[第1実施形態]
以下添付図面を参照しながら、本発明の実施の形態について説明し、本発明の理解に供する。なお、以下の実施の形態は、本発明を具体化した一例であって、本発明の技術的範囲を限定する性格のものではない。
First Embodiment
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings for understanding of the present invention. The following embodiment is an example embodying the present invention, and is not of the nature to limit the technical scope of the present invention.
[配薬支援システム10]
図1に示すように、本発明の実施の形態に係る配薬支援システム10は、調剤支援装置1、読取端末2、薬品分包装置3、プリンタ4、配薬支援装置5、携帯端末6、及び読取端末7などを備える。前記調剤支援装置1、前記読取端末2、前記薬品分包装置3、及び前記プリンタ4は、ネットワークN1を介して無線又は有線で通信可能に接続されている。また、前記配薬支援装置5、前記携帯端末6、及び前記読取端末7は、ネットワークN2を介して無線又は有線で通信可能に接続されている。なお、前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2は、LAN、WAN、インターネット、又はイントラネットなどである。
[Dispensing support system 10]
As shown in FIG. 1, the drug dispensing support system 10 according to the embodiment of the present invention includes a dispensing support device 1, a reading terminal 2, a medicine packaging device 3, a printer 4, a drug dispensing support device 5, a portable terminal 6, And the reading terminal 7 and the like. The dispensing support device 1, the reading terminal 2, the medicine package device 3, and the printer 4 are communicably connected wirelessly or by wire via a network N1. Moreover, the said medicine distribution assistance apparatus 5, the said portable terminal 6, and the said reading terminal 7 are connected so that communication is possible by radio | wireless or a wire communication via the network N2. The network N1 and the network N2 are a LAN, a WAN, the Internet, an intranet, or the like.
前記調剤支援装置1、前記読取端末2、前記薬品分包装置3、及び前記プリンタ4は、薬品の調剤が行われる薬局Aに配置される。なお、前記調剤支援装置1は薬局側端末の一例であるが、その配置場所は、前記ネットワークN1に接続可能であれば前記薬局Aの外部であってもよい。一方、前記配薬支援装置5、前記携帯端末6、及び前記読取端末7は、前記薬局Aで調剤された薬品の配送先となる老健施設B各々に配置される。前記老健施設Bには、前記薬局Aで調剤された薬品を服用する複数の服用者が入居する施設である。なお、前記老健施設Bは、予め定められた配薬グループの一例に過ぎず、例えば予め定められた複数の服用者の自宅を含む地域又は配送ルートも前記配薬グループの一例である。また、前記配薬支援装置5は、施設側端末の一例であるが、その配置場所は、前記ネットワークN2に接続されて前記老健施設Bで使用可能であれば前記老健施設Bの外部であってもよい。さらに、前記調剤支援装置1が前記配薬支援装置5の機能を兼ねることも考えられる。
The dispensing support device 1, the reading terminal 2, the medicine package device 3, and the printer 4 are disposed in the pharmacy A where medicine dispensing is performed. The dispensing support device 1 is an example of a pharmacy-side terminal, but the location may be outside the pharmacy A as long as it can be connected to the network N1. On the other hand, the medicine distribution support device 5, the portable terminal 6, and the reading terminal 7 are disposed in each of the health facilities B serving as a delivery destination of the medicine dispensed by the pharmacy A. The health care facility B is a facility in which a plurality of users who take the medicine dispensed at the pharmacy A enter. The old-age facility B is only an example of a predetermined drug distribution group, and for example, a region including the homes of a plurality of predetermined dosers or a delivery route is also an example of the drug distribution group. Moreover, although the said medicine distribution assistance apparatus 5 is an example of a plant | facility side terminal, if the arrangement | positioning location is connected to the said network N2 and it can use it with the said elderly care facility B, it is the said elderly care facility B outside. It is also good. Furthermore, it is also conceivable that the dispensing support device 1 doubles as the function of the drug distribution support device 5.
[薬品分包装置3]
前記薬品分包装置3は、前記調剤支援装置1から入力される処方データに基づいて薬品を服用時期ごとに薬包81(図4参照)で分包することが可能な調剤機器である。例えば、前記薬品分包装置3は、錠剤を分包する錠剤分包機又は散薬を分包する散薬分包機である。具体的に、前記錠剤分包機は、複数種類の錠剤が収容された複数の薬剤カセットを有し、処方データに従って前記薬剤カセットから錠剤を払い出して服用時期ごとに前記薬包81で包装する分包動作を実行する。また、前記散薬分包機は、投入された散薬を処方データに従って服用時期ごとに前記薬包81で包装する分包動作を実行する。これらの分包動作に用いられる前記薬包81が分包容器の一例である。さらに、前記錠剤分包機又は前記散薬分包機が、錠剤及び散薬を服用時期ごとに一包化することが可能な構成も考えられる。なお、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬品分包装置3に設けられた連続する長尺状の薬包シートの一部の加熱溶融により前記薬包81が形成され、前記薬包81各々の間には切り離しを容易に行うためのミシン目が形成される。
[Drug Packaging Device 3]
The medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 is a dispensing apparatus capable of packaging the medicine in the medicine package 81 (see FIG. 4) at each dosing timing based on the prescription data input from the dispensing support apparatus 1. For example, the medicine dispensing device 3 is a tablet dispensing machine for dispensing tablets or a powder dispensing machine for dispensing powders. Specifically, the tablet packaging machine has a plurality of drug cassettes containing a plurality of types of tablets, and the tablets are taken out from the drug cassette according to prescription data and packaged with the drug package 81 at each dosing time Execute the action. In addition, the powder packager carries out a packaging operation in which the input powder is packaged with the medicine package 81 at each dosing time according to the prescription data. The medicine package 81 used for these packaging operations is an example of the packaging container. Furthermore, a configuration is also conceivable in which the tablet dispensing machine or the powder dispensing machine can package tablets and powders at each dose. In the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3, the medicine package 81 is formed by heating and melting a part of the continuous long medicine package sheet provided in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3. Perforations are formed between them to facilitate separation.
前記薬品分包装置3は、前記薬品分包装置3を制御する制御部31、及び前記薬包81に情報を印刷する分包プリンタ32を備える。前記制御部31は、CPU、ROM、及びRAMなどを備える。前記分包プリンタ32は、前記制御部31からの制御指示に従って、前記薬包81に、前記薬包81に収容される薬品を服用する服用者を示す服用者ID(服用者識別情報の一例)、前記薬包81に収容される薬品の服用時期、及び予め定められた配送先識別情報を含む第1配薬情報を印刷する。前記配送先識別情報は、前記薬包81の薬品の服用者が入居している前記老健施設Bを示す配送先ID又は配送先名などの情報であって、後述の服用者マスターに登録されている。なお、前記服用時期を示す文字に代えて、又は前記服用時期を示す文字と共に、前記服用時期ごとに予め定められた服用時期コードの数字(例えば2桁の数字)又は前記服用時期を示すピクトグラムなどの画像が前記薬袋81に印刷されることも考えられる。ここで、前記服用時期コードの数字は文字として印刷されてもよいが、前記薬品分包装置3が前記ピクトグラムを印刷する機能を有する場合には、前記制御部31がその機能を利用して、前記服用時期コードの数字の画像として予め登録された画像を前記ピクトグラムに代えて印刷することも考えられる。これにより、既存のシステムにおいて前記薬包81に前記服用時期コードの数字を印刷させることが可能である。
The medicine dispensing apparatus 3 includes a control unit 31 that controls the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 and a dispensing printer 32 that prints information on the medicine package 81. The control unit 31 includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and the like. The dispensing package 32 indicates a doser ID (an example of doser identification information) indicating a doser who takes the medicine contained in the medicine package 81 in the medicine package 81 according to a control instruction from the control unit 31. The first drug distribution information including the dosing timing of the medicine contained in the medicine package 81 and the predetermined delivery destination identification information is printed. The delivery destination identification information is information such as a delivery destination ID or delivery destination name indicating the health care facility B in which the person taking the medicine of the medicine package 81 resides, and is registered in the dosing person master described later There is. In addition, instead of the letter indicating the dosing time, or together with the letter indicating the dosing time, a number (for example, a two-digit number) of a dosing time code predetermined for each dosing time or a pictogram indicating the dosing time It is also conceivable that an image of the image is printed on the medicine bag 81. Here, the numeral of the dosing timing code may be printed as characters, but when the medicine packaging device 3 has a function of printing the pictogram, the control unit 31 utilizes the function, It is also conceivable to replace the pictogram with an image registered in advance as an image of the number of the dosing timing code in place of the pictogram. Thereby, it is possible to make the medicine package 81 print the number of the dose timing code in the existing system.
特に、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記分包プリンタ32により、前記第1配薬情報を示す一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコード811(図4参照)が前記薬包81に印刷される。ここに、前記分包プリンタ32を用いて前記薬包81に前記第1配薬情報を印刷するときの前記制御部31が第1記録手段の一例である。なお、前記薬包81に貼付されるラベルなどの第1記録媒体に前記第1配薬情報が印刷されることも他の実施形態として考えられる。また、前記薬包81にICタグのような第1記録媒体が付されることも考えられる。この場合、前記薬品分包装置3が、前記第1記録媒体に前記第1配薬情報を記録するICリーダーライタのような記録手段を備える構成が考えられる。
In particular, in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3, the dispensing package 32 prints a code 811 (see FIG. 4) such as a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code indicating the first medicine information on the medicine package 81. . Here, the control unit 31 when printing the first medicine distribution information on the medicine package 81 using the package printer 32 is an example of a first recording unit. In addition, it is also considered as another embodiment that the first drug distribution information is printed on a first recording medium such as a label attached to the medicine package 81. It is also conceivable that a first recording medium such as an IC tag is attached to the medicine package 81. In this case, a configuration is conceivable in which the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 includes recording means such as an IC reader / writer that records the first medicine distribution information on the first recording medium.
また、前記薬品分包装置3は、一の服用者が服用する薬品を服用時期ごとに一連の前記薬包81に連続して分包する服用者別分包処理と、予め定められた配薬グループに属する複数の服用者が服用する薬品を服用時期ごとに並べて一連の前記薬包81に連続して分包する時期別分包処理とを実行可能である。前記薬品分包装置3では、前記服用者別分包処理及び前記時期別分包処理のいずれが実行される場合でも、前記分包プリンタ32によって前記薬包81各々に前記コード811が印刷される。
In addition, the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 performs a pack separation process according to the user for continuously dispensing and packing the medicine taken by one doser in a series of the medicine package 81 at each dosing time, and a predetermined distribution. It is possible to arrange the medicines taken by a plurality of users who belong to the group at different times, and to carry out the time-wise distribution process in which the medicine packages 81 are continuously divided. In the medicine packager 3, the package 8 prints the code 811 on each medicine package 81 by the packager 32 regardless of whether the packager by user or the package by period is executed. .
なお、前記時期別分包処理が実行される場合には、前記一連の薬包81を切り離すことなく配送することも考えられるため、前記分包プリンタ32により最初又は最後の前記薬包81のみに前記コード811が印刷されることも他の実施形態として考えられる。この場合、後述の収容時照合処理(図10参照)において、前記服用時期ごとに連なった前記薬包81のうち最初又は最後の前記薬包81に印刷された前記第1配薬情報が照合の対象となる。
In addition, since it is also considered that the said series of medicine package 81 is delivered without cutting off when the said time-sorted packing process is performed, only the first or last medicine package 81 by the packing printer 32 is considered. It is also conceivable as another embodiment that the code 811 is printed. In this case, the first drug information printed on the first or last medicine package 81 out of the medicine packages 81 connected at each dosing time in the accommodation verification process (see FIG. 10), which will be described later, It becomes an object.
[プリンタ4]
前記プリンタ4は、予め定められた配薬グループに属する複数の服用者の前記薬包81を同一服用時期ごとに纏めて収容する際に使用される薬袋82(配送容器の一例:図4参照)に貼付されるラベル821(第2記録媒体の一例:図4参照)に情報を印刷するために用いられる。具体的に、前記プリンタ4は、前記調剤支援装置1からの制御指示に従って、前記ラベル821に、前記薬袋82に収容される前記薬包81に対応する服用時期及び予め定められた配送先識別情報を含む第2配薬情報を印刷(記録)する。特に、前記プリンタ4は、前記ラベル821に、前記第2配薬情報を示す一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコード822(図4参照)を印刷する。そして、前記ラベル821は、前記薬袋82に貼付して用いられる。なお、前記配送先識別情報は、前記薬包81の薬品の服用者が入居している前記老健施設Bを示す情報であって、後述の服用者マスターに予め登録されている。
[Printer 4]
The printer 4 is a medicine bag 82 (an example of a delivery container: see FIG. 4) used when collectively storing the medicine packages 81 of a plurality of users belonging to a predetermined medicine distribution group at the same time of dosing. Is used to print information on a label 821 (an example of the second recording medium: see FIG. 4) attached to the. Specifically, the printer 4 uses the label 821 in accordance with the control instruction from the dispensing support device 1 to determine the dosing timing and the predetermined delivery destination identification information corresponding to the medicine package 81 contained in the medicine bag 82. Print (record) the second drug information including In particular, the printer 4 prints on the label 821 a code 822 (see FIG. 4) such as a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code indicating the second drug distribution information. The label 821 is used by being attached to the medicine bag 82. The delivery destination identification information is information indicating the health care facility B in which the person taking the medicine of the medicine package 81 is located, and is registered in advance in the person taking the medicine master described later.
前記ラベル821は、前記薬袋82に前記第2配薬情報を記録するための手段の一例であり、前記プリンタ4によって前記薬袋82に前記第2配薬情報が直接印刷されることも他の実施形態として考えられる。また、前記薬袋82にICタグのような第2記録媒体が付されることも考えられる。この場合、前記調剤支援装置1が、前記第2記録媒体に前記第2配薬情報を記録するICリーダーライタのような記録手段を備える構成が考えられる。なお、前記プリンタ4は、前記調剤支援装置1から受信するプリントデータに従って、前記処方データに対応する処方箋を印刷するためにも利用される。
The label 821 is an example of means for recording the second drug distribution information in the drug bag 82, and the printer 4 directly prints the second drug distribution information on the drug bag 82 in another embodiment. It can be considered as a form. It is also conceivable that a second recording medium such as an IC tag is attached to the medicine bag 82. In this case, a configuration is conceivable in which the dispensing support device 1 includes recording means such as an IC reader / writer that records the second drug supply information on the second recording medium. The printer 4 is also used to print a prescription corresponding to the prescription data according to the print data received from the dispensing support device 1.
[調剤支援装置1]
前記調剤支援装置1は、制御部11、データ記憶部12、通信インターフェース13、表示装置14、操作装置15、及びドライブ装置16などを備えるパーソナルコンピュータである。前記調剤支援装置1の単体を本発明に係る配薬支援システムとして捉えてもよい。また、前記調剤支援装置1には、前記調剤支援装置1に処方データを入力する電子カルテシステム又は処方入力端末などの上位システム(不図示)が前記ネットワークN1を介して接続されている。なお、前記調剤支援装置1において前記操作装置15を用いて処方データが入力可能な構成も考えられる。
[Dispensing support device 1]
The dispensing support device 1 is a personal computer including a control unit 11, a data storage unit 12, a communication interface 13, a display device 14, an operation device 15, a drive device 16, and the like. The single substance of the dispensing support device 1 may be regarded as a medicine dispensing support system according to the present invention. In addition, a high-level system (not shown) such as an electronic medical record system or a prescription input terminal for inputting prescription data to the dispensing support device 1 is connected to the dispensing support device 1 via the network N1. In addition, the composition which can input prescription data in the said dispensing assistance apparatus 1 using the said operating device 15 is also considered.
前記制御部11は、CPU、ROM、及びRAM等を備える。前記CPUは、各種の制御プログラムに従って処理を実行することにより前記調剤支援装置1を制御するプロセッサーである。前記ROMは、前記CPUにより実行されるBIOS等のプログラムが予め記憶された不揮発性メモリである。前記RAMは、前記CPUによる各種の制御プログラムの展開及びデータの一時記憶に用いられる揮発性メモリ又は不揮発性メモリである。
The control unit 11 includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and the like. The CPU is a processor that controls the dispensing support device 1 by executing processing in accordance with various control programs. The ROM is a non-volatile memory in which a program such as a BIOS executed by the CPU is stored in advance. The RAM is a volatile memory or a non-volatile memory used for expansion of various control programs by the CPU and temporary storage of data.
前記データ記憶部12は、前記制御部11によって実行される各種のアプリケーションプログラム及び各種のデータを記憶するハードディスク又はSSD等の不揮発性の記憶手段である。具体的に、前記データ記憶部12には、後述の処方データ発行処理(図5参照)、収容時照合処理(図10参照)及び配送時照合処理(図11参照)などを前記制御部11に実行させるための調剤支援プログラムが記憶されている。
The data storage unit 12 is a non-volatile storage unit such as a hard disk or an SSD that stores various application programs executed by the control unit 11 and various data. Specifically, the data storage unit 12 includes a prescription data issuing process (see FIG. 5), an accommodation verification process (see FIG. 10), a delivery verification process (see FIG. 11), etc. A dispensing support program for execution is stored.
例えば、前記制御部11は、前記調剤支援プログラムに従って各種の処理を実行することにより、第2記録部111、判定部112、及び第1報知部113として機能する。ここに、前記第2記録部111、前記判定部112、及び前記第1報知部113として機能するときの前記制御部11が第2記録手段、判定手段、及び第1報知手段の一例である。
For example, the control unit 11 functions as a second recording unit 111, a determination unit 112, and a first notification unit 113 by executing various processes in accordance with the dispensing support program. Here, the control unit 11 when functioning as the second recording unit 111, the determination unit 112, and the first notification unit 113 is an example of a second recording unit, a determination unit, and a first notification unit.
前記第2記録部111は、前記プリンタ4を用いて、予め定められた前記老健施設B(配薬グループ)に属する複数の服用者の前記薬包81を同一服用時期ごとに収容する際に用いられる前記薬袋82に付される前記ラベル821に、前記服用時期及び前記老健施設Bの配送先識別情報を含む前記第2配薬情報である前記コード822を印刷(記録)する。
The second recording unit 111 is used when storing the medicine package 81 of a plurality of dosers belonging to the predetermined health care facility B (drug distribution group) using the printer 4 at the same dose timing. On the label 821 attached to the medicine bag 82, the code 822 which is the second drug delivery information including the dosing time and the delivery destination identification information of the old-life facility B is printed (recorded).
前記判定部112は、前記薬包81から読み取られる前記第1配薬情報の前記服用時期及び前記配送先識別情報と前記薬袋82から読み取られる前記第2配薬情報の前記服用時期及び前記配送先識別情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。なお、前記第1配薬情報及び前記第2配薬情報の読み取りは前記読取端末2によって行われる。
The determination unit 112 determines the dosing timing and delivery destination identification information of the first drug distribution information read from the medicine package 81 and the dosing timing and delivery destination of the second drug distribution information read from the medicine bag 82. It is determined whether the identification information matches. The reading of the first drug distribution information and the second drug distribution information is performed by the reading terminal 2.
前記第1報知部113は、前記判定部112の判定結果を報知する。例えば、前記第1報知部113は、前記判定部112の判定結果が一致であるか否かを、前記読取端末2又は前記表示装置14に表示させる。なお、前記第1報知部113は、前記判定部112の判定結果が一致でない場合にのみエラーメッセージを表示させることも考えられる。
The first notification unit 113 notifies the determination result of the determination unit 112. For example, the first notification unit 113 causes the reading terminal 2 or the display device 14 to display whether the determination result of the determination unit 112 is the same. The first notification unit 113 may display an error message only when the determination result of the determination unit 112 is not the same.
また、前記データ記憶部12には、薬品マスター、服用者マスター、薬剤師マスター、処方箋区分マスター、診療科マスター、及び病棟マスターなどの各種データベースも記憶されている。例えば、前記薬品マスターには、薬品コード、薬品名、JANコード(又はRSS)、薬瓶コード、区分(剤形:散薬、錠剤、水剤、外用薬など)、比重、薬品種(普通薬、毒薬、麻薬、劇薬、抗精神薬、治療薬など)、配合変化、賦形薬品、注意事項などの情報が含まれる。さらに、前記薬品マスターには、薬品ごとに発現するおそれのある副作用に関する副作用関連情報も含まれる。これにより、前記調剤支援装置1において、前記制御部11は、例えば副作用の内容が選択された場合に、その副作用の原因となっている可能性の高い薬品を前記副作用関連情報と前記処方データとに基づいて特定する被疑薬特定処理を実行することも可能である。また、前記服用者マスターには、服用者各々の服用者ID、氏名、性別、年齢、住所、既往歴、家族情報、診療科、及び入院病棟と共に、入居先の前記老健施設Bに対応する前記配送先識別情報などの情報が含まれる。なお、前記服用者とは、前記老健施設Bに入居している入居者、及び医療機関で診療を受けている患者を含む概念である。
The data storage unit 12 also stores various databases such as a medicine master, a user master, a pharmacist master, a prescription division master, a medical department master, and a ward master. For example, the drug master includes drug code, drug name, JAN code (or RSS), vial code, classification (dosage form: powder, tablet, liquid, external medicine, etc.), specific gravity, drug type (conventional drug, It contains information such as poisons, narcotics, opiates, antipsychotics, remedies etc., formulation changes, excipients, and precautions. Furthermore, the drug master also includes side effect related information on side effects that may occur for each drug. Thereby, in the dispensing support device 1, when the content of the side effect is selected, for example, the control unit 11 selects a drug having a high possibility of causing the side effect, the side effect related information and the prescription data. It is also possible to execute a suspected drug identification process that identifies based on the In addition, the doser master corresponds to the patient's old health facility B along with the doser ID, name, sex, age, address, medical history, family information, medical department, and hospital ward of each doser. Information such as delivery destination identification information is included. In addition, the said doser is the concept including the resident | tenant who has entered the said nursing home B, and the patient who is receiving medical treatment at a medical institution.
また、前記データ記憶部12は、処方データ記憶部121及び配薬管理情報記憶部122を有する。前記処方データ記憶部121は、前記上位システム(不図示)から取得する前記処方データをデータベース形式で記憶する。前記処方データには、例えば処方箋交付年月日、オーダーナンバー、処方区分、BCD、服用者ID、服用者名、服用者生年月日、薬品情報(薬品コード、薬品名、用量など)、剤形情報(内服、外用など)、用法情報(服用時期を含む)、診療種別(外来、入院など)、診療科などの情報が含まれる。
Further, the data storage unit 12 includes a prescription data storage unit 121 and a medicine distribution management information storage unit 122. The prescription data storage unit 121 stores the prescription data acquired from the upper system (not shown) in a database format. The prescription data includes, for example, prescription delivery date, order number, prescription classification, BCD, doser ID, doser name, doser birth date, drug information (drug code, drug name, dose, etc.), dosage form Information (internal use, external use, etc.), usage information (including dosing time), medical treatment type (outpatient, hospitalization, etc.), medical treatment department, etc. information is included.
前記配薬管理情報記憶部122は、配送先識別情報と服用時期と服用者識別情報とが対応付けられた配薬管理情報D1を記憶する。ここに、図2は、前記配薬管理情報D1の一例を示す図である。図2に示すように、前記配薬管理情報D1では、配送日と、配送先識別情報である前記老健施設Bの配送先ID及び老健施設名と、服用時期と、前記服用者識別情報である前記服用者ID及び氏名とが対応付けて記憶されている。
The medicine distribution management information storage unit 122 stores medicine distribution management information D1 in which delivery destination identification information, dosing timing, and dosing person identification information are associated. Here, FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of the medicine distribution management information D1. As shown in FIG. 2, in the drug distribution management information D1, the delivery date, the delivery destination ID of the aging facility B and the name of the aging facility which are delivery destination identification information, the dosing time, and the doser identification information The doser ID and the name are stored in association with each other.
具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記上位システム(不図示)から入力される複数の服用者の処方データ及び前記服用者マスターに基づいて、前記配薬管理情報D1を生成する。なお、図2に示す前記配薬管理情報D1では、1日分の服用時期に対応する情報が示されているが、これに限定されない。例えば、前記制御部11は、複数日分又は1週間分など、前記薬局Aから前記老健施設Bに同時に配送される予め定められた任意の服用期間に対応する前記配薬管理情報D1を生成する。
Specifically, the control unit 11 generates the medicine distribution management information D1 based on prescription data of a plurality of dosers input from the upper system (not shown) and the doser master. In addition, in the said medicine distribution management information D1 shown in FIG. 2, although the information corresponding to the dosing time for one day is shown, it is not limited to this. For example, the control unit 11 generates the medicine distribution management information D1 corresponding to a predetermined arbitrary dosing period simultaneously delivered from the pharmacy A to the health care facility B, such as a plurality of days or a week. .
また、図2に示す前記配薬管理情報D1では、前記老健施設Bとして二つの老健施設B1及び老健施設B2が登録されている場合を例に挙げて説明するが、一つ又は三つ以上の前記老健施設Bが配送先として予め登録されていてもよい。さらに、本実施の形態では、前記老健施設Bが一つの配薬グループとして設定されている場合について説明するが、例えば前記老健施設Bにおいて複数の服用者が入居している部屋又はフロアを前記配薬グループとして設定することも可能である。
Further, in the case of the medicine distribution management information D1 shown in FIG. 2, although the case where two long-term health facilities B1 and long-term health facilities B2 are registered as the long-term health facilities B is described as an example, one or three or more The health care facility B may be registered in advance as a delivery destination. Furthermore, in the present embodiment, although the case where the health care facility B is set as one drug distribution group is described, for example, the room or floor in which a plurality of dosers are moving in the health care facility B is arranged. It is also possible to set it as a drug group.
前記通信インターフェース13は、前記ネットワークN1を介して前記読取端末2、前記薬品分包装置3、及び前記プリンタ4との間で、予め定められた通信プロトコルに従って無線又は有線でデータ通信を実行するネットワークカード等を有する。前記表示装置14は、前記制御部11からの制御指示に従って各種の情報を表示する液晶ディスプレイ又は有機ELディスプレイなどの表示手段である。前記操作装置15は、前記調剤支援装置1に各種の情報を入力するためにユーザーによって操作される操作手段である。具体的に、前記操作装置15は、前記表示装置14の表示画面に従った各種の情報の入力操作を受け付けるキーボード及びマウス(ポインティングデバイス)を含む。
The communication interface 13 performs data communication wirelessly or by wire according to a predetermined communication protocol between the reading terminal 2, the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 and the printer 4 via the network N1. I have a card etc. The display device 14 is a display unit such as a liquid crystal display or an organic EL display which displays various information in accordance with a control instruction from the control unit 11. The operating device 15 is an operating means operated by the user to input various information to the dispensing support device 1. Specifically, the controller device 15 includes a keyboard and a mouse (pointing device) that receive input operations of various information according to the display screen of the display device 14.
前記ドライブ装置16は、前記調剤支援プログラムが記録されたコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体17から前記調剤支援プログラムを読み取ることが可能である。前記記録媒体17は、CD、DVD、BD、又はUSBメモリなどである。そして、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11により、前記記録媒体17から前記ドライブ装置16で読み取られた前記調剤支援プログラムが前記データ記憶部12にインストールされる。
The drive device 16 can read the dispensing support program from a computer readable recording medium 17 in which the dispensing support program is recorded. The recording medium 17 is a CD, a DVD, a BD, a USB memory, or the like. Then, in the dispensing support device 1, the dispensing support program read from the recording medium 17 by the drive device 16 is installed in the data storage unit 12 by the control unit 11.
[読取端末2]
前記読取端末2は、前記薬包81及び前記薬袋82に付されている前記コード811及び前記コード822から前記第1配薬情報及び前記第2配薬情報を読み取るバーコードリーダーなどの読取手段である。前記読取端末2により読み取られる前記第1配薬情報及び前記第2配薬情報は、前記調剤支援装置1に入力される。なお、前記薬包81又は前記薬袋82に前記第1配薬情報又は前記第2配薬情報が記録されるICタグなどの第1記録媒体又は第2記録媒体が付される場合、前記読取端末2は、前記第1記録媒体又は前記第2記録媒体から情報を読み取るICリーダーライタのような読取手段である。また、前記読取端末2は、前記コード811及び前記コード822から情報を読み取ることができるものであれば、携帯電話、スマートフォン、PDA、メディアプレーヤー、又はタブレット端末などの携帯端末であってもよい。
[Reading terminal 2]
The reading terminal 2 is a reading means such as a bar code reader which reads the first drug information and the second drug information from the code 811 attached to the medicine package 81 and the medicine bag 82 and the code 822. is there. The first drug distribution information and the second drug distribution information read by the reading terminal 2 are input to the dispensing support device 1. In addition, when the first recording medium or the second recording medium such as an IC tag in which the first drug distribution information or the second drug distribution information is recorded is attached to the medicine package 81 or the medicine bag 82, the reading terminal Reference numeral 2 denotes reading means such as an IC reader / writer for reading information from the first recording medium or the second recording medium. The reading terminal 2 may be a portable terminal such as a mobile phone, a smart phone, a PDA, a media player, or a tablet terminal as long as it can read information from the code 811 and the code 822.
[配薬支援装置5]
一方、前記配薬支援装置5は、制御部51、データ記憶部52、通信インターフェース53、表示装置54、操作装置55、及びドライブ装置56などを備えるパーソナルコンピュータである。
[Drug dispensing support device 5]
On the other hand, the dispensing assistance device 5 is a personal computer provided with a control unit 51, a data storage unit 52, a communication interface 53, a display device 54, an operating device 55, a drive device 56, and the like.
前記制御部51は、CPU、ROM、及びRAM等を備える。前記CPUは、各種の制御プログラムに従って処理を実行することにより前記配薬支援装置5を制御するプロセッサーである。前記ROMは、前記CPUにより実行されるBIOS等のプログラムが予め記憶された不揮発性メモリである。前記RAMは、前記CPUによる各種の制御プログラムの展開及びデータの一時記憶に用いられる揮発性メモリ又は不揮発性メモリである。
The control unit 51 includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and the like. The CPU is a processor that controls the medicine dispensing support device 5 by executing processing in accordance with various control programs. The ROM is a non-volatile memory in which a program such as a BIOS executed by the CPU is stored in advance. The RAM is a volatile memory or a non-volatile memory used for expansion of various control programs by the CPU and temporary storage of data.
前記データ記憶部52は、前記制御部51によって実行される各種のアプリケーションプログラム及び各種のデータを記憶するハードディスク又はSSD等の不揮発性の記憶手段である。具体的に、前記データ記憶部52には、後述の受取時照合処理(図12参照)及び配薬時照合処理(図13参照)などを前記制御部51に実行させるための配薬支援プログラムが記憶されている。
The data storage unit 52 is a non-volatile storage unit such as a hard disk or an SSD that stores various application programs executed by the control unit 51 and various data. Specifically, the data storage unit 52 has a drug distribution support program for causing the control unit 51 to execute a later-described on-reception check process (see FIG. 12) and a on-drug check process (see FIG. 13). It is memorized.
例えば、前記制御部51は、前記配薬支援プログラムに従って各種の処理を実行することにより、表示制御部511、配送先判定部512、及び第2報知部513として機能する。ここに、前記表示制御部511、前記配送先判定部512、及び前記第2報知部513として機能するときの前記制御部51が表示制御手段、配送先判定手段、及び第2報知手段の一例である。
For example, the control unit 51 functions as a display control unit 511, a delivery destination determination unit 512, and a second notification unit 513 by executing various processes according to the medicine distribution support program. Here, the control unit 51 when functioning as the display control unit 511, the delivery destination determination unit 512, and the second notification unit 513 is an example of a display control unit, a delivery destination determination unit, and a second notification unit. is there.
前記表示制御部511は、前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られた場合に前記第1配薬情報の前記服用者IDに対応する前記服用者の顔画像を前記データ記憶部52から読み出して表示する。具体的に、前記表示制御部511は、前記携帯端末6によって前記第1配薬情報が読み取られた場合に、前記マスター記憶部521に記憶されている後述の入居者マスターに基づいて前記服用者の顔画像を前記携帯端末6に表示させる。
The display control unit 511, when the first drug distribution information is read from the drug package 81, the face image of the doser corresponding to the doser ID of the first drug distribution information in the data storage unit 52. Read from and display. Specifically, when the first drug distribution information is read by the portable terminal 6, the display control unit 511 determines the doser based on a resident master described later stored in the master storage unit 521. The face image of is displayed on the portable terminal 6.
前記配送先判定部512は、前記配送先において前記薬袋82から読み取られる前記第2配薬情報の前記配送先識別情報と前記配送先に対応する前記配送先識別情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。即ち、前記配送先判定部512は、前記配送先が前記薬袋82を配送するべき配送先として正しいか否かを判定する。
The delivery destination determination unit 512 determines whether or not the delivery destination identification information of the second drug delivery information read from the medicine bag 82 at the delivery destination matches the delivery destination identification information corresponding to the delivery destination. judge. That is, the delivery destination determination unit 512 determines whether the delivery destination is correct as the delivery destination to which the medicine bag 82 should be delivered.
前記第2報知部513は、前記配送先判定部512による判定結果を報知する。例えば、前記第2報知部513は、前記配送先判定部512の判定結果が一致であるか否かを、前記表示装置54又は前記読取端末7に表示させることが考えられる。なお、前記第2報知部513は、前記配送先判定部512の判定結果が一致でない場合にのみエラーメッセージを表示させることも考えられる。
The second notification unit 513 notifies the determination result by the delivery destination determination unit 512. For example, it is conceivable that the second notification unit 513 causes the display device 54 or the reading terminal 7 to display whether or not the determination result of the delivery destination determination unit 512 is the same. The second notification unit 513 may display an error message only when the determination result of the delivery destination determination unit 512 does not match.
また、前記データ記憶部52は、マスター記憶部521及び変換情報記憶部522を有する。前記マスター記憶部521には、前記老健施設Bに入居している入居者について、入居者ID、入居者名、顔画像、病歴、又は薬歴などの情報を含む入居者マスターが記憶される。なお、前記顔画像は、入居者の外観を示す顔写真又は似顔絵などの画像として予め登録される。
Further, the data storage unit 52 includes a master storage unit 521 and a conversion information storage unit 522. In the master storage unit 521, a resident master including information such as a resident ID, a resident name, a face image, a medical history, or a medicine history is stored for a resident who is in the health care facility B. The face image is registered in advance as an image such as a face picture or a portrait showing the appearance of the resident.
前記変換情報記憶部522には、前記薬局Aで管理されている前記服用者マスターと前記老健施設Bで管理されている前記入居者マスターとの互換を実現するために予め定められた変換情報が記憶されている。例えば、前記変換情報は、前記服用者IDと前記入居者IDとの対応関係を示す情報である。なお、前記服用者マスターにおける前記服用者IDが、前記老健施設Bに対応する前記配送先識別情報及び前記入居者IDを結合したものであることも考えられる。
In the conversion information storage unit 522, conversion information determined in advance to realize compatibility between the doser master managed by the pharmacy A and the resident master managed by the health care facility B is used. It is memorized. For example, the conversion information is information indicating a correspondence between the doser ID and the resident ID. In addition, it is also conceivable that the doser ID in the doser master is a combination of the delivery destination identification information corresponding to the health care facility B and the resident ID.
これにより、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、前記薬局Aで管理されている前記服用者マスターにおける前記服用者IDを前記変換情報に基づいて前記入居者IDに変換することが可能である。従って、前記配薬支援システム10では、前記薬局A側のシステムと前記老健施設B側のシステムとを切り離して構成することが可能であり、前記老健施設B側の前記入居者マスターの情報を前記薬局A側に伝える必要がない。
Thereby, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 converts the doser ID in the doser master managed by the pharmacy A into the resident ID based on the conversion information. It is possible. Therefore, in the medicine distribution support system 10, the system on the pharmacy A side and the system on the nursing home B side can be separated and configured, and the information of the resident master on the nursing home B side can be There is no need to tell the pharmacy A side.
前記通信インターフェース53は、前記ネットワークN1を介して前記調剤支援装置1等との間で、予め定められた通信プロトコルに従って無線又は有線でデータ通信を実行するネットワークカード等を有する。前記表示装置54は、前記制御部51からの制御指示に従って各種の情報を表示する液晶ディスプレイ又は有機ELディスプレイなどの表示手段、及び前記制御部51からの制御指示に従って音声を出力するスピーカー等を備える端末表示手段の一例である。前記操作装置55は、前記配薬支援装置5に各種の情報を入力するためにユーザーによって操作される操作手段である。具体的に、前記操作装置55は、前記表示装置54の表示画面に従った各種の情報の入力操作を受け付けるキーボード及びマウス(ポインティングデバイス)を含む。
The communication interface 53 has a network card or the like that executes data communication with the dispensing support device 1 or the like via the network N1 in a wireless or wired manner according to a predetermined communication protocol. The display device 54 includes display means such as a liquid crystal display or an organic EL display for displaying various information in accordance with a control instruction from the control unit 51, and a speaker for outputting sound in accordance with the control instruction from the control unit 51. It is an example of a terminal display means. The operating device 55 is an operating means operated by the user in order to input various types of information to the drug distribution support device 5. Specifically, the operation device 55 includes a keyboard and a mouse (pointing device) that receive input operations of various information according to the display screen of the display device 54.
前記ドライブ装置56は、前記配薬支援プログラムが記録されたコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体57から前記配薬支援プログラムを読み取ることが可能である。前記記録媒体57は、CD、DVD、BD、又はUSBメモリなどである。そして、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51により、前記記録媒体57から前記ドライブ装置56で読み取られた前記配薬支援プログラムが前記データ記憶部52にインストールされる。
The drive device 56 can read the medicine distribution support program from a computer readable recording medium 57 in which the medicine distribution support program is recorded. The recording medium 57 is a CD, a DVD, a BD, a USB memory, or the like. Then, in the medicine dispensing support device 5, the medicine dispensing support program read from the recording medium 57 by the drive device 56 is installed in the data storage unit 52 by the control unit 51.
[携帯端末6]
前記携帯端末6は、例えば携帯電話、スマートフォン、PDA、メディアプレーヤー、又はタブレット端末などであって、前記老健施設Bにおいて、前記薬袋82に収容された前記薬包81を服用者に配薬する配薬担当者によって持ち運ばれる。前記携帯端末6は、制御部61及びカメラ62を備える。
[Mobile terminal 6]
The mobile terminal 6 is, for example, a mobile phone, a smart phone, a PDA, a media player, or a tablet terminal, and in the health care facility B, a distribution for distributing the medicine package 81 contained in the medicine bag 82 to the user. Carried by a drug representative. The portable terminal 6 includes a control unit 61 and a camera 62.
前記制御部61は、CPU、RAM、及びROMなどを備え、前記携帯端末6を制御する。なお、前記携帯端末6では、前記制御部61により、予めインストールされたアプリケーションプログラムに従って各種の処理が実行される。前記カメラ62は、画像又は映像を撮影する撮影手段である。そして、前記制御部61は、前記カメラ62で撮影される画像又は映像に含まれる一次元コード又は二次元コードを読み取るコード読取機能を有する。具体的に、前記携帯端末6では、前記コード読取機能を用いて、前記薬包81及び前記薬袋82に印刷されている一次元コード又は二次元コードから情報を読み取ることが可能である。そして、前記制御部61は、前記カメラ62を用いて読み取った情報を前記配薬支援装置5に送信する。なお、前記携帯端末6は、各種の情報を表示する表示部及び各種の操作を受け付ける操作部なども備えている。
The control unit 61 includes a CPU, a RAM, and a ROM, and controls the mobile terminal 6. In the mobile terminal 6, various processes are executed by the control unit 61 in accordance with an application program installed in advance. The camera 62 is an imaging unit that captures an image or a video. The control unit 61 has a code reading function of reading a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code included in an image or video captured by the camera 62. Specifically, the portable terminal 6 can read information from the one-dimensional code or the two-dimensional code printed on the medicine package 81 and the medicine bag 82 using the code reading function. Then, the control unit 61 transmits the information read using the camera 62 to the medicine dispensing support device 5. The portable terminal 6 also includes a display unit for displaying various information, an operation unit for receiving various operations, and the like.
[読取端末7]
前記読取端末7は、前記読取端末2と同様に、前記薬包81又は前記薬袋82などに印刷されている一次元コード又は二次元コードから情報を読み取るバーコードリーダーなどの読取手段である。そして、前記読取端末7により読み取られる情報は、前記配薬支援装置5に入力される。なお、前記薬包81又は前記薬袋82にICタグなどの記録媒体が付される場合、前記読取端末7は、前記記録媒体から情報を読み取るICリーダーライタのような読取手段である。なお、前記携帯端末6を前記読取端末7として利用し、前記読取端末7を省略することも可能である。
[Reading terminal 7]
Similar to the reading terminal 2, the reading terminal 7 is a reading unit such as a bar code reader which reads information from a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code printed on the medicine package 81 or the medicine bag 82 or the like. Then, the information read by the reading terminal 7 is input to the medicine dispensing support device 5. When a recording medium such as an IC tag is attached to the medicine package 81 or the medicine bag 82, the reading terminal 7 is a reading means such as an IC reader / writer which reads information from the recording medium. It is also possible to use the portable terminal 6 as the reading terminal 7 and omit the reading terminal 7.
[配薬作業の一例]
続いて、図3及び図4を参照しつつ、前記配薬支援システム10が使用される前記薬局A及び前記老健施設Bにおいて実行される配薬作業のフローについて説明する。具体的に、図3に示すステップS1〜S5は前記薬局Aで実行され、ステップS6〜S7は前記老健施設Bで実行される。なお、図4は、前記薬局Aから前記老健施設Bの一例である前記老健施設B1及び前記老健施設B2に薬品が配送される場合の前記配薬作業のフローを模式的に示す図である。
[Example of drug administration work]
Subsequently, with reference to FIGS. 3 and 4, a flow of a drug dispensing operation performed in the pharmacy A and the health-care facility B in which the drug dispensing support system 10 is used will be described. Specifically, steps S1 to S5 shown in FIG. 3 are executed by the pharmacy A, and steps S6 to S7 are executed at the health care facility B. FIG. 4 is a view schematically showing a flow of the medicine distribution operation when the medicine is delivered from the pharmacy A to the aging facility B1 and the aging facility B2 which are examples of the aging facility B. As shown in FIG.
<ステップS1>
まず、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11が、前記操作装置15のユーザー操作に応じて、薬品を配送する前記老健施設Bを選択し、前記老健施設Bに対応する処方データを発行する処方データ発行処理を実行する(S1)。
<Step S1>
First, in the dispensing support device 1, the control unit 11 selects the old care facility B to which medicine is to be delivered according to the user operation of the operation device 15, and issues prescription data corresponding to the old care facility B. Prescription data issuance processing is executed (S1).
<ステップS2>
そして、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11が、前記ステップS1で発行された前記処方データ各々に基づいて分包データを生成し、その分包データを前記薬品分包装置3に入力することにより、前記薬品分包装置3による自動調剤が開始される(S2)。これにより、図4に示すように、前記老健施設B各々に属する服用者が服用する薬品が収容された前記薬包81各々が得られる。
<Step S2>
Then, in the dispensing support device 1, the control unit 11 generates packaging data based on each of the prescription data issued in the step S 1, and inputs the packaging data into the medicine dispensing device 3. Thus, the automatic dispensing by the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 is started (S2). As a result, as shown in FIG. 4, the medicine package 81 containing each medicine taken by the user belonging to each of the health care facilities B can be obtained.
また、前記ステップS2において、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記制御部31が、前記分包プリンタ32を用いて、図4に示すように、前記第1配薬情報を示す前記コード811を前記薬包81に印刷させる。前記第1配薬情報には、前記服用者ID、前記服用時期及び前記配送先識別情報が含まれる。なお、前記薬包81には、服用者名、服用日時、及び服用時期なども印刷される。また、前記第1配薬情報に、服用日時の情報が含まれていることも考えられる。
Further, in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 in the step S2, as shown in FIG. 4, the control unit 31 uses the packaging and packaging printer 32 to perform the code 811 indicating the first drug distribution information. The medicine package 81 is printed. The first drug distribution information includes the doser ID, the dose timing, and the delivery destination identification information. In the medicine package 81, the name of the user, the date and time of taking, and the taking time are also printed. In addition, it is also conceivable that the first drug information contains information on the dosing date and time.
さらに、前記ステップS2において、前記制御部11は、前記プリンタ4を用いて、図4に示すように、前記第2配薬情報を示す前記コード822を、前記薬袋82に貼付される前記ラベル821に印刷させる。前記第2配薬情報には、前記服用時期及び前記配送先識別情報が含まれる。なお、前記薬袋82には、老健施設名、服用日時、及び服用時期なども印刷される。
Furthermore, in the step S2, as shown in FIG. 4, the control unit 11 uses the printer 4 to label the code 822, which indicates the second medicine distribution information, to the medicine bag 82. Make it print. The second drug delivery information includes the dosing timing and the delivery destination identification information. In the medicine bag 82, the name of the health care facility, the date and time of taking, and the taking time are also printed.
<ステップS3>
前記薬品分包装置3による調剤作業が完了すると、続いて、鑑査担当の薬剤師は、前記薬品分包装置3で調剤された薬品の鑑査を行う(S3)。なお、前記鑑査には、前記薬品分包装置3により調剤された薬品を撮像し、その撮像された画像に基づいて自動的に鑑査を行う画像鑑査システムが利用されることも考えられる。例えば、前記薬品分包処理において前記時期別分包処理が実行された場合、前記画像鑑査システムでは、老健施設単位で前記服用時期ごとに並べられた前記薬包81各々の画像が分割され、前記服用者単位で前記服用時期ごとに並べた鑑査用画像が生成される。そして、前記画像鑑査システムは、前記鑑査用画像に基づいて前記薬品分包装置3により調剤された薬品を鑑査する。
<Step S3>
When the dispensing operation by the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 is completed, the pharmacist in charge of inspection then inspects the medicine dispensed by the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 (S3). In addition, it is also considered that the image inspection system which images the medicine dispensed by the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 and performs inspection automatically based on the imaged image is used for the inspection. For example, when the time-sorted packing process is performed in the medicine packing process, in the image inspection system, the images of the medicine package 81 arranged at each dosing stage are divided in units of old health facilities, An inspection image is generated which is arranged for each dosing period on a per doser basis. Then, the image inspection system inspects the medicine dispensed by the medicine packaging device 3 based on the inspection image.
<ステップS4>
次に、配送担当者は、図4に示すように、前記老健施設B各々に配送するべき前記薬包81各々を前記薬包81の服用時期及び配送先に対応する前記薬袋82に収容する(S4)。このとき、配送担当者は、前記読取端末2を用いて、前記薬包81及び前記薬袋82各々から前記第1配薬情報及び前記第2配薬情報を読み取る。これにより、前記調剤管理装置1の制御部11は、後述の収容時照合処理において前記第1配薬情報と前記第2配薬情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。
<Step S4>
Next, as shown in FIG. 4, the person in charge of delivery stores each of the medicine package 81 to be delivered to each of the health care facilities B in the medicine bag 82 corresponding to the dosing timing and delivery destination of the medicine package 81 ( S4). At this time, the person in charge of delivery reads the first drug delivery information and the second drug delivery information from the medicine package 81 and the medicine bag 82 using the reading terminal 2. As a result, the control unit 11 of the dispensing management device 1 determines whether or not the first drug delivery information and the second drug delivery information match in the storage comparison process described later.
<ステップS5>
その後、配送担当者は、前記薬袋82各々を前記配送先に配送する(S5)。このとき、配送担当者は、前記読取端末2を用いて、前記薬袋82各々から前記第2配薬情報を読み取る。これにより、前記調剤管理装置1の制御部11は、後述の配送時照合処理において前記配送先に配送するべき前記薬袋82に漏れがあるか否かを判定する。
<Step S5>
Thereafter, the delivery person in charge delivers each of the medicine bags 82 to the delivery destination (S5). At this time, the delivery person in charge reads the second drug delivery information from each medicine bag 82 using the reading terminal 2. Thereby, the control unit 11 of the dispensing management device 1 determines whether or not the medicine bag 82 to be delivered to the delivery destination has a leak in the delivery comparison process described later.
<ステップS6>
次に、前記老健施設B各々では、前記薬局Aから前記薬袋82各々を受け取ると、配薬担当者が、前記読取端末7を用いて前記薬袋82のコード822から前記第2配薬情報を読み取る(S6)。これにより、前記配薬支援装置51の制御部51は、後述の薬品受取処理において、前記第2配薬情報に含まれる配送先識別情報と前記読取端末7が配置された前記老健施設Bの配送先識別情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。
<Step S6>
Next, in each of the old-age facilities B, when each medicine bag 82 is received from the pharmacy A, the person in charge of medicine distribution reads the second medicine distribution information from the code 822 of the medicine bag 82 using the reading terminal 7 (S6). Thereby, the control unit 51 of the medicine distribution support device 51 delivers the delivery destination identification information included in the second medicine distribution information and the delivery of the old health facility B in which the reading terminal 7 is disposed in the medicine receiving process described later. It is determined whether or not the previous identification information matches.
<ステップS7>
その後、前記老健施設Bの配薬担当者は、服用時期ごとに、その服用時期に対応する前記薬袋82に収容されている前記薬包81各々を入居者に配薬する(S7)。このとき、前記配薬作業では、複数の服用者の前記薬包81が前記服用時期ごとに纏めて前記薬袋82に収容されているため、配送先である前記老健施設Bでは、服用時期ごとに前記薬袋82から複数の服用者の前記薬包81を取り出して服用者各々に容易に投薬することが可能である。また、前記ステップS7において、配薬担当者は、前記携帯端末6を用いて前記薬包81各々から前記第1配薬情報を読み取る。これにより、前記配薬支援装置51の制御部51は、後述の配薬時照合処理において、前記第1配薬情報に含まれる前記服用者IDに基づいて前記服用者IDに対応する入居者の顔画像63を前記データ記憶部52の前記服用者情報記憶部521から読み出して前記携帯端末6に表示させる。
<Step S7>
After that, the person in charge of drug distribution in the old-age facility B distributes the medicine package 81 contained in the medicine bag 82 corresponding to the time of taking the medicine to the resident for each taking time (S7). At this time, in the dispensing operation, the medicine packages 81 of a plurality of users are collectively contained in the medicine bag 82 at each dosing time, so in the health care facility B which is a delivery destination, every dosing time It is possible to take out the medicine package 81 of a plurality of users from the medicine bag 82 and to easily dispense each medicine. Further, in the step S7, the person in charge of drug distribution reads the first drug distribution information from each of the medicine package 81 using the portable terminal 6. As a result, the control unit 51 of the medicine distribution support device 51 performs the patient identification corresponding to the doser ID based on the doser ID included in the first drug distribution information in the distribution check process described later. The face image 63 is read from the user information storage unit 521 of the data storage unit 52 and displayed on the mobile terminal 6.
[配薬支援システム10で実行される各種の処理]
以下、図5〜図13を参照しつつ、前記配薬作業(図3参照)が実行される場合に、前記配薬支援システム10において実行される各種の処理の一例について説明する。なお、前記配薬支援システム10において実行される各種の処理の実行主体はここで説明するものに限らず、前記配薬支援システム10を構成する各種の装置の制御部により実行されればよい。
[Various processing executed by drug distribution support system 10]
Hereinafter, with reference to FIGS. 5 to 13, an example of various processes performed in the medicine distribution support system 10 when the medicine distribution operation (see FIG. 3) is performed will be described. In addition, the execution subject of the various processes performed in the said medicine distribution assistance system 10 should just be performed by the control part of the various apparatuses which comprise the said medicine distribution assistance system 10 not only what is demonstrated here.
[処方データ発行処理]
まず、図5を参照しつつ、前記ステップS1において前記調剤支援装置1の制御部11によって実行される処方データ発行処理について説明する。
[Prescription data issuance process]
First, prescription data issuance processing executed by the control unit 11 of the dispensing support device 1 in step S1 will be described with reference to FIG.
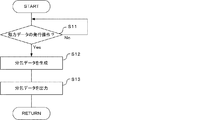
<ステップS11>
ステップS11において、前記制御部11は、一又は複数の前記老健施設Bについて処方データの発行操作が行われたか否かを判断する。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記調剤支援装置1における前記操作装置15のユーザー操作に応じて、一又は複数の前記老健施設Bを選択し、前記老健施設B各々の処方データの発行操作を受け付ける。そして、前記処方データの発行操作が行われると(S11:Yes)、処理がステップS12に移行する。なお、前記処方データの発行操作が行われるまでの間は(S11:No)、処理が前記ステップS11で待機する。
<Step S11>
In step S11, the control unit 11 determines whether or not the operation of issuing prescription data has been performed for one or more of the old facilities B. Specifically, the control unit 11 selects one or a plurality of the old facilities B in accordance with the user operation of the operation device 15 in the dispensing support device 1, and issues an operation of issuing prescription data of each of the old facilities B. Accept Then, when the operation for issuing the prescription data is performed (S11: Yes), the process proceeds to step S12. In addition, until the issue operation of the said prescription data is performed (S11: No), a process waits at the said step S11.
<ステップS12>
ステップS12において、前記制御部11は、前記老健施設B各々に属する前記服用者各々の前記処方データを、当該服用者が属する老健施設単位で同一服用時期ごとに分解して並べた分包データを生成する。
<Step S12>
In step S12, the control unit 11 divides package data in which the prescription data of each of the dosers belonging to each of the health facilities B are disassembled and arranged at the same dose timing in the health facility unit to which the dosers belong. Generate
例えば、前記制御部11は、図6に示すように、「老健施設B1」及び「老健施設B2」ごとに属する複数の服用者の処方データをグループ化したグループ処方データを生成する。その後、前記制御部11は、図7に示すように、前記グループ処方データに基づいて、「老健施設B1」及び「老健施設B2」に属する服用者各々に対応する処方データを服用時期ごとに並び替えた分包データを生成する。また、前記分包データには、服用時期に対応する薬品が存在しない服用者についてもその旨を示すデータ(空データ)が含まれている。
For example, as shown in FIG. 6, the control unit 11 generates group prescription data in which prescription data of a plurality of users who belong to each of the “care facility B1” and the “care facility B2” are grouped. Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 7, the control unit 11 arranges, based on the group prescription data, prescription data corresponding to each of the users who belong to the “care facility B1” and the “care facility B2” at each dosing time. Generate replaced package data. Further, the package data includes data (empty data) indicating that the person who takes the medicine corresponding to the taking time does not exist.
<ステップS13>
そして、ステップS13において、前記制御部11は、前記薬品分包装置3に前記分包データを出力する。これにより、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記分包データに従って後述の薬品分包処理(図8参照)が実行される。なお、前記調剤支援装置1が接続された前記プリンタ4等により前記分包データを示す一次元コード又は二次元コードなどを印刷出力することも他の実施形態として考えられる。これにより、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記印刷された用紙から前記分包データをハーコードリーダー等によって読み取ることにより、前記分包データに従った分包動作を行うことが可能である。
<Step S13>
Then, in step S13, the control unit 11 outputs the packing data to the medicine packing device 3. Thereby, in the medicine dispensing and packing apparatus 3, the medicine dispensing and packing process (see FIG. 8) described later is executed according to the packing data. It is also conceivable as another embodiment to print out a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code or the like indicating the package data by the printer 4 or the like to which the dispensing support device 1 is connected. Thereby, in the medicine dispensing and packing apparatus 3, it is possible to perform the packaging operation according to the packaging data by reading the packaging data from the printed sheet by the Harcode reader or the like.
[薬品分包処理]
次に、図8を参照しつつ、前記ステップS2において前記薬品分包装置3の制御部31によって実行される薬品分包処理について説明する。なお、本実施の形態では、前記薬品分包処理として前記時期別分包処理が実行される場合を例に挙げて説明するが、前記服用者別分包処理が実行されてもよい。
[Drug packaging process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 8, the medicine packaging process performed by the control unit 31 of the medicine packaging apparatus 3 in the step S2 will be described. In the present embodiment, although the case where the time-sorted packing process is performed is described as an example, the medicine-packed processing may be performed according to the user.
<ステップS21>
まず、ステップS21において、前記制御部31は、前記調剤支援装置1からの前記分包データの入力を待ち受ける(S21:No)。そして、前記分包データが入力されたと判断すると(S21:Yes)、前記制御部31は、処理をステップS22に移行させる。
<Step S21>
First, in step S21, the control unit 31 waits for input of the package data from the dispensing support device 1 (S21: No). Then, if it is determined that the packaging data has been input (S21: Yes), the control unit 31 shifts the processing to step S22.
<ステップS22>
ステップS22において、前記制御部31は、前記分包データのうち一つ目の前記老健施設B1を分包対象として設定する。具体的に、図7に示した前記分包データが入力された場合、前記制御部11は、初めの前記ステップS22において、「老健施設B1」を分包対象として設定する。そして、二回目以降に前記ステップS22が実行された場合、前記制御部11は二つ目以降の前記病室を順に分包対象として設定する。即ち、図7に示した前記分包データが入力された場合、前記制御部31は、二回目の前記ステップS22において、「老健施設B2」を分包対象として設定する。
<Step S22>
In step S22, the control unit 31 sets the first health care facility B1 among the packaging data as a packaging target. Specifically, when the packaging data shown in FIG. 7 is input, the control unit 11 sets “senior facility B1” as a packaging target in the first step S22. Then, when the step S22 is executed for the second time and thereafter, the control unit 11 sequentially sets the second and subsequent patient rooms as a packing target. That is, when the packaging data shown in FIG. 7 is input, the control unit 31 sets “senior facility B2” as a packaging target in the second step S22.
<ステップS23>
ステップS23において、前記制御部31は、前記分包データのうち前記ステップS22で分包対象として選択された前記老健施設Bに対応する一つ目の服用時期を分包対象として分包を開始する。
<Step S23>
In step S23, the control unit 31 starts the packing process with the first taking time corresponding to the health care facility B selected as the packing object in the step S22 among the packing data as a packing object. .
具体的に、図7に示した前記分包データが入力されている場合、前記制御部31は、初めの前記ステップS23において、「老健施設B1」の「△月△日朝食後」の服用時期を分包対象として分包を開始する。そして、二回目以降に前記ステップS23が実行された場合、前記制御部31は、二つ目以降の前記服用時期について順に分包対象として分包を開始する。即ち、図7に示した前記分包データが入力されている場合、前記制御部31は、二回目の前記ステップS23において、「老健施設B1」の「△月△日昼食後」の服用時期を分包対象として分包を開始する。
Specifically, when the package data shown in FIG. 7 is input, the control unit 31 calculates the dose timing of “after month Δday breakfast” of “eldery facility B1” in the first step S23. Start packing as a target for packing. And when the said step S23 is performed after the 2nd time, the said control part 31 starts a packing as a packing object in order about the said dosing timing after the 2nd. That is, when the package data shown in FIG. 7 is input, the control unit 31 performs the second “Don't take care of lunch on the day of Δmonthly day” of “the old nursing facility B1” in the second step S23. Start packing as packing target.
ここに、図9(A)は、図7に示した前記分包データに基づいて前記薬品分包処理が実行された場合の分包結果の一例を示す図である。図9(A)に示す分包結果では、同一の前記老健施設Bに属する複数の服用者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに連続して分包されている。具体的に、前記老健施設B1の服用者「湯山一郎」、「湯山二郎」、「湯山三郎」に対応する前記薬包81が、△月△日の朝食後、昼食後、夕食後ごとに連続して形成されている。なお、△月△日の後には、次の日である△月□日についても同様の形態で分包される。
Here, FIG. 9A is a view showing an example of the packing result when the medicine packing processing is performed based on the packing data shown in FIG. 7. In the packing result shown in FIG. 9 (A), medicines taken by a plurality of users who belong to the same health care facility B are continuously packing at each dosing timing. More specifically, the medicine package 81 corresponding to the users "Yuyama Ichiro", "Yuyama Jiro", and "Yuyama Saburo" of the old health facility B1 continues after breakfast, after lunch and after dinner on the day of. It is formed. Note that after the month and day, the next day, the month and day are also packaged in the same manner.
また、前記処方データに、前記薬包81に分包されない目薬、水剤、又は外用薬などの分包外薬品の情報(種類、使用時期など)が含まれる場合には、前記分包データに、前記薬品分包装置3で分包される薬品のデータに加えて前記分包外薬品の情報が含まれることが考えられる。この場合、前記制御部31は、前記分包外薬品の使用時期に対応する前記薬包81に、前記分包外薬品が存在する旨及び前記分包外薬品の内容などの情報を文字又はピクトグラム(画像)で印刷することが考えられる。これにより、前記薬包81の配薬時に前記分包外薬品の存在を容易に把握することができ、前記分包外薬品の使用忘れを抑制することができる。また、前記分包外薬品の使用時期に対応する前記薬包81が存在しない場合でも、前記制御部31が、空の前記薬包81を出力してその薬包81に前記分包外薬品が存在する旨及び前記分包外薬品の内容などの情報を文字又はピクトグラム(画像)で印刷することが考えられる。これにより、前記薬包81の服用時期と異なる時期に使用するべき前記分包外薬品が存在する場合でも、前記薬包81を参照することにより前記分包外薬品の存在を容易に把握することができ、前記分包外薬品の使用忘れを抑制することができる。
If the prescription data includes information (type, time of use, etc.) of an extra-packaged medicine such as an eye drop, a liquid medicine, or an external preparation not packaged in the medicine package 81, the package data includes In addition to the data of the medicine to be packaged by the medicine packaging device 3, it is conceivable that the information on the extra-packed medicine is included. In this case, the control unit 31 displays information such as the presence of the medicine outside the package in the medicine package 81 corresponding to the usage time of the medicine outside the package and the contents of the medicine outside the package with characters or pictograms. It is conceivable to print with (image). This makes it possible to easily grasp the presence of the extracapsular medicine at the time of dispensing the medicine package 81, and to suppress the forgetful use of the extracapsular medicine. In addition, even when the medicine package 81 corresponding to the use time of the medicine outside the package does not exist, the control unit 31 outputs the empty medicine package 81 and the medicine outside the medicine package is in the medicine package 81. It is conceivable to print information such as the existence and the contents of the medicine outside the package in characters or pictograms (images). Thereby, even when the extra-fraction medicine to be used at a time different from the time of taking the medicine package 81 exists, the presence of the extra-package medicine can be easily grasped by referring to the medicine package 81. It is possible to suppress the forgetful use of the extra-packaged medicine.
<ステップS24>
次に、ステップS24において、前記制御部31は、前記分包データに含まれた前記服用者各々のデータについて当該服用時期に服用するべき薬品が存在するか否かを順に判断する。そして、前記制御部31は、当該データに服用時期に服用するべき薬品が存在しない場合、即ち当該データが空データである場合(S24:No)、処理をステップS241に移行させる。一方、当該データに服用時期に服用するべき薬品が存在している場合、即ち当該データが空データではない場合(S24:Yes)、処理をステップS25に移行させる。
<Step S24>
Next, in step S24, the control unit 31 sequentially determines whether or not there is a drug to be taken at the relevant dosing timing for the data of each of the dosing persons included in the package data. Then, the control unit 31 shifts the process to step S241 when there is no medicine to be taken at the dosing time in the data, that is, when the data is empty data (S24: No). On the other hand, if there is a drug to be taken at the dosing time in the data, that is, if the data is not empty (S24: Yes), the process proceeds to step S25.
<ステップS25>
ステップS25において、前記制御部31は、前記分包データに含まれた当該データについて分包動作を実行する。具体的に、前記制御部31は、前記分包プリンタ32により、服用者の氏名及び服用時期と前記第1配薬情報を示す前記コード811とを前記薬包81に印刷すると共に、当該データに対応する薬品を前記薬包81に分包する。
<Step S25>
In step S25, the control unit 31 executes a packing operation on the data included in the packing data. Specifically, the control unit 31 causes the packager printer 32 to print the name and dosing timing of the user and the code 811 indicating the first drug distribution information on the medicine package 81, and The corresponding medicine is packaged in the medicine package 81.
<ステップS241>
一方、ステップS241において、前記制御部31は、当該服用時期に服用するべき薬品が存在しない旨が前記分包プリンタ32により印刷された空の前記薬包81を作成する。具体的に、空の前記薬包81には、服用者の氏名及び服用時期と、前記コード811と、薬がない旨を示す情報(お薬はありません)とが印刷される。
<Step S241>
On the other hand, in step S241, the control unit 31 creates the empty medicine package 81 printed by the package printer 32 that there is no medicine to be taken at the time of taking the medicine. Specifically, in the empty medicine package 81, the name of the person taking the medicine, the timing of taking the medicine, the code 811 and information indicating that there is no medicine (there is no medicine) are printed.
<ステップS26>
そして、ステップS26において、前記制御部31は、前記ステップS23で開始された同一服用時期についての分包が終了したか否かを判断する。ここで、前記同一服用時期の分包が終了したと判断すると(S26:Yes)、前記制御部31は処理をステップS27に移行させる。一方、前記同一服用時期の分包が終了していないと判断すると(S26:No)、前記制御部31は処理を前記ステップS24に戻す。
<Step S26>
Then, in step S26, the control unit 31 determines whether or not the packing for the same dose timing started in step S23 has ended. Here, when it is determined that the packing of the same dosing time has ended (S26: Yes), the control unit 31 shifts the process to step S27. On the other hand, if it is determined that the packing of the same dosing time has not ended (S26: No), the control unit 31 returns the process to the step S24.
<ステップS27>
ステップS27において、前記制御部31は、前記ステップS22で分包対象として設定された同一の前記老健施設Bについての全服用時期の分包が終了したか否かを判断する。ここで、前記全服用時期の分包が終了したと判断すると(S27:Yes)、前記制御部31は処理をステップS28に移行させる。一方、前記全服用時期の分包が終了していないと判断すると(S27:No)、前記制御部31は処理をステップS271に移行させる。
<Step S27>
In step S27, the control unit 31 determines whether or not the packaging at the full dose timing for the same old health care facility B set as the packaging target in step S22 has ended. Here, when it is determined that the packing of the full dose time has ended (S27: Yes), the control unit 31 shifts the process to step S28. On the other hand, when it is determined that the packing of the full dose time is not completed (S27: No), the control unit 31 shifts the process to step S271.
<ステップS271>
ステップS271において、前記制御部31は、前記服用時期が切り替わるタイミングを明示するための分包の区切り処理を実行し、処理を前記ステップS23に戻す。例えば、前記区切り処理は、空の前記薬包81を一つ設けることである。これにより、当該薬品分包処理による分包結果として得られる前記薬包81が連続して形成された薬包シートにおいて服用時期の切り替わりのタイミングを容易に把握することができる。なお、空の前記薬包81には、その前に連なっている各薬包81の内容に関する検薬用、鑑査用の各種情報が印字されてもよい。また、前記区切り処理は、前記薬包81が連続して形成された薬包シートを一度切断することであってもよい。これにより、前記薬品分包装置3において、自動的に服用時期ごとの前記薬包81の連続体を得ることができる。なお、前記区切り処理を省略することも他の実施形態として考えられる。
<Step S271>
In step S 271, the control unit 31 executes a dividing process of the package to clearly indicate the timing at which the dosing time changes, and returns the process to step S 23. For example, the separation process is to provide one empty medicine package 81. Thereby, it is possible to easily grasp the timing of the switching of the dosing time in the medicine package sheet in which the medicine package 81 obtained as a result of the packaging by the medicine packaging process is continuously formed. In addition, on the empty medicine package 81, various information for inspection and inspection regarding the contents of each medicine package 81 connected in front may be printed. In addition, the dividing process may be to cut the medicine package sheet, in which the medicine package 81 is continuously formed, once. Thereby, in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3, it is possible to automatically obtain a continuous body of the medicine package 81 for each dosing time. Note that omitting the dividing process is also considered as another embodiment.
<ステップS28>
そして、ステップS28では、前記分包データに含まれた全ての前記老健施設Bについての分包が終了したか否かを判断する。ここで、前記老健施設B各々の分包が終了したと判断すると(S28:Yes)、前記制御部31は一連の当該薬品分包処理を終了して処理を前記ステップS21に戻す。一方、前記老健施設B各々の分包が終了していないと判断すると(S28:No)、前記制御部31は処理を前記ステップS22に移行させ、次の前記老健施設Bについての分包動作を開始する。
<Step S28>
Then, in step S28, it is determined whether or not packing for all the old facilities B included in the packing data has ended. Here, if it is determined that the packing of each of the old facilities B is completed (S28: Yes), the control unit 31 ends the series of medicine packaging processing and returns the process to the step S21. On the other hand, when it is determined that the packing of each of the old facilities B is not completed (S28: No), the control unit 31 shifts the process to step S22, and performs the next packing operation for the old facilities B. Start.
なお、本実施の形態では、前記薬品分包処理において前記時期別分包処理が実行される場合を例に挙げて説明したが、前記薬品分包処理において前記服用者別分包処理が実行されてもよい。ここに、図9(B)は、図6に示した前記グループ処方データに従って「老健施設B1」を対象に前記服用者別分包処理が実行された場合の分包結果を示す図である。図9(B)に示す分包結果では、一の服用者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに連続して分包されている。具体的に、図9(B)に示す例では、服用者「湯山一郎」の△月△日の朝食後、昼食後、夕食後、△月□日の朝食後、昼食後、夕食後のそれぞれに対応する前記薬包81が連続して形成されている。そして、服用者「湯山一郎」の後は、同一の前記老健施設B1に属する服用者「湯山二郎」についても同様に、服用時期ごとに対応する前記薬包81が連続して形成される。
In the present embodiment, although the case where the time-sorted packing process is performed is described as an example in the medicine packing process, the medicine-classified packing process is executed in the medicine packing process. May be Here, FIG. 9 (B) is a view showing a result of the packing when the packing processing according to the user is executed on the “care facility B1” according to the group prescription data shown in FIG. In the packing result shown in FIG. 9 (B), the medicine taken by one doser is divided into packs continuously at each dosing timing. Specifically, in the example shown in FIG. 9B, after breakfast, after lunch, after dinner, after breakfast, after lunch, after lunch, after dinner on the day of the month on the day of Mr. Ichiro Ichiro The medicine package 81 corresponding to is continuously formed. Then, after the user “Yuichiro Ichiro”, the medicine package 81 corresponding to each dosing time is continuously formed similarly for the user “Yuyama Jiro” who belongs to the same old health care facility B1.
[収容時照合処理]
続いて、図10のフローチャートを参照しつつ、前記ステップS3において前記調剤支援装置1の前記制御部11によって実行される収容時照合処理について説明する。
Capacity matching process
Subsequently, the storage time check process executed by the control unit 11 of the dispensing support device 1 in step S3 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
なお、前記服用者別分包処理が実行された場合には、前記ステップS3における前記薬包81の前記薬袋82への収容時に、前記薬包81各々が切り離されて前記薬袋82各々に収容される。一方、前記時期別分包処理が実行された場合には、前記ステップS3における前記薬包81の前記薬袋82への収容時に、前記薬包81各々を切り離して前記薬袋82各々に収容してもよいが、服用時期ごとに連なった複数の前記薬包81を切り離さずに前記薬袋82に収容してもよい。このような収容作業により、前記薬局Aでは、前記服用時期ごとに対応する複数の服薬者の前記薬包81が纏めて収容された前記薬袋82が複数準備される。
In addition, when the packing process according to the user is executed, each medicine packet 81 is separated and accommodated in each medicine bag 82 when the medicine package 81 is accommodated in the medicine bag 82 in the step S3. Ru. On the other hand, when the time-divisional packing process is performed, the medicine package 81 is cut off and accommodated in each medicine bag 82 when the medicine package 81 is accommodated in the medicine bag 82 in step S3. Although it is preferable, the plurality of medicine packages 81 connected at each dosing time may be stored in the medicine bag 82 without being separated. By such a storing operation, in the pharmacy A, a plurality of medicine bags 82 in which the medicine packages 81 of a plurality of medication users corresponding to the respective dosing times are collectively stored are prepared.
<ステップS31>
ステップS31において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2によって、前記薬袋82の前記コード822から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたと判断すると(S31:Yes)、処理をステップS32に移行させる。一方、前記第2配薬情報が読み取られるまでの間は(S31:No)、処理が前記ステップS31で待機する。なお、前記制御部11は、前記薬包81の第1配薬情報と前記薬袋82の第2配薬情報との違いを、例えば前記第1配薬情報にのみ存在する前記服用者IDの有無に応じて判断可能である。もちろん、前記第1配薬情報及び前記第2配薬情報にその識別が可能な情報が含まれていてもよい。
<Step S31>
In step S31, the control unit 11 determines whether the second drug delivery information has been read from the code 822 of the medicine bag 82 by the reading terminal 2. Here, when the control unit 11 determines that the second drug supply information has been read (S31: Yes), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S32. On the other hand, until the second drug supply information is read (S31: No), the process waits in the step S31. In addition, the control unit 11 determines the difference between the first drug distribution information of the drug package 81 and the second drug distribution information of the drug bag 82, for example, the presence or absence of the doser ID existing only in the first drug distribution information. It can be judged according to Of course, the first drug information and the second drug information may include information that can be identified.
<ステップS32>
ステップS32において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS31で読み取られた前記薬袋82の第2配薬情報と前記配薬管理情報D1とに基づいて、同一の前記薬袋82に収容される薬包81として予め定められた一又は複数の前記薬包81を特定する。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記配薬管理情報D1において前記配送先識別情報及び前記服用時期が前記第2配薬情報と同一である前記服用者IDの薬品が収容される前記薬包81を前記薬袋82に収容するべき前記薬包81として特定する。
<Step S32>
In step S32, the control unit 11 stores the medicine package 81 contained in the same medicine bag 82 based on the second medicine distribution information of the medicine bag 82 read in step S31 and the medicine distribution management information D1. One or more medicine packages 81 predetermined as. Specifically, the control unit 11 is configured to store the medicine of the doser ID whose delivery destination identification information and the dose timing are the same as the second drug delivery information in the drug distribution management information D1. 81 is identified as the medicine package 81 to be contained in the medicine bag 82.
<ステップS33>
そして、ステップS33において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2によって、前記薬包81の前記コード811から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたと判断すると(S33:Yes)、処理をステップS34に移行させ、前記第1配薬情報が読み取られるまでの間は(S33:No)、前記ステップS33の判断を繰り返す。
<Step S33>
Then, in step S33, the control unit 11 determines whether the first drug delivery information is read from the code 811 of the medicine package 81 by the reading terminal 2. Here, when the control unit 11 determines that the first drug distribution information has been read (S33: Yes), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S34 and continues until the first drug distribution information is read (S33). No), repeat the determination of step S33.
<ステップS34>
ステップS34において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS31で読み取られた前記第2配薬情報の前記配送先識別情報及び前記服用時期と前記ステップS33で読み取られた前記第1配薬情報の前記配送先識別情報及び前記服用時期とが一致するか否かを判定する。ここに、前記ステップS34は、前記制御部11の前記判定部112によって実行される処理である。また、前記ステップS34において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS33で読み取られた前記第1配薬情報と、前記ステップS34における判定結果とを読取履歴として前記データ記憶部12に記憶させる。これにより、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記読取履歴を参照及び出力することが可能である。
<Step S34>
In step S34, the control unit 11 transmits the delivery destination identification information of the second drug delivery information read in step S31, the dosing timing, and the delivery of the first drug delivery information read in step S33. It is determined whether or not the preceding identification information and the dosing time match. Here, step S34 is a process executed by the determination unit 112 of the control unit 11. In step S34, the control unit 11 causes the data storage unit 12 to store the first medicine distribution information read in step S33 and the determination result in step S34 as a reading history. Thus, the dispensing support device 1 can refer to and output the reading history.
<ステップS35>
そして、ステップS35において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS34における判定結果を報知する。ここに、前記ステップS35は、前記制御部11の前記第1報知部113によって実行される処理である。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記判定結果を前記表示装置14又は前記読取端末2に表示させることにより、前記判定結果をユーザーに報知する。これにより、ユーザーが前記判定結果を認識することができる。従って、複数の服用者の前記薬包81を服用時期ごとに纏めて前記薬袋82に収容して配送先に配送する配薬作業における人為的ミスが抑制される。なお、前記判定結果の報知方法は表示に限らず、音声又は発光態様などによって前記判定結果の報知が行われてもよい。
<Step S35>
Then, in step S35, the control unit 11 reports the determination result in step S34. Here, the step S35 is a process executed by the first notification unit 113 of the control unit 11. Specifically, the control unit 11 notifies the user of the determination result by displaying the determination result on the display device 14 or the reading terminal 2. Thus, the user can recognize the determination result. Therefore, human error in the drug dispensing operation in which the medicine package 81 of a plurality of users is collectively collected at each dosing time, stored in the medicine bag 82 and delivered to the delivery destination is suppressed. In addition, the notification method of the said determination result may alert | report the said determination result not only by display but the audio | voice or the light emission aspect.
<ステップS36>
その後、ステップS36において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2による前記薬袋82に収容する前記薬包81からの前記第1配薬情報の読取作業を終了するか否かを判断する。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2に対するユーザーの継続操作、又は次の前記薬包81からの前記第1配薬情報の読取作業が行われた場合に、前記読取作業を終了しないと判断し(S36:No)、処理を前記ステップS33に移行させる。これにより、前記薬袋82に収容する前記薬包81各々からの前記第1配薬情報の読み取りが順に実行される。一方、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2に対するユーザーの終了操作に応じて前記読取端末2から終了信号が入力された場合、又は前記ステップS31で読み取られた前記薬袋82と異なる前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られた場合に、前記読取作業を終了すると判断し(S36:Yes)、処理をステップS37に移行させる。
<Step S36>
Thereafter, in step S36, the control unit 11 determines whether or not the reading operation of the first medicine distribution information from the medicine package 81 stored in the medicine bag 82 by the reading terminal 2 is finished. Specifically, the control unit 11 ends the reading operation when the user's continuous operation on the reading terminal 2 or the reading operation of the first drug supply information from the next medicine package 81 is performed. It judges that it does not do (S36: No) and makes processing shift to the above-mentioned step S33. Thereby, the reading of the first drug distribution information from each of the medicine package 81 contained in the medicine bag 82 is sequentially executed. On the other hand, when the end signal is input from the reading terminal 2 in response to the user's closing operation to the reading terminal 2, the control unit 11 or from the medicine bag 82 different from the medicine bag 82 read in the step S31. When the second drug supply information is read, it is determined that the reading operation is to be ended (S36: Yes), and the process proceeds to step S37.
<ステップS37>
ステップS37において、前記制御部11は、前記配薬管理情報D1に基づいて、同一の前記薬袋82に収容するべき全ての前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判定する。ここに、前記ステップS37は、前記制御部11の前記判定部112によって実行される処理である。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記薬袋82に収容するべき全ての前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたと判定すると(S37:Yes)、当該収容時照合処理を終了させて処理を前記ステップS31に戻す。なお、異なる前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られることにより読取終了と判断した場合には、続く前記ステップS31以降において当該第2配薬情報に基づいて同様の処理が実行される。一方、前記制御部11は、前記薬袋82に収容するべき全ての前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られていないと判定すると(S37:No)、処理をステップS38に移行させる。
<Step S37>
In step S37, the control unit 11 determines, based on the medicine distribution management information D1, whether or not the first medicine distribution information has been read from all the medicine packages 81 to be accommodated in the same medicine bag 82. Do. Here, step S37 is processing executed by the determination unit 112 of the control unit 11. Here, when the control unit 11 determines that the first medicine distribution information has been read from all the medicine packages 81 to be stored in the medicine bag 82 (S37: Yes), the accommodation verification process is ended. The process returns to step S31. When it is determined that the reading is completed by reading the second drug supply information from different medicine bags 82, the same processing is executed based on the second drug supply information in the subsequent step S31. On the other hand, when the control unit 11 determines that the first medicine distribution information has not been read from all the medicine packages 81 to be stored in the medicine bag 82 (S37: No), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S38.
<ステップS38>
ステップS38において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS37における判定結果を報知し、処理を前記ステップS33に戻す。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記配薬管理情報D1に基づいて、前記薬袋82に収容するべき前記薬包81のうち前記ステップS33で読み取られていない前記薬包81が存在する旨、及びその未読取の前記薬包81の情報を前記表示装置14又は前記読取端末2に表示させる。これにより、前記薬袋82への前記薬包81の収容漏れが抑制される。例えば、前記制御部11は、前記薬袋82に収容するべき前記薬包81のうち前記ステップS33で読み取られていない前記薬包81に対応する服用者のID又は氏名などを前記服用時期と共に表示させる。
<Step S38>
In step S38, the control unit 11 notifies the determination result in step S37, and returns the process to step S33. Specifically, based on the medicine distribution management information D1, the control unit 11 indicates that the medicine package 81 not read in the step S33 exists among the medicine packages 81 to be stored in the medicine bag 82, The information on the medicine package 81 not read yet is displayed on the display device 14 or the reading terminal 2. Thereby, the accommodation leak of the said medicine package 81 to the said medicine bag 82 is suppressed. For example, the control unit 11 displays an ID or a name of a user corresponding to the medicine package 81 not read in the step S33 among the medicine packages 81 to be stored in the medicine bag 82 along with the medicine taking time. .
[配送時照合処理]
続いて、図11のフローチャートを参照しつつ、前記ステップS5において前記調剤支援装置1の前記制御部11によって実行される配送時照合処理について説明する。
[Delivery check process]
Subsequently, the delivery time check process executed by the control unit 11 of the dispensing support device 1 in step S5 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
<ステップS41>
ステップS41において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2によって、前記配送先識別情報が入力されたか否かを判断する。具体的に、配送担当者は、前記読取端末2に対して、これから出荷する前記薬袋82の配送先である前記老健施設Bを示す前記配送先識別情報を入力する。また、配送担当者は、前記読取端末2を用いて、これから出荷する前記薬袋82が配送する際に収容されるコンテナなどの容器に予め付された前記配送先識別情報を読み取ることにより前記配送先識別情報を入力することも考えられる。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記配送先識別情報が入力されたと判断すると(S41:Yes)、処理をステップS42に移行させる。一方、前記配送先識別情報が入力されるまでの間は(S41:No)、処理が前記ステップS41で待機する。
<Step S41>
In step S41, the control unit 11 determines whether the delivery destination identification information has been input by the reading terminal 2. Specifically, the delivery person in charge inputs, to the reading terminal 2, the delivery destination identification information indicating the health care facility B which is the delivery destination of the medicine bag 82 to be shipped from now. In addition, the delivery person in charge uses the reading terminal 2 to read the delivery destination identification information by reading the delivery destination identification information attached in advance to a container such as a container accommodated when the medicine bag 82 to be delivered from now is delivered. It is also conceivable to input identification information. Here, when the control unit 11 determines that the delivery destination identification information is input (S41: Yes), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S42. On the other hand, until the delivery destination identification information is input (S41: No), the process waits at the step S41.
<ステップS42>
ステップS42において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS41で入力された前記配送先識別情報と前記配薬管理情報D1とに基づいて、前記配送先識別情報が示す同一の前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき一又は複数の前記薬袋82を特定する。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記配送先識別情報及び前記配送日が同一である前記薬袋82を前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき前記薬袋82として特定する。
<Step S42>
In step S42, the control unit 11 simultaneously delivers to the same old care facility B indicated by the delivery destination identification information, based on the delivery destination identification information input in the step S41 and the medicine supply management information D1. The one or more medicine bags 82 to be identified are identified. Specifically, the control unit 11 specifies the medicine bag 82 having the same delivery destination identification information and the delivery date as the medicine bag 82 to be simultaneously delivered to the health care facility B.
<ステップS43>
そして、ステップS43において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2によって、前記薬袋82の前記コード822から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたと判断すると(S43:Yes)、処理をステップS44に移行させ、前記第2配薬情報が読み取られるまでの間は(S43:No)、前記ステップS43の判断を繰り返す。
<Step S43>
Then, in step S43, the control unit 11 determines whether the second drug delivery information has been read from the code 822 of the medicine bag 82 by the reading terminal 2. Here, when the control unit 11 determines that the second drug supply information has been read (S43: Yes), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S44 and continues until the second drug supply information is read (S43). No), repeat the determination of step S43.
<ステップS44>
ステップS44において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS41で入力された前記配送先識別情報と前記ステップS43で読み取られた前記第2配薬情報の前記配送先識別情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。ここに、前記ステップS44は、前記制御部11の前記判定部112によって実行される処理である。また、前記ステップS44において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS43で読み取られた前記第2配薬情報と、前記ステップS44における判定結果とを読取履歴として前記データ記憶部12に記憶させる。これにより、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記読取履歴を参照及び出力することが可能である。
<Step S44>
In step S44, the control unit 11 determines whether or not the delivery destination identification information input in the step S41 matches the delivery destination identification information of the second drug delivery information read in the step S43. judge. Here, step S44 is a process executed by the determination unit 112 of the control unit 11. In step S44, the control unit 11 causes the data storage unit 12 to store the second medicine distribution information read in step S43 and the determination result in step S44 as a reading history. Thus, the dispensing support device 1 can refer to and output the reading history.
<ステップS45>
そして、ステップS45において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS44における判定結果を報知する。ここに、前記ステップS45は、前記制御部11の前記第1報知部113によって実行される処理である。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記判定結果を前記表示装置14又は前記読取端末2に表示させることにより、前記判定結果をユーザーに報知する。これにより、ユーザーが前記判定結果を認識することができる。従って、複数の服用者の前記薬包81を服用時期ごとに纏めて前記薬袋82に収容して配送先に配送する配薬作業における人為的ミスが抑制される。なお、前記判定結果の報知方法は表示に限らず、音声又は発光態様などによって前記判定結果の報知が行われてもよい。
<Step S45>
Then, in step S45, the control unit 11 reports the determination result in step S44. Here, the step S45 is a process executed by the first notification unit 113 of the control unit 11. Specifically, the control unit 11 notifies the user of the determination result by displaying the determination result on the display device 14 or the reading terminal 2. Thus, the user can recognize the determination result. Therefore, human error in the drug dispensing operation in which the medicine package 81 of a plurality of users is collectively collected at each dosing time, stored in the medicine bag 82 and delivered to the delivery destination is suppressed. In addition, the notification method of the said determination result may alert | report the said determination result not only by display but the audio | voice or the light emission aspect.
<ステップS46>
その後、ステップS46において、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2による同一の前記老健施設Bに配送する前記薬袋82からの前記第2配薬情報の読取作業を終了するか否かを判断する。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2に対するユーザーの継続操作、又は次の前記薬袋82からの前記第2配薬情報の読取作業が行われた場合に、前記読取作業を終了しないと判断し(S46:No)、処理を前記ステップS43に移行させる。これにより、同一の前記老健施設Bに配送する前記薬袋82各々からの前記第2配薬情報の読み取りが順に実行される。一方、前記制御部11は、前記読取端末2に対するユーザーの終了操作に応じて前記読取端末2から終了信号が入力された場合、又は前記ステップS41で入力された前記配送先識別情報とは異なる前記配送先識別情報が入力された場合に、前記読取作業を終了すると判断し(S46:Yes)、処理をステップS47に移行させる。
<Step S46>
Thereafter, in step S46, the control unit 11 determines whether the reading operation of the second drug supply information from the medicine bag 82 to be delivered to the same old care facility B by the reading terminal 2 is finished. Specifically, the control unit 11 does not end the reading operation when the user's continuous operation on the reading terminal 2 or the reading operation of the second drug supply information from the medicine bag 82 next is performed. It is determined that (S46: No), and the process proceeds to step S43. Thereby, the reading of the second drug delivery information from each of the medicine bags 82 delivered to the same health care facility B is sequentially executed. On the other hand, when the end signal is input from the reading terminal 2 in response to the user's end operation to the reading terminal 2, the control unit 11 is different from the delivery destination identification information input in the step S41. When the delivery destination identification information is input, it is determined that the reading operation is finished (S46: Yes), and the process proceeds to step S47.
<ステップS47>
ステップS47において、前記制御部11は、前記配薬管理情報D1に基づいて、前記配送先識別情報に対応する同一の前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき全ての前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判定する。ここに、前記ステップS47は、前記制御部11の前記判定部112によって実行される処理である。ここで、前記制御部11は、前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき全ての前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたと判定すると(S47:Yes)、当該配送時照合処理を終了させて処理を前記ステップS41に移行させる。なお、異なる前記配送先識別情報の入力により読取終了と判断した場合には、続く前記ステップS41以降において当該配送先識別情報に基づいて同様の処理が実行される。一方、前記制御部11は、前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき全ての前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られていないと判定すると(S47:No)、処理をステップS48に移行させる。
<Step S47>
In step S47, based on the medicine distribution management information D1, the control unit 11 performs the second medicine supply from all the medicine bags 82 to be simultaneously delivered to the same old care facility B corresponding to the delivery destination identification information. It is determined whether the information has been read. Here, step S47 is a process executed by the determination unit 112 of the control unit 11. Here, if the control unit 11 determines that the second drug delivery information has been read from all the medicine bags 82 to be delivered simultaneously to the health care facility B (S47: Yes), the delivery verification process is ended. Then, the process proceeds to step S41. When it is determined that the reading is ended by the input of different delivery destination identification information, the same processing is executed based on the delivery destination identification information in the subsequent step S41. On the other hand, when the control unit 11 determines that the second drug delivery information is not read from all the medicine bags 82 to be simultaneously delivered to the health care facility B (S47: No), the control unit 11 shifts the process to step S48. .
<ステップS48>
ステップS48において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS47における判定結果を報知し、処理を前記ステップS43に戻す。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記配薬管理情報D1に基づいて、前記配送先識別情報に対応する前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき前記薬袋82のうち前記ステップS43で読み取られていない前記薬袋82が存在する旨、及びその未読取の前記薬袋82の情報を前記表示装置14又は前記読取端末2に表示させる。これにより、前記老健施設Bへの前記薬袋82の配送漏れが抑制される。例えば、前記制御部11は、前記配送先識別情報に対応する前記老健施設Bに同時に配送するべき前記薬袋82のうち前記ステップS43で読み取られていない前記薬袋82に対応する服用時期などを前記配送先識別情報と共に表示させる。
<Step S48>
In step S48, the control unit 11 reports the determination result in step S47, and returns the process to step S43. Specifically, based on the medicine distribution management information D1, the control unit 11 does not read in the step S43 in the medicine bag 82 to be simultaneously delivered to the health care facility B corresponding to the delivery destination identification information. The display device 14 or the reading terminal 2 displays that the drug bag 82 is present and information of the drug bag 82 which has not been read. Thereby, the delivery leak of the medicine bag 82 to the health care facility B is suppressed. For example, the control unit 11 delivers the dosing timing and the like corresponding to the medicine bag 82 not read in the step S43 among the medicine bags 82 to be simultaneously delivered to the health care facility B corresponding to the delivery destination identification information. Display along with the previous identification information.
[受取時処理]
次に、図12のフローチャートを参照しつつ、前記ステップS6において前記配薬支援装置5の制御部51によって実行される受取時処理の手順の一例について説明する。
[Process on receipt]
Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 12, an example of the procedure of the receiving process performed by the control unit 51 of the medicine distribution supporting device 5 in the step S6 will be described.
<ステップS51>
ステップS51において、前記制御部51は、前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られるまでの間は(S51:No)、処理が前記ステップS51で待機する。一方、前記薬袋82から前記第2配薬情報が読み取られたと判断すると(S51:Yes)、処理はステップS52に移行する。
<Step S51>
In step S51, the control unit 51 determines whether the second drug supply information has been read from the medicine bag 82 or not. Here, until the second drug supply information is read from the medicine bag 82 (S51: No), the process waits in the step S51. On the other hand, if it is determined that the second drug supply information has been read from the medicine bag 82 (S51: Yes), the process proceeds to step S52.
<ステップS52>
ステップS52において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS51で読み取られた前記第2配薬情報に含まれる前記配送先識別情報と、前記配薬支援装置5が設置されている前記老健施設Bを示す情報として前記配薬支援装置5に予め登録された配送先識別情報とが一致するか否かを判定する。ここに、前記ステップS52は、前記制御部51の前記配送先判定部512によって実行される処理である。また、前記ステップS52において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS51で読み取られた前記第2配薬情報と、前記ステップS52における判定結果とを読取履歴として前記データ記憶部52に記憶させる。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記読取履歴を参照及び出力することが可能である。
<Step S52>
In step S52, the control unit 51 indicates the delivery destination identification information included in the second drug delivery information read in step S51, and the health care facility B in which the drug delivery support device 5 is installed. It is determined whether the delivery destination identification information registered in advance in the medicine distribution support device 5 as information matches. Here, the step S52 is a process executed by the delivery destination determination unit 512 of the control unit 51. In step S52, the control unit 51 causes the data storage unit 52 to store the second medicine distribution information read in step S51 and the determination result in step S52 as a reading history. Thus, the medicine distribution support device 5 can refer to and output the reading history.
<ステップS53>
そして、ステップS53において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS52における前記判定結果を報知する。具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記判定結果を前記表示装置54又は前記読取端末7に表示させる。ここに、前記ステップS53は、前記制御部51の前記第2報知部513によって実行される処理である。これにより、配薬担当者は、前記判定結果を確認することにより、前記老健施設Bが前記薬袋82の配送先として正しい旨を容易かつ確実に認識することができる。従って、前記薬袋82の誤配送が抑制される。
<Step S53>
Then, in step S53, the control unit 51 notifies the determination result in the step S52. Specifically, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 or the reading terminal 7 to display the determination result. Here, step S53 is processing executed by the second notification unit 513 of the control unit 51. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily and surely recognize that the health care facility B is correct as the delivery destination of the medicine bag 82 by confirming the determination result. Therefore, erroneous delivery of the medicine bag 82 is suppressed.
[配薬時照合処理]
次に、図13のフローチャートを参照しつつ、前記ステップS7において前記配薬支援装置5の制御部51によって実行される配薬時照合処理の手順の一例について説明する。
[Drug matching process]
Next, an example of the procedure of the dispensing time check process executed by the control unit 51 of the drug dispensing support device 5 in step S7 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
<ステップS61>
ステップS61において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られるまでの間は(S61:No)、処理が前記ステップS61で待機する。一方、前記薬包81から前記第1配薬情報が読み取られたと判断すると(S61:Yes)、処理はステップS62に移行する。
<Step S61>
In step S61, the control unit 51 determines whether the first medicine distribution information has been read from the medicine package 81 or not. Here, until the first medicine distribution information is read from the medicine package 81 (S61: No), the process waits in the step S61. On the other hand, if it is determined that the first drug distribution information has been read from the medicine package 81 (S61: Yes), the process proceeds to step S62.
<ステップS62>
ステップS62において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS61で読み取られた前記第1配薬情報に含まれる前記服用者IDと前記変換情報と前記入居者マスターとに基づいて前記服用者に対応する入居者を特定する。また、前記ステップS62において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS61で読み取られた前記第1配薬情報と、前記ステップS62における特定結果とを読取履歴として前記データ記憶部52に記憶させる。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記読取履歴を参照及び出力することが可能である。
<Step S62>
In step S62, the control unit 51 moves in accordance with the doser based on the doser ID, the conversion information, and the resident master included in the first medicine information read in step S61. Identify the In step S62, the control unit 51 causes the data storage unit 52 to store the first drug supply information read in step S61 and the identification result in step S62 as a reading history. Thus, the medicine distribution support device 5 can refer to and output the reading history.
<ステップS63>
そして、ステップS63において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81の服用時期と、前記ステップS62で特定された前記服用者に対応する入居者の氏名及び顔画像63と、を前記携帯端末6に表示させる(図4参照)。ここに、前記ステップS63は、前記制御部51の前記表示制御部511によって実行される処理である。これにより、配薬担当者は、前記入居者の顔画像63を確認することにより、前記入居者が前記薬包81の薬品を服用する服用者として正しい旨を容易かつ確実に認識することができるため、配薬担当者による配薬ミスが抑制される。また、前記配薬支援システム10の構成によれば、前記顔画像63を表示されることにより、前記入居者各々が当該入居者を識別するためのリストバンドなどを装着する必要がないため、前記老健施設Bの運営に好適である。なお、前記入居者マスターに、1人の前記入居者について表情又は撮影角度の異なる複数の前記顔画像63が予め登録されていることも他の実施形態として考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者が前記顔画像63各々に基づいて前記入居者をより正確に判断することができる。
<Step S63>
Then, in step S 63, the control unit 51 uses the portable terminal 6 to take the medication time of the medicine package 81 and the name and face image 63 of the tenant corresponding to the taker identified in the step S 62. Display (see FIG. 4). Here, step S63 is processing executed by the display control unit 511 of the control unit 51. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily and surely recognize that the resident is correct as the user who takes the medicine of the medicine package 81 by checking the face image 63 of the tenant. As a result, it is possible to suppress drug delivery errors by drug delivery personnel. Further, according to the configuration of the medicine distribution support system 10, the face image 63 is displayed, so that the tenants do not need to wear a wrist band or the like for identifying the tenants, so that It is suitable for the management of the aged facility B. In addition, it is also conceivable as another embodiment that a plurality of face images 63 having different expressions or photographing angles are registered in advance for one resident of the resident master. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can more accurately determine the resident based on each of the face images 63.
[第2実施形態]
前述したように、前記老健施設Bで実行される前記ステップS7の配薬作業では、配薬担当者により薬品と入居者とが照合されながら配薬が行われる。以下、本実施形態では、配薬担当者による薬品の配薬作業を支援することにより配薬時における人為的ミスの抑制を図る構成について説明する。
Second Embodiment
As described above, in the dispensing operation in step S7 performed in the health care facility B, the dispensing is performed while the medicine and the resident are collated by the person in charge of drug distribution. Hereinafter, in the present embodiment, a configuration for suppressing human error at the time of drug distribution by supporting the drug distribution operation of the drug by the drug distributor will be described.
まず、図14を参照しつつ、本実施形態に係る配薬支援システム100の構成について説明する。なお、前記配薬支援システム100について、前記配薬支援システム10(図1参照)と同様の構成には同じ符号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
First, the configuration of the medicine distribution support system 100 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. In addition, about the said medicine distribution assistance system 100, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the structure similar to the said medicine distribution assistance system 10 (refer FIG. 1), and the description is abbreviate | omitted.
図14に示すように、前記調剤支援装置1は、USBポート18を備える。前記USBポート18は、USBメモリ19を着脱可能であって、前記USBメモリ19に対するデータの書き込み及び前記USBメモリ19からのデータの読み出しが可能である。なお、前記USBメモリ19に限らず、CD、DVD、BDなどの他の記録メディアを利用することも考えられる。
As shown in FIG. 14, the dispensing support device 1 includes a USB port 18. The USB port 18 can attach and detach the USB memory 19, and can write data to the USB memory 19 and read data from the USB memory 19. Not only the USB memory 19 but also other recording media such as CD, DVD, BD, etc. may be used.
また、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11が、前記調剤支援プログラムに従って各種の処理を実行することにより配薬データ出力部114、残薬情報入力部115、及び残薬通知部116として機能する。なお、前記配薬データ出力部114が配薬データ出力手段の一例、前記残薬情報入力部115が残薬情報入力手段の一例、前記残薬通知部116が残薬通知手段の一例である。
Further, in the dispensing support device 1, the control unit 11 functions as a drug distribution data output unit 114, a residual medicine information input unit 115, and a residual medicine notification unit 116 by executing various processes according to the dispensing support program. Do. The drug distribution data output unit 114 is an example of a drug distribution data output unit, the residual drug information input unit 115 is an example of a residual drug information input unit, and the residual drug notification unit 116 is an example of a residual drug notification unit.
前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記薬包81各々に薬品を分包する際に用いられ、前記処方データ記憶部121に記憶されている処方データに基づく配薬データを前記USBポート18に出力し、前記USBポート18から前記USBメモリ19に記録させることが可能である。特に、前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記配薬データを前記配薬グループの単位で出力することが可能である。具体的に、前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記操作装置15に対するユーザー操作により前記老健施設Bが指定された場合に、その老健施設Bに入居している入居者各々に対応する処方データを抽出し、その処方データに基づく配薬データを出力可能である。これにより、前記処方データのうち必要な処方データだけを容易に利用することが可能である。
The medicine distribution data output unit 114 is used when the medicine is packaged in each medicine package 81, and the medicine distribution data based on the prescription data stored in the prescription data storage unit 121 is output to the USB port 18 It is possible to make the USB memory 19 record data from the USB port 18. In particular, the drug distribution data output unit 114 can output the drug distribution data in units of the drug distribution group. Specifically, when the nursing home B is designated by the user operation on the operation device 15, the medicine distribution data output unit 114 specifies prescription data corresponding to each resident in the nursing home B. It is possible to extract and output drug distribution data based on the prescription data. Thus, it is possible to easily use only the necessary prescription data of the prescription data.
そのため、前記調剤支援装置1の前記データ記憶部12には、施設マスター及び入居者マスターが記憶されており、前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記施設マスター及び前記入居者マスターに基づいて必要な前記処方データを抽出する。なお、前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記配薬データに前記施設マスター及び前記入居者マスターの情報の一部又は全部を付加して出力することも可能である。
Therefore, a facility master and a resident master are stored in the data storage unit 12 of the dispensing support device 1, and the medicine distribution data output unit 114 is required based on the facility master and the tenant master. The prescription data is extracted. Note that the drug distribution data output unit 114 can add and output a part or all of the information of the facility master and the resident master to the drug distribution data.
ここに、図15は、前記施設マスター及び前記入居者マスターの一例を示す図である。なお、前記施設マスター及び前記入居者マスター各々の登録作業は、例えば前記調剤支援装置1の初期設定又はマスターメンテナンスなどにおいて、前記調剤支援装置1の前記表示装置14及び前記操作装置15などを用いて行われる。
Here, FIG. 15 is a diagram showing an example of the facility master and the resident master. The registration work of each of the facility master and the resident master may be performed, for example, using the display device 14 and the operation device 15 of the dispensing support device 1 in initial setting or master maintenance of the dispensing support device 1 or the like. To be done.
図15に示すように、前記施設マスターには、前記老健施設Bごとに対応する施設コード、施設名称、及び印字フォーマットが関連付けて記憶されている。前記施設コード及び前記施設名称は、前記老健施設Bを識別するための識別情報の一例であって、前記印字フォーマットは、前記薬品分包装置3において前記薬包81に印刷する項目のフォーマットの種類を識別するための情報である。なお、前記施設コードは、例えば前記配送先ID(図2参照)と同一である。
As shown in FIG. 15, in the facility master, a facility code, a facility name, and a print format corresponding to each old facility B are associated and stored. The facility code and the facility name are an example of identification information for identifying the health care facility B, and the print format is a type of format of an item to be printed on the medicine package 81 in the medicine packaging device 3 Is information for identifying The facility code is, for example, the same as the delivery destination ID (see FIG. 2).
また、図15に示すように、前記入居者マスター各々は、前記施設マスターに登録されている前記老健施設B各々に関連付けて記憶される。具体的に、前記入居者マスターには、入居者ごとに対応する服用者ID、服用者名、入居者ID、グループ、及び印字フォーマットが記憶されている。前記服用者ID、前記服用者名、及び前記入居者IDは前記老健施設Bに入居する入居者を識別するための識別情報の一例である。特に、前記服用者IDは、前記薬局A側の前記調剤支援装置1などにおいて前記入居者(服用者)を識別するために予め登録される識別情報であり、前記入居者IDは、前記老健施設B側の前記配薬支援装置5などにおいて前記入居者を識別するために予め登録される識別情報である。例えば、前記マスター記憶部521に記憶されている前記入居者マスターが前記老健施設B側から前記薬局A側に提供されることにより、前記薬局A側で前記調剤支援装置1の前記入居者マスターに前記入居者IDが登録される。なお、前記入居者マスターにおける前記服用者IDと前記入居者IDとの対応関係は、前記配薬支援装置5で用いられる前記変換情報における前記服用者IDと前記入居者IDとの対応関係と同じである。
Further, as shown in FIG. 15, the resident masters are stored in association with the old facilities B registered in the facility master. Specifically, in the resident master, a doser ID, a doser name, a resident ID, a group, and a print format corresponding to each resident are stored. The doser ID, the doser's name, and the resident ID are an example of identification information for identifying a resident who moves into the health care facility B. In particular, the doser ID is identification information registered in advance for identifying the resident (patient) in the dispensing support device 1 or the like on the pharmacy A side, and the resident ID is the health care facility The identification information is registered in advance to identify the resident in the medicine distribution support device 5 or the like on the B side. For example, when the resident master stored in the master storage unit 521 is provided from the health care facility B side to the pharmacy A side, the resident master of the dispensing support device 1 at the pharmacy A side The resident ID is registered. The correspondence relationship between the doser ID and the resident ID in the resident master is the same as the correspondence relationship between the doser ID and the resident ID in the conversion information used in the medicine distribution support device 5 It is.
また、前記グループは、前記老健施設Bにおける病棟、病室、又はフロアなどにより一連の配薬グループとして分類されたグループを識別するための識別情報である。なお、前記老健施設Bでは、入居者への配薬作業が前記グループごとに行われる。さらに、前記印字フォーマットは、前記薬品分包装置3において前記薬包81及び前記薬袋82などに印刷する項目及び配置などのフォーマットの種類を識別するための情報である。なお、前記入居者マスターに登録された前記印字フォーマットは、例えば前記施設マスターにおいて前記印字フォーマットが登録されている場合でも優先的に採用される。
The group is identification information for identifying a group classified as a series of drug distribution groups by a ward, a hospital room, a floor, or the like in the health care facility B. In addition, in the said elderly care facility B, the medicine distribution operation to a resident is performed for every said group. Furthermore, the print format is information for identifying the type of format such as an item and arrangement to be printed on the medicine package 81 and the medicine bag 82 in the medicine dispensing apparatus 3. The print format registered in the resident master is preferentially adopted, for example, even when the print format is registered in the facility master.
このように構成された前記配薬支援システム100では、前記調剤支援装置1において、前記服用者IDと前記入居者IDとの対応関係を把握することが可能である。そのため、前記制御部11が、前記第1配薬情報に含まれる前記服薬者IDに代えて又は前記服薬者IDと共に、前記入居者IDを前記薬品分包装置3によって前記薬包81に印刷させることが考えられる。
In the medicine distribution support system 100 configured as described above, the dispensing support device 1 can grasp the correspondence between the doser ID and the resident ID. Therefore, the control unit 11 causes the medicine package 81 to print the resident ID by the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 in place of or together with the patient ID included in the first drug distribution information. It is conceivable.
また、前記残薬情報入力部115は、前記配薬支援装置5において後述の残薬情報出力部516によって出力される残薬情報を入力可能である。例えば、前記残薬情報入力部115は、前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して、前記残薬情報の送信を前記配薬支援装置5に要求し、前記配薬支援装置5から送信される前記残薬情報を取得する。また、前記残薬情報入力部115は、前記USBメモリ19などの記録媒体から前記残薬情報を読み取って入力することも可能であり、前記配薬支援装置5からメールなどによって送信された前記残薬情報を入力することも可能である。
Further, the residual medicine information input unit 115 can input residual medicine information output from the residual medicine information output unit 516 described later in the medicine distribution support device 5. For example, the residual drug information input unit 115 requests the drug distribution support device 5 to transmit the residual drug information via the network N1 and the network N2 or the like, and is transmitted from the drug distribution support device 5 The remaining drug information is acquired. The residual medicine information input unit 115 can also read and input the residual medicine information from a recording medium such as the USB memory 19 or the like, and the residual medicine transmitted from the medicine distribution support device 5 by e-mail or the like. It is also possible to enter drug information.
前記残薬通知部116は、前記残薬情報入力部115により入力された前記残薬情報と前記処方データとに基づいて、前記処方データに含まれる処方薬として使用可能な残薬の情報を通知可能である。例えば、前記残薬通知部116は、前記処方データの発行処理(図4のステップS1)において、調剤対象の前記処方データで使用可能な残薬が存在する旨の注意喚起を表示することが可能である。なお、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11が、前記操作装置15のユーザー操作に応じて任意のタイミングで前記表示装置14などに前記残薬情報を表示させることも可能である。また、前記残薬通知部116は、前記残薬情報を前記調剤支援装置1に通信可能に接続された前記電子カルテシステム又は前記処方入力端末などの上位システム(不図示)に送信することも可能である。これにより、前記上位システムを使用する医師に前記残薬情報を通知して前記処方データの修正などを促すことができ、薬品の無駄を抑制することが可能である。なお、前記薬局A側の薬剤師が、前記調剤支援装置1で表示される前記残薬情報を参照し、残薬の量を医師に連絡して、新たな処方入力時に残薬を除いた処方入力を促すこと、又は入力済みの処方から残薬を除く修正(再発行)を促すことが可能である。
The residual medicine notification unit 116 notifies information on residual medicine that can be used as a prescription medicine included in the prescription data, based on the residual medicine information and the prescription data input by the residual medicine information input unit 115. It is possible. For example, the remaining drug notification unit 116 can display a warning that there is a usable remaining drug in the prescription data to be dispensed in the process of issuing the prescription data (step S1 in FIG. 4). It is. In addition, in the said dispensing assistance apparatus 1, it is also possible for the said control part 11 to display the said residual medicine information on the said display apparatus 14 etc. at arbitrary timing according to the user operation of the said operating device 15. FIG. Further, the remaining drug notification unit 116 can also transmit the remaining drug information to a high level system (not shown) such as the electronic medical record system communicably connected to the dispensing support device 1 or the prescription input terminal. It is. As a result, it is possible to notify a doctor who uses the upper level system of the remaining drug information to urge correction of the prescription data and the like, and it is possible to suppress waste of medicine. The pharmacist on the pharmacy A side refers to the remaining drug information displayed on the dispensing support device 1, communicates the amount of the remaining drug to the doctor, and inputs the prescription excluding the remaining drug at the time of new prescription input It is possible to prompt a correction (reissue) to remove the remaining drug from the input prescription.
一方、図14に示すように、前記配薬支援装置5は、USBポート58を備える。前記USBポート58は、前記USBメモリ19が着脱可能であり、前記USBメモリ19に対するデータの書き込み及び前記USBメモリ19からのデータの読み出しが可能である。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 14, the drug distribution support device 5 includes a USB port 58. The USB memory 19 is attachable to and detachable from the USB port 58, and data can be written to the USB memory 19 and data can be read from the USB memory 19.
また、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記データ記憶部52に配薬データ記憶部523が含まれる。前記配薬データ記憶部523には、前記調剤支援装置1から出力され、前記USBポート58によって前記USBメモリ19から読み出される前記配薬データが記憶される。
Further, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the data storage unit 52 includes a medicine distribution data storage unit 523. The drug-dispensing data storage unit 523 stores the drug-dispensing data output from the dispensing support device 1 and read from the USB memory 19 by the USB port 58.
また、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、前記配薬支援プログラムに従って各種の処理を実行することにより配薬データ入力部514、服薬完了入力部515、及び残薬情報出力部516として機能する。なお、前記配薬データ入力部514が配薬データ入力手段の一例、前記服薬完了入力部515が服薬完了入力手段の一例、前記残薬情報出力部516が残薬情報出力手段の一例である。
Further, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 executes various processes according to the medicine distribution support program, and the medicine distribution data input unit 514, the medicine administration complete input unit 515, and the remaining medicine information output unit 516. Act as. The drug distribution data input unit 514 is an example of a drug distribution data input unit, the medication completion input unit 515 is an example of a drug administration completion input unit, and the residual medicine information output unit 516 is an example of a residual medicine information output unit.
前記配薬データ入力部514は、前記調剤支援装置1により出力された前記配薬データを、薬品の配送先である前記老健施設Bに設けられた前記配薬支援装置5に入力することが可能である。具体的に、前記配薬データ入力部514は、前記操作装置55のユーザー操作に応じて、前記USBポート58に接続される前記USBメモリ19から前記配薬データを読み出すことにより前記配薬データを前記配薬支援装置5に入力する。
The medicine distribution data input unit 514 can input the medicine distribution data output by the medicine distribution support device 1 to the medicine distribution support device 5 provided in the health care facility B, which is a medicine delivery destination. It is. Specifically, the drug delivery data input unit 514 reads the drug delivery data by reading out the drug delivery data from the USB memory 19 connected to the USB port 58 according to the user operation of the operation device 55. The information is input to the medicine distribution support device 5.
前記服薬完了入力部515は、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6により後述の入居者一覧画面211(図23参照)に表示された服用者ごとの服薬完了の入力操作を受け付ける。具体的に、前記服薬完了入力部515は、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6に対する前記服用者の服薬完了の入力操作を受け付ける。
The medication completion input unit 515 receives an input operation of dosing completion for each doser displayed on the tenant list screen 211 (see FIG. 23) described later by the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6. Specifically, the medication completion input unit 515 receives an input operation on the manipulation device 55 or the portable terminal 6 for the dosing completion of the user.
前記残薬情報出力部516は、前記服用者が服用しなかった残薬に関する残薬情報の入力操作を受け付けると共に、前記残薬情報を出力可能である。具体的に、前記残薬情報出力部516は、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6に対する前記残薬情報の入力操作を受け付ける。そして、前記残薬情報出力部516は、前記残薬情報を前記データ記憶部52に記憶すると共に、前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して前記調剤支援装置1に送信出力する。
The residual medicine information output unit 516 can output the residual medicine information as well as accepting input operation of residual medicine information on the residual medicine that the user did not take. Specifically, the residual medicine information output unit 516 receives an input operation of the residual medicine information to the operation device 55 or the portable terminal 6. The remaining drug information output unit 516 stores the remaining drug information in the data storage unit 52, and transmits and outputs the remaining drug information to the dispensing support device 1 via the network N1 and the network N2.
また、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部11が前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6のユーザー操作に応じて初期設定情報として前記老健施設B及び入居者の情報を登録可能である。ここに、図16は施設登録画面の一例を示す図、図17は入居者登録画面の一例を示す図である。
Further, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 11 can register the information on the aged facility B and the resident as initial setting information according to the user operation of the operation device 55 or the portable terminal 6. Here, FIG. 16 is a view showing an example of the facility registration screen, and FIG. 17 is a view showing an example of the resident registration screen.
図16に示すように、前記制御部11は、前記操作装置55のユーザー操作に応じて、施設コード及び施設名称を登録するための施設登録画面を表示させる。前記施設登録画面では、前記施設コード及び前記施設名称が入力された後、登録キーが操作されることにより、それらの情報が施設マスターとして前記マスター記憶部521に記憶される。なお、前記施設コード及び前記施設名称は、前記調剤支援装置1の前記施設マスター(図15参照)に登録される施設コード及び施設名称と同じである。
As shown in FIG. 16, the control unit 11 displays a facility registration screen for registering a facility code and a facility name in accordance with a user operation of the operation device 55. In the facility registration screen, after the facility code and the facility name are input, when the registration key is operated, the information is stored in the master storage unit 521 as a facility master. The facility code and the facility name are the same as the facility code and the facility name registered in the facility master (see FIG. 15) of the dispensing support device 1.
また、図17に示すように、前記制御部11は、前記操作装置55のユーザー操作に応じて、入居者の情報を登録するための入居者登録画面を表示させる。具体的に、前記入居者登録画面では、入居者ID、入居者の名前、仮名、生年月日、性別、管理区分、グループ、部屋コード、コメント、及び顔画像(写真)の入力が可能である。前記管理区分では、例えば、薬品の服用を自己で管理する自己管理であるか否かなどが選択される。前記管理区分には、服薬時の配薬及び服薬の有無の確認が必要である「服薬確認要」、所定期間の薬品が服用者に預けられ、服薬時の配薬は不要であるが服薬の有無の確認が必要である「服薬確認要(自己管理)」、及び所定期間の薬品が服用者に預けられ、服薬時の配薬及び服用の確認が共に不要である「服薬確認不要(自己管理)」などが含まれる。前記コメントには、入居者について注意すべき事項などが任意に記載可能であり、前記コメントは後述の入居者確認画面213(図25参照)に表示可能である。また、顔画像(写真)の入力手法としては、予め撮影された写真を一覧から選択して取り込む取込入力、及び入居者の情報を登録する際に前記携帯端末6の前記カメラ62を用いて撮影する撮影入力がある。そして、前記入居者登録画面では、入居者の情報が入力された後、登録キーが操作されることによりそれらの情報が前記入居者マスターとして前記マスター記憶部521に記憶される。なお、入居者の情報に含まれる入居者ID、入居者の名前(仮名)、及びグループなどは、前記調剤支援装置1の前記入居者マスター(図15参照)に登録される入居者ID、服用者名、及びグループと同じである。また、前記入居者登録画面において、データキーが操作された場合には、前記制御部11は、その後の操作に応じて入居者の情報のインポート又はエクスポートを実行する。
Further, as shown in FIG. 17, the control unit 11 displays a resident registration screen for registering resident information in accordance with the user operation of the operation device 55. Specifically, on the resident registration screen, the resident ID, the name of the resident, pseudonym, date of birth, gender, management classification, group, room code, comment, and face image (photograph) can be input. . In the management category, for example, it is selected whether or not self-management for self-administration of medicine taking. In the above management classification, “Confirmation of medication required”, which requires drug distribution at the time of drug administration and confirmation of the presence or absence of medication, medicines for a predetermined period are deposited by the user, and drug dispensing at the time of drug administration is unnecessary "Confirmation of medication required (self-management)", which requires confirmation of presence / absence, and medication for a prescribed period of time is deposited by the person taking the medication, and confirmation of medication and taking at the time of medication is unnecessary. ) Etc. The comment can optionally describe matters to be noted about the resident, and the comment can be displayed on a resident confirmation screen 213 (see FIG. 25) described later. In addition, as a method of inputting a face image (photograph), using a camera 62 of the portable terminal 6 when registering a taken-in input by selecting a photograph taken in advance from a list and taking in the information of a resident There is a shooting input to shoot. Then, on the resident registration screen, after the information of the resident is input, when the registration key is operated, the information is stored in the master storage unit 521 as the tenant master. The resident ID included in the information of the resident, the name (temporary name) of the resident, the group, etc. is the resident ID registered in the resident master (see FIG. 15) of the dispensing support device 1, the dose It is the same as the person's name and group. When the data key is operated on the resident registration screen, the control unit 11 performs import or export of tenant information according to the subsequent operation.
以下、このように構成された前記配薬支援システム100において実行される各種の処理について説明する。なお、前記配薬支援システム100においても、前記薬品分包処理(図8参照)、前記収容時照合処理(図10参照)、前記配送時照合処理(図11参照)、及び前記受取時処理(図12参照)などが実行される。
Hereinafter, various processes performed in the medicine distribution support system 100 configured as described above will be described. In the drug distribution support system 100 as well, the medicine package process (see FIG. 8), the accommodation check process (see FIG. 10), the delivery check process (see FIG. 11), and the reception process (see FIG. 11). 12) and the like are executed.
[処方データの発行処理]
まず、図18を参照しつつ、前記配薬支援システム100で実行される前記処方データ発行処理について説明する。なお、前記処方データの発行処理について、図5で説明した処理手順と同様の処理手順については同じ符号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
[Prescription data issuance process]
First, the prescription data issuance process performed by the medicine distribution support system 100 will be described with reference to FIG. In addition, about the issue process of the said prescription data, about the process sequence similar to the process sequence demonstrated in FIG. 5, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected and the description is abbreviate | omitted.
<ステップS111>
図18に示すように、前記ステップS11において前記処方データの発行操作が行われると、続くステップS111において、前記制御部11は、前記残薬情報を入力するための残薬情報入力処理を実行する。ここに、前記ステップS111は、前記制御部11の前記残薬情報入力部115によって実行される。
<Step S111>
As shown in FIG. 18, when the operation for issuing the prescription data is performed in the step S11, the control unit 11 executes a residual medicine information input process for inputting the residual medicine information in the subsequent step S111. . Here, the step S111 is executed by the residual drug information input unit 115 of the control unit 11.
例えば、前記ステップS111では、前記制御部11が、前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して前記配薬支援装置5に前記残薬情報の送信を要求する。そして、前記制御部11は、前記配薬支援装置5から前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して送信される前記残薬情報を受信する。なお、前記配薬支援装置5から予め設定された期間ごと又は予め定められたタイミングで自動的に前記残薬情報が前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して送信され、前記残薬情報入力部115が前記残薬情報を取得することも考えられる。また、前記配薬支援装置5において前記USBメモリ19などの記録媒体に前記残薬情報が記録され、前記調剤支援装置1において前記USBメモリ19などの記録媒体から前記残薬情報が読み出されることも考えられる。これにより、前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2を介した連携を伴うことなく前記残薬情報を前記調剤支援装置1で活用することが可能となる。
For example, in step S111, the control unit 11 requests the medicine distribution support apparatus 5 to transmit the residual medicine information via the network N1, the network N2, and the like. Then, the control unit 11 receives the residual medicine information transmitted from the medicine distribution support device 5 via the network N1 and the network N2. The remaining drug information is automatically transmitted from the drug distribution support device 5 at predetermined intervals or at predetermined timings via the network N1 and the network N2, etc., and the residual drug information input unit It is also conceivable that 115 acquires the remaining drug information. Further, the residual medicine information may be recorded in a recording medium such as the USB memory 19 in the medicine dispensing support device 5, and the residual medicine information may be read out from the recording medium such as the USB memory 19 in the dispensing assistance device 1. Conceivable. As a result, the remaining drug information can be used by the dispensing support device 1 without involving cooperation via the network N1 and the network N2.
<ステップS112>
次に、ステップS112において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS111で取得した前記残薬情報と前記処方データとに基づいて、前記処方データに含まれる処方薬として使用可能な残薬の情報を通知する。ここに、前記ステップ112は、前記制御部11の前記残薬通知部116によって実行される。また、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS112において、前記処方データにおける処方日が、前記残薬情報に含まれる残薬の有効期限内であるか否かを判断し、前記有効期限内であるか否かを前記表示装置14などに表示させることも考えられる。
<Step S112>
Next, in step S112, the control unit 11 notifies, based on the residual drug information acquired in the step S111 and the prescription data, information on residual medicine usable as a prescription drug contained in the prescription data. Do. Here, the step 112 is executed by the remaining drug notification unit 116 of the control unit 11. Further, the control unit 11 determines in step S112 whether or not the prescription date in the prescription data is within the expiration date of the residual medicine included in the residual drug information, and is within the expiration date. It is also conceivable to display on the display device 14 etc.
例えば、前記ステップS112では、前記制御部11が、前記残薬情報と前記処方データとに基づいて、前記処方データのうち前記残薬情報において残薬として存在するため分包が不要な薬品を判断する。そして、前記残薬として存在する薬品の情報を前記表示装置14などに表示させる。これにより、前記表示装置14を参照する薬剤師などが、前記残薬を利用可能である旨を容易に認識することが可能であり、例えば医師への前記処方データの修正照会を行うことにより薬品の無駄を抑制することが可能になる。具体的には、前記残薬情報を確認した上で服用日数又は服用回数などが調整されることが考えられる。
For example, in the step S112, the control unit 11 determines a drug which does not require a package because it exists as a residual drug in the residual drug information among the prescription data, based on the residual drug information and the prescription data. Do. Then, the display device 14 or the like displays information on the medicine existing as the residual drug. As a result, a pharmacist or the like who refers to the display device 14 can easily recognize that the remaining drug can be used. It becomes possible to control waste. Specifically, it is conceivable that the number of days taken, the number of times taken, etc. are adjusted after confirming the remaining drug information.
なお、このとき医師が、前記処方データから前記残薬を使用可能な服用時期又は薬品を除いた場合には、前記残薬を使用することが前提になるため、前記老健施設Bに配送される薬品が不足した状態となる。そこで、例えば前記ステップS12における前記分包データの生成時に、前記残薬の存在により分包対象から除かれた薬品についても空の前記薬包81が発行されるように前記分包データが生成されることが考えられる。具体的には、前記分包データのうち前記残薬の存在により分包対象から除かれた薬品に対応する分包データに、その服用時期と、その服用時期に使用する残薬を特定するための残薬特定情報(例えば、服用時期など)とが含まれることが考えられる。
In addition, since it becomes a premise to use the said remaining drug at this time when a doctor removes the dosing timing or medicine which can use the said remaining drug from the said prescription data, it is delivered to the said health care facility B. The medicine runs out. Therefore, for example, the package data is generated so that the empty drug package 81 is issued also for the medicine that is excluded from the package target due to the presence of the residual drug when the package data is generated in the step S12. It is conceivable that Specifically, in the package data corresponding to the drug removed from the package target due to the presence of the residual drug among the package data, to specify the dosing period and the remaining drug to be used for the dosing period It is considered that the remaining drug specific information (for example, the dosing time etc.) is included.
そして、前記薬品分包装置3では、残薬を使用する前記服用時期及び前記残薬特定情報が空の前記薬包81に印刷される。例えば、空の前記薬包81には、「△月△日夕食後は、○月○日夕食後の薬品を服用して下さい」などのメッセージが表示されることが考えられる。これにより、前記老健施設Bでは、空の前記薬包81を参照することにより前記服用時期ごとに使用するべき残薬を判断することが可能である。なお、前記残薬が使用可能であるか否かの判断は、前記服用時期ごとに行われること、即ち前記薬包81の単位で行われることが考えられる。これにより、前記薬包81内の薬品と残薬として残っている薬品とを合わせて服用する必要がなく、配薬ミスの発生を抑制することができる。また、前記分包データの生成時に、分包対象から除かれた薬品に関する情報が前記操作装置15の操作入力によって入力されることが考えられる。さらに、前記調剤支援装置1の前記制御部11が、前記残薬を使用する旨の修正が医師によって行われた場合に、その修正前後の前記処方データに基づいて、分包対象から除かれた薬品の服用時期などを判断することも考えられる。
Then, in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3, the taking time for using the remaining drug and the remaining drug specifying information are printed on the empty drug package 81. For example, it is possible that a message such as "Please take medicine after O Mon O Sun dinner after O Mon O Sun dinner" is displayed in the empty medicine package 81. Thereby, in the health care facility B, it is possible to determine the remaining medicine to be used at each dosing time by referring to the empty medicine package 81. In addition, it is conceivable that the determination as to whether or not the remaining drug can be used is performed at each dosing time, that is, performed in units of the medicine package 81. As a result, it is not necessary to take together the medicine in the medicine pack 81 and the medicine remaining as a residual medicine, and it is possible to suppress the occurrence of a medication error. Further, it is conceivable that, at the time of generation of the packing data, information on the medicine removed from the packing object is inputted by the operation input of the operating device 15. Furthermore, when a correction to use the residual drug is performed by a doctor, the control unit 11 of the dispensing support device 1 is excluded from the subject of packaging based on the prescription data before and after the correction. It is also conceivable to determine the timing of taking medicines.
<ステップS14>
その後、ステップS14において、前記制御部11は、前記老健施設B側で利用される配薬データの出力操作を待ち受ける(S14:No側)。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記操作装置15に対するユーザー操作によって前記配薬データの出力操作が実行されたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記配薬データの出力操作が行われたと判断すると(S14:Yes側)、処理はステップS15に移行する。
<Step S14>
After that, in step S14, the control unit 11 waits for the output operation of the medicine distribution data used on the health care facility B side (S14: No side). Specifically, the control unit 11 determines whether or not the output operation of the medicine distribution data has been executed by the user operation on the operation device 15. Here, if it is determined that the output operation of the drug distribution data has been performed (S14: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S15.
<ステップS15>
ステップS15において、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS11で発行操作が行われた前記処方データに基づいて前記配薬データを生成し、前記配薬データを前記USBポート18に出力して前記USBメモリ19に記録する。即ち、前記制御部11は、前記処方データ及び前記分包データと同様に、前記配薬グループである前記老健施設B又は前記グループなどの単位で前記配薬データを出力する。これにより、前記薬包81及び前記薬袋82等と共に前記USBメモリ19を前記配薬支援装置5に配送することにより、前記USBメモリ19に記憶されている前記配薬データを前記配薬支援装置5で利用し、配薬担当者による配薬作業の効率化及び配薬ミスの抑制を図ることが可能となる。また、前記ステップS11で発行操作が行われた前記処方データを対象として前記配薬データが生成されるため、前記配薬データを生成するための抽出条件などを再度設定する手間が軽減され、また、調剤対象であって前記処方データと異なる前記配薬データが生成されることが防止される。
<Step S15>
In step S15, the control unit 11 generates the drug distribution data based on the prescription data for which the issuing operation has been performed in step S11, and outputs the drug distribution data to the USB port 18 for the USB memory Record at 19. That is, the control unit 11 outputs the drug distribution data in units of the health care facility B which is the drug distribution group or the group, as in the case of the prescription data and the package data. As a result, the medicine distribution data stored in the USB memory 19 is stored in the medicine distribution support unit 5 by delivering the USB memory 19 to the medicine distribution support unit 5 together with the medicine package 81 and the medicine bag 82 and the like. It is possible to improve the efficiency of drug distribution work by drug distribution personnel and to control the distribution error. Further, since the drug distribution data is generated for the prescription data for which the issuing operation has been performed in step S11, it is possible to reduce the time and effort for setting extraction conditions and the like for generating the drug distribution data, and And preventing the generation of the drug distribution data which is a dispensing target and is different from the prescription data.
前記配薬データには、入居者ID、入居者名(服用者名)、グループ、仮名、薬品コード(YJコード)、薬品名、服用日、服用時期(用法)、用量、剤形、一包化区分、副作用関連情報、及び頓服の1日最大用量(最大回数)などが含まれる。ここに、前記一包化区分は、同じ前記薬包81内に分包される薬品を識別するための区分である。前記副作用関連情報は、薬品の添付文書に記載されている副作用に関する情報、又は前記薬局Aなどにおいて予め薬品に対応付けて任意に登録された副作用に関する情報などである。なお、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記薬局A側の前記調剤支援装置1においても前記配薬支援装置5側で管理される入居者ID及びグループなどの情報が前記入居者マスターに登録される。そのため、前記制御部11は、前記入居者マスターを参照して前記入居者ID及び前記グループなどの情報を前記配薬データに付加して出力することが可能である。これにより、複数の前記薬局Aと複数の前記老健施設Bとの間で薬品の授受が行われる場合でも、前記配薬支援装置5が、前記配薬データに基づいて入居者を特定することが可能である。なお、前記配薬データに前記服用者IDが含まれており、前記老健施設B各々において前記配薬支援装置5が前記服用者IDと前記入居者IDとの対応関係(前記変換情報)に基づいて前記服用者IDに対応する入居者を判断することも他の実施形態として考えられる。
The drug distribution data includes resident ID, resident name (patient name), group, pseudonym, drug code (YJ code), drug name, dose date, dose timing (usage), dose, dosage form, package Category, adverse-effect related information, and daily maximum dose (maximum number of doses) of oral treatment. Here, the single-packed category is a category for identifying a drug to be packaged in the same drug package 81. The side effect related information is information related to the side effect described in the package insert of the drug, or information related to the side effect registered in advance in the pharmacy A or the like in association with the drug. In the dispensing support system 100, information such as resident ID and group managed by the dispensing support device 5 is also registered in the resident master in the dispensing support device 1 on the pharmacy A side. . Therefore, the control unit 11 can add the tenant ID and information such as the group to the medicine distribution data with reference to the tenant master, and can output the information. Thus, even when medicines are exchanged between the plurality of the pharmacies A and the plurality of the old facilities B, the medicine distribution support device 5 identifies the resident based on the medicine distribution data. It is possible. In addition, the doser ID is included in the drug distribution data, and in each of the health care facilities B, the drug distribution support device 5 is based on the correspondence (the conversion information) between the doser ID and the resident ID Determining the resident corresponding to the doser ID is also considered as another embodiment.
ここに、図19は、前記老健施設B1で利用される配薬データの一例を示す図である。図19に示すように、前記配薬データには、前記分包データ(図6参照)に加えて、入居者ID、入居者名(服用者名)、グループ、剤形、一包化区分が含まれている。なお、前記一包化区分について、図19に示す例では、「湯山一郎」の医薬品M1と医薬品M3とは共に一包化区分が「1」であり同じ前記薬包81に分包されることが示されており、「湯山三郎」の医薬品M7と医薬品M8とは一包化区分が「1」、「2」であって異なる前記薬包81に分包されることを示している。また、図19では省略しているが、前述したように、前記配薬データには、副作用関連情報及び頓服の1日最大用量(最大回数)なども含まれる。
FIG. 19 is a diagram showing an example of drug distribution data used in the health care facility B1. As shown in FIG. 19, in addition to the package data (see FIG. 6), in the drug distribution data, a resident ID, a resident name (patient's name), a group, a dosage form, and a package division include. In the example shown in FIG. 19, the medicine M1 and the medicine M3 of “Yuyama Ichiro” are both packaged in the same medicine package 81, which is “1” in the one packing division. The medicine M7 and the medicine M8 of “Yuyama Saburo” indicate that the one-packed division is “1”, “2” and is divided into different medicine packages 81. Further, although omitted in FIG. 19, as described above, the drug distribution data also includes side effect related information and the daily maximum dose (maximum number of times) of oral treatment.
なお、前記USBメモリ19は、前記配薬データの移動に利用される記録媒体の一例であって、前記USBメモリ19に代えて他のフラッシュメモリ又はハードディスクドライブなどの各種の記録媒体を用いることが可能である。また、本実施形態では、前記USBメモリ19のような記録媒体を用いて前記配薬データを移動可能な構成について説明するが、前記配薬データを前記配薬支援装置5に伝達することができればその手法はこれに限らない。例えば、前記配薬データ出力部114が、前記配薬データを前記通信インターフェース13に出力し、前記通信インターフェース13からインターネット等の前記ネットワークN1を通じて前記配薬支援装置5に送信出力な構成も考えられる。なお、前記配薬データ出力部114は、前記配薬データに対応する前記処方データを前記配薬支援装置5に送信出力することが可能な構成も考えられる。
The USB memory 19 is an example of a recording medium used to move the drug-dispensing data, and may be replaced with the USB memory 19 to use various recording media such as another flash memory or a hard disk drive. It is possible. Further, in the present embodiment, a configuration in which the drug distribution data can be moved using a recording medium such as the USB memory 19 will be described, but if the drug distribution data can be transmitted to the drug distribution support device 5 The method is not limited to this. For example, the composition data output unit 114 may output the composition data to the communication interface 13 and transmit output from the communication interface 13 to the composition assistance device 5 through the network N1 such as the Internet. . The configuration in which the medicine distribution data output unit 114 can transmit and output the prescription data corresponding to the medicine distribution data to the medicine distribution support device 5 is also conceivable.
さらに、前記制御部11は、前記調剤支援装置1及び前記配薬支援装置5が前記ネットワークN1及び前記ネットワークN2などを介して通信可能に接続されたサーバーなどの記憶部に前記配薬データを出力して記憶させることも考えられる。即ち、前記調剤支援装置1及び前記配薬支援装置5がクラウド上で前記配薬データを共有する構成が考えられる。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5の前記制御部51は、前記サーバーなどの記憶部から前記配薬データを読み出して入力することが可能となる。また、前記薬品分包装置3において服用時期各々に対応する前記薬包81が連続する前記薬包シートが服用者ごとに出力され、その薬包シートに検薬用の情報が印刷される前記薬包81が付加される場合などには、その薬包81に当該服用者に関する前記配薬データを示す一次元コード又は二次元コードなどのコードが印刷出力されることが考えられる。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5において、前記制御部51が、前記検薬用の前記薬包81から前記コードを読み取ることにより、服用者ごとに前記配薬データを入力することが可能となる。なお、前記コードは、前記薬包81に限らず、例えば前記薬包81と共に配送される紙媒体に印刷されることも考えられる。前記コードに含まれる前記配薬データには、当該服用者に対応する今回の前記配薬データにおける最初の服用時期である服用開始時期及び最後の服用時期を示す服用終了時期も含まれる。また、前記配薬データに代えて当該服用者に対応する前記処方データ(例えば、薬品名、用法、用量、服用開始日、服用終了日など)が前記検薬用の前記薬包81に印刷出力される前記コードに含まれることも考えられる。
Furthermore, the control unit 11 outputs the drug distribution data to a storage unit such as a server to which the dispensing support device 1 and the drug distribution support device 5 are communicably connected via the network N1, the network N2, and the like. It is also conceivable to memorize it. That is, a configuration is conceivable in which the dispensing support device 1 and the drug distribution support device 5 share the drug distribution data on the cloud. Thus, the control unit 51 of the medicine distribution support device 5 can read out and input the medicine distribution data from the storage unit such as the server. Further, the medicine package sheet in which the medicine package 81 corresponding to each dosing time in the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 is continuously output for each user, and the medicine package information is printed on the medicine package sheet When 81 is added, etc., it is conceivable that a code such as a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code indicating the above-mentioned drug distribution data regarding the user concerned is printed out on the medicine package 81. Thereby, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 can input the medicine distribution data for each user by reading the code from the medicine package 81 for the test. The code is not limited to the medicine package 81. For example, the code may be printed on a paper medium to be delivered together with the medicine package 81. The drug distribution data included in the code also includes a dose start time, which is the first dose time in the current drug distribution data corresponding to the doser, and a dose end time indicating the last dose time. In addition, the prescription data (for example, drug name, usage, dose, dosing start date, dosing end date, etc.) corresponding to the patient in place of the drug distribution data is printed out on the medicine package 81 for the test. May be included in the code.
また、前記調剤支援装置1では、前述したように残薬の使用を前提とする前記処方データに基づいて前記分包データが生成された場合には、前記制御部11が、その残薬の服用時期と新たな服用時期との関係を示す前記残薬特定情報を含む前記配薬データを出力することが考えられる。そして、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、残薬に対応する前記薬包81に付されている前記コード811が読み取られた場合に、前記残薬特定情報を参照して前記薬包81に対応する服用時期を新たな服用時期として認識する。これにより、残薬を使用する場合にも、前記配薬支援システム100において、前記薬包81に対応する服用時期及び入居者などを照合すること、又は前記入居者の服用の有無などを管理することが可能となる。
Further, in the dispensing support device 1, as described above, when the packaging data is generated based on the prescription data premised on the use of the remaining drug, the control unit 11 takes the remaining drug. It is conceivable to output the drug distribution data including the residual drug specific information indicating the relationship between the time and the new dosing time. Then, in the medicine distribution supporting device 5, when the control unit 51 reads the code 811 attached to the medicine package 81 corresponding to the remaining medicine, the control unit 51 refers to the remaining medicine specifying information and refers to the remaining medicine specifying information. The dose timing corresponding to the medicine package 81 is recognized as a new dose time. Thereby, even when using the remaining drug, the medicine distribution support system 100 collates the dosing timing and the resident corresponding to the medicine package 81, or manages the presence or absence of the resident, etc. It becomes possible.
なお、ここでは、図18に示した処方データ発行処理において前記分包データが出力されるタイミングで前記配薬データが出力可能な構成について説明したが、前記制御部11は、前記配薬データを、任意のタイミングで前記操作装置15の操作などに応じて出力することも可能である。具体的に、前記制御部11は、前記処方データ記憶部121に記憶されている前記処方データのうち出力対象となる処方データを抽出するための抽出条件の設定操作を待ち受ける。例えば、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11が、前記操作装置15に対する設定開始操作に応じて、前記表示装置14に前記抽出条件を設定するための設定画面を表示する。そして、前記制御部11は、前記設定画面に従った前記操作装置15の操作に応じて前記抽出条件を設定する。例えば、前記施設コード、前記施設名称、前記グループ、前記服用者ID、前記服用者名、及び前記入居者IDのうち一又は複数の条件が設定可能である。ここで、前記抽出条件が設定されたと判断すると、前記制御部11は、前記処方データ記憶部121に記憶されている前記処方データに基づいて前記抽出条件に対応する前記配薬データを生成する。
In addition, although the structure which can output the said medication data at the timing which the said package data is output in the prescription data issue process shown in FIG. 18 was demonstrated here, the said control part 11 said the medication data. It is also possible to output at any timing according to the operation of the operating device 15 or the like. Specifically, the control unit 11 waits for the setting operation of the extraction condition for extracting the prescription data to be output among the prescription data stored in the prescription data storage unit 121. For example, in the dispensing support device 1, the control unit 11 displays a setting screen for setting the extraction condition on the display device 14 in accordance with a setting start operation on the operation device 15. Then, the control unit 11 sets the extraction condition in accordance with the operation of the operation device 15 in accordance with the setting screen. For example, one or more conditions can be set among the facility code, the facility name, the group, the doser ID, the doser name, and the resident ID. Here, if it is determined that the extraction condition is set, the control unit 11 generates the medicine distribution data corresponding to the extraction condition based on the prescription data stored in the prescription data storage unit 121.
具体的に、前記施設コードが選択された場合には、前記処方データ記憶部121に記憶されている前記処方データから、前記施設コードに対応する前記老健施設Bに入居している服用者各々の処方データが抽出される。また、前記抽出条件として前記グループが選択された場合には、前記処方データ記憶部121に記憶されている前記処方データから、前記グループに属する服用者各々の処方データが抽出される。そして、前記制御部11は、前記処方データのうち予め定められた一部又は全部の項目を前記配薬データとして抽出する。これにより、前記処方データのうち前記配薬データとして不要な情報を省略することによりデータ量を減少させ、又は前記服用者の個人情報の利用を最小限に抑制しつつ前記処方データを利用することが可能である。その後、前記制御部11は、前記ステップS15と同様に前記配薬データを出力する。これにより、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記処方データの発行タイミングに限らず任意のタイミングで前記配薬データを出力することが可能である。
Specifically, when the facility code is selected, each of the users who are in the elderly facility B corresponding to the facility code from the prescription data stored in the prescription data storage unit 121 Prescription data is extracted. Further, when the group is selected as the extraction condition, prescription data of each of the users belonging to the group is extracted from the prescription data stored in the prescription data storage unit 121. Then, the control unit 11 extracts a part or all of predetermined items of the prescription data as the medicine distribution data. Thereby, the amount of data can be reduced by omitting unnecessary information as the drug distribution data among the prescription data, or the prescription data can be used while minimizing the use of the personal information of the user. Is possible. Thereafter, the control unit 11 outputs the drug supply data, as in step S15. Thereby, in the said dispensing assistance apparatus 1, it is possible not only the issue timing of the said prescription data to output the said drug-delivery data at arbitrary timings.
[配薬時照合処理]
次に、図20のフローチャートを参照しつつ、前記配薬支援システム100において前記配薬支援装置5の制御部51によって実行される配薬時照合処理について説明する。
[Drug matching process]
Next, the dispensing-time checking process executed by the control unit 51 of the dispensing support system 5 in the dispensing support system 100 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
<ステップS81>
ステップS81において、前記制御部51は、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6に対して予め定められた配薬開始操作が行われたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記配薬開始操作が行われたと判断すると、処理がステップS82に移行し、前記配薬開始操作が行われていない場合には、処理がステップS811に移行する。
<Step S81>
In step S81, the control unit 51 determines whether or not a predetermined dispensing start operation has been performed on the controller device 55 or the portable terminal 6. Here, if it is determined that the drug dispensing start operation has been performed, the process proceeds to step S82. If the drug dispensing start operation is not performed, the process proceeds to step S811.
ところで、前記配薬開始操作では、予め定めた職員などの配薬担当者のログイン操作が行われることが考えられる。この場合、前記データ記憶部52には、前記配薬担当者各々の識別コード及びパスワードなどが設定されていることが考えられる。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記配薬開始操作が行われた後、前記読取端末7によって前記配薬担当者が有する名札などに記載された一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコードが読み取られ、そのコードの情報が前記配薬担当者の識別コードと一致する場合に、その配薬担当者をログインさせることが考えられる。さらに、前記制御部51は、前記識別コードが読み取られた後、その識別コードに対応する前記パスワードが入力された場合に、そのパスワードを照合してから前記配薬担当者をログインさせることも考えられる。これにより、前記制御部51は、前記配薬担当者ごとに当該配薬時照合処理で表示させる情報を制限すること、又は前記配薬担当者ごとに当該配薬時照合処理で表示させる入居者の範囲(例えば自己担当の入居者のみ)を変更することなどが可能になる。
By the way, it is possible that login operation of persons in charge of medicine distribution, such as a predetermined staff member, is performed in the said medicine distribution start operation. In this case, it is conceivable that an identification code and a password of each person in charge of medicine distribution are set in the data storage unit 52. For example, after the drug distribution start operation is performed, the control unit 51 causes the reading terminal 7 to read a code such as a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code described in a name tag or the like possessed by the drug distributor If the information of the code matches the identification code of the drug distributor, it is conceivable to log in the drug distributor. Furthermore, after the identification code is read, when the password corresponding to the identification code is input, the control unit 51 may consider that the password is compared and then the person in charge of medication can be logged in. Be Thereby, the control unit 51 limits the information to be displayed in the matching process at the time of dispensing for each person in charge of dispensing, or the resident who is displayed in the process of matching at the time of dispensing for each person in charge of dispensing It is possible to change the range of (for example, only the resident in charge of oneself).
<ステップS811〜S812>
ステップS811〜ステップS812では、前記調剤支援装置1から出力された前記配薬データを入力するための入力処理が実行される。ここに、前記ステップS811〜S812は、前記配薬データ入力部514によって実行される。
<Steps S811 to S812>
In steps S <b> 811 to S <b> 812, an input process for inputting the drug distribution data output from the dispensing support device 1 is executed. Here, the steps S811 to S812 are executed by the drug distribution data input unit 514.
具体的に、まずステップS811において、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データの入力タイミングを待ち受ける(S811:No側)。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記USBメモリ19が前記USBポート58に装着され、前記操作装置55に対するユーザー操作が行われた場合に、前記配薬データの入力タイミングであると判断する。また、前記制御部51は、前記通信インターフェース53により前記ネットワークN2などを介して前記配薬データが受信された場合にも、前記配薬データの入力タイミングであると判断する。そして、前記配薬データの入力タイミングが到来したと判断すると(S811:Yes側)、処理はステップS812に移行する。
Specifically, first, in step S811, the control unit 51 waits for the input timing of the drug distribution data (S811: No side). For example, when the USB memory 19 is attached to the USB port 58 and a user operation on the controller device 55 is performed, the control unit 51 determines that it is the input timing of the medication data. The control unit 51 also determines that it is the input timing of the medication data, even when the medication data is received by the communication interface 53 via the network N2 or the like. Then, when it is determined that the input timing of the drug distribution data has come (S811: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S812.
ステップS812において、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データを前記調剤支援装置1に入力する。例えば、前記制御部51は、当該配薬時照合処理を実行するために必要な情報を予め定められたデータベース形式に従って前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶する。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記調剤支援装置1における調剤時に用いられていた前記配薬データを利用して各種の処理を実行することが可能となる。
In step S812, the control unit 51 inputs the drug distribution data to the dispensing support device 1. For example, the control unit 51 stores the information necessary for performing the medicine distribution matching process in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523 according to a predetermined database format. As a result, the medicine distribution support device 5 can execute various processes using the medicine distribution data used at the time of dispensing in the medicine distribution support device 1.
<ステップS82>
一方、前記ステップS81において、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6に対して予め定められた配薬開始操作が行われたと判断した場合、続くステップS82において、前記制御部51は配薬担当者が配薬時に参照する初期画面210(第1表示画面の一例)を表示させる。具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記操作装置55により前記配薬開始操作が行われた場合には、前記表示装置54に前記初期画面210を表示させる。また、前記制御部51は、前記携帯端末6により前記配薬開始操作が行われた場合には、前記携帯端末6の表示部に前記初期画面210を表示させる。なお、これ以降の処理についても同様に、前記操作装置55による操作は前記表示装置54の表示に反映され、前記携帯端末6における操作は前記携帯端末6の表示部の表示に反映される。
<Step S82>
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S81 that a predetermined dispensing start operation has been performed on the operation device 55 or the portable terminal 6, in the subsequent step S82, the control unit 51 is a person in charge of dispensing An initial screen 210 (an example of a first display screen) to be referred to at the time of drug administration is displayed. Specifically, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 to display the initial screen 210 when the dispensing start operation is performed by the operation device 55. Further, the control unit 51 causes the display unit of the mobile terminal 6 to display the initial screen 210 when the drug supply start operation is performed by the mobile terminal 6. Similarly, in the subsequent processing, the operation by the operation device 55 is reflected on the display of the display device 54, and the operation in the portable terminal 6 is reflected on the display of the display unit of the portable terminal 6.
ここに、図21は、前記初期画面210の一例である。図21に示すように、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データに基づいて、これから服用する服用時期を選択するための選択キーが表示される。具体的に、図21に示す例では、前記制御部51が、本日に対応する服用時期が選択候補として前記初期画面210に表示される。前記初期画面210では、朝食、昼食、夕食ごとに「前」、「後」、「間」がツリー表示されており、配薬担当者が目的の服用時期を見つけやすい。なお、前記初期画面210の前段で服用日時が選択可能な構成も他の実施形態として考えられる。
Here, FIG. 21 is an example of the initial screen 210. As shown in FIG. 21, the control unit 51 displays a selection key for selecting a dose timing to be taken from now on the basis of the drug distribution data. Specifically, in the example shown in FIG. 21, the control unit 51 displays the dosing timing corresponding to the current day on the initial screen 210 as a selection candidate. In the initial screen 210, “before”, “after”, and “between” are displayed in a tree view for each of breakfast, lunch, and dinner, and the person in charge of medication can easily find a desired dosing time. In addition, the structure which can select a dosing date on the front | former stage of the said initial screen 210 is also considered as another embodiment.
また、図21に示すように、前記制御部51は、前記初期画面210において、服用すべき薬品が存在する服用時期と、服用すべき薬品が存在しない服用時期とを異なる表示態様で表示させる。これにより、配薬担当者は、服用時期ごとにおける服用すべき薬品の存在の有無を容易に判断することが可能である。なお、図21における服用時期の背景模様の違いが表示態様に差があることを示している。例えば、服用すべき薬品が存在する服用時期(図21の夕食後、夕食間など)はハイライト表示し、服用すべき薬品が存在しない服用時期(図21の朝食前、朝食後、朝食間など)はハイライト表示しないことが考えられる。また、服用すべき薬品が存在する服用時期の表示色と、服用すべき薬品が存在しない服用時期の表示色とが異なることも考えられる。さらに、服用すべき薬品が存在する服用時期の表示サイズが大きく、服用すべき薬品が存在しない服用時期の表示サイズが小さいことも考えられる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 21, the control unit 51 causes the initial screen 210 to display, in different display modes, the dosing time when the medicine to be taken is present and the dosing time when the medicine to be taken is not present. This allows the person in charge of drug distribution to easily determine the presence or absence of the drug to be taken at each dosing time. In addition, the difference in the background pattern of the dosing time in FIG. 21 shows that there is a difference in the display mode. For example, when the drug to be taken is present (after dinner, after dinner, etc. in FIG. 21) is highlighted, and when the drug to be taken is not present (before breakfast, after breakfast, between breakfast, etc. ) May not be highlighted. In addition, it may be considered that the indication color of the dosing time when the medicine to be taken is present differs from the indication color of the dosing time when the medicine to be taken does not exist. Furthermore, it is also conceivable that the display size of the dosing time when the drug to be taken is present is large and the display size of the dosing time when the drug to be taken is not present is small.
さらに、図21に示すように、前記制御部51は、前記初期画面210において、現在時刻に最も近い服用時期を他の服用時期とは異なる表示態様で表示させることが考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者による服用時期の選択ミスを抑制すると共に、選択する服用時期を探す手間を軽減することができる。なお、このような表示処理を実現するため、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記データ記憶部52に、服用時期ごとに対応する服用時期名、服用時刻、服用時期コード、及び服用区分などの服用時期情報が予め記憶されている。これにより、前記制御部51は、前記服用時期情報に基づいて、現時点で服用するべき服用時期を判断することが可能である。前記服用時期コードは、前記薬包81に印刷される前記服用時期コードと同じ内容を示す情報であり、前記調剤支援装置1及び前記配薬支援装置5において共通で用いられる統一された情報である。なお、前記制御部51は、前記配薬支援装置5の初期設定などにおいてユーザー操作に応じて前記服用時期情報を変更可能である。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 21, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 causes the initial screen 210 to display the dosing timing closest to the current time in a display mode different from the other dosing timings. As a result, it is possible to suppress the selection error of the dosing time by the person in charge of drug distribution and to reduce the time and effort for searching for the dosing time to be selected. In addition, in order to realize such display processing, in the drug distribution support device 5, the data storage unit 52 stores the dose timing name, the dose time, the dose timing code, and the dose category corresponding to each dose timing. The time information is stored in advance. Thereby, the control unit 51 can determine the dosing timing to be taken at the present time based on the dosing timing information. The dose timing code is information indicating the same content as the dose timing code printed on the medicine package 81, and is unified information commonly used in the dispensing support device 1 and the drug distribution support device 5. . In addition, the control unit 51 can change the dose timing information according to the user operation in the initial setting of the medicine distribution support device 5 or the like.
ところで、図21では、服用時期がツリー表示された初期画面210が示されているが、服用時期を選択するための初期画面210の他の例として、例えば図22に示すように、服用時期各々が個別に配列して表示されることも考えられる。さらに、前記制御部51が、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作に応じて、前記初期画面210における前記服用時期各々の表示位置、表示サイズ、及び表示色を予め任意に設定可能な構成が考えられる。また、前記制御部51が、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作に応じて、前記初期画面210に表示される前記服用時期の種類を予め任意に設定可能な構成も考えられる。これにより、例えばユーザーが前記初期画面210を任意にカスタマイズして自己にとって見やすい画面構成にすること、又は前記初期画面210における不要な情報の表示を排除することが可能である。
By the way, although FIG. 21 shows the initial screen 210 in which the dosing time is displayed in a tree view, as another example of the initial screen 210 for selecting the dosing time, for example, as shown in FIG. It is also conceivable that the may be displayed separately. Furthermore, the control unit 51 can arbitrarily set in advance the display position, display size, and display color of each of the dosing periods on the initial screen 210 in accordance with the operation of the operating device 55 or the portable terminal 6. Is considered. In addition, a configuration is also conceivable in which the control unit 51 can arbitrarily set in advance the type of dosing timing displayed on the initial screen 210 in accordance with the operation of the operating device 55 or the portable terminal 6. Thereby, for example, it is possible for the user to customize the initial screen 210 arbitrarily to make the screen configuration easy for the user to view, or to eliminate the display of unnecessary information on the initial screen 210.
また、前記老健施設Bでは、特定の前記薬局Aのみならず他の薬局からも薬品が持ち込まれ、その薬品の配薬の管理が行われることが考えられる。そのため、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、複数の前記薬局Aから取得する前記配薬データを合成することも可能である。また、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作に応じて前記配薬データを任意に入力可能な構成が考えられる。具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記操作装置55の操作に応じて、入居者、医療機関、医師、用法(服用時期)、薬品の種類、用量、及びコメントなどの情報を登録するための登録画面を表示させ、その登録画面に入力された情報を前記配薬データとして入力する。
In addition, in the health care facility B, it is conceivable that medicines are brought in not only from the specific pharmacy A but also from other pharmacies, and management of the medicine distribution is performed. Therefore, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 can also synthesize the medicine distribution data acquired from a plurality of the pharmacies A. Moreover, in the said medicine distribution assistance apparatus 5, the said control part 51 can consider the structure which can input the said medicine distribution data arbitrarily according to operation of the said operating device 55 or the said portable terminal 6. FIG. Specifically, the control unit 51 is configured to register information such as a resident, a medical institution, a doctor, usage (time of dosing), type of medicine, dose, and comment according to the operation of the operation device 55. A registration screen is displayed, and the information input on the registration screen is input as the drug supply data.
<ステップS83>
そして、ステップS83において、前記制御部51は、服用対象となる服用時期の選択を待ち受ける(S83:No側)。ここで、服用時期が選択されたと判断すると(S83:Yes側)、処理がステップS84に移行する。
<Step S83>
Then, in step S83, the control unit 51 waits for selection of a dosing time to be taken (S83: No side). Here, if it is determined that the dosing time has been selected (S83: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S84.
具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記初期画面210における服用時期を選択するための操作が前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作部によって行われた場合に服用時期が選択されたと判断する。また、前記制御部51は、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7により、服用時期ごとに対応する前記薬包81が収容された配薬ボックスに予め付されている服用時期を示す一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコードが読み取られた場合に、その服用時期が選択されたと判断することが考えられる。
Specifically, the control unit 51 determines that the dosing time is selected when the operation for selecting the dosing time on the initial screen 210 is performed by the operation device 55 or the operation unit of the portable terminal 6 . In addition, the control unit 51 may be a one-dimensional code indicating a dosing timing previously attached to a medicine dispensing box containing the medicine package 81 corresponding to each dosing timing by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 or When a code such as a two-dimensional code is read, it may be determined that the dosing time has been selected.
ところで、前記配薬支援システム100が、複数の服用者の各服用時期に対応する前記薬包81などの薬品を各服用時期に対応する前記配薬ボックスに自動的に収容する自動収容装置を備える構成も考えられる。これにより、複数の服用者に処方される薬品が服用時期ごとに纏めて前記配薬ボックスに自動的に収容されるため、前記薬局A又は前記老健施設Bで前記薬包81を前記配薬ボックスに収容する手間が省略される。なお、前記自動収容装置は、前記薬品分包装置3に搭載されるものであってもよい。ところで、前記配薬ボックスは、例えば区画された複数の収容部を備えるボックスであるが、所謂ブリスターパックであってもよい。前記ブリスターパックとは、一面が開放された包装領域を複数有する包装部材を平板状の部材に接合することにより閉鎖された複数の包装部が形成される収容部材である。また、前記ブリスターパックでは、前記包装部各々を容易に切り離すための切り取り点線(ミシン目)が形成されている。
By the way, the medicine distribution support system 100 is provided with an automatic storage device for automatically containing medicines such as the medicine package 81 corresponding to each dosing time of a plurality of dosing persons in the medicine dispensing box corresponding to each dosing time A configuration is also conceivable. As a result, medicines prescribed to a plurality of users are collectively contained at each dosing time and automatically stored in the medicine distribution box. The time and effort to store in is omitted. The automatic storage device may be mounted on the medicine packaging device 3. By the way, although the said medicine distribution box is a box provided with the some accommodating part divided, for example, it may be what is called a blister pack. The blister pack is a housing member in which a plurality of packaging parts closed by joining a packaging member having a plurality of packaging areas with one surface open to a flat plate member is formed. Further, in the blister pack, cut dotted lines (perforations) are formed to easily separate the packaging portions.
ここで、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS83で選択された服用時期が、前記配薬支援装置5で計時される現在日時に対応する適正な服用時期であるか否かを判断し、適正でない場合にその旨を報知可能である。具体的に、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記服用時期ごとに対応する服用時刻又は服用時間帯が予め設定されて前記データ記憶部52に記憶されている。例えば、服用時期「昼食後」に対応する服用時刻が「13時」に設定され、服用時期「昼食間」に対応する服用時刻が「15時」に設定され、服用時期「夕食前」に対応する服用時間帯が「18時」に設定されていることが考えられる。この場合、前記制御部51は、現在時刻が、前記ステップS83で選択された前記服用時期に対応する前記服用時刻から前後30分のような所定の許容範囲内であるか否かを判断することが考えられる。なお、現在時刻には、例えば前記配薬支援装置5のシステムクロックとして計時されている時刻、又は前記ネットワークN2などを介して所定の時刻報知機関から取得可能な時刻が用いられる。また、服用時期「昼食後」に対応する服用時間帯が「12時30分〜13時」に設定され、服用時期「昼食間」に対応する服用時間帯が「15時〜16時」に設定され、服用時期「夕食前」に対応する服用時間帯が「18時30分〜19時」に設定されていることが考えられる。この場合、前記制御部51は、現在時刻が、前記ステップS83で選択された前記服用時期に対応する前記服用時間帯であるか否かを判断することが考えられる。
Here, the control unit 51 determines whether or not the dose timing selected in the step S83 is an appropriate dose timing corresponding to the current date and time counted by the drug distribution support device 5, and is not appropriate. In that case, it can be informed. Specifically, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the dosing time or dosing time zone corresponding to each dosing time is set in advance and stored in the data storage unit 52. For example, the dosing time corresponding to the dosing time "after lunch" is set to "13 o'clock", the dosing time corresponding to the dosing time "during lunch" is set to "15 o'clock", and the dosing time "before dinner" is supported It is conceivable that the dosage period to be taken is set to "18 o'clock". In this case, the control unit 51 determines whether or not the current time is within a predetermined allowable range such as 30 minutes before and after the dosing time corresponding to the dosing time selected in the step S83. Is considered. As the current time, for example, the time counted as the system clock of the medicine distribution support device 5, or the time obtainable from a predetermined time announcing agency via the network N2 or the like is used. In addition, the dosing time zone corresponding to the dosing time "after lunch" is set to "12:30 to 13 o'clock", and the dosing time zone corresponding to the dosing time "during lunch" is set to "15 o'clock to 16 o'clock" It is conceivable that the dosing time zone corresponding to the dosing time “before dinner” is set to “18:30 to 19:00”. In this case, it can be considered that the control unit 51 determines whether the current time is in the dosing period corresponding to the dosing time selected in step S83.
さらに、前記制御部51が、前記初期画面210において選択される服用時期と、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7で読み取られた前記配薬ボックスに付された一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコードの服用時期とを照合可能であり、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。この場合、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、前記操作装置55の操作に応じて、例えば服用日時、服用時期、及びグループなどの前記配薬ボックスに貼付する情報を含む一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコードを任意のプリンタによってラベルなどに印刷可能であることが考えられる。また、前記制御部51が、前記初期画面210の表示前に選択される服用日時と、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7で読み取られた前記配薬ボックスに付された前記コードの服用日時とを照合可能であり、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。同じく、前記制御部51が、前記初期画面210に表示されるグループと、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7で読み取られた前記配薬ボックスに付された前記コードのグループとを照合可能であり、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。
Furthermore, the control unit 51 selects a dosing time selected on the initial screen 210 and a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code attached to the dispensing box read by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7. A configuration is also conceivable that can collate with the dose timing of the code, and can notify that effect when the collation results do not match. In this case, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 includes one-dimensional information including information to be attached to the medicine distribution box such as, for example, dosing date, dosing time, and group according to the operation of the operating device 55. It is contemplated that a code, such as a code or a two-dimensional code, can be printed on a label or the like by any printer. Further, the dosing date and time selected before the display of the initial screen 210 by the control unit 51, and the dosing date and time of the code attached to the medication box read by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 A configuration is also conceivable in which it is possible to collate and to notify that effect when the collated results are not identical. Similarly, the control unit 51 can collate the group displayed on the initial screen 210 with the group of codes attached to the dispensing box read by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7. A configuration is also conceivable that can notify that effect when the comparison results do not match.
<ステップS84>
ステップS84において、前記制御部51は、入居者の一覧が表示される入居者一覧画面211(第2表示画面の一例)を前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部に表示させる。ここに、図23は、前記入居者一覧画面211の一例を示す図である。具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記マスター記憶部521に記憶されている前記入居者マスターと前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データとに基づいて前記入居者一覧画面211を表示させる。
<Step S84>
In step S84, the control unit 51 causes the display unit of the display device 54 or the mobile terminal 6 to display an occupant list screen 211 (an example of a second display screen) on which a list of occupants is displayed. Here, FIG. 23 is a view showing an example of the resident list screen 211. Specifically, the control unit 51 displays the tenant list screen based on the resident master stored in the master storage unit 521 and the medicine distribution data stored in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523. Display 211.
特に、図23に示すように、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211において、前記ステップS83で選択されたと判断した服用時期に服用する薬品が存在する入居者と、その服用時期に服用する薬品が存在しない入居者とを異なる表示態様で表示させる。即ち、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS81〜S84を実行することにより、前記入居者各々と前記服用時期各々との関係を表示させることが可能である。ここに、係る表示処理は前記表示制御部511によって実行され、前記表示制御部511が処方表示手段の一例である。特に、前記ステップS81〜S82において前記服用時期を選択するための前記初期画面210を表示させるときの前記表示制御部511が第1表示処理手段の一例であり、前記ステップS83〜S84において前記初期画面210における前記服用時期の選択に応じて前記服用時期における前記入居者各々の配薬の要否を表示する前記入居者一覧画面211を表示するときの前記表示制御部511が第2表示処理手段の一例である。
In particular, as shown in FIG. 23, the control unit 51 takes the resident who has the medicine to be taken at the dosing timing determined at the step S83 in the tenant list screen 211 and the dosing at that dosing timing. The resident who has no medicine to be displayed is displayed in a different display mode. That is, the control unit 51 can display the relationship between each tenant and each dosing period by executing the steps S81 to S84. Here, the display processing is executed by the display control unit 511, and the display control unit 511 is an example of a prescription display unit. In particular, the display control unit 511 when displaying the initial screen 210 for selecting the dose timing in the steps S81 to S82 is an example of the first display processing means, and the initial screen in the steps S83 to S84. The display control unit 511 of the second display processing means displays the tenant list screen 211 for displaying necessity / unnecessity of drug distribution for each tenant at the dosing timing according to the selection of the dosing timing at 210. It is an example.
これにより、配薬担当者は、前記初期画面210及び前記入居者一覧画面211を用いて、服用時期各々において服用すべき薬品が存在する入居者を容易に判断することが可能である。なお、図23における入居者の背景模様の違いが表示態様に差があることを示している。例えば、服用すべき薬品が存在する入居者(「湯山一郎」など)はハイライト表示し、服用すべき薬品が存在しない入居者(「湯山三郎」など)はハイライト表示しないことが考えられる。また、服用すべき薬品が存在する入居者の表示色と、服用すべき薬品が存在しない入居者の表示色とが異なることも考えられる。さらに、服用すべき薬品が存在する入居者の表示サイズが大きく、服用すべき薬品が存在しない入居者の表示サイズが小さいことも考えられる。
Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily determine the resident who has the medicine to be taken at each dosing time, using the initial screen 210 and the resident list screen 211. In addition, the difference in the background pattern of the resident in FIG. 23 indicates that there is a difference in the display mode. For example, it is conceivable that a resident who has a medicine to be taken (such as "Yuyama Ichiro") is highlighted, and a tenant who does not have a medicine to be taken (such as "Yuyama Saburo") is not highlighted. In addition, the display color of the resident who has the drug to be taken may be different from the display color of the resident who does not have the drug to be taken. Furthermore, the display size of the resident who has the medicine to be taken may be large, and the display size of the tenant who does not have the medicine to be taken may be small.
また、前記入居者一覧画面211では、入居者の服薬の状況に関するステータス情報として、前述した前記服用時期に服用すべき薬品の有無の他に、「未服薬」、「服薬済」、「外出」、「未服薬完了」、「自己管理確認無」、「自己管理未確認」、「自己管理確認済」、「仕事中」、「服薬不能」、「入院中」などの情報が表示されることも考えられる。即ち、前記入居者一覧画面211では、これらの複数のステータス情報が、異なる配色又は表示サイズなどの異なる表示態様で表示可能である。
Further, in the resident list screen 211, as status information on the status of the patient's medication, in addition to the presence or absence of the medicine to be taken at the above-mentioned dosing timing, "unused drug", "medicated", "going out" Also, information such as "Not yet taken", "No self-control confirmed", "Self-managed unconfirmed", "Self-managed confirmed", "At work", "Unavailable", "Hospitalized", etc. Conceivable. That is, on the resident list screen 211, the plurality of pieces of status information can be displayed in different display modes such as different color arrangements or display sizes.
例えば、図23に示す例では、「湯山八郎」が「服薬完了」に対応する表示態様で表示されており、「湯山九郎」などの入居者は「未服薬」に対応する表示態様で表示されている。具体的には、服薬完了に対応する表示態様がグレーアウトであり、未服薬に対応する表示態様がグレーアウトを除く他の配色表示であることが考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者が、選択した服用時期における配薬の要否を入居者ごとに容易に判断することが可能である。また、図23に示す例では、「湯山七太」が「外出」に対応する表示態様で表示されており、配薬担当者は、「湯山七太」が外出中又は外泊中などであるために配薬が不要である旨を容易に判断することが可能である。ここで、入居者各々の外出の有無などのステータス情報は、前記制御部51により、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作部などの操作に応じて予め前記マスター記憶部521の前記入居者マスターの一部として記憶されることが考えられる。
For example, in the example shown in FIG. 23, "Yuyama Hachiro" is displayed in the display mode corresponding to "Drug intake completed", and tenants such as "Yuyama Kuro" are displayed in the display mode corresponding to "Unused drug" ing. Specifically, it is conceivable that the display mode corresponding to the completion of the medication is grayed out and the display mode corresponding to the non-drug is the other color display except grayed out. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily determine the necessity of drug distribution at the selected dosing time for each resident. Moreover, in the example shown in FIG. 23, "Yutasan" is displayed in a display mode corresponding to "Going out", and the person in charge of drug administration is "Yutasan" while he is outing or staying out, etc. It is possible to easily judge that drug delivery is unnecessary. Here, the status information such as the presence or absence of each resident is determined in advance by the control unit 51 according to the operation of the operation unit of the operation device 55 or the portable terminal 6 or the like, the tenant of the master storage unit 521 It is considered to be stored as part of the master.
なお、「仕事中」は、前記入居者が仕事に出ていることを示し、「服薬不能」は、前記入居者が服用困難な健康状態であることを示し、「入院中」は、前記入居者が病院に入院中であることを示す。また、「未服薬完了」は、服用者が薬品を服薬していないがその薬品が残薬として処理されて服薬が完了状態になっていることを示す。さらに「自己管理確認無」は、服用者に所定期間の薬品を予め預けて服用者を自己管理する場合であってその服薬の有無の確認の必要がないことを示す。一方、「自己管理未確認」、「自己管理確認済」は、服用者に所定期間の薬品を予め預けて服用者を自己管理するがその服薬の有無の確認の必要があることを示し、「自己管理未確認」は、まだ服薬が確認されていないことを示し、「自己管理確認済」は、既に服薬が確認されてその旨の入力操作が行われていることを示す。
“At work” indicates that the resident is out of work, “impossible to take a drug” indicates that the resident is in a difficult health condition to take, and “in hospital” indicates the move Indicates that the person is admitted to the hospital. Also, "unused drug complete" indicates that the user who has not taken the drug has treated the drug as a residual drug and the drug is in the completed state. Further, “no self-management confirmation” indicates that the medicine for the predetermined period is deposited in advance for the medicine management to self-manage the medicine, and it is not necessary to confirm the presence or absence of the medication. On the other hand, "Self-management unconfirmed" and "Self-management confirmed" indicate that the drug is kept in advance for the prescribed period and the drug is self-managed, but it is necessary to confirm the presence or absence of the drug. “Management unconfirmed” indicates that the medication has not been confirmed yet, and “self-management confirmed” indicates that the medication has already been confirmed and an input operation to that effect has been performed.
図23に示す前記入居者一覧画面211では、同一画面に表示されない入居者はスクロールによって表示可能であり、前記入居者一覧画面211における入居者の表示順は例えば五十音順又はアルファベット順などである。また、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211における「全員」の操作キーの選択に応じて、前記入居者一覧画面211における入居者の表示を、未服用の入居者のみが表示される状態と入居者全員が表示される状態とに交互に切換可能である。さらに、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211における「完了」の操作キーの選択に応じて前記入居者一覧画面211に表示中の入居者についてステータス情報を「未服薬完了」の状態に変更し、その服用時期に対応する未服用の薬品(薬包81)を残薬情報として前記データ記憶部52に記憶することが考えられる。また、前記制御部51は、前記残薬情報を前記データ記憶部52に蓄積して記憶する際、前記残薬情報の合計を算出することなく、前記薬包81に収容された錠剤の状態をそのままの情報として記憶する。例えば、ある入居者の薬品として1錠及び0.5錠(半錠)の薬品が薬包81に分包されており、その薬包81が3回分残っている場合、前記データ記憶部52では、4.5錠ではなく、1.5錠×3の情報が前記残薬情報として記憶される。
In the tenant list screen 211 shown in FIG. 23, tenants not displayed on the same screen can be displayed by scrolling, and the display order of the tenants in the tenant list screen 211 is, for example, in the order of the Japanese syllabary or in alphabetical order is there. Further, according to the selection of the operation key "all members" in the resident list screen 211, only the resident who has not taken the display of the resident in the resident list screen 211 is displayed on the control section 51. It is possible to switch between the state and the state in which all the residents are displayed. Furthermore, the control unit 51 changes the status information of the tenant currently displayed on the tenant list screen 211 into the status of "not yet taken" in response to the selection of the operation key "completion" on the resident list screen 211. It is possible to change and store in the data storage unit 52 a drug (drug package 81) which has not been taken corresponding to the dose timing as the remaining drug information. In addition, when the control unit 51 accumulates and stores the residual drug information in the data storage unit 52, the state of the tablet contained in the medicine package 81 is calculated without calculating the total of the residual drug information. It stores as the information as it is. For example, in the case where one tablet and one half tablet (half tablet) of medicine as a medicine for a certain resident is packaged in medicine package 81 and the medicine package 81 remains for three times, the data storage unit 52 Information of 1.5 tablets × 3 instead of 4.5 tablets is stored as the residual drug information.
ところで、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記入居者マスター(図15参照)及び前記入居者登録画面(図17参照)に示したように、前記入居者を複数のグループに分類することも可能である。この場合、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211を前記グループごとに表示させることが他の実施形態として考えられる。ここに、図24は、前記入居者各々をグループごとに表示させる場合の入居者一覧画面211の一例を示す図である。
By the way, in the medicine distribution support system 100, as shown on the resident master (see FIG. 15) and the resident registration screen (see FIG. 17), the resident can be classified into a plurality of groups. is there. In this case, it may be considered as another embodiment that the control unit 51 displays the tenant list screen 211 for each group. Here, FIG. 24 is a view showing an example of the resident list screen 211 in the case of displaying each of the above tenants by group.
図24に示す前記入居者一覧画面211では、各グループに対応するタブが表示されており、前記タブが選択された場合にそのタブのグループに属する入居者の一覧が表示される。なお、この場合も図23に示した前記入居者の表示態様は、前記入居者一覧画面211と同様であるため説明を省略する。一方、前記制御部51は、例えばグループに属する入居者全員の服用が完了した場合に、その旨を前記入居者一覧画面211に表示させることも考えられる。例えば、前記制御部51は、入居者全員の服用が完了したグループのタブをグレーアウト表示させ、入居者全員の服用が完了していないグループのタブをグレーアウトを除く他の配色態様で表示させることが考えられる。これにより、前記入居者一覧画面211において、服用が完了したか否かをグループ単位で容易に把握することが可能である。なお、前記制御部51が、入居者全員の服用が完了したグループのタブが選択された場合に前記入居者一覧画面211の全体をグレーアウト表示させてもよい。また、前述したように、前記配薬ボックスに付された前記コードが前記グループを示す情報を含む場合、前記制御部51は前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7によって読み取られた前記コードが示す前記グループに対応する前記入居者一覧画面211を表示させることが考えられる。また、前記制御部51が、前記図24における前記入居者一覧画面211で選択された前記タブのグループと、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7によって前記配薬ボックスから読み取られる前記コードが示すグループとが一致しているか否かを照合可能であり、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。
In the tenant list screen 211 shown in FIG. 24, a tab corresponding to each group is displayed, and when the tab is selected, a list of tenants belonging to the group of the tab is displayed. Also in this case, the display mode of the resident shown in FIG. 23 is the same as that of the tenant list screen 211 and thus the description thereof is omitted. On the other hand, it is also conceivable that, for example, when taking of all the residents belonging to the group is completed, the control unit 51 causes the tenant list screen 211 to display a message to that effect. For example, the control unit 51 grays out the tab of the group in which all the residents have taken the drug, and displays the tab of the group in which the patient does not take the drug in the other color arrangement except graying out. Conceivable. Thereby, it is possible to easily grasp in the group unit whether or not taking has been completed on the resident list screen 211. In addition, the said control part 51 may gray out the whole resident | tenant list screen 211, when the tab of the group which taking-in of all the tenants completed is selected. In addition, as described above, when the code attached to the dispensing box includes the information indicating the group, the control unit 51 is configured to indicate the code read by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7. It is conceivable to display the resident list screen 211 corresponding to the group. In addition, the group indicated by the code read from the dispensing box by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 by the control unit 51 is the group of tabs selected on the tenant list screen 211 in FIG. A configuration is also conceivable that can check whether or not matches, and can notify that effect when the matching results do not match.
<ステップS85>
次に、ステップS85において、前記制御部51は、服用対象となる入居者の選択を待ち受ける(S85:No側)。ここで、入居者が選択されたと判断すると(S85:Yes側)、処理がステップS86に移行する。
<Step S85>
Next, in step S85, the control unit 51 waits for the selection of the resident to be dosed (S85: No side). Here, if it is determined that a resident is selected (S85: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S86.
具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211における入居者を選択するための操作が前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作部によって行われた場合に入居者が選択されたと判断する。また、前記制御部51は、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7により、例えば入居者が所有する名札、リストバンド、又は前記薬包81に付された一次元コード又は二次元コード等のコードが読み取られた場合に、そのコードが示す入居者IDに対応する入居者が選択されたと判断することが考えられる。さらに、前記制御部51が、前記入居者一覧画面211において選択される入居者と、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7で読み取られた前記コードが示す入居者とを照合可能であり、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。なお、前記制御部51は、前記入居者の照合方法として、例えば静脈、指紋、網膜、又は顔などを用いて前記入居者を照合する生体認証を実行することも考えられる。この場合、前記生体認証に必要な情報が予め前記入居者マスターなどに登録されており、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7は、前記生体認証に必要な情報を読取可能なセンサーなどを備える。
Specifically, when the operation unit 55 or the operation unit of the portable terminal 6 performs an operation for selecting the tenant in the tenant list screen 211, the control unit 51 selects the tenant. to decide. In addition, the control unit 51 may use a code such as a name tag owned by a resident, a wrist band, or a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code attached to the medicine package 81 by the mobile terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7. When read, it can be considered that the tenant corresponding to the tenant ID indicated by the code is selected. Furthermore, the control unit 51 can collate the tenant selected on the tenant list screen 211 with the tenant indicated by the code read by the mobile terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7, and the collation result There is also conceivable a configuration capable of notifying that effect when there is a mismatch. Note that the control unit 51 may consider performing biometric authentication in which the tenants are collated using, for example, a vein, a fingerprint, a retina, or a face as a collation method of the tenants. In this case, the information necessary for the biometric authentication is registered in advance in the resident master or the like, and the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 includes a sensor or the like capable of reading the information necessary for the biometric authentication.
なお、前記ステップS85において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211におけるメニューキーが操作された場合には、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示を前記配薬開始操作が行われる前のメニュー画面などに戻す。また、前記制御部51は、戻るキーが操作された場合には、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示を前記初期画面210に戻す。
In the step S85, when the menu key in the tenant list screen 211 is operated, the control unit 51 performs the dispensing start operation to display the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 Return to the previous menu screen etc. Further, when the return key is operated, the control unit 51 returns the display of the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 to the initial screen 210.
<ステップS86>
ステップS86において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS85で選択されたと判断した入居者を確認するための入居者確認画面213を前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部に表示させる。具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記マスター記憶部521に記憶されている前記入居者マスター及び前記配薬データに基づいて入居者の情報及び服薬する薬品の情報などを前記入居者確認画面213に表示させる。ここに、図25は、前記入居者確認画面213の一例を示す図である。
<Step S86>
In step S86, the control unit 51 causes the display unit 54 or the display unit of the portable terminal 6 to display an occupant confirmation screen 213 for confirming the occupant determined to be selected in step S85. Specifically, based on the resident master stored in the master storage unit 521 and the drug distribution data, the control unit 51 displays resident information and information on medicines to be taken on the resident confirmation screen 213. Display on. Here, FIG. 25 is a view showing an example of the resident confirmation screen 213. As shown in FIG.
図25に示すように、前記入居者確認画面213では、入居者の情報として、入居者の名前、顔画像(写真)、及びコメントが表示されている。また、前記入居者確認画面213では、配薬データのうち用法及び薬品情報が表示されている。これにより、配薬担当者は、配薬対象となる入居者及び薬品などの適否を容易に把握することが可能である。また、前記入居者確認画面213には、確認キー、取消キー、未服用キーが表示される。前記確認キーは、入居者が適切であることを確認したことを入力するための操作キーである。前記取消キーは、前記入居者の選択を解除して前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部の表示を前記入居者一覧画面211に戻すための操作キーである。前記未服用キーは、前記入居者が薬品を服用しなかった場合の未服薬理由を入力して未服薬のまま完了させるための操作キーである。なお、前記配薬確認データが前記処方データそのものの一部又は全部である場合には、実際に調剤された後の薬品の内容(例えば分包状態など)が把握できないことも考えられ、この場合、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213における薬品情報の表示を省略することが考えられる。
As shown in FIG. 25, on the resident confirmation screen 213, the resident's name, face image (photograph) and comment are displayed as the resident's information. Further, on the resident confirmation screen 213, usage and drug information among the drug distribution data are displayed. As a result, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily grasp the suitability of the resident and drug or the like to be subjected to drug distribution. Further, on the resident confirmation screen 213, a confirmation key, a cancel key, and a non-dose key are displayed. The confirmation key is an operation key for inputting that the tenant has confirmed that it is appropriate. The cancel key is an operation key for canceling the selection of the tenant and returning the display of the display unit of the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 to the tenant list screen 211. The non-dose key is an operation key for inputting a reason for non-drug when the resident does not take a drug and completing the non-drug. In addition, when the said medicine distribution confirmation data is a part or all of the said prescription data itself, it is also considered that the content (for example, the packaging condition etc.) of the medicine after being actually dispensed can not be grasped, The control unit 51 may omit the display of medicine information on the resident confirmation screen 213.
さらに、前記データ記憶部52に薬品各々について注意すべき副作用に関する前記副作用関連情報を含む薬品マスターなどが記憶されており、前記入居者確認画面213では、前記入居者が服用する薬品の前記副作用関連情報が表示されることが考えられる。また、前記制御部51が、前記ネットワークN1を通じて前記調剤支援装置1にアクセスし、前記調剤支援装置1に記憶されている前記薬品マスターを参照して前記薬品の前記副作用関連情報を表示することも考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者は、前記入居者への配薬時に前記副作用関連情報を参照して前記入居者の状態について注意すべき事項を容易に把握することができ、例えば前記入居者の異常などを早期発見することが可能となる。また、前記入居者確認画面213では、前記服用時期を識別するための情報として、前記服用時期を示す文字に代えて、又は前記服用時期と共に前記服用時期コードが表示されることも考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者は、前記薬包81にも前記服用時期コードが印刷されている場合にその服用時期コードを参照して服用時期を容易に確認することが可能となる。さらに、前記入居者確認画面213では、前記入居者の服薬に関する前記ステータス情報(「未服薬」、「服薬済」、「外出」、「未服薬完了」、「自己管理確認無」、「自己管理未確認」、「自己管理確認済」、「仕事中」、「服薬不能」、又は「入院中」など)が表示されることも考えられる。なお、前記薬品マスターに薬品各々の写真などの薬品画像データが含まれている場合には、前記制御部51は、前記薬品画像データを前記入居者確認画面213で表示させることも可能である。
Furthermore, a drug master or the like including the side effect related information on the side effects to be careful about each drug is stored in the data storage unit 52, and the side effect related relation of the drug to be taken by the tenant is Information may be displayed. The control unit 51 may also access the dispensing support device 1 through the network N1 and display the side effect related information of the drug with reference to the drug master stored in the dispensing support device 1. Conceivable. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily grasp the matter to be noted about the condition of the resident by referring to the side effect related information at the time of drug distribution to the resident, for example, the abnormality of the resident It will be possible to detect early. In the resident confirmation screen 213, it is also considered that the dosing time code is displayed as information for identifying the dosing time, instead of the letter indicating the dosing time, or together with the dosing time. As a result, when the medication timing code is printed on the medicine package 81, the person in charge of medication can easily confirm the dosing timing with reference to the dosing timing code. Furthermore, in the resident confirmation screen 213, the status information on the medication of the resident ("unused drug," "taken medicine," "going out," "not yet taken medicine completed," "no self-management confirmation," "self-management It is also conceivable that “unconfirmed”, “self-management confirmed”, “at work”, “impossible to take medicine”, “in hospital”, etc. are displayed. When the medicine master includes medicine image data such as a picture of each medicine, the control unit 51 can also display the medicine image data on the resident confirmation screen 213.
<ステップS87>
続いて、ステップS87において、前記制御部51は確認操作を待ち受ける(S87:No側)。ここで、前記確認操作が行われたと判断すると、処理はステップS871に移行し、前記確認操作が行われていない場合には、処理がステップS88に移行する。
<Step S87>
Subsequently, in step S87, the control unit 51 waits for a confirmation operation (S87: No side). Here, if it is determined that the confirmation operation has been performed, the process proceeds to step S871. If the confirmation operation is not performed, the process proceeds to step S88.
具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213の前記確認キーが操作された場合に前記確認操作が行われたと判断する。このとき、前記制御部51は、前記確認キーの操作に応じて入居者IDを入力するための入力画面を表示させ、その入力画面において入力される入居者IDを前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている入居者に対応する入居者IDと照合し、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知可能な構成も考えられる。例えば、前記照合結果が不一致である場合、前記制御部51は、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6にエラーメッセージを表示させた後、表示画面を前記入居者一覧画面211に戻す。
Specifically, the control unit 51 determines that the confirmation operation has been performed when the confirmation key of the resident confirmation screen 213 is operated. At this time, the control unit 51 displays an input screen for inputting the resident ID in response to the operation of the confirmation key, and displays the resident ID input on the input screen on the resident confirmation screen 213. A configuration is also conceivable in which it can be collated with the resident ID corresponding to the resident who is being carried out, and if the result of the collation does not match, this can be notified. For example, if the comparison result is not identical, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 to display an error message, and then returns the display screen to the tenant list screen 211.
さらに、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS86で前記入居者確認画面213を表示する前に、前記確認キーの操作に応じて入居者IDを入力するための入力画面を表示させ、その入力画面において入力される入居者IDを前記ステップS85で選択された入居者に対応する入居者IDと照合することも考えられる。この場合、前記制御部51は、照合結果が一致である場合は処理を前記ステップS86に移行させて前記入居者確認画面213を表示させ、照合結果が不一致である場合にその旨を報知することが考えられる。なお、前記制御部51が、前記入居者一覧画面211において選択される入居者と、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7で読み取られた前記コードが示す入居者とを照合する構成でも同様に、照合結果が一致であることが確認された後に前記入居者確認画面213を表示させることが考えられる。
Furthermore, before the resident confirmation screen 213 is displayed in the step S86, the control unit 51 displays an input screen for inputting the resident ID according to the operation of the confirmation key, and the input screen is displayed. It is also conceivable to collate the resident ID inputted with the resident ID corresponding to the resident selected in the step S85. In this case, the control unit 51 shifts the process to the step S86 to display the resident confirmation screen 213 when the collation result is the same, and notifies that effect when the collation result is not the same. Is considered. In the same manner, the control unit 51 collates the tenant selected on the tenant list screen 211 with the tenant indicated by the code read by the mobile terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 in the same manner. It is conceivable to display the resident confirmation screen 213 after it is confirmed that the matching results are identical.
また、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81に付された前記コード811が前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7によって読み取られ、そのコード811が示す入居者が、前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている入居者と一致する場合に前記確認操作が行われたと判断することも考えられる。なお、前記入居者が一致しない場合、前記制御部51は、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6にエラーメッセージを表示させた後、表示画面を前記入居者一覧画面211に戻す。さらに、前記制御部51が、前記薬包81のコード811が示す入居者及び服用時期が、前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている入居者及び服用時期と一致するか否かを判断してもよい。また、前記制御部51が、前記薬包81のコード811が示す服用時期が、前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている服用時期と一致するか否かを判断してもよい。ところで、前記ステップS87では、このように前記入居者及び前記服用時期のいずれか一方又は両方が照合されることにより、服用日が異なる前記薬包81であっても使用可能である。即ち、前記制御部51は、前記コード811に服用日時の情報が含まれている場合でも、前記服用日時が一致しているか否かをあえて判断しないことが考えられる。もちろん、前記制御部51が、前記服用日時が一致しているか否かを判断することも他の実施形態として考えられる。ところで、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7による前記薬包81の読取確認を徹底するため、前記入居者確認画面213における前記確認キーの表示を省略することも他の実施形態として考えられる。
In addition, the control unit 51 causes the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 to read the code 811 attached to the medicine package 81, and the tenant indicated by the code 811 displays the resident confirmation screen 213. It is also conceivable to judge that the confirmation operation has been performed when the user agrees with the resident. If the tenants do not match, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 or the mobile terminal 6 to display an error message, and then returns the display screen to the tenant list screen 211. Furthermore, the control unit 51 determines whether the resident indicated by the code 811 of the medicine package 81 and the dosing time coincide with the resident and dosing time displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213. It is also good. Further, the control unit 51 may determine whether or not the dosing time indicated by the code 811 of the medicine package 81 matches the dosing time displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213. By the way, in the step S87, even if the medicine package 81 having a different dose date can be used by checking one or both of the resident and the dose timing in this way. That is, even when the code 811 includes information on the date and time of dosing, the control unit 51 may not judge whether or not the dosing date and time match. Of course, it may be considered as another embodiment that the control unit 51 determines whether the dosing date and time match. By the way, it is also conceivable as another embodiment to omit the display of the confirmation key on the resident confirmation screen 213 in order to thoroughly confirm the reading of the medicine package 81 by the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7.
また、前記制御部51が、前記ステップS83で選択される服用時期と前記ステップS85で選択される入居者との組み合わせについて既に前記確認処理が終了している場合には、重複投与である旨を報知することが考えられる。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記表示装置54、前記携帯端末6、又は前記読取端末7などに、「既に服用済みです。」のような重複投与である旨のメッセージを表示させることが考えられる。これにより、同じ服用時期の同じ入居者への重複投与が防止される。また、前記メッセージの表示時には、既に服用済みの前記薬包81の情報として、例えば薬包番号、服用時期、服用日時、薬品名などが表示されてもよい。
In addition, when the confirmation process has already been completed for the combination of the dosing time selected in step S83 and the tenant selected in step S85, the control unit 51 indicates that the administration is a duplicate administration. It is conceivable to notify. For example, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 causes the display device 54, the portable terminal 6, the reading terminal 7 or the like to display a message to the effect that duplicate administration such as "already taken." . This prevents multiple doses to the same resident at the same dosing time. In addition, at the time of displaying the message, for example, a medicine package number, a dosing time, a dosing date, a medicine name and the like may be displayed as information of the medicine package 81 already taken.
<ステップS871>
ステップS871において、前記制御部51は、入居者への投薬開始を促す投薬開始メッセージを前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6に表示させる。そして、配薬担当者は、入居者に対して前記薬包81を配薬する。なお、前記入居者確認画面213に、入居者の管理区分として自己管理であるか否かの情報が表示されることも考えられる。これにより、配薬担当者は、前記薬包81の配薬時に入居者の管理区分を容易に判断することができる。
<Step S871>
In step S 871, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 to display a dosing start message for prompting a tenant to start dosing. The person in charge of drug distribution then distributes the medicine package 81 to the resident. In addition, it is also conceivable that information on whether the self-management is performed is displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 as the management division of the resident. Thereby, the person in charge of drug distribution can easily judge the management classification of the resident when the medicine package 81 is distributed.
<ステップS872>
また、ステップS872において、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データに関連付けて、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者への配薬結果として「服薬完了」を記録し、処理を前記ステップS81に戻す。これにより、次に前記入居者一覧画面211が表示される場合、既に服用が完了した服用時期については服薬が不要であることを示す表示態様で入居者の名前が表示されることになる。ここに、前記ステップS87、S871、S872において、前記確認操作を前記入居者各々の服薬完了の入力操作として受け付ける処理は、前記服薬完了入力部515によって実行される。なお、前記ステップS87が省略されることも考えられる。即ち、前記薬包81に付された前記コードが読み取られて入居者が選択された場合に(S85:Yes側)、前記入居者確認画面213が表示されると共に(S86)、前記コードによって識別される前記入居者の前記薬包81の服用時期の服用完了が自動的に記録されることも考えられる(S872)。
<Step S872>
Further, in step S 872, the control unit 51 associates the medicine distribution data stored in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523 with the medicine distribution results for the tenant displayed on the tenant confirmation screen 213. "Completion of medication" is recorded, and the process returns to step S81. As a result, when the resident list screen 211 is displayed next, the name of the resident is displayed in a display mode indicating that taking the medication is not necessary for the dosing time when the dosing has already been completed. Here, in the steps S87, S871 and S872, the process of accepting the confirmation operation as the input operation of the patient's respective medication completion is executed by the medication completion input unit 515. It is also conceivable that the step S87 is omitted. That is, when the code attached to the medicine package 81 is read and a resident is selected (S85: Yes side), the resident confirmation screen 213 is displayed (S86) and identification is performed by the code It is also conceivable that the completion of the dose taking of the medicine package 81 of the resident who has been done is automatically recorded (S 872).
<ステップS88>
また、ステップS88において、前記制御部51は、前記未服用キーの操作を待ち受ける(S88:No側)。ここで、前記未服用キーが操作されたと判断すると、処理はステップS881に移行し、前記未服用キーが操作されていない場合には、処理がステップS89に移行する。なお、前記制御部51は、前記未服用キーが操作された場合には、「未服用で良いか?」などの確認メッセージを表示させることも考えられる。
<Step S88>
Further, in step S88, the control unit 51 waits for the operation of the non-dosing key (S88: No side). Here, if it is determined that the non-dose key has been operated, the process proceeds to step S881. If the non-dose key is not operated, the process proceeds to step S89. In addition, when the said undosed key is operated, the said control part 51 is also considered to display a confirmation message, such as "is it undosed?"
<ステップS881>
ステップS881において、前記制御部51は、図26に示すように、前記入居者が薬品を服用しなかった未服薬理由を入力するための未服薬入力画面214を前記入居者確認画面213上にポップアップで表示させた後、前記未服薬入力に入力される未服薬理由を、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データに関連付けて記憶させる。例えば、前記未服薬理由の入力は、図26に示すように、予め登録された未服薬理由の一覧が表示され、その未服薬理由を選択することによって行われる。ここで、前記未服薬理由は、プルダウン形式で表示される予め定められた複数の候補から選択によって入力可能であることも考えられる。なお、前記未服薬理由としては、例えば外出中、就寝、又は服用拒否などが考えられる。また、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データに関連付けて、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者への配薬結果として「未服薬完了」を記録する。これにより、次に前記入居者一覧画面211が表示される場合、既に服薬しなかった未服薬理由が入力された服用時期については服薬が不要であることを示す表示態様で入居者の名前が表示されることになる。
<Step S881>
In step S 881, as shown in FIG. 26, the control unit 51 pops up an unmedicated drug input screen 214 for inputting the unmedicated drug reasons for which the resident did not take medicine on the resident confirmation screen 213. After being displayed, the reason for the non-drug to be input to the non-drug input is stored in association with the drug distribution data stored in the drug-distribution data storage unit 523. For example, as shown in FIG. 26, the input of the non-drug reason is performed by displaying a list of non-drug reasons registered in advance and selecting the non-drug reason. Here, it is also conceivable that the non-drug reason can be input by selection from a plurality of predetermined candidates displayed in a pull-down format. In addition, as said non-drug reason, for example, going out, going to bed, or taking refusal etc. can be considered. In addition, the control unit 51 relates to the medicine distribution data stored in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523 and as a result of the medicine distribution to the tenant displayed on the tenant confirmation screen 213, Record "Done". Thereby, when the resident list screen 211 is displayed next, the name of the resident is displayed in a display mode indicating that the drug is not necessary for the dosing timing when the reason for the non-drug that has not been taken is input. It will be done.
ところで、入居者が外出(仕事、外泊、入院など)する予定が予め決まっていることも考えられる。そのため、前記配薬支援装置5では、入居者の未服薬の予定を入力可能な構成が考えられる。具体的に、図27は、入居者の未服薬の予定を入力するための予定入力画面215の一例を示す図である。図27に示すように、前記予定入力画面215では、前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作によって、任意の日程が選択され、予め登録された服用時期が選択されると共に、未服薬理由が入力される。なお、図27には、前記予定入力画面215上で2014年3月12日〜14日が選択された状態が示されている。このようにして未服薬の予定が入力されている場合、前記制御部51は、前記未服薬キーが操作されたときに(S88:Yes側)、前記ステップS881における未服薬理由の入力処理を省略して、既登録である未服用の予定の情報を表示させることが考えられる。また、前記制御部51は、未服用の予定が入力されている場合には、前記入居者一覧画面211において未服薬完了である旨を表示させることにより、その入居者の服薬の確認作業を省略させることも考えられる。
By the way, it is conceivable that a plan for the resident to go out (work, overnight, hospitalization, etc.) is decided in advance. Therefore, in the said medicine distribution assistance apparatus 5, the structure which can input the schedule of a resident | patient's unmedicated medicine can be considered. Specifically, FIG. 27 is a diagram showing an example of a schedule input screen 215 for inputting a schedule of an unmedicated drug for a resident. As shown in FIG. 27, on the schedule input screen 215, an arbitrary schedule is selected by the operation of the operation device 55 or the portable terminal 6, and a pre-registered dose timing is selected, and the reason for non-delivery is It is input. Note that FIG. 27 shows a state where March 12-14, 2014, is selected on the schedule input screen 215. Thus, when the schedule of the non-drug has been input, when the non-drug key is operated (S 88: Yes side), the control unit 51 omits the input process of the non-drug reason in the step S 881. Then, it is conceivable to display the information of the already taken unscheduled dose. Further, when a schedule for taking a dose has not been taken, the control unit 51 displays a message indicating that the medication has not been completed on the resident list screen 211, thereby omitting the patient's medication confirmation operation. It is also conceivable to
<ステップS882>
そして、ステップS882において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者が服薬しなかった残薬に関する残薬情報として、前記入居者が服薬するべきであった薬品の情報を前記入居者の情報(配薬データなど)と共に出力する。ここに、係る処理は前記残薬情報出力部516によって実行される。
<Step S882>
Then, in step S 882, the control unit 51 causes the tenant to take the medicine as residual medicine information on the residual medicine which the tenant did not take and displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213. Information is output together with the resident's information (drug supply data etc.). Here, such processing is executed by the residual drug information output unit 516.
具体的に、前記ステップS882において、前記制御部51は、前記残薬情報を前記通信インターフェース53に出力し、前記通信インターフェース53からインターネット等の前記ネットワークN2を通じて前記調剤支援装置1に送信出力することが考えられる。また、前記残薬情報を前記調剤支援装置1に伝達することができればその手法はこれに限らず、例えば前記制御部51が、前記USBポート58を介して前記USBメモリ19に記録出力することも考えられる。これにより、前記調剤支援装置1では、次の薬品の処方時に医師又は薬剤師などが前記残薬情報を参照することが可能となり、例えば処方する薬品の無駄を防止することができる。なお、前記残薬情報は、前記データ記憶部52にも記憶される。これにより、前記配薬支援装置5又は前記携帯端末6においても前記残薬情報を参照することが可能になる。
Specifically, in step S 882, the control unit 51 outputs the remaining medicine information to the communication interface 53, and transmits and outputs the remaining medicine information from the communication interface 53 to the dispensing support device 1 through the network N 2 such as the Internet. Is considered. Further, the method is not limited to this as long as the remaining drug information can be transmitted to the dispensing support device 1, for example, the control unit 51 can also record and output the USB memory 19 via the USB port 58. Conceivable. Thereby, in the dispensing support device 1, a doctor or a pharmacist can refer to the remaining drug information at the time of prescription of the next medicine, and for example, it is possible to prevent waste of the medicine to be prescribed. The residual drug information is also stored in the data storage unit 52. Thereby, it becomes possible to refer to the remaining medicine information also in the medicine distribution support device 5 or the portable terminal 6.
<ステップS89>
なお、ステップS89において、前記制御部51は、前記取消キーの操作を待ち受ける(S89:No側)。ここで、前記取消キーが操作されたと判断すると(S89:Yes側)、処理は前記ステップS84に移行して前記入居者一覧画面211が再表示される。なお、前記取消キーが操作されていない場合には(S89:No側)、処理が前記ステップS87に移行する。
<Step S89>
In step S89, the control unit 51 waits for the operation of the cancel key (S89: No side). Here, if it is determined that the cancel key has been operated (S89: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S84, and the tenant list screen 211 is displayed again. When the cancel key is not operated (S89: No side), the process proceeds to step S87.
以上、説明したように、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記配薬データが前記調剤支援装置1から前記配薬支援装置5に提供されることにより、前記配薬支援装置5において実行される前記配薬時照合処理などにおいて前記配薬データを考慮した表示及び操作を実現することが可能になる。これにより、配薬担当者による入居者への配薬作業を効率的に実行することが可能になると共に、配薬担当者の配薬ミスを抑制することができる。
As described above, in the medicine distribution support system 100, the medicine distribution support device 5 provides the medicine distribution data to the medicine distribution support device 5, whereby the medicine distribution support device 5 is executed. It becomes possible to realize display and operation in consideration of the drug distribution data in drug distribution matching processing and the like. As a result, it becomes possible to efficiently carry out the drug distribution operation to the tenants by the drug distribution staff, and it is possible to suppress the distribution error of the drug distribution staff.
[その他の機能]
なお、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記配薬データが前記配薬支援装置5に提供されることにより、下記のような他の機能も実現可能である。
[Other features]
In addition, in the said medicine distribution support system 100, the following other functions are realizable by the said medicine distribution data being provided to the said medicine distribution support apparatus 5. FIG.
[副作用情報入力機能]
例えば、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に、前記入居者の健康状態又は副作用の状態などを任意に入力可能であることが考えられる。この場合、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213の表示スペースを考慮して、予め定められた複数の項目をプルダウン形式で入力可能であることが考えられる。特に、前記制御部51は、前記副作用関連情報と前記配薬データとに基づいて当該入居者が服用する薬品に対応する副作用の候補を絞り込んで表示させることも考えられる。これにより、前記老健施設B側では、前記候補から選択することにより前記副作用の入力を容易に行うことが可能である。また、前記制御部51は、前記入居者の健康状態又は副作用の状態などの入力開始キーを前記入居者確認画面213に表示させ、その入力開始キーの操作に応じて前記入居者確認画面213から副作用情報入力画面216をポップアップで表示させることも考えられる。ここに、図28は、前記副作用情報入力画面216の一例を示す図である。また、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213とは別のメニュー画面などにおいて、副作用情報を入力する所定の操作が行われた場合に、図29に示すように、入居者名、写真、副作用情報、及びコメントなどが表示される入居者状態画面217を表示させ、前記入居者状態画面217における副作用情報の入力操作が行われた場合に前記副作用情報入力画面216をポップアップで表示させることも考えられる。なお、前記副作用情報入力画面216は、入居者ごとに予め任意のコメント情報を入力するためにも用いられる。
[Side effect information input function]
For example, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 can arbitrarily input the state of health or side effects of the resident on the resident confirmation screen 213. In this case, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 can input a plurality of predetermined items in a pull-down form in consideration of the display space of the resident confirmation screen 213. In particular, it may be considered that the control unit 51 narrows down and displays the side effect candidates corresponding to the medicine taken by the resident based on the side effect related information and the drug distribution data. Thus, the side effects can be input easily by selecting from the candidates on the health care facility B side. In addition, the control unit 51 causes the resident confirmation screen 213 to display an input start key such as the state of health or side effects of the resident, and from the resident confirmation screen 213 in accordance with the operation of the input start key. It is also conceivable to display the side effect information input screen 216 in a pop-up manner. Here, FIG. 28 is a view showing an example of the side effect information input screen 216. Further, as shown in FIG. 29, when the predetermined operation for inputting the side effect information is performed on the menu screen or the like different from the resident confirmation screen 213, the control unit 51 displays the resident name and the photograph. , A side effect information, a resident status screen 217 on which a comment, etc. are displayed, and the side effect information input screen 216 is displayed in a pop-up when the side effect information input operation on the above resident state screen 217 is performed. Is also conceivable. The side effect information input screen 216 is also used to input arbitrary comment information in advance for each resident.
そして、前記制御部51は、前記副作用情報入力画面216で前記入居者の健康状態又は副作用の状態などに関する副作用情報が入力された場合には、その副作用情報を前記データ記憶部52に記憶させると共に、前記通信インターフェース53により前記調剤支援装置1に送信することが考えられる。なお、前記副作用情報が前記USBメモリ19などの記録媒体に記録され、前記USBメモリ19が前記調剤支援装置1又は前記上位システム(不図示)などに接続されることによって前記調剤支援装置1又は前記上位システム(不図示)などに前記副作用情報が入力されることも考えられる。これらの構成によれば、例えば医師が前記入居者の診察を行う際に、前記入居者の健康状態又は副作用の状態などの副作用情報を前記配薬支援装置5又は前記携帯端末6などで参照することが可能となる。
When the side effect information related to the resident's health condition or the side effect condition is input on the side effect information input screen 216, the control unit 51 stores the side effect information in the data storage unit 52. It is conceivable to transmit to the dispensing support device 1 by the communication interface 53. The side effect information is recorded in a recording medium such as the USB memory 19 and the USB memory 19 is connected to the dispensing support device 1 or the upper system (not shown) or the like, whereby the dispensing support device 1 or the dispensing support device 1 or It is also conceivable that the side effect information is input to a host system (not shown) or the like. According to these configurations, for example, when a doctor examines the resident, the side effect information such as the state of health or the side effect of the resident is referred to by the medicine distribution support device 5 or the portable terminal 6 or the like. It becomes possible.
また、前記制御部51が、前記副作用情報と前記副作用関連情報とに基づいて発現している副作用の原因となっている可能性の高い被疑薬を特定して表示可能であることも考えられる。ここで、前記薬品マスターに薬品各々の写真などの薬品画像データが含まれている場合には、前記制御部51は、前記被疑薬の前記薬品画像データを前記入居者確認画面213で表示させることも可能である。これにより、例えば複数の薬品が一包化されている前記薬包81から前記被疑薬を抜き出す際の人為的ミスが抑制される。
In addition, it is also conceivable that the control unit 51 can identify and display a suspected drug that is highly likely to be the cause of the side effect that has occurred based on the side effect information and the side effect related information. Here, when the medicine master includes medicine image data such as a picture of each medicine, the control unit 51 displays the medicine image data of the suspected medicine on the resident confirmation screen 213. Is also possible. As a result, for example, human error in extracting the suspected drug from the medicine package 81 in which a plurality of medicines are packaged is suppressed.
さらに、前記調剤支援装置1に送信されることにより、薬局側でも前記入居者の健康状態又は副作用の状態などの情報を容易に把握することができる。特に、前記調剤支援装置1では、前記制御部11によって前記副作用情報を前記上位システム(不図示)に送信可能であることが考えられる。これにより、前記入居者の薬品を処方する医師も前記上位システム(不図示)において前記副作用情報を参照することが可能であり、病院(医師)、薬局(薬剤師)、及び老健施設(配薬担当者)が密接に連携した医療システムが実現される。
Further, by being transmitted to the dispensing support device 1, the pharmacy side can easily grasp information such as the state of health or side effects of the resident. In particular, in the dispensing support device 1, it is conceivable that the side effect information can be transmitted to the upper system (not shown) by the control unit 11. Thereby, a doctor who prescribes the medicine of the resident can refer to the side effect information in the upper system (not shown), and a hospital (doctor), a pharmacy (pharmacist), and a health care facility (distribution staff) Medical system in which the persons in close cooperation) is realized.
さらに、前記調剤支援装置1又は前記上位システム(不図示)などで前記副作用情報を参照することが可能であるため、例えば前記入居者の次の処方データに基づく調剤時に、薬剤師が前記副作用情報に基づいて特定の薬品の調剤を省略することが可能である。また、前記調剤支援装置1において、前記制御部11が、自動的に前記副作用情報の対象となっている薬品を調剤対象から除外して前記分包データなどを生成することも考えられる。なお、前記副作用情報として、前記副作用の発現により服用が中止された日時又は未服用の薬品量などが含まれている場合には、前記調剤支援装置1において、前記制御部11が、前記副作用情報に基づいて未服用の薬品及び残量を特定し、次の前記分包データの生成時に前記未服用の薬品の処方量から前記残量を除いて前記分包データを生成することも考えられる。なお、前記薬局A側の薬剤師が、前記調剤支援装置1で表示される前記副作用情報を参照し、副作用の原因となっている可能性のある被疑薬を医師に連絡して、新たな処方入力時に前記被疑薬を除いた処方入力を促すこと、又は入力済みの処方から前記被疑薬を除く修正(再発行)を促すことが可能である。また、未服用の薬品量を医師に連絡して、新たな処方入力時に前記未服用の薬品量を除いた処方入力を促すこと、又は入力済みの処方から前記未服用の薬品量を除く修正(再発行)を促すことも可能である。
Furthermore, since it is possible to refer to the side effect information by the dispensing support device 1 or the upper system (not shown) or the like, for example, at the time of dispensing based on the next prescription data of the resident, the pharmacist It is possible to dispense with the dispensing of certain medicines based on that. In addition, in the dispensing support device 1, it is also conceivable that the control unit 11 automatically excludes the medicine targeted for the side effect information from the dispensing target to generate the packaging data and the like. In the case where the side effect information includes the date and time when dosing was discontinued due to the occurrence of the side effect or the amount of drug not yet taken, the control unit 11 in the dispensing support device 1 determines the side effect information. It is also conceivable to specify the medicine not yet taken and the remaining amount based on the above, and generate the packing data by removing the remaining amount from the prescribed amount of the medicine not yet taken at the time of the next generation of the packing data. In addition, the pharmacist on the pharmacy A side refers to the side effect information displayed on the dispensing support device 1 and notifies the doctor of the suspected drug that may cause the side effect, and inputs a new prescription. It is sometimes possible to prompt for prescription input excluding the suspect drug, or to prompt correction (reissue) for removing the suspect drug from the entered prescription. In addition, notify the doctor of the amount of drug that has not been taken, and encourage prescription entry excluding the amount of the drug that has not been taken at the time of new prescription input, or correct the amount of drug that has not been taken yet It is also possible to encourage reissue.
[配薬ボックス開閉機能]
また、服用時期ごとに対応する前記薬包81が収容される収容部を備え、前記収容部ごとに開閉制御が可能な配薬ボックスが前記配薬支援装置5と通信可能に接続されて用いられることが考えられる。この場合、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データに基づいて、服用時期が到来しないとその服用時期に対応する薬品を取り出すことができないように前記配薬ボックスにおける前記収容部各々の開閉を制御することが考えられる。これにより、前記入居者に対する配薬ミスを抑制することができる。
[Medication box opening and closing function]
In addition, a medicine dispensing box is provided, which contains the medicine package 81 corresponding to each dosing time, and the medicine dispensing box capable of opening / closing control for each of the medicine accommodating units is communicably connected to the medicine dispensing support device 5 and used. It is conceivable. In this case, based on the drug distribution data, the control unit 51 controls the opening and closing of each of the storage units in the drug distribution box so that the drug corresponding to the dosing time can not be taken out unless the dosing time arrives. It is possible to do. Accordingly, it is possible to suppress drug administration errors for the resident.
[服薬履歴表示機能]
また、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶される前記配薬データ及び服薬結果の履歴を表示させる服薬履歴表示機能を有することが考えられる。ここに、図30〜図33は、前記服薬履歴表示機能によって表示可能な履歴画面の一例を示す図である。
[Medication history display function]
Further, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 has a medication history display function of displaying a history of the medication data and medication results stored in the medication data storage unit 523. FIGS. 30 to 33 are views showing an example of a history screen that can be displayed by the medication history display function.
まず、前記制御部51は、前記表示装置54などにメニュー画面が表示された状態で、服薬履歴を表示する所定の操作が行われた場合に、図30に示す履歴画面218を表示させる。前記履歴画面218では、入居者各々の服薬結果が1日単位で表示される。前記履歴画面218では、「○」のマークが服薬、「△」のマークが一部未服薬、「×」のマークが未服薬を示している。なお、前記一部未服薬とは、1日に含まれる複数の服用時期に服薬及び未服薬が含まれている状態を示す。例えば、前記一部未服薬とは、1日に朝、昼、晩の3回の服用時期が含まれている場合に、朝、昼、晩のいずれか一つ又は二つの服用時期が未服用である場合である。また、前記履歴画面218では、服薬有無などに関する情報を除く例えば残薬の情報又は副作用の情報などの情報が記録されている日に対応するマークの背景色又は形状が通常とは異なる背景色又は形状で表示される。
First, when the menu screen is displayed on the display device 54 or the like, the control unit 51 causes the history screen 218 shown in FIG. 30 to be displayed when a predetermined operation for displaying the medication history is performed. On the history screen 218, medication results for each resident are displayed on a daily basis. On the history screen 218, the mark of "o" indicates medication, the mark of "f" partially indicates non-drug, and the mark of "x" indicates non-drug. Here, the term "partially non-administered drug" refers to a state in which drug administration and non-drug are included in a plurality of dosing periods included in one day. For example, in the case where the partially unmedicated drug includes three dosage periods of morning, noon and evening on one day, any one or two doses in the morning, noon, and evening have not been taken. Is the case. In the history screen 218, the background color or the shape of the mark corresponding to the day on which the information such as the information on remaining medicine or the information on the side effects is recorded except the information on the presence or absence of medication etc. Displayed in shape.
ところで、服用開始日、服用終了日、及び服用時期(朝食前、昼食後など)などを含む前記配薬データ又は前記処方データが前記配薬支援装置5に入力されている場合、前記制御部51は、前記履歴画面218において、服用者各々に対応する服用の要否予定を表示することが考えられる。なお、前述したように、前記配薬データ又は前記処方データは、例えば前記調剤支援装置1から入力され、前記USBメモリ19から読み取られ、又は前記薬包81から読み取られる。具体的に、前記制御部51は、服用の必要がある日付に対応する欄に、服用の必要がある旨を示すために予め定められた菱形のマークなどを表示させることが考えられる。また、前記制御部51は、前記履歴画面218において、入居者の外出予定又は外泊予定などのように服用の必要がない予定が先に入力されている場合には、前記履歴画面218において、その予定日に対応する欄に、服用の必要がない予定である旨を示すために予め定められた「外」のマークなどを表示させることが考えられる。
By the way, when the drug distribution data or the prescription data including the dose start date, the dose end date, and the dose timing (before breakfast, after lunch, etc.) are input to the drug delivery support device 5, the control unit 51 In the history screen 218, it is conceivable to display the necessity / unnecessary schedule of the dose corresponding to each doser. As described above, the drug distribution data or the prescription data is input from, for example, the dispensing support device 1, read from the USB memory 19, or read from the medicine package 81. Specifically, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 displays a diamond-shaped mark or the like, which is determined in advance, to indicate that it is necessary to take a dose, in a field corresponding to a date on which the need to take a dose. In the case where a schedule for which taking is not necessary is previously input, such as a going-out schedule or a stay-time schedule of the resident on the history screen 218, the control unit 51 is configured on the history screen 218. It is conceivable to display an "outside" mark or the like, which is determined in advance, to indicate that it is not necessary to take a dose, in the column corresponding to the scheduled date.
そして、前記履歴画面218で入居者を選択するための操作が行われると、前記制御部51は、前記履歴画面218に代えて図31に示す履歴画面219を表示させる。図31に示す前記履歴画面219では、選択された入居者が服薬した薬品各々の履歴が1日単位で表示される。また、前記履歴画面219では、最下段に「その他の情報」の表示欄が設けられており、その表示欄では、残薬の情報又は副作用の情報などの情報が記録されている日に「○」が記載される。そして、前記制御部51は、「その他の情報」の表示欄のうち「○」が記載されている領域が選択された場合、又はその領域に前記操作装置55又は前記携帯端末6の操作ポインターが存在する場合などに、その表示欄に対応する残薬の情報又は副作用の情報などの情報をポップアップで表示させることが考えられる。
Then, when an operation for selecting a resident on the history screen 218 is performed, the control unit 51 causes the history screen 219 shown in FIG. 31 to be displayed instead of the history screen 218. In the history screen 219 shown in FIG. 31, the history of each medicine taken by the selected tenant is displayed on a daily basis. Further, in the history screen 219, a display column of "other information" is provided at the bottom, and in the display column, "○" is displayed on the day when information such as information on residual medicine or information on side effects is recorded. "Is described. Then, when the area where “o” is described in the display column of “other information” is selected, the control unit 51 selects the operation pointer of the operating device 55 or the portable terminal 6 in that area. If it exists, it is conceivable to display information such as information on residual medicine or information on side effects corresponding to the display column in a pop-up.
また、前記履歴画面219で日付が選択されると、前記制御部51は、前記履歴画面219に代えて図32に示す履歴画面220を表示させる。図32に示す前記履歴画面220では、選択された入居者が服薬した薬品各々の履歴が服用時期単位で表示される。なお、前記履歴画面220でも前記履歴画面219と同様に「その他の情報」の表示欄が表示されている。
Further, when a date is selected on the history screen 219, the control unit 51 displays a history screen 220 shown in FIG. 32 in place of the history screen 219. In the history screen 220 shown in FIG. 32, the history of each medicine taken by the selected tenant is displayed in dosage unit units. In the history screen 220, as in the case of the history screen 219, a display column of "other information" is displayed.
なお、前記履歴画面219又は前記履歴画面220で、「その他の情報」の表示欄において残薬の情報が記録されている箇所が選択された場合、前記制御部51は、前記残薬の情報を前記配薬データ記憶部523から読み出して図33に示す履歴画面221に表示させることが考えられる。図33に示す前記履歴画面221では、薬品M1の残薬状況として「2錠」が示されており、薬品M2の残薬状況として「1.5錠×3」が示されている。ここで、前記薬品M2の残薬状況として1.5錠×3の算出結果である「4.5錠」と表示することも考えられるが、前記制御部51は、前記薬品M2の剤形を考慮して「1.5錠×3」と表示する。これにより、前記薬品M2の残薬が4錠及び0.5錠の合計5粒ではなく、1錠及び0.5錠が3組で合計6粒であることが明示され、例えば次の処方データに含まれる処方薬として使用するか否かの判断を容易に行うことが可能である。このため、前記配薬支援装置5において、前記制御部51は、入居者の薬品各々の残薬情報における薬品の残量を調剤時の状態で管理しており、前記調剤支援装置1にも同様の前記残薬情報を送信する。
In addition, when the location where information on residual medicine is recorded in the display column of "other information" is selected on the history screen 219 or the history screen 220, the control unit 51 selects information on the residual medicine. It is conceivable to read out from the medicine distribution data storage unit 523 and to display it on the history screen 221 shown in FIG. On the history screen 221 shown in FIG. 33, “2 tablets” are shown as the residual drug status of the medicine M1, and “1.5 tablets × 3” are shown as the residual drug status of the medicine M2. Here, it may be considered to display “4.5 tablets” which is a calculation result of 1.5 tablets × 3 as the residual medicine condition of the medicine M2, but the control unit 51 may use a dosage form of the medicine M2. In consideration of this, "1.5 tablets x 3" is displayed. As a result, it is clearly shown that the remaining drug M2 is not a total of 5 tablets of 4 tablets and 0.5 tablets, but 3 tablets of 1 tablet and 0.5 tablets are 6 tablets in total, for example, the following prescription data It is possible to easily determine whether to use as a prescription drug included in Therefore, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 manages the remaining amount of medicine in the remaining medicine information of each medicine of the resident in the state at the time of dispensing, and the same applies to the medicine preparation support device 1 as well. Of the remaining drug information of
[アラーム機能]
ところで、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶される前記配薬データに基づいてアラームを自動的に設定するアラーム機能を有することが考えられる。ここに、図34〜図35は、前記配薬データが入力された場合に表示される服薬予定画面の一例を示す図である。
[Alarm function]
By the way, it is conceivable that the control unit 51 has an alarm function of automatically setting an alarm based on the medicine distribution data stored in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523. Here, FIGS. 34 to 35 are diagrams showing an example of a medication schedule screen displayed when the drug distribution data is input.
ここでは、前記薬品分包装置3において前記服用者別分包処理が実行され、一の服用者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに一連の前記薬包81に分包された場合に、その最初又は最後の前記薬包81に一次元コード又は二次元コードによって検薬コードが印刷される場合について説明する。ここに、図36は、最初の前記薬包81に検薬コードが印刷された一連の前記薬包81の一例を示す図である。図36に示す例では、最初の前記薬包81に前記検薬コードとして二次元コードが印刷されており、二つ目以後の前記薬包81には、前記第1配薬情報を示す前記コード811として一次元コードが印刷されている。前記検薬コードには、前記薬包81の検薬に必要な予め定められた情報と共に、入居者ID、入居者名称、服用開始日、服用終了日、及び服用時期コードなどの配薬データが含まれる。前記服用時期コードは、前記服用開始日から前記服用終了日の間に服用する必要がある服用時期(朝食前、朝食後、昼食前など)を示す数字又は記号などである。即ち、ここでは、入居者各々に対応する一連の前記薬包81の最初又は最後の前記薬包81の前記検薬コードが読み取られることによって前記入居者各々に対応する前記配薬データが順に前記配薬管理装置5に入力されるものとする。なお、一連の前記薬包81は、そのままの状態で前記薬局A側から前記老健施設B側に配送され、又は、前記薬包81が個別に切り離された状態で前記薬局A側から前記老健施設B側に配送される。
In this case, if the medicine packaging process by the user is executed in the medicine packaging apparatus 3 and the medicine taken by one user is divided into a series of medicine packages 81 at each dosing time, the first process Alternatively, a case where a test drug code is printed on the last medicine package 81 by a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code will be described. Here, FIG. 36 is a view showing an example of a series of the medicine package 81 in which a test drug code is printed on the first medicine package 81. In the example shown in FIG. 36, a two-dimensional code is printed on the first drug package 81 as the test drug code, and on the second and subsequent drug packages 81, the code indicating the first drug information is displayed. A one-dimensional code is printed as 811. In the examination drug code, together with predetermined information necessary for the examination of the medicine package 81, drug distribution data such as a resident ID, a resident name, a dosing start date, a dosing end date, and a dosing timing code included. The dosing period code is a number or a symbol indicating a dosing period (before breakfast, after breakfast, before lunch, etc.) which needs to be taken between the dosing start date and the dosing end date. That is, here, the medicine distribution data corresponding to each tenant is sequentially read by reading the test code of the first or last medicine package 81 of the series of medicine packages 81 corresponding to each tenant. It is assumed that the medicine supply management device 5 is input. In addition, a series of the medicine package 81 is delivered as it is from the pharmacy A side to the health care facility B side, or in a state where the medicine package 81 is separated individually, the health care facility from the pharmacy A side It is delivered to B side.
そして、前記配薬管理装置5において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81の前記検薬コードから前記配薬データが読み取られた場合に、前記配薬データに基づいて、前記薬包81に対応する入居者の服薬予定を前記データ記憶部52に登録させる。ここで、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データが読み取られたことを確認するための服用予定画面222を、前記配薬データを読み取った前記読取端末7又は前記表示装置54に表示させることが考えられる。また、前記服用予定画面222は、前記携帯端末6及び前記読取端末7などにおいて、服薬予定を確認するための所定のユーザー操作が行われた場合にも前記携帯端末6及び前記読取端末7などに表示される。
Then, in the medicine distribution management device 5, when the medicine distribution data is read from the test drug code of the medicine pack 81, the control unit 51 selects the medicine medicine pack 81 based on the medicine distribution data. The corresponding patient's medication schedule is registered in the data storage unit 52. Here, the control unit 51 may cause the reading terminal 7 or the display device 54 that has read the medicine distribution data to display a dosing schedule screen 222 for confirming that the medicine distribution data has been read. Conceivable. In addition, the dose schedule screen 222 is displayed on the portable terminal 6 and the reading terminal 7 or the like even when a predetermined user operation for checking the dosing schedule is performed on the portable terminal 6 and the reading terminal 7 or the like. Is displayed.
ここに、図34は、前記服用予定画面222の一例を示す図である。図34に示されているように、前記服用予定画面222の上段には、最後に前記薬包81から読み取られた前記配薬データに対応する入居者の入居者ID、入居者名称、服用開始日、服用終了日などが表示されている。また、前記服用予定画面222には、下段に、既に読み取られて前記データ記憶部52に記憶されている一又は複数の入居者に対応する前記配薬データの一覧が表示されている。なお、前記服用予定画面222において、特定の前記配薬データが選択され、詳細キーが操作されると、前記配薬データに対応する服用予定の詳細が表示される服用詳細画面223が表示される。なお、前記制御部51は、特定の前記配薬データが選択され、削除キーが操作されると、前記配薬データに対応する服薬予定を削除することも可能である。また、前記服用予定画面222の上段に表示される情報は、前記服用予定画面222の下段における前記配薬データの選択に応じてその選択された配薬データに対応する情報に切り換えられてもよい。
Here, FIG. 34 is a view showing an example of the dose schedule screen 222. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 34, in the upper part of the dose schedule screen 222, the resident ID, the resident name, and the dose start of the resident corresponding to the drug distribution data read from the medicine package 81 lastly The day, the end date of taking, etc. are displayed. Further, on the lower side of the dose schedule screen 222, a list of the drug supply data corresponding to one or more tenants read and stored in the data storage unit 52 is displayed. In the dose schedule screen 222, when the specific drug distribution data is selected and the detail key is operated, a dose detail screen 223 is displayed in which details of the dose schedule corresponding to the drug dose data are displayed. . The control unit 51 can also delete the medication schedule corresponding to the drug distribution data when the specific drug distribution data is selected and the delete key is operated. Further, the information displayed on the upper stage of the dose schedule screen 222 may be switched to information corresponding to the selected drug delivery data according to the selection of the drug distribution data on the lower stage of the dose schedule screen 222. .
ここに、図35は、前記服用詳細画面223の一例を示す図である。図35に示されているように、前記服用詳細画面223には、上段に、読み取られた前記配薬データに対応する入居者の入居者ID、入居者名称、服用開始日、服用終了日などが表示されている。また、前記服用詳細画面223には、下段に、1人の入居者に対応する前記配薬データに対応する服用開始日から服用終了日までの服用予定日及び服用時期が表示される。
Here, FIG. 35 is a view showing an example of the dose detail screen 223. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 35, in the upper part of the dose details screen 223, the resident ID of the resident corresponding to the read drug distribution data, resident name, resident start date, dose end date Is displayed. In the lower part of the dose details screen 223, scheduled dose dates and dose dates from the dose start date to the dose finish date corresponding to the drug distribution data corresponding to one resident are displayed.
そして、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データが入力されると、前記配薬データに基づいて、前記配薬データに対応する前記入居者の服用時期各々について予め定められたアラーム条件に従って自動的にアラーム時刻を設定するアラーム設定処理を実行する。ここに、係る処理を実行するときの前記制御部51がアラーム設定手段の一例である。具体的に、前記アラーム条件として、服用時期「昼食後」に対応するアラーム時刻が「13時」、服用時期「昼食間」に対応するアラーム時刻が「15時」、服用時期「夕食前」に対応するアラーム時刻が「18時」であることが考えられる。また、前記アラーム条件として、服用時期「昼食後」に対応するアラーム時刻が「12時30分」、服用時期「昼食間」に対応するアラーム時刻が「15時」、服用時期「夕食前」に対応するアラーム時刻が「18時30分」であることが考えられる。
Then, when the drug distribution data is input, the control unit 51 automatically performs, on the basis of the drug distribution data, the alarm condition predetermined for each of the tenants taking time corresponding to the drug distribution data. Execute alarm setting processing to set the alarm time to. Here, the control unit 51 when executing the processing is an example of the alarm setting unit. Specifically, as the alarm condition, the alarm time corresponding to the taking time "after lunch" is "13 o'clock", the alarming time corresponding to the taking time "between lunch" is "15 o'clock", and the taking time "before dinner" It is conceivable that the corresponding alarm time is "18 o'clock". Also, as the alarm condition, the alarm time corresponding to the taking time "after lunch" is "12:30", the alarming time corresponding to the taking time "between lunch" is "15 o'clock", and the taking time "before dinner" It is conceivable that the corresponding alarm time is "18:30".
その後、前記制御部51は、前記アラーム設定処理によって設定された前記服用時期各々の前記アラーム時刻に、当該服用時期に対応する服用完了が入力されていない場合、当該服用時期の服用を促すメッセージ等を前記携帯端末6、前記読取端末7、又は前記配薬支援装置5の表示装置54などに表示させるアラーム報知処理を実行する。ここに、係る処理を実行するときの前記制御部51がアラーム報知手段の一例である。これにより、前記入居者各々について前記服用時期各々における服用漏れが抑制される。なお、前記アラーム報知処理の内容は表示に限らず、例えば音声などによる報知であってもよい。また、前記制御部51は、前記メッセージ等を表示する際、前記服用完了が入力されていない服用者の一覧を表示させること、又は前記服用完了が入力されていない服用者ごとに順にメッセージ等を表示させることが考えられる。
Thereafter, when the dose completion corresponding to the dose timing is not input at the alarm time of each dose timing set by the alarm setting process, the control unit 51 displays a message prompting the user to take the dose timing, etc. An alarm notification process is performed to cause the display unit 54 of the portable terminal 6, the reading terminal 7, or the medicine dispensing support device 5 to display the information. Here, the control unit 51 when executing the processing is an example of the alarm notification unit. Thereby, the dose leak at each of the dosing periods is suppressed for each of the tenants. In addition, the content of the said alarm alerting | reporting process may be alerting | reporting not only by display but audio | voice etc., for example. Further, when displaying the message etc., the control unit 51 displays a list of users who have not received the dose completion, or sequentially displays a message etc. for each doser who has not received the dose completion. It is conceivable to display.
そして、前記制御部51は、前記アラーム時刻に前記アラーム報知処理を実行した後、その報知の対象であった前記服用時期の服用が行われなかったと判断した場合、前記服用時期の服用を未服用として前記データ記憶部52に記録する。これにより、前記制御部51は、前記服用予定画面222が表示される場合、前記未服用の服用時期に該当する欄に「×」のマークを表示させる。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記アラーム報知処理の実行後、予め設定された所定時間内に前記服用時期に対応する前記コード情報811が読み取られなかった場合、又は前記服用時期における服用が不要である旨の操作が行われた場合に、前記服用時期の服用が行われなかったと判断する。また、前記制御部51が、前記服用完了が入力されていない服用者の一覧が表示された状態で配薬対象を順に移動させる場合には、現在の配薬対象の服用者とは異なる服用者に対応する前記コード情報811が読み取られた場合に、現在の配薬対象の服用者の服用が行われなかったと判断することも考えられる。なお、前記制御部51は、服用者の一覧が表示された状態で配薬対象を順に移動させる場合、現在の配薬対象の服用者に対応する前記コード情報811が読み取られた場合に、当該服用者の服用が行われたと判断し、次の服用者を配薬対象として選択する。同じく、前記制御部51が、前記服用完了が入力されていない服用者ごとに順にメッセージ等を表示させる場合には、現在表示中のメッセージ等に対応する服用者とは異なる服用者に対応する前記コード情報811が読み取られた場合に、表示中のメッセージ等に対応する服用者の服用が行われなかったと判断することも考えられる。なお、前記制御部51は、服用者ごとに対応するメッセージ等を順に表示させる場合、現在表示中のメッセージ等に対応する服用者の前記コード情報811が読み取られた場合に、当該服用者の服用が行われたと判断し、次の服用者に対応する前記メッセージ等を表示させる。
Then, after the control unit 51 executes the alarm notification process at the alarm time, if it is determined that the taking of the taking time that was the target of the notification is not performed, the taking of the taking time is not taken. As the data storage unit 52. Thus, when the dosing schedule screen 222 is displayed, the control unit 51 displays a mark of “x” in the column corresponding to the dosing period not yet taken. For example, when the code information 811 corresponding to the dosing time is not read within a predetermined time set in advance after execution of the alarm notification process, the control unit 51 does not need to take the dosing time at the dosing time. If an operation has been performed, it is determined that the dose has not been taken. In addition, when the control unit 51 sequentially moves the drug distribution target in a state where the list of dosers who has not received the dose completion is displayed, the doser different from the doser of the current drug distribution target When the code information 811 corresponding to is read, it may be considered that it is determined that the current drug recipient has not taken the drug. When the control unit 51 sequentially moves the drug distribution target in a state where the list of dosers is displayed, the control unit 51 may read the code information 811 corresponding to the doser of the current drug distribution target. It is determined that the doser has taken the drug, and the next doser is selected for drug delivery. Similarly, when the control unit 51 sequentially displays a message or the like for each doser who has not received the dose completion, the control unit 51 corresponds to a doser different from the doser corresponding to the currently displayed message or the like. When the code information 811 is read, it can be considered that it is determined that the user of the dose corresponding to the displayed message has not been taken. When the control unit 51 sequentially displays a message or the like corresponding to each doser, when the code information 811 of the doser corresponding to the currently displayed message or the like is read, the dose of the doser It is determined that the above-mentioned message etc. corresponding to the next doser are displayed.
[第3実施形態]
以下、本実施形態では、前記第2実施形態に係る配薬支援システム1において、服用者が一回の服用時期に服用する薬品が複数の薬包81に分包される運用に対応可能な構成について説明する。なお、本実施の形態では、前記第2実施形態で説明した構成及び処理と同様の構成及び処理については説明を省略する。
Third Embodiment
Hereinafter, in the present embodiment, in the medicine distribution support system 1 according to the second embodiment, a configuration that can cope with the operation in which the medicine taken by the user at the time of single taking is divided into a plurality of medicine packages 81. Will be explained. In the present embodiment, the description of the same configuration and processing as the configuration and processing described in the second embodiment will be omitted.
本実施形態では、前記第2実施形態と同様に、前記薬局Aで分包された前記薬包81の薬品が前記老健施設Bに配送され、前記老健施設Bの入居者(服用者の一例)によって服用される場合を例に挙げて説明する。なお、本実施形態に対応する発明は、前記薬局Aで分包された前記薬包81の薬品が病院の入院患者(服用者の一例)によって服用される場合、前記薬局Aで分包された前記薬包81の薬品が自宅等で患者(服用者の一例)によって服用される場合にも適用可能である。
In the present embodiment, as in the second embodiment, the medicine of the medicine package 81 packaged in the pharmacy A is delivered to the health care facility B, and the resident of the health care facility B (an example of the person taking the medicine) The case where it is taken by will be described as an example. In the invention corresponding to the present embodiment, when the medicine in the medicine package 81 packaged in the pharmacy A is taken by a hospitalized patient (an example of a user) in the hospital, the medicine is packaged in the pharmacy A The present invention is also applicable to the case where the medicine of the medicine package 81 is taken by a patient (an example of a user) at home or the like.
ここに、図37及び図38は、前記配薬支援システム1において、一又は複数の前記薬品分包装置3で実行される薬品分包処理の分包結果の一例を示す図である。図37及び図38に示されている例では、1人の入居者に対応する分包結果として複数の薬包シート81A〜81C(分包容器群の一例)が得られている。なお、以下の説明において前記薬包シート81A〜81Cのような一連の薬包81を単に薬包シートと総称することがある。
Here, FIG. 37 and FIG. 38 are diagrams showing an example of the result of the packaging process of the medicine packaging process performed by one or more medicine packaging apparatuses 3 in the medicine distribution support system 1. In the example shown in FIGS. 37 and 38, a plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C (an example of a package container group) are obtained as a result of packaging corresponding to one tenant. In the following description, a series of medicine package 81 such as the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C may be simply referred to as a medicine package sheet.
具体的に、図37には、同一の前記薬品分包装置3で複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する薬品の薬品分包処理が実行された場合の分包結果の一例が示されている。なお、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬局Aから前記老健施設Bに配送される薬品について、予め設定された締めタイミングが到来した場合、又はユーザー操作による締め要求が行われた場合に締め処理が実行され、入居者各々が服用する薬品が確定されるものとする。即ち、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに関する前記薬品分包処理の実行時に、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの存在が認識可能である。また、前記薬品分包装置3に処方データが入力され、前記処方データに複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する薬品が含まれている場合にも、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに関する前記薬品分包処理の実行時に、前記処方データに基づいて前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの存在が認識可能である。
Specifically, FIG. 37 shows an example of the result of packing when medicine packing processing of medicine corresponding to a plurality of medicine pack sheets 81A to 81C is executed by the same medicine packing apparatus 3. ing. The medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3 performs a tightening process when a preset tightening timing arrives for a medicine delivered from the pharmacy A to the health care facility B or when a tightening request is made by a user operation. Shall be carried out, and the medicine taken by each resident shall be determined. That is, in the medicine packaging device 3, the existence of the medicine packaging sheets 81A to 81C can be recognized when the medicine packaging processing for the medicine packaging sheets 81A to 81C is performed. Further, even when the prescription data is input to the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 and the prescription data includes medicines corresponding to the plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C, the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 further includes When the medicine packaging process for medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is performed, the presence of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C can be recognized based on the prescription data.
このような場合、図37に示されているように、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々において、先頭に付される検薬用の空包である検薬包810(配薬記録媒体の一例)に検薬コード831が記録される。また、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々において、前記薬包81各々に薬包コード832が記録される。なお、前記検薬コード831及び前記薬包コード832は、前記薬品分包装置3の前記分包プリンタ32を用いて前記検薬包810及び前記薬包81に印刷される。
In such a case, as shown in FIG. 37, in the medicine dispensing and packaging apparatus 3, in each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C, a test packet package 810 (an empty package for an examination) attached at the top. A test drug code 831 is recorded in an example of the drug distribution recording medium). Further, in the medicine packing device 3, the medicine package code 832 is recorded in each medicine package 81 in each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C. The test drug code 831 and the medicine package code 832 are printed on the test medicine package 810 and the medicine package 81 by using the packaging printer 32 of the medicine package 3.
前記検薬コード831は、複数の前記薬包81を含む前記薬包シート81A〜81Cごとに対応する配薬データが纏めて記録された一次元コード又は二次元コードである。具体的に、前記配薬データは、一の前記入居者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに分包された複数の前記薬包81の分包内容を含む。前記分包内容には、薬包番号、入居者ID、入居者名称、服用開始日、服用終了日、服用時期コード、服用時期などの情報が含まれる。例えば、前記薬包番号は、前記薬品分包装置3を識別可能な号機番号と前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々の前記薬包81であることを識別可能な薬種番号とを含む予め設定される3桁の数字である。なお、前記配薬データには、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの前記薬包81に収容されている薬品コード及び薬品名称などの情報が含まれていてもよい。
The test drug code 831 is a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code in which drug delivery data corresponding to each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C including the plurality of medicine packages 81 are collectively recorded. Specifically, the drug distribution data includes the contents of the plurality of medicine packages 81 into which the medicine taken by one resident is divided at each dosing time. The contents of the package include information such as a medicine package number, a resident ID, a resident name, a dosing start date, a dosing end date, a dosing timing code, and a dosing timing. For example, the medicine package number is set in advance including a machine number capable of identifying the medicine dispensing apparatus 3 and a medicine type number capable of identifying the medicine package 81 of each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C. It is a 3-digit number. The drug distribution data may include information such as a drug code and a drug name stored in the drug package 81 of the drug package sheets 81A to 81C.
また、前記薬包コード832は、前記薬包81を識別可能な識別データの一例である。具体的に、前記薬包コード832は、薬包番号、入居者ID、入居者名称、服用時期コード、服用時期などの情報を含む一次元コード又は二次元コードなどである。なお、前記薬包コード832に、前記薬包81に収容されている薬品の薬品コード及び薬品名称などの情報が含まれていてもよい。
Further, the medicine package code 832 is an example of identification data capable of identifying the medicine package 81. Specifically, the medicine package code 832 is a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code including information such as medicine package number, resident ID, resident name, dosing time code, dosing time and the like. The medicine package code 832 may include information such as a medicine code and a medicine name of a medicine contained in the medicine package 81.
また、図38には、複数の前記薬品分包装置3で複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する薬品分包処理が実行された場合の分包結果の一例が示されている。例えば、同一の服用時期に服用する薬品の薬品分包処理が、錠剤を分包する錠剤分包機及び散薬を分包する散薬分包機を含む複数の前記薬品分包装置3によって個別に実行されることがある。この場合、前記薬品分包装置3各々では、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々に対応する前記薬品分包処理の実行時に、他の装置で実行される前記薬品分包処理の内容を認識することができない場合がある。なお、同一の前記薬品分包装置3で前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々に対応する処方データについて異なるタイミングで前記薬品分包処理が実行される場合にも、前記薬品分包装置3が前記薬品分包処理各々の内容を認識することができないことがある。
Further, FIG. 38 shows an example of the result of the packaging when the medicine packaging process corresponding to the plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is executed by the plurality of medicine packaging devices 3. For example, the drug packaging process of the drug to be taken at the same dosing time is separately performed by the plurality of drug packaging devices 3 including a tablet packaging machine that packages tablets and a powder packaging machine that packages powders. Sometimes. In this case, each of the medicine dispensing and packing apparatus 3 recognizes the contents of the medicine dispensing and packing process performed by another apparatus when the medicine dispensing and packing process corresponding to each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is performed. There are times when you can not. In addition, even when the medicine packaging process is performed at different timings with respect to prescription data corresponding to each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C in the same medicine packaging apparatus 3, the medicine packaging apparatus 3 performs the medicine The contents of each packaging process may not be recognized.
このような場合、図38に示されているように、前記薬品分包装置3では、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々の前記検薬包810に、前記検薬コード831に代えて検薬コード831A〜831Cが記録される。なお、前述したように、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々の前記薬包81各々には前記薬包コード832が記録される。
In such a case, as shown in FIG. 38, in the medicine dispensing and packing apparatus 3, instead of the test medicine code 831, the test medicine code 810 of each medicine package sheet 81A to 81C is replaced with a test medicine code. 831A to 831C are recorded. As described above, the medicine package code 832 is recorded in each medicine package 81 of each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C.
前記検薬コード831A〜831Cは、複数の前記薬包81を含む前記薬包シート81A〜81Cごとに対応する配薬データが個別に記録された一次元コード又は二次元コードである。具体的に、前記検薬コード831Aには、前記薬包シート81Aに対応する前記配薬データが記録されている。また、前記検薬コード831Bには、前記薬包シート81Bに対応する前記配薬データが記録されており、前記検薬コード831Cには、前記薬包シート81Cに対応する前記配薬データが記録されている。前述したように、前記配薬データは、一の前記入居者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに分包された複数の前記薬包81の分包内容を含む。前記分包内容には、薬包番号、入居者ID、入居者名称、服用開始日、服用終了日、服用時期コード、服用時期などの情報が含まれる。
The test drug codes 831A to 831C are one-dimensional codes or two-dimensional codes in which drug distribution data corresponding to each of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C including the plurality of medicine packages 81 are individually recorded. Specifically, the drug distribution data corresponding to the medicine package sheet 81A is recorded in the test drug code 831A. Further, the drug distribution data corresponding to the medicine package sheet 81B is recorded in the test drug code 831B, and the drug distribution data corresponding to the medicine package sheet 81C is recorded in the test drug code 831C. It is done. As described above, the drug distribution data includes the contents of the plurality of medicine packages 81 into which the medicine taken by the one resident is divided at each dosing time. The contents of the package include information such as a medicine package number, a resident ID, a resident name, a dosing start date, a dosing end date, a dosing timing code, and a dosing timing.
なお、複数の前記薬品分包装置3で複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの薬品分包処理が個別に実行される場合であっても、前記薬品分包装置3各々が複数の前記薬品分包装置3で実行される前記薬品分包処理の内容を特定可能な構成も考えられる。例えば、前記調剤支援装置1から複数の前記薬品分包装置3に同じ処方データ(調剤データ)が入力され、前記薬品分包装置3各々によって前記処方データに基づいて自機に割り当てられた薬品分包処理のみが実行されることが考えられる。この場合は、図37と同様に、複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々に共通の前記配薬コード831が記録される。
In addition, even if the medicine packaging process for the plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is individually performed by the plurality of medicine packaging apparatuses 3, each of the medicine packaging apparatuses 3 is for the plurality of medicines. A configuration capable of specifying the contents of the medicine packaging process performed by the packaging device 3 is also conceivable. For example, the same prescription data (dispensing data) is input from the dispensing support device 1 to the plurality of medicine packaging devices 3, and each medicine division assigned to the machine based on the prescription data by each of the medicine packaging devices 3 It is conceivable that only the packaging process is performed. In this case, as in FIG. 37, the medication code 831 common to the plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is recorded.
そして、前記配薬支援装置5では、前記制御部51が、前記配薬時照合処理において、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ複数の前記薬包81について前記識別データの読み取りが完了したか否かを判定する判定処理を実行することが可能である。より具体的に、前記制御部51は、予め設定された第1判定モード及び第2判定モードのいずれかを選択して前記判定処理を実行する。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記配薬支援装置5の初期設定等におけるユーザー操作に従って前記第1判定モード及び前記第2判定モードのいずれかを選択する。
Then, in the medicine distribution support device 5, the control unit 51 determines whether the reading of the identification data is completed for the resident and the plurality of medicine packages 81 having the same dosing timing in the medicine distribution matching process It is possible to execute determination processing to determine whether the More specifically, the control unit 51 selects one of the first determination mode and the second determination mode set in advance and executes the determination process. For example, the control unit 51 selects one of the first determination mode and the second determination mode in accordance with a user operation in initial setting and the like of the medicine distribution support device 5.
ここに、前記第1判定モードでは、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ全ての前記薬包81から個別に前記薬包コード832が読み取られた場合に、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したと判定される。また、前記第2判定モードでは、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ複数の前記薬包81のいずれか一つの前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られた場合に、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したと判定される。即ち、同一の前記入居者について同一の前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81が複数存在する場合、前記第1判定モードでは全ての前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られる必要があり、前記第2判定モードではいずれか一つの前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られればよい。
Here, in the first determination mode, when the medicine package code 832 is individually read from the medicine pack 81 having the same tenant and the same dosing time, a plurality of the tenant and the taking time are the same. It is determined that reading of the medicine package code 832 is completed for the medicine package 81 of In the second determination mode, when the medicine package code 832 is read from the medicine package 81 of the resident and any one medicine package 81 of the plurality of medicine packages 81 having the same dosing time, It is determined that the reading of the medicine package code 832 has been completed for the plurality of medicine packages 81 having the same dosing time. That is, when there are a plurality of medicine packages 81 corresponding to the same taking time for the same resident, the medicine package code 832 needs to be read from all the medicine packages 81 in the first determination mode. In the second determination mode, the medicine package code 832 may be read from any one medicine package 81.
[配薬時照合処理]
以下、図39を参照しつつ、前記配薬時照合処理(図20参照)の他の例について説明する。本実施形態に係る配薬時照合処理では、前記ステップS81で前記配薬開始操作が行われていない場合と判断された場合に、処理がステップS91に移行する。
[Drug matching process]
Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 39, another example of the medicine distribution matching process (see FIG. 20) will be described. In the medicine distribution matching process according to the present embodiment, when it is determined in step S81 that the case where the medicine distribution start operation has not been performed, the process proceeds to step S91.
<ステップS91>
前記ステップS91において、前記制御部5は、前記調剤支援装置1から出力される配薬データの入力タイミングが到来したか否かを判断する。前記配薬データは、前述したように、一の服用者が服用する薬品が服用時期ごとに分包された複数の前記薬包81の分包内容を含む配薬データである。換言すれば、前記配薬データは、服用者が服用する薬品を服用時期ごとに一又は複数の前記薬包81に分包する前記薬品分包処理の内容を示すデータである。
<Step S91>
In step S91, the control unit 5 determines whether or not the input timing of the medicine distribution data output from the dispensing support device 1 has come. As described above, the medicine distribution data is medicine distribution data including the contents of the plurality of medicine packages 81 into which the medicine to be taken by one doser is packaged at each time of the medicine administration. In other words, the drug distribution data is data indicating the contents of the medicine packaging process in which the medicine taken by the user is divided into one or more medicine packages 81 every time the medicine is taken.
具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7などを用いて、前記配薬コード831又は前記配薬コード831A〜831Cが読み取られた場合に、前記配薬データの入力タイミングであると判断する。ここで、前記配薬データの入力タイミングが到来していないと判断されると(S91:No側)、処理は前記ステップS81に戻る。また、前記配薬データの入力タイミングが到来したと判断されると(S91:Yes側)、処理はステップS92に移行する。
Specifically, when the drug delivery code 831 or the drug delivery codes 831A to 831C are read using the mobile terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 or the like, the control unit 51 inputs the drug delivery data. It is determined that it is timing. Here, if it is determined that the input timing of the drug distribution data has not arrived (S91: No side), the process returns to the step S81. If it is determined that the input timing of the drug distribution data has arrived (S91: Yes side), the process proceeds to step S92.
<ステップS92>
ステップS92において、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データを取得するための処理を実行する。ここに、係る処理は、前記制御部51の配薬データ入力部514によって実行され、前記配薬データ入力部514が本発明における取得処理部の一例である。
<Step S92>
In step S92, the control unit 51 executes a process for acquiring the drug distribution data. Here, the processing is executed by the medicine distribution data input unit 514 of the control unit 51, and the medicine distribution data input unit 514 is an example of the acquisition processing unit in the present invention.
具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記携帯端末6又は前記読取端末7などを用いて読み取られた前記配薬コード831又は前記配薬コード831A〜831Cを前記配薬データとして取得し、前記データ記憶部52の配薬データ記憶部523に記憶する。これにより、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データに基づいて、前記入居者が各服用時期に服用するべき前記薬包81の数及び種類などを認識することが可能である。
Specifically, the control unit 51 acquires, as the medication data, the medication code 831 or the medication codes 831A to 831C read using the portable terminal 6 or the reading terminal 7 or the like, and the data It is stored in the drug distribution data storage unit 523 of the storage unit 52. Thereby, the control unit 51 can recognize the number, type, and the like of the medicine package 81 to be taken by the resident at each taking time based on the drug distribution data.
より具体的に、前記配薬コード831には、複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する前記薬品分包処理の内容を示す前記配薬データが纏めて含まれている。そのため、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cのいずれか一つの前記検薬包810から前記配薬コード831が読み取られることにより、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する前記配薬データが纏めて取得されることになる。
More specifically, the medicine distribution code 831 collectively includes the medicine distribution data indicating the contents of the medicine packing process corresponding to the plurality of medicine pack sheets 81A to 81C. Therefore, the medicine distribution data corresponding to the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C are collectively acquired by reading the medicine distribution code 831 from the test medicine package 810 of any one of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C. It will be
一方、前記配薬コード831A〜831Cには、複数の前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する前記薬品分包処理の内容を示す前記配薬データが個別に含まれている。そのため、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々の前記検薬包810から前記配薬コード831A〜831Cが読み取られることにより、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cに対応する前記配薬データが個別に取得されることになる。
On the other hand, the drug distribution data 831A to 831C individually include the drug distribution data indicating the contents of the medicine package processing corresponding to the plurality of medicine package sheets 81A to 81C. Therefore, the medicine distribution data corresponding to the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C are individually acquired by reading the medicine distribution codes 831A to 831C from the test packet packages 810 of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C. It will be.
このように、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの配薬データを、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cのいずれか一つの前記検薬包810から取得する運用と、前記薬包シート81A〜81C各々の前記検薬包810から取得する運用とが実現可能である。
Thus, in the medicine distribution support system 100, an operation of acquiring medicine distribution data of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C from any one of the medicine package sheets 810 of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C and the medicine An operation of acquiring each of the package sheets 81A to 81C from the test packet package 810 can be realized.
なお、前記薬包シート81A及び81Bの前記検薬包810の前記配薬コード831に、前記薬包シート81A及び81Bに対応する前記薬品分包処理の内容を示す配薬コードが記憶されており、前記薬包シート81Cの前記検薬包810の前記配薬コード831に、前記薬包シート81Cに対応する前記薬品分包処理の内容を示す配薬コードが記憶されていることも考えられる。この場合、前記配薬支援システム100では、前記薬包シート81A及び81Bのいずれか一方の前記検薬包810の前記配薬コードが読み取られ、前記薬包シート81Cの前記検薬包810の前記配薬コードが読み取られることにより、前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの情報が取得される。
In addition, in the medicine code of the medicine package sheet 810 of the medicine package sheets 81A and 81B, a medicine distribution code indicating contents of the medicine package processing corresponding to the medicine package sheets 81A and 81B is stored. It is also conceivable that the drug distribution code 831 of the test packet package 810 of the drug package sheet 81C stores a drug distribution code corresponding to the drug package sheet 81C and indicating the contents of the medicine packaging process. In this case, in the drug delivery support system 100, the drug delivery code of the test packet package 810 of one of the drug package sheets 81A and 81B is read, and the drug delivery code of the drug delivery package 810 of the drug package sheet 81C is read. Information on the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C is acquired by reading the drug distribution code.
また、予め設定された配薬データ登録開始操作が行われた後、前記薬包81各々から前記薬包データ832が読み取られることにより前記薬包81各々の前記薬包データ832が前記配薬データとして取得されることも考えられる。さらに、前記薬包81各々に当該薬包81のみに対応する前記配薬データが薬包データ832とは別に記憶されており、前記薬包81各々から前記配薬データが読み取られることによって前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの配薬データが取得されることも考えられる。なお、前記配薬データの取得方法は、これらに限られず、例えば一又は複数の入居者に対応する前記薬包シート81A〜81Cの前記配薬データを示す一次元コード又は二次元コードなどのコードが印刷された印刷物から前記コードが読み取られてもよい。
In addition, after the drug distribution data registration start operation set in advance is performed, the medicine package data 832 of each of the medicine packages 81 is read by the medicine package data 832 of each medicine package 81 by reading the medicine package data 832 from each of the medicine packages 81. It is also conceivable to be acquired as Furthermore, the drug distribution data corresponding to only the drug package 81 is stored in each of the drug package 81 separately from the drug package data 832, and the drug distribution data is read from each of the drug package 81 and the drug It is also conceivable that drug distribution data of the package sheets 81A to 81C is acquired. The method of acquiring the drug distribution data is not limited thereto, and, for example, a code such as a one-dimensional code or a two-dimensional code indicating the drug distribution data of the medicine package sheets 81A to 81C corresponding to one or more tenants. The code may be read from a printed matter on which is printed.
<ステップS86>
また、本実施形態に係る配薬時照合処理では、前記ステップS86において予め設定された前記入居者確認画面213が表示された後、ステップS93が実行される。ここに、図41Aは、本実施形態に係る前記入居者確認画面213の一例である。図41Aに示されているように、前記入居者確認画面213には、入居者名の表示領域、服用時期の表示領域、顔画像(写真)の表示領域、入居者ID入力欄、服用時期入力欄、薬包番号入力欄、及びコメント表示領域などが表示されている。前記入居者ID入力欄、前記服用時期入力欄、及び前記薬包番号入力欄では、ユーザー操作による情報の入力を受け付けることが可能である。特に、前記薬包番号入力欄では、前記薬包81の薬包番号の入力が可能である。また、前記入居者確認画面213には、既に読み取られた前記薬包81の薬包番号が表示される表示領域A11、ユーザー操作を受け付ける確認キーK11及び取消キーK12も表示されている。なお、前記薬包81の薬包番号が読み取られるまでの間、前記表示領域A11は空白である。
<Step S86>
In addition, in the dispensing-time verification process according to the present embodiment, after the resident confirmation screen 213 set in advance in the step S86 is displayed, the step S93 is executed. Here, FIG. 41A is an example of the resident confirmation screen 213 according to the present embodiment. As shown in FIG. 41A, in the resident confirmation screen 213, a display area of a resident name, a display area of dosing time, a display area of a face image (photograph), a resident ID input field, dosing time input A column, medicine package number input column, comment display area, etc. are displayed. It is possible to receive input of information by user operation in the resident ID input field, the dose timing input field, and the medicine package number input field. In particular, the medicine package number of the medicine package 81 can be input in the medicine package number input field. Further, on the resident confirmation screen 213, a display area A11 in which the medicine package number of the medicine package 81 already read is displayed, a confirmation key K11 for accepting a user operation, and a cancel key K12 are also displayed. The display area A11 is blank until the medicine package number of the medicine package 81 is read.
<ステップS93>
ステップS93において、前記制御部51は前記配薬支援装置5で使用される判定モードとして前記第1判定モードが選択されているか否かを判断する。ここで、前記第1判定モードが選択されていると判断すると(S93:Yes)、処理が後述のステップS101(図40参照)に移行して前記第1判定モードで判定処理が実行される。また、前記第1判定モードが選択されていないと判断すると(S93:No)、処理がステップS94に移行して前記第2判定モードで判定処理が実行される。
<Step S93>
In step S93, the control unit 51 determines whether the first determination mode is selected as the determination mode to be used by the medicine distribution assistance device 5. Here, if it is determined that the first determination mode is selected (S93: Yes), the process proceeds to later-described step S101 (see FIG. 40), and the determination process is executed in the first determination mode. If it is determined that the first determination mode is not selected (S93: No), the process proceeds to step S94, and the determination process is executed in the second determination mode.
また、前記制御部51が、前記ステップS93の実行前に、前記入居者、又は前記薬包81に収容されている薬品の種類などについて予め設定された選択条件に従って前記第1判定モード及び前記第2判定モードを自動的に選択することも考えられる。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS85で選択された入居者が、厳重な薬品の服用管理が必要な入居者として予め設定された特定の入居者であるという選択条件を満たす場合に前記第1判定モードを選択し、前記選択条件を満たさない場合に前記第2判定モードを選択することが考えられる。また、前記制御部51は、前記入居者が服用する予定の薬品が、厳重な服用管理が必要な薬品として予め設定された特定の薬品であるという選択条件を満たす場合に前記第1判定モードを選択し、前記選択条件を満たさない場合に前記第2判定モードを選択することが考えられる。さらに、前記制御部51は、同一の前記入居者の同一の前記服用時期について一つの前記配薬コード831が読み取られていた場合は前記第2判定モードを選択し、同一の前記入居者の同一の前記服用時期について複数の前記配薬コード831A〜831Cなどが読み取られていた場合は前記第1判定モードを選択することが考えられる。なお、前記第1判定モード及び前記第2判定モードが選択できず、予め設定されたいずれか一方の判定モードで判定処理を実行可能な構成も他の実施形態として考えられる。
In addition, before the execution of step S93, the control unit 51 performs the first determination mode and the first determination mode according to a selection condition set in advance for the resident or the type of medicine contained in It is also conceivable to automatically select the two determination modes. For example, when the tenant selected in step S85 is a specific tenant set in advance as a resident who needs strict drug administration, the control unit 51 satisfies the selection condition. It is conceivable to select the first determination mode and to select the second determination mode when the selection condition is not satisfied. Further, the control unit 51 sets the first determination mode in the case where the medicine scheduled to be taken by the resident satisfies the selection condition that the medicine which is predetermined as the medicine requiring strict dose management is prescribed It is conceivable to select and select the second determination mode when the selection condition is not satisfied. Furthermore, the control unit 51 selects the second determination mode when one medicine code 831 is read for the same taking time of the same resident, and the same control for the same resident. It is conceivable to select the first determination mode when a plurality of the drug supply codes 831A to 831C and the like have been read for the dosing timing of. A configuration in which the first determination mode and the second determination mode can not be selected and the determination processing can be executed in any one of the determination modes set in advance is also conceivable as another embodiment.
[第2判定モードの判定処理]
まず、前記制御部51によってステップS94以後で前記第2判定モードの判定処理について説明し、前記ステップS101以降に実行される前記第1判定モードの判定処理については後述する。
[Determination process of second judgment mode]
First, the determination process of the second determination mode will be described by the control unit 51 after step S94, and the determination process of the first determination mode performed after the step S101 will be described later.
<ステップS94>
ステップS94において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記薬包コード832が読み取られたと判断すると(S94:Yes)、処理がステップS941に移行し、前記薬包コード832が読み取られていないと判断された場合には(S94:No)、処理がステップS95に移行する。
<Step S94>
In step S94, the control unit 51 determines whether the medicine package code 832 has been read from the medicine package 81 or not. Here, if it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has been read (S94: Yes), the process proceeds to step S941, and if it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has not been read (S94: No) The process proceeds to step S95.
<ステップS941>
ステップS941において、前記制御部51は、前記ステップS92で取得される前記配薬データと前記薬包81から読み取られる前記薬包コード832とに基づいて、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ一又は複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したか否かを判定する。具体的に、ここでは前記第2判定モードが選択されている。そのため、前記制御部51は、一つの前記薬包81から読み取られた前記薬包コード832が、現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれる場合に、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ一又は複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したと判定する。
<Step S941>
In step S941, the control unit 51 determines whether the tenant and the dose timing are the same, based on the medicine distribution data acquired in step S92 and the medicine package code 832 read from the medicine package 81. It is determined whether the reading of the medicine package code 832 has been completed for a plurality of medicine packages 81. Specifically, the second determination mode is selected here. Therefore, when the medicine package code 832 read from one medicine package 81 is included in the medicine distribution data corresponding to the currently selected resident and the time of taking the medicine, the control unit 51 It is determined that the reading of the medicine package code 832 has been completed for the patient and the medicine package 81 having the same dose timing.
即ち、前記ステップS941では、同一の前記入居者について同一の前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81が複数存在する場合、そのいずれか一つの前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られたか否かが判断される。例えば、前記薬包81から読み取られた前記薬包コード832の前記薬包番号が、前記配薬データのうち現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81の前記薬包番号に含まれるか否かが判断される。そして、前記ステップS941において、前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したと判断されると(S941:Yes)、処理がステップS942に移行する。なお、前記ステップS941で、前記薬包コード832が前記配薬データに含まれていないと判断された場合には(S941:No)、例えばエラーメッセージ等が表示された後、処理が前記ステップS94に戻される。また、前記ステップS87で説明したように、前記ステップS941においても、前記制御部51が、同一の入居者及び服用時期について同一の前記薬包番号が読み取られた場合に重複投与である旨を報知することが考えられる。
That is, in the step S941, if there are a plurality of medicine packages 81 corresponding to the same dosing time for the same resident, is the medicine package code 832 read from any one of the medicine packages 81? It is judged whether or not. For example, the medicine package number of the medicine package code 832 read from the medicine package 81 is the medicine of the medicine package 81 corresponding to the tenant currently selected from the medicine distribution data and the dosing time. It is determined whether or not it is included in the package number. When it is determined in step S941 that reading of the medicine package code 832 is completed (S941: Yes), the process proceeds to step S942. If it is determined in step S941 that the medicine package code 832 is not included in the drug distribution data (S941: No), for example, an error message or the like is displayed, and then the process proceeds to step S94. Will be returned to Further, as described in the step S87, also in the step S941, the control unit 51 notifies that the medicine package number is the same when the same package number is read for the same resident and taking time. It is possible to do.
<ステップS942>
ステップS942において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に投薬開始メッセージを表示させることにより、前記ステップS941における判定結果を報知する。なお、係る処理は、前記制御部51の表示制御部511によって実行され、係る処理を実行するときの前記表示制御部511が報知処理部の一例である。
<Step S942>
In step S 942, the control unit 51 notifies the determination result in step S 941 by displaying a medication start message on the resident confirmation screen 213. The processing is executed by the display control unit 511 of the control unit 51, and the display control unit 511 when executing the processing is an example of a notification processing unit.
ここに、図42は、前記投薬開始メッセージが表示されるときの前記入居者確認画面213の一例を示す図である。図42に示されるように、前記入居者確認画面213には、前記投薬開始メッセージとして「お薬を投薬して下さい。」の文字が表示される。また、前記入居者確認画面213には、現在の服用対象となっている前記入居者及び前記服用時期について服用されるべき前記薬包81の数を示すメッセージとして「2種類の薬包があります。」の文字も表示される。これにより、前記入居者が一回の前記服用時期に複数の前記薬包81の薬品を服用する必要がある場合に、前記薬包81の数が入居者又は配薬担当者などに報知されるため、複数の前記薬包81の服用漏れが抑制される。なお、前記入居者確認画面213に、前記投薬開始メッセージと共に前記服用時期に服用する必要のある一又は複数の前記薬包81の薬包番号が表示されてもよい。
FIG. 42 is a diagram showing an example of the resident confirmation screen 213 when the medication start message is displayed. As shown in FIG. 42, on the resident confirmation screen 213, the characters “Please dispense medicine.” Are displayed as the medication start message. Further, the resident confirmation screen 213 has “two types of medicine packages as a message indicating the number of the medicine package 81 to be taken for the current accommodation subject and the taking time for the administration. The letter "is also displayed. Thereby, when the resident needs to take a plurality of medicines of the medicine package 81 at the time of one taking of the medicine, the number of the medicine package 81 is notified to the resident or the person in charge of medicine distribution, etc. Therefore, the dose leakage of the plurality of medicine packages 81 is suppressed. In addition, on the resident confirmation screen 213, the medicine package number of the one or more medicine packages 81 which need to be taken at the time of taking the medicine may be displayed together with the medication start message.
また、図42に示されているように、前記投薬開始メッセージが表示される際、前記入居者確認画面213には、確認キーK21、取消キーK22、及び戻るキーK23が表示されている。そして、前記確認キーK21が操作されると、処理が前記ステップS943に移行する。一方、前記取消キーK22が操作されると、処理が前記ステップS84に戻されて前記入居者の再選択が可能となる。なお、前記戻るキーK23が操作されると、処理は、処理が前記ステップS86に戻され、前記入居者確認画面213が前記薬包コード832の読取前の状態で表示される。
Further, as shown in FIG. 42, when the medication start message is displayed, the resident confirmation screen 213 displays a confirmation key K21, a cancel key K22, and a return key K23. Then, when the confirmation key K21 is operated, the process proceeds to the step S943. On the other hand, when the cancel key K22 is operated, the process is returned to the step S84, and the tenant can be reselected. When the return key K23 is operated, the process returns to the step S86, and the resident confirmation screen 213 is displayed in a state before the medicine package code 832 is read.
<ステップS943>
前記ステップS943では、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データに関連付けて、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する全ての薬品の配薬結果として「服薬完了」が記録される。
<Step S943>
In the step S943, in relation to the drug distribution data stored in the drug distribution data storage unit 523, distribution of all the medicines corresponding to the tenant and the dose timing displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 As medication result "completion of medication" is recorded.
<ステップS95>
また、ステップS95において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている前記確認キーK11の操作が行われた否かを判断する。ここで、前記確認キーK11が操作されたと判断すると(S95:Yes)、処理は前記ステップS881に移行し、前記確認キーK812が操作されていない場合には(S95:No)、処理が前記ステップS89に移行する。即ち、本実施形態に係る前記入居者確認画面213では、前記第2実施形態における前記未服用キーに代えて前記確認キーK11が表示されている。
<Step S95>
In step S95, the control unit 51 determines whether the operation of the confirmation key K11 displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 has been performed. Here, if it is determined that the confirmation key K11 has been operated (S95: Yes), the process proceeds to the step S881. If the confirmation key K812 has not been operated (S95: No), the process proceeds to the step Move to S89. That is, on the resident confirmation screen 213 according to the present embodiment, the confirmation key K11 is displayed in place of the untaken key in the second embodiment.
<ステップS881>
前記ステップS881では、前記制御部51が、予め設定された確認メッセージ等を含むポップアップ画面224を、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部に表示させる。ここに、図43は、前記ポップアップ画面224の一例を示す図である。図43に示されているように、前記ポップアップ画面224には、前記確認メッセージとして、前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81のうち既に前記薬包コード832が読み取られた前記薬包81の数に不足が生じていること、前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81の数、及び前記薬包コード832がまだ読み取られていない前記薬包81を未服用として処理するか否かの確認メッセージなどが表示されている。
<Step S881>
In the step S881, the control unit 51 causes the display unit of the display device 54 or the portable terminal 6 to display a pop-up screen 224 including a confirmation message and the like set in advance. Here, FIG. 43 is a view showing an example of the pop-up screen 224. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 43, the pop-up screen 224 displays, as the confirmation message, the medicine for which the medicine package code 832 has already been read out of the medicine package 81 corresponding to the tenant and the taking time. Treat the number of packets 81 as insufficient, the number of the drug packages 81 corresponding to the resident and the dosing time, and the drug package 81 for which the drug package code 832 has not been read yet A confirmation message of whether or not to be displayed is displayed.
また、前記ポップアップ画面224には、肯定キーK31及び否定キーK32が表示されている。そして、前記制御部51は、前記肯定キーK31が操作されると、現在の服用対象として選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する全ての薬品の配薬結果として未服用完了及び未服用の理由を入力するための前記未服薬入力画面214(図28参照)が表示され、前記第2実施形態と同様に処理される。即ち、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者及び前記服用時期の全体としての服用結果は「未服用」となる。一方、前記否定キーK32が操作されると、処理が前記ステップS86に戻され、前記入居者確認画面213が前記確認キーK11の操作前の状態で表示される。
Further, on the pop-up screen 224, a positive key K31 and a negative key K32 are displayed. Then, when the affirmation key K31 is operated, the control unit 51 has not completed taking and not taking as a result of the dispensing of all the medicines corresponding to the tenant and the taking time selected as the current taking target. The non-drug input screen 214 (see FIG. 28) for inputting the reason for taking is displayed and processed in the same manner as the second embodiment. That is, the tenant and the dosing result as a whole of the dosing time displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 are "not yet taken". On the other hand, when the negative key K32 is operated, the process is returned to the step S86, and the resident confirmation screen 213 is displayed in a state before the operation of the confirmation key K11.
[第1判定モードの判定処理]
続いて、図40を参照しつつ、前記制御部51によって前記ステップS101以降で実行される第1判定モードの判定処理について説明する。
[Determination process of first determination mode]
Subsequently, the determination process of the first determination mode performed by the control unit 51 after the step S101 will be described with reference to FIG.
<ステップS101>
ステップS101において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、前記薬包コード832が読み取られたと判断すると(S101:Yes)、処理がステップS102に移行し、前記薬包コード832が読み取られていないと判断された場合には(S101:No)、処理がステップS104に移行する。
<Step S101>
In step S101, the control unit 51 determines whether the medicine package code 832 has been read from the medicine package 81 or not. Here, if it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has been read (S101: Yes), the process proceeds to step S102, and if it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has not been read (S101: No) The process proceeds to step S104.
前記薬包コード832が読み取られた場合、前記制御部51は、続くステップS102〜S103において、前記ステップS92で取得される前記配薬データと前記薬包81から読み取られる前記薬包コード832とに基づいて、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ一又は複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したか否かを判定する。具体的に、ここでは前記第1判定モードが選択されている。そのため、前記制御部51は、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ全ての前記薬包81から個別に前記薬包コード832が読み取られた場合に、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ一又は複数の前記薬包81について前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了したと判定する。
When the medicine package code 832 is read, in the subsequent steps S102 to S103, the control unit 51 uses the medicine distribution data acquired in the step S92 and the medicine package code 832 read from the medicine package 81. Based on the determination, it is determined whether the reading of the medicine package code 832 has been completed for the patient and the one or more medicine packages 81 having the same dosing time. Specifically, the first determination mode is selected here. Therefore, when the medicine package code 832 is individually read from the medicine package 81 having the same time as the resident and the time for taking the medicine, the control unit 51 determines one or more of the tenant and the time for taking the medicine. It is determined that reading of the medicine package code 832 has been completed for the medicine package 81 of
<ステップS102>
具体的に、ステップS102において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包81から読み取られた前記薬包コード832が、現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれるか否かを判定する。例えば、前記薬包81から読み取られた前記薬包コード832の前記薬包番号が、前記配薬データのうち現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81の前記薬包番号に含まれるか否かが判断される。ここで、前記薬包コード832が現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれる場合、前記制御部51は、前記薬包コード832に対応する前記薬包81の薬包番号を読み取り済みの薬包番号として記録し、前記表示領域A11に前記薬包コード832に含まれる前記薬包番号を表示させる。その後、処理は前記ステップS103に移行する。なお、前記薬包コード832が現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれない場合は、例えばエラーメッセージ等が表示された後、処理が前記ステップS101に戻される。また、前記ステップS87で説明したように、前記ステップS102においても、前記制御部51が、同一の入居者及び服用時期について同一の前記薬包番号が読み取られた場合に重複投与である旨を報知することが考えられる。
<Step S102>
Specifically, in step S102, the control unit 51 causes the medicine package code 832 read from the medicine package 81 to be included in the medicine distribution data corresponding to the currently-selected resident and the dosing time. It is determined whether the For example, the medicine package number of the medicine package code 832 read from the medicine package 81 is the medicine of the medicine package 81 corresponding to the tenant currently selected from the medicine distribution data and the dosing time. It is determined whether or not it is included in the package number. Here, when the medicine package code 832 is included in the drug distribution data corresponding to the currently selected resident and the dosing time, the control unit 51 determines the medicine package corresponding to the medicine package code 832. The medicine package number 81 is recorded as a read medicine package number, and the medicine package number included in the medicine package code 832 is displayed on the display area A11. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S103. If the medicine package code 832 is not included in the drug distribution data corresponding to the currently selected resident and the dosing period, an error message or the like is displayed, for example, and then the process proceeds to step S101. Will be returned. Further, as described in the step S87, also in the step S102, the control unit 51 notifies that the medicine package number is the same when the medicine package number is read for the same resident and taking time. It is possible to do.
<ステップS103>
ステップS103において、前記制御部51は、現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する全ての前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られたか否かを判断する。ここで、現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する全ての前記薬包81の前記薬包コード832の読み取りが完了していないと判断されると(S103:No側)、処理は前記ステップS101に戻される。
<Step S103>
In step S103, the control unit 51 determines whether the medicine package code 832 has been read from the medicine package 81 corresponding to the currently selected resident and the dosing time. Here, if it is determined that reading of the medicine package code 832 of the medicine package 81 corresponding to the currently selected resident and all the medicine packages 81 corresponding to the dosing time has not been completed (S103: No side), processing Are returned to step S101.
一方、全ての前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られたと判断されると(S103:Yes側)、処理は前記ステップS942に移行する。これにより、前記ステップS942では、前記入居者確認画面213に前記服薬開始メッセージが表示される。そして、前記ステップS943では、前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶されている前記配薬データに関連付けて、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する全ての薬品の配薬結果として「服薬完了」が記録される。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has been read from all the medicine packages 81 (S103: Yes side), the process proceeds to the step S942. As a result, in step S 942, the medication start message is displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213. Then, in the step S943, in association with the drug distribution data stored in the drug distribution data storage unit 523, all the medicines corresponding to the tenant and the dosing time displayed on the tenant confirmation screen 213 As a result of drug delivery, “completion of medication” is recorded.
<ステップS104>
また、ステップS104において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に表示されている前記確認キーK11の操作が行われた否かを判断する。ここで、前記確認キーK11が操作されたと判断すると(S104:Yes)、処理は前記ステップS881に移行し、前記確認キーK11が操作されていない場合には(S104:No)、処理が前記ステップS106に移行する。
<Step S104>
In step S104, the control unit 51 determines whether the operation of the confirmation key K11 displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 has been performed. Here, if it is determined that the confirmation key K11 has been operated (S104: Yes), the process proceeds to the step S881. If the confirmation key K11 has not been operated (S104: No), the process proceeds to the step It transfers to S106.
なお、前記ステップS881では、前記制御部51が、前記ポップアップ画面224を前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部に表示させる。そして、前記制御部51は、前記確認キーK31が操作されると、現在の服用対象として選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する複数の薬品のうち前記薬包コード832が読み取られていない前記薬包81に対応する薬品を抽出する。そして、前記制御部51は、前記抽出された薬品の配薬結果として未服用完了及び未服用の理由を入力するための前記未服薬入力画面214(図28参照)が表示され、前記第2実施形態と同様に処理される。一方、前記取消キーK32が操作されると、処理が前記ステップS86に戻され、前記入居者確認画面213が前記確認キーK11の操作前の状態で表示される。
In the step S881, the control unit 51 causes the display device 54 or the display unit of the mobile terminal 6 to display the pop-up screen 224. Then, when the confirmation key K31 is operated, the control unit 51 reads the medicine package code 832 out of the tenant selected as the current dose target and the plurality of medicines corresponding to the dose timing. The medicine corresponding to the medicine package 81 not extracted is extracted. Then, the control unit 51 displays the non-drug input screen 214 (refer to FIG. 28) for inputting the non-taking completion and non-taking reason as the dispensing result of the extracted medicine, and the second embodiment is performed. It is processed in the same way as the form. On the other hand, when the cancel key K32 is operated, the process is returned to the step S86, and the resident confirmation screen 213 is displayed in a state before the operation of the confirmation key K11.
<ステップS105>
続いて、ステップS105において、前記制御部51は、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記薬包81のうち、前記ステップS102において記録された読み取り済みの薬包番号に対応する前記薬包81の薬品の配薬結果として「服薬完了」を記録する。このように、前記ステップS105、S881では、前記薬包コード832が読み取られた前記薬包81については配薬結果として「服用完了」が記録され、前記薬包コード832が読み取られなかった前記薬包81については配薬結果として「未服用」が記録される。即ち、前記入居者確認画面213に表示された前記入居者及び前記服用時期の全体としての服用結果は「一部未服用」となる。
<Step S105>
Subsequently, in step S105, the control unit 51 reads the one recorded in the step S102 among the patient and the medicine package 81 corresponding to the dose timing displayed on the patient confirmation screen 213. Record “Drug Ingestion” as the result of dispensing the medicine in the medicine pack 81 corresponding to the medicine pack number. As described above, in the steps S105 and S881, for the medicine package 81 from which the medicine package code 832 has been read, “dosing completion” is recorded as a result of dispensing, and the medicine whose medicine package code 832 has not been read For the package 81, "not yet taken" is recorded as a result of the drug distribution. That is, the tenant and the dosing result as a whole of the dosing time displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 become “partially undosed”.
<ステップS106>
一方、前記確認キーK11が操作されていない場合(S104:No)、続くステップS106において、前記制御部51は、前記薬包コード832の手動入力が行われたか否かを判断する。具体的に、前記操作画面上において、入居者ID、服用時期、及び薬包番号が入力された場合に、前記薬包コード832の手動入力が行われたと判断する。なお、前記入居者ID及び前記服用時期の入力が省略され、前記薬包番号のみが入力される構成も他の実施形態として考えられる。ここで、前記薬包コード832の手動入力が行われたと判断すると(S106:Yes)、処理はステップS107に移行し、前記薬包コード832の手動入力が行われていないと判断すると(S106:No)、処理は前記ステップS89に移行する。
<Step S106>
On the other hand, when the confirmation key K11 is not operated (S104: No), in the subsequent step S106, the control unit 51 determines whether or not the medicine package code 832 has been manually input. Specifically, when the resident ID, the taking time, and the medicine package number are input on the operation screen, it is determined that the medicine package code 832 has been manually input. In addition, the input of the said resident | tenant ID and the said dosing period is abbreviate | omitted, and the structure where only the said medicine package number is input is also considered as another embodiment. Here, when it is determined that the manual input of the medicine package code 832 is performed (S106: Yes), the process proceeds to step S107, and when it is determined that the manual input of the medicine package code 832 is not performed (S106: No), the process proceeds to step S89.
<ステップS107>
ステップS107において、前記制御部51は、手動入力された前記薬包コード832が、現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれるか否かを判定する。ここで、前記薬包コード832が現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれる場合、前記制御部51は、前記薬包コード832に対応する前記薬包81の薬包番号を読み取り済みの薬包番号として記録し、前記表示領域A11に前記薬包コード832に含まれる前記薬包番号を表示させる。その後、処理は前記ステップS103に移行する。なお、前記薬包コード832が現在選択されている前記入居者及び前記服用時期に対応する前記配薬データに含まれない場合は、例えばエラーメッセージ等が表示された後、処理が前記ステップS101に戻される。
<Step S107>
In step S107, the control unit 51 determines whether the medicine package code 832 manually input is included in the medicine distribution data corresponding to the currently selected tenant and the dose timing. Here, when the medicine package code 832 is included in the drug distribution data corresponding to the currently selected resident and the dosing time, the control unit 51 determines the medicine package corresponding to the medicine package code 832. The medicine package number 81 is recorded as a read medicine package number, and the medicine package number included in the medicine package code 832 is displayed on the display area A11. Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S103. If the medicine package code 832 is not included in the drug distribution data corresponding to the currently selected resident and the dosing period, an error message or the like is displayed, for example, and then the process proceeds to step S101. Will be returned.
これにより、前記薬包81に印刷された前記薬包コード832の汚損などにより前記薬包コード832を正常に読み取ることができない場合にも、前記制御部51に、前記薬包81から前記薬包コード832が読み取られた場合と同様の処理を実行させることが可能である。また、この場合には、前記薬包コード832が前記薬包81から読み取られたか否かに関する情報が前記配薬データに関連付けて記録されることも考えられる。
As a result, even when the medicine package code 832 can not be read normally due to contamination or the like of the medicine package code 832 printed on the medicine package 81, the control unit 51 checks the medicine package 81 from the medicine package 81. It is possible to execute the same process as when the code 832 is read. In this case, it is also conceivable that information on whether or not the medicine package code 832 has been read from the medicine package 81 is recorded in association with the drug distribution data.
さらに、図41Aに示されるように、前記入居者確認画面213には、前記配薬データに含まれていない薬包、錠剤、PTPシート(ヒート)、水剤などの予定外薬品を登録するための操作キーK13が表示されている。そして、前記制御部51は、前記操作キーK13が操作されると、前記配薬データとの照合を行うことなく、例えば「予定が存在しない薬品です。続行しますか?」のような前記予定外薬品を登録する旨の確認メッセージなどを表示させる。その後、前記制御部51は、確認メッセージに対する確認操作が行われた場合、図41Bに示されるように、前記入居者確認画面213の表示領域A12に前記予定外薬品の数(包数、錠数、シート数、本数など)を表示させる。なお、前記入居者確認画面213に表示される前記予定外薬品の数は、前記操作キーK13の操作に応じて1ずつ加算される。また、前記制御部51が、前記操作キーK13の操作後に前記予定外薬品の数の入力を受け付けて表示させてもよい。さらに、前記制御部51は、前記予定外薬品の内容として、例えば薬品名及び服用量などの入力を受付可能であることも考えられる。そして、前記制御部51は、前記予定外薬品の数又は前記予定外薬品の内容などを前記配薬データに関連付けて記録する。これにより、前記制御部51は、前記服用履歴表示機能によって、前記予定外薬品の有無及び数などを前記服用結果として表示させることが可能となる。したがって、前記制御部51は、例えば前記入居者が持参薬、他の薬局等から受け取った薬品、OTC医薬品(一般用医薬品)などのように前記薬包番号が付されていない薬品を服用する場合に、その服用の記録を残すことが可能となる。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 41A, in the resident confirmation screen 213, for registering unscheduled medicines such as medicine package, tablets, PTP sheet (heat), liquid medicine and the like not included in the medicine distribution data. The operation key K13 of is displayed. Then, when the operation key K13 is operated, the control unit 51 does not check the drug distribution data, for example, the schedule such as "a drug for which there is no schedule. Do you want to continue?" Display a confirmation message to register external medicine. Thereafter, when a confirmation operation is performed on the confirmation message, the control unit 51 displays the number of unscheduled medicines (the number of packages and the number of tablets) in the display area A12 of the tenant confirmation screen 213 as shown in FIG. , Number of sheets, number of sheets, etc.). The number of the unscheduled medicines displayed on the resident confirmation screen 213 is incremented by one according to the operation of the operation key K13. In addition, the control unit 51 may receive and display the input of the number of unscheduled medicines after the operation of the operation key K13. Furthermore, it is also conceivable that the control unit 51 can receive an input of, for example, a drug name and a dose as the contents of the unscheduled drug. Then, the control unit 51 records the number of the unplanned medicine or the content of the unplanned medicine in association with the drug distribution data. Thereby, the control unit 51 can display the presence, the number, and the like of the unscheduled medicine as the dosing result by the dosing history display function. Therefore, the control unit 51, for example, takes the medicine which the tenant does not have the medicine package number attached thereto, such as a brought medicine, a medicine received from another pharmacy, an OTC medicine (general medicine), etc. It is possible to keep a record of the dose.
以上説明したように、本実施形態に係る前記配薬支援システム100によれば、前記入居者が一回の前記服用時期に服用するべき前記薬包81が複数存在する場合に、その複数の前記薬包81の漏れのない服用を支援することが可能である。
As described above, according to the medicine distribution support system 100 according to the present embodiment, when there are a plurality of medicine packages 81 to be taken by the resident at one taking time of the dose, the plurality of medicine packages 81 It is possible to support the leak-free taking of the medicine package 81.
ところで、前記第1判定モードが選択されている場合、前記配薬時照合処理の前記ステップS881及び前記ステップS105において、一回の服用時期に対応する複数の前記薬包81の一部について配薬結果が服用完了である旨が記録され、残りの前記薬包81については配薬結果が未服用である旨が記録されることがある。そのため、前記制御部51は、前記服用履歴表示機能により、各服用時期に服用される薬品の服用結果として、それらの情報を表示可能であることが考えられる。ここに、図44は、前記服用履歴表示機能によって表示可能な履歴画面225の一例を示す図である。
By the way, when the first determination mode is selected, in the step S881 and the step S105 of the medication matching process, the medicine is dispensed for a part of the plurality of medicine packages 81 corresponding to one dosing timing. It may be recorded that the result is completion of taking, and it may be recorded that the result of drug delivery has not been taken for the remaining medicine package 81. Therefore, it is considered that the control unit 51 can display those pieces of information as the result of taking the medicine taken at each taking time by the taking history display function. FIG. 44 is a diagram showing an example of a history screen 225 that can be displayed by the dose history display function.
図44に示されているように、前記履歴画面225では、入居者各々の服用時期各々の配薬結果及び服用予定が表示されている。また、前記入居者及び前記服用時期のいずれかの組み合わせが選択されると、その組み合わせに対応する配薬結果及び服用予定を示す吹き出し画面226が表示される。具体的に、図44に示されているように、前記吹き出し画面226では、前記配薬結果又は前記服用予定として、前記薬包番号とコメント(効能)と配薬結果とが対応付けられている。例えば、前記薬包番号が「01」の前記薬包81は風邪薬であり、30日の朝食後に服用されていること、前記薬包番号が「02」の前記薬包81は胃薬であり、30日の朝食後に服用されていることが表示されている。また、前記薬包番号が「03」の前記薬包81は咳止めであり、30日の朝食後に未服用であったことが表示されている。
As shown in FIG. 44, on the history screen 225, the drug distribution results and the dosing schedule for each dosing period of each resident are displayed. In addition, when any combination of the resident and the dosing period is selected, a balloon screen 226 indicating the drug distribution result and the dosing schedule corresponding to the combination is displayed. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 44, on the balloon screen 226, the medicine package number, the comment (efficacy), and the drug distribution result are associated as the drug distribution result or the dose schedule. . For example, the medicine package 81 having the medicine package number “01” is a cold medicine, and is taken after breakfast for 30 days, and the medicine package 81 having the medicine package number “02” is a stomach medicine, It is indicated that it is taken after breakfast for 30 days. In addition, it is indicated that the medicine package 81 whose medicine package number is "03" is a cough medicine and has not been taken after breakfast for 30 days.
なお、前記薬包81各々に分包されている薬品の種類及び効能などが前記配薬データに含まれている場合、前記制御部51は、前記コメントの内容が前記配薬データに基づいて判断可能である。また、前記薬包81各々に分包されている薬品の種類及び効能などが前記配薬データに含まれていない場合であっても、前記制御部51は、ユーザー操作に応じて前記薬包81各々の前記薬包番号に対応する前記コメントを予め任意に登録することが可能である。ここに、図45は、前記入居者ごとの前記配薬データを確認するための服用予定登録画面227の一例を示す図である。前記服用予定登録画面227は、前記配薬支援装置5及び前記携帯端末6に対するユーザー操作により表示対象の前記入居者が選択された場合に、前記表示装置54又は前記携帯端末6の表示部に表示される。
In the case where the medicine distribution data includes the type and efficacy of medicines packaged in each medicine package 81, the control unit 51 determines the content of the comment based on the medicine distribution data. It is possible. In addition, even if the medicine distribution data does not include the type and effect of the medicines packaged in each medicine package 81, the control unit 51 can change the medicine package 81 according to the user operation. The comment corresponding to each medicine package number can be arbitrarily registered in advance. Here, FIG. 45 is a view showing an example of a dosing schedule registration screen 227 for confirming the drug supply data for each resident. The dose schedule registration screen 227 is displayed on the display unit 54 or the display unit of the mobile terminal 6 when the tenant to be displayed is selected by the user operation on the drug distribution support device 5 and the mobile terminal 6. Be done.
図45に示されているように、前記服用予定登録画面227では、前記配薬データに基づいて、前記薬包番号、前記薬品種別、服用予定日、及び外泊予定などの一覧が前記入居者の服用予定として表示される。また、前記服用予定登録画面227には、前記入居者の服用予定を編集するための操作キーとして操作キーK41〜K43が表示されている。そして、前記制御部51は、前記操作キーK41〜K43の操作に応じて、前記入居者の服用予定の削除、新規登録、変更などの各種の処理を実行するための操作画面を表示させ、前記操作画面における操作に従って前記各種の処理を実行する。また、前記制御部51は、前記服用予定登録画面227において、前記薬包番号各々に対応する前記コメントを、ユーザーによるテキスト入力操作などに応じて任意に登録することが可能である。
As shown in FIG. 45, on the dosing schedule registration screen 227, based on the drug distribution data, a list of the medicine package number, the medicine type, the scheduled dosing date, and the plan for staying overnight is provided by the resident It will be displayed as a dose schedule. Further, on the dose schedule registration screen 227, operation keys K41 to K43 are displayed as operation keys for editing the dose schedule of the resident. Then, in response to the operation of the operation keys K41 to K43, the control unit 51 displays an operation screen for executing various processes such as deletion, new registration, and change of the dose schedule of the resident. The various processes are executed in accordance with the operation on the operation screen. Further, the control unit 51 can arbitrarily register the comments corresponding to the medicine package numbers in the dose schedule registration screen 227 in accordance with a text input operation or the like by the user.
なお、前記入居者及び前記服用時期が同じ複数の前記薬包81を識別するために前記薬包81に前記薬包番号が付されている場合を例に挙げて説明した。一方、前記ステップS941及び前記ステップS103において前記服用者及び前記服用時期が同じ前記薬包81の数と同数の前記薬包コードが読み取られたか否かが判定される構成であれば、前記配薬コード831、831A〜831C、及び前記薬包コード832などに前記薬包番号が含まれていなくてもよい。また、前記配薬コード831、831A〜831C、及び前記薬包コード832などに前記薬包番号が含まれている場合であっても、前記薬包番号を考慮せずに、前記ステップS941及び前記ステップS103において前記服用者及び前記服用時期が同じ前記薬包81の数と同数の前記薬包コードが読み取られたか否かが判定されてもよい。
The case where the medicine package number is attached to the medicine package 81 has been described as an example in order to identify the resident and the plurality of medicine packages 81 having the same dosing time. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S941 and step S103 whether or not the medicine package codes have been read in the same number as that of the doser and the medicine package 81 at the same time of administration, the drug supply The medicine package number may not be included in the codes 831, 831A to 831C, the medicine package code 832, and the like. Further, even if the medicine package number is included in the drug distribution codes 831, 831A to 831C, the medicine package code 832, etc., the step S941 and the step S941 and the medicine package number are not taken into consideration. In step S103, it may be determined whether or not the medicine package codes have been read as many as the number of the medicine packages 81 with the same dose timing and the doser.
[新規登録機能]
ところで、前記配薬支援システム10では、前記配薬支援装置5において、前記調剤支援装置1から出力された前記配薬データに基づく各種の処理が実行される。一方、前記配薬支援装置5が、前記配薬データを新規に登録する新規登録機能を有することが考えられる。
[New registration function]
By the way, in the medicine distribution support system 10, various processes based on the medicine distribution data output from the dispensing support apparatus 1 are executed in the medicine distribution support apparatus 5. On the other hand, it is conceivable that the medicine distribution support device 5 has a new registration function for newly registering the medicine distribution data.
より具体的に、前記制御部51は、前記配薬データを新規に登録するための新規登録処理を実行することにより前記新規登録機能を具現する。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記服用予定登録画面227の前記操作キーK42の操作に応じて前記新規登録処理を実行する。また、前記制御部51は、前記入居者一覧画面211(図23等)において、前記入居者が選択された場合に、前記入居者に対応する前記配薬データが存在しない場合に、前記新規登録処理を実行することも考えられる。なお、前記制御部51は、前記初期画面210に前記新規登録処理を実行するための操作キーを表示させ、前記操作キーの操作に応じて前記新規登録処理を実行してもよい。
More specifically, the control unit 51 implements the new registration function by executing a new registration process for newly registering the drug distribution data. For example, the control unit 51 executes the new registration process in response to the operation of the operation key K42 on the dose schedule registration screen 227. Further, when the tenant is selected on the tenant list screen 211 (FIG. 23, etc.), the control unit 51 performs the new registration when the medicine distribution data corresponding to the tenant does not exist It is also conceivable to execute the process. The control unit 51 may display an operation key for executing the new registration process on the initial screen 210 and execute the new registration process according to the operation of the operation key.
そして、前記制御部51は、前記新規登録処理において、前記配薬データを登録するための新規登録画面301を表示させる。ここに、図46は、前記新規登録画面301の一例を示す図である。図46に示すように、前記新規登録画面301には、登録対象となる前記薬包81に対応する前記配薬データに必要な各種の情報を入力するための入力インターフェースが表示される。例えば、図46に示すように、前記新規登録画面301では、登録対象の前記薬包81に対応する入居者識別情報(入居者ID、入居者名)、薬包番号、薬包の説明、服用日数、服用開始日、服用終了日、隔日、曜日指定、服用時期、服用開始時期、服用終了時期などが入力可能である。なお、図46に示す例では、既に前記入居者が選択された状態を示しているが、前記新規登録画面301において入居者が入力又は選択されてもよい。
Then, the control unit 51 displays a new registration screen 301 for registering the medicine distribution data in the new registration process. Here, FIG. 46 is a view showing an example of the new registration screen 301. As shown in FIG. 46, the new registration screen 301 displays an input interface for inputting various types of information necessary for the medicine distribution data corresponding to the medicine package 81 to be registered. For example, as shown in FIG. 46, on the new registration screen 301, resident identification information (resident ID, resident name) corresponding to the medicine package 81 to be registered, medicine package number, medicine package description, medication The number of days, dosing start date, dosing end date, alternate day, designated day of the week, dosing timing, dosing start timing, dosing end timing, etc. can be input. In the example shown in FIG. 46, the tenant is already selected, but the tenant may be input or selected on the new registration screen 301.
なお、前記薬包の説明の入力欄には、前記薬包81に収容されている薬品の説明が入力される。前記新規登録画面301では、1回分の服用時期に対応する前記薬包81の配薬データを登録することも可能であるが、複数回分の服用時期に対応する前記薬包81の配薬データを登録することも可能である。
In the input column of the description of the medicine package, the explanation of the medicine contained in the medicine package 81 is input. In the new registration screen 301, it is possible to register drug distribution data of the medicine package 81 corresponding to a single dose timing, but distribution data of the medicine package 81 corresponding to a plurality of dose timings. It is also possible to register.
具体的に、前記新規登録画面301の左側では、前記服用日数の入力欄において、予め設定された服用日数(3日分、7日分、14日分)からの選択、又は任意の数値入力によって前記薬包81の服用日数が入力される。また、前記服用開始日の入力欄には、前記薬包81の服用開始日が入力される。例えば、前記服用開始日の入力時には、カレンダーが表示されて前記カレンダーから任意に選択可能である。前記服用終了日の入力欄には、前記服用開始日から前記服用日数の経過後の日付が入力される。なお、前記隔日、前記曜日指定などが選択された場合には、前記服用終了日が、前記隔日及び前記曜日指定を考慮して計算された服用終了日の日付が入力される。前記隔日の入力欄では、服用間隔及び連続服用期間などが入力可能である。また、前記曜日指定の入力欄では、服用曜日が指定可能である。
Specifically, on the left side of the new registration screen 301, selection from the number of days (3 days, 7 days, 14 days) set in advance is made in the input field of the number of days taken, or by arbitrary numerical value input The number of days taken for the medicine package 81 is input. Moreover, the dosing start date of the medicine package 81 is input in the entry field of the dosing start date. For example, at the time of input of the dose start date, a calendar is displayed and can be arbitrarily selected from the calendar. The date after the lapse of the dosing days from the dosing start date is entered in the entry field of the dosing end date. In addition, when the alternate day, the designated day of the week, or the like is selected, the date on which the dose end date is calculated taking into account the alternate day and the designated day is input. In the alternate-day input field, it is possible to input a dosing interval, a continuous dosing period, and the like. Further, in the input column for specifying the day of the week, it is possible to specify the day of taking the medication.
また、前記新規登録画面301の右側では、前記服用時期の入力欄において、前記薬包81を服用する服用時期の選択操作が行われる。前記服用時期の入力欄では、予め設定された服用時期がグレーアウトで初期表示されており、選択された場合に前記グレーアウトとは異なる白色又は緑色などの任意の色に変更される。また、前記服用開始時期の入力欄には、前記服用開始日における服用開始時期が入力され、前記服用終了時期の入力欄には、前記服用終了日における服用終了時期が入力される。例えば、前記制御部51は、前記服用時期の入力欄で選択されている服用時期のうち1日における最初の服用時期を前記服用開始時期として自動的に入力し、1日における最後の服用時期を前記服用終了時期として自動的に入力する。また、前記服用開始時期の入力欄が選択された場合、前記制御部51は、前記服用時期の入力欄で選択されている服用時期の一覧を表示させ、その服用時期のいずれかの選択操作によって前記服用開始時期を変更する。さらに、前記制御部51は、前記服用開始時期の変更に応じて、前記服用時期の入力欄で選択されている前記服用時期のうち前記服用開始時期の一つ前の時期の前記服用時期を前記服用終了時期として自動的に変更する。
Further, on the right side of the new registration screen 301, in the input field for the dosing time, a selection operation of the dosing time for taking the medicine package 81 is performed. In the entry column of the dosing period, a preset dosing period is initially displayed in gray out, and when selected, it is changed to any color such as white or green different from the gray out. Further, the dosing start time on the dosing start date is input in the dosing start time input field, and the dosing end time on the dosing end date is input in the dosing end time input field. For example, the control unit 51 automatically inputs, as the dose start time, the first dose time in one day among the dose times selected in the dose period input field, and the last dose time in one day is It is automatically input as the said dosing end time. In addition, when the input field for the dosing start time is selected, the control unit 51 displays a list of the dosing times selected in the dosing column for the dosing time, and one of the dosing operations is selected. Change the dosing start time. Furthermore, the control unit 51 is configured to, according to a change in the dose start time, select the dose time before the dose start time from the dose times selected in the input box for the dose time. It changes automatically as the taking end time.
そして、前記制御部51は、前記新規登録画面301の入力が終了し、登録操作が行われた場合に、前記新規登録画面301の入力内容を前記配薬データとして前記配薬データ記憶部523に記憶させる。このように構成された前記配薬支援システム10では、前記配薬支援装置5において、前記配薬データを新規に登録することが可能であり、持参薬、他の薬局の薬、OTC医薬品などについても前記配薬支援装置5で管理することが可能となる。
Then, when the input of the new registration screen 301 is completed and the registration operation is performed, the control unit 51 uses the input contents of the new registration screen 301 as the medicine distribution data in the medicine distribution data storage unit 523. Remember. In the medicine distribution support system 10 configured as described above, the medicine distribution support device 5 can newly register the medicine distribution data, and it is possible to take a drug, medicine of another pharmacy, OTC medicine, etc. Can be managed by the medicine distribution support device 5 as well.