JP6593802B2 - Inorganic coordination polymers as gelling agents - Google Patents
Inorganic coordination polymers as gelling agents Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6593802B2 JP6593802B2 JP2016554436A JP2016554436A JP6593802B2 JP 6593802 B2 JP6593802 B2 JP 6593802B2 JP 2016554436 A JP2016554436 A JP 2016554436A JP 2016554436 A JP2016554436 A JP 2016554436A JP 6593802 B2 JP6593802 B2 JP 6593802B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- general formula
- lithium
- cyclic
- compound
- substituted
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/056—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte characterised by the materials used as electrolytes, e.g. mixed inorganic/organic electrolytes
- H01M10/0564—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte characterised by the materials used as electrolytes, e.g. mixed inorganic/organic electrolytes the electrolyte being constituted of organic materials only
- H01M10/0565—Polymeric materials, e.g. gel-type or solid-type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
- H01M10/0525—Rocking-chair batteries, i.e. batteries with lithium insertion or intercalation in both electrodes; Lithium-ion batteries
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2300/00—Electrolytes
- H01M2300/0017—Non-aqueous electrolytes
- H01M2300/0065—Solid electrolytes
- H01M2300/0082—Organic polymers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2300/00—Electrolytes
- H01M2300/0085—Immobilising or gelification of electrolyte
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Description
本発明は、非プロトン性有機溶媒にゲル化剤として、一般式(I)のフルオロアルキルリン酸リチウム、
及び電気化学電池の電解質の添加剤としてそれらの使用方法に関する。さらに、本発明は、前記フルオロアルキルリン酸リチウムを含む電解質組成物、及び前記電解質組成物を含む電気化学電池に関する。
The present invention provides a lithium fluoroalkyl phosphate of general formula (I) as a gelling agent in an aprotic organic solvent,
And their use as an additive for electrolytes in electrochemical cells. Furthermore, the present invention relates to an electrolyte composition containing the lithium fluoroalkyl phosphate, and an electrochemical cell containing the electrolyte composition.
電気エネルギーの貯蔵に対する関心は、依然として高まっている。電気エネルギーの効率的貯蔵は、有利な場合には電気エネルギーを生成し、必要な場合には電気エネルギーを使用することを許容する。現在、しばしばリチウムイオン電池とも称されるリチウムイオン蓄電池は、特にノートパソコン及び携帯電話などの携帯型装置において、電気エネルギーの提供に広く使用されており、電動移動体(electric mobility)にも使用されている。鉛又はより低い活性の重金属をベースとする蓄電池より、リチウムイオン電池はより高いエネルギー密度を提供している。 There is still a growing interest in storing electrical energy. Efficient storage of electrical energy produces electrical energy when advantageous and allows the use of electrical energy when necessary. Currently, lithium ion batteries, often referred to as lithium ion batteries, are widely used to provide electrical energy, especially in portable devices such as notebook computers and mobile phones, and are also used in electric mobility. ing. Lithium ion batteries offer higher energy densities than batteries based on lead or lower activity heavy metals.
リチウムイオン電池などの電気化学電池には、カソード、アノード、及び、カソードとアノードとの間のイオン交換のための導電性塩を含有する電解質組成物が含まれている。様々な電解質組成物が知られており、最もよく使用されているのは液体電解質であるが、固体電解質及びゲル電解質も使用されている。 Electrochemical cells, such as lithium ion cells, include an electrolyte composition that includes a cathode, an anode, and a conductive salt for ion exchange between the cathode and the anode. Various electrolyte compositions are known and most commonly used are liquid electrolytes, but solid electrolytes and gel electrolytes are also used.
固体電解質は、イオン拡散により電気を伝導する物質である。好適な物質としては、例えば、ポリエチレンオキシド又はポリフッ化ビニリデンなどのポリマーがある。該ポリマーは導電性塩と混合される。ポリマー電解質は機械的安定性及び低い揮発特性を示すが、電気伝導性が低い。一般的には、液体電解質は、1種以上の溶媒、それに溶媒和する導電性塩及び任意のさらなる添加剤からなる。一般的には、液体電解質は良好なイオン伝導性を示すが、電解質の損失を避けるためには電気化学電池を密封しなければならない。ゲル電解質は、上記の2種の中間にあり、ポリマーなどの固体物質、及びゲルを生成する固体物質に係り、導電性塩を含有する液体溶媒により生成される。通常、ゲルを生成するために、少量の液体溶媒のみが必要である。固体電解質と比較すると、大量の溶媒はゲル電解質の電気伝導性の増大をもたらす。しかも、溶媒はゲル中に固定され、液体電解質より溶媒漏出の危険性が低い。 A solid electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity by ion diffusion. Suitable materials include, for example, polymers such as polyethylene oxide or polyvinylidene fluoride. The polymer is mixed with a conductive salt. Polymer electrolytes exhibit mechanical stability and low volatility properties, but have low electrical conductivity. In general, the liquid electrolyte is composed of one or more solvents, conductive salts solvating thereto, and any additional additives. In general, liquid electrolytes exhibit good ionic conductivity, but electrochemical cells must be sealed to avoid electrolyte loss. The gel electrolyte is in the middle of the above two types, and relates to a solid substance such as a polymer and a solid substance that forms a gel, and is generated by a liquid solvent containing a conductive salt. Usually only a small amount of liquid solvent is required to produce a gel. Compared to a solid electrolyte, a large amount of solvent results in an increase in the electrical conductivity of the gel electrolyte. In addition, the solvent is fixed in the gel and has a lower risk of solvent leakage than the liquid electrolyte.
現在、リチウムイオン電池領域において、より高いエネルギー密度をもたらすより高い電圧の電池に向けて開発が進んでいる。LiCoPO4及びマンガン含有のスピネルなどの高電圧カソード物質はLi/Li+に対して4.5Vを超える電圧を示す。これらの物質と組み合わせで使用される電解質は、良好な電気化学安定性、及び電気化学電池に長い寿命を与えるための電極物質との良好な適合性を示さなければならない。これらの要求は、溶媒、導電性塩、及び電気化学電池の寿命にわたって消耗されない電解質組成物の他の使用可能な成分にも求められる。さらに、良好な電気伝導性及び電解質組成物の高い安全性の要求を満たさなければならない。 Currently, development is progressing towards higher voltage batteries that provide higher energy densities in the lithium ion battery area. High voltage cathode materials such as LiCoPO 4 and manganese-containing spinels exhibit voltages in excess of 4.5V relative to Li / Li + . The electrolyte used in combination with these materials must exhibit good electrochemical stability and good compatibility with the electrode material to give the electrochemical cell a long life. These requirements are also sought for solvents, conductive salts, and other usable components of the electrolyte composition that are not consumed over the life of the electrochemical cell. Furthermore, the requirements for good electrical conductivity and high safety of the electrolyte composition must be met.
本発明は、電気化学電池、特に良好な電気伝導性、安全特性及び高電圧で良好な電気化学安定性を示すリチウムイオン電池の電解質組成物を提供することを目的とする。さらに、本発明は、電気化学電池、特に良好な安全特性及び長い寿命を示すリチウムイオン電池、特に高いエネルギー密度を有する電気化学電池を提供することを目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to provide an electrolyte composition for an electrochemical cell, in particular, a lithium ion battery exhibiting good electrical conductivity, safety characteristics and good electrochemical stability at a high voltage. Furthermore, it is an object of the present invention to provide an electrochemical cell, in particular a lithium ion battery exhibiting good safety characteristics and a long life, in particular an electrochemical cell having a high energy density.
この目的は、一般式(I)、
又は、
R1及びR2は、一緒に結合しており、F及び任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C10−アルキルから選択された1つ以上の置換基により置換されることが可能である、五員又は六員ヘテロ環基を、基−OPO−と共に形成するC2〜C3−アルカンジイルから選択される)
の化合物の使用により達成される。
For this purpose, the general formula (I),
Or
R 1 and R 2 are bonded together and can be substituted with one or more substituents selected from F and optionally fluorinated C 1 -C 10 -alkyl. Selected from C 2 -C 3 -alkanediyl, which forms a membered or six-membered heterocyclic group with the group —OPO—)
Is achieved by the use of
また、この目的は、
(i)少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒、
(ii)少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物、
(iii)少なくとも1種の、一般式(I)の化合物と異なる導電性塩、及び、
(iv)任意に、少なくとも1種のさらなる添加剤、
を含む電解質組成物(A)により、
並びに、電解質組成物(A)を含む電気化学電池により達成される。
This purpose is also
(I) at least one aprotic organic solvent,
(Ii) at least one compound of general formula (I),
(Iii) at least one conductive salt different from the compound of general formula (I), and
(Iv) optionally at least one further additive;
By the electrolyte composition (A) containing
Moreover, it is achieved by an electrochemical cell containing the electrolyte composition (A).
一般式(I)の化合物は、炭酸塩などの有機非プロトン性溶媒の添加により配位ポリマーを生成する。これは、一般式(I)の低分子量化合物が、配位ポリマーと呼ばれる大分子をもたらす配位結合により加えられる溶媒中のLi金属錯体を生成すると理解される。低分子化合物によりの配位ポリマーの生成は、非プロトン性有機溶媒にゲル化剤の効果を有する。非プロトン性有機溶媒中にただ少量の一般式(I)の化合物を存在することは、溶媒(単数又は複数)により充填される配位ポリマーのネットワークにより生成されたゲルを得ることに十分である。非プロトン性有機溶媒、及び一般的に電気化学電池の電解質組成物に使用される溶媒混合物、例えば炭酸塩及びエーテル、の使用が可能である。通例の導電性塩は容易にゲルに加えられる。その結果として、これらのゲルは、溶媒の漏出のより低いリスクを有する電解質組成物の良好な基礎を提供する。電池にNa+又は遷移金属イオンなどの有害なイオンを導入していないので、一般式(I)の化合物をゲル化剤として使用することは、リチウムイオン電池又はリチウム硫黄電池などの、リチウムイオンがアノードとカソードとの間のイオン移動に使用される電気化学電池の電解質組成物に特に有利である。一般式(I)の化合物は、5V以下で電気化学的に安定する。 The compound of general formula (I) produces a coordination polymer by the addition of an organic aprotic solvent such as carbonate. It is understood that the low molecular weight compound of general formula (I) produces a Li metal complex in a solvent that is added by a coordination bond that results in a large molecule called a coordination polymer. Formation of a coordination polymer with a low molecular weight compound has the effect of a gelling agent in an aprotic organic solvent. The presence of only a small amount of a compound of general formula (I) in an aprotic organic solvent is sufficient to obtain a gel produced by a network of coordination polymers filled with solvent (s). . It is possible to use aprotic organic solvents and solvent mixtures such as carbonates and ethers commonly used in electrochemical cell electrolyte compositions. Conventional conductive salts are easily added to the gel. As a result, these gels provide a good basis for electrolyte compositions that have a lower risk of solvent leakage. Since no harmful ions such as Na + or transition metal ions are introduced into the battery, the use of the compound of general formula (I) as a gelling agent is that lithium ions such as lithium ion batteries or lithium sulfur batteries are anodes. It is particularly advantageous for electrochemical cell electrolyte compositions used for ion transfer between the cathode and the cathode. The compound of the general formula (I) is electrochemically stable at 5 V or less.
無機部分の原因で、一般式(I)の化合物及び一般式(I)の化合物により生成する配位ポリマーは、特に置換基R1及び/又はR2がFに置換される場合には、従来の有機ポリマーより低い可燃性を有する。また、電解質組成物の向上された難燃性をもたらす。 Due to the inorganic moiety, the coordination polymer produced by the compound of the general formula (I) and the compound of the general formula (I) is conventionally used when the substituents R 1 and / or R 2 are substituted with F. Lower flammability than other organic polymers. It also provides improved flame retardancy of the electrolyte composition.
本発明の電解質組成物(A)は、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)、好ましくは少なくとも2種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)を含有する。一実施態様によれば、電解質組成物(A)は、10種以下の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)を含有してもよい。 The electrolyte composition (A) of the present invention contains at least one aprotic organic solvent (i), preferably at least two aprotic organic solvents (i). According to one embodiment, the electrolyte composition (A) may contain 10 or less aprotic organic solvents (i).
好ましくは、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)は、
(a)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状及び非環状有機炭酸塩、
(b)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、ジ−C1〜C10−アルキルエーテル、
(c)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、ジ−C1〜C4−アルキル−C2〜C6−アルキレンエーテル及びポリエーテル、
(d)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状エーテル、
(e)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状及び非環状アセタール及びケタール、
(f)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、オルトエステル、
(g)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状及び非環状のカルボン酸エステル、
(h)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状及び非環状スルホン、
(i)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、環状及び非環状ニトリル及びジニトリル、並びに、
(j)部分的にハロゲン化されてもよい、イオン液体、
から選択される。
Preferably, at least one aprotic organic solvent (i) is
(A) cyclic and acyclic organic carbonates, which may be partially halogenated,
(B) may be partially halogenated, di -C 1 -C 10 - alkyl ethers,
(C) may be partially halogenated, di -C 1 -C 4 - alkyl -C 2 -C 6 - alkylene ether and polyethers,
(D) a cyclic ether, which may be partially halogenated,
(E) cyclic and acyclic acetals and ketals, which may be partially halogenated,
(F) orthoesters, which may be partially halogenated,
(G) cyclic and acyclic carboxylic esters that may be partially halogenated,
(H) cyclic and acyclic sulfones, which may be partially halogenated,
(I) cyclic and acyclic nitriles and dinitriles, which may be partially halogenated, and
(J) an ionic liquid, which may be partially halogenated,
Selected from.
より好ましくは、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)は、環状及び非環状有機炭酸塩(a)、ジ−C1〜C10−アルキルエーテル(b)ジ−C1〜C4−アルキル−C2〜C6−アルキレンエーテル及びポリエーテル(c)、並びに、環状エーテル(d)から選択され、さらにより好ましくは、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)は環状及び非環状有機炭酸塩(a)から選択され、最も好ましくは、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)は環状及び非環状有機炭酸塩(a)から選択される少なくとも2種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)の混合物であり、特に好ましくは、少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)は少なくとも1種の環状有機炭酸塩と少なくとも1種の非環状有機炭酸塩との混合物である。 More preferably, at least one aprotic organic solvent (i) is cyclic and acyclic organic carbonates (a), di -C 1 -C 10 - alkyl ether (b) di -C 1 -C 4 - Selected from alkyl-C 2 -C 6 -alkylene ethers and polyethers (c) and cyclic ethers (d), even more preferably, at least one aprotic organic solvent (i) is cyclic and acyclic Selected from organic carbonates (a), most preferably at least one aprotic organic solvent (i) is at least two aprotic organic solvents selected from cyclic and acyclic organic carbonates (a) It is a mixture of (i), particularly preferably the at least one aprotic organic solvent (i) is a mixture of at least one cyclic organic carbonate and at least one acyclic organic carbonate. It is.
非プロトン性有機溶媒(a)〜(j)は部分的にハロゲン化されてもよく、例えば、部分的にフッ素化され、部分的に塩素化され又は部分的に臭素化されてもよく、好ましくは部分的にフッ素化されてもよい。「部分的にハロゲン化され」という用語は、個々の分子の1つ以上のHがハロゲン原子(例えば、F、Cl又はBr)に置換されることを意味する。少なくとも1種の溶媒(i)は部分的にハロゲン化及び非ハロゲン化の非プロトン性有機溶媒(a)〜(j)から選択されてもよく、換言すれば、電解質組成物は部分的にハロゲン化及び非ハロゲン化の非プロトン性有機溶媒の混合物を含んでもよい。 The aprotic organic solvents (a) to (j) may be partially halogenated, for example, partially fluorinated, partially chlorinated or partially brominated, preferably May be partially fluorinated. The term “partially halogenated” means that one or more H of an individual molecule is replaced with a halogen atom (eg, F, Cl or Br). The at least one solvent (i) may be selected from partially halogenated and non-halogenated aprotic organic solvents (a) to (j), in other words, the electrolyte composition is partially halogenated A mixture of halogenated and non-halogenated aprotic organic solvents may be included.
好適な有機炭酸塩(a)の例は、一般式(a1)、(a2)又は(a3)、
の環状有機炭酸塩である。
Examples of suitable organic carbonates (a) are those of the general formula (a1), (a2) or (a3),
The cyclic organic carbonate.
「C1〜C4−アルキル」という用語は、メチル、エチル、n−プロピル、イソ−プロピル、n−ブチル、イソ−ブチル、sec.−ブチル、及びtert.−ブチルを含むことを意味する。 The term “C 1 -C 4 -alkyl” refers to methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, iso-butyl, sec. -Butyl, and tert. -Means containing butyl.
好ましい環状有機炭酸塩(a)は、Ra、Rb及びRcがHである一般式(a1)、(a2)又は(a3)のものである。例としては、炭酸エチレン、炭酸ビニレン及び炭酸プロピレンが挙げられる。好ましい環状有機炭酸塩(a)は炭酸エチレンである。さらに好ましい環状有機炭酸塩(a)は、ジフルオロ炭酸エチレン(a4)及びモノフルオロ炭酸エチレン(a5)である。 Preferred cyclic organic carbonates (a) are those of general formula (a1), (a2) or (a3) where R a , R b and R c are H. Examples include ethylene carbonate, vinylene carbonate and propylene carbonate. A preferred cyclic organic carbonate (a) is ethylene carbonate. Further preferred cyclic organic carbonates (a) are difluoroethylene carbonate (a4) and monofluoroethylene carbonate (a5).
好適な非環状有機炭酸塩(a)の例は、炭酸ジメチル、炭酸ジエチル、炭酸メチルエチル及びそれらの混合物である。 Examples of suitable acyclic organic carbonates (a) are dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate, methyl ethyl carbonate and mixtures thereof.
本発明の一実施態様において、電解質組成物(A)は、1:10〜10:1、好ましくは3:1〜1:1の質量比の、非環状有機炭酸塩(a)と環状有機炭酸塩(a)との混合物を含有する。 In one embodiment of the invention, the electrolyte composition (A) comprises an acyclic organic carbonate (a) and a cyclic organic carbonate in a mass ratio of 1:10 to 10: 1, preferably 3: 1 to 1: 1. Contains a mixture with salt (a).
好適な非環状ジ−C1〜C10−アルキルエーテル(b)の例は、ジメチルエーテル、エチルメチルエーテル、ジエチルエーテル、ジイソプロピルエーテル及びジ−n−ブチルエーテルである。 Examples of suitable acyclic di-C 1 -C 10 -alkyl ethers (b) are dimethyl ether, ethyl methyl ether, diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether and di-n-butyl ether.
ジ−C1〜C4−アルキル−C2〜C6−アルキレンエーテル(c)の例は、1,2−ジメトキシエタン、1,2−ジエトキシエタン、ジグリム(ジエチレングリコールジメチルエーテル)、トリグリム(トリエチレングリコールジメチルエーテル)、テトラグリム(テトラエチレングリコールジメチルエーテル)及びジエチレングリコールジエチルエーテルである。 Examples of di-C 1 -C 4 -alkyl-C 2 -C 6 -alkylene ethers (c) are 1,2-dimethoxyethane, 1,2-diethoxyethane, diglyme (diethylene glycol dimethyl ether), triglyme (triethylene). Glycol dimethyl ether), tetraglyme (tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether) and diethylene glycol diethyl ether.
好適なポリエーテル(c)の例は、ポリアルキレングリコールであり、好ましくはポリ−C1〜C4−アルキレングリコール、特にポリエチレングリコールである。ポリエチレングリコールは、20モル%以下の、1種以上の共重合形態のエチレングリコールを含んでもよい。好ましくは、ポリアルキレングリコールは、ジメチル−又はジエチル−端部キャップされるポリアルキレングリコールである。好適なポリアルキレングリコール及び特に好適なポリエチレングリコールの分子量MWは、少なくとも400g/molであってもよい。好適なポリアルキレングリコール及び特に好適なポリエチレングリコールの分子量MWは、5000000g/mol以下、好ましくは2000000g/mol以下であってもよい。 Examples of suitable polyethers (c) are polyalkylene glycols, preferably poly-C 1 -C 4 -alkylene glycols, especially polyethylene glycol. The polyethylene glycol may contain 20 mol% or less of one or more copolymerized forms of ethylene glycol. Preferably, the polyalkylene glycol is a dimethyl- or diethyl-end-capped polyalkylene glycol. The molecular weight M W of suitable polyalkylene glycols and particularly preferred polyethylene glycol may be at least 400 g / mol. The molecular weight M W of suitable polyalkylene glycols and particularly preferred polyethylene glycol, 5 000 000 g / mol or less, preferably may be less than or equal to 2,000,000 g / mol.
好適な環状エーテル(d)の例は、テトラヒドロフラン及び1,4−ジオキサンである。 Examples of suitable cyclic ethers (d) are tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane.
好適な非環状アセタール(e)の例は、1,1−ジメトキシメタン及び1,1−ジエトキシメタンである。好適な環状アセタール(e)の例は、1,3−ジオキサン及び1,3−ジオキソランである。 Examples of suitable acyclic acetals (e) are 1,1-dimethoxymethane and 1,1-diethoxymethane. Examples of suitable cyclic acetals (e) are 1,3-dioxane and 1,3-dioxolane.
好適なオルトエステル(f)の例は、トリ−C1〜C4−アルコキシメタン、特にトリメトキシメタン及びトリエキシメタンである。好適な環状オルトエステル(f)の例は、1,4−ジメチル−3,5,8−トリオキサビシクロ[2.2.2]オクタン及び4−エチル−1−メチル−3,5,8−トリオキサビシクロ[2.2.2]オクタンである。 Examples of suitable orthoesters (f) are tri-C 1 -C 4 -alkoxymethanes, in particular trimethoxymethane and trieximethane. Examples of suitable cyclic orthoesters (f) are 1,4-dimethyl-3,5,8-trioxabicyclo [2.2.2] octane and 4-ethyl-1-methyl-3,5,8- Trioxabicyclo [2.2.2] octane.
好適な非環状のカルボン酸エステル(g)の例は、酢酸エチル、ブタン酸メチル、及び1,3−プロパン酸二酸ジメチルなどのカルボン酸エステルである。好適な環状のカルボン酸エステルの例はγ−ブチロラクトンである。
Examples of suitable acyclic carboxylic acid esters (g) are carboxylic acid esters such as ethyl acetate, methyl butanoate, and
好適な環状及び非環状スルホンの例は、エチルメチルスルホン、ジメチルスルホン及びテトラヒドロチオフェン−S,S−二酸である。 Examples of suitable cyclic and acyclic sulfones are ethyl methyl sulfone, dimethyl sulfone and tetrahydrothiophene-S, S-dioic acid.
好適な環状及び非環状ニトリル及びジニトリル(i)の例は、アデポジニトリル、アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル及びブチロニトリルである。 Examples of suitable cyclic and acyclic nitriles and dinitriles (i) are adepositonitrile, acetonitrile, propionitrile and butyronitrile.
本発明の電解質組成物の水含有量は、電解質組成物の質量に基づいて、好ましくは100ppm未満、より好ましくは50ppm未満、最も好ましくは30ppm未満である。水含有量は、例えばDIN 51777又はISO760:1978に詳しく記載されているカールフィッシャー滴定により測定することが可能である。 The water content of the electrolyte composition of the present invention is preferably less than 100 ppm, more preferably less than 50 ppm, and most preferably less than 30 ppm, based on the weight of the electrolyte composition. The water content can be measured, for example, by Karl Fischer titration as described in detail in DIN 51777 or ISO 760: 1978.
本発明の電解質組成物のHF含有量は、電解質組成物の質量に基づいて、好ましくは60ppm未満、より好ましくは40ppm未満、最も好ましくは20ppm未満である。HF含有量は、電位差滴定法又は電位グラフ滴定法により測定することが可能である。 The HF content of the electrolyte composition of the present invention is preferably less than 60 ppm, more preferably less than 40 ppm, and most preferably less than 20 ppm based on the mass of the electrolyte composition. The HF content can be measured by potentiometric titration or potential graph titration.
本発明の電解質組成物(A)は、成分(ii)としての少なくとも1種の一般式(I)
又は、R1及びR2は、一緒に結合しており、F及び任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C10−アルキルから選択された1つ以上の置換基により置換されることが可能である、五員又は六員ヘテロ環基を、基−OPO−と共に形成するC2〜C3−アルカンジイルから選択される)
の化合物を含む。
The electrolyte composition (A) of the present invention contains at least one general formula (I) as component (ii).
Or, R 1 and R 2 are bonded together and can be substituted with one or more substituents selected from F and optionally fluorinated C 1 -C 10 -alkyl. , Selected from C 2 -C 3 -alkanediyl which forms a 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic group with the group —OPO—
Of the compound.
R1及びR2は、一緒に結合しており、五員又は六員ヘテロ環基を、基−OPO−と共に形成するC2〜C3−アルカンジイルから選択される一般式(I)の化合物の例は、下記、
である。
Compounds of general formula (I) wherein R 1 and R 2 are bonded together and selected from C 2 -C 3 -alkanediyl which together with the group —OPO— form a 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic group Examples of
It is.
好ましくは、R1及びR2は、互いに独立し、1つ以上のFにより置換されることが可能であるC1〜C4−アルキルから選択され、又は、R 1 及びR 2 は結合しており、及び一緒にF及び任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C10−アルキルから選択された1つ以上の置換基により置換されることが可能であるC2−アルカンジイルから選択される。
Preferably, R 1 and R 2 are, independently of one another, C 1 is capable of being substituted by one or more F -C 4 - is selected from alkyl, or, R 1 and R 2 forming combined and it has, and fluorinated C 1 -
ここで使用された「C1〜C10−アルキル」という用語は、1個〜10個の炭素原子を備え、1の自由原子価を有する直鎖又は分岐の飽和炭化水素を意味し、且つ、例えばメチル、エチル、n−プロピル、イソプロピル、n−ブチル、sec−ブチル、イソ−ブチル、tert−ブチル、n−ペンチル、イソ−ペンチル、2,2−ジメチルプロピル、n−ヘキシル、イソ−ヘキシル、2−エチルヘキシル、n−ヘプチル、イソ−ヘプチル、n−オクチル、イソ−オクチル、n−ノニル、n−デシル及び類似物を含む。好ましくは、C1〜C4−アルキルである。 The term “C 1 -C 10 -alkyl” as used herein means a straight or branched saturated hydrocarbon having 1 to 10 carbon atoms and having a free valence of 1; For example, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, iso-butyl, tert-butyl, n-pentyl, iso-pentyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, n-hexyl, iso-hexyl, 2-ethylhexyl, n-heptyl, iso-heptyl, n-octyl, iso-octyl, n-nonyl, n-decyl and the like. Preferably, C 1 ~C 4 - alkyl.
ここで使用された「C2〜C3−アルカンジイル」という用語は、2個〜3個の炭素原子を備え2の自由原子価を有する飽和炭化水素を意味する。C2〜C3−アルカンジイルは、例えば、−CH2CH2−及び−CH2CH2CH2−を含む。 The term “C 2 -C 3 -alkanediyl” as used herein refers to a saturated hydrocarbon having 2 to 3 carbon atoms and having a free valence of 2. C 2 -C 3 - alkanediyl is, for example, -CH 2 CH 2 - containing - and -CH 2 CH 2 CH 2.
少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物は、好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも1つのFにより置換され、より好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも2つのFにより置換され、最も好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも3つのFにより置換される一般式(I)の化合物から選択される。特に好ましくは、R1及びR2の少なくとも1つは、少なくとも1つのCF3−基を含む。 At least one compound of general formula (I) is preferably substituted at least one of R 1 and R 2 by at least one F, more preferably at least one of R 1 and R 2 is substituted by at least two F And most preferably selected from compounds of general formula (I) in which at least one of R 1 and R 2 is substituted by at least 3 F. Particularly preferably, at least one of R 1 and R 2 comprises at least one CF 3 — group.
本発明の一実施態様により、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物は、R1及びR2が互いに独立し任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C4−アルキルから選択される一般式(I)の化合物から選択される。好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも1つのFにより置換され、より好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも2つのFにより置換され、最も好ましくはR1及びR2の少なくとも1つが少なくとも3つのFにより置換される。特に好ましくは、R1及びR2の少なくとも1つは、少なくとも1つのCF3−基を含む。 According to one embodiment of the present invention, at least one compound of general formula (I) is selected from general formula (1) wherein R 1 and R 2 are independently of one another and optionally fluorinated C 1 -C 4 -alkyl. Selected from compounds of I). Preferably at least one of R 1 and R 2 is substituted by at least one F, more preferably at least one of R 1 and R 2 is substituted by at least two F, and most preferably at least one of R 1 and R 2 Are replaced by at least three Fs. Particularly preferably, at least one of R 1 and R 2 comprises at least one CF 3 — group.
他の実施態様により、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物は、R1及びR2が、一緒に結合しており、F及び任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C10−アルキルから選択された1つ以上の置換基により置換されることが可能である、五員又は六員ヘテロ環基を、基−OPO−と共に形成するC2−アルカンジイルから選択される。該C2−アルカンジイルは、好ましくは少なくとも1つのF、より好ましくは少なくとも2つのF、さらにより好ましくは少なくとも3つのFを含む。特に好ましくは、五員ヘテロ環は少なくとも1つのCF3−基を含む。
According to another embodiment, the at least one compound of general formula (I) is selected from
好ましい一般式(I)の化合物は、LiOOP(OCH2CF3)2、LiOOP(OCH(CF3)2)2、LiOOP(On−C4F9)2及びLiOOP(OC(CF3)3)2である。 Preferred compounds of the general formula (I) are LiOOP (OCH 2 CF 3 ) 2 , LiOOP (OCH (CF 3 ) 2 ) 2 , LiOOP (On-C 4 F 9 ) 2 and LiOOP (OC (CF 3 ) 3 ). 2 .
任意に一般式(I)のフッ素化されたアルキルリン酸リチウム化合物の異なる製造方法が知られている。一案としては、対応する(フルオロ)アルキルリン酸をリチウム水酸化物又はブチルリチウムなどの脱プロトン化剤と反応させることにより製造することである。対応する(フルオロ)アルキルリン酸の製造は、例えば、Mahmood,T.及びShreeve,J.M.、Inorg.Chem.25、3830〜3837頁(1986)に記載されている。もう1つの可能性としては、個々のリチウム(フルオロ)アルコキシドを五酸化リンと反応させることである。本発明のもう1つの課題は、LiOR1、LiOR2及び/又はLiOR1R2OLiを五酸化リンと反応させることであり、R1及びR2が上記のように定義され、R1R2が、一緒に結合しており、1つ以上のF及び/又は任意にフッ素化されたC1〜C10−アルキルにより置換されることが可能であるC2〜C3−アルカンジイルから選択される部分である。LiOR1、LiOR2及び/又はLiOR1R2OLiは、対応するアルコールをリチウム水酸化物又はブチルリチウムなどの脱プロトン化剤と反応させることにより容易に製造される。一般的には、LiOR1、LiOR2及び/又はLiOR1R2OLi及び五酸化リンは、炭酸ジメチルなどの炭酸塩のような非プロトン性溶媒の存在下で反応される。一般的には、反応温度は室温を超え、例えば、好適な温度範囲は50〜120℃である。また、ビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸リチウムは、対応するアルコールを、リチウム水酸化物又はブチルリチウムなどの脱プロトン化剤で脱プロトン化した五酸化リンと直接に反応させることにより製造される。 Different processes are known for the preparation of optionally fluorinated lithium alkyl phosphate compounds of general formula (I). One idea is to produce the corresponding (fluoro) alkyl phosphoric acid by reacting with a deprotonating agent such as lithium hydroxide or butyl lithium. The preparation of the corresponding (fluoro) alkyl phosphate is described, for example, in Mahmood, T .; And Shreeve, J .; M.M. Inorg. Chem. 25, pages 3830-3837 (1986). Another possibility is to react individual lithium (fluoro) alkoxides with phosphorus pentoxide. Another subject of the present invention is to react LiOR 1 , LiOR 2 and / or LiOR 1 R 2 OLi with phosphorus pentoxide, R 1 and R 2 are defined as above and R 1 R 2 Are selected from C 2 -C 3 -alkanediyl bonded together and capable of being substituted by one or more F and / or optionally fluorinated C 1 -C 10 -alkyl. This is the part. LiOR 1 , LiOR 2 and / or LiOR 1 R 2 OLi are easily produced by reacting the corresponding alcohol with a deprotonating agent such as lithium hydroxide or butyl lithium. In general, LiOR 1 , LiOR 2 and / or LiOR 1 R 2 OLi and phosphorus pentoxide are reacted in the presence of an aprotic solvent such as a carbonate such as dimethyl carbonate. Generally, the reaction temperature exceeds room temperature, for example, a suitable temperature range is 50-120 ° C. In addition, lithium bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate directly reacts with the corresponding alcohol by phosphorus pentoxide deprotonated with a deprotonating agent such as lithium hydroxide or butyl lithium. Manufactured.
一般的には、電解質組成物(A)は、少なくとも0.01mol/Lの少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物を含む。一般的には、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物の最大濃度は5mol/Lである。一般式(I)の化合物がゲル化剤として電解質組成物に使用される場合、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物の濃度は、電解質組成物(A)の総体積に基づいて、好ましくは0.1〜5mol/L、より好ましくは0.15〜3mol/L、最も好ましくは0.2〜2mol/Lの範囲である。 Generally, the electrolyte composition (A) comprises at least 0.01 mol / L of at least one compound of general formula (I). In general, the maximum concentration of at least one compound of general formula (I) is 5 mol / L. When the compound of general formula (I) is used in the electrolyte composition as a gelling agent, the concentration of at least one compound of general formula (I) is preferably based on the total volume of the electrolyte composition (A) Is 0.1 to 5 mol / L, more preferably 0.15 to 3 mol / L, and most preferably 0.2 to 2 mol / L.
一般式(I)の小分子フルオロアルキルリン酸リチウムは、配位ポリマーのネットワーク、及びポリマーの全体のネットワークのうちに分布する溶媒分子からなるゲルをもたらす溶媒中の配位ポリマーを生成する。該ゲルは、有限降伏応力を有し、弾性と粘性との両方を示す。これは、レオロジー振動実験(rheological oscillation experiments)により測定された貯蔵弾性率G’及び損失弾性率G’’の発展により反映される。変形掃引(deformation sweep)において、微小変形(small deformation)での損失弾性率より、貯蔵弾性率G’はより大きく、これはむしろ固相物質に近い。これは、高い変形値で変化するので、ゲルがむしろ液体に近いことを示す。微小変形での周波数掃引実験(frequency sweep experiment)において、ゲルの貯蔵弾性率G’は損失弾性率G’’より大きく、少なくとも、理想的なゲルにおいて両方とも並行して進む。本発明の好ましい実施態様により、電解質組成物(A)はゲル電解質である。 The small molecule lithium fluoroalkyl phosphate of general formula (I) produces a coordination polymer in solvent that results in a gel consisting of a network of coordination polymers and solvent molecules distributed within the overall network of polymers. The gel has finite yield stress and exhibits both elasticity and viscosity. This is reflected by the development of storage modulus G 'and loss modulus G "measured by rheological oscillation experiments. In a deformation sweep, the storage elastic modulus G 'is larger than the loss elastic modulus in small deformation, which is rather close to a solid phase material. This indicates that the gel is more like a liquid because it changes with higher deformation values. In a frequency sweep experiment with small deformations, the storage modulus G 'of the gel is greater than the loss modulus G "and at least both proceed in parallel in an ideal gel. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the electrolyte composition (A) is a gel electrolyte.
さらに、本発明の電解質組成物(A)は、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物と異なる導電性塩(iii)を含む。電解質組成物(A)は、電気化学電池に行う電気化学反応に関与するイオンを伝導するための媒質となる。一般的には、電解質に存在する導電性塩(単数又は複数)(iii)は、非プロトン性有機溶媒(単数又は複数)(i)に溶媒和される。好ましくは、導電性塩(iii)は、導電性塩を含有するリチウムイオンである。好ましくは、導電性塩は、
Li[F6−xP(CyF2y+1)x](式中、xは0〜6の範囲の整数であり、yは1〜20の範囲の整数である);
Li[B(RI)4]、Li[B(RI)2(ORIIO)]及びLi[B(ORIIO)2](式中、個々のRIは、互いに独立し、F、Cl、Br、I、C1〜C4−アルカリ、C2〜C4−アルケニル、C2〜C4−アルキニル、OC1〜C4−アルカリ、OC2〜C4−アルケニル及びOC2〜C4−アルキニルから選択され、アルカリ、アルケニル及びアルキニルは1つ以上のORIIIにより置換されてもよく、RIIIはC1〜C6−アルカリ、C2〜C6−アルケニル及びC2〜C6−アルキニルから選択され、且つ、
(ORIIO)は、1,2−若しくは1,3−ジオール、1,2−若しくは1,3−ジカルボン酸、又は、1,2−若しくは1,3−ヒドロキシカルボン酸に由来する二価基であり、該二価基は両方の酸素原子により中心のB−原子と5−又は6員環を形成する);
LiClO4;LiAsF6;LiCF3SO3;Li2SiF6;LiSbF6;LiAlCl4、テトラフルオロ(オキサラト)リン酸リチウム;シュウ酸リチウム;LiN(SO2F)2;並びに、
一般式Li[Z(CnF2n+1SO2)m](式中、m及びnは、下記、
Zが酸素及び硫黄から選択される場合、mが1であり、
Zが窒素及びリンから選択される場合、mが2であり、
Zが炭素及びシリコンから選択される場合、mが3であり、
nが1〜20の範囲の整数である、
ように定義される)、
からなる群から選択される。
Furthermore, the electrolyte composition (A) of the present invention contains a conductive salt (iii) different from at least one compound of the general formula (I). The electrolyte composition (A) serves as a medium for conducting ions involved in the electrochemical reaction performed in the electrochemical cell. In general, the conductive salt (s) (iii) present in the electrolyte are solvated in the aprotic organic solvent (s) (i). Preferably, the conductive salt (iii) is a lithium ion containing a conductive salt. Preferably, the conductive salt is
Li [F 6-x P ( C y F 2y + 1) x] ( where, x is an integer in the range of Less than six, y is an integer ranging from 1 to 20);
Li [B (R I ) 4 ], Li [B (R I ) 2 (OR II O)] and Li [B (OR II O) 2 ] (wherein each R I is independent of each other and
(OR II O) is a divalent group derived from 1,2- or 1,3-diol, 1,2- or 1,3-dicarboxylic acid, or 1,2- or 1,3-hydroxycarboxylic acid And the divalent group forms a 5- or 6-membered ring with the central B-atom by both oxygen atoms);
LiClO 4 ; LiAsF 6 ; LiCF 3 SO 3 ; Li 2 SiF 6 ; LiSbF 6 ; LiAlCl 4 , lithium tetrafluoro (oxalate) lithium phosphate; lithium oxalate; LiN (SO 2 F) 2 ;
General formula Li [Z (CnF 2n + 1 SO 2 ) m ] (where m and n are
When Z is selected from oxygen and sulfur, m is 1.
When Z is selected from nitrogen and phosphorus, m is 2.
When Z is selected from carbon and silicon, m is 3;
n is an integer in the range of 1-20,
Defined)),
Selected from the group consisting of
二価基(ORIIO)を生成する好適な1,2−又は1,3−ジオールは、脂肪族又は芳香族のものであり、例えば、1つ以上のFに、及び/又は少なくとも1つの直鎖又は分岐のフッ素化されない、部分的にフッ素化される又は完全にフッ素化されるC1〜C4−アルカリ基により任意に置換される1,2−ジヒドロキシベンゼン、プロパン−1,2−ジオール、ブタン−1,2−ジオール、プロパン−1,3−ジオール、ブタン−1,3−ジオール、シクロヘキシル−トランス−1,2−ジオール及びナフタレン−2,3−ジオールから選択されてもよい。このような1,2−又は1,3−ジオールの例としては、1,1,2,2−テトラ(トリフルオロメチル)−1,2−エタンジオールが挙げられる。 Suitable 1,2- or 1,3-diols that generate divalent groups (OR II O) are aliphatic or aromatic, eg, one or more F and / or at least one 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, propane-1,2-optionally substituted with linear or branched non-fluorinated, partially fluorinated or fully fluorinated C 1 -C 4 -alkali groups It may be selected from diols, butane-1,2-diol, propane-1,3-diol, butane-1,3-diol, cyclohexyl-trans-1,2-diol and naphthalene-2,3-diol. Examples of such 1,2- or 1,3-diol include 1,1,2,2-tetra (trifluoromethyl) -1,2-ethanediol.
「完全にフッ素化されるC1〜C4−アルカリ基」という用語は、全てのアルキル基のH−原子がFにより置換されることを意味する。 The term “fully fluorinated C 1 -C 4 -alkali group” means that the H-atoms of all alkyl groups are replaced by F.
二価基(ORIIO)を生成する好適な1,2−又は1,3−ジカルボン酸は、肪族又は芳香族の、例えば、シュウ酸、マロン酸(プロパン−1,3−ジカルボン酸)、フタル酸又はイソフタル酸であり、好ましくはシュウ酸である。該1,2−又は1,3−ジカルボン酸は、任意に、1つ以上のFに、及び/又は少なくとも1つの直鎖又は分岐のフッ素化されない、部分的にフッ素化される又は完全にフッ素化されたC1〜C4−アルカリ基に置換される。 Suitable 1,2- or 1,3-dicarboxylic acids that generate divalent groups (OR II O) are aliphatic or aromatic, such as oxalic acid, malonic acid (propane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid) Phthalic acid or isophthalic acid, preferably oxalic acid. The 1,2- or 1,3-dicarboxylic acid optionally has one or more F and / or at least one linear or branched, non-fluorinated, partially fluorinated or fully fluorinated. The substituted C 1 -C 4 -alkali group is substituted.
二価基(ORIIO)を生成する好適な1,2−又は1,3−ヒドロキシカルボン酸は、肪族又は芳香族の、例えば、1つ以上のFに、及び/又は少なくとも1つの直鎖又は分岐のフッ素化されない、部分的にフッ素化される又は完全にフッ素化されたC1〜C4−アルカリ基により任意に置換されるサリチル酸、テトラヒドロサリチル酸、リンゴ酸及び2−ヒドロキシ酢酸であってもよい。このような1,2−又は1,3−ヒドロキシカルボン酸の例としては、2,2−ビス(トリフルオロメチル)−2−ヒドロキシ−酢酸が挙げられる。 Suitable 1,2- or 1,3-hydroxycarboxylic acids that form divalent groups (OR II O) are aliphatic or aromatic, eg, one or more F, and / or at least one straight chain. not fluorinated chain or branched, partially fluorinated is or completely fluorinated C 1 -C 4 - salicylic acid, which is optionally substituted by an alkali base, tetrahydrophthalic acid, a malic acid and 2-hydroxy acetic acid May be. Examples of such 1,2- or 1,3-hydroxycarboxylic acids include 2,2-bis (trifluoromethyl) -2-hydroxy-acetic acid.
Li[B(RI)4]、Li[B(RI)2(ORIIO)]及びLi[B(ORIIO)2]の例としては、LiBF4、ジフルオロオキサラトホウ酸リチウム及びジオキサラトホウ酸リチウムが挙げられる。 Examples of Li [B (R I ) 4 ], Li [B (R I ) 2 (OR II O)] and Li [B (OR II O) 2 ] include LiBF 4 , lithium difluorooxalatoborate and Examples include lithium dioxalatoborate.
好ましくは、少なくとも1種の導電性塩(iii)は、LiBF4、ジフルオロオキサラトホウ酸リチウム、ジオキサラトホウ酸リチウム、Li[N(FSO2)2]、Li[N(CF3SO2)2]、LiClO4、LiPF6及びLiPF3(CF2CF3)3から、より好ましくはLiPF6、LiBF4及びLiPF3(CF2CF3)3から選択され、さらにより好ましくは導電性塩(iii)はLiPF6及びLiBF4から選択され、最も好ましくは導電性塩(iii)はLiPF6である。 Preferably, the at least one conductive salt (iii) is LiBF 4 , lithium difluorooxalatoborate, lithium dioxalatoborate, Li [N (FSO 2 ) 2 ], Li [N (CF 3 SO 2 ) 2 ]. , LiClO 4 , LiPF 6 and LiPF 3 (CF 2 CF 3 ) 3 , more preferably selected from LiPF 6 , LiBF 4 and LiPF 3 (CF 2 CF 3 ) 3 , and even more preferably a conductive salt (iii) Is selected from LiPF 6 and LiBF 4 , most preferably the conductive salt (iii) is LiPF 6 .
一般的には、少なくとも1種の導電性塩(iii)は、少なくとも0.1mol/Lの最小濃度で存在する。一般的には、最大濃度は、電解質組成物の総体積に基づいて2mol/Lである。 Generally, at least one conductive salt (iii) is present at a minimum concentration of at least 0.1 mol / L. In general, the maximum concentration is 2 mol / L based on the total volume of the electrolyte composition.
電解質組成物(A)は、ビニレンカーボネート及びその誘導体、ビニルエチレンカーボネート及びその誘導体、メチルエチレンカーボネート及びその誘導体、(ビスオキサラト)ホウ酸リチウム、ジフルオロ(オキサラト)ホウ酸リチウム、テトラフルオロ(オキサラト)リン酸リチウム、シュウ酸リチウム、2−ビニルピリジン、4−ビニルピリジン、環状エキソ−メチレンカーボネート、スルトン、環状及び非環状スルホン酸塩、環状及び非環状亜硫酸塩、無機酸の有機エステル、1バールで少なくとも36℃の沸点を有する非環状及び環状アルカン、並びに、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状スルホニルイミド、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状リン酸エステル、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状ホスフィン、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状亜リン酸塩、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状ホスファゼン、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状シリルアミン、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状ハロゲン化エステル、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状アミド、任意にハロゲン化の環状及び非環状無水物、イオン液体、及び任意にハロゲン化の複素環を含む芳香族化合物からなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の添加剤(iv)を含んでもよい。好ましくは、添加剤(iv)は、個々の電解質組成物(A)に存在している導電性塩(iii)から選択された化合物と異なるように選択される。好ましくは、添加剤(iv)は、個々の電解質組成物(A)に存在している前記少なくとも1種の有機非プロトン性溶媒(i)とも異なる。 The electrolyte composition (A) is composed of vinylene carbonate and its derivatives, vinyl ethylene carbonate and its derivatives, methyl ethylene carbonate and its derivatives, (bisoxalato) lithium borate, difluoro (oxalato) lithium borate, tetrafluoro (oxalato) phosphoric acid Lithium, lithium oxalate, 2-vinylpyridine, 4-vinylpyridine, cyclic exo-methylene carbonate, sultone, cyclic and acyclic sulfonates, cyclic and acyclic sulfites, organic esters of inorganic acids, at least 36 at 1 bar Acyclic and acyclic alkanes having boiling points of ° C, and optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic sulfonylimides, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic phosphate esters, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic phosphines, optional Halogenated Cyclic and acyclic phosphites, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic phosphazenes, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic silylamines, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic halogenated esters, optionally halogenated cyclic And at least one additive (iv) selected from the group consisting of acyclic amides, optionally halogenated cyclic and acyclic anhydrides, ionic liquids, and optionally aromatic compounds containing halogenated heterocycles May be included. Preferably, additive (iv) is selected to be different from the compound selected from the conductive salt (iii) present in the individual electrolyte composition (A). Preferably, additive (iv) is also different from said at least one organic aprotic solvent (i) present in the individual electrolyte composition (A).
本発明の好ましいイオン液体は式[K]+[L]−のイオン液体から選択され、[K]+が、好ましくは還元安定性の、一般式(II)〜(IX)、
Rは、H、C1−〜C6−アルキル、C2−〜C6−アルケニル及びフェニル、好ましくはメチル、エチル及びプロピルを示す;
RAは、−(CH2)s−O−C(O)−R、−(CH2)s−C(O)−OR, −(CH2)s−S(O)2−OR、−(CH2)s−O−S(O)2−OR、−(CH2)s−O−C(O)−OR、−(CH2)s−HC=CH−R、−(CH2)s −CN、
を示す;
XAは、CH2、O、S又はNRBを示す;
RBは、H、C1−〜C6−アルキル、C2−〜C6−アルケニル、フェニル、及び、sが1〜8、好ましくは1〜3である−(CH2)s−CNを示す;好ましくは、RBは、メチル、エチル、プロピル又はHである)
のカチオン群から選択されたカチオンを示し、
[L]−が、BF4 −、PF6 −、[B(C2O4)2]−、[F2B(C2O4)]−、[N(S(O)2F)2]−、[FpP(CqF2q+1)6−p]−、[N(S(O)2CqF2q+1)2]−、[(CqF2q+1)2P(O)O]−、[CqF2q+1P(O)O2]2−、[OC(O)CqF2q+1]−、[OS(O)2CqF2q+1]−;[N(C(O)CqF2q+1)2]−;[N(C(O)CqF2q+1)(S(O)2CqF2q+1)]−;[N(C(O)CqF2q+1)(C(O))F]−;[N(S(O)2CqF2q+1)(S(O)2F)]−;[C(C(O)CqF2q+1)3]−及び[C(S(O)2CqF2q+1)3N(SO2CF3)2]−、
(式中、pが0〜6の範囲の整数であり、qが1〜20の範囲の整数であり、好ましくはqが1〜4の範囲の整数である)
の群から選択されたアニオンを示す。
Preferred ionic liquids of the present invention are selected from ionic liquids of the formula [K] + [L] − , wherein [K] + is preferably of general formula (II) to (IX)
R represents H, C 1-to C 6 -alkyl, C 2-to C 6 -alkenyl and phenyl, preferably methyl, ethyl and propyl;
R A is — (CH 2 ) s —O—C (O) —R, — (CH 2 ) s —C (O) —OR, — (CH 2 ) s —S (O) 2 —OR, — (CH 2) s -O-S (O) 2 -OR, - (CH 2) s -O-C (O) -OR, - (CH 2) s -HC = CH-R, - (CH 2) s- CN,
Indicates;
X A represents CH 2 , O, S or NR B ;
R B is, H, C 1 -~C 6 - alkyl, C 2 -~C 6 - alkenyl, phenyl, and, s is 1-8, is preferably 1 to 3 - a (CH 2) s -CN shown; preferably, R B is methyl, ethyl, propyl or H)
A cation selected from the cation group of
[L] − is BF 4 − , PF 6 − , [B (C 2 O 4 ) 2 ] − , [F 2 B (C 2 O 4 )] − , [N (S (O) 2 F) 2 ] -, [F p P ( C q F 2q + 1) 6-p] -, [N (S (O) 2 C q F 2q + 1) 2] -, [(C q F 2q + 1) 2 P (O) O] − , [C q F 2q + 1 P (O) O 2 ] 2− , [OC (O) C q F 2q + 1 ] − , [OS (O) 2 CqF 2q + 1 ] − ; [N (C (O) C q F 2q + 1) 2] -; [N (C (O) C q F 2q + 1) (S (O) 2 C q F 2q + 1)] -; [N (C (O) C q F 2q + 1) (C (O)) F] -; [N (S (O) 2 C q F 2q + 1) (S (O) 2 F)] -; [C (C (O) C q F 2q + 1) 3] - , and [C (S (O 2 C q F 2q + 1) 3 N (SO 2 CF 3) 2] -,
(Wherein p is an integer in the range of 0-6, q is an integer in the range of 1-20, and preferably q is an integer in the range of 1-4)
An anion selected from the group of
添加剤(iv)として使用される好ましいイオン液体は、式[K][L](式中、[K]は、XがCH2であり、sが1〜3の範囲の整数である一般式(II)のピロリジニウムカチオンから選択され、[L]は、BF4 −、PF6 −、[B(C2O4)2]−、[F2B(C2O4)]−、[N(S(O)2F)2]−、[N(SO2C2F5)2 2]−、[F3P(C2F5)3]−及び[F3P(C4F9)3]−からなる群から選択される)のイオン液体である。 Preferred ionic liquids used as additives (iv) are those of the formula [K] [L] (wherein [K] is a general formula wherein X is CH 2 and s is an integer in the range of 1 to 3). Selected from the pyrrolidinium cations of (II), [L] is BF 4 − , PF 6 − , [B (C 2 O 4 ) 2 ] − , [F 2 B (C 2 O 4 )] − , [N (S (O) 2 F) 2 ] − , [N (SO 2 C 2 F 5 ) 2 2 ] − , [F 3 P (C 2 F 5 ) 3 ] − and [F 3 P (C 4 F 9 ) 3 ] - )).
1種以上のさらなる添加剤(iv)が電解質組成物(A)に存在する場合、さらなる添加剤(iv)の総濃度は、電解質組成物(A)の総質量に基づいて、少なくとも0.001質量%、好ましくは0.005〜5質量%、より好ましくは0.01〜2質量%である。 When one or more additional additives (iv) are present in the electrolyte composition (A), the total concentration of the additional additives (iv) is at least 0.001 based on the total mass of the electrolyte composition (A). It is mass%, Preferably it is 0.005-5 mass%, More preferably, it is 0.01-2 mass%.
電解質組成物(A)は、少なくとも1種の溶媒(i)と少なくとも1種の導電性塩(iii)と任意に1種以上の添加剤(iv)との混合物を提供する工程、一般式(I)の化合物を添加する工程、及び、全ての成分を混合する工程により製造されてもよい。ある場合には、ゲルの均一性を確保するために超音波浴で溶液を処理することが有用である。 The electrolyte composition (A) provides a mixture of at least one solvent (i), at least one conductive salt (iii) and optionally one or more additives (iv), having the general formula ( It may be produced by adding the compound of I) and mixing all the components. In some cases, it is useful to treat the solution in an ultrasonic bath to ensure gel uniformity.
本発明のさらなる目的は、好ましい実施態様を含んで上記で詳しく定義したような一般式(I)の化合物をゲル化剤として非プロトン性有機溶媒又は溶媒混合物に使用する方法である。典型的な非プロトン性有機溶媒は、非プロトン性有機溶媒(i)としての、好ましい実施態様を含めて上記で詳しく記載された溶媒である。好ましい非プロトン性有機溶媒(単数又は複数)は環状及び非環状有機炭酸塩から選択される。一般的には、一般式(I)の化合物は、非プロトン性有機溶媒(単数又は複数)及び一般式(I)の化合物(単数又は複数)を含有する組成物の総体積に基づいて、0.1〜5mol/L、より好ましくは0.15〜3mol/L、最も好ましくは0.2〜2mol/Lの範囲の濃度の少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物をゲル化剤として使用される。好ましくは、一般式(I)の化合物は、ゲル化剤として、非プロトン性有機溶媒(単数又は複数)を含有する非水性電解質組成物に使用される。本発明のさらなる目的は、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物を非プロトン性有機溶媒又は上記のような非プロトン性有機溶媒の混合物に添加することにより、非プロトン性有機溶媒又は非プロトン性有機溶媒の混合物をゲル化する方法である。「ゲル化する」という用語は、プロトン性有機溶媒又は非プロトン性有機溶媒の混合物のゲル化を誘導して、プロトン性有機溶媒又は非プロトン性有機溶媒の混合物と、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物と、任意に上記の導電性塩(iii)及び添加剤(iv)のような導電性塩及び添加剤などのさらなる化合物とを含むゲルを得る。 A further object of the invention is a process for using a compound of general formula (I) as defined in detail above, including preferred embodiments, as a gelling agent in an aprotic organic solvent or solvent mixture. Typical aprotic organic solvents are those described in detail above, including preferred embodiments, as aprotic organic solvent (i). Preferred aprotic organic solvent (s) are selected from cyclic and acyclic organic carbonates. Generally, the compound of general formula (I) is 0 based on the total volume of the composition containing the aprotic organic solvent (s) and the compound (s) of general formula (I). Use at least one compound of general formula (I) as a gelling agent at a concentration in the range of 1-5 mol / L, more preferably 0.15-3 mol / L, most preferably 0.2-2 mol / L Is done. Preferably, the compound of general formula (I) is used as a gelling agent in non-aqueous electrolyte compositions containing an aprotic organic solvent (s). A further object of the present invention is to add an aprotic organic solvent or an aprotic compound by adding at least one compound of general formula (I) to an aprotic organic solvent or a mixture of aprotic organic solvents as described above. It is the method of gelatinizing the mixture of an organic solvent. The term “gelling” induces gelation of a mixture of a protic organic solvent or an aprotic organic solvent to produce a mixture of a protic organic solvent or an aprotic organic solvent and at least one general formula ( A gel is obtained comprising a compound of I) and optionally further compounds such as conductive salts and additives such as the conductive salts (iii) and additives (iv) described above.
本発明のもう1つの目的は、少なくとも1種の一般式(I)の化合物を電気化学電池用の電解質の添加剤として使用する方法である。一般的には、一般式(I)の化合物は、本発明の電解質組成物(A)に対して上記の範囲の濃度で使用される。 Another object of the invention is a method of using at least one compound of general formula (I) as an additive for electrolytes for electrochemical cells. In general, the compound of the general formula (I) is used at a concentration within the above range with respect to the electrolyte composition (A) of the present invention.
本発明のもう1つの目的は、上記で詳しく記載されたような電解質組成物(A)を含む電気化学電池である。特に、該電気化学電池は、
(A)上記の電解質組成物、
(B)少なくとも1種のカソード活物質を含む少なくとも1つのカソード、及び、
(C)少なくとも1種のアノード活物質を含む少なくとも1つのアノード、
を含む。
Another object of the present invention is an electrochemical cell comprising an electrolyte composition (A) as described in detail above. In particular, the electrochemical cell is
(A) the above electrolyte composition,
(B) at least one cathode comprising at least one cathode active material; and
(C) at least one anode comprising at least one anode active material;
including.
好ましくは、本発明の電気化学電池は、リチウム電池であり、換言すれば、アノードが電池の値充電/放電の間のどこかにリチウム金属又はリチウムイオンを含む電気化学電池である。アノードは、リチウム金属又はリチウム金属合金(リチウムを含有する化合物又はリチウムイオンを組み込む物質)を含むことが可能であり、例えばリチウムイオン電池、リチウム/硫黄電池又はリチウム/セレン硫黄電池である。好ましくは、電気化学電池は、リチウムイオン二次電池又はリチウム硫黄電池である。 Preferably, the electrochemical cell of the present invention is a lithium cell, in other words, an electrochemical cell in which the anode contains lithium metal or lithium ions somewhere during the value charge / discharge of the cell. The anode can include lithium metal or a lithium metal alloy (a lithium-containing compound or a material that incorporates lithium ions), such as a lithium ion battery, a lithium / sulfur battery, or a lithium / selenium sulfur battery. Preferably, the electrochemical battery is a lithium ion secondary battery or a lithium sulfur battery.
リチウム/硫黄電池は、カソード活物質としての硫黄含有物質を含む。一般的には、硫黄は、導電性物質と、特に好ましくはカーボンブラック、黒鉛、膨張黒鉛、グラフェン、炭素繊維、カーボンナノチューブ、活性炭、コルク又はピッチの熱処理により製造された炭素などの炭素質導電性物質との混合物又は複合物として存在している。また、金属粉末、金属フレーク、金属化合物又はそれらの混合物なとの他の導電性物質を使用することが可能である。硫黄を含有する混合物又は複合物は、しばしば、元素硫黄又は硫黄を含有するポリマーから製造される。 Lithium / sulfur batteries include a sulfur-containing material as a cathode active material. In general, sulfur is a conductive material and particularly preferably carbonaceous conductivity such as carbon black, graphite, expanded graphite, graphene, carbon fiber, carbon nanotube, activated carbon, carbon produced by heat treatment of cork or pitch. It exists as a mixture or complex with the substance. It is also possible to use other conductive materials such as metal powders, metal flakes, metal compounds or mixtures thereof. Mixtures or composites containing sulfur are often made from elemental sulfur or a polymer containing sulfur.
一般的には、リチウムアノードはリチウム金属及び/又はリチウム金属合金を含む。リチウム/硫黄電池において、リチウム−アルミニウム合金、リチウム−スズ合金、Li−Mg−合金及びLi−Ag−合金を使用してもよい。 Generally, the lithium anode includes lithium metal and / or a lithium metal alloy. In lithium / sulfur batteries, lithium-aluminum alloys, lithium-tin alloys, Li-Mg alloys and Li-Ag alloys may be used.
好ましくは、電気化学電池は、二次リチウムイオン電気化学電池又はリチウム硫黄電池であり、換言すれば、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得るカソード活物質を含むカソード、並びに、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得るアノード活物質を含むアノードを含む二次リチウムイオン電気化学電池である。本発明の範囲内で、「二次リチウムイオン電気化学電池」及び「(二次)リチウムイオン電池」は交互に用いられる。 Preferably, the electrochemical cell is a secondary lithium ion electrochemical cell or a lithium sulfur battery, in other words, a cathode including a cathode active material capable of reversibly occluding and releasing lithium ions, and reversible lithium ions. A secondary lithium ion electrochemical cell including an anode containing an anode active material that can be occluded and released. Within the scope of the present invention, “secondary lithium ion electrochemical cells” and “(secondary) lithium ion cells” are used alternately.
好ましくは、少なくとも1種のカソード活物質は、リチウム化リン酸遷移金属及びリチウムイオンを挿入する遷移金属酸化物から選択される、且つ、リチウムイオンを吸蔵及び放出できる物質を含む。 Preferably, the at least one cathode active material comprises a material selected from lithiated phosphate transition metals and transition metal oxides that insert lithium ions and capable of occluding and releasing lithium ions.
リチウム化リン酸遷移金属の例はLiCoPO4であり、リチウムイオンを挿入する遷移金属酸化物の例は、一般式(X)Li(1+z)[NiaCobMnc](1−z)O2+e(式中、zは0〜0.3である;a、b及びcは、同一又は異なり、それぞれに0〜0.8であり、a+b+c=1;−0.1≦e≦0.1)の層構造を有する遷移金属酸化物、並びに、一般式(XI)Li1+tM2−tO4−d(式中、dは0〜0.4であり、tは0〜0.4であり、MはMn、並びに、Co及びNiからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種のさらなる金属である)及びLi(1+g)[NihCoiAlj](1−g)O2+k(g、h、I、j及びkの標準値は下記である:g=0、h=0.8〜0.85、i=0.15〜0.20、j=0.02〜0.03及びk=0)のマンガン含有スピネルである。 An example of a lithiated phosphate transition metal is LiCoPO 4 , and an example of a transition metal oxide that inserts lithium ions is the general formula (X) Li (1 + z) [Ni a Co b Mn c ] (1-z) 2 O 2 + e (wherein z is 0 to 0.3; a, b and c are the same or different and each is 0 to 0.8, a + b + c = 1; −0.1 ≦ e ≦ 0.1) ) And a transition metal oxide having a layer structure of general formula (XI) Li 1 + t M 2-t O 4-d (wherein d is 0 to 0.4, and t is 0 to 0.4. And M is Mn and at least one further metal selected from the group consisting of Co and Ni) and Li (1 + g) [Ni h Co i Al j ] (1-g) O 2 + k (g, Standard values for h, I, j and k are: g = 0, h = 0.8-0.85, i = 0.15 to 0.20, j = 0.02 to 0.03 and k = 0).
1つの好ましい実施態様において、カソード活物質はLiCoPO4から選択される。また、カソード活物質としてのLiCoPO4を含むカソードはLiCoPO4カソードとも称される。LiCoPO4は、Fe、Mn、Ni、V、Mg、Al、Zr、Nb、Tl、Ti、K、Na、Ca、Si、Sn、Ge、Ga、B、As、Cr、Sr、又は希土類元素、換言すれば、ランタニド、スカンジウム及びイットリウムでドープされてもよい。特に、オリビン構造を備えるLiCoPO4は、高い動作電圧(4.8Vの酸化還元電位vs.Li/Li+)、平らな電圧プロフィール、及び約170mAh/gの高い理論容量を有するので、本発明に好適である。カソードはLiCoPO4/C複合物質を含んでもよい。LiCoPO4/C複合物質を含む好適なカソードの製造は、Markevich et al.,Electrochem.Comm.,2012,15,22−25に記載されている。 In one preferred embodiment, the cathode active material is selected from LiCoPO 4 . A cathode containing LiCoPO 4 as a cathode active material is also referred to as a LiCoPO 4 cathode. LiCoPO 4 is Fe, Mn, Ni, V, Mg, Al, Zr, Nb, Tl, Ti, K, Na, Ca, Si, Sn, Ge, Ga, B, As, Cr, Sr, or a rare earth element, In other words, it may be doped with lanthanides, scandium and yttrium. In particular, LiCoPO 4 with an olivine structure has a high operating voltage (4.8 V redox potential vs. Li / Li + ), a flat voltage profile, and a high theoretical capacity of about 170 mAh / g. Is preferred. The cathode may include a LiCoPO 4 / C composite material. The manufacture of suitable cathodes containing LiCoPO 4 / C composites is described in Markevich et al. Electrochem. Comm. 2012, 15, 22-25.
本発明のもう1つの好ましい実施態様において、カソード活物質は、一般式(X)Li(1+z)[NiaCobMnc](1−z)O2+e(式中、zは0〜0.3である;a、b及びcは、同一又は異なり、それぞれに0〜0.8であり、a+b+c=1;−0.1≦e≦0.1)の層構造を有する遷移金属酸化物から選択される。好ましくは、一般式(X)Li(1+z)[NiaCobMnc](1−z)O2+e(式中、zは0.05〜0.3であり、aは0.2〜0.5であり、bは0〜0.3であり、cは0.4〜0.8であり、a+b+c=1;−0.1≦e≦0.1)の層構造を有する遷移金属酸化物である。本発明の一実施態様において、一般式(X)の層構造を有する遷移金属酸化物は、[NiaCobMnc]がNi0.33Co0Mn0.66、Ni0.25Co0Mn0.75、Ni0.35Co0.15Mn0.5、Ni0,21Co0,08Mn0,71及びNi0,22Co0,12Mn0,66から選択されるものから選択され、特に好ましくはNi0,21Co0,08Mn0,71及びNi0,22Co0,12Mn0,66である。また、一般式(X)の遷移金属酸化物は、通常のNCMsより高いエネルギー密度を備えるので、高エネルギーNCM(HE−NCM)とも呼ばれる。HE−NCMとNCMとの両方ともLi/Li+対して約2.3〜3.8Vの動作電圧を有するが、確実にフル充電を達成しそのより高いエネルギー密度から利益を受けるために、HE−NCMS充電に高いカットオフ電圧(>4.6V)を使用しなければならない。 In another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the cathode active material has the general formula (X) Li (1 + z) [Ni a Co b Mn c ] (1-z) O 2 + e (wherein z is 0 to 0.00). A, b and c are the same or different and each is 0 to 0.8, and a transition metal oxide having a layer structure of a + b + c = 1; −0.1 ≦ e ≦ 0.1) Selected. Preferably, the general formula (X) Li (1 + z) [Ni a Co b Mn c ] (1-z) O 2 + e (wherein z is 0.05 to 0.3 and a is 0.2 to 0) 0.5, b is 0 to 0.3, c is 0.4 to 0.8, and a transition metal oxide having a layer structure of a + b + c = 1; −0.1 ≦ e ≦ 0.1) It is a thing. In one embodiment of the present invention, the transition metal oxide having a layer structure represented by the general formula (X) includes [Ni a Co b Mn c ] having Ni 0.33 Co 0 Mn 0.66 and Ni 0.25 Co 0. Mn 0.75, selected from Ni 0.35 Co 0.15 Mn 0.5, those selected from Ni 0,21 Co 0,08 Mn 0,71 and Ni 0,22 Co 0,12 Mn 0,66 it is, particularly preferably Ni 0,21 Co 0,08 Mn 0,71 and Ni 0,22 Co 0,12 Mn 0,66. Moreover, since the transition metal oxide of general formula (X) is provided with an energy density higher than normal NCMs, it is also called high energy NCM (HE-NCM). Both HE-NCM and NCM have an operating voltage of about 2.3-3.8V versus Li / Li +, but to ensure full charge and benefit from its higher energy density, HE -A high cut-off voltage (> 4.6V) must be used for NCMS charging.
本発明のさらなる好ましい実施態様により、カソード活物質は、一般式(XI)Li1+tM2−tO4−d(式中、dは0〜0.4であり、tは0〜0.4であり、MはMn、並びに、Co及びNiからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種のさらなる金属である)のマンガン含有スピネルから選択される。好適な一般式(XI)のマンガン含有スピネルの例はLiNi0,5Mn1,5O4−dである。これらのスピネルは、HE(高エネルギー)−スピネルとも呼ばれる。 According to a further preferred embodiment of the present invention, the cathode active material has the general formula (XI) Li 1 + t M 2−t O 4-d where d is 0 to 0.4 and t is 0 to 0.4. And M is Mn and at least one further metal selected from the group consisting of Co and Ni). An example of a suitable manganese-containing spinel of the general formula (XI) is LiNi 0,5 Mn 1,5 O 4-d . These spinels are also called HE (high energy) -spinels.
多くの成分は遍在する。例えば、ナトリウム、カリウム及び塩化物は、わずかの非常に少ない割合で、実質的に全ての無機物質中で検出できる。この明細書において、0.5質量%未満の割合のカチオン又はアニオンを無視し、換言すれば、0.5質量%未満の割合のカチオン又はアニオンは有意でないことと見なされる。従って、この明細書において、0.5質量%未満のナトリウムを含む任意のリチウムイオン含有の遷移金属酸化物は無ナトリウムと見なされる。相応には、この明細書において、0.5質量%未満の硫酸イオンを含む任意のリチウムイオン含有の混合遷移金属酸化物は無硫酸と見なされる。 Many components are ubiquitous. For example, sodium, potassium and chloride can be detected in virtually all inorganic materials in only a very small proportion. In this specification, a proportion of cations or anions of less than 0.5% by weight is ignored, in other words a proportion of cations or anions of less than 0.5% by weight is considered insignificant. Therefore, in this specification, any lithium ion-containing transition metal oxide containing less than 0.5% by weight of sodium is considered sodium free. Correspondingly, in this specification any lithium ion-containing mixed transition metal oxide containing less than 0.5% by weight of sulfate ions is considered sulfuric-free.
カソードは、導電性炭素などの導電性物質及び結合剤などの通常成分をさらに含んでもよい。導電性物質及び結合剤として好適な化合物は当業者に公知である。例えば、カソードは、例えばグラファイト、カーボンブラック、カーボンナノチューブ、グラフェン又は前記物質の少なくとも2種の混合物から選択される導電性多形体中の炭素を含んでもよい。さらに、カソードは、1種以上の結合剤、例えば、ポリエチレン、ポリアクリロニトリル、ポリブタジエン、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリアクリレート、ポリビニルアルコール、ポリイソプレン、並びに、エチレン、プロピレン、スチレン、(メタ)アクリロニトリル及び1,3−ブタジエンから選択された少なくとも2種のコモノマーのコポリマー、特にエチレン−ブタジエンコポリマー、並びに、塩化ポリビニリデン、塩化ポリビニル、フッ化ポリビニル、フッ化ポリビニリデン(PVdF)、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン、テトラフルオロエチレンとヘキサフルオロプロピレンとのコポリマー、テトラフルオロエチレンとフッ化ビニリデン及びポリアクリルニトリル等のハロゲン化(コ)ポリマー等の1種以上の有機ポリマーを含んでもよい。 The cathode may further include conventional components such as a conductive material such as conductive carbon and a binder. Compounds suitable as conductive materials and binders are known to those skilled in the art. For example, the cathode may comprise carbon in a conductive polymorph selected from, for example, graphite, carbon black, carbon nanotubes, graphene, or a mixture of at least two of the foregoing materials. In addition, the cathode may include one or more binders such as polyethylene, polyacrylonitrile, polybutadiene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyacrylate, polyvinyl alcohol, polyisoprene, and ethylene, propylene, styrene, (meth) acrylonitrile and 1,3. A copolymer of at least two comonomers selected from butadiene, in particular ethylene-butadiene copolymer, and polyvinylidene chloride, polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl fluoride, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF), polytetrafluoroethylene, tetrafluoroethylene and One or more organic polymers such as copolymers with hexafluoropropylene, halogenated (co) polymers such as tetrafluoroethylene and vinylidene fluoride and polyacrylonitrile It may also include a.
さらに、カソードは集電体を含んでもよく、該集電体が金属線、金属グリッド、金属ウェブ、金属シート、金属ホイル又は金属プレートであってもよい。好適な金属ホイルはアルミホイルである。 Further, the cathode may include a current collector, which may be a metal wire, metal grid, metal web, metal sheet, metal foil or metal plate. The preferred metal foil is aluminum foil.
本発明の一実施態様により、カソードは、集電体の厚さを含まずにカソードの全体厚さに基づいて、25〜200μm、好ましくは30〜100μmの厚さを有する。 According to one embodiment of the invention, the cathode has a thickness of 25 to 200 μm, preferably 30 to 100 μm, based on the total thickness of the cathode without including the thickness of the current collector.
本発明のリチウムイオン二次電池中に含まれるアノード(C)は、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出するアノード活物質を含む。特に、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得る炭素質物質がアノード活物質として使用される。好適な炭素質物質は、結晶性炭素、例えばグラファイト物質、より特に天然グラファイト、黒鉛化コークス、黒鉛化MCMB及び黒鉛化MPCF、非晶質炭素、例えばコークス、1500℃未満で燃やしたメソカーボンマイクロビーズ及びピッチの中間相をベースとする炭素繊維(MPCF)、並びに、硬質炭素及び炭素のアノード活物質(熱分解される炭素、コークス、グラファイト)、例えば炭素複合物、燃やした有機ポリマー及び炭素繊維である。 The anode (C) contained in the lithium ion secondary battery of the present invention contains an anode active material that reversibly occludes and releases lithium ions. In particular, a carbonaceous material capable of reversibly occluding and releasing lithium ions is used as the anode active material. Suitable carbonaceous materials are crystalline carbon such as graphite materials, more particularly natural graphite, graphitized coke, graphitized MCMB and graphitized MPCF, amorphous carbon such as coke, mesocarbon microbeads burned below 1500 ° C. And carbon fibers (MPCF) based on intermediate phases of pitch and hard carbon and carbon anode active materials (carbons to be pyrolyzed, coke, graphite), such as carbon composites, burned organic polymers and carbon fibers is there.
さらなるアノード活物質は、リチウム金属、又はリチウムと合金を生成できる成分を含む物質である。リチウムと合金を生成できる成分を含む物質の限定されない例は、金属、半金属又はそれらの合金である。ここで使用された「合金」という用語は、2種以上の金属の合金にも、1種以上の金属と1種以上の半金属との合金にも関すると理解されるべきである。合金が全体として金属特性を備える場合、該合金は非金属成分を含んでもよい。合金の質感において、固体溶液、共融物(共融混合物)、金属間化合物又はそれらの2種以上は共存する。このような金属又は半金属成分の例は、制限されず、チタン(Ti)、スズ(Sn)、鉛(Pb)、アルミニウム、インジウム(In)、亜鉛(Zn)、アンチモン(Sb)、ビスマス(Bi)、ガリウム(Ga)、ゲルマニウム(Ge)、ヒ素(As)、銀(Ag)、ハフニウム(Hf)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イットリウム(Y)、及びシリコン(Si)を含む。好ましくは、長周期型周期表の元素中の4〜14族の金属及び半金属元素であり、特に好ましくはチタン、シリコン及びスズ、特にシリコンである。スズ合金の例は、スズ以外の第2成分元素としての、シリコン、マグネシウム(Mg)、ニッケル、銅、鉄、コバルト、マンガン、亜鉛、インジウム、銀、チタン(Ti)、ゲルマニウム、ビスマス、アンチモン及びクロム(Cr)からなる群から選択された1種以上の元素を有するものを含む。シリコン合金の例は、シリコン以外の第2成分元素としての、スズ、マグネシウム、ニッケル、銅、鉄、コバルト、マンガン、亜鉛、インジウム、銀、チタン、ゲルマニウム、ビスマス、アンチモン及びクロムからなる群から選択された1種以上の元素を有するものを含む。 Further anode active materials are materials containing components that can form lithium metal or alloys with lithium. Non-limiting examples of materials containing components that can form alloys with lithium are metals, metalloids or alloys thereof. As used herein, the term “alloy” should be understood to relate to alloys of two or more metals as well as alloys of one or more metals and one or more metalloids. If the alloy has overall metallic properties, the alloy may contain non-metallic components. In the texture of the alloy, a solid solution, a eutectic material (eutectic mixture), an intermetallic compound, or two or more of them coexist. Examples of such metal or metalloid components are not limited, and titanium (Ti), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), aluminum, indium (In), zinc (Zn), antimony (Sb), bismuth ( Bi), gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), silver (Ag), hafnium (Hf), zirconium (Zr), yttrium (Y), and silicon (Si). Preferred are group 4-14 metal and metalloid elements in the elements of the long-period periodic table, and particularly preferred are titanium, silicon and tin, especially silicon. Examples of tin alloys include silicon, magnesium (Mg), nickel, copper, iron, cobalt, manganese, zinc, indium, silver, titanium (Ti), germanium, bismuth, antimony and second component elements other than tin. Including those having one or more elements selected from the group consisting of chromium (Cr). Examples of silicon alloys are selected from the group consisting of tin, magnesium, nickel, copper, iron, cobalt, manganese, zinc, indium, silver, titanium, germanium, bismuth, antimony and chromium as second component elements other than silicon Including those having one or more elements.
アノード活物質のさらなる可能なものはリチウムイオンを貯蔵できるシリコンである。該シリコンは、例えばナノワイヤー、ナノチューブ、ナノ粒子、フィルム、ナノ多孔性シリコン又はシリコンナノチューブの様々な形態で使用される。該シリコンは集電体に堆積されてもよい。集電体は、金属線、金属グリッド、金属ウェブ、金属シート、金属ホイル又は金属プレートであってもよい。好ましい集電体は、金属ホイル、例えば銅ホイルである。シリコンの薄膜は、当業者に公知の任意の技術(例えば、スパッタリング技術)により金属ホイルに堆積されてもよい。Si薄膜電極の一案は、R.Elazari et al.;Electrochem.Comm.(2012),14,21−24に記載されている。また、本発明により、シリコン/炭素複合物をアノード活物質として使用することが可能である。 A further possible anode active material is silicon capable of storing lithium ions. The silicon is used in various forms, for example nanowires, nanotubes, nanoparticles, films, nanoporous silicon or silicon nanotubes. The silicon may be deposited on a current collector. The current collector may be a metal wire, metal grid, metal web, metal sheet, metal foil or metal plate. A preferred current collector is a metal foil, such as a copper foil. The thin film of silicon may be deposited on the metal foil by any technique known to those skilled in the art (eg, sputtering techniques). One proposal for a Si thin film electrode is R.A. Elazari et al. Electrochem. Comm. (2012), 14 , 21-24. Further, according to the present invention, it is possible to use a silicon / carbon composite as an anode active material.
アノード活物質の他の可能なものはTiのリチウムイオン挿入の酸化物である。 Another possible anode active material is an oxide of Ti lithium ion insertion.
好ましくは、本発明のリチウムイオン二次電池に存在するアノード活物質は、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得る炭素質物質から選択され、特に好ましくは、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得る炭素質物質は、結晶性炭素、硬質炭素及び非晶質炭素から選択され、特に好ましくはグラファイトである。他の好ましい実施態様において、本発明のリチウムイオン二次電池に存在するアノード活物質は、リチウムイオンを可逆的に吸蔵及び放出し得るシリコンから選択され、好ましくは、アノードは、シリコン又はシリコン/炭素複合物の薄膜を含む。さらなる好ましい実施態様において、本発明のリチウムイオン二次電池に存在するアノード活物質は、Tiのリチウムイオン挿入の酸化物から選択される。 Preferably, the anode active material present in the lithium ion secondary battery of the present invention is selected from carbonaceous materials capable of reversibly occluding and releasing lithium ions, and particularly preferably reversibly occluding and releasing lithium ions. The carbonaceous material which can be selected is selected from crystalline carbon, hard carbon and amorphous carbon, particularly preferably graphite. In another preferred embodiment, the anode active material present in the lithium ion secondary battery of the present invention is selected from silicon capable of reversibly occluding and releasing lithium ions, preferably the anode is silicon or silicon / carbon. Including thin films of composites. In a further preferred embodiment, the anode active material present in the lithium ion secondary battery of the present invention is selected from oxides of lithium ion insertion of Ti.
アノード及びカソードは、電極活物質、結合剤、任意に導電性物質及び増粘剤を分散させることにより、必要な場合に、溶媒中で、電極スラリー組成物を製造する工程、及び、該スラリー組成物を集電体の表面に塗布する工程により製造される。集電体は、金属線、金属グリッド、金属ウェブ、金属シート、金属ホイル又は金属プレートであってもよい。好ましくは、集電体は金属ホイル、例えば銅ホイル又はアルミホイルである。 The anode and cathode are prepared by dispersing an electrode active material, a binder, and optionally a conductive material and a thickener to produce an electrode slurry composition in a solvent, if necessary, and the slurry composition It is manufactured by a process of applying an object to the surface of the current collector. The current collector may be a metal wire, metal grid, metal web, metal sheet, metal foil or metal plate. Preferably, the current collector is a metal foil, such as a copper foil or an aluminum foil.
本発明の電気化学電池は、通例のさらなる構成要素、例えばセパレータ、筺体、ケーブル接続などを含んでもよい。筺体は、任意の形状、例えば立方体状又は円筒状、プリズム状であってもよく、或いは、使用された筺体は、ポーチとして加工された金属−プラスチックの複合フィルムである。好適なセパレータは、例えば、ガラス繊維セパレータ及びポリオレフィンセパレータなどのポリマー系セパレータである。 The electrochemical cell of the present invention may include customary additional components such as separators, enclosures, cable connections, and the like. The housing may be any shape, for example, cubic or cylindrical, prismatic, or the housing used is a metal-plastic composite film processed as a pouch. Suitable separators are, for example, polymer separators such as glass fiber separators and polyolefin separators.
複数の本発明の電気化学電池は、例えば直列接続又は並列接続で互いに接続されてもよい。好ましくは直列接続である。さらに、本発明は、本発明の電気化学電池を上記の装置に、例えばモバイル機器に使用する方法を提供する。モバイル機器の例としては、車両、例えば自動車、自転車及び航空機、又は、水上乗り物、例えばボート若しくは船舶が挙げられる。モバイル機器の他の例は、携帯用の、例えば、パソコン、特にノートパソコン、電話、電動工具、例えば建設業からのもの、特にドリル、電池式スクリュードライバー又は電池式鋲打ち機である。ただし、本発明のリチウムイオン電池は固定エネルギー貯蔵(stationary energy stores)にも使用し得る。 A plurality of electrochemical cells of the present invention may be connected to each other, for example, in series connection or parallel connection. A series connection is preferable. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method of using the electrochemical cell of the present invention in the above apparatus, for example, in a mobile device. Examples of mobile devices include vehicles such as cars, bicycles and aircraft, or water vehicles such as boats or ships. Other examples of mobile devices are portable, for example personal computers, in particular notebook computers, telephones, power tools, such as those from the construction industry, in particular drills, battery-powered screwdrivers or battery-powered nailers. However, the lithium ion battery of the present invention can also be used for stationary energy stores.
以下、実施例を参照して本発明を説明するが、ただ本発明に制限されない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described with reference to examples, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
1.一般式(I)の化合物の製造
1a) ビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸リチウム LiOOP(OCH2CF3)2(化合物1)
8モルの2,2,2−トリフルオロエタノールを1モルのP4O10(両物質ともAlfa Aesar社製)と反応させることによりビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸リチウムを製造した。精留(rectification)により該反応生成物を精製し、無色結晶の形態でビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸を得た。その酸をジエチルエーテルに溶解して冷却した、ジエチルエーテル中LiHのスラリーを添加した。溶媒を蒸発した後に、白色粉末のビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸リチウムを得た。
1. Production of compounds of general formula (I) 1a) Lithium bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate LiOOP (OCH 2 CF 3 ) 2 (compound 1)
Lithium bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate by reacting 8 moles of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol with 1 mole of P 4 O 10 (both materials from Alfa Aesar) Manufactured. The reaction product was purified by rectification to give bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphoric acid in the form of colorless crystals. The acid was dissolved in diethyl ether and cooled, and a slurry of LiH in diethyl ether was added. After evaporating the solvent, white powder lithium bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate was obtained.
1b) ビス−(1,1,1,3,3,3−ヘキサフルオロイソプロピル)リン酸リチウム LiOOP(OCH(CF3)2)2(化合物2)
ジメチル炭酸塩中の1モルのP4O10の氷で冷やした混合物に8モルのLi[OCH(CF3)2]懸濁液を投入する。その後、冷却を取り外し、該混合物を還流下で3時間加熱する。その後、真空中で反応混合物の体積を80%減少する。CH2Cl2を添加し、該混合物を4時間撹拌する。LiOOP(OCH(CF3)2)2の白色沈殿物を濾過し、冷たいCH2Cl2で洗浄し、真空中で乾燥する。
1b) Lithium bis- (1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl) phosphate LiOOP (OCH (CF 3 ) 2 ) 2 (Compound 2)
8 mol of Li [OCH (CF 3 ) 2 ] suspension is charged into a mixture of 1 mol of P 4 O 10 in dimethyl carbonate cooled with ice. The cooling is then removed and the mixture is heated under reflux for 3 hours. Thereafter, the volume of the reaction mixture is reduced by 80% in vacuo. CH 2 Cl 2 is added and the mixture is stirred for 4 hours. The white precipitate of LiOOP (OCH (CF 3 ) 2 ) 2 is filtered, washed with cold CH 2 Cl 2 and dried in vacuo.
2.電解質組成物
1:1の容積比の炭酸エチレン(EC)と炭酸ジメチル(DMC)、及び1MのLiPF6又は1MのLiBF4との混合物、比較例として製造した。LiPF6を含有する混合物は、また、本発明のゲル電解質組成物の製造に使用した。異なる量のビス−(2,2,2−トリフルオロエチル)リン酸リチウムを、LiPF6含有の混合物に添加した。その混合物を任意に超音波浴で数時間処理した。デカンテーションにより又は任意に遠心分離により、余分な溶媒を分離した。この場合には、ごく僅かな量の余分な溶媒を除去した。上記の濃度は、余分な溶媒を分離する前の試料に言及する。全ての本発明の組成物は均質ゲルの外観を有していた。
2. Electrolyte composition A 1: 1 volume ratio of a mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and 1M LiPF 6 or 1M LiBF 4 was prepared as a comparative example. The mixture containing LiPF 6 was also used in the production of the gel electrolyte composition of the present invention. Different amounts of lithium bis- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate were added to the LiPF 6 containing mixture. The mixture was optionally treated for several hours in an ultrasonic bath. Excess solvent was separated by decantation or optionally by centrifugation. In this case, a negligible amount of excess solvent was removed. The above concentrations refer to the sample before separating the excess solvent. All inventive compositions had the appearance of a homogeneous gel.
2a) 導電性
InLab710プローブを備えるMetrohm SevenMulti電気伝動度測定器により、25℃で導電性を測定した。結果を表1に示す。
2a) Conductivity Conductivity was measured at 25 ° C. with a Metrohm SevenMulti electrical conductivity meter equipped with an InLab710 probe. The results are shown in Table 1.
本発明の実施例5は、導電性塩含有の組成物より低い導電性を示すが、ゲルであった。 Example 5 of the present invention showed a lower conductivity than the conductive salt-containing composition, but was a gel.
2b) レオロジー
室温で本発明の実施例1についてレオロジー測定を行った。25mmの直径及び200ミクロンのギャップを備えるプレート−ペイト配置(plate-pate geometry)を有する回転レオメータを使用した。試料の蒸発を避けるために、シリコン油で試料を囲んだ。変形スイープ(deformation sweep)の結果を図1に示し、振動スイープ(oscillation sweep)の結果を図2に示す。G’は弾性率を表し、G’’は損失弾性率を表し、γは変形率であり、ωは角周波数である。図1(周波数スイープ、貯蔵及び損失弾性率(パスカル)対半径周波数(rad/s))及び図2(変形率スイープ、貯蔵及び損失弾性率(パスカル)対変形率(%))から分かるように、本発明の電解質組成物1はゲルのレオロジー挙動を示す。
2b) Rheology Rheology measurements were performed on Example 1 of the present invention at room temperature. A rotary rheometer with a plate-pate geometry with a diameter of 25 mm and a gap of 200 microns was used. The sample was surrounded by silicone oil to avoid sample evaporation. The result of the deformation sweep is shown in FIG. 1, and the result of the oscillation sweep is shown in FIG. G ′ represents an elastic modulus, G ″ represents a loss elastic modulus, γ is a deformation rate, and ω is an angular frequency. As can be seen from FIG. 1 (frequency sweep, storage and loss modulus (pascal) vs. radial frequency (rad / s)) and FIG. 2 (deformation rate sweep, storage and loss modulus (pascal) vs. deformation rate (%)). The
2c) サイクリックボルタンメトリー
プラチナ作用電極(直径が1mm)とリチウムホイルからなる作用及び参照電極とを備えるMetrohm Autolab PGStat101により、サイクリックボルタンメトリー測定を行った。走査速度(scan rate)を1秒当たり10mVに設定した。電解質は、1mol/LのLiOOP(OCH2CF3)2と混合したEC/DMC(1:1)中の1mol/LのLi[PF6]からなるものであった。結果を図3及び4(EC/DMC(1:1)中の1mol/LのLi[PF6]中のLiOOP(OCH2CF3)2のサイクリックボルタモグラム)に示す。
2c) Cyclic voltammetry Cyclic voltammetry measurement was performed with a
2d) 性能試験
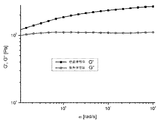
2mAh/cm2の電気容量を有するリチウムニッケルコバルトマンガン酸化物(NCM111)電極及び2.15mAh/cm2の電気容量を有するグラファイト電極を用いて、ボタン電池を組み立てた。ガラス繊維フィルターセパレータ(Whatmann GF/D)をセパレータとして使用した。該セパレータを100μlの電解質に浸漬した。電極は、0.235mol/LのLiOOP2(OCH2CF3)2と混合したEC/DMC(1:1)中の1mol/LのLi[PF6]からなるものであった。全ての電気化学測定は、25℃で人工気候室中で行った。表2に示した手順により、サイクル数に関しての該電池の性能を測定した。
2d) lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese oxide having a capacitance of performance test 2mAh / cm 2 (NCM111) with graphite electrodes having a capacitance of the electrode and 2.15mAh / cm 2, were assembled button cell. A glass fiber filter separator (Whatmann GF / D) was used as the separator. The separator was immersed in 100 μl of electrolyte. The electrode consisted of 1 mol / L Li [PF 6 ] in EC / DMC (1: 1) mixed with 0.235 mol / L LiOOP 2 (OCH 2 CF 3 ) 2 . All electrochemical measurements were performed in an artificial climate room at 25 ° C. According to the procedure shown in Table 2, the performance of the battery with respect to the number of cycles was measured.
サイクル数による、0.235mol/LのLiOOP2(OCH2CF3)2と混合したEC/DMC(1:1)中の1mol/LのLi[PF6]からなる電解質の比電気容量を図5に示し、中空三角形(open triangles)が充電の間の比電気容量を表し、中空でない三角形(full triangles)が放電の間の比電気容量を表す。 The specific capacity of an electrolyte composed of 1 mol / L Li [PF 6 ] in EC / DMC (1: 1) mixed with 0.235 mol / L LiOOP 2 (OCH 2 CF 3 ) 2 according to the number of cycles. In FIG. 5, hollow triangles represent the specific capacitance during charging, and full triangles represent the specific capacitance during discharge.
Claims (6)
の化合物を、環状及び非環状の有機炭酸塩から選択される少なくとも1種の非プロトン性有機溶媒又は溶媒混合物、一般式(I)の化合物、少なくとも1種の、一般式(I)の化合物とは異なる導電性塩及びさらなる添加剤
を含む電解質組成物中のゲル化剤として使用する方法。 Formula (I),
The compounds, cyclic and at least one aprotic organic solvent Nakadachimata selected from acyclic organic carbonate is a solvent mixture, compounds of general formula (I), at least one of the general formula (I) Conductive salts different from the compounds and further additives
How to use as a gelling agent in the electrolyte composition comprising.
の化合物を製造する方法。 By reacting LiOR 1 , LiOR 2 and / or LiOR 1 R 2 OLi with phosphorus pentoxide, the general formula (I),
The method of manufacturing the compound of this.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14156852 | 2014-02-26 | ||
| EP14156852.7 | 2014-02-26 | ||
| PCT/EP2015/053905 WO2015128363A1 (en) | 2014-02-26 | 2015-02-25 | Inorganic coordination polymers as gelling agents |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017515919A JP2017515919A (en) | 2017-06-15 |
| JP2017515919A5 JP2017515919A5 (en) | 2018-03-22 |
| JP6593802B2 true JP6593802B2 (en) | 2019-10-23 |
Family
ID=50156681
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016554436A Active JP6593802B2 (en) | 2014-02-26 | 2015-02-25 | Inorganic coordination polymers as gelling agents |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10074873B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3111502B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6593802B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102460283B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106463764B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015128363A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6299357B2 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2018-03-28 | Dic株式会社 | Non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium ion secondary battery using the same |
| JP6458803B2 (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2019-01-30 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | Electrolytic solution and method for producing phosphate |
| PL3396768T3 (en) * | 2015-12-25 | 2020-11-16 | Stella Chemifa Corporation | Non-aqueous electrolyte solution for secondary battery, and secondary battery provided therewith |
| KR102209829B1 (en) * | 2016-07-25 | 2021-01-29 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Additive for electrolyte of lithium battery, electrolyte including the same and lithium battery using the electrolyte |
| US10707531B1 (en) | 2016-09-27 | 2020-07-07 | New Dominion Enterprises Inc. | All-inorganic solvents for electrolytes |
| KR102546609B1 (en) | 2018-07-13 | 2023-06-23 | 오씨아이 주식회사 | Etching solution for silicon substrate |
| CN111628219A (en) * | 2020-06-05 | 2020-09-04 | 宁德新能源科技有限公司 | Electrolyte solution, electrochemical device containing electrolyte solution, and electronic device |
| EP4183742A1 (en) | 2021-11-19 | 2023-05-24 | Technische Universität Dresden | Ligand-assisted deoxygenation of phosphates to nitrogenous phosphorous (v) precursors and their conversion to various oxyphosphorus compounds |
| DE102022120599A1 (en) | 2022-08-16 | 2024-02-22 | Technische Universität Dresden, Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts | Process for recycling organophosphates |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4039636A (en) | 1973-06-28 | 1977-08-02 | The Dow Chemical Company | Magnesium dialkyl phosphates and their preparation |
| JP2832794B2 (en) * | 1993-11-17 | 1998-12-09 | 花王株式会社 | Phosphoric acid diester polyvalent metal salt, method for producing the same, and oil gelling agent containing the phosphoric acid diester polyvalent metal salt |
| IT1318460B1 (en) * | 2000-04-11 | 2003-08-25 | Ausimont Spa | PRESERVATIVES OF FORMULATIONS FOR TOPICAL USE. |
| JP4529274B2 (en) * | 2000-04-18 | 2010-08-25 | ソニー株式会社 | Non-aqueous electrolyte battery |
| JP4542232B2 (en) | 2000-06-07 | 2010-09-08 | 日本化学工業株式会社 | Koji Stabilizer and Koji Stabilizing Method |
| JP2003301164A (en) * | 2002-02-05 | 2003-10-21 | Nitto Denko Corp | Polymerizable gelling agent |
| JP4097261B2 (en) * | 2003-06-02 | 2008-06-11 | 竹本油脂株式会社 | Synthetic fiber treating agent and synthetic fiber treating method for use in spinning process or non-woven fabric production by dry method |
| JP4820993B2 (en) | 2006-01-20 | 2011-11-24 | 国立大学法人山口大学 | Organic liquid gelling agent comprising aromatic compound having perfluoroalkyl group |
| CN102473919A (en) * | 2009-07-16 | 2012-05-23 | 住友精化株式会社 | Gelling agent for an electrolyte solution for an alkaline battery |
| CN101702449B (en) * | 2009-11-03 | 2011-08-17 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Gel electrolyte of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof |
| JP2014022333A (en) * | 2012-07-23 | 2014-02-03 | Asahi Kasei Corp | Electrolyte for nonaqueous electricity storage device |
| JP6673639B2 (en) * | 2014-02-14 | 2020-03-25 | ステラケミファ株式会社 | Non-aqueous electrolyte for secondary battery and secondary battery having the same |
| CN103915647B (en) * | 2014-03-31 | 2017-02-15 | 绍兴安卡汽车配件有限公司 | Low-temperature lithium ion battery |
-
2015
- 2015-02-25 WO PCT/EP2015/053905 patent/WO2015128363A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-02-25 US US15/121,613 patent/US10074873B2/en active Active
- 2015-02-25 EP EP15706475.9A patent/EP3111502B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2015-02-25 JP JP2016554436A patent/JP6593802B2/en active Active
- 2015-02-25 KR KR1020167023576A patent/KR102460283B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2015-02-25 CN CN201580010468.1A patent/CN106463764B/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102460283B1 (en) | 2022-10-27 |
| EP3111502B1 (en) | 2018-11-14 |
| KR20160127007A (en) | 2016-11-02 |
| CN106463764B (en) | 2019-07-09 |
| CN106463764A (en) | 2017-02-22 |
| EP3111502A1 (en) | 2017-01-04 |
| JP2017515919A (en) | 2017-06-15 |
| US20160365605A1 (en) | 2016-12-15 |
| WO2015128363A1 (en) | 2015-09-03 |
| US10074873B2 (en) | 2018-09-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6593802B2 (en) | Inorganic coordination polymers as gelling agents | |
| EP3022797B1 (en) | Use of reactive lithium alkoxyborates as electrolyte additives in electrolytes for lithium ion batteries | |
| CN105556728B (en) | Ethylene oxide derivatives as additives for electrolytes in lithium ion batteries | |
| EP3357115A1 (en) | Non-aqueous electrolytes for high energy lithium-ion batteries | |
| US10249906B2 (en) | Use of fluoroisopropyl derivatives as additives in electrolytes | |
| US10541446B2 (en) | Acrylonitrile derivatives as additive for electrolytes in lithium ion batteries | |
| EP3391453B1 (en) | Cyanoalkyl sulfonylfluorides for electrolyte compositions for high energy lithium-ion batteries | |
| EP2768064A1 (en) | Use of substituted alkynyl sulfonates, carbonates and oxalates as additives in electrolytes of secondary lithium-ion batteries | |
| JP6522004B2 (en) | Method of using reactive ionic liquid as additive for electrolyte of lithium ion secondary battery | |
| CN109716578B (en) | Electrochemical cell comprising difunctional silyl phosphonate | |
| EP3449524A1 (en) | Electrolyte comprising cyclic dinitriles and fluoroethers | |
| KR102540018B1 (en) | Substituted isoxazoles for lithium batteries |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180209 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180209 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190125 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190129 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20190426 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20190626 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190724 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190820 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20190917 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6593802 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |