JP6730264B2 - UV blocking to improve glass transparency - Google Patents
UV blocking to improve glass transparency Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6730264B2 JP6730264B2 JP2017516308A JP2017516308A JP6730264B2 JP 6730264 B2 JP6730264 B2 JP 6730264B2 JP 2017516308 A JP2017516308 A JP 2017516308A JP 2017516308 A JP2017516308 A JP 2017516308A JP 6730264 B2 JP6730264 B2 JP 6730264B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- mol
- glass article
- glass
- zno
- sno
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 title claims description 195
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 title 1
- 238000002835 absorbance Methods 0.000 claims description 47
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 37
- 229910006404 SnO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 34
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 23
- 229910021645 metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910018068 Li 2 O Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 23
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 17
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 17
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 15
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 14
- 239000005358 alkali aluminosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000005354 aluminosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 9
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000006025 fining agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 238000001429 visible spectrum Methods 0.000 description 6
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 229910000272 alkali metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000005407 aluminoborosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000002845 discoloration Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000007654 immersion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- -1 phosphate silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001491 alkali aluminosilicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000006059 cover glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005341 toughened glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 2
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Orthosilicate Chemical compound [O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ozone Chemical compound [O-][O+]=O CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- AFCIMSXHQSIHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O].[P] Chemical compound [O].[P] AFCIMSXHQSIHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011481 absorbance measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001413 alkali metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000323 aluminium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013405 beer Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005388 borosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003426 chemical strengthening reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003841 chloride salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001627 detrimental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002823 nitrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005191 phase separation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009832 plasma treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005368 silicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003283 slot draw process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002791 soaking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005728 strengthening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003467 sulfuric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005496 tempering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009281 ultraviolet germicidal irradiation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005382 zinc containing phosphate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C4/00—Compositions for glass with special properties
- C03C4/08—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths
- C03C4/085—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths for ultraviolet absorbing glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/083—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound
- C03C3/085—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound containing an oxide of a divalent metal
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/083—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound
- C03C3/085—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound containing an oxide of a divalent metal
- C03C3/087—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound containing an oxide of a divalent metal containing calcium oxide, e.g. common sheet or container glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/089—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing boron
- C03C3/091—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing boron containing aluminium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/089—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing boron
- C03C3/091—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing boron containing aluminium
- C03C3/093—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing boron containing aluminium containing zinc or zirconium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/097—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing phosphorus, niobium or tantalum
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Glass Compositions (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Description
本出願は、その内容が依拠され、その全体がここに参照することによって本願に援用される、2014年9月25日出願の米国仮特許出願第62/055,275号の米国法典第35編特許法第119条に基づく優先権の利益を主張する。 This application is incorporated by reference in its entirety herein, and is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety into U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/055,275, filed Sep. 25, 2014, 35th U.S. Code. Claims the benefit of priority under Article 119 of the Patent Act.
本開示は、概略的にはガラス物品に関し、詳細には、紫外線(UV)フォトダークニングに対して耐性のある、カバー又はディスプレイガラスとして用いられるガラス物品に関する。 The present disclosure relates generally to glass articles, and in particular to glass articles used as covers or display glasses that are resistant to ultraviolet (UV) photodarkening.
ガラス、例えば強化ガラスは、携帯電話、スマートフォン、タブレット、ビデオ再生装置、情報端末(IT)装置、ラップトップ型コンピュータ等の携帯用又は移動用電子通信及びエンタテイメント装置のためのカバープレート又はウィンドウとして使用されうる。本明細書において用いられる場合、用語「カバープレート」又は「カバーガラス」には、ディスプレイ及びタッチスクリーン用途、並びに、透明性、高強度及び耐摩耗性を必要とする他の用途におけるウィンドウ等が含まれる。加えて、カバーガラスは、電子機器の背面及び側面等の装飾片として使用されうる。加えて、化学的に強化されていない他のガラスは、ディスプレイガラスとして使用される。 Glass, such as tempered glass, is used as a cover plate or window for portable or mobile electronic communication and entertainment devices such as mobile phones, smartphones, tablets, video playback devices, information terminal (IT) devices, laptop computers and the like. Can be done. As used herein, the term "cover plate" or "cover glass" includes windows and the like in display and touch screen applications, as well as other applications requiring transparency, high strength and abrasion resistance. Be done. In addition, the cover glass can be used as a decorative piece such as a back surface and a side surface of an electronic device. In addition, other glasses that are not chemically strengthened are used as display glasses.
紫外線光への曝露によってガラスに変色を生じ、ディスプレイガラスの鮮明性及び解像度にも影響が及ぶことが分かっている。ガラスは、これらの電子機器に利用されることが多くなっていることから、色の鮮明性及び明瞭なディスプレイ解像度を維持するガラス物品の開発がますます重要になってきている。 It has been found that exposure to ultraviolet light causes discoloration of the glass, which also affects the sharpness and resolution of the display glass. With the increasing use of glass in these electronic devices, it is becoming increasingly important to develop glass articles that maintain color clarity and clear display resolution.
本開示の実施形態は、ガラス物品のUVフォトダークニングを最小限に低減又は排除するUV吸収剤を有するガラス物品を対象とする。本明細書において用いられる場合、「UVフォトダークニング」とは、UV光への曝露の際のガラス物品の変色のことを指す。 Embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to glass articles having UV absorbers that minimize or eliminate UV photodarkening of glass articles. As used herein, "UV photodarkening" refers to the discoloration of a glass article upon exposure to UV light.
一実施形態によれば、ガラス物品が提供される。このガラス物品は、1.3mm以下の厚さを有し、かつ、54〜75モル%のSiO2;8〜17モル%のAl2O3;B2O3及びP2O5のうちの少なくとも1つ、ここで、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である;10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、該R2OはNa2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1種類以上を含む;0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び、無機UV吸収剤を含む。無機UV吸収剤は、0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属イオンがTi、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択されるもの;0超〜500質量ppmまでの1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属が、Mo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択されるもの;又はそれらの組合せを含みうる。
According to one embodiment, a glass article is provided. The glass article has a thickness of 1.3 mm, and, SiO 2 of 54 to 75 mole%; of
別の実施形態によれば、1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品は、0〜12モル%のB2O3;0〜7モル%のP2O5;及び、無機UV吸収剤を含み、3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15モル%である。 According to another embodiment, the glass article having a thickness of less than 1.3mm is from 0 to 12 mole% B 2 O 3; 0~7 mole% of P 2 O 5; and an inorganic UV absorber Including 3 mol%≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦15 mol %.
さらに別の実施形態によれば、アルカリ金属及び酸化物を実質的に含まないガラス物品が提供される。無アルカリガラスは、65〜74モル%のSiO2;11〜13モル%のAl2O3;11〜16モル%のRO、ここで、該ROはMgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1種類以上である;2〜11モル%のB2O3;0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び、無機UV吸収剤を含み、該無機UV吸収剤は、0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属イオンがTi、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択されるもの;0超〜500質量ppmまでの1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属がMo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択されるもの;又はそれらの組合せを含む。
According to yet another embodiment, there is provided a glass article that is substantially free of alkali metals and oxides. Alkali-free glass is 65 to 74 mol% of SiO 2; 11 to 13 mol% of Al 2 O 3; 11~16 mol% of RO, wherein said RO is MgO, CaO, SrO, of BaO and
さらなる実施形態は、ZnO UV吸収剤を対象とする。例えば、一実施形態において、ガラス物品は、54〜75モル%のSiO2;8〜17モル%のAl2O3;0.1〜9モル%のB2O3;場合によってはP2O5、ここで0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である;10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、R2OはNa2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1種類以上を含む;0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び、0.5〜10モル%のZnOを含む。 A further embodiment is directed to ZnO UV absorbers. For example, in one embodiment, the glass article is from 54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2; 8 to 17 mol% of Al 2 O 3; 0.1~9 mol% of B 2 O 3; Optionally P 2 O 5 , where 0.1 mol%≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦19 mol%; 10-20 mol% R 2 O, where R 2 O is Na 2 O, K 2 O, and one or more of Li 2 O; 0 SnO 2 to super to 1 mol%; and containing 0.5 to 10 mol% of ZnO.
さらなる実施形態において、ガラス物品は、54〜75モル%のSiO2;8〜14モル%のAl2O3;0〜12モル%のB2O3;0.1〜7モル%のP2O5;10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、R2OはNa2O、K2O、又はLi2Oのうちの1種類以上を含む;3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15モル%;及び、0.5〜10モル%のZnOを含む。 In a further embodiment, the glass article is from 54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2; 8 to 14 mol% of Al 2 O 3; 0~12 mol% of B 2 O 3; 0.1~7 mol% of P 2 O 5 ; 10 to 20 mol% of R 2 O, where R 2 O includes one or more of Na 2 O, K 2 O, or Li 2 O; 3 mol% ≦B 2 O 3 +P. 2 O 5 ≦15 mol%; and 0.5 to 10 mol% ZnO.
さらに別の実施形態によれば、ガラス物品は、アルカリ金属及び酸化物を実質的に含まず、かつ、65〜74モル%のSiO2;11〜13モル%のAl2O3;11〜16モル%のRO、ここで、該ROはMgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1種類以上であり、かつ、該ガラス物品は0.5〜10モル%のZnOを含む;2〜11モル%のB2O3;及び、0超〜1モル%までのSnO2を含む。 According to yet another embodiment, the glass article is free of alkali metals and oxides substantially, and, SiO 2 of 65 to 74 mol%; 11 to 13 mol% of Al 2 O 3; 11 to 16 Mol% RO, wherein the RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO and ZnO, and the glass article comprises 0.5-10 mol% ZnO; 2-11 2 O 3 mole% of B; and, including SnO 2 of greater than 0 up to 1 mol%.
本開示の特定の実施形態の以下の詳細な説明は、添付の図面と併せて読まれた場合に最も良く理解されうる。 The following detailed description of specific embodiments of the present disclosure can be best understood when read in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
図面に記載される実施形態は、本質的に説明のためのものであって、特許請求の範囲に定義される本発明を限定することは意図されていない。さらには、図面の個々の特徴は、詳細な説明を勘案して、さらに十分に明らかになり、かつ理解されよう。 The embodiments described in the drawings are illustrative in nature and are not intended to limit the invention defined in the claims. Furthermore, the individual features of the drawings will be more fully apparent and understood in view of the detailed description.
ガラス物品の実施形態は、UVフォトダークニングを低減するのに適したUV吸収剤を含む。これらのUV吸収剤がそれら自体にフォトダークニングする傾向がないことを前提条件として、多くのUV吸収剤が、ガラス物品におけるUVフォトダークニングを低減するために予定されている。理論に束縛されるものではないが、UV吸収剤をより低レベルにすることにより、さまざまなガラスにおけるフォトダークニングは、ガラスが強化されているか否かにかかわらず、大幅に低減又は排除されうる。特定の実施形態では、UVフォトダークニングの低減は、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラスに関して達成される。1つ以上の実施形態において、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラスは、アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩、無アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩、アルミノホウケイ酸塩、又はアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラスでありうる。 Embodiments of glass articles include UV absorbers suitable for reducing UV photodarkening. Many UV absorbers are designed to reduce UV photodarkening in glass articles, provided that these UV absorbers do not tend to photodarken to themselves. Without wishing to be bound by theory, lower levels of UV absorbers can significantly reduce or eliminate photodarkening in various glasses, whether or not the glasses are tempered. .. In certain embodiments, UV photodarkening reduction is achieved for aluminosilicate glasses. In one or more embodiments, the aluminosilicate glass can be an alkali aluminosilicate, non-alkali aluminosilicate, aluminoborosilicate, or aluminophosphosilicate glass.
一実施形態において、無機UV吸収剤は、Ti、V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Mo、Ce、Geの1種類以上の金属又は酸化物、又はそれらの組合せを含みうる。特定の実施形態において、無機UV吸収剤は、0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物を含んでよく、該金属イオンは、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択される。これらのUV吸収剤の代替物としては、ガラスの内部に、他の金属のUV吸収剤を、より少ない量で含むことが望ましいであろう。例えば、無機UV吸収剤は、0超(すなわち、ゼロを超える)〜500質量ppm以下までの1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物を含んでよく、該金属は、Mo、Cr、Co及びNi、又はそれらの組合せからなる群より選択される。さらに別の実施形態では、無機UV吸収剤は、150質量ppm以下の1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物を含んでよく、該金属は、Mo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択される。 In one embodiment, the inorganic UV absorber may include one or more metals or oxides of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Mo, Ce, Ge, or combinations thereof. In certain embodiments, the inorganic UV absorber may comprise 0.1-1.0 mol% of one or more metal ions or oxides thereof, wherein the metal ions are Ti, V, Mn, Fe. , Cu, Ce, Ge, and combinations thereof. As an alternative to these UV absorbers, it may be desirable to include smaller amounts of other metallic UV absorbers inside the glass. For example, the inorganic UV absorber may include one or more metals or their oxides from greater than 0 (ie, greater than zero) up to 500 ppm by weight, the metals being Mo, Cr, Co and Ni. , Or a combination thereof. In yet another embodiment, the inorganic UV absorber may comprise up to 150 ppm by weight of one or more metals or oxides thereof, the metals being selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cr, Co and Ni. It
例となる実施形態では、無機UV吸収剤はTiO2である。さまざまな量のUV吸収剤が本明細書において予定されている。例えば、ガラス物品は、0.1〜2モル%の無機UV吸収剤、又は0.1〜1モル%の無機UV吸収剤、又は0.2〜1モル%の無機UV吸収剤、又は約0.3〜0.9モル%の無機UV吸収剤を含みうる。特定の例となる実施形態では、ガラス物品は、0.2〜1モル%のTiO2、又は約0.3〜0.9モル%のTiO2を含みうる。下記の例のほとんどはTiO2の影響について示しているが、有益な影響は、Sb2O3、CeO2、Fe2O3等の他のUV吸収剤によっても達成されうることが、添付の図面に示され、かつ、以下に説明されている。 In an exemplary embodiment, the inorganic UV absorber is TiO 2 . Various amounts of UV absorbers are contemplated herein. For example, a glass article may have 0.1 to 2 mol% inorganic UV absorber, or 0.1 to 1 mol% inorganic UV absorber, or 0.2 to 1 mol% inorganic UV absorber, or about 0. It may contain from 0.3 to 0.9 mol% of inorganic UV absorbers. In embodiments where a particular example, the glass article may comprise 0.2 to 1 mol% of TiO 2, or from about 0.3 to 0.9 mole% of TiO 2. Although most of the examples below show the effect of TiO 2 , it is noted that the beneficial effect can also be achieved with other UV absorbers such as Sb 2 O 3 , CeO 2 , Fe 2 O 3 . Shown in the drawings and described below.
代替的な取り組みは、紫外線(UV)光又はプラズマ洗浄プロセスに曝露されたときに誘起される着色に対して耐性である亜鉛を、ガラスにドープすることである。亜鉛の添加は、深UVへの曝露の間又はプラズマ洗浄による色中心形成に起因した着色を防止するために、任意のガラス組成物に適用することができる。さらに多い量も予定されているが、ガラスは、1つ以上の実施形態において、0.5〜10モル%のZnO、又は1〜10モル%のZnO、又は2〜10モル%のZnO、又は3〜10モル%のZnO、又は5〜10モル%のZnOを含みうる。 An alternative approach is to dope the glass with zinc that is resistant to coloration induced when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light or plasma cleaning processes. The addition of zinc can be applied to any glass composition to prevent coloration during exposure to deep UV or due to color center formation by plasma cleaning. Glass is, in one or more embodiments, 0.5-10 mol% ZnO, or 1-10 mol% ZnO, or 2-10 mol% ZnO, or even higher amounts are contemplated. It may contain 3-10 mol% ZnO, or 5-10 mol% ZnO.
理論に束縛されるものではないが、MgOに替えてZnOを使用することは、軟化点近くでの加熱処理において相分離に対して追加の耐性をもたらすことから、有利である。 Without wishing to be bound by theory, the use of ZnO instead of MgO is advantageous because it provides additional resistance to phase separation during heat treatment near the softening point.
さらには、理論に束縛されるものではないが、UVフォトダークニングの低減を実証するガラス物品は、UV照射への曝露の際に、約270nmのスペクトル波長において2以上のUV吸光度/mm、及び、可視スペクトルにおいて0.025未満の誘起された吸光度を有する。本明細書において用いられる場合、可視スペクトルは400ナノメートル〜700ナノメートルの波長を含み、紫外線(UV)スペクトルは、可視スペクトル未満(すなわち、400nm以下)の波長を含み、特に100〜400nmの波長を含む。さらなる実施形態では、ガラス物品は、約270nmのスペクトル波長において2.2以上のUV吸光度/mm、又は、約270nmのスペクトル波長において2.5以上のUV吸光度/mmを有しうる。さらなる実施形態では、ガラスは、可視スペクトルにおいて0.02以下、又は、可視スペクトルにおいて0.01以下の誘起された吸光度を有しうる。 Furthermore, without wishing to be bound by theory, glass articles demonstrating a reduction in UV photodarkening show that upon exposure to UV radiation, a UV absorbance of 2 or more/mm at a spectral wavelength of about 270 nm, and , Has an induced absorbance of less than 0.025 in the visible spectrum. As used herein, the visible spectrum includes wavelengths from 400 nanometers to 700 nanometers, and the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum includes wavelengths below the visible spectrum (ie, 400 nm or less), particularly wavelengths from 100 to 400 nm. including. In a further embodiment, the glass article can have a UV absorbance/mm of 2.2 or greater at a spectral wavelength of about 270 nm, or a UV absorbance/mm of 2.5 or greater at a spectral wavelength of about 270 nm. In a further embodiment, the glass can have an induced absorbance of 0.02 or less in the visible spectrum, or 0.01 or less in the visible spectrum.
当業者にはよく知られているように、UV吸収剤を使用しない限り、さまざまなUV照射波長が、ガラス物品にUVフォトダークニングを生じさせうる。例えば、UV吸収剤を使用しない場合、28mW cm−1の放射照度で16分間照射される、ある範囲の波長を有するUVオゾン照射への曝露の際に、UVフォトダークニングが生じる可能性がありうる。 As is well known to those skilled in the art, various UV irradiation wavelengths can cause UV photodarkening in glass articles unless a UV absorber is used. For example, without the use of UV absorbers, UV photodarkening can occur upon exposure to UV ozone radiation having a range of wavelengths, which is illuminated for 16 minutes at an irradiance of 28 mW cm −1 . sell.
多くのガラス厚及び組成が予定されている。例えば、ガラス物品は、1.3mm以下の厚さ、又は0.1mm〜1.0mm、又は0.2mm〜0.8mmの厚さを有しうる。例となる実施形態では、ガラス板の厚さは0.7ミリメートル未満であり、主面の各々の面積は、60平方センチメートルより大きい。 Many glass thicknesses and compositions are planned. For example, the glass article may have a thickness of 1.3 mm or less, or 0.1 mm to 1.0 mm, or 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm. In an exemplary embodiment, the glass sheet has a thickness of less than 0.7 millimeters and the area of each major surface is greater than 60 square centimeters.
上述のように、本ガラス物品は、例えばアルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品などのアルミノケイ酸塩ガラスである。一実施形態において、ガラス物品は、54〜75モル%のSiO2及び8〜17モル%のAl2O3を含む。加えて、ガラス物品は、B2O3及びP2O5のうちの少なくとも1つを含み、ここで、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である。さらには、ガラス物品は、12〜20モル%のR2Oを含み、該R2Oは、Na2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1つ以上を含む。
As mentioned above, the glass article is an aluminosilicate glass, such as an alkali aluminosilicate glass article. In one embodiment, the glass article comprises SiO 2 and 8-17
代替的な成分量が、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品について予定されている。例えば、ガラス物品は、約54〜72モル%のSiO2、又は約54〜70モル%のSiO2、又は約54〜65モル%のSiO2を含みうる。あるいは、ガラス物品は、約63〜75モル%のSiO2を含みうる。さらには、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品は、8〜14%のAl2O3、又は、代替的に、11〜17モル%のAl2O3、又は11〜13モル%のAl2O3など、他の予定されている範囲を含みうる。さらには、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品は、13〜19モル%のR2O、又は14〜18モル%のR2Oの範囲のアルカリ量を含みうる。
Alternative component amounts are planned for aluminosilicate glass articles. For example, the glass article may comprise about 54 to 72 mol% of SiO 2, or from about 54 to 70 mole% of SiO 2, or about 54 to 65 mol% of SiO 2. Alternatively, the glass article may include about 63-75 mol% SiO 2 . Further, silicate glass article aluminosilicate, 8 to 14% Al 2 O 3, or, alternatively, 11 to 17
上記実施形態において、アルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品は、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19を含みうる;しかしながら、アルミノホウケイ酸塩又はアルミノリンケイ酸塩については、ガラス物品は、1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15、又は3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15モル%、又は2モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦10、又は3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦8を含みうる。特定の実施形態において、アルミノリンケイ酸塩が、最大で7モル%のP2O5、又は0.1〜7モル%のP2O5、又は2〜7モル%のP2O5を含みうるのに対し、アルミノホウケイ酸塩は、最大で8モル%のB2O3、又は2〜8モル%のB2O3を含みうる。さらには、ガラス物品は、Al2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>12モル%、又はAl2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>16モル%、又はAl2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>19モル%を定めうる。
In the above embodiments, the aluminosilicate glass article may include 0.1 mol% ≤ B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≤ 19; however, for aluminoborosilicate or aluminoline silicate, the glass article is 1 mol% ≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦ 15, or 3 mol% ≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦15 mol%, or 2 mol% ≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦10, or 3 mol%≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦8 may be included. Include In certain embodiments, alumino phosphate silicates, up to 7 mol% of P 2 O 5, or 0.1 to 7 mol% of P 2 O 5, or 2 to 7 mol% of P 2 O 5 to sell, aluminoborosilicate may include an 8
別の実施形態では、ガラス物品はアルカリ土類成分を含みうる。これらのアルカリ土類成分は、最大で17モル%のRO量で含まれてよく、該ROは、MgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1種類以上である。さらなる実施形態では、ガラス物品は、0〜7モル%のRO、又は0〜4モル%のROを含みうる。 In another embodiment, the glass article may include an alkaline earth component. These alkaline earth components may be contained in a maximum amount of 17 mol% RO, which RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO and ZnO. In a further embodiment, the glass article may comprise 0-7 mol% RO, or 0-4 mol% RO.
さらには、ガラス物品の組成は、式:−3.5<R2O+RO−Al2O3<10によって定められうる。さらなる実施形態では、ガラス物品は、式:−3.5<R2O+RO−Al2O3<3.5によって定められうる。 Furthermore, the composition of the glass article, wherein: -3.5 <may be defined by the R 2 O + RO-Al 2 O 3 <10. In a further embodiment, the glass article has the formula: -3.5 <may be defined by the R 2 O + RO-Al 2 O 3 <3.5.
加えて、ガラス物品は、0超〜1モル%までのSn又はSnO2、若しくは0.05〜1モル%のSn又はSnO2、若しくは0.1〜1モル%のSn又はSnO2、若しくは0.1〜0.5モル%のSn又はSnO2を含みうる。Snをベースとする清澄剤に加えて、CeO2などの他の清澄剤を使用することが予定されている。ガラス製造業者による、環境に配慮した清澄剤の使用が増大し、As2O3及びSb2O3などの環境に有害な清澄剤の使用が低減してきている。よって、1つ以上の実施形態において、ガラス物品は、As2O3又はSb2O3のうち少なくとも一方を実質的に含まない場合がある。追加の実施形態はまた、フッ素などの他の清澄剤を実質的に含まない場合がある。清澄剤としての有効性に加えて、SnO2は、フォトダークニングの低減にも有効である。例えば、SnO2の包含により、400nmにおいて約0.02の誘起された吸光度を生じる。 In addition, the glass article comprises more than 0 and up to 1 mol% Sn or SnO 2 , or 0.05 to 1 mol% Sn or SnO 2 , or 0.1 to 1 mol% Sn or SnO 2 , or 0. 0.1 to 0.5 mol% Sn or SnO 2 may be included. In addition to Sn-based fining agents, it is planned to use other fining agents such as CeO 2 . The use of environmentally friendly fining agents by glass manufacturers is increasing and the use of environmentally harmful fining agents such as As 2 O 3 and Sb 2 O 3 is decreasing. Thus, in one or more embodiments, the glass article may be substantially free of at least one of As 2 O 3 or Sb 2 O 3 . Additional embodiments may also be substantially free of other fining agents such as fluorine. In addition to its effectiveness as a fining agent, SnO 2 is also effective in reducing photodarkening. For example, the inclusion of SnO 2 results in an induced absorbance at 400 nm of about 0.02.
UVフォトダークニングに対する耐性の改善は、無アルカリのアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品についても達成されうる。これらの無アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス組成物は、65〜72モル%のSiO2、11〜13モル%のAl2O3;11〜16モル%のRO、ここで、該ROはMgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1種類以上である;2〜11モル%のB2O3;0超〜1モル%までのSn又はSnO2;及び、0.1〜1モル%の先に挙げた無機UV吸収剤を含みうる。別の実施形態において、無アルカリのアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品は、0〜3モル%のP2O5又は0〜2モル%のP2O5を含みうる。 Improved resistance to UV photodarkening can also be achieved for alkali-free aluminosilicate glass articles. These alkali-free aluminosilicate glass composition, 65 to 72 mol% of SiO 2, 11 to 13 mol% of Al 2 O 3; 11~16 mol% of RO, wherein said RO is MgO, CaO, One or more of SrO, BaO and ZnO; 2 to 11 mol% B 2 O 3 ; more than 0 to 1 mol% Sn or SnO 2 ; and 0.1 to 1 mol% first. The inorganic UV absorbers mentioned may be included. In another embodiment, aluminosilicate glass article of alkali-free may include P 2 O 5 0-3 mol% of P 2 O 5, or 0-2 mol%.
上述のように、本開示のガラス物品の幾つかは、強化されたガラス物品である。典型的には、ガラス物品、特にアルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス物品は、イオン交換によって化学的に強化されうる。このプロセスにおいて、ガラスの表層内のイオンは、同じ価数又は酸化状態を有する、より大きいイオンで置換又は交換される。ガラス物品が、アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラスを含む、アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラスから本質的になる、又はアルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラスからなる実施形態において、ガラスの表層内のイオン及びより大きいイオンの両方は、例えばLi+(ガラス中に存在する場合)、Na+、K+、Rb+、及びCs+などの一価のアルカリ金属カチオンである。あるいは、表層内の一価のカチオンは、例えばAg+等のアルカリ金属カチオン以外の一価のカチオンに置き換えられうる。 As mentioned above, some of the glass articles of the present disclosure are toughened glass articles. Typically, glass articles, especially alkali aluminosilicate glass articles, can be chemically strengthened by ion exchange. In this process, the ions in the surface of the glass are replaced or exchanged with larger ions having the same valence or oxidation state. In embodiments where the glass article comprises, consists essentially of, or consists of, an alkali aluminosilicate glass, both the ions in the surface of the glass and the larger ions are, for example, Monovalent alkali metal cations such as Li + (when present in glass), Na + , K + , Rb + , and Cs + . Alternatively, the monovalent cations in the surface layer can be replaced with monovalent cations other than alkali metal cations such as Ag + .
イオン交換プロセスは、典型的には、ガラス内のより小さいイオンと交換されるより大きいイオンを含む溶融塩浴中にガラス物品を浸漬させることによって行われる。浴の組成及び温度、浸漬時間、塩浴(1つ又は複数)中へのガラスの浸漬回数、複数の塩浴の使用、例えばアニール、洗浄等の追加の工程などを含むがそれらに限られない、イオン交換プロセスのパラメータは、概して、ガラスの組成及び層の所望の深さ、並びに、強化作業の結果生じるガラスの圧縮応力によって決定されることが当業者に認識されよう。例として、アルカリ金属含有ガラスのイオン交換は、より大きいアルカリ金属イオンの硝酸塩、硫酸塩、及び塩化物などの塩を含むがこれらに限定されない、少なくとも1つの溶融浴に浸漬することによって達成されうる。浸漬時間は約15分間から最大で約40時間である一方、溶融塩浴の温度は、典型的には、約380℃から最高で約450℃の範囲内にある。しかしながら、上記のものと異なる温度及び浸漬時間も用いられうる。 The ion exchange process is typically performed by immersing the glass article in a molten salt bath containing larger ions that are exchanged for smaller ions in the glass. Including but not limited to bath composition and temperature, soaking time, number of times the glass is soaked in salt bath(s), use of multiple salt baths, additional steps such as annealing, cleaning, etc. It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the parameters of the ion exchange process are generally determined by the composition of the glass and the desired depth of the layers, and the compressive stress in the glass resulting from the tempering operation. By way of example, ion exchange of alkali metal-containing glasses can be accomplished by immersion in at least one molten bath, including but not limited to salts of larger alkali metal ions such as nitrates, sulfates, and chlorides. .. Immersion times range from about 15 minutes up to about 40 hours, while molten salt bath temperatures are typically in the range of about 380°C up to about 450°C. However, different temperatures and immersion times than those described above may also be used.
加えて、ガラスが、浸漬と浸漬との間に洗浄及び/又はアニール工程を有する、複数のイオン交換浴に浸漬される、イオン交換プロセスの非限定的な例は、ガラスが異なる濃度の塩浴中での複数の連続したイオン交換処理において浸漬される、2008年7月11日出願の米国仮特許出願第61/079,995号の優先権を主張する、「民生用途のための圧縮表面を有するガラス(Glass with Compressive Surface for Consumer Applications)」という発明の名称の下、Douglas C.Allanらによる2009年7月10日出願の米国特許出願第12/500,650号明細書;及び、第1の浴でのイオン交換によるガラスが流出イオンで希釈され、その後、第1の浴よりも流出イオンの濃度が低い第2の浴に浸漬される、2008年7月29日出願の米国仮特許出願第61/084,398号の優先権を主張する、「ガラスの科学的強化のための二段イオン交換(Dual Stage Ion Exchange for Chemical Strengthening of Glass)」という発明の名称の下、2012年11月20日に発行されたChristopher M.Leeらによる米国特許第8,312,739号明細書に記載されている。米国特許出願第12/500,650号明細書及び米国特許第8,312,739号明細書の内容は、その全体が、参照することによって本願に援用される。さらには、本開示のガラス組成物は、例えばスロットドロー、フュージョンドロー、再ドロー等の当技術分野で知られたプロセスによって下方に延伸可能であり、少なくとも13000Pa・s(130キロポアズ)の液相粘度を有する。 In addition, a non-limiting example of an ion exchange process in which the glass is immersed in multiple ion exchange baths with a cleaning and/or annealing step between the immersions is a salt bath in which the glass has different concentrations. Claiming priority of US Provisional Patent Application No. 61/079,995, filed Jul. 11, 2008, which is immersed in multiple sequential ion exchange treatments in "compressed surfaces for consumer applications. Under the name of the invention "Glass with Compressive Surface for Consumer Applications". Allan et al., U.S. patent application Ser. No. 12/500,650, filed Jul. 10, 2009; and the glass from the ion exchange in the first bath was diluted with effluent ions and then from the first bath. Also claims priority to US Provisional Patent Application No. 61/084,398, filed July 29, 2008, which is immersed in a second bath having a low concentration of effluent ions, "for scientific strengthening of glass. Under the title of the invention "Dual Stage Ion Exchange for Chemical Strengthening of Glass", Christopher M., published on November 20, 2012. See Lee et al., U.S. Pat. No. 8,312,739. The contents of US patent application Ser. No. 12/500,650 and US Pat. No. 8,312,739 are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. Further, the glass compositions of the present disclosure can be drawn downward by processes known in the art such as slot draw, fusion draw, redraw, and the like, and have a liquidus viscosity of at least 13000 Pa·s (130 kilopoise). Have.
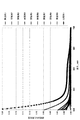
表1〜5に記載される組成物を含む実験の試料を、1mm厚の約2.54cm(1インチ)直径のディスクにカットし、表面を研磨した。16分間のUVへの曝露(米国カリフォルニア州アーバイン所在のJelight Co.のUVO cleaner model 7576)の前後に、分光光度計によって試料のスペクトルを得た。図1〜7のグラフは、さまざまなガラスについてのUVへの曝露後の可視スペクトルを示している。 Experimental samples containing the compositions described in Tables 1-5 were cut into 1 mm thick discs of approximately 2.54 cm (1 inch) diameter and the surface was polished. Spectra of the samples were obtained by a spectrophotometer before and after 16 minutes of UV exposure (UVO cleaner model 7576, Jelight Co., Irvine, Calif., USA). The graphs of Figures 1-7 show the visible spectra after exposure to UV for various glasses.
本図面及び開示に実証されるように、ガラス試料を、吸光度及び誘起された吸光度測定に基づいて比較した。吸光度は、ベールの法則を使用してスペクトルから計算し、ここで、吸光度=−log(透過度)である。試料における誘起された吸光度は、コンピュータによって次のように算出される:誘起された吸光度(A)=−log(試験後の透過度/試験前の透過度) As demonstrated in this figure and disclosure, glass samples were compared based on absorbance and induced absorbance measurements. Absorbance was calculated from the spectrum using Beer's law, where Absorbance=−log(transmittance). The induced absorbance in the sample is calculated by the computer as follows: Induced absorbance (A)=-log (permeability after test/permeability before test).
TiO2含量に対する吸光度が、これらの試料について図1〜3にプロットされている。 The absorbance against TiO 2 content is plotted in Figures 1-3 for these samples.
実施例1〜9を参照すると、実施例1から実施例9までTiO2の組成が増大している。図1を参照すると、実施例1における0.1のTiO2の添加により、TiO2を含まない比較例1と比較して、270nmのUV波長において、吸光度/mmがおよそ1.0から1.5まで増加している。さらには、実施例1から実施例2〜9へのTiO2の増加により、270nmのUV波長において、吸光度/mmがおよそ1.0から少なくとも2.0まで増加している。図2及び3に示されるものと同様に、TiO2の添加は、誘起された吸光度におけるかなりの改善を示している。図3に示されるように、TiO2の添加は、誘起された吸光度を大いにかつ望ましく低下させる。特に、実施例2〜9では、400nmにおける誘起された吸光度は、比較例1と比較して、0.0に近い。 Referring to Examples 1-9, the composition of TiO 2 is increased from Example 1 to Example 9. Referring to FIG. 1, the addition of 0.1 TiO 2 in Example 1 results in an absorbance/mm of approximately 1.0 to 1. at a UV wavelength of 270 nm as compared to Comparative Example 1 which does not contain TiO 2 . It has increased to 5. Furthermore, the increase in TiO 2 from Example 1 to Examples 2-9 increases the absorbance/mm from approximately 1.0 to at least 2.0 at the UV wavelength of 270 nm. Similar to that shown in Figures 2 and 3, the addition of TiO 2 show a significant improvement in the induced absorbance. As shown in FIG. 3, the addition of TiO 2 is greatly and thereby desirably reduces the induced absorbance. In particular, in Examples 2-9, the induced absorbance at 400 nm is closer to 0.0 compared to Comparative Example 1.
図4は、これらの試料についてのTiO2含量の影響のプロットを示している。 FIG. 4 shows a plot of the effect of TiO 2 content for these samples.
上記表2における実施例10〜16を参照すると、TiO2の増加により、強化されていない無アルカリのディスプレイガラスにおけるUVフォトダークニングも低下する。示されるように、実施例10から実施例16までTiO2の組成が増加している。図4を参照すると、TiO2を含まない比較例2では、400nmにおいて0.01より大きく、より長い可視波長において0.01未満に低下するにすぎないのに対し、実施例10〜16におけるTiO2の添加にでは、UVで誘起された吸光度は400〜450nmの可視範囲において0.01(1%)未満に低下する。
Referring to examples 10 to 16 in Table 2, the increase in TiO 2, also decreases UV photodarkening in display glass alkali-free unreinforced. As shown, the composition of TiO 2 increases from Example 10 to Example 16. Referring to FIG. 4, Comparative Example 2 containing no TiO 2 only dropped to greater than 0.01 at 400 nm and less than 0.01 at longer visible wavelengths, whereas
図5は、表3の試料についてのUVフォトダークニングにおけるZnO含量の影響を示している。 FIG. 5 shows the effect of ZnO content in UV photodarkening for the samples in Table 3.
上記表3における実施例17〜19を参照すると、ZnOの増加により、UVフォトダークニングが低下している。図5に示されるように、ZnOを含まない比較例3では、400nmにおいて0.01より大きく、より長い可視波長、すなわち、約600nm以上において0.01未満に低下するにすぎないのに対し、実施例17〜19におけるZnOの添加では、UVで誘起された吸光度は、400〜700nmの可視範囲において0.01(1%)未満に低下する。 Referring to Examples 17 to 19 in Table 3 above, UV photodarkening is decreased due to an increase in ZnO. As shown in FIG. 5, in Comparative Example 3 containing no ZnO, the wavelength is more than 0.01 at 400 nm and longer than visible wavelength, that is, less than 0.01 at about 600 nm or more. With the addition of ZnO in Examples 17-19, the UV-induced absorbance drops below 0.01 (1%) in the visible range of 400-700 nm.
図6は、表4の試料についてのUVフォトダークニングにおけるZnO含量の影響を示している。 FIG. 6 shows the effect of ZnO content in UV photodarkening for the samples in Table 4.
上記表4における実施例20〜26を参照すると、ZnOの増加により、また、強化されていない無アルカリのディスプレイガラスにおけるUVフォトダークニングも低減される。図6に示されるように、ZnOを含まない比較例4の誘起された吸光度が400nmにおいて0.01より大きく、より長い可視波長において0.01未満に低下するにすぎないのに対し、実施例20〜26におけるZnOの添加では、UVで誘起された吸光度は、400〜700nmの可視範囲において0.01(1%)未満に低下する。 Referring to Examples 20-26 in Table 4 above, increasing ZnO also reduces UV photodarkening in unreinforced, alkali-free display glass. As shown in FIG. 6, the induced absorbance of Comparative Example 4 without ZnO is greater than 0.01 at 400 nm and only drops to less than 0.01 at longer visible wavelengths. With the addition of ZnO at 20-26, the UV-induced absorbance drops below 0.01 (1%) in the visible range of 400-700 nm.
図7は、表5のアルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラスにおけるZnO及びTiO2の影響を示している。 FIG. 7 shows the effect of ZnO and TiO 2 in the alkali aluminosilicate glass of Table 5.
上記表5における実施例27〜35を参照すると、ZnO及びTiO2の増加によって、UVフォトダークニングは、比較例5の400nmにおける約0.06(6%)から、2.44モル%のZnO及び0.29モル%のTiO2を有する実施例35ではほぼ0まで相乗的に低下する。 Referring to examples 27 to 35 in Table 5, the increase of ZnO and TiO 2, UV photodarkening from about 0.06 (6%) in the 400nm Comparative Example 5, 2.44 mol% of ZnO And Example 35 with 0.29 mol% TiO 2 decreases synergistically to almost zero.
理論に束縛されるものではないが、Zn含有リン酸ガラスは、UV光、並びにX−線照射に曝露される場合に、非常に安定でありうる。比較例5は、主にZnOと交換されるMgOを含む。UVへの曝露は、電子を受け取ることによってFe3+をFe2+へと光還元する。MgOは、次に、生じたFe2+を安定化することができ、リン−酸素正孔中心(POHC)の生成を有害な方法で促進する。UV曝露下において、これらの電子は励起され、電子の色中心及び/又は正孔中心を形成しうる。これらの色中心は、特定の波長の光、特に可視範囲の光を吸収し、それによって変色を生じる。POHC集団もまた、酸素プラズマ処理で処理した後に大幅に増加しうる。ここでは、MgOをZnOで置換することによって、このFe2+のMgO安定化を最小限にし、それによって、可視範囲の変色につながる電子の色中心の数を実質的に最小限に抑える。 Without being bound by theory, Zn-containing phosphate glasses can be very stable when exposed to UV light as well as X-ray irradiation. Comparative Example 5 mainly contains MgO that is exchanged with ZnO. Exposure to UV photoreduces Fe 3+ to Fe 2+ by accepting electrons. MgO, in turn, can stabilize the resulting Fe 2+ and promote the formation of phosphorus-oxygen hole centers (POHC) in a detrimental way. Under UV exposure, these electrons may be excited to form electron color centers and/or hole centers. These color centers absorb light of a particular wavelength, especially in the visible range, thereby causing discoloration. POHC populations can also increase significantly after treatment with oxygen plasma treatment. Here, substitution of MgO with ZnO minimizes the MgO stabilization of this Fe 2+ , thereby substantially minimizing the number of electron color centers that lead to discoloration in the visible range.
図8は、表6のアルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラスにおけるSnO2の影響を示している。 FIG. 8 shows the effect of SnO 2 in the alkali aluminosilicate glass of Table 6.
上記表6における実施例36〜44を参照すると、SnO2の増加により、例えば、アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラス(実施例36及び37)、アルカリアルミノホウケイ酸塩ガラス(実施例38及び39)、及びアルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラス(実施例40〜42)、無アルカリのディスプレイガラス(実施例43及び44)などのすべての種類のガラスについてUVフォトダークニングが相乗的に低下する。アルカリアルミノケイ酸塩ガラスの例と比較して、0.2モル%のSnO2を含む試料37が400nmにおいて約0.02の誘起された吸光度を有するのに対し、0モル%のSnO2を含む試料36は、400nmにおいて、約0.06の誘起された吸光度を有する。同様に、0.2モル%のSnO2を含むアルカリアルミノホウケイ酸塩ガラスの試料39が400nmにおいて約0.02の誘起された吸光度を有するのに対し、0モル%のSnO2を含むアルカリアルミノホウケイ酸塩ガラスの試料38は、400nmにおいて約0.12の誘起された吸光度を有する。 Referring to examples 36 to 44 in Table 6, the increase of SnO 2, for example, the alkali aluminosilicate glass (Examples 36 and 37), alkali aluminoborosilicate glass (Examples 38 and 39), and alkali UV photodarkening is synergistically reduced for all types of glass, including aluminosilicate glass (Examples 40-42), alkali-free display glass (Examples 43 and 44). Sample 37, which contains 0.2 mol% SnO 2 has an induced absorbance of about 0.02 at 400 nm, compared to the example of an alkali aluminosilicate glass, while it contains 0 mol% SnO 2 . Sample 36 has an induced absorbance at 400 nm of about 0.06. Similarly, sample 39 of an alkali aluminoborosilicate glass containing 0.2 mol% SnO 2 has an induced absorbance at 400 nm of about 0.02, whereas alkali aluminoborosilicate glass containing 0 mol% SnO 2 was used. Borosilicate glass sample 38 has an induced absorbance at 400 nm of about 0.12.
最も際立った改善は、アルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラス試料について実証されている。特に、0.1モル%のSnO2を含むアルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラス試料41が400nmにおいて約0.04の誘起された吸光度を有するのに対し、0モル%のSnO2を含む試料40は、400nmにおいて約0.16の誘起された吸光度を有する。さらには、より多くのSnO2、すなわち0.2モル%のSnO2を含むアルカリアルミノリンケイ酸塩ガラス試料42は、400nmにおいて約0.02の誘起された吸光度を有する。イオン交換されたアルカリ含有ガラス(実施例36〜42)と同様に、SnO2はまた、無アルカリの強化されていないディスプレイガラス(実施例43及び44)におけるフォトダークニングも低減させる。特に、0.2モル%のSnO2を含むディスプレイガラス試料44は、400nmにおいて約0.01の誘起された吸光度を有するのに対し、0モル%のSnO2を含む試料43は、400nmにおいて約0.04の誘起された吸光度を有する。 The most significant improvement is demonstrated for the alkali aluminosilicate glass samples. In particular, the alkali aluminosilicate glass sample 41 with 0.1 mol% SnO 2 has an induced absorbance at 400 nm of about 0.04, while the sample 40 with 0 mol% SnO 2 has It has an induced absorbance of about 0.16 at 400 nm. Moreover, the alkali aluminosilicate glass sample 42 with more SnO 2 , ie 0.2 mol% SnO 2, has an induced absorbance of about 0.02 at 400 nm. Like the ion-exchanged alkali-containing glass (Example 36 - 42), SnO 2 also photodarkening in display glass unreinforced non-alkali (Examples 43 and 44) also reduces. In particular, the display glass sample 44 containing 0.2 mol% SnO 2 has an induced absorbance of about 0.01 at 400 nm, while the sample 43 containing 0 mol% SnO 2 has about 400 nm. It has an induced absorbance of 0.04.
さらには、「好ましくは」、「概して」、「一般に」、及び「典型的には」等の用語は、本明細書では、特許請求される本発明の範囲を限定する目的、又は、ある特定の特徴が、特許請求される本発明の構造又は機能にとって重大、本質的、又は重要であるという意味を含める目的では用いられないことに留意されたい。むしろ、これらの用語は、単に、本開示の特定の実施形態に用いられても用いられなくてもよい、代替的又は追加的な特徴を強調することが意図されている。 Furthermore, terms such as "preferably," "generally," "generally," and "typically" are used herein to limit the scope of the invention as claimed, or to a certain extent. It should be noted that the above features are not used for the purpose of including meanings which are significant, essential, or important to the structure or function of the claimed invention. Rather, these terms are merely intended to highlight alternative or additional features that may or may not be used in particular embodiments of the present disclosure.
添付の特許請求の範囲に定められる本開示の範囲から逸脱することなく、修正及び変形が可能であることは明白であろう。より詳細には、本開示の一部の態様は、ここでは、好ましい又は特に有利であるとして認定されているが、本開示は、これらの態様に必ずしも限定する必要がないことが予定されている。 It will be apparent that modifications and variations are possible without departing from the scope of the disclosure as defined by the appended claims. More particularly, some aspects of the present disclosure have been identified herein as preferred or particularly advantageous, but it is contemplated that the present disclosure need not necessarily be limited to these aspects. ..
以下、本発明の好ましい実施形態を項分け記載する。 The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below item by item.
実施形態1
1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品において、
54〜75モル%のSiO2;
8〜17モル%のAl2O3;
B2O3及びP2O5のうちの少なくとも1つ、ここで、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である;
10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、該R2OはNa2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1つ以上を含む;
0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び
無機UV吸収剤であって、
0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はその酸化物であって、該金属イオンが、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択される、金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物;
0超〜500質量ppmまでの1種類以上の金属又はその酸化物であって、該金属が、Mo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択される、金属又はそれらの酸化物;又は
それらの組合せ
を含む、無機UV吸収剤
を含む、ガラス物品。
Embodiment 1
In a glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less,
54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2;
8 to 17 mole% of Al 2 O 3;
At least one of B 2 O 3 and P 2 O 5 , where 0.1 mol% ≤ B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≤ 19 mol%;
10-20 mol% of R 2 O, wherein said R 2 O comprises one or more of Na 2 O, K 2 O, and Li 2 O;
A and inorganic UV absorbers,; 0 SnO 2 to super to 1 mole%
0.1-1.0 mol% of one or more metal ions or oxides thereof, wherein the metal ions consist of Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ce, Ge, and combinations thereof. Selected from metal ions or their oxides;
More than 0 to 500 ppm by mass of one or more metals or oxides thereof, the metals being selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cr, Co and Ni; or their oxides; or their A glass article comprising an inorganic UV absorber, including a combination.
実施形態2
前記ガラス物品が、式:−3.5<R2O+RO−Al2O3<10
によって定められることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
It said glass article has the formula: -3.5 <R 2 O + RO -Al 2 O 3 <10
2. The glass article according to embodiment 1, characterized by being defined by:
実施形態3
前記ガラス物品が強化されたガラス物品であることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 3
The glass article according to embodiment 1, wherein the glass article is a reinforced glass article.
実施形態4
前記ガラス物品が、約270nmのスペクトル波長において2以上のUV吸光度/mm、及び400〜700nmの少なくとも1つの波長について0.025未満の誘起された吸光度を有することを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 4
In embodiment 1, wherein the glass article has a UV absorbance of 2 or more/mm at a spectral wavelength of about 270 nm and an induced absorbance of less than 0.025 for at least one wavelength of 400-700 nm. The glass article described.
実施形態5
前記無機UV吸収剤が、0.2〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物を含み、前記金属イオンが、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択されることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 5
The inorganic UV absorber contains 0.2 to 1.0 mol% of one or more kinds of metal ions or oxides thereof, and the metal ions are Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ce, Ge, And the glass article according to Embodiment 1, which is selected from the group consisting of: and a combination thereof.
実施形態6
前記ガラス物品が、0.05〜1モル%のSnO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 6
Said glass article, characterized in that it comprises a SnO 2 of 0.05 to 1 mol%, the glass article according to the first embodiment.
実施形態7
0.1〜17モル%のROをさらに含み、該ROが、MgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1つ以上であることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 7
The glass article according to embodiment 1, further comprising 0.1 to 17 mol% RO, wherein the RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO and ZnO.
実施形態8
前記ガラス物品の前記厚さが0.1〜1.0mmであることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 8
The glass article according to embodiment 1, wherein the thickness of the glass article is 0.1 to 1.0 mm.
実施形態9
前記ガラス物品が、54〜65モル%のSiO2、11〜17モル%のAl2O3、0〜8モル%のB2O3、0〜4モル%のRO、0〜7モル%のP2O5、13〜19モル%のR2Oを含み、かつ、Al2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>19モル%であることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 9
Said glass article, 54-65 mol% of SiO 2, 11 to 17 mol% of Al 2 O 3, 0 to 8
実施形態10
前記無機UV吸収剤が、150質量ppm以下の1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物を含み、該金属がMo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択されることを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiments characterized in that the inorganic UV absorber comprises 150 ppm or less by mass of one or more metals or oxides thereof, the metals being selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cr, Co and Ni. 1. The glass article according to 1.
実施形態11
前記ガラス物品が、0〜12モル%のB2O3、0〜7モル%のP2O5、及び、3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15モル%を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態1に記載のガラス物品。
Characterized in that said glass article, 0-12 mol% of B 2 O 3, 0 to 7 mol% of P 2 O 5, and containing 3 mol% ≦ B 2 O 3 + P 2 O 5 ≦ 15 mol% The glass article according to Embodiment 1.
実施形態12
1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品であって、該ガラス物品がアルカリ金属及び酸化物を実質的に含まず、かつ、
65〜74モル%のSiO2;
11〜13モル%のAl2O3;
11〜16モル%のRO、ここで、該ROはMgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1種類以上である;
2〜11モル%のB2O3;
0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び
無機UV吸収剤において、
0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属イオンが、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択される、金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物;
0超〜500質量ppmまでの1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物であって、該金属が、Mo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択される、金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物;又は
それらの組合せ
を含む無機UV吸収剤
を含む、ガラス物品。
A glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less, the glass article being substantially free of alkali metals and oxides, and
65 to 74 mol% of SiO 2;
11-13 mol% Al 2 O 3 ;
11-16 mol% RO, where the RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO and ZnO;
2 to 11 mol% of B 2 O 3;
In and inorganic UV absorbers,; 0 SnO 2 to super to 1 mole%
0.1-1.0 mol% of one or more metal ions or oxides thereof, wherein the metal ions consist of Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ce, Ge, and combinations thereof. Metal ions or their oxides selected from the group;
More than 0 to 500 ppm by mass of one or more metals or their oxides, wherein the metal is selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cr, Co and Ni; metal ions or their oxides; or A glass article comprising an inorganic UV absorber comprising a combination thereof.
実施形態13
前記無機UV吸収剤が、150質量ppm以下の1種類以上の金属又はそれらの酸化物を含み、該金属が、Mo、Cr、Co及びNiからなる群より選択されることを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
Implementation, characterized in that the inorganic UV absorber comprises one or more metals or oxides thereof in an amount of 150 mass ppm or less, the metal being selected from the group consisting of Mo, Cr, Co and Ni. A glass article according to
実施形態14
前記無機UV吸収剤が、0.2〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物を含み、該金属イオンが、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択されることを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
The inorganic UV absorber contains 0.2 to 1.0 mol% of one or more kinds of metal ions or oxides thereof, and the metal ions are Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ce, Ge, And a combination thereof, the glass article according to
実施形態15
前記ガラス物品が、0.1〜1モル%のSnO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
Said glass article, characterized in that it comprises a SnO 2 of 0.1 to 1 mol%, the glass article of
実施形態16
前記ガラス物品が、約270nmのスペクトル波長において2以上のUV吸光度/mm、及び400〜700nmの少なくとも1つの波長について0.025未満の誘起された吸光度を有することを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
In
実施形態17
前記ガラス物品の前記厚さが0.1〜1.0mmであることを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
The glass article according to
実施形態18
前記ガラス物品が0〜3モル%のP2O5を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態12に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 18.
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a P 2 O 5 0-3 mol%, the glass article of
実施形態19
1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品において、
54〜75モル%のSiO2;
8〜17モル%のAl2O3;
0.1〜9モル%のB2O3;
場合によっては、P2O5、ここで、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である;
10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、該R2OはNa2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1つ以上を含む;
0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;及び
0.5〜10モル%のZnO
を含む、ガラス物品。
Embodiment 19.
In a glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less,
54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2;
8 to 17 mole% of Al 2 O 3;
0.1 to 9 mol% of B 2 O 3;
Optionally P 2 O 5 , where 0.1 mol% ≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦19 mol%;
10-20 mol% of R 2 O, wherein said R 2 O comprises one or more of Na 2 O, K 2 O, and Li 2 O;
0 SnO up super to 1 mole% 2; and 0.5 to 10 mol% of ZnO
Including glass articles.
実施形態20
前記ガラス物品が、63〜75モル%のSiO2及び8〜14モル%のAl2O3を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Said glass article, characterized in that it comprises SiO 2 and 8 to 14
実施形態21
前記ガラス物品が、式:−3.5<R2O+RO−Al2O3<10によって定められることを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Said glass article has the formula: -3.5 <characterized in that it is defined by R 2 O + RO-Al 2 O 3 <10, the glass article of embodiment 19.
実施形態22
前記ガラス物品が1〜10モル%のZnOを含むことを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Glass article according to embodiment 19, characterized in that said glass article comprises 1 to 10 mol% ZnO.
実施形態23
前記ガラス物品が強化されたガラス物品であることを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
20. A glass article according to embodiment 19, characterized in that the glass article is a reinforced glass article.
実施形態24
前記ガラス物品が、400〜700nmの少なくとも1つの波長について0.01未満の誘起された吸光度を有することを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Glass article according to embodiment 19, characterized in that the glass article has an induced absorbance of less than 0.01 for at least one wavelength between 400 and 700 nm.
実施形態25
前記ガラス物品が0.05〜1モル%のSnO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a SnO 2 of 0.05 to 1 mol%, the glass article of embodiment 19.
実施形態26
前記ガラス物品が0.5〜17モル%のROを含み、該ROが、MgO、CaO、SrO、ZnO、及びBaOのうちの1つ以上であることを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
20. Embodiment 19 characterized in that the glass article comprises 0.5 to 17 mol% RO, which RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, ZnO, and BaO. Glass articles.
実施形態27
前記ガラス物品の前記厚さが0.1〜1.0であることを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 27
Glass article according to embodiment 19, characterized in that the thickness of the glass article is 0.1-1.0.
実施形態28
前記ガラス物品が、54〜65モル%のSiO2、11〜17モル%のAl2O3、0.1〜8モル%のB2O3、0〜4モル%のRO、0〜7モル%のP2O5、13〜19モル%のR2O、及び、Al2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>19モル%を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態19に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 28
Said glass article, 54-65 mol% of SiO 2, 11 to 17 mol% of Al 2 O 3, 0.1 to 8 mole% of B 2 O 3, 0 to 4 mol% of RO, 0 to 7 mol % P 2 O 5 , 13-19 mol% R 2 O, and the total of Al 2 O 3 +B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 >19 mol%. Glass articles.
実施形態29
1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品において、
54〜75モル%のSiO2;
8〜14モル%のAl2O3;
0〜12モル%のB2O3;
0.1〜7モル%のP2O5;
10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、該R2OはNa2O、K2O、又はLi2Oのうち1つ以上を含む;
3モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦15モル%;及び
0.5〜10モル%のZnO
を含む、ガラス物品。
Embodiment 29
In a glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less,
54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2;
Of 8 to 14
0-12 mol% of B 2 O 3;
0.1-7 mol% P 2 O 5 ;
10-20 mol% R 2 O, wherein the R 2 O comprises one or more of Na 2 O, K 2 O, or Li 2 O;
3 mol%≦B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≦15 mol%; and 0.5-10 mol% ZnO
Including glass articles.
実施形態30
前記ガラス物品が63〜75モル%のSiO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 30
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a SiO 2 of 63 to 75 mol%, the glass article of embodiment 29.
実施形態31
前記ガラス物品が1〜10モル%のZnOを含むことを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 31
30. The glass article of embodiment 29, wherein the glass article comprises 1-10 mol% ZnO.
実施形態32
前記ガラス物品が式:−3.5<R2O+RO−Al2O3<10によって定められることを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 32
Said glass article has the formula: -3.5 <characterized in that it is defined by R 2 O + RO-Al 2 O 3 <10, the glass article of embodiment 29.
実施形態33
前記ガラス物品が強化されたガラス物品であることを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 33
30. The glass article according to embodiment 29, wherein the glass article is a reinforced glass article.
実施形態34
前記ガラス物品が400〜700nmの少なくとも1つの波長について0.01未満の誘起された吸光度を有することを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 34
Glass article according to embodiment 29, characterized in that the glass article has an induced absorbance of less than 0.01 for at least one wavelength between 400 and 700 nm.
実施形態35
前記ガラス物品が0.05〜1モル%のSnO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 35
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a SnO 2 of 0.05 to 1 mol%, the glass article of embodiment 29.
実施形態36
前記ガラス物品が0.5〜17モル%のROを含み、該ROが、MgO、CaO、SrO、ZnO、及びBaOのうちの1種類以上であることを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 36
Embodiment 29, wherein the glass article comprises 0.5 to 17 mol% RO, wherein the RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, ZnO, and BaO. Glass articles.
実施形態37
前記ガラス物品の前記厚さが0.1〜1.0mmであることを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 37
30. The glass article according to embodiment 29, wherein the thickness of the glass article is 0.1-1.0 mm.
実施形態38
前記ガラス物品が、54〜65モル%のSiO2、11〜17モル%のAl2O3、0〜8モル%のB2O3、0〜4モル%のRO、0.1〜7モル%のP2O5、13〜19モル%のR2O、及びAl2O3+B2O3+P2O5の合計>19モル%を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態29に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 38
Said glass article, 54-65 mol% of SiO 2, 11 to 17 mol% of Al 2 O 3, 0 to 8 mol% of B 2 O 3, 0 to 4 mol% of RO, 0.1 to 7 moles % of P 2 O 5, characterized in that it contains 13 to 19 mol% of R 2 O, and the sum of the Al 2 O 3 + B 2 O 3 + P 2 O 5> 19 mol%, of embodiment 29 Glass articles.
実施形態39
1.3mm以下の厚さを有するガラス物品であって、該ガラス物品がアルカリ金属及び酸化物を実質的に含まず、かつ、
65〜74モル%のSiO2;
11〜13モル%のAl2O3;
11〜16モル%のRO、ここで、該ROはMgO、CaO、SrO、BaO及びZnOのうちの1つ以上であり、かつ、前記ガラス物品は0.5〜10モル%のZnOを含む;
2〜11モル%のB2O3;及び
0超〜1モル%までのSnO2
を含む、ガラス物品。
Embodiment 39
A glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less, the glass article being substantially free of alkali metals and oxides, and
65 to 74 mol% of SiO 2;
11-13 mol% Al 2 O 3 ;
11-16 mol% RO, wherein the RO is one or more of MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO and ZnO, and the glass article comprises 0.5-10 mol% ZnO;
2 to 11 mol% of B 2 O 3; and 0 SnO 2 to super to 1 mole%
Including glass articles.
実施形態40
前記ガラス物品が1〜10モル%のZnOを含むことを特徴とする、実施形態39に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 40
40. The glass article of embodiment 39, wherein the glass article comprises 1-10 mol% ZnO.
実施形態41
前記ガラス物品が400〜700nmの少なくとも1つの波長について0.01未満の誘起された吸光度を有することを特徴とする、実施形態39に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 41
40. The glass article according to embodiment 39, wherein the glass article has an induced absorbance of less than 0.01 for at least one wavelength of 400-700 nm.
実施形態42
前記ガラス物品が0.1〜1モル%のSn又はSnO2を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態39に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 42
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a 0.1 to 1 mole percent of Sn or SnO 2, glass article of embodiment 39.
実施形態43
前記ガラス物品の前記厚さが0.1〜1.0mmであることを特徴とする、実施形態39に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 43
The glass article according to embodiment 39, wherein the thickness of the glass article is 0.1-1.0 mm.
実施形態44
前記ガラス物品が0〜3モル%のP2O5を含むことを特徴とする、実施形態39に記載のガラス物品。
Embodiment 44
It said glass article is characterized in that it comprises a P 2 O 5 0-3 mol%, the glass article of embodiment 39.
Claims (8)
54〜75モル%のSiO2;
8〜17モル%のAl2O3;
B2O3及びP2O5のうちの少なくとも1つ、ここで、0.1モル%≦B2O3+P2O5≦19モル%である;
10〜20モル%のR2O、ここで、該R2OはNa2O、K2O、及びLi2Oのうちの1つ以上を含む;
0超〜1モル%までのSnO2;
0.5〜10モル%のZnO;及び
0.1〜1.0モル%の1種類以上の金属イオン又はその酸化物であって、該金属イオンが、Ti、V、Mn、Fe、Cu、Ce、Ge、及びそれらの組合せからなる群より選択される、金属イオン又はそれらの酸化物を含む無機UV吸収剤;
を含む、ガラス物品。 In a glass article having a thickness of 1.3 mm or less,
54 to 75 mol% of SiO 2;
8 to 17 mole% of Al 2 O 3;
At least one of B 2 O 3 and P 2 O 5 , where 0.1 mol% ≤ B 2 O 3 +P 2 O 5 ≤ 19 mol%;
10-20 mol% of R 2 O, wherein said R 2 O comprises one or more of Na 2 O, K 2 O, and Li 2 O;
0 SnO up super to 1 mole% 2;
0.5-10 mol% ZnO; and
0 . 1 to 1.0 mol% of one or more metal ions or oxides thereof, wherein the metal ions are selected from the group consisting of Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ce, Ge, and combinations thereof. is the metal ion or including no machine UV absorbers and their oxides;
Including glass articles.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201462055275P | 2014-09-25 | 2014-09-25 | |
| US62/055,275 | 2014-09-25 | ||
| PCT/US2015/052103 WO2016049400A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 | 2015-09-25 | Uv blocking for improved transmission glasses |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017533877A JP2017533877A (en) | 2017-11-16 |
| JP2017533877A5 JP2017533877A5 (en) | 2018-11-15 |
| JP6730264B2 true JP6730264B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 |
Family
ID=54291647
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017516308A Active JP6730264B2 (en) | 2014-09-25 | 2015-09-25 | UV blocking to improve glass transparency |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US10501365B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3197841B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6730264B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102530039B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN107001113B (en) |
| TW (2) | TWI695821B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2016049400A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI695821B (en) * | 2014-09-25 | 2020-06-11 | 美商康寧公司 | Glass articles |
| WO2016069821A1 (en) * | 2014-10-31 | 2016-05-06 | Corning Incorporated | Dimensionally stable fast etching glasses |
| EP3390313A1 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2018-10-24 | Corning Incorporated | Ion exchangeable glass with fast diffusion |
| EP3490950A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2019-06-05 | Corning Incorporated | Glasses having resistance to photo-darkening |
| CN106746601B (en) * | 2016-12-30 | 2019-06-04 | 东旭集团有限公司 | It is used to prepare the composition, glassware and purposes of glass |
| CN107032604A (en) | 2017-04-18 | 2017-08-11 | 东旭科技集团有限公司 | Glass composition, alkaline earth aluminates glass and its preparation method and application |
| CN107226614A (en) * | 2017-05-16 | 2017-10-03 | 东旭科技集团有限公司 | A kind of glass composition and glass and its preparation method and application |
| US11028007B2 (en) | 2017-06-22 | 2021-06-08 | Corning Incorporated | Automotive glass compositions, articles and hybrid laminates |
| KR102673755B1 (en) | 2018-06-19 | 2024-06-11 | 코닝 인코포레이티드 | High strain point and high Young's modulus glass |
| DE102018116483A1 (en) | 2018-07-06 | 2020-01-09 | Schott Ag | Chemically toughened glasses with high chemical resistance and crack resistance |
| US11634354B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 | 2023-04-25 | Corning Incorporated | Colored glass articles having improved mechanical durability |
| US11597674B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 | 2023-03-07 | Corning Incorporated | Colored glass articles having improved mechanical durability |
| US12054422B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 | 2024-08-06 | Corning Incorporated | Colored glass articles having improved mechanical durability |
| US11667562B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 | 2023-06-06 | Corning Incorporated | Colored glass articles having improved mechanical durability |
| US11560329B1 (en) | 2021-10-04 | 2023-01-24 | Corning Incorporated | Colored glass articles having improved mechanical durability |
| US11802072B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 | 2023-10-31 | Corning Incorporated | Gold containing silicate glass |
Family Cites Families (44)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1393118A (en) | 1971-09-16 | 1975-05-07 | Pilkington Brothers Ltd | Manufacture of flat glass |
| US4287380A (en) | 1979-09-18 | 1981-09-01 | Emhart Industries, Inc. | Electrode assembly for molten glass forehearth |
| US4429402A (en) | 1981-11-04 | 1984-01-31 | Corning Glass Works | Devices for use in a glass-melting furnace |
| US4433419A (en) | 1982-04-23 | 1984-02-21 | Owens-Corning Fiberglas Corporation | Electrode purge sleeve for glass melting furnaces |
| US4862477A (en) | 1988-09-01 | 1989-08-29 | Manville Corporation | Apparatus and method for melting and homogenizing batch material |
| US5151918A (en) | 1990-08-28 | 1992-09-29 | Argent Ronald D | Electrode blocks and block assemblies |
| US5153151A (en) * | 1991-05-06 | 1992-10-06 | Corning Incorporated | High index fluorine-free phosphate glasses |
| KR100262115B1 (en) | 1995-09-28 | 2000-07-15 | 기시다 기요사쿠 | Alkali-free glass substrate |
| US5932501A (en) | 1995-10-18 | 1999-08-03 | Corning Incorporated | High-index glasses that absorb UV radiation |
| DE19616633C1 (en) | 1996-04-26 | 1997-05-07 | Schott Glaswerke | Chemically toughenable alumino-silicate glass |
| DE19916296C1 (en) | 1999-04-12 | 2001-01-18 | Schott Glas | Alkali-free aluminoborosilicate glass and its use |
| DE19934072C2 (en) * | 1999-07-23 | 2001-06-13 | Schott Glas | Alkali-free aluminoborosilicate glass, its uses and processes for its manufacture |
| DE19939789A1 (en) * | 1999-08-21 | 2001-02-22 | Schott Glas | Alkali-free aluminoborosilicate glasses and their uses |
| JP2001316128A (en) | 2000-03-02 | 2001-11-13 | Nippon Sheet Glass Co Ltd | Pale colored high transmittance plate-glass and method for manufacturing same |
| KR20050025182A (en) * | 2002-05-16 | 2005-03-11 | 쇼오트 아게 | Uv-blocking borosilicate glass, the use of the same, and a fluorescent lamp |
| DE102004007436B4 (en) | 2004-02-16 | 2017-11-16 | Schott Ag | Use of a B2O3-free crystallization-stable aluminosilicate glass and its preparation |
| DE102004022629B9 (en) * | 2004-05-07 | 2008-09-04 | Schott Ag | Flooded lithium aluminosilicate flat glass with high temperature resistance, which can be preloaded chemically and thermally and its use |
| US7435696B2 (en) | 2005-07-15 | 2008-10-14 | Vidrio Plano De Mexico, S.A. De C.V. | Glass composition with high visible light transmission and low ultraviolet light transmission |
| EP2075237B1 (en) * | 2006-10-10 | 2019-02-27 | Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd. | Reinforced glass substrate |
| JP5282572B2 (en) | 2006-11-10 | 2013-09-04 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Glass substrate for flat panel display, manufacturing method thereof, and display panel using the same |
| FR2909374B1 (en) | 2006-11-30 | 2016-11-25 | Soc En Nom Collectif Dite : Eurokera | CLEAR, COLORLESS, COLORLESS BETA-QUARTZ GLAZE WITH LOW TIO2 CONTENT; ARTICLES THEREOF VITROCERAMIC; PRECURSOR GLASSES, METHODS OF PREPARATION |
| US7666511B2 (en) | 2007-05-18 | 2010-02-23 | Corning Incorporated | Down-drawable, chemically strengthened glass for cover plate |
| CN101074146B (en) | 2007-06-16 | 2010-10-06 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Low-expansion coefficient glass for absorbing ultraviolet |
| JP5467490B2 (en) | 2007-08-03 | 2014-04-09 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Method for producing tempered glass substrate and tempered glass substrate |
| EP2307328A1 (en) | 2008-07-11 | 2011-04-13 | Corning Incorporated | Glass with compressive surface for consumer applications |
| US8504330B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2013-08-06 | Nec Laboratories America, Inc. | Parallelizing bounded model checking using tunnels over a distributed framework |
| WO2010014163A1 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2010-02-04 | Corning Incorporated | Dual stage ion exchange for chemical strengthening of glass |
| US8341976B2 (en) | 2009-02-19 | 2013-01-01 | Corning Incorporated | Method of separating strengthened glass |
| TWI543948B (en) | 2009-05-07 | 2016-08-01 | 日本電氣硝子股份有限公司 | Glass substrate and fabricating method thereof |
| US8361915B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2013-01-29 | Vidrio Plano De Mexico, S.A. De C.V. | Glass composition |
| US8759238B2 (en) | 2010-05-27 | 2014-06-24 | Corning Incorporated | Ion exchangeable glasses |
| JPWO2011158366A1 (en) | 2010-06-17 | 2013-08-15 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Glass substrate and manufacturing method thereof |
| US8916487B2 (en) | 2010-06-30 | 2014-12-23 | Hoya Corporation | Glass substrate for information recording medium |
| US20120052271A1 (en) * | 2010-08-26 | 2012-03-01 | Sinue Gomez | Two-step method for strengthening glass |
| TW201245080A (en) * | 2011-03-17 | 2012-11-16 | Asahi Glass Co Ltd | Glass for chemical strengthening |
| CN102690059B (en) * | 2011-03-23 | 2016-08-03 | 肖特玻璃科技(苏州)有限公司 | Aluminosilicate glass for chemical tempering and glass ceramics |
| BR112014011561A2 (en) | 2011-11-16 | 2017-05-09 | Corning Inc | cracking initiation high threshold ion exchange glass |
| JP5954690B2 (en) * | 2012-06-18 | 2016-07-20 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Non-contact power supply support member |
| WO2014042244A1 (en) * | 2012-09-14 | 2014-03-20 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Glass for chemical toughening, chemically toughened glass and method for producing glass for chemical toughening |
| US9403716B2 (en) * | 2012-09-27 | 2016-08-02 | Corning Incorporated | Glass-ceramic(s); associated formable and/or color-tunable, crystallizable glass(es); and associated process(es) |
| WO2014120641A2 (en) * | 2013-01-31 | 2014-08-07 | Corning Incorporated | Transition metal-containing, ion exchangeable colored glasses |
| CN103641309B (en) * | 2013-11-01 | 2018-10-16 | 何开生 | Absorb glass composition and its application of ultraviolet light and infrared ray |
| EP3107875B1 (en) | 2014-02-20 | 2018-06-13 | Corning Incorporated | Uv photobleaching of glass having uv-induced colorization |
| TWI695821B (en) * | 2014-09-25 | 2020-06-11 | 美商康寧公司 | Glass articles |
-
2015
- 2015-09-25 TW TW104131888A patent/TWI695821B/en active
- 2015-09-25 EP EP15778477.8A patent/EP3197841B1/en active Active
- 2015-09-25 TW TW108118895A patent/TWI771589B/en active
- 2015-09-25 KR KR1020177010799A patent/KR102530039B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2015-09-25 US US14/865,295 patent/US10501365B2/en active Active
- 2015-09-25 WO PCT/US2015/052103 patent/WO2016049400A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-09-25 CN CN201580063781.1A patent/CN107001113B/en active Active
- 2015-09-25 JP JP2017516308A patent/JP6730264B2/en active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-13 US US16/681,960 patent/US11498865B2/en active Active
-
2022
- 2022-10-27 US US17/974,686 patent/US20230061747A1/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3197841A1 (en) | 2017-08-02 |
| TWI771589B (en) | 2022-07-21 |
| TWI695821B (en) | 2020-06-11 |
| US10501365B2 (en) | 2019-12-10 |
| JP2017533877A (en) | 2017-11-16 |
| CN107001113A (en) | 2017-08-01 |
| CN107001113B (en) | 2021-09-10 |
| KR20170058423A (en) | 2017-05-26 |
| US20230061747A1 (en) | 2023-03-02 |
| US20200079682A1 (en) | 2020-03-12 |
| EP3197841B1 (en) | 2021-12-08 |
| US20160090321A1 (en) | 2016-03-31 |
| TW201940447A (en) | 2019-10-16 |
| TW201619089A (en) | 2016-06-01 |
| US11498865B2 (en) | 2022-11-15 |
| KR102530039B1 (en) | 2023-05-08 |
| WO2016049400A1 (en) | 2016-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6730264B2 (en) | UV blocking to improve glass transparency | |
| JP5689075B2 (en) | Glass substrate for display cover glass and method for producing the same | |
| US10865140B2 (en) | X-ray induced coloration in glass or glass-ceramic articles | |
| US10676394B2 (en) | Antimicrobial glass articles and methods of making and using same | |
| JP5589379B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of glass substrate for display cover glass | |
| JP2017511785A (en) | Glass with enhanced strength and antibacterial properties and method for producing the same | |
| US10723652B2 (en) | Tempered and colorless antimicrobial soda lime glass and methods of making and using same | |
| WO2016028554A1 (en) | Antimicrobial articles with copper nanoparticles and methods of making and using same | |
| CN106458723B (en) | Antimicrobial articles having silver-containing alkali silicate coatings and methods of making the same | |
| US11407675B2 (en) | Glasses having resistance to photo-darkening |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180925 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180925 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20181018 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190830 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190911 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20191211 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20200212 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200310 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200603 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200702 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6730264 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |