JP6493721B2 - Light source optical device and projector - Google Patents
Light source optical device and projector Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6493721B2 JP6493721B2 JP2014059531A JP2014059531A JP6493721B2 JP 6493721 B2 JP6493721 B2 JP 6493721B2 JP 2014059531 A JP2014059531 A JP 2014059531A JP 2014059531 A JP2014059531 A JP 2014059531A JP 6493721 B2 JP6493721 B2 JP 6493721B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light
- light source
- lens
- incident
- optical system
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Projection Apparatus (AREA)
- Non-Portable Lighting Devices Or Systems Thereof (AREA)
- Transforming Electric Information Into Light Information (AREA)
Description
本発明は、マイクロレンズアレイを用いて光源光を表示素子に照射する光源光学装置及びこの光源光学装置を備えたプロジェクタに関する。 The present invention relates to a light source optical device that irradiates a display element with light source light using a microlens array and a projector including the light source optical device.
今日、パーソナルコンピュータの画面やビデオ画像、さらにメモリカード等に記憶されている画像データによる画像等をスクリーンに投影する画像投影装置としてのデータプロジェクタが会議等においても用いられて多用されるようになっている。このようなプロジェクタでは、良好な携帯性を備えると共に明るい室内での画像投影が要求され、従来、高輝度の放電ランプを光源とするものが主流であったが、近年、省電力、高寿命、高輝度のレーザーダイオードを用いたプロジェクタの提案がなされている。 2. Description of the Related Art Today, data projectors as image projection devices for projecting personal computer screens, video images, and images based on image data stored in a memory card or the like onto a screen are also frequently used in conferences and the like. ing. In such projectors, image projection in a bright room is required with good portability. Conventionally, projectors using a high-intensity discharge lamp as the light source have been mainstream, but in recent years, power saving, long life, Projectors using high-intensity laser diodes have been proposed.
そして、プロジェクタの小型軽量化や光学系の簡素化を促進するため、DMD(デジタルマイクロミラーデバイス)等の表示素子に光源光を照射するに際して、マイクロレンズアレイと照明レンズを用いて光源光を均一化することにより表示素子に照射することを本件出願人は提案している(例えば特許文献1)。 In order to promote the reduction in size and weight of the projector and the simplification of the optical system, when irradiating the light source light to a display element such as a DMD (digital micromirror device), the light source light is made uniform using a microlens array and an illumination lens. The present applicant has proposed to irradiate the display element by making it (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、マイクロレンズアレイと照明レンズとを用いて光源光の均一性と光の利用率を高めるプロジェクタに関する改良提案も、行われている(例えば特許文献2)。 In addition, an improvement proposal has been made on a projector that uses a microlens array and an illumination lens to increase the uniformity of light source light and the utilization factor of light (for example, Patent Document 2).
前述の様に、マイクロレンズアレイを用いた光学系により光源光を表示素子に照射するプロジェクタでは、光源光学系の各要素の配置、ひいてはプロジェクタの小型化を容易とすることができる。 As described above, in the projector that irradiates the display element with the light source light by the optical system using the microlens array, the arrangement of each element of the light source optical system and the downsizing of the projector can be facilitated.
また、高輝度の半導体光源を用いたプロジェクタは、明るい画像の投影を可能としているが、光利用効率を高くし、明るい室内であっても、より明るく鮮明な画像の投影を行うために、光の利用効率を一層高めることが要求されている。 In addition, projectors using high-intensity semiconductor light sources are capable of projecting bright images. However, in order to increase light utilization efficiency and project brighter and clearer images even in a bright room, There is a demand to further increase the efficiency of use.
本発明は、上記従来技術の問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、光源の光利用効率を向上させる光学系を備えた光源光学装置及びこの光源光学装置を備えたプロジェクタを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems of the prior art, and an object thereof is to provide a light source optical device including an optical system that improves the light utilization efficiency of a light source, and a projector including the light source optical device. And
本発明の光源光学装置は、光源と、前記光源から出射された光を均一化するマイクロレンズアレイと、このマイクロレンズアレイを透過した光を屈折させる照明光学系と、前記照明光学系からの出射光が入射するTIRプリズムと、を備え、前記照明光学系は、2枚の凸レンズの間に1枚の凹レンズが配置されている3枚のレンズを含み、前記3枚のレンズの内の前記マイクロレンズアレイから最も離れたレンズは、前記照明光学系からの出射光の前記TIRプリズムの全反射面への入射角が大きくなるように光軸がシフトされていることを特徴とする。
また、本発明の光源光学装置は、光源と、前記光源から出射された光を均一化するマイクロレンズアレイと、このマイクロレンズアレイを透過した光を屈折させる照明光学系と、前記照明光学系からの出射光が入射する入射プリズムと、前記入射プリズムからの出射光が入射するTIRプリズムと、を備え、前記照明光学系は、2枚の凸レンズの間に1枚の凹レンズが配置されている3枚のレンズを含み、前記入射プリズムは、前記照明光学系からの出射光の前記TIRプリズムの全反射面への入射角が大きくなるような向きに配置されていることを特徴とする。
The light source optical device of the present invention includes a light source, a microlens array that uniformizes light emitted from the light source, an illumination optical system that refracts light transmitted through the microlens array, and an output from the illumination optical system. The illumination optical system includes three lenses in which one concave lens is disposed between two convex lenses, and the micro lens among the three lenses is provided. The lens farthest from the lens array is characterized in that the optical axis is shifted so that the incident angle of the light emitted from the illumination optical system to the total reflection surface of the TIR prism is increased.
The light source optical device of the present invention includes a light source, a microlens array that uniformizes the light emitted from the light source, an illumination optical system that refracts light transmitted through the microlens array, and the illumination optical system. an incident prism that of the outgoing light is incident, and a TIR prisms that light emitted from the incident prism is incident, said illumination optical system includes a single concave lens between two convex lenses are arranged The incident prism includes three lenses, and is arranged in such a direction that an incident angle of light emitted from the illumination optical system to a total reflection surface of the TIR prism is increased.
本発明のプロジェクタは、上述の光源光学装置と、前記光源光学装置からの出射光が照射されて投影光を生成する表示素子と、前記表示素子で形成された画像光をスクリーンに投影する投影光学系と、前記表示素子や前記光源光学装置の制御を行うプロジェクタ制御手段と、を有することを特徴とする。 The projector according to the present invention includes the above-described light source optical device, a display element that emits light emitted from the light source optical device to generate projection light, and projection optical that projects image light formed by the display element onto a screen. And a projector control means for controlling the display element and the light source optical device.
本発明における光源光学装置は、光利用効率の高い光源光学装置とすることができ、光利用率が高く、明るい画像投影が可能な光学系を備えた小型のプロジェクタとすることができる。 The light source optical device according to the present invention can be a light source optical device with high light utilization efficiency, and can be a small projector having an optical system with a high light utilization factor and capable of projecting a bright image.
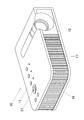
以下、本発明の実施形態を図に基づいて詳説する。図1は、プロジェクタ10の外観斜視図である。なお、本実施形態において、プロジェクタ10における左右とは投影方向に対しての左右方向を示し、前後とはプロジェクタ10のスクリーン側方向及び光線群の進行方向に対しての前後方向を示す。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is an external perspective view of the
そして、プロジェクタ10は、図1に示すように、略直方体形状であって、プロジェクタ筐体の前方の側板とされる正面板12の側方に投影部を有すると共に、この正面板12には複数の排気孔17を設けている。さらに、図示しないがリモートコントローラからの制御信号を受信するIr受信部を備えている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
また、筐体の上ケース11にはキー/インジケータ部37が設けられ、このキー/インジケータ部37には、電源スイッチキーや電源のオン又はオフを報知するパワーインジケータ、投影のオン、オフを切りかえる投影スイッチキー、光源ユニット60や表示素子51又は制御回路等が過熱したときに報知をする過熱インジケータ等のキーやインジケータが配置されている。また、上ケース11は、プロジェクタ10における筐体の上面と左側面の一部までを覆っており、故障時等には上ケース11を下ケース16から取り外せる構成とされている。
The
さらに、筐体の背面には、図示されない背面板にUSB端子やアナログRGB映像信号が入力される映像信号入力用のD−SUB端子、S端子、RCA端子、音声出力端子等を設ける入出力コネクタ部及び電源アダプタプラグ等の各種端子が設けられている。また、背面板には、複数の吸気孔が形成されている。 In addition, an input / output connector is provided on the rear surface of the housing, which is provided with a D-SUB terminal, an S terminal, an RCA terminal, an audio output terminal, etc. for inputting a USB terminal or an analog RGB video signal on a back plate (not shown). And various terminals such as a power adapter plug are provided. In addition, a plurality of intake holes are formed in the back plate.
次に、プロジェクタ10のプロジェクタ制御手段について図2の機能ブロック図を用いて述べる。プロジェクタ制御手段は、制御部38、入出力インターフェース22、画像変換部23、表示エンコーダ24、表示駆動部26等から構成される。
Next, projector control means of the
この制御部38は、プロジェクタ10内の各回路の動作制御を司るものであって、CPU、各種セッティング等の動作プログラムを固定的に記憶したROM及びワークメモリとして使用されるRAM等により構成されている。
The
そして、このプロジェクタ制御手段により、入出力コネクタ部21から入力された各種規格の画像信号は、入出力インターフェース22、システムバス(SB)を介して画像変換部23で表示に適した所定のフォーマットの画像信号に統一するように変換された後、表示エンコーダ24に出力される。
Then, the image signals of various standards input from the input /
また、表示エンコーダ24は、入力された画像信号をビデオRAM25に展開記憶させた上でこのビデオRAM25の記憶内容からビデオ信号を生成して表示駆動部26に出力する。
The
表示駆動部26は、表示素子制御手段として機能するものであり、表示エンコーダ24から出力された画像信号に対応して適宜フレームレートで空間的光変調素子(SOM)である表示素子51を駆動するものである。
The
そして、このプロジェクタ10では、赤色波長帯域、緑色波長帯域、青色波長帯域の各光線群を時分割で出射する光源とした光源ユニット60からの出射光を、照明光学系110及びTIRプリズム(全反射プリズム)120を介して表示素子51に照射することにより、DMD等の表示素子51の反射光で光像を形成し、投影光学系を介して図示しないスクリーンに画像を投影表示する。なお、この投影光学系の可動レンズ群235は、レンズモータ45によりズーム調整やフォーカス調整のための駆動が行われる。
In the
また、画像圧縮/伸長部31は、画像信号の輝度信号及び色差信号をADCT及びハフマン符号化等の処理によりデータ圧縮して着脱自在な記録媒体とされるメモリカード32に順次書き込む記録処理を行う。
The image compression /
さらに、画像圧縮/伸長部31は、再生モード時にメモリカード32に記録された画像データを読み出し、一連の動画を構成する個々の画像データを1フレーム単位で伸長し、この画像データを、画像変換部23を介して表示エンコーダ24に出力し、メモリカード32に記憶された画像データに基づいて動画等の表示を可能とする処理を行う。
Further, the image compression /
そして、筐体の上ケース11に設けられるメインキー及びインジケータ等により構成されるキー/インジケータ部37の操作信号は、直接に制御部38に送出され、リモートコントローラからのキー操作信号は、Ir受信部35で受信され、Ir処理部36で復調されたコード信号が制御部38に出力される。
Then, the operation signal of the key /
なお、制御部38にはシステムバス(SB)を介して音声処理部47が接続されている。この音声処理部47は、PCM音源等の音源回路を備えており、投影モード及び再生モード時には音声データをアナログ化し、スピーカ48を駆動して拡声放音させる。
Note that an
また、制御部38は、光源制御手段としての光源制御回路41を制御しており、この光源制御回路41は、画像生成時に要求される所定波長帯域の光が光源ユニット60から出射されるように、光源ユニット60の緑色光源装置61、赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95の発光を個別に制御する。
Further, the
さらに、制御部38は、冷却ファン駆動制御回路43に光源ユニット60等に設けた複数の温度センサによる温度検出を行わせ、この温度検出の結果から冷却ファンの回転速度を制御させている。また、制御部38は、冷却ファン駆動制御回路43にタイマー等によりプロジェクタ本体の電源オフ後も冷却ファンの回転を持続させる、あるいは、温度センサによる温度検出の結果によってはプロジェクタ本体の電源をオフにする等の制御も行う。
Further, the
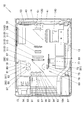
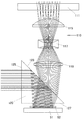
次に、このプロジェクタ10の内部構造について述べる。図3は、プロジェクタ10の内部構造を示す平面模式図である。プロジェクタ10は、中央部分に光源とする光源ユニット60を備え、光源ユニット60の左側方に照明光学系110を備え、更に照明光学系110の左にTIRプリズム120と表示素子51とを備え、光源ユニット60と照明光学系110により光源光学装置を形成している。
Next, the internal structure of the
そして、光源光学装置から出射される光源光を、TIRプリズム120を介して表示素子51に照射し、画像光をTIRプリズム120によりTIRプリズム120の前方に配置される投影光学系が内装されたレンズ鏡筒140の入射口に入射させることとしている。
The light source light emitted from the light source optical device is irradiated onto the
また、プロジェクタ10は、光源ユニット60の下方に主制御回路基板を備えると共に、左側板14の内側には、光源制御回路41や冷却ファン駆動制御回路43、更にフォーカスモータやズームモータの駆動制御回路等を組み込む各種の制御基板を備えている。
The
そして、プロジェクタ10は、背面板13の内側における左側板14の近傍には、表示素子51を冷却させる冷却ファン55を備え、背面板13及び左側板14の内側に配置したヒートシンク53により表示素子51を冷却している。
The
また、この光源ユニット60は、赤色光源装置91として赤色レーザーダイオード93を用い、青色光源装置95として青色レーザーダイオード97を用いて発光手段を形成し、赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95を冷却するヒートシンク83を光源ユニット60の右側板15側に備えている。
In addition, the
この光源ユニット60は、緑色光源装置61と、赤色光源装置91と、青色光源装置95と、ダイクロイックミラー101と、を備えるものである。緑色光源装置61は、背面板13の近傍においてプロジェクタ10筐体の左右方向における略中央部分に配置される励起光照射装置63とこの励起光照射装置63から出射される光線群上に配置される蛍光発光装置73とで発光手段を構成し、青色光源装置95と赤色光源装置91とは、プロジェクタ10の筐体の略中央やや右側寄りの位置に配置するものとしている。
The
この励起光照射装置63は、背面板13と光軸が垂直になるよう配置された半導体発光素子による励起光源65とする青色レーザーダイオード66と、励起光源65と背面板13との間に配置されたヒートシンク81と、を備え、青色レーザーダイオード66の前方にコリメータレンズ67を有している。
The excitation
励起光源65は、半導体発光素子である青色レーザーダイオード66を左右方向へ2個並べたものを上下に2組配置することによる4(=2×2)個の半導体発光素子で構成しており、各青色レーザーダイオード66の光軸上には、各青色レーザーダイオード66からの出射光を平行光に変換する集光レンズであるコリメータレンズ67が夫々配置されている。
The
ヒートシンク81と背面板13との間には、冷却媒体として外気を吸入してヒートシンク側に送風する送風ファンである冷却ファン85が配置されており、この冷却ファン85とヒートシンク81とによって励起光源65が冷却される。
Between the
また、緑色光源装置61における蛍光発光装置73は、正面板12と平行となるように、つまり、励起光照射装置63からの出射光の光軸と直交するように配置された蛍光ホイール75と、この蛍光ホイール75を回転駆動するホイールモータ77と、蛍光ホイール75から背面板13方向に出射される光線群を集光する集光レンズ群79と、を備える。ホイールモータ77と正面板12との間には冷却ファン89が配置されており、正面板12の排気孔17から排気を行うことよって蛍光ホイール75が冷却される。
Further, the fluorescent
蛍光ホイール75は、円板状の金属基材であって、励起光源65からの出射光を励起光として緑色波長帯域の蛍光発光光を出射する環状の蛍光発光領域が凹部として形成され、励起光を受けて蛍光発光する蛍光体層が設けられる。そして、蛍光発光領域を含む蛍光ホイール75の励起光源65側の表面は、銀蒸着等によってミラー加工されることで光を反射する反射面が形成され、この反射面上に緑色蛍光体の層が敷設されている。
The
蛍光ホイール75の緑色蛍光体層に照射された励起光照射装置63からの出射光は、緑色蛍光体層における緑色蛍光体を励起する。そして、緑色蛍光体から全方位に蛍光発光された光線群は、直接、励起光源65側へ、あるいは、蛍光ホイール75の反射面で反射した後に励起光源65側へ出射される。
The outgoing light from the excitation
また、蛍光体層の蛍光体に吸収されることなく、金属基材に照射された励起光は、反射面により反射されて再び蛍光体層に入射し、蛍光体を励起することとなる。よって、蛍光ホイール75の凹部の表面を反射面とすることにより、緑色波長帯域光の励起光源65から出射される励起光の利用効率を上げることができ、より明るく発光させることができる。
Moreover, the excitation light irradiated to the metal substrate without being absorbed by the phosphor of the phosphor layer is reflected by the reflecting surface and is incident on the phosphor layer again to excite the phosphor. Therefore, by using the surface of the concave portion of the
赤色光源装置91と青色光源装置95とは、その出射光の光軸と励起光源65からの光の光軸とが直交するように、すなわち緑色光源装置61である蛍光発光装置73からの蛍光発光光の光軸と直交するようにして、赤色レーザーダイオード93と青色レーザーダイオード97とが並設されている。青色光源装置95は、青色レーザーダイオード97と、青色レーザーダイオード97からの出射光を所定範囲の光に集光して出射するコリメータレンズ98と、を備える。青色レーザーダイオード97は、上下方向に並べて二個が配置されている。
The red
そして、青色レーザーダイオード97の前後の両側には、赤色光源装置91の赤色レーザーダイオード93が前後それぞれ上下方向に並べて二個ずつ、合計四個が配置されている。赤色光源装置91は、赤色レーザーダイオード93と、赤色レーザーダイオード93からの出射光を所定範囲の光に集光して出射するコリメータレンズ94と、を備える。そして、赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95は、励起光照射装置63からの出射光及び蛍光ホイール75から出射される緑色波長帯域光と光軸が交差するように配置されている。
On both sides of the
この赤色レーザーダイオード93や青色レーザーダイオード97から出射されるレーザー光は、光軸に垂直な断面形状が長楕円形のコヒーレント光である。そして、これら赤色レーザーダイオード93及び青色レーザーダイオード97については、コリメータレンズとの距離調整を行って、照明光学系110のマイクロレンズアレイ111への照射光を所定範囲に集光させて出射させる。異なる波長帯域光である赤色波長帯域光及び青色波長帯域光の両発光光は、近接平行で同一方向に出射される。
The laser light emitted from the
赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95の右側板15側に設けたヒートシンク83と正面板12との間には、ヒートシンク83によって暖められた空気を吸い込んで装置外部に排出するための冷却ファン87が配置されており、この冷却ファン87によって赤色レーザーダイオード93及び青色レーザーダイオード97が冷却される。
Between the
そして、赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95から出射される赤色波長帯域光及び青色波長帯域光の光軸と、励起光照射装置63から出射される青色波長帯域光及び蛍光発光装置73から出射される緑色波長帯域光の光軸と、が直交して交差する位置に、青色及び赤色波長帯域光を透過し、緑色波長帯域光を反射してこの緑色光の光軸を左側板14方向に90度変換するダイクロイックミラー101が配置されている。
The red wavelength band light and the blue wavelength band light emitted from the red
従って、1枚のダイクロイックミラー101により、赤色波長帯域光、緑色波長帯域光及び青色波長帯域光の各光を同一の光路に重ね合わせるようにして高輝度の光源光とし、各色の光源光を時分割により光源としての光源ユニット60から出射し、照明光学系110のマイクロレンズアレイ111に入射することができる。
Therefore, a single
そして、ダイクロイックミラー101の左方には、導光手段としてのマイクロレンズアレイ111と3数のレンズとによる照明光学系110が配置されている。このマイクロレンズアレイ111は、光源ユニット60からの出射光を拡散させ、輝度分布を均一化させるものである。
On the left side of the
本実施形態におけるマイクロレンズアレイ111のマイクロレンズ112は、レンズ形状として平面視横長矩形形状として表示素子51と相似形状であって、各マイクロレンズ112は、同一大きさにして入射面と出射面を同一曲率とした両凸レンズを格子状に配列しているものである。そして、マイクロレンズアレイ111の左側板14側には、照明レンズとして3枚のレンズが配置される。3枚のレンズは、マイクロレンズアレイ111を透過した拡散均一光を表示素子51の有効サイズに集光させるものである。
The
即ち、光源としての光源ユニット60から出射された光源光は、マイクロレンズアレイ111により、均一な強度分布とされ、凸レンズである第1レンズ115や第3レンズ119及び凹レンズである第2レンズ117を介してTIRプリズム120に入射される。
That is, the light source light emitted from the
TIRプリズム120に入射された光源光は、前方にカバーガラスを有する表示素子51に入射され、表示素子51で反射されたオン光は、再度TIRプリズム120に入射され、画像光としてレンズ鏡筒140に入射されて投影光学系によりスクリーンに投影される。
The light source light incident on the
この投影光学系としては、レンズ鏡筒140に内蔵する固定レンズ群と可動鏡筒に内蔵する可動レンズ群235とを備えてズーム機能を備えた可変焦点型レンズとされ、レンズモータ45により可動レンズ群235が移動されることにより、ズーム調整やフォーカス調整が可能とされている。
The projection optical system includes a fixed lens group built in the
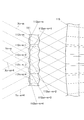
この照明光学系110では、図4に示すように、光源ユニット60から出射された光源光がマイクロレンズアレイ111の各マイクロレンズ112に入射され、各マイクロレンズ112に入射された光は、射出して第1レンズ115に入射される。
In the illumination
尚、図4では、一列(図で上下方向)にn個のマイクロレンズ112が配置されるマイクロレンズアレイ111の最後(図示しない下端)であるn番目のマイクロレンズ112nからm番目であるマイクロレンズ112n−mと、このm番目のマイクロレンズ112mを含む5個のマイクロレンズ112n−m+1、112n−m+2、112n−m+3、112n−m+4を図示している。
In FIG. 4, the mth microlens from the
このように、レンズ面の曲率や厚さを共通として同一の光学特性とされた各マイクロレンズ112に入射された光が射出したのち第1レンズ115に入射さる。
As described above, the light incident on each
また、各マイクロレンズ112を両凸レンズとすることにより、各マイクロレンズ112で同一状態の透過光を形成する。両凸レンズの焦点は互いの面付近にあり、マイクロレンズ112n−m+1の入射側セルに当たった光線群はマイクロレンズ112n−m+1の射出側のセル以外つまりたとえばマイクロレンズ112n−mやマイクロレンズ112n−m+2の射出側レンズ面になるべく向かわないようにマイクロレンズ112n−m+1の射出側凸レンズ面光軸付近により集光されている。そして、図5、6に示すように、マイクロレンズ112n−m+1の射出側凸レンズ面によりマイクロレンズ112n−m+1の入射側マイクロレンズセル面の共役面113がはるか遠くになるようになる。
Further, by making each microlens 112 a biconvex lens, transmitted light in the same state is formed by each
そして、マイクロレンズ112が複数行で複数列に配置されたマイクロレンズアレイ111における1列のマイクロレンズ112において、例えば、先頭のマイクロレンズ1121から最後のマイクロレンズ112nまでの途中での最後からm番目のマイクロレンズ112n−m、及び、このm番目から5個目までのマイクロレンズ112n−m+4についての透過光は、図4に示したように、各マイクロレンズ112の入射面で屈折して第1レンズ115に入射され、図5に示すように、射出したのち第1レンズ115に入射される。
In the
このため、マイクロレンズアレイ111を透過して第1レンズ115に入射される光線群における各入射側マイクロレンズセル面とその虚像は、図6に示すように、ほぼ等価とすることができ、1番目のマイクロレンズ1121による一方の稜線光X1と最後のn番目のマイクロレンズ112nの稜線光Xnとの差は、マイクロレンズアレイ111における1番目のマイクロレンズ1121とn番目のマイクロレンズ112nとの実寸と同一となり、他方の稜線光における1番目のマイクロレンズ1121による稜線光Y1とn番目のマイクロレンズ112nの稜線光Ynとの差もマイクロレンズアレイ111における実寸の差と同一となり、ひいては各マイクロレンズ112の射出側マイクロレンズによる各入射側マイクロレンズ光軸の虚像点M1、・・、Mn−m、Mn−m+1、・・、Mn−m+4、・・、Mnも、各マイクロレンズ112の実寸大の大きさのずれに合わせたずれとなる。共役面113の虚像は遠くにあるのでとても大きなものとなりそのずれは無視でき、重ね合わせた虚像の明るさの分布は、各マイクロレンズの入射側セルの照射分布を拡大し重ね合わせたものとなり、ほぼ一様となる。
For this reason, each incident side microlens cell surface and its virtual image in the light ray group transmitted through the
従って、各マイクロレンズ112を透過した光線群を3枚の照明レンズにより表示素子51に照射して光源像を表示素子51の画像形成面にこの共役面113において重なっている虚像を結像させたとき、効果的に均一な照度の照射光とすることができる。
Therefore, the light beam transmitted through each
このように遠くにある虚像である共役面113をDMDに結像する形で照射するので、第1レンズ115、第2レンズ117、第3レンズ119で形成される組レンズによる照明光学系110の照明レンズとしては、まるであたかも遠くにある物を、DMDまでプリズムや鏡が設置できるだけのある程度のスペース(つまりはバックフォーカス)をとって、DMDに結像させるような構成とすればよい。
Since the
そして、投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140に一般的な投射レンズを使用する場合、DMDの位置による周辺光線と主光線のなす角の表示素子51の位置によるばらつきを小さくするために、球面収差、コマ収差、非点収差、像面湾曲等の各収差を小さくし、各マイクロレンズ112の形状である矩形の像を正確に表示素子51の画像形成面に一致させて結像させるために、歪曲を小さくする。これらを小さなスペースで簡易に実現できる照明光学系は2枚の凸レンズである第1レンズ115と第3レンズ119との間に凹レンズである第2レンズ117を配置する構成となる。
When a general projection lens is used for the
図7に、本発明の実施形態に係る照明光学系によりTIRプリズムを介して表示素子に光源光を入射して表示素子から出射させる光線追跡図を模式的に示す。(なお、正確な光線追跡図は、後述の図13に示す。) FIG. 7 schematically shows a ray tracing diagram in which light source light is incident on the display element via the TIR prism and emitted from the display element by the illumination optical system according to the embodiment of the present invention. (An accurate ray tracing diagram is shown in FIG. 13 described later.)
図7に示すように、マイクロレンズアレイ111と3枚の組みレンズによる照明光学系110を介してTIRプリズム120により表示素子51に光源光を照射し、表示素子51で画像光を形成するに際し、表示素子51の形状と相似形状である矩形とされた各マイクロレンズ112の入射側セルの像が主光線と周辺光線のなす角が表示素子51の位置によるばらつきが小さく、歪曲の少ない像として表示素子51の画像形成面に形成することができる。
As shown in FIG. 7, when the
そのため、画像形成面の全体に各マイクロレンズ112の像を重ねるようにしつつ、後の投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140でのオン光の利用率が高く投影画像を形成し、表示素子51の周囲に照射される無駄な光を少なくすることができる。
Therefore, while superimposing the image of each
そして、効率よく照射された光源光による明るい画像光を形成し、この画像光をTIRプリズム120の全反射面とされた傾斜面123で反射して投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140の入射口に入射させることができる。
Then, bright image light is formed by the efficiently irradiated light source light, and this image light is reflected by the
このように、この照明光学系110は、第1レンズ115、第2レンズ117、更に第3レンズ119で光源光を屈折させてTIRプリズム120に入射させるものである。
As described above, the illumination
そして、このTIRプリズム120は、直角二等辺三角柱の単プリズムであって、柱底面の斜辺を含む側面を斜辺面123とし、柱底面の直角を挟む側面である二隣辺面の内の一面を隣辺面127とし、この隣辺面127をカバーガラス52を備えた表示素子51に対向させるとともに、この二隣辺面の内の他のもう一面を隣辺面125として投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140の入射口に対向させる。
The
また、入射面とする傾斜面123は、表示素子51からのオン光に対して全反射面を兼ねるものである。
In addition, the
従って、表示素子51により画像光として形成されるオン光は、図7に示したようにTIRプリズム120の隣辺面127から入射されて傾斜面123で反射されてレンズ鏡筒140に入射される方向へ隣辺面125から出射されることとなり、TIRプリズム120に入射されたオフ光は、図示していないが、傾斜面123で反射されてレンズ鏡筒140の入射口以外の方向に出射されるものである。
Therefore, the ON light formed as image light by the
このように、表示素子51から出射されるオン光の光軸をTIRプリズム120の隣辺面127に対して垂直とすれば、全反射面である傾斜面123での全反射による光軸の変化角は90度となり、TIRプリズム120の隣辺面125に対して光軸を垂直とし、隣辺面125で屈折することなく直進させて投影光学系を備えたレンズ鏡筒140に入射させることができる。
Thus, if the optical axis of the on-light emitted from the
従って、投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140の光軸を、表示素子51の画像形成面の法線に対して90度で交わる方向、且つ、照明光学系110の光軸と90度交わる方向としてレンズ鏡筒140を配置することができ、プロジェクタ10内の各部材の配置設計を容易とすることができる。
Therefore, the direction in which the optical axis of the
また、この光源光学装置では、マイクロレンズアレイ111により光源光を均一化し、第1レンズ115や第2レンズ117及び第3レンズ119により屈折させ、主光線と周辺光線のなす角が表示素子51の位置によるばらつきが小さく、且つ、歪曲の少ない各マイクロレンズ112入射側セルの像を表示素子51の画像形成面に結像させることができる。
Further, in this light source optical device, the light source light is made uniform by the
この本実施の形態に対し、2枚のレンズのみを組み合わせた従来の照明光学系では、マイクロレンズアレイ111による光源像を表示素子51に結像させるに際し、歪曲が生じることになり、表示素子51の画像形成面の周囲に照射される光源光が増加し、表示素子51への集光効率が低下することになる。
In contrast to this embodiment, in the conventional illumination optical system in which only two lenses are combined, distortion occurs when the light source image by the
また、表示素子51への入射光において、収差より主光線と周辺光線のなす角に関しても、位置によるばらつきが増加することになる。
In addition, in the incident light to the
図8に、比較例として、一般的な照明光学系である凸レンズ2枚によりTIRプリズムを介して表示素子に光源光を入射して表示素子から出射させる光線追跡図を模式的に示す。(なお、正確な光線追跡図は、後述の図14に示す。) FIG. 8 schematically shows a ray tracing diagram in which light source light is incident on a display element via a TIR prism and emitted from the display element by two convex lenses, which are general illumination optical systems, as a comparative example. (An accurate ray tracing diagram is shown in FIG. 14 described later.)
表示素子51から出射される画像光がTIRプリズム120の傾斜面123で反射されてレンズ鏡筒140の入射口に向かう際、各オン光の光は傾斜面123に入射するときに臨界角を越えないこともあり、傾斜面123を透過屈折する光成分が増加していた。また、TIRプリズムの隣辺面125から射出しても投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140に入らなかったり、入っても内蔵する吸収部品に当たったりして投影画像形成に使用されなくなる光成分が増加していた。これらの増加により投影画像が暗くなってしまっていた。
When the image light emitted from the
しかし、本実施の形態の照明光学系110は、凹レンズを第2レンズ117として第1レンズ115と第3集光レンズ119との間に配置することにより、表示素子51の画像形成面にマイクロレンズ112の入射側形状を結像させるに際して収差や歪曲を相殺により少なくし、各マイクロミラーで反射される各オン光の主光線と周辺光線のなす角のばらつきを減少させ、傾斜面123で画像光が反射される際に透過屈折するなど無駄になってしまう光成分を減少させることができるため、明るい投影画像を形成することができることになる。
However, the illumination
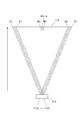
そして、上記のような照明レンズを組み合わせるに際し、収差等を小さくするためには、通常、組レンズの半画角を30度以下とすることが好ましい。 In order to reduce aberrations and the like when combining the illumination lenses as described above, it is usually preferable to set the half angle of view of the combined lens to 30 degrees or less.
このため、このマイクロレンズアレイ111におけるマイクロレンズ112は、図9に示すように、各マイクロレンズ112の一方の面の端部から他方の面の光軸上点までの光軸に沿った距離をlとし、面の中心から有効当該面の端部までの最大距離をhとし、レンズ硝材の屈折率をnとするとき、出射側の面の中央から出射される出射光のマイクロレンズ112の光軸と交わる角をθ'が30度以下となるようにしているものである。
Therefore, the
即ち、マイクロレンズ112の略厚みである一方の面の端部から他方の面の光軸上点までの距離lとマイクロレンズ112の口径の大きさである距離hの関係において、
l>h√(4n 2 −1) (式1)
を満たすようにしている。
That is, in the relationship between the distance l from the end of one surface, which is substantially the thickness of the
l> h√ (4n 2 −1) (Formula 1)
To meet.
これは、照明光学系110の第1レンズ115に入射する光線群における光軸と交わる光線の角度は、マイクロレンズ112から出射する出射光における光軸と交わる角度θ'であり、この出射角θ'の最大を30度とすると、このマイクロレンズ112を透過する有効光の出射面への入射角θは、入射面又は出射面の中心から端部までの距離hと、レンズの厚みである一方の面の中心から他方の面の端部までの光軸に沿った距離lとの関係において、
tanθ=h/l (式2)
で表される。
This is because the angle of the light ray intersecting with the optical axis in the light ray group incident on the
tan θ = h / l (Formula 2)
It is represented by
また、出射面における入射角θと出射角θ'とは、レンズの硝材の屈折率をnとすると、
n・sinθ=sinθ' (式3)
で表されることになる。
更に、θ'は最大角が30度あるため、
0.5>sinθ' (式3)
となる。
Further, the incident angle θ and the exit angle θ ′ on the exit surface are expressed as follows, where n is the refractive index of the glass material of the lens.
n · sin θ = sin θ ′ (Formula 3)
It will be represented by
Furthermore, since θ ′ has a maximum angle of 30 degrees,
0.5> sin θ ′ (Formula 3)
It becomes.
従って、
0.5>sinθ'=n・sinθ=n・h/√(h2+l2) (式4)
となり、lとhとの関係は(式1)で表され、レンズの厚さlが、入射面の口径2hとの関係において、h√(4n2−1)よりも大きいとき、各マイクロレンズ112からの出射光における光軸からの傾きを30度以内とすることができる。
Therefore,
0.5> sin θ ′ = n · sin θ = n · h / √ (h 2 + l 2 ) (Formula 4)
The relationship between l and h is expressed by (Equation 1). When the lens thickness l is larger than h√ (4n 2 −1) in relation to the aperture 2h of the incident surface, each microlens The inclination of the emitted light from 112 from the optical axis can be within 30 degrees.
従って、上記記載の3枚の組レンズにおいて、各種収差、歪曲を小さくして各マイクロレンズ112の矩形の像を表示素子51の画像形成面に結像させることができる。
Therefore, in the above-described three lens groups, various aberrations and distortions can be reduced, and a rectangular image of each
また、前述の実施形態は、TIRプリズム120を介して表示素子51に光源光を照射しているも、図10に示すように、照明光学系110の光軸上に照射ミラー135を配置し、表示素子51をプロジェクタ10の背面板113の内側において背面板13に沿って設け、照射ミラー135により照明光学系110を介した光源光をコンデンサレンズ137、カバーガラス52を通して表示素子51に照射し、画像光とするオン光をプロジェクタ10の正面板12の方向に出射させるようにしてもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the
尚、ヒートシンク53及び冷却ファン55を背面板13の内側で表示素子51の背面板13側に設けて表示素子51の冷却を行っている。
A
この場合も、マイクロレンズアレイ111と凸レンズ2枚の間に凹レンズを配置した3枚のレンズとによる照明光学系110により、各マイクロレンズ112の収差や歪の少ない矩形の像を重ねて表示素子51の画像形成面に結像させることができる。
Also in this case, the illumination
従って、マイクロレンズアレイ111を介した光を無駄なく表示素子51に照射し、表示素子51からのオン光の多くを投影光学系に入射そして射出させることができ、明るい画像を投影可能とすることができる。
Therefore, the
そして、TIRプリズム120として、前述の様な単独プリズムに限ることなく、図11に示すように、全反射面とする傾斜面123や隣辺面125を有する主プリズム121と入射プリズム130とを備える2枚プリズムとしてもよい。
The
この場合は、画像光の傾斜面123における全反射率を高くして明るい画像を形成することができる。
In this case, a bright image can be formed by increasing the total reflectance of the
また、図12に示すように、照明光学系110の最前方の集光レンズである第3レンズ119の中心を、TIRプリズム120における入射面が照明光学系110から離れる方向にずらすように第3レンズ119の中心をシフトさせることにより、照明光学系110から出射される光源光の光軸を最前方のレンズにより曲げ、TIRプリズム120への入射角を大きくするように調整するようにしてもよい。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 12, the
この場合、第3レンズ119の中心をシフトさせない場合に比較してTIRプリズム120の傾斜面123への入射角が大きくなり、傾斜面123での透過屈折による角度変化を大きく、即ち屈折率の高い光学ガラスを用いてTIRプリズム120とすることにより、傾斜面123を透過する際の屈折量を大きくし、ひいては臨界角を大きくして、全反射する光量を増大させつつ、光源とする光源ユニット60や照明光学系110、表示素子51、投影光学系の配置設計等を容易とすることができる。
In this case, compared with the case where the center of the
尚、照明光学系110のレンズ枚数を、上記第1レンズ115、第2レンズ117、第3レンズ119の構成を含む4枚以上としてもよい。
The number of lenses of the illumination
このように、上記のような照明光学系110として4枚以上のレンズを用いれば、マイクロレンズアレイ111により均一化された光線によるマイクロレンズ112の入射側セルの像を、主光線と周辺光線のなす角のばらつき収差や歪曲のより一層少ない状態で、表示素子51の画像形成面に結像させ、効率良く表示素子51に集光することができる。
As described above, if four or more lenses are used as the illumination
尤も、上記のような2枚の凸レンズと1枚の凹レンズの組レンズとすれば、照明光学系110を小型化することが容易であり、且つ、主光線と周辺光線のなす角のばらつきや歪曲の少ない組レンズとすることができる。
However, if the combined lens of two convex lenses and one concave lens as described above is used, it is easy to reduce the size of the illumination
また、図3に示した光源ユニット60は、半導体発光素子である励起光源65及び蛍光体による緑色光源装置61と、半導体発光素子としてのレーザーダイオード(LD)による赤色光源装置91及び青色光源装置95と、を組み合わせた三原色の光源としているも、光源としては、赤色発光ダイオード(LED)、緑色発光ダイオード(LED)、青色発光ダイオード(LED)などの半導体発光素子を用いる場合や、更に、三原色以外の黄色波長帯域光などの補色の波長帯域光を発する発光素子を追加してもよい。
Further, the
このように、半導体発光素子を光源に用いれば、省電力にして寿命の長い光源とすることができ、励起光源と緑色蛍光体を用いた光源を組み合わせれば、明るい三原色を容易に得ることができる。そして、三原色の画像光を形成することにより、フルカラーの画像を形成することができる。 Thus, if a semiconductor light-emitting element is used as a light source, it can be a light source that saves power and has a long life, and if a light source using an excitation light source and a green phosphor is combined, bright three primary colors can be easily obtained. it can. A full-color image can be formed by forming image light of the three primary colors.
更に、半導体発光素子を用いた光源ユニット60に換え、高圧放電ランプ等の白色光源とカラーホイールとを組み合わせ、少なくとも三原色を同一光軸として出射する光源としてもよい。
Furthermore, instead of the
このように、赤色波長帯域光、緑色波長帯域光、青色波長帯域光の各光線群を時分割で出射する光源ユニット60からの光源光を、マイクロレンズアレイ111と照明光学系110とにより輝度を均一化しつつ収差や歪の小さな像として表示素子51の画像形成面に結像させる光源光学装置を備えたプロジェクタ10は、小型にして光の利用効率が高く、明るい画像投影が可能なプロジェクタ10とすることができる。
In this way, the light source light from the
なお、光源は、例えば、白色光源1つであって白黒の投影装置に用いられるような光源装置であってもよい。つまり、本発明は、光源の構成を限定するものではない。
また、上記実施形態では、複数枚のレンズの各レンズを単レンズの図で説明したが、各レンズが張り合わされた複合的なレンズであっても一つのレンズ(ユニット)として取り扱うことのできるものであれば、本発明における各レンズと同等であることは、は言うまでもない。
The light source may be, for example, a light source device that is a white light source and is used in a black and white projection device. That is, the present invention does not limit the configuration of the light source.
In the above embodiment, each lens of a plurality of lenses has been described as a single lens. However, even a compound lens in which each lens is bonded can be handled as one lens (unit). Needless to say, it is equivalent to each lens in the present invention.
<実施例及び比較例>
図13に、本実施形態の図7の構成による光線追跡の正確なシミュレーション結果を示す。これは、模式的な図である図7に対応するものである。
図14に、比較例として、図8の構成による光線追跡の正確なシミュレーション結果を示す。これは、模式的な図である図8に対応するものである。
なお、図13及び図14においては、図の奥行き方向(紙面に垂直な方向)の光線も紙面に重畳して示している。
<Examples and Comparative Examples>
FIG. 13 shows an accurate simulation result of ray tracing according to the configuration of FIG. 7 of the present embodiment. This corresponds to FIG. 7, which is a schematic diagram.
FIG. 14 shows an accurate simulation result of ray tracing by the configuration of FIG. 8 as a comparative example. This corresponds to FIG. 8, which is a schematic diagram.
In FIGS. 13 and 14, light rays in the depth direction (direction perpendicular to the paper surface) are also superimposed on the paper surface.
図14においては、TIRプリズムで全反射されない光が迷光として、かなり発生してしまっているが、図13では、この迷光が少なくなっている。
また、図14においては、TIRプリズムの隣辺面125から射出しても投影光学系を内蔵するレンズ鏡筒140に入らなかったり、入っても内蔵する吸収部品に当たったりして投影画像形成に使用されなくなる光成分が増加していたが、図13では、そのような光成分が少なくなっている。
したがって、図7の構成が、光の利用効率が高く、明るい投影を可能にしていることがわかる。
In FIG. 14, light that is not totally reflected by the TIR prism is considerably generated as stray light, but in FIG. 13, this stray light is reduced.
Further, in FIG. 14, even if it exits from the
Therefore, it can be seen that the configuration of FIG. 7 has high light utilization efficiency and enables bright projection.
以上説明した実施形態は、例として提示したものであり、発明の範囲を限定することは意図していない。これら新規な実施形態は、その他の様々な形態で実施されることが可能であり、発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で、種々の省略、置き換え、変更を行うことができる。これらの実施形態やその変形は、発明の範囲や要旨に含まれるとともに、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明とその均等の範囲に含まれる。 The embodiment described above is presented as an example, and is not intended to limit the scope of the invention. These novel embodiments can be implemented in various other forms, and various omissions, replacements, and changes can be made without departing from the spirit of the invention. These embodiments and modifications thereof are included in the scope and gist of the invention, and are included in the invention described in the claims and the equivalents thereof.
以下に、本願出願の最初の特許請求の範囲に記載された発明を付記する。
[1]光源と、
前記光源から出射された光を均一化するマイクロレンズアレイと、
このマイクロレンズアレイを透過した光を屈折させる照明光学系と、
を備え、
前記照明光学系は、2枚の凸レンズの間に1枚の凹レンズが配置されている3枚のレンズを含むことを特徴とする光源光学装置。
[2]前記マイクロレンズアレイの各マイクロレンズは、入射面の焦点及び出射面の焦点が、それぞれ前記出射面付近及び前記入射面付近にある凸レンズであることを特徴とする前記[1]に記載の光源光学装置。
[3]前記各マイクロレンズは、入射面の有効部端部から出射面の光軸上点までの光軸に沿った距離をlとし、入射面の光軸上点から入射面の有効部端部までの最大距離をhとし、硝材の屈折率をnとするとき、
l>h√(4n 2 −1) (式1)
を満足することを特徴とする前記[2]に記載の光源光学装置。
[4]前記マイクロレンズアレイの前記各マイクロレンズは、表示素子の矩形と相似形状とされていることを特徴とする前記[1]乃至前記[3]の何れかに記載の光源光学装置。
[5]前記3枚のレンズの内の前記マイクロレンズアレイから最も離れたレンズは、光軸がシフトされていることを特徴とする前記[1]乃至前記[4]の何れかに記載の光源光学装置。
[6]前記光源は、赤色波長帯域光を出射する半導体発光素子と、緑色波長帯域光を出射する半導体発光素子と、青色波長帯域光を出射する半導体発光素子と、を含むことを特徴とする前記[1]乃至前記[5]の何れかに記載の光源光学装置。
[7]前記光源は、赤色波長帯域光を出射する半導体発光素子と、青色波長帯域光を出射する半導体発光素子と、励起光源及び緑色蛍光体による緑色波長帯域光を出射する発光手段と、を含むことを特徴とする前記[1]乃至前記[5]の何れかに記載の光源光学装置。
何れかに記載の光源光学装置。
[8]前記[1]乃至前記[7]の何れか記載の光源光学装置と、
前記光源光学装置からの出射光が照射されて投影光を生成する表示素子と、
前記表示素子で形成された画像光をスクリーンに投影する投影光学系と、
前記表示素子や前記光源光学装置の制御を行うプロジェクタ制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とするプロジェクタ。
The invention described in the first claim of the present application will be appended below.
[1] a light source;
A microlens array for uniformizing the light emitted from the light source;
An illumination optical system that refracts light transmitted through the microlens array;
With
The illumination optical system includes a light source optical device including three lenses in which one concave lens is disposed between two convex lenses.
[2] Each microlens of the microlens array is a convex lens in which the focal point of the incident surface and the focal point of the emission surface are in the vicinity of the emission surface and the vicinity of the incident surface, respectively. Light source optical device.
[3] In each microlens, a distance along the optical axis from the effective portion end of the incident surface to the point on the optical axis of the output surface is set to l, and the effective portion end of the incident surface from the point on the optical axis of the incident surface. When the maximum distance to the part is h and the refractive index of the glass material is n,
l> h√ (4n 2 −1) (Formula 1)
The light source optical device according to [2], wherein:
[4] The light source optical device according to any one of [1] to [3], wherein each of the microlenses of the microlens array has a shape similar to a rectangle of the display element.
[5] The light source according to any one of [1] to [4], wherein a lens farthest from the microlens array among the three lenses has an optical axis shifted. Optical device.
[6] The light source includes a semiconductor light emitting element that emits red wavelength band light, a semiconductor light emitting element that emits green wavelength band light, and a semiconductor light emitting element that emits blue wavelength band light. The light source optical device according to any one of [1] to [5].
[7] The light source includes: a semiconductor light emitting element that emits red wavelength band light; a semiconductor light emitting element that emits blue wavelength band light; and a light emitting unit that emits green wavelength band light from an excitation light source and a green phosphor. The light source optical device according to any one of [1] to [5], including:
The light source optical device according to any one of the above.
[8] The light source optical device according to any one of [1] to [7],
A display element that emits light emitted from the light source optical device to generate projection light;
A projection optical system that projects image light formed by the display element onto a screen;
Projector control means for controlling the display element and the light source optical device;
A projector comprising:
10 プロジェクタ 11 上ケース
12 正面板 13 背面板
14 左側板 15 右側板
16 下ケース 17 排気孔
21 入出力コネクタ部 22 入出力インターフェース
23 画像変換部 24 表示エンコーダ
25 ビデオRAM 26 表示駆動部
31 画像圧縮/伸長部 32 メモリカード
35 受信部 36 処理部
37 キー/インジケータ部
38 制御部 41 光源制御回路
43 冷却ファン駆動制御回路 45 レンズモータ
47 音声処理部 48 スピーカ
51 表示素子 52 カバーガラス
53 ヒートシンク 55 冷却ファン
60 光源ユニット
61 緑色光源装置
63 励起光照射装置 65 励起光源
66 青色レーザーダイオード 67 コリメータレンズ
73 蛍光発光装置
75 蛍光ホイール 77 ホイールモータ
79 集光レンズ群
81、83 ヒートシンク 85、87、89 冷却ファン
91 赤色光源装置
93 赤色レーザーダイオード 94 コリメータレンズ
95 青色光源装置
97 青色レーザーダイオード 98 コリメータレンズ
110 照明光学系
101 ダイクロイックミラー
111 マイクロレンズアレイ 112 マイクロレンズ
112a セル面
113 共役面
115 第1レンズ 117 第2レンズ
119 第3レンズ
120 TIRプリズム
121 主プリズム 123 傾斜面
125 隣辺面 127 隣辺面
129 吸収板
130 入射プリズム
135 照射ミラー 137 コンデンサレンズ
140 レンズ鏡筒 235 可動レンズ群
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
前記光源から出射された光を均一化するマイクロレンズアレイと、
このマイクロレンズアレイを透過した光を屈折させる照明光学系と、
前記照明光学系からの出射光が入射するTIRプリズムと、
を備え、
前記照明光学系は、2枚の凸レンズの間に1枚の凹レンズが配置されている3枚のレンズを含み、
前記3枚のレンズの内の前記マイクロレンズアレイから最も離れたレンズは、前記照明光学系からの出射光の前記TIRプリズムの全反射面への入射角が大きくなるように光軸がシフトされていることを特徴とする光源光学装置。 A light source;
A microlens array for uniformizing the light emitted from the light source;
An illumination optical system that refracts light transmitted through the microlens array;
A TIR prism on which light emitted from the illumination optical system is incident;
With
The illumination optical system includes three lenses in which one concave lens is disposed between two convex lenses,
Among the three lenses, the lens farthest from the microlens array has its optical axis shifted so that the incident angle of the light emitted from the illumination optical system to the total reflection surface of the TIR prism is increased. A light source optical device.
前記光源から出射された光を均一化するマイクロレンズアレイと、
このマイクロレンズアレイを透過した光を屈折させる照明光学系と、
前記照明光学系からの出射光が入射する入射プリズムと、
前記入射プリズムからの出射光が入射するTIRプリズムと、
を備え、
前記照明光学系は、2枚の凸レンズの間に1枚の凹レンズが配置されている3枚のレンズを含み、
前記入射プリズムは、前記照明光学系からの出射光の前記TIRプリズムの全反射面への入射角が大きくなるような向きに配置されていることを特徴とする光源光学装置。 A light source;
A microlens array for uniformizing the light emitted from the light source;
An illumination optical system that refracts light transmitted through the microlens array;
An incident prism on which light emitted from the illumination optical system is incident ;
A TIR prisms that light emitted from the incident prism is incident,
With
The illumination optical system includes three lenses in which one concave lens is disposed between two convex lenses,
The light source optical device , wherein the incident prism is arranged in such a direction that an incident angle of light emitted from the illumination optical system to a total reflection surface of the TIR prism is increased.
l>h√(4n2−1) (式1)
を満足することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の光源光学装置。 Each of the microlenses has a distance along the optical axis from the end of the effective portion of the entrance surface to the point on the optical axis of the exit surface, and is from the point on the optical axis of the entrance surface to the end of the effective portion of the entrance surface. When the maximum distance is h and the refractive index of the glass material is n,
l> h√ (4n 2 −1) (Formula 1)
The light source optical device according to claim 3, wherein:
前記光源光学装置からの出射光が照射されて投影光を生成する表示素子と、
前記表示素子で形成された画像光をスクリーンに投影する投影光学系と、
前記表示素子や前記光源光学装置の制御を行うプロジェクタ制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とするプロジェクタ。
A light source optical device according to any one of claims 1 to 7,
A display element that emits light emitted from the light source optical device to generate projection light;
A projection optical system that projects image light formed by the display element onto a screen;
Projector control means for controlling the display element and the light source optical device;
A projector comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014059531A JP6493721B2 (en) | 2014-03-24 | 2014-03-24 | Light source optical device and projector |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014059531A JP6493721B2 (en) | 2014-03-24 | 2014-03-24 | Light source optical device and projector |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015184401A JP2015184401A (en) | 2015-10-22 |
| JP2015184401A5 JP2015184401A5 (en) | 2017-04-27 |
| JP6493721B2 true JP6493721B2 (en) | 2019-04-03 |
Family
ID=54351019
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014059531A Active JP6493721B2 (en) | 2014-03-24 | 2014-03-24 | Light source optical device and projector |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6493721B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115280234A (en) * | 2020-03-18 | 2022-11-01 | 夏普Nec显示器解决方案株式会社 | Light source device and projector |
| JP7424246B2 (en) * | 2020-08-19 | 2024-01-30 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Light source device, image display device, and projector |
| JP7223287B2 (en) | 2020-09-17 | 2023-02-16 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Light source device, projection device, and light source control method |
| WO2022195761A1 (en) * | 2021-03-17 | 2022-09-22 | シャープNecディスプレイソリューションズ株式会社 | Light source device and projector |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11281914A (en) * | 1998-03-26 | 1999-10-15 | Fuji Photo Optical Co Ltd | Illuminating optical system and projector device using the system |
| JP2001109070A (en) * | 1999-10-12 | 2001-04-20 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Illuminating optical device and projection type display device using it |
| JP4041700B2 (en) * | 2002-06-25 | 2008-01-30 | フジノン株式会社 | Illumination optical system and projection display device using the same |
| JP2005165137A (en) * | 2003-12-04 | 2005-06-23 | Canon Inc | Illuminating optical system and image display device |
| US7245436B2 (en) * | 2005-02-09 | 2007-07-17 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Illumination device and projector |
| JP4337826B2 (en) * | 2005-02-09 | 2009-09-30 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Lighting device and projector |
| JP2008003270A (en) * | 2006-06-22 | 2008-01-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Illuminator and projection-type image display device using the same |
| JP4901656B2 (en) * | 2007-09-04 | 2012-03-21 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Illumination device and projection display device |
| JP4962405B2 (en) * | 2008-05-12 | 2012-06-27 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | projector |
| JP2013120250A (en) * | 2011-12-07 | 2013-06-17 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Projection video display device |
| JP5920095B2 (en) * | 2012-07-31 | 2016-05-18 | 株式会社Jvcケンウッド | Image display device |
-
2014
- 2014-03-24 JP JP2014059531A patent/JP6493721B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015184401A (en) | 2015-10-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109143746B (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP4711155B2 (en) | Light source device and projector | |
| JP6390922B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP5429543B2 (en) | Light source unit and projector | |
| JP5910868B2 (en) | Light source device and projector | |
| JP6270045B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP2015184303A (en) | Light source optical device and projector | |
| JP6260819B2 (en) | Light source device and projector | |
| JP6380813B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP5333472B2 (en) | Light source unit, light source device and projector | |
| JP2017156619A (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP6493721B2 (en) | Light source optical device and projector | |
| JP6447881B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP2008145510A (en) | Light source unit and projector | |
| JP2009237455A (en) | Light source device and projector | |
| CN106918979B (en) | Projection device | |
| JP6701531B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP6135904B2 (en) | Light source device and projector | |
| JP6332678B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP2009031717A (en) | Optical system unit and projector | |
| JP6669192B2 (en) | Light source device and projection device | |
| JP6880442B2 (en) | Multi-chip package, light source device and projection device | |
| JP7223287B2 (en) | Light source device, projection device, and light source control method | |
| JP5348455B2 (en) | LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE, PROJECTOR, AND LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE MANUFACTURING METHOD | |
| JP2018060223A (en) | Light source device and projector |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170323 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170323 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20180222 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180301 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180416 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180712 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180905 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190207 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20190220 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6493721 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |