JP6848669B2 - Robots and gears - Google Patents
Robots and gears Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6848669B2 JP6848669B2 JP2017096344A JP2017096344A JP6848669B2 JP 6848669 B2 JP6848669 B2 JP 6848669B2 JP 2017096344 A JP2017096344 A JP 2017096344A JP 2017096344 A JP2017096344 A JP 2017096344A JP 6848669 B2 JP6848669 B2 JP 6848669B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- gear
- teeth
- internal
- external
- lubricant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Manipulator (AREA)
- Retarders (AREA)
- General Details Of Gearings (AREA)
Description
本発明は、ロボットおよび歯車装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to robots and gears.
少なくとも1つのアームを含んで構成されたロボットアームを備えるロボットでは、例えば、ロボットアームの関節部をモーターにより駆動するが、一般に、そのモーターからの駆動力(回転力)による回転を減速機により減速することが行われている。このような減速機として、例えば、特許文献1に記載されている波動歯車装置のような歯車装置が知られている。
In a robot including a robot arm including at least one arm, for example, a joint portion of the robot arm is driven by a motor, but in general, rotation due to a driving force (rotational force) from the motor is decelerated by a speed reducer. Is being done. As such a speed reducer, for example, a gear device such as the wave gear device described in
特許文献1に記載の波動歯車装置は、環形状をした剛性の内歯歯車と、環形状をした可撓性の外歯歯車と、この外歯歯車を半径方向にて内歯歯車に部分的に噛み合わせるとともに当該噛み合わせ位置を円周方向に移動させる波動発生器と、を備える。そして、内歯歯車および外歯歯車の歯面部には、グリースが充填されている。
The strain wave gearing described in
特許文献1に記載の波動歯車装置では、内歯歯車および外歯歯車が極めて少ないバックラッシュで互いに噛み合う。従来、このような噛み合い部における潤滑剤の潤滑寿命が短く、かかる波動歯車装置をロボットに用いた場合、焼き付きや摩耗等が比較的早期に生じやすいという問題があった。
In the strain wave gearing described in
本発明の目的は、歯車装置に用いる潤滑剤の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができるロボットおよび歯車装置を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a robot and a gear device capable of effectively improving the lubrication life of a lubricant used in the gear device.
上記目的は、下記の本発明により達成される。
本発明のロボットは、第1部材と、
前記第1部材に対して回動可能に設けられた第2部材と、
前記第1部材および前記第2部材の一方側から他方側へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置と、を備え、
前記歯車装置は、
前記駆動力の伝達経路の途中に設けられ、互いに噛み合う内歯および外歯と、
前記内歯と前記外歯との間に配置されている潤滑剤と、を有し、
前記外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が前記内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さいことを特徴とする。
The above object is achieved by the following invention.
The robot of the present invention includes the first member and
A second member rotatably provided with respect to the first member,
A gear device for transmitting a driving force from one side of the first member and the second member to the other side is provided.
The gear device
Internal and external teeth that are provided in the middle of the driving force transmission path and mesh with each other,
With a lubricant disposed between the internal teeth and the external teeth,
The average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the outer tooth is smaller than the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the inner tooth.
このようなロボットによれば、外歯の結晶粒径を小さくして、潤滑剤を外歯上に保持させやすくすることができる。そのため、潤滑剤を外歯の回転による遠心力に抗して外歯上に留めておくことができる。その一方で、内歯の結晶粒径を大きくして、潤滑剤を内歯上に沿って流動させやすくすることができる。そのため、潤滑剤が内歯上で偏ったり固化したりするのを低減することができる。そして、前述したような、潤滑剤を外歯上に留めておく効果、および、潤滑剤が内歯上で偏ったり固化したりするのを低減する効果の2つの効果が相乗して、潤滑剤の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。 According to such a robot, the crystal grain size of the outer teeth can be reduced to facilitate holding of the lubricant on the outer teeth. Therefore, the lubricant can be retained on the external teeth against the centrifugal force due to the rotation of the external teeth. On the other hand, the crystal grain size of the internal teeth can be increased to facilitate the flow of the lubricant along the internal teeth. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the bias and solidification of the lubricant on the internal teeth. Then, as described above, the two effects of the effect of retaining the lubricant on the outer teeth and the effect of reducing the bias and solidification of the lubricant on the inner teeth are synergistic, and the lubricant The lubrication life of the product can be effectively improved.
本発明のロボットでは、前記内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が20μm以上150μm以下の範囲内にあることが好ましい。 In the robot of the present invention, it is preferable that the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the internal teeth is in the range of 20 μm or more and 150 μm or less.
これにより、潤滑剤を内歯上に沿ってより効果的に流動させることができる。また、内歯が金属で構成されている場合において、内歯の機械的強度を優れたものとすることができる。 This allows the lubricant to flow more effectively along the internal teeth. Further, when the internal teeth are made of metal, the mechanical strength of the internal teeth can be made excellent.
本発明のロボットでは、前記外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が0.5μm以上30μm以下の範囲内にあることが好ましい。 In the robot of the present invention, it is preferable that the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the external tooth is in the range of 0.5 μm or more and 30 μm or less.
これにより、潤滑剤を外歯上により効果的に保持させることができる。また、外歯が金属で構成されている場合において、外歯の機械的強度を優れたものとすることができる。 This allows the lubricant to be more effectively retained on the external teeth. Further, when the external teeth are made of metal, the mechanical strength of the external teeth can be made excellent.
本発明のロボットでは、前記内歯および前記外歯は、それぞれ、金属材料で構成されていることが好ましい。 In the robot of the present invention, it is preferable that the internal teeth and the external teeth are each made of a metal material.
一般に、金属は、優れた機械的特性を有するとともに、比較的簡単に機械加工でき、また、その加工精度も高い。そのため、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する内歯および外歯を簡単に実現することができる。 In general, metals have excellent mechanical properties, can be machined relatively easily, and have high processing accuracy. Therefore, internal teeth and external teeth having excellent characteristics (mechanical strength, accuracy, etc.) can be easily realized.
本発明のロボットでは、前記内歯は、鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方で構成されていることが好ましい。 In the robot of the present invention, it is preferable that the internal teeth are made of either cast iron or precipitation hardening stainless steel.
これにより、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する内歯を簡単に実現することができる。特に、鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼は、それぞれ、潤滑剤を内歯上に沿って効果的に流動させる適切な結晶粒径を実現しやすく、また、機械的強度および加工性のバランスに優れている。そのため、内歯を鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方で構成することで、内歯の機械的強度を優れたものとしつつ、潤滑剤を内歯上に沿ってより効果的に流動させることができる。 Thereby, an internal tooth having excellent characteristics (mechanical strength, accuracy, etc.) can be easily realized. In particular, cast iron and precipitation hardening stainless steel, respectively, can easily achieve an appropriate grain size that allows the lubricant to effectively flow along the internal teeth, and have an excellent balance between mechanical strength and workability. There is. Therefore, by constructing the internal teeth with either cast iron or precipitation hardening stainless steel, the mechanical strength of the internal teeth is improved, and the lubricant is more effectively applied along the internal teeth. Can be fluidized.
本発明のロボットでは、前記外歯は、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つで構成されていることが好ましい。 In the robot of the present invention, the external teeth are preferably made of any one of nickel chrome molybdenum steel, maraging steel and precipitation hardening stainless steel.
これにより、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する外歯を簡単に実現することができる。特に、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼は、それぞれ、潤滑剤を外歯上に効果的に保持させる適切な結晶粒径を実現しやすく、また、機械的強度および加工性のバランスに優れている。そのため、外歯をニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つで構成することで、外歯の機械的強度を優れたものとしつつ、潤滑剤を外歯上により効果的に保持させることができる。 Thereby, an external tooth having excellent characteristics (mechanical strength, accuracy, etc.) can be easily realized. In particular, nickel-chromium molybdenum steel, maraging steel and precipitation hardening stainless steel, respectively, are easy to achieve appropriate grain boundaries that effectively hold the lubricant on the external teeth, and have mechanical strength and workability, respectively. Excellent balance. Therefore, by configuring the outer teeth with any one of nickel-chromium molybdenum steel, maraging steel, and precipitation hardening stainless steel, the mechanical strength of the outer teeth is made excellent, and the lubricant is used as the outer teeth. It can be held more effectively on the top.
本発明のロボットでは、前記歯車装置は、
前記内歯を有する内歯車と、
前記内歯に部分的に噛み合う前記外歯を有する可撓性の外歯車と、
前記外歯車を撓めて前記内歯車と前記外歯車との噛み合い位置を周方向に移動させる波動発生器と、を有することが好ましい。
In the robot of the present invention, the gear device is
The internal gear having the internal teeth and
A flexible external gear having the external teeth that partially meshes with the internal teeth,
It is preferable to have a wave generator that bends the external gear to move the meshing position between the internal gear and the external gear in the circumferential direction.
このような歯車装置では、一般に、内歯車および外歯車が極めて少ないバックラッシュで互いに噛み合うため、潤滑剤の潤滑寿命に対する要求が極めて高い。そのため、このような歯車装置に本発明を適用すると、その効果が顕著となる。 In such a gear device, the internal gear and the external gear generally mesh with each other with extremely few backlashes, so that the requirement for the lubrication life of the lubricant is extremely high. Therefore, when the present invention is applied to such a gear device, the effect becomes remarkable.
本発明の歯車装置は、互いに噛み合う内歯および外歯と、
前記内歯と前記外歯との間に配置されている潤滑剤と、を有し、
前記外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が前記内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さいことを特徴とする。
このような歯車装置によれば、潤滑剤の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。
The gear device of the present invention includes internal and external teeth that mesh with each other.
With a lubricant disposed between the internal teeth and the external teeth,
The average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the outer tooth is smaller than the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the inner tooth.
According to such a gear device, the lubrication life of the lubricant can be effectively improved.
以下、本発明のロボットおよび歯車装置を添付図面に示す好適な実施形態に基づいて詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, the robot and the gear device of the present invention will be described in detail based on the preferred embodiments shown in the accompanying drawings.
1.ロボット
まず、本発明のロボットの実施形態について説明する。
1. 1. Robot First, an embodiment of the robot of the present invention will be described.
図1は、本発明のロボットの実施形態の概略構成を示す図である。
図1に示すロボット100は、精密機器やこれを構成する部品(対象物)の給材、除材、搬送および組立等の作業を行うことができる。
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an embodiment of the robot of the present invention.
The
ロボット100は、6軸の垂直多関節ロボットであり、基台111と、基台111に接続されたロボットアーム120と、ロボットアーム120の先端部に設けられた力検出器140およびハンド130と、を有する。また、ロボット100は、ロボットアーム120を駆動させる動力を発生させる複数の駆動源(モーター150および歯車装置1を含む)を制御する制御装置110と、を有している。
The
基台111は、ロボット100を任意の設置箇所に取り付ける部分である。なお、基台111の設置箇所は、特に限定されず、例えば、床、壁、天井、移動可能な台車上などが挙げられる。
The
ロボットアーム120は、第1アーム121(アーム)と、第2アーム122(アーム)と、第3アーム123(アーム)と、第4アーム124(アーム)と、第5アーム125(アーム)と、第6アーム126(アーム)とを有し、これらが基端側(基台側)から先端側に向ってこの順に連結されている。第1アーム121は、基台111に接続されている。第6アーム126の先端には、例えば、各種部品等を把持するハンド130(エンドエフェクター)が着脱可能に取り付けられている。このハンド130は、2本の指131、132を有しており、指131、132で例えば各種部品等を把持することができる。
The
基台111には、第1アーム121を駆動するサーボモーター等のモーター150および歯車装置1(減速機)を有する駆動源が設けられている。また、図示しないが、各アーム121〜126にも、それぞれ、モーターおよび減速機を有する複数の駆動源が設けられている。そして、各駆動源は、制御装置110により制御される。
The
このようなロボット100では、歯車装置1が、基台111(第1部材)および第1アーム121(第2部材)の一方から他方へ駆動力を伝達する。より具体的には、歯車装置1が、第1アーム121を基台111に対して回動させる駆動力を基台111側から第1アーム121側へ伝達する。ここで、歯車装置1が減速機として機能することにより、駆動力の回転を減速して第1アーム121を基台111に対して回動させることができる。なお、「回動」とはある中心点に対して一方向またはその反対方向を含めた双方向に動くこと、および、ある中心点に対して回転することを含むものである。
In such a
このように、ロボット100は、「第1部材」である基台111と、基台111に対して回動可能に設けられた「第2部材」である第1アーム121と、基台111(第1部材)および第1アーム121(第2部材)の一方側から他方側へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置1と、を備えている。なお、第2〜第6アーム122〜126のうち第1アーム121側から順次選択した任意の数のアームを「第2部材」と捉えてもよい。すなわち、第1アーム121、および、第2〜第6アーム122〜126のうち第1アーム121側から順次選択した任意の数のアームからなる構造体が「第2部材」であるとも言える。例えば、第1、第2アーム121、122からなる構造体が「第2部材」であるとも言えるし、ロボットアーム120全体が「第2部材」であるとも言える。また、「第2部材」がハンド130を含んでいてもよい。すなわち、ロボットアーム120およびハンド130からなる構造体が「第2部材」であるとも言える。
As described above, the
以上説明したようなロボット100は、以下に説明するような歯車装置1を備えることにより、歯車装置1に用いる潤滑剤の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。
By providing the
2.歯車装置
以下、本発明の歯車装置の実施形態について説明する。
2. Gear device Hereinafter, embodiments of the gear device of the present invention will be described.
<第1実施形態>
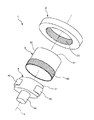
図2は、本発明の第1実施形態に係る歯車装置を示す分解斜視図である。図3は、図2に示す歯車装置の縦断面図である。図4は、図2に示す歯車装置の正面図である。なお、各図では、説明の便宜上、必要に応じて各部の寸法を適宜誇張して図示しており、各部間の寸法比は実際の寸法比とは必ずしも一致しない。
<First Embodiment>
FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view showing a gear device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a vertical cross-sectional view of the gear device shown in FIG. FIG. 4 is a front view of the gear device shown in FIG. In each drawing, for convenience of explanation, the dimensions of each part are exaggerated as necessary, and the dimensional ratio between the parts does not always match the actual dimensional ratio.
図2ないし図4に示す歯車装置1は、波動歯車装置であり、例えば減速機として用いられる。この歯車装置1は、内歯車である剛性歯車2と、剛性歯車2の内側に配置されているカップ型の外歯車である可撓性歯車3と、可撓性歯車3の内側に配置されている波動発生器4と、を有している。
The
この歯車装置1では、可撓性歯車3の横断面が波動発生器4により楕円形または長円形に変形した部分を有し、当該部分の長軸側の両端部において可撓性歯車3が剛性歯車2と噛み合っている。そして、剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3の歯数が互いに異なっている。
In this
本実施形態では、剛性歯車2が前述したロボット100の基台111(第1部材)側に固定され、可撓性歯車3が前述したロボット100の第1アーム121(第2部材)側に接続され、波動発生器4が前述したロボット100のモーター150の回転軸側に接続されている。
In the present embodiment, the rigid gear 2 is fixed to the base 111 (first member) side of the
このような歯車装置1において、例えば、波動発生器4に駆動力(例えば、前述したモーター150からの駆動力)が入力されると、剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3は、互いの噛み合い位置が周方向に移動しながら、歯数差に起因して軸線aまわりに相対的に回転する。これにより、駆動源から波動発生器4に入力された駆動力(回転力)による回転を減速して可撓性歯車3から出力することができる。すなわち、波動発生器4を入力軸側、可撓性歯車3を出力軸側とする減速機を実現することができる。
In such a
なお、剛性歯車2、可撓性歯車3および波動発生器4の接続形態は、前述した形態に限定されず、例えば、可撓性歯車3を基台111側に固定し、剛性歯車2を第1アーム121側に接続しても、歯車装置1を減速機として用いることができる。また、可撓性歯車3をモーター150の回転軸側に接続しても、歯車装置1を減速機として用いることができ、この場合、波動発生器4を基台111側に固定し、剛性歯車2を第1アーム121側に接続すればよい。また、歯車装置1を増速機として用いる場合(入力された駆動力の回転を増速させる場合)、前述した入力側(モーター150側)と出力側(第1アーム121側)との関係を反対にすればよい。
The connection form of the rigid gear 2, the flexible gear 3, and the wave generator 4 is not limited to the above-mentioned form. For example, the flexible gear 3 is fixed to the base 111 side, and the rigid gear 2 is connected to the first. The
以下、歯車装置1の構成を簡単に説明する。
図2ないし図4に示すように、剛性歯車2は、径方向に実質的に撓まない剛体で構成された歯車であって、内歯23を有するリング状の内歯車である。本実施形態では、剛性歯車2が、平歯車である。すなわち、内歯23は、軸線aに対して平行な歯スジを有する。
Hereinafter, the configuration of the
As shown in FIGS. 2 to 4, the rigid gear 2 is a gear made of a rigid body that does not substantially bend in the radial direction, and is a ring-shaped internal gear having
可撓性歯車3は、剛性歯車2の内側に挿通されている。この可撓性歯車3は、径方向に撓み変形可能な可撓性を有する歯車であって、剛性歯車2の内歯23に噛み合う外歯33(歯)を有する外歯車である。また、可撓性歯車3の歯数は、剛性歯車2の歯数よりも少ない。このように可撓性歯車3および剛性歯車2の歯数が互いに異なることにより、減速機を実現することができる。
The flexible gear 3 is inserted inside the rigid gear 2. The flexible gear 3 is a gear having flexibility that can be flexed and deformed in the radial direction, and is an external gear having external teeth 33 (teeth) that mesh with the
本実施形態では、可撓性歯車3は、一端が開口したカップ状をなし、その開口側の端部に外歯33が形成されている。ここで、可撓性歯車3は、軸線aまわりの筒状(より具体的には円筒状)の胴部31(筒部)と、胴部31の軸線a方向での一端部側に接続されている底部32と、を有する。これにより、胴部31の底部32とは反対側の端部を径方向に撓み易くすることができる。そのため、剛性歯車2に対する可撓性歯車3の良好な撓み噛み合いを実現することができる。また、胴部31の底部32側の端部の剛性を高めることができる。そのため、底部32に入力軸または出力軸を安定的に接続することができる。
In the present embodiment, the flexible gear 3 has a cup shape with one end open, and
また、図3に示すように、底部32には、軸線aに沿って貫通した孔321と、孔321の周囲において貫通した複数の孔322と、が形成されている。孔321には、出力側の軸体を挿通することができる。また、孔322には、出力側の軸体を底部32に固定するためのネジを挿通するネジ孔として用いることができる。なお、これらの孔は、適宜設ければよく、省略することもできる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 3, the
図3に示すように、波動発生器4は、可撓性歯車3の内側に配置され、軸線aまわりに回転可能である。そして、波動発生器4は、可撓性歯車3の底部32とは反対側の部分の横断面を長軸Laおよび短軸Lbとする楕円形または長円形に変形させて外歯33を剛性歯車2の内歯23に噛み合わせる(図4参照)。ここで、可撓性歯車3および剛性歯車2は、同一の軸線aまわりに回転可能に互いに内外で噛み合わされることとなる。
As shown in FIG. 3, the wave generator 4 is arranged inside the flexible gear 3 and is rotatable around the axis a. Then, the wave generator 4 deforms the cross section of the portion of the flexible gear 3 opposite to the bottom 32 into an elliptical shape or an oval shape having a long axis La and a short axis Lb, and makes the external teeth 33 a rigid gear. It meshes with the
本実施形態では、波動発生器4は、本体部41と、本体部41から軸線aに沿って突出した軸部42と、本体部41に対して軸線aに平行な軸線a1まわりに回転可能に設けられた1対のローラー43と、を有する。このような波動発生器4は、1対のローラー43が可撓性歯車3の内周面上を転動しながら可撓性歯車3を内側から押し広げて、本体部41、軸部42および1対のローラー43が軸線aまわりに回転可能である。したがって、例えば、駆動源から波動発生器4に駆動力が入力されると、剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3の互いの噛み合い位置が周方向に移動する。
In the present embodiment, the wave generator 4 can rotate around the
以上、歯車装置1の構成を簡単に説明した。このような歯車装置1では、前述したように、例えば、波動発生器4に駆動力(例えば、前述したモーター150からの駆動力)が入力されると、剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3は、互いの噛み合い位置が周方向に移動しながら、歯数差に起因して軸線aまわりに相対的に回転する。ここで、歯車装置1の各部の摩擦を低減するため、潤滑剤が用いられるが、歯車装置1は、剛性歯車2と可撓性歯車3との噛み合い部において、潤滑剤を良好な状態で長期にわたり保持するため、以下に述べるような構成を有する。
The configuration of the
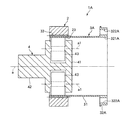
図5は、図2に示す歯車装置の噛合部および摺動部に配置された潤滑剤を説明する図である。 FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a lubricant arranged in a meshing portion and a sliding portion of the gear device shown in FIG.
前述したように、歯車装置1は、内歯23を有する「内歯車」である剛性歯車2と、内歯23に部分的に噛み合う外歯33を有する可撓性の「外歯車」である可撓性歯車3と、可撓性歯車3を撓めて剛性歯車2と可撓性歯車3との噛み合い位置を周方向に移動させる波動発生器4と、を有する。ここで、図5に示すように、剛性歯車2の内歯23の歯面231と可撓性歯車3の外歯33の歯面331との間の領域である噛合部61には、潤滑剤51が配置されている。すなわち、歯車装置1は、駆動力(例えばモーター150からの駆動力)の伝達経路の途中に設けられ、互いに噛み合う内歯23および外歯33と、内歯23と外歯33との間に配置されている潤滑剤51と、を有する。ここで、「駆動力の伝達経路の途中」とは、駆動力の伝達経路の始点から終点までの任意の位置を言う。
As described above, the
内歯23および外歯33は、それぞれ、後述するような金属材料で構成されており、その金属組織内に結晶粒を有する。そして、外歯33の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が内歯23の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さい。
The
このような内歯23および外歯33の構成材料の平均結晶粒径の大小関係により、外歯33の結晶粒径を小さくして、潤滑剤51を外歯33上に保持させやすくすることができる。そのため、潤滑剤51を外歯33の回転による遠心力に抗して外歯33上に留めておくことができる。ここで、潤滑剤51は、外歯33の表面に存在する結晶粒界に優先的に保持される。これは、当該結晶粒界が潤滑剤51を収容する微細な凹部や溝のような役割を果たすためと考えられる。したがって、外歯33の結晶粒径を小さくすることで、外歯33の表面に存在する結晶粒界の密度が高くなり、それに伴って、外歯33の表面に潤滑剤51が保持されやすくなる。
Due to the magnitude relationship of the average crystal grain size of the constituent materials of the
また、外歯33の結晶粒径を小さくすると、外歯33の機械的強度を高めるとともに、外歯33の靱性を高めることができる。外歯33は、前述したように剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3の互いの噛み合い位置の移動に伴って変形を繰り返すことから、内歯23に比べて高い機械的強度および靱性が要求される。そのため、外歯33の機械的強度および靱性を高めることは極めて有益である。なお、一般に、金属の機械的強度は、結晶粒径の1/2乗に反比例して高まる。
Further, by reducing the crystal grain size of the
その一方で、内歯23の結晶粒径を大きくして、潤滑剤51を内歯23上に沿って流動させやすくすることができる。そのため、潤滑剤51が内歯23上で偏ったり固化したりするのを低減することができる。ここで、内歯23は非回転であるため、内歯23上において、前述した外歯33のような遠心力が働かないため、もともと潤滑剤51を保持しやすい傾向にある。そこで、内歯23上の潤滑剤51を流動しやすくすることで、潤滑剤51の固着や必要箇所での油切れを防ぐ。これにより、潤滑剤51の性能を十分に発揮させることが可能となる。
On the other hand, the crystal grain size of the
このように、歯車装置1では、前述したような、潤滑剤51を外歯33上に留めておく効果、および、潤滑剤51が内歯23上で偏ったり固化したりするのを低減する効果の2つの効果を同時に発揮させることができる。そして、この2つの効果が相乗して、潤滑剤51の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。特に、歯車装置1のような波動歯車装置では、一般に、内歯車および外歯車が極めて少ないバックラッシュで互いに噛み合うため、潤滑剤の潤滑寿命に対する要求が極めて高い。そのため、このような歯車装置に本発明を適用すると、その効果が顕著となる。
As described above, in the
なお、詳細な説明は省略するが、可撓性歯車3の胴部31の内周面311と波動発生器4のローラー43の外周面431との間の領域である摺動部62には、潤滑剤52が配置されている。また、図示しないが、波動発生器4内の摺動部にも潤滑剤が配置されている。
Although detailed description will be omitted, the sliding
ここで、「平均結晶粒径」は、JIS G 0551「鋼−結晶粒度の顕微鏡試験方法」に準拠して測定されるものである。この平均結晶粒径の測定に際しては、試験片(内歯または外歯)の表面を腐食液によりエッチングすることで結晶粒界を出現させ、その出現した結晶粒界を顕微鏡観察することにより行うが、腐食液としては、5%ナイタール(5%硝酸−エチルアルコール)を用いる。また、前述したような平均結晶粒径の大小関係は、少なくとも内歯23および外歯33において満たしていればよく、剛性歯車2および可撓性歯車3の他の部分同士において満たしていなくてもよいが、他の部分同士においても満たしていると、その効果が顕著となる。また、内歯23および外歯33の結晶粒径は、例えば、これらを構成する材料(金属組成)および製造時の熱処理等に応じて調整が可能である。
Here, the "average crystal grain size" is measured in accordance with JIS G 0551 "Steel-Crystal Grain Size Microscopic Test Method". The average crystal grain size is measured by etching the surface of the test piece (inner tooth or outer tooth) with a corrosive solution to make grain boundaries appear, and observing the appearing grain boundaries under a microscope. As the corrosive liquid, 5% nital (5% nitrate-ethyl alcohol) is used. Further, the magnitude relationship of the average crystal grain size as described above may be satisfied at least in the
外歯33の構成材料の平均結晶粒径をAとし、内歯23の構成材料の平均結晶粒径をBとしたとき、A<Bなる関係を満たせばよいが、前述したような2つの効果を好適に発揮させる上で、好ましくは、1.2≦B/A≦100、より好ましくは、2≦B/A≦50とされる。これに対し、B/Aが小さすぎると、前述した2つの効果のバランスが悪くなる傾向を示し、一方、B/Aが大きすぎると、内歯23と外歯33の強度差が大きくなりすぎて、内歯23および外歯33のうちの一方の摩耗が早くなる傾向を示す。
When the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the
内歯23の構成材料の平均結晶粒径(B)は、特に限定されないが、20μm以上150μm以下の範囲内にあることが好ましく、30μm以上100μm以下の範囲内にあることがより好ましく、30μm以上50μm以下の範囲内にあることがさらに好ましい。これにより、潤滑剤51を内歯23上に沿ってより効果的に流動させることができる。また、内歯23が金属で構成されている場合において、内歯23の機械的強度を優れたものとすることができる。これに対して、かかる平均結晶粒径が小さすぎると、内歯23上での潤滑剤51の流動性が低下する傾向を示す。一方、かかる平均結晶粒径が大きすぎると、内歯23の構成材料によっては、内歯23の強度が不足する場合がある。なお、剛性歯車2の全体において、前述した平均結晶粒径の範囲を満たしていると、前述した効果が顕著となる。
The average crystal grain size (B) of the constituent material of the
一方、外歯33の構成材料の平均結晶粒径(A)は、前述したA<Bを満たす限り特に限定されないが、0.5μm以上30μm以下の範囲内にあることが好ましく、5μm以上20μm以下の範囲内にあることがより好ましく、5μm以上15μm以下の範囲内にあることがさらに好ましい。これにより、潤滑剤51を外歯33上により効果的に保持させることができる。また、外歯33が金属で構成されている場合において、外歯33の機械的強度を優れたものとすることができる。これに対し、かかる平均結晶粒径が小さすぎると、外歯33を製造する際の加工性が悪く、また、外歯33の表面に存在する結晶粒界に起因する凹部の深さも小さくなるため、かえって、潤滑剤51を外歯33上に保持し難くなってしまう。一方、かかる平均結晶粒径が大きすぎると、潤滑剤51を外歯33上に保持する効果が低下する傾向を示し、また、外歯33に必要な機械的強度および靱性を確保することが難しい。なお、可撓性歯車3の全体において、前述した平均結晶粒径の範囲を満たしていると、前述した効果が顕著となる。
On the other hand, the average crystal grain size (A) of the constituent material of the
ここで、内歯23および外歯33は、それぞれ、金属材料で構成されていることが好ましく、特に、機械的特性および加工性に優れ、かつ、比較的安価であることから、鉄系材料を用いることが好ましい。一般に、金属は、優れた機械的特性を有するとともに、比較的簡単に機械加工でき、また、その加工精度も高い。そのため、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する内歯23および外歯33を簡単に実現することができる。特に、外歯33は、前述したように高い靱性を有することが好ましいため、金属材料で構成されていることが好ましい。なお、内歯23は、実質的な剛体であるため、セラミックス材料で構成することも可能であるが、外歯33との強度のバランスから、金属材料を用いることが好ましい。
Here, it is preferable that the
また、内歯23を構成する金属材料は、前述したA<Bを満たす限り特に限定されず、種々の金属材料を用いることができるが、特に、鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方であることが好ましい。内歯23が鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方で構成されていることにより、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する内歯23を簡単に実現することができる。特に、鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼は、それぞれ、前述したような潤滑剤51を内歯23上に沿って効果的に流動させる適切な結晶粒径を実現しやすく、また、機械的強度および加工性のバランスに優れている。そのため、内歯23を鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方で構成することで、内歯23の機械的強度を優れたものとしつつ、潤滑剤51を内歯23上に沿ってより効果的に流動させることができる。なお、剛性歯車2の内歯23の少なくとも表面が前述したような材料で構成されていればよいが、前述したような効果を顕著なものとするために、歯底部まで前述したような材料で構成することが好ましい。更には剛性歯車2全体を前述したような材料で構成すれば同様な効果を得つつ製造が比較的容易になる。また、鋳鉄および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか一方に他の物質を添加した材料で内歯23を構成してもよい。
The metal material constituting the
また、外歯33を構成する金属材料は、前述したA<Bを満たす限り特に限定されず、種々の金属材料を用いることができるが、特に、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つであることが好ましい。外歯33がニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つで構成されていることにより、優れた特性(機械的強度、精度等)を有する外歯33を簡単に実現することができる。特に、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼は、それぞれ、前述したような潤滑剤51を外歯33上に効果的に保持させる適切な結晶粒径を実現しやすく、また、機械的強度および加工性のバランスに優れている。そのため、外歯33をニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つで構成することで、外歯33の機械的強度を優れたものとしつつ、潤滑剤51を外歯33上により効果的に保持させることができる。なお、可撓性歯車3の外歯33の表面が前述したような材料で構成されていればよいが、前述したような効果を顕著なものとするため、歯底部まで前述したような材料で構成することが好ましい。更には可撓性歯車3全体を前述したような材料で構成すれば同様な効果を得つつ製造が比較的容易になる。また、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼、マルエージング鋼および析出硬化型ステンレス鋼のうちのいずれか1つに他の物質を添加した材料で外歯33を構成してもよい。
The metal material constituting the
また、潤滑剤51は、グリースであっても潤滑油であってもよいが、グリースであることが好ましい。すなわち、潤滑剤51は、基油および増ちょう剤を含んでいることが好ましい。これにより、潤滑剤51を固体状または半固体状のグリースとすることができる。したがって、潤滑剤51を必要箇所に留まらせやすくすることができる。ここで、増ちょう剤としては、例えば、カルシウム石けん、カルシウム複合石けん、ナトリウム石けん、アルミニウム石けん、リチウム石けん、リチウム複合石けん等の石けん系、また、ポリウレア、ナトリウムテレフタメート、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)、有機ベントナイト、シリカゲル等の非石けん系等が挙げられ、これらのうちの1種を単独でまたは2種以上を組み合わせて用いることができるが、リチウム石けんを用いることが好ましい。増ちょう剤としてリチウム石けんを用いることにより、潤滑剤51のせん断安定性を優れたものとすることができる。また、潤滑剤51の潤滑剤としての特性のバランスを優れたものとすることができる。
The
また、基油としては、例えば、パラフィン系、ナフテン系等の鉱油(精製鉱物油)、ポリオレフィン、エステル、シリコーン等の合成油が挙げられ、これらのうちの1種を単独でまたは2種以上を組み合わせて用いることができる。 Examples of the base oil include mineral oils such as paraffin-based and naphthen-based oils (refined mineral oils), synthetic oils such as polyolefins, esters, and silicones, and one of these may be used alone or in combination of two or more. Can be used in combination.
また、潤滑剤51が基油および増ちょう剤を含む場合、潤滑剤51は、酸化防止剤、極圧剤、防錆剤等の添加剤、また、黒鉛、硫化モリブデン、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)等の固体潤滑剤等を含んでいることが好ましい。これにより、長期にわたり高い最大非焼付き荷重および融着荷重を発揮可能な潤滑剤51を容易に得ることができる。
When the
特に、潤滑剤51が極圧剤を含んでいることが好ましい。これにより、潤滑対象部が極圧潤滑状態となっても、焼き付きやスカッフィングを効果的に防止することができる。特に、極圧剤として、有機モリブデン化合物、ジアルキルジチオリン酸亜鉛を用いることが好ましい。
In particular, it is preferable that the
潤滑剤51が有機モリブデン化合物を含んでいることにより、潤滑対象部における摩擦を効果的に低減することができる。特に、有機モリブデンは、二硫化モリブデンと同等の極圧性および耐摩耗性を発揮し、しかも、二硫化モリブデンに比べて酸化安定性に優れる。そのため、潤滑剤51の長寿命化を図ることができる。ここで、潤滑剤51中における有機モリブデン化合物の含有量は、例えば、1質量%以上5質量%以下の範囲内にあることが好ましい。また、潤滑剤51中におけるジアルキルジチオリン酸亜鉛の含有量は、例えば、1質量%以上5質量%以下の範囲内にあることが好ましい。
Since the
<第2実施形態>
次に、本発明の第2実施形態について説明する。
図6は、本発明の第2実施形態に係る歯車装置を示す縦断面図である。
<Second Embodiment>
Next, the second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
FIG. 6 is a vertical sectional view showing a gear device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
なお、以下の説明では、本実施形態に関し、前述した実施形態との相違点を中心に説明し、同様の事項に関してはその説明を省略する。 In the following description, the present embodiment will be mainly described with respect to the differences from the above-described embodiment, and the description of the same matters will be omitted.
図6に示す歯車装置1Aは、剛性歯車2の内側に配置されているハット型の外歯車である可撓性歯車3Aを有している。
The
この可撓性歯車3Aは、軸線aまわりに筒状をなす胴部31の軸線a方向での一端部側に軸線aとは反対側に突出して設けられたフランジ部32Aを有する。このような形状の可撓性歯車3Aによっても、剛性歯車2に対する可撓性歯車3Aの良好な撓み噛み合いを実現することができる。また、フランジ部32Aに入力軸または出力軸を安定的に接続することができる。
The
本実施形態では、フランジ部32Aには、軸線aに沿って貫通した複数の孔322Aが形成されている。この孔322Aには、出力側の軸体をフランジ部32Aに固定するためのネジを挿通するネジ孔として用いることができる。また、フランジ部32Aの内周部321Aには、出力側の軸体を挿通することができる。
In the present embodiment, the
このように、歯車装置1Aは、内歯23を有する「内歯車」である剛性歯車2と、内歯23に部分的に噛み合う外歯33を有する可撓性の「外歯車」である可撓性歯車3Aと、可撓性歯車3Aを撓めて剛性歯車2と可撓性歯車3Aとの噛み合い位置を周方向に移動させる波動発生器4と、を有する。ここで、歯車装置1Aは、互いに噛み合う内歯23および外歯33と、内歯23と外歯33との間に配置されている潤滑剤51と、を有する。そして、前述した第1実施形態と同様、外歯33の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が内歯23の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さい。
As described above, the
以上説明したような第2実施形態によっても、潤滑剤51の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。
The lubrication life of the
<第3実施形態>
次に、本発明の第3実施形態について説明する。
<Third Embodiment>
Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
図7は、本発明の第3実施形態に係る歯車装置を示す分解斜視図である。図8は、図7に示す歯車装置の縦断面図である。 FIG. 7 is an exploded perspective view showing a gear device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 8 is a vertical cross-sectional view of the gear device shown in FIG. 7.
なお、以下の説明では、本実施形態に関し、前述した実施形態との相違点を中心に説明し、同様の事項に関してはその説明を省略する。 In the following description, the present embodiment will be mainly described with respect to the differences from the above-described embodiment, and the description of the same matters will be omitted.
図7および図8に示す歯車装置200は、円柱状の外形を有する本体部202を備えている。本体部202の軸線方向での一方側には、第1回転軸203が設けられ、一方、本体部202の軸線方向での他方側には、第2回転軸204が設けられている。第1回転軸203および第2回転軸204は、互いに同一の中心軸205を中心として回動する。ここで、中心軸205は、本体部202の軸線と同一線上に配置されている。本体部202を固定した状態で第1回転軸203を回動させると、その回動が後述するような本体部202内の機構によって減速されて第2回転軸204から出力される。つまり、第1回転軸203が高速回転する入力軸であり、第2回転軸204が低速回転する出力軸となる。
The
図7に示すように、歯車装置200は、空洞部206cを有する円筒形のリングギア206を備えている。リングギア206の内周には、複数のギア歯206aが形成されている。また、リングギア206の内側には、リングギア206の内周よりも少し小さい外周を有する第1公転ギア207および第2公転ギア208が設置されている。第1公転ギア207の外周には、ギア歯206aの歯数よりも少ない数の複数のギア歯207aが配置され、第2公転ギア208の外周には、ギア歯207aの歯数と同じ数の複数のギア歯208aが配置されている。そして、ギア歯207aおよびギア歯208aがギア歯206aと噛み合っている。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
第1公転ギア207の中央には、軸孔207bが設けられ、同様に、第2公転ギア208の中央には、軸孔208bが設けられている。軸孔207bには、第1ベアリング209が設置され、同様に、軸孔208bには、第2ベアリング210が設置されている。
A shaft hole 207b is provided in the center of the
第1回転軸203には、中心軸205に対して互いに反対側に同量偏心している円形カムである第1偏心カム211および第2偏心カム212が設置されている。そして、第1偏心カム211が第1ベアリング209の内輪に設置され、同様に、第2偏心カム212が第2ベアリング210の内輪に設置されている。これにより、ギア歯207aがギア歯206aと噛み合う部分と、ギア歯208aがギア歯206aと噛み合う部分との間に、中心軸205が位置している。
The first
第1公転ギア207には、第1公転ギア207の中央を中心とする同心円上の4か所に第1貫通孔207cが設けられている。同様に、第2公転ギア208には、第2公転ギア208の中央を中心とする同心円上の4か所に第2貫通孔208cが設けられている。各第1貫通孔207cおよび各第2貫通孔208cには、それぞれ、第1公転ギア207の自転の動きを取り出すための貫通ピン213が挿入されている。各第1貫通孔207cの内周壁には、弾性を有する略円筒形の第1弾性部214が圧入により嵌めこまれている。同様に、各第2貫通孔208cの内周壁には、弾性を有する略円筒形の第2弾性部215が圧入により嵌めこまれている。ここで、貫通ピン213は、第1弾性部214および第2弾性部215の内側を貫通している。
The
各貫通ピン213は、本体部202の第1回転軸203側において、円板状の下蓋板216に取り付けられ、第2回転軸204側において、ナット217によって円板状の上蓋板218に固定されている。下蓋板216および上蓋板218は、中心軸205の軸方向に沿って並んでおり、リングギア206に対して回動可能となるように隙間をもってリングギア206を挟んでいる。
Each through
下蓋板216の中央には、第1回転軸203が挿入されている中心孔216aが形成されている。そして、第1回転軸203の第1偏心カム211および第2偏心カム212側の一端部が下蓋板216から本体部202内へ突出し、第1回転軸203の他端部が下蓋板216から本体部202外に突出している。上蓋板218の中央には、第2回転軸204が固定されている。そして、上蓋板218の回転に伴って、上蓋板218の回転トルクが第2回転軸204に伝達される。
A
以上のように構成された歯車装置200において、「内歯車」であるリングギア206と「外歯車」である第1公転ギア207および第2公転ギア208との噛み合い部には、図示しないが、前述した第1実施形態の潤滑剤51と同様の潤滑剤が配置されている。そして、第1公転ギア207および第2公転ギア208のそれぞれの外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径は、リングギア206の内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さい。
In the
以上説明したような第3実施形態によっても、潤滑剤の潤滑寿命を効果的に向上させることができる。 The lubrication life of the lubricant can also be effectively improved by the third embodiment as described above.
以上、本発明のロボットおよび歯車装置を、図示の実施形態に基づいて説明したが、本発明は、これに限定されるものではなく、各部の構成は、同様の機能を有する任意の構成のものに置換することができる。また、本発明に、他の任意の構成物が付加されていてもよい。また、各実施形態を適宜組み合わせてもよい。 The robot and the gear device of the present invention have been described above based on the illustrated embodiment, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the configuration of each part is an arbitrary configuration having the same function. Can be replaced with. Further, any other constituents may be added to the present invention. Moreover, each embodiment may be combined appropriately.
前述した実施形態では、ロボットが備える基台が「第1部材」、第1アームが「第2部材」であり、第1部材から第2部材へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置について説明したが、本発明は、これに限定されず、第n(nは1以上の整数)アームが「第1部材」、第(n+1)アームが「第2部材」であり、第nアームおよび第(n+1)アームの一方から他方へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置についても適用可能である。また、第2部材から第1部材へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置についても適用可能である。 In the above-described embodiment, the gear device in which the base provided by the robot is the "first member" and the first arm is the "second member" and the driving force is transmitted from the first member to the second member has been described. The present invention is not limited to this, and the nth arm (n is an integer of 1 or more) is the "first member", the first (n + 1) arm is the "second member", and the nth arm and the (n + 1) th arm. It is also applicable to a gear device that transmits a driving force from one arm to the other. It is also applicable to a gear device that transmits a driving force from a second member to a first member.
また、前述した実施形態では、6軸の垂直多関節ロボットについて説明したが、本発明は、可撓性歯車を有する歯車装置を用いるものであれば、これに限定されず、例えば、ロボットの関節数は任意であり、また、水平多関節ロボット(スカラロボット)にも適用可能である。 Further, in the above-described embodiment, the 6-axis vertical articulated robot has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this as long as it uses a gear device having a flexible gear, for example, a robot joint. The number is arbitrary, and it can also be applied to a horizontal articulated robot (SCARA robot).
また、本発明は、互いに噛み合う内歯および外歯を有する各種歯車装置に適用可能であり、歯車装置の構成は、前述した実施形態に限定されない。例えば、波動発生器が、玉軸受において内輪の外周面を楕円形とするとともに外輪を弾性変形な薄肉としたような形態であってもよい。 Further, the present invention can be applied to various gear devices having internal teeth and external teeth that mesh with each other, and the configuration of the gear device is not limited to the above-described embodiment. For example, the wave generator may have a ball bearing in which the outer peripheral surface of the inner ring has an elliptical shape and the outer ring has an elastically deformed thin wall.
以下、本発明の具体的な実施例について説明する。
1.歯車装置(減速機)の製造
(実施例1)
図2に示すような構成の歯車装置を製造した。
Hereinafter, specific examples of the present invention will be described.
1. 1. Manufacture of gear device (reducer) (Example 1)
A gear device having a configuration as shown in FIG. 2 was manufactured.
ここで、製造した歯車装置は、内歯車の外径φ60、内歯車の内径および外歯車の外径(かみ合い基準円直径)φ45、減速比50であった。また、内歯車の構成材料として鋳鉄、外歯車の構成材料としてニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼を用いた。また、内歯車の内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径(B)は、20μmであり、外歯車の外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径(A)は、0.5μmであった。 Here, the manufactured gear device had an outer diameter of the internal gear of φ60, an inner diameter of the internal gear and an outer diameter of the external gear (meshing reference circle diameter) of φ45, and a reduction ratio of 50. Cast iron was used as the constituent material of the internal gear, and nickel-chromium molybdenum steel was used as the constituent material of the external gear. The average crystal grain size (B) of the constituent material of the internal teeth of the internal gear was 20 μm, and the average crystal grain size (A) of the constituent material of the external teeth of the external gear was 0.5 μm.
(実施例2〜13、比較例)
内歯車および外歯車の構成材料および平均結晶粒径を表1に示すようにした以外は、前述した実施例1と同様にして歯車装置を製造した。
(Examples 2 to 13, comparative example)
A gear device was manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 described above, except that the constituent materials and the average crystal grain size of the internal gear and the external gear were shown in Table 1.
なお、表1中、SNCM439は、ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼であり、SUS630は、析出硬化型ステンレス鋼であり、鋳鉄は、ダクタイル鋳鉄である。 In Table 1, SNCM439 is nickel-chromium molybdenum steel, SUS630 is precipitation hardening stainless steel, and cast iron is ductile cast iron.
2.評価
前述した1.で得られた各歯車装置について、入力軸回転数:2000rpm、負荷トルク1000Nmにて連続運転を行い、寿命(50%故障確率の入力軸総回転数)を測定した。その結果を表1に併せて示す。
2. Evaluation The above-mentioned 1. For each gear device obtained in the above, continuous operation was performed at an input shaft rotation speed of 2000 rpm and a load torque of 1000 Nm, and the service life (total input shaft rotation speed with a 50% failure probability) was measured. The results are also shown in Table 1.
表1から明らかなように、各実施例は、比較例に比べて、寿命が格段に長くなっていることがわかる。 As is clear from Table 1, each of the examples has a significantly longer life than the comparative example.
1…歯車装置、1A…歯車装置、2…剛性歯車(内歯車)、3…可撓性歯車(外歯車)、3A…可撓性歯車(外歯車)、4…波動発生器、23…内歯、31…胴部、32…底部、32A…フランジ部、33…外歯、41…本体部、42…軸部、43…ローラー、51…潤滑剤、52…潤滑剤、61…噛合部、62…摺動部、100…ロボット、110…制御装置、111…基台(第1部材)、120…ロボットアーム、121…第1アーム(第2部材)、122…第2アーム、123…第3アーム、124…第4アーム、125…第5アーム、126…第6アーム、130…ハンド、131…指、132…指、140…力検出器、150…モーター、200…歯車装置、202…本体部、203…第1回転軸、204…第2回転軸、205…中心軸、206…リングギア、206a…ギア歯、206c…空洞部、207…第1公転ギア、207a…ギア歯、207b…軸孔、207c…第1貫通孔、208…第2公転ギア、208a…ギア歯、208b…軸孔、208c…第2貫通孔、209…第1ベアリング、210…第2ベアリング、211…第1偏心カム、212…第2偏心カム、213…貫通ピン、214…第1弾性部、215…第2弾性部、216…下蓋板、216a…中心孔、217…ナット、218…上蓋板、231…歯面、311…内周面、321…孔、321A…内周部、322…孔、322A…孔、331…歯面、431…外周面、La…長軸、Lb…短軸、a…軸線、a1…軸線 1 ... Gear device, 1A ... Gear device, 2 ... Rigid gear (internal gear), 3 ... Flexible gear (external gear), 3A ... Flexible gear (external gear), 4 ... Wave generator, 23 ... Internal Gears, 31 ... Body, 32 ... Bottom, 32A ... Flange, 33 ... External teeth, 41 ... Main body, 42 ... Shaft, 43 ... Roller, 51 ... Lubricant, 52 ... Lubricant, 61 ... Mesh, 62 ... Sliding part, 100 ... Robot, 110 ... Control device, 111 ... Base (first member), 120 ... Robot arm, 121 ... First arm (second member), 122 ... Second arm, 123 ... First 3 arm, 124 ... 4th arm, 125 ... 5th arm, 126 ... 6th arm, 130 ... hand, 131 ... finger, 132 ... finger, 140 ... force detector, 150 ... motor, 200 ... gear device, 202 ... Main body, 203 ... 1st rotation shaft, 204 ... 2nd rotation shaft, 205 ... Central shaft, 206 ... Ring gear, 206a ... Gear teeth, 206c ... Cavity, 207 ... First revolution gear, 207a ... Gear teeth, 207b ... Shaft hole, 207c ... 1st through hole, 208 ... 2nd revolving gear, 208a ... Gear tooth, 208b ... Shaft hole, 208c ... 2nd through hole, 209 ... 1st bearing, 210 ... 2nd bearing, 211 ... 1 eccentric cam, 212 ... 2nd eccentric cam, 213 ... through pin, 214 ... first elastic part, 215 ... second elastic part, 216 ... lower lid plate, 216a ... center hole, 217 ... nut, 218 ... upper lid plate , 231 ... Tooth surface, 311 ... Inner peripheral surface, 321 ... Hole, 321A ... Inner peripheral part, 322 ... Hole, 322A ... Hole, 331 ... Tooth surface, 431 ... Outer surface, La ... Long axis, Lb ... Short axis, a ... Axis, a1 ... Axis
Claims (8)
前記第1部材に対して回動可能に設けられた第2部材と、
前記第1部材および前記第2部材の一方側から他方側へ駆動力を伝達する歯車装置と、
を備え、
前記歯車装置は、
前記駆動力の伝達経路の途中に設けられ、互いに噛み合う内歯および外歯と、
前記内歯と前記外歯との間に配置されている潤滑剤と、を有し、
前記外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が前記内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さいことを特徴とするロボット。 The first member and
A second member rotatably provided with respect to the first member,
A gear device that transmits a driving force from one side of the first member and the second member to the other side.
With
The gear device
Internal and external teeth that are provided in the middle of the driving force transmission path and mesh with each other,
With a lubricant disposed between the internal teeth and the external teeth,
A robot characterized in that the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the outer tooth is smaller than the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the inner tooth.
前記内歯を有する内歯車と、
前記内歯に部分的に噛み合う前記外歯を有する可撓性の外歯車と、
前記外歯車を撓めて前記内歯車と前記外歯車との噛み合い位置を周方向に移動させる波動発生器と、を有する請求項1ないし6のいずれか1項に記載のロボット。 The gear device
The internal gear having the internal teeth and
A flexible external gear having the external teeth that partially meshes with the internal teeth,
The robot according to any one of claims 1 to 6, further comprising a wave generator that bends the external gear to move the meshing position between the internal gear and the external gear in the circumferential direction.
前記内歯と前記外歯との間に配置されている潤滑剤と、を有し、
前記外歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径が前記内歯の構成材料の平均結晶粒径よりも小さいことを特徴とする歯車装置。 With internal and external teeth that mesh with each other,
With a lubricant disposed between the internal teeth and the external teeth,
A gear device characterized in that the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the outer tooth is smaller than the average crystal grain size of the constituent material of the internal tooth.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/658,798 US10451174B2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2017-07-25 | Robot and gear device |
| CN201710621883.1A CN107662203B (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2017-07-27 | Robot and gear device |
| EP17183492.2A EP3275601B1 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2017-07-27 | Gear device and robot |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016149796 | 2016-07-29 | ||
| JP2016149796 | 2016-07-29 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018025291A JP2018025291A (en) | 2018-02-15 |
| JP2018025291A5 JP2018025291A5 (en) | 2020-06-25 |
| JP6848669B2 true JP6848669B2 (en) | 2021-03-24 |
Family
ID=61195600
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017096344A Active JP6848669B2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2017-05-15 | Robots and gears |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6848669B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108626379B (en) * | 2018-05-10 | 2023-10-20 | 杭州新松机器人自动化有限公司 | Wrist gear transmission side clearance adjusting structure of industrial robot and using method thereof |
| JP7127367B2 (en) * | 2018-06-05 | 2022-08-30 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | ROBOT, GEAR DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING GEAR DEVICE |
| JP7251118B2 (en) * | 2018-11-28 | 2023-04-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | gears and robots |
| CN110842427A (en) * | 2019-12-11 | 2020-02-28 | 金华市乐道门业有限公司 | Novel anti-theft door frame full-automatic welding mechanical arm and working method |
| JP7396178B2 (en) * | 2020-04-13 | 2023-12-12 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | gearing and robots |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5613421A (en) * | 1979-07-09 | 1981-02-09 | Riken Corp | Tough and hard spheroidal graphite cast iron and its manufacture |
| JPS59168045U (en) * | 1983-04-27 | 1984-11-10 | 三菱電機株式会社 | reduction gear |
| JP2002307237A (en) * | 2001-04-09 | 2002-10-23 | Harmonic Drive Syst Ind Co Ltd | Method of manufacturing rigid internal tooth gear for wave motive gear |
| JP2006083905A (en) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-03-30 | Kyushu Institute Of Technology | Wave motion gear device |
| JP2013170295A (en) * | 2012-02-21 | 2013-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method for producing gear, the gear, reduction gear, and robot |
-
2017
- 2017-05-15 JP JP2017096344A patent/JP6848669B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018025291A (en) | 2018-02-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6848669B2 (en) | Robots and gears | |
| US10451174B2 (en) | Robot and gear device | |
| JP6790648B2 (en) | Manufacturing methods for robots, gear devices and gear devices | |
| JP7127367B2 (en) | ROBOT, GEAR DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING GEAR DEVICE | |
| US11067159B2 (en) | Robot, gear device, and gear device unit | |
| CN108687752B (en) | Robot and gear unit | |
| EP3249261B1 (en) | Method for lubricating strain wave gearing | |
| JP6756214B2 (en) | Manufacturing methods for robots, gear devices and gear devices | |
| JP2009041747A (en) | Power transmission device and sliding part structure for power transmission device | |
| US20180031109A1 (en) | Robot, gear device, and manufacturing method for gear device | |
| US11441661B2 (en) | Gear device and robot | |
| US10036463B2 (en) | Robot and gear device | |
| US11285601B2 (en) | Gearing, gearing unit, and robot | |
| US11529731B2 (en) | Gearing and robot | |
| JP2017180526A (en) | Robot, gear device and manufacturing method for gear device | |
| JP2018194094A (en) | Robot, gear unit, and method of manufacturing the gear unit | |
| JP7251118B2 (en) | gears and robots | |
| JP2019078292A (en) | Robot and gear box | |
| JP2019076975A (en) | robot | |
| JP2018199203A (en) | Robot and gear device | |
| JP2018194034A (en) | Robot, gear device, and gear unit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200424 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200424 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20210129 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210202 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210215 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6848669 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |