Of the above aspects, in a configuration in which the setting change mode can be executed, a configuration may be adopted in which, during the setting change mode, a notification is given that the setting change mode is in progress. Specific explanations will be given below.
本態様では、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードを開始すると、設定変更モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。
In this embodiment, when the
音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定変更モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
When the voice-
そして、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードを終了すると、設定変更モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定変更モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
Then, when the
このように、本態様によれば、設定変更モード中であることをスピーカー46や図柄表示装置41、各種ランプ47によって報知するので、パチンコ機10の管理者は、パチンコ機10が設定変更モード中であることを容易に認識することができる。また、仮に、不正な者がパチンコ機10を不正に設定変更モードに移行させた場合であっても、当該パチンコ機10は、設定変更モード中であることをスピーカー46や図柄表示装置41によって報知するので、周囲の遊技者や管理者が、当該パチンコ機10が不正な者によって設定変更モード中となっていることに気付くことができる。したがって、不正な者による抽選設定の変更を抑制することが可能となる。
In this manner, according to this embodiment, the setting change mode is notified by the
さらに、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードを開始すると、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。そして、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードを終了した場合には、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。
Furthermore, when the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の管理者が当該パチンコ機10の近辺にいない場合であっても、設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10が存在していることをホールコンピュータによる管理画面によって認識することが可能となる。したがって、例えば、不正な者によってパチンコ機10が設定変更モードとなっている場合であっても、管理者は、設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10が存在していることをホールコンピュータによる管理画面によって認識することができる。したがって、不正な者による抽選設定の変更を抑制することが可能となる。
With this configuration, even if the administrator of the
<態様80>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更された場合には、当該設定変更モードの終了後に、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、遊技状態に関する情報を除いて初期化する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode, when the lottery setting is changed in the setting change mode, the information stored in the
本態様では、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更された場合には、遊技状態に関する情報を除いて主側RAM64を初期化し、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更されずにそのまま設定変更モードが終了した場合には、主側RAM64の初期化を実行せずに、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行する。なお、本態様において、初期化されない「遊技状態に関する情報」とは、高確率モードフラグの状態や、高頻度サポートモードフラグの状態、開閉実行モード中(大当たり中)であるか否かを示すフラグの状態である。
In this embodiment, when the lottery setting is changed in the setting change mode, the
このように、本態様によれば、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更された場合には主側RAM64を初期化するので、抽選設定が変更された後に主側RAM64に記憶される情報と、抽選設定が変更される前に主側RAM64に記憶されていた情報との間で不整合が生じ、遊技の進行に不具合が発生してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this way, according to this embodiment, when the lottery setting is changed in the setting change mode, the
さらに、本態様によれば、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更され、主側RAM64が初期化された場合であっても、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、遊技状態に関する情報は消去されないので、例えば、遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態は維持しつつ、当該パチンコ機10における抽選設定を変更することが可能となる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, even if the lottery setting is changed in the setting change mode and the
なお、本態様では、設定変更モードの終了後に主側RAM64を初期化する構成としたが、パチンコ機10の電源OFF時に設定変更モードとして起動するための操作を受け付けた場合には、設定変更モードとして起動する前に、遊技状態に関する情報を除いて主側RAM64を初期化する構成としてもよい。このような構成としても、抽選設定が変更された後に主側RAM64に記憶される情報と、抽選設定が変更される前に主側RAM64に記憶されていた情報との間で不整合が生じ、遊技の進行に不具合が発生してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this embodiment, the
また、本態様では、主側RAM64を初期化する際に、遊技状態に関する情報は消去しない構成としたが、主側RAM64に記憶されている全ての情報(遊技状態に関する情報を含む)を初期化する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the
また、初期化されない「遊技状態に関する情報」は、上記に限られず、例えば、保留情報を含む構成としてもよい。 In addition, the "information regarding the game state" that is not initialized is not limited to the above, and may include, for example, pending information.
<態様81>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、ノイズ等によって主側RAM64に記憶されている情報に不整合が生じ、主側RAM64の初期化を実行した際には、遊技を進行可能な遊技進行モードに復帰する前に、設定変更モードに移行する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode, when an inconsistency occurs in the information stored in the
本態様では、主制御装置60は、タイマ割込み処理において、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報に不整合等の異常が生じていないかを監視する監視処理を実行している。具体的には、例えば、監視処理では、主側RAM64の各領域において記憶されるはずのない範囲の値が記憶されていないか等を監視する。そして、監視処理において主側RAM64に異常が生じていると判定した場合には、遊技の進行に関する処理を中止し、主側RAM64を強制的に初期化する。そして、主側RAM64の初期化が完了した後は、主制御装置60は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行する前に、上述した設定変更モードに移行する。なお、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報に不整合等の異常が生じる原因としては、例えば、電磁波等のノイズや、不正な意図を持った遊技者がパチンコ機10に磁石等を近づけたこと等を挙げることができる。
In this embodiment, the
そして、上述した態様79と同様に、パチンコ機10が設定変更モード中であることを報知する構成とすれば、パチンコ機10の管理者は、当該パチンコ機10が設定変更モードに移行したことに気付くことができる。そして、管理者は、設定変更モードにおいて当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定を決定し、その後、当該パチンコ機10は、遊技進行モードに移行する。
As in the above-mentioned aspect 79, if the
このような構成とした理由について説明する。ノイズ等に起因して主側RAM64を強制的に初期化する状況となった場合には、抽選設定の設定情報も管理者が本来意図した設定情報とは異なる設定情報に書き換わってしまっている可能性がある。そして、主側RAM64を初期化しても抽選設定の設定情報は初期化されない(変更されない)構成である場合には、依然として管理者が本来意図した設定情報とは異なる設定情報に維持されるおそれがある。そこで、本態様のように、ノイズ等に起因して主側RAM64を強制的に初期化した際には、遊技を進行可能な遊技進行モードに復帰する前に、設定変更モードに移行する構成とすれば、管理者は、パチンコ機10が遊技進行モードに復帰する前に、抽選設定の設定情報を本来意図した設定情報に修正することが可能となる。
The reason for this configuration will be explained. In the event that the
さらに、本態様において、ノイズ等に起因して主側RAM64を強制的に初期化する際に、上述した遊技状態に関する情報は初期化しない構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、ノイズ等に起因して主側RAM64が強制的に初期化された場合であっても、遊技状態に関する情報は初期化されない(消去されない)ので、遊技者は、遊技状態を維持しつつ遊技を再開することが可能となる。したがって、ノイズ等に起因した主側RAM64の強制的な初期化によって遊技者に不利益を与えてしまうことを抑止することが可能となる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, when the
なお、本態様では、主側RAM64の初期化後に設定変更モードに移行する構成としたが、主側RAM64の初期化後に設定変更モードに移行せず、抽選設定を初期値(例えば、「抽選設定1」)に設定した上で、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行する構成としてもよい。
In this embodiment, the setting change mode is entered after the
また、本態様では、主側RAM64を初期化する際に、遊技状態に関する情報は消去しない構成としたが、主側RAM64を初期化する際に遊技状態に関する情報も消去する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the information regarding the game status is not erased when the
<態様82>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、当該設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更されたのか、変更されていないのかを報知する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 82>
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode, a configuration may be adopted in which it is notified whether the lottery setting has been changed or not in the setting change mode. Specific explanations will be given below.
本態様では、パチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定が変更されたことを示唆する音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、抽選設定が変更されたことを示唆する文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させることによって、抽選設定が変更されたことを報知する。
In this embodiment, when the lottery settings are changed in the setting change mode, the
具体的には、例えば、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードに移行すると、現在の抽選設定の設定情報を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、設定変更モードにおいて新たに決定された抽選設定の設定情報と、退避させておいた変更前の抽選設定の設定情報とを比較し、これらの設定情報が異なっている場合には、抽選設定が変更されたことを示すコマンドである設定変更コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。
Specifically, for example, when the
音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更コマンドを受信すると、抽選設定が変更されたことを示唆する音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「抽選設定が変更されました」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更コマンドを受信すると、抽選設定が変更されたことを示唆する情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「抽選設定が変更されました」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「抽選設定が変更されました」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47が最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
When the audio/light-emitting
一方、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたまま設定変更モードを終了する場合には、パチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを示唆する音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを示唆する文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させることによって、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを報知する。
On the other hand, when the setting change mode is ended with the lottery settings remaining unchanged, the
具体的には、例えば、主制御装置60は、設定変更モードに移行すると、現在の抽選設定の設定情報を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、設定変更モードにおいて新たに決定された抽選設定の設定情報と、退避させておいた変更前の抽選設定の設定情報とを比較し、これらの設定情報が一致している場合には、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを示すコマンドである設定維持コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。
Specifically, for example, when the
音声発光制御装置90は、設定維持コマンドを受信すると、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを示唆する音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「抽選設定が変更されませんでした」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定維持コマンドを受信すると、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを示唆する情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「抽選設定が変更されませんでした」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「抽選設定が変更されませんでした」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定維持コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47が点滅ではなく点灯するように制御する。
When the audio/light-emitting
このように、本態様によれば、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定が変更されたことを報知するので、管理者や遊技者は、抽選設定が変更されたか否かを確認することができる。 In this way, according to this embodiment, when the lottery settings are changed in the setting change mode, a notification is issued that the lottery settings have been changed, so that the administrator or player can check whether the lottery settings have been changed.
特に、上記の態様81において、ノイズ等に起因した主側RAM64の強制的な初期化の後の設定変更モードにおいて、当該パチンコ機10において遊技を行なっていた遊技者は、管理者によって抽選設定が変更されてしまったのか否か、疑心暗鬼になることが想定される。しかしながら、本態様によれば、抽選設定が変更された場合には、抽選設定が変更されたことを報知するので、遊技者は、抽選設定が変更されたか否かを確認することができる。より具体的には、遊技者に、現在の抽選設定がどのような設定情報になっているのかは把握させずに、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定が変更されたか否かに関してのみ把握させることができる。この結果、遊技者が、管理者によって抽選設定が変更されてしまったのか否か不明なまま不安な気持ちで遊技を再開しなくてはいけないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。
In particular, in the above-mentioned
なお、本態様では、抽選設定が変更されなかった場合には、抽選設定が変更されずに維持されたことを報知する構成としたが、抽選設定が変更されなかった場合には、何も報知をしない構成としてもよく、又は、「設定変更モードを終了します」といったように、抽選設定が変更された場合とは異なる態様の報知をする構成としてもよい。このような構成としても、遊技者は、「抽選設定が変更されました」といった報知がない場合には抽選設定は変更されなかったと判断することができるので、遊技者が不安な気持ちで遊技を再開しなくてはいけないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。 In this embodiment, if the lottery setting has not been changed, a notification is given that the lottery setting has been maintained without change. However, if the lottery setting has not been changed, no notification may be given, or a different notification may be given than when the lottery setting has been changed, such as "setting change mode will be terminated." Even with this configuration, if there is no notification such as "lottery setting has been changed," the player can determine that the lottery setting has not been changed, and this prevents the player from having to resume play with anxiety.
<態様83>
上記態様82において、主制御装置60は、抽選設定が変更されたことを示すコマンドである設定変更コマンドに、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を含める構成としてもよい。そして、音声発光制御装置90は、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を含んだ設定変更コマンドを受信する毎に、自身が備える記憶手段としてのRAMに当該変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を順次記憶する構成としてもよい。そして、音声発光制御装置90は、パチンコ機10の管理者等から所定の操作を受け付けた場合には、抽選設定の変更の履歴を図柄表示装置41に表示させる構成としてもよい。
<Aspect 83>
In the above aspect 82, the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の主制御装置60の主側RAM64の限られた記憶容量を使用することなく、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の変更の履歴を記憶することができるとともに、パチンコ機10の管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定がどのように運用されてきたのかを図柄表示装置41に表示される抽選設定の変更の履歴によって容易に確認することが可能となる。
With this configuration, it is possible to store the history of changes to the lottery settings of the
<態様84>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モードを実行可能な構成において、抽選設定を変更することはできないが管理者等が現在の抽選設定を確認することが可能な設定確認モードを実行可能な構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 84>
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in the configuration capable of executing the setting change mode, a configuration capable of executing a setting confirmation mode in which the lottery setting cannot be changed but the administrator or the like can confirm the current lottery setting may be also used. A specific description will be given below.
本態様のパチンコ機10は、特定の条件下において特定の操作が実行された場合に、遊技の進行が不可能な遊技停止状態とした上で、設定確認モードに移行する。
When a specific operation is performed under specific conditions, the
本態様において、特定の条件下とは、以下の条件を全て満たしている状態をいう。
条件1:特図ユニット37において特別図柄の変動中ではないこと
条件2:普図ユニット38において普通図柄の変動中ではないこと
条件3:特別電動役物としての可変入賞装置36が動作していないこと
条件4:普通電動役物としての電動役物34aが動作していないこと
条件5:最後に遊技球が発射されてから所定時間(例えば20秒)が経過していること
すなわち、特定の条件下とは、遊技の進行を停止(中断)しても遊技の結果に影響を与えない状態である。
In this embodiment, "under specific conditions" refers to a state in which all of the following conditions are met.
Condition 1: The special pattern is not changing in the special pattern unit 37.Condition 2: The normal pattern is not changing in the normal pattern unit 38.Condition 3: The
また、本態様において、特定の操作とは、パチンコ機10の背面に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下する操作である。
In addition, in this embodiment, the specific operation is the operation of pressing the RAM clear button located on the back of the
すなわち、本態様のパチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モード中においてRAMクリアボタンが押下された状態になったことを検知すると、上記の特定の条件下であるか否かを判定し、上記の特定の条件下であると判定した場合には、設定確認モードに移行する。そして、当該RAMクリアボタンが再び押下されていない状態になったことを検知すると、設定確認モードを終了し、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに復帰する。
In other words, when the
主制御装置60は、設定確認モード中においては、大当たり乱数カウンタ等を更新する乱数更新処理や電源の監視処理は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(タイマ割込み処理における各種の入球処理等)は実行せずに遊技停止状態(遊技の進行が不可能な状態)とした上で、現在の抽選設定を示す設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させる。例えば、パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定が「抽選設定1」である場合には、情報表示部45zに「1」を表示させる。
During the setting confirmation mode, the
さらに、遊技進行モード中において、大当たり抽選の結果や電動役物開放抽選の結果に関わらずに常に一定の動作(予め定められた動作)を継続する役物(以下、常時動作役物とも呼ぶ)を備えるパチンコ機10においては、主制御装置60は、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行した場合であっても、当該常時動作役物の動作をそのまま継続させる。具体的には、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードに移行後は、乱数更新処理や電源の監視処理に加えて、常時動作役物の制御処理の実行を継続する構成とする。そして、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを終了し、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに復帰する際には、実行を回避していた遊技の進行に必要な他の処理の実行を再開する。
Furthermore, in a
このような構成によれば、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行したタイミング及び設定確認モードから遊技進行モードに復帰したタイミングにおいても常時動作役物の動作が停止したり変化したりせずに一定の動作を継続するので、例えば、常時動作役物の動作が停止したり変化したりするタイミングを狙って遊技者が遊技球を発射して不正に有利な結果を得てしまうことを抑制することができる。 With this configuration, the operation of the constantly operating device continues at a constant rate without stopping or changing even when the game progress mode is switched to the setting confirmation mode and when the setting confirmation mode is returned to the game progress mode. This prevents, for example, a player from obtaining an unfair advantage by firing a game ball at a time when the operation of the constantly operating device stops or changes.
なお、本態様では、設定確認モード中においても常時動作役物の動作をそのまま継続する構成としたが、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行したタイミングで常時動作役物の動作を一時的に停止させ、設定確認モードから遊技進行モードに復帰したタイミングで停止させていた常時動作役物の動作を再開させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、常時動作役物の動作を継続する構成と比較して処理を簡易化することができる。また、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モード中においては常時動作役物の動作が連続的に繋がっていることを担保することができる。また、このような構成によれば、設定確認モードから遊技進行モードに復帰する際に、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行したタイミングにおける状態と同じ状態から常時動作役物の動作が再開されるので、設定確認モードから遊技進行モードに復帰する際に、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行したタイミングにおける状態と異なる状態(例えば、遊技者に不利な状態又は有利な状態)から常時動作役物の動作が再開されてしまい、遊技者が遊技を停止した状態とは異なる状態から遊技を再開しなくてはいけないことを回避することができる。 In this embodiment, the operation of the constantly operating role continues even during the setting confirmation mode, but the operation of the constantly operating role may be temporarily stopped when the game progress mode is switched to the setting confirmation mode, and the operation of the constantly operating role that was stopped may be resumed when the game progress mode is returned to from the setting confirmation mode. This configuration simplifies the processing compared to a configuration in which the operation of the constantly operating role continues. It is also possible to ensure that the operation of the constantly operating role is continuously connected during the game progress mode in which game progress is possible. Furthermore, with this configuration, when returning from the setting confirmation mode to the game progress mode, the operation of the constantly operating device is resumed from the same state as when the game progress mode was switched to the setting confirmation mode. This avoids the situation where the operation of the constantly operating device is resumed from a state different from the state when the game progress mode was switched to the setting confirmation mode (for example, a state that is disadvantageous or advantageous to the player) when returning from the setting confirmation mode to the game progress mode, and the player has to resume play from a state different from the state when the game was stopped.
また、本態様では、設定確認モードに移行させるための特定の操作として、RAMクリアボタンを押下する操作を採用する構成としたが、当該特定の操作としては種々の操作を採用することができる。例えば、当該特定の操作として、設定変更用の鍵を設定変更用の鍵穴に挿入して設定変更側に回す操作を採用してもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を確認するためには設定変更用の鍵が必要となるので、設定変更用の鍵を有していない者がパチンコ機10の抽選設定を確認できてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, the specific operation for transitioning to the setting confirmation mode is the operation of pressing the RAM clear button, but various operations can be used as the specific operation. For example, the specific operation may be the operation of inserting a setting change key into a setting change keyhole and turning it to the setting change side. With this configuration, a setting change key is required to check the lottery settings of the
<態様85>
上記態様84では、設定確認モード中においても常時動作役物の動作をそのまま継続する構成としたが、設定確認モードに移行した場合には、常時動作役物を予め定められた初期状態に移行(又は初期位置に移動)させてから動作を停止させる構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 84, the operation of the constantly operating role is continued even during the setting confirmation mode, but when the setting confirmation mode is entered, the constantly operating role may be moved to a predetermined initial state (or moved to an initial position) and then stopped. This will be specifically described below.
本態様のパチンコ機10の主制御装置60は、遊技進行モードから設定確認モードに移行した場合には、常時動作役物が初期状態に移行(又は初期位置に移動)するまで当該常時動作役物の制御処理を継続する。そして、主制御装置60は、常時動作役物が初期状態に移行(又は初期位置に移動)したことを検出すると、常時動作役物の制御処理の実行を中止して常時動作役物の動作を停止させる。その後、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを終了し、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに復帰する際には、常時動作役物の制御処理と、回避していた遊技の進行に必要な他の処理の実行を再開する。
When the
なお、主制御装置60は、常時動作役物が初期状態に移行(又は初期位置に移動)したことを検出する前に設定確認モードから遊技進行モードに復帰する際には、当該常時動作役物の制御処理をそのまま継続する。すなわち、本態様では、常時動作役物は、初期状態以外の状態(又は初期位置以外の位置)で動作を停止することがないように構成されている。
When the
このような構成によれば、例えば、初期状態以外の状態(又は初期位置以外の位置)で動作を停止させると不具合が発生する可能性のある常時動作役物において、不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 This configuration makes it possible to prevent malfunctions, for example, in constantly operating devices that may malfunction if their operation is stopped in a state other than the initial state (or in a position other than the initial position).
<態様86>
上記各態様のうち、設定確認モードを実行可能な構成において、設定確認モード中には、当該設定確認モード中であることを報知する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Of the above aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting check mode, a configuration may be adopted in which, during the setting check mode, a notification is given that the setting check mode is in progress. Specific examples will be described below.
本態様では、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを開始すると、設定確認モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。
In this embodiment, when the
音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定確認モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
When the audio/light-emitting
そして、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを終了すると、設定確認モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定確認モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
Then, when the
このように、本態様によれば、設定確認モード中であることをスピーカー46や図柄表示装置41、各種ランプ47によって報知するので、パチンコ機10の管理者は、パチンコ機10が設定確認モード中であることを容易に認識することができる。また、仮に、不正な者がパチンコ機10を不正に設定確認モードに移行させた場合であっても、当該パチンコ機10は、設定確認モード中であることをスピーカー46や図柄表示装置41、各種ランプ47によって報知するので、周囲の遊技者や管理者が、当該パチンコ機10が不正な者によって設定確認モード中となっていることに気付くことができる。したがって、不正な者による抽選設定の確認を抑制することが可能となる。
In this manner, according to this embodiment, the
さらに、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを開始すると、設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。そして、主制御装置60は、設定確認モードを終了した場合には、設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。
Furthermore, when the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の管理者が当該パチンコ機10の近辺にいない場合であっても、設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10が存在していることをホールコンピュータによる管理画面によって認識することが可能となる。したがって、例えば、不正な者によってパチンコ機10が設定確認モードとなっている場合であっても、管理者は、設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10が存在していることをホールコンピュータによる管理画面によって認識することができる。したがって、不正な者による抽選設定の確認を抑制することが可能となる。
With this configuration, even if the administrator of the
<態様87>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行可能な構成において、パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにした後でなければ設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行することができない構成としてもよい。すなわち、パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、当該パチンコ機10の電源をONにする際に所定の操作が為された場合に、当該パチンコ機10が設定変更モード又は設定確認モードを実行する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in the configuration capable of executing the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the configuration may be such that the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode cannot be executed unless the power supply of the
なお、上記各態様における「設定変更用の鍵穴」及び「設定変更用の鍵」は、本態様及び以下に説明する態様では、抽選設定を変更する設定変更モードに移行させる場合に限らず、抽選設定を確認する設定確認モードに移行させる場合にも用いられるため、それぞれ単に「設定用の鍵穴」及び「設定用の鍵」とも呼ぶ。 In addition, in this embodiment and the embodiments described below, the "keyhole for changing settings" and "key for changing settings" in each of the above embodiments are also referred to simply as the "keyhole for changing settings" and the "key for changing settings", respectively, because they are used not only when transitioning to a setting change mode for changing the lottery settings, but also when transitioning to a setting confirmation mode for confirming the lottery settings.
本態様では、パチンコ機10の背面側に位置する主制御基板61には、電源スイッチと、RAMクリアボタンと、設定用の鍵穴と、設定変更用のボタンと、情報表示部45zとが設けられている。本態様のパチンコ機10は、電源スイッチが操作されて電源がONにされ、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードの実行が開始された後は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにした後でなければ、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードには移行できないように構成されている。そして、当該パチンコ機10の電源がONにされた際に所定の条件が満たされている場合に、設定変更モード又は設定確認モードが実行されるように構成されている。
In this embodiment, the
具体的には、本態様のパチンコ機10は、電源の投入時(ON時)に、以下の条件A1~A3の全てを満たしている場合に、設定変更モードを実行する。
条件A1:内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態であること
条件A2:設定用の鍵が設定用の鍵穴に挿入されてON側に位置していること
条件A3:RAMクリアボタンが押下されていること
Specifically, the
Condition A1: The
また、本態様のパチンコ機10は、電源の投入時(ON時)に、以下の条件B1~B3の全てを満たしている場合に、設定確認モードを実行する。
条件B1:内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態であること
条件B2:設定用の鍵が設定用の鍵穴に挿入されてON側に位置していること
条件B3:RAMクリアボタンが押下されていないこと
In addition, the
Condition B1: The
以下では、パチンコ機10の管理者が、遊技進行モードの実行が開始された後のパチンコ機10を設定変更モード又は設定確認モードに移行させるための作業工程の一例について説明した後、当該パチンコ機10において実行される処理の一例について説明する。
Below, we will explain an example of the work process that an administrator of the
図49は、管理者がパチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更する場合の作業工程を示す工程図である。
Figure 49 is a process diagram showing the work process when an administrator changes the lottery settings of the
工程W101では、管理者は、抽選設定を変更する対象のパチンコ機10のシリンダ錠17に鍵を挿入して開放側に回し、内枠13を外枠11に対して回動させて開放状態にするとともに、前扉枠14を内枠13に対して回動させて開放状態にする。内枠13を外枠11に対して回動させることによって、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた各種の操作部にアクセスすることが可能となる。次に、工程W102に進み、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた電源スイッチを操作して電源をOFFにする。次に工程W103に進む。
In step W101, the administrator inserts a key into the
工程W103では、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた設定用の鍵穴に、設定用の鍵を挿入して設定変更側(以下ではON側ともいう)に回す。次に、工程W104に進み、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源スイッチを操作してパチンコ機10の電源をONにする。そうすると、パチンコ機10は、起動後に設定変更モードに移行し(工程W105)、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報が表示される(工程W106)。具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の現在の設定情報が「1」である場合には、情報表示部45zに「1」が点灯表示される。次に工程W107に進む。
In step W103, the administrator inserts the setting key into the setting keyhole on the back side of the
工程W107では、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた設定変更用ボタンを押下して設定情報を変更する。具体的には、例えば、管理者が設定変更用ボタンを押下する度に、情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が「1」→「2」→「3」→「4」→「5」→「6」→「1」→「2」...といった順序で切り替わるので、管理者は、情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報が所望の設定情報となるまで設定変更用ボタンを押下する。次に工程W108に進む。
In step W107, the administrator changes the setting information by pressing a setting change button provided on the back side of the
工程W108では、管理者は、情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報が所望の設定情報となっていることを確認した上で、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられたRAMクリアボタンを押下して変更後の設定情報を確定させる。次に工程W109に進み、管理者は、設定用の鍵をOFF側に戻し、当該鍵を設定用の鍵穴から抜く。そうすると、パチンコ機10は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行し(工程W110)、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報が表示される(工程W111)。次に工程W112に進み、管理者は、内枠13及び前扉枠14を閉鎖状態としてシリンダ錠17から鍵を抜く。このような工程によって、管理者は、パチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更することができる。
In step W108, the administrator confirms that the setting information displayed on the
図50は、管理者がパチンコ機10の抽選設定を確認する場合の作業工程を示す工程図である。
Figure 50 is a process diagram showing the work process when an administrator checks the lottery settings of the
工程W201では、管理者は、抽選設定を確認する対象のパチンコ機10のシリンダ錠17に鍵を挿入して開放側に回し、内枠13を外枠11に対して回動させて開放状態にするとともに、前扉枠14を内枠13に対して回動させて開放状態にする。内枠13を外枠11に対して回動させることによって、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた各種の操作部にアクセスすることが可能となる。次に、工程W202に進み、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた電源スイッチを操作して電源をOFFにする。次に工程W203に進む。
In step W201, the administrator inserts a key into the
工程W203では、管理者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた設定用の鍵穴に、設定用の鍵を挿入してON側に回す。次に、工程W204に進み、管理者は、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチを操作してパチンコ機10の電源をONにする。そうすると、パチンコ機10は、起動後に設定確認モードに移行し(工程W205)、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報が表示される(工程W206)。具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機10の現在の設定情報が「1」である場合には、情報表示部45zに「1」が点滅表示される。管理者は、この情報表示部45zに点滅表示される設定情報を確認することによって、当該パチンコ機10の現在の設定情報を確認することができる。次に工程W207に進む。
In step W203, the administrator inserts a setting key into a setting keyhole provided on the back side of the
工程W207では、管理者は、情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報を確認した上で、設定用の鍵をOFF側に戻し、当該鍵を設定用の鍵穴から抜く。そうすると、パチンコ機10は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行し(工程W208)、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報が表示される(工程W209)。次に工程W210に進み、管理者は、内枠13及び前扉枠14を閉鎖状態としてシリンダ錠17から鍵を抜く。このような工程によって、管理者は、パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定を確認することができる。
In step W207, the administrator checks the setting information displayed on the
次に、本態様のパチンコ機10の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する処理について説明する。
Next, we will explain the processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
図51は、第1実施形態の態様87の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理の一部を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 51 is a flowchart showing a part of the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11201では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11202に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11203に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11203を実行した後、ステップS11204に進む。
In step S11201, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11204では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11204, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11204において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11204:YES)、ステップS11205に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11206に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11206において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11206:YES)、後述するステップS11208に進む。
If it is determined in step S11204 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11204: YES), the process proceeds to step S11205, where a RAM judgment value of the
一方、上述したステップS11204において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11204:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11206においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11206:NO)、ステップS11207に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合又は復電フラグはONであるがRAM判定値が正常ではない場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。ステップS11207を実行した後、ステップS11208に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11204 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11204: NO), and if it is determined in step S11206 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11206: NO), the process proceeds to step S11207, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF or when the power recovery flag is ON but the RAM judgment value is not normal, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
ステップS11208では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11208において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11208:NO)、ステップS11209に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S11208, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S11208 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11208: NO), the process proceeds to step S11209, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. The frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11209において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11209:NO)、ステップS11210に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11209 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S11209: NO), proceed to step S11210 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11210において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11210:NO)、ステップS11211に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11211を実行した後、ステップS11212に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11210, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11210: NO), the process proceeds to step S11211, where a power recovery process is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery process, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、ステップS11210において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11210:YES)、ステップS11213に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11213を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11210 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11210: YES), the process proceeds to step S11213, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
一方、上述したステップS11209において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11209:YES)、ステップS11214に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11209 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11209: YES), proceed to step S11214 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11214において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11214:NO)、ステップS11215に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細については後述する。ステップS11215を実行した後、ステップS11216に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11217に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11214, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11214: NO), the process proceeds to step S11215, where a setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11214において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11214:YES)、ステップS11218に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11218を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、上述したように、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11214 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11214: YES), the process proceeds to step S11218, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11208において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11208:YES)、ステップS11219に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11208 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11208: YES), proceed to step S11219 and determine whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON.
ステップS11219において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11219:NO)、ステップS11220に進み、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11220において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11220:NO)、ステップS11221に進む。 If it is determined in step S11219 that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S11219: NO), proceed to step S11220 to determine whether the RAM abnormality flag described above is ON. If it is determined in step S11220 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11220: NO), proceed to step S11221.
ステップS11221では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11221を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11221, the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
一方、ステップS11220において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11220:YES)、ステップS11222に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11222を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、上述したように、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11220 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11220: YES), the process proceeds to step S11222, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11219において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11219:YES)、ステップS11223に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11219 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11219: YES), proceed to step S11223 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11223において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11223:NO)、ステップS11224に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11225に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細については後述する。ステップS11225を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
If it is determined in step S11223 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11223: NO), the process proceeds to step S11224, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S11225, where the setting change process is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11223において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11223:YES)、ステップS11226に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11226を実行した後、ステップS11227に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11223 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11223: YES), the process proceeds to step S11226, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11227では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。ここで、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、第1RAMクリア処理ではなく、設定情報も消去する第2RAMクリア処理を実行する理由について説明する。RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報も正常でない可能性があり、例えば、ノイズ等によって管理者の意図しない設定情報に書き換わっていたり、設定情報としては所定の範囲内の数値(例えば1から6までの数値)しか取り得ないにも関わらず、所定の範囲以外の数値が記憶されていたりする可能性があるためである。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。また、第2RAMクリア処理によって、RAM異常フラグもOFFとなる。その後、ステップS11228に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細については後述する。ステップS11228を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11227, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
図52は、第1実施形態の態様87の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定変更処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定変更処理は、図51のステップS11225及びステップS11228のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 52 is a flowchart showing the setting change process executed by the master MPU 62 (
ステップS11301では、設定変更報知開始処理を実行する。設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定変更モード中です。設定を変更して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定変更モード中です。設定を変更して下さい。」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です。設定を変更して下さい。」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S11301, a setting change notification start process is executed. In the setting change notification start process, a setting change mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has been started, is sent to the voice and light
さらに、設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。ステップS11301を実行した後、ステップS11302に進む。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification start process, information indicating that the setting change mode has started is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has started displays information about the
ステップS11302では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる。その後、ステップS11303に進み、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。ステップS11303において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS11303:YES)、ステップS11305に進む。一方、ステップS11303において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS11303:NO)、例えば、設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、ステップS11304に進み、設定情報を初期値に変更する。本態様では、設定情報に初期値として「1」を格納する。その後、ステップS11305に進む。
In step S11302, control is started to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
ステップS11305では、RAMクリアボタンが押下されたか否かを判定する。ステップS11305において、RAMクリアボタンが押下されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11305:NO)、ステップS11306に進み、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたか否かを判定する。ステップS11306において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたと判定した場合には(ステップS11306:YES)、ステップS11307に進み、抽選設定の設定情報を更新する。具体的には、設定情報として格納されている数値情報に1を加算する。ただし、設定情報として格納されている数値情報が「6」である状況において設定変更用ボタンが押下された場合には当該数値情報は「1」に更新される。その後、上述したステップS11303に戻り、更新した設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。一方、ステップS11306において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11306:NO)、ステップS11307の処理を実行することなく、上述したステップS11303に戻り、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。 In step S11305, it is determined whether the RAM clear button has been pressed. If it is determined in step S11305 that the RAM clear button has not been pressed (step S11305: NO), the process proceeds to step S11306, where it is determined whether the setting change button has been pressed. If it is determined in step S11306 that the setting change button has been pressed (step S11306: YES), the process proceeds to step S11307, where the setting information of the lottery setting is updated. Specifically, 1 is added to the numerical information stored as the setting information. However, if the setting change button is pressed when the numerical information stored as the setting information is "6", the numerical information is updated to "1". After that, it returns to the above-mentioned step S11303, and it is determined whether the updated setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11306 that the setting change button has not been pressed (step S11306: NO), the process returns to step S11303 described above without executing the processing of step S11307, and it is determined whether the setting information is a numerical value within the predetermined range.
上述したステップS11305において、RAMクリアボタンが押下されたと判定した場合には(ステップS11305:YES)、ステップS11308に進み、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったか否かを判定する。ステップS11308において、設定用の鍵がOFF側になっていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11308:NO)、再びステップS11308を実行する。一方、ステップS11308において、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったと判定した場合には(ステップS11308:YES)、ステップS11309に進む。すなわち、RAMクリアボタンが押下された後は、設定用の鍵がOFF側になるまでは無限ループを繰り返してステップS11309に進まず、設定用の鍵がOFF側になるとステップS11309に進む。 If it is determined in step S11305 described above that the RAM clear button has been pressed (step S11305: YES), the process proceeds to step S11308, where it is determined whether or not the setting key has been turned to the OFF side. If it is determined in step S11308 that the setting key has not been turned to the OFF side (step S11308: NO), step S11308 is executed again. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11308 that the setting key has been turned to the OFF side (step S11308: YES), the process proceeds to step S11309. In other words, after the RAM clear button is pressed, an infinite loop is repeated until the setting key is turned to the OFF side, and the process does not proceed to step S11309, and once the setting key is turned to the OFF side, the process proceeds to step S11309.
ステップS11309では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS11310に進む。
In step S11309, control for displaying the lottery setting information on the
ステップS11310では、設定変更報知終了処理を実行する。設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定変更モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
In step S11310, a setting change notification end process is executed. In the setting change notification end process, a setting change mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定変更モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する。ステップS11310を実行した後、本設定変更処理を終了する。なお、設定変更報知終了処理を実行した後、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成とし、当該情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification end process, information indicating that the setting change mode has ended is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has ended displays information indicating that the setting change mode of the
図53は、第1実施形態の態様87の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定確認処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定確認処理は、図51のステップS11215のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 53 is a flowchart showing the setting confirmation process executed by the master MPU 62 (
ステップS11401では、設定確認報知開始処理を実行する。設定確認報知開始処理では、設定確認モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定確認モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S11401, the setting confirmation notification start process is executed. In the setting confirmation notification start process, a setting confirmation mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting confirmation mode has been started, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定確認報知開始処理では、設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。ステップS11401を実行した後、ステップS11402に進む。
Furthermore, in the setting check notification start process, information indicating that the setting check mode has started is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting check mode has started displays information about the
ステップS11402では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに点滅表示させる。その後、ステップS11403に進む。
In step S11402, control is started to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
ステップS11403では、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったか否かを判定する。ステップS11403において、設定用の鍵がOFF側になっていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11403:NO)、再びステップS11403を実行する。一方、ステップS11403において、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったと判定した場合には(ステップS11403:YES)、ステップS11404に進む。すなわち、設定用の鍵がOFF側になるまでは無限ループを繰り返してステップS11404に進まず、設定用の鍵がOFF側になるとステップS11404に進む。 In step S11403, it is determined whether the setting key has been turned OFF. If it is determined in step S11403 that the setting key has not been turned OFF (step S11403: NO), step S11403 is executed again. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11403 that the setting key has been turned OFF (step S11403: YES), the process proceeds to step S11404. In other words, an infinite loop is repeated until the setting key is turned OFF, and the process does not proceed to step S11404, and once the setting key is turned OFF, the process proceeds to step S11404.
ステップS11404では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS11405に進む。
In step S11404, control for displaying the lottery setting information on the
ステップS11405では、設定確認報知終了処理を実行する。設定確認報知終了処理では、設定確認モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定確認モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
In step S11405, a setting confirmation notification end process is executed. In the setting confirmation notification end process, a setting confirmation mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定確認報知終了処理では、設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定確認モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する。ステップS11405を実行した後、本設定確認処理を終了する。
Furthermore, in the setting confirmation notification end process, information indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via the external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended displays information indicating that the setting confirmation mode of the
以上説明したように、本態様では、パチンコ機10は、電源が投入された際(電源ON時)に、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONになっており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチがONになっている場合に設定変更モードを実行し、一方、電源が投入された際(電源ON時)に、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONになっており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチがOFFになっている場合に設定確認モードを実行する。すなわち、本態様では、起動済み(例えば、遊技進行モードを実行中)のパチンコ機10の電源をONの状態としたまま設定変更モードや設定確認モードに移行させることはできない構成となっており、起動済みのパチンコ機10を設定変更モードや設定確認モードに移行させるためには、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにした後、上記の所定の操作を行ないながら再び電源をONにしなければならないように構成されている。
As described above, in this embodiment, when the power is turned on (power ON), the
一般に、遊技ホールでは管理者以外の者がパチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた電源スイッチを操作することができないような設備配置となっているため、仮に、不正な利益を得る目的を持ってパチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更したり確認しようとする者(以下、不正な者ともいう)が存在したとしても、管理者ではない不正な者は、パチンコ機10の背面側に設けられた電源スイッチを操作することは困難である。したがって、不正な者が、パチンコ機10を設定変更モードや設定確認モードに不正に移行させてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In general, gaming halls are equipped with equipment that prevents anyone other than the administrator from operating the power switch located on the back side of the
さらに、本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源がONになると、スピーカー46から当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す音声や警報音が出力されるので、不正な者が周囲に気付かれずに抽選設定を変更したり確認することをさらに困難にすることができる。この結果、不正な者が不正に抽選設定を変更したり確認することを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, when the power of the
さらに、本態様では、パチンコ機10を設定変更モードや設定確認モードに移行させるためには、内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態とする必要があるため、不正な者が周囲に気付かれずに抽選設定を変更したり確認することをさらに困難にすることができる。この結果、不正な者が不正に抽選設定を変更したり確認することを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, in order to transition the
さらに、本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされてから遊技進行モードの実行が開始されるまでの立ち上げ処理中(図51のステップS11201からステップS11228までの処理が実行されている期間中)は、情報表示部45zには、遊技履歴情報は表示されず、設定変更モード又は設定確認モードが実行された場合に抽選設定の設定情報が表示される。すなわち、立ち上げ処理中は、情報表示部45zに遊技履歴情報が表示されることがなく、抽選設定の設定情報のみが表示され得ることになる。したがって、管理者が、立ち上げ処理中に、情報表示部45zに表示されている情報が抽選設定の設定情報であるのか、それとも遊技履歴情報であるのか迷ってしまうことを抑制することができるとともに、管理者が、情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報を、遊技履歴情報であると誤解して認識してしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, during the start-up process from when the power of the
さらに、本態様では、電源のON時に設定確認モードを実行させるための操作が為されていた場合であっても、主側RAM64のRAM判定値が正常であるか否かを判定し、RAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、当該設定確認モードを実行せず、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、遊技を進行可能な遊技進行モードに移行させない。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま設定確認モード及び遊技進行モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, even if an operation to execute the setting check mode is performed when the power is turned on, it is determined whether the RAM judgment value of the
さらに、本態様では、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作には、RAMクリアボタンを押下するという操作が含まれており、パチンコ機10は、設定変更モードを実行する際にはRAMクリア処理(第1RAMクリア処理又は第2RAMクリア処理)を実行する。すなわち、パチンコ機10に設定変更モードを実行させるためには、管理者は、RAMクリアボタンを操作することになり、パチンコ機10は、設定変更モードを実行する際にRAMクリア処理も実行する。一般に、パチンコ機10を管理する管理者は、RAMクリアボタンを押下した状態でパチンコ機10の電源をONにした場合にはRAMクリア処理が実行されることを認識している。したがって、本態様の構成によれば、管理者に対して、RAMクリアボタンを操作して設定変更モードを実行させた場合には、設定変更モードが実行されるだけでなく、RAMクリア処理も実行されるということを強く認識させることが可能となる。この結果、例えば、管理者は、高確率モード等の遊技状態を維持させたままパチンコ機10を起動させて前回の電源OFF時の状態から遊技進行モードを再開させたい場合、すなわちパチンコ機10の起動時にRAMクリア処理を実行させてはいけない場合には、RAMクリア処理の実行が伴う設定変更モードを実行させてはいけないといった判断を確実にすることができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the operation for executing the setting change mode includes the operation of pressing the RAM clear button, and the
さらに、本態様では、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報は消去しない第1RAMクリア処理と、設定情報も含めて消去する第2RAMクリア処理とを実行可能であるので、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、設定情報を残して他の情報は消去すべき処理工程、及び、設定情報も含めて消去すべき処理工程のいずれの場合にも対応した処理工程を実現することができる。例えば、設定情報は正常であるため維持させたまま、他の情報は消去すべき処理工程である場合には第1RAMクリア処理を実行し、設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性のある処理工程である場合には第2RAMクリア処理を実行する構成を実現することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, it is possible to execute a first RAM clear process that does not erase the setting information for the lottery setting among the information stored in the
さらに、本態様では、パチンコ機10は、電源がONにされた際に、復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合及びRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない。そして、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにした後、再び電源をONにする際に、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作が為されて設定変更モードを実行した後でなければ、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードを実行しないように構成されている。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま遊技進行モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, when the
さらに、本態様では、設定変更モードを実行する際には、RAMクリア処理を実行するので、抽選設定が変更された後に主側RAM64に記憶される情報と、抽選設定が変更される前に主側RAM64に記憶されていた情報との間で不整合が生じ、遊技の進行に不具合が発生してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the setting change mode is executed, a RAM clear process is executed, so that it is possible to prevent an inconsistency from occurring between the information stored in the
なお、本態様では、図51のステップS11224において第1RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、ステップS11225において設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行した後に、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成とすれば、設定変更処理によって設定された抽選設定の設定情報を維持したまま、主側RAM64に記憶されている遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等を消去することができる。さらに、図51のステップS11223においてRAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合に、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行した後に、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する構成とした上で、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)において抽選設定を変更せずに(又は変更した設定情報を確定させずに)設定用の鍵をOFF側に回して設定用の鍵穴から抜いた場合には、第1RAMクリア処理を実行せずに遊技進行モードに移行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、意図せずに誤って設定用の鍵をON側に回した状態でRAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源をONにして設定変更処理(設定変更モード)が実行された場合であっても、抽選設定の設定情報を変更しない(又は変更した設定情報を確定させない)ようにすることによって、第1RAMクリア処理の実行を回避し、前回の電源OFF時の状態から遊技進行モードを再開させることが可能となる。
In this embodiment, the first RAM clear process is executed in step S11224 of FIG. 51, and then the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed in step S11225. However, instead of this configuration, the first RAM clear process may be executed after the setting change process (setting change mode). With such a configuration, it is possible to erase various flag information and various control information indicating the game state stored in the
また、本態様では、図51のステップS11224において第1RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、ステップS11225において設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、第2RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成としても、第2RAMクリア処理によって抽選設定が消去されて設定情報として初期値(例えば「1」)が格納された後、設定変更処理によって抽選設定を所望の設定情報に変更することができるので、抽選設定の設定情報が初期値(例えば「1」)となったまま遊技進行モードが実行されることを回避することができる。 In addition, in this embodiment, the first RAM clear process is executed in step S11224 of FIG. 51, and then the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed in step S11225. However, instead of this configuration, the setting change process (setting change mode) may be executed after the second RAM clear process is executed. Even with this configuration, the lottery setting can be erased by the second RAM clear process and an initial value (e.g., "1") is stored as the setting information, and then the lottery setting can be changed to the desired setting information by the setting change process, so that it is possible to avoid the game progress mode being executed with the setting information of the lottery setting at its initial value (e.g., "1").
また、本態様では、図51のステップS11227において第2RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、ステップS11228において設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行した後に、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成とすれば、設定変更処理によって設定された抽選設定の設定情報を維持したまま、異常と判定された主側RAM64に記憶されている各種の情報を消去することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, the second RAM clear process is executed in step S11227 of FIG. 51, and then the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed in step S11228. However, instead of this configuration, the first RAM clear process may be executed after the setting change process (setting change mode). With such a configuration, various information stored in the
また、本態様では、図51のステップS11227において第2RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、ステップS11228において設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、第1RAMクリア処理を実行した後に、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、仮に、抽選設定の設定情報が異常な値であり、第1RAMクリア処理の実行後にも抽選設定の設定情報が異常な値となったまま維持された場合であっても、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)によって抽選設定の設定情報を適切な値に再設定することができる。 In addition, in this embodiment, the second RAM clear process is executed in step S11227 of FIG. 51, and then the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed in step S11228. However, instead of this configuration, the setting change process (setting change mode) may be executed after the first RAM clear process is executed. With this configuration, even if the setting information for the lottery setting is an abnormal value and remains abnormal even after the first RAM clear process is executed, the setting information for the lottery setting can be reset to an appropriate value by the setting change process (setting change mode).
また、本態様では、図51のステップS11210、ステップS11214及びステップS11220においてRAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には、RAM異常報知処理を実行し、遊技進行モードには移行しない構成としたが、この構成に代えて、ステップS11210、ステップS11214及びステップS11220においてRAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には、RAM異常報知処理を実行した後、第2RAMクリア処理を実行して抽選設定の設定情報を初期値(例えば「1」)に設定した上で、遊技進行モードに移行する構成としてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, if it is determined in steps S11210, S11214, and S11220 in FIG. 51 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON, a RAM abnormality notification process is executed and the game progress mode is not entered. However, instead of this configuration, if it is determined in steps S11210, S11214, and S11220 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the RAM abnormality notification process may be executed, and then a second RAM clear process may be executed to set the setting information for the lottery setting to an initial value (e.g., "1"), and then the game progress mode may be entered.
また、本態様では、図51のステップS11215において設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行した後、ステップS11216において復電処理を実行し、ステップS11217において復電フラグをOFFにする構成としたが、この構成に代えて、復電処理及び復電フラグをOFFにする処理を実行した後に、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行する構成としてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, after the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is executed in step S11215 in FIG. 51, the power recovery process is executed in step S11216, and the power recovery flag is turned OFF in step S11217. However, instead of this configuration, the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) may be executed after the power recovery process and the process of turning OFF the power recovery flag are executed.
また、本態様では、図52のステップS11306において設定変更用ボタンが押下された場合に設定情報を更新し、ステップS11305においてRAMクリアボタンが押下された場合に設定情報を確定させる構成としたが、設定情報を更新、確定させる操作はこれに限らず、例えば、RAMクリアボタンが押下された場合に設定情報を更新し、RAMクリアボタンが所定時間以上継続して押下された場合に設定情報を確定させる構成としてもよい。この構成によれば、設定変更用ボタンを省略することができるので、パチンコ機10の製造コストを低減することができる。また、設定用の鍵がOFFにされた場合に設定情報を確定させる構成としてもよく、所定の入球口に設けられた入球検知センサーによって遊技球が検知された場合に設定情報を確定させる構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the setting information is updated when the setting change button is pressed in step S11306 of FIG. 52, and the setting information is confirmed when the RAM clear button is pressed in step S11305. However, the operation of updating and confirming the setting information is not limited to this, and for example, the setting information may be updated when the RAM clear button is pressed, and the setting information may be confirmed when the RAM clear button is pressed for a predetermined time or more. With this configuration, the setting change button can be omitted, and the manufacturing cost of the
また、本態様では、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行させるための条件に、内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態であることが含まれている構成としたが、内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態であることは当該条件に必須ではなく、例えば、内枠13が開放状態であることが当該条件に含まれており前扉枠14が開放状態であることは当該条件に含まれていない構成としてもよく、また、前扉枠14が開放状態であることが当該条件に含まれており内枠13が開放状態であることは当該条件に含まれていない構成としてもよく、また、内枠13及び前扉枠14のいずれも当該条件には含まれていない構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the conditions for executing the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode include the
また、本態様では、設定変更モード中において情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報は点灯する表示態様であり、設定確認モード中において情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報は点滅する表示態様である構成としたが、各モード中の設定情報の表示態様はこれらに限られず、例えば、設定変更モード中において情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報は点滅する表示態様であり、設定確認モード中において情報表示部45zに表示される設定情報は点灯する表示態様である構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the setting information displayed on the
また、本態様では、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードが終了した後は、そのまま遊技進行モードを実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードが終了した後は、遊技進行モードは実行せずに、遊技を進行させることができない待機状態に移行する構成とし、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行させるための所定の操作をせずに電源をONにした場合に、遊技進行モードを実行する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the game progress mode is executed immediately after the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode are terminated. However, instead of this configuration, the game progress mode is not executed after the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode are terminated, and the game progress mode can be executed when the power of the
また、本態様では、設定変更処理(図52)のステップS11302において、主側RAM64に格納されている抽選設定の設定情報(例えば前回の電源OFF時における設定情報)を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、当該設定変更処理の開始時に、主側RAM64に格納されている抽選設定の設定情報がどのような値であるかに関わらず、抽選設定の設定情報を初期値(例えば「1」)に設定し、当該初期値に設定された設定情報を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる構成としてもよい。このような構成とすれば、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)RAMクリア処理を、設定変更処理の実行前に実行することが可能となる。
In addition, in this embodiment, in step S11302 of the setting change process (FIG. 52), the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the main RAM 64 (e.g., the setting information at the time of the previous power OFF) is displayed by lighting on the
また、本態様において、内枠13が開放状態である期間中は、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)や設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中であるか否かに関わらず、内枠13が開放状態であることを報知し続ける構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、「内枠が開いています」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。同様に、前扉枠14が開放状態である期間中は、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)や設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中であるか否かに関わらず、前扉枠14が開放状態であることを報知し続ける構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、「扉が開いています」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。このような構成によれば、不正な者が周囲に気付かれずにパチンコ機10に設定変更処理(設定変更モード)や設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させることをより一層困難にすることができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, while the
<態様88>
上記態様87では、パチンコ機10は、電源がONにされた際に、復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合及びRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない構成としたが、この構成に代えて、電源がONにされた際に、復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合及びRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、設定変更モードを実行するための操作が為されていない場合であっても、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、設定変更モードを実行し、その後、遊技進行モードに移行する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 88>
In the above-mentioned
図54は、第1実施形態の態様88の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理の一部を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 54 is a flowchart showing a part of the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11501では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11502に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11503に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11503を実行した後、ステップS11504に進む。
In step S11501, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11504では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11504, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11504において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11504:YES)、ステップS11505に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11506に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11506において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11506:YES)、ステップS11507に進む。
If it is determined in step S11504 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11504: YES), the process proceeds to step S11505, where the RAM judgment value of the
ステップS11507では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11507において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11507:NO)、ステップS11508に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S11507, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S11507 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11507: NO), the process proceeds to step S11508, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. The frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11508において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11508:NO)、ステップS11509に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11509を実行した後、ステップS11510に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11508, if it is determined that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S11508: NO), the process proceeds to step S11509, where a power recovery process is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery process, the value of the stack pointer stored in the
一方、上述したステップS11508において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11508:YES)、ステップS11511に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図53に示した設定確認処理と同じである。ステップS11511を実行した後、ステップS11512に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11513に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11508 that the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON (step S11508: YES), the process proceeds to step S11511, where the setting confirmation process is executed. The details of the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) are the same as those shown in FIG. 53 of the above-mentioned
上述したステップS11507において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11507:YES)、ステップS11514に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11507 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11507: YES), proceed to step S11514 and determine whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON.
ステップS11514において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11514:NO)、ステップS11515に進む。 If it is determined in step S11514 that at least one of the setting key, frame opening switch, and door opening switch is not ON (step S11514: NO), proceed to step S11515.
ステップS11515では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11515を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11515, the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
上述したステップS11514において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11514:YES)、ステップS11516に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11517に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11517kを実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
If it is determined in step S11514 above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11514: YES), the process proceeds to step S11516, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S11517, where the setting change process is executed. Details of the setting change process (setting change mode) are the same as the setting change process shown in FIG. 52 of
一方、上述したステップS11504において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11504:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11506においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11506:NO)、ステップS11518に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11518を実行した後、ステップS11519に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11504 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11504: NO), and if it is determined in step S11506 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11506: NO), the process proceeds to step S11518, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11519では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。その後、ステップS11520に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11520を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11519, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、電源のON時に、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作が為されていない場合であっても、復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合、及び、主側RAM64のRAM判定値が正常であるか否かを判定し、RAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、第2RAMクリア処理及び設定変更モードを実行して設定情報を確定させた後、遊技を進行可能な遊技進行モードに移行する。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま遊技進行モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, even if no operation is performed to execute the setting change mode when the power is ON, if it is determined that the power recovery flag is not ON, and if it is determined that the RAM judgment value of the
例えば、電源のON時に、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作が為されていた場合であっても、復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合、及び、主側RAM64のRAM判定値が正常であるか否かを判定し、RAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には、当該設定確認モードを実行せず、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知した上で、第2RAMクリア処理及び設定変更モードを実行して設定情報を確定させた後、遊技を進行可能な遊技進行モードに移行する。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま遊技進行モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
For example, even if an operation to execute the setting check mode has been performed when the power is ON, if it is determined that the power recovery flag is not ON, and if it is determined that the RAM judgment value of the
<態様89>
上記態様87におけるメイン処理(図51)では、RAMクリアボタンが押下されているか否かを判定した後に(ステップS11208)、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する(ステップS11209及びステップS11219)構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定した後に、RAMクリアボタンが押下されているか否かを判定する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 89>
In the main process (FIG. 51) in the
図55は、第1実施形態の態様89の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理の一部を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 55 is a flowchart showing a part of the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11601では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11602に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11603に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11603を実行した後、ステップS11604に進む。
In step S11601, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11604では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11604, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11604において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11604:YES)、ステップS11605に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11606に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11606において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11606:YES)、後述するステップS11608に進む。
If it is determined in step S11604 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11604: YES), the process proceeds to step S11605, where a RAM judgment value of the
一方、上述したステップS11604において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11604:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11606においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11606:NO)、ステップS11607に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合又は復電フラグはONであるがRAM判定値が正常ではない場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。ステップS11607を実行した後、ステップS11608に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11604 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11604: NO), and if it is determined in step S11606 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11606: NO), the process proceeds to step S11607, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF or when the power recovery flag is ON but the RAM judgment value is not normal, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
ステップS11608では、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。ステップS11608において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11608:NO)、ステップS11609に進み、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。
In step S11608, it is determined whether the setting key, frame opening switch, and door opening switch are all ON. The frame opening switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11609において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11609:NO)、ステップS11610に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11609 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11609: NO), proceed to step S11610 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11610において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11610:NO)、ステップS11611に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11611を実行した後、ステップS11612に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11610, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11610: NO), the process proceeds to step S11611, where a power recovery process is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery process, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、ステップS11610において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11610:YES)、ステップS11613に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11613を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11610 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11610: YES), the process proceeds to step S11613, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
一方、上述したステップS11609において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11609:YES)、ステップS11614に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11614において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11614:NO)、ステップS11615に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11609 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11609: YES), the process proceeds to step S11614, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S11614 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11614: NO), the process proceeds to step S11615.
ステップS11615では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11615を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11615, the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
一方、ステップS11614において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11614:YES)、ステップS11616に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11616を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、上述したように、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11614 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11614: YES), the process proceeds to step S11616 and RAM abnormality notification processing is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification processing, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11608において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11608:YES)、ステップS11617に進み、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11608 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11608: YES), proceed to step S11617 and determine whether the RAM clear button is ON.
上述したステップS11617において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11617:YES)、ステップS11618に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11617 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11617: YES), the process proceeds to step S11618, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11618において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11618:NO)、ステップS11619に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図53に示した設定確認処理と同じである。ステップS11619を実行した後、ステップS11620に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11621に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11618, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11618: NO), the process proceeds to step S11619, where a setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11618において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11618:YES)、ステップS11622に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11622を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。ただし、上述したように、本態様のパチンコ機10では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)は実行するが、遊技の進行に必要な他の処理(例えば始動口用の入球処理や遊技回制御処理等)は実行しない。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、タイマ割り込みの許可設定を行なわない。したがって、見かけ上は通常の遊技進行モードと同等であるが、遊技者が遊技を進行させることはできない状態となる。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11618 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11618: YES), the process proceeds to step S11622, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11217において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11217:YES)、ステップS11223に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11217 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11217: YES), proceed to step S11223 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11623において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11623:NO)、ステップS11624に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11625に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11625を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
If it is determined in step S11623 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11623: NO), the process proceeds to step S11624, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. After that, the process proceeds to step S11625, where the setting change process is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11623において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11623:YES)、ステップS11626に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11626を実行した後、ステップS11627に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11623 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11623: YES), the process proceeds to step S11626, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11627では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。ここで、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、第1クリア処理ではなく、設定情報も消去する第2クリア処理を実行する理由について説明する。RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報も正常でない可能性があり、例えば、ノイズ等によって管理者の意図しない設定情報に書き換わっていたり、設定情報としては所定の範囲内の数値(例えば1から6までの数値)しか取り得ないにも関わらず、所定の範囲以外の数値が記憶されていたりする可能性があるためである。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。また、第2クリア処理によって、RAM異常フラグもOFFとなる。その後、ステップS11628に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11628を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11627, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
以上説明した本態様の構成によっても、上記態様87と同様の効果を奏することができる。また、上記態様87において説明した各種の変形的な構成も本態様に適用することができる。
The configuration of this aspect described above can achieve the same effect as
<態様90>
上記態様88におけるメイン処理(図54)では、RAMクリアボタンが押下されているか否かを判定した後に(ステップS11507)、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する(ステップS11508及びステップS11514)構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定した後に、RAMクリアボタンが押下されているか否かを判定する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
In the main process (FIG. 54) in the above aspect 88, after determining whether the RAM clear button is pressed (step S11507), it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (steps S11508 and S11514), but instead of this configuration, it may be configured to determine whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON, and then determine whether the RAM clear button is pressed. This will be explained in detail below.
図56は、第1実施形態の態様90の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理の一部を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 56 is a flowchart showing a part of the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11701では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11702に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11703に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11703を実行した後、ステップS11704に進む。
In step S11701, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11704では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11704, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11704において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11704:YES)、ステップS11705に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11706に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11706において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11706:YES)、ステップS11707に進む。
If it is determined in step S11704 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11704: YES), the process proceeds to step S11705, where the RAM judgment value of the
ステップS11707では、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。ステップS11707において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11707:NO)、ステップS11708に進み、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。
In step S11707, it is determined whether the setting key, frame opening switch, and door opening switch are all ON. The frame opening switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11708において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11708:NO)、ステップS11709に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11709を実行した後、ステップS11710に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11708, if it is determined that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11708: NO), the process proceeds to step S11709, where a power recovery process is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery process, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、上述したステップS11708において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11708:YES)、ステップS11711に進み、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11711を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
On the other hand, in the above-mentioned step S11708, if it is determined that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11708: YES), the process proceeds to step S11711, and the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) the information stored in the
上述したステップS11707において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11707:YES)、ステップS11712に進み、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11707 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11707: YES), the process proceeds to step S11712, where it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON.
ステップS11712において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11712:NO)、ステップS11713に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図53に示した設定確認処理と同じである。ステップS11713を実行した後、ステップS11714に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11715に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、通常の遊技処理へ移行する。具体的には、例えば、上述した各態様において説明したタイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、乱数更新処理、電源監視処理(停電監視処理)を実行する。タイマ割込み処理の割り込みを許可し、上述したタイマ割込み処理が実行されることによって、遊技の進行が可能となる(遊技進行モードが開始される)。
In step S11712, if it is determined that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11712: NO), the process proceeds to step S11713, where the setting confirmation process is executed. The details of the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) are the same as those shown in FIG. 53 of the above-mentioned
上述したステップS11712において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11712:YES)、ステップS11716に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11717に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11717を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
If it is determined in step S11712 above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11712: YES), the process proceeds to step S11716, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S11717, where the setting change process is executed. Details of the setting change process (setting change mode) are the same as the setting change process shown in FIG. 52 of
一方、上述したステップS11704において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11704:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11706においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11706:NO)、ステップS11718に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11718を実行した後、ステップS11719に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11704 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11704: NO), and if it is determined in step S11706 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11706: NO), the process proceeds to step S11718, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11719では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。その後、ステップS11720に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、上述した態様87の図52に示した設定変更処理と同じである。ステップS11720を実行した後、上述した通常の遊技処理へ移行する。
In step S11719, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
以上説明した本態様の構成によっても、上記態様88と同様の効果を奏することができる。また、上記態様88において説明した各種の変形的な構成も本態様に適用することができる。 The configuration of this embodiment described above can achieve the same effect as embodiment 88. In addition, the various modified configurations described in embodiment 88 can also be applied to this embodiment.
<態様91>
上記各態様における設定変更処理(図52)では、RAMクリアボタンが押下された場合に抽選設定の設定情報が確定する(ステップS11305)構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定用の鍵がOFFになった場合に抽選設定の設定情報が確定する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
In the setting change process (FIG. 52) in each of the above aspects, the setting information for the lottery setting is confirmed when the RAM clear button is pressed (step S11305), but instead of this configuration, the setting information for the lottery setting may be confirmed when the setting key is turned OFF. This will be specifically described below.
図57は、第1実施形態の態様91の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定変更処理を示すフローチャートである。図52に示した設定変更処理に含まれる処理と同一の処理については同一のステップ番号を付している。図52に示した設定変更処理との主な相違点は、図52では、変更した設定情報を確定させる処理がRAMクリアボタンを押下することであるのに対し(ステップS11305)、本態様では、変更した設定情報を確定させる処理が設定用の鍵をOFF側にすること(ステップS11305a)である点と、これに伴って図52のステップS11308の処理が省略されている点である。以下、具体的に説明する。
Figure 57 is a flowchart showing the setting change process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11301では、設定変更報知開始処理を実行する。設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定変更モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S11301, the setting change notification start process is executed. In the setting change notification start process, a setting change mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has been started, is sent to the voice and light
さらに、設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。ステップS11301を実行した後、ステップS11302に進む。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification start process, information indicating that the setting change mode has started is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has started displays information about the
ステップS11302では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる。その後、ステップS11303に進み、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。ステップS11303において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS11303:YES)、ステップS11305aに進む。一方、ステップS11303において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS11303:NO)、例えば、設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、ステップS11304に進み、設定情報を初期値に変更する。本態様では、設定情報に初期値として「1」を格納する。その後、ステップS11305aに進む。
In step S11302, control is started to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
ステップS11305aでは、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったか否かを判定する。ステップS11305aにおいて、設定用の鍵がOFF側になっていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11305a:NO)、ステップS11306に進み、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたか否かを判定する。ステップS11306において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたと判定した場合には(ステップS11306:YES)、ステップS11307に進み、抽選設定の設定情報を更新する。具体的には、設定情報として格納されている数値情報に1を加算する。ただし、設定情報として格納されている数値情報が「6」である状況において設定変更用ボタンが押下された場合には当該数値情報は「1」に更新される。その後、上述したステップS11303に戻り、更新した設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。一方、ステップS11306において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS11306:NO)、ステップS11307の処理を実行することなく、上述したステップS11303に戻り、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。 In step S11305a, it is determined whether the setting key has been turned OFF. If it is determined in step S11305a that the setting key has not been turned OFF (step S11305a: NO), the process proceeds to step S11306, where it is determined whether the setting change button has been pressed. If it is determined in step S11306 that the setting change button has been pressed (step S11306: YES), the process proceeds to step S11307, where the setting information for the lottery setting is updated. Specifically, 1 is added to the numerical information stored as the setting information. However, if the setting change button is pressed when the numerical information stored as the setting information is "6", the numerical information is updated to "1". After that, it returns to the above-mentioned step S11303, and it is determined whether the updated setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11306 that the setting change button has not been pressed (step S11306: NO), the process returns to step S11303 described above without executing the processing of step S11307, and it is determined whether the setting information is a numerical value within the predetermined range.
上述したステップS11305aにおいて、設定用の鍵がOFF側になったと判定した場合には(ステップS11305a:YES)、ステップS11309に進み、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS11310に進む。
If it is determined in step S11305a described above that the setting key has been turned to the OFF side (step S11305a: YES), the process proceeds to step S11309, where control for displaying the setting information for the lottery setting on the
ステップS11310では、設定変更報知終了処理を実行する。設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定変更モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
In step S11310, a setting change notification end process is executed. In the setting change notification end process, a setting change mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定変更モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する。ステップS11310を実行した後、本設定変更処理を終了する。なお、設定変更報知終了処理を実行した後、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成とし、当該情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification end process, information indicating that the setting change mode has ended is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has ended displays information indicating that the setting change mode of the
以上説明した本態様の構成によれば、変更した設定情報を確定させるためにRAMクリアボタンを押下するという操作を省略することができるので、管理者が設定情報を変更させるために必要となる作業工程を簡易化することができる。 According to the configuration of this aspect described above, the operation of pressing the RAM clear button to confirm the changed setting information can be omitted, simplifying the work process required for the administrator to change the setting information.
<態様92>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行可能な構成において、設定変更モードの実行中及び設定確認モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードの実行中には表示されない表示パターン(表示態様)を表示する構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 92>
Among the above-mentioned modes, in a configuration in which the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode can be executed, during execution of the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the
上述したように、メイン表示部45は、複数の発光部によって構成されている。具体的には、メイン表示部45は、複数のセグメント発光部からなる第1図柄表示部37aと、複数のセグメント発光部からなる第2図柄表示部37bと、複数のLEDランプからなる第1保留表示部37cと、複数のLEDランプからなる第2保留表示部37dと、複数のLEDランプからなる普図ユニット38と、複数のLEDランプからなるラウンド表示部39とによって構成されている。
As described above, the
そして、メイン表示部45は、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードの実行中においては、遊技の進行の状況を反映した表示態様となるように各発光部を制御するが、本態様では、遊技進行モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部が同時に点灯した状態となったり、全ての発光部が同期して点滅した状態となることはない。
The
そこで、本態様では、メイン表示部45は、抽選設定の設定情報を変更可能な設定変更モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部を同時に点灯させる制御を実行し、抽選設定の設定情報を確認可能な設定確認モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部を同期して点滅させる制御を実行する。
In this embodiment, the
このような構成によれば、現在のパチンコ機10が遊技進行モード中であるのか、設定変更モード中であるのか、設定確認モード中であるのかを管理者等に識別させることが可能となる。さらに、このような構成によれば、例えば、パチンコ機10の現在のモードを識別させるためのモード表示用の発光部をメイン表示部45に新たに追加しなくてもよいため、パチンコ機10のハードウェア構成を変更することなく、パチンコ機10の制御プログラムを変更することのみによって、パチンコ機10の現在のモードを管理者等に識別させることが可能な構成に変更することができる。
This configuration allows the administrator, etc., to identify whether the
なお、メイン表示部45は、抽選設定の設定情報を変更可能な設定変更モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部を同期して点滅させる制御を実行し、抽選設定の設定情報を確認可能な設定確認モードの実行中においては、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部を同時に点灯させる制御を実行する構成としてもよい。
The
また、設定変更モードの実行中及び設定確認モードの実行中においてメイン表示部45が表示する表示態様は、遊技進行モードの実行中には表示されない表示態様(点灯パターン)であれば、メイン表示部45を構成する全ての発光部を点灯、点滅させる構成に限らず、他の表示態様であってもよい。
In addition, the display mode displayed by the
また、メイン表示部45にモード表示用の発光部(例えばLED)を1つ追加し、遊技進行モードの実行中は当該発光部を消灯させ、設定変更モードの実行中は当該発光部を点灯させ、設定確認モードの実行中は当該発光部を点滅させる構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の現在のモードを管理者等に明確に認識させることが可能となるとともに、音声発光制御装置90や表示制御装置100、図柄表示装置41を用いてパチンコ機10の現在のモードを報知する構成と比較して、構成の簡略化を実現することができる。
In addition, a light-emitting unit (e.g., an LED) for displaying the mode may be added to the
また、メイン表示部45にモード表示用の発光部(例えばLED)を2つ(第1発光部及び第2発光部)追加し、遊技進行モードの実行中は第1発光部及び第2発光部の両方を消灯させた状態とし、設定変更モードの実行中は第1発光部を点灯させて第2発光部は消灯させた状態とし、設定確認モードの実行中は第2発光部を点灯させて第1発光部を消灯させた状態とする構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の現在のモードを管理者等に明確に認識させることが可能となるとともに、音声発光制御装置90や表示制御装置100、図柄表示装置41を用いてパチンコ機10の現在のモードを報知する構成と比較して、構成の簡略化を実現することができる。さらに、メイン表示部45に追加した2つの発光部を制御するだけでよいので、制御プログラムや点灯パターンを追加することによるデータ容量の増加を抑制することができる。
In addition, two light-emitting units (e.g., LEDs) for displaying the mode (first and second light-emitting units) may be added to the
<態様93>
上記各態様のうち、情報表示部45zが4個の7セグメント表示器45z1~45z4を備える構成において、当該パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる構成としてもよい。
<
Among the above aspects, in a configuration in which the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、情報表示部45zを構成する発光部に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができる。例えば、仮に、右中7セグメント表示器45z3のセグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが不具合によって点灯しない場合には、右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「3」を表示させる制御が実行されている場合であっても、セグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが点灯しないことによって、右中7セグメント表示器45z3には「7」が表示されてしまうことになる。この結果、管理者は、遊技履歴情報の数値情報を誤認してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本態様の構成によれば、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、情報表示部45zを構成する発光部に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができるので、このような誤認を抑制することができる。
According to this configuration, when the power supply of the
さらに、情報表示部45zを検査するための情報表示部検査ボタンを設け、当該情報表示部検査ボタンが押下された場合には、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, an information display unit inspection button for inspecting the
このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の電源投入時ではなくても、情報表示部検査ボタンを押下することによって、情報表示部45zを構成する発光部に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができる。すなわち、情報表示部45zに不具合が発生していないかを確認するためにパチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにしてからONにしなくてもよいため、管理者の作業効率を向上させることができる。
With this configuration, even when the
また、上述したベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶し、記憶したベース(通常モード中)を情報表示部45zに表示させる構成において、主制御装置60は、計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達する毎に区間を分け、区間毎にベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶する構成とし、情報表示部45zは、算出対象となった区間の異なる複数種類のベース(通常モード中)を切り替えて表示する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in a configuration in which the above-mentioned base (during normal mode) is calculated and stored and the stored base (during normal mode) is displayed on the
具体的には、本態様のパチンコ機10は、最大で7つの区間のベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶し、情報表示部45zは、最大で7つの区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を切り替えて表示する。7つの区間は以下のとおりである。
Specifically, the
・「bL」:計測中のベース(通常モード中)
現在計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達するまでの現在の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b1」:1つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の1つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b2」:2つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の2つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b3」:3つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の3つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b4」:4つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の4つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b5」:5つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の5つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・「b6」:6つ前の区間において計測済みのベース(通常モード中)
計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した区間であって、現在計測中の区間の6つ前の区間において算出された出球率(通常モード中)
・"bL": Base being measured (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate calculated in the current section until the number of balls passing through the discharge passage currently being measured N OUT reaches 60,000 (in normal mode)
"b1": Base already measured in the previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section immediately preceding the section currently being measured in which the number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT has reached 60,000.
・"b2": Base already measured in the previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section two sections before the section currently being measured in which the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches 60,000.
・"b3": Base already measured in the third previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section three sections before the section currently being measured in which the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches 60,000.
"b4": Base already measured in the fourth previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section four sections before the section currently being measured in which the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches 60,000.
・"b5": Base measured in the 5th previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section where the number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches 60,000 balls and is 5 sections before the section currently being measured.
"b6": Base measured in the 6th previous section (in normal mode)
The ball discharge rate (in normal mode) calculated in the section 6 before the section currently being measured in which the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches 60,000.
各入球部への入球個数情報等の遊技履歴基礎情報が記憶されていない初期状態において「bL」に対応する区間の計測を開始し、所定のタイミングで随時「bL」に対応する区間におけるベース(通常モード中)を算出する。計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達すると、「bL」に対する区間として記憶した遊技履歴基礎情報を「b1」に対応する区間にシフトさせ、新たに「bL」に対応する区間の計測を開始する。そして、新たに計測を開始した「bL」に対応する区間において排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達すると、「b1」に対する区間として記憶していた遊技履歴基礎情報を「b2」に対応する区間にシフトさせ、「bL」に対する区間として記憶した遊技履歴基礎情報を「b1」に対応する区間にシフトさせ、新たに「bL」に対応する区間の計測を開始する。このようにして、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達する毎に、区間毎の遊技履歴基礎情報をシフトさせていき、最大で「b6」に対応する区間まで遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶しておく。そして、「b6」に対応する区間として遊技履歴基礎情報が記憶されている状態で、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達すると、「b6」に対応する区間として記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を消去し、「b5」に対応する区間として記憶されていた遊技履歴基礎情報を「b6」に対応する区間にシフトさせる。 In the initial state where the game history basic information such as the number of balls entering each entry section is not stored, the measurement of the section corresponding to "bL" is started, and the base (in normal mode) in the section corresponding to "bL" is calculated at a predetermined timing. When the number of balls passing through the discharge passage during measurement N OUT reaches 60,000, the game history basic information stored as the section corresponding to "bL" is shifted to the section corresponding to "b1", and the measurement of the section corresponding to "bL" is started. Then, when the number of balls passing through the discharge passage N OUT reaches 60,000 in the section corresponding to "bL" where the measurement is started, the game history basic information stored as the section corresponding to "b1" is shifted to the section corresponding to "b2", the game history basic information stored as the section corresponding to "bL" is shifted to the section corresponding to "b1", and the measurement of the section corresponding to "bL" is started. In this way, the game history basic information for each section is shifted every time the number of balls passing through the discharge passage during measurement N OUT reaches 60,000, and the game history basic information is stored up to the section corresponding to "b6" at the maximum. Then, when the number N OUT of balls passing through the discharge passage during measurement reaches 60,000 while the game history basic information is stored as the section corresponding to "b6", the game history basic information stored as the section corresponding to "b6" is erased, and the game history basic information stored as the section corresponding to "b5" is shifted to the section corresponding to "b6".
すなわち、本態様では、最大で60000個×7区間の排出通路通過個数NOUTが計測されるまでの遊技履歴基礎情報が蓄積されて記憶される。 That is, in this embodiment, the basic game history information is accumulated and stored until the maximum number N OUT of balls passing through the discharge passage (60,000 balls×7 sections) is measured.
そして、本態様では、情報表示部45zは、記憶されている複数の区間のベース(通常モード中)を5秒毎に切り替えて表示する。具体的には、例えば、「bL」、「b1」、「b2」、「b3」、「b4」の5つの区間のベース(通常モード中)が記憶されている場合には、情報表示部45zは、「bL.31」→「b1.31」→「b2.30」→「b3.31」→「b4.30」→「bL.31」→「b1.31」...といった順序で5秒毎に切り替えながら各区間のベース(通常モード中)を繰り返し表示する。
In this embodiment, the
このような構成によれば、遊技機の検査者又は管理者は、情報表示部45zの表示を確認することによって、各区間毎のベース(通常モード中)を比較することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、パチンコ機10に不具合が発生したり不正が施されたりすることによってベース(通常モード中)の値が異常値になった場合に、過去のどのタイミングで不具合等が発生したのかを予測することが可能となる。
With this configuration, the inspector or manager of the gaming machine can compare the base (during normal mode) for each section by checking the display on the
なお、本態様では、計測した排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達する毎に区間を分け、区間毎にベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶し、区間毎に記憶したベース(通常モード中)を所定時間毎(例えば5秒毎)に切り替えて情報表示部45zに表示させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、RTC96を設け、日付が変わる毎に区間を分け、日付毎に区分けされた区間毎にベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶し、日付毎(区間毎)に記憶したベース(通常モード中)を所定時間毎(例えば5秒毎)に切り替えて情報表示部45zに表示させる構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、「bL」は当日の区間、「b1」は1日前の区間、「b2」は2日前の区間、「b3」は3日前の区間、「b4」は4日前の区間、「b5」は5日前の区間、「b6」は6日前の区間として定義する。
In this embodiment, the section is divided every time the measured number N OUT of passing through the discharge passage reaches 60,000, the base (in normal mode) is calculated and stored for each section, and the base (in normal mode) stored for each section is switched every predetermined time (for example, every 5 seconds) to be displayed on the
このような構成によれば、遊技機の検査者又は管理者は、情報表示部45zの表示を確認することによって、日付毎に区切られた各区間毎のベース(通常モード中)を比較することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、パチンコ機10に不具合が発生したり不正が施されたりすることによってベース(通常モード中)の値が異常値になった場合に、不具合等が発生した日付を予測することが可能となる。
With this configuration, an inspector or manager of the gaming machine can compare the base (during normal mode) for each section divided by date by checking the display on the
また、各入球部への入球個数情報等の遊技履歴基礎情報及びベース(通常モード中)等の遊技履歴情報が主側RAM64に記憶されており、RAMクリアボタンを押下した状態でパチンコ機10の電源をONにすることによって実行されるRAMクリア処理によって、遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が消去される(クリアされる)構成において、遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が消去された後、計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数(例えば300個)に達するまでは、遊技履歴情報を情報表示部45zに表示させる際に、遊技履歴情報の種別情報は表示させるが、遊技履歴情報の数値情報は表示させない構成としてもよい。
In addition, in a configuration in which basic game history information such as the number of balls entering each entry section and game history information such as the base (during normal mode) are stored in the
具体的には、例えば、遊技履歴情報としてベース(通常モード中)を算出して記憶し、記憶したベース(通常モード中)を情報表示部45zに表示させる構成において、RAMクリア処理によって遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が消去された後、計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが300個に達するまでは、情報表示部45zの種別情報表示エリアに「bL.」を表示させ、数値情報表示エリアに「--(2個のハイフン)」を表示させる構成としてもよい。
Specifically, for example, in a configuration in which a base (during normal mode) is calculated and stored as game history information and the stored base (during normal mode) is displayed on the
このような構成によれば、遊技機の検査者又は管理者は、情報表示部45zに「bL.--」が表示されている場合には、遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報が消去された後、又はメーカーの工場から当該パチンコ機10が出荷された後に計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが300個に達していないと認識することができる。また、例えば、メーカーがパチンコ機10を出荷する際には、数個の遊技球を各入球部に入球させたりして動作をチェックする場合がある。この場合には、正当に遊技を行なった場合ではない状況において各入球部に入球した遊技球の個数が計測されてしまうので、例えば、最初に計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが300個に達するまでは、遊技履歴基礎情報及び遊技履歴情報に、メーカーによるチェックの影響が大きく出てしまう可能性がある。そこで、本態様の構成によれば、計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが300個に達するまでは、情報表示部45zに「bL.--」を表示させて、ベース(通常モード中)の数値情報は表示させないので、管理者が、メーカーによるチェックの影響を大きく受けた数値を確認し、パチンコ機10に不具合等が発生してしまったのではないかといった誤解をしてしまうことを抑制することができる。
According to this configuration, when "bL.--" is displayed on the
<態様94>
上記各態様のうち、複数の区間毎に遊技履歴情報を算出する構成において、区間に対応する遊技履歴基礎情報が上限まで記憶されて遊技履歴情報を算出して記憶した後は、当該区間の遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となった遊技履歴基礎情報は消去する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達して遊技履歴情報を算出して記憶した後は、当該遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となった遊技履歴基礎情報は消去する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶するために必要となる記憶容量を低減することができる。
<Aspect 94>
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in the configuration in which the gaming history information is calculated for each of a plurality of sections, after the gaming history basic information corresponding to the section is stored up to an upper limit and the gaming history information is calculated and stored, the gaming history basic information that was the basis for the calculation of the gaming history information for that section may be erased. Specifically, for example, after the number of balls passing through the discharge passage N OUT during measurement reaches 60,000 and the gaming history information is calculated and stored, the gaming history basic information that was the basis for the calculation of the gaming history information may be erased. With such a configuration, the storage capacity required for storing the gaming history basic information can be reduced.
<態様95>
上記各態様のうち、複数の区間のそれぞれに対応した複数のベース(通常モード中)を情報表示部45zが切り替えて順次表示する構成において、当該切り替えの際に、所定時間、情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~H及びDP発光部)を所定時間消灯させる構成としてもよい。以下、本態様の構成について具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 95>
Among the above aspects, in a configuration in which the
図58は、情報表示部45zの表示態様の変化の一例を示すタイムチャートである。この図58には、「bL」、「b1」、「b2」の3つの区間のベース(通常モード中)が算出されて主側RAM64に記憶されており、これら3つの区間のベース(通常モード中)が情報表示部45zによって切り替えて表示される例が示されている。
Figure 58 is a time chart showing an example of a change in the display mode of the
本態様では、情報表示部45zは、過去の区間に遡る順序でベース(通常モード中)を循環させて繰り返し表示する。より具体的には、直近の区間に対応した計測中のベース(通常モード中)である「bL」を所定の表示継続時間(例えば5000ms)が経過するまで表示した後、1つ前の区間に遡る順序でベース(通常モード中)を順次表示し、主側RAM64に記憶されている区間のうちの最も過去の区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)を表示した後は、再び直近の計測中の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)である「bL」を表示する。
In this embodiment, the
さらに、本態様では、情報表示部45zは、複数の区間のうちの一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)の表示を開始して当該ベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間(例えば5000ms)が経過した際には、当該情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~H及びDP発光部)を所定時間(例えば300ms)消灯させた後に、1つ前の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)の表示を開始する。すなわち、本態様では、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)の表示を他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)の表示に切り替える際に、情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~H及びDP発光部)を所定時間(例えば300ms)消灯させる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, when the
図58に示した例では、情報表示部45zは、現在計測中の区間に対応する計測中のベース(通常モード中)である「bL」を「bL.31」といった表示態様で5000ms継続して点灯表示し、その後、全ての発光部を300ms消灯する。その後、1つ前の区間に対応する計測済みのベース(通常モード中)である「b1」を「b1.30」といった表示態様で5000ms継続して点灯表示し、その後、全ての発光部を300ms消灯する。その後、さらに1つ前の区間に対応する計測済みのベース(通常モード中)である「b2」を「b2.31」といった表示態様で5000ms継続して点灯表示し、その後、全ての発光部を300ms消灯する。その後、再び、現在計測中の区間に対応する計測中のベース(通常モード中)である「bL」を「bL.31」といった表示態様で5000ms継続して点灯表示する。このように、情報表示部45zは、300msの全消灯状態を挟みながら、主側RAM64に記憶されている各区間のベース(通常モード中)を循環させて繰り返し表示する。
In the example shown in FIG. 58, the
次に、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合について説明する。 Next, a case where the number N OUT of particles passing through the discharge passage during measurement reaches 60,000 will be described.
図59は、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合における情報表示部45zの表示態様の変化の一例を示すタイムチャートである。この図59には、「bL」、「b1」、「b2」の3つの区間のベース(通常モード中)が算出されて主側RAM64に記憶されており、情報表示部45zが「b1」を表示中に、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した例が示されている。
Fig. 59 is a time chart showing an example of a change in the display mode of the
本態様では、いずれかの区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)を表示中に、現在計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過する前であっても、当該表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示を終了する。そして、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様による表示を開始し、当該表示態様を所定時間(例えば2000ms)継続する。本態様では、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様として、4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様を採用している。そして、4個のハイフンを点灯させている所定期間(例えば2000ms)が経過するまでの期間に、主制御装置60の主側CPU62xは、現在計測中の区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)である「bL」としての最終値を算出する処理と、各区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を1つずつ過去の区間にシフトさせる処理とを実行した上で、新たな「bL」を算出するための現在の区間における各入球口への遊技球の入球個数の計測、及び「bL」の現在の値を算出する処理を開始する。
In this embodiment, when the number NOUT of passing through the discharge passage in the currently measured section reaches 60,000 while a base (in normal mode) corresponding to any section is being displayed, the
図59に示した例では、「b1」を表示中であって当該「b1」の表示継続時間である5000msが経過する前のタイミングで、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したため、情報表示部45zは、当該「b1」の表示を終了し、4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様による表示を開始し、当該表示態様を2000ms継続する。
In the example shown in FIG. 59, while "b1" is being displayed, the number NOUT of pieces passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 pieces before the display duration of 5,000 ms for "b1" has elapsed, so the
その後、本態様では、4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様を開始してから所定時間(例えば2000ms)が経過したことに基づいて、新たに計測を開始した「bL」から循環表示を開始する。すなわち、4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様による表示を終了した後は、表示が中断されたベース(通常モード中)の区間に関わらず、新たに計測を開始した「bL」から表示を再開する。 In this embodiment, the display then starts cyclically from "bL" which has just started to be measured, based on the fact that a predetermined time (e.g., 2000 ms) has elapsed since the display mode in which the four hyphens are lit has started. In other words, after the display mode in which the four hyphens are lit has ended, the display resumes from "bL" which has just started to be measured, regardless of the base (in normal mode) section in which the display was interrupted.
なお、本態様において、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を消灯させる表示態様を開始してから300msが経過する前のタイミングで、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、当該全ての発光部を消灯させる表示態様を終了し、上述した4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様に移行する。
In this embodiment, if the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 before 300 ms has elapsed since the start of the display mode in which all of the light-emitting elements constituting the
以上説明したように、本態様では、情報表示部45zは、複数の区間のうちの一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様(例えば「bL」を表示する表示態様)から、いずれのベース(通常モード中)も表示しない表示態様(例えば全てのセグメント発光部を消灯させた表示態様)に移行した後、他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様(例えば「b1」を表示する表示態様)に移行する。したがって、本態様によれば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者に対して、情報表示部45zに表示されているベース(通常モード中)が他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)に切り替わったことを明確に認識させることができる。この結果、管理者等が、表示されているベース(通常モード中)の区間が切り替わったことに気付かずに、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の区間を誤って認識してしまうことを抑制することができる。特に、本態様では、ベース(通常モード中)の区間が異なっていても、ベース(通常モード中)の数値自体は同じになっている状況があり、この状況において表示中のベース(通常モード中)の区間が切り替わった場合には、ベース(通常モード中)の区間を示す2文字目(例えば、L、1、2等)の表示のみが変化することになる。仮に、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様から他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に直接移行する構成とすると、管理者等は、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の区間が切り替わったことに気付くのが困難となる。これに対して、本態様では、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様から他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に移行する前に、いずれのベース(通常モード中)も表示しない表示態様(例えば全てのセグメント発光部を消灯させた表示態様)に移行するので、切り替わり前後のベース(通常モード中)の数値自体が同じであっても、管理者等に対して、情報表示部45zに表示されているベース(通常モード中)が他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)に切り替わったことを明確に認識させることができる。
As described above, in this embodiment, the
また、本態様では、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様から、他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に移行する場合の移行態様は、全ての発光部を300ms消灯させる移行態様である。一方、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合の移行態様は、4個のハイフンを2000ms点灯させる移行態様である。すなわち、本態様では、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様から他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に移行する場合の移行態様と、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合の移行態様とが異なっている。したがって、本態様によれば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者は、移行態様の違いを認識することによって、他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に移行するのか、それとも、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様が移行するのかを明確に区別して認識することができる。この結果、例えば、管理者等が、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことによって各区間のベース(通常モード中)が1つずつ過去の区間にシフトしたことに気付かずにベース(通常モード中)の確認作業を継続してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this embodiment, the transition mode when switching from a display mode displaying a base (in normal mode) corresponding to one section to a display mode displaying a base (in normal mode) corresponding to another section is a transition mode in which all light-emitting units are turned off for 300 ms. On the other hand, the transition mode when switching the display mode based on the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000 is a transition mode in which four hyphens are turned on for 2000 ms. In other words, in this embodiment, the transition mode when switching from a display mode displaying a base (in normal mode) corresponding to one section to a display mode displaying a base (in normal mode) corresponding to another section is different from the transition mode when switching the display mode based on the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000. Therefore, according to this embodiment, the manager or inspector of the
また、本態様では、ベース(通常モード中)を表示中に、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間が経過する前であっても、当該計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様(4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様)に移行する。したがって、本態様によれば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者に対して、当該計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことを早期に認識させることができる。また、本態様によれば、当該計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことによるシフト後の各区間のベース(通常モード中)を早期に表示することが可能となるので、管理者等は、当該計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことによるシフト後の各区間毎のベース(通常モード中)を早期に確認することができるので、パチンコ機10に対する検査の効率を向上させることができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 while the base (in normal mode) is being displayed, even before the display duration of the displayed base (in normal mode) has elapsed, the display mode is switched to a display mode (a display mode in which four hyphens are lit) corresponding to the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000. Therefore, according to this embodiment, the manager or inspector of the
また、本態様では、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、当該計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様(4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様)を所定時間(本態様では2000ms)継続するので、当該所定時間が経過するまでの期間を利用して、主側CPU62xが「bL」としての最終値を算出する処理及び各区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を1つずつ過去の区間にシフトさせる処理を実行するための時間を確保することができる。また、「bL」としての最終値を算出した後に、当該「bL」の算出の基礎となった遊技履歴基礎情報を消去する構成とすれば、遊技履歴基礎情報を記憶するために必要となる記憶容量を低減することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000, the display mode (the display mode in which four hyphens are lit) corresponding to the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 is continued for a predetermined time (2000 ms in this embodiment), so that the period until the predetermined time has elapsed can be used to secure time for the
また、本態様では、複数の区間のそれぞれに対応した複数のベース(通常モード中)を、1つ前の区間に遡るといった所定の順序に従って順次切り替えて表示しており、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、所定の順序に従って次に表示すべきベース(通常モード中)の区間がどの区間であるのかに関わらず、新たに計測を開始した直近の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)である「bL」から表示を開始する。したがって、本態様によれば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者は、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことを認識することができるとともに、「bL」から優先的に確認することが可能となる。
In addition, in this embodiment, the display switches between a plurality of bases (in normal mode) corresponding to each of the plurality of sections in a predetermined order, such as going back to the previous section, and when the number of balls passing through the discharge passage N OUT in the section being measured reaches 60,000, the display starts from "bL", which is the base (in normal mode) corresponding to the most recent section in which the measurement has just started, regardless of which section the next base (in normal mode) to be displayed in the predetermined order is. Therefore, according to this embodiment, the manager or inspector of the
なお、本態様では、複数の区間のうちの一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様と他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様との間における表示態様として、全てのセグメント発光部を消灯させる表示態様を採用したが、いずれの区間のベース(通常モード中)も表示しない表示態様であれば、他の表示態様を採用してもよい。例えば、4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様や、4個のハイフンを点滅させる表示態様を採用してもよい。このような構成によれば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者に対して、情報表示部45zに表示されているベース(通常モード中)が他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)に切り替わったことをさらに明確に認識させることができる。
In this embodiment, a display mode in which all segment light emitting units are turned off is used as a display mode between a display mode that displays a base (in normal mode) corresponding to one of the multiple sections and a display mode that displays a base (in normal mode) corresponding to another section. However, other display modes may be used as long as they do not display the base (in normal mode) of any section. For example, a display mode in which four hyphens are lit or a display mode in which four hyphens flash may be used. This configuration allows the manager or inspector of the
また、本態様では、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様として、4個のハイフンを点灯させる表示態様を採用したが、他の表示態様を採用してもよい。例えば、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様として、4個のハイフンを点滅させる表示態様を採用してもよい。また、例えば、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様として、情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~H及びDP発光部)を消灯させる表示態様を採用してもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, a display mode in which four hyphens are lit is adopted as a display mode corresponding to the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000, but other display modes may be adopted. For example, a display mode in which four hyphens flash may be adopted as a display mode corresponding to the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000. Also, for example, a display mode in which all light-emitting parts (segment light-emitting parts A to H and the DP light-emitting part) of the seven-segment display constituting the
また、本態様では、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合の移行態様として、4個のハイフンを2000ms点灯させる移行態様を採用したが、他の移行態様を採用してもよい。例えば、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合の移行態様として、情報表示部45zを構成する7セグメント表示器の全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~H及びDP発光部)を300ms消灯させる移行態様を採用してもよい。このような構成によれば、一の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様から他の区間に対応したベース(通常モード中)を表示する表示態様に移行する場合の移行態様と、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて表示態様が移行する場合の移行態様とを同じにすることができるので、管理者等に対して違和感を与えることなく表示態様を移行させることができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, the transition mode in which four hyphens are lit for 2000 ms is adopted as the transition mode when the display mode is changed based on the number N OUT passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaching 60,000, but other transition modes may be adopted. For example, the transition mode in which all light-emitting parts (segment light-emitting parts A to H and DP light-emitting part) of the 7-segment display constituting the
また、本態様では、遊技履歴情報としてベース(通常モード中)を表示する構成としたが、表示する遊技履歴情報はベース(通常モード中)に限られず、第1実施形態に示した種々の遊技履歴情報(例えば役物比率や連続役物比率等)を表示する構成としてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the game history information is configured to display the base (in normal mode), but the game history information to be displayed is not limited to the base (in normal mode), and various game history information shown in the first embodiment (for example, the ratio of roles and the ratio of consecutive roles) may be displayed.
また、本態様では、排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに基づいて区間を分ける構成としたが、他の所定の条件が満たされたことに基づいて区間を分ける構成としてもよい。例えば、排出通路通過個数NOUTが10000個に達したことに基づいて区間を分ける構成としてもよく、また、日付が変わったことに基づいて区間を分ける構成としてもよい。 In this embodiment, the section is divided based on the number of pieces passing through the discharge passage N OUT reaching 60,000, but the section may be divided based on the satisfaction of other predetermined conditions. For example, the section may be divided based on the number of pieces passing through the discharge passage N OUT reaching 10,000, or based on a change in the date.
<態様96>
上記態様95では、いずれかの区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)を表示中に、現在計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過する前であっても、当該表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示を終了し、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様による表示を開始する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、いずれかの区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)を表示中に、現在計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過した後に、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様による表示を開始する構成としてもよい。以下、本態様の構成について具体的に説明する。
<
In the above-mentioned aspect 95, when the number N OUT of passing through the discharge passage in the currently measured section reaches 60,000 while a base (in normal mode) corresponding to any section is being displayed, the
図60は、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合における情報表示部45zの表示態様の変化の一例を示すタイムチャートである。この図60には、「bL」、「b1」、「b2」の3つの区間のベース(通常モード中)が算出されて主側RAM64に記憶されており、情報表示部45zが「b1」を表示中に、計測中の排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した例が示されている。
Fig. 60 is a time chart showing an example of a change in the display mode of the
上述したように、本態様では、いずれかの区間に対応するベース(通常モード中)を表示中に、現在計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過した後に、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様による表示を開始する。本態様では、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達したことに対応した表示態様として、4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様を採用している。 As described above, in this embodiment, when the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the currently measured section reaches 60,000 while the base (in normal mode) corresponding to any section is being displayed, the information display unit 45z starts displaying in a display mode corresponding to the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the currently measured section reaching 60,000 after the display duration (5,000 ms) of the displayed base (in normal mode) has elapsed. In this embodiment, a display mode in which four hyphens are lit is adopted as the display mode corresponding to the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the currently measured section reaching 60,000.
図60に示した例では、「b1」を表示中であって当該「b1」の表示継続時間である5000msが経過する前のタイミングで、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達しており、情報表示部45zは、当該「b1」の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過した後に、4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様による表示を開始し、当該表示態様を2000ms継続する。その後、上述した態様95と同様に、新たに計測を開始した「bL」から循環表示を開始する。
In the example shown in Fig. 60, while "b1" is being displayed, the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 before the display duration of "b1" of 5,000 ms has elapsed, and the
なお、本態様において、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を消灯させる表示態様を開始してから300msが経過する前のタイミングで、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合には、情報表示部45zは、当該全ての発光部を消灯させる表示態様を開始してから300msが経過した後に、上述した4個のハイフンが点灯した表示態様に移行する。
In this embodiment, if the number NOUT of particles passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 before 300 ms has elapsed since the start of the display mode in which all of the light-emitting elements constituting the
以上説明したように、本態様では、ベース(通常モード中)の表示中に、計測中の区間における排出通路通過個数NOUTが60000個に達した場合であっても、当該表示中のベース(通常モード中)の表示継続時間が経過するまでは当該ベース(通常モード中)の表示が継続されるので、例えば、当該パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者が、表示中のベース(通常モード中)を確認して検査表に転記しようとしたタイミングで当該ベース(通常モード中)の表示が終了してしまい、当該ベース(通常モード中)を検査表に転記することができなかったといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。
As explained above, in this embodiment, even if the number N OUT of balls passing through the discharge passage in the section being measured reaches 60,000 while the base (in normal mode) is being displayed, the display of the base (in normal mode) continues until the display duration of the displayed base (in normal mode) has elapsed. This prevents, for example, a situation in which the display of the base (in normal mode) ends just as the manager or inspector of the
<態様97>
上記態様93において説明した、電源投入時に情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる構成を実現するための処理フローとして、以下の処理フローを採用してもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
The following process flow may be adopted as a process flow for realizing the configuration described in the above-mentioned
図61及び図62は、第1実施形態の態様97の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。図51に示したメイン処理との主な相違点は、復電処理の実行後に、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を点灯、点滅させる処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する点である。
Figures 61 and 62 are flowcharts showing the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11801では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11802に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11803に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11803を実行した後、ステップS11804に進む。
In step S11801, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11804では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11804, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11804において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11804:YES)、ステップS11805に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11806に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11806において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11806:YES)、後述するステップS11808に進む。
If it is determined in step S11804 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11804: YES), the process proceeds to step S11805, where a RAM judgment value of the
一方、上述したステップS11804において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11804:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11806においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11806:NO)、ステップS11807に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合又は復電フラグはONであるがRAM判定値が正常ではない場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。ステップS11807を実行した後、ステップS11808に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11804 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11804: NO), and if it is determined in step S11806 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11806: NO), the process proceeds to step S11807, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF or when the power recovery flag is ON but the RAM judgment value is not normal, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
ステップS11808では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11808において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11808:NO)、ステップS11809に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S11808, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S11808 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11808: NO), the process proceeds to step S11809, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. The frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11809において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11809:NO)、ステップS11810に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11809 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S11809: NO), proceed to step S11810 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11810において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11810:NO)、ステップS11811に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11811を実行した後、ステップS11812に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、ステップS11812-2に進み、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を点灯、点滅させる処理である点灯点滅処理を実行する。点灯点滅処理では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる。ステップS11812-2を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
In step S11810, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11810: NO), the process proceeds to step S11811, where a power recovery process is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery process, the value of the stack pointer stored in the
一方、ステップS11810において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11810:YES)、ステップS11813に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11813を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理へ移行する。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11810 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11810: YES), the process proceeds to step S11813, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
一方、上述したステップS11809において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11809:YES)、ステップS11814に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11809 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11809: YES), the process proceeds to step S11814, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11814において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11814:NO)、ステップS11815に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細は、図53に示した設定確認処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11815を実行した後、ステップS11816に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11817に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、ステップS11817-2に進み、上述した点灯点滅処理を実行する。ステップS11817-2を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理へ移行する。
If it is determined in step S11814 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11814: NO), the process proceeds to step S11815, where the setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11814において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11814:YES)、ステップS11818に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11818を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11814 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11814: YES), the process proceeds to step S11818, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11808において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11808:YES)、ステップS11819に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11808 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11808: YES), proceed to step S11819 and determine whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON.
ステップS11819において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11819:NO)、ステップS11820に進み、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11820において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11820:NO)、ステップS11821に進む。 If it is determined in step S11819 that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S11819: NO), the process proceeds to step S11820, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag described above is ON. If it is determined in step S11820 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11820: NO), the process proceeds to step S11821.
ステップS11821では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11821を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
In step S11821, the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
一方、ステップS11820において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11820:YES)、ステップS11822に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11822を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11820 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11820: YES), the process proceeds to step S11822, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11819において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11819:YES)、ステップS11823に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11819 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11819: YES), proceed to step S11823 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11823において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11823:NO)、ステップS11824に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11825に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、図52に示した設定変更処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11825を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
If it is determined in step S11823 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11823: NO), the process proceeds to step S11824, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S11825, where the setting change process is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11823において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11823:YES)、ステップS11826に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11826を実行した後、ステップS11827に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11823 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11823: YES), the process proceeds to step S11826, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11827では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。ここで、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、第1RAMクリア処理ではなく、設定情報も消去する第2RAMクリア処理を実行する理由について説明する。RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報も正常でない可能性があり、例えば、ノイズ等によって管理者の意図しない設定情報に書き換わっていたり、設定情報としては所定の範囲内の数値(例えば1から6までの数値)しか取り得ないにも関わらず、所定の範囲以外の数値が記憶されていたりする可能性があるためである。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。また、第2RAMクリア処理によって、RAM異常フラグもOFFとなる。その後、ステップS11828に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、図52に示した設定変更処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11828を実行した後、後述するステップS11829(図62)の処理に進む。
In step S11827, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
図62に示すステップS11829以降の処理においては、RAM異常フラグがONではない場合には、タイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、各種乱数更新処理、停電監視処理(電源監視処理)が実行され、上述したタイマ割込み処理(図27)も実行される。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONではない場合には、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行する。一方、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、各種乱数更新処理、停電監視処理は実行されるが、タイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定は実行されないので、上述したタイマ割込み処理(図27)は実行されない。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。以下、ステップS11829以降の処理を具体的に説明する。
In the processing after step S11829 shown in FIG. 62, if the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, the timer interrupt processing interrupt permission setting, interrupt prohibition setting, various random number update processing, and power outage monitoring processing (power supply monitoring processing) are executed, and the above-mentioned timer interrupt processing (FIG. 27) is also executed. That is, if the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, the game progress mode in which the game can progress is entered. On the other hand, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, various random number update processing and power outage monitoring processing are executed, but the timer interrupt processing interrupt permission setting is not executed, so the above-mentioned timer interrupt processing (FIG. 27) is not executed. That is, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the game progress mode in which the game can progress is not entered. In this state, the administrator can turn off the power of the
図62に示すステップS11829では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11829において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11829:NO)、ステップS11830に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、ステップS11831に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止する割込み禁止設定を実行する。その後、後述するステップS11832に進む。一方、ステップS11829において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11829:YES)、ステップS11830及びステップS11831の処理を実行せずに、ステップS11832に進む。 In step S11829 shown in FIG. 62, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S11829 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11829: NO), the process proceeds to step S11830, where an interrupt permission setting is executed to permit the occurrence of timer interrupt processing. Then, the process proceeds to step S11831, where an interrupt prohibition setting is executed to prohibit the occurrence of timer interrupt processing. Then, the process proceeds to step S11832, which will be described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11829 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11829: YES), the process proceeds to step S11832 without executing the processes of steps S11830 and S11831.
ステップS11832では、各種乱数更新処理を実行する。各種乱数更新処理では、主側RAM64における各カウンタから現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報に1を加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに加算後の数値情報を上書きする処理を実行する。なお、読み出した数値情報が当該カウンタの最大値である場合には、読み出し元のカウンタに0を上書きする処理を実行する。ステップS11832を実行した後、ステップS11833に進む。
In step S11832, various random number update processes are executed. In the various random number update processes, the current numerical information is read from each counter in the
ステップS11833では、停電監視処理を実行する。停電監視処理では、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧を監視しており、当該駆動電圧が所定値(例えば10ボルト)を下回ったと判定した場合には、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた又は停電が発生したと判断して、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。その後、後述するステップS11834には進まずに、供給される駆動電圧が低下して動作不能となるまで無限ループ処理を繰り返す。なお、本態様の電源装置85は、主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回るまで低下した場合であっても、主制御装置60などの制御系において駆動電圧として使用される5ボルトの安定化電圧が出力されるように構成されている。この安定化電圧が出力される時間としては、上述したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶するまでの処理を実行するに十分な時間が確保されている。
In step S11833, a power failure monitoring process is executed. In the power failure monitoring process, the drive voltage supplied from the
一方、ステップS11833の停電監視処理において、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回っていないと判定した場合には、そのままステップS11834に進む。
On the other hand, if the power outage monitoring process in step S11833 determines that the drive voltage supplied from the
ステップS11834では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11834において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11834:NO)、上述したステップS11835に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、上述したステップS11831に戻り、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止する割込み禁止設定を実行する。一方、ステップS11834において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11834:YES)、割込み許可設定を実行するステップS11835には進まず、各種乱数更新処理を実行するステップS11832に戻る。 In step S11834, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S11834 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11834: NO), the process proceeds to step S11835 described above, where an interrupt permission setting is performed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. Thereafter, the process returns to step S11831 described above, where an interrupt prohibition setting is performed to prohibit timer interrupt processing from occurring. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11834 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11834: YES), the process does not proceed to step S11835 where the interrupt permission setting is performed, but returns to step S11832 where various random number update processes are performed.
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上述した点灯点滅処理が実行されるので、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。例えば、仮に、右中7セグメント表示器45z3のセグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが不具合によって点灯しない場合には、右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「3」を表示させる制御が実行されている場合であっても、セグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが点灯しないことによって、右中7セグメント表示器45z3には「7」が表示されてしまうことになる。この結果、管理者は、例えば、情報表示部45zに表示される遊技履歴情報の数値情報を誤認してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本態様の構成によれば、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるので、このような誤認を抑制することができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the above-mentioned lighting and blinking process is executed, so that it is possible to check whether there is a light-emitting part that does not light due to a malfunction such as a broken wire among the multiple light-emitting parts that make up the
さらに、本態様では、復電処理の実行を契機として点灯点滅処理を実行する。したがって、パチンコ機10の管理者又は検査者が、電源がONとなっているパチンコ機10の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにして再びONにすると、上述した復電処理が実行され、当該復電処理の実行を契機として点灯点滅処理が実行される。すなわち、管理者又は検査者は、電源スイッチをOFF、ONとする簡易な操作によって当該パチンコ機10に点灯点滅処理を実行させることができる。さらに、管理者又は検査者が、パチンコ機10に点灯点滅処理を実行させるために、電源スイッチをOFF、ONとする操作を行なった場合には、当該パチンコ機10において復電処理が実行されるため、当該パチンコ機10の遊技状態(高確率モードフラグの状態等)も維持される。したがって、本態様によれば、仮に当該パチンコ機10において遊技者が遊技を行なっている状況であったとしても、遊技者に不利益を与えずに点灯点滅処理を実行させることができ、管理者又は検査者は、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the lighting and blinking process is executed in response to the execution of the power recovery process. Therefore, when the manager or inspector of the
<態様98>
上記態様93において説明した、電源投入時に情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる構成を実現するための処理フローとして、以下の処理フローを採用してもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<Aspect 98>
The following process flow may be adopted as a process flow for realizing the configuration described in the above-mentioned
図63及び図64は、第1実施形態の態様98の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。図61及び図62に示したメイン処理との主な相違点は、復電処理の実行を契機として点灯点滅処理を実行するのではなく、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行した場合であっても点灯点滅処理を実行する点である。
Figures 63 and 64 are flowcharts showing the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS11901では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS11902に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11903に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11903を実行した後、ステップS11904に進む。
In step S11901, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS11904では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S11904, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS11904において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11904:YES)、ステップS11905に進み、主側RAM64のRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS11906に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS11906において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS11906:YES)、後述するステップS11908に進む。
If it is determined in step S11904 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S11904: YES), the process proceeds to step S11905, where a RAM judgment value of the
一方、上述したステップS11904において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS11904:NO)、及び、上述したステップS11906においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11906:NO)、ステップS11907に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合又は復電フラグはONであるがRAM判定値が正常ではない場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。ステップS11907を実行した後、ステップS11908に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11904 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S11904: NO), and if it is determined in step S11906 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S11906: NO), the process proceeds to step S11907, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF or when the power recovery flag is ON but the RAM judgment value is not normal, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
ステップS11908では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11908において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11908:NO)、ステップS11909に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S11908, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S11908 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S11908: NO), the process proceeds to step S11909, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. The frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS11909において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11909:NO)、ステップS11910に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11909 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S11909: NO), proceed to step S11910 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11910において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11910:NO)、ステップS11911に進み、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS11911を実行した後、ステップS11912に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
If it is determined in step S11910 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11910: NO), the process proceeds to step S11911, where power recovery processing is executed to restore the state at the time of the previous power OFF. Specifically, in the power recovery processing, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、ステップS11910において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11910:YES)、ステップS11913に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11913を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11910 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11910: YES), the process proceeds to step S11913, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
一方、上述したステップS11909において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11909:YES)、ステップS11914に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11909 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11909: YES), the process proceeds to step S11914, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11914において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11914:NO)、ステップS11915に進み、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細は、図53に示した設定確認処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11915を実行した後、ステップS11916に進み、上述した復電処理を実行して前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる。その後、ステップS11917に進み、復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
If it is determined in step S11914 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11914: NO), the process proceeds to step S11915, where a setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11914において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11914:YES)、ステップS11918に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11918を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11914 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11914: YES), the process proceeds to step S11918, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11908において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11908:YES)、ステップS11919に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11908 described above that the RAM clear button is ON (step S11908: YES), proceed to step S11919 and determine whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON.
ステップS11919において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11919:NO)、ステップS11920に進み、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11920において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11920:NO)、ステップS11921に進む。 If it is determined in step S11919 that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S11919: NO), the process proceeds to step S11920, where it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag described above is ON. If it is determined in step S11920 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11920: NO), the process proceeds to step S11921.
ステップS11921では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11921を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
In step S11921, the first RAM clear process is executed. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
一方、ステップS11920において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11920:YES)、ステップS11922に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS11922を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11920 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11920: YES), the process proceeds to step S11922, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
上述したステップS11919において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11919:YES)、ステップS11923に進み、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 If it is determined in step S11919 described above that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S11919: YES), proceed to step S11923 and determine whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS11923において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11923:NO)、ステップS11924に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。その後、ステップS11925に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、図52に示した設定変更処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11925を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
If it is determined in step S11923 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11923: NO), the process proceeds to step S11924, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S11925, where the setting change process is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
一方、ステップS11923において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11923:YES)、ステップS11926に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS11926を実行した後、ステップS11927に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11923 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11923: YES), the process proceeds to step S11926, where a RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS11927では、第2RAMクリア処理を実行する。第2RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を含む全ての情報を消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第2RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等に加えて、抽選設定の設定情報も消去される。ここで、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、第1RAMクリア処理ではなく、設定情報も消去する第2RAMクリア処理を実行する理由について説明する。RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報も正常でない可能性があり、例えば、ノイズ等によって管理者の意図しない設定情報に書き換わっていたり、設定情報としては所定の範囲内の数値(例えば1から6までの数値)しか取り得ないにも関わらず、所定の範囲以外の数値が記憶されていたりする可能性があるためである。なお、本態様の第2RAMクリア処理では、設定情報が消去された後、設定情報の初期値として「1」が格納される。また、第2RAMクリア処理によって、RAM異常フラグもOFFとなる。その後、ステップS11928に進み、設定変更処理を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細は、図52に示した設定変更処理と同じであるため、説明を省略する。ステップS11928を実行した後、後述するステップS11928-2(図64)の処理に進む。
In step S11927, the second RAM clear process is executed. The second RAM clear process is a process for erasing (clearing to 0) all information stored in the
図64に示すステップS11928-2では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を点灯、点滅させる処理である点灯点滅処理を実行する。点灯点滅処理では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる。ステップS11928-2を実行した後、ステップS11929に進む。
In step S11928-2 shown in FIG. 64, a lighting and blinking process is executed, which is a process for lighting and blinking all the light-emitting elements (segment light-emitting elements A to G and DP light-emitting element) that make up the
ステップS11929以降の処理においては、RAM異常フラグがONではない場合には、タイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定、割込み禁止設定、各種乱数更新処理、停電監視処理(電源監視処理)が実行され、上述したタイマ割込み処理(図27)も実行される。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONではない場合には、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードに移行する。一方、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、各種乱数更新処理、停電監視処理は実行されるが、タイマ割込み処理の割込み許可設定は実行されないので、上述したタイマ割込み処理(図27)は実行されない。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない。この状態の場合には、管理者は、当該パチンコ機10の電源を一旦OFFにし、設定用の鍵を設定用の鍵穴に挿入してON側に回し、RAMクリアボタンを押下したまま電源をONにして当該パチンコ機10を設定変更モードで起動させればよい。以下、ステップS11929以降の処理を具体的に説明する。
In the processing from step S11929 onwards, if the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, the timer interrupt processing interrupt permission setting, interrupt prohibition setting, various random number update processing, and power failure monitoring processing (power supply monitoring processing) are executed, and the timer interrupt processing (FIG. 27) described above is also executed. That is, if the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, the game progress mode in which the game can progress is entered. On the other hand, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, various random number update processing and power failure monitoring processing are executed, but the timer interrupt processing interrupt permission setting is not executed, so the timer interrupt processing (FIG. 27) described above is not executed. That is, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the game progress mode in which the game can progress is not entered. In this state, the administrator can turn off the power of the
図64に示すステップS11929では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11929において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11929:NO)、ステップS11930に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、ステップS11931に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止する割込み禁止設定を実行する。その後、後述するステップS11932に進む。一方、ステップS11929において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11929:YES)、ステップS11930及びステップS11931の処理を実行せずに、ステップS11932に進む。 In step S11929 shown in FIG. 64, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S11929 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11929: NO), the process proceeds to step S11930, where an interrupt permission setting is executed to permit the occurrence of timer interrupt processing. Then, the process proceeds to step S11931, where an interrupt prohibition setting is executed to prohibit the occurrence of timer interrupt processing. Then, the process proceeds to step S11932, which will be described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11929 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11929: YES), the process proceeds to step S11932 without executing the processes of steps S11930 and S11931.
ステップS11932では、各種乱数更新処理を実行する。各種乱数更新処理では、主側RAM64における各カウンタから現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報に1を加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに加算後の数値情報を上書きする処理を実行する。なお、読み出した数値情報が当該カウンタの最大値である場合には、読み出し元のカウンタに0を上書きする処理を実行する。ステップS11932を実行した後、ステップS11933に進む。
In step S11932, various random number update processes are executed. In the various random number update processes, the current numerical information is read from each counter in the
ステップS11933では、停電監視処理を実行する。停電監視処理では、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧を監視しており、当該駆動電圧が所定値(例えば10ボルト)を下回ったと判定した場合には、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた又は停電が発生したと判断して、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、RAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。その後、後述するステップS11934には進まずに、供給される駆動電圧が低下して動作不能となるまで無限ループ処理を繰り返す。なお、本態様の電源装置85は、主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回るまで低下した場合であっても、主制御装置60などの制御系において駆動電圧として使用される5ボルトの安定化電圧が出力されるように構成されている。この安定化電圧が出力される時間としては、上述したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶するまでの処理を実行するに十分な時間が確保されている。
In step S11933, a power failure monitoring process is executed. In the power failure monitoring process, the drive voltage supplied from the
一方、ステップS11933の停電監視処理において、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回っていないと判定した場合には、そのままステップS11934に進む。
On the other hand, if the power outage monitoring process in step S11933 determines that the drive voltage supplied from the
ステップS11934では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS11934において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS11934:NO)、上述したステップS11935に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、上述したステップS11931に戻り、タイマ割込み処理の発生を禁止する割込み禁止設定を実行する。一方、ステップS11934において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS11934:YES)、割込み許可設定を実行するステップS11935には進まず、各種乱数更新処理を実行するステップS11932に戻る。 In step S11934, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S11934 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S11934: NO), the process proceeds to step S11935 described above, where an interrupt permission setting is performed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. Thereafter, the process returns to step S11931 described above, where an interrupt prohibition setting is performed to prohibit timer interrupt processing from occurring. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S11934 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S11934: YES), the process does not proceed to step S11935 where the interrupt permission setting is performed, but returns to step S11932 where various random number update processes are performed.
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上述した点灯点滅処理を実行するので、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。例えば、仮に、右中7セグメント表示器45z3のセグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが不具合によって点灯しない場合には、右中7セグメント表示器45z3に「3」を表示させる制御が実行されている場合であっても、セグメント発光部G及びセグメント発光部Dが点灯しないことによって、右中7セグメント表示器45z3には「7」が表示されてしまうことになる。この結果、管理者は、例えば、情報表示部45zに表示される遊技履歴情報の数値情報を誤認してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本態様の構成によれば、パチンコ機10の電源投入時に、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるとともに、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができるので、このような誤認を抑制することができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the above-mentioned lighting and blinking process is executed, so that it is possible to check whether there is a light-emitting part that does not light due to a malfunction such as a broken wire among the multiple light-emitting parts that make up the
また、本態様では、電源スイッチがONにされて外部からの電力の供給が開始された際における各操作部(RAMクリアスイッチ、設定用の鍵)の操作態様に基づいて、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれかの処理フローを実行する。例えば、電源がONにされた際にRAMクリアスイッチがON、設定用の鍵がON側となっており、かつ、内枠13及び前扉枠14が開放状態である場合には、設定変更処理が含まれる処理フローを実行する。そして、本態様では、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行する場合であっても点灯点滅処理を実行する。したがって、本態様によれば、電源がONにされた際に各操作部がどのような操作態様を受け付けている場合であっても、当該パチンコ機10に点灯点滅処理を実行させることができる。具体的には、例えば、メーカーがパチンコ機10を出荷する際には、RAMクリアスイッチをON、設定用の鍵をON側とし、かつ、内枠13及び前扉枠14を開放状態とした上で電源をONとすることによって、当該パチンコ機10に設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させて抽選設定を変更することが可能であるか否か等の動作確認をする場合がある。この場合であっても、当該パチンコ機10は、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行した後に、上述した点灯点滅処理を実行するので、メーカーの管理者は、設定変更モードにおける動作確認を行なった後にそのまま当該パチンコ機10の情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。したがって、パチンコ機10の出荷時における検査効率を飛躍的に向上させることができる。このように、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、電源がONにされた際に各操作部が受け付けている操作態様に関わらず、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。すなわち、電源がONにされた際に各操作部が受け付けている操作態様次第では当該検査を実施することができないといったことを抑制することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, one of the multiple branched processing flows is executed based on the operation mode of each operation unit (RAM clear switch, setting key) when the power switch is turned ON and the supply of power from the outside is started. For example, if the RAM clear switch is ON, the setting key is on the ON side, and the
また、本態様によれば、電源スイッチがONにされて外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、点灯点滅処理を含むメイン処理(図63、図64)のステップS11901からステップS11928-2までの処理群を実行し、当該処理群の実行が終了した後に、割込み許可設定を実行してタイマ割込み処理に含まれる処理群を繰り返し実行するので、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後に点灯点滅処理を1回だけ実行させることができる。仮に、点灯点滅処理がタイマ割込み処理の処理群に含まれる構成とした場合には、点灯点滅処理が繰り返し実行されることとなってしまい、パチンコ機10の処理負荷が大きくなってしまう。また、点灯点滅処理が繰り返し実行されてしまうと、情報表示部45zに各種情報を表示させることが可能な期間が少なくなってしまう虞がある。これに対して、本態様によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後に点灯点滅処理を1回だけ実行させることができるので、パチンコ機10の処理負荷を低減することができるとともに、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, when the power switch is turned ON and the supply of power from the outside is started, the process group from step S11901 to step S11928-2 of the main process (FIGS. 63 and 64) including the lighting and blinking process is executed, and after the execution of the process group is completed, the interrupt permission setting is executed to repeatedly execute the process group included in the timer interrupt process, so that the lighting and blinking process can be executed only once after the supply of power from the outside is started. If the lighting and blinking process were configured to be included in the process group of the timer interrupt process, the lighting and blinking process would be executed repeatedly, which would increase the processing load of the
また、本態様によれば、電源スイッチがONにされて外部からの電力の供給が開始された後、割込み許可設定を実行してタイマ割込み処理(図27)の実行が開始される前に、点灯点滅処理を実行する。したがって、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において遊技の進行が可能となる前に、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。仮に、タイマ割込み処理の実行が開始された後に点灯点滅処理を実行する構成とした場合には、管理者または検査者が情報表示部45zの検査をすることが可能となる前に、遊技者が当該パチンコ機10において遊技を始めることが可能となる。この場合、遊技者がパチンコ機10において遊技を始めた後に、管理者または検査者が当該パチンコ機10の情報表示部45zの検査を行なって、当該情報表示部45zの発光部に不具合を発見してしまう虞がある。管理者または検査者が当該パチンコ機10の情報表示部45zの発光部に不具合を発見した場合には、当該情報表示部45zを修理又は交換するために、当該遊技者に遊技を中断又は中止してもらう必要が生じる。この結果、遊技者に強い不快感を与えてしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本態様によれば、遊技者がパチンコ機10において遊技を始めることが可能となる前に、管理者または検査者が当該パチンコ機10の情報表示部45zの検査をすることが可能となるので、遊技を中断又は中止させて遊技者に不快感を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。
According to this embodiment, after the power switch is turned on and the supply of power from the outside is started, the lighting and blinking process is executed before the timer interrupt process (FIG. 27) is started by executing the interrupt permission setting. Therefore, the manager or inspector of the
また、本態様によれば、点灯点滅処理を実行した後に、割込み許可設定を実行して、タイマ割込み処理に含まれる遊技履歴用処理(図27のステップS10616)を実行する。すなわち、本態様では、ベース(通常モード中)等の遊技履歴情報が情報表示部45zに表示される前に点灯点滅処理を実行するので、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において遊技履歴情報が情報表示部45zに表示される前に、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。この結果、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していることに気付かずに、当該情報表示部45zに表示されている遊技履歴情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, after the lighting and blinking process is executed, the interrupt permission setting is executed to execute the game history process included in the timer interrupt process (step S10616 in FIG. 27). That is, in this embodiment, the lighting and blinking process is executed before the game history information of the base (in normal mode) etc. is displayed on the
なお、本態様では、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)(図63のステップS11925、ステップS11928)を実行した後に点灯点滅処理(図64のステップS11928-2)を実行する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)において抽選設定の設定情報が情報表示部45zに表示されるよりも前に、点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としてもよい。具体的には、例えば、図64のステップS11928-2における点灯点滅処理を省略し、図63のステップS11908の処理(RAMクリアボタンの状態を判定する処理)の実行に先立って点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、当該パチンコ機10において設定情報が情報表示部45zに表示される前に、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。この結果、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって正常に動作しない発光部が存在していることに気付かずに、当該情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。また、同様に、この構成によれば、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)において抽選設定の設定情報が情報表示部45zに表示されるよりも前に、点灯点滅処理を実行することになるので、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって正常に動作しない発光部が存在していることに気付かずに、当該情報表示部45zに表示されている設定情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。
In this embodiment, the lighting and blinking process (step S11928-2 in FIG. 64) is executed after the setting change process (setting change mode) (steps S11925 and S11928 in FIG. 63). However, instead of this configuration, the lighting and blinking process may be executed before the setting information of the lottery setting is displayed on the
また、本態様では、図64のステップS11928-2において点灯点滅処理を実行する構成とすることによって、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行する場合であっても点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としたが、この構成に限らず他の構成を採用することによって、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行する場合であっても点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としてもよい。例えば、図64のステップS11928-2における点灯点滅処理を省略し、図63のステップS11908の処理(RAMクリアボタンの状態を判定する処理)の実行に先立って点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としてもよい。また、例えば、図64のステップS11928-2における点灯点滅処理を省略し、図63のステップS11909とステップS11910との間、図63のステップS11909とステップS11914との間、図63のステップS11919とステップS11920との間、及び、図63のステップS11919とステップS11923との間において、点灯点滅処理を実行する構成としてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the lighting blinking process is executed in step S11928-2 of FIG. 64, regardless of which of the multiple branched processing flows is executed, but this is not limited to this configuration, and other configurations may be adopted to execute the lighting blinking process regardless of which of the multiple branched processing flows is executed. For example, the lighting blinking process in step S11928-2 of FIG. 64 may be omitted, and the lighting blinking process may be executed prior to the execution of the processing in step S11908 of FIG. 63 (processing for determining the state of the RAM clear button). Also, for example, the lighting blinking process in step S11928-2 in FIG. 64 may be omitted, and the lighting blinking process may be performed between step S11909 and step S11910 in FIG. 63, between step S11909 and step S11914 in FIG. 63, between step S11919 and step S11920 in FIG. 63, and between step S11919 and step S11923 in FIG. 63.
<態様99>
上記態様97及び態様98では、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを管理者や検査者が検査するための検査用処理として、上述した点灯点滅処理を採用したが、検査用処理としては点灯点滅処理に限定されず、様々な制御の態様を採用することができる。例えば、検査用処理として、発光部を点滅させる制御は実行せず、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を消灯した状態から点灯した状態に同時に移行させ、所定時間経過後に点灯した状態から消灯した状態に同時に移行させる制御を実行してもよい。また、例えば、検査用処理として、全ての発光部を同期して点滅させる制御を実行してもよい。また、例えば、検査用処理として、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部に対して順番に点灯させた後に消灯させる制御を実行してもよい。すなわち、検査用処理としては、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を少なくとも1回ずつ消灯状態から点灯状態に移行させた後に消灯状態に移行させる制御を実行すればよい。このような制御の態様の検査用処理を実行することによっても、パチンコ機10の管理者または検査者は、情報表示部45zを構成する複数の発光部の中に不具合によって点灯しない発光部や消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを検査することができる。
<Aspect 99>
In the above-mentioned
<態様100>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行可能な構成においては、種々のメイン処理及びタイマ割込み処理を採用することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode and the setting check mode, various main processes and timer interrupt processes can be adopted. Specific explanations will be given below.
図65は、第1実施形態の態様100の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 65 is a flowchart showing the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12001では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS12002に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12003に進み、当該パチンコ機10に電源が投入されて起動したことを報知するための処理を実行する。具体的には、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを示す起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、例えば、「起動中です」といった音声や所定の警報音をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS12003を実行した後、ステップS12004に進む。
In step S12001, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS12004では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S12004, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS12004において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12004:YES)、ステップS12005に進み、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS12006に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS12006において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS12006:YES)、ステップS12007に進む。
If it is determined in step S12004 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S12004: YES), the process proceeds to step S12005, where a RAM judgment value is calculated by performing a predetermined calculation based on a predetermined group of information stored in the
ステップS12007では、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値である場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定し、一方、設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定する。ステップS12007において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS12007:YES)、ステップS12008に進む。
In step S12007, the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the
一方、上述したステップS12004において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12004:NO)、上述したステップS12006においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12006:NO)、及び、上述したステップS12007において設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12007:NO)には、ステップS12015に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合、RAM判定値が正常ではない場合、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない場合のいずれかの場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。
On the other hand, if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12004 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S12004: NO), if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12006 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S12006: NO), or if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12007 that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range (step S12007: NO), the process proceeds to step S12015, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF, when the RAM judgment value is not normal, or when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
以下では、RAM異常フラグがONにならなかった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明し、その後、RAM異常フラグがONになった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明する。 Below, we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, and then we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS12008では、設定変更中フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。設定変更中フラグは、後述する設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の開始の際にONとなり、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の終了の際にOFFになるフラグである。ここで、ステップS12008において設定変更中フラグがONとなっている状況とは、本パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に、後述する設定変更処理(設定変更モード)が実行され、当該設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定変更中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている状況である。
In step S12008, it is determined whether the setting change in progress flag is ON. The setting change in progress flag is a flag that is set ON when the setting change process (setting change mode) described below is started, and is set OFF when the setting change process (setting change mode) is ended. Here, a situation in which the setting change in progress flag is ON in step S12008 means that the setting change process (setting change mode) described below was executed when the
ステップS12008において設定変更中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12008:YES)、ステップS12018に進み、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細については後述する。一方、ステップS12008において設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12008:NO)、ステップS12009に進む。
If it is determined in step S12008 that the setting change in progress flag is ON (step S12008: YES), the process proceeds to step S12018, where the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
ステップS12009では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12009において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12009:NO)、ステップS12010に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、「設定用の鍵がON」とは、設定用の鍵が設定用の鍵穴に挿入されてON側に位置していることを意味する。また、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S12009, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S12009 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S12009: NO), the process proceeds to step S12010, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. Note that "setting key is ON" means that the setting key is inserted into the setting keyhole and positioned on the ON side. In addition, the frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS12010において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12010:NO)、ステップS12011に進む。 If it is determined in step S12010 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S12010: NO), proceed to step S12011.
ステップS12011では、設定確認中フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。設定確認中フラグは、後述する設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の開始の際にONとなり、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の終了の際にOFFになるフラグである。ここで、ステップS12011において設定確認中フラグがONとなっている状況とは、本パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に、後述する設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が実行され、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定確認中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている状況である。
In step S12011, it is determined whether the setting confirmation flag is ON. The setting confirmation flag is a flag that is set ON when the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) described below starts, and is set OFF when the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) ends. Here, a situation in which the setting confirmation flag is ON in step S12011 means that the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) described below was executed when the
ステップS12011において、設定確認中フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12011:NO)、後述するステップS12013に進む。 If it is determined in step S12011 that the setting confirmation flag is not ON (step S12011: NO), the process proceeds to step S12013, which will be described later.
一方、上述したステップS12010において設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合(ステップS12010:YES)、及び、ステップS12011において設定確認中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12011:YES)、ステップS12012に進む。すなわち、パチンコ機10の電源投入時にRAMクリアボタンがOFFとなっており、かつ、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONである場合、及び、パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が実行され、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定確認中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている場合に、ステップS12012に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12010 that the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON (step S12010: YES), and if it is determined in step S12011 that the setting confirmation flag is ON (step S12011: YES), the process proceeds to step S12012. That is, if the RAM clear button is OFF when the
ステップS12012では、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細については後述する。ステップS12012を実行した後、ステップS12013に進む。
In step S12012, a setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
ステップS12013では、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS12013を実行した後、ステップS12014に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、後述するステップS12022の処理に進む。
In step S12013, a power restoration process is executed to restore the state when the power was last turned off. Specifically, in the power restoration process, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、上述したステップS12009において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12009:YES)、ステップS12017に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12017において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12017:YES)、上述したステップS12018に進み、上述した設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。その後、後述するステップS12022に進む。一方、ステップS12017において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12017:NO)、ステップS12019に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12009 that the RAM clear button is ON (step S12009: YES), the process proceeds to step S12017, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. If it is determined in step S12017 that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S12017: YES), the process proceeds to step S12018, where the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S12022, which will be described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12017 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S12017: NO), the process proceeds to step S12019.
ステップS12019では、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12019において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12019:NO)、ステップS12020に進み、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドである第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、第1RAMクリア処理実行コマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAMをクリアしました。」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS12020を実行した後、後述するステップS12022に進む。
In step S12019, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. In step S12019, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12019: NO), the process proceeds to step S12020 and executes the first RAM clear process. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) the information stored in the
一方、ステップS12019において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12019:YES)、ステップS12021に進み、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS12021を実行した後、ステップS12022に進む。ただし、本説明の流れでは、RAM異常フラグはONになっていないため、ステップS12021には進まない。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12019 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12019: YES), the process proceeds to step S12021, where the RAM abnormality notification process is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification process, a RAM abnormality command, which is a command indicating that the
ステップS12022では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を点灯、点滅させる処理である点灯点滅処理を実行する。点灯点滅処理では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる。ステップS12022を実行した後、ステップS12023に進む。
In step S12022, a lighting and blinking process is executed, which is a process for lighting and blinking all the light-emitting elements (segment light-emitting elements A to G and DP light-emitting element) that make up the
ステップS12023では、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、無限ループを繰り返して待機するとともに、後述するタイマ割込み処理が定期的に(本態様では4ms毎に)実行される。 In step S12023, an interrupt permission setting is executed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. After that, an infinite loop is repeated while waiting, and the timer interrupt processing described below is executed periodically (every 4 ms in this embodiment).
次に、ステップS12015においてRAM異常フラグがONになった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明する。 Next, we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON in step S12015.
上述したように、ステップS12004において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12004:NO)、ステップS12006においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12006:NO)、及び、ステップS12007において設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12007:NO)には、ステップS12015に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。その後、ステップS12016に進む。 As described above, if it is determined in step S12004 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S12004: NO), if it is determined in step S12006 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S12006: NO), or if it is determined in step S12007 that the setting information is not a numerical value within a predetermined range (step S12007: NO), the process proceeds to step S12015, where the RAM abnormality flag is set ON. Then, the process proceeds to step S12016.
ステップS12016では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12016において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12016:YES)、ステップS12017に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12017において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12017:YES)、上述したステップS12018に進み、上述した設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。その後、ステップS12022に進む。一方、ステップS12016においてRAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12016:NO)、及び、ステップS12017において設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12017:NO)には、ステップS12019に進む。 In step S12016, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S12016 that the RAM clear button is ON (step S12016: YES), the process proceeds to step S12017, where it is determined whether the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON. If it is determined in step S12017 that the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON (step S12017: YES), the process proceeds to the above-mentioned step S12018, where the above-mentioned setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S12022. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12016 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S12016: NO), and if it is determined in step S12017 that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S12017: NO), the process proceeds to step S12019.
ステップS12019では、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12019において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12019:NO)、ステップS12020に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。ステップS12020を実行した後、ステップS12022に進む。ただし、本説明の流れでは、RAM異常フラグはONになっているため、ステップS12020には進まない。 In step S12019, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag described above is ON. If it is determined in step S12019 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12019: NO), the process proceeds to step S12020, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. After executing step S12020, the process proceeds to step S12022. However, in the flow of this explanation, since the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the process does not proceed to step S12020.
一方、ステップS12019において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12019:YES)、ステップS12021に進み、上述したRAM異常報知処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12022に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12019 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12019: YES), the process proceeds to step S12021, where the RAM abnormality notification process described above is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S12022.
ステップS12022では、上述した点灯点滅処理を実行する。ステップS12022を実行した後、ステップS12023に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、無限ループ処理を繰り返して待機するとともに、後述するタイマ割込み処理が定期的に(本態様では4ms毎に)実行される。 In step S12022, the above-mentioned lighting and blinking process is executed. After executing step S12022, the process proceeds to step S12023, where an interrupt permission setting is executed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. Thereafter, the process waits by repeating an infinite loop process, and the timer interrupt process described below is executed periodically (every 4 ms in this embodiment).
以上説明したように、本態様においては、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。また、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下していない状態とし(OFF状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。また、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチのいずれかをOFFにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。 As described above, in this embodiment, the operation for executing the setting change process (setting change mode) is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch pressed (ON state) and with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON. Also, the operation for executing the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch not pressed (OFF state) and with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON. Also, the operation for executing the first RAM clear process is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch pressed (ON state) and with any of the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch turned OFF.
以下に、上述したメイン処理が実行されることによって実現される処理の流れの一例をまとめて説明する。 Below is a summary of an example of the process flow that is realized by executing the main process described above.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定するが(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かに関わらず、また、設定確認中フラグの状態に関わらず、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する(ステップS12018)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, and S12007). If an operation has been performed to execute the setting change process (setting change mode), the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed (step S12018) regardless of whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and regardless of the state of the setting checking flag.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12008:YES)、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作、及び、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれているか否かに関わらず、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する(ステップS12018)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met and the setting change flag is ON (step S12008: YES), the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed (step S12018) regardless of whether an operation for executing a setting change process (setting change mode), an operation for executing a setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), or an operation for executing a first RAM clear process has been performed.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12008:NO)、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には(ステップS12009:YES、ステップS12017:NO、ステップS12019:NO)、設定確認中フラグの状態に関わらず、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する(ステップS12020)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12008: NO) and an operation has been performed to execute the first RAM clear process (step S12009: YES, step S12017: NO, step S12019: NO), and the first RAM clear process is executed (step S12020) regardless of the state of the setting confirmation flag.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12008:NO)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には(ステップS12009:NO、ステップS12010:YES)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行する(ステップS12012)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12008: NO). If an operation has been performed to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) (step S12009: NO, step S12010: YES), the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is executed (step S12012).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12008:NO)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていない場合であっても、設定確認中フラグがONであった場合には(ステップS12011:YES)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行する(ステップS12012)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12008: NO). Even if no operation has been performed to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), if the setting confirmation flag is ON (step S12011: YES), the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is executed (step S12012).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していると判定してRAM異常フラグをONにした場合には(ステップS12015)、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合であっても、第1RAMクリア処理を実行せず、RAM異常報知処理を実行する(ステップS12021)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON (step S12015), the first RAM clear process is not executed and a RAM abnormality notification process is executed (step S12021) even if an operation for executing the first RAM clear process has been performed.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12004、ステップS12006、ステップS12007)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していると判定してRAM異常フラグをONにした場合には(ステップS12015)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合であっても、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行せず、RAM異常報知処理を実行する(ステップS12021)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12004, S12006, S12007). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON (step S12015), even if an operation has been performed to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is not executed and a RAM abnormality notification process is executed (step S12021).
次に、図65のステップS12018に示した設定変更処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the setting change process shown in step S12018 of Figure 65.
図66は、第1実施形態の態様100の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定変更処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定変更処理は、図65のステップS12018のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 66 is a flowchart showing the setting change process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12101では、主側RAM64における設定変更中フラグをONにする。設定変更中フラグは、上述したように、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)が開始されたことを示すフラグであるとともに、当該設定変更処理(設定変更モード)がまだ終了していないことを示すフラグである。ステップS12101を実行した後、ステップS12102に進む。
In step S12101, the setting change in progress flag in the
ステップS12102では、設定変更開始時初期設定処理を実行する。設定変更開始時初期設定処理では、設定変更処理を開始するにあたって必要な初期設定を実行する。また、本態様では、設定変更開始時初期設定処理において、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定し、当該RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には、当該RAM異常フラグをOFFにする。ステップS12102を実行した後、ステップS12103に進む。 In step S12102, the initial setting process at the start of the setting change is executed. In the initial setting process at the start of the setting change, the initial settings required to start the setting change process are executed. In this embodiment, in the initial setting process at the start of the setting change, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON, and if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the RAM abnormality flag is turned OFF. After executing step S12102, the process proceeds to step S12103.
ステップS12103では、設定変更報知開始処理を実行する。設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定変更モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S12103, a setting change notification start process is executed. In the setting change notification start process, a setting change mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has been started, is sent to the voice and light
さらに、設定変更報知開始処理では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。ステップS12103を実行した後、ステップS12104に進む。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification start process, information indicating that the setting change mode has started is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has started displays information about the
ステップS12104では、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、更新用設定情報として保存する。具体的には、本態様では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ設定情報を、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域以外の他の領域である更新用設定情報記憶領域にコピーする。ステップS12104を実行した後、ステップS12105に進む。
In step S12104, the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the
ステップS12105では、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる。その後、ステップS12106に進み、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、更新用設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。ステップS12106において、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS12106:YES)、ステップS12108に進む。一方、ステップS12106において、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12106:NO)、例えば、更新用設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、ステップS12107に進み、更新用設定情報を初期値に変更する。本態様では、更新用設定情報に初期値として「1」を格納する。その後、ステップS12108に進む。
In step S12105, the update setting information stored in the update setting information storage area of the
ステップS12108では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側になっている期間中はHighレベルを示す信号であって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になっている期間中はLowレベルを示す信号を監視しており、当該信号がHighレベルからLowレベルに立ち下がる立下がりエッジを検出した場合に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になったと判定する。ステップS12108において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行していないと判定した場合には(ステップS12108:NO)、ステップS12109に進み、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたか否かを判定する。ステップS12109において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたと判定した場合には(ステップS12109:YES)、ステップS12110に進み、更新用設定情報を更新する。具体的には、更新用設定情報として格納されている数値情報に1を加算する。ただし、更新用設定情報として格納されている数値情報が「6」である状況において設定変更用ボタンが押下された場合には当該数値情報は「1」に更新される。その後、上述したステップS12106に戻り、更新した更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。一方、ステップS12109において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS12109:NO)、ステップS12110の処理を実行することなく、上述したステップS12106に戻り、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。 In step S12108, it is determined whether the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. Specifically, in this embodiment, a signal indicating a high level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the ON side, and a signal indicating a low level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the OFF side, and when a falling edge of the signal falling from a high level to a low level is detected, it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has become the OFF side. In step S12108, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has not shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12108: NO), the process proceeds to step S12109, where it is determined whether the setting change button has been pressed. In step S12109, if it is determined that the setting change button has been pressed (step S12109: YES), the process proceeds to step S12110, where the update setting information is updated. Specifically, 1 is added to the numerical information stored as the updated setting information. However, if the setting change button is pressed when the numerical information stored as the updated setting information is "6", the numerical information is updated to "1". Thereafter, the process returns to step S12106 described above, and it is determined whether the updated updated setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12109 that the setting change button has not been pressed (step S12109: NO), the process returns to step S12106 described above without executing the processing of step S12110, and it is determined whether the updated setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range.
上述したステップS12108において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定した場合には(ステップS12108:YES)、ステップS12111に進む。 If it is determined in step S12108 described above that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12108: YES), proceed to step S12111.
ステップS12111では、主側RAM64に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、設定情報として保存する。具体的には、本態様では、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ更新用設定情報を、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域にコピーする。ステップS12111を実行した後、ステップS12112に進み、更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS12113に進む。
In step S12111, the update setting information stored in the
ステップS12113では、設定変更報知終了処理を実行する。設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定変更モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
In step S12113, a setting change notification end process is executed. In the setting change notification end process, a setting change mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定変更報知終了処理では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定変更モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する。ステップS12113を実行した後、ステップS12114に進む。なお、設定変更報知終了処理を実行した後、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成とし、当該情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
Furthermore, in the setting change notification end process, information indicating that the setting change mode has ended is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting change mode has ended displays information indicating that the setting change mode of the
ステップS12114では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報以外の情報を消去する。この第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、上述した設定変更中フラグも消去される(OFFとなる)。ステップS12114を実行した後、本設定変更処理を終了する。
In step S12114, a first RAM clear process is executed. In the first RAM clear process, information other than the setting information of the lottery setting stored in the setting information storage area of the
次に、図65のステップS12012に示した設定確認処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the setting confirmation process shown in step S12012 of Figure 65.
図67は、第1実施形態の態様100の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定確認処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定確認処理は、図65のステップS12012のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 67 is a flowchart showing the setting confirmation process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12201では、主側RAM64における設定確認中フラグをONにする。設定確認中フラグは、上述したように、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が開始されたことを示すフラグであるとともに、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)がまだ終了していないことを示すフラグである。ステップS12201を実行した後、ステップS12202に進む。
In step S12201, the setting confirmation flag in the
ステップS12202では、設定確認報知開始処理を実行する。設定確認報知開始処理では、設定確認モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、例えば、「設定確認モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、例えば、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S12202, the setting confirmation notification start process is executed. In the setting confirmation notification start process, a setting confirmation mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting confirmation mode has been started, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定確認報知開始処理では、設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する。ステップS12202を実行した後、ステップS12203に進む。
Furthermore, in the setting check notification start process, information indicating that the setting check mode has started is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer that receives the information indicating that the setting check mode has started displays information about the
ステップS12203では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに点滅表示させる。その後、ステップS12204に進む。
In step S12203, control is started to display the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the setting information storage area of the
ステップS12204では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側になっている期間中はHighレベルを示す信号であって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になっている期間中はLowレベルを示す信号を監視しており、当該信号がHighレベルからLowレベルに立ち下がる立下がりエッジを検出した場合に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定する。ステップS12204において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行していないと判定した場合には(ステップS12204:NO)、再びステップS12204を実行する。一方、ステップS12204において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定した場合には(ステップS12204:YES)、ステップS12205に進む。すなわち、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行するまでは無限ループを繰り返してステップS12205に進まず、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行するとステップS12205に進む。 In step S12204, it is determined whether the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. Specifically, in this embodiment, a signal indicating a High level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the ON side, and a signal indicating a Low level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the OFF side, and when a falling edge of the signal falling from a High level to a Low level is detected, it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. In step S12204, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has not shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12204: NO), step S12204 is executed again. On the other hand, in step S12204, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12204: YES), proceed to step S12205. In other words, an infinite loop is repeated until the setting key (keyhole) transitions from the ON side to the OFF side, and the process does not proceed to step S12205. When the setting key (keyhole) transitions from the ON side to the OFF side, the process proceeds to step S12205.
ステップS12205では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS12206に進む。
In step S12205, control for displaying the lottery setting information on the
ステップS12206では、設定確認報知終了処理を実行する。設定確認報知終了処理では、設定確認モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信すると、上述した設定確認モード中であることを報知するための各種の制御を終了する。
In step S12206, a setting confirmation notification end process is executed. In the setting confirmation notification end process, a setting confirmation mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
さらに、設定確認報知終了処理では、設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する。設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定確認モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する。ステップS12206を実行した後、ステップS12207に進み、主側RAM64における設定変更中フラグをOFFにする。その後、本設定確認処理を終了する。
Furthermore, in the setting confirmation notification end process, information indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended is sent to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal. The hall computer, which has received the information indicating that the setting confirmation mode has ended, displays information indicating that the setting confirmation mode of the
次に、主側MPU62(CPU62x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理について説明する。
Next, we will explain the timer interrupt processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
図68は、第1実施形態の態様100の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。本態様では、主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)は、4ms周期でタイマ割込み処理を実行する。
Figure 68 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12301では、各種乱数更新処理を実行する。各種乱数更新処理では、主側RAM64における各カウンタ(大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3、電動役物開放カウンタC4等)から現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報に1を加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに加算後の数値情報を上書きする処理を実行する。なお、読み出した数値情報が当該カウンタの最大値である場合には、読み出し元のカウンタに0を上書きする処理を実行する。ステップS12301を実行した後、ステップS12302に進む。 In step S12301, various random number update processes are executed. In the various random number update processes, the current numerical information is read from each counter in the main RAM 64 (jackpot random number counter C1, jackpot type counter C2, reach random number counter C3, electric role release counter C4, etc.), a process is executed to add 1 to the read numerical information, and then a process is executed to overwrite the read-out counter with the added numerical information. Note that if the read-out numerical information is the maximum value of the counter, a process is executed to overwrite the read-out counter with 0. After executing step S12301, proceed to step S12302.
ステップS12302では、停電監視処理を実行する。停電監視処理では、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧を監視しており、当該駆動電圧が所定値(例えば10ボルト)を下回ったと判定した場合には、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた又は停電が発生したと判断して、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。その後、後述するステップS12303には進まずに、供給される駆動電圧が低下して動作不能となるまで無限ループ処理を繰り返す。なお、本態様の電源装置85は、主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回るまで低下した場合であっても、主制御装置60などの制御系において駆動電圧として使用される5ボルトの安定化電圧が出力されるように構成されている。この安定化電圧が出力される時間としては、上述したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶するまでの処理を実行するに十分な時間が確保されている。
In step S12302, a power failure monitoring process is executed. In the power failure monitoring process, the drive voltage supplied from the
一方、ステップS12302の停電監視処理において、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回っていないと判定した場合には、そのままステップS12303に進む。
On the other hand, if the power outage monitoring process in step S12302 determines that the drive voltage supplied from the
ステップS12303では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12303において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12303:NO)、ステップS12304に進む。一方、ステップS12303において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12303:YES)、ステップS12304以降の処理を実行せずに、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、ステップS12304以降の遊技の進行を可能とするための処理が実行されないこととなり、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない構成となっている。以下、遊技の進行を可能とするための処理であるステップS12304以降の処理について説明する。 In step S12303, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S12303 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12303: NO), the process proceeds to step S12304. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12303 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12303: YES), the process from step S12304 onwards is not executed and this timer interrupt process is terminated. In other words, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the process from step S12304 onwards to enable game progress is not executed, and the system is configured not to transition to a game progress mode in which game progress is possible. Below, the process from step S12304 onwards, which is the process to enable game progress, is explained.
ステップS12304では、ポート出力処理を実行する。ポート出力処理では、前回のタイマ割込み処理において出力情報の設定が行われている場合に、その出力情報に対応した出力を各種駆動部36c,34bに行うための処理を実行する。例えば、大入賞口36aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には可変入賞駆動部36cへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。また、第2始動口34の電動役物34aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には電動役物駆動部34bへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。その後、ステップS12305に進む。
In step S12304, port output processing is executed. In the port output processing, when output information has been set in the previous timer interrupt processing, processing is executed to output corresponding to the output information to the
ステップS12305では、読み込み処理を実行する。読み込み処理では、入球信号以外の信号の読み込みを実行し、その読み込んだ情報を今後の処理にて利用するために記憶する。その後、ステップS12306に進む。 In step S12305, a read process is executed. In the read process, signals other than the ball-entering signal are read, and the read information is stored for use in future processes. Then, the process proceeds to step S12306.
ステップS12306では、各入球検知センサー44a~44hから受信している信号を読み込むとともに、その読み込んだ情報に対応した処理を行うための入球検知処理を実行する。入球検知処理は、図28に示した入球検知処理と同じであるため、詳細な説明は省略する。ステップS12306を実行した後、ステップS12307に進む。
In step S12306, the signals received from each
ステップS12307では、主側RAM64に設けられている所定のタイマカウンタの数値情報をまとめて更新するためのタイマ更新処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12308に進み、賞球コマンドの出力設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12309に進む。
In step S12307, a timer update process is executed to collectively update the numerical information of a predetermined timer counter provided in the
ステップS12309では、第1始動口33及び第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に伴う始動口用の入球処理を実行する。始動口用の入球処理では、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34に遊技球が入球したと判定されたことに基づいて大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2及びリーチ乱数カウンタC3の値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の保留情報記憶エリア64bに記憶する。ステップS12309を実行した後、ステップS12310に進む。
In step S12309, a ball entry process for the start port is executed in response to the entry of the game ball into the
ステップS12310では、スルーゲート35への遊技球の入球(通過)に伴うスルーゲート用の入球処理を実行する。スルーゲート用の入球処理では、スルーゲート35に遊技球が入球(通過)したと判定されたことに基づいて変動種別カウンタCSの値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の電役保留エリア64dに記憶する。ステップS12310を実行した後、ステップS12311に進む。
In step S12310, a ball entry process for the through gate is executed in response to the entry (passage) of a game ball into the through
ステップS12311では、各遊技回における遊技を制御するための遊技回制御処理を実行する。遊技回制御処理では、大当たり抽選や、第1図柄表示部37a,第2図柄表示部37bの表示制御などを行う。ステップS12311を実行した後、ステップS12312に進む。
In step S12311, a game round control process is executed to control the game in each game round. In the game round control process, a jackpot lottery is performed, and display control of the first
ステップS12312では、遊技状態を移行させるための遊技状態移行処理を実行する。遊技状態移行処理では、遊技状態を開閉実行モード、高確率モード、高頻度サポートモードなどへ移行させる処理を実行する。ステップS12312を実行した後、ステップS12313に進む。 In step S12312, a game state transition process is executed to transition the game state. In the game state transition process, a process is executed to transition the game state to an open/close execution mode, a high probability mode, a high frequency support mode, or the like. After executing step S12312, the process proceeds to step S12313.
ステップS12313では、電動役物34aを制御するための電役サポート用処理を実行する。電役サポート用処理では、電動役物34aを開放状態とするか否かの判定(電動役物開放抽選)を行なうとともに、開放状態とすると判定した場合には電動役物34aを駆動制御する。ステップS12313を実行した後、ステップS12314に進む。 In step S12313, an electric role support process is executed to control the electric role 34a. In the electric role support process, a determination is made as to whether or not the electric role 34a is to be opened (electric role opening lottery), and if it is determined that the electric role 34a is to be opened, the electric role 34a is driven and controlled. After executing step S12313, the process proceeds to step S12314.
ステップS12314では、遊技球発射制御処理を実行する。遊技球発射制御処理では、遊技者によって操作ハンドル25が操作された際に遊技球を遊技領域PAに発射するための処理を実行する。ステップS12314を実行した後、ステップS12315に進む。
In step S12314, a game ball launch control process is executed. In the game ball launch control process, a process is executed to launch a game ball into the game area PA when the player operates the operating
ステップS12315では、今回のタイマ割込み処理にて実行された各種処理の処理結果に応じた外部信号の出力の開始及び終了を制御するように外部情報設定処理を実行する。ステップS12315を実行した後、ステップS12316に進む。 In step S12315, an external information setting process is executed to control the start and end of the output of an external signal according to the results of the various processes executed in the current timer interrupt process. After executing step S12315, proceed to step S12316.
ステップS12316では、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための遊技履歴用処理を実行する。遊技履歴用処理は、図29に示した遊技履歴用処理と同じであるため、詳細な説明は省略する。ステップS12316を実行した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。 In step S12316, a game history process is executed to calculate and display game history information. The game history process is the same as the game history process shown in FIG. 29, so a detailed description is omitted. After step S12316 is executed, this timer interrupt process is terminated.
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上記の他の態様において説明した効果に加えて、以下の効果を奏することができる。 As explained above, this embodiment has the following advantages in addition to those explained in the other embodiments above.
本態様によれば、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させ、設定変更モードの開始の際に設定変更中フラグをONの状態とし、設定変更モードの終了の際に設定変更中フラグをOFFの状態に遷移させる。そして、主側RAM64は、外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても設定変更中フラグの状態を維持することが可能である。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したこと等によって、設定変更モードの実行中に当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定変更中フラグはONの状態に維持される。
According to this embodiment, the setting change mode is started based on the reception of an operation to execute the setting change mode, the setting change flag is set to ON when the setting change mode is started, and the setting change flag is transitioned to OFF when the setting change mode is terminated. The
そして、本態様によれば、外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が開始された際に設定変更中フラグがONの状態であると判定したことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させる(図65のステップS12008)。すなわち、本態様によれば、設定変更モードの実行中に当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が再開された場合には、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けていない場合であっても、設定変更モードが開始されることになる。
According to this aspect, the setting change mode is started based on the determination that the setting change in progress flag is ON when power supply to the
したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該パチンコ機10に再び設定変更モードを開始させるためには、当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が再開された後に管理者が再び設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を行なわなければいけないといった手間を省くことができる。
Therefore, if the power supply to the
また、設定変更モードの実行中に外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない状態となっている可能性があるが、本態様によれば、外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が再開された場合には、パチンコ機10の管理者が再び設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を行なわなくても設定変更モードが開始されるので、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図しない状態となったまま見過ごされてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, if the power supply to the
また、本態様によれば、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定確認モードを開始させ、設定確認モードの開始の際に設定確認中フラグをONの状態とし、設定確認モードの終了の際に設定確認中フラグをOFFの状態に遷移させる。そして、主側RAM64は、外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても設定確認中フラグの状態を維持することが可能である。したがって、例えば、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したこと等によって、設定確認モードの実行中に当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定確認中フラグはONの状態に維持される。
In addition, according to this embodiment, the setting check mode is started based on the reception of an operation to execute the setting check mode, the setting check flag is set to ON when the setting check mode is started, and the setting check flag is transitioned to OFF when the setting check mode is terminated. The
そして、本態様によれば、外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が開始された際に設定確認中フラグがONの状態であると判定したことに基づいて設定確認モードを開始させる(図65のステップS12011)。すなわち、本態様によれば、設定確認モードの実行中に当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が再開された場合には、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けていない場合であっても、設定確認モードが開始されることになる。
According to this aspect, the setting check mode is started based on the determination that the setting check flag is ON when power supply to the
したがって、設定確認モードの実行中に外部から当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該パチンコ機10に再び設定確認モードを開始させるためには、当該パチンコ機10への電力の供給が再開された後に管理者が再び設定確認モードを実行させるための操作を行なわなければいけないといった手間を省くことができる。
Therefore, if the power supply to the
また、本態様によれば、設定変更モードの開始の際に、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報を読み込み、当該設定情報と同じ情報を更新用設定情報として主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶する。そして、設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作を受け付けることによって、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報に記憶されている更新用設定情報を更新し、設定変更モードの終了の際に、更新用設定情報と同じ情報を設定情報として主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶する。したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合であっても、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報を、設定変更モードが開始される前の値のまま維持させることができる。この結果、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれることによって当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまうことを抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。
In addition, according to this embodiment, when the setting change mode is started, the setting information stored in the setting information storage area of the
仮に、設定変更モードの実行中に更新用設定情報を用いない構成であって、設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作を受け付けることによって、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報を直接変更する構成を採用した場合において、設定変更モードの実行中に設定情報が当該パチンコ機10の管理者の意図した値とは異なる値になっているタイミングで外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合には、当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報は、管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまう。
If a configuration is adopted in which update setting information is not used while the setting change mode is being executed, and the setting information stored in the setting information storage area of the
これに対して、本態様によれば、設定変更モードが終了するまでは、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報そのものは変更されず、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報が変更されるので、設定変更モードの実行中に更新用設定情報が当該パチンコ機10の管理者の意図した値とは異なる値になっているタイミングで外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合であっても、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報は、設定変更モードが開始される前の値のまま維持される。したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれることによって当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報が管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまうことを抑制することができる。
In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the setting information stored in the setting information storage area of the
また、本態様によれば、設定変更モードの実行中に、主側RAM64の更新用情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報が情報表示部45zに表示されるので、管理者は、情報表示部45zに表示されている更新用設定情報を確認しながら、設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作を行なうことができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, while the setting change mode is being executed, the update setting information stored in the update information storage area of the
また、本態様によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定し、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合には、RAM異常フラグをONにし、遊技を進行させる遊技進行処理(図68のステップS12304からステップS12316の処理)を実行しない。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態のまま遊技進行処理が実行されてしまい、当該パチンコ機10における遊技の進行に不具合が生じてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、例えば、遊技者や管理者に想定外の損失を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, according to this embodiment, when the supply of external power is started, it is determined whether the setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range, and if it is determined that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON, and the game progress process (the process from step S12304 to step S12316 in FIG. 68) that allows the game to proceed is not executed. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the game progress process from being executed while the setting information stored in the
また、本態様によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定し、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合には、RAM異常フラグをONにし、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作を受け付けた場合であっても、第1RAMクリア処理を実行しない。したがって、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態のまま第1RAMクリア処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 Furthermore, according to this aspect, when the supply of power from the outside is started, it is determined whether the setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range, and if it is determined that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON, and the first RAM clear process is not executed even if an operation to execute the first RAM clear process is received. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of a malfunction caused by the first RAM clear process being executed when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range. This will be explained in detail below.
仮に、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合であっても第1RAMクリア処理を実行する構成を採用した場合には、主側RAM64に記憶されている各種情報のうち、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定したことを示す情報であるRAM異常フラグまで消去されてしまい(OFFとなり)、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず、第1RAMクリア処理の実行後に、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であることを前提とした遊技進行処理(図68のステップS12304からステップS12316の処理)が実行されてしまい、不具合が発生してしまう可能性がある。
If a configuration is adopted in which the first RAM clear process is executed even when it is determined that the setting information is not within the specified range, even the RAM abnormality flag, which is information indicating that it has been determined that the setting information is not within the specified range, will be erased (turned OFF) from among the various information stored in the
これに対して、本態様によれば、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合には、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作を受け付けた場合であっても、第1RAMクリア処理を実行しないので、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず第1RAMクリア処理が実行されてしまい、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であることを前提とした遊技進行処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態のまま第1RAMクリア処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to the present embodiment, if it is determined that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, the first RAM clear process is not executed even if an operation to execute the first RAM clear process is received, so that it is possible to prevent the first RAM clear process from being executed even when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, and to prevent the game progress process from being executed on the assumption that the setting information is a numerical value within the predetermined range. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions caused by the first RAM clear process being executed when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range.
また、本態様によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定し、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合には、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けた場合であっても、設定確認モードを実行しない。したがって、主側RAM64に記憶されている設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず、当該設定情報を表示する設定確認モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。
In addition, according to this aspect, when the supply of power from the outside is started, it is determined whether the setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range, and if it is determined that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, the setting confirmation mode is not executed even if an operation to execute the setting confirmation mode is received. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the setting confirmation mode that displays the setting information from being executed even if the setting information stored in the
また、本態様によれば、外部からの電力の供給が断たれる際に、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群(本態様では設定情報を含む)に基づいて所定の演算を実行し、当該所定の演算の結果であるRAM判定値(以下、第1RAM判定値とも呼ぶ)を主側RAM64に記憶させる。そして、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群(本態様では設定情報を含み、第1RAM判定値は含まない)に基づいて所定の演算を実行し、当該所定の演算の結果であるRAM判定値(以下では第2RAM判定値とも呼ぶ)と、主側RAM64に記憶されている第1RAM判定値とが一致するか否かを判定する。さらに、本態様では、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致すると判定した場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致すると判定し(図65のステップS12006:YES)、かつ、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(図65のステップS12007:YES)、RAM異常フラグはONにならず、遊技進行処理(図68のステップS12304からステップS12316の処理)を実行する。換言すれば、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致すると判定したが(図65のステップS12006:YES)、設定情報は所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合には(図65のステップS12007:NO)、RAM異常フラグがONになり(図65のステップS12015)、遊技進行処理(図68のステップS12304からステップS12316の処理)は実行しない。したがって、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とは一致しているが設定情報は所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず、遊技進行処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず遊技進行処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。
Also, according to this embodiment, when the supply of power from the outside is cut off, a predetermined calculation is performed based on a predetermined information group (including the setting information in this embodiment) stored in the
第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致している場合には、外部からの電力供給が開始された際に主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群の内容と、前回の電力供給が断たれる際に主側RAM64に記憶されていた所定の情報群の内容とが同じである可能性が高く、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群が、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても正常に維持されていた可能性が高い。しかしながら、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群が正常に維持されていない場合であっても、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが偶然に一致してしまう場合がある。
If the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value match, it is highly likely that the contents of the specified information group stored in the
このため、仮に、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致するか否かは判定するが、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かは判定しない構成を採用した場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない場合であっても、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが偶然に一致してしまい、遊技進行処理が実行されてしまう可能性がある。この結果、遊技の進行に致命的な不具合が生じてしまうおそれがある。 For this reason, if a configuration were adopted in which it was determined whether the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value matched each other but whether the setting information was a numerical value within a predetermined range was not determined, even if the setting information was a numerical value within the predetermined range, the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value could coincidentally match, and game progress processing could be executed. This could result in a fatal malfunction in the progress of the game.
これに対して、本態様によれば、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とが一致すると判定し、かつ、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定したことに基づいて、遊技進行処理を実行する。換言すれば、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とは一致しているが、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態では、遊技進行処理を実行しない。したがって、第2RAM判定値と第1RAM判定値とは一致しているが設定情報は所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず、遊技進行処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない状態であるにもかかわらず遊技進行処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the game progress process is executed based on the determination that the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value match and that the setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range. In other words, when the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value match but the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, the game progress process is not executed. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the game progress process from being executed even when the second RAM judgment value and the first RAM judgment value match but the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions caused by the game progress process being executed even when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range.
また、本態様によれば、設定変更モードの実行中に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)のONの状態からOFFの状態への移行を検出したことに基づいて、設定変更モードを終了させるので(図66のステップS12108:YES)、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまうことを回避することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 In addition, according to this embodiment, the setting change mode is terminated based on the detection of the transition of the setting key (keyhole) from the ON state to the OFF state while the setting change mode is being executed (step S12108 in FIG. 66: YES), so it is possible to prevent the setting change mode from ending immediately after it has started. This will be explained in detail below.
例えば、仮に、本態様とは異なる構成であって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFFの状態であることを検出した場合に設定変更モードを終了させる構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成を採用した場合において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がONの状態であることを含む設定変更モードを開始させるための操作が行なわれたことに基づいて設定変更モードが開始された場合には、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がONの状態からOFFの状態に移行するまで、当該設定変更モードは継続する。しかしながら、電力の供給が開始された際に設定変更中フラグがONであったことに基づいて設定変更モードが開始された場合には、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFFの状態のまま設定変更モードが開始される場合もある。この場合には、設定変更モードが開始された直後に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFFの状態であることが検出され、当該設定変更モードが終了してしまう。すなわち、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまい、設定変更モードにおいて抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが困難となってしまう。 For example, a description will be given of a case where a configuration different from the present embodiment is adopted, in which the setting change mode is terminated when it is detected that the setting key (keyhole) is in the OFF state. In the case where this configuration is adopted, if the setting change mode is initiated based on an operation for starting the setting change mode, including the setting key (keyhole) being in the ON state, the setting change mode continues until the setting key (keyhole) transitions from the ON state to the OFF state. However, if the setting change mode is initiated based on the setting change flag being ON when power supply is initiated, the setting change mode may be initiated with the setting key (keyhole) in the OFF state. In this case, immediately after the setting change mode is initiated, it is detected that the setting key (keyhole) is in the OFF state, and the setting change mode is terminated. In other words, the setting change mode is terminated immediately after it is initiated, making it difficult to change the setting information of the lottery setting in the setting change mode.
これに対して、本態様によれば、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)のONの状態からOFFの状態への移行を検出したことに基づいて、設定変更モードを終了させるので、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFFの状態のまま設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、パチンコ機10の管理者等が設定用の鍵(鍵穴)をOFFの状態からONの状態に移行させ、再度、ONの状態からOFFの状態に移行させるまでは、設定変更モードが継続することになる。したがって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFFの状態のまま設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、設定変更モードが開始された直後に当該設定変更モードが終了してしまうことを回避することができる。この結果、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまうことによって抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが困難となってしまうことを抑制することができる。
In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the setting change mode is terminated based on the detection of the transition of the setting key (keyhole) from the ON state to the OFF state. Therefore, even if the setting change mode is started with the setting key (keyhole) in the OFF state, the setting change mode will continue until the administrator of the
また、本態様によれば、電力の供給が開始された際に設定変更中フラグがONであったことに基づいて設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、設定用の鍵を有している者のみが設定変更モードを終了させることができる。したがって、パチンコ機10のセキュリティを向上させることができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, even if the setting change mode is started because the setting change flag is ON when power supply is started, only a person who has the setting key can end the setting change mode. Therefore, the security of the
また、本態様によれば、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がONの状態であることを含む設定変更モードを開始させるための操作が行なわれたことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させるだけでなく、電力の供給が開始された際に設定変更中フラグがONであったことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させる。したがって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がONの状態である場合に限らず、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がONの状態ではない場合であっても、設定変更モードを開始させることができる。 In addition, according to this embodiment, the setting change mode is not only started based on an operation to start the setting change mode, including the setting key (keyhole) being in the ON state, but also based on the setting change flag being ON when power supply is started. Therefore, the setting change mode can be started not only when the setting key (keyhole) is in the ON state, but also when the setting key (keyhole) is not in the ON state.
なお、本態様では、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用したが、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作としては種々の操作を採用することができる。例えば、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)をONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用してもよい。 In this embodiment, the operation for executing the setting change mode is to press the RAM clear switch (to the ON state), turn the power switch ON with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON, but various operations can be used for executing the setting change mode. For example, the operation for executing the setting change mode can be to press the RAM clear switch (to the ON state), turn the setting key (keyhole) ON, and turn the power switch ON.
また、本態様では、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下していない状態とし(OFF状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用したが、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作としては種々の操作を採用することができる。例えば、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下していない状態とし(OFF状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)をONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用してもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the operation for executing the setting check mode is to turn on the power switch with the RAM clear switch not pressed (OFF state) and with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON, but various operations can be used as the operation for executing the setting check mode. For example, the operation for executing the setting check mode can be to turn on the power switch with the RAM clear switch not pressed (OFF state) and with the setting key (keyhole) turned ON.
また、本態様では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチのいずれかをOFFにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用したが、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作としては種々の操作を採用することができる。例えば、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作としては、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)をOFFにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作を採用してもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the operation for executing the first RAM clear process is to turn the power switch ON while the RAM clear switch is pressed (ON state) and any one of the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch is OFF, but various operations can be used as the operation for executing the first RAM clear process. For example, the operation for executing the first RAM clear process may be to turn the power switch ON while the RAM clear switch is pressed (ON state) and the setting key (keyhole) is OFF.
また、本態様では、RAM判定値(チェックサム値)を算出する対象に設定情報を含める構成としたが、この構成に代えて、RAM判定値(チェックサム値)を算出する対象に設定情報を含めない構成としてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the configuration is such that the setting information is included in the calculation of the RAM judgment value (checksum value), but instead of this configuration, the configuration may be such that the setting information is not included in the calculation of the RAM judgment value (checksum value).
また、本態様では、電力の供給が断たれる際に算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)を主側RAM64に記憶させる構成としたが、この構成に代えて、電力の供給が断たれる際に算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)を、主側RAM64とは別の不揮発性の記憶手段に記憶させる構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, the RAM judgment value (checksum value) calculated when the power supply is cut off is stored in the
また、本態様では、設定変更モードの開始の際に、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている設定情報と同じ情報を更新用設定情報として主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶する構成としたが、更新用設定情報として記憶する情報は、設定情報と完全に同じでなくてもよく、設定情報に対応した情報であればよい。例えば、設定情報が「1」である場合には設定情報に対応した値として「A」を更新用設定情報として記憶し、設定情報が「2」である場合には設定情報に対応した値として「B」を更新用設定情報として記憶する構成としてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, when the setting change mode is started, the same information as the setting information stored in the setting information storage area of the
同様に、本態様では、設定変更モードの終了の際に、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報と同じ情報を設定情報として主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶する構成としたが、設定情報として記憶する情報は、更新用設定情報と完全に同じでなくてもよく、更新用設定情報に対応した情報であればよい。例えば、更新用設定情報が「A」である場合には設定情報に対応した値として「1」を設定情報として記憶し、更新用設定情報が「B」である場合には更新用設定情報に対応した値として「2」を設定情報として記憶する構成としてもよい。
Similarly, in this embodiment, when the setting change mode is terminated, the same information as the update setting information stored in the update setting information storage area of the
<態様101>
上記各態様のうち、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードを実行可能な構成において、音声発光制御装置90が現在の日時を計時可能なRTC97(リアルタイムクロック)を備える構成を採用してもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
Among the above-mentioned aspects, in a configuration capable of executing the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the audio and light
図69は、第1実施形態の態様101の音声発光制御装置90及び表示制御装置100の電気的構成を中心として示すブロック図である。なお、電源装置85等の一部の構成は省略されている。
Figure 69 is a block diagram showing mainly the electrical configuration of the audio and light
音声発光制御装置90に設けられた音声発光制御基板91には、音声発光制御装置90の全体の制御を司る演算装置であるMPU92と、現在の日時を特定可能な情報である現在日時情報を出力可能なRTC97(リアルタイムクロック)とが搭載されている。MPU92とRTC97とは、信号線を介して相互通信可能に接続されている。
The audio/light
MPU92は、CPU92x、ROM93、RAM94、割込回路、タイマ回路、データ入出力回路などが内蔵された素子である。CPU92xは、主側ROM63に記憶されている各種制御プログラムを実行する。ROM93は、CPU92xにより実行される各種の制御プログラムや固定値データ、テーブル等を記憶するメモリである。例えば、ROM93のエリアの一部には、演出パターンテーブル等が記憶された各種テーブル記憶エリアが設けられている。RAM94は、CPU92xが制御プログラムを実行する際に各種データ等を一時的に記憶するためのメモリである。例えば、RAM94のエリアの一部には、各種のフラグが記憶される各種フラグ記憶エリア94aや、後述する起動日時情報が記憶される起動日時情報記憶エリア94b等が設けられている。なお、CPU92x、ROM93及びRAM94が1チップ化されていることは必須の構成ではなく、それぞれが個別にチップ化された構成としてもよい。
The MPU 92 is an element that incorporates a
RTC97は、現在の日時を計時することができる機能を有しており、RTC制御部97aと、レジスタ97bと、RTC用電源97cとを有している。
The
RTC制御部97aは、レジスタ97bを利用(制御)して、現在の日時の計時など各種の制御を行う。レジスタ97bは、複数のレジスタからなるレジスタテーブルを有しており、このレジスタテーブルには、計時レジスタ97b1と、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2とが含まれている。
The
計時レジスタ97b1は、現在の日時を計時するためのレジスタであり、現在日時情報としてのレジスタ値が1秒毎に更新される。本態様では、計時レジスタ97b1における現在日時情報には、現在の「年」、「月」、「日」、「時」、「分」、「秒」を特定可能な情報が含まれている。 The clock register 97b1 is a register for clocking the current date and time, and the register value as the current date and time information is updated every second. In this embodiment, the current date and time information in the clock register 97b1 includes information that can identify the current "year", "month", "day", "hour", "minute", and "second".
起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2は、パチンコ機10が起動した直後のタイミングで、計時レジスタ97b1にて計時されている現在日時情報が書き込まれる記憶領域である。以下では、計時レジスタ97b1から読み込まれて起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に書き込まれた現在日時情報を、起動日時情報と呼ぶ。本態様では、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶される起動日時情報には、上述したパチンコ機10が起動した後の所定のタイミングにおける「年」、「月」、「日」、「時」、「分」、「秒」を特定可能な情報が含まれている。計時レジスタ97b1にて計時されている現在日時情報が起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報として書き込まれる処理の詳細については後述する。
The start-up date and time information storage area 97b2 is a storage area in which the current date and time information kept by the clock register 97b1 is written immediately after the
RTC用電源97cは、パチンコ機10の電源とは異なるRTC97専用の電源であり、パチンコ機10の電源が断たれた電断状態でもRTC制御部97a及びレジスタ97bに電力を供給することができる。したがって、計時レジスタ97b1は、電断状態であっても現在日時情報を更新可能であり、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2は、電断状態であっても、記憶している起動日時情報を保持することが可能である。本態様では、RTC用電源97cには、ボタン型電池が用いられている。
The RTC power supply 97c is a power supply dedicated to the
音声発光制御基板91には、入出力ポートがそれぞれ設けられている。音声発光制御基板91の入力側には主制御装置60及び演出操作ボタン24が接続されており、MPU92は、主制御装置60から各種コマンドを受信し、演出操作ボタン24から所定の信号を受信する。音声発光制御基板91の出力側には、スピーカー46、各種ランプ47が接続されているとともに、表示制御装置100が接続されている。
The audio and light
表示制御装置100に設けられた表示制御基板101には、プログラムROM103及びワークRAM104が複合的にチップ化された素子であるMPU102と、ビデオディスプレイプロセッサ(VDP)105と、キャラクタROM106と、ビデオRAM107とが搭載されている。なお、MPU102に対してプログラムROM103及びワークRAM104が1チップ化されていることは必須の構成ではなく、それぞれが個別にチップ化された構成としてもよい。
The
MPU102は、音声発光制御装置90から受信した各種コマンドを解析し又は受信した各種コマンドに基づいて所定の演算処理を行って、VDP105の制御(具体的にはVDP105に対する内部コマンドの生成)を実施する。
The
プログラムROM103は、MPU102により実行される各種の制御プログラムや固定値データを記憶するためのメモリであり、背景画像用のJPEG形式画像データも併せて記憶されている。
The
ワークRAM104は、MPU102による各種プログラムの実行時に使用されるワークデータやフラグ等を一時的に記憶するためのメモリである。
The work RAM 104 is a memory for temporarily storing work data, flags, etc. used when the
VDP105は、一種の描画回路であり、図柄表示装置41に組み込まれた液晶表示部ドライバとしての画像処理デバイスを直接操作する。VDP105は、ICチップ化されているため「描画チップ」とも呼ばれ、描画処理専用のファームウェアを内蔵した一種のマイコンチップである。VDP105は、MPU102、ビデオRAM107等のそれぞれのタイミングを調整してデータの読み書きに介在するとともに、ビデオRAM107に記憶させる画像データを、キャラクタROM106から所定のタイミングで読み出して図柄表示装置41に表示させる。
The
キャラクタROM106は、図柄表示装置41に表示される図柄などのキャラクタデータを記憶するための画像データライブラリとしての役割を担うものである。このキャラクタROM106には、各種の表示図柄のビットマップ形式画像データ、ビットマップ画像の各ドットでの表現色を決定する際に参照される色パレットテーブル等が記憶されている。なお、キャラクタROM106を複数設け、各キャラクタROM106に分担して画像データ等を記憶させておくことも可能である。また、プログラムROM103に記憶した背景画像用のJPEG形式画像データをキャラクタROM106に記憶する構成とすることも可能である。
The
ビデオRAM107は、図柄表示装置41に表示させる表示データを記憶するためのメモリであり、ビデオRAM107の内容を書き替えることにより図柄表示装置41の表示内容が変更される。
以下では、主制御装置60のMPU62、ROM63、RAM64をそれぞれ主側MPU62、主側ROM63、主側RAM64とも呼び、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92、ROM93、RAM94をそれぞれ音光側MPU92、音光側ROM93、音光側RAM94とも呼び、表示制御装置100のMPU102を表示側MPU102とも呼ぶ。
In the following, the
図70は、第1実施形態の態様101の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が電源ON時に実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 70 is a flowchart showing the main processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12401では、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理を実行する。具体的には、主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに予め決められた所定値を設定すると共に、サブ側の制御装置(音声発光制御装置90、表示制御装置100、払出制御装置70等)が動作可能な状態になるのを待つために例えば1秒程度、ウェイト処理を実行する。そして、主側RAM64へのアクセスを許可する。その後、ステップS12402に進み、内部機能レジスタの設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12403に進む。
In step S12401, the initial setting process associated with power-on is executed. Specifically, a predetermined value is set in the stack pointer of the
ステップS12403では、復電フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。 In step S12403, it is determined whether the power recovery flag is ON.
ここで復電フラグについて説明する。本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた場合や停電が発生した場合には、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。なお、商用電源からの電源の供給が断たれた後は、コンデンサ等のバックアップ電源からの電源供給に切り替わる。このように、復電フラグは、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させるための情報が主側RAM64に記憶されているか否かを電源投入時に識別するためのフラグである。
Now, the power recovery flag will be explained. In this embodiment, when the power switch of the
ステップS12403において、復電フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12403:YES)、ステップS12404に進み、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値を算出する。本態様では、RAM判定値として、主側RAM64のチェックサム値を算出する。その後、ステップS12405に進み、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)が正常であるか否か、すなわち、算出したRAM判定値(チェックサム値)と主側RAM64に記憶されているRAM判定値(チェックサム値)とが一致するか否かを判定する。ステップS12405において、RAM判定値が正常であると判定した場合には(ステップS12405:YES)、ステップS12406に進む。
If it is determined in step S12403 that the power recovery flag is ON (step S12403: YES), the process proceeds to step S12404, where a RAM judgment value is calculated by performing a predetermined calculation based on a predetermined group of information stored in the
ステップS12406では、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値である場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定し、一方、設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定する。ステップS12406において、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS12406:YES)、ステップS12407に進む。
In step S12406, the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the
一方、上述したステップS12403において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12403:NO)、上述したステップS12405においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12405:NO)、及び、上述したステップS12406において設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12406:NO)には、ステップS12415に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。すなわち、RAM異常フラグは、復電フラグがOFFである場合、RAM判定値が正常ではない場合、設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではない場合のいずれかの場合にONになるフラグであり、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報が正常ではない状態であることを示すフラグである。
On the other hand, if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12403 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S12403: NO), if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12405 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S12405: NO), or if it is determined in the above-mentioned step S12406 that the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range (step S12406: NO), the process proceeds to step S12415, where the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON. In other words, the RAM abnormality flag is a flag that is set to ON when the power recovery flag is OFF, when the RAM judgment value is not normal, or when the setting information is not a numerical value within the predetermined range, and is a flag that indicates that the information stored in the
以下では、RAM異常フラグがONにならなかった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明し、その後、RAM異常フラグがONになった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明する。 Below, we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is not ON, and then we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is ON.
ステップS12407では、設定変更中フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。設定変更中フラグは、後述する設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の開始の際にONとなり、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の終了の際にOFFになるフラグである。ここで、ステップS12407において設定変更中フラグがONとなっている状況とは、本パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に、後述する設定変更処理(設定変更モード)が実行され、当該設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定変更中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている状況である。
In step S12407, it is determined whether the setting change in progress flag is ON. The setting change in progress flag is a flag that is set ON when the setting change process (setting change mode) described below is started, and is set OFF when the setting change process (setting change mode) is ended. Here, a situation in which the setting change in progress flag is ON in step S12407 means that the setting change process (setting change mode) described below was executed when the
ステップS12407において設定変更中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12407:YES)、ステップS12418に進み、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)では、情報表示部45zに抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行するとともに、抽選設定の設定情報の変更を受け付ける処理を実行する。すなわち、設定変更モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の抽選設定の設定情報を変更することが可能なモードである。設定変更処理(設定変更モード)の詳細については後述する。一方、ステップS12407において設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12407:NO)、ステップS12408に進む。
If it is determined in step S12407 that the setting change flag is ON (step S12407: YES), the process proceeds to step S12418, where the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. In the setting change process (setting change mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the lottery setting on the
ステップS12408では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12408において、RAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12408:NO)、ステップS12409進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。なお、「設定用の鍵がON」とは、設定用の鍵が設定用の鍵穴に挿入されてON側に位置していることを意味する。また、枠開放スイッチは、内枠13が外枠11に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチであり、扉開放スイッチは、前扉枠14が内枠13に対して開放状態であるときにONとなるスイッチである。
In step S12408, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S12408 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S12408: NO), the process proceeds to step S12409, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. Note that "setting key is ON" means that the setting key is inserted into the setting keyhole and is positioned on the ON side. In addition, the frame open switch is a switch that is ON when the
ステップS12409において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12409:NO)、ステップS12410に進む。 If it is determined in step S12409 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S12409: NO), proceed to step S12410.
ステップS12410では、設定確認中フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。設定確認中フラグは、後述する設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の開始の際にONとなり、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の終了の際にOFFになるフラグである。ここで、ステップS12410において設定確認中フラグがONとなっている状況とは、本パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に、後述する設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が実行され、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定確認中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている状況である。
In step S12410, it is determined whether the setting confirmation flag is ON. The setting confirmation flag is a flag that is set ON when the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) described below starts, and is set OFF when the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) ends. Here, a situation in which the setting confirmation flag is ON in step S12410 means that the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) described below was executed when the
ステップS12410において、設定確認中フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12410:NO)、ステップS12411に進み、通常起動コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。通常起動コマンドは、RAM異常であると判定されず、かつ、後述する設定変更処理、設定確認処理、第1RAMクリア処理のいずれの処理も実行しない通常の状態でパチンコ機10(主制御装置60)が起動したことを示すコマンドである。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、通常起動コマンドを受信すると、当該パチンコ機10が通常の状態で起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「通常起動します」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS12411を実行した後、後述するステップS12413に進む。
If it is determined in step S12410 that the setting confirmation flag is not ON (step S12410: NO), the process proceeds to step S12411, where a normal startup command is sent to the audio and light
一方、上述したステップS12409において設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合(ステップS12409:YES)、及び、ステップS12410において設定確認中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12410:YES)、ステップS12412に進む。すなわち、パチンコ機10の電源投入時にRAMクリアボタンがOFFとなっており、かつ、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONである場合、及び、パチンコ機10の前回の電源投入時に設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が実行され、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の実行中に当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したことにより、当該設定確認中フラグがONとなったまま維持されている場合に、ステップS12412に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12409 that the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON (step S12409: YES), and if it is determined in step S12410 that the setting confirmation flag is ON (step S12410: YES), the process proceeds to step S12412. That is, if the RAM clear button is OFF when the
ステップS12412では、設定確認処理を実行する。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)では、情報表示部45zに現在の抽選設定の設定情報を表示させる処理を実行する。すなわち、設定確認モードは、管理者等が当該パチンコ機10の現在の抽選設定の設定情報を確認することが可能なモードである。設定確認処理(設定確認モード)の詳細については後述する。ステップS12412を実行した後、ステップS12413に進む。
In step S12412, a setting confirmation process is executed. In the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), a process is executed to display the setting information of the current lottery setting on the
ステップS12413では、前回の電源OFF時の状態に復帰させる復電処理を実行する。具体的には、復電処理では、主側RAM64に保存されたスタックポインタの値を主側CPU62xのスタックポインタに書き込み、主側RAM64に退避されたデータを主側CPU62xのレジスタに復帰させることによって、主側CPU62xのレジスタの状態を電源が遮断される前の状態に復帰させる。ステップS12413を実行した後、ステップS12414に進み、主側RAM64の復電フラグをOFFにする。その後、後述するステップS12423の処理に進む。
In step S12413, a power restoration process is executed to restore the state when the power was last turned off. Specifically, in the power restoration process, the value of the stack pointer saved in the
一方、上述したステップS12408において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12408:YES)、ステップS12417に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12417において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12417:YES)、上述したステップS12418に進み、上述した設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。その後、後述するステップS12423に進む。一方、ステップS12417において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12417:NO)、ステップS12419に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12408 that the RAM clear button is ON (step S12408: YES), the process proceeds to step S12417, where it is determined whether the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON. If it is determined in step S12417 that the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON (step S12417: YES), the process proceeds to step S12418, where the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S12423, which will be described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12417 that at least one of the setting key, frame open switch, and door open switch is not ON (step S12417: NO), the process proceeds to step S12419.
ステップS12419では、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12419において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12419:NO)、ステップS12420に進み、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理は、主側RAM64に記憶されている情報のうち、抽選設定の設定情報を除いて消去する(0クリアする)処理である。すなわち、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、遊技状態を示す各種フラグ情報や各種の制御情報等は消去されるが、抽選設定の設定情報は消去されず、設定情報はそのまま維持される。ステップS12420を実行した後、ステップS12421に進み、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドであるRAMクリアコマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、RAMクリアコマンドを受信すると、第1RAMクリア処理が実行されたことを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、本態様では、「主制御装置のRAMをクリアしました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS12421を実行した後、後述するステップS12423に進む。
In step S12419, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. In step S12419, if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12419: NO), the process proceeds to step S12420 and executes the first RAM clear process. The first RAM clear process is a process of erasing (clearing to 0) the information stored in the
一方、ステップS12419において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12419:YES)、ステップS12422に進み、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、主側RAM64が異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、本態様では、「主制御装置のRAMが異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS12422を実行した後、ステップS12423に進む。ただし、本説明の流れでは、RAM異常フラグはONになっていないため、上述したステップS12422には進まない。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12419 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12419: YES), the process proceeds to step S12422, where a RAM abnormality command is sent to the audio/light-emitting
ステップS12423では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部(セグメント発光部A~G及びDP発光部)を点灯、点滅させる処理である点灯点滅処理を実行する。点灯点滅処理では、情報表示部45zを構成する全ての発光部を所定時間(例えば3秒間)点灯させ、その後、所定時間(例えば2秒間)同期して点滅させる。ステップS12423を実行した後、ステップS12424に進む。
In step S12423, a lighting and blinking process is executed, which is a process for lighting and blinking all the light-emitting elements (segment light-emitting elements A to G and DP light-emitting element) that make up the
ステップS12424では、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、無限ループを繰り返して待機するとともに、後述するタイマ割込み処理が定期的に(本態様では4ms毎に)実行される。 In step S12424, an interrupt permission setting is executed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. After that, an infinite loop is repeated while waiting, and the timer interrupt processing described below is executed periodically (every 4 ms in this embodiment).
次に、ステップS12415においてRAM異常フラグがONになった場合に実行する処理の流れについて説明する。 Next, we will explain the process flow that is executed when the RAM abnormality flag is set to ON in step S12415.
上述したように、ステップS12403において復電フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12403:NO)、ステップS12405においてRAM判定値が正常ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12405:NO)、及び、ステップS12406において設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12406:NO)には、ステップS12415に進み、RAM異常フラグをONにする。その後、ステップS12416に進む。 As described above, if it is determined in step S12403 that the power recovery flag is not ON (step S12403: NO), if it is determined in step S12405 that the RAM judgment value is not normal (step S12405: NO), or if it is determined in step S12406 that the setting information is not a numerical value within a predetermined range (step S12406: NO), the process proceeds to step S12415, where the RAM abnormality flag is set ON. Then, the process proceeds to step S12416.
ステップS12416では、RAMクリアボタンがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12416において、RAMクリアボタンがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12416:YES)、ステップS12417に進み、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12417において、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12417:YES)、上述したステップS12418に進み、上述した設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する。その後、ステップS12422に進む。一方、ステップS12416においてRAMクリアボタンがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12416:NO)、及び、ステップS12417において設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの少なくとも1つがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS12417:NO)には、ステップS12419に進む。 In step S12416, it is determined whether the RAM clear button is ON. If it is determined in step S12416 that the RAM clear button is ON (step S12416: YES), the process proceeds to step S12417, where it is determined whether the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON. If it is determined in step S12417 that the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch are all ON (step S12417: YES), the process proceeds to the above-mentioned step S12418, where the above-mentioned setting change process (setting change mode) is executed. Then, the process proceeds to step S12422. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12416 that the RAM clear button is not ON (step S12416: NO), and if it is determined in step S12417 that at least one of the setting key, the frame open switch, and the door open switch is not ON (step S12417: NO), the process proceeds to step S12419.
ステップS12419では、上述したRAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12419において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12419:NO)、ステップS12420に進み、上述した第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。ステップS12420を実行した後、ステップS12421に進み、第1RAMクリア処理を実行したことを示すコマンドであるRAMクリアコマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。ステップS12421を実行した後、ステップS12422に進む。ただし、本説明の流れでは、RAM異常フラグはONになっているため、上述したステップS12420には進まない。
In step S12419, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag described above is ON. If it is determined in step S12419 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12419: NO), the process proceeds to step S12420, where the first RAM clear process described above is executed. After executing step S12420, the process proceeds to step S12421, where a RAM clear command, which is a command indicating that the first RAM clear process has been executed, is sent to the audio and light
一方、ステップS12419において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12419:YES)、ステップS12422に進み、主側RAM64が異常であることを示すコマンドであるRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、RAM異常コマンドを受信すると、RAMが異常であることを示す音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。具体的には、本態様では、「主制御装置のRAMが異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。ステップS12422を実行した後、ステップS12423に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12419 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12419: YES), the process proceeds to step S12422, where a RAM abnormality command is sent to the audio/light-emitting
ステップS12423では、上述した点灯点滅処理を実行する。ステップS12423を実行した後、ステップS12424に進み、タイマ割込み処理の発生を許可する割込み許可設定を実行する。その後、無限ループ処理を繰り返して待機するとともに、後述するタイマ割込み処理が定期的に(本態様では4ms毎に)実行される。 In step S12423, the above-mentioned lighting and blinking process is executed. After executing step S12423, the process proceeds to step S12424, where an interrupt permission setting is executed to allow timer interrupt processing to occur. Thereafter, an infinite loop process is repeated while waiting, and the timer interrupt processing described below is executed periodically (every 4 ms in this embodiment).
以上説明したように、本態様においては、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。また、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下していない状態とし(OFF状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てをONにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。また、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作は、RAMクリアスイッチを押下した状態とし(ON状態とし)、かつ、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチのいずれかをOFFにした状態で、電源スイッチをONにする操作である。 As described above, in this embodiment, the operation for executing the setting change process (setting change mode) is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch pressed (ON state) and with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON. Also, the operation for executing the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch not pressed (OFF state) and with the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch all turned ON. Also, the operation for executing the first RAM clear process is to turn the power switch ON with the RAM clear switch pressed (ON state) and with any of the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch turned OFF.
以下に、上述したメイン処理が実行されることによって実現される処理の流れの一例をまとめて説明する。 Below is a summary of an example of the process flow that is realized by executing the main process described above.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定するが(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かに関わらず、また、設定確認中フラグの状態に関わらず、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する(ステップS12418)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406), but if an operation has been performed to execute the setting change process (setting change mode), the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed (step S12418) regardless of whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and regardless of the state of the setting confirmation flag.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12407:YES)、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作、及び、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれているか否かに関わらず、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行する(ステップS12418)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met and the setting change flag is ON (step S12407: YES), the setting change process (setting change mode) is executed regardless of whether an operation for executing a setting change process (setting change mode), an operation for executing a setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), or an operation for executing a first RAM clear process has been performed (step S12418).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12407:NO)、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には(ステップS12408:YES、ステップS12417:NO、ステップS12419:NO)、設定確認中フラグの状態に関わらず、第1RAMクリア処理を実行し(ステップS12420)、RAMクリアコマンドを送信する(ステップS12421)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12407: NO). If an operation has been performed to execute the first RAM clear process (step S12408: YES, step S12417: NO, step S12419: NO), the first RAM clear process is executed (step S12420) and a RAM clear command is sent (step S12421) regardless of the state of the setting confirmation flag.
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12407:NO)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合には(ステップS12408:NO、ステップS12409:YES)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行する(ステップS12412)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12407: NO). If an operation has been performed to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) (step S12408: NO, step S12409: YES), the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is executed (step S12412).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していないと判定した場合において、設定変更中フラグがONではないと判定し(ステップS12407:NO)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていない場合であっても、設定確認中フラグがONであった場合には(ステップS12410:YES)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行する(ステップS12412)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for turning the RAM abnormality flag ON are not met, it is determined that the setting change flag is not ON (step S12407: NO). Even if no operation has been performed to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode), if the setting confirmation flag is ON (step S12410: YES), the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is executed (step S12412).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していると判定してRAM異常フラグをONにした場合には(ステップS12415)、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合であっても、第1RAMクリア処理を実行せず、RAM異常コマンドを送信する(ステップS12422)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for setting the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for setting the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and the RAM abnormality flag is set ON (step S12415), even if an operation to execute the first RAM clear process has been performed, the first RAM clear process is not executed and a RAM abnormality command is sent (step S12422).
・電力の供給が開始された際に、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立しているか否かを判定し(ステップS12403、ステップS12405、ステップS12406)、RAM異常フラグをONにすべき条件が成立していると判定してRAM異常フラグをONにした場合には(ステップS12415)、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作が行なわれていた場合であっても、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行せず、RAM異常コマンドを送信する(ステップS12422)。 - When power supply is started, it is determined whether the conditions for setting the RAM abnormality flag ON are met (steps S12403, S12405, S12406). If it is determined that the conditions for setting the RAM abnormality flag ON are met and the RAM abnormality flag is set ON (step S12415), even if an operation to execute the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) has been performed, the setting confirmation process (setting confirmation mode) is not executed and a RAM abnormality command is sent (step S12422).
次に、図70のステップS12418に示した設定変更処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the setting change process shown in step S12418 of Figure 70.
図71は、第1実施形態の態様101の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定変更処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定変更処理は、図70のステップS12418のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 71 is a flowchart showing the setting change process executed by the master MPU 62 (
ステップS12501では、設定変更モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モードが開始されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「設定変更モードを開始しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、その後、「設定変更モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、本態様では、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S12501, a setting change mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has started, is sent to the voice and light
なお、設定変更モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信した後に、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成としてもよい。この場合、設定変更モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定変更モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する構成としてもよい。ステップS12501を実行した後、ステップS12502に進む。
In addition, after the setting change mode start command is sent to the audio and light
ステップS12502では、主側RAM64における設定変更中フラグをONにする。設定変更中フラグは、上述したように、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)が開始されたことを示すフラグであるとともに、当該設定変更処理(設定変更モード)がまだ終了していないことを示すフラグである。ステップS12502を実行した後、ステップS12503に進む。
In step S12502, the setting change in progress flag in the
ステップS12503では、設定変更開始時初期設定処理を実行する。設定変更開始時初期設定処理では、設定変更処理を開始するにあたって必要な初期設定を実行する。また、本態様では、設定変更開始時初期設定処理において、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定し、当該RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には、当該RAM異常フラグをOFFにする。ステップS12503を実行した後、ステップS12504に進む。 In step S12503, the initial setting process at the start of the setting change is executed. In the initial setting process at the start of the setting change, the initial settings required to start the setting change process are executed. In this embodiment, in the initial setting process at the start of the setting change, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON, and if it is determined that the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the RAM abnormality flag is turned OFF. After executing step S12503, the process proceeds to step S12504.
ステップS12504では、主側RAM64に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、更新用設定情報として保存する。具体的には、本態様では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ設定情報を、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域以外の他の領域である更新用設定情報記憶領域にコピーする。ステップS12504を実行した後、ステップS12505に進む。
In step S12504, the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the
ステップS12505では、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに点灯表示させる。その後、ステップS12506に進み、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。本態様では、パチンコ機10に設定される設定情報は「1」から「6」までの6段階であるため、更新用設定情報が「1」から「6」までの範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。ステップS12506において、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であると判定した場合には(ステップS12506:YES)、ステップS12508に進む。一方、ステップS12506において、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値ではないと判定した場合(ステップS12506:NO)、例えば、更新用設定情報として「0」や「7」が格納されている場合や、ノイズ等によって数値以外の情報が格納されている場合には、ステップS12507に進み、更新用設定情報を初期値に変更する。本態様では、更新用設定情報に初期値として「1」を格納する。その後、ステップS12508に進む。
In step S12505, the update setting information stored in the update setting information storage area of the
ステップS12508では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側になっている期間中はHighレベルを示す信号であって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になっている期間中はLowレベルを示す信号を監視しており、当該信号がHighレベルからLowレベルに立ち下がる立下がりエッジを検出した場合に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になったと判定する。ステップS12508において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行していないと判定した場合には(ステップS12508:NO)、ステップS12509に進み、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたか否かを判定する。ステップS12509において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されたと判定した場合には(ステップS12509:YES)、ステップS12510に進み、更新用設定情報を更新する。具体的には、更新用設定情報として格納されている数値情報に1を加算する。ただし、更新用設定情報として格納されている数値情報が「6」である状況において設定変更用ボタンが押下された場合には当該数値情報は「1」に更新される。その後、上述したステップS12506に戻り、更新した更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。一方、ステップS12509において、設定変更用ボタンが押下されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS12509:NO)、ステップS12510の処理を実行することなく、上述したステップS12506に戻り、更新用設定情報が所定の範囲内の数値であるか否かを判定する。 In step S12508, it is determined whether the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. Specifically, in this embodiment, a signal indicating a High level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the ON side, and a signal indicating a Low level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the OFF side, and when a falling edge of the signal falling from a High level to a Low level is detected, it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has become the OFF side. In step S12508, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has not shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12508: NO), the process proceeds to step S12509, where it is determined whether the setting change button has been pressed. In step S12509, if it is determined that the setting change button has been pressed (step S12509: YES), the process proceeds to step S12510, where the update setting information is updated. Specifically, 1 is added to the numerical information stored as the update setting information. However, if the setting change button is pressed when the numerical information stored as the update setting information is "6", the numerical information is updated to "1". Thereafter, the process returns to step S12506 described above, and it is determined whether the updated update setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12509 that the setting change button has not been pressed (step S12509: NO), the process returns to step S12506 described above without executing the processing of step S12510, and it is determined whether the update setting information is a numerical value within a predetermined range.
上述したステップS12508において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定した場合には(ステップS12508:YES)、ステップS12511に進む。 If it is determined in step S12508 described above that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12508: YES), proceed to step S12511.
ステップS12511では、主側RAM64に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、設定情報として保存する。具体的には、本態様では、主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている更新用設定情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ更新用設定情報を、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域にコピーする。ステップS12511を実行した後、ステップS12512に進み、更新用設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS12513に進む。
In step S12511, the update setting information stored in the
ステップS12513では、第1RAMクリア処理を実行する。第1RAMクリア処理では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報以外の情報を消去する。この第1RAMクリア処理が実行されると、上述した設定変更中フラグも消去される(OFFとなる)。ステップS12513を実行した後、ステップS12514に進む。
In step S12513, a first RAM clear process is executed. In the first RAM clear process, information other than the setting information of the lottery setting stored in the setting information storage area of the
ステップS12514では、設定変更モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モードが終了されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、スピーカー46からの「設定変更モード中です」といった音声の出力を終了させ、「設定変更モードを終了しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。また、図柄表示装置41や各種ランプ47における設定変更モード中であることを報知する制御を終了させる。
In step S12514, a setting change mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting change mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
なお、設定変更モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信した後、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成としてもよい。この場合、設定変更モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定変更モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
In addition, after sending the setting change mode end command to the audio and light
ステップS12514を実行した後、本設定変更処理を終了する。なお、設定変更報知終了処理を実行した後、変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成とし、当該情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の変更後の抽選設定の設定情報を表示する構成としてもよい。
After executing step S12514, this setting change process is terminated. Note that after executing the setting change notification termination process, the setting information of the changed lottery setting may be transmitted to the hall computer of the gaming hall via an external terminal, and the hall computer that receives the information may be configured to display the setting information of the changed lottery setting of the
次に、図70のステップS12412に示した設定確認処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the setting confirmation process shown in step S12412 of Figure 70.
図72は、第1実施形態の態様101の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行する設定確認処理を示すフローチャートである。この設定確認処理は、図70のステップS12412のサブルーチンとして実行される。
Figure 72 is a flowchart showing the setting confirmation process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12601では、設定確認モードを開始したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モードが開始されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「設定確認モードを開始しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、その後、「設定確認モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、本態様では、音声発光制御装置90は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード開始コマンドを受信すると、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。
In step S12601, a setting check mode start command, which is a command indicating that the setting check mode has started, is sent to the audio/light-emitting
なお、設定確認モード開始コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信した後、設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成としてもよい。この場合、設定確認モードを開始したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に設定確認モード中のパチンコ機10の情報を表示する構成としてもよい。ステップS12601を実行した後、ステップS12602に進む。
In addition, after sending the setting check mode start command to the audio and light
ステップS12602では、主側RAM64における設定確認中フラグをONにする。設定確認中フラグは、上述したように、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)が開始されたことを示すフラグであるとともに、当該設定確認処理(設定確認モード)がまだ終了していないことを示すフラグである。ステップS12602を実行した後、ステップS12603に進む。
In step S12602, the setting confirmation flag in the
ステップS12603では、主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域に記憶されている抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を開始する。具体的には、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに点滅表示させる。その後、ステップS12604に進む。
In step S12603, control is started to display the setting information for the lottery setting stored in the setting information storage area of the
ステップS12604では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側になっている期間中はHighレベルを示す信号であって、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がOFF側になっている期間中はLowレベルを示す信号を監視しており、当該信号がHighレベルからLowレベルに立ち下がる立下がりエッジを検出した場合に、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定する。ステップS12604において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行していないと判定した場合には(ステップS12604:NO)、再びステップS12604を実行する。一方、ステップS12604において、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行したと判定した場合には(ステップS12604:YES)、ステップS12605に進む。すなわち、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行するまでは無限ループを繰り返してステップS12605に進まず、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)がON側からOFF側に移行するとステップS12605に進む。 In step S12604, it is determined whether the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. Specifically, in this embodiment, a signal indicating a High level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the ON side, and a signal indicating a Low level is monitored during the period when the setting key (keyhole) is on the OFF side, and when a falling edge of the signal falling from a High level to a Low level is detected, it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side. In step S12604, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has not shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12604: NO), step S12604 is executed again. On the other hand, in step S12604, if it is determined that the setting key (keyhole) has shifted from the ON side to the OFF side (step S12604: YES), proceed to step S12605. In other words, an infinite loop is repeated until the setting key (keyhole) transitions from the ON side to the OFF side, and the process does not proceed to step S12605. When the setting key (keyhole) transitions from the ON side to the OFF side, the process proceeds to step S12605.
ステップS12605では、抽選設定の設定情報を情報表示部45zに表示させるための制御を終了する。その後、ステップS12606に進む。
In step S12605, control for displaying the lottery setting information on the
ステップS12606では、主側RAM64における設定変更中フラグをOFFにする。その後、ステップS12607に進む。
In step S12606, the setting change in progress flag in the
ステップS12607では、設定確認モードを終了したことを示すコマンドである設定確認モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信する。後述するように、音声発光制御装置90は、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モードが終了されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、スピーカー46からの「設定確認モード中です」といった音声の出力を終了させ、「設定確認モードを終了しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。また、図柄表示装置41や各種ランプ47における設定確認モード中であることを報知する制御を終了させる。
In step S12607, a setting check mode end command, which is a command indicating that the setting check mode has ended, is sent to the audio and light
なお、設定確認モード終了コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信した後、設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を外部端子を介して遊技ホールのホールコンピュータに送信する構成としてもよい。この場合、設定確認モードを終了したことを示す情報を受信したホールコンピュータは、管理画面に当該パチンコ機10の設定確認モードが終了したことを示す情報を表示する構成としてもよい。ステップS12607を実行した後、本設定確認処理を終了する。
In addition, after sending the setting check mode end command to the audio and light
次に、主側MPU62(CPU62x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理について説明する。
Next, we will explain the timer interrupt processing executed by the main MPU 62 (
図73は、第1実施形態の態様101の主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。本態様では、主側MPU62(主側CPU62x)は、4ms周期でタイマ割込み処理を実行する。
Figure 73 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt process executed by the main MPU 62 (
ステップS12701では、各種乱数更新処理を実行する。各種乱数更新処理では、主側RAM64における各カウンタ(大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2、リーチ乱数カウンタC3、電動役物開放カウンタC4等)から現状の数値情報を読み出し、その読み出した数値情報に1を加算する処理を実行した後に、読み出し元のカウンタに加算後の数値情報を上書きする処理を実行する。なお、読み出した数値情報が当該カウンタの最大値である場合には、読み出し元のカウンタに0を上書きする処理を実行する。ステップS12701を実行した後、ステップS12702に進む。 In step S12701, various random number update processes are executed. In the various random number update processes, the current numerical information is read from each counter in the main RAM 64 (jackpot random number counter C1, jackpot type counter C2, reach random number counter C3, electric role release counter C4, etc.), a process is executed to add 1 to the read numerical information, and then a process is executed to overwrite the read-out counter with the added numerical information. Note that if the read-out numerical information is the maximum value of the counter, a process is executed to overwrite the read-out counter with 0. After executing step S12701, proceed to step S12702.
ステップS12702では、停電監視処理を実行する。停電監視処理では、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧を監視しており、当該駆動電圧が所定値(例えば10ボルト)を下回ったと判定した場合には、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされた又は停電が発生したと判断して、主側CPU62xのレジスタに格納されている各種情報(遊技状態を示す情報や制御情報等)を主側RAM64の所定の領域に退避させる。そして、これらの情報の主側RAM64への退避が完了した場合に、復電フラグをONにするとともに、主側RAM64に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行することによってRAM判定値(例えばチェックサム値)を算出し、算出したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶する。その後、後述するステップS12703には進まずに、供給される駆動電圧が低下して動作不能となるまで無限ループ処理を繰り返す。なお、本態様の電源装置85は、主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回るまで低下した場合であっても、主制御装置60などの制御系において駆動電圧として使用される5ボルトの安定化電圧が出力されるように構成されている。この安定化電圧が出力される時間としては、上述したRAM判定値を主側RAM64に記憶するまでの処理を実行するに十分な時間が確保されている。
In step S12702, a power failure monitoring process is executed. In the power failure monitoring process, the drive voltage supplied from the
一方、ステップS12702の停電監視処理において、電源装置85から主制御装置60に供給される駆動電圧が所定値を下回っていないと判定した場合には、そのままステップS12703に進む。
On the other hand, if the power outage monitoring process in step S12702 determines that the drive voltage supplied from the
ステップS12703では、RAM異常フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12703において、RAM異常フラグがONではないと判定した場合には(ステップS12703:NO)、ステップS12704に進む。一方、ステップS12703において、RAM異常フラグがONであると判定した場合には(ステップS12703:YES)、ステップS12704以降の処理を実行せずに、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。すなわち、RAM異常フラグがONである場合には、ステップS12704以降の遊技の進行を可能とするための処理が実行されないこととなり、遊技の進行が可能な遊技進行モードには移行しない構成となっている。以下、遊技の進行を可能とするための処理であるステップS12704以降の処理について説明する。 In step S12703, it is determined whether the RAM abnormality flag is ON. If it is determined in step S12703 that the RAM abnormality flag is not ON (step S12703: NO), the process proceeds to step S12704. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12703 that the RAM abnormality flag is ON (step S12703: YES), the process from step S12704 onwards is not executed and this timer interrupt process is terminated. In other words, if the RAM abnormality flag is ON, the process from step S12704 onwards to enable game progress is not executed, and the system is configured not to transition to a game progress mode in which game progress is possible. Below, the process from step S12704 onwards, which is the process to enable game progress, is explained.
ステップS12704では、ポート出力処理を実行する。ポート出力処理では、前回のタイマ割込み処理において出力情報の設定が行われている場合に、その出力情報に対応した出力を各種駆動部36c,34bに行うための処理を実行する。例えば、大入賞口36aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には可変入賞駆動部36cへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。また、第2始動口34の電動役物34aを開放状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には電動役物駆動部34bへの駆動信号の出力を開始させ、閉鎖状態に切り換えるべき情報が設定されている場合には当該駆動信号の出力を停止させる。その後、ステップS12705に進む。
In step S12704, port output processing is executed. In the port output processing, when output information has been set in the previous timer interrupt processing, processing is executed to output corresponding to the output information to the
ステップS12705では、読み込み処理を実行する。読み込み処理では、入球信号以外の信号の読み込みを実行し、その読み込んだ情報を今後の処理にて利用するために記憶する。その後、ステップS12706に進む。 In step S12705, a read process is executed. In the read process, signals other than the ball-entering signal are read, and the read information is stored for use in future processes. Then, the process proceeds to step S12706.
ステップS12706では、各入球検知センサー44a~44hから受信している信号を読み込むとともに、その読み込んだ情報に対応した処理を行うための入球検知処理を実行する。入球検知処理は、図28に示した入球検知処理と同じであるため、詳細な説明は省略する。ステップS12706を実行した後、ステップS12707に進む。
In step S12706, the signals received from each
ステップS12707では、主側RAM64に設けられている所定のタイマカウンタの数値情報をまとめて更新するためのタイマ更新処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12708に進み、賞球コマンドの出力設定処理を実行する。その後、ステップS12709に進む。
In step S12707, a timer update process is executed to collectively update the numerical information of a predetermined timer counter provided in the
ステップS12709では、第1始動口33及び第2始動口34への遊技球の入球に伴う始動口用の入球処理を実行する。始動口用の入球処理では、第1始動口33又は第2始動口34に遊技球が入球したと判定されたことに基づいて大当たり乱数カウンタC1、大当たり種別カウンタC2及びリーチ乱数カウンタC3の値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の保留情報記憶エリア64bに記憶する。ステップS12709を実行した後、ステップS12710に進む。
In step S12709, a ball entry process for the start port is executed in response to the entry of the game ball into the
ステップS12710では、スルーゲート35への遊技球の入球(通過)に伴うスルーゲート用の入球処理を実行する。スルーゲート用の入球処理では、スルーゲート35に遊技球が入球(通過)したと判定されたことに基づいて変動種別カウンタCSの値を取得するとともに、取得したカウンタ値をRAM64の電役保留エリア64dに記憶する。ステップS12710を実行した後、ステップS12711に進む。
In step S12710, a ball entry process for the through gate is executed in response to the entry (passage) of a game ball into the through
ステップS12711では、各遊技回における遊技を制御するための遊技回制御処理を実行する。遊技回制御処理では、大当たり抽選や、第1図柄表示部37a,第2図柄表示部37bの表示制御などを行う。ステップS12711を実行した後、ステップS12712に進む。
In step S12711, a game round control process is executed to control the game in each game round. In the game round control process, a jackpot lottery is performed, and display control of the first and second
ステップS12712では、遊技状態を移行させるための遊技状態移行処理を実行する。遊技状態移行処理では、遊技状態を開閉実行モード、高確率モード、高頻度サポートモードなどへ移行させる処理を実行する。ステップS12712を実行した後、ステップS12713に進む。 In step S12712, a game state transition process is executed to transition the game state. In the game state transition process, a process is executed to transition the game state to an open/close execution mode, a high probability mode, a high frequency support mode, or the like. After executing step S12712, the process proceeds to step S12713.
ステップS12713では、電動役物34aを制御するための電役サポート用処理を実行する。電役サポート用処理では、電動役物34aを開放状態とするか否かの判定(電動役物開放抽選)を行なうとともに、開放状態とすると判定した場合には電動役物34aを駆動制御する。ステップS12713を実行した後、ステップS12714に進む。 In step S12713, an electric role support process is executed to control the electric role 34a. In the electric role support process, a determination is made as to whether or not the electric role 34a is to be opened (electric role opening lottery), and if it is determined that the electric role 34a is to be opened, the electric role 34a is driven and controlled. After executing step S12713, the process proceeds to step S12714.
ステップS12714では、遊技球発射制御処理を実行する。遊技球発射制御処理では、遊技者によって操作ハンドル25が操作された際に遊技球を遊技領域PAに発射するための処理を実行する。ステップS12714を実行した後、ステップS12715に進む。
In step S12714, a game ball launch control process is executed. In the game ball launch control process, a process is executed to launch a game ball into the game area PA when the player operates the operating
ステップS12715では、今回のタイマ割込み処理にて実行された各種処理の処理結果に応じた外部信号の出力の開始及び終了を制御するように外部情報設定処理を実行する。ステップS12715を実行した後、ステップS12716に進む。 In step S12715, an external information setting process is executed to control the start and end of the output of an external signal according to the results of the various processes executed in the current timer interrupt process. After executing step S12715, proceed to step S12716.
ステップS12716では、遊技履歴情報を算出・表示するための遊技履歴用処理を実行する。遊技履歴用処理は、図29に示した遊技履歴用処理と同じであるため、詳細な説明は省略する。ステップS12716を実行した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。 In step S12716, a game history process is executed to calculate and display game history information. The game history process is the same as the game history process shown in FIG. 29, so a detailed description is omitted. After step S12716 is executed, this timer interrupt process is terminated.
以上説明したように、本態様では、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがONにされて当該パチンコ機10が起動すると、上述した通常起動コマンド、RAM異常コマンド、RAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドの5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドが主制御装置60から音声発光制御装置90へ向けて送信される。これらの5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信した音声発光制御装置90は、受信したコマンドの種別に基づいて、主制御装置60がどのような態様で起動したのか(どのような種別の起動処理を実行したのか)を把握することができる。すなわち、上述した通常起動コマンド、RAM異常コマンド、RAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドの5個のコマンドは、主制御装置60が実行した起動処理の種別を示すコマンドであることから、これらの5個のコマンドをまとめて「起動種別コマンド」とも呼ぶ。
As described above, in this embodiment, when the power switch of the
次に、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92が実行する処理について説明する。
Next, we will explain the processing performed by the MPU 92 of the audio and light
図74は、第1実施形態の態様101の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。ステップS12801では、立ち上げ処理を実行する。具体的には、電源投入に伴う初期設定処理や、音光側RAM94が正常に機能するか否かの判定等を実行する。ステップS12801を実行した後、ステップS12802に進む。
Figure 74 is a flowchart showing the main processing executed by the audio/optical side MPU 92 (audio/
ステップS12802では、起動日時情報取得処理を実行する。起動日時情報取得処理では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2から起動日時情報を読み出して主側RAM64の起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに記憶させる処理を実行する。起動日時情報取得処理の詳細については後述する。ステップS12802を実行した後、ステップS12803に進む。
In step S12802, a startup date and time information acquisition process is executed. In the startup date and time information acquisition process, the startup date and time information is read from the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
ステップS12803では、起動種別報知処理を実行する。起動種別報知処理では、主制御装置60の主側MPU62から受信した起動種別コマンドに基づいて、当該主制御装置60の起動の種別を報知する。起動種別報知処理の詳細については後述する。ステップS12803を実行した後、ステップS12804に進む。
In step S12803, the start-up type notification process is executed. In the start-up type notification process, the start-up type of the
ステップS12804では、タイマ割込みの許可を設定する。これにより、後述するタイマ割込み処理の実行が許可される。その後、無限ループに突入する。 In step S12804, timer interrupt permission is set. This allows execution of the timer interrupt process described below. After that, the process enters an infinite loop.
次に、図74のステップS12802に示した起動日時情報取得処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the startup date and time information acquisition process shown in step S12802 of Figure 74.
図75は、第1実施形態の態様101の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行する起動日時情報取得処理を示すフローチャートである。ステップS12901では、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、主側MPU62から、上述した通常起動コマンド、RAM異常コマンド、RAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドの5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。ステップS12901において、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定した場合には(ステップS12901:YES)、ステップS12902に進む。一方、ステップS12901において、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれのコマンドも受信していないと判定した場合には(ステップS12901:NO)、再びステップS12901に戻る。すなわち、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定するまで待機し、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定した場合に、ステップS12902に進む。
Figure 75 is a flowchart showing the start date and time information acquisition process executed by the sound/light side MPU 92 (sound/
ステップS12902では、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンド又はRAM異常コマンドのいずれかであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12902において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンド又はRAM異常コマンドのいずれかであると判定した場合には(ステップS12902:YES)、ステップS12903に進む。ここで、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンド又はRAM異常コマンドである場合とは、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作、及び、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作のいずれの操作も受け付けていなかった場合である。このような場合に、ステップS12903に進む。
In step S12902, it is determined whether the command received as the startup type command from the
ステップS12903では、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ現在日時情報をRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に書き込む(記憶する)。その後、後述するステップS12905に進む。
In step S12903, the current date and time information is read from the clock register 97b1 of the
一方、ステップS12902において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンド又はRAM異常コマンドのいずれでもないと判定した場合(ステップS12902:NO)、すなわち、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドのうちのいずれかであった場合には、ステップS12904に進む。ここで、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドのうちのいずれかであった場合とは、主に、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、設定変更処理(設定変更モード)を実行させるための操作、設定確認処理(設定確認モード)を実行させるための操作、及び、第1RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作のいずれかの操作を受け付けていた場合である。このような場合に、ステップS12904に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S12902 that the command received as the startup type command from the
ステップS12904では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されているか否かを判定する。ここで、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されている場合とは、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている情報から日時を読み出すことが可能な場合であり、一方、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていない場合とは、例えば、当該パチンコ機10に初めて電源が投入された場合や、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている情報がノイズ等によって破壊されていて正常に日時が読み出せない場合である。ステップS12904において、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていると判定した場合には(ステップS12904:YES)、上述したステップS12903の処理(現在日時情報を起動日時情報として上書きする処理)を実行せずに(回避して)ステップS12905に進む。
In step S12904, it is determined whether or not the start-up date and time information is stored in the start-up date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
ステップS12905では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2から起動日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ起動日時情報を音光側RAM94の起動日時情報記起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに書き込む(記憶する)。その後、本起動日時情報取得処理を終了する。
In step S12905, the startup date and time information is read from the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
なお、上述したステップS12904において、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS12904:NO)、上述したステップS12903の処理(現在日時情報を読み込んで起動日時情報に上書きする処理)を実行してから、上述したステップS12905に進む。この理由は、仮に、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていない状態のまま上述したステップS12905に進む構成とすると、音光側RAM94の起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに書き込むべき対象の起動日時情報が存在しないという不具合が生じてしまうからである。
If it is determined in step S12904 that no startup date and time information is stored in the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97 (step S12904: NO), the process of step S12903 described above (process of reading the current date and time information and overwriting it with the startup date and time information) is executed, and then the process proceeds to step S12905 described above. The reason for this is that if the process proceeds to step S12905 described above without any startup date and time information stored in the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
次に、図74のステップS12803に示した起動種別報知処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the startup type notification process shown in step S12803 of Figure 74.
図76は、第1実施形態の態様101の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行する起動種別報知処理を示すフローチャートである。ステップS13001では、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンドであるか否かを判定する。ステップS13001において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンドであると判定した場合には(ステップS13001:YES)、ステップS13002に進む。
Figure 76 is a flowchart showing the startup type notification process executed by the sound/light side MPU 92 (sound/
ステップS13002では、通常起動報知処理を実行する。通常起動報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であると判定されず、かつ、上述した設定変更処理、設定確認処理、第1RAMクリア処理のいずれの処理も実行しない通常の状態でパチンコ機10(主制御装置60)が起動したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「通常起動します」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。ステップS13002を実行した後、本起動種別報知処理を終了する。
In step S13002, normal startup notification processing is executed. In the normal startup notification processing, the
一方、ステップS13001において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが通常起動コマンドではないと判定した場合には(ステップS13001:NO)、ステップS13003に進み、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAM異常コマンドであるか否かを判定する。ステップS13003において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAM異常コマンドであると判定した場合には(ステップS13003:YES)、ステップS13004に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13001 that the command received as the startup type command from the
ステップS13004では、RAM異常報知処理を実行する。RAM異常報知処理では、主側RAM64が異常であることを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「主制御装置のRAMが異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい」といった音声がスピーカー46から繰り返し出力されるように制御して無限ループに突入する。すなわち、RAM異常報知処理では、当該パチンコ機10において次に起動させるべき種別の報知を、当該パチンコ機10の電源スイッチがOFFにされて電源の供給が断たれるまで継続する。
In step S13004, RAM abnormality notification processing is executed. In the RAM abnormality notification processing, processing is executed to notify that the
一方、ステップS13003において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAM異常コマンドではないと判定した場合には(ステップS13003:NO)、ステップS13005に進み、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAMクリアコマンドであるか否かを判定する。ステップS12005において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAMクリアコマンドであると判定した場合には(ステップS13005:YES)、ステップS13006に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13003 that the command received as the activation type command from the
ステップS13006では、RAMクリア報知処理を実行する。RAMクリア報知処理では、主側RAM64に対してRAMクリア処理を実行したことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「主制御装置のRAMをクリアしました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。その後、本起動種別報知処理を終了する。
In step S13006, a RAM clear notification process is executed. In the RAM clear notification process, a process is executed to notify the user that a RAM clear process has been executed on the
一方、ステップS13005において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドがRAMクリアコマンドではないと判定した場合には(ステップS13005:NO)、ステップS13007に進み、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが設定変更モード開始コマンドであるか否かを判定する。ステップS13007において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが設定変更モード開始コマンドであると判定した場合には(ステップS13007:YES)、ステップS13008に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13005 that the command received as the startup type command from the
ステップS13008では、設定変更モード開始報知処理を実行する。設定変更モード開始報知処理では、設定変更モードが開始されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「設定変更モードを開始しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、その後、「設定変更モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、設定変更モード開始報知処理では、設定変更モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、本態様では、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定変更モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、設定変更モード開始報知処理では、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。その後、ステップS13009に進み、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。ステップS13009において、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定した場合には(ステップS13009:YES)、ステップS13010に進む。一方、ステップS13009において、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信していないと判定した場合には(ステップS13009:NO)、再びステップS13009に戻る。すなわち、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定するまで待機し、設定変更モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定した場合に、ステップS13010に進む。
In step S13008, a setting change mode start notification process is executed. In the setting change mode start notification process, a process of notifying that the setting change mode has started is executed. Specifically, in this embodiment, a voice such as "The setting change mode has started" is output from the
ステップS13010では、設定変更モード終了報知処理を実行する。設定変更モード終了報知処理では、設定変更モードが終了されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、スピーカー46からの「設定変更モード中です」といった音声の出力を終了させ、「設定変更モードを終了しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。また、図柄表示装置41や各種ランプ47における設定変更モード中であることを報知する制御を終了させる。その後、本起動種別報知処理を終了する。
In step S13010, a setting change mode end notification process is executed. In the setting change mode end notification process, a process is executed to notify that the setting change mode has ended. Specifically, in this embodiment, the output of a voice such as "You are in setting change mode" from the
一方、ステップS13007において、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが設定変更モード開始コマンドではないと判定した場合(ステップS13007:NO)、換言すれば、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドとして受信したコマンドが設定確認モード開始コマンドである場合には、ステップS13011に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13007 that the command received as the activation type command from the
ステップS13011では、設定確認モード開始報知処理を実行する。設定確認モード開始報知処理では、設定確認モードが開始されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、「設定確認モードを開始しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させ、その後、「設定確認モード中です」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。また、設定確認モード開始報知処理では、設定確認モード中であることを示す情報を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。具体的には、本態様では、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に送信し、当該コマンドを受信した表示制御装置100は、「設定確認モード中です」といった文字列を図柄表示装置41に表示させる。また、設定確認モード開始報知処理では、各種ランプ47を最大輝度による点灯と消灯とを交互に繰り返して点滅するように制御する。その後、ステップS13012に進み、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。ステップS13012において、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定した場合には(ステップS13012:YES)、ステップS13013に進む。一方、ステップS13012において、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信していないと判定した場合には(ステップS13012:NO)、再びステップS13012に戻る。すなわち、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定するまで待機し、設定確認モード終了コマンドを受信したと判定した場合に、ステップS13013に進む。
In step S13011, a setting check mode start notification process is executed. In the setting check mode start notification process, a process of notifying that the setting check mode has started is executed. Specifically, in this embodiment, a voice such as "The setting check mode has started" is output from the
ステップS13013では、設定確認モード終了報知処理を実行する。設定確認モード終了報知処理では、設定確認モードが終了されたことを報知する処理を実行する。具体的には、本態様では、スピーカー46からの「設定変更モード中です」といった音声の出力を終了させ、「設定変更モードを終了しました」といった音声をスピーカー46から出力させる。また、図柄表示装置41や各種ランプ47における設定確認モード中であることを報知する制御を終了させる。その後、本起動種別報知処理を終了する。
In step S13013, a setting check mode end notification process is executed. In the setting check mode end notification process, a process is executed to notify that the setting check mode has ended. Specifically, in this embodiment, the output of a voice such as "You are in setting change mode" from the
図77は、第1実施形態の態様101の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行するタイマ割込み処理を示すフローチャートである。タイマ割込み処理は、比較的短い周期(本態様では2msec)で繰り返し実行される。以下、タイマ割込み処理において実行される各ステップの処理について説明する。
Figure 77 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt process executed by the sound/light side MPU 92 (sound/
ステップS13101では、コマンド記憶処理を実行する。コマンド記憶処理は、主側MPU62からコマンドを受信した場合に、受信したコマンドを音光側RAM94に記憶するための処理である。音光側RAM94には、主側MPU62から受信したコマンドの記憶及び読み出しを可能とするためのリングバッファが設けられており、主側MPU62から受信したコマンドは、当該リングバッファに順次記憶されるとともに、記憶された順序に従って順次読み出される。ステップS13101を実行した後、ステップS13102に進む。
In step S13101, a command storage process is executed. The command storage process is a process for storing a received command in the audio/light side RAM 94 when a command is received from the
ステップS13102では、RTC演出用処理を実行する。RTC演出用処理では、当該パチンコ機10が起動してから(電力の供給が開始されてから)所定時間毎(本態様では1時間毎)に所定時間(本態様では5分間)のRTC演出を実行するための処理を行なう。RTC演出用処理の詳細については後述する。ステップS13102を実行した後、ステップS13103に進む。
In step S13102, the RTC effect processing is executed. In the RTC effect processing, processing is performed to execute an RTC effect for a predetermined time (in this embodiment, 5 minutes) at predetermined time intervals (in this embodiment, every hour) after the
ステップS13103では、遊技回演出用処理を実行する。遊技回演出用処理では、図柄の変動が開始してから停止するまでの遊技回において実行する演出に関する処理を行なう。ステップS13103を実行した後、ステップS13104に進む。 In step S13103, processing for game round presentation is executed. In the processing for game round presentation, processing is performed for presentation to be executed in the game round from when the pattern change starts to when it stops. After executing step S13103, proceed to step S13104.
ステップS13104では、開閉実行モード演出用処理を実行する。開閉実行モード演出用処理では、オープニング期間における演出や、開閉処理期間における演出、エンディング期間における演出に関する処理を行なう。ステップS13104を実行した後、ステップS13105に進む。 In step S13104, processing for the opening and closing execution mode presentation is executed. In the opening and closing execution mode presentation processing, processing related to the presentation during the opening and closing processing period, and the presentation during the ending period is performed. After executing step S13104, proceed to step S13105.
ステップS13105では、客待ち用処理を実行する。客待ち用処理では、遊技回が所定時間実行されていない場合に図柄表示装置41にデモ動画を表示させるための処理を実行する。ステップS13105を実行した後、ステップS13106に進む。
In step S13105, a customer waiting process is executed. In the customer waiting process, a process is executed to display a demo video on the
ステップS13106では、各種ランプ47の発光制御を行うための発光制御処理を実行する。発光制御処理では、上記の各演出用処理において読み出された発光データに基づいて、各種ランプ47の発光制御を行う。ステップS13106を実行した後、ステップS13107に進む。
In step S13106, a light emission control process is executed to control the light emission of the
ステップS13107では、スピーカー46の音声出力制御を行うための音声出力制御処理を実行する。音声出力制御処理では、上記のBGM用処理及び各演出用処理において読み出された音声データに基づいて、スピーカー46の音声出力制御を行う。ステップS13107を実行した後、本タイマ割込み処理を終了する。
In step S13107, an audio output control process is executed to control the audio output of the
次に、図77のステップS13102に示したRTC演出用処理の詳細について説明する。 Next, we will explain the details of the RTC performance processing shown in step S13102 of Figure 77.
図78は、第1実施形態の態様101の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行するRTC演出用処理を示すフローチャートである。
Figure 78 is a flowchart showing the RTC performance process executed by the sound/light side MPU 92 (sound/
ステップS13201では、主側RAM64に記憶されているRTC演出実行中フラグがONであるか否かを判定する。RTC演出実行中フラグは、後述するRTC演出が実行中であるか否かを判定するためのフラグであり、RTC演出の開始の際にONとなり、RTC演出の終了の際にOFFとなる。ステップS13201において、RTC演出実行中フラグがONではないと判定した場合(ステップS13201:NO)、すなわち、RTC演出が実行中ではない場合には、ステップS13202に進む。
In step S13201, it is determined whether the RTC performance execution flag stored in the
ステップS13202では、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込む。その後、ステップS13203に進み、読み込んだ現在日時情報と、音光側RAM94の起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに記憶されている起動日時情報とに基づいて、起動日時から現在の日時までの経過時間である起動経過時間を算出する。具体的には、例えば、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から読み込んだ現在日時情報が「2017年12月15日11時53分45秒」を示しており、音光側RAM94に記憶されている起動日時情報が「2017年12月15日08時42分35秒」を示している場合には、起動経過時間は、「3時間11分10秒」となる。なお、算出した起動経過時間が24時間00分00秒を超える値となる場合には、起動経過時間が24時間00分00秒以下の値となるまで、当該起動経過時間から24時間00分00秒に対応する値を減算する。例えば、算出した起動経過時間が「51時間35分24秒」である場合には、24時間00分00秒に対応する値を2回減算して、新たな起動経過時間が「3時間35分24秒」となる。このような処理を採用する理由については後述する。ステップS13203を実行した後、ステップS13204に進む。
In step S13202, the current date and time information is read from the clock register 97b1 of the
ステップS13204では、音光側ROM93に記憶されているRTC演出実行判定テーブルを参照し、ステップS13205においてRTC演出を開始するタイミングであるか否かを判定する。RTC演出実行判定テーブルには、起動経過時間と、RTC演出の種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。
In step S13204, the RTC performance execution judgment table stored in the sound/
図79は、RTC演出実行判定テーブルを説明する説明図である。上述したように、RTC演出実行判定テーブルには、起動経過時間と、RTC演出の種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。具体的には、本態様では、図79に示すように、起動経過時間の1時間毎に異なる種別のRTC演出が設定されている。例えば、起動経過時間「1時間00分00秒」に対応して「RTC演出A」が設定されており、起動経過時間「2時間00分00秒」に対応して「RTC演出B」が設定されている。上述したように、本態様では、起動経過時間が24時間00分00秒を超える値となる場合には、起動経過時間が24時間00分00秒以下の値となるまで、当該起動経過時間から24時間00分00秒に対応する値を減算する。したがって、RTC演出実行判定テーブルを起動経過時間が24時間00分00秒を超える部分に対応させなくてもよいため、RTC演出実行判定テーブルを記憶するために必要となる音光側ROM93の記憶容量を低減することができる。
79 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the RTC performance execution judgment table. As described above, the RTC performance execution judgment table stores the elapsed time from startup in association with the type of RTC performance. Specifically, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 79, a different type of RTC performance is set for each hour of the elapsed time from startup. For example, "RTC performance A" is set corresponding to the elapsed time from startup of "1
図78に説明を戻す。ステップS13205では、RTC演出を開始するタイミングであるか否かを判定する。具体的には、ステップS13203において算出した起動経過時間が、RTC演出実行判定テーブルに設定されている起動経過時間と一致している場合にはRTC演出の開始タイミングであると判定し、一致していない場合にはRTC演出の開始タイミングではないと判定する。例えば、ステップS13203において算出した起動経過時間が「1時間00分00秒」である場合にはRTC演出Aの開始タイミングであると判定する。
Returning to FIG. 78 for explanation, in step S13205, it is determined whether it is the timing to start an RTC performance. Specifically, if the elapsed time from startup calculated in step S13203 matches the elapsed time from startup set in the RTC performance execution determination table, it is determined that it is the timing to start an RTC performance, and if they do not match, it is determined that it is not the timing to start an RTC performance. For example, if the elapsed time from startup calculated in step S13203 is "1
ステップS13205において、RTC演出を開始するタイミングではないと判定した場合には(ステップS13205:NO)、本RTC演出用処理を終了する。一方、ステップS13205において、RTC演出を開始するタイミングであると判定した場合には(ステップS13205:YES)、ステップS13206に進む。 If it is determined in step S13205 that it is not the time to start the RTC performance (step S13205: NO), the RTC performance process ends. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13205 that it is the time to start the RTC performance (step S13205: YES), the process proceeds to step S13206.
ステップS13206では、RTC演出実行判定テーブルにおいて設定されている起動経過時間に対応した種別のRTC演出を開始するように設定する。例えば、起動経過時間が「1時間00分00秒」である場合にはRTC演出Aに対応した演出態様となるようにスピーカー46及び各種ランプ47の制御を開始し、RTC演出Aに対応した動画の表示を開始させるためのコマンドを表示制御装置100に対して送信する。本態様では、RTC演出Aは、5分間、キャラクターAが登場して楽曲Aを歌う演出である。RTC演出実行判定テーブルにおいて設定されている他のRTC演出は、5分間、他のキャラクターが登場して他の楽曲を歌う演出である。すなわち、RTC演出の種別毎に登場するキャラクター及び楽曲が異なっている。その後、ステップS13207に進む。
In step S13206, the RTC performance corresponding to the elapsed time from startup set in the RTC performance execution judgment table is set to start. For example, if the elapsed time from startup is "1
ステップS13207では、RTC演出実行中フラグをONにする。その後、ステップS13208に進み、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrに「150000」をセットする。RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrは、RTC演出の残時間を管理するためのカウンタであり、後述するように、本タイマ割込み処理が実行される毎に1減算される。本態様では、タイマ割込み処理は2ms毎に実行されるので、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrにセットされる「150000」は、5分間に相当する。その後、本RTC演出用処理を終了する。 In step S13207, the RTC performance execution flag is turned ON. Then, the process proceeds to step S13208, where the timer counter Tr for the RTC performance is set to "150000". The timer counter Tr for the RTC performance is a counter for managing the remaining time of the RTC performance, and as described below, is decremented by 1 each time this timer interrupt process is executed. In this embodiment, the timer interrupt process is executed every 2 ms, so the "150000" set in the timer counter Tr for the RTC performance corresponds to 5 minutes. Then, this RTC performance process is terminated.
上述したステップS13201において、RTC演出実行中フラグがONであると判定した場合(ステップS13201:YES)、すなわち、上述したステップS13207においてRTC演出実行中フラグをONにした後のタイマ割込み処理にて本ステップS13201に進んだ場合には、ステップS13209に進む。 If it is determined in step S13201 above that the RTC performance execution flag is ON (step S13201: YES), that is, if the process proceeds to this step S13201 in the timer interrupt process after the RTC performance execution flag is set ON in step S13207 above, the process proceeds to step S13209.
ステップS13209では、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrにセットされている値から1を減算する。その後、ステップS13210に進み、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrの値が0であるか否かを判定する。ステップS13210において、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrの値が0ではないと判定した場合(ステップS13210:NO)、すなわち、まだRTC演出の終了タイミングではないと判定した場合には、本RTC演出用処理を終了する。一方、ステップS13210において、RTC演出用タイマカウンタTrの値が0であると判定した場合(ステップS13210:YES)、すなわち、RTC演出の終了タイミングであると判定した場合には、ステップS13211に進み、実行中のRTC演出を終了するように設定する。その後、ステップS13212に進み、RTC演出実行中フラグをOFFにして、本RTC演出用処理を終了する。 In step S13209, 1 is subtracted from the value set in the timer counter Tr for RTC performance. Then, proceed to step S13210 and determine whether the value of the timer counter Tr for RTC performance is 0 or not. In step S13210, if it is determined that the value of the timer counter Tr for RTC performance is not 0 (step S13210: NO), that is, if it is determined that it is not yet time to end the RTC performance, this RTC performance processing is terminated. On the other hand, in step S13210, if it is determined that the value of the timer counter Tr for RTC performance is 0 (step S13210: YES), that is, if it is determined that it is time to end the RTC performance, proceed to step S13211 and set the ongoing RTC performance to end. Then, proceed to step S13212, turn off the RTC performance execution flag, and terminate this RTC performance processing.
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上記の他の態様において説明した効果に加えて、以下の効果を奏することができる。 As explained above, this embodiment has the following advantages in addition to those explained in the other embodiments above.
なお、本態様の効果の説明に先立って、パチンコ機10が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数のパチンコ機10がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。
Before describing the effects of this embodiment, an amusement hall in which
本態様によれば、パチンコ機10は、当該パチンコ機10への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ現在日時情報を起動日時情報としてRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶させる処理(図75のステップS12903に示す処理、以下では、「起動日時情報記憶処理」とも呼ぶ)を実行する。そして、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行された年月日及び時刻を含む起動日時情報と、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1にて計時されている現在日時情報とに基づいて、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間である起動経過時間を算出し(図78のステップS13203)、算出した起動経過時間に基づいてRTC演出の実行を開始する(図78のステップS13204~ステップS13206)。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。
According to this aspect, the
仮に、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行されてからの起動経過時間ではなく、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1において計時されている現在日時情報に基づいてRTC演出の実行を開始する構成(例えば、現在日時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングでRTC演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10の現在日時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間においてパチンコ機10Aの現在日時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、パチンコ機10Bの現在日時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、RTC演出が開始されるタイミングが各パチンコ機10毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において一斉に(同時に)RTC演出が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。
We will now explain a case where the RTC performance is started based on the current date and time information clocked in the clock register 97b1 of the
これに対して、本態様によれば、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、当該パチンコ機10への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ現在日時情報を起動日時情報として起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶させる起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。
In contrast, according to this embodiment, when the supply of power from an external source to the
そして、本態様によれば、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行された年月日及び時刻を含む起動日時情報と、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1において計時されている現在日時情報とに基づいて、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行されてからの起動経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行するので、各パチンコ機10において算出される起動日時情報記憶処理が実行されてからの起動経過時間は、各パチンコ機10のRTC97の計時レジスタ97b1において計時されている現在日時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。
According to this embodiment, each
そして、本態様によれば、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、算出した起動経過時間に基づいてRTC演出を開始するので、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において一斉に(同時に)RTC演出を開始させることが可能となる。
And according to this embodiment, each
さらに、本態様のパチンコ機10は、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶した起動日時情報を外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態の間も保持することが可能に構成されており、また、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92は、主制御装置60のMPU62が実行する起動処理の種別が特定の起動処理である場合には上述した起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避するように構成されている(図75のステップS12902)。具体的には、本態様では、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92は、主制御装置60のMPU62からRAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モードのいずれかの起動種別コマンドを受信した場合には、上述した起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。
Furthermore, the
仮に、上述した起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避する機能を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10のうちの一のパチンコ機10に特定の起動処理(例えば、設定変更モードや、設定確認モード、RAMクリア処理)を実行させるために、当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一のパチンコ機10を特定の起動処理が実行される状態(例えば、設定変更モードや設定確認モード、RAMクリア処理を実行させるための操作を受け付けている状態)として当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにして特定の起動処理を実行させる場合がある。この場合、当該一のパチンコ機10は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一のパチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間が、他のパチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一のパチンコ機10においてRTC演出が開始されるタイミングが、他のパチンコ機10においてRTC演出が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一のパチンコ機10において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。
We will now explain a case where a configuration that does not have the function of avoiding the execution of the above-mentioned start date and time information storage process is adopted. In this configuration, when the supply of power to each
これに対して、本態様によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一のパチンコ機10のRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2において記憶されている起動日時情報は保持される。その後、管理者が当該一のパチンコ機10を特定の起動処理が実行される状態として電源スイッチをONにすると、当該一のパチンコ機10において特定の起動処理が実行され、起動日時情報記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一のパチンコ機10のRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている起動日時情報が上書きされず、他のパチンコ機10と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された起動日時情報記憶処理において記憶された起動日時情報が維持される。この結果、当該一のパチンコ機10を含む当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。
In contrast, according to this embodiment, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the
そして、本態様によれば、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、算出した起動経過時間に基づいてRTC演出を開始するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにしたパチンコ機10を含む当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において一斉に(同時に)RTC演出を開始させることが可能となる。
And according to this embodiment, each
また、本態様によれば、特定の起動処理が主制御装置60によって実行される場合に、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報を報知する。具体的には、本態様では、RAM異常コマンドを送信する処理(図70のステップS12422)を含む起動処理が主制御装置60によって実行された場合に、音声発光制御装置90は、「RAM異常です。設定変更モードで起動して下さい。」といった音声をスピーカー46から繰り返し出力させる。したがって、管理者は、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別を把握することができ、当該パチンコ機10への電力供給を終了させた後、再度、当該パチンコ機10への電力供給を開始させる際に、報知された種別の起動処理(本態様では設定変更モード)を実行させるようにすることができる。
In addition, according to this embodiment, when a specific startup process is executed by the
特に、本態様では、図70のステップS12415においてRAM異常フラグがONとなったパチンコ機10への電力供給を終了させた後、再度、当該パチンコ機10への電力供給を開始させる際に、報知された種別の起動処理(設定変更モード)を実行させなかった場合には、再びRAM異常であると判定されて主制御装置60がRAM異常コマンドを音声発光制御装置90に送信してしまう(図70のステップS12422)。そうすると、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92は、上述した起動日時情報記憶処理(図75のステップS12903)を再び実行してしまい、当該パチンコ機10において実行されるRTC演出の開始のタイミングが他の複数のパチンコ機10において実行されるRTC演出の開始のタイミングとずれてしまう。しかしながら、本態様では、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報を報知するので、管理者が当該パチンコ機10に別の種別の起動処理を実行させてしまうことを抑制することができ、この結果、当該パチンコ機10におけるRTC演出の開始のタイミングが他の複数のパチンコ機10とずれてしまうことを抑制することが可能となる。
In particular, in this embodiment, if the power supply to a
また、本態様では、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を、当該パチンコ機10への外部からの電力供給が断たれるまで(例えば、電源スイッチがOFFにされるまで)継続するように構成されている。このような構成とすることによる効果について説明する。
In addition, in this embodiment, the notification of information regarding the type of startup process to be executed when the next power supply is started is configured to continue until the external power supply to the
仮に、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を所定時間(例えば10秒)で終了する構成とした場合には、例えば、広い遊技ホールにおいて、管理者が島設備の島電源スイッチの電源をONにしてパチンコ機10への外部からの電力供給が開始された後、管理者が当該パチンコ機10に到達する前に当該報知が終了してしまい、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別を管理者が把握することができない場合がある。
If the notification of information regarding the type of startup process to be executed when the next power supply is started were configured to end after a predetermined time (e.g., 10 seconds), for example, in a large amusement hall, after an administrator turns on the island power switch of the island equipment and starts the external power supply to the
これに対して、本態様によれば、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を当該パチンコ機10への外部からの電力供給が断たれるまで継続するので、管理者が当該パチンコ機10に到達する前に当該報知が終了してしまい、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別を管理者が把握することができないといった事態の発生を回避することができる。
In contrast, according to the present embodiment, the notification of information regarding the type of startup process to be executed when the next power supply is started continues until the external power supply to the
なお、本態様では、図75のステップS12905において、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2から起動日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ起動日時情報を音光側RAM94の起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに書き込む(記憶する)処理を実行する構成としたが、このステップS12905の処理を省略する構成としてもよい。この場合には、図78のステップS13203において、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から読み込んだ現在日時情報と、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2から読み込んだ起動日時情報とに基づいて、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行された日時から現在の日時までの経過時間である起動経過時間を算出する構成とすればよい。ただし、ステップS12905の処理を実行する構成とした方が、音光側MPU92によるRTC97へのアクセスの頻度を減らすことができるので、音光側MPU92の処理負荷を低減することができる。
In this embodiment, in step S12905 of FIG. 75, the startup date and time information is read from the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
また、本態様では、図78のステップS13202において、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込むことによって現在の日時を把握する構成としたが、この構成に代えて、パチンコ機10の起動時にRTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、その後は、当該起動時に読み込んだ現在日時情報からの経過時間を内部クロックに基づいてカウントすることによって現在の日時を把握する構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、RTC97へのアクセスの頻度を減らすことができるので、音光側MPU92の処理負荷を低減することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, in step S13202 of FIG. 78, the current date and time is ascertained by reading the current date and time information from the clock register 97b1 of the
また、本態様では、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定変更モードが実行された場合に限らず、設定変更中フラグがONであることに基づいて設定変更モードが実行された場合であっても、起動日時情報記憶処理の実行が回避される構成としたが、設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定変更モードが実行された場合に限り、起動日時情報記憶処理の実行が回避される構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにして、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された場合において、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行すべき状況であるにもかかわらず、設定変更中フラグがONとなっているパチンコ機10が起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避してしまうといったことを抑制することができる。
In addition, in this embodiment, the execution of the start date and time information storage process is avoided not only when the setting change mode is executed based on the reception of an operation to execute the setting change mode, but also when the setting change mode is executed based on the setting change flag being ON. However, the execution of the start date and time information storage process may be avoided only when the setting change mode is executed based on the reception of an operation to execute the setting change mode. With this configuration, when the manager of the game hall turns on the island power switch and power is supplied to
同様に、設定確認モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定確認モードが実行された場合に限り、起動日時情報記憶処理の実行が回避される構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにして、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された場合において、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行すべき状況であるにもかかわらず、設定確認中フラグがONとなっているパチンコ機10が起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避してしまうといったことを抑制することができる。
Similarly, the configuration may be such that the execution of the start date and time information storage process is avoided only when the setting check mode is executed based on the receipt of an operation to execute the setting check mode. With such a configuration, when the manager of the gaming hall turns on the island power switch and power is supplied to
<態様102>
上記態様101の図75に示した起動日時情報取得処理を、以下の図79に示す起動日時情報取得処理に置き換えた構成としてもよい。以下、具体的に説明する。
<
The startup date and time information acquisition process shown in Fig. 75 in the
図80は、第1実施形態の態様102の音光側MPU92(音光側CPU92x)が実行する起動日時情報取得処理を示すフローチャートである。ステップS13301では、主側MPU62から起動種別コマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。具体的には、本態様では、主側MPU62から、上述した通常起動コマンド、RAM異常コマンド、RAMクリアコマンド、設定変更モード開始コマンド、設定確認モード開始コマンドの5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したか否かを判定する。ステップS13301において、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定した場合には(ステップS13301:YES)、ステップS13302に進む。一方、ステップS13301において、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれのコマンドも受信していないと判定した場合には(ステップS13301:NO)、再びステップS13301に戻る。すなわち、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定するまで待機し、上述した5個のコマンドのうちのいずれかのコマンドを受信したと判定した場合に、ステップS13302に進む。
Figure 80 is a flowchart showing the start date and time information acquisition process executed by the sound/light side MPU 92 (sound/
ステップS13302では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されているか否かを判定する。ここで、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されている場合とは、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている情報から日時を読み出すことが可能な場合であり、一方、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていない場合とは、例えば、当該パチンコ機10に初めて電源が投入された場合や、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている情報がノイズ等によって破壊されていて正常に日時が読み出せない場合である。ステップS13302において、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていると判定した場合には(ステップS13302:YES)、ステップS13303に進む。
In step S13302, it is determined whether or not the start-up date and time information is stored in the start-up date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
ステップS13303では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2から起動日時情報を読み込み、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込む。そして、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過しているか否かを判定する。具体的には、例えば、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が「2017年12月8日08時12分32秒」であり、起動日時情報が示す日時が、次の日である「2017年12月9日08時15分11秒」である場合には、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過していると判定する。一方、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が「2017年12月8日08時12分32秒」であり、起動日時情報が示す日時が、同日の「2017年12月8日08時25分21秒」である場合には、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過していないと判定する。ステップS13303において、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過していると判定した場合には(ステップS13303:YES)、ステップS13304に進む。
In step S13303, the startup date and time information is read from the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
ステップS13304では、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ現在日時情報をRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に書き込む(記憶する)。その後、後述するステップS13305に進む。すなわち、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過している場合には、パチンコ機10が起動したタイミングの日時を示す情報(現在日時情報)が、起動日時情報として起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶される。その後、後述するステップS13305に進む。
In step S13304, the current date and time information is read from the clock register 97b1 of the
一方、ステップS13303において、現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過していないと判定した場合には(ステップS13303:NO)、上述したステップS13304の処理(現在日時情報を読み込んで起動日時情報として上書きする処理)を実行せずに(回避して)ステップS13305に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S13303 that the current date and time indicated by the current date and time information is not more than 30 minutes after the date and time indicated by the startup date and time information (step S13303: NO), the process of step S13304 described above (the process of reading the current date and time information and overwriting it as startup date and time information) is not executed (avoided) and the process proceeds to step S13305.
ステップS13305では、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている起動日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ起動日時情報を音光側RAMの起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに書き込む(記憶する)。その後、本起動日時情報取得処理を終了する。
In step S13305, the startup date and time information stored in the startup date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
なお、上述したステップS13302において、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていないと判定した場合には(ステップS13302:NO)、上述したステップS13303の処理(現在日時情報が示す現在の日時が、起動日時情報が示す日時から30分以上経過しているか否かを判定する処理)を回避して、ステップS13304の処理に進む。この理由は、仮に、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていない状態のまま上述したステップS13303に進む構成とすると、現在日時情報と比較すべき対象の起動日時情報が存在しないという不具合が生じてしまうからである。また、ステップS13304の処理を実行する理由は、仮に、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に起動日時情報が記憶されていない状態のまま上述したステップS13305に進む構成とすると、音光側RAM94の起動日時情報記憶エリア94bに書き込むべき対象の起動日時情報が存在しないという不具合が生じてしまうからである。
In the above-mentioned step S13302, if it is determined that the start-up date and time information is not stored in the start-up date and time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97 (step S13302: NO), the above-mentioned step S13303 processing (processing to determine whether the current date and time indicated by the current date and time information is 30 minutes or more after the date and time indicated by the start-up date and time information) is avoided and the processing proceeds to step S13304. The reason for this is that if the above-mentioned step S13303 is proceeded to while the start-up date and time information storage area 97b2 of the
以上説明したように、本態様によれば、上記の他の態様において説明した効果に加えて、以下の効果を奏することができる。 As explained above, this embodiment provides the following advantages in addition to the advantages explained in the other embodiments above.
本態様によれば、パチンコ機10は、当該パチンコ機10への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1から現在日時情報を読み込み、当該読み込んだ現在日時情報を起動日時情報としてRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶させる処理(図79のステップS13304に示す処理、以下では、「起動日時情報記憶処理」とも呼ぶ)を実行する。そして、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行された年月日及び時刻を含む起動日時情報と、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1にて計時されている現在日時情報とに基づいて、起動日時情報記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間である起動経過時間を算出し(図78のステップS13203)、算出した起動経過時間に基づいてRTC演出の実行を開始する(図78のステップS13204~ステップS13206)。この構成を採用したことによる効果は、上記の態様102において説明した効果と同じであるため、説明を省略する。
According to this aspect, the
さらに、本態様のパチンコ機10は、RTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶した起動日時情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能に構成されており、また、音声発光制御装置90のMPU92は、主制御装置60のMPU62から起動種別コマンドを受信した際に、RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1における現在日時情報に含まれる日時が、起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている起動日時情報に含まれる日時から所定時間(本態様では30分)が経過していない場合には上述した起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避するように構成されている(図79のステップS13303)。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。
Furthermore, the
仮に、上述した起動日時情報記憶処理の実行を回避する機能を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、一斉に(同時に)起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、種々の理由により、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10のうちの一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、再度、当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする場合がある。具体的には、例えば、設定変更モードを実行させてパチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更するために、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10のうちの一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一のパチンコ機10を設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けている状態として当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにして設定変更モードを実行させる場合がある。この場合、当該一のパチンコ機10は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び起動日時情報記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一のパチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間が、他のパチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一のパチンコ機10においてRTC演出が開始されるタイミングが、他のパチンコ機10においてRTC演出が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一のパチンコ機10において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。
We will now explain a case where a configuration that does not have the function of avoiding the execution of the above-mentioned start date and time information storage process is adopted. In this configuration, when the supply of power to each
これに対して、本態様によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一のパチンコ機10のRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2において記憶されている起動日時情報は保持される。その後、管理者が所定時間(本態様では30分)以内に当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにすると、起動日時情報記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一のパチンコ機10のRTC97の起動日時情報記憶エリア97b2に記憶されている起動日時情報が上書きされず、他のパチンコ機10と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された起動日時情報記憶処理において記憶された起動日時情報が維持される。この結果、当該一のパチンコ機10を含む当該島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において算出される起動経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。
In contrast, according to this embodiment, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the
そして、本態様によれば、島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10は、算出した起動経過時間に基づいてRTC演出を開始するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにしたパチンコ機10を含む島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において一斉に(同時に)RTC演出を開始させることが可能となる。
And according to this embodiment, each
すなわち、管理者は、島設備の島電源スイッチをONにして、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始させた後、所定時間(本態様では30分)以内に、当該島設備に設置されている複数のパチンコ機10のうち、抽選設定を変更しようとする一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一のパチンコ機10を設定変更モードを実行させるための操作を受け付けている状態として当該一のパチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにして設定変更モードを実行させれば、当該一のパチンコ機10の抽選設定を変更することが可能であるとともに、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした当該一のパチンコ機10を含む島設備に設置されている各パチンコ機10において一斉に(同時に)RTC演出を開始させることが可能となる。
In other words, the administrator turns on the island power switch of the island equipment to start supplying power to the
なお、本態様では、図80のステップS13303において、起動日時情報記憶処理(ステップS13304)の実行を回避するか否かの判定基準となる時間は30分に設定されていたが、当該判定基準となる時間の長さを変更可能な構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技ホールに設置されているパチンコ機10の台数や広さ等に応じて、当該判定基準となる時間の長さを適宜変更することができるので、例えば、当該遊技ホールに設置されている複数のパチンコ機10に対する抽選設定の変更作業が完了する前に、当該判定基準となる時間が経過してしまうといった事態の発生を抑制することが可能となる。
In this embodiment, in step S13303 of FIG. 80, the time criterion for determining whether or not to avoid execution of the startup date and time information storage process (step S13304) was set to 30 minutes, but the length of the criterion may be made changeable. With such a configuration, the length of the criterion can be changed appropriately depending on the number and size of the
<態様103>
上記の各態様において説明した各種の機能(例えば、各入球口への遊技球の入球個数を記憶する機能や、各入球口への遊技球の入球に基づいて賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数を算出する機能、賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数を記憶する機能、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報を算出する機能、算出した遊技履歴情報を記憶する機能、記憶した遊技履歴情報を表示する機能、RAMやフラッシュメモリ等の各種の記憶手段に記憶された各種の情報を消去する機能等)の少なくとも一部の機能を、遊技履歴管理チップ300が実現する構成としてもよく、主側CPU62x(遊技履歴管理チップ300を除いた主側MPU62)が実現する構成としてもよく、検査機320が実現する構成としてもよい。また、遊技履歴管理チップ300、主側CPU62x(遊技履歴管理チップ300を除いた主側MPU62)及び検査機320がこれらの各種の機能の少なくとも一部の機能を分担又は協働して実現する構成としてもよい。
<
At least some of the various functions described in each of the above aspects (for example, a function for storing the number of game balls entering each ball entrance, a function for calculating the number of game balls paid out as prize balls based on the game balls entering each ball entrance, a function for storing the number of game balls paid out as prize balls, a function for calculating game history information such as a ratio of game balls, a function for storing the calculated game history information, a function for displaying the stored game history information, a function for erasing various information stored in various storage means such as a RAM or a flash memory, etc.) may be realized by the game
<態様104>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様は、パチンコ機10に限らず、他の種別の遊技機に対しても適用することができる。例えば、パチンコ型スロットマシン等の回胴式遊技機に対しても適用することができる。具体的には、例えば、ボーナス時に当選して得た遊技メダルの枚数と、通常区間中に引いた子役で得られる遊技メダルの枚数と、ボーナスとは別の有利区間(AT、ART)中に得られる遊技メダルの枚数との比率を算出し、当該比率を液晶表示装置に表示する構成や、当該比率を検査機に出力し、当該検査機の表示部に当該比率を表示させる構成に対して適用することができる。
<Aspect 104>
The first embodiment and the other aspects described above can be applied not only to the
<態様105>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の他の態様において、ソフトウェアによって実現(CPUがプログラムを実行することによって実現)されている機能の一部又は全部をハードウェアによって実現する構成としてもよい。例えば、遊技履歴管理チップ300は、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算処理を実行するために設計された専用のハードウェアを備える構成としてもよい。このような構成によれば、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算処理を高速化することができるとともに、演算用のプログラムが不正に改竄されて正しい遊技履歴情報が算出されない等といった不正の発生を抑制することができる。なお、当該ハードウェアは、デジタル回路で構成されていてもよく、アナログ回路で構成されていてもよい。アナログ回路で構成されていれば、デジタル回路よりもさらに演算処理を高速化することができる。
<
In the first embodiment and other aspects, some or all of the functions realized by software (by the CPU executing a program) may be realized by hardware. For example, the gaming
<態様106>
上記第1実施形態及び上記の態様1から態様105に含まれる1又は複数の構成を適宜差し替えたり組み合わせた構成を採用してもよい。また、上記第1実施形態及び上記の態様1から態様105に含まれる1又は複数の構成と第1実施形態以外の実施形態に含まれる1又は複数の構成とを組み合わせてもよい。また、上記第1実施形態及び上記の態様1から態様105に含まれる構成のうち、必須でない構成は、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において適宜省略することが可能である。
<
A configuration may be adopted in which one or more configurations included in the first embodiment and
B.他の構成への適用:
上記各実施形態とは異なる他のタイプのパチンコ機等、例えば特別装置の特定領域に遊技球が入ると電動役物が所定回数開放するパチンコ機や、特別装置の特定領域に遊技球が入ると権利が発生して大当たりとなるパチンコ機、他の役物を備えたパチンコ機、アレンジボール機、雀球等の遊技機にも、本発明を適用できる。
B. Application to other configurations:
The present invention can also be applied to other types of pachinko machines different from the above embodiments, such as pachinko machines in which an electric device opens a predetermined number of times when a gaming ball enters a specific area of a special device, pachinko machines in which a right is generated and a jackpot is awarded when a gaming ball enters a specific area of a special device, pachinko machines equipped with other devices, arrange ball machines, mahjong ball machines, and other gaming machines.
また、弾球式でない遊技機、例えば、複数種類の図柄が周方向に付された複数のリールを備え、メダルの投入及びスタートレバーの操作によりリールの回転を開始し、ストップスイッチが操作されるか所定時間が経過することでリールが停止した後に、表示窓から視認できる有効ライン上に特定図柄又は特定図柄の組合せが成立していた場合にはメダルの払い出し等といった特典を遊技者に付与するスロットマシンにも本発明を適用できる。 The present invention can also be applied to non-pinball gaming machines, such as slot machines, which have multiple reels with multiple types of symbols circumferentially attached, and which start the rotation of the reels by inserting a medal and operating a start lever, and which, after the reels stop when a stop switch is operated or a predetermined time has passed, award the player with a special privilege, such as a medal payout, if a specific symbol or combination of specific symbols appears on a winning line visible through a display window.
また、外枠に開閉可能に支持された遊技機本体に貯留部及び取込装置を備え、貯留部に貯留されている所定数の遊技球が取込装置により取り込まれた後にスタートレバーが操作されることによりリールの回転を開始する、パチンコ機とスロットマシンとが融合された遊技機にも、本発明を適用できる。 The present invention can also be applied to a gaming machine that combines a pachinko machine and a slot machine, in which the gaming machine body is supported on an outer frame so that it can be opened and closed, has a storage section and an intake device, and the reels start to rotate when a start lever is operated after a predetermined number of gaming balls stored in the storage section have been taken in by the intake device.
また、上記実施形態においてソフトウェアで実現されている機能の一部をハードウェアで実現してもよく、あるいは、ハードウェアで実現されている機能の一部をソフトウェアで実現してもよい。 In addition, some of the functions realized by software in the above embodiments may be realized by hardware, or some of the functions realized by hardware may be realized by software.
C.上記各実施形態等から抽出される発明群について:
以下、上述した各実施形態から抽出される発明群の特徴について、必要に応じて効果等を示しつつ説明する。なお、以下においては、理解の容易のため、上記各実施形態において対応する構成を括弧書き等で適宜示すが、この括弧書き等で示した具体的構成に限定されるものではない。
C. Regarding the inventions extracted from the above embodiments:
The following describes the features of the inventions extracted from each of the above-mentioned embodiments, while indicating, as necessary, the effects, etc. In the following, for ease of understanding, the corresponding configurations in each of the above-mentioned embodiments are appropriately indicated in parentheses, but the present invention is not limited to the specific configurations indicated in parentheses.
<特徴A群>
特徴A群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Features Group A>
The group of features A is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴A1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
当該遊技機本体の筐体の内部に格納されるともに、前記検知手段による検知に基づいて取得された情報である検知情報を不揮発的に記憶する情報記憶手段(レジスタ304、演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶された情報を当該遊技機と接続された所定の装置に対して送信する送信手段(CPU308)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
An information storage means (register 304, memory for storing calculation results 309) that is stored inside the cabinet of the gaming machine main body and stores in a non-volatile manner the detection information obtained based on the detection by the detection means;
A transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the information stored in the information storage means to a predetermined device connected to the gaming machine;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴A1によれば、処理実行手段は、検知手段による検知に基づいて取得された情報である検知情報を不揮発的に記憶する情報記憶手段を備える。検知情報は、実行された遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該検知情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、検知情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴A1によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体内部に格納された処理実行手段の情報記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から検知情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を保持することができない。特徴A1の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体内部に格納された処理実行手段の情報記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴A1の遊技機は、当該遊技機がいかなる状態(遊技ホールに設置されている状態や流通状態)に置かれても、遊技機と検知情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature A1, the processing execution means includes information storage means for non-volatilely storing detection information, which is information acquired based on detection by the detection means. Since the detection information is information that correlates with the behavior of the game ball in the executed game, the detection information differs for each game machine and is information specific to the game machine. In other words, the detection information is information that reflects the characteristics of the game machine. According to feature A1, the detection information, which is information that reflects the characteristics of the game machine, is stored in the information storage means of the processing execution means stored inside the housing of the game machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the game machine, the characteristics of the game machine can be inspected by acquiring the detection information from the game machine main body itself. When the game machine is installed in a game hall, information on the characteristics of the game machine can be acquired by the hall computer installed in the game hall. However, since game machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where they are not connected to the hall computer, in which case, conventional game machines cannot retain information on the characteristics of the game machine. The gaming machine of Feature A1 stores detection information, which is information reflecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, in the information storage means of the processing execution means housed inside the cabinet of the gaming machine main body, so that the detection information can be acquired from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, the gaming machine of Feature A1 can always keep the gaming machine and the detection information linked one-to-one, regardless of the state of the gaming machine (the state of being installed in an amusement hall or the state of circulation), and the characteristics of the gaming machine can be managed and inspected. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴A2]
特徴A1に記載の遊技機であって、
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、前記制御手段と同一の電源によって動作する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A2]
A gaming machine according to feature A1,
A control means (
The processing execution means is operated by the same power source as the control means.
特徴A2によれば、処理実行手段は、制御手段と同一の電源によって動作するので、例えば、当該遊技機が遊技ホールに設置されている場合であって、ホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得していた場合に、当該ホールコンピュータの電源系統に不具合が生じた場合や、当該ホールコンピュータの処理に不具合が生じた場合であっても、遊技機に電源が供給されている状況であれば、検知情報を取得することができる。仮に、制御手段と処理実行手段とが異なる電源によって動作している場合、処理実行手段の電源供給に不具合があった場合に、遊技機によって遊技が実行されているにも関わらず検知情報が取得できないといった不具合が生じる。これに対して、特徴A2によれば、制御手段と処理実行手段とが同一の電源によって動作しているので、遊技が実行可能な状況であれば必ず検知情報を取得することができる。よって、検知情報の信頼性を向上させることができる。 According to feature A2, the process execution means operates on the same power source as the control means. Therefore, for example, when the gaming machine is installed in an amusement hall and a hall computer is acquiring information about the characteristics of the gaming machine, even if a malfunction occurs in the power supply system of the hall computer or in the processing of the hall computer, the detection information can be acquired as long as power is being supplied to the gaming machine. If the control means and the process execution means operate on different power sources, a malfunction in the power supply to the process execution means will result in a malfunction in which the detection information cannot be acquired even though a game is being played by the gaming machine. In contrast, according to feature A2, the control means and the process execution means operate on the same power source, so that the detection information can always be acquired as long as a game can be played. This improves the reliability of the detection information.
[特徴A3]
特徴A1または特徴A2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、所定の検知手段(排出通路検知センサー44h)によって規定個数(500個)の遊技球が検知されるまでの期間毎の前記検知情報を記憶する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A3]
A gaming machine according to feature A1 or feature A2,
The information storage means stores the detection information for each period until a specified number (500) of gaming balls are detected by a predetermined detection means (discharge
特徴A3によれば、所定の検知手段によって規定個数の遊技球が検知されるまでの期間毎の検知情報を記憶するので、各遊技機によって規定個数の遊技球が検知されるまでの時間にバラつきがあったとしても、その時間のバラつきに影響しない検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、遊技球が発射される頻度に高低差がある場合であっても、その影響を受けにくい精度の高い検知情報を取得することができる。 According to feature A3, since detection information for each period until a specified number of game balls is detected by a specified detection means is stored, even if there is variation in the time until a specified number of game balls is detected by each gaming machine, it is possible to obtain detection information that is not affected by the variation in time. In other words, even if there is a difference in the frequency at which game balls are released, it is possible to obtain highly accurate detection information that is not easily affected by this.
[特徴A4]
特徴A1または特徴A2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、予め設定された規定期間毎(1時間毎)の前記検知情報を記憶する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A4]
A gaming machine according to feature A1 or feature A2,
The information storage means stores the detection information for each preset specified period (every hour).
特徴A4によれば、情報記憶手段は、予め設定された規定期間毎の検知情報を記憶するので、当該検知情報を用いて時間の概念を用いた統計処理を行うことができる。 According to feature A4, the information storage means stores the detection information for each predetermined period, and the detection information can be used to perform statistical processing using the concept of time.
[特徴A5]
特徴A1または特徴A2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、当該遊技機への電源の供給が開始されてから前記電源が遮断されるまでの期間毎の前記検知情報を記憶する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A5]
A gaming machine according to feature A1 or feature A2,
The information storage means stores the detection information for each period from when power supply to the gaming machine is started to when the power is cut off.
特徴A5によれば、情報記憶手段は、当該遊技機への電源の供給が開始されてから電源の遮断が発生するまでの期間毎の検知情報を記憶するので、例えば、遊技機が遊技ホールに設置されている場合には、遊技ホールの営業日ごとの検知情報を取得することができる。 According to feature A5, the information storage means stores detection information for each period from when power supply to the gaming machine starts to when power is cut off. For example, if the gaming machine is installed in an amusement hall, it is possible to obtain detection information for each business day of the amusement hall.
[特徴A6]
特徴A1から特徴A5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として前記払出手段から払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を取得する賞球数情報取得手段と、
前記検知情報と前記賞球数情報とに基づいて所定の演算を実行する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
を備え、
前記情報記憶手段は、前記演算実行手段による演算結果(役物比率等)に関する情報である演算結果情報を記憶する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature A6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features A1 to A5,
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
Equipped with
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information acquisition means for acquiring prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) paid out from the payout means as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A calculation execution means (CPU 308) that executes a predetermined calculation based on the detection information and the winning ball number information;
Equipped with
The information storage means stores calculation result information which is information regarding the calculation result (such as the ratio of game elements) by the calculation execution means.
特徴A6によれば、処理実行手段は、演算結果情報を記憶する。演算結果情報は、検知情報と賞球数情報とに基づいて演算された情報であるので、遊技機が払い出した賞球数に関する情報が反映されている。よって、特徴A6によれば、払い出した賞球に関する遊技機の特性を取得することができる。この結果、払い出した賞球に関する遊技機の特性を管理することができる。 According to feature A6, the processing execution means stores calculation result information. The calculation result information is information calculated based on the detection information and the prize ball number information, and therefore reflects information regarding the number of prize balls paid out by the gaming machine. Therefore, according to feature A6, it is possible to obtain the characteristics of the gaming machine related to the prize balls paid out. As a result, it is possible to manage the characteristics of the gaming machine related to the prize balls paid out.
<特徴B群>
特徴B群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group B>
The group of features B is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴B1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された第1の情報と予め設定されている第2の情報とに基づいて演算処理を実行し第3の情報を取得する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
前記第3の情報を不揮発的に記憶する情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記演算実行手段と前記情報記憶手段とは、前記制御手段と同一の電源によって動作する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature B1]
A control means (
A calculation execution means (CPU 308) for executing a calculation process based on first information acquired based on a game that has been executed and second information that has been set in advance, and acquiring third information;
an information storage means (a
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine, wherein the calculation execution means and the information storage means are operated by the same power source as the control means.
特徴B1によれば、第1の情報は実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であり、第3の情報は第1の情報に基づいて取得された情報である。よって、第3の情報は、実行された遊技に関する情報を含んでいる。したがって、情報記憶手段は、実行された遊技に関する情報を含んだ第3の情報を記憶しているので、情報記憶手段に記憶された第3の情報を用いて、過去に実行された遊技に関する情報を取得することが可能である。よって、第3の情報を用いることによって、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理することが可能となる。そして、演算実行手段と情報記憶手段とは、制御手段と同一の電源によって動作するので、遊技機に電源が供給されている状況であれば、第3の情報を取得することができる。仮に、演算実行手段および情報記憶手段と制御手段とが異なる電源によって動作している場合、演算実行手段および情報記憶手段の電源供給に不具合があった場合に、遊技機によって遊技が実行されているにも関わらず第3の情報が取得できないといった不具合が生じる。これに対して、特徴B2によれば、演算実行手段および情報記憶手段と制御手段とが同一の電源によって動作しているので、遊技が実行可能な状況であれば必ず第3の情報を取得することができる。よって、第3の情報の信頼性を向上させることができる。この結果、遊技機の検査の信頼性を向上させることができ、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature B1, the first information is information acquired based on the executed game, and the third information is information acquired based on the first information. Thus, the third information includes information on the executed game. Therefore, since the information storage means stores the third information including information on the executed game, it is possible to acquire information on the games executed in the past using the third information stored in the information storage means. Thus, by using the third information, it is possible to manage the characteristics of the game of the gaming machine. And since the calculation execution means and the information storage means are operated by the same power source as the control means, the third information can be acquired if the gaming machine is supplied with power. If the calculation execution means, the information storage means, and the control means are operated by different power sources, if there is a problem with the power supply of the calculation execution means and the information storage means, a problem occurs in which the third information cannot be acquired even though the gaming machine is executing a game. In contrast, according to feature B2, since the calculation execution means, the information storage means, and the control means are operated by the same power source, the third information can be acquired without fail if the game is executable. Thus, the reliability of the third information can be improved. As a result, the reliability of gaming machine inspections can be improved, and the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴B2]
特徴B1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶された前記第3の情報を、前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に送信する送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature B2]
A gaming machine according to feature B1,
A gaming machine comprising a transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the third information stored in the information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴B2によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶された第3の情報を、遊技機に接続された所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備えるので、所定の装置を利用して、第3の情報を用いた遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理することが可能となる。 According to feature B2, a transmission means is provided for transmitting the third information stored in the information storage means to a specified device connected to the gaming machine, so that it is possible to use the specified device to manage the characteristics related to the gaming machine's play using the third information.
[特徴B3]
特徴B1または特徴B2に記載の遊技機であって、
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
を備え、
前記第1の情報は、前記検知手段による検知に基づいて取得された情報であり、
前記第2の情報は、前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として前記払出手段から払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報であり、
前記第3の情報は、実行された遊技において遊技機が払い出した賞球数に関する情報である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature B3]
A gaming machine according to feature B1 or feature B2,
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
Equipped with
the first information is information acquired based on detection by the detection means,
The second information is information regarding the number of game balls (number of prize balls) paid out from the payout means as prize balls set in each of the plurality of detection means,
The gaming machine, characterized in that the third information is information regarding the number of winning balls paid out by the gaming machine in the executed game.
特徴B3によれば、第3の情報は、実行された遊技において遊技機が払い出した賞球数に関する情報である。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている第3の情報を用いて、実際に払い出した賞球に関する遊技機の特性を管理することができる。 According to feature B3, the third information is information regarding the number of prize balls paid out by the gaming machine in the executed game. Therefore, the third information stored in the information storage means can be used to manage the characteristics of the gaming machine regarding the prize balls actually paid out.
<特徴C群>
特徴C群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group C>
The group of features C is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴C1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された第1の情報を不揮発的に記憶する情報記憶手段(レジスタ304、演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature C1]
A control means (
An information storage means (register 304, memory for storing calculation results 309) for non-volatilely storing first information acquired based on a game that has been executed;
A gaming machine comprising:
The information storage means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a seal sticker affixed) that shows signs of opening and closing.
特徴C1によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、情報記憶手段を格納している。したがって、情報記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、情報記憶手段に記憶されている第1の情報が情報記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、第1の情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に情報記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる第1の情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、第1の情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、第1の情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴C1によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した第1の情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature C1, the information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when the information storage means is physically touched, traces of opening the cabinet are left. Therefore, if the first information stored in the information storage means is altered through physical contact with the information storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the cabinet. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the first information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution. However, since the information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the first information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the first information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the first information. Therefore, according to feature C1, unauthorized alteration of the first information reflecting the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine can be prevented, and the gaming machine can be properly managed and inspected. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴C2]
特徴C1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、前記制御手段と同一の電源によって動作する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature C2]
A gaming machine according to feature C1,
The gaming machine, wherein the information storage means is operated by the same power source as the control means.
特徴C2によれば、情報記憶手段は、制御手段と同一の電源によって動作するので、遊技機に電源が供給されている状況であれば、第1の情報を取得することができる。仮に、情報記憶手段と制御手段とが異なる電源によって動作している場合、情報記憶手段の電源供給に不具合があった場合に、遊技機によって遊技が実行されているにも関わらず第1の情報が取得できないといった不具合が生じる。これに対して、特徴C2によれば、情報記憶手段と制御手段とが同一の電源によって動作しているので、遊技が実行可能な状況であれば必ず第1の情報を取得することができる。よって、第1の情報の信頼性を向上させることができる。この結果、遊技機の検査の信頼性を向上させることができ、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature C2, since the information storage means and the control means are operated by the same power source, the first information can be acquired as long as power is being supplied to the gaming machine. If the information storage means and the control means were operated by different power sources, a malfunction in the power supply to the information storage means would result in a malfunction in which the first information cannot be acquired even though a game is being played by the gaming machine. In contrast, according to feature C2, since the information storage means and the control means are operated by the same power source, the first information can be acquired without fail as long as a game can be played. This makes it possible to improve the reliability of the first information. As a result, it is possible to improve the reliability of inspections of gaming machines and improve the soundness of play.
[特徴C3]
特徴C1または特徴C2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第1の情報を、前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に送信する送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature C3]
A gaming machine according to feature C1 or feature C2,
A gaming machine comprising: a transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the first information to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴C3によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶された第1の情報を、遊技機に接続された所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備えるので、所定の装置を利用して、第1の情報を用いた遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。 According to feature C3, a transmission means is provided for transmitting the first information stored in the information storage means to a specified device connected to the gaming machine, so that it is possible to use the specified device to manage and inspect the characteristics related to play of the gaming machine using the first information.
<特徴D群>
特徴D群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature D group>
The group of features D is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴D1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する第1の賞球数情報記憶手段(主側ROM63)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記第1の賞球数記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報を取得する賞球数情報取得手段と、
前記賞球数情報取得手段によって取得された前記賞球数情報を記憶する第2の賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶する個数情報記憶手段(レジスタ304)と、
前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技球の個数に関する情報と前記第2の賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて演算を実行することによって、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
前記演算実行手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature D1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A first prize ball number information storage means (main ROM 63) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information acquisition means for acquiring the prize ball number information stored in the first prize ball number storage means;
A second prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing the prize ball number information acquired by the prize ball number information acquisition means;
A number information storage means (register 304) for storing information regarding the number of game balls detected by the detection means;
a calculation execution means (CPU 308) for calculating game history information (such as a ratio of prize balls) which is information relating to a game history by performing calculations based on information relating to the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means and the prize ball number information stored in the second prize ball number information storage means;
a game history information storage means (a calculation result storage memory 309) for storing the game history information calculated by the calculation execution means;
A gaming machine comprising:
遊技機に設定されている賞球数情報は、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に異なる値が設定されていることが一般的である。 The number of prize balls information set for gaming machines is generally set to a different value for each type (model) of gaming machine.
特徴D1によれば、処理実行手段は、第1の賞球数記憶手段に記憶されている賞球数情報を取得するので、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に異なる賞球数情報が設定されていても、処理実行手段は、遊技機の種類毎に設定された賞球数情報を用いて正しい遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。 According to feature D1, the processing execution means acquires the prize ball number information stored in the first prize ball number storage means, so that even if different prize ball number information is set for each type (model) of gaming machine, the processing execution means can calculate correct gaming history information using the prize ball number information set for each type of gaming machine.
遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていると、算出された遊技履歴情報が、想定された値とは異なる不自然な値になる場合がある。したがって、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 If a gaming machine has been illegally tampered with, the calculated gaming history information may have unnatural values that differ from expected values. Therefore, by checking the gaming history information, an inspector of the gaming machine can properly determine whether or not the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴D2]
特徴D1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第1の賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報を含む信号を前記処理実行手段に送信する賞球数情報送信手段(CPU62x)を備え、
前記取得手段は、前記賞球数情報送信手段から送信された前記信号を受信することによって前記賞球数情報を取得する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature D2]
A gaming machine according to feature D1,
a prize ball number information transmission means (
A gaming machine characterized in that the acquisition means acquires the prize ball number information by receiving the signal transmitted from the prize ball number information transmission means.
特徴D2によれば、第1の賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている賞球数情報を含む信号を処理実行手段に送信するので、処理実行手段が第1の賞球数記憶手段にアクセスすることができない構成や、処理実行手段が第1の賞球数記憶手段に記憶されている賞球数情報の記憶位置(メモリアドレス)を把握することができない構成であっても、処理実行手段が第1の賞球数記憶手段に記憶されている賞球数情報を取得することが可能となる。 According to feature D2, a signal including the prize ball number information stored in the first prize ball number information storage means is transmitted to the processing execution means, so that even in a configuration in which the processing execution means is unable to access the first prize ball number storage means or in which the processing execution means is unable to grasp the storage location (memory address) of the prize ball number information stored in the first prize ball number storage means, the processing execution means is able to obtain the prize ball number information stored in the first prize ball number storage means.
[特徴D3]
特徴D1または特徴D2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を送信する遊技履歴情報送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature D3]
A gaming machine according to feature D1 or feature D2,
A gaming machine comprising: a gaming history information transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴D3によれば、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の装置に送信されるので、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature D3, the gaming history information of the gaming machine is transmitted to a specified device, which is then capable of displaying the gaming history information of the gaming machine. Then, an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information displayed on the specified device.
[特徴D4]
特徴D1から特徴D3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature D4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features D1 to D3,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means.
特徴D4によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature D4, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
[特徴D5]
特徴D1から特徴D4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記発射手段は、前記処理実行手段において前記賞球数情報の前記第2の賞球数情報記憶手段への記憶が完了するまでは遊技球の発射を実行することができないように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature D5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features D1 to D4,
A gaming machine characterized in that the launching means is configured such that it cannot execute the launch of gaming balls until the processing execution means has completed storing the prize ball number information in the second prize ball number information storage means.
特徴D5によれば、賞球数情報の第2の賞球数情報記憶手段への記憶が完了するまでは遊技球が発射されないので、演算実行手段による遊技履歴情報の算出対象から遊技球が漏れてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature D5, the game balls are not released until the storage of the prize ball number information in the second prize ball number information storage means is completed, so that it is possible to prevent the game balls from being omitted from the calculation of the game history information by the calculation execution means.
<特徴E群>
特徴E群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Features Group E>
The group of features E is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴E1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶する個数情報記憶手段(レジスタ304)と、
前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている所定の検知手段(排出通路検知センサー44h)によって検知された遊技球の個数(排出通路通過個数NOUT)が規定値(500個)に達する毎に、前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技球の個数に関する情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて演算を実行することによって、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
前記演算実行手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature E1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A number information storage means (register 304) for storing information regarding the number of game balls detected by the detection means;
a calculation execution means (CPU 308) for calculating game history information ( such as a ratio of game devices) which is information relating to a game history, by executing calculations based on information relating to the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means and the prize ball number information stored in the prize ball number information storage means each time the number of game balls (the number of game balls passing through the discharge passage N OUT ) detected by a predetermined detection means (the discharge
a game history information storage means (a calculation result storage memory 309) for storing the game history information calculated by the calculation execution means;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴E1によれば、所定の検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数が規定値に達する毎に遊技履歴情報を算出するので、各遊技機によって検知された遊技球の個数が規定値に達するまでの時間にバラつきがあったとしても、その時間のバラつきに影響しない遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。すなわち、遊技球が検知される頻度に高低差がある場合であっても、その影響を受けにくい精度の高い遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。この結果、遊技機の検査者は、精度の高い遊技履歴情報を確認することができ、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature E1, game history information is calculated each time the number of game balls detected by a specified detection means reaches a specified value. Therefore, even if there is variation in the time it takes for the number of game balls detected by each gaming machine to reach the specified value, game history information that is not affected by the variation in time can be calculated. In other words, even if there is a difference in the frequency with which game balls are detected, highly accurate game history information that is less affected by this can be calculated. As a result, an inspector of the gaming machine can confirm highly accurate game history information and can properly determine whether the gaming machine has been tampered with. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴E2]
特徴E1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記演算を実行する条件である演算実行条件として、前記所定の検知手段(排出通路検知センサー44h)及び前記規定値(500個)に関する情報を記憶する第1の演算実行条件記憶手段(主側ROM63)を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記第1の演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている前記演算実行条件を取得する演算実行条件取得手段と、
前記取得された前記演算実行条件を記憶する第2の演算実行条件記憶手段(演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307)と、
を備え、
前記演算実行手段は、前記第2の演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている前記演算実行条件が成立した場合に、前記演算を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature E2]
A gaming machine according to feature E1,
a first calculation execution condition storage means (main ROM 63) for storing information regarding the predetermined detection means (the discharge
The process execution means includes:
an operation execution condition acquisition means for acquiring the operation execution condition stored in the first operation execution condition storage means;
a second calculation execution condition storage means (a calculation execution condition storage memory 307) for storing the obtained calculation execution condition;
Equipped with
The operation execution means executes the operation when the operation execution condition stored in the second operation execution condition storage means is established.
遊技機の種類(機種)が異なると、遊技の特性も異なるため、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行する最適な条件も異なることになる。このため、演算実行条件は、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に異なる条件が記憶されている。 Differing types (models) of gaming machines have different game characteristics, and therefore the optimal conditions for executing the calculations to calculate the gaming history information also differ. For this reason, different calculation execution conditions are stored for each type (model) of gaming machine.
特徴E2によれば、処理実行手段は、第1の演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている演算実行条件を取得するので、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に設定された演算実行条件が成立した場合に演算を実行することができる。 According to feature E2, the process execution means acquires the calculation execution conditions stored in the first calculation execution condition storage means, and can execute a calculation when the calculation execution conditions set for each type (model) of gaming machine are met.
[特徴E3]
特徴E1または特徴E2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記演算実行手段が前記演算を実行した後に、前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている遊技球の個数に関する情報を消去する消去手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature E3]
A gaming machine according to feature E1 or feature E2,
The process execution means includes:
a deletion means for deleting information regarding the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means after the calculation execution means executes the calculation.
特徴E3によれば、演算実行手段が演算を実行した後に、個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている遊技球の個数に関する情報を消去するので、再び個数情報記憶手段に遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶することが可能となる。したがって、個数情報記憶手段に必要な記憶容量を低減することができる。 According to feature E3, after the calculation execution means executes a calculation, the information regarding the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means is erased, so that it becomes possible to store information regarding the number of game balls in the number information storage means again. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the storage capacity required for the number information storage means.
[特徴E4]
特徴E1から特徴E3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を送信する遊技履歴情報送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature E4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features E1 to E3,
A gaming machine comprising: a gaming history information transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴E4によれば、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の装置に送信されるので、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature E4, the gaming history information of the gaming machine is transmitted to a specified device, which is then capable of displaying the gaming history information of the gaming machine. Then, an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information displayed on the specified device.
[特徴E5]
特徴E1から特徴E4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature E5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features E1 to E4,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means.
特徴E5によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature E5, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
<特徴F群>
特徴F群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature Group F>
The group of features F is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴F1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶する個数情報記憶手段(レジスタ304)と、
所定時間(1時間)が経過する毎に、前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技球の個数に関する情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて演算を実行することによって、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
前記演算実行手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature F1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A number information storage means (register 304) for storing information regarding the number of game balls detected by the detection means;
a calculation execution means (CPU 308) for calculating game history information (such as a ratio of game devices) which is information relating to a game history by performing calculations based on information relating to the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means and the number of prize balls information stored in the number of prize balls information storage means every time a predetermined time (one hour) has elapsed;
a game history information storage means (a calculation result storage memory 309) for storing the game history information calculated by the calculation execution means;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴F1によれば、所定時間が経過する毎に遊技履歴情報を算出するので、遊技機の検査者は、時間の概念を用いた統計処理によって算出された遊技履歴情報を確認することができ、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature F1, the gaming history information is calculated every time a predetermined time has elapsed, so that the gaming machine inspector can check the gaming history information calculated by statistical processing using the concept of time, and can properly determine whether the gaming machine has been tampered with in any way. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴F2]
特徴F1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記演算を実行する条件である演算実行条件として、前記演算を実行する時間的間隔に関する情報を記憶する第1の演算実行条件記憶手段(主側ROM63)を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている前記演算実行条件を取得する演算実行条件取得手段と、
前記取得された前記演算実行条件を記憶する第2の演算実行条件記憶手段(演算実行条件記憶用メモリ307)と、
を備え、
前記演算実行手段は、前記第2の演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている前記演算実行条件が成立した場合に、前記演算を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature F2]
A gaming machine according to feature F1,
a first calculation execution condition storage means (main ROM 63) for storing information on a time interval for executing the calculation as a calculation execution condition that is a condition for executing the calculation;
The process execution means includes:
a calculation execution condition acquisition means for acquiring the calculation execution conditions stored in the calculation execution condition storage means;
a second calculation execution condition storage means (a calculation execution condition storage memory 307) for storing the obtained calculation execution condition;
Equipped with
The operation execution means executes the operation when the operation execution condition stored in the second operation execution condition storage means is established.
遊技機の種類(機種)が異なると、遊技の特性も異なるため、遊技履歴情報を算出するための演算を実行する最適な条件も異なることになる。このため、演算実行条件は、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に異なる条件が記憶されている。 Differing types (models) of gaming machines have different game characteristics, and therefore the optimal conditions for executing the calculations to calculate the gaming history information also differ. For this reason, different calculation execution conditions are stored for each type (model) of gaming machine.
特徴F2によれば、処理実行手段は、第1の演算実行条件記憶手段に記憶されている演算実行条件を取得するので、遊技機の種類(機種)毎に設定された演算実行条件が成立した場合に演算を実行することができる。 According to feature F2, the process execution means acquires the calculation execution conditions stored in the first calculation execution condition storage means, and can execute a calculation when the calculation execution conditions set for each type (model) of gaming machine are met.
[特徴F3]
特徴F1または特徴F2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記演算が実行されてからの経過時間を計測する計測手段と、
遊技者によって遊技が行なわれているか否かを判定する判定手段と、
を備え、
前記計測手段は、前記判定手段によって遊技が行なわれていないと判定されている期間は、前記経過時間の計測を中断する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature F3]
A gaming machine according to feature F1 or feature F2,
A measuring means for measuring an elapsed time since the execution of the calculation;
A determination means for determining whether or not a game is being played by a player;
Equipped with
The measuring means interrupts measurement of the elapsed time during a period during which the determining means determines that a game is not being played.
特徴F3によれば、遊技が行なわれていないと判定されている期間は、演算が実行されてからの経過時間の計測を中断するので、実際に遊技が行なわれている期間のみを対象として遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。 According to feature F3, during the period when it is determined that no play is being performed, measurement of the elapsed time since the calculation is performed is suspended, so that the game history information can be calculated only for the period when the game is actually being performed.
[特徴F4]
特徴F1から特徴F3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を送信する遊技履歴情報送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature F4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features F1 to F3,
A gaming machine comprising: a gaming history information transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴F4によれば、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の装置に送信されるので、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature F4, the gaming history information of the gaming machine is transmitted to a specified device, which makes it possible for the specified device to display the gaming history information of the gaming machine. Then, an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information displayed on the specified device.
[特徴F5]
特徴F1から特徴F4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature F5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features F1 to F4,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means.
特徴F5によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature F5, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
<特徴G群>
特徴G群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature Group G>
The group of features G is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴G1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
電源の遮断の発生を監視する監視手段(停電監視回路86)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶する個数情報記憶手段(レジスタ304)と、
前記監視手段が電源の遮断の発生を検知した場合に、前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技球の個数に関する情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて演算を実行することによって、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する演算実行手段(CPU308)と、
前記演算実行手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature G1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A monitoring means (power failure monitoring circuit 86) for monitoring the occurrence of a power interruption;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A number information storage means (register 304) for storing information regarding the number of game balls detected by the detection means;
a calculation execution means (CPU 308) for calculating game history information (such as a ratio of game devices) which is information relating to a game history, by executing calculations based on information relating to the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means and the number of prize balls information stored in the number of prize balls information storage means when the monitoring means detects a power interruption;
a game history information storage means (a calculation result storage memory 309) for storing the game history information calculated by the calculation execution means;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴G1によれば、電源の遮断の発生を検知した場合に遊技履歴情報を算出するので、遊技機への電源の供給が開始されてから電源の遮断が発生するまでの期間中において検知された遊技球の個数に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。すなわち、遊技ホールの営業が開始してから終了するまでの期間毎に遊技履歴情報が算出されるので、遊技ホールの営業日毎に遊技履歴情報が算出されることになる。したがって、遊技機の検査者は、遊技ホールの営業日を跨いで遊技履歴情報の特性に変化があったか否かを容易に把握することができるので、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature G1, the gaming history information is calculated when a power interruption is detected, so that the gaming history information can be calculated based on the number of gaming balls detected during the period from when power is supplied to the gaming machine to when a power interruption occurs. In other words, the gaming history information is calculated for each period from when the amusement hall opens to when it closes, so that the gaming history information is calculated for each business day of the amusement hall. Therefore, an inspector of the gaming machine can easily determine whether there has been a change in the characteristics of the gaming history information across business days of the amusement hall, making it possible to properly determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴G2]
特徴G1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記電源の遮断が発生した後においても前記演算実行手段に対して電源を供給する供給手段(コンデンサ)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature G2]
A gaming machine according to feature G1,
A gaming machine comprising a supply means (capacitor) for supplying power to the calculation execution means even after a power interruption occurs.
特徴G2によれば、電源の遮断が発生した後においても演算実行手段に対して電源を供給する供給手段を備えるので、演算実行手段による遊技履歴情報の算出及び遊技履歴情報の遊技履歴情報記憶手段への記憶を確実に完了させることができる。 According to feature G2, since a supply means is provided for supplying power to the calculation execution means even after a power interruption occurs, it is possible to reliably complete the calculation of the game history information by the calculation execution means and the storage of the game history information in the game history information storage means.
[特徴G3]
特徴G1または特徴G2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を送信する遊技履歴情報送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature G3]
A gaming machine according to feature G1 or feature G2,
A gaming machine comprising: a gaming history information transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴G3によれば、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の装置に送信されるので、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature G3, the gaming history information of the gaming machine is transmitted to a specified device, which is then able to display the gaming history information of the gaming machine. Then, an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information displayed on the specified device.
[特徴G4]
特徴G1から特徴G3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature G4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features G1 to G3,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means.
特徴G4によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature G4, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
<特徴H群>
特徴H群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature H Group>
The group of features H is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴H1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
所定の場合に報知をする報知手段と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の個数に関する情報を記憶する個数情報記憶手段(レジスタ304)と、
前記個数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技球の個数に関する情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する算出手段(CPU308)と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309)と、
を備え、
前記報知手段は、前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶された前記遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A notification means for notifying in a predetermined case;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A number information storage means (register 304) for storing information regarding the number of game balls detected by the detection means;
A calculation means (CPU 308) for calculating game history information (such as a ratio of game features) which is information regarding a game history based on information regarding the number of game balls stored in the number information storage means and the prize ball number information stored in the prize ball number information storage means;
a game history information storage means (a memory for storing calculation results 309) for storing the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
Equipped with
The notification means issues a notification when the game history information stored in the game history information storage means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴H1によれば、遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature H1, an alert is issued when the gaming history information does not satisfy a predetermined condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose gaming history information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. Then, by checking the gaming history information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴H2]
特徴H1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶された前記遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H2]
A gaming machine according to feature H1,
The notification means is configured to provide a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴H2によれば、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature H2, an alert is issued when a specific value included in the gaming history information falls outside of a predetermined range, allowing a gaming machine inspector to easily find a gaming machine whose specific value included in the gaming history information falls outside of the predetermined range. Then, by checking the gaming history information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴H3]
特徴H2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H3]
A gaming machine according to feature H2,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴H3によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature H3, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value included in the gaming history information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴H4]
特徴H1から特徴H3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features H1 to H3,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴H4によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature H4, since a display means is provided that displays a predetermined display as a notification, an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the gaming history information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
[特徴H5]
特徴H1から特徴H4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を送信する遊技履歴情報送信手段(CPU308)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features H1 to H4,
A gaming machine comprising: a gaming history information transmitting means (CPU 308) for transmitting the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine.
特徴H5によれば、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の装置に送信されるので、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。そして、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置に表示された遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature H5, the gaming history information of the gaming machine is transmitted to a specified device, which is then capable of displaying the gaming history information of the gaming machine. Then, an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information displayed on the specified device.
[特徴H6]
特徴H1から特徴H5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature H6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features H1 to H5,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means.
特徴H6によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature H6, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
<特徴I群>
特徴I群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group I>
The group I of features is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴I1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて賞球として遊技球を払い出す払出手段(払出装置71)と、
所定の処理を実行する処理実行手段(遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(賞球数データ記憶用メモリ306)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知される毎に、当該検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことを示す情報である入球情報を順次記憶する入球情報記憶手段(入球情報記憶用メモリ309b)と、
前記遊技機に接続された所定の装置(検査機320)に対して、前記入球情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記入球情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とを送信する送信手段(CPU308)と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature I1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A payout means (payout device 71) that pays out game balls as prize balls based on the game balls detected by the detection means;
A processing execution means (game history management chip 300) for executing a predetermined process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
A prize ball number information storage means (a prize ball number data storage memory 306) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
A ball entry information storage means (a ball entry
a transmission means (CPU 308) for transmitting the winning ball information stored in the winning ball information storage means and the number of winning balls information stored in the number of winning balls information storage means to a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) connected to the gaming machine;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴I1によれば、所定の装置に対して入球情報と賞球数情報とを送信するので、所定の装置は、入球情報と賞球数情報とに基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報を任意の範囲で算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の検査者は、所定の装置によって、任意の範囲で算出された当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができ、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを適切に判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature I1, ball entry information and prize ball count information are transmitted to a specified device, so that the specified device can calculate gaming history information, which is information about the gaming history, within any range based on the ball entry information and prize ball count information. Therefore, a gaming machine inspector can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine calculated within any range by the specified device, and can properly determine whether the gaming machine has been tampered with or not. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴I2]
特徴I1に記載の遊技機であって、
日時に関する情報である日時情報を取得する日時情報取得手段(RTC96)を備え、
前記入球情報記憶手段は、前記入球情報を記憶する際に、前記遊技球が前記検知手段によって検知された日時に対応した前記日時情報を付加して記憶する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature I2]
A gaming machine according to feature I1,
A time and date information acquisition unit (RTC 96) is provided for acquiring time and date information, which is information related to time and date;
A gaming machine characterized in that, when storing the ball entry information, the ball entry information storage means stores the ball entry information by adding the date and time information corresponding to the date and time when the gaming ball was detected by the detection means.
特徴I2によれば、日時情報が付加された入球情報を受信した所定の装置は、日時の範囲を指定して遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。したがって、遊技機の検査者は、日時の範囲を指定した遊技履歴情報に基づいて詳細な検査をすることができる。また、日時情報が付加された入球情報を所定の装置が表示する構成とすれば、遊技機の検査者は、各検知手段によって遊技球が検知された日時についても把握することが可能となる。 According to feature I2, a specified device that receives ball entry information with date and time information attached can specify a date and time range and calculate game history information. Therefore, a gaming machine inspector can perform a detailed inspection based on the game history information with a specified date and time range. Furthermore, if the specified device is configured to display the ball entry information with date and time information attached, the gaming machine inspector can also know the date and time when the gaming ball was detected by each detection means.
[特徴I3]
特徴I1または特徴I2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記入球情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記入球情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature I3]
A gaming machine according to feature I1 or feature I2,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the winning information stored in the winning information storage means.
特徴I3によれば、入球情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、入球情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の入球情報を確認することができる。 According to feature I3, the winning ball information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that the person inspecting the gaming machine can check the winning ball information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the winning ball information.
<特徴J群>
特徴J群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group J>
The group of features J is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴J1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記複数の検知手段のそれぞれに設定された賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数(賞球数)に関する情報である賞球数情報(賞球数データ)を記憶する賞球数情報記憶手段(主側ROM63)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)を実行するとともに、前記検知手段によって検知された遊技球の検知情報と前記賞球数情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記賞球数情報とに基づいて演算を実行することによって遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等)を算出する処理を実行する処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記処理実行手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段(主側RAM64、フラッシュメモリ64x)と、
を備えることを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A prize ball number information storage means (main ROM 63) for storing prize ball number information (prize ball number data) which is information regarding the number of game balls (prize ball number) to be paid out as prize balls set for each of the plurality of detection means;
a processing execution means (
A game history information storage means (
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴J1によれば、遊技履歴情報を記憶する遊技履歴情報記憶手段を備える。遊技履歴情報は、遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該遊技履歴情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、遊技履歴情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴J1によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である遊技履歴情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から遊技履歴情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができない。特徴J1の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である遊技履歴情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から遊技履歴情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴J1によれば、遊技機と遊技履歴情報とを1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature J1, the gaming machine is provided with a gaming history information storage means for storing gaming history information. Since the gaming history information is information that correlates with the behavior of the gaming ball in a game, the gaming history information differs for each gaming machine and is information specific to the gaming machine. In other words, the gaming history information is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine. According to feature J1, the gaming history information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine is stored in a gaming history information storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, the characteristics of the gaming machine can be inspected by acquiring the gaming history information from the gaming machine main body itself. When the gaming machine is installed in a gaming hall, information on the characteristics of the gaming machine can be acquired by the hall computer installed in the gaming hall. However, since gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where the gaming machine is not connected to the hall computer, in which case, with a conventional gaming machine, information on the characteristics of the gaming machine cannot be acquired. A gaming machine with feature J1 stores gaming history information, which is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine, in a gaming history information storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body, so that the gaming history information can be obtained from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, feature J1 makes it possible to link the gaming machine and the gaming history information one-to-one, and to manage and inspect the characteristics of the gaming machine. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
さらに、特徴J1によれば、単一の処理実行手段が遊技進行処理と遊技履歴情報を算出する処理とを実行するので、当該算出処理を実行するための別の演算用チップ等を設ける必要がなく、遊技機の製造コストを低減させることができる。 Furthermore, according to feature J1, a single processing execution means executes the game progress processing and the processing for calculating the game history information, so there is no need to provide a separate arithmetic chip or the like for executing the calculation processing, and the manufacturing costs of the gaming machine can be reduced.
[特徴J2]
特徴J1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第2のモードでは、遊技球が前記所定の領域を通過した場合であっても、前記遊技進行処理を実行しないように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J2]
A gaming machine according to feature J1,
The process execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
The gaming machine is characterized in that, in the second mode, the gaming progress process is not executed even if the gaming ball passes through the specified area.
特徴J2によれば、遊技球が所定の領域を通過した場合であっても遊技進行処理を実行しない第2のモードを実行可能であるので、遊技進行処理と並行して実行することが好ましくない処理や、遊技進行処理と並行して実行した場合に不具合が生じやすい処理等を第2のモードにおいて実行することができる。また、特徴J2によれば、第2のモードにおいては遊技進行処理を実行しないので、第2のモードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムを開発する際に、遊技進行処理が並行して実行された場合における対策を考慮しなくてもよいため、第2のモードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムの開発効率を大幅に向上させることができる。 According to feature J2, it is possible to execute a second mode in which game progress processing is not executed even when the game ball passes through a specified area, so that it is possible to execute in the second mode processes that are undesirable to execute in parallel with game progress processing or processes that are likely to cause malfunctions when executed in parallel with game progress processing. In addition, according to feature J2, since game progress processing is not executed in the second mode, when developing a program for processing to be executed in the second mode, it is not necessary to consider measures to be taken in the event that game progress processing is executed in parallel, so that it is possible to significantly improve the development efficiency of programs for processing to be executed in the second mode.
[特徴J3]
特徴J2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2のモードは、前記遊技履歴情報を出力するモードである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J3]
A gaming machine according to feature J2,
The gaming machine, wherein the second mode is a mode for outputting the gaming history information.
遊技履歴情報は、遊技球が検知されて遊技進行処理が実行されると内容が変化する情報である。したがって、仮に、遊技進行処理と並行して遊技履歴情報を出力する処理を実行する構成を採用すると、遊技機の検査者が遊技履歴情報によって当該遊技機の特性を検査している間に遊技進行処理が実行されて当該遊技履歴情報の内容が随時変化してしまい、円滑に検査を実施することが困難になってしまう場合がある。これに対して、特徴J3によれば、遊技球が所定の領域を通過した場合であっても遊技進行処理を実行しない第2のモードにおいて遊技履歴情報を出力するので、遊技履歴情報を出力している間に当該遊技履歴情報の内容が変化してしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、遊技機の検査者は円滑に検査を実施することができる。 The game history information is information whose contents change when a game ball is detected and game progress processing is executed. Therefore, if a configuration is adopted in which a process for outputting game history information is executed in parallel with the game progress processing, the game progress processing may be executed while an inspector of the gaming machine is inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine using the game history information, causing the contents of the game history information to change from time to time, making it difficult to carry out the inspection smoothly. In contrast, according to feature J3, the game history information is output in a second mode in which the game progress processing is not executed even if a game ball has passed through a specified area, so that it is possible to prevent the contents of the game history information from changing while it is being output. As a result, an inspector of the gaming machine can carry out the inspection smoothly.
[特徴J4]
特徴J1から特徴J3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第1のモードにおいて前記遊技進行処理の実行中に、前記第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合)には、第2の条件が成立したタイミング(図柄の変動表示処理が終了したタイミング等の遊技進行処理が予め定められた処理段階まで完了したタイミング、実行中の各遊技進行処理の全ての処理が完了したタイミング)で、前記第1のモードから前記第2のモードに移行するように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J3,
The process execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
a gaming machine configured to transition from the first mode to the second mode when the first condition is met during execution of the game progress processing in the first mode (when the operation of pressing the mode switching button is performed, when the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the mode switching button is performed, when an
特徴J4によれば、第1のモードにおいて第1の条件が成立した場合には、第2の条件が成立したタイミングで、第1のモードから第2のモードに移行するように構成されているので、第2の条件が成立したか否かに関わらずに第1の条件が満たされた直後のタイミングで第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する構成と比較して、第2のモードに移行する際の処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature J4, when the first condition is satisfied in the first mode, the first mode is switched to the second mode at the timing when the second condition is satisfied. This can reduce the occurrence of processing errors when switching to the second mode, compared to a configuration in which the first mode is switched to the second mode immediately after the first condition is satisfied, regardless of whether the second condition is satisfied or not.
例えば、仮に、第2の条件が成立したか否かに関わらずに第1の条件が成立した直後のタイミングで第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する構成を採用した場合において、第1のモードにおいて遊技進行処理としての図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、所定の操作が実行されたという第1の条件が成立した場合には、図柄の変動表示の途中で第2のモードに移行することになり、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となる。これに対して、特徴J4によれば、例えば、第1のモードにおいて遊技進行処理としての図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、所定の操作が実行されたという第1の条件が成立した場合には、図柄の変動表示処理が実行されていないという第2の条件が成立したタイミング、すなわち、変動表示中の図柄が停止した後のタイミングで第2のモードに移行することになる。したがって、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となるといった処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the first mode is switched to the second mode immediately after the first condition is satisfied, regardless of whether the second condition is satisfied or not, if the first condition that a predetermined operation is executed during the period in which the variable display process of the pattern is being executed as the game progress process in the first mode is satisfied, the mode will be switched to the second mode in the middle of the variable display of the pattern, making it difficult to control the timing of the stop of the pattern and the variable time of the pattern. In contrast, according to feature J4, for example, if the first condition that a predetermined operation is executed during the period in which the variable display process of the pattern is being executed as the game progress process in the first mode is satisfied, the mode will be switched to the second mode at the timing when the second condition that the variable display process of the pattern is not being executed is satisfied, that is, after the variable display of the pattern has stopped. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of processing malfunctions such as making it difficult to control the timing of the stop of the pattern and the variable time of the pattern.
[特徴J5]
特徴J1から特徴J4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第2のモード中に第3の条件が成立した場合(検査モードに移行してから10分が経過した場合)には、前記第2のモードから前記第1のモードに移行させるための操作である移行操作(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作)が実行されていない場合であっても、前記第2のモードから前記第1のモードに移行するように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J4,
The process execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
a gaming machine configured to transition from the second mode to the first mode when a third condition is met during the second mode (when 10 minutes have passed since transitioning to the inspection mode), even if a transition operation (an operation of pressing a mode switching button, an operation of pressing a power button while pressing a mode switching button) for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode has not been performed.
特徴J5によれば、第2のモード中に第3の条件が成立した場合には、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させるための移行操作が実行されていない場合であっても、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行するように構成されているので、移行操作の実行がされずに第1のモードに復帰しないことを抑制することができる。例えば、第2のモードへの移行後に遊技機の管理者や検査者等が移行操作の実行を失念してしまい、遊技機が遊技進行処理を実行可能な第1のモードに復帰せず、遊技者が当該遊技機で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature J5, when the third condition is met during the second mode, even if the transition operation for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode is not performed, the system is configured to transition from the second mode to the first mode, so that it is possible to prevent a situation in which the transition operation is not performed and the system does not return to the first mode. For example, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which an administrator or inspector of the gaming machine forgets to perform the transition operation after transitioning to the second mode, causing the gaming machine to not return to the first mode in which game progress processing can be performed, and the player is unable to play on the gaming machine.
[特徴J6]
特徴J5に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第3の条件は、所定の時点から所定の時間が経過すること(検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過すること)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J6]
A gaming machine according to feature J5,
The gaming machine according to the present invention, wherein the third condition is that a predetermined time has elapsed from a predetermined point in time (10 minutes has elapsed from the point in time when the mode was changed to the inspection mode).
特徴J6によれば、第2のモード中に所定の時点から所定の時間が経過した場合には、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させるための移行操作が実行されていない場合であっても、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行するように構成されているので、移行操作の実行がされずに第1のモードに復帰しないことを確実に抑制することができる。例えば、第2のモードへの移行後に遊技機の管理者や検査者等が移行操作の実行を失念してしまった場合であっても、所定の時点から所定の時間が経過すれば第1のモードに復帰するので、遊技機が遊技進行処理を実行可能な第1のモードに復帰せず、遊技者が当該遊技機で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature J6, when a predetermined time has passed from a predetermined point in time during the second mode, the system is configured to transition from the second mode to the first mode even if a transition operation for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode has not been performed, so that it is possible to reliably prevent a situation in which the transition operation is not performed and the system does not return to the first mode. For example, even if an administrator or inspector of the gaming machine forgets to perform a transition operation after transitioning to the second mode, the system will return to the first mode when a predetermined time has passed from a predetermined point in time, so that it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the gaming machine does not return to the first mode in which game progress processing can be performed and the player is unable to play on the gaming machine.
[特徴J7]
特徴J1から特徴J6のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記遊技進行処理に関する情報を記憶する遊技進行処理情報記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するための操作である消去操作(RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作)が実行されたことに基づいて、前記遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記消去手段は、前記第2のモードに移行後であって前記第1のモードに移行する前の状態(検査モード中の状態、検査モードに移行後にそのまま電源がOFFになった状態)では、前記消去操作が実行された場合であっても、前記遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶された情報を消去しないように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J7]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J6,
A game progress processing information storage means (main RAM 64) that is stored in the cabinet of the gaming machine main body and stores information related to the game progress processing;
an erasing means for erasing the information stored in the game progress processing information storage means based on the execution of an erasing operation (an operation of pressing a power button while pressing a RAM clear button) for erasing the information stored in the game progress processing information storage means;
Equipped with
The process execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
The erasing means is configured not to erase the information stored in the game progress processing information storage means even if the erasing operation is executed in a state after transition to the second mode and before transition to the first mode (a state during the inspection mode, or a state in which the power is turned off after transition to the inspection mode).
特徴J7によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態では、遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するための消去操作が実行された場合であっても、遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶された情報を消去しないので、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態において、第1のモードに移行させようとして誤って消去操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature J7, even if an erase operation is performed to erase information stored in the game progress processing information storage means after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, the information stored in the game progress processing information storage means is not erased. Therefore, even if an erase operation is mistakenly performed in an attempt to transition to the first mode after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, the information can be prevented from being mistakenly erased.
例えば、遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するための消去操作が、消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作であり、第1のモードと第2のモードとの間でモードを移行させるための操作が、移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作である構成においては、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させようとして移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまう虞がある。しかしながら、特徴J7によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態では、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 For example, in a configuration in which the erase operation for erasing information stored in the game progress processing information storage means is the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the erase button, and the operation for transitioning between the first mode and the second mode is the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the transition button, there is a risk that when trying to transition from the second mode to the first mode by pressing the power button while pressing the transition button, the player may mistakenly press the power button while pressing the erase button. However, according to feature J7, even if the operation of accidentally pressing the power button while pressing the erase button is performed after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, it is possible to prevent the information from being mistakenly erased.
より具体的には、例えば、第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する際に、第1のモードにおいて実行していた遊技進行処理を一時的に停止させるとともに、当該停止させた遊技進行処理を第2のモードへの復帰後に再開させるための情報を遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶させる構成を採用した場合において、第2のモードから第1のモードに復帰させようとして移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合には、遊技進行処理を再開するための情報が消去されてしまい、第2のモードへの復帰後に遊技進行処理を再開させることができなくなり、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまう虞がある。これに対して、特徴J7によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態において、第1のモードに移行させようとして誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合であっても、遊技進行処理情報記憶手段に記憶された情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができるので、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 More specifically, for example, in a configuration in which the game progress processing being executed in the first mode is temporarily stopped when transitioning from the first mode to the second mode, and information for resuming the stopped game progress processing after returning to the second mode is stored in the game progress processing information storage means, if a player intends to press the power button while pressing the transition button to return from the second mode to the first mode, but accidentally presses the power button while pressing the erase button, the information for resuming the game progress processing is erased, and the game progress processing cannot be resumed after returning to the second mode, which may cause a disadvantage to the player. In contrast, according to feature J7, even if the player accidentally presses the power button while pressing the erase button to transition to the first mode after transitioning to the second mode but before transitioning to the first mode, the information stored in the game progress processing information storage means can be prevented from being erroneously erased, thereby preventing a disadvantage to the player.
[特徴J8]
特徴J1から特徴J7のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J8]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J7,
The gaming machine is characterized by comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the gaming history information.
特徴J8によれば、遊技履歴情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することができる。 According to feature J8, the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the gaming history information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the gaming history information.
[特徴J9]
特徴J1から特徴J8のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリ(フラッシュメモリ64x)によって構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J9]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J8,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the game history information storage means is composed of a non-volatile memory (
特徴J9によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれても遊技履歴情報が保持されるので、当該遊技機がいかなる状態(例えば、遊技機に電源が供給されない流通状態等)に置かれても、遊技機と遊技履歴情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。 According to feature J9, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the gaming history information is retained. Therefore, no matter what state the gaming machine is in (for example, a distribution state where the gaming machine is not supplied with power, etc.), it is possible to always keep the gaming machine and the gaming history information linked one-to-one, and the characteristics of the gaming machine can be managed and inspected.
[特徴J10]
特徴J1から特徴J9のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J10]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J9,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the game history information storage means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a sealing sticker affixed) that retains traces of opening and closing.
特徴J10によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、遊技履歴情報記憶手段が格納されている。したがって、遊技履歴情報記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶されている遊技履歴情報が遊技履歴情報記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に遊技履歴情報記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、遊技履歴情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、遊技履歴情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴J10によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した遊技履歴情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature J10, the gaming history information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when physical contact is made with the gaming history information storage means, traces of opening the cabinet are left. Therefore, if the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means is altered through physical contact with the gaming history information storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the cabinet. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the gaming history information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution, but since the gaming history information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the gaming history information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the gaming history information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the gaming history information. Therefore, according to feature J10, unauthorized alteration of the gaming history information reflecting the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine is prevented, so that the gaming machine can be properly managed and inspected. As a result, the quality of the game can be improved.
[特徴J11]
特徴J1から特徴J10のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶された前記遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J11]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J1 to J10,
a notification means for notifying a player when the game history information stored in the game history information storage means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴J11によれば、遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature J11, an alert is issued when the gaming history information does not satisfy a predetermined condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose gaming history information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. Then, by checking the gaming history information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴J12]
特徴J11に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記遊技履歴情報記憶手段に記憶された前記遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J12]
A gaming machine according to feature J11,
The notification means is configured to provide a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the gaming history information stored in the gaming history information storage means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴J12によれば、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の遊技履歴情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature J12, an alert is issued when a specific value included in the gaming history information falls outside of a predetermined range, allowing a gaming machine inspector to easily find a gaming machine whose specific value included in the gaming history information falls outside of the predetermined range. Then, by checking the gaming history information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴J13]
特徴J12に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J13]
A gaming machine according to feature J12,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴J13によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技履歴情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature J13, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value included in the gaming history information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴J14]
特徴J11から特徴J13のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature J14]
A gaming machine according to any one of features J11 to J13,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴J14によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の遊技履歴情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature J14, since a display means is provided that displays a predetermined display as a notification, an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the gaming history information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
<特徴K群>
特徴K群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature K group>
The group of features K is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴K1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
を備え、
前記遊技進行処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
所定の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第2のモードでは、遊技球が前記所定の領域を通過した場合であっても、前記遊技進行処理を実行しないように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A game progress processing execution means (
Equipped with
The game progress processing execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a certain condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
The gaming machine is characterized in that, in the second mode, the gaming progress process is not executed even if the gaming ball passes through the specified area.
特徴K1によれば、遊技球が所定の領域を通過した場合であっても遊技進行処理を実行しない第2のモードを実行可能であるので、遊技進行処理と並行して実行することが好ましくない処理や、遊技進行処理と並行して実行した場合に不具合が生じやすい処理等を第2のモードにおいて実行することができる。また、特徴K1によれば、第2のモードにおいては遊技進行処理を実行しないので、第2のモードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムを開発する際に、遊技進行処理が並行して実行された場合における対策を考慮しなくてもよいため、第2のモードにおいて実行する処理のプログラムの開発効率を大幅に向上させることができる。 According to feature K1, it is possible to execute a second mode in which game progress processing is not executed even if the game ball passes through a specified area, so that it is possible to execute in the second mode processes that are undesirable to be executed in parallel with game progress processing or processes that are likely to cause malfunctions when executed in parallel with game progress processing. In addition, according to feature K1, since game progress processing is not executed in the second mode, when developing a program for processing to be executed in the second mode, it is not necessary to consider measures to be taken in the event that game progress processing is executed in parallel, so that it is possible to significantly improve the development efficiency of programs for processing to be executed in the second mode.
[特徴K2]
特徴K1に記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、役物比率等を含む遊技履歴情報)を記憶する記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、主側RAM64、フラッシュメモリ64x)を備え、
前記第2のモードは、前記検知情報を出力するモードである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K2]
A gaming machine according to feature K1,
The gaming machine includes a storage means (a
The gaming machine, wherein the second mode is a mode in which the detection information is output.
特徴K2によれば、検知情報を記憶するとともに、第2のモードにおいて検知情報を出力することができる。検知情報は、遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該検知情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、検知情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴K2によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から検知情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができない。特徴K2の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴K2によれば、遊技機と検知情報とを1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature K2, the detection information can be stored and output in the second mode. Since the detection information is information that correlates with the behavior of the gaming ball in a game, the detection information differs for each gaming machine and is information specific to the gaming machine. In other words, the detection information is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine. According to feature K2, the detection information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine is stored in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, the characteristics of the gaming machine can be inspected by obtaining the detection information from the gaming machine main body itself. When the gaming machine is installed in a gaming hall, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine can be obtained by the hall computer installed in the gaming hall. However, since gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where the gaming machines are not connected to the hall computer, in which case, with conventional gaming machines, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine cannot be obtained. A gaming machine with Feature K2 stores detection information, which is information reflecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body, so that the detection information can be obtained from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, Feature K2 makes it possible to link the gaming machine and the detection information one-to-one, and to manage and inspect the characteristics of the gaming machine. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
また、検知情報は、遊技球が検知されて遊技進行処理が実行されると内容が変化する情報である。したがって、仮に、遊技進行処理と並行して検知情報を出力する処理を実行する構成を採用すると、遊技機の検査者が検知情報によって当該遊技機の特性を検査している間に遊技進行処理が実行されて当該検知情報の内容が随時変化してしまい、円滑に検査を実施することが困難になってしまう場合がある。これに対して、特徴K2によれば、遊技球が所定の領域を通過した場合であっても遊技進行処理を実行しない第2のモードにおいて検知情報を出力するので、検知情報を出力している間に当該検知情報の内容が変化してしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、遊技機の検査者は円滑に検査を実施することができる。 Furthermore, the detection information is information whose contents change when a gaming ball is detected and a game progress process is executed. Therefore, if a configuration is adopted in which a process for outputting detection information is executed in parallel with a game progress process, the game progress process may be executed while an inspector of the gaming machine is inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine using the detection information, causing the contents of the detection information to change from time to time, making it difficult to carry out the inspection smoothly. In contrast, according to feature K2, the detection information is output in a second mode in which the game progress process is not executed even if the gaming ball has passed through a specified area, so that it is possible to prevent the contents of the detection information from changing while the detection information is being output. As a result, an inspector of the gaming machine can carry out the inspection smoothly.
[特徴K3]
特徴K2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2のモードにおいて出力される前記検知情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K3]
A gaming machine according to feature K2,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the detection information output in the second mode.
特徴K3によれば、検知情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することができる。 According to feature K3, the detection information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the detection information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the detection information.
[特徴K4]
特徴K2または特徴K3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリ(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、フラッシュメモリ64x)によって構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K4]
A gaming machine according to feature K2 or feature K3,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the storage means is composed of non-volatile memory (
特徴K4によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれても検知情報が保持されるので、当該遊技機がいかなる状態(例えば、遊技機に電源が供給されない流通状態等)に置かれても、遊技機と検知情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。 According to feature K4, the detection information is retained even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off. Therefore, no matter what state the gaming machine is in (for example, a distribution state where the gaming machine is not supplied with power, etc.), it is possible to always keep the gaming machine and the detection information linked one-to-one, and the characteristics of the gaming machine can be managed and inspected.
[特徴K5]
特徴K2から特徴K4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features K2 to K4,
The gaming machine, wherein the memory means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a seal sticker affixed) that shows signs of opening and closing.
特徴K5によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、記憶手段が格納されている。したがって、記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、記憶手段に記憶されている検知情報が記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、検知情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる検知情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、検知情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、検知情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴K5によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した検知情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature K5, the storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when the storage means is physically touched, traces of opening the cabinet are left. Therefore, if the detection information stored in the storage means is altered through physical contact with the storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the cabinet. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the detection information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution. However, since the storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the detection information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the detection information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the detection information. Therefore, according to feature K5, it is possible to properly manage and inspect the gaming machine by preventing unauthorized alteration of the detection information reflecting the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to improve the soundness of the game.
[特徴K6]
特徴K2から特徴K5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features K2 to K5,
A gaming machine comprising: a notification means for providing a notification when the detection information stored in the memory means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴K6によれば、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature K6, an alert is issued when the detection information does not satisfy a specified condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose detection information does not satisfy the specified condition. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴K7]
特徴K6に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K7]
A gaming machine according to feature K6,
The notification means issues a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the detection information stored in the memory means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴K7によれば、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature K7, an alert is issued when a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of a predetermined range, allowing an inspector of a gaming machine to easily find a gaming machine in which a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of the predetermined range. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴K8]
特徴K7に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K8]
A gaming machine according to feature K7,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴K8によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature K8, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value contained in the detection information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴K9]
特徴K6から特徴K8のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature K9]
A gaming machine according to any one of features K6 to K8,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴K9によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature K9, a display means is provided that displays a specified message as a notification, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the detection information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a specified condition.
<特徴L群>
特徴L群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature L group>
The group of features L is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴L1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
を備え、
前記遊技進行処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第1のモードにおいて前記遊技進行処理の実行中に、前記第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合)には、第2の条件が成立したタイミング(図柄の変動表示処理が終了したタイミング等の遊技進行処理が予め定められた処理段階まで完了したタイミング、実行中の各遊技進行処理の全ての処理が完了したタイミング)で、前記第1のモードから前記第2のモードに移行するように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A game progress processing execution means (
Equipped with
The game progress processing execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
a gaming machine configured to transition from the first mode to the second mode when the first condition is met during execution of the game progress processing in the first mode (when the operation of pressing the mode switching button is performed, when the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the mode switching button is performed, when an
特徴L1によれば、第1のモードにおいて第1の条件が成立した場合には、第2の条件が成立したタイミングで、第1のモードから第2のモードに移行するように構成されているので、第2の条件が成立したか否かに関わらずに第1の条件が満たされた直後のタイミングで第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する構成と比較して、第2のモードに移行する際の処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature L1, when the first condition is satisfied in the first mode, the first mode is switched to the second mode at the timing when the second condition is satisfied. This can reduce the occurrence of processing errors when switching to the second mode, compared to a configuration in which the first mode is switched to the second mode immediately after the first condition is satisfied, regardless of whether the second condition is satisfied or not.
例えば、仮に、第2の条件が成立したか否かに関わらずに第1の条件が成立した直後のタイミングで第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する構成を採用した場合において、第1のモードにおいて遊技進行処理としての図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、所定の操作が実行されたという第1の条件が成立した場合には、図柄の変動表示の途中で第2のモードに移行することになり、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となる。これに対して、特徴L1によれば、例えば、第1のモードにおいて遊技進行処理としての図柄の変動表示処理が実行されている期間中に、所定の操作が実行されたという第1の条件が成立した場合には、図柄の変動表示処理が実行されていないという第2の条件が成立したタイミング、すなわち、変動表示中の図柄が停止した後のタイミングで第2のモードに移行することになる。したがって、図柄の停止のタイミングや、図柄の変動時間の制御等が困難となるといった処理上の不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the first mode is switched to the second mode immediately after the first condition is satisfied, regardless of whether the second condition is satisfied or not, if the first condition that a predetermined operation is executed during the period in which the variable display process of the pattern is executed as the game progress process in the first mode is satisfied, the mode will be switched to the second mode in the middle of the variable display of the pattern, making it difficult to control the timing of the stop of the pattern and the variable time of the pattern. In contrast, according to feature L1, for example, if the first condition that a predetermined operation is executed during the period in which the variable display process of the pattern is executed as the game progress process in the first mode is satisfied, the mode will be switched to the second mode at the timing when the second condition that the variable display process of the pattern is not executed is satisfied, that is, after the variable display of the pattern stops. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of processing malfunctions such as difficult to control the timing of the stop of the pattern and the variable time of the pattern.
[特徴L2]
特徴L1に記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、役物比率等を含む遊技履歴情報)を記憶する記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、主側RAM64、フラッシュメモリ64x)を備え、
前記第2のモードは、前記検知情報を出力するモードである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L2]
A gaming machine according to feature L1,
The gaming machine includes a storage means (a
The gaming machine, wherein the second mode is a mode in which the detection information is output.
特徴L2によれば、検知情報を記憶するとともに、第2のモードにおいて検知情報を出力することができる。検知情報は、遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該検知情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、検知情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴L2によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から検知情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができない。特徴L2の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴L2によれば、遊技機と検知情報とを1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature L2, the detection information can be stored and output in the second mode. Since the detection information is information that has a correlation with the behavior of the gaming ball in the game, the detection information differs for each gaming machine and is information specific to the gaming machine. In other words, the detection information is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine. According to feature L2, the detection information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine is stored in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, the characteristics of the gaming machine can be inspected by obtaining the detection information from the gaming machine main body itself. When the gaming machine is installed in a gaming hall, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine can be obtained by the hall computer installed in the gaming hall. However, since gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where the gaming machines are not connected to the hall computer, in which case, with conventional gaming machines, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine cannot be obtained. The gaming machine of feature L2 stores detection information, which is information reflecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body, so that the detection information can be obtained from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, feature L2 makes it possible to link the gaming machine and the detection information one-to-one, and to manage and inspect the characteristics of the gaming machine. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴L3]
特徴L2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2のモードにおいて出力される前記検知情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L3]
A gaming machine according to feature L2,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the detection information output in the second mode.
特徴L3によれば、検知情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することができる。 According to feature L3, the detection information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the detection information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the detection information.
[特徴L4]
特徴L2または特徴L3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリ(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、フラッシュメモリ64x)によって構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L4]
A gaming machine according to feature L2 or feature L3,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the storage means is composed of non-volatile memory (
特徴L4によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれても検知情報が保持されるので、当該遊技機がいかなる状態(例えば、遊技機に電源が供給されない流通状態等)に置かれても、遊技機と検知情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。 According to feature L4, the detection information is retained even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off. Therefore, no matter what state the gaming machine is in (for example, a distribution state where the gaming machine is not supplied with power, etc.), it is possible to always keep the gaming machine and the detection information linked one-to-one, and the characteristics of the gaming machine can be managed and inspected.
[特徴L5]
特徴L2から特徴L4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features L2 to L4,
The gaming machine, wherein the memory means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a seal sticker affixed) that shows signs of opening and closing.
特徴L5によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、記憶手段が格納されている。したがって、記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、記憶手段に記憶されている検知情報が記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、検知情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる検知情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、検知情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、検知情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴L5によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した検知情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature L5, the storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when the storage means is physically touched, traces of opening the cabinet are left. Therefore, if the detection information stored in the storage means is altered through physical contact with the storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the cabinet. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the detection information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution. However, since the storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the detection information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the detection information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the detection information. Therefore, according to feature L5, it is possible to properly manage and inspect the gaming machine by preventing unauthorized alteration of the detection information reflecting the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to improve the soundness of the game.
[特徴L6]
特徴L2から特徴L5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features L2 to L5,
A gaming machine comprising: a notification means for providing a notification when the detection information stored in the memory means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴L6によれば、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature L6, an alert is issued when the detection information does not satisfy a predetermined condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose detection information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴L7]
特徴L6に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L7]
A gaming machine according to feature L6,
The notification means issues a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the detection information stored in the memory means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴L7によれば、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature L7, an alert is issued when a specific value contained in the detection information is no longer within a predetermined range, so that an inspector of a gaming machine can easily find a gaming machine in which a specific value contained in the detection information is no longer within the predetermined range. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴L8]
特徴L7に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L8]
A gaming machine according to feature L7,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴L8によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature L8, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value contained in the detection information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴L9]
特徴L6から特徴L8のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature L9]
A gaming machine according to any one of features L6 to L8,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴L9によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature L9, a display means is provided that displays a predetermined display as a notification, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the detection information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
<特徴M群>
特徴M群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature M group>
The group of features M is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴M1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
を備え、
前記遊技進行処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
第1の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記第2のモード中に第2の条件が成立した場合(検査モードに移行してから10分が経過した場合)には、前記第2のモードから前記第1のモードに移行させるための所定の操作(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作)が実行されていない場合であっても、前記第2のモードから前記第1のモードに移行するように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A game progress processing execution means (
Equipped with
The game progress processing execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a first condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
The gaming machine is configured such that when a second condition is met during the second mode (when 10 minutes have passed since the transition to the inspection mode), the gaming machine transitions from the second mode to the first mode even if a predetermined operation for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode (an operation of pressing a mode switching button, an operation of pressing a power button while pressing a mode switching button) has not been performed.
特徴M1によれば、第2のモード中に第2の条件が成立した場合には、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させるための所定の操作が実行されていない場合であっても、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行するように構成されているので、所定の操作の実行がされずに第1のモードに復帰しないことを抑制することができる。例えば、第2のモードへの移行後に遊技機の管理者や検査者等が所定の操作の実行を失念してしまい、遊技機が遊技進行処理を実行可能な第1のモードに復帰せず、遊技者が当該遊技機で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature M1, when the second condition is met during the second mode, even if the specified operation for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode is not performed, the system is configured to transition from the second mode to the first mode, so that it is possible to prevent a situation in which the specified operation is not performed and the system does not return to the first mode. For example, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which an administrator or inspector of the gaming machine forgets to perform the specified operation after transitioning to the second mode, causing the gaming machine to not return to the first mode in which game progress processing can be performed, and the player is unable to play on the gaming machine.
[特徴M2]
特徴M1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2の条件は、所定の時点から所定の時間が経過すること(検査モードに移行した時点から10分が経過すること)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M2]
A gaming machine according to feature M1,
The gaming machine according to the present invention, wherein the second condition is that a predetermined time has elapsed from a predetermined point in time (10 minutes has elapsed from the point in time when the mode was changed to the inspection mode).
特徴M2によれば、第2のモード中に所定の時点から所定の時間が経過した場合には、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させるための所定の操作が実行されていない場合であっても、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行するように構成されているので、所定の操作の実行がされずに第1のモードに復帰しないことを確実に抑制することができる。例えば、第2のモードへの移行後に遊技機の管理者や検査者等が所定の操作の実行を失念してしまった場合であっても、所定の時点から所定の時間が経過すれば第1のモードに復帰するので、遊技機が遊技進行処理を実行可能な第1のモードに復帰せず、遊技者が当該遊技機で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature M2, when a predetermined time has elapsed from a predetermined point during the second mode, the second mode is configured to transition to the first mode even if a predetermined operation for transitioning from the second mode to the first mode has not been performed, so that it is possible to reliably prevent a situation in which the predetermined operation is not performed and the first mode is not returned to. For example, even if an administrator or inspector of the gaming machine forgets to perform a predetermined operation after transitioning to the second mode, the first mode will be returned to once a predetermined time has elapsed from a predetermined point, so that it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the gaming machine does not return to the first mode in which game progress processing can be performed and the player is unable to play on the gaming machine.
[特徴M3]
特徴M1または特徴M2に記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、役物比率等を含む遊技履歴情報)を記憶する記憶手段(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、主側RAM64、フラッシュメモリ64x)を備え、
前記第2のモードは、前記検知情報を出力するモードである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M3]
A gaming machine according to feature M1 or feature M2,
The gaming machine includes a storage means (a
The gaming machine, wherein the second mode is a mode in which the detection information is output.
特徴M3によれば、検知情報を記憶するとともに、第2のモードにおいて検知情報を出力することができる。検知情報は、遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該検知情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、検知情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴M3によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から検知情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができない。特徴M3の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴M3によれば、遊技機と検知情報とを1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature M3, the detection information can be stored and output in the second mode. Since the detection information is information that correlates with the behavior of the gaming ball in a game, the detection information differs for each gaming machine and is information specific to the gaming machine. In other words, the detection information is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine. According to feature M3, the detection information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine is stored in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, the characteristics of the gaming machine can be inspected by obtaining the detection information from the gaming machine main body itself. When the gaming machine is installed in a gaming hall, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine can be obtained by the hall computer installed in the gaming hall. However, since gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where they are not connected to the hall computer, in which case, with conventional gaming machines, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine cannot be obtained. A gaming machine with Feature M3 stores detection information, which is information reflecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, in a storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body, so that the detection information can be obtained from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, Feature M3 makes it possible to link the gaming machine and the detection information one-to-one, and to manage and inspect the characteristics of the gaming machine. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
また、特徴M3によれば、遊技機の検査者が第2のモードにおいて出力される検知情報によって当該遊技機の特性を検査した後、所定の操作の実行を失念してしまい、遊技機が遊技進行処理を実行可能な第1のモードに復帰せず、遊技者が当該遊技機で遊技をできないといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 Furthermore, according to feature M3, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which an inspector of a gaming machine inspects the characteristics of the gaming machine using the detection information output in the second mode, and then forgets to perform a specified operation, causing the gaming machine to not return to the first mode in which game progress processing can be performed, and the player is unable to play on the gaming machine.
[特徴M4]
特徴M3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2のモードにおいて出力される前記検知情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M4]
A gaming machine according to feature M3,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the detection information output in the second mode.
特徴M4によれば、検知情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することができる。 According to feature M4, the detection information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the detection information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the detection information.
[特徴M5]
特徴M3または特徴M4に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能な不揮発性のメモリ(演算結果記憶用メモリ309、入球個数記憶用メモリ309a、入球情報記憶用メモリ309b、フラッシュメモリ64x)によって構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M5]
A gaming machine according to feature M3 or feature M4,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the storage means is composed of non-volatile memory (
特徴M5によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれても検知情報が保持されるので、当該遊技機がいかなる状態(例えば、遊技機に電源が供給されない流通状態等)に置かれても、遊技機と検知情報とを常に1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。 According to feature M5, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the detection information is retained. Therefore, no matter what state the gaming machine is in (for example, a distribution state where the gaming machine is not supplied with power), it is possible to always keep the gaming machine and the detection information linked one-to-one, and the characteristics of the gaming machine can be managed and inspected.
[特徴M6]
特徴M3から特徴M5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features M3 to M5,
The gaming machine, wherein the memory means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a seal sticker affixed) that shows signs of opening and closing.
特徴M6によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、記憶手段が格納されている。したがって、記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、記憶手段に記憶されている検知情報が記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、検知情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる検知情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、検知情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、検知情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴M6によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した検知情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature M6, the storage means is stored inside the housing that leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when the storage means is physically touched, traces of opening the housing are left. Therefore, if the detection information stored in the storage means is altered through physical contact with the storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the housing. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the detection information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution. However, since the storage means is stored inside the housing that leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the detection information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the detection information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the detection information. Therefore, according to feature M6, it is possible to properly manage and inspect the gaming machine by preventing unauthorized alteration of the detection information that reflects the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to improve the soundness of the game.
[特徴M7]
特徴M3から特徴M6のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M7]
A gaming machine according to any one of features M3 to M6,
A gaming machine comprising: a notification means for providing a notification when the detection information stored in the memory means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴M7によれば、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature M7, an alert is issued when the detection information does not satisfy a specified condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose detection information does not satisfy the specified condition. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴M8]
特徴M7に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M8]
A gaming machine according to feature M7,
The notification means issues a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the detection information stored in the memory means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴M8によれば、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature M8, an alert is issued when a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of a predetermined range, allowing an inspector of a gaming machine to easily find a gaming machine in which a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of the predetermined range. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴M9]
特徴M8に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M9]
A gaming machine according to feature M8,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴M9によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature M9, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value contained in the detection information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴M10]
特徴M7から特徴M9のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature M10]
A gaming machine according to any one of features M7 to M9,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴M10によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature M10, a display means is provided that displays a predetermined display as a notification, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the detection information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
<特徴N群>
特徴N群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature N group>
The group of N features is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴N1]
遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段(遊技球発射機構81)と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づいて遊技を進行するための処理である遊技進行処理(大当たり抽選処理、電役開放抽選処理、賞球の払出処理、メイン表示部45における図柄の変動表示処理、開閉扉36bや電動役物34aの開閉処理等)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記遊技進行処理に関する情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
所定の操作(RAMクリアボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作)が実行されたことに基づいて、前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備え、
前記遊技進行処理実行手段は、
前記遊技進行処理を実行可能なモードである第1のモード(遊技モード)と、
所定の条件が成立した場合(モード切替ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、モード切替ボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行された場合、検査用端子65に検査機320が接続された場合、所定の時刻になった場合、ホールコンピュータから所定の信号を受信した場合)に実行されるモードである第2のモード(検査モード)と、
を実行可能であり、
前記消去手段は、前記第2のモードに移行後であって前記第1のモードに移行する前の状態(検査モード中の状態、検査モードに移行後にそのまま電源がOFFになった状態)では、前記所定の操作が実行された場合であっても、前記記憶手段に記憶された情報を消去しないように構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N1]
A launching means (a game ball launching mechanism 81) for launching a game ball toward a game area;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A game progress processing execution means (
A storage means (main RAM 64) that is stored in the cabinet of the gaming machine main body and stores information related to the game progress processing;
an erasing means for erasing information stored in the storage means based on a predetermined operation (an operation of pressing a power button while pressing a RAM clear button);
Equipped with
The game progress processing execution means includes:
A first mode (game mode) in which the game progress process can be executed;
A second mode (inspection mode) is executed when a certain condition is met (when the mode switching button is pressed, when the power button is pressed while the mode switching button is pressed, when the
It is possible to execute
The gaming machine is characterized in that the erasing means is configured not to erase the information stored in the memory means after transition to the second mode and before transition to the first mode (a state during the inspection mode, or a state in which the power is turned off after transition to the inspection mode), even if the specified operation is performed.
特徴N1によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態では、記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するための所定の操作が実行された場合であっても、記憶手段に記憶された情報を消去しないので、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態において、第1のモードに移行させようとして誤って所定の操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature N1, even if a predetermined operation for erasing information stored in the storage means is performed after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, the information stored in the storage means is not erased. Therefore, even if a predetermined operation is mistakenly performed in an attempt to transition to the first mode after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, the information can be prevented from being mistakenly erased.
例えば、記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するための所定の操作が、消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作であり、第1のモードと第2のモードとの間でモードを移行させるための操作が、移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下する操作である構成においては、第2のモードから第1のモードに移行させようとして移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまう虞がある。しかしながら、特徴N1によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態では、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するという操作が実行されてしまった場合であっても、当該情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 For example, in a configuration in which the predetermined operation for erasing information stored in the storage means is the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the erase button, and the operation for transitioning between the first mode and the second mode is the operation of pressing the power button while pressing the transition button, there is a risk that when the user intends to press the power button while pressing the transition button to transition from the second mode to the first mode, he or she may mistakenly press the power button while pressing the erase button. However, according to feature N1, even if the operation of accidentally pressing the power button while pressing the erase button is performed after transition to the second mode but before transition to the first mode, it is possible to prevent the information from being mistakenly erased.
より具体的には、例えば、第1のモードから第2のモードに移行する際に、第1のモードにおいて実行していた遊技進行処理を一時的に停止させるとともに、当該停止させた遊技進行処理を第2のモードへの復帰後に再開させるための情報を記憶手段に記憶させる構成を採用した場合において、第2のモードから第1のモードに復帰させようとして移行用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下するつもりが、誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合には、遊技進行処理を再開するための情報が消去されてしまい、第2のモードへの復帰後に遊技進行処理を再開させることができなくなり、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまう虞がある。これに対して、特徴N1によれば、第2のモードに移行後であって第1のモードに移行する前の状態において、第1のモードに移行させようとして誤って消去用のボタンを押下しながら電源ボタンを押下してしまった場合であっても、記憶手段に記憶された情報が誤って消去されてしまうことを抑制することができるので、遊技者に不利益を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 More specifically, for example, in a configuration in which the game progress processing being executed in the first mode is temporarily stopped when transitioning from the first mode to the second mode, and information for resuming the stopped game progress processing after returning to the second mode is stored in the storage means, if a player intends to press the power button while pressing the transition button to return from the second mode to the first mode, but accidentally presses the power button while pressing the erase button, the information for resuming the game progress processing is erased, and the game progress processing cannot be resumed after returning to the second mode, which may cause a disadvantage to the player. In contrast, according to feature N1, even if the player accidentally presses the power button while pressing the erase button to transition to the first mode after transitioning to the second mode but before transitioning to the first mode, the information stored in the storage means can be prevented from being erroneously erased, and therefore, it is possible to prevent a disadvantage from being caused to the player.
[特徴N2]
特徴N1に記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機本体の筐体に格納されるともに、前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、役物比率等を含む遊技履歴情報)を記憶する検知情報記憶手段を備え、
前記第2のモードは、前記検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、役物比率等を含む遊技履歴情報)を出力するモードである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N2]
A gaming machine according to feature N1,
A detection information storage means is provided which is stored in the housing of the gaming machine body and stores detection information (game history information including ball entry information, ball number information, and bonus item ratios) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
The second mode is a mode for outputting the detection information (game history information including ball entry information, ball number information, and bonus item ratios, etc.).
特徴N2によれば、検知情報を記憶するとともに、第2のモードにおいて検知情報を出力することができる。検知情報は、遊技における遊技球の挙動と相関を有する情報であるため、当該検知情報は遊技機毎に異なるとともに、遊技機固有の情報である。すなわち、検知情報は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である。特徴N2によれば、当該遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された検知情報記憶手段に記憶する。よって、例えば、当該遊技機の特性を検査する場合には、当該遊技機本体自身から検知情報を取得することによって、当該遊技機の特性を検査することができる。遊技機は、遊技ホールに設置されている状態においては、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータによって遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができる。しかしながら、遊技機は、転々流通するものであるので、ホールコンピュータに接続されていない状態に置かれる場合があり、この場合、従来の遊技機では、当該遊技機の特性に関する情報を取得することができない。特徴N2の遊技機は、遊技機の特性が反映された情報である検知情報を遊技機本体の筐体に格納された検知情報検知情報記憶手段に記憶するので、遊技機がホールコンピュータと接続されていない状態であっても、当該遊技機本体から検知情報を取得することができる。すなわち、特徴N2によれば、遊技機と検知情報とを1対1で紐付けした状態にすることが可能であり、当該遊技機の特性を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature N2, the detection information can be stored and output in the second mode. Since the detection information is information that has a correlation with the behavior of the gaming ball in the game, the detection information differs for each gaming machine and is information specific to the gaming machine. In other words, the detection information is information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine. According to feature N2, the detection information that reflects the characteristics of the gaming machine is stored in a detection information storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body. Therefore, for example, when inspecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, the characteristics of the gaming machine can be inspected by obtaining the detection information from the gaming machine main body itself. When the gaming machine is installed in an amusement hall, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine can be obtained by the hall computer installed in the amusement hall. However, since gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, there are cases where the gaming machines are not connected to the hall computer, in which case, with conventional gaming machines, information regarding the characteristics of the gaming machine cannot be obtained. The gaming machine of feature N2 stores detection information, which is information reflecting the characteristics of the gaming machine, in a detection information storage means stored in the housing of the gaming machine main body, so that the detection information can be obtained from the gaming machine main body even when the gaming machine is not connected to a hall computer. In other words, feature N2 makes it possible to link the gaming machine and the detection information one-to-one, and to manage and inspect the characteristics of the gaming machine. As a result, the soundness of the game can be improved.
[特徴N3]
特徴N2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2のモードにおいて出力される前記検知情報を表示する表示手段(図柄表示装置41)を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N3]
A gaming machine according to feature N2,
A gaming machine comprising a display means (a symbol display device 41) for displaying the detection information output in the second mode.
特徴N3によれば、検知情報が遊技機の表示手段に表示されるので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報を確認するための専用の装置を用いることなく、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することができる。 According to feature N3, the detection information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can check the detection information of the gaming machine without using a dedicated device for checking the detection information.
[特徴N4]
特徴N2または特徴N3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記検知情報記憶手段は、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックス)の内部に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N4]
A gaming machine according to feature N2 or feature N3,
The detection information storage means is stored inside a housing (a base box with a seal sticker affixed) that retains traces of opening and closing.
特徴N4によれば、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に、検知情報記憶手段が格納されている。したがって、検知情報記憶手段に対して物理的な接触をした場合には、筐体を開いた痕跡が残る。よって、仮に、検知情報記憶手段に記憶されている検知情報が検知情報記憶手段への物理的な接触を介して改変された場合、改変されたことを筐体の痕跡から把握することが可能になる。したがって、検知情報の不正な改変を防止することができる。遊技機は、転々流通するものあるので、流通されている過程においては、様々な外的な接触が行われるが、開閉の痕跡が残る筐体の内部に検知情報記憶手段を格納するので、遊技機が転々流通する状況であっても、何者かによる検知情報の不正な改変を抑制することができる。また、検知情報は、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報であるので、検知情報を用いて遊技機の遊技に関する特性を管理、検査することが可能となる。よって、特徴N4によれば、遊技機の遊技に関する特性を反映した検知情報の不正な改変を防止することで、適正に遊技機を管理、検査することができる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature N4, the detection information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing. Therefore, when the detection information storage means is physically touched, traces of opening the cabinet are left. Therefore, if the detection information stored in the detection information storage means is altered through physical contact with the detection information storage means, it is possible to know that the alteration has been made from the traces on the cabinet. Therefore, it is possible to prevent unauthorized alteration of the detection information. Since some gaming machines are circulated from one place to another, various external contacts are made during the course of distribution. However, since the detection information storage means is stored inside the cabinet, which leaves traces of opening and closing, unauthorized alteration of the detection information by someone can be suppressed even in a situation where the gaming machine is circulated from one place to another. In addition, since the detection information is information acquired based on the executed game, it is possible to manage and inspect the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine using the detection information. Therefore, according to feature N4, it is possible to properly manage and inspect the gaming machine by preventing unauthorized alteration of the detection information reflecting the characteristics related to the game of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to improve the soundness of the game.
[特徴N5]
特徴N2から特徴N4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記検知情報記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知をする報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features N2 to N4,
A gaming machine comprising: a notification means for providing a notification when the detection information stored in the detection information storage means does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
特徴N5によれば、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていない遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature N5, an alert is issued when the detection information does not satisfy a specified condition, so that a gaming machine inspector can easily find a gaming machine whose detection information does not satisfy the specified condition. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴N6]
特徴N5に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記検知情報記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報に含まれる特定の値(払出比率等)が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知をする
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N6]
A gaming machine according to feature N5,
The notification means issues a notification when a specific value (such as a payout ratio) included in the detection information stored in the detection information storage means falls outside a predetermined range.
特徴N6によれば、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった場合に報知するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲に含まれなくなった遊技機を容易に発見することができる。そして、当該遊技機の検知情報を確認することによって、遊技機に不正な改造等が施されていないかを判断することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature N6, an alert is issued when a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of a predetermined range, allowing an inspector of a gaming machine to easily find a gaming machine in which a specific value contained in the detection information falls outside of the predetermined range. Then, by checking the detection information of the gaming machine, it becomes possible to determine whether the gaming machine has been illegally modified. As a result, the soundness of gaming can be improved.
[特徴N7]
特徴N6に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記特定の値の前記所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様(LEDランプの色)を決定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N7]
A gaming machine according to feature N6,
The notification means determines a notification mode (color of an LED lamp) according to a deviation degree of the specific value from the predetermined range.
特徴N7によれば、特定の値の所定の範囲からの乖離度に応じて報知の態様を決定するので、遊技機の検査者は、検知情報に含まれる特定の値が所定の範囲からどの程度乖離しているのかを容易に把握することができる。 According to feature N7, the manner of notification is determined according to the degree of deviation of a specific value from a predetermined range, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily grasp the degree to which a specific value contained in the detection information deviates from the predetermined range.
[特徴N8]
特徴N5から特徴N7のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature N8]
A gaming machine according to any one of features N5 to N7,
The gaming machine, wherein the notification means includes a display means for displaying a predetermined display as the notification.
特徴N8によれば、報知として所定の表示をする表示手段を備えるので、遊技機の検査者は、遊技機の検知情報が所定の条件を満たしていないことを容易に知ることができる。 According to feature N8, a display means is provided that displays a predetermined message as a notification, so that an inspector of the gaming machine can easily know that the detection information of the gaming machine does not satisfy a predetermined condition.
なお、上記特徴A群~特徴N群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature groups A to N solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, including structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the entertainment value of the game.
また、遊技の興趣向上に加え、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition to making games more entertaining, various technical improvements are being made to improve the integrity of games, such as by detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
例えば、遊技者によって不正な行為(いわゆるゴト行為)が行われたり、パチンコ遊技機の遊技盤に設けられた釘が不正に曲げられて改造されたりすると、一般入賞口や始動口等の各入球口への遊技球の入球割合等が当初に想定されたものとは異なるようになってしまい、パチンコ遊技機に想定された性能や遊技性が損なわれてしまう場合があった。しかしながら、このような不正の発見は非常に困難であった。 For example, if a player commits fraudulent acts (so-called cheating), or if the nails on the game board of a pachinko machine are fraudulently bent and modified, the ratio of game balls that enter each entry port, such as the general entry port and the starting port, may differ from what was originally expected, and the performance and playability expected of the pachinko machine may be impaired. However, it has been very difficult to detect such fraud.
このような不正は、遊技ホールの営業時間中に遊技者によって行われる場合がある。また、遊技ホールの営業時間後に、何者かによって不正な改造が行われる場合もある。さらには、遊技ホールに設置される前の輸送中の遊技機に対して不正な改造が行われる場合もある。さらには、遊技ホールに出荷される前の遊技機に対して不正な改造が行われる場合もある。また、それよりも前に不正な改造が行われる可能性もある。 This type of fraud may be committed by a player while the amusement parlor is open. In addition, unauthorized modifications may be made by someone after the amusement parlor is open. Furthermore, unauthorized modifications may be made to gaming machines while they are being transported before they are installed in the amusement parlor. Furthermore, unauthorized modifications may be made to gaming machines before they are shipped to the amusement parlor. There is also the possibility that unauthorized modifications may be made even earlier than that.
このような状況を踏まえ、遊技機に対する不正な行為や不正な改造を発見し、遊技の健全性を向上させることを目的とする。 In light of this situation, the aim is to discover fraudulent activities and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines and improve the integrity of gaming.
<特徴O群>
特徴O群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様23から抽出される。
<Characteristic group O>
The group of features O is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴O1]
所定の間隔(4msecの間隔)で所定の処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行を開始する処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、前記所定の処理に含まれる一の処理として、特定の処理(遊技履歴情報を算出する処理である演算処理)を実行可能であり、
前記特定の処理は、複数の処理段階(図29のタスク1及びタスク2)によって構成されており、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記所定の処理の1回の実行においては前記特定の処理を構成する前記複数の処理段階のうちの一の処理段階を実行可能であり、
前記所定の処理を複数回実行することによって、前記特定の処理を構成する前記複数の処理段階の全てを実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature O1]
A gaming machine having a process execution means (
the process execution means is capable of executing a specific process (a computation process which is a process for calculating game history information) as one process included in the predetermined process;
The specific process is composed of a plurality of process steps (
The process execution means includes:
In one execution of the predetermined process, one processing step among the plurality of processing steps constituting the specific process can be executed,
A gaming machine characterized in that all of the plurality of processing steps constituting the specific processing are executed by executing the predetermined processing a plurality of times.
特徴O1によれば、所定の処理の1回の実行においては特定の処理を構成する複数の処理段階のうちの一の処理段階を実行可能であり、所定の処理を複数回実行することによって、特定の処理を構成する複数の処理段階の全てを実行するので、所定の処理の1回の実行において特定の処理を構成する複数の処理段階の全てを実行する構成に比べて、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、所定の処理の実行を開始する所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまい、所定の処理を所定の間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。 According to feature O1, one of the multiple processing steps constituting the specific process can be executed in one execution of the specified process, and all of the multiple processing steps constituting the specific process are executed by executing the specified process multiple times. Therefore, the time required for one execution of the specified process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which all of the multiple processing steps constituting the specific process are executed in one execution of the specified process. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for one execution of the specified process from becoming longer than the specified interval for starting the execution of the specified process, which makes it impossible to execute the specified process at the specified interval.
[特徴O2]
特徴O1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、実行する順序が定められた一連の処理によって構成されており、
前記複数の処理段階は、前記特定の処理を構成する前記一連の処理を分割したものであり、
前記処理実行手段は、前記複数の処理段階のうちの一の処理段階(図29のタスク1)を実行した後、当該一の処理段階の次に実行する前記処理段階(図29のタスク2)を指定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature O2]
A gaming machine according to feature O1,
The specific process is composed of a series of processes whose execution order is determined,
the plurality of processing steps are obtained by dividing the series of processing steps constituting the specific processing step,
The processing execution means executes one of the plurality of processing steps (
特徴O2によれば、実行する順序が定められた一連の処理を分割し、所定の処理の1回の実行においては、複数の処理段階のうちの一の処理段階を実行した後、当該一の処理段階の次に実行する処理段階を指定するので、所定の処理に組み込んだ場合に当該所定の処理の実行に要する時間が所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまうような一連の処理であっても、所定の間隔で実行される所定の処理に組み込んで実行することができる。 According to feature O2, a series of processes with a set execution order is divided, and in one execution of the specified process, one of the multiple processing steps is executed, and then the processing step to be executed after the one processing step is specified. Therefore, even if a series of processes would take longer to execute than the specified interval when incorporated into the specified process, they can be incorporated into the specified process that is executed at the specified interval and executed.
[特徴O3]
特徴O2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、前記所定の処理に含まれる処理として、遊技の進行に関する処理である遊技進行処理を実行可能であり、
前記特定の処理は、前記遊技進行処理とは異なる処理(演算処理)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature O3]
A gaming machine according to feature O2,
The process execution means is capable of executing a game progress process, which is a process related to the progress of a game, as a process included in the predetermined process;
The specific processing is processing (arithmetic processing) different from the game progress processing.
特徴O3によれば、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理(遊技進行処理以外の処理)を所定の処理に組み込んだ場合に当該所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまうような構成の遊技機においても、所定の間隔で実行される所定の処理に当該遊技進行処理とは異なる処理を組み込んで実行することができる。また、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理は、所定の処理の1回の実行において全ての処理段階を実行しなくても遊技の進行に影響はないため、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を、当該所定の処理に含まれる遊技進行処理の実行時間に割り振ることができ、遊技機の設計の自由度を向上させることができる。なお、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理としては、種々の任意の処理を採用することが可能であり、例えば、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報を算出する処理や、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータに対して遊技の状況に関する情報を所定のタイミングで送信する送信処理等を採用することができる。 According to feature O3, even in a gaming machine configured such that when a process other than the game progress process is incorporated into a predetermined process, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process becomes longer than the predetermined interval, the process other than the game progress process can be incorporated into the predetermined process executed at a predetermined interval and executed. Furthermore, since the process other than the game progress process does not affect the progress of the game even if not all processing steps are executed in one execution of the predetermined process, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process can be allocated to the execution time of the game progress process included in the predetermined process, thereby improving the freedom of design of the gaming machine. Note that various arbitrary processes can be adopted as the process other than the game progress process, and for example, a process for calculating game history information, which is information related to the game history, or a transmission process for transmitting information related to the game status to a hall computer installed in the game hall at a predetermined timing can be adopted.
[特徴O4]
特徴O3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報を算出する処理である算出処理(演算処理)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature O4]
A gaming machine according to feature O3,
The specific process is a calculation process (arithmetic process) for calculating game history information, which is information relating to a game history.
特徴O4によれば、遊技履歴情報を算出する算出処理を所定の処理に組み込んだ場合に当該所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまうような構成の遊技機においても、所定の間隔で実行される所定の処理に当該算出処理を組み込んで実行することができる。また、遊技履歴情報を算出する算出処理は、所定の処理の1回の実行において全ての処理段階を実行しなくても遊技の進行に影響はないため、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を、当該所定の処理に含まれる遊技進行処理の実行時間に割り振ることができ、遊技機の設計の自由度を向上させることができる。 According to Feature O4, even in a gaming machine configured such that when a calculation process for calculating game history information is incorporated into a predetermined process, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process becomes longer than the predetermined interval, the calculation process can be incorporated into the predetermined process executed at a predetermined interval and executed. Furthermore, since the calculation process for calculating game history information does not affect the progress of the game even if not all processing steps are executed in one execution of the predetermined process, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process can be allocated to the execution time of the game progress process included in the predetermined process, thereby improving the freedom of design of the gaming machine.
<特徴P群>
特徴P群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様23から抽出される。
<Feature P group>
The group of features P is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴P1]
所定の間隔(4msecの間隔)で所定の処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行を開始する処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記所定の処理に含まれる一の処理として、特定の処理(賞球集計処理)を実行可能であり、
前記所定の処理の1回の実行においては、複数の処理対象候補(バッファエリアの8個のビット)の中から一部の処理対象候補(2個のビット)を、前記特定の処理(賞球集計処理)の処理対象として設定し、当該設定した処理対象に対して前記特定の処理を実行可能であり、
前記所定の処理を複数回実行することによって、前記複数の処理対象候補の全てに対して前記特定の処理を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature P1]
A gaming machine having a process execution means (
The process execution means includes:
As one process included in the predetermined process, a specific process (a prize ball counting process) can be executed,
In one execution of the predetermined process, a part of the process target candidates (two bits) from among a plurality of process target candidates (eight bits in the buffer area) is set as a process target of the specific process (a prize ball counting process), and the specific process can be executed on the set process target.
The gaming machine is characterized in that the specific process is executed for all of the plurality of process target candidates by executing the predetermined process multiple times.
特徴P1によれば、所定の処理の1回の実行においては、複数の処理対象候補の中から一部の処理対象候補を、特定の処理の処理対象として設定し、当該設定した処理対象に対して特定の処理を実行可能であり、所定の処理を複数回実行することによって、複数の処理対象候補の全てに対して特定の処理を実行する。したがって、所定の処理の1回の実行において複数の処理対象候補の全てに対して特定の処理を実行する構成に比べて、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、所定の処理の実行を開始する所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまい、所定の処理を所定の間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。 According to feature P1, in one execution of a specified process, some of the multiple processing target candidates are set as processing targets for a specific process, and the specific process can be executed on the set processing targets, and the specified process is executed on all of the multiple processing target candidates by executing the specified process multiple times. Therefore, the time required for one execution of the specified process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the specific process is executed on all of the multiple processing target candidates in one execution of the specified process. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for one execution of the specified process from becoming longer than the specified interval for starting the execution of the specified process, making it impossible to execute the specified process at the specified interval.
[特徴P2]
特徴P1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の処理対象候補は、予め固定されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature P2]
A gaming machine according to feature P1,
The gaming machine, characterized in that the plurality of processing target candidates are fixed in advance.
特徴P2によれば、複数の処理対象候補は予め固定されているので、複数の処理対象候補を選択する処理を実行する必要がなく、処理を簡易化することができ、この結果、処理速度を向上させることができる。さらに、複数の処理対象候補を選択するために必要なプログラムやパラメータなどの情報を記憶するための記憶容量を削減することができる。 According to feature P2, since the multiple processing target candidates are fixed in advance, there is no need to execute a process for selecting the multiple processing target candidates, and the process can be simplified, thereby improving the processing speed. Furthermore, the memory capacity for storing information such as programs and parameters required for selecting the multiple processing target candidates can be reduced.
[特徴P3]
特徴P1または特徴P2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理対象設定手段は、前記複数の処理対象候補の中から前記一部の処理対象候補を前記特定の処理の処理対象として設定する際に、予め定められた順序で設定する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature P3]
A gaming machine according to feature P1 or feature P2,
The processing target setting means, when setting the part of the processing target candidates from among the plurality of processing target candidates as processing targets for the specific processing, sets the part in a predetermined order.
特徴P3によれば、複数の処理対象候補の中から一部の処理対象候補を特定の処理の処理対象として設定する際に、予め定められた順序で設定するので、特定の処理の処理対象をいずれの処理対象候補に設定するかの判定処理を実行する必要がなく、処理を簡易化することができ、この結果、処理速度を向上させることができる。さらに、判定処理を実行するために必要なプログラムやパラメータなどの情報を記憶するための記憶容量を削減することができる。 According to feature P3, when some of the processing target candidates from among multiple processing target candidates are set as the processing target for a specific process, they are set in a predetermined order, so there is no need to perform a determination process to determine which processing target candidate to set as the processing target for the specific process, which simplifies the process and, as a result, improves the processing speed. Furthermore, it is possible to reduce the memory capacity required to store information such as programs and parameters required to perform the determination process.
[特徴P4]
特徴P1から特徴P3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な入球部を複数備え、
前記複数の処理対象候補のそれぞれは、前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応しており、
前記各処理対象候補は、前記各入球部への遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報(バッファエリアの各ビットに格納された入球検知情報)であり、
前記処理実行手段は、1つの前記入球部に2個の遊技球が連続して入球して検知される最短の間隔(18msec程度)よりも短い時間で、前記所定の処理を複数回(4回)実行することによって前記処理対象候補の全てに対して前記特定の処理を実行することが可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature P4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features P1 to P3,
Equipped with multiple ball entry areas where game balls can enter,
Each of the plurality of processing target candidates corresponds to each of the plurality of ball entry portions,
Each of the candidates for processing is information (ball entry detection information stored in each bit of the buffer area) that is updated based on detection of a ball entering each of the ball entry sections,
The processing execution means is capable of executing the specific processing on all of the processing target candidates by executing the predetermined processing multiple times (four times) in a time shorter than the shortest interval (approximately 18 msec) between two gaming balls successively entering one entry section.
特徴P4によれば、処理対象候補の全てに対して特定の処理が実行されるまでに要する時間を、1つの入球部に2個の遊技球が連続して入球して検知される最短の間隔よりも短くすることができるので、各入球部への遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報を、1個の遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報として記憶することができる。具体的に説明すると、入球部に2個の遊技球が連続して入球した場合に、最初の1個目の遊技球の入球が入球部において検知されることに基づいて更新された情報が処理対象として設定されて特定の処理が実行され、さらにその後に残りの他の処理対象候補が処理対象として設定されて特定の処理が実行されたとしても、次の2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球部において検知されるよりも先にこれら全ての特定の処理を終了することができる。すなわち、2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球部において検知されることに基づいて更新された情報が処理対象として設定されて特定の処理が実行された時点においては、既に、1個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球部において検知されることに基づいて更新された情報に対する特定の処理は終了しており、2個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球部において検知されることに基づいて更新された情報は、新たな1個目の遊技球の入球が当該入球部において検知されることに基づいて更新された情報として扱うことができる。よって、各入球部への遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報は、1個の遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報として記憶することができる。その結果、例えば、各入球部への遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報を、入球の有無を示す2値の情報として記憶することが可能となる。この場合、各入球部への遊技球の入球が検知されることに基づいて更新される情報を記憶するための記憶容量を小さくすることができるとともに、特定の処理の処理速度を向上させることができる。 According to feature P4, the time required for the specific processing to be performed on all of the candidates for processing can be made shorter than the shortest interval between the detection of two consecutive game balls entering one ball entry section, so that the information updated based on the detection of the entry of a game ball into each ball entry section can be stored as information updated based on the detection of the entry of one game ball. To be more specific, when two game balls enter a ball entry section in succession, even if the information updated based on the detection of the entry of the first game ball at the ball entry section is set as the processing target and a specific processing is performed, and then the remaining candidates for processing can be set as the processing targets and a specific processing is performed, all of these specific processing can be completed before the entry of the next second game ball at the ball entry section is detected. That is, at the time when the information updated based on the detection of the entry of the second game ball in the ball entry section is set as the processing target and the specific processing is executed, the specific processing for the information updated based on the detection of the entry of the first game ball in the ball entry section has already been completed, and the information updated based on the detection of the entry of the second game ball in the ball entry section can be treated as information updated based on the detection of the entry of the new first game ball in the ball entry section. Therefore, the information updated based on the detection of the entry of a game ball into each ball entry section can be stored as information updated based on the detection of the entry of one game ball. As a result, for example, the information updated based on the detection of the entry of a game ball into each ball entry section can be stored as binary information indicating the presence or absence of a ball entry. In this case, the memory capacity for storing the information updated based on the detection of the entry of a game ball into each ball entry section can be reduced, and the processing speed of the specific processing can be improved.
<特徴Q群>
特徴Q群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様23から抽出される。
<Feature Q group>
The group of features Q is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴Q1]
特定の処理(遊技履歴用処理)と前記特定の処理以外の他の処理(遊技の進行に関する処理)とを実行可能な処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
情報の書き込みが可能な記憶領域(主側RAM64)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、処理の実行のための情報(レジスタ情報)を保持する保持手段(レジスタ)を備え、
前記特定の処理は、
前記保持手段が保持する情報であって前記他の処理の実行のための情報(レジスタ情報)を前記記憶領域に書き込む第1の処理(退避処理)と、
前記第1の処理において前記記憶領域に書き込まれた情報を前記保持手段に保持させる第2の処理(復帰処理)と、
を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Q1]
A process execution means (
A storage area (main RAM 64) into which information can be written;
A gaming machine comprising:
the process execution means includes a storage means (register) for storing information for executing the process (register information);
The specific processing is
a first process (saving process) for writing information (register information) held by the holding means for executing the other process into the memory area;
a second process (recovery process) for causing the holding means to hold the information written in the storage area in the first process;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴Q1によれば、特定の処理は、保持手段が保持する情報であって他の処理の実行のための情報を記憶領域に書き込む第1の処理を含むので、処理実行手段が特定の処理の開始時に、保持手段が特定の処理の開始直前に実行していた他の処理の実行のための情報を保持している場合には、保持手段が保持していた他の処理の実行のための情報を記憶領域に書き込むことによって一時的に移動(退避)させることができる。よって、保持手段に保持されていた他の処理の実行のための情報を消去し、処理実行手段が特定の処理の実行時には、保持手段に特定の処理の実行のための情報を保持させることができる。また、特定の処理は、第1の処理において記憶領域に書き込まれた情報を保持手段に保持させる第2の処理を含むので、特定の処理を終了する際に、他の処理の実行のための情報を保持手段に再び保持させ、特定の処理の開始以前に実行していた他の処理を、特定の処理の開始直前の状態から再び実行することができる。さらに、第1の処理と第2の処理は特定の処理に含まれるので、特定の処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを削除しても特定の処理以外の他の処理が問題なく実行される遊技機を提供することができる。すなわち、特定の処理以外の他の処理を実行するためのプログラムを改変せずに、特定の処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを容易に削除することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、特定の処理を実行させないように当該遊技機を改良する場合や、当該遊技機に基づいて特定の処理を実行しない新たな遊技機を開発する場合において、設計変更を最小限にすることが可能となる。 According to feature Q1, the specific process includes a first process of writing information for executing other processes, which is information held by the holding means, into the storage area. Therefore, when the process execution means starts the specific process, if the holding means holds information for executing other processes that were executed immediately before the start of the specific process, the information for executing the other processes held by the holding means can be temporarily moved (evacuated) by writing it into the storage area. Therefore, the information for executing other processes held in the holding means can be erased, and when the process execution means executes the specific process, the information for executing the specific process can be held in the holding means. In addition, the specific process includes a second process of causing the holding means to hold the information written in the storage area in the first process. Therefore, when the specific process is terminated, the information for executing the other processes can be held again in the holding means, and the other processes that were executed before the start of the specific process can be executed again from the state immediately before the start of the specific process. Furthermore, since the first process and the second process are included in the specific process, it is possible to provide a gaming machine in which processes other than the specific process can be executed without problems even if only the program for executing the specific process is deleted. In other words, it is possible to easily delete only the program for executing the specific process without modifying the program for executing other processes other than the specific process. As a result, for example, when improving the gaming machine so that it does not execute a specific process, or when developing a new gaming machine based on the gaming machine that does not execute a specific process, it is possible to minimize design changes.
[特徴Q2]
特徴Q1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記特定の処理に含まれる前記第1の処理において、前記他の処理の実行のための情報を、前記記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域(第2エリア)に書き込み、かつ、前記特定の処理における情報の書き込みを、前記記憶領域のうちの前記特定の領域(第2エリア)に対してのみ実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Q2]
A gaming machine according to feature Q1,
The process execution means includes:
A gaming machine characterized in that, in the first process included in the specific process, information for executing the other process is written to a predetermined specific area (second area) of the memory area, and the writing of information in the specific process is executed only to the specific area (second area) of the memory area.
特徴Q2によれば、処理実行手段は、特定の処理に含まれる第1の処理において、他の処理の実行のための情報を、記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域に書き込み、かつ、特定の処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域に対してのみ実行するので、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域以外の他の領域に書き込まれている情報が、特定の処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、当該他の領域を用いた処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該処理に対して特定の処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature Q2, in a first process included in a specific process, the process execution means writes information for executing other processes to a predetermined specific area of the storage area, and executes writing of information for the specific process only to the specific area of the storage area, so that information written to areas other than the specific area of the storage area can be prevented from being rewritten by the execution of the specific process. Therefore, when a process using the other area is executed by the process execution means, it is possible to prevent the specific process from affecting the process.
[特徴Q3]
特徴Q1または特徴Q2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記他の処理における情報の書き込みを、前記記憶領域のうちの前記特定の領域以外の他の領域(第1エリア)に対してのみ実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Q3]
A gaming machine according to feature Q1 or feature Q2,
The process execution means includes:
a first area of the memory area other than the specific area, and a second area of the memory area other than the specific area of the memory area.
特徴Q3によれば、他の処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域以外の他の領域に対してのみ実行するので、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域に書き込まれている情報が、他の処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、特定の領域を用いて特定の処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該特定の処理に対して当該他の処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature Q3, writing of information in other processes is executed only to areas other than the specific area of the storage area, so that information written in the specific area of the storage area can be prevented from being rewritten by the execution of other processes. Therefore, when a specific process is executed by a process execution means using a specific area, it is possible to prevent the other processes from affecting the specific process.
[特徴Q4]
特徴Q1から特徴Q3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、遊技の進行に関する処理である遊技進行処理とは異なる処理であり、
前記他の処理は、前記遊技進行処理である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Q4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features Q1 to Q3,
The specific processing is different from a game progress processing, which is a processing related to the progress of a game,
The gaming machine, wherein the other process is the game progress process.
特徴Q4によれば、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを削除しても遊技進行処理が問題なく実行される遊技機を提供することができる。すなわち、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを容易に削除することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理を実行させないように当該遊技機を改良する場合や、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理を実行しない新たな遊技機を開発する場合において、設計変更を最小限にすることが可能となる。なお、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理としては、種々の任意の処理を採用することが可能であり、例えば、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報の算出及び表示を行なう処理や、遊技ホールに設置されているホールコンピュータに対して遊技の状況に関する情報を所定のタイミングで送信する送信処理等を採用することができる。 According to feature Q4, it is possible to provide a gaming machine in which the game progress process can be executed without any problems even if only the program for executing the process different from the game progress process is deleted. In other words, it is possible to easily delete only the program for executing the process different from the game progress process. As a result, it is possible to minimize design changes, for example, when improving the gaming machine so that it does not execute the process different from the game progress process, or when developing a new gaming machine that does not execute the process different from the game progress process. Note that various arbitrary processes can be adopted as the process different from the game progress process, and for example, a process for calculating and displaying game history information, which is information about the game history, or a transmission process for transmitting information about the game status to a hall computer installed in the game hall at a predetermined timing can be adopted.
[特徴Q5]
特徴Q4に記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率)の算出及び表示を行なう処理である遊技履歴情報関連処理(遊技履歴用処理)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Q5]
A gaming machine according to feature Q4,
The specific process is a game history information related process (game history process) that calculates and displays game history information (role ratio, consecutive role ratio), which is information related to the game history.
特徴Q5によれば、遊技履歴情報関連処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを削除しても遊技進行処理が問題なく実行される遊技機を提供することができる。すなわち、遊技履歴情報関連処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを容易に削除することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、遊技履歴情報関連処理を実行させないように当該遊技機を改良する場合や、遊技履歴情報関連処理を実行しない新たな遊技機を開発する場合において、設計変更を最小限にすることが可能となる。 According to feature Q5, it is possible to provide a gaming machine in which game progress processing can be executed without problems even if only the program for executing the gaming history information related processing is deleted. In other words, it is possible to easily delete only the program for executing the gaming history information related processing. As a result, it is possible to minimize design changes, for example, when improving the gaming machine so that it does not execute the gaming history information related processing, or when developing a new gaming machine that does not execute the gaming history information related processing.
<特徴R群>
特徴R群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様23から抽出される。
<Feature R group>
The group of features R is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴R1]
特定の処理(遊技履歴用処理)を含む複数の処理を実行可能な処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と、
情報の書き込みが可能な記憶領域(主側RAM64)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記特定の処理における情報の書き込みを、前記記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域(第2エリア)に対してのみ実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature R1]
A process execution means (
A storage area (main RAM 64) into which information can be written;
A gaming machine comprising:
The process execution means includes:
The gaming machine is characterized in that writing of information in the specific process is executed only to a predetermined specific area (second area) of the memory area.
特徴R1によれば、処理実行手段は特定の処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域に対してのみ実行するので、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域以外の他の領域に書き込まれている情報が、特定の処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域以外の他の領域を用いた処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該処理に対して特定の処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature R1, the process execution means writes information for a specific process only to a predetermined specific area of the storage area, so that information written in areas other than the specific area of the storage area can be prevented from being rewritten by the execution of the specific process. Therefore, when a process using areas other than the specific area of the storage area is executed by the process execution means, it is possible to prevent the specific process from affecting that process.
[特徴R2]
特徴R1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記特定の処理以外の他の処理(遊技の進行に関する処理)における情報の書き込みを、前記記憶領域のうちの前記特定の領域以外の他の領域(第1エリア)に対してのみ実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature R2]
A gaming machine according to feature R1,
The process execution means includes:
A gaming machine characterized in that writing of information for processes other than the specific process (processing related to the progress of the game) is executed only to an area (first area) other than the specific area of the memory area.
特徴R2によれば、処理実行手段は、特定の処理以外の他の処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域以外の他の領域に対してのみ実行するので、記憶領域のうちの特定の領域に書き込まれている情報が、当該他の処理の実行によって書き換えられてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、特定の領域を用いて特定の処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該特定の処理に対して当該他の処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature R2, the process execution means writes information for processes other than the specific process only to areas other than the specific area of the storage area, so that it is possible to prevent information written in the specific area of the storage area from being rewritten by the execution of the other process. Therefore, when a specific process is executed by the process execution means using the specific area, it is possible to prevent the other process from affecting the specific process.
[特徴R3]
特徴R1または特徴R2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
処理の実行のための情報(レジスタ情報)を保持する保持手段(レジスタ)を備え、かつ、前記特定の処理と前記他の処理とを排他的に実行し、
前記特定の処理は、
前記保持手段が保持する情報であって前記他の処理の実行のための情報(レジスタ情報)を前記特定の領域に書き込む第1の処理(退避処理)と、
前記第1の処理において前記特定の領域に書き込まれた情報を前記保持手段に保持させる第2の処理(復帰処理)と、
を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature R3]
A gaming machine according to feature R1 or feature R2,
The process execution means includes:
a storage unit (register) for storing information (register information) for executing a process, and the specific process and the other process are exclusively executed;
The specific processing is
a first process (saving process) for writing information (register information) held by the holding means for executing the other process into the specific area;
a second process (recovery process) for causing the storage unit to store the information written in the specific area in the first process;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴R3によれば、特定の処理は第1の処理を含むので、処理実行手段が特定の処理の開始時に、保持手段が特定の処理の開始直前に実行していた他の処理の実行のための情報を保持している場合には、保持手段が保持していた他の処理の実行のための情報を特定の領域に書き込むことによって一時的に移動(退避)させることができる。よって、保持手段に保持されていた他の処理の実行のための情報を消去し、処理実行手段が特定の処理の実行時には、保持手段に特定の処理の実行のための情報を保持させることができる。また、特定の処理は第2の処理を含むので、特定の処理を終了する際に、他の処理の実行のための情報を保持手段に再び保持させ、特定の処理の開始以前に実行していた他の処理を、特定の処理の開始直前の状態から再び実行することができる。さらに、第1の処理と第2の処理は特定の処理に含まれるので、特定の処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを削除しても特定の処理以外の他の処理が問題なく実行される遊技機を提供することができる。すなわち、特定の処理以外の他の処理を実行するためのプログラムを改変せずに、特定の処理を実行するためのプログラムのみを容易に削除することが可能となる。この結果、例えば、特定の処理を実行させないように当該遊技機を改良する場合や、当該遊技機に基づいて特定の処理を実行しない新たな遊技機を開発する場合において、設計変更を最小限にすることが可能となる。 According to feature R3, the specific process includes the first process, so if the storage means stores information for the execution of other processes that were executed immediately before the start of the specific process when the process execution means starts the specific process, the information for the execution of the other processes stored in the storage means can be temporarily moved (evacuated) by writing it to a specific area. Thus, the information for the execution of other processes stored in the storage means can be erased, and when the process execution means executes the specific process, the information for the execution of the specific process can be stored in the storage means. In addition, since the specific process includes the second process, when the specific process is terminated, the information for the execution of the other processes can be stored again in the storage means, and the other processes that were executed before the start of the specific process can be executed again from the state immediately before the start of the specific process. Furthermore, since the first process and the second process are included in the specific process, it is possible to provide a gaming machine in which processes other than the specific process can be executed without problems even if only the program for executing the specific process is deleted. In other words, it is possible to easily delete only the program for executing the specific process without modifying the program for executing other processes other than the specific process. As a result, for example, when improving the gaming machine so that it does not execute a specific process, or when developing a new gaming machine based on the gaming machine that does not execute a specific process, it is possible to minimize design changes.
[特徴R4]
特徴R1から特徴R3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、遊技の進行に関する処理である遊技進行処理とは異なる処理であり、
前記特定の処理以外の他の処理は、前記遊技進行処理である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature R4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features R1 to R3,
The specific processing is different from a game progress processing, which is a processing related to the progress of a game,
The gaming machine, characterized in that the processing other than the specific processing is the game progress processing.
特徴R4によれば、処理実行手段は、遊技進行処理とは異なる処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域に対してのみ実行するので、遊技進行処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該遊技進行処理に対して、当該遊技進行処理とは異なる処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature R4, the process execution means writes information for a process other than the game progress process only to a predetermined specific area of the memory area, so that when the game progress process is executed by the process execution means, it is possible to prevent the process other than the game progress process from affecting the game progress process.
[特徴R5]
特徴R4に記載の遊技機であって、
前記特定の処理は、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率)の算出及び表示を行なう処理である遊技履歴情報関連処理(遊技履歴用処理)である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature R5]
A gaming machine according to feature R4,
The specific process is a game history information related process (game history process) that calculates and displays game history information (role ratio, consecutive role ratio), which is information related to the game history.
特徴R5によれば、処理実行手段は、遊技履歴情報関連処理における情報の書き込みを、記憶領域のうちの予め定められた特定の領域に対してのみ実行するので、遊技進行処理が処理実行手段によって実行される場合に、当該遊技進行処理に対して遊技履歴情報関連処理が影響を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature R5, the process execution means writes information in the game history information related process only to a predetermined specific area of the memory area, so that when the game progress process is executed by the process execution means, the game history information related process can be prevented from affecting the game progress process.
<特徴S群>
特徴S群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様23から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group S>
The group of features S is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴S1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球を検知する入球検知手段(入球検知センサー)と、
所定のパラメータ(賞球集計値)を記憶するパラメータ記憶手段(賞球集計用バッファ)と、
所定の間隔(4msecの間隔)で所定の処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行を開始する処理実行手段(主側CPU62x)と
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記所定の処理として、
前記パラメータ記憶手段に記憶されている前記所定のパラメータを前記入球部への遊技球の入球を契機として更新するパラメータ更新処理(賞球集計処理)と、
前記パラメータ記憶手段に記憶されている前記所定のパラメータに基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報を算出する算出処理(図29のタスク1及びタスク2)と、
を実行可能であり、
1回の前記所定の処理において、前記パラメータ更新処理を実行する場合には前記算出処理を実行しない
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature S1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A ball entry detection means (ball entry detection sensor) for detecting a game ball entering the ball entry section;
A parameter storage means (a prize ball tally buffer) for storing a predetermined parameter (a prize ball tally value);
A processing execution means (
The process execution means includes:
As the predetermined processing,
A parameter update process (a prize ball tallying process) for updating the predetermined parameters stored in the parameter storage means when a game ball enters the ball entry section;
A calculation process (
It is possible to execute
The gaming machine is characterized in that, in one of the predetermined processes, when the parameter update process is executed, the calculation process is not executed.
特徴S1によれば、1回の所定の処理においてパラメータ更新処理を実行する場合には算出処理を実行しない。すなわち、1回の所定の処理においてはパラメータ更新処理と算出処理の両方の処理を実行することはないので、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が、所定の処理の実行を開始する所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまい、所定の処理を所定の間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。さらに、特徴S1によれば、遊技球の入球状況と処理負荷とが相関するパラメータ更新処理を、遊技球の入球状況と処理負荷とが相関しない算出処理よりも優先して実行するので、パラメータ更新処理の実行の間隔が大きくなることを抑制し、その結果として当該パラメータ更新処理の処理結果(賞球集計値)が遊技球の入球状況を正確に反映することができなくなってしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature S1, when a parameter update process is executed in one predetermined process, a calculation process is not executed. In other words, since both a parameter update process and a calculation process are not executed in one predetermined process, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process can be shortened. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for one execution of the predetermined process from becoming longer than the predetermined interval for starting the execution of the predetermined process, which makes it impossible to execute the predetermined process at the predetermined interval. Furthermore, according to feature S1, a parameter update process in which the ball entry status and the processing load are correlated are executed in preference to a calculation process in which the ball entry status and the processing load are not correlated, which prevents the interval between the execution of the parameter update process from becoming too long, and as a result, it is possible to prevent the processing result of the parameter update process (prize ball tally value) from being unable to accurately reflect the ball entry status.
[特徴S2]
特徴S1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記算出処理を実行するか否かを判定する判定手段(図29のステップS10810の処理)を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記パラメータ更新処理を実行しない場合であって、前記判定手段によって前記算出処理を実行すると判定された場合に、前記算出処理を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature S2]
A gaming machine according to feature S1,
A determination means for determining whether or not to execute the calculation process (the process of step S10810 in FIG. 29 ),
The process execution means includes:
a parameter update process being not executed and, when the determination means determines that the calculation process is to be executed, executing the calculation process.
特徴S2によれば、パラメータ更新処理を実行しない場合であって判定手段によって算出処理を実行すると判定された場合に算出処理を実行するので、所定の処理においてパラメータ更新処理も算出処理も実行せずに、当該状況において、パラメータ更新処理及び算出処理の代わりに、これらの処理とは独立した他の処理(例えば、更新されたパラメータや、算出処理の算出結果の有効性を判定する処理等)を実行することが可能となる。さらに、1回の所定の処理においてパラメータ更新処理または算出処理のいずれかを実行した場合に当該所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が所定の間隔よりも短くなる構成であれば、当該状況において、パラメータ更新処理及び算出処理よりも処理時間の短い処理を実行することによって、当該所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間が所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまうことを確実に抑制することができる。 According to feature S2, when the parameter update process is not executed and the determination means determines that the calculation process is executed, the calculation process is executed. Therefore, it is possible to execute other processes independent of the parameter update process and the calculation process in the given situation (e.g., a process for determining the validity of the updated parameters or the calculation result of the calculation process, etc.) instead of the parameter update process and the calculation process without executing either the parameter update process or the calculation process in the given situation. Furthermore, if the configuration is such that when either the parameter update process or the calculation process is executed in one given process, the time required for one execution of the given process is shorter than the given interval, by executing a process with a shorter processing time than the parameter update process and the calculation process in the given situation, it is possible to reliably prevent the time required for one execution of the given process from becoming longer than the given interval.
[特徴S3]
特徴S1または特徴S2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、前記算出処理において複数の種別の前記遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率)を算出可能であるにも関わらず、1回の前記所定の処理における前記算出処理においては、一の種別の前記遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理(図29のタスク1またはタスク2)を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature S3]
A gaming machine according to feature S1 or feature S2,
The processing execution means is capable of calculating a plurality of types of the gaming history information (role ratio, consecutive role ratio) in the calculation process, but in the calculation process in one of the predetermined processes, executes processing (
特徴S3によれば、算出処理において複数の種別の遊技履歴情報を算出可能であるにも関わらず、1回の所定の処理における算出処理においては、一の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理を実行するので、1回の所定の処理における算出処理において複数の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理を実行する構成と比較して、所定の処理の1回の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、所定の処理の実行に要する時間が、所定の処理の実行を開始する所定の間隔よりも長くなってしまい、所定の処理を所定の間隔で実行することができなくなってしまうといったことを抑制することができる。また、算出した遊技履歴情報を一時的に記憶するための記憶容量を削減することができる。 According to feature S3, although multiple types of game history information can be calculated in the calculation process, the calculation process in one predetermined process executes the process for calculating one type of game history information. Therefore, the time required for one execution of the predetermined process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the calculation process in one predetermined process executes the process for calculating multiple types of game history information. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required for execution of the predetermined process from becoming longer than the predetermined interval for starting the execution of the predetermined process, making it impossible to execute the predetermined process at the predetermined interval. In addition, the storage capacity for temporarily storing the calculated game history information can be reduced.
[特徴S4]
特徴S3に記載の遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記一の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理(図29のタスク1またはタスク2)を、複数回の前記所定の処理に亘って実行することによって、当該一の種別の遊技履歴情報を算出する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature S4]
A gaming machine according to feature S3,
The process execution means includes:
A gaming machine characterized by calculating the one type of gaming history information by executing a process for calculating the one type of gaming history information (
特徴S4によれば、一の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出についての処理を、複数回の所定の処理に亘って実行することによって、当該一の種別の遊技履歴情報を算出するので、1回の所定の処理における算出処理において一の種別の遊技履歴情報の算出が完了する構成と比較して、1回の所定の処理の実行に要する時間を短縮することができる。この結果、所定の処理の実行に要する時間が、所定の処理の実行の間隔を超えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature S4, the process for calculating one type of gaming history information is executed over multiple predetermined processes to calculate the one type of gaming history information, so the time required to execute one predetermined process can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the calculation of one type of gaming history information is completed in a calculation process in a single predetermined process. As a result, it is possible to prevent the time required to execute the predetermined process from exceeding the interval between executions of the predetermined process.
なお、上記特徴O群~特徴S群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group O to feature group S solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, and simplifying control.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like the ones mentioned above, further technological improvements are desired in order to increase the enjoyment of the game, reduce the processing load of the gaming machine, optimize processing, simplify control, and provide a more sound gaming experience.
<特徴T群>
特徴T群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature T group>
The group of features T is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴T1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様38の主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)を記憶する情報記憶手段(フラッシュメモリ64x)と、
所定の操作を受け付ける操作手段(フラッシュメモリクリアボタン)と、
前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段(消去処理用ICチップ)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記操作手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature T1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
An information storage means (
an operation means (a flash memory clear button) for accepting a predetermined operation;
an erasing means (an IC chip for erasing) for erasing the information stored in the information storage means based on the operation of the operating means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine, wherein the operating means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a base box with a sealing sticker affixed thereto).
特徴T1によれば、操作手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして操作手段を操作することになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。 According to feature T1, since the operating means is stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening, in order to erase information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine, the space of the gaming machine is opened and the operating means is operated, so that traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether or not traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to know whether or not the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been erased.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不正な改造が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。遊技機によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該遊技機に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該遊技機に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。 If a gaming machine is illegally tampered with, the illegal tampering may affect the game that is played, and may also affect the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine. A person who inspects whether a gaming machine is playing a normal game (hereinafter also referred to as an "inspector") can discover any illegal tampering that has been applied to the gaming machine by checking the information stored in the information storage means. For this reason, there may be a person (hereinafter also referred to as an "illegal person") who wishes to erase the information in order to prevent the inspector from discovering that the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with.
しかしながら、本特徴によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして操作手段を操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、遊技機に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、遊技機に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 However, according to this feature, in order to erase the information stored in the information storage means, it is necessary to open the space of the gaming machine and operate the operating means. In that case, a trace of the opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine, and even if the information stored in the information storage means is erased, there will remain traces that the information may have been erased to conceal fraud. This makes it difficult to conceal fraudulent modifications made to the gaming machine, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivation to make fraudulent modifications to the gaming machine, thereby improving the soundness of play.
なお、遊技機は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのある遊技機(いわゆる中古の遊技機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者のみが、当該空間の開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、遊技機の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。 Gaming machines may be traded and circulated, and a person wishing to distribute a gaming machine that has already been used in play (a so-called used gaming machine) may have a legitimate request to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine before distributing it. If a distribution system were established in which only a person who has a legitimate request to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine could erase the traces of the opening of the space, it would be possible to promote the smooth distribution of gaming machines while ensuring the soundness of gaming.
[特徴T2]
特徴T1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature T2]
A gaming machine according to feature T1,
The gaming machine, wherein the information storage means is capable of retaining stored information even when the power supply is cut off.
特徴T2によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれた場合であっても、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を保持することができるので、例えば、流通過程において遊技機に電源が供給されない場合であっても、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature T2, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the information acquired based on the game that was played can be retained. Therefore, for example, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is not supplied during the distribution process, it is possible to check whether or not normal play was performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴T3]
特徴T1または特徴T2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報(賞球集計値)を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature T3]
A gaming machine according to feature T1 or feature T2,
The information acquired based on the executed game includes information regarding the number of game balls already paid out as prize balls (a prize ball tally).
特徴T3によれば、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報を利用することによって、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature T3, by using information regarding the number of game balls that have already been paid out as prize balls, it is possible to check whether normal play has been performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴T4]
特徴T1から特徴T3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature T4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features T1 to T3,
The information storage means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a base box with a sealing sticker affixed thereto).
特徴T4によれば、情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、当該情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうとするためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にすることになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変が施された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に施された不正な改変の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature T4, since the information storage means is stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening, in order to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, the space of the gaming machine must be opened, and traces of opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to grasp whether the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been unauthorizedly changed. This makes it difficult to conceal unauthorized changes made to the information stored in the information storage means, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivations to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, thereby improving the soundness of the game.
<特徴U群>
特徴U群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic U group>
The group of features U is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴U1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様39の主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)を記憶する情報記憶手段(フラッシュメモリ64x)と、
所定の装置(検査機320)を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段(消去処理用ICチップ)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置から所定の信号(消去命令信号)を受信したことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature U1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
An information storage means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) can be connected;
an erasing means (an IC chip for erasing) for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The erasing means comprises means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means based on receipt of a predetermined signal (erasing command signal) from the predetermined device connected to the connection means.
特徴U1によれば、消去手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する手段を備えるので、所定の装置を有する者が、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去することができる。すなわち、所定の装置を有さない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。 According to feature U1, the erasing means includes means for erasing information stored in the information storage means based on receipt of a specified signal from a specified device connected to the connection means, so that a person who has the specified device can erase the information stored in the information storage means. In other words, it is possible to restrict the erasure of the information by a person who does not have the specified device.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不正な改造が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。遊技機によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該遊技機に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該遊技機に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。 If a gaming machine is illegally tampered with, the illegal tampering may affect the game that is played, and may also affect the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine. A person who inspects whether a gaming machine is playing a normal game (hereinafter also referred to as an "inspector") can discover any illegal tampering that has been applied to the gaming machine by checking the information stored in the information storage means. For this reason, there may be a person (hereinafter also referred to as an "illegal person") who wishes to erase the information in order to prevent the inspector from discovering that the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with.
しかしながら、本特徴によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の接続手段に接続可能な所定の装置が必要となる。そして、当該所定の装置を有することができる者を制限すれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができ、ひいては、遊技機に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 However, according to this feature, in order to erase the information stored in the information storage means, a specific device that can be connected to the connection means of the gaming machine is required. Then, by restricting who can have the specific device, it is possible to prevent information stored in the information storage means from being erased by unauthorized persons, which in turn makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of motivation to make unauthorized modifications to the gaming machine, thereby improving the soundness of gaming.
なお、遊技機は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのある遊技機(いわゆる中古の遊技機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者のみが、所定の装置を有することが可能な流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、遊技機の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。 Gaming machines may be traded and circulated, and a person wishing to distribute a gaming machine that has already been used in play (a so-called used gaming machine) may have a legitimate request to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine before distributing it. Therefore, if a distribution system is established in which only those who wish to erase the information stored in the information storage means of a gaming machine for a legitimate reason can own the required equipment, it will be possible to promote the smooth distribution of gaming machines while ensuring the soundness of gaming.
[特徴U2]
特徴U1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記消去手段が前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去することに先立って、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature U2]
A gaming machine according to feature U1,
a transmission means for transmitting the information stored in the information storage means to the specified device connected to the connection means before the erasing means erases the information stored in the information storage means.
特徴U2によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去手段が消去することに先立って、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を接続手段に接続された所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備えるので、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が、所定の装置を有する者の意思に反した操作によって誤って消去されてしまった場合であっても、情報記憶手段から消去されてしまった当該情報を当該所定の装置によって確認することができる。 According to feature U2, a transmission means is provided for transmitting the information stored in the information storage means to a specified device connected to the connection means before the erasing means erases the information stored in the information storage means. Therefore, even if the information stored in the information storage means is mistakenly erased by an operation against the will of the owner of the specified device, the information erased from the information storage means can be confirmed by the specified device.
[特徴U3]
特徴U1または特徴U2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature U3]
A gaming machine according to feature U1 or feature U2,
The gaming machine, wherein the information storage means is capable of retaining stored information even when the power supply is cut off.
特徴U3によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれた場合であっても、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を保持することができるので、例えば、流通過程において遊技機に電源が供給されない場合であっても、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature U3, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the information acquired based on the game that was played can be retained. For example, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is not supplied during the distribution process, it is possible to check whether or not normal play was performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴U4]
特徴U1から特徴U3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報(賞球集計値)を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature U4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features U1 to U3,
The information acquired based on the executed game includes information regarding the number of game balls already paid out as prize balls (a prize ball tally).
特徴U4によれば、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報を利用することによって、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature U4, by using information regarding the number of game balls that have already been paid out as prize balls, it is possible to check whether normal play has been performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴U5]
特徴U1から特徴U4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature U5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features U1 to U4,
The information storage means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a base box with a sealing sticker affixed thereto).
特徴U5によれば、情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、当該情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうとするためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にすることになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変が施された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に施された不正な改変の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature U5, since the information storage means is stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening, in order to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, the space of the gaming machine must be opened, and traces of opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to grasp whether the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been unauthorizedly changed. This makes it difficult to conceal unauthorized changes made to the information stored in the information storage means, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivations to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, thereby improving the soundness of the game.
<特徴V群>
特徴V群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature V Group>
The group of features V is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴V1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様40の主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)を記憶する情報記憶手段(フラッシュメモリ64x)と、
所定の装置(検査機320)を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
所定の操作を受け付ける操作手段(フラッシュメモリクリアボタン)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段(消去処理用ICチップ)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記操作手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されており、
前記消去手段は、前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付け、かつ、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置から所定の信号(消去命令信号)を受信したことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature V1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
An information storage means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device (inspection machine 320) can be connected;
an operation means (a flash memory clear button) for accepting a predetermined operation;
an erasing means (an IC chip for erasing) for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The operating means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a board box with a seal attached thereto),
The erasing means comprises means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means accepting the specified operation and receiving a specified signal (erase command signal) from the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴V1によれば、操作手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして操作手段を操作することになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。さらに、消去手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する手段を備えるので、所定の装置を有する者が、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去することができる。したがって、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となるとともに、所定の装置を有さない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。 According to feature V1, since the operating means is stored inside the space where traces of opening remain, in order to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine, the space of the gaming machine is opened and the operating means is operated, so that traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine. Furthermore, since the erasing means includes a means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means based on receiving a predetermined signal from a predetermined device connected to the connection means, a person who has the predetermined device can erase the information stored in the information storage means. Therefore, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to know whether the space of the gaming machine may have been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been erased, and it is also possible to restrict the erasure of the information by a person who does not have the predetermined device.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不正な改造が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。遊技機によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該遊技機に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該遊技機に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。 If a gaming machine is illegally tampered with, the illegal tampering may affect the game that is played, and may also affect the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine. A person who inspects whether a gaming machine is playing a normal game (hereinafter also referred to as an "inspector") can discover any illegal tampering that has been applied to the gaming machine by checking the information stored in the information storage means. For this reason, there may be a person (hereinafter also referred to as an "illegal person") who wishes to erase the information in order to prevent the inspector from discovering that the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with.
しかしながら、本特徴によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の接続手段に接続可能な所定の装置が必要となる。そして、当該所定の装置を有することができる者を制限すれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。さらに、仮に不正な者が所定の装置を有してしまった場合であっても、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして操作手段を操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができるとともに、遊技機に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができる。この結果、遊技機に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生をさらに抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 However, according to this feature, in order to erase the information stored in the information storage means, a specific device that can be connected to the connection means of the gaming machine is required. If the persons who can have the specific device are restricted, it is possible to prevent the information stored in the information storage means from being erased by an unauthorized person. Furthermore, even if an unauthorized person has the specific device, in order to erase the information stored in the information storage means, it is necessary to open the space of the gaming machine and operate the operation means. In that case, a trace of the opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine, so that even if the information stored in the information storage means is erased, a trace will remain that indicates that the information may have been erased to conceal fraud. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the information stored in the information storage means from being erased by an unauthorized person, and it is also possible to make it difficult to conceal fraudulent modifications made to the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to further suppress the occurrence of motivations to make fraudulent modifications to the gaming machine, and the soundness of the game can be improved.
なお、遊技機は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのある遊技機(いわゆる中古の遊技機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者のみが、所定の装置を有することが可能であるとともに当該空間の開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、遊技機の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。 Gaming machines may be traded and circulated, and a person wishing to distribute a gaming machine that has already been used for gaming (a so-called used gaming machine) may have a legitimate request to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine before distributing it. Therefore, if a distribution system were established in which only those who wish to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine for a legitimate reason could have the required equipment and in which traces of the opening of the space could be erased, it would be possible to promote the smooth distribution of gaming machines while ensuring the soundness of gaming.
[特徴V2]
特徴V1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記消去手段が前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去することに先立って、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature V2]
A gaming machine according to feature V1,
a transmission means for transmitting the information stored in the information storage means to the specified device connected to the connection means before the erasing means erases the information stored in the information storage means.
特徴V2によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去手段が消去することに先立って、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を接続手段に接続された所定の装置に送信する送信手段を備えるので、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が、所定の装置を有する者の意思に反した操作によって誤って消去されてしまった場合であっても、情報記憶手段から消去されてしまった当該情報を当該所定の装置によって確認することができる。 According to feature V2, a transmission means is provided for transmitting the information stored in the information storage means to a specified device connected to the connection means before the erasing means erases the information stored in the information storage means. Therefore, even if the information stored in the information storage means is erroneously erased by an operation against the will of the owner of the specified device, the information erased from the information storage means can be confirmed by the specified device.
[特徴V3]
特徴V1または特徴V2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature V3]
A gaming machine according to feature V1 or feature V2,
The gaming machine, wherein the information storage means is capable of retaining stored information even when the power supply is cut off.
特徴V3によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれた場合であっても、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を保持することができるので、例えば、流通過程において遊技機に電源が供給されない場合であっても、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature V3, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the information acquired based on the game that was played can be retained. Therefore, for example, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is not supplied during the distribution process, it is possible to check whether the game was played normally on the gaming machine.
[特徴V4]
特徴V1から特徴V3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報(賞球集計値)を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature V4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features V1 to V3,
The information acquired based on the executed game includes information regarding the number of game balls already paid out as prize balls (a prize ball tally).
特徴V4によれば、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報を利用することによって、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature V4, by using information regarding the number of game balls that have already been paid out as prize balls, it is possible to check whether normal play has been performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴V5]
特徴V1から特徴V4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature V5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features V1 to V4,
The information storage means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a base box with a sealing sticker affixed thereto).
特徴V5によれば、情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、当該情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうとするためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にすることになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変が施された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に施された不正な改変の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature V5, since the information storage means is stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening, in order to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, the space of the gaming machine must be opened, and traces of opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to grasp whether the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been unauthorizedly changed. This makes it difficult to conceal unauthorized changes made to the information stored in the information storage means, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivations to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, thereby improving the soundness of the game.
<特徴W群>
特徴W群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature W group>
The group of features W is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴W1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様46の主側CPU62x)と、
前記制御手段による前記遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている遊技進行処理に用いられる情報)と、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)とを記憶する情報記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第2の情報を消去する際には前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第1の情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature W1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
an information storage means (main RAM 64) for storing first information (information used for game progress processing stored in a first area of the main RAM 64) which is information used for controlling the execution of the game by the control means, and second information (game history information such as the prize ball tally, the ratio of roles, and the number of winning balls, stored in a second area of the main RAM 64) which is information acquired based on the executed game;
an erasing means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
said erasing means further comprising means for erasing said first information stored in said information storage means when erasing said second information stored in said information storage means.
特徴W1によれば、消去手段は、第2の情報を消去する際には第1の情報を消去する手段を備えるので、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報が消去されたにも関わらず、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報が消去されずにそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature W1, the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information when erasing the second information, so that it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the first information, which is information used to control the execution of the game, is not erased but is maintained as is even though the second information, which is information acquired based on the executed game, has been erased.
具体的には、例えば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報は、当該遊技機において実行された遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる情報であるため、当該第2の情報が消去された場合には、当該遊技機における遊技の実行の制御に用いられる第1の情報(例えば、遊技状態を示す高確率モードフラグや高頻度サポートモードフラグに関する情報)を消去して当該遊技機の遊技状態を初期化することが好ましい。本特徴によれば、消去手段は、第2の情報を消去する際には第1の情報を消去する手段を備えるので、遊技の公正さを判断するための担保となる第2の情報が消去されたにも関わらず、第1の情報が消去されないことによって当該遊技機の遊技状態がそのまま維持されるといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 Specifically, for example, the second information, which is information acquired based on an executed game, is information that serves as a guarantee for judging the fairness of the game executed on the gaming machine, so when the second information is erased, it is preferable to erase the first information (e.g., information on a high probability mode flag or a high frequency support mode flag that indicates the game state) used to control the execution of the game on the gaming machine to initialize the game state of the gaming machine. According to this feature, since the erasing means includes a means for erasing the first information when erasing the second information, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of a situation in which the game state of the gaming machine is maintained as it is because the first information is not erased even though the second information that serves as a guarantee for judging the fairness of the game has been erased.
[特徴W2]
特徴W1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、前記第1の情報を消去し、前記第2の情報は消去しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature W2]
A gaming machine according to feature W1,
the erasing means comprises means for erasing the first information and not erasing the second information among the information stored in the information storage means.
特徴W2によれば、消去手段は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、第1の情報を消去し、第2の情報は消去しない手段を備えるので、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去することが可能となる。 According to feature W2, the erasing means includes a means for erasing the first information and not erasing the second information among the information stored in the information storage means, so that it is possible to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of the game, while leaving the second information, which is information obtained based on the executed game.
具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や、遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したいが、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報は消去したくないといった要望がある。本特徴によれば、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去して当該遊技機の制御の初期化を実行することが可能となる。 Specifically, for example, when a problem occurs in controlling the execution of a game or when an amusement parlor starts or closes its business hours, there is a desire to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of a game, and initialize the control of the gaming machine, but not to erase the second information, which is information acquired based on the game that has been executed. With this feature, it is possible to initialize the control of the gaming machine by erasing the first information, which is information used to control the execution of a game, while leaving the second information, which is information acquired based on the game that has been executed.
<特徴X群>
特徴X群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group X>
The group of features X is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴X1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様42の主側CPU62x)と、
前記制御手段による前記遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている遊技進行処理に用いられる情報)と、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)とを記憶する情報記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
第1の操作(RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態でパチンコ機10の電源をONにする操作)を受け付ける第1の操作手段(RAMクリアボタン及び電源スイッチ)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記第1の操作手段が前記第1の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、前記第1の情報を消去し、前記第2の情報は消去しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature X1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
an information storage means (main RAM 64) for storing first information (information used for game progress processing stored in a first area of the main RAM 64) which is information used for controlling the execution of the game by the control means, and second information (game history information such as the prize ball tally, the ratio of roles, and the number of winning balls, stored in a second area of the main RAM 64) which is information acquired based on the executed game;
A first operation means (a RAM clear button and a power switch) for accepting a first operation (an operation of turning on the power of the
an erasing means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information and not erasing the second information among the information stored in the information storage means, based on the first operation means accepting the first operation.
特徴X1によれば、消去手段は、第1の操作手段が第1の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、第1の情報を消去し、第2の情報は消去しない手段を備えるので、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去することが可能となる。 According to feature X1, the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information and not erasing the second information among the information stored in the information storage means based on the first operation being received by the first operating means, so that it is possible to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of the game, while leaving the second information, which is information obtained based on the executed game.
具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や、遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したいが、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報は消去したくないといった要望がある。本特徴によれば、第1の操作手段を操作することによって、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報を残しつつ、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去して当該遊技機の制御の初期化を実行することが可能となる。 Specifically, for example, when a malfunction occurs in controlling the execution of a game or when an amusement parlor starts or closes its business hours, there is a desire to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of a game, and initialize the control of the gaming machine, but not to erase the second information, which is information acquired based on the executed game. According to this feature, by operating the first operating means, it is possible to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of a game, while leaving the second information, which is information acquired based on the executed game, and initialize the control of the gaming machine.
[特徴X2]
特徴X1に記載の遊技機であって、
第2の操作(パチンコ機10の電源のON中に第2RAMクリアボタンを所定時間押下するという操作)を受け付ける第2の操作手段(第2RAMクリアボタン)を備え、
前記消去手段は、前記第2の操作手段が前記第2の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第2の情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature X2]
A gaming machine according to feature X1,
a second operation means (a second RAM clear button) for accepting a second operation (an operation of pressing the second RAM clear button for a predetermined period of time while the power of the
the erasing means comprising means for erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the second operation being accepted by the second operation means.
特徴X2によれば、消去手段は、第2の操作手段が第2の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去する手段を備えるので、第1の操作手段を操作することによっては消去することのできない第2の情報を、第2の操作手段を操作することによって消去することができる。 According to feature X2, the erasing means includes means for erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the second operation being accepted by the second operating means, so that the second information that cannot be erased by operating the first operating means can be erased by operating the second operating means.
[特徴X3]
特徴X2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2の操作手段(第2RAMクリアボタン)は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature X3]
A gaming machine according to feature X2,
The second operating means (second RAM clear button) is stored inside a space that shows signs of being opened (inside a board box with a seal sticker affixed thereto).
特徴X3によれば、第2の操作手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして第2の操作手段を操作することになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報が消去された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。 According to feature X3, since the second operating means is stored inside the space where traces of opening remain, in order to erase the second information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine, the space of the gaming machine is opened and the second operating means is operated, and traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to know whether the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the second information stored in the information storage means may have been erased.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不正な改造が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。遊技機によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該遊技機に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該遊技機に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。 If a gaming machine is illegally tampered with, the illegal tampering may affect the game that is played, and may also affect the second information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine. A person who inspects whether a game is being played normally on a gaming machine (hereinafter also referred to as an "inspector") can discover any illegal tampering that has been applied to the gaming machine by checking the information stored in the information storage means. For this reason, there may be a person (hereinafter also referred to as an "illegal person") who wishes to erase the information in order to prevent the inspector from discovering that the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with.
しかしながら、本特徴によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去するためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にして第2の操作手段を操作する必要がある。そうすると、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになるので、情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去したとしても、当該情報を不正の隠蔽のために消去した可能性があるといった痕跡が残ることになる。したがって、遊技機に施された不正な改造の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、遊技機に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 However, according to this feature, in order to erase the second information stored in the information storage means, it is necessary to open the space of the gaming machine and operate the second operating means. In that case, a trace of the opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine, so even if the second information stored in the information storage means is erased, there will remain traces that the information may have been erased to conceal fraud. This makes it difficult to conceal fraudulent modifications made to the gaming machine, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivations to make fraudulent modifications to the gaming machine, thereby improving the soundness of play.
なお、遊技機は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのある遊技機(いわゆる中古の遊技機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者のみが、当該空間の開放の痕跡を消すことのできる流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、遊技機の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。 Gaming machines may be traded and circulated, and a person who wishes to distribute a gaming machine that has already been used for gaming (a so-called used gaming machine) may have a legitimate request to erase the second information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine before distributing it. Therefore, if a distribution system is established in which only a person who has a legitimate request to erase the second information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine can erase the traces of the opening of the space, it will be possible to promote the smooth distribution of gaming machines while ensuring the soundness of gaming.
<特徴Y群>
特徴Y群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic Group Y>
The group of features Y is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴Y1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様43、44の主側CPU62x)と、
前記制御手段による前記遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報(主側RAM64の第1エリアに記憶されている遊技進行処理に用いられる情報)と、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報(主側RAM64の第2エリアに記憶されている賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)とを記憶する情報記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
所定の操作を受け付ける操作手段(RAMクリアボタン及び電源スイッチ)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、
前記操作手段が第1の操作(RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにし、パチンコ機10の電源がONにされてから所定時間以内にRAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態にするという操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第1の情報を消去し、
前記操作手段が前記第1の操作とは異なる第2の操作(RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにし、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態をそのまま所定時間継続させるという操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第2の情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Y1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
an information storage means (main RAM 64) for storing first information (information used for game progress processing stored in a first area of the main RAM 64) which is information used for controlling the execution of the game by the control means, and second information (game history information such as prize ball tally, role ratio, number of winning balls, etc. stored in a second area of the main RAM 64) which is information acquired based on the executed game;
Operation means for accepting predetermined operations (RAM clear button and power switch);
an erasing means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The erasing means is
The first information stored in the information storage means is erased based on the fact that the operation means has accepted a first operation (an operation of turning on the power of the
A gaming machine characterized in that it is provided with a means for erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means accepting a second operation different from the first operation (an operation of turning on the power of the
特徴Y1によれば、消去手段は、操作手段が第1の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第1の情報を消去し、操作手段が第1の操作とは異なる第2の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、情報記憶手段に記憶されている第2の情報を消去する手段を備えるので、操作手段に対して異なる操作を実行することによって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することが可能となる。すなわち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択するための他の操作手段を設けなくても、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することができるので、遊技機の構造の簡素化を図ることができる。 According to feature Y1, the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means receiving a first operation, and for erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means receiving a second operation different from the first operation, so that by executing different operations on the operation means, it becomes possible to select information to be erased from among the information stored in the information storage means. In other words, since it is possible to select information to be erased without providing another operation means for selecting information to be erased, the structure of the gaming machine can be simplified.
具体的には、例えば、遊技の実行の制御に不具合が生じた場合や遊技ホールの営業の開始時または終了時において、遊技の実行の制御に用いられる情報である第1の情報を消去して遊技機の制御の初期化を実行したい場合には、第1の操作を実行し、一方、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報である第2の情報を消去して当該遊技機を新たに流通させたい場合には、第2の操作を実行すればよい。このように、操作手段に対して異なる操作を実行することによって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、消去すべき対象の情報を選択することが可能となる。 Specifically, for example, if it is desired to erase the first information, which is information used to control the execution of games, and initialize the control of the gaming machine when a malfunction occurs in the control of the execution of games or when the business hours of the gaming hall are opened or closed, a first operation is executed, whereas if it is desired to erase the second information, which is information acquired based on the executed games, and to newly distribute the gaming machine, a second operation is executed. In this way, by executing different operations on the operating means, it is possible to select the information to be erased from the information stored in the information storage means.
[特徴Y2]
特徴Y1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記操作手段が前記第2の操作(RAMクリアボタンを押下しながらパチンコ機10の電源をONにし、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態をそのまま所定時間継続させるという操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第2の情報を消去することに加えて前記第1の情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Y2]
A gaming machine according to feature Y1,
The gaming machine is characterized in that the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information in addition to erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means accepting the second operation (an operation of turning on the power of the
特徴Y2によれば、消去手段は、操作手段が第2の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記第2の情報を消去することに加えて前記第1の情報を消去する手段を備えるので、操作手段に対して第2の操作を実行することによって、第1の情報と第2の情報の両方を消去することができる。 According to feature Y2, the erasing means includes means for erasing the first information in addition to erasing the second information stored in the information storage means based on the operation means receiving a second operation, so that both the first information and the second information can be erased by executing the second operation on the operation means.
<特徴Z群>
特徴Z群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics Group Z>
The group of features Z is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴Z1]
遊技の実行を制御する制御手段(第1実施形態の態様41の主側CPU62x)と、
実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報(賞球集計値、役物比率等の遊技履歴情報、入球個数情報等)を記憶する情報記憶手段(フラッシュメモリ64x)と、
前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去手段(消去処理用ICチップ)と、
認証情報(暗証番号)を受け付ける受付手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記受付手段が受け付けた認証情報が所定の条件を満たしたことに基づいて、前記情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Z1]
A control means for controlling the execution of a game (
An information storage means (
an erasing means (an IC chip for erasing) for erasing the information stored in the information storage means;
A reception means for receiving authentication information (a personal identification number);
A gaming machine comprising:
the erasing means comprising means for erasing the information stored in the information storage means based on the authentication information accepted by the accepting means satisfying a predetermined condition.
特徴Z1によれば、消去手段は、受付手段が受け付けた認証情報が所定の条件を満たしたことに基づいて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する手段を備えるので、当該所定の条件を満たす認証情報を有する者が、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去することができる。すなわち、当該所定の条件を満たす認証情報を有しない者による当該情報の消去を制限することが可能となる。 According to feature Z1, the erasing means includes means for erasing information stored in the information storage means based on the fact that the authentication information accepted by the accepting means satisfies a predetermined condition, so that a person who has authentication information that satisfies the predetermined condition can erase the information stored in the information storage means. In other words, it is possible to restrict the erasure of the information by a person who does not have authentication information that satisfies the predetermined condition.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不正な改造が施されている場合には、実行された遊技に当該不正な改造による影響が表れ、さらに、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に当該不正な改造による影響が表れる場合がある。遊技機によって正常な遊技が実行されているか否かを検査する者(以下、「検査者」ともいう)は、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を確認することによって、当該遊技機に施された不正な改造を発見することができる。このため、当該情報を消去することによって当該遊技機に不正な改造が施されていることを検査者に発見されないようにしたいといった要望を抱く者(以下、「不正な者」ともいう)が存在する可能性がある。 If a gaming machine is illegally tampered with, the illegal tampering may affect the game that is played, and may also affect the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine. A person who inspects whether a gaming machine is playing a normal game (hereinafter also referred to as an "inspector") can discover any illegal tampering that has been applied to the gaming machine by checking the information stored in the information storage means. For this reason, there may be a person (hereinafter also referred to as an "illegal person") who wishes to erase the information in order to prevent the inspector from discovering that the gaming machine has been illegally tampered with.
しかしながら、本特徴によれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去するためには、当該所定の条件を満たす認証情報を有していることが必要となる。そして、当該所定の条件を満たす認証情報を有することができる者を制限すれば、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報が不正な者によって消去されてしまうことを抑制することができ、ひいては、遊技機に不正な改造を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 However, according to this feature, in order to erase information stored in the information storage means, it is necessary to have authentication information that satisfies the specified conditions. Then, by restricting those who can have authentication information that satisfies the specified conditions, it is possible to prevent information stored in the information storage means from being erased by unauthorized persons, which in turn makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of motivation to make unauthorized modifications to gaming machines, thereby improving the soundness of gaming.
なお、遊技機は取引によって転々流通する場合があり、既に遊技が実行されたことのある遊技機(いわゆる中古の遊技機)を新たに流通させたい者は、当該遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去してから流通させたいといった正当な要望を抱く場合もある。そこで、遊技機の情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報を正当な理由で消去したいといった要望を抱く者のみが、当該所定の条件を満たす認証情報を有することが可能な流通体制を構築すれば、遊技の健全性を確保しつつ、遊技機の円滑な流通を促すことが可能となる。 Gaming machines may be traded and circulated, and a person who wishes to distribute a gaming machine that has already been used in play (a so-called used gaming machine) may have a legitimate request to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine before distributing it. Therefore, if a distribution system is established in which only those who wish to erase the information stored in the information storage means of the gaming machine for a legitimate reason can obtain authentication information that satisfies the specified conditions, it will be possible to promote the smooth distribution of gaming machines while ensuring the soundness of gaming.
[特徴Z2]
特徴Z1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、電源の供給が断たれても記憶を保持することが可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Z2]
A gaming machine according to feature Z1,
The gaming machine, wherein the information storage means is capable of retaining stored information even when the power supply is cut off.
特徴Z2によれば、遊技機への電源の供給が断たれた場合であっても、実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報を保持することができるので、例えば、流通過程において遊技機に電源が供給されない場合であっても、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature Z2, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, the information acquired based on the game that was played can be retained. For example, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is not supplied during the distribution process, it is possible to check whether or not normal play was performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴Z3]
特徴Z1または特徴Z2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記実行された遊技に基づいて取得された情報は、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報(賞球集計値)を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Z3]
A gaming machine according to feature Z1 or feature Z2,
The information acquired based on the executed game includes information regarding the number of game balls already paid out as prize balls (a prize ball tally).
特徴Z3によれば、既に賞球として払い出された遊技球の個数に関する情報を利用することによって、当該遊技機において正常な遊技が実行されていたか否かを検査することが可能となる。 According to feature Z3, by using information regarding the number of game balls that have already been paid out as prize balls, it is possible to check whether normal play has been performed on the gaming machine.
[特徴Z4]
特徴Z1から特徴Z3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部(封印シールが貼付された基板ボックスの内部)に格納されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature Z4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features Z1 to Z3,
The information storage means is stored inside a space that shows signs of having been opened (inside a base box with a sealing sticker affixed thereto).
特徴Z4によれば、情報記憶手段は、開放の痕跡が残る空間の内部に格納されているので、当該情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうとするためには、当該遊技機の当該空間を開放状態にすることになり、当該遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残ることになる。すなわち、遊技機の当該空間に開放の痕跡が残っているか否かに基づいて、当該遊技機の当該空間が開放状態にされて情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変が施された可能性があるか否かを把握することが可能となる。したがって、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に施された不正な改変の隠蔽を困難にすることができ、ひいては、情報記憶手段に記憶されている情報に不正な改変を施そうといった動機の発生を抑制することが可能となり、遊技の健全性を向上させることができる。 According to feature Z4, since the information storage means is stored inside a space that leaves traces of opening, in order to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, the space of the gaming machine must be opened, and traces of opening will remain in the space of the gaming machine. In other words, based on whether traces of opening remain in the space of the gaming machine, it is possible to grasp whether the space of the gaming machine has been opened and the information stored in the information storage means may have been unauthorizedly changed. This makes it difficult to conceal unauthorized changes made to the information stored in the information storage means, and ultimately makes it possible to suppress the occurrence of motivations to make unauthorized changes to the information stored in the information storage means, thereby improving the soundness of the game.
なお、上記特徴T群~特徴Z群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature groups T to Z solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, and simplifying the structure.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those mentioned above, further technological improvements are desired in order to increase the enjoyment of the game, reduce the processing load of the gaming machine, optimize processing, simplify control, simplify the structure, and provide a more sound game experience.
<特徴αA群>
特徴αA群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αA group>
The group of features αA is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αA1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する信号出力手段(各入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記信号に基づいて前記入球部に遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報である判定情報(入球情報)を出力する判定情報出力手段(入球検知用IC62c)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の進行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
所定の装置を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記制御手段を介さずに前記判定情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αA1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A signal output means (each of the ball
a judgment information output means (ball
A control means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device can be connected;
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine, wherein the determination information output means comprises means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means without going through the control means.
特徴αA1によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報を受信することが可能となる。 According to feature αA1, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that the specific device can receive judgment information that is not affected by the control means.
例えば、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介して判定情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、所定の装置に出力される判定情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。 For example, if the configuration of this characteristic were not adopted, but rather a configuration were adopted in which judgment information was output via a control means to a specific device connected to the connection means, and if the control means had a malfunction or was tampered with illegally, there is a risk that the malfunction or tampering would affect the judgment information output to the specific device.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、所定の装置に出力される判定情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to the specified device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that even if the control means has a malfunction or has been illegally tampered with, the malfunction or illegal tampering will not affect the judgment information output to the specified device. As a result, the specified device connected to the connection means can execute processing based on judgment information that is not affected by the malfunction or illegal tampering.
[特徴αA2]
特徴αA1に記載の遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な前記入球部と、前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する前記信号出力手段とをそれぞれ複数備え、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記複数の信号出力手段のそれぞれから出力された前記信号に基づいて前記複数の入球部のぞれぞれに遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報であって前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した情報である前記判定情報(入球情報)を、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、シリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αA2]
A gaming machine according to feature αA1,
a plurality of ball entry sections into which game balls can enter, and a plurality of signal output means for outputting a signal based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
The gaming machine is characterized in that the judgment information output means is provided with a means for judging whether or not a gaming ball has entered each of the multiple ball entry points based on the signals output from each of the multiple signal output means, and for outputting the judgment information (ball entry information), which is information based on the judgment and corresponds to each of the multiple ball entry points, to the specified device connected to the connection means via a serial transmission method.
特徴αA2によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、例えば、判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合と比較して、当該判定情報を所定の装置に経由させる接続手段の構成を簡略化することができるとともに、当該判定情報を受信する所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。 According to feature αA2, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to a specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method. Therefore, compared to a configuration in which judgment information is output by a parallel transmission method, for example, it is possible to simplify the configuration of the connection means that routes the judgment information to the specified device, and also to simplify the configuration of the specified device that receives the judgment information.
具体的には、仮に、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合には、接続手段は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した出力部を備える必要がある。同様に、所定の装置は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した入力部を備える必要がある。また、遊技機が備える入球部の個数は、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なるため、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なる個数の端子を備えた所定の装置を用意する必要が生じる。 Specifically, if a configuration is adopted in which judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections is output using a parallel transmission method, the connection means must have an output section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Similarly, the specified device must have an input section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Furthermore, since the number of ball entry sections provided in a gaming machine differs for each type (model) of gaming machine, it becomes necessary to prepare a specified device with a different number of terminals for each type (model) of gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、接続手段は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって判定情報を出力することのできる出力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよい。したがって、接続手段の構成を簡略化することができる。同様に、所定の装置は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって出力された判定情報を入力することのできる入力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよいので、所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。さらに、入球部の個数の異なる遊技機に所定の装置を接続した場合であっても、当該所定の装置は、シリアル伝送方式によって複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報を入力することができる。すなわち、所定の装置を、入球部の個数の異なる他の遊技機に対しても利用することが可能となる。この結果、所定の装置の汎用性を高めることが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to the specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method, so the connection means may be configured to include at least one output section that can output judgment information by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine. Therefore, the configuration of the connection means can be simplified. Similarly, the specified device may be configured to include at least one input section that can input judgment information output by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine, so the configuration of the specified device can be simplified. Furthermore, even if the specified device is connected to a gaming machine with a different number of ball entry sections, the specified device can input judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections by a serial transmission method. In other words, the specified device can be used for other gaming machines with a different number of ball entry sections. As a result, it is possible to increase the versatility of the specified device.
[特徴αA3]
特徴αA1または特徴αA2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段は、前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出可能な前記所定の装置を接続可能に構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αA3]
A gaming machine according to feature αA1 or feature αA2,
The connection means is configured to be capable of connecting to the specified device capable of calculating gaming history information (gaming history information such as device ratios), which is information regarding the history of gaming, based on the judgment information.
特徴αA3によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の性能を検査する検査者は、制御手段による影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を所定の装置によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。 According to feature αA3, a specified device connected to the connection means can calculate game history information based on judgment information that is not affected by the control means. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the performance of the gaming machine can check game history information that is not affected by the control means using the specified device. As a result, the soundness of the game can be ensured.
<特徴αB群>
特徴αB群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αB group>
The group of features αB is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αB1]
遊技球が入球可能な複数の入球部と、
前記複数の入球部のそれぞれへの遊技球の入球に基づいた信号をそれぞれ出力する複数の信号出力手段(各入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記複数の信号出力手段のそれぞれから出力された前記信号に基づいて前記複数の入球部のぞれぞれに遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報であって前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した情報である判定情報(入球情報)を出力する判定情報出力手段(入球検知用IC62c)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の進行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
所定の装置を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した前記判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αB1]
A plurality of ball entry sections into which game balls can enter;
A plurality of signal output means (ball
a judgment information output means (ball
A control means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device can be connected;
A gaming machine comprising:
A gaming machine characterized in that the judgment information output means includes means for outputting the judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to the specified device connected to the connection means via a serial transmission method.
特徴αB1によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、例えば、判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合と比較して、当該判定情報を所定の装置に経由させる接続手段の構成を簡略化することができるとともに、当該判定情報を受信する所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。 According to feature αB1, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to a specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method. Therefore, compared to a configuration in which judgment information is output by a parallel transmission method, for example, it is possible to simplify the configuration of the connection means that routes the judgment information to the specified device, and also to simplify the configuration of the specified device that receives the judgment information.
具体的には、仮に、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合には、接続手段は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した出力部を備える必要がある。同様に、所定の装置は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した入力部を備える必要がある。また、遊技機が備える入球部の個数は、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なるため、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なる個数の端子を備えた所定の装置を用意する必要が生じる。 Specifically, if a configuration is adopted in which judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections is output using a parallel transmission method, the connection means must have an output section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Similarly, the specified device must have an input section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Furthermore, since the number of ball entry sections provided in a gaming machine differs for each type (model) of gaming machine, it becomes necessary to prepare a specified device with a different number of terminals for each type (model) of gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、接続手段は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって判定情報を出力することのできる出力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよい。したがって、接続手段の構成を簡略化することができる。同様に、所定の装置は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって出力された判定情報を入力することのできる入力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよいので、所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。さらに、入球部の個数の異なる遊技機に所定の装置を接続した場合であっても、当該所定の装置は、シリアル伝送方式によって複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報を入力することができる。すなわち、所定の装置を、入球部の個数の異なる他の遊技機に対しても利用することが可能となる。この結果、所定の装置の汎用性を高めることが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to the specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method, so the connection means may be configured to include at least one output section that can output judgment information by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine. Therefore, the configuration of the connection means can be simplified. Similarly, the specified device may be configured to include at least one input section that can input judgment information output by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine, so the configuration of the specified device can be simplified. Furthermore, even if the specified device is connected to a gaming machine with a different number of ball entry sections, the specified device can input judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections by a serial transmission method. In other words, the specified device can be used for other gaming machines with a different number of ball entry sections. As a result, it is possible to increase the versatility of the specified device.
[特徴αB2]
特徴αB1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段は、前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出可能な前記所定の装置を接続可能に構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αB2]
A gaming machine according to feature αB1,
The connection means is configured to be capable of connecting to the specified device capable of calculating gaming history information (gaming history information such as device ratios), which is information regarding the history of gaming, based on the judgment information.
特徴αB2によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の性能を検査する検査者は、制御手段による影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を所定の装置によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。 According to feature αB2, a specified device connected to the connection means can calculate game history information based on judgment information that is not affected by the control means. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the performance of the gaming machine can check game history information that is not affected by the control means using the specified device. As a result, the soundness of the game can be ensured.
[特徴αB3]
特徴αB1または特徴αB2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記制御手段を介さずに前記判定情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αB3]
A gaming machine according to feature αB1 or feature αB2,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination information output means comprises means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means without going through the control means.
特徴αB3によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報を受信することが可能となる。 According to feature αB3, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that the specific device can receive judgment information that is not affected by the control means.
例えば、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介して判定情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、所定の装置に出力される判定情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。 For example, if the configuration of this characteristic were not adopted, but rather a configuration were adopted in which judgment information was output via a control means to a specific device connected to the connection means, and if the control means had a malfunction or was tampered with illegally, there is a risk that the malfunction or tampering would affect the judgment information output to the specific device.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、所定の装置に出力される判定情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to the specified device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that even if the control means has a malfunction or has been illegally tampered with, the malfunction or illegal tampering will not affect the judgment information output to the specified device. As a result, the specified device connected to the connection means can execute processing based on judgment information that is not affected by the malfunction or illegal tampering.
<特徴αC群>
特徴αC群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αC Group>
The group of features αC is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αC1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する信号出力手段(各入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記信号に基づいて前記入球部に遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報である判定情報(入球情報)を出力する判定情報出力手段(入球検知用IC62c)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の進行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
所定の装置を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置との関係が所定の条件を満たしている場合(検査機320からHiレベルの信号が入力されている場合)に限り当該所定の装置に対して前記判定情報を出力する出力制御手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αC1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A signal output means (each of the ball
a judgment information output means (ball
A control means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device can be connected;
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine is characterized in that the judgment information output means is equipped with an output control means for outputting the judgment information to the specified device only when the relationship with the specified device connected to the connection means satisfies a specified condition (when a Hi level signal is input from the inspection machine 320).
特徴αC1によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置との関係が所定の条件を満たしている場合に限り当該所定の装置に対して判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、当該所定の条件を満たしている場合以外において当該遊技機の判定情報が外部に出力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、当該遊技機の判定情報が悪意のある者に解析されて悪用されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αC1, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means only when the relationship with the specific device satisfies a specific condition, so that it is possible to prevent the judgment information of the gaming machine from being output to the outside in cases other than when the specific condition is satisfied. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the judgment information of the gaming machine from being analyzed and misused by malicious individuals.
[特徴αC2]
特徴αC1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記所定の条件は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置から所定の信号を受信することを含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αC2]
A gaming machine according to feature αC1,
The gaming machine, wherein the predetermined condition includes receiving a predetermined signal from the predetermined device connected to the connection means.
特徴αC2によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置から所定の信号を受信することを含む所定の条件が満たされていない場合において当該遊技機の判定情報が外部に出力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。したがって、当該遊技機の判定情報が悪意のある者に解析されて悪用されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 Feature αC2 makes it possible to prevent the judgment information of the gaming machine from being output to the outside when certain conditions, including receiving a certain signal from a certain device connected to the connection means, are not met. This makes it possible to prevent the judgment information of the gaming machine from being analyzed and misused by malicious individuals.
[特徴αC3]
特徴αC1または特徴αC2に記載の遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な前記入球部と、前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する前記信号出力手段とをそれぞれ複数備え、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記複数の信号出力手段のそれぞれから出力された前記信号に基づいて前記複数の入球部のぞれぞれに遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報であって前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した情報である前記判定情報(入球情報)を、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、シリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αC3]
A gaming machine according to feature αC1 or feature αC2,
a plurality of ball entry sections into which game balls can enter; and a plurality of signal output means for outputting a signal based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
The gaming machine is characterized in that the judgment information output means is provided with a means for judging whether or not a gaming ball has entered each of the multiple ball entry points based on the signals output from each of the multiple signal output means, and for outputting the judgment information (ball entry information), which is information based on the judgment and corresponds to each of the multiple ball entry points, to the specified device connected to the connection means via a serial transmission method.
特徴αC3によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、例えば、判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合と比較して、当該判定情報を所定の装置に経由させる接続手段の構成を簡略化することができるとともに、当該判定情報を受信する所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。 According to feature αC3, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to a specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method. Therefore, compared to a configuration in which judgment information is output by a parallel transmission method, for example, it is possible to simplify the configuration of the connection means that routes the judgment information to the specified device, and also to simplify the configuration of the specified device that receives the judgment information.
具体的には、仮に、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合には、接続手段は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した出力部を備える必要がある。同様に、所定の装置は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した入力部を備える必要がある。また、遊技機が備える入球部の個数は、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なるため、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なる個数の入力部を備えた所定の装置を用意する必要が生じる。 Specifically, if a configuration is adopted in which judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections is output by a parallel transmission method, the connection means must have an output section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Similarly, the specified device must have an input section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Furthermore, since the number of ball entry sections provided in a gaming machine differs for each type (model) of gaming machine, it becomes necessary to prepare a specified device with a different number of input sections for each type (model) of gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、接続手段は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって判定情報を出力することのできる出力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよい。したがって、接続手段の構成を簡略化することができる。同様に、所定の装置は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって出力された判定情報を入力することのできる入力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよいので、所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。さらに、入球部の個数の異なる遊技機に所定の装置を接続した場合であっても、当該所定の装置は、シリアル伝送方式によって複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報を入力することができる。すなわち、所定の装置を、入球部の個数の異なる他の遊技機に対しても利用することが可能となる。この結果、所定の装置の汎用性を高めることが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to the specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method, so the connection means may be configured to include at least one output section that can output judgment information by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine. Therefore, the configuration of the connection means can be simplified. Similarly, the specified device may be configured to include at least one input section that can input judgment information output by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine, so the configuration of the specified device can be simplified. Furthermore, even if the specified device is connected to a gaming machine with a different number of ball entry sections, the specified device can input judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections by a serial transmission method. In other words, the specified device can be used for other gaming machines with a different number of ball entry sections. As a result, it is possible to increase the versatility of the specified device.
[特徴αC4]
特徴αC1から特徴αC3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段は、前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出可能な前記所定の装置を接続可能に構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αC4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αC1 to αC3,
The connection means is configured to be capable of connecting to the specified device capable of calculating gaming history information (gaming history information such as device ratios), which is information regarding the history of gaming, based on the judgment information.
特徴αC4によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の性能を検査する検査者は、制御手段による影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を所定の装置によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。 According to feature αC4, a specified device connected to the connection means can calculate game history information based on judgment information that is not affected by the control means. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the performance of the gaming machine can check game history information that is not affected by the control means using the specified device. As a result, the soundness of the game can be ensured.
[特徴αC5]
特徴αC1から特徴αC4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記制御手段を介さずに前記判定情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αC5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αC1 to αC4,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination information output means comprises means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means without going through the control means.
特徴αC5によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報を受信することが可能となる。 According to feature αC5, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that the specific device can receive judgment information that is not affected by the control means.
例えば、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介して判定情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、所定の装置に出力される判定情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。 For example, if the configuration of this characteristic were not adopted, but rather a configuration were adopted in which judgment information was output via a control means to a specific device connected to the connection means, and if the control means had a malfunction or was tampered with illegally, there is a risk that the malfunction or tampering would affect the judgment information output to the specific device.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、所定の装置に出力される判定情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to the specified device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that even if the control means has a malfunction or has been illegally tampered with, the malfunction or illegal tampering will not affect the judgment information output to the specified device. As a result, the specified device connected to the connection means can execute processing based on judgment information that is not affected by the malfunction or illegal tampering.
<特徴αD群>
特徴αD群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αD group>
The group of features αD is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αD1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する信号出力手段(各入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記信号に基づいて前記入球部に遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報である判定情報(入球情報)を出力する判定情報出力手段(入球検知用IC62c)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の進行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
所定の装置を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記判定情報を出力する手段を備え、
前記遊技機は、さらに、
前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、前記入球部に1個の遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数を特定可能な情報である賞球数情報を出力する賞球数情報出力手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A signal output means (each of the ball
a judgment information output means (ball
A control means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device can be connected;
A gaming machine comprising:
the determination information output means includes means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means,
The gaming machine further comprises:
A gaming machine comprising a prize ball number information output means for outputting prize ball number information, which is information capable of identifying the number of gaming balls to be paid out as prize balls when one gaming ball enters the ball entry section, to the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴αD1によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して賞球数情報を出力する賞球数情報出力手段を備えるので、所定の装置に対して賞球数情報を手入力する手間を省くことができるとともに、所定の装置に対して誤った賞球数情報が入力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、所定の装置は、判定情報と賞球数情報出力手段から出力された正確な賞球数情報とに基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 According to feature αD1, a prize ball number information output means is provided that outputs prize ball number information to a specified device connected to the connection means, thereby eliminating the need to manually input prize ball number information to the specified device and preventing incorrect prize ball number information from being input to the specified device. As a result, the specified device is able to execute processing based on the judgment information and the accurate prize ball number information output from the prize ball number information output means.
[特徴αD2]
特徴αD1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、前記入球部の種別を特定可能な情報である種別情報を出力する種別情報出力手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD2]
A gaming machine according to feature αD1,
A gaming machine comprising a type information output means for outputting type information, which is information capable of identifying the type of the ball entry section, to the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴αD2によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して種別情報を出力する種別情報出力手段を備えるので、所定の装置に対して種別情報を手入力する手間を省くことができるとともに、所定の装置に対して誤った種別情報が入力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、所定の装置は、判定情報出力手段から出力された判定情報と種別情報出力手段から出力された正確な種別情報とに基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。なお、入球部の種別とは、例えば、第1始動口や第2始動口、大入賞口、排出通路といった信号出力手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)が設けられている入球部の種別である。
According to feature αD2, a type information output means is provided that outputs type information to a specified device connected to the connection means, which eliminates the need to manually input type information to the specified device and prevents incorrect type information from being input to the specified device. As a result, the specified device is able to execute processing based on the judgment information output from the judgment information output means and the accurate type information output from the type information output means. The type of ball entry section is, for example, the type of ball entry section that is provided with signal output means (ball
[特徴αD3]
特徴αD1または特徴αD2に記載の遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な前記入球部と、前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する前記信号出力手段とをそれぞれ複数備え、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記複数の信号出力手段のそれぞれから出力された前記信号に基づいて前記複数の入球部のぞれぞれに遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報であって前記複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した情報である前記判定情報(入球情報)を、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、シリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD3]
A gaming machine according to feature αD1 or feature αD2,
a plurality of ball entry sections into which game balls can enter; and a plurality of signal output means for outputting a signal based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
The gaming machine is characterized in that the judgment information output means is provided with a means for judging whether or not a gaming ball has entered each of the multiple ball entry points based on the signals output from each of the multiple signal output means, and for outputting the judgment information (ball entry information), which is information based on the judgment and corresponds to each of the multiple ball entry points, to the specified device connected to the connection means via a serial transmission method.
特徴αD3によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、例えば、判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合と比較して、当該判定情報を所定の装置に経由させる接続手段の構成を簡略化することができるとともに、当該判定情報を受信する所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。 According to feature αD3, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to a specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method. Therefore, compared to a configuration in which judgment information is output by a parallel transmission method, for example, it is possible to simplify the configuration of the connection means that routes the judgment information to the specified device, and also to simplify the configuration of the specified device that receives the judgment information.
具体的には、仮に、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をパラレル伝送方式によって出力する構成を採用した場合には、接続手段は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した出力部を備える必要がある。同様に、所定の装置は、当該複数の入球部の個数に対応した入力部を備える必要がある。また、遊技機が備える入球部の個数は、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なるため、遊技機の種別毎(機種毎)に異なる個数の端子を備えた所定の装置を用意する必要が生じる。 Specifically, if a configuration is adopted in which judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections is output using a parallel transmission method, the connection means must have an output section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Similarly, the specified device must have an input section corresponding to the number of the multiple ball entry sections. Furthermore, since the number of ball entry sections provided in a gaming machine differs for each type (model) of gaming machine, it becomes necessary to prepare a specified device with a different number of terminals for each type (model) of gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報をシリアル伝送方式によって出力する手段を備えるので、接続手段は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって判定情報を出力することのできる出力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよい。したがって、接続手段の構成を簡略化することができる。同様に、所定の装置は、当該遊技機が備える入球部の個数に関わらず、シリアル伝送方式によって出力された判定情報を入力することのできる入力部を少なくとも1つ備える構成とすればよいので、所定の装置の構成を簡略化することができる。さらに、入球部の個数の異なる遊技機に所定の装置を接続した場合であっても、当該所定の装置は、シリアル伝送方式によって複数の入球部のそれぞれに対応した判定情報を入力することができる。すなわち、所定の装置を、入球部の個数の異なる他の遊技機に対しても利用することが可能となる。この結果、所定の装置の汎用性を高めることが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections to the specified device connected to the connection means by a serial transmission method, so the connection means may be configured to include at least one output section that can output judgment information by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine. Therefore, the configuration of the connection means can be simplified. Similarly, the specified device may be configured to include at least one input section that can input judgment information output by a serial transmission method regardless of the number of ball entry sections included in the gaming machine, so the configuration of the specified device can be simplified. Furthermore, even if the specified device is connected to a gaming machine with a different number of ball entry sections, the specified device can input judgment information corresponding to each of the multiple ball entry sections by a serial transmission method. In other words, the specified device can be used for other gaming machines with a different number of ball entry sections. As a result, it is possible to increase the versatility of the specified device.
[特徴αD4]
特徴αD1から特徴αD3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記賞球数情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置から所定の信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を受信したことに基づいて前記賞球数情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αD1 to αD3,
A gaming machine characterized in that the prize ball number information output means includes a means for outputting the prize ball number information based on receiving a specified signal (a ball entrance information transmission request command) from the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴αD4によれば、賞球数情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいて賞球数情報を出力する手段を備えるので、不適切な状況やタイミングにおいて賞球数情報が外部に出力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αD4, the prize ball number information output means includes a means for outputting prize ball number information based on receiving a specified signal from a specified device connected to the connection means, thereby preventing prize ball number information from being output to the outside in inappropriate circumstances or at inappropriate times.
[特徴αD5]
特徴αD1から特徴αD4のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記賞球数情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に前記所定の装置が接続されたことを契機として前記賞球数情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD5]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αD1 to αD4,
A gaming machine characterized in that the prize ball number information output means includes a means for outputting the prize ball number information when the specified device is connected to the connection means.
特徴αD5によれば、賞球数情報出力手段は、接続手段に所定の装置が接続されたことを契機として賞球数情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、接続手段に接続された後に速やかに賞球数情報を取得することができる。したがって、例えば、所定の装置は、接続手段に接続された後に、当該賞球数情報を必要とする処理を速やかに実行することが可能となる。 According to feature αD5, the prize ball number information output means includes a means for outputting prize ball number information when a specific device is connected to the connection means, so that the specific device can quickly obtain the prize ball number information after being connected to the connection means. Therefore, for example, after being connected to the connection means, the specific device can quickly execute a process that requires the prize ball number information.
[特徴αD6]
特徴αD1から特徴αD5のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段は、前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出可能な前記所定の装置を接続可能に構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD6]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αD1 to αD5,
The connection means is configured to be capable of connecting to the specified device capable of calculating gaming history information (gaming history information such as device ratios), which is information regarding the history of gaming, based on the judgment information.
特徴αD6によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の性能を検査する検査者は、制御手段による影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を所定の装置によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。 According to feature αD6, a specified device connected to the connection means can calculate game history information based on judgment information that is not affected by the control means. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the performance of the gaming machine can check game history information that is not affected by the control means using the specified device. As a result, the soundness of the game can be ensured.
[特徴αD7]
特徴αD1から特徴αD6のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記制御手段を介さずに前記判定情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD7]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αD1 to αD6,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination information output means comprises means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means without going through the control means.
特徴αD7によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報を受信することが可能となる。 According to feature αD7, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that the specific device can receive judgment information that is not affected by the control means.
例えば、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介して判定情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、所定の装置に出力される判定情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。 For example, if the configuration of this characteristic were not adopted, but rather a configuration were adopted in which judgment information was output via a control means to a specific device connected to the connection means, and if the control means had a malfunction or was tampered with illegally, there is a risk that the malfunction or tampering would affect the judgment information output to the specific device.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、所定の装置に出力される判定情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to the specified device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that even if the control means has a malfunction or has been illegally tampered with, the malfunction or illegal tampering will not affect the judgment information output to the specified device. As a result, the specified device connected to the connection means can execute processing based on judgment information that is not affected by the malfunction or illegal tampering.
[特徴αD8]
特徴αD2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記種別情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置から所定の信号(入球口情報送信要求コマンド)を受信したことに基づいて前記種別情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD8]
A gaming machine according to feature αD2,
The type information output means comprises a means for outputting the type information based on receiving a specified signal (entrance information transmission request command) from the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴αD8によれば、種別情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置から所定の信号を受信したことに基づいて種別情報を出力する手段を備えるので、不適切な状況やタイミングにおいて種別情報が外部に出力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αD8, the type information output means includes a means for outputting type information based on receiving a specified signal from a specified device connected to the connection means, thereby making it possible to prevent type information from being output to the outside in inappropriate circumstances or at inappropriate times.
[特徴αD9]
特徴αD2または特徴D8に記載の遊技機であって、
前記種別情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に前記所定の装置が接続されたことを契機として前記種別情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αD9]
A gaming machine according to feature αD2 or feature D8,
The gaming machine, wherein the type information output means comprises means for outputting the type information when the specified device is connected to the connection means.
特徴αD9によれば、種別情報出力手段は、接続手段に所定の装置が接続されたことを契機として種別情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、接続手段に接続された後に速やかに種別情報を取得することができる。したがって、例えば、所定の装置は、接続手段に接続された後に、当該種別情報を必要とする処理を速やかに実行することが可能となる。 According to feature αD9, the type information output means includes means for outputting type information when a specific device is connected to the connection means, so that the specific device can quickly obtain type information after being connected to the connection means. Therefore, for example, the specific device can quickly execute a process that requires the type information after being connected to the connection means.
<特徴αE群>
特徴αE群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αE group>
The group of features αE is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αE1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいた信号を出力する信号出力手段(各入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記信号に基づいて前記入球部に遊技球が入球したか否かを判定し、当該判定に基づいた情報である判定情報(入球情報)を出力する判定情報出力手段(入球検知用IC62c)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の進行を制御する制御手段(主側CPU62x)と、
前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段(主側CPU62x、遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を記憶する記憶手段(フラッシュメモリ64x、遊技履歴管理チップ300)と、
所定の装置を接続可能な接続手段(検査用端子65)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記判定情報を出力する手段を備え、
前記遊技機は、さらに、
前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記遊技履歴情報を出力する遊技履歴情報出力手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αE1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A signal output means (each of the ball
a judgment information output means (ball
A control means (
A calculation means (
A storage means (
a connection means (terminals for inspection 65) to which a predetermined device can be connected;
A gaming machine comprising:
the determination information output means includes means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means,
The gaming machine further comprises:
a game history information output means for outputting the game history information stored in the storage means to the predetermined device connected to the connection means.
特徴αE1によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して、記憶手段に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を出力する手段と、判定情報を出力する手段とを備えるので、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、記憶手段に記憶されている遊技履歴情報を受信することができ、また、判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 According to feature αE1, the device is provided with a means for outputting game history information stored in the storage means and a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means, so that the specific device connected to the connection means can receive the game history information stored in the storage means and can execute processing based on the judgment information.
具体的には、例えば、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の記憶手段に記憶されている遊技履歴情報(以下、第1遊技履歴情報とも呼ぶ)を表示することができる。また、所定の装置は、当該遊技機の接続手段に接続されている所定の検査期間において受信した判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出し、当該遊技履歴情報(以下、第2遊技履歴情報とも呼ぶ)を表示することが可能となる。したがって、例えば、遊技機を検査する検査者は、遊技機が備える記憶手段に記憶されている第1遊技履歴情報と、所定の装置が所定の検査期間において受信した判定情報に基づいた第2遊技履歴情報とを比較することが可能となる。 Specifically, for example, a specified device can display the gaming history information (hereinafter also referred to as the first gaming history information) stored in the storage means of the gaming machine. In addition, the specified device can calculate the gaming history information based on the judgment information received during a specified inspection period when connected to the connection means of the gaming machine, and display the gaming history information (hereinafter also referred to as the second gaming history information). Therefore, for example, an inspector inspecting the gaming machine can compare the first gaming history information stored in the storage means provided in the gaming machine with the second gaming history information based on the judgment information received by the specified device during the specified inspection period.
ここで、仮に、遊技機に不具合が発生したり、不正な改造(例えば釘の改変等)が施されたりしたこと等によって当該遊技機における遊技の特性に変化が生じた場合には、遊技機が備える記憶手段に記憶されている第1遊技履歴情報(過去の所定期間における判定情報に基づいて算出手段によって算出された遊技履歴情報)と、所定の装置が所定の検査期間における判定情報に基づいて算出した第2遊技履歴情報とに差が生じることがある。したがって、遊技機を検査する検査者は、2つの遊技履歴情報の差分に注目することによって、当該遊技機において不具合や不正な改造(例えば、釘の改変)が発生していないかを検査することができる。 If a malfunction occurs in the gaming machine or unauthorized modifications (e.g., tampering with the nails) are made to the gaming machine, causing a change in the gaming characteristics of the gaming machine, a difference may occur between the first gaming history information stored in the memory means provided in the gaming machine (the gaming history information calculated by the calculation means based on the judgment information for a specified period in the past) and the second gaming history information calculated by a specified device based on the judgment information for a specified inspection period. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the gaming machine can inspect whether a malfunction or unauthorized modifications (e.g., tampering with the nails) have occurred in the gaming machine by focusing on the difference between the two pieces of gaming history information.
[特徴αE2]
特徴αE1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して、前記入球部に1個の遊技球が入球した場合に賞球として払い出される遊技球の個数を特定可能な情報である賞球数情報を出力する賞球数情報出力手段を備えることを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αE2]
A gaming machine according to feature αE1,
A gaming machine characterized in that it is equipped with a prize ball number information output means for outputting prize ball number information, which is information that can identify the number of gaming balls to be paid out as prize balls when one gaming ball enters the ball entry section, to the specified device connected to the connection means.
特徴αE2によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して賞球数情報を出力する賞球数情報出力手段を備えるので、所定の装置に対して賞球数情報を手入力する手間を省くことができるとともに、所定の装置に対して誤った賞球数情報が入力されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、所定の装置は、判定情報出力手段から出力された判定情報と賞球数情報出力手段から出力された正確な賞球数情報とに基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 According to feature αE2, a prize ball number information output means is provided that outputs prize ball number information to a specified device connected to the connection means, thereby eliminating the need to manually input prize ball number information to the specified device and preventing incorrect prize ball number information from being input to the specified device. As a result, the specified device is able to execute processing based on the judgment information output from the judgment information output means and the accurate prize ball number information output from the prize ball number information output means.
[特徴αE3]
特徴αE1または特徴αE2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記接続手段は、前記判定情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出可能な前記所定の装置を接続可能に構成されている
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αE3]
A gaming machine according to feature αE1 or αE2,
The connection means is configured to be capable of connecting to the specified device capable of calculating gaming history information (gaming history information such as device ratios), which is information regarding the history of gaming, based on the judgment information.
特徴αE3によれば、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報に基づいて遊技履歴情報を算出することができる。したがって、遊技機の性能を検査する検査者は、制御手段による影響を受けていない遊技履歴情報を所定の装置によって確認することが可能となる。この結果、遊技の健全性を確保することができる。 According to feature αE3, a specified device connected to the connection means can calculate game history information based on judgment information that is not affected by the control means. Therefore, an inspector who inspects the performance of the gaming machine can check game history information that is not affected by the control means using the specified device. As a result, the soundness of the game can be ensured.
[特徴αE4]
特徴αE1から特徴αE3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記判定情報出力手段は、前記接続手段に接続された前記所定の装置に対して前記制御手段を介さずに前記判定情報を出力する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αE4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αE1 to αE3,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination information output means comprises means for outputting the determination information to the predetermined device connected to the connection means without going through the control means.
特徴αE4によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、所定の装置は、制御手段による影響を受けていない判定情報を受信することが可能となる。 According to feature αE4, the judgment information output means includes a means for outputting judgment information to a specific device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that the specific device can receive judgment information that is not affected by the control means.
例えば、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介して判定情報を出力する構成を採用した場合において、当該制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合には、所定の装置に出力される判定情報にも当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及んでしまうおそれがある。 For example, if the configuration of this characteristic were not adopted, but rather a configuration were adopted in which judgment information was output via a control means to a specific device connected to the connection means, and if the control means had a malfunction or was tampered with illegally, there is a risk that the malfunction or tampering would affect the judgment information output to the specific device.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、判定情報出力手段は、接続手段に接続された所定の装置に対して制御手段を介さずに判定情報を出力する手段を備えるので、制御手段に不具合が発生していたり不正な改造が施されている場合であっても、所定の装置に出力される判定情報には当該不具合や不正な改造の影響が及ばない。この結果、接続手段に接続された所定の装置は、当該不具合や不正な改造の影響の及んでいない判定情報に基づいた処理を実行することが可能となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the judgment information output means includes means for outputting judgment information to the specified device connected to the connection means without going through the control means, so that even if the control means has a malfunction or has been illegally tampered with, the malfunction or illegal tampering will not affect the judgment information output to the specified device. As a result, the specified device connected to the connection means can execute processing based on judgment information that is not affected by the malfunction or illegal tampering.
<特徴αF群>
特徴αF群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αF group>
The group of features αF is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αF1]
第1の処理群(メイン処理の残余処理)を繰り返し実行する第1処理群実行手段と、
所定の条件が成立したこと(第2の処理群の前回の実行の開始から所定時間が経過したこと)に基づいて、第2の処理群(遊技回制御処理等を含む遊技進行処理)を前記第1の処理群に割り込んで実行する第2処理群実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記第1処理群実行手段は、一の前記第2の処理群の実行の終了後から次の前記第2の処理群の実行の開始までの期間(残余時間)において前記第1の処理群を繰り返し実行する手段を備え、
前記第1の処理群は、遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率等)の算出に関連した処理である遊技履歴情報関連処理(遊技履歴用処理)を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αF1]
a first process group execution means for repeatedly executing a first process group (a remaining process of the main process);
a second process group execution means for interrupting the first process group and executing a second process group (a game progress process including a game number control process, etc.) based on the establishment of a predetermined condition (a predetermined time has elapsed since the start of the previous execution of the second process group);
A gaming machine comprising:
the first process group execution means includes means for repeatedly executing the first process group during a period (a remaining time) from the end of execution of one of the second process groups to the start of execution of the next of the second process group;
The first processing group includes a gaming history information related process (processing for gaming history) which is a process related to the calculation of gaming history information (role ratio, consecutive role ratio, etc.), which is information regarding the gaming history.
特徴αF1によれば、一の第2の処理群の実行の終了後から次の第2の処理群の実行の開始までの期間において遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群を繰り返し実行するので、一の第2の処理群の実行が終了していないにも関わらず遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群の実行が開始されてしまうことを抑制することができる。すなわち、第2の処理群の実行を優先しつつ、第2の処理群が実行されていない期間において遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 According to feature αF1, the first process group including the gaming history information related processing is repeatedly executed in the period from the end of execution of one second process group to the start of execution of the next second process group, so that it is possible to prevent the first process group including the gaming history information related processing from being started even though the execution of one second process group has not been completed. In other words, while prioritizing the execution of the second process group, it is possible to quickly calculate the gaming history information by repeatedly executing the first process group including the gaming history information related processing in the period when the second process group is not being executed.
また、仮に、本特徴の構成を採用せずに、遊技履歴情報関連処理を第2の処理群に含めて実行する構成を採用した場合には、当該第2の処理群の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間が長くなってしまい、例えば、次の第2の処理群の実行の開始の契機となる所定の条件が成立したタイミングにおいて未だ一の第2の処理群の実行が終了しておらず、当該一の第2の処理群の実行が終了するまで次の第2の処理群の実行を開始することができなくなってしまう場合がある。この場合には、次の第2の処理群の実行の開始が遅れてしまったことによって不具合が発生するおそれがある。 Furthermore, if this characteristic configuration were not adopted, and a configuration were adopted in which the game history information-related processing is included in the second process group and executed, the time required from start to finish of one execution of the second process group would be long, and for example, the execution of one second process group may not have finished when a predetermined condition that triggers the start of execution of the next second process group is met, and it may not be possible to start execution of the next second process group until the execution of the one second process group finishes. In this case, there is a risk of a malfunction occurring due to the delay in starting the execution of the next second process group.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技履歴情報関連処理を第1の処理群に含めて実行するので、遊技履歴情報関連処理を第2の処理群に含めて実行する構成と比較して、第2の処理群の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間を短くすることができる。したがって、例えば、次の第2の処理群の実行の開始の契機となる所定の条件が成立したタイミングにおいて未だ一の第2の処理群の実行が終了していないといった事態の発生を抑制することができ、当該一の第2の処理群の実行が終了するまで次の第2の処理群の実行を開始することができないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。この結果、次の第2の処理群の実行の開始の遅れによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the game history information related processing is executed as part of the first processing group, so the time required from start to finish of one execution of the second processing group can be shortened compared to a configuration in which the game history information related processing is executed as part of the second processing group. Therefore, for example, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the execution of one second processing group has not yet finished at the timing when a predetermined condition that triggers the start of execution of the next second processing group is met, and it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the execution of the next second processing group cannot be started until the execution of the one second processing group is finished. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions due to a delay in the start of execution of the next second processing group.
以上より、本特徴によれば、次の第2の処理群の実行の開始が遅れてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制しつつ、第2の処理群が実行されていない期間において遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群を繰り返し実行することによって効率的かつ速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 As described above, this feature makes it possible to efficiently and quickly calculate gaming history information by repeatedly executing the first processing group, which includes gaming history information-related processing, during periods when the second processing group is not being executed, while suppressing the occurrence of malfunctions caused by delays in the start of execution of the next second processing group.
[特徴αF2]
特徴αF1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2の処理群は、遊技の進行に関する処理である遊技進行処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αF2]
A gaming machine according to feature αF1,
The gaming machine, wherein the second process group includes a game progress process which is a process related to the progress of a game.
特徴αF2によれば、遊技の進行に関する処理である遊技進行処理を含む第2の処理群の実行の開始が遅れてしまうことを抑制することができるので、遊技の進行に不具合が発生してしまうことを抑制しつつ、第2の処理群が実行されていない期間において遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 Feature αF2 makes it possible to prevent delays in the start of execution of the second processing group, which includes game progress processing, which is processing related to the progress of the game, and therefore makes it possible to quickly calculate game history information by repeatedly executing the first processing group, which includes game history information-related processing, during periods when the second processing group is not being executed, while preventing malfunctions from occurring in the progress of the game.
[特徴αF3]
特徴αF1または特徴αF2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記遊技履歴情報関連処理は、順次実行することによって前記遊技履歴情報の算出が完了する複数の処理段階(複数種類のタスク)を含んでおり、
前記第1処理群実行手段は、前記遊技履歴情報関連処理の1回の実行では、前記複数の処理段階のうちの一部の処理段階を実行する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αF3]
A gaming machine according to feature αF1 or feature αF2,
the game history information-related process includes a plurality of processing steps (a plurality of types of tasks) that are executed in sequence to complete the calculation of the game history information;
The first process group execution means executes a part of the plurality of process steps in one execution of the game history information related process.
特徴αF3によれば、第1処理群実行手段は、遊技履歴情報関連処理の1回の実行では、複数の処理段階のうちの一部の処理段階を実行するので、例えば、遊技履歴情報関連処理の1回の実行において複数の処理段階の全てを実行する構成と比較して、遊技履歴情報関連処理の1回の実行の開始から終了までに要する時間を短くすることができる。具体的には、例えば、遊技履歴情報関連処理の実行中に所定の条件が成立した場合においても、実行中の遊技履歴情報関連処理が短時間で終了するので、当該所定の条件の成立から第2の処理群の実行が開始されるまでの時間を短くすることができる。この結果、第2の処理群の実行の開始が遅れてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制しつつ、第1の処理群を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 According to feature αF3, the first processing group execution means executes some of the multiple processing steps in one execution of the gaming history information related process, so that the time required from start to finish of one execution of the gaming history information related process can be shortened, for example, compared to a configuration in which all of the multiple processing steps are executed in one execution of the gaming history information related process. Specifically, for example, even if a predetermined condition is met during the execution of the gaming history information related process, the gaming history information related process being executed ends in a short time, so that the time from the fulfillment of the predetermined condition to the start of execution of the second processing group can be shortened. As a result, it is possible to quickly calculate the gaming history information by repeatedly executing the first processing group while suppressing the occurrence of malfunctions caused by a delay in the start of execution of the second processing group.
[特徴αF4]
特徴αF1から特徴αF3のいずれか一つに記載の遊技機であって、
前記所定の条件は、前記第2の処理群の前回の実行の開始から所定時間が経過したことを含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αF4]
A gaming machine according to any one of features αF1 to αF3,
The gaming machine, wherein the predetermined condition includes a predetermined time having elapsed since the start of a previous execution of the second process group.
特徴αF4によれば、所定の条件は、第2の処理群の前回の実行の開始から所定時間が経過したことを含むので、第2の処理群を定期的に実行することができる。そして、第2の処理群の実行が終了した後であって当該第2の処理群の実行の開始から所定時間が経過するまでの期間において、遊技履歴情報関連処理を含む第1の処理群を繰り返し実行することによって速やかに遊技履歴情報を算出することが可能となる。 According to feature αF4, the predetermined condition includes the passage of a predetermined time from the start of the previous execution of the second process group, so that the second process group can be executed periodically. Then, during the period after the execution of the second process group is completed and before the predetermined time has elapsed from the start of the execution of the second process group, the first process group including the game history information related process can be repeatedly executed, thereby quickly calculating the game history information.
なお、上記特徴αA群~特徴αF群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group αA to feature group αF solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている(例えば、特許文献1)。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements have been made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the entertainment value of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, and simplifying control (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like the ones mentioned above, further technological improvements are desired in order to increase the enjoyment of the game, reduce the processing load of the gaming machine, simplify control, and provide a more sound game experience.
<特徴αG群>
特徴αG群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αG group>
The group of features αG is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αG1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、前記当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間における前記検知情報を記憶する手段を備え、
前記算出手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて前記複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αG1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, etc.) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means for displaying the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The storage means includes a means for storing the detection information for a plurality of periods each including a boundary between the change in the winning probability,
The calculation means includes means for calculating game history information for each of the plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the plurality of periods;
The display means comprises a display means for displaying information based on the game history information for each of the plurality of periods.
特徴αG1によれば、遊技機の検査者は、当該遊技機における当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報に基づく表示を確認することが可能となる。例えば、遊技履歴情報に基づく表示が遊技履歴情報そのものの数値である場合には、検査者は、当該遊技機において当選確率が過去に変更されてきた過程において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。 According to feature αG1, an inspector of a gaming machine can check the display based on the gaming history information for each of multiple periods bounded by changes in the winning probability of the gaming machine. For example, if the display based on the gaming history information is the numerical value of the gaming history information itself, the inspector can check whether there was a situation in which the gaming history information was not within an appropriate range during the process in which the winning probability of the gaming machine was changed in the past.
<特徴αH群>
特徴αH群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αH group>
The group of features αH is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αH1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする表示手段と、
前記当選確率が変更された後に前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積される前に前記当選確率が再び変更された場合に、所定の情報(短期変更情報)を表示する所定情報表示手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αH1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, etc.) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means for displaying the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
a predetermined information display means for displaying predetermined information (short-term change information) when the winning probability is changed again before the detection information stored in the storage means is accumulated to a predetermined amount after the winning probability is changed;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αH1によれば、遊技機の検査者は、所定の情報を確認することによって、検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積される前に当選確率が再び変更されたか否かを確認することができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 According to feature αH1, the gaming machine inspector can check the specified information to see whether the winning probability has been changed again before the detection information has accumulated to a specified amount. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from changing the winning probability with fraudulent intent.
例えば、仮に、当選確率が変更されたことに基づいて当該当選確率の変更の前に記憶されていた検知情報が消去される構成を採用した場合には、遊技機が検査者によって検査される前に、当該遊技機の管理者が、当選確率の変更後に当該遊技機において遊技があまり実行されていない状況であるにも関わらず、再び当選確率の変更を行なって、当該遊技機に記憶されている検知情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。しかしながら、本態様によれば、当選確率の変更後に当該遊技機において遊技があまり実行されていない状況であるにも関わらず、再び当選確率の変更が短期間で行なわれた場合には、上述した短期変更情報が記録され、表示されることになる。したがって、検査者は、短期変更情報を確認することによって、検知情報の消去といった不正な意図によって当選確率の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかと認識することが可能となる。この結果、遊技機の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the detection information stored before the change in the winning probability is erased based on the change in the winning probability, the manager of the gaming machine may change the winning probability again before the gaming machine is inspected by an inspector, even though not many games are being played on the gaming machine after the change in the winning probability, and erase the detection information stored in the gaming machine. However, according to this embodiment, if the winning probability is changed again in a short period of time even though not many games are being played on the gaming machine after the change in the winning probability, the above-mentioned short-term change information is recorded and displayed. Therefore, by checking the short-term change information, the inspector can recognize that the winning probability may have been changed in a short period of time with the fraudulent intention of erasing the detection information. As a result, it is possible to suppress changes to the winning probability based on fraudulent intentions by the manager of the gaming machine.
[特徴αH2]
特徴αH1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記検知情報を消去する消去手段を備え、
前記記憶手段は、前記当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間における前記検知情報を記憶する手段を備え、
前記算出手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする手段を備え、
前記消去手段は、前記当選確率が変更された場合には、前記複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における前記検知情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αH2]
A gaming machine according to feature αH1,
an erasing means for erasing the detection information stored in the storage means,
The storage means includes a means for storing the detection information for a plurality of periods each including a boundary between the change in the winning probability,
The calculation means includes means for calculating the game history information for each of the plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the plurality of periods,
the display means includes means for displaying based on the game history information for each of the plurality of periods,
The erasing means comprises a means for erasing the detection information for the oldest period among the plurality of periods when the winning probability is changed.
特徴αH2によれば、遊技機の検査者は、当該遊技機における当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報に基づく表示を確認することが可能となる。例えば、遊技履歴情報に基づく表示が遊技履歴情報そのものの数値である場合には、検査者は、当該遊技機において当選確率が過去に変更されてきた過程において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。 According to feature αH2, an inspector of a gaming machine can check the display based on the gaming history information for each of multiple periods bounded by changes in the winning probability of the gaming machine. For example, if the display based on the gaming history information is the numerical value of the gaming history information itself, the inspector can check whether or not there was a situation in which the gaming history information was not within an appropriate range during the process in which the winning probability of the gaming machine was changed in the past.
さらに、本特徴によれば、遊技機の検査者は、所定の情報を確認することによって、検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積される前に当選確率が再び変更されたか否かを確認することができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the gaming machine inspector can check the specified information to see whether the winning probability has been changed again before the detection information has accumulated to a specified amount. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from changing the winning probability with fraudulent intent.
具体的には、例えば、遊技機が検査者によって検査される前に、当該遊技機の管理者が、当選確率の変更を短期間に繰り返し行なって、当該遊技機の当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間における検知情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。しかしながら、本特徴によれば、当選確率の変更が短期間で繰り返し行なわれた場合には、上述した短期変更情報が記録され、表示されることになる。したがって、検査者は、短期変更情報を確認することによって、不正な意図によって当選確率の変更が短期間に行なわれた可能性があるのではないかと認識することが可能となる。この結果、遊技機の管理者による不正な意図に基づいた当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 Specifically, for example, before a gaming machine is inspected by an inspector, the manager of the gaming machine may repeatedly change the winning probability in a short period of time, erasing detection information for multiple periods bounded by the change in the winning probability of the gaming machine. However, according to this feature, when the winning probability is repeatedly changed in a short period of time, the above-mentioned short-term change information is recorded and displayed. Therefore, by checking the short-term change information, the inspector can recognize that the winning probability may have been changed in a short period of time with fraudulent intent. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from changing the winning probability with fraudulent intent.
<特徴αI群>
特徴αI群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αI group>
The group of features αI is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αI1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする表示手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記検知情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、前記当選確率が変更された場合には、前記当選確率が変更された後に前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積された後に、前記当選確率が変更される前に前記記憶手段に記憶されていた前記検知情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αI1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, etc.) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means for displaying the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
an erasing means for erasing the detection information stored in the storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The erasing means includes means for erasing, when the winning probability is changed, the detection information stored in the storage means before the winning probability was changed after the detection information stored in the storage means after the winning probability was changed has accumulated to a predetermined amount.
特徴αI1によれば、当選確率が変更された後に記憶手段に記憶された検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは、当選確率が変更される前に記憶手段に記憶されていた検知情報は消去されないので、当選確率の変更の前に記憶されていた検知情報が、遊技機の当選確率の変更を行なうことによって意図的に消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。例えば、仮に、当選確率の変更の前に取得されて記憶されていた検知情報が、遊技機の当選確率の変更が行なわれた直後に消去される構成を採用すると、遊技機が検査者によって検査される前に、当該遊技機の管理者が、当選確率の変更を行なって、当該当選確率の変更の前に記憶されていた検知情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本特徴によれば、当選確率の変更の前に記憶されていた検知情報は、当選確率が変更された後に取得されて記憶された検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは消去されないので、遊技機機の管理者による不正な意図による当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 According to feature αI1, the detection information stored in the storage means before the change in the winning probability is not erased until the detection information stored in the storage means after the change in the winning probability has accumulated to a predetermined amount, so that it is possible to prevent the detection information stored before the change in the winning probability of the gaming machine from being intentionally erased by changing the winning probability of the gaming machine. For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the detection information acquired and stored before the change in the winning probability of the gaming machine is erased immediately after the change in the winning probability of the gaming machine is made, there is a possibility that the manager of the gaming machine changes the winning probability and erases the detection information stored before the change in the winning probability before the gaming machine is inspected by an inspector. In contrast, according to this feature, the detection information stored before the change in the winning probability is not erased until the detection information acquired and stored after the change in the winning probability has accumulated to a predetermined amount, so that it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from changing the winning probability with improper intentions.
[特徴αI2]
特徴αI1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記検知情報を消去する消去手段を備え、
前記記憶手段は、前記当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間における前記検知情報を記憶する手段を備え、
前記算出手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする手段を備え、
前記消去手段は、前記当選確率が変更された場合には、前記当選確率が変更された後に前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積された後に、前記複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における前記検知情報を消去する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αI2]
A gaming machine according to feature αI1,
an erasing means for erasing the detection information stored in the storage means,
The storage means includes a means for storing the detection information for a plurality of periods each including a boundary between the change in the winning probability,
The calculation means includes means for calculating the game history information for each of the plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the plurality of periods,
the display means includes means for displaying based on the game history information for each of the plurality of periods,
The erasing means is provided with a means for erasing the detection information for the oldest period among the plurality of periods when the winning probability is changed and the detection information stored in the memory means after the winning probability is changed is accumulated to a predetermined amount.
特徴αI2によれば、遊技機の検査者は、当該遊技機における当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間毎における遊技履歴情報に基づく表示を確認することが可能となる。例えば、遊技履歴情報に基づく表示が遊技履歴情報そのものの数値である場合には、検査者は、当該遊技機において当選確率が過去に変更されてきた過程において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。 According to feature αI2, the inspector of the gaming machine can check the display based on the gaming history information for each of multiple periods bounded by changes in the winning probability of the gaming machine. For example, if the display based on the gaming history information is the numerical value of the gaming history information itself, the inspector can check whether there was a situation in which the gaming history information was not within an appropriate range during the process in which the winning probability of the gaming machine was changed in the past.
さらに、本特徴によれば、当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間における検知情報が、遊技機の当選確率の変更が繰り返し行なわれることによって意図的に消去されてしまうことを抑制することができる。例えば、仮に、当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における検知情報が、遊技機の当選確率の変更が行なわれた直後に消去される構成を採用すると、遊技機が検査者によって検査される前に、当該遊技機の管理者が、当選確率の変更を繰り返し行なって、当該遊技機の複数の期間における検知情報を消去してしまう可能性がある。これに対して、本特徴によれば、当選確率の変更を境界とした複数の期間のうちの最も古い期間における検知情報は、当選確率が変更された後に取得されて記憶された検知情報が所定の量まで蓄積されるまでは消去されないので、遊技機の管理者による不正な意図による当選確率の変更を抑制することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, it is possible to prevent the detection information for multiple periods bounded by a change in the winning probability from being intentionally erased by repeatedly changing the winning probability of the gaming machine. For example, if a configuration is adopted in which the detection information for the oldest period of multiple periods bounded by a change in the winning probability is erased immediately after the winning probability of the gaming machine is changed, there is a possibility that the manager of the gaming machine will repeatedly change the winning probability and erase the detection information for the multiple periods of the gaming machine before the gaming machine is inspected by an inspector. In contrast, according to this feature, the detection information for the oldest period of multiple periods bounded by a change in the winning probability is not erased until a predetermined amount of detection information is accumulated after the winning probability is changed, so it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from changing the winning probability with fraudulent intentions.
<特徴αJ群>
特徴αJ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αJ group>
The group of features αJ is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αJ1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、前記検知情報を、前記検知手段が遊技球を検知した時点における前記当選確率毎に区別して記憶する手段を備え、
前記算出手段は、前記当選確率毎に前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、前記当選確率毎に前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示をする手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αJ1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, etc.) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means for displaying the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The storage means includes a means for storing the detection information by distinguishing the winning probability at the time when the detection means detects the gaming ball,
the calculation means includes means for calculating the game history information for each of the winning probabilities,
The display means comprises a display means for displaying information based on the game history information for each of the winning probabilities.
特徴αJ1によれば、例えば、遊技履歴情報に基づく表示が遊技履歴情報そのものの数値である場合には、遊技機の検査者は、当選確率毎に算出されて表示された各遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲内に収まっているか否かを確認することができる。すなわち、検査者は、当該遊技機において遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲内に収まっていない当選確率の設定が存在しないか否かを確認することが可能となる。 According to feature αJ1, for example, when the display based on the gaming history information is the numerical value of the gaming history information itself, the inspector of the gaming machine can check whether each piece of gaming history information calculated and displayed for each winning probability falls within an appropriate range. In other words, the inspector can check whether there is a winning probability setting in the gaming machine where the gaming history information does not fall within an appropriate range.
なお、上記特徴αG群~特徴αJ群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group αG to feature group αJ solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている(例えば、特許文献1)。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements have been made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the entertainment value of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, and simplifying control (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like the ones mentioned above, further technological improvements are desired in order to increase the enjoyment of the game, reduce the processing load of the gaming machine, simplify control, and provide a more sound game experience.
<特徴αK群>
特徴αK群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αK group>
The group of features αK is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αK1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成された第1の表示領域及び第2の表示領域を有し、当該第1の表示領域及び当該第2の表示領域に所定の情報を表示可能な表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、
前記遊技履歴情報を表示する際に、前記第1の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を前記表示要素を使用して表示し、前記第2の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の数値情報を前記表示要素を使用して表示する手段と、
前記当選確率の変更の際に、前記第1の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示する際には表示されない表示態様であって、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示する際に使用される表示要素のみを使用した表示態様を表示し、前記第2の表示領域に、前記当選確率の設定に関する数値情報を前記表示要素を使用して表示する手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αK1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means having a first display area and a second display area constituted by a plurality of display elements (segment light emitting units, CP light emitting units) and capable of displaying predetermined information in the first display area and the second display area;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes:
a means for displaying, when displaying the gaming history information, information relating to a type of the gaming history information in the first display area by using the display elements, and displaying, in the second display area, numerical information of the gaming history information by using the display elements;
a means for displaying, in the first display area, a display mode that is not displayed when displaying information related to the type of the game history information, and that uses only display elements that are used when displaying information related to the type of the game history information, when changing the winning probability, and displaying, in the second display area, numerical information related to the setting of the winning probability using the display elements;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αK1によれば、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、第1の表示領域の表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、遊技機の管理者に、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者が、第2の表示領域に表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と当選確率の設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αK1, the display mode of the first display area is clearly different when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means from when the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. Therefore, for example, it is possible to allow the manager of the gaming machine to clearly distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means or whether the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from mistaking the numerical information displayed in the second display area for the numerical information of the game history information or the numerical information of the winning probability setting.
さらに、本特徴によれば、遊技履歴情報を表示する際に使用されない第1の表示領域の表示要素(例えば、左端7セグメント表示器45z1のセグメント発光部A、B、DP発光部、左中7セグメント表示器45z2のセグメント発光部B)は、当選確率の変更の際にも使用されないので、第1の表示領域には、使用されない表示要素(以下、不使用表示要素)が存在することになる。したがって、例えば、第1の表示領域の不使用表示要素に不具合が発生したとしても、第1の表示領域における表示態様には影響がない。この結果、第1の表示領域の表示要素に不具合が発生した場合に表示態様に影響が生じてしまう可能性を低減することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the display elements of the first display area that are not used when displaying game history information (for example, the segment light emitting units A and B and the DP light emitting unit of the leftmost seven-segment display 45z1, and the segment light emitting unit B of the left-center seven-segment display 45z2) are not used when changing the winning probability either, so the first display area has display elements that are not used (hereinafter, unused display elements). Therefore, for example, even if a malfunction occurs in an unused display element of the first display area, the display mode in the first display area is not affected. As a result, it is possible to reduce the possibility that the display mode will be affected if a malfunction occurs in a display element of the first display area.
また、例えば、表示要素としてLED等の発光素子を採用した場合には、不使用表示要素となる発光素子は発光する必要がないため、当該発光素子を発光させるために必要な部品を省略することができる。したがって、表示手段のコストを低減することができる。 In addition, for example, when light-emitting elements such as LEDs are used as display elements, the light-emitting elements that are unused display elements do not need to emit light, so the components required to make the light-emitting elements emit light can be omitted. This allows the cost of the display means to be reduced.
<特徴αL群>
特徴αL群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αL group>
The group of features αL is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αL1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
第1の表示領域及び第2の表示領域を有し、当該第1の表示領域及び当該第2の表示領域に所定の情報を表示可能な表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、
前記遊技履歴情報を表示する際に、前記第1の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示し、前記第2の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の数値情報を表示する手段と、
前記当選確率の変更の際に、前記第1の表示領域には何も表示せず、前記第2の表示領域に、前記当選確率の設定に関する数値情報を表示する手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αL1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means having a first display area and a second display area and capable of displaying predetermined information in the first display area and the second display area;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes:
a means for displaying information on a type of the gaming history information in the first display area and displaying numerical information of the gaming history information in the second display area when displaying the gaming history information;
a means for displaying nothing in the first display area and displaying numerical information related to the setting of the winning probability in the second display area when the winning probability is changed;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αL1によれば、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、第1の表示領域の表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、遊技機の管理者に、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者が、第2の表示領域に表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と当選確率の設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αL1, the display mode of the first display area is clearly different when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means from when the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. Therefore, for example, it is possible to allow the manager of the gaming machine to clearly distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means or whether the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from mistaking the numerical information displayed in the second display area for the numerical information of the game history information or the numerical information of the winning probability setting.
さらに、本特徴によれば、例えば、第1の表示領域を複数の発光素子(LED)によって構成し、所定の発光素子が発光することによって所定の情報を表示し、全ての発光素子が消灯することで何も表示しない構成とした場合において、仮に第1の表示領域を構成する一部の発光素子が発光しないといった不具合が発生していたとしても、全ての発光素子が発光しないといった重大な不具合が発生していない限りは、第1の表示領域の表示態様が、遊技履歴情報を表示している場合と当選確率の設定に関する数値情報を表示している場合とで異なることになる。したがって、本特徴によれば、管理者に対して、仮に第1の表示領域を構成する一部の発光素子が発光しない不具合が発生していたとしても、全ての発光素子が発光しないといった重大な不具合が発生していない限りは、第2の表示領域に表示されている数値情報が遊技履歴情報であるのか、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報であるのかを区別して認識させることができる。すなわち、管理者は、第1の表示領域において少なくとも一部の発光素子が発光している場合には第2の表示領域に表示されている数値が遊技履歴情報であると判断し、第1の表示領域を構成する全ての発光素子が消灯している場合に限り第2の表示領域に表示されている数値が当選確率の設定に関する数値情報であると判断することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, for example, in a case where the first display area is composed of a plurality of light-emitting elements (LEDs), and a specific light-emitting element emits light to display specific information, and all the light-emitting elements are turned off to display nothing, even if a malfunction occurs in which some of the light-emitting elements constituting the first display area do not emit light, as long as there is no serious malfunction in which all the light-emitting elements do not emit light, the display mode of the first display area will be different between when it displays game history information and when it displays numerical information related to the setting of the winning probability. Therefore, according to this feature, even if a malfunction occurs in which some of the light-emitting elements constituting the first display area do not emit light, as long as there is no serious malfunction in which all the light-emitting elements do not emit light, the administrator can distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information displayed in the second display area is game history information or numerical information related to the setting of the winning probability. In other words, the administrator can determine that the numerical value displayed in the second display area is game history information when at least some of the light-emitting elements in the first display area are emitting light, and can determine that the numerical value displayed in the second display area is numerical information related to the setting of the winning probability only when all the light-emitting elements constituting the first display area are turned off.
<特徴αM群>
特徴αM群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αM group>
The group of features α M is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αM1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
所定の表示領域を有し、当該所定の表示領域に所定の情報を表示可能な表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、
前記遊技履歴情報を表示する際に、前記所定の表示領域に前記遊技履歴情報の数値情報を所定の桁数(2桁)で表示する手段と、
前記当選確率の変更の際に、前記所定の表示領域に前記当選確率の設定に関する数値情報を前記所定の桁数とは異なる桁数(1桁)で表示する手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αM1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means having a predetermined display area and capable of displaying predetermined information in the predetermined display area;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes:
a display unit for displaying, in the predetermined display area, numerical information of the gaming history information with a predetermined number of digits (two digits) when the gaming history information is displayed;
a means for displaying, in the predetermined display area, numerical information regarding the setting of the winning probability with a number of digits (one digit) different from the predetermined number of digits when the winning probability is changed;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αM1によれば、所定の表示領域に遊技履歴情報に関する数値情報が表示されている場合と、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、表示されている数値の桁数が異なることになる。したがって、例えば、遊技機の管理者に、表示手段の所定の表示領域に遊技履歴情報に関する数値情報が表示されているのか、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者が、表示手段の所定の表示領域に表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と当選確率の設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αM1, the number of digits of the displayed numerical value differs when numerical information related to game history information is displayed in the specified display area from when numerical information related to the winning probability setting is displayed. Therefore, for example, it is possible to allow the manager of the gaming machine to clearly distinguish and recognize whether numerical information related to game history information or numerical information related to the winning probability setting is displayed in the specified display area of the display means. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from mistaking the numerical information displayed in the specified display area of the display means for numerical information related to game history information or numerical information related to the winning probability setting.
<特徴αN群>
特徴αN群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αN group>
The group of features αN is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αN1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更手段と、
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
第1の表示領域及び第2の表示領域を有し、当該第1の表示領域及び当該第2の表示領域に所定の情報を表示可能な表示手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、
前記遊技履歴情報を表示する際に、前記第1の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示し、前記第2の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の数値情報を表示する手段と、
前記当選確率の変更の際に、前記第1の表示領域に、前記遊技履歴情報の種別に関する情報を表示する際には表示されない複数種類の表示態様(表示パターンA及び表示パターンB)を切り替えて繰り返し表示し、前記第2の表示領域に、前記当選確率の設定に関する数値情報を表示する手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αN1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
A change means for changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from outside;
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means having a first display area and a second display area and capable of displaying predetermined information in the first display area and the second display area;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes:
a means for displaying information on a type of the gaming history information in the first display area and displaying numerical information of the gaming history information in the second display area when displaying the gaming history information;
a means for repeatedly displaying, in the first display area, a plurality of display modes (display pattern A and display pattern B) which are not displayed when displaying information relating to the type of the game history information, by switching between them when changing the winning probability, and displaying, in the second display area, numerical information relating to the setting of the winning probability;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αN1によれば、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されている場合と、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されている場合とで、第1の表示領域の表示態様が明確に異なることになる。したがって、例えば、遊技機の管理者に、表示手段の第2の表示領域に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されているのか、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が表示されているのかを明確に区別して認識させることができる。この結果、遊技機の管理者が、第2の表示領域に表示されている数値情報を、遊技履歴情報の数値情報と当選確率の設定に関する数値情報との間で誤認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αN1, the display mode of the first display area is clearly different when the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means from when the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. Therefore, for example, it is possible to allow the manager of the gaming machine to clearly distinguish and recognize whether the numerical information of the game history information is displayed in the second display area of the display means or whether the numerical information of the winning probability setting is displayed. As a result, it is possible to prevent the manager of the gaming machine from mistaking the numerical information displayed in the second display area for the numerical information of the game history information or the numerical information of the winning probability setting.
さらに、本特徴によれば、当選確率の設定に関する数値情報が第2の表示領域に表示されている期間においては第1の表示領域における表示態様が動的に変化することになるので、遊技機の管理者に対して、当選確率の変更を慎重に行なうべき重要な状態であるといった注意を喚起することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the display mode in the first display area changes dynamically while the numerical information regarding the winning probability setting is displayed in the second display area, so that the administrator of the gaming machine can be alerted to an important state in which changes to the winning probability should be made with caution.
<特徴αO群>
特徴αO群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αO group>
The group of features αO is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αO1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示(種別情報及び数値情報の表示)をする表示手段と、
前記遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる前記検知情報の情報量(通常モード中に排出通路を通過した遊技球の個数(通常モード中のアウト数))に基づいて、前記表示手段における前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示の表示態様(点灯表示か点滅表示か)を決定する決定手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αO1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the game ball detected by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
a display means for displaying (displaying type information and numerical value information) based on the game history information calculated by the calculation means;
a determination means for determining a display mode (whether to light or flash) of a display based on the game history information on the display means, based on an amount of information of the detection information (the number of game balls passing through the discharge passage during the normal mode (the number of outs during the normal mode)) that is the basis for calculating the game history information;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αO1によれば、遊技機の管理者は、表示手段における表示態様を確認することによって、遊技履歴情報の算出の基礎となる検知情報がどの程度蓄積されているのかを把握することができ、例えば、表示されている遊技履歴情報の数値が、十分な量の統計データが蓄積された状態で算出されたものであるのか否かを判断することが可能となる。 According to feature αO1, the manager of the gaming machine can ascertain how much detection information has been accumulated that is the basis for calculating the gaming history information by checking the display mode on the display means, and can determine, for example, whether the numerical value of the displayed gaming history information has been calculated when a sufficient amount of statistical data has been accumulated.
なお、上記特徴αK群~特徴αO群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature αK group to feature αO group solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている(例えば、特許文献1)。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements have been made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the entertainment value of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, and simplifying control (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、制御の簡易化、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like the ones mentioned above, further technological improvements are desired in order to increase the enjoyment of the game, reduce the processing load of the gaming machine, simplify control, and provide a more sound game experience.
<特徴αP群>
特徴αP群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αP group>
The group of features αP is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αP1]
遊技を制御する制御手段を備える遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、
フラグレジスタを含む複数のレジスタと、スタックポインタとを備え、第1プログラムおよび第2プログラムを含む複数種類のプログラムを実行するCPU(主側CPU62x)と、
前記第1プログラムを記憶する第1プログラム記憶領域と、前記第1プログラム記憶領域と異なる領域であって、前記第2プログラムを記憶する第2プログラム記憶領域とを有するプログラム記憶手段(主側ROM63のプログラム記憶手段63a)と、
前記スタックポインタに格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1スタック領域と、前記第1スタック領域と異なる領域であって、前記スタックポインタに格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2スタック領域とを有するスタック手段(主側RAM64のスタック手段64b)と、
データを更新可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1データ記憶領域と、前記第1データ記憶領域と異なる領域であって、データを更新可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2データ記憶領域とを有するデータ記憶手段(主側RAM64のデータ記憶手段64a)とを備え、
前記フラグレジスタは、所定の場合に値が変化するレジスタであり、
前記第1プログラムによる処理では前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記第2プログラムによる処理では前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記CPUは、
前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第1処理(遊技進行処理)を実施し、
前記第1処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記フラグレジスタの値を前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶する記憶処理を実施し、
前記記憶処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記スタックポインタに格納されている前記第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶し、前記スタックポインタに前記第2スタック領域参照用アドレスを格納し、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶する退避処理を実施し、
前記退避処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第2処理(遊技履歴情報算出表示処理)を実施し、
前記第2処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を前記退避処理により前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶した値に設定し、前記退避処理により前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶した前記第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを前記スタックポインタに格納する復帰処理を実施し、
前記復帰処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記復帰処理により値が設定された前記複数のレジスタのうち前記フラグレジスタの値を、前記記憶処理により前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶した値に変更する変更処理を実施する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αP1]
A gaming machine having a control means for controlling a game,
The control means
a CPU (
a program storage means (program storage means 63a of the main ROM 63) having a first program storage area for storing the first program and a second program storage area that is an area different from the first program storage area and stores the second program;
a stack means (stack means 64b of the main RAM 64) having a first stack area corresponding to the first program and accessible by a first stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer, and a second stack area different from the first stack area and corresponding to the second program and accessible by a second stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer;
a data storage means (data storage means 64a of the main RAM 64) having a first data storage area corresponding to the first program capable of updating data, and a second data storage area which is an area different from the first data storage area and corresponds to the second program capable of updating data;
The flag register is a register whose value changes in a predetermined case,
In a process by the first program, data in the first stack area and the first data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the second stack area and the second data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
In a process by the second program, data in the second stack area and the second data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the first stack area and the first data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
The CPU includes:
A first process (game progress process) is carried out by executing a program included in the first program;
After performing the first process, a storage process is performed to store the value of the flag register in the first stack area or the first data storage area by executing a program included in the first program;
after carrying out the storage process, executing a program included in the second program to carry out a save process of storing the address for referring to the first stack area stored in the stack pointer in the second data storage area, storing the address for referring to the second stack area in the stack pointer, and storing the values of each of the plurality of registers in the second data storage area;
After carrying out the saving process, a second process (a game history information calculation and display process) is carried out by executing a program included in the second program;
a program included in the second program is executed after the second process is performed, thereby performing a return process in which the values of the plurality of registers are set to the values stored in the second data storage area by the save process, and the address for referring to the first stack area stored in the second data storage area by the save process is stored in the stack pointer;
A gaming machine characterized in that, after performing the return process, a program included in the first program is executed to perform a change process in which the value of the flag register, one of the multiple registers whose values were set by the return process, is changed to a value stored in the first stack area or the first data memory area by the storage process.
特徴αP1によれば、退避処理及び復帰処理を実施するので、第2プログラムから第1プログラムへ復帰した際に、第1プログラムにおいて利用していたレジスタの値が変化してしまっていることによる不具合の発生を回避することができる。 Feature αP1 performs save and restore processes, which makes it possible to avoid problems caused by changes to the register values used in the first program when returning from the second program to the first program.
また、本特徴によれば、記憶処理を実施した後であって退避処理を実施する前のタイミングにおいてフラグレジスタの値が変化した場合であっても、変更処理を実施することによって、フラグレジスタの値が第1プログラムによる第1処理の終了直後と同じ値に復帰するので、第2プログラムによる処理から復帰した後に実施する第1プログラムによる処理に影響を及ぼすおそれがない。この結果、複数のプログラムを独立して構成することが可能となる。 In addition, according to this feature, even if the value of the flag register changes after the storage process is performed but before the save process is performed, the value of the flag register is restored to the same value as immediately after the end of the first process by the first program by performing the change process, so there is no risk of affecting the process by the first program that is performed after returning from the process by the second program. As a result, it becomes possible to configure multiple programs independently.
また、本特徴によれば、第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを第2プログラムに追加するだけで、第1プログラムによる処理に影響を与えずに、第2処理を追加することができる。したがって、第1プログラムとは独立して第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを容易に作成することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the second process can be added without affecting the processing by the first program, simply by adding a program for performing the second process to the second program. Therefore, a program for performing the second process independently of the first program can be easily created.
また、例えば、スタック領域に記憶させようとするデータの容量が、スタック領域の記憶容量の上限値を超える場合には、当該スタック領域に記憶されている全データを消去するリセット処理が実施される構成である場合において、仮に、退避処理において複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を第2スタック領域に記憶させる構成とすると、当該リセット処理が実施されてしまうおそれがある。これに対して、本特徴によれば、退避処理において複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域に記憶するので、スタック領域のリセット処理が実施されてしまうリスクを回避することができる。 In addition, for example, in a configuration in which a reset process is performed to erase all data stored in the stack area when the amount of data to be stored in the stack area exceeds the upper limit of the storage capacity of the stack area, if the values of each of the multiple registers are stored in the second stack area during the evacuation process, there is a risk that the reset process will be performed. In contrast, according to this feature, the values of each of the multiple registers are stored in the second data storage area during the evacuation process, so the risk of the stack area resetting being performed can be avoided.
<特徴αQ群>
特徴αQ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αQ group>
The group of features αQ is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αQ1]
遊技を制御する制御手段を備える遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、
フラグレジスタを含む複数のレジスタと、スタックポインタとを備え、第1プログラムおよび第2プログラムを含む複数種類のプログラムを実行するCPU(主側CPU62x)と、
前記第1プログラムを記憶する第1プログラム記憶領域と、前記第1プログラム記憶領域と異なる領域であって、前記第2プログラムを記憶する第2プログラム記憶領域とを有するプログラム記憶手段(主側ROM63のプログラム記憶手段63a)と、
前記スタックポインタに格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1スタック領域と、前記第1スタック領域と異なる領域であって、前記スタックポインタに格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2スタック領域とを有するスタック手段(主側RAM64のスタック手段64b)と、
データを更新可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1データ記憶領域と、前記第1データ記憶領域と異なる領域であって、データを更新可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2データ記憶領域とを有するデータ記憶手段(主側RAM64のデータ記憶手段64a)とを備え、
前記フラグレジスタは、所定の場合に値が変化するレジスタであり、
前記第1プログラムによる処理では前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記第2プログラムによる処理では前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記CPUは、
前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第1処理(遊技進行処理)を実施し、
前記第1処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記フラグレジスタの値を前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶する記憶処理を実施し、
前記記憶処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記スタックポインタに前記第2スタック領域参照用アドレスを格納し、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶する退避処理を実施し、
前記退避処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第2処理(遊技履歴情報算出表示処理)を実施し、
前記第2処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を前記退避処理により前記第2データ記憶領域に記憶した値に設定し、固定値である前記第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを前記スタックポインタに格納する復帰処理を実施し、
前記復帰処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記復帰処理により値が設定された前記複数のレジスタのうち前記フラグレジスタの値を、前記記憶処理により前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶した値に変更する変更処理を実施する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αQ1]
A gaming machine having a control means for controlling a game,
The control means
a CPU (
a program storage means (program storage means 63a of the main ROM 63) having a first program storage area for storing the first program and a second program storage area that is an area different from the first program storage area and stores the second program;
a stack means (stack means 64b of the main RAM 64) having a first stack area corresponding to the first program and accessible by a first stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer, and a second stack area different from the first stack area and corresponding to the second program and accessible by a second stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer;
a data storage means (data storage means 64a of the main RAM 64) having a first data storage area corresponding to the first program capable of updating data, and a second data storage area which is an area different from the first data storage area and corresponds to the second program capable of updating data;
The flag register is a register whose value changes in a predetermined case,
In a process by the first program, data in the first stack area and the first data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the second stack area and the second data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
In a process by the second program, data in the second stack area and the second data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the first stack area and the first data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
The CPU includes:
A first process (game progress process) is carried out by executing a program included in the first program;
After performing the first process, a storage process is performed to store the value of the flag register in the first stack area or the first data storage area by executing a program included in the first program;
after carrying out the storage process, a program included in the second program is executed to store an address for referring to the second stack area in the stack pointer and to carry out a save process for storing the respective values of the plurality of registers in the second data storage area;
After the save process is performed, a program included in the second program is executed to perform a second process (a game history information calculation and display process);
a program included in the second program is executed after the second process is performed, thereby performing a return process in which the values of the plurality of registers are set to the values stored in the second data storage area by the save process, and the address for referring to the first stack area, which is a fixed value, is stored in the stack pointer;
A gaming machine characterized in that, after performing the return process, a program included in the first program is executed to perform a change process in which the value of the flag register, one of the multiple registers whose values were set by the return process, is changed to a value stored in the first stack area or the first data memory area by the storage process.
特徴αQ1によれば、退避処理及び復帰処理を実施するので、第2プログラムから第1プログラムへ復帰した際に、第1プログラムにおいて利用していたレジスタの値が変化してしまっていることによる不具合の発生を回避することができる。 Feature αQ1 performs save and restore processes, which makes it possible to avoid problems caused by changes to the register values used in the first program when returning from the second program to the first program.
また、本特徴によれば、記憶処理を実施した後であって退避処理を実施する前のタイミングにおいてフラグレジスタの値が変化した場合であっても、変更処理を実施することによって、フラグレジスタの値が第1プログラムによる第1処理の終了直後と同じ値に復帰するので、第2プログラムによる処理から復帰した後に実施する第1プログラムによる処理に影響を及ぼすおそれがない。この結果、複数のプログラムを独立して構成することが可能となる。 In addition, according to this feature, even if the value of the flag register changes after the storage process is performed but before the save process is performed, the value of the flag register is restored to the same value as immediately after the end of the first process by the first program by performing the change process, so there is no risk of affecting the process by the first program that is performed after returning from the process by the second program. As a result, it becomes possible to configure multiple programs independently.
また、本特徴によれば、第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを第2プログラムに追加するだけで、第1プログラムによる処理に影響を与えずに、第2処理を追加することができる。したがって、第1プログラムとは独立して第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを容易に作成することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the second process can be added without affecting the processing by the first program, simply by adding a program for performing the second process to the second program. Therefore, a program for performing the second process independently of the first program can be easily created.
また、例えば、スタック領域に記憶させようとするデータの容量が、スタック領域の記憶容量の上限値を超える場合には、当該スタック領域に記憶されている全データを消去するリセット処理が実施される構成である場合において、仮に、退避処理において複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を第2スタック領域に記憶させる構成とすると、当該リセット処理が実施されてしまうおそれがある。これに対して、本特徴によれば、退避処理において複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を第2データ記憶領域に記憶するので、スタック領域のリセット処理が実施されてしまうリスクを回避することができる。 In addition, for example, in a configuration in which a reset process is performed to erase all data stored in the stack area when the amount of data to be stored in the stack area exceeds the upper limit of the storage capacity of the stack area, if the values of each of the multiple registers are stored in the second stack area during the evacuation process, there is a risk that the reset process will be performed. In contrast, according to this feature, the values of each of the multiple registers are stored in the second data storage area during the evacuation process, so the risk of the stack area resetting being performed can be avoided.
また、本特徴によれば、復帰処理において固定値である第1スタック領域参照用アドレスをスタックポインタに格納するので、退避処理においてスタックポインタに格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを第2データ記憶領域に退避させる必要がない。したがって、CPUの処理を簡略化することができるとともに、スタックポインタに格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを退避させるために必要となる第2データ記憶領域の記憶容量を低減することができる。 In addition, according to this feature, the address for referencing the first stack area, which is a fixed value, is stored in the stack pointer during the return process, so there is no need to save the address for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer to the second data storage area during the save process. This makes it possible to simplify the CPU processing and reduce the storage capacity of the second data storage area required to save the address for referencing the first stack area stored in the stack pointer.
<特徴αR群>
特徴αR群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αR group>
The group of features αR is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αR1]
遊技を制御する制御手段を備える遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、
フラグレジスタを含む複数のレジスタと、スタックポインタとを備え、第1プログラムおよび第2プログラムを含む複数種類のプログラムを実行するCPU(主側CPU62x)と、
前記第1プログラムを記憶する第1プログラム記憶領域と、前記第1プログラム記憶領域と異なる領域であって、前記第2プログラムを記憶する第2プログラム記憶領域とを有するプログラム記憶手段(主側ROM63のプログラム記憶手段63a)と、
前記スタックポインタに格納される第1スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1スタック領域と、前記第1スタック領域と異なる領域であって、前記スタックポインタに格納される第2スタック領域参照用アドレスによりアクセス可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2スタック領域とを有するスタック手段(主側RAM64のスタック手段64b)と、
データを更新可能な前記第1プログラムに対応した第1データ記憶領域と、前記第1データ記憶領域と異なる領域であって、データを更新可能な前記第2プログラムに対応した第2データ記憶領域とを有するデータ記憶手段(主側RAM64のデータ記憶手段64a)とを備え、
前記フラグレジスタは、所定の場合に値が変化するレジスタであり、
前記第1プログラムによる処理では前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記第2プログラムによる処理では前記第2スタック領域および前記第2データ記憶領域のデータを更新および参照可能であり、前記第1スタック領域および前記第1データ記憶領域のデータを更新できないが参照可能になっており、
前記CPUは、
前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第1処理(遊技進行処理)を実施し、
前記第1処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記フラグレジスタの値を前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶する記憶処理を実施し、
前記記憶処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する第1クリア処理を実施し、
前記第1クリア処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記スタックポインタに前記第2スタック領域参照用アドレスを格納する第1格納処理を実施し、
前記第1格納処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、第2処理(遊技履歴情報算出表示処理)を実施し、
前記第2処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、固定値である前記第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを前記スタックポインタに格納する第2格納処理を実施し、
前記第2格納処理を実施した後に、前記第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記複数のレジスタそれぞれの値を0に設定する第2クリア処理を実施し、
前記第2クリア処理を実施した後に、前記第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムを実行することによって、前記フラグレジスタの値を、前記記憶処理により前記第1スタック領域または前記第1データ記憶領域に記憶した値に変更する変更処理を実施する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αR1]
A gaming machine having a control means for controlling a game,
The control means
a CPU (
a program storage means (program storage means 63a of the main ROM 63) having a first program storage area for storing the first program and a second program storage area that is an area different from the first program storage area and stores the second program;
a stack means (stack means 64b of the main RAM 64) having a first stack area corresponding to the first program and accessible by a first stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer, and a second stack area different from the first stack area and corresponding to the second program and accessible by a second stack area reference address stored in the stack pointer;
a data storage means (data storage means 64a of the main RAM 64) having a first data storage area corresponding to the first program capable of updating data, and a second data storage area which is an area different from the first data storage area and corresponds to the second program capable of updating data;
The flag register is a register whose value changes in a predetermined case,
In a process by the first program, data in the first stack area and the first data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the second stack area and the second data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
In a process by the second program, data in the second stack area and the second data storage area can be updated and referenced, and data in the first stack area and the first data storage area cannot be updated but can be referenced,
The CPU includes:
A first process (game progress process) is carried out by executing a program included in the first program;
After performing the first process, a storage process is performed to store the value of the flag register in the first stack area or the first data storage area by executing a program included in the first program;
After the storage process is performed, a first clear process is performed in which a program included in the first program is executed to set each value of the plurality of registers to 0;
performing a first storing process of storing an address for referring to the second stack area in the stack pointer by executing a program included in the second program after performing the first clearing process;
After carrying out the first storage process, a program included in the second program is executed to carry out a second process (a game history information calculation and display process);
performing a second storing process of storing the address for referring to the first stack area, which is a fixed value, in the stack pointer by executing a program included in the second program after performing the second process;
After the second storing process is performed, a second clearing process is performed in which a value of each of the plurality of registers is set to 0 by executing a program included in the second program;
A gaming machine characterized in that, after performing the second clear process, a change process is performed by executing a program included in the first program, changing the value of the flag register to a value stored in the first stack area or the first data memory area by the storage process.
特徴αR1によれば、第1プログラムに含まれるプログラムによって第1クリア処理を実施し、第2プログラムに含まれるプログラムによって第2クリア処理を実施するので、第2プログラムの実行の開始直前の時点における複数のレジスタそれぞれの値と、第2プログラムの実行の終了直後の時点における複数のレジスタそれぞれの値とを一致させることができる。したがって、第2プログラムから第1プログラムへ復帰した際に、第1プログラムにおいて利用していた複数のレジスタそれぞれの値が変化してしまっていることによる不具合の発生を回避することができる。 According to feature αR1, the first clear process is performed by a program included in the first program, and the second clear process is performed by a program included in the second program, so that the values of each of the multiple registers immediately before the start of execution of the second program can be made to match the values of each of the multiple registers immediately after the end of execution of the second program. Therefore, when returning from the second program to the first program, it is possible to avoid problems caused by the values of each of the multiple registers used in the first program having changed.
また、本特徴によれば、記憶処理及び変更処理を実施するので、フラグレジスタの値が第1プログラムによる第1処理の終了直後と同じ値に復帰する。したがって、第2プログラムによる処理から復帰した後に実施する第1プログラムによる処理に影響を及ぼすおそれがない。この結果、複数のプログラムを独立して構成することが可能となる。 In addition, according to this feature, since the storage process and change process are performed, the value of the flag register is restored to the same value as immediately after the end of the first process by the first program. Therefore, there is no risk of affecting the process by the first program that is performed after returning from the process by the second program. As a result, it becomes possible to configure multiple programs independently.
また、本特徴によれば、第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを第2プログラムに追加するだけで、第1プログラムによる処理に影響を与えずに、第2処理を追加することができる。したがって、第1プログラムとは独立して第2処理を実施するためのプログラムを容易に作成することができる。 Furthermore, according to this feature, the second process can be added without affecting the processing by the first program, simply by adding a program for performing the second process to the second program. Therefore, a program for performing the second process independently of the first program can be easily created.
また、本特徴によれば、復帰処理において、固定値である第1スタック領域参照用アドレスをスタックポインタに格納するので、退避処理において、スタックポインタに格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを第2データ記憶領域に退避させる必要がない。したがって、CPUの処理を簡略化することができるとともに、スタックポインタに格納されている第1スタック領域参照用アドレスを退避させるために必要となる第2データ記憶領域の記憶容量を低減することができる。 In addition, according to this feature, in the return process, the address for referring to the first stack area, which is a fixed value, is stored in the stack pointer, so in the save process, there is no need to save the address for referring to the first stack area stored in the stack pointer to the second data storage area. This makes it possible to simplify the CPU processing and reduce the storage capacity of the second data storage area required to save the address for referring to the first stack area stored in the stack pointer.
<特徴αS群>
特徴αS群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αS group>
The group of features αS is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αS1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更モードを実行する変更モード実行手段と、
遊技の進行に関する情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記記憶手段の異常を検知する検知手段と、
前記検知手段が前記異常を検知した場合に前記記憶手段を初期化する初期化手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記変更モード実行手段は、前記初期化が実行された場合には、前記所定の操作を受け付けていない場合であっても前記変更モードを実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αS1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a change mode execution means for executing a change mode capable of changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from an outside;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing information regarding the progress of a game;
A detection means for detecting an abnormality in the storage means;
an initialization means for initializing the storage means when the detection means detects the abnormality;
A gaming machine comprising:
The change mode execution means is provided with a means for executing the change mode when the initialization is executed, even if the specified operation is not accepted.
記憶手段の異常によって当該記憶手段を初期化する状況となった場合には、当選確率の設定情報も管理者が本来意図した設定情報とは異なる設定情報に書き換わってしまっている可能性がある。そして、記憶手段を初期化しても当選確率の設定情報は初期化されない(変更されない)構成である場合には、依然として管理者が本来意図した設定情報とは異なる設定情報に維持されるおそれがある。 If an abnormality in the storage means causes the storage means to be initialized, the winning probability setting information may also be rewritten to setting information different from the setting information originally intended by the administrator. Furthermore, if the winning probability setting information is configured so that it is not initialized (changed) even when the storage means is initialized, there is a risk that the setting information may still be maintained as different from the setting information originally intended by the administrator.
特徴αS1によれば、記憶手段の異常によって当該記憶手段を初期化した際には、変更モードを実行するので、遊技機の管理者は、当該遊技機において遊技が再開される前に、変更モードにおいて、当選確率の設定情報を本来意図した設定情報に変更することが可能となる。 According to feature αS1, when the storage means is initialized due to an abnormality in the storage means, the change mode is executed, so that the manager of the gaming machine can change the winning probability setting information to the originally intended setting information in the change mode before play is resumed on the gaming machine.
[特徴αS2]
特徴αS1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記初期化手段は、前記記憶手段を初期化する際に、前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、遊技状態に関する情報は初期化しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αS2]
A gaming machine according to feature αS1,
The initialization means includes a means for initializing information relating to a game state among information stored in the storage means when initializing the storage means.
特徴αS2によれば、記憶手段が初期化された場合であっても、遊技状態に関する情報は初期化されないので、遊技者は、遊技状態を維持しつつ遊技を再開することが可能となる。したがって、記憶手段の初期化によって遊技者に不利益を与えてしまうことを抑止することが可能となる。 According to feature αS2, even if the storage means is initialized, information about the game status is not initialized, so the player can resume playing while maintaining the game status. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the player from being disadvantaged by the initialization of the storage means.
[特徴αS3]
特徴αS1または特徴αS2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記変更モードにおいて前記当選確率が変更された場合に、前記当選確率が変更されたことを報知する報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αS3]
A gaming machine according to feature αS1 or feature αS2,
The gaming machine further comprises a notification means for notifying a player that the winning probability has been changed when the winning probability is changed in the change mode.
記憶手段の異常によって当該記憶手段が初期化され、変更モードが実行された場合には、当該遊技機において遊技を行なっていた遊技者は、記憶手段の初期化の後の変更モードにおいて、管理者によって当選確率が変更されてしまったのか否か、疑心暗鬼になることが想定される。しかしながら、本特徴によれば、当選確率が変更された場合には、当選確率が変更されたことを報知するので、遊技者は、当選確率が変更されたか否かを確認することができる。より具体的には、遊技者に、現在の当選確率の設定情報がどのような設定情報になっているのかは把握させずに、変更モードにおいて当選確率が変更されたか否かに関してのみ把握させることができる。この結果、遊技者が、管理者によって当選確率が変更されてしまったのか否か不明なまま不安な気持ちで遊技を再開しなくてはいけないといった事態の発生を抑制することができる。 When an abnormality in the storage means causes the storage means to be initialized and the change mode is executed, it is expected that a player playing on the gaming machine will become suspicious as to whether or not the winning probability has been changed by the administrator in the change mode after the initialization of the storage means. However, according to this feature, when the winning probability has been changed, the fact that the winning probability has been changed is notified, so the player can confirm whether or not the winning probability has been changed. More specifically, the player can be made to understand only whether or not the winning probability has been changed in the change mode, without being made to understand what the current setting information for the winning probability is. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which a player must resume playing in a state of anxiety, not knowing whether or not the winning probability has been changed by the administrator.
<特徴αT群>
特徴αT群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic αT group>
The group of features α T is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αT1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から所定の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更モードを実行する変更モード実行手段と、
前記変更モードにおいて前記当選確率が変更された場合に、前記当選確率が変更されたことを報知する報知手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αT1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a change mode execution means for executing a change mode capable of changing the probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different probability by accepting a predetermined operation from an outside;
a notification means for notifying a user that the winning probability has been changed when the winning probability is changed in the change mode;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴αT1によれば、遊技者は、変更モードにおいて当選確率が変更されたことを認識することができる。具体的には、例えば、遊技者に、現在の当選確率の設定がどのような設定になっているのかは把握させずに、変更モードにおいて当選確率が変更されたか否かに関してのみ把握させることができる。 According to feature αT1, the player can recognize that the winning probability has been changed in the change mode. Specifically, for example, the player can be made to understand only whether the winning probability has been changed in the change mode, without being made to understand what the current winning probability setting is.
[特徴αT2]
特徴αT1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記変更モートにおいて前記当選確率が変更されなかった場合に、前記報知手段による報知とは異なる態様の報知をする第2報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αT2]
A gaming machine according to feature αT1,
a second notification means for notifying a player in a manner different from that notified by the notification means when the winning probability is not changed in the change mode.
特徴αT2によれば、遊技者は、変更モードにおいて当選確率が変更されなかったことを認識することができる。 Feature αT2 allows the player to recognize that the winning probability has not changed in the change mode.
[特徴αT3]
特徴αT1または特徴αT2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記第2報知手段は、前記変更モードにおいて前記当選確率が変更されなかった場合に、前記当選確率が変更されなかったことを報知する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αT3]
A gaming machine according to feature αT1 or feature αT2,
The second notification means comprises a means for notifying that the winning probability has not been changed when the winning probability has not been changed in the change mode.
特徴αT3によれば、遊技者は、変更モードにおいて当選確率が変更されなかったことを明確に認識することができる。 Feature αT3 allows the player to clearly recognize that the winning probability has not been changed in the change mode.
<特徴αU群>
特徴αU群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αU group>
The group of features αU is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αU1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から第1の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更モードを実行する変更モード実行手段と、
前記第1の操作とは異なる第2の操作を外部から受け付けることによって、遊技の進行を停止したモードであって前記当選確率に関する情報を表示する情報表示モードを実行する情報表示モード実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理の結果に関わらず一定の動作を継続する役物と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記役物は、前記情報表示モード中であっても、前記一定の動作を継続する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αU1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a change mode execution means for executing a change mode capable of changing the winning probability of winning a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different winning probability by receiving a first operation from an outside;
an information display mode execution means for executing an information display mode in which the progress of a game is stopped and information regarding the winning probability is displayed by receiving a second operation different from the first operation from the outside;
A role that continues a certain operation regardless of the result of the predetermined lottery process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine is characterized in that the reel continues the certain operation even during the information display mode.
特徴αU1によれば、遊技の進行を停止した情報表示モードの開始及び終了のタイミングにおいても役物の動作が停止したり変化したりせずに一定の動作を継続するので、例えば、役物の動作が停止したり変化したりするタイミングを狙って遊技者が遊技球を発射して不正に有利な結果を得てしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αU1, the action of the reel does not stop or change even when the information display mode that stops the game progress starts or ends, but continues to operate in a certain way. This prevents, for example, a player from gaining an unfair advantage by firing a game ball at a time when the action of the reel stops or changes.
<特徴αV群>
特徴αV群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αV group>
The group of features αV is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αV1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
外部から第1の操作を受け付けることによって、前記所定の抽選処理において所定の結果に当選する当選確率を異なる当選確率に変更可能な変更モードを実行する変更モード実行手段と、
前記第1の操作とは異なる第2の操作を外部から受け付けることによって、遊技の進行を停止したモードであって前記当選確率に関する情報を表示する情報表示モードを実行する情報表示モード実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理の結果に関わらず一定の動作を継続する役物と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記役物は、前記情報表示モード中は、予め定められた状態となって前記一定の動作を停止する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αV1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a change mode execution means for executing a change mode capable of changing a winning probability of a predetermined result in the predetermined lottery process to a different winning probability by receiving a first operation from an outside;
an information display mode execution means for executing an information display mode in which the progress of a game is stopped and information regarding the winning probability is displayed by receiving a second operation different from the first operation from the outside;
A role that continues a certain operation regardless of the result of the predetermined lottery process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine is characterized in that the reel is in a predetermined state and stops the fixed operation during the information display mode.
特徴αV1によれば、例えば、予め定められた状態以外の状態で動作を停止させると不具合が発生する可能性のある役物において、不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 Feature αV1 makes it possible to suppress malfunctions in, for example, parts that may malfunction if their operation is stopped in a state other than a predetermined state.
なお、上記特徴αP群~特徴αV群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group αP to feature group αV solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
<特徴αW群>
特徴αW群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αW group>
The group of features αW is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αW1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、当該遊技機に電源が投入された時点において第1の条件(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンがONであること)が成立している場合に前記設定変更モードを実行するが、電源が投入された後に前記第1の条件が成立した場合であっても前記設定変更モードを実行しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αW1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
A gaming machine comprising:
The setting change mode execution means executes the setting change mode when a first condition (the setting key, the frame opening switch and the door opening switch are all ON, and the RAM clear button is ON) is satisfied at the time the gaming machine is powered on, but is further provided with a means for not executing the setting change mode even if the first condition is satisfied after the power is turned on.
特徴αW1によれば、電源が投入済みの遊技機に設定変更モードを実行させるためには、当該遊技機の電源を一旦OFFにして再度電源をONにする必要がある。一般に、遊技ホールにおいて、遊技機の管理者以外の者は、遊技機の背面に設けられた電源スイッチを操作して電源を一旦OFFにして再度電源をONにすることは困難である。したがって、遊技機の管理者でない不正な意図を持つ者によって遊技機の当選確率の設定が不正に変更されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αW1, in order to execute the setting change mode on a gaming machine that has already been turned on, it is necessary to turn the power of the gaming machine OFF once and then ON again. Generally, in an amusement parlor, it is difficult for anyone other than the manager of the gaming machine to operate the power switch on the back of the gaming machine to turn the power OFF once and then ON again. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the winning probability setting of the gaming machine from being illegally changed by a person with illegal intentions who is not the manager of the gaming machine.
[特徴αW2]
特徴αW1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段を備え、
前記設定情報表示モード実行手段は、当該遊技機に電源が投入された時点において第2の条件(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンがOFFであること)が成立している場合に前記設定情報表示モードを実行するが、電源が投入された後に前記第2の条件が成立した場合であっても前記設定情報表示モードを実行しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αW2]
A gaming machine according to feature αW1,
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
The setting information display mode execution means executes the setting information display mode when a second condition (the setting key, the frame opening switch, and the door opening switch are all ON, and the RAM clear button is OFF) is satisfied at the time the gaming machine is powered on, but is further provided with a means for not executing the setting information display mode even if the second condition is satisfied after the power is turned on.
特徴αW2によれば、電源が投入済みの遊技機に設定情報表示モードを実行させるためには、当該遊技機の電源を一旦OFFにして再度電源をONにする必要がある。一般に、遊技ホールにおいて、遊技機の管理者以外の者は、遊技機の背面に設けられた電源スイッチを操作して電源を一旦OFFにして再度電源をONにすることは困難である。したがって、遊技機の管理者でない不正な意図を持つ者によって遊技機の当選確率の設定が不正に知られてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature αW2, in order to execute the setting information display mode on a gaming machine that is already powered on, it is necessary to turn the power of the gaming machine OFF once and then ON again. Generally, in an amusement parlor, it is difficult for anyone other than the manager of the gaming machine to operate the power switch on the back of the gaming machine to turn the power OFF once and then ON again. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the winning probability setting of the gaming machine from being illegally known by a person with illegal intentions who is not the manager of the gaming machine.
[特徴αW3]
特徴αW1または特徴αW2に記載の遊技機であって、
当該遊技機に電源が投入された場合に報知する報知手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αW3]
A gaming machine according to feature αW1 or feature αW2,
A gaming machine comprising a notification means for notifying when the power to the gaming machine is turned on.
特徴αW3によれば、遊技機の管理者でない不正な意図を持つ者が、周囲に気付かれずに当該遊技機の電源を一旦OFFにして再度電源をONにすることを困難にすることができる。したがって、遊技機の管理者でない不正な意図を持つ者が遊技機の当選確率の設定を変更したり確認したりすることをさらに抑制することができる。 Feature αW3 makes it difficult for a person with fraudulent intentions who is not the administrator of the gaming machine to turn the power of the gaming machine OFF and then ON again without being noticed by those around. This makes it possible to further prevent a person with fraudulent intentions who is not the administrator of the gaming machine from changing or checking the settings of the winning probability of the gaming machine.
<特徴αX群>
特徴αX群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αX group>
The group of features αX is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αX1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段と、
前記設定情報を含む情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいて所定の判定処理(RAM判定値を算出して正常か否かを判定する処理)を実行する判定処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定情報表示モード実行手段は、前記設定情報表示モードを実行する条件が成立している場合であっても、前記所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果(RAM判定値が正常ではないという結果)である場合には、前記設定情報表示モードを実行しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αX1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing information including the setting information;
a determination process execution means for executing a predetermined determination process (a process for calculating a RAM determination value and determining whether or not the RAM is normal) based on the information stored in the storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
A gaming machine characterized in that the setting information display mode execution means includes a means for not executing the setting information display mode when the result of the specified judgment process is a specified result (a result that the RAM judgment value is not normal) even if the condition for executing the setting information display mode is met.
記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいた所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果である場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報が、当該遊技機の管理者の意図しない異常な値になっている可能性がある。特徴αX1によれば、記憶手段に記憶されている当選確率の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま設定情報表示モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 When the result of a predetermined judgment process based on the information stored in the storage means is a predetermined result, there is a possibility that the setting information stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator of the gaming machine. According to feature αX1, it is possible to prevent the setting information display mode from being executed while leaving open the possibility that the setting information for the winning probability stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator.
<特徴αY群>
特徴αY群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αY group>
The group of features αY are extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and are mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αY1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
所定の操作(押下する操作)を受け付ける操作手段(RAMクリアボタン)と、
遊技の進行に関する情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けた状態(RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態)で電源が投入された場合に前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記情報を消去する消去処理(RAMクリア処理)を実行する消去処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けた状態であることを含む所定の条件(電源の投入時に、設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態であること)が成立した場合に、前記設定変更モードを実行する手段を備え、
前記消去処理実行手段は、前記所定の条件が成立した場合には、前記設定変更モードの実行前または実行後に前記消去処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αY1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
An operation means (RAM clear button) for accepting a predetermined operation (pressing operation);
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing information regarding the progress of a game;
an erasure process execution means for executing an erasure process (RAM clear process) for erasing the information stored in the storage means when the power is turned on in a state in which the operation means has accepted the predetermined operation (a state in which the RAM clear button is pressed);
A gaming machine comprising:
The setting change mode execution means includes a means for executing the setting change mode when a predetermined condition is met, including the operation means accepting the predetermined operation (when the power is turned on, the setting key, the frame opening switch, and the door opening switch are all ON, and the RAM clear button is pressed);
The erasure process execution means comprises means for executing the erasure process before or after execution of the setting change mode when the predetermined condition is met.
一般に、遊技機を管理する管理者は、操作手段が所定の操作を受け付けた状態で当該遊技機の電源を投入した場合には記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する消去処理が実行されることを認識している。したがって、特徴αY1によれば、管理者に対して、操作手段が所定の操作を受け付けた状態であることを含む所定の条件を成立させて設定変更モードを実行させた場合には、設定変更モードが実行されるだけでなく、消去処理も実行されるということを強く認識させることが可能となる。この結果、例えば、管理者は、高確率モード等の遊技状態を維持させたまま遊技機を起動させて前回の電源OFF時の状態から遊技を再開させたい場合、すなわち遊技機の起動時に消去処理を実行させてはいけない場合には、設定変更モードを実行させてはいけないといった判断を確実にすることができる。すなわち、本特徴によれば、管理者が操作を理解しやすい遊技機を提供することができる。 In general, the administrator who manages the gaming machine is aware that when the power of the gaming machine is turned on with the operation means accepting a predetermined operation, an erasure process is executed to erase the information stored in the storage means. Therefore, according to feature αY1, it is possible to make the administrator strongly aware that when a setting change mode is executed by establishing a predetermined condition including the operation means accepting a predetermined operation, not only the setting change mode is executed but also the erasure process is executed. As a result, for example, when the administrator wants to start the gaming machine while maintaining a game state such as a high probability mode and resume playing from the state when the power was last turned off, that is, when the erasure process should not be executed when the gaming machine is started, the administrator can reliably determine that the setting change mode should not be executed. In other words, according to this feature, a gaming machine whose operation is easy for the administrator to understand can be provided.
<特徴αZ群>
特徴αZ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature αZ group>
The group of features αZ is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴αZ1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を含む情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去手段は、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、前記設定情報は消去せず、前記設定情報以外の情報を消去する第1消去処理(第1RAMクリア処理)と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、前記設定情報を含む情報を消去する第2消去処理(第2RAMクリア処理)と、
を実行可能である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αZ1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing information including setting information which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability;
an erasing means for erasing the information stored in the storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The erasing means is
a first erasure process (first RAM clear process) for erasing information other than the setting information, without erasing the setting information, among the information stored in the storage means;
a second erasing process (second RAM clearing process) for erasing information including the setting information from among the information stored in the storage means;
A gaming machine characterized by being capable of executing the above.
特徴αZ1によれば、記憶手段に記憶されている情報のうち、設定情報を残して他の情報は消去すべき処理工程、及び、設定情報も含めて消去すべき処理工程のいずれの場合にも対応した処理工程を実現することができる。例えば、設定情報は正常であるため維持させたまま、他の情報は消去すべき処理工程である場合には設定情報は消去せず、設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性のある処理工程である場合には設定情報を含む情報を消去する構成を実現することができる。 According to feature αZ1, it is possible to realize a processing process that can handle both a processing process in which the setting information should be left and the other information should be deleted from the information stored in the storage means, and a processing process in which the setting information should be deleted as well. For example, it is possible to realize a configuration in which the setting information is not deleted in a processing process in which the setting information is normal and therefore should be maintained, and the setting information is not deleted in a processing process in which the setting information may have become an abnormal value unintended by the administrator, and the information including the setting information is deleted.
[特徴αZ2]
特徴αZ1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいて所定の判定処理(RAM判定値を算出して正常か否かを判定する処理)を実行する判定処理実行手段を備え、
前記消去手段は、前記所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果(RAM判定値が正常ではないという結果)である場合には、前記第2消去処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature αZ2]
A gaming machine according to feature αZ1,
a determination process execution means for executing a predetermined determination process (a process for calculating a RAM determination value and determining whether or not the RAM is normal) based on the information stored in the storage means,
The erasing means is provided with a means for executing the second erasing process when the result of the predetermined judgment process is a predetermined result (a result that the RAM judgment value is abnormal).
記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいた所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果である場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報が、当該遊技機の管理者の意図しない異常な値になっている可能性がある。特徴αZ2によれば、記憶手段に記憶されている当選確率の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま遊技が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 When the result of a predetermined judgment process based on the information stored in the storage means is a predetermined result, there is a possibility that the setting information stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator of the gaming machine. According to feature αZ2, it is possible to prevent a game from being played while leaving the possibility that the setting information for the winning probability stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator.
<特徴βA群>
特徴βA群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics of βA group>
The feature group βA is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βA1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記抽選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を含む情報を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいて所定の判定処理(RAM判定値を算出して正常か否かを判定する処理)を実行する判定処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、前記設定変更モードを実行するための所定の操作(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下された状態で、パチンコ機10の電源をONにする操作)を受け付けていない場合であっても、前記所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果(RAM判定値が正常ではないという結果)である場合には、前記設定変更モードを実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βA1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing information including setting information which is information regarding the setting of the lottery probability;
a determination process execution means for executing a predetermined determination process (a process for calculating a RAM determination value and determining whether or not the RAM is normal) based on the information stored in the storage means;
A gaming machine comprising:
A gaming machine characterized in that the setting change mode execution means is provided with a means for executing the setting change mode when a predetermined operation for executing the setting change mode (an operation of turning on the power of the
記憶手段に記憶されている情報に基づいた所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果である場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報が、当該遊技機の管理者の意図しない異常な値になっている可能性がある。特徴βA1によれば、所定の判定処理の結果が所定の結果である場合には、設定変更モードが実行されるので、管理者は、当選確率の設定を変更することができる。したがって、記憶手段に記憶されている当選確率の設定情報が管理者の意図しない異常な値になってしまっている可能性を残したまま遊技が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 If the result of a predetermined judgment process based on the information stored in the storage means is a predetermined result, there is a possibility that the setting information stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator of the gaming machine. According to feature βA1, if the result of the predetermined judgment process is a predetermined result, a setting change mode is executed, so that the administrator can change the winning probability setting. Therefore, it is possible to prevent a game from being played while leaving the possibility that the winning probability setting information stored in the storage means has an abnormal value that is not intended by the administrator.
<特徴βB群>
特徴βB群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βB group>
The feature group βB is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βB1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理の結果を含む遊技に関する情報を表示する表示手段(メイン表示部45)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、
前記設定変更モードの実行中は、前記遊技に関する情報を表示する際には表示されない第1の表示態様(全LEDが点灯する表示パターン)を表示する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βB1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
A display means (main display unit 45) for displaying information regarding the game including the result of the predetermined lottery process;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes:
The gaming machine is characterized by comprising a means for displaying a first display mode (a display pattern in which all LEDs are lit) that is not displayed when displaying information related to the game while the setting change mode is being executed.
特徴βB1によれば、設定変更モードが実行されていることを、遊技に関する情報を表示する表示手段を用いて管理者や遊技者に報知することができる。また、例えば、遊技に関する情報を表示する表示手段を備える遊技機である場合には、遊技機のハードウェア構成を変更することなく、遊技機の制御プログラムを変更することのみによって、設定変更モードが実行されていることを管理者や遊技者に報知することが可能な構成に変更することができる。したがって、例えば、設定変更モードが実行されていることを報知するための専用の表示手段を追加で設ける構成と比較して、遊技機の製造コストを低減することができる。 According to feature βB1, the setting change mode can be notified to an administrator or a player by using a display means that displays information about the game. Furthermore, for example, in the case of a gaming machine that is equipped with a display means that displays information about the game, the configuration can be changed to one that can notify an administrator or a player that the setting change mode is being executed by simply changing the control program of the gaming machine, without changing the hardware configuration of the gaming machine. Therefore, for example, the manufacturing costs of the gaming machine can be reduced compared to a configuration in which a dedicated display means is additionally provided for notifying that the setting change mode is being executed.
[特徴βB2]
特徴βB1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記設定情報表示モードの実行中は、前記遊技に関する情報を表示する際には表示されない表示態様であって前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(全LEDが同時に点滅する表示態様)を表示する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βB2]
A gaming machine according to feature βB1,
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
The display means is
A gaming machine comprising a means for displaying a second display mode (a display mode in which all LEDs flash simultaneously) different from the first display mode and not displayed when displaying information related to the game during execution of the setting information display mode.
特徴βB2によれば、設定変更モードではなく設定情報表示モードが実行されていることを、遊技に関する情報を表示する表示手段を用いて管理者や遊技者に報知することができる。また、例えば、遊技に関する情報を表示する表示手段を備える遊技機である場合には、遊技機のハードウェア構成を変更することなく、遊技機の制御プログラムを変更することのみによって、設定情報表示モードが実行されていることを管理者や遊技者に報知することが可能な構成に変更することができる。したがって、例えば、設定情報表示モードが実行されていることを報知するための専用の表示手段を追加で設ける構成と比較して、遊技機の製造コストを低減することができる。 According to feature βB2, it is possible to notify an administrator or a player that the setting information display mode is being executed instead of the setting change mode, by using a display means that displays information about the game. Furthermore, for example, in the case of a gaming machine that is equipped with a display means that displays information about the game, it is possible to change the configuration to one that can notify an administrator or a player that the setting information display mode is being executed by simply changing the control program of the gaming machine, without changing the hardware configuration of the gaming machine. Therefore, for example, it is possible to reduce the manufacturing costs of the gaming machine compared to a configuration in which a dedicated display means is additionally provided for notifying that the setting information display mode is being executed.
<特徴βC群>
特徴βC群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βC group>
The group of features βC is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βC1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示(種別情報及び数値情報の表示)をする表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記表示手段を制御する制御手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、複数の発光部によって構成されており、
前記制御手段は、当該遊技機に電源が投入されたことに基づいて、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の発光部の全てが点灯した状態となるように制御する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βC1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A control means for controlling the display means;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means is composed of a plurality of light emitting units,
The control means is provided with a control means for controlling all of the plurality of light-emitting elements constituting the display means to be lit up when power is applied to the gaming machine.
特徴βC1によれば、遊技機の管理者は、遊技機の電源を投入した際に、表示手段を構成する発光部に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができる。 According to feature βC1, when the gaming machine is powered on, the manager of the gaming machine can check whether any of the light-emitting elements constituting the display means are not lit due to a malfunction such as a broken wire.
[特徴βC2]
特徴βC1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、当該遊技機に電源が投入されたことに基づいて、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の発光部の全てが点滅した状態となるように制御する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βC2]
A gaming machine according to feature βC1,
The control means is provided with a control means for controlling all of the plurality of light-emitting elements constituting the display means to flash when power is applied to the gaming machine.
特徴βC2によれば、遊技機の管理者は、遊技機の電源を投入した際に、表示手段を構成する発光部に、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかを確認することができる。 According to feature βC2, when the gaming machine manager turns on the gaming machine, he or she can check whether any of the light-emitting elements constituting the display means are constantly lit due to a malfunction and do not turn off.
<特徴βD群>
特徴βD群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βD group>
The group of features βD is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βD1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報に基づく表示(種別情報及び数値情報の表示)をする表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記表示手段を制御する制御手段と、
外部からの所定の操作を受け付ける操作手段(情報表示部検査ボタン)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、複数の発光部によって構成されており、
前記制御手段は、前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の発光部の全てが点灯した状態となるように制御する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βD1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A control means for controlling the display means;
an operating means (information display unit inspection button) for accepting a predetermined operation from the outside;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means is composed of a plurality of light emitting units,
The control means is provided with a control means for controlling all of the plurality of light-emitting elements constituting the display means to be lit up based on the operation means accepting the specified operation.
特徴βD1によれば、遊技機の管理者は、操作手段を操作することによって、表示手段を構成する発光部に、断線等の不具合によって点灯しない発光部が存在していないかをいつでも確認することができる。 According to feature βD1, the manager of the gaming machine can check at any time whether any of the light-emitting elements constituting the display means are not lit due to a malfunction such as a broken wire by operating the operating means.
[特徴βD2]
特徴βD1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、前記操作手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の発光部の全てが点滅した状態となるように制御する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βD2]
A gaming machine according to feature βD1,
The control means is provided with a control means for controlling all of the plurality of light-emitting elements constituting the display means to flash on and off based on the operation means accepting the specified operation.
特徴βD2によれば、遊技機の管理者は、操作手段を操作することによって、表示手段を構成する発光部に、不具合によって常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部が存在していないかをいつでも確認することができる。 According to feature βD2, the manager of the gaming machine can, by operating the operating means, check at any time whether any of the light-emitting elements constituting the display means are constantly lit and do not turn off due to a malfunction.
<特徴βE群>
特徴βE群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βE group>
The group of features βE is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βE1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、所定のタイミングを境界とした複数の期間における前記検知情報を記憶する手段を備え、
前記算出手段は、前記複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて前記複数の期間毎における前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、前記複数の期間毎における複数の前記遊技履歴情報を切り替えて表示する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βE1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
the storage means includes means for storing the detection information for a plurality of periods with a predetermined timing as a boundary;
The calculation means includes means for calculating the game history information for each of the plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the plurality of periods,
The display means includes a means for switching between and displaying the plurality of pieces of game history information for each of the plurality of periods.
特徴βE1によれば、遊技機の検査者は、当該遊技機における所定のタイミングを境界とした複数の期間毎における複数の遊技履歴情報を確認することが可能となる。例えば、検査者は、当該遊技機において所定のタイミングを境界とした複数の期間において、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを確認することが可能となる。 According to feature βE1, an inspector of a gaming machine can check multiple pieces of gaming history information for multiple periods bounded by a predetermined timing on the gaming machine. For example, the inspector can check whether or not there was a situation in which the gaming history information was not within an appropriate range for multiple periods bounded by a predetermined timing on the gaming machine.
[特徴βE2]
特徴βE1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記所定のタイミングは、日付が変わったタイミングである
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βE2]
A gaming machine according to feature βE1,
The gaming machine, wherein the predetermined timing is a timing when the date changes.
特徴βE2によれば、遊技機の検査者は、当該遊技機における日付毎における複数の遊技履歴情報を確認することが可能となる。例えば、検査者は、遊技履歴情報が適正な範囲に収まっていない状況が存在したか否かを日付毎に確認することが可能となる。 According to feature βE2, the inspector of the gaming machine can check multiple pieces of gaming history information for each date on the gaming machine. For example, the inspector can check for each date whether there was a situation in which the gaming history information was not within the appropriate range.
<特徴βF群>
特徴βF群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βF group>
The feature group βF is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βF1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
所定の操作を受け付けた場合に前記記憶手段に記憶された前記検知情報を消去する消去手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、前記消去手段によって前記検知手段が消去された後、所定の条件が成立するまでは(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達するまでは)、前記遊技履歴情報の数値情報は表示しない手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βF1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
an erasing means for erasing the detection information stored in the storage means when a predetermined operation is received;
A gaming machine comprising:
The display means includes a means for not displaying the numerical information of the game history information until a predetermined condition is satisfied (until the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number) after the detection means is erased by the erasing means.
特徴βF1によれば、遊技機の検査者は、表示手段に遊技履歴情報の数値情報が表示されていない場合には、消去手段によって検知手段が消去された後、所定の条件が成立していないと認識することができる。 According to feature βF1, if the display means does not display numerical information of the gaming history information, the gaming machine inspector can recognize that the specified condition is not met after the detection means is erased by the erasing means.
なお、上記特徴αW群~特徴βF群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group αW to feature group βF solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
<特徴βG群>
特徴βG群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristics of βG group>
The group of features βG is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βG1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記算出手段は、所定の条件が満たされたこと(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達したこと)を境界とした複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて、当該複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した複数の前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した前記複数の遊技履歴情報を切り替えて表示する手段であって、前記遊技履歴情報の表示を切り替える際に、前記複数の期間のうちの一の期間に対応した前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様(bLの区間に対応するベースを表示する表示態様)から、前記複数の遊技履歴情報のいずれも表示しない表示態様(全消灯)に移行した後、前記複数の期間のうちの他の期間に対応した前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様(b1の区間に対応するベースを表示する表示態様)に移行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βG1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The calculation means includes a means for calculating a plurality of pieces of the game history information corresponding to each of a plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the periods, the boundaries of which are determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied (when the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number);
The display means includes:
a display mode for displaying the game history information corresponding to one of the plurality of periods (a display mode displaying a base corresponding to the bL section) to a display mode for displaying none of the game history information (all lights off), and then to a display mode for displaying the game history information corresponding to another of the plurality of periods (a display mode displaying a base corresponding to the b1 section), when switching the display of the game history information.
特徴βG1によれば、表示手段は、遊技履歴情報の表示を切り替える際に、複数の期間のうちの一の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様から、複数の遊技履歴情報のいずれも表示しない表示態様に移行した後、複数の期間のうちの他の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様に移行するので、当該遊技機の管理者又は検査者に対して、表示手段に表示されている遊技履歴情報が他の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報に切り替わったことを明確に認識させることができる。この結果、例えば、管理者等が、表示されている遊技履歴情報の期間が他の期間に切り替わったことに気付かずに、期間を誤認識して遊技履歴情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βG1, when switching the display of the game history information, the display means transitions from a display mode that displays game history information corresponding to one of the multiple periods to a display mode that does not display any of the multiple game history information, and then transitions to a display mode that displays game history information corresponding to another of the multiple periods, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can clearly recognize that the game history information displayed on the display means has switched to game history information corresponding to another period. As a result, for example, it is possible to prevent the manager or the like from misidentifying the period and checking the game history information without realizing that the period of the displayed game history information has switched to another period.
<特徴βH群>
特徴βH群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βH group>
The group of features βH is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βH1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記算出手段は、所定の条件が満たされたこと(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達したこと)を境界とした複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて、当該複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した複数の前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記複数の期間のうちの一の期間に対応した前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様(bLを表示する表示態様)から、前記複数の期間のうちの他の期間に対応した前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様(b1を表示する表示態様)に移行する場合には、第1の移行態様(300msの全消灯を挟んで移行させる移行態様)で表示態様を移行する手段と、
前記所定の条件が満たされたことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合には、前記第1の移行態様とは異なる第2の移行態様(3000msのハイフン点灯表示を挟んで移行させる移行態様)で表示態様を移行する手段とを備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βH1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The calculation means includes a means for calculating a plurality of pieces of the game history information corresponding to each of a plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the periods, the boundaries of which are determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied (when the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number);
The display means includes:
a means for transitioning the display mode in a first transition mode (a transition mode in which a transition is made with a full light-off period of 300 ms) when transitioning from a display mode (a display mode displaying bL) in which the game history information corresponding to one of the plurality of periods is displayed to a display mode (a display mode displaying b1) in which the game history information corresponding to another of the plurality of periods is displayed;
and when the display mode is to be changed based on the specified condition being satisfied, a means for changing the display mode in a second change mode (a change mode in which a hyphen is lit for 3000 ms and a change mode is made) different from the first change mode.
特徴βH1によれば、一の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様から他の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様に移行する場合の移行態様と、所定の条件が満たされたことに基づいて表示態様を移行する場合の移行態様とが異なるので、当該遊技機の管理者又は検査者は、移行態様の違いを認識することによって、他の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報を表示する表示態様に移行するのか、それとも、所定の条件が満たされたことに基づいて表示態様が移行するのかを明確に区別して認識することができる。したがって、例えば、管理者等が、所定の条件が満たされたことに気付かずに、遊技履歴情報の確認作業を継続してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βH1, the transition mode when switching from a display mode that displays game history information corresponding to one period to a display mode that displays game history information corresponding to another period is different from the transition mode when switching the display mode based on the satisfaction of a specified condition, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can clearly distinguish and recognize whether the display mode is switching to a display mode that displays game history information corresponding to another period, or whether the display mode is switching based on the satisfaction of a specified condition, by recognizing the difference between the transition modes. Therefore, for example, it is possible to prevent the manager, etc. from continuing the task of checking game history information without realizing that the specified condition has been satisfied.
<特徴βI群>
特徴βI群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βI group>
The feature group βI is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βI1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記算出手段は、所定の条件が満たされたこと(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達したこと)を境界とした複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて、当該複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した複数の前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した前記複数の遊技履歴情報を所定の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過したことに基づいて切り替えて表示する手段であって、前記遊技履歴情報を表示中に前記所定の条件が満たされた場合には、表示中の前記遊技履歴情報の前記所定の表示継続時間が経過する前であっても、当該所定の条件が満たされたことに対応した表示態様(ハイフン点灯、全消灯)に移行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βI1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The calculation means includes a means for calculating a plurality of pieces of the game history information corresponding to each of a plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the periods, the boundaries of which are determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied (when the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number);
The display means includes:
A gaming machine comprising: a means for switching and displaying the plurality of pieces of game history information corresponding to each of the plurality of periods based on the lapse of a predetermined display duration (5000 ms), and when the predetermined condition is satisfied while the game history information is being displayed, a means for transitioning to a display mode (hyphen lit, all lights off) corresponding to the satisfaction of the predetermined condition even before the predetermined display duration of the game history information being displayed has elapsed.
特徴βI1によれば、遊技履歴情報を表示中に所定の条件が満たされた場合には、表示中の遊技履歴情報の所定の表示継続時間が経過する前であっても、当該所定の条件が満たされたことに対応した表示態様に移行するので、当該遊技機の管理者又は検査者に対して、所定の条件が満たされたことを早期に認識させることができる。また、例えば、所定の条件が満たされたことに対応した表示態様に移行した後、早期に、当該所定の条件が満たされた後における各期間毎の遊技履歴情報を表示することが可能となる。この結果、管理者等は、当該所定の条件が満たされた後における各期間毎の遊技履歴情報を早期に確認することができるので、遊技機の検査効率を向上させることができる。 According to feature βI1, if a predetermined condition is met while the game history information is being displayed, the display mode changes to one corresponding to the predetermined condition being met, even before the predetermined display duration of the displayed game history information has elapsed, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can quickly recognize that the predetermined condition has been met. Furthermore, for example, after the display mode changes to one corresponding to the predetermined condition being met, it is possible to quickly display the game history information for each period after the predetermined condition was met. As a result, the manager or inspector can quickly check the game history information for each period after the predetermined condition was met, thereby improving the inspection efficiency of the gaming machine.
<特徴βJ群>
特徴βJ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βJ group>
The group of features βJ is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βJ1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記算出手段は、所定の条件が満たされたこと(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達したこと)を境界とした複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて、当該複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した複数の前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した前記複数の遊技履歴情報を所定の表示継続時間(5000ms)が経過したことに基づいて切り替えて表示する手段であって、前記遊技履歴情報を表示中に前記所定の条件が満たされた場合には、表示中の前記遊技履歴情報の前記所定の表示継続時間が経過した後に、当該所定の条件が満たされたことに対応した表示態様(ハイフン点灯、全消灯)に移行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βJ1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The calculation means includes a means for calculating a plurality of pieces of the game history information corresponding to each of a plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the periods, the boundaries of which are determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied (when the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number);
The display means includes:
A gaming machine comprising: a means for switching and displaying the plurality of pieces of game history information corresponding to each of the plurality of periods based on the lapse of a predetermined display duration (5000 ms), and when the predetermined condition is satisfied while the game history information is being displayed, a means for transitioning to a display mode (hyphen lit, all lights off) corresponding to the satisfaction of the predetermined condition after the predetermined display duration of the game history information being displayed has elapsed.
特徴βJ1によれば、遊技履歴情報の表示中に所定の条件が満たされた場合であっても、当該表示中の遊技履歴情報の表示継続時間が経過するまでは当該遊技履歴情報の表示が継続されるので、例えば、当該遊技機の管理者又は検査者が、表示中の遊技履歴情報を確認して検査表に転記しようとしたタイミングで当該遊技履歴情報の表示が終了してしまい、当該遊技履歴情報を検査表に転記することができなかったといった状況の発生を抑制することができる。 According to feature βJ1, even if a predetermined condition is satisfied while the game history information is being displayed, the game history information continues to be displayed until the display duration of the game history information being displayed has elapsed. This makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which, for example, the display of the game history information ends just as the manager or inspector of the gaming machine is about to check the game history information being displayed and transcribe it onto an inspection sheet, making it impossible to transcribe the game history information onto the inspection sheet.
<特徴βK群>
特徴βK群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βK group>
The group of features βK is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βK1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
前記算出手段によって算出された前記遊技履歴情報を表示する表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記算出手段は、所定の条件が満たされたこと(計測された排出通路通過個数NOUTが所定の個数に達したこと)を境界とした複数の期間毎における前記検知情報に基づいて、当該複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した複数の前記遊技履歴情報を算出する手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
前記複数の期間のそれぞれに対応した前記複数の遊技履歴情報を所定の順序に従って切り替えて表示する手段であって、前記所定の条件が満たされた場合には、前記所定の順序に関わらず、前記複数の期間のうちの特定の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報(bL)から表示を開始する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βK1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The calculation means includes a means for calculating a plurality of pieces of the game history information corresponding to each of a plurality of periods based on the detection information for each of the periods, the boundaries of which are determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied (when the measured number of balls passing through the discharge passage NOUT reaches a predetermined number);
The display means includes:
a means for switching and displaying the plurality of pieces of game history information corresponding to each of the plurality of periods in a predetermined order, and a means for starting display from game history information (bL) corresponding to a specific period among the plurality of periods, regardless of the predetermined order, when the predetermined condition is satisfied.
特徴βK1によれば、所定の条件が満たされた場合には、所定の順序に関わらず、複数の期間のうちの特定の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報から表示を開始するので、当該遊技機の管理者又は検査者は、所定の条件が満たされたことを認識することができるとともに、特定の期間に対応した遊技履歴情報から優先して確認することが可能となる。 According to feature βK1, when a specified condition is met, the display starts from the gaming history information corresponding to a specific period among multiple periods, regardless of the specified order. This allows the manager or inspector of the gaming machine to recognize that the specified condition has been met, and allows the manager or inspector of the gaming machine to prioritize checking the gaming history information corresponding to the specific period.
なお、上記特徴βG群~特徴βK群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group βG to feature group βK solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
<特徴βL群>
特徴βL群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature βL group>
The group of features βL is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βL1]
遊技機であって、
外部からの電力の供給が断たれる際に、所定の情報(各種フラグ情報等)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記所定の情報に基づいて、当該遊技機を電力の供給が断たれる前の状態に復帰させる復帰処理(復電処理)を実行する復帰手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、各種情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する検査用処理実行手段と、
を備え、
前記検査用処理実行手段は、前記復帰処理の実行を契機として、前記検査用処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βL1]
A gaming machine,
A storage unit (main RAM 64) for storing predetermined information (various flag information, etc.) when the supply of power from the outside is cut off;
a recovery means for executing a recovery process (power restoration process) for recovering the gaming machine to a state before the power supply is cut off based on the predetermined information when the power supply from an external source is started;
A display means (
a test process execution means for executing a test process (a lighting and blinking process) which is a process for operating the plurality of display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined mode;
Equipped with
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process execution means comprises a means for executing the inspection process in response to execution of the return process.
特徴βL1によれば、復帰処理の実行を契機として検査用処理を実行するので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、当該遊技機に対して復帰処理を実行させる操作(例えば、電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後に再びONにする操作)を行なうことによって、当該遊技機に検査用処理を実行させることができる。そして、管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βL1, the execution of the recovery process triggers the execution of the inspection process, so the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can cause the gaming machine to execute the inspection process by performing an operation to execute the recovery process on the gaming machine (for example, turning the power switch OFF and then ON again). The manager or inspector can then inspect whether any of the multiple display elements that make up the display means are malfunctioning and not operating in a specified manner.
[特徴βL2]
特徴βL1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βL2]
A gaming machine according to feature βL1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βL2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βL2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βL3]
特徴βL1または特徴βL2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βL3]
A gaming machine according to feature βL1 or feature βL2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βL3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βL3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
<特徴βM群>
特徴βM群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βM group>
The group of features β M is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βM1]
外部からの操作を受け付ける操作受付手段(RAMクリアボタン、設定用の鍵穴、設定変更用ボタン)と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記操作受付手段が受け付けている操作態様に基づいて、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれかの処理フローを実行する処理実行手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、各種情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記処理実行手段は、前記複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行する場合であっても、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βM1]
An operation reception means for receiving an operation from the outside (a RAM clear button, a keyhole for settings, and a button for changing settings);
a process execution means for executing one of a plurality of branched process flows based on an operation mode accepted by the operation acceptance means when the supply of electric power from an external source is started;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The gaming machine is characterized in that the processing execution means is provided with a means for executing an inspection process (lighting and flashing process) which is a process for operating the multiple display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined manner, regardless of which of the multiple branched processing flows is executed.
特徴βM1によれば、複数に分岐した処理フローのうちのいずれの処理フローを実行する場合であっても検査用処理を実行するので、電力の供給が開始された際に操作受付手段がどのような操作態様を受け付けている場合であっても、当該遊技機に検査用処理を実行させることができる。したがって、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、電力の供給が開始された際に操作受付手段が受け付けている操作態様に関わらず、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。すなわち、電力の供給が開始された際に操作受付手段が受け付けている操作態様次第では当該検査を実施することができないといったことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βM1, the inspection process is executed regardless of which of the multiple branched processing flows is executed, so that the gaming machine can be made to execute the inspection process regardless of the operation mode accepted by the operation acceptance means when power supply is started. Therefore, the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that does not operate in a predetermined mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means, regardless of the operation mode accepted by the operation acceptance means when power supply is started. In other words, it is possible to prevent the inspection from being unable to be performed depending on the operation mode accepted by the operation acceptance means when power supply is started.
[特徴βM2]
特徴βM1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βM2]
A gaming machine according to feature βM1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βM2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βM2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βM3]
特徴βM1または特徴βM2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βM3]
A gaming machine according to feature βM1 or feature βM2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βM3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βM3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
<特徴βN群>
特徴βN群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Feature βN group>
The group of features βN is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βN1]
外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、第1の処理群(図63及び図64のステップS12001~ステップS12028までの処理)を実行する第1処理群実行手段と、
前記第1の処理群の実行が終了した後、第2の処理群(タイマ割込み処理に含まれる各種処理、各種乱数更新処理、停電監視処理)を繰り返し実行する第2処理群実行手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、各種情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記第1処理群実行手段は、前記第1の処理群に含まれる一の処理として、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βN1]
a first process group execution means for executing a first process group (the processes from step S12001 to step S12028 in FIG. 63 and FIG. 64) based on the start of the supply of electric power from an external source;
A second process group execution means for repeatedly executing a second process group (various processes included in timer interrupt processing, various random number update processes, and power outage monitoring processing) after the execution of the first process group is completed;
A display means (
A gaming machine comprising:
The first process group executing means is provided with a means for executing an inspection process (lighting and flashing process) as one process included in the first process group, the inspection process being a process for operating the plurality of display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined manner.
特徴βN1によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、検査用処理を含む第1の処理群を実行し、当該第1の処理群の実行が終了した後に、第2の処理群を繰り返し実行するので、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後に検査用処理を1回だけ実行させることができる。仮に、検査用処理が第2の処理群に含まれる構成とした場合には、検査用処理が繰り返し実行されることとなってしまい、遊技機の処理負荷が大きくなってしまう。また、検査用処理が繰り返し実行されてしまうと、表示手段に各種情報を表示させることが可能な期間が少なくなってしまう虞がある。これに対して、本特徴によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後に検査用処理を1回だけ実行させることができるので、遊技機の処理負荷を低減することができるとともに、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βN1, a first process group including a test process is executed based on the start of the supply of external power, and after the execution of the first process group is completed, a second process group is repeatedly executed, so that the test process can be executed only once after the supply of external power is started. If the test process were included in the second process group, the test process would be repeatedly executed, which would increase the processing load of the gaming machine. Furthermore, if the test process is repeatedly executed, there is a risk that the period during which various information can be displayed on the display means will be shortened. In contrast, according to this feature, the test process can be executed only once after the supply of external power is started, so that the processing load of the gaming machine can be reduced, and the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can check whether there is any display element that does not operate in a predetermined manner due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements that make up the display means.
[特徴βN2]
特徴βN1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βN2]
A gaming machine according to feature βN1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βN2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βN2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βN3]
特徴βN1または特徴βN2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βN3]
A gaming machine according to feature βN1 or feature βN2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βN3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βN3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
<特徴βO群>
特徴βO群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βO group>
The group of features βO is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modified examples, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βO1]
遊技の進行を可能とするための処理である遊技進行処理(タイマ割込み処理に含まれる入球検知処理、始動口用の入球処理、遊技回制御処理等)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、各種情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する検査用処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記検査用処理実行手段は、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後、前記遊技進行処理の実行が開始される前に、前記検査用処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βO1]
A game progress processing execution means for executing game progress processing (a ball entry detection process included in a timer interrupt process, a ball entry process for a starting hole, a game number control process, etc.) which is a process for enabling the progress of a game;
A display means (
a test process execution means for executing a test process (a lighting and blinking process) which is a process for operating the plurality of display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined mode;
A gaming machine comprising:
The inspection process execution means comprises a means for executing the inspection process after the supply of power from an external source is started and before the execution of the game progress process is started.
特徴βO1によれば、外部からの電力の供給が開始された後、遊技進行処理の実行が開始される前に、検査用処理を実行するので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、当該遊技機において遊技の進行が可能となる前に、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βO1, after the supply of external power has begun and before the execution of the game progress process begins, the inspection process is executed, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether any of the multiple display elements constituting the display means are malfunctioning and not operating in a predetermined manner before game progress can be made on the gaming machine.
仮に、遊技進行処理の実行が開始された後に検査用処理を実行する構成とした場合には、管理者または検査者が表示手段の検査をすることが可能となる前に、遊技者が遊技を始めることが可能となる。この場合、遊技者が遊技機において遊技を始めた後に、管理者または検査者が当該遊技機の表示手段の検査を行なって、当該表示手段の表示要素に不具合を発見してしまう虞がある。管理者または検査者が当該遊技機の表示手段の表示要素に不具合を発見した場合には、当該表示手段を修理又は交換するために、当該遊技者に遊技を中断又は中止してもらう必要が生じる。この結果、遊技者に強い不快感を与えてしまう可能性がある。 If the inspection process were to be executed after the game progress process had begun, the player would be able to start playing before the manager or inspector could inspect the display means. In this case, there is a risk that after the player has started playing on the gaming machine, the manager or inspector would inspect the display means of the gaming machine and discover a defect in the display elements of the display means. If the manager or inspector discovers a defect in the display elements of the display means of the gaming machine, it will be necessary to have the player suspend or stop playing in order to repair or replace the display means. This could result in a strong sense of discomfort to the player.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技者が遊技機において遊技を始めることが可能となる前に、管理者または検査者が当該遊技機の表示手段の検査をすることが可能となるので、遊技を中断又は中止させて遊技者に不快感を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 In response to this, this feature allows an administrator or inspector to inspect the display means of a gaming machine before the player is able to start playing on the gaming machine, which prevents the player from having to interrupt or stop playing, causing discomfort to the player.
[特徴βO2]
特徴βO1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βO2]
A gaming machine according to feature βO1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βO2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βO2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βO3]
特徴βO1または特徴βO2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βO3]
A gaming machine according to feature βO1 or feature βO2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βO3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βO3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
<特徴βP群>
特徴βP群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βP group>
The group of features βP is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βP1]
所定の領域を通過した遊技球を検知する複数の検知手段(入球検知センサー44a~44h)と、
前記検知手段によって遊技球が検知されたことに基づく情報である検知情報(入球情報、入球個数情報、賞球集計値等の遊技履歴基礎情報)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記検知情報に基づいて遊技の履歴に関する情報である遊技履歴情報(役物比率、連続役物比率、出球率等の遊技履歴情報)を算出する算出手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、各種情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記遊技履歴情報に対応した情報を前記表示手段に表示させる処理である遊技履歴情報表示処理(タイマ割込み処理に含まれる遊技履歴用処理)を実行する遊技履歴情報表示処理実行手段と、
前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する検査用処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記検査用処理実行手段は、前記遊技履歴情報表示処理が実行されることによって前記遊技履歴情報に対応した情報が前記表示手段に表示される前に、前記検査用処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βP1]
A plurality of detection means (ball
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing detection information (basic game history information such as ball entry information, ball number information, and prize ball tally value) based on the detection of game balls by the detection means;
A calculation means for calculating game history information (game history information such as a combination ratio, a consecutive combination ratio, and a ball payout rate) which is information related to a game history based on the detection information;
A display means (
a game history information display process execution means for executing a game history information display process (a game history process included in a timer interrupt process) which is a process for displaying information corresponding to the game history information on the display means;
a test process execution means for executing a test process (a lighting and blinking process) which is a process for operating the plurality of display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined mode;
A gaming machine comprising:
The inspection process execution means includes a means for executing the inspection process before information corresponding to the gaming history information is displayed on the display means by executing the gaming history information display process.
特徴βP1によれば、遊技履歴情報に対応した情報が表示手段に表示される前に検査用処理を実行するので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、当該遊技機において遊技履歴情報に対応した情報が表示手段に表示される前に、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。この結果、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって正常に動作しない表示要素が存在していることに気付かずに、当該表示手段に表示されている遊技履歴情報に対応した情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βP1, the inspection process is executed before the information corresponding to the gaming history information is displayed on the display means, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that does not operate in a predetermined manner due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means before the information corresponding to the gaming history information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to prevent a player from checking the information corresponding to the gaming history information displayed on the display means without realizing that there is a display element that does not operate normally due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means.
[特徴βP2]
特徴βP1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βP2]
A gaming machine according to feature βP1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βP2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βP2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βP3]
特徴βP1または特徴βP2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βP3]
A gaming machine according to feature βP1 or feature βP2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βP3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βP3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
<特徴βQ群>
特徴βQ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態から抽出される。
<Characteristic βQ group>
The group of features βQ is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment.
[特徴βQ1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部からの操作を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
複数の表示要素(セグメント発光部、CP発光部)によって構成され、前記設定変更モードの実行中に前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を表示可能な表示手段(情報表示部45z)と、
前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素を所定の態様で動作させる処理である検査用処理(点灯点滅処理)を実行する検査用処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記検査用処理実行手段は、前記設定変更モードが実行されることによって前記設定情報が前記表示手段に表示される前に、前記検査用処理を実行する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βQ1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which a setting of a winning probability in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by receiving an external operation;
A display means (
a test process execution means for executing a test process (a lighting and blinking process) which is a process for operating the plurality of display elements constituting the display means in a predetermined mode;
A gaming machine comprising:
The inspection process execution means comprises a means for executing the inspection process before the setting information is displayed on the display means by executing the setting change mode.
特徴βQ1によれば、設定情報が表示手段に表示される前に検査用処理を実行するので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、当該遊技機において設定情報が表示手段に表示される前に、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって所定の態様で動作しない表示要素が存在していないかを検査することができる。この結果、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって正常に動作しない表示要素が存在していることに気付かずに、当該表示手段に表示されている設定情報を確認してしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βQ1, the inspection process is executed before the setting information is displayed on the display means, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there are any display elements that do not operate in a predetermined manner due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements that make up the display means before the setting information is displayed on the display means of the gaming machine. As a result, it is possible to prevent the user from checking the setting information displayed on the display means without realizing that there is a display element that does not operate normally due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements that make up the display means.
[特徴βQ2]
特徴βQ1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βQ2]
A gaming machine according to feature βQ1,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode.
特徴βQ2によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第2の表示態様となるように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様になることができない表示要素(例えば、断線によって点灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βQ2, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to be in the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is any display element that cannot be in the second display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting part that does not light up due to a broken wire).
[特徴βQ3]
特徴βQ1または特徴βQ2に記載の遊技機であって、
前記複数の表示要素のそれぞれは、第1の表示態様(消灯状態)と、前記第1の表示態様とは異なる第2の表示態様(点灯状態)とになることが可能であり、
前記検査用処理は、前記表示手段を構成する前記複数の表示要素の全てが前記第1の表示態様と前記第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含む
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βQ3]
A gaming machine according to feature βQ1 or feature βQ2,
Each of the plurality of display elements is capable of being in a first display state (off state) and a second display state (on state) different from the first display state,
The gaming machine, wherein the inspection process includes a process of controlling all of the plurality of display elements constituting the display means to alternately repeat the first display mode and the second display mode.
特徴βQ3によれば、検査用処理は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の全てが第1の表示態様と第2の表示態様とを交互に繰り返すように制御する処理を含むので、遊技機の管理者または検査者は、表示手段を構成する複数の表示要素の中に不具合によって第2の表示態様から第1の表示態様に移行することができない表示要素(例えば、常時点灯状態となって消灯しない発光部)が存在していないかを検査することができる。 According to feature βQ3, the inspection process includes a process for controlling all of the multiple display elements constituting the display means to alternate between the first display mode and the second display mode, so that the manager or inspector of the gaming machine can inspect whether there is a display element that cannot transition from the second display mode to the first display mode due to a malfunction among the multiple display elements constituting the display means (for example, a light-emitting element that is always on and does not turn off).
なお、上記特徴βL群~特徴βQ群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group βL to feature group βQ solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
<特徴βR群>
特徴βR群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βR group>
The group of features βR is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βR1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
所定の識別情報(設定変更中フラグ)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記設定変更モードの開始の際に前記識別情報を第1の状態(ON)とし、前記設定変更モードの終了の際に前記識別情報を前記第1の状態とは異なる第2の状態(OFF)に遷移させる識別情報遷移手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記識別情報の状態を維持することが可能であり、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、
所定の開始操作(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態で、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記設定変更モードを開始させる第1開始手段と、
外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が開始された際に前記識別情報が前記第1の状態であると判定したことに基づいて、前記設定変更モードを開始させる第2開始手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βR1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing predetermined identification information (setting change in progress flag);
an identification information transition means for setting the identification information to a first state (ON) when the setting change mode is started, and transitioning the identification information to a second state (OFF) different from the first state when the setting change mode is ended;
A gaming machine comprising:
The storage means is capable of maintaining the state of the identification information even when the supply of power to the gaming machine from an external source is cut off,
The setting change mode execution means is
A first starting means for starting the setting change mode based on the reception of a predetermined starting operation (an operation of turning on the power switch of the
a second starting means for starting the setting change mode based on the determination that the identification information is in the first state when the supply of power to the gaming machine is started from an external source;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βR1によれば、第1開始手段は、所定の開始操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させ、識別情報遷移手段は、設定変更モードの開始の際に識別情報を第1の状態とし、設定変更モードの終了の際に識別情報を第2の状態に遷移させる。そして、記憶手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても識別情報の状態を維持することが可能である。したがって、例えば、遊技機の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したこと等によって、設定変更モードの実行中に当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている識別情報は第1の状態に維持される。 According to feature βR1, the first starting means starts the setting change mode based on receipt of a predetermined starting operation, and the identification information transition means sets the identification information to a first state when the setting change mode starts and transitions the identification information to a second state when the setting change mode ends. The storage means is capable of maintaining the state of the identification information even when the supply of power to the gaming machine from the outside is cut off. Therefore, for example, if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off while the setting change mode is being executed because the power switch of the gaming machine is turned off or a power outage occurs, the identification information stored in the storage means is maintained in the first state.
そして、本特徴によれば、第2開始手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が開始された際に識別情報が第1の状態であると判定したことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させる。すなわち、本特徴によれば、設定変更モードの実行中に当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該遊技機への電力の供給が再開された場合には、所定の開始操作を受け付けていない場合であっても、設定変更モードが開始されることになる。 According to this feature, the second starting means starts the setting change mode based on determining that the identification information is in the first state when the supply of power to the gaming machine from the outside is started. In other words, according to this feature, if the supply of power to the gaming machine is cut off while the setting change mode is being executed, and the supply of power to the gaming machine is resumed, the setting change mode will be started even if a predetermined start operation has not been received.
したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該遊技機に再び設定変更モードを開始させるためには、当該遊技機への電力の供給が再開された後に管理者が再び所定の開始操作を行なわなければいけないといった手間を省くことができる。 Therefore, if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off from the outside while the setting change mode is being executed, the administrator can eliminate the trouble of having to perform the specified start operation again after the power supply to the gaming machine is resumed in order to restart the setting change mode on the gaming machine.
また、設定変更モードの実行中に外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、当該遊技機の当選確率の設定が管理者の意図しない状態となっている可能性があるが、本特徴によれば、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が再開された場合には、遊技機の管理者が再び所定の開始操作を行なわなくても設定変更モードが開始されるので、当該遊技機の当選確率の設定が管理者の意図しない状態となったまま見過ごされてしまうことを抑制することができる。 In addition, if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off from the outside while the setting change mode is running, the winning probability setting of the gaming machine may be in a state that the administrator did not intend. However, according to this feature, when the power supply to the gaming machine is resumed from the outside, the setting change mode is started without the administrator of the gaming machine having to perform the specified start operation again, so it is possible to prevent the winning probability setting of the gaming machine from being left in a state that the administrator did not intend and being overlooked.
<特徴βS群>
特徴βS群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βS group>
The group of features βS is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βS1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段と、
所定の識別情報(設定確認中フラグ)を記憶する記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
前記設定情報表示モードの開始の際に前記識別情報を第1の状態(ON)とし、前記設定情報表示モードの終了の際に前記識別情報を前記第1の状態とは異なる第2の状態(OFF)に遷移させる識別情報遷移手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記記憶手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記識別情報の状態を維持することが可能であり、
前記設定情報表示モード実行手段は、
所定の開始操作(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態で、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記設定情報表示モードを開始させる第1開始手段と、
外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が開始された際に前記識別情報が前記第1の状態であると判定したことに基づいて、前記設定情報表示モードを開始させる第2開始手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βS1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
A storage means (main RAM 64) for storing predetermined identification information (setting confirmation flag);
an identification information transition means for setting the identification information to a first state (ON) when the setting information display mode is started, and transitioning the identification information to a second state (OFF) different from the first state when the setting information display mode is ended;
A gaming machine comprising:
The storage means is capable of maintaining the state of the identification information even when the supply of power to the gaming machine from an external source is cut off,
The setting information display mode execution means
A first starting means for starting the setting information display mode based on the reception of a predetermined starting operation (an operation of turning on the power switch of the
a second starting means for starting the setting information display mode based on the determination that the identification information is in the first state when the supply of power to the gaming machine is started from an external source;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βS1によれば、第1開始手段は、所定の開始操作を受け付けたことに基づいて設定情報表示モードを開始させ、識別情報遷移手段は、設定情報表示モードの開始の際に識別情報を第1の状態とし、設定情報表示モードの終了の際に識別情報を第2の状態に遷移させる。そして、記憶手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても識別情報の状態を維持することが可能である。したがって、例えば、遊技機の電源スイッチがOFFにされたり停電が発生したこと等によって、設定情報表示モードの実行中に当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている識別情報は第1の状態に維持される。 According to feature βS1, the first starting means starts the setting information display mode based on receipt of a predetermined starting operation, and the identification information transition means sets the identification information to a first state when the setting information display mode starts and transitions the identification information to a second state when the setting information display mode ends. The storage means is capable of maintaining the state of the identification information even when the supply of power to the gaming machine from the outside is cut off. Therefore, for example, if the supply of power to the gaming machine is cut off while the setting information display mode is being executed because the power switch of the gaming machine is turned off or a power outage occurs, the identification information stored in the storage means is maintained in the first state.
そして、本特徴によれば、第2開始手段は、外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が開始された際に識別情報が第1の状態であると判定したことに基づいて設定情報表示モードを開始させる。すなわち、本特徴によれば、設定情報表示モードの実行中に当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該遊技機への電力の供給が再開された場合には、所定の開始操作を受け付けていない場合であっても、設定情報表示モードが開始されることになる。 According to this feature, the second starting means starts the setting information display mode based on determining that the identification information is in the first state when power supply to the gaming machine is started from the outside. In other words, according to this feature, if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off while the setting information display mode is being executed, and the power supply to the gaming machine is resumed, the setting information display mode will be started even if a predetermined start operation has not been received.
したがって、設定情報表示モードの実行中に外部から当該遊技機への電力の供給が断たれた場合において、当該遊技機に再び設定情報表示モードを開始させるためには、当該遊技機への電力の供給が再開された後に管理者が再び所定の開始操作を行なわなければいけないといった手間を省くことができる。 Therefore, if the power supply to the gaming machine is cut off from the outside while the setting information display mode is being executed, the administrator can eliminate the trouble of having to perform the specified start operation again after the power supply to the gaming machine is resumed in order to restart the setting information display mode on the gaming machine.
<特徴βT群>
特徴βT群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βT group>
The feature group βT is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βT1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を記憶する記憶手段であって、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記設定情報の状態を維持することが可能な第1記憶手段(主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域)と、
前記設定変更モードの実行中に用いられる情報である変更用設定情報(更新用設定情報)を記憶する第2記憶手段(主側RAM64の更新用設定情報記憶領域)と、
前記設定変更モードの実行中に前記変更用設定情報を変更可能な変更手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記第2記憶手段は、前記設定変更モードの開始の際に、前記設定情報に対応する情報を前記変更用設定情報として記憶する手段を備え、
前記変更手段は、前記所定の変更操作を受け付けることによって、前記第2記憶手段に記憶されている前記変更用設定情報を変更する手段を備え、
前記第1記憶手段は、前記設定変更モードの終了の際に、前記変更用設定情報に対応する情報を前記設定情報として記憶する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βT1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A first storage means (a setting information storage area of the main RAM 64) that stores setting information, which is information related to the setting of the winning probability, and that can maintain the state of the setting information even when the supply of power from the outside is cut off;
A second storage means (an update setting information storage area of the main RAM 64) for storing change setting information (update setting information) which is information used during execution of the setting change mode;
a change means for changing the change setting information during execution of the setting change mode;
A gaming machine comprising:
the second storage means includes means for storing information corresponding to the setting information as the change setting information when the setting change mode is started,
the change means includes means for changing the change setting information stored in the second storage means by accepting the predetermined change operation,
The first storage means comprises means for storing, as the setting information, information corresponding to the change setting information when the setting change mode is terminated.
特徴βT1によれば、第2記憶手段は、設定変更モードの開始の際に、設定情報に対応する情報を変更用設定情報として記憶し、変更手段は、所定の変更操作を受け付けることによって、第2記憶手段に記憶されている変更用設定情報を変更し、第1記憶手段は、設定変更モードの終了の際に、変更用設定情報に対応する情報を設定情報として記憶する。したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合であっても、第1記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報を、設定変更モードが開始される前の値のまま維持させることができる。この結果、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれることによって当該遊技機の当選確率の設定情報が管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまうことを抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 According to feature βT1, when the setting change mode is started, the second storage means stores information corresponding to the setting information as change setting information, the change means changes the change setting information stored in the second storage means by accepting a predetermined change operation, and the first storage means stores information corresponding to the change setting information as setting information when the setting change mode is terminated. Therefore, even if the supply of external power is cut off during the execution of the setting change mode, the setting information stored in the first storage means can be maintained at the value before the setting change mode was started. As a result, it is possible to prevent the setting information of the winning probability of the gaming machine from becoming a value different from the value intended by the administrator due to the supply of external power being cut off during the execution of the setting change mode. A specific explanation will be given below.
仮に、設定変更モードの実行中に変更用設定情報を用いない構成であって、所定の変更操作を受け付けることによって、第1記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報を直接変更する構成を採用した場合において、設定変更モードの実行中に設定情報が当該遊技機の管理者の意図した値とは異なる値になっているタイミングで外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合には、当該遊技機の当選確率の設定情報は、管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまう。 If a configuration is adopted in which change setting information is not used during execution of the setting change mode, and the setting information stored in the first storage means is directly changed by accepting a specified change operation, if the external power supply is cut off at a time when the setting information is a value different from the value intended by the manager of the gaming machine during execution of the setting change mode, the setting information of the winning probability of the gaming machine will become a value different from the value intended by the manager.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、設定変更モードが終了するまでは、第1記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報そのものは変更されず、第2記憶手段に記憶されている変更用設定情報が変更されるので、設定変更モードの実行中に変更用設定情報が当該遊技機の管理者の意図した値とは異なる値になっているタイミングで外部からの電力の供給が断たれた場合であっても、第1記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報は、設定変更モードが開始される前の値のまま維持される。したがって、設定変更モードの実行中に外部からの電力の供給が断たれることによって当該遊技機の当選確率の設定情報が管理者の意図した値とは異なる値となってしまうことを抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the setting information stored in the first storage means itself is not changed until the setting change mode is terminated, and the change setting information stored in the second storage means is changed. Therefore, even if the external power supply is cut off at a time when the change setting information is a value different from the value intended by the manager of the gaming machine during execution of the setting change mode, the setting information stored in the first storage means is maintained at the value it had before the setting change mode was started. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the winning probability setting information of the gaming machine from becoming a value different from the value intended by the manager due to the external power supply being cut off during execution of the setting change mode.
[特徴βT2]
特徴βT1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モードの実行中に、前記第2記憶手段に記憶されている前記変更用設定情報を表示する表示手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βT2]
A gaming machine according to feature βT1,
a display means for displaying the change setting information stored in the second storage means while the setting change mode is being executed.
特徴βT2によれば、表示手段は、設定変更モードの実行中に、第2記憶手段に記憶されている変更用設定情報を表示するので、管理者は、表示手段に表示されている変更用設定情報を確認しながら、所定の変更操作を行なうことができる。 According to feature βT2, the display means displays the change setting information stored in the second storage means while the setting change mode is being executed, so that the administrator can carry out the specified change operation while checking the change setting information displayed on the display means.
<特徴βU群>
特徴βU群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βU group>
The group of features βU are extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and are mainly extracted from the first embodiment (e.g., aspect 100).
[特徴βU1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を記憶する記憶手段であって、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記設定情報の状態を維持することが可能な記憶手段(主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域)と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定する(図65のステップS12007の処理を実行する)設定情報判定手段と、
遊技を進行させる処理である遊技進行処理(図68のステップS12304~ステップS12316の処理)を実行する遊技進行処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記遊技進行処理実行手段は、前記設定情報判定手段によって前記設定情報が前記所定の条件を満たさないと判定された場合(図65のステップS12007において設定情報が所定の範囲内ではないと判定され、ステップS12015においてRAM異常フラグがONとなった場合)には、前記遊技進行処理を実行しない
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βU1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A storage means for storing setting information, which is information related to the setting of the winning probability, capable of maintaining the state of the setting information even when the supply of power from the outside is cut off (a setting information storage area of the main RAM 64);
A setting information determination means for determining whether or not the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of electric power from an external source is started (executing the process of step S12007 in FIG. 65 );
A game progress processing execution means for executing a game progress processing (the processing of steps S12304 to S12316 in FIG. 68) which is a processing for progressing a game;
A gaming machine comprising:
A gaming machine characterized in that the game progress processing execution means does not execute the game progress processing when the setting information determination means determines that the setting information does not satisfy the specified condition (when the setting information is determined to be not within the specified range in step S12007 of Figure 65 and the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON in step S12015).
特徴βU1によれば、記憶手段は、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても設定情報の状態を維持しており、遊技進行処理実行手段は、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定し、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定した場合には、遊技を進行させる遊技進行処理を実行しない。したがって、記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態のまま遊技進行処理が実行されてしまい、当該遊技機における遊技の進行に不具合が生じてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、例えば、遊技者や管理者に想定外の損失を与えてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βU1, the storage means maintains the state of the setting information even when the supply of external power is cut off, and the game progress processing execution means determines whether the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of external power is started, and does not execute the game progress processing to progress the game if it is determined that the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the game progress processing from being executed while the setting information stored in the storage means does not satisfy the predetermined condition, which would cause a malfunction in the progress of the game on the gaming machine. As a result, for example, it is possible to prevent unexpected losses from being caused to players or managers.
<特徴βV群>
特徴βV群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βV group>
The group of features βV is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βV1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を含む各種情報を記憶可能な記憶手段であって、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記各種情報を維持することが可能な記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定する(図65のステップS12007の処理を実行する)設定情報判定手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記各種情報のうち前記設定情報を除いて消去する消去処理(第1RAMクリア処理)を実行する消去処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記消去処理実行手段は、
所定の消去操作(設定用の鍵がOFFであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態で、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記消去処理を実行する手段と、
前記設定情報判定手段によって前記設定情報が前記所定の条件を満たさないと判定された場合(図65のステップS12007において設定情報が所定の範囲内ではないと判定され、ステップS12015においてRAM異常フラグがONとなった場合)には、前記所定の消去操作を受け付けた場合であっても、前記消去処理を実行しない手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βV1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A storage means (main RAM 64) capable of storing various information including setting information which is information related to the setting of the winning probability, and capable of maintaining the various information even when the supply of power from the outside is cut off;
A setting information determination means for determining whether or not the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of electric power from an external source is started (executing the process of step S12007 in FIG. 65 );
an erasure process execution means for executing an erasure process (first RAM clear process) for erasing the various information stored in the storage means except for the setting information;
A gaming machine comprising:
The erasure process execution means includes:
A means for executing the erasure process based on receipt of a predetermined erasure operation (an operation of turning on the power switch of the
means for not executing the erasure process when it is determined by the setting information determination means that the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition (when it is determined in step S12007 of FIG. 65 that the setting information is not within a predetermined range and a RAM abnormality flag is ON in step S12015), even if the predetermined erasure operation is accepted;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βV1によれば、記憶手段は、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても設定情報の状態を維持しており、消去処理実行手段は、外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定し、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定した場合には、所定の消去操作を受け付けた場合であっても、消去処理を実行しない。したがって、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態のまま消去処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 According to feature βV1, the storage means maintains the state of the setting information even when the supply of external power is cut off, and the erasure process execution means determines whether the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of external power is started, and if it is determined that the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition, does not execute the erasure process even if a predetermined erasure operation is received. Therefore, it is possible to prevent malfunctions caused by the erasure process being executed while the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. This is explained in detail below.
仮に、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定した場合であっても消去処理を実行する構成を採用した場合には、記憶手段に記憶されている各種情報のうち、例えば、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定したことを示す情報(例えばRAM異常フラグ)まで消去されてしまい、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず、消去処理の実行後に、設定情報が所定の条件を満たしていることを前提とした処理(例えば遊技を進行させる遊技進行処理)が実行されてしまい、不具合が発生してしまう可能性がある。 If a configuration is adopted in which an erasure process is executed even when it is determined that the setting information does not satisfy a predetermined condition, then, among the various information stored in the storage means, even information indicating that it has been determined that the setting information does not satisfy a predetermined condition (e.g., a RAM abnormality flag) may be erased. Even though the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition, after the erasure process is executed, a process that assumes that the setting information satisfies the predetermined condition (e.g., a game progress process that progresses the game) may be executed, which may result in a malfunction.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定した場合には、所定の消去操作を受け付けた場合であっても、消去処理を実行しないので、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず消去処理が実行されてしまい、設定情報が所定の条件を満たしていることを前提とした処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態のまま消去処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to this feature, if it is determined that the setting information does not satisfy the specified conditions, the erasure process is not executed even if a specified erasure operation is received. This makes it possible to prevent the erasure process from being executed even when the setting information does not satisfy the specified conditions, and to prevent processing that is based on the assumption that the setting information satisfies the specified conditions from being executed. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of problems caused by the erasure process being executed when the setting information does not satisfy the specified conditions.
<特徴βW群>
特徴βW群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βW group>
The group of features βW is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βW1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段と、
前記設定情報を含む各種情報を記憶可能な記憶手段であって、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記各種情報を維持することが可能な記憶手段(主側RAM64の設定情報記憶領域)と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定する(図65のステップS12007の処理を実行する)設定情報判定手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定情報表示モード実行手段は、
所定の開始操作(設定用の鍵、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下されていない状態で、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする操作)を受け付けたことに基づいて、前記設定情報表示モードを実行する手段と、
前記設定情報判定手段によって前記設定情報が前記所定の条件を満たさないと判定された場合(図65のステップS12007において設定情報が所定の範囲内ではないと判定され、ステップS12015においてRAM異常フラグがONとなった場合)には、前記所定の開始操作を受け付けた場合であっても、前記設定情報表示モードを実行しない手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βW1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
A lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
A storage means capable of storing various information including the setting information, and capable of maintaining the various information even when the supply of power from the outside is cut off (a setting information storage area of the main RAM 64);
A setting information determination means for determining whether or not the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of electric power from an external source is started (executing the process of step S12007 in FIG. 65 );
A gaming machine comprising:
The setting information display mode execution means
A means for executing the setting information display mode based on receipt of a predetermined start operation (an operation of turning on the power switch of the
means for not executing the setting information display mode when the setting information determination means determines that the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition (when the setting information is determined to be outside the predetermined range in step S12007 of FIG. 65 and the RAM abnormality flag is turned ON in step S12015), even when the predetermined start operation is accepted;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βW1によれば、記憶手段は、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても設定情報を含む各種情報の状態を維持しており、設定情報表示モード実行手段は、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさないと判定された場合には、所定の開始操作を受け付けた場合であっても、設定情報表示モードを実行しない。したがって、記憶手段に記憶されている設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず、当該設定情報を表示する設定情報表示モードが実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。 According to feature βW1, the storage means maintains the state of various information including the setting information even when the supply of external power is cut off, and the setting information display mode execution means does not execute the setting information display mode even if a specified start operation is received when it is determined that the setting information does not satisfy a specified condition. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the setting information display mode that displays the setting information from being executed even when the setting information stored in the storage means does not satisfy the specified condition.
<特徴βX群>
特徴βX群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βX group>
The feature βX group is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βX1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報を含む各種情報を記憶可能な記憶手段であって、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても前記各種情報を維持することが可能な記憶手段(主側RAM64)と、
外部からの電力の供給が断たれる際に、前記記憶手段に記憶されている所定の情報群に基づいて所定の演算を実行し、当該所定の演算の結果である第1演算結果を前記記憶手段に記憶させる(停電監視処理においてRAM判定値を算出して主側RAM64に記憶させる)演算実行手段と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記記憶手段に記憶されている前記所定の情報群に基づいて前記所定の演算を実行し、当該所定の演算の結果である第2演算結果と、前記第1演算結果とが一致するか否かを判定する(図65のステップS12005からステップS12006の処理を実行する)演算結果判定手段と、
外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かを判定する(図65のステップS12007の処理を実行する)設定情報判定手段と、
前記演算結果判定手段によって前記第2演算結果と前記第1演算結果とが一致すると判定され、かつ、前記設定情報判定手段によって前記設定情報が前記所定の条件を満たすと判定されたことに基づいて、所定の処理(遊技を進行させる処理である図68のステップS12304~ステップS12316の処理)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βX1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A storage means (main RAM 64) capable of storing various information including setting information which is information related to the setting of the winning probability, and capable of maintaining the various information even when the supply of power from the outside is cut off;
When the supply of power from the outside is cut off, a predetermined calculation is performed based on a predetermined information group stored in the storage means, and a first calculation result, which is the result of the predetermined calculation, is stored in the storage means (a RAM determination value is calculated in the power outage monitoring process and stored in the main RAM 64). Calculation execution means;
a calculation result determination means for, when the supply of electric power from an external source is started, executing the predetermined calculation based on the predetermined information group stored in the storage means and determining whether or not a second calculation result, which is a result of the predetermined calculation, matches the first calculation result (performing the processing of steps S12005 to S12006 in FIG. 65 );
A setting information determination means for determining whether or not the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition when the supply of electric power from an external source is started (executing the process of step S12007 in FIG. 65 );
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (the process of steps S12304 to S12316 in FIG. 68, which is a process for progressing a game) based on the determination by the calculation result determination means that the second calculation result and the first calculation result match, and the determination by the setting information determination means that the setting information satisfies the predetermined condition;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βX1によれば、所定処理実行手段は、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが一致すると判定され、かつ、設定情報が所定の条件を満たすと判定されたことに基づいて、所定の処理を実行する。したがって、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とは一致しているが設定情報は所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず、所定の処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず所定の処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 According to feature βX1, the predetermined processing execution means executes the predetermined processing based on the determination that the second calculation result matches the first calculation result and that the setting information satisfies the predetermined condition. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the predetermined processing from being executed even when the second calculation result matches the first calculation result but the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a malfunction caused by the predetermined processing being executed even when the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. This is explained in detail below.
第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが一致している場合には、外部からの電力供給が開始された際に記憶手段に記憶されている所定の情報群の内容と、前回の電力供給が断たれる際に記憶手段に記憶されていた所定の情報群の内容とが同じである可能性が高く、記憶手段に記憶されている所定の情報群が、外部からの電力の供給が断たれた状態であっても正常に維持されていた可能性が高い。しかしながら、記憶手段に記憶されている所定の情報群が正常に維持されていない場合であっても、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが偶然に一致してしまう場合がある。 If the second calculation result and the first calculation result match, it is highly likely that the contents of the specified information group stored in the storage means when the external power supply is started are the same as the contents of the specified information group stored in the storage means when the previous power supply was cut off, and it is highly likely that the specified information group stored in the storage means was maintained normally even when the external power supply was cut off. However, even if the specified information group stored in the storage means is not maintained normally, the second calculation result and the first calculation result may coincidentally match.
このため、仮に、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが一致するか否かは判定するが、設定情報が所定の条件を満たすか否かは判定しない構成を採用した場合には、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない場合であっても、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが偶然に一致してしまい、所定の処理が実行されてしまう可能性がある。所定の処理が、例えば、遊技の進行を可能とする処理を含む場合には、遊技の進行に致命的な不具合が生じてしまうおそれがある。 For this reason, if a configuration were adopted in which it was determined whether the second calculation result and the first calculation result matched each other but whether the setting information satisfied a predetermined condition was not determined, even if the setting information did not satisfy the predetermined condition, the second calculation result and the first calculation result could coincidentally match, and a predetermined process could be executed. If the predetermined process included, for example, a process that allowed the game to proceed, there was a risk of a fatal malfunction occurring in the progress of the game.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とが一致すると判定され、かつ、設定情報が所定の条件を満たすと判定されたことに基づいて、所定の処理を実行する、換言すれば、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とは一致しているが、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態では、所定の処理を実行しない。したがって、第2演算結果と第1演算結果とは一致しているが設定情報は所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず、所定の処理が実行されてしまうことを抑制することができる。この結果、設定情報が所定の条件を満たさない状態であるにもかかわらず所定の処理が実行されてしまうことによる不具合の発生を抑制することができる。 In response to this, according to this feature, a predetermined process is executed based on the determination that the second calculation result matches the first calculation result and that the setting information satisfies a predetermined condition. In other words, when the second calculation result matches the first calculation result but the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition, the predetermined process is not executed. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the predetermined process from being executed even when the second calculation result matches the first calculation result but the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition. As a result, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions caused by the predetermined process being executed even when the setting information does not satisfy the predetermined condition.
<特徴βY群>
特徴βY群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態(例えば態様100)から抽出される。
<Characteristic βY group>
The feature group βY is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from the first embodiment (eg, aspect 100).
[特徴βY1]
遊技球が入球可能な入球部と、
前記入球部への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
所定の操作(設定用の鍵穴に設定用の鍵を挿入して回す操作)を受け付けることによって、第1の状態(OFF側の状態)から、前記第1の状態とは異なる第2の状態(ON側の状態)に移行可能な操作受付手段(設定用の鍵穴)と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、
前記設定変更モードの実行中に、前記操作受付手段の前記第2の状態から前記第1の状態への移行(ON側の状態からOFF側の状態に立ち下がるOFFエッジ)を検出したことに基づいて、前記設定変更モードを終了させる終了手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βY1]
An entry section into which game balls can enter;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of the game ball into the ball entry section;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
an operation receiving means (a setting keyhole) that can transition from a first state (an OFF state) to a second state (an ON state) different from the first state by receiving a predetermined operation (an operation of inserting a setting key into a setting keyhole and turning it);
A gaming machine comprising:
The setting change mode execution means includes:
a termination means for terminating the setting change mode based on detection of a transition of the operation receiving means from the second state to the first state (an OFF edge falling from an ON state to an OFF state) during execution of the setting change mode.
特徴βY1によれば、設定変更モード実行手段は、設定変更モードの実行中に、操作受付手段の第2の状態から第1の状態への移行を検出したことに基づいて、設定変更モードを終了させるので、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまうことを回避することができる。以下、具体的に説明する。 According to feature βY1, the setting change mode execution means terminates the setting change mode based on detection of a transition of the operation acceptance means from the second state to the first state while the setting change mode is being executed, so that it is possible to prevent the setting change mode from being terminated immediately after it has been started. This will be described in detail below.
例えば、操作受付手段が第2の状態であることを含む第1の開始条件(例えば、設定用の鍵(鍵穴)、枠開放スイッチ及び扉開放スイッチの全てがONであり、かつ、RAMクリアボタンが押下されている状態で、パチンコ機10の電源スイッチをONにする操作が行なわれたこと)が成立した場合、及び、操作受付手段が第2の状態であるか否かに関わらない第2の開始条件(例えば、電源ON時に設定変更中フラグがONであること)が成立した場合に、設定変更モードが開始される構成において、仮に、本特徴とは異なる構成であって、操作受付手段が第1の状態であることを検出した場合に設定変更モードを終了させる構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成を採用した場合において、操作受付手段が第2の状態であることを含む第1の開始条件の成立に基づいて設定変更モードが開始された場合には、操作受付手段が第2の状態から第1の状態に移行するまで、当該設定変更モードは継続する。しかしながら、操作受付手段が第2の状態であるか否かに関わらない第2の開始条件の成立に基づいて設定変更モードが開始された場合には、操作受付手段が第1の状態のまま設定変更モードが開始される場合もある。この場合には、設定変更モードが開始された直後に、操作受付手段が第1の状態であることが検出され、当該設定変更モードが終了してしまう。すなわち、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまい、設定変更モードにおいて当選確率の設定を変更することが困難となってしまう。
For example, in a configuration in which the setting change mode is started when a first start condition including the operation acceptance means being in the second state (for example, when the setting key (keyhole), frame open switch, and door open switch are all ON and the RAM clear button is pressed, and the power switch of the
これに対して、本特徴によれば、操作受付手段の第2の状態から第1の状態への移行を検出したことに基づいて、設定変更モードを終了させるので、例えば、第2の開始条件の成立によって設定変更モードが開始された場合であって、操作受付手段が第1の状態のまま設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、遊技機の管理者等が操作受付手段を第1の状態から第2の状態に移行させ、再度、第2の状態から第1の状態に移行させるまでは、設定変更モードが継続することになる。したがって、操作受付手段が第1の状態のまま設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、設定変更モードが開始された直後に当該設定変更モードが終了してしまうことを回避することができる。この結果、設定変更モードが開始直後に終了してしまうことによって当選確率の設定を変更することが困難となってしまうことを抑制することができる。 In contrast, according to this feature, the setting change mode is terminated based on the detection of a transition of the operation acceptance means from the second state to the first state. Therefore, even if the setting change mode is initiated by the establishment of the second start condition and the setting change mode is initiated while the operation acceptance means is still in the first state, the setting change mode will continue until an administrator of the gaming machine or the like transitions the operation acceptance means from the first state to the second state, and then transitions it again from the second state to the first state. Therefore, even if the setting change mode is initiated while the operation acceptance means is still in the first state, it is possible to avoid the setting change mode being terminated immediately after it is initiated. As a result, it is possible to prevent the setting change mode from being terminated immediately after it is initiated, making it difficult to change the winning probability setting.
また、本特徴によれば、第2の開始条件の成立によって設定変更モードが開始された場合であっても、操作受付手段の状態を移行させることのできる者のみが設定変更モードを終了させることができる。したがって、遊技機のセキュリティを向上させることができる。 In addition, according to this feature, even if the setting change mode is started by the establishment of the second start condition, only a person who can change the state of the operation reception means can end the setting change mode. Therefore, the security of the gaming machine can be improved.
[特徴βY2]
特徴βY1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、
前記操作受付手段が前記第2の状態であること(設定用の鍵穴がON側の状態であること)を含む第1の開始条件が成立したことに基づいて、前記設定変更モードを開始させる第1開始手段と、
前記操作受付手段が前記第2の状態であるか否かに関わらない第2の開始条件(電源ON時に設定変更中フラグがONであること)が成立したことに基づいて、前記設定変更モードを開始させる第2開始手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βY2]
A gaming machine according to feature βY1,
The setting change mode execution means is
a first starting means for starting the setting change mode based on the establishment of a first starting condition including that the operation accepting means is in the second state (that is, that the setting keyhole is in an ON state);
a second starting means for starting the setting change mode based on the establishment of a second starting condition (a setting change in progress flag being ON when the power is ON) that is not related to whether the operation receiving means is in the second state or not;
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴βY2によれば、第1開始手段は、操作受付手段が第2の状態であることを含む第1の開始条件が成立したことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させ、第2開始手段は、操作受付手段が第2の状態であるか否かに関わらない第2の開始条件が成立したことに基づいて設定変更モードを開始させる。したがって、操作受付手段が第2の状態である場合に限らず、操作受付手段が第2の状態ではない場合であっても、設定変更モードを開始させることができる。 According to feature βY2, the first starting means starts the setting change mode based on the satisfaction of a first starting condition including the operation receiving means being in the second state, and the second starting means starts the setting change mode based on the satisfaction of a second starting condition that is independent of whether the operation receiving means is in the second state. Therefore, the setting change mode can be started not only when the operation receiving means is in the second state, but also when the operation receiving means is not in the second state.
なお、上記特徴βR群~特徴βY群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group βR to feature group βY solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
<特徴βZ群>
特徴βZ群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様101から抽出される。
<Characteristic βZ group>
The feature βZ group is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴βZ1]
遊技機であって、
時刻を特定可能な情報を含む計時情報(現在日時情報)を当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態であっても更新可能な計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)と、
前記計時情報を起動時刻情報(起動日時情報)として記憶可能な手段であって、前記記憶した前記起動時刻情報を前記電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段(RTC97の起動時刻情報記憶エリア97b2)と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、前記計時情報更新手段から前記計時情報を取得し、取得した前記計時情報を前記起動時刻情報として前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する記憶処理実行手段と、
前記起動時刻情報に基づいて、前記記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する経過時間算出手段と、
前記経過時間に基づいて所定の処理(RTC演出)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、処理の内容が異なる複数の種別の起動処理(図70の通常起動コマンドを送信する処理を含む起動処理、設定変更モードの実行を含む起動処理、設定確認モードの実行を含む起動処理等)のうちのいずれかの起動処理を実行する起動処理実行手段と、
を備え、
前記記憶処理実行手段は、前記起動処理実行手段が実行する前記起動処理の種別が前記複数の起動処理のうちの特定の起動処理(設定変更モードの実行を含む起動処理、設定確認モードの実行を含む起動処理等)である場合には前記記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature βZ1]
A gaming machine,
A time information updating means (a time register 97b1 of the RTC 97) capable of updating time information (current date and time information) including information that can identify the time even in a power failure state in which the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is cut off;
a start-up time information storage means (a start-up time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97) capable of storing the timekeeping information as start-up time information (start-up date and time information), and capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during the power interruption state;
a storage process execution means for executing a storage process which is a process of acquiring the timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine, and storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as the startup time information;
an elapsed time calculation means for calculating an elapsed time from the execution of the storage process based on the start time information;
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (RTC effect) based on the elapsed time;
a startup process execution means for executing one of a plurality of types of startup processes having different process contents (a startup process including a process for transmitting a normal startup command shown in FIG. 70, a startup process including an execution of a setting change mode, a startup process including an execution of a setting check mode, etc.) based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine;
Equipped with
A gaming machine characterized in that the memory process execution means is provided with an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the memory process when the type of the startup process executed by the startup process execution means is a specific startup process among the multiple startup processes (a startup process including execution of a setting change mode, a startup process including execution of a setting confirmation mode, etc.).
特徴βZ1の効果の説明に先立って、遊技機が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数の遊技機がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。 Before explaining the effect of feature βZ1, we will explain an amusement hall where multiple gaming machines are installed. Generally, in an amusement hall, power supply to multiple gaming machines starts all at once (simultaneously). Specifically, for example, multiple gaming machines are installed in a so-called island facility with their respective power switches turned on, and when the power switch of the island facility (hereinafter also referred to as the island power switch) is turned on, power supply starts all at once (simultaneously) to the multiple gaming machines installed in the island facility.
以上説明した遊技ホールにおける遊技機の運用を踏まえて、特徴βZ1の遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。そして、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出し、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 In light of the operation of gaming machines in the gaming hall described above, a gaming machine with feature βZ1 acquires timing information from a timing information update means when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information. Then, based on the startup time information stored in the startup time information storage means, the time that has elapsed since the storage process was executed is calculated, and a predetermined process is executed based on the calculated elapsed time. We will now explain the effects of adopting this configuration.
仮に、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間ではなく、計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)において更新されている計時情報(現在日時情報)に基づいて所定の処理を実行する構成(例えば、計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングで所定の演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間において遊技機Aの計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、遊技機Bの計時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが各遊技機毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration is adopted in which a predetermined process is executed based on the timing information (current date and time information) updated in the timing information update means (timing register 97b1 of RTC97) rather than the elapsed time since the storage process was executed (for example, a configuration in which a predetermined presentation is started when the time included in the timing information becomes 11:00:00). In this configuration, if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine installed on the island equipment (for example, if at a certain moment the time included in the timing information of gaming machine A is 11:00:00 and the time included in the timing information of gaming machine B is 10:59:52), the timing at which the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) is started will differ for each gaming machine, which will cause a problem of discomfort to players who were expecting the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) to be started simultaneously (simultaneously) on all gaming machines installed on the island equipment.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。
したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。
In contrast, according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment acquires timing information from a timing information update means based on the start of external power supply to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process which is a process of storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information.
Therefore, for example, when the manager of an amusement hall turns on the island power switch, power begins to be supplied to multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment all at once (simultaneously), and each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes memory processing all at once (simultaneously).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行するので、各遊技機において算出される記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間は、各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。 According to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment calculates the elapsed time since the memory process was executed based on the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. As described above, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes the memory process simultaneously, so the elapsed time since the memory process was executed calculated by each gaming machine will be the same (or approximately the same) even if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so the manner in which the predetermined process is executed on each gaming machine can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment.
さらに、本特徴の遊技機は、記憶した起動時刻情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段と、起動処理実行手段が実行する起動処理の種別が複数の起動処理のうちの特定の起動処理である場合には記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段とを備える。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 Furthermore, the gaming machine of this characteristic includes a start-up time information storage means capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during a power outage, and an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the stored process when the type of start-up process executed by the start-up process execution means is a specific start-up process among a plurality of start-up processes. The effects of adopting this configuration are explained below.
仮に、上述した回避手段を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機に特定の起動処理(例えば、設定変更モードの実行を含む起動処理)を実行させるために、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を特定の起動処理が実行される状態として当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにして特定の起動処理を実行させる場合がある。この場合、当該一の遊技機は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一の遊技機において算出される経過時間が、他の遊技機において算出される経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが、他の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 A hypothetical example will be described in which a configuration not equipped with the above-mentioned avoidance means is adopted. In this configuration, when power supply is started simultaneously (at the same time) to each gaming machine installed on an island facility, each gaming machine installed on the island facility simultaneously (at the same time) executes a storage process. After that, the manager of the gaming hall may turn off the power switch of one of the multiple gaming machines installed on the island facility in order to have the one gaming machine execute a specific startup process (for example, a startup process including execution of a setting change mode), and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine to place the one gaming machine in a state in which the specific startup process is executed and execute the specific startup process. In this case, the one gaming machine executes the storage process again based on the fact that the power switch has been turned on and the supply of power has been started. This causes the elapsed time calculated on that one gaming machine to differ from the elapsed time calculated on the other gaming machines, and the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on that one gaming machine to differ from the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on the other gaming machines, creating an awkward feeling for the player playing on that one gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段において記憶されている起動時刻情報は保持される。その後、管理者が当該一の遊技機を特定の起動処理が実行される状態として電源スイッチをONにすると、当該一の遊技機において特定の起動処理が実行され、記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報が上書きされず、他の遊技機と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された記憶処理において記憶された起動時刻情報が維持される。この結果、当該一の遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において算出される経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the gaming machine and cuts off the power, the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means of the gaming machine is retained. If the manager then turns on the power switch of the gaming machine to put it in a state in which a specific start-up process is to be executed, the specific start-up process is executed in the gaming machine and execution of the storage process is avoided, so that the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means of the gaming machine is not overwritten, and the start-up time information stored in the storage process executed when the power supply to the other gaming machines was started all at once (simultaneously) is maintained. As a result, the elapsed time calculated for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including the gaming machine, is the same (or approximately the same).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。この結果、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so that the manner in which the predetermined process is executed can be made the same for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. As a result, it is possible to increase the interest in the game.
<特徴γA群>
特徴γA群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様101から抽出される。
<Characteristic γA group>
The feature group γA is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴γA1]
遊技機であって、
時刻を特定可能な情報を含む計時情報(現在日時情報)を当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態であっても更新可能な計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)と、
前記計時情報を起動時刻情報(起動日時情報)として記憶可能な手段であって、前記記憶した前記起動時刻情報を前記電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段(RTC97の起動時刻情報記憶エリア97b2)と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、前記計時情報更新手段から前記計時情報を取得し、取得した前記計時情報を前記起動時刻情報として前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する記憶処理実行手段と、
前記起動時刻情報に基づいて、前記記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する経過時間算出手段と、
前記経過時間に基づいて所定の処理(RTC演出)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
所定の操作を受け付ける操作受付手段(設定用の鍵穴)と、
を備え、
前記記憶処理実行手段は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に前記操作受付手段が前記所定の操作を受け付けていた場合には前記記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γA1]
A gaming machine,
A time information updating means (a time register 97b1 of the RTC 97) capable of updating time information (current date and time information) including information that can identify the time even in a power failure state in which the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is cut off;
a start-up time information storage means (a start-up time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97) capable of storing the timekeeping information as start-up time information (start-up date and time information), and capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during the power interruption state;
a storage process execution means for executing a storage process which is a process of acquiring the timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine, and storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as the startup time information;
an elapsed time calculation means for calculating an elapsed time from the execution of the storage process based on the start time information;
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (RTC effect) based on the elapsed time;
an operation receiving means (a keyhole for setting) for receiving a predetermined operation;
Equipped with
The memory process execution means is provided with an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the memory process if the operation receiving means has received the specified operation when the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is started.
特徴γA1の効果の説明に先立って、遊技機が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数の遊技機がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。 Before explaining the effect of feature γA1, we will explain an amusement hall where multiple gaming machines are installed. Generally, in an amusement hall, power supply to multiple gaming machines starts all at once (simultaneously). Specifically, for example, multiple gaming machines are installed in a so-called island facility with their respective power switches turned on, and when the power switch of the island facility (hereinafter also referred to as the island power switch) is turned on, power supply starts all at once (simultaneously) to the multiple gaming machines installed in the island facility.
以上説明した遊技ホールにおける遊技機の運用を踏まえて、特徴γA1の遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。そして、起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出し、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 In light of the operation of gaming machines in the gaming hall described above, a gaming machine with feature γA1 acquires timing information from a timing information update means when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information. Then, based on the startup time information, the time that has elapsed since the storage process was executed is calculated, and a predetermined process is executed based on the calculated elapsed time. The effects of adopting this configuration will be explained below.
仮に、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間ではなく、計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)において更新されている計時情報(現在日時情報)に基づいて所定の処理を実行する構成(例えば、計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングで所定の演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間において遊技機Aの計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、遊技機Bの計時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが各遊技機毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration is adopted in which a predetermined process is executed based on the timing information (current date and time information) updated in the timing information update means (timing register 97b1 of RTC97) rather than the elapsed time since the storage process was executed (for example, a configuration in which a predetermined presentation is started when the time included in the timing information becomes 11:00:00). In this configuration, if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine installed on the island equipment (for example, if at a certain moment the time included in the timing information of gaming machine A is 11:00:00 and the time included in the timing information of gaming machine B is 10:59:52), the timing at which the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) is started will differ for each gaming machine, which will cause a problem of discomfort to players who were expecting the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) to be started simultaneously (simultaneously) on all gaming machines installed on the island equipment.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。 In response to this, according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment acquires timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of external power to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as startup time information. Therefore, for example, when the manager of the gaming hall turns on the island power switch, the supply of power starts simultaneously to the multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment, and each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a storage process simultaneously.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行するので、各遊技機において算出される記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間は、各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。 According to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment calculates the elapsed time since the memory process was executed based on the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. As described above, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes the memory process simultaneously, so the elapsed time since the memory process was executed calculated by each gaming machine will be the same (or approximately the same) even if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so the manner in which the predetermined process is executed on each gaming machine can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment.
さらに、本特徴の遊技機は、記憶した起動時刻情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段と、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に操作受付手段が所定の操作を受け付けていた場合には記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段とを備える。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 Furthermore, the gaming machine of this feature includes a start time information storage means capable of holding the stored start time information even during a power outage, and an avoidance means for avoiding the execution of the storage process if the operation acceptance means has accepted a predetermined operation when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started. The effects of adopting this configuration are explained below.
仮に、上述した回避手段を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、種々の理由により、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を所定の操作を受け付けた状態としたまま当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにする場合がある。この場合、当該一の遊技機は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一の遊技機において算出される経過時間が、他の遊技機において算出される経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが、他の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 A hypothetical case where a configuration without the above-mentioned avoidance means is adopted will be described. In this configuration, when power supply to each gaming machine installed on an island facility starts at the same time, each gaming machine installed on the island facility executes a storage process at the same time. After that, for various reasons, the manager of the game hall may turn off the power switch of one of the multiple gaming machines installed on the island facility, and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine while the one gaming machine is in a state where it accepts a predetermined operation. In this case, the one gaming machine executes a storage process again based on the fact that the power switch has been turned on and the supply of power has started. In this case, the elapsed time calculated on the one gaming machine differs from the elapsed time calculated on the other gaming machines, and the timing at which the one gaming machine starts a predetermined process (predetermined performance) differs from the timing at which the other gaming machines start a predetermined process (predetermined performance), causing a problem that the player playing on the one gaming machine feels uncomfortable.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段において記憶されている起動時刻情報は保持される。その後、管理者が当該一の遊技機を所定の操作を受け付けた状態としたまま電源スイッチをONにすると、記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報が上書きされず、他の遊技機と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された記憶処理において記憶された起動時刻情報が維持される。この結果、当該一の遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において算出される経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the gaming machine in question and cuts off the power, the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine in question is retained. If the manager then turns on the power switch of the gaming machine while it is in a state where it is accepting a specified operation, the execution of the storage process is avoided, so that the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine in question is not overwritten, and the start time information stored in the storage process executed when the supply of power to the other gaming machines is started all at once (simultaneously) is maintained. As a result, the elapsed time calculated for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including the gaming machine in question, is the same (or approximately the same).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。この結果、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so that the manner in which the predetermined process is executed can be made the same for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. As a result, it is possible to increase the interest in the game.
<特徴γB群>
特徴γB群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様101から抽出される。
<Characteristic gamma B group>
The feature group γ B is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴γB1]
遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な入球手段と、
前記入球手段への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
時刻を特定可能な情報を含む計時情報(現在日時情報)を当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態であっても更新可能な計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)と、
前記計時情報を起動時刻情報(起動日時情報)として記憶可能な手段であって、前記記憶した前記起動時刻情報を前記電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段(RTC97の起動時刻情報記憶エリア97b2)と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、前記計時情報更新手段から前記計時情報を取得し、取得した前記計時情報を前記起動時刻情報として前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する記憶処理実行手段と、
前記起動時刻情報に基づいて、前記記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する経過時間算出手段と、
前記経過時間に基づいて所定の処理(RTC演出)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
を備え、
前記設定変更モード実行手段は、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に所定の開始条件が成立するか否かを判定する判定手段と、
前記所定の開始条件の成立に基づいて前記設定変更モードを開始させる設定変更モード開始手段と、
を備え、
前記記憶処理実行手段は、前記設定変更モードが開始される場合には前記記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γB1]
A gaming machine,
A ball entry means capable of entering the game ball;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of a game ball into the ball entry means;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
A time information updating means (a time register 97b1 of the RTC 97) capable of updating time information (current date and time information) including information that can identify the time even in a power failure state in which the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is cut off;
a start-up time information storage means (a start-up time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97) capable of storing the timekeeping information as start-up time information (start-up date and time information), and capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during the power interruption state;
a storage process execution means for executing a storage process which is a process of acquiring the timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine, and storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as the startup time information;
an elapsed time calculation means for calculating an elapsed time from the execution of the storage process based on the start time information;
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (RTC effect) based on the elapsed time;
Equipped with
The setting change mode execution means is
a determination means for determining whether or not a predetermined start condition is satisfied when the supply of electric power from an external source to the gaming machine is started;
a setting change mode starting means for starting the setting change mode when the predetermined starting condition is satisfied;
Equipped with
The storage process execution means comprises an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the storage process when the setting change mode is started.
特徴γB1の効果の説明に先立って、遊技機が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数の遊技機がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。 Before explaining the effect of feature γB1, we will explain an amusement hall where multiple gaming machines are installed. Generally, in an amusement hall, power supply to multiple gaming machines starts all at once (simultaneously). Specifically, for example, multiple gaming machines are installed in a so-called island facility with their respective power switches turned on, and when the power switch of the island facility (hereinafter also referred to as the island power switch) is turned on, power supply starts all at once (simultaneously) to the multiple gaming machines installed in the island facility.
以上説明した遊技ホールにおける遊技機の運用を踏まえて、特徴γB1の遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。そして、起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出し、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 In light of the operation of gaming machines in the gaming hall described above, a gaming machine with feature γB1 acquires timing information from a timing information update means when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information. Then, based on the startup time information, the time that has elapsed since the storage process was executed is calculated, and a predetermined process is executed based on the calculated elapsed time. The effects of adopting this configuration will be explained below.
仮に、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間ではなく、計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)において更新されている計時情報(現在日時情報)に基づいて所定の処理を実行する構成(例えば、計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングで所定の演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間において遊技機Aの計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、遊技機Bの計時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが各遊技機毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration is adopted in which a predetermined process is executed based on the timing information (current date and time information) updated in the timing information update means (timing register 97b1 of RTC97) rather than the elapsed time since the storage process was executed (for example, a configuration in which a predetermined presentation is started when the time included in the timing information becomes 11:00:00). In this configuration, if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine installed on the island equipment (for example, if at a certain moment the time included in the timing information of gaming machine A is 11:00:00 and the time included in the timing information of gaming machine B is 10:59:52), the timing at which the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) is started will differ for each gaming machine, which will cause a problem of discomfort to players who were expecting the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) to be started simultaneously (simultaneously) on all gaming machines installed on the island equipment.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。
したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。
In contrast, according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment acquires timing information from a timing information update means based on the start of external power supply to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process which is a process of storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information.
Therefore, for example, when the manager of an amusement hall turns on the island power switch, power begins to be supplied to multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment all at once (simultaneously), and each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes memory processing all at once (simultaneously).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行するので、各遊技機において算出される記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間は、各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。 According to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment calculates the elapsed time since the memory process was executed based on the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. As described above, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes the memory process simultaneously, so the elapsed time since the memory process was executed calculated by each gaming machine will be the same (or approximately the same) even if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so the manner in which the predetermined process is executed on each gaming machine can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment.
さらに、本特徴の遊技機は、記憶した起動時刻情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段と、設定変更モードが開始される場合には記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段とを備える。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 Furthermore, this gaming machine is equipped with a start time information storage means capable of retaining the stored start time information even during a power outage, and an avoidance means for avoiding the execution of the storage process when the setting change mode is started. The effects of adopting this configuration are explained below.
仮に、上述した回避手段を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、設定変更モードを実行させて遊技機の当選確率の設定を変更するために、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を設定変更モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにして設定変更モードを開始させる場合がある。この場合、当該一の遊技機は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一の遊技機において算出される経過時間が、他の遊技機において算出される経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが、他の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 A hypothetical case will be described where a configuration not including the above-mentioned avoidance means is adopted. In this configuration, when power supply to each gaming machine installed on an island facility starts all at once (at the same time), each gaming machine installed on the island facility executes a storage process all at once (at the same time). After that, the manager of the game hall may turn off the power switch of one of the gaming machines installed on the island facility once in order to execute the setting change mode and change the winning probability setting of the gaming machine, and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine to start the setting change mode, with the starting condition for starting the setting change mode being satisfied. In this case, the one gaming machine executes the storage process again based on the fact that the power switch has been turned on and the supply of power has started. This causes the elapsed time calculated on that one gaming machine to differ from the elapsed time calculated on the other gaming machines, and the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on that one gaming machine to differ from the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on the other gaming machines, creating an awkward feeling for the player playing on that one gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段において記憶されている起動時刻情報は保持される。その後、管理者が当該一の遊技機を設定変更モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として電源スイッチをONにすると、当該一の遊技機において設定変更モードが開始され、記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報が上書きされず、他の遊技機と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された記憶処理において記憶された起動時刻情報が維持される。この結果、当該一の遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において算出される経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the gaming machine, the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine is maintained. Thereafter, when the manager turns on the power switch of the gaming machine with the start condition for starting the setting change mode being satisfied, the setting change mode is started in the gaming machine and the execution of the storage process is avoided, so that the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine is not overwritten, and the start time information stored in the storage process executed when the power supply to the other gaming machines was started all at once (simultaneously) is maintained. As a result, the elapsed time calculated for each gaming machine installed in the island equipment, including the gaming machine, is the same (or approximately the same).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。この結果、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so that the manner in which the predetermined process is executed can be made the same for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. As a result, it is possible to increase the interest in the game.
<特徴γC群>
特徴γC群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様101から抽出される。
<Characteristic γC group>
The feature group γ C is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴γC1]
遊技機であって、
遊技球が入球可能な入球手段と、
前記入球手段への遊技球の入球に基づいて所定の抽選処理を実行する抽選処理実行手段と、
前記所定の抽選処理における当選確率の設定を外部から所定の変更操作(設定変更用ボタンを押下する操作)を受け付けることによって変更可能な設定変更モードを実行する設定変更モード実行手段と、
前記当選確率の設定に関する情報である設定情報は表示するが、前記当選確率の設定は変更することができない設定情報表示モード(設定確認モード)を実行する設定情報表示モード実行手段と、
時刻を特定可能な情報を含む計時情報(現在日時情報)を当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態であっても更新可能な計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)と、
前記計時情報を起動時刻情報(起動日時情報)として記憶可能な手段であって、前記記憶した前記起動時刻情報を前記電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段(RTC97の起動時刻情報記憶エリア97b2)と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、前記計時情報更新手段から前記計時情報を取得し、取得した前記計時情報を前記起動時刻情報として前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する記憶処理実行手段と、
前記起動時刻情報に基づいて、前記記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する経過時間算出手段と、
前記経過時間に基づいて所定の処理(RTC演出)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
を備え、
前記設定情報表示モード実行手段は、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に所定の開始条件が成立するか否かを判定する判定手段と、
前記所定の開始条件の成立に基づいて前記設定情報表示モードを開始させる設定情報表示モード開始手段と、
を備え、
前記記憶処理実行手段は、前記設定情報表示モードが開始される場合には前記記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γC1]
A gaming machine,
A ball entry means capable of entering the game ball;
a lottery process execution means for executing a predetermined lottery process based on the entry of a game ball into the ball entry means;
a setting change mode execution means for executing a setting change mode in which the winning probability setting in the predetermined lottery process can be changed by accepting a predetermined change operation (operation of pressing a setting change button) from the outside;
a setting information display mode execution means for executing a setting information display mode (setting confirmation mode) in which setting information, which is information regarding the setting of the winning probability, is displayed but the setting of the winning probability cannot be changed;
A time information updating means (a time register 97b1 of the RTC 97) capable of updating time information (current date and time information) including information that can identify the time even in a power failure state in which the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is cut off;
a start-up time information storage means (a start-up time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97) capable of storing the timekeeping information as start-up time information (start-up date and time information), and capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during the power interruption state;
a storage process execution means for executing a storage process which is a process of acquiring the timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine, and storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as the startup time information;
an elapsed time calculation means for calculating an elapsed time from the execution of the storage process based on the start time information;
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (RTC effect) based on the elapsed time;
Equipped with
The setting information display mode execution means
a determination means for determining whether or not a predetermined start condition is satisfied when the supply of electric power from an external source to the gaming machine is started;
a setting information display mode starting means for starting the setting information display mode when the predetermined starting condition is satisfied;
Equipped with
The storage process execution means comprises an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the storage process when the setting information display mode is started.
特徴γC1の効果の説明に先立って、遊技機が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数の遊技機がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。 Before explaining the effect of feature γC1, we will explain an amusement hall where multiple gaming machines are installed. Generally, in an amusement hall, power supply to multiple gaming machines starts all at once (simultaneously). Specifically, for example, multiple gaming machines are installed in a so-called island facility with their respective power switches turned on, and when the power switch of the island facility (hereinafter also referred to as the island power switch) is turned on, power supply starts all at once (simultaneously) to the multiple gaming machines installed in the island facility.
以上説明した遊技ホールにおける遊技機の運用を踏まえて、特徴γC1の遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。そして、起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出し、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 In light of the operation of gaming machines in the gaming hall described above, a gaming machine with feature γC1 acquires timing information from a timing information update means when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information. Then, based on the startup time information, the time that has elapsed since the storage process was executed is calculated, and a predetermined process is executed based on the calculated elapsed time. The effects of adopting this configuration will be explained below.
仮に、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間ではなく、計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)において更新されている計時情報(現在日時情報)に基づいて所定の処理を実行する構成(例えば、計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングで所定の演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間において遊技機Aの計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、遊技機Bの計時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが各遊技機毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration is adopted in which a predetermined process is executed based on the timing information (current date and time information) updated in the timing information update means (timing register 97b1 of RTC97) rather than the elapsed time since the storage process was executed (for example, a configuration in which a predetermined presentation is started when the time included in the timing information becomes 11:00:00). In this configuration, if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine installed on the island equipment (for example, if at a certain moment the time included in the timing information of gaming machine A is 11:00:00 and the time included in the timing information of gaming machine B is 10:59:52), the timing at which the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) is started will differ for each gaming machine, which will cause a problem of discomfort to players who were expecting the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) to be started simultaneously (simultaneously) on all gaming machines installed on the island equipment.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。
したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。
In contrast, according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment acquires timing information from a timing information update means based on the start of external power supply to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process which is a process of storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information.
Therefore, for example, when the manager of an amusement hall turns on the island power switch, power begins to be supplied to multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment all at once (simultaneously), and each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes memory processing all at once (simultaneously).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行するので、各遊技機において算出される記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間は、各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。 According to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment calculates the elapsed time since the memory process was executed based on the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. As described above, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes the memory process simultaneously, so the elapsed time since the memory process was executed calculated by each gaming machine will be the same (or approximately the same) even if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so the manner in which the predetermined process is executed on each gaming machine can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment.
さらに、本特徴の遊技機は、記憶した起動時刻情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段と、設定情報表示モードが開始される場合には記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段とを備える。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 Furthermore, this gaming machine is equipped with a start time information storage means capable of retaining the stored start time information even during a power outage, and an avoidance means for avoiding the execution of the storage process when the setting information display mode is started. The effects of adopting this configuration are explained below.
仮に、上述した回避手段を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、設定情報表示モードを実行させて遊技機の当選確率の設定を確認するために、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を設定情報表示モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにして設定情報表示モードを開始させる場合がある。この場合、当該一の遊技機は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一の遊技機において算出される経過時間が、他の遊技機において算出される経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが、他の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration that does not include the above-mentioned avoidance means is adopted. In this configuration, when power supply to each gaming machine installed on an island facility starts all at once (at the same time), each gaming machine installed on the island facility executes a storage process all at once (at the same time). After that, the manager of the game hall may turn off the power switch of one of the gaming machines installed on the island facility once in order to execute the setting information display mode and check the winning probability setting of the gaming machine, and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine to start the setting information display mode, with the starting condition for starting the setting information display mode being satisfied. In this case, the one gaming machine executes the storage process again based on the fact that the power switch has been turned on and the supply of power has started. This causes the elapsed time calculated on that one gaming machine to differ from the elapsed time calculated on the other gaming machines, and the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on that one gaming machine to differ from the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on the other gaming machines, creating an awkward feeling for the player playing on that one gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段において記憶されている起動時刻情報は保持される。その後、管理者が当該一の遊技機を設定情報表示モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として電源スイッチをONにすると、当該一の遊技機において設定情報表示モードが開始され、記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報が上書きされず、他の遊技機と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された記憶処理において記憶された起動時刻情報が維持される。この結果、当該一の遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において算出される経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the gaming machine and cuts off the power, the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine is retained. If the manager then turns on the power switch of the gaming machine after satisfying the start condition for starting the setting information display mode, the setting information display mode is started in the gaming machine and the execution of the storage process is avoided, so that the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine is not overwritten, and the start time information stored in the storage process executed when the power supply to the other gaming machines is started all at once (simultaneously) is maintained. As a result, the elapsed time calculated for each gaming machine installed in the island equipment, including the gaming machine, is the same (or approximately the same).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。この結果、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so that the manner in which the predetermined process is executed can be made the same for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again. As a result, it is possible to increase the interest in the game.
<特徴γD群>
特徴γD群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様102から抽出される。
<Feature γD group>
The group of features γD is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴γD1]
遊技機であって、
時刻を特定可能な情報を含む計時情報(現在日時情報)を当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が断たれた電断状態であっても更新可能な計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)と、
前記計時情報を起動時刻情報(起動日時情報)として記憶可能な手段であって、前記記憶した前記起動時刻情報を前記電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段(RTC97の起動時刻情報記憶エリア97b2)と、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、前記計時情報更新手段から前記計時情報を取得し、取得した前記計時情報を前記起動時刻情報として前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する記憶処理実行手段と、
前記起動時刻情報に基づいて、前記記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する経過時間算出手段と、
前記経過時間に基づいて所定の処理(RTC演出)を実行する所定処理実行手段と、
を備え、
前記記憶処理実行手段は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、前記計時情報更新手段における前記計時情報に含まれる時刻が、前記起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記起動時刻情報に含まれる時刻から所定時間(30分)が経過していない場合には前記記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γD1]
A gaming machine,
A time information updating means (a time register 97b1 of the RTC 97) capable of updating time information (current date and time information) including information that can identify the time even in a power failure state in which the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine is cut off;
a start-up time information storage means (a start-up time information storage area 97b2 of the RTC 97) capable of storing the timekeeping information as start-up time information (start-up date and time information), and capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during the power interruption state;
a storage process execution means for executing a storage process which is a process of acquiring the timing information from the timing information update means based on the start of the supply of power from an external source to the gaming machine, and storing the acquired timing information in the startup time information storage means as the startup time information;
an elapsed time calculation means for calculating an elapsed time from the execution of the storage process based on the start time information;
A predetermined process execution means for executing a predetermined process (RTC effect) based on the elapsed time;
Equipped with
The gaming machine is characterized in that the memory processing execution means is provided with an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the memory processing if, when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, the time contained in the timing information in the timing information update means is not a predetermined time (30 minutes) after the time contained in the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means.
特徴γD1の効果の説明に先立って、遊技機が複数台設置されている遊技ホールについて説明する。一般に、遊技ホールでは、複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始する。具体的には、例えば、複数の遊技機がそれぞれの電源スイッチがONになっている状態でいわゆる島設備に設置されており、当該島設備の電源スイッチ(以下、島電源スイッチとも呼ぶ)をONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始される。 Before explaining the effect of feature γD1, we will explain an amusement hall where multiple gaming machines are installed. Generally, in an amusement hall, power supply to multiple gaming machines starts all at once (simultaneously). Specifically, for example, multiple gaming machines are installed in a so-called island facility with their respective power switches turned on, and when the power switch of the island facility (hereinafter also referred to as the island power switch) is turned on, power supply starts all at once (simultaneously) to the multiple gaming machines installed in the island facility.
以上説明した遊技ホールにおける遊技機の運用を踏まえて、特徴γD1の遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。そして、起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出し、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行する。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 In light of the operation of gaming machines in the gaming hall described above, a gaming machine with feature γD1 acquires timing information from a timing information update means based on the start of the supply of external power to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process, which is a process for storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information. Then, based on the startup time information, the time that has elapsed since the storage process was executed is calculated, and a predetermined process is executed based on the calculated elapsed time. The effects of adopting this configuration will be explained below.
仮に、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間ではなく、計時情報更新手段(RTC97の計時レジスタ97b1)において更新されている計時情報(現在日時情報)に基づいて所定の処理を実行する構成(例えば、計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒となったタイミングで所定の演出を開始する構成)を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じている場合(例えば、ある瞬間において遊技機Aの計時情報に含まれている時刻が11時00分00秒であり、遊技機Bの計時情報に含まれている時刻が10時59分52秒である場合)には、所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが各遊技機毎に異なってしまい、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されることを期待していた遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 We will now explain a case where a configuration is adopted in which a predetermined process is executed based on the timing information (current date and time information) updated in the timing information update means (timing register 97b1 of RTC97) rather than the elapsed time since the storage process was executed (for example, a configuration in which a predetermined presentation is started when the time included in the timing information becomes 11:00:00). In this configuration, if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine installed on the island equipment (for example, if at a certain moment the time included in the timing information of gaming machine A is 11:00:00 and the time included in the timing information of gaming machine B is 10:59:52), the timing at which the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) is started will differ for each gaming machine, which will cause a problem of discomfort to players who were expecting the predetermined process (predetermined presentation) to be started simultaneously (simultaneously) on all gaming machines installed on the island equipment.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて、計時情報更新手段から計時情報を取得し、取得した計時情報を起動時刻情報として起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶させる処理である記憶処理を実行する。
したがって、例えば、遊技ホールの管理者が島電源スイッチをONにすると、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始され、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。
In contrast, according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment acquires timing information from a timing information update means based on the start of external power supply to the gaming machine, and executes a storage process which is a process of storing the acquired timing information in a startup time information storage means as startup time information.
Therefore, for example, when the manager of an amusement hall turns on the island power switch, power begins to be supplied to multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment all at once (simultaneously), and each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes memory processing all at once (simultaneously).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に基づいて、記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間を算出する。上述したように、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行するので、各遊技機において算出される記憶処理が実行されてからの経過時間は、各遊技機の計時情報に含まれている時刻にずれが生じていたとしても、同一(又は略同一)となる。 According to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment calculates the elapsed time since the memory process was executed based on the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. As described above, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes the memory process simultaneously, so the elapsed time since the memory process was executed calculated by each gaming machine will be the same (or approximately the same) even if there is a discrepancy in the time included in the timing information of each gaming machine.
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so the manner in which the predetermined process is executed on each gaming machine can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment.
さらに、本特徴の遊技機は、記憶した起動時刻情報を電断状態の間も保持することが可能な起動時刻情報記憶手段と、当該遊技機への外部からの電力の供給が開始された際に、計時情報更新手段における計時情報に含まれる時刻が、起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報に含まれる時刻から所定時間(例えば30分)が経過していない場合には記憶処理の実行を回避する回避手段とを備える。この構成を採用したことによる効果について説明する。 Furthermore, the gaming machine of this feature includes a start-up time information storage means capable of holding the stored start-up time information even during a power outage, and an avoidance means for avoiding execution of the storage process if, when the supply of external power to the gaming machine is started, the time included in the timing information in the timing information update means is less than a predetermined time (e.g., 30 minutes) after the time included in the start-up time information stored in the start-up time information storage means. The effects of adopting this configuration are explained below.
仮に、上述した回避手段を備えない構成を採用した場合について説明する。この構成において、島設備に設置されている各遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始されると、当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、一斉に(同時に)記憶処理を実行する。その後、遊技ホールの管理者が、種々の理由により、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、再度、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにする場合がある。具体的には、例えば、設定変更モードを実行させて遊技機の当選確率の設定を変更するために、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を設定変更モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにして設定変更モードを開始させる場合がある。この場合、当該一の遊技機は、電源スイッチがONにされて電力の供給が開始されたことに基づいて再び記憶処理を実行する。そうすると、当該一の遊技機において算出される経過時間が、他の遊技機において算出される経過時間と異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングが、他の遊技機において所定の処理(所定の演出)が開始されるタイミングと異なってしまい、当該一の遊技機において遊技を行なっている遊技者に違和感を与えてしまうといった課題がある。 A hypothetical case will be described where a configuration not including the above-mentioned avoidance means is adopted. In this configuration, when the supply of power to each gaming machine installed on an island facility starts all at once (at the same time), each gaming machine installed on the island facility executes the storage process all at once (at the same time). After that, for various reasons, the manager of the gaming hall may turn off the power switch of one of the multiple gaming machines installed on the island facility once, and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine again. Specifically, for example, in order to execute the setting change mode and change the setting of the winning probability of the gaming machine, the manager may turn off the power switch of one of the multiple gaming machines installed on the island facility once, and then turn on the power switch of the one gaming machine to start the setting change mode with the starting condition for starting the setting change mode being satisfied. In this case, the one gaming machine executes the storage process again based on the fact that the power switch is turned on and the supply of power is started. This causes the elapsed time calculated on that one gaming machine to differ from the elapsed time calculated on the other gaming machines, and the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on that one gaming machine to differ from the timing at which a specific process (specific presentation) starts on the other gaming machines, creating an awkward feeling for the player playing on that one gaming machine.
これに対して、本特徴によれば、遊技ホールの管理者が、当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをOFFにして電断状態としても、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段において記憶されている起動時刻情報は保持される。その後、管理者が所定時間(例えば30分)以内に当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにすると、記憶処理の実行が回避されるので、当該一の遊技機の起動時刻情報記憶手段に記憶されている起動時刻情報が上書きされず、他の遊技機と一斉に(同時に)電力の供給が開始された際に実行された記憶処理において記憶された起動時刻情報が維持される。この結果、当該一の遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において算出される経過時間は同一(又は略同一)となる。 In contrast, according to this feature, even if the manager of the gaming hall turns off the power switch of the gaming machine in question, the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine in question is retained. If the manager then turns on the power switch of the gaming machine within a predetermined time (e.g., 30 minutes), the execution of the storage process is avoided, so that the start time information stored in the start time information storage means of the gaming machine in question is not overwritten, and the start time information stored in the storage process executed when the supply of power to the other gaming machines is started all at once (simultaneously) is maintained. As a result, the elapsed time calculated for each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including the gaming machine in question, is the same (or approximately the same).
そして、本特徴によれば、島設備に設置されている各遊技機は、算出した経過時間に基づいて所定の処理を実行するので、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む当該島設備に設置されている各遊技機において実行される所定の処理の実行の態様を同じにすることができる。具体的には、例えば、経過時間が所定時間となった場合に特定の演出を開始する構成を採用した場合には、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。 And according to this feature, each gaming machine installed on the island equipment executes a predetermined process based on the calculated elapsed time, so that the manner of execution of the predetermined process executed by each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again, can be made the same. Specifically, for example, if a configuration is adopted in which a specific presentation is started when a predetermined time has elapsed, it becomes possible to simultaneously (simultaneously) start a specific presentation on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including gaming machines whose power switches have been turned OFF and then ON again.
すなわち、管理者は、島設備の島電源スイッチをONにして、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機に対して一斉に(同時に)電力の供給を開始させた後、所定時間(例えば30分)以内に、当該島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうち、当選確率の設定を変更しようとする一の遊技機の電源スイッチを一旦OFFにした後、当該一の遊技機を設定変更モードを開始させる開始条件を成立させた状態として当該一の遊技機の電源スイッチをONにして設定変更モードを開始させれば、当該一の遊技機の当選確率の設定を変更することが可能であるとともに、一旦電源スイッチをOFFにした後再度電源スイッチをONにした当該一の遊技機を含む島設備に設置されている各遊技機において一斉に(同時に)特定の演出を開始させることが可能となる。この結果、遊技の興趣向上を図ることができる。 That is, the manager turns on the island power switch of the island equipment to start supplying power to the multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment all at once (simultaneously), then within a predetermined time (e.g. 30 minutes), turns off the power switch of one of the multiple gaming machines installed on the island equipment for which the winning probability setting is to be changed, and then turns on the power switch of the one gaming machine to start the setting change mode with the start condition for starting the setting change mode of the one gaming machine being satisfied, thereby making it possible to change the winning probability setting of the one gaming machine and to start a specific presentation all at once (simultaneously) on each gaming machine installed on the island equipment, including the one gaming machine whose power switch was turned off and then turned on again. As a result, it is possible to increase the interest in the game.
[特徴γD2]
特徴γD1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記所定時間の長さを変更する変更手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γD2]
A gaming machine according to feature γD1,
A gaming machine comprising a change means for changing the length of the predetermined time.
特徴γD2によれば、遊技ホールに設置されている遊技機の台数や広さ等に応じて所定時間の長さを適宜変更することができるので、例えば、当該遊技ホールに設置されている複数の遊技機に対する当選確率の設定の変更作業が完了する前に所定時間が経過してしまうといった事態の発生を抑制することが可能となる。 According to feature γD2, the length of the specified time can be changed appropriately depending on the number of gaming machines installed in the gaming hall, the size of the hall, etc., so that it is possible to prevent the occurrence of a situation in which the specified time has elapsed before the work to change the winning probability settings for multiple gaming machines installed in the gaming hall is completed, for example.
<特徴γE群>
特徴γE群は、上述した各実施形態、変形例、又はこれらの組み合わせから抽出され、主に第1実施形態の態様101から抽出される。
<Feature γE group>
The group of features γ E is extracted from each of the above-described embodiments, modifications, or combinations thereof, and is mainly extracted from
[特徴γE1]
遊技機であって、
当該遊技機への外部からの電力供給が開始されたことに基づいて、処理の内容が異なる複数の種別の起動処理のうちのいずれかの起動処理を実行する起動処理実行手段と、
前記複数の種別の起動処理のうちの特定の起動処理が前記起動処理実行手段によって実行される場合(RAM異常コマンドを送信する処理を含む起動処理が主制御装置によって実行される場合)に、次回の電力供給の開始の際に前記起動処理実行手段に実行させるべき前記起動処理の種別に関する情報を報知する(「設定変更モードで起動して下さい」と報知する)報知手段と、
を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γE1]
A gaming machine,
a startup process execution means for executing one of a plurality of types of startup processes having different contents based on the start of power supply from an external source to the gaming machine;
a notification means for notifying information on the type of the startup process to be executed by the startup process execution means when the next power supply is started (notifying "Please start in setting change mode") when a specific startup process among the multiple types of startup processes is executed by the startup process execution means (when a startup process including a process for transmitting a RAM abnormality command is executed by a main control device);
A gaming machine comprising:
特徴γE1によれば、次回の電力供給の開始の際に実行させるべき起動処理の種別に関する情報を報知するので、遊技機の管理者は、当該遊技機への電力供給を終了させた後、再度、当該遊技機への電力供給を開始させる際に、報知された種別の起動処理を実行させるようにすることができる。したがって、遊技機の管理性を向上させることができる。 According to feature γE1, information regarding the type of startup process to be executed when the next power supply is started is notified, so that the manager of the gaming machine can execute the notified type of startup process when starting the power supply to the gaming machine again after terminating the power supply to the gaming machine. This improves the manageability of the gaming machine.
具体的には、例えば、島設備に設置されている複数の遊技機のうちの一の遊技機への電力供給を終了させた後、再度、当該一の遊技機への電力供給を開始させる際に、報知された種別の起動処理を実行させなければ当該一の遊技機において実行される特定の演出の開始のタイミングが他の複数の遊技機において実行される特定の演出の開始のタイミングとずれてしまう構成において、管理者が当該一の遊技機に別の種別の起動処理を実行させてしまうことを抑制することができ、この結果、当該一の遊技機において実行される特定の演出の開始のタイミングが他の複数の遊技機において実行される特定の演出の開始のタイミングとずれてしまうことを抑制することが可能となる。 Specifically, for example, in a configuration in which, when the power supply to one of a number of gaming machines installed on an island facility is terminated and then the power supply to the one gaming machine is started again, if the notified type of startup process is not executed, the timing of the start of a specific effect executed on the one gaming machine will be shifted from the timing of the start of a specific effect executed on the other multiple gaming machines, it is possible to prevent the manager from causing the one gaming machine to execute a different type of startup process, and as a result, it is possible to prevent the timing of the start of a specific effect executed on the one gaming machine from being shifted from the timing of the start of a specific effect executed on the other multiple gaming machines.
[特徴γE2]
特徴γE1に記載の遊技機であって、
前記報知手段は、前記起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を当該遊技機への外部からの電力供給が断たれるまで(電源スイッチがOFFにされるまで)継続する手段を備える
ことを特徴とする遊技機。
[Feature γE2]
A gaming machine according to feature γE1,
The notification means comprises a means for continuing to notify information regarding the type of startup process until the external power supply to the gaming machine is cut off (until the power switch is turned off).
特徴γE2によれば、起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を当該遊技機への外部からの電力供給が断たれるまで継続する。この効果について説明する。仮に、起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を所定時間(例えば10秒)で終了する構成とした場合には、例えば、広い遊技ホールにおいて、管理者が島設備の島電源スイッチの電源をONにして遊技機への外部からの電力供給が開始された後、管理者が当該遊技機に到達する前に当該報知が終了してしまい、次回の電力供給の開始の際に起動処理実行手段に実行させるべき起動処理の種別を管理者が把握することができない場合がある。これに対して、特徴γE2によれば、起動処理の種別に関する情報の報知を当該遊技機への外部からの電力供給が断たれるまで継続するので、管理者が当該遊技機に到達する前に当該報知が終了してしまい、次回の電力供給の開始の際に起動処理実行手段に実行させるべき起動処理の種別を管理者が把握することができないといった事態の発生を回避することができる。 According to feature γE2, the notification of information on the type of startup process continues until the external power supply to the gaming machine is cut off. The effect of this is explained below. If the notification of information on the type of startup process is configured to end after a predetermined time (for example, 10 seconds), for example, in a large gaming hall, after the manager turns on the island power switch of the island equipment to start the external power supply to the gaming machine, the notification may end before the manager reaches the gaming machine, and the manager may not be able to grasp the type of startup process to be executed by the startup process execution means when the next power supply starts. In contrast, according to feature γE2, the notification of information on the type of startup process continues until the external power supply to the gaming machine is cut off, so that it is possible to avoid the occurrence of a situation in which the notification ends before the manager reaches the gaming machine and the manager is unable to grasp the type of startup process to be executed by the startup process execution means when the next power supply starts.
なお、上記特徴βZ群~特徴γE群の発明は、以下の課題を解決する。 The inventions of the above feature group βZ to feature group γE solve the following problems:
パチンコ遊技機やスロットマシン等の遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供等を目的として、構造、制御、演出等の様々な観点から技術的な改良が行われている。 In gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines, technical improvements are being made from various perspectives, such as structure, control, and presentation, with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of the gaming machine, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying the structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, and providing gaming machines that are considerate of the player.
また、遊技者による不正な行為や遊技機に対する不正な改造の発見や抑止といった遊技の健全性の向上を目的とした様々な技術的な改良も行われている。 In addition, various technical improvements are being made to improve the soundness of gaming, such as detecting and preventing fraudulent behavior by players and unauthorized modifications to gaming machines.
上記のような遊技機においては、遊技の興趣向上や、遊技機の処理負荷の低減、処理の最適化、制御の簡易化、構造の簡素化、遊技機の開発の効率化、不具合が発生しにくい遊技機の提供、遊技者に配慮した遊技機の提供、より健全な遊技の提供等を目的として、さらなる技術の向上が望まれている。 In gaming machines like those described above, further technological improvements are desired with the aim of increasing the enjoyment of the game, reducing the processing load of gaming machines, optimizing processing, simplifying control, simplifying structure, making gaming machine development more efficient, providing gaming machines that are less prone to malfunctions, providing gaming machines that are considerate of players, and providing a more wholesome experience.
なお、上記特徴A群~特徴γE群に含まれる1又は複数の構成を適宜組み合わせた構成を採用してもよい。これにより、その組み合わせた構成による相乗的な効果を奏することが可能となる。 It is also possible to adopt a configuration in which one or more of the configurations included in the above-mentioned feature group A to feature group γE are appropriately combined. This makes it possible to achieve a synergistic effect by the combined configuration.
以下に、上記の各特徴を適用し得る又は各特徴に適用される遊技機の基本構成を示す。 The following shows the basic configuration of a gaming machine to which each of the above features can be applied or to which each feature can be applied.
パチンコ遊技機:遊技者による発射操作に基づいて、遊技領域に向けて遊技球を発射する発射手段と、前記遊技領域に設けられ、当該遊技領域を流下する遊技球が入球可能な始動入球部と、前記始動入球部に遊技球が入球したことに基づいて、特別情報を取得する情報取得手段と、前記情報取得手段が取得した特別情報を記憶する取得情報記憶手段とを備える遊技機。 Pachinko gaming machine: A gaming machine that includes a launching means for launching gaming balls toward a gaming area based on a launching operation by a player, a starting ball entry section that is provided in the gaming area and into which a gaming ball flowing down the gaming area can enter, an information acquisition means for acquiring special information based on a gaming ball entering the starting ball entry section, and an acquired information storage means for storing the special information acquired by the information acquisition means.
スロットマシン等の回胴式遊技機:複数の絵柄を可変表示させる絵柄表示手段と、始動操作手段の操作に起因して前記複数の絵柄の可変表示を始動させる始動手段と、停止操作手段の操作に起因して又は所定時間の経過に起因して前記複数の絵柄の可変表示を停止させる停止手段と、停止後の絵柄に応じて遊技者に特典を付与する特典付与手段とを備える遊技機。 Slot machine or other reel-type gaming machine: A gaming machine that includes a pattern display means for variably displaying multiple patterns, a start means for starting the variable display of the multiple patterns due to the operation of a start operation means, a stop means for stopping the variable display of the multiple patterns due to the operation of a stop operation means or due to the passage of a predetermined time, and a bonus granting means for granting a bonus to a player according to the pattern after the stop.
本発明は、上述の実施形態や変形例に限られるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の構成で実現することができる。例えば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments and modifications, and can be realized in various configurations without departing from the spirit of the present invention. For example, the technical features in the embodiments and modifications corresponding to the technical features in each aspect described in the Summary of the Invention column can be replaced or combined as appropriate to solve some or all of the above-mentioned problems or to achieve some or all of the above-mentioned effects. Furthermore, if a technical feature is not described as essential in this specification, it can be deleted as appropriate.
10...パチンコ機
11...外枠
12...パチンコ機本体
13...内枠
14...前扉枠
15...ヒンジ
16...ヒンジ
17...シリンダ錠
18...窓部
19...ガラスユニット
20...上皿
21...下皿
22...排出口
23...レバー
24...演出操作ボタン
25...操作ハンドル
25a...タッチセンサー
25b...ウェイトボタン
25c...可変抵抗器
26...遊技球発射ボタン
30...遊技盤
31...誘導レール
31a...内レール部
31b...外レール部
32...一般入賞口
32a...第1入賞口
32b...第2入賞口
32c...第3入賞口
33...第1始動口
34...第2始動口
34a...電動役物
34b...電動役物駆動部
35...スルーゲート
36...可変入賞装置
36a...大入賞口
36b...開閉扉
36c...可変入賞駆動部
37...特図ユニット
37a...第1図柄表示部
37b...第2図柄表示部
37c...第1保留表示部
37d...第2保留表示部
38...普図ユニット
39...ラウンド表示部
40...可変表示ユニット
41...図柄表示装置
42...釘
43...アウト口
45...メイン表示部
45z...遊技履歴情報表示部(情報表示部)
46...スピーカー
47...各種ランプ
51...第1制御ユニット
52...第2制御ユニット
53...第3制御ユニット
54...タンク
55...タンクレール
56...ケースレール
60...主制御装置
61...主制御基板
62...主側MPU
62x...主側CPU
63...主側ROM
64...主側RAM
64x...フラッシュメモリ
70...払出制御装置
71...払出装置
80...発射制御装置
81...遊技球発射機構
85...電源装置
86...停電監視回路
90...音声発光制御装置
91...音声発光制御基板
96...RTC
100...表示制御装置
300...遊技履歴管理チップ
302...バッファ
304...レジスタ
306...賞球数データ記憶用メモリ
307...演算実行条件記憶用メモリ
307a...記憶実行条件記憶用メモリ
308...CPU
309...演算結果記憶用メモリ
309a...入球個数記憶用メモリ
309b...入球情報記憶用メモリ
320...検査機
321...CPU
328...表示部
329...接続ケーブル
LIST OF
46...
62x...Main CPU
63...Main ROM
64...Main RAM
64x...
100...
309...Memory for storing
328...
Claims (1)
前記複数の所定検出手段と電気的に接続され、遊技に対する遊技価値を付与するための処理を実行する遊技価値付与手段と、
前記遊技価値付与手段と電気的に接続され、前記遊技価値付与手段からの信号であって付与すべき賞球数に関する賞球付与信号に基づいて、前記遊技価値としての賞球を払い出すための払出処理を実行する払出手段と、
前記遊技価値付与手段と各種信号を送信可能な信号線によって電気的に接続され、前記払出処理とは別の異なる処理であって前記賞球付与信号に基づくことのない所定の遊技に関する所定の数値情報の出力に関する特定処理を少なくとも実行する処理実行手段と、
を備える遊技機であって、
前記遊技価値付与手段は、
前記遊技に対する遊技価値を付与するための処理に用いられる情報であって、前記所定検出手段の検出に対して参照される参照用情報を記憶する第1参照用情報記憶手段と、
本遊技機への電力の所定の供給が開始された後であって少なくとも遊技を進行させるために定期的に繰り返される所定の遊技処理の実行を開始する前に、前記第1参照用情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記参照用情報に対応した参照用情報信号を前記処理実行手段に対して送信する第1送信手段と、
前記所定検出手段による検出に基づいて取得された情報である入球情報に基づく所定情報信号を前記処理実行手段に対して送信する第2送信手段と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、
前記遊技価値付与手段から送信された前記参照用情報信号に対応した参照用情報を記憶する第2参照用情報記憶手段と、
前記第2送信手段から送信された前記所定情報信号と、前記第2参照用情報記憶手段に記憶された前記参照用情報とに基づいて前記特定処理を実行する実行手段と、
前記実行手段による前記特定処理の処理結果に関する情報である処理結果情報を記憶する処理結果情報記憶手段と、
を備え、
本遊技機は、
本遊技機の前方から視認可能であり、所定の抽選処理の結果を告知する処理の1単位である遊技回毎に実行される遊技回演出を表示する演出用表示手段と、
前記処理結果情報を前記演出用表示手段に出力する手段と、
を備え、
前記処理実行手段は、前記遊技価値付与手段の前記第1参照用情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記参照用情報を書き換え不能に構成されており、
前記遊技価値付与手段は、前記処理結果情報記憶手段に記憶されている前記処理結果情報を直接的に変更不能であり、
遊技機前面体が開放されて所定状態が発生した場合に、前記遊技価値付与手段から前記遊技機前面体の開放に対応する開放情報が送信され、前記処理実行手段において前記開放情報に対応した情報が記憶され、
前記複数の所定検出手段は、遊技球を検出したことに基づいて付与する遊技価値が異なる所定検出手段を少なくとも含んでおり、
前記実行手段は、前記遊技価値が異なる前記所定検出手段に基づいた前記所定情報信号と、前記第2参照用情報記憶手段に記憶された前記参照用情報とに基づいて前記特定処理を実行する手段を備え、
前記特定処理の終了後の所定タイミングで前記所定情報信号に基づいて記憶された情報が消去される構成である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。 A plurality of predetermined detection means for detecting game balls that have passed through a predetermined area;
a game value providing means electrically connected to the plurality of predetermined detection means and configured to execute a process for providing a game value for a game;
a payout means electrically connected to the game value providing means, and executing a payout process for paying out prize balls as the game value based on a prize ball providing signal from the game value providing means, the prize ball providing signal being related to the number of prize balls to be provided;
a process execution means that is electrically connected to the game value providing means by a signal line capable of transmitting various signals, and that executes at least a specific process related to the output of predetermined numerical information related to a predetermined game, which is a process different from the payout process and is not based on the prize ball providing signal ;
A gaming machine comprising:
The game value providing means includes:
a first reference information storage means for storing reference information used in a process for providing a game value to the game, the reference information being referenced in response to detection by the predetermined detection means;
a first transmitting means for transmitting a reference information signal corresponding to the reference information stored in the first reference information storage means to the process executing means after a predetermined supply of power to the gaming machine is started and before the start of execution of a predetermined game process that is periodically repeated at least to progress a game;
a second transmitting means for transmitting a predetermined information signal based on the ball-entering information, which is information acquired based on the detection by the predetermined detecting means, to the processing executing means;
Equipped with
The process execution means includes:
a second reference information storage means for storing reference information corresponding to the reference information signal transmitted from the game value providing means;
an execution means for executing the specific process based on the predetermined information signal transmitted from the second transmission means and the reference information stored in the second reference information storage means;
a processing result information storage means for storing processing result information which is information regarding a processing result of the specific processing performed by the execution means;
Equipped with
This gaming machine is
A presentation display means for displaying a presentation to be executed for each game round, which is one unit of a process for notifying the result of a predetermined lottery process, and which is visible from the front of the gaming machine;
a means for outputting the processing result information to the performance display means;
Equipped with
The processing execution means is configured to make the reference information stored in the first reference information storage means of the game value providing means non-rewritable,
the game value providing means cannot directly change the processing result information stored in the processing result information storage means;
When a front body of the gaming machine is opened and a predetermined state occurs, opening information corresponding to the opening of the front body of the gaming machine is transmitted from the gaming value providing means, and information corresponding to the opening information is stored in the processing execution means;
The plurality of predetermined detection means include at least a predetermined detection means which provides different game values based on the detection of a game ball,
The execution means includes a means for executing the specific process based on the predetermined information signal based on the predetermined detection means having different game values and the reference information stored in the second reference information storage means;
The information stored based on the predetermined information signal is erased at a predetermined timing after the specific process is completed.
A gaming machine characterized by:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023096609A JP7473060B2 (en) | 2021-12-18 | 2023-06-12 | Gaming Machines |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021205616A JP2022027983A (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2021-12-18 | Game machine |
| JP2023096609A JP7473060B2 (en) | 2021-12-18 | 2023-06-12 | Gaming Machines |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021205616A Division JP2022027983A (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2021-12-18 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2023107874A JP2023107874A (en) | 2023-08-03 |
| JP2023107874A5 JP2023107874A5 (en) | 2024-01-12 |
| JP7473060B2 true JP7473060B2 (en) | 2024-04-23 |
Family
ID=80265085
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023096609A Active JP7473060B2 (en) | 2021-12-18 | 2023-06-12 | Gaming Machines |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7473060B2 (en) |
Citations (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005065858A (en) | 2003-08-21 | 2005-03-17 | Takao:Kk | Pinball game machine |
| JP2013094245A (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-05-20 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game system and game device |
| JP2023021372A (en) | 2017-09-15 | 2023-02-10 | 株式会社三洋物産 | game machine |
| JP7375862B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375865B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375863B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375864B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392799B2 (en) | 2021-03-19 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392796B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392800B2 (en) | 2021-03-19 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392798B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392797B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7424413B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2024-01-30 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
-
2023
- 2023-06-12 JP JP2023096609A patent/JP7473060B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005065858A (en) | 2003-08-21 | 2005-03-17 | Takao:Kk | Pinball game machine |
| JP2013094245A (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-05-20 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game system and game device |
| JP7375864B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375862B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375865B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7375863B2 (en) | 2017-09-06 | 2023-11-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP2023021372A (en) | 2017-09-15 | 2023-02-10 | 株式会社三洋物産 | game machine |
| JP7392796B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392798B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392797B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7424413B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2024-01-30 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392799B2 (en) | 2021-03-19 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
| JP7392800B2 (en) | 2021-03-19 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社三洋物産 | gaming machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2023107874A (en) | 2023-08-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7424429B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7473051B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7392796B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7392798B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7392797B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7424412B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7375873B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7375879B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP2024045771A (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7473053B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7473052B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7405203B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7473060B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485159B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485163B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485162B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485168B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485161B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485166B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485164B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485167B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485160B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7485165B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7405204B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7424430B2 (en) | gaming machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20230703 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20231228 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240116 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240224 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20240312 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20240325 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7473060 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |