JP6435895B2 - Elevator control system - Google Patents
Elevator control system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6435895B2 JP6435895B2 JP2015021402A JP2015021402A JP6435895B2 JP 6435895 B2 JP6435895 B2 JP 6435895B2 JP 2015021402 A JP2015021402 A JP 2015021402A JP 2015021402 A JP2015021402 A JP 2015021402A JP 6435895 B2 JP6435895 B2 JP 6435895B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- door
- magnetic pole
- pole position
- elevator
- phase
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 claims description 50
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 30
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 22
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 21
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 20
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 101710165590 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100024828 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 101710165595 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 2 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100025031 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 2 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 101710101695 Probable mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101710101698 Probable mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 2 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004397 blinking Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Elevator Door Apparatuses (AREA)
Description
本発明は、エレベータのドアを開閉駆動する電動機の制御を中心とした、エレベータの制御に係るシステムを対象とする。 The present invention is directed to a system related to elevator control centering on control of an electric motor that drives an elevator door to open and close.
エレベータのかごを昇降駆動する電動機として、永久磁石を備えた回転子と電機子巻線を備えた固定子を有する永久磁石同期電動機を採用した例が、特許文献1に記載されている。
その電動機の制御としてはベクトル制御方式を採り、電流指令値として3要素(一次周波数角、d軸電流指令値、q軸電流指令値)を指令するとしている。そのうち一次周波数角については、電動機の磁極軸位置を計測して定めるが、その計測が何らかの原因でうまく行かず、一次周波数角と磁極軸位置の間にずれが生じた場合には、磁極軸推定制御を起動するという技術が提示されている。
Patent Document 1 describes an example in which a permanent magnet synchronous motor having a rotor having permanent magnets and a stator having armature windings is adopted as an electric motor that drives an elevator car up and down.
The electric motor is controlled by a vector control method, and three elements (primary frequency angle, d-axis current command value, q-axis current command value) are commanded as current command values. Of these, the primary frequency angle is determined by measuring the magnetic pole axis position of the motor, but if the measurement does not work for some reason and there is a deviation between the primary frequency angle and the magnetic pole axis position, the magnetic pole axis position is estimated. Techniques for activating control are presented.
そして、この磁極軸推定制御をどういうときに起動するかという起動条件について、特許文献1ではエレベータの異常検出やエレベータ制御電源の立上げを挙げており、異常検出や制御電源立上げが生じた場合には、その前段階で一次周波数角と磁極軸位置の間にずれが生じている可能性を想定していると考えられる。 And as for the starting condition of when to start this magnetic pole axis estimation control, Patent Document 1 mentions the detection of an abnormality in the elevator and the startup of the elevator control power supply, and when the abnormality detection or the control power supply startup occurs. Is considered to assume the possibility of a deviation between the primary frequency angle and the magnetic pole axis position in the previous stage.
なお以下の記述では、磁極軸推定制御の用語に代えて磁極位置推定制御を使用する。また、一次周波数角、d軸電流指令値、q軸電流指令値についてもそれぞれ、d軸電流の位相、d軸電流の振幅、q軸電流の振幅と称することにする。 In the following description, magnetic pole position estimation control is used in place of the term magnetic pole axis estimation control. The primary frequency angle, the d-axis current command value, and the q-axis current command value are also referred to as the d-axis current phase, the d-axis current amplitude, and the q-axis current amplitude, respectively.
特許文献1のような、かごを昇降駆動する電動機ではなく、ドアを開閉駆動する電動機として永久磁石同期電動機を採用するとした場合にも、磁極位置推定制御をする必要がある。その場合、磁極位置推定制御の起動条件としてどういう条件を設定するかは、ドア開閉用の電動機に特有の考慮が必要になると考えられる。 Even when a permanent magnet synchronous motor is adopted as an electric motor for opening and closing a door, instead of an electric motor for raising and lowering a car as in Patent Document 1, it is necessary to perform magnetic pole position estimation control. In this case, it is considered that what kind of condition is set as the starting condition of the magnetic pole position estimation control needs to be considered specifically for the door opening / closing motor.
そこで、ドア開閉用の永久磁石同期電動機に対する磁極位置推定制御としてどのような起動条件とすべきかを考察し、その条件によって的確に磁極位置推定制御を実施するエレベータ制御システムをどのように構成するかを発明課題とする。 Therefore, the starting conditions for magnetic pole position estimation control for a permanent magnet synchronous motor for opening and closing the door are considered, and how to configure an elevator control system that performs magnetic pole position estimation control accurately according to the conditions. Is an invention subject.
本発明のエレベータ制御システムは、永久磁石を備えた回転子及び電機子巻線を備えた固定子を有し、その回転子が回転することによってエレベータのドアを開閉駆動する永久磁石同期電動機と、前記ドアを開ける方向や閉める方向に前記回転子を回転させるために前記電機子巻線に電流を流すドア制御部と、前記ドア制御部に対して前記ドアを開けるための戸開指令および前記ドアを閉めるための戸閉指令を出すエレベータ制御装置を備える。以上の構成を共通とする第一の態様と第二の態様がある。 The elevator control system of the present invention has a rotor having a permanent magnet and a stator having an armature winding, and a permanent magnet synchronous motor that drives the door of the elevator to open and close by rotating the rotor, A door control unit for passing an electric current through the armature winding to rotate the rotor in a direction for opening or closing the door, a door opening command for opening the door to the door control unit, and the door An elevator control device for issuing a door closing command for closing the door. There is a first mode and a second mode that share the above configuration.
第一の態様では、前記エレベータ制御装置は、エレベータが給電されていない状態から給電されている状態に切換ったと検出した場合、前記永久磁石の磁極位置の認識を更新するための磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう前記ドア制御部に指令することを特徴とする。また第二の態様では、前記エレベータ制御装置は、前記戸開指令を出しても前記ドアが全開位置にならないと検出した場合、または前記戸閉指令を出しても前記ドアが全閉位置にならないと検出した場合、前記永久磁石の磁極位置の認識を更新するための磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう前記ドア制御部に指令することを特徴とする。 In the first aspect, when the elevator control device detects that the elevator is switched from a state in which power is not supplied to a state in which power is supplied, the magnetic pole position estimation control for updating the recognition of the magnetic pole position of the permanent magnet. The door control unit is instructed to perform the following. In the second aspect, the elevator control device detects that the door is not in the fully open position even if the door open command is issued, or does not enter the fully closed position even if the door close command is issued. Is detected, the door control unit is commanded to perform magnetic pole position estimation control for updating the recognition of the magnetic pole position of the permanent magnet.
本発明のエレベータ制御システムによれば、エレベータが給電されていない状態において何らかの原因で回転子が回転してしまった場合には、回転子の磁極の位置変動をドア制御部が認識できないので、給電されている状態に切り換わるのをエレベータ制御装置が検出してからドア制御部に磁極位置の認識更新を指令することによって、その後ドア制御部は電動機を的確に制御することができる。また、ドアを戸開させて全開位置にしたり、戸閉させて全閉位置にしたりしようとするのに、そうならない場合、エレベータ制御装置がドア制御部に磁極位置の認識更新を指令することによって、その後のドア制御部が電動機を制御したときにドアが全開位置や全閉位置となるようにできる可能性が出てくる。 According to the elevator control system of the present invention, when the rotor is rotated for some reason in a state where the elevator is not supplied with power, the door control unit cannot recognize the position fluctuation of the magnetic pole of the rotor. After the elevator control device detects that the state is switched to the current state, the door control unit can accurately control the electric motor thereafter by instructing the door control unit to update the recognition of the magnetic pole position. If the door is opened to the fully open position, or the door is closed to the fully closed position, if that is not the case, the elevator controller instructs the door control unit to update the recognition of the magnetic pole position. Then, there is a possibility that the door can be in the fully open position or the fully closed position when the subsequent door control unit controls the electric motor.
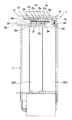
本発明に係るエレベータのドア制御システムについて、一つの実施形態を以下に述べる。まずは、「図面の簡単な説明」の項で述べた図1ないし図8の説明を踏まえつつ、かごドア3や乗場ドア1と、ドア開閉装置4と、自閉装置14と、終端保持装置38のそれぞれについて述べると共に、お互いの間の関係について述べる。
One embodiment of an elevator door control system according to the present invention will be described below. First, the
<かごドアと乗場ドアの連動>
図1に示すように、乗場に面して乗場ドア1が設けられ、かご2にかごドア3が設けられている。かごドア3には、乗場ドア1側に突出する係合部31が設けられる。乗場ドア1には、かごドア3側に突出する被係合部11が設けられる。かご2が乗場の位置に到着すると、係合部31と被係合部11とが係合するので、かご2側に設けられたドア開閉装置4によってかごドア3が開くと、連動して乗場ドア1も開く。その後ドア開閉装置4によってかごドア3が閉まると、連動して乗場ドア1も閉まる。
<Linkage of car door and landing door>
As shown in FIG. 1, a landing door 1 is provided facing the landing, and a
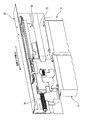
<ドア開閉装置によるかごドアの駆動>
図2を参照しつつ、ドア開閉装置4を構成する永久磁石同期電動機41の駆動力がかごドア3に伝達される機構について説明する。
<Driving the car door by the door opening and closing device>
A mechanism for transmitting the driving force of the permanent magnet
まずは、ドア開閉装置4が備える永久磁石同期電動機41と、駆動プーリ42と、従動プーリ43と、駆動ベルト44について以下に述べる。なお、ドア開閉装置4が備えている全閉位置検出部39aや全開位置検出部39bについては、終端保持装置38の説明箇所で説明する。また、ドア開閉装置4が備えるドア制御部45やエンコーダ46については、終端保持装置38の説明箇所の後で説明する。
First, the permanent magnet
永久磁石同期電動機41は、永久磁石を備えた回転子と電機子巻線を備えた固定子とを有し、上部フレーム21の正面の一端側に配置されている。回転子の駆動軸には駆動プーリ42が直結されている(ダイレクトドライブと称する)。従動プーリ43は、上部フレーム21の正面の他端側に取り付けられている。駆動ベルト44は、駆動プーリ42及び従動プーリ43の間に巻き掛けられている。このような構成により、永久磁石同期電動機41の駆動軸が回転すれば駆動ベルト44が循環する。
The permanent magnet
本実施形態に係るエレベータは、図2に示すように、かご2の出入口が一方の端から開く、いわゆるサイドオープンタイプのエレベータであり、一対のかごドア3fとかごドア3sとが同じ方向に移動し、かごドア3fがかごドア3sよりも多く移動する構造となっている(かごドア3fは、移動量が多い、即ち移動速度が速いということで“ファストドア”と称し、かごドア3sは、移動量が少ない、即ち移動速度が遅いということで“スロードア”と称する)。
The elevator according to the present embodiment is a so-called side open type elevator in which the doorway of the
かごドア3fは、ドアハンガ32fを介してドアレール33fに吊り下げられている。ドアハンガ32fには一対のローラ34f,34fが取り付けられ、これらはドアレール33f上に載置されている。同様にかごドア3sもドアハンガ32sを介してドアレール33sに吊り下げられている。ドアハンガ32sには一対のローラ34s,34sが取り付けられ、これらはドアレール33s上に載置されている。
The car door 3f is suspended from the
かごドア3fは、ドアハンガ32f及び、ドアハンガ32fに取り付けられた連結具35fを介して、ドア開閉装置4の駆動ベルト44に連結されている。一方、かごドア3sは、後述の減速機構37を介してかごドア3fに連結されている。従って、永久磁石同期電動機41により駆動ベルト44が循環すると、ドアハンガ32fを介してかごドア3fがドアレール33fに沿って移動すると共に、減速機構37を介してかごドア3sが連動し、ドアレール33sに沿ってかごドア3fの半分の速度で移動する。
The car door 3f is connected to the
なお、減速機構37は、アーム37aと、一対の減速プーリ37b,37bと、減速ワイヤ37cと、ブラケット37dとを備える。アーム37aは、ドアハンガ32sに取り付けられ、かご2の出入口の間口方向に沿って延びている。一対の減速プーリ37b,37bは、アーム37aの一端側及び他端側に取り付けられている。減速ワイヤ37cは、一対の減速プーリ37b,37b間に巻き掛けられている。減速ワイヤ37cの一部は、ブラケット37dによって上部フレーム21の正面に固定されている。減速ワイヤ37cには、ドアハンガ32fに取り付けられた連結具35sを介してかごドア3fが連結されている。
The
<乗場ドアを付勢する自閉装置>
図3に示すように、乗場ドア1は、左側のファストドアと右側のスロードアで構成されている。右側のスロードアは、ドアレールに載置されたドアハンガ12で吊下がっている。図3でドアハンガ12は、左側のファストドアを吊下げるドアハンガが載置されたドアレールに遮られて、上下に分断された形で見えている(その下部のほうを13で示している)。ドアハンガ12の左端には、弾性体の右端が連結されている(その連結部は、左側のファストドアを吊下げるドアハンガに遮られて見えない)。弾性体の左端は、上部フレーム21の左端に連結されている。このようにドアハンガ12と弾性体と上部フレーム21が連結されて自閉装置14が構成され、乗場ドア1に付勢力(自閉力と称する)を付与する。この付勢力により、乗場ドア1に何の外力も作用しないとき自動的に全閉位置へ推移させて、出入口が閉塞した状態に保持する。
<Self-closing device for energizing the landing door>
As shown in FIG. 3, the landing door 1 is composed of a left fast door and a right slow door. The right throw door is suspended by a
以上の記載から分るように、永久磁石同期電動機41の駆動力が伝わってかごドア3が開閉すると、かごドア3と乗場ドア1とが係合していれば乗場ドア1も開閉することになるが、このような駆動力の伝達経路(永久磁石同期電動機41→かごドア3→乗場ドア1)を逆方向にたどって、自閉装置14による乗場ドア1の自閉力が、かごドア3を経て永久磁石同期電動機41にまで影響することになる。これを模式図で示すと、図8(a)のようになる。
As can be seen from the above description, when the
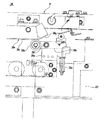
<かごドアを付勢する終端保持装置、および全閉/全開位置検出部>
乗場ドア1に付与される自閉力は、ドアの全行程(全開位置〜全閉位置)にわたって作用するが、かごドア3に対しては、全開位置の付近や、全閉位置の付近だけで作用する力がある。その力は、図4ないし図7に示す終端保持装置38によって付与される。すなわち、終端保持装置38は、かごドア3を開く方向(戸開方向)に力を付与して全開位置に保持したり、かごドア3を閉じる方向(戸閉方向)に力を付与して全閉位置に保持したりするものである。
<Terminal holding device for energizing the car door and fully closed / fully opened position detecting unit>
The self-closing force applied to the landing door 1 acts over the entire stroke of the door (fully open position to fully closed position), but for the
終端保持装置38によるかごドア3の保持力も、駆動力の伝達経路(永久磁石同期電動機41→かごドア3)を逆方向にたどって、永久磁石同期電動機41にまで影響することになる。これを模式図で示すと、図8(b)のようになる。
The holding force of the
終端保持装置38は、図5と図6に示すように、ベース38aと、ローラ38bと、レバー38cと、弾性部38dとを備える。ベース38aは、ドアハンガ32fに固定されている。ローラ38bは、上部フレーム21に支持されたガイドレール38eに回動可能に当接され、かごドア3の移動に伴ってガイドレール38e上を走行する。レバー38cは、ベース38aに設けられる軸38fに軸支されている。弾性部38dは、軸38fを支点としてレバー38cの一端を下方に引っ張るので、レバー38cの他端に設けられるローラ38bからは、ガイドレール38eに向かって押圧力が発生する。
As shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, the
図4に示すように、ガイドレール38eの両端部には傾斜部38g,38hが設けられ、傾斜部38gと傾斜部38hとの間には平坦部38iが設けられている。
As shown in FIG. 4,
ローラ38bが傾斜部38gに達すると、ローラ38bの押圧力が水平方向の分力をもつので、それに対するガイドレール38eからの反作用が、ローラ38bから、レバー38c、軸38f、ベース38a、ドアハンガ32fと伝わり、かごドア3が全閉位置に向けて誘導される。また、ローラ38bが傾斜部38hに達したときも同様にして、かごドア3が全開位置に向けて誘導される。
When the
ガイドレール38eには、図7に示すように、かごドア3が出入口を完全に閉塞するまで閉じた位置に対応した全閉位置P1と、かごドア3が出入口を完全に開放するまで開いた位置に対応した全開位置P2とが設定されている。また、かごドア3には、ローラ38bが全閉位置P1に到達したときに全閉位置信号を出力する全閉位置検出部39aと、全開位置P2に到達したときに全開位置信号を出力する全開位置検出部39bが設けられている(図示省略)。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
なお、傾斜部38gと平坦部38iとの境界位置は、閉側保持解除位置P3と呼び、傾斜部38hと平坦部38iとの境界位置は、開側保持解除位置P4と呼ぶ。全閉位置P1と閉側保持解除位置P3との間にあるガイドレール38e上の領域は閉保持ゾーンZ1と呼び、全開位置P2と開側保持解除位置P4との間にあるガイドレール38e上の領域は開保持ゾーンZ2と呼び、閉側保持解除位置P3と開側保持解除位置P4との間にあるガイドレール38e上の領域は保持解除ゾーンZ3と呼ぶ。
The boundary position between the
以上、かごドア3や乗場ドア1と、ドア開閉装置4と、自閉装置14と、終端保持装置38について述べてきたが、次に、図9ないし図13を参照しつつ、ドア開閉装置4を構成するドア制御部45とエンコーダ46について述べる。
The
<ドア制御部の周辺と内部>
図9を参照しつつ、エレベータ制御装置5とドア制御部45の関係、ドア制御部45と永久磁石同期電動機41やエンコーダ46の関係について説明する。ドア制御部45は、エレベータの運行全体を管理し制御するエレベータ制御装置5から、かごドア3を戸開せよという指令(戸開指令)または戸閉せよという指令(戸閉指令)を受ける。そして、これらの指令に基いて、永久磁石同期電動機41の電機子巻線に所要の電流を出力し、戸開させる方向または戸閉させる方向へと回転子を回転させる。
<Around and inside the door control unit>
The relationship between the elevator control device 5 and the
ドア制御部45が回転制御をスタートする際には、永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置を確認するため、その回転軸に取り付けられているエンコーダ46を利用する。ドア制御部45はまた、かごドア3の移動目標とする位置や速度に対して実際の位置や速度が追従しているかどうかを見るためにも、エンコーダ46を利用する。ドア制御部45はさらに、かごドア3の実際位置をエンコーダ46によって正しく認識できているかを確認するため、かごドア3が全閉位置に来たときに全閉位置検出部39aの全閉位置信号を利用し、全開位置に来たときに全開位置検出部39bの全開位置信号を利用する。
When the
次に、図9を参照しつつ、ドア制御部45の内部について説明する。ドア制御部45は、速度制御部451と、電流制御部452と、電力変換部453と、電流検出部454と、磁極位置推定部456を備えており、以下のように機能する。なおドア制御部45は単純カウンタ455も備えているが、これについては後で述べる。
Next, the inside of the
速度制御部451は、自らが設定する開閉速度パターンに沿うような電流指令値を生成し、電流制御部452に出力する。なお、永久磁石同期電動機41に対する制御方式としてはベクトル制御を採用し、電流指令値を3要素(d軸電流の位相、d軸電流の振幅、q軸電流の振幅)で構成する。なお、d軸電流の位相が0度になるのは、例えば、永久磁石同期電動機41のU相巻線とV相巻線とW相巻線のうち、U相巻線に流れる電流が最大になるときであると定義する。
The speed control unit 451 generates a current command value that follows the opening / closing speed pattern set by the speed control unit 451 and outputs the current command value to the current control unit 452. Note that vector control is adopted as a control method for the permanent
電流制御部452は、この電流指令値と、電流検出部454からフィードバックされる電流検出値を比較し、両者の差分量に対応した電圧指令値を電力変換部453に指令する。電力変換部453は、電圧指令値に応じた可変電圧・可変周波数の三相交流電圧を生成し、永久磁石同期電動機41を可変速駆動する。電流検出部454は、永久磁石同期電動機41に流れる電流を検出し、電流制御部452にフィードバックする。
The current control unit 452 compares the current command value with the current detection value fed back from the current detection unit 454, and commands the power conversion unit 453 with a voltage command value corresponding to the difference between the two. The power conversion unit 453 generates a variable voltage / variable frequency three-phase AC voltage according to the voltage command value, and drives the permanent
速度制御部451は、磁極位置カウンタ451cと補正情報記憶部451dを備えている。永久磁石同期電動機41の回転をスタートさせる際のd軸電流の位相を定めるに当っては、速度制御部451は、磁極位置カウンタ451cが保持する磁極位置情報MPと、補正情報記憶部451dが保持する補正情報MPCの加算値(MP+MPC)を用いる。これらは所定の条件・タイミングで校正する必要がある。そのための制御を「磁極位置推定制御」と称する。なお速度制御部451は、磁極位置カウンタ451c以外にドア位置カウンタ451aやドア速度カウンタ451bも備えているが、これらについては<速度制御部の各カウンタ>という見出しの段落群で詳しく述べる。また補正情報記憶部451dについては<磁極位置推定モード時のフェーズ移行>という見出しの段落群やそれ以降で述べる。
The speed control unit 451 includes a magnetic pole position counter 451c and a correction information storage unit 451d. In determining the phase of the d-axis current when starting the rotation of the permanent
磁極位置推定制御の際は、永久磁石同期電動機41に一定位相の直流電流が流れるような電流指令値を、速度制御部451が生成する。一定位相の直流電流が永久磁石同期電動機41に流れると、その位相の起磁力が発生し、その位相へ磁極位置が一致しようとして回転子が回転することになる。この一定位相とは、電流指令値の3要素のうちでd軸電流の位相について、その一定値を磁極位置推定部456がその都度指定するものである。その指定方法は、磁極位置推定部456の構成部位(磁極固定部456a、磁極情報取得部456b、磁極情報演算部456c)と共に、後で述べる。
In the magnetic pole position estimation control, the speed control unit 451 generates a current command value that allows a constant phase DC current to flow through the permanent
他の2要素(d軸電流の振幅、q軸電流の振幅)については毎回同じ値をとるものと決めておく。d軸電流の振幅のほうは、電流位相に磁極位置が一致する動作が安定して確保されるような一定値に決めておく。q軸電流の振幅のほうは、ゼロ値と決めておく。これらの値は速度制御部451で記憶している。 The other two elements (d-axis current amplitude and q-axis current amplitude) are determined to have the same value every time. The amplitude of the d-axis current is determined to be a constant value so that an operation in which the magnetic pole position matches the current phase is stably secured. The q-axis current amplitude is determined to be a zero value. These values are stored in the speed control unit 451.
<エンコーダ>
ここでエンコーダ46について述べる。エンコーダ46としては、インクリメンタル式ロータリーエンコーダを適用した例で以下説明する。エンコーダ46は、永久磁石同期電動機41が回転するのに従って、回転した量(回転角)に比例した数のパルス信号を出力するものである。パルス信号はA相パルスとB相パルスの2種類あり、90度の位相差をもって出力される。このA相パルスから90度遅れてB相パルスが出力された場合の回転方向を、かごドア3を戸開させる方向に対応付け、B相パルスから90度遅れてA相パルスが出力された場合の回転方向を、かごドア3を戸閉させる方向に対応付けたシステム構成で以下説明する。ただし、逆の対応付けであっても技術的に支障は無い。
<Encoder>
Here, the
エンコーダ46が出力するパルス数としては、永久磁石同期電動機41が1回転するとA相が5400パルス(B相も5400パルス)出力するものを例にして以下の説明をする。このように機械角の1回転で5400パルスを出力するわけであるが、永久磁石同期電動機41としては2極のものを採用し、電気角の1回転でも5400パルス出力となる例で以下説明する。なお、2極に限定せず、極数に応じて「機械角÷極数の半分=電気角」の関係式により換算される電気角で述べることも可能である。
The number of pulses output by the
<単純カウンタ>
エンコーダ46が出力するパルスを、ドア制御部45は単純カウンタ455で受け取り、パルスカウント値N0として保持する。すなわち、パルスカウント値N0は、エンコーダ46からのA相パルスやB相パルスが立上ったり立下ったりするときに、カウントアップ(加算)したりカウントダウン(減算)したりする。例えば次のようなカウントの仕方である。
<Simple counter>
The
カウントアップするのは、B相パルスがLow状態でA相パルスが立上る時、A相がパルスHigh状態でB相パルスが立上る時、B相パルスがHigh状態でA相パルスが立下る時、A相パルスがLow状態でB相パルスが立下る時である。これと逆にカウントダウンするのは、B相パルスがLow状態でA相パルスが立下る時、A相パルスがLow状態でB相パルスが立上る時、B相パルスがHigh状態でA相パルスが立上る時、A相パルスがHigh状態でB相パルスが立下る時である。 Counts up when the A-phase pulse rises when the B-phase pulse is low, when the A-phase pulse is high and when the B-phase pulse rises, or when the B-phase pulse is high and the A-phase pulse falls , When the B-phase pulse falls while the A-phase pulse is in the low state. Conversely, the countdown occurs when the A-phase pulse falls when the B-phase pulse is in the Low state, when the A-phase pulse is Low and the B-phase pulse rises, when the B-phase pulse is High and the A-phase pulse is when rises, is when the A-phase pulse B phase pulse falls in a High state.
<速度制御部の各カウンタ>
単純カウンタ455が保持するパルスカウント値N0に基づいて、速度制御部451の各カウンタ(ドア位置カウンタ451a、ドア速度カウンタ451b、磁極位置カウンタ451c)は、下記のように、それぞれの情報を保持している。
<Each counter of speed controller>
Based on the pulse count value N0 held by the
ドア位置カウンタ451aを参照しながら、速度制御部451は開閉速度パターンを設定する。ドア位置カウンタ451aはドア位置情報DP’を保持している。そして、単純カウンタ455のパルスカウント値N0を一定の周期ΔTごとに読み出し、今回読み出した値から前回読み出した値を引き算した値ΔN0をドア位置情報DP’に加算し、新たなドア位置情報DPとして保持する(DP’+ΔN0=DP)。
While referring to the door position counter 451a, the speed control unit 451 sets an opening / closing speed pattern. The door position counter 451a holds door position information DP ′. Then, the pulse count value N0 of the
なお、速度制御部451には、かごドア3が全閉位置P1にあるとき全閉位置信号が全閉位置検出部39aから入力されるが、その入力時、ドア位置カウンタ451aのドア位置情報DPを、全閉位置に対応する全閉位置情報DPCに書き換える。また、かごドア3が全開位置P2にあるとき全開位置信号が全開位置検出部39bから入力されるが、その入力時、ドア位置カウンタ451aのドア位置情報DPを、全開位置に対応する全開位置情報DPOに書き換える。
The speed control unit 451 receives a fully closed position signal from the fully closed position detection unit 39a when the
ドア速度カウンタ451bと開閉速度パターンを参照しながら、速度制御部451は電流指令値を生成する。ドア速度カウンタ451bは、単純カウンタ455のパルスカウント値N0を一定の周期ΔTごとに読み出し、今回読み出した値から前回読み出した値を引き算し、その絶対値|ΔN0|を周期ΔTで割り算した値をドア速度情報Vとして保持する(|ΔN0|/ΔT=V)。
The speed controller 451 generates a current command value while referring to the door speed counter 451b and the opening / closing speed pattern. The door speed counter 451b reads the pulse count value N0 of the
磁極位置カウンタ451cと補正情報記憶部451dを参照して、速度制御部451は、永久磁石同期電動機41の回転制御をスタートするときのd軸位相を決定する。補正情報記憶部451dが保持する情報は磁極位置推定制御の時だけ変動するが、磁極位置カウンタ451cが保持する情報は磁極位置推定制御の時でなくても平常時に永久磁石同期電動機41が回転するに連れて変動する。磁極位置カウンタ451cは、磁極位置情報MP’を保持している。そして、単純カウンタ455のパルスカウント値N0を一定の周期ΔTごとに読み出し、今回読み出した値から前回読み出した値を引き算した値ΔN0を磁極位置情報MP’に加算し、新たな磁極位置情報MPとして保持する(MP’+ΔN0=MP)。
With reference to the magnetic pole position counter 451c and the correction information storage unit 451d, the speed control unit 451 determines the d-axis phase when starting the rotation control of the permanent
ただし、電気角の1回転で5400パルスが出力されることに基いて、磁極位置情報MPが5400以上となる場合は、5400を引き算した剰余を磁極位置カウンタ451cで記憶し、0〜5399の範囲で変動する値としている。つまり、0からカウントアップして5399に達した直後のカウントアップでは0に戻ることになる。この0からカウントアップして0に戻る一周で辿る各カウント値を、電気角の0度から0度(=360度)へと一周するときに辿る各角度を表すものと読みとることにする。すると、カウント値と角度が「カウント値=15×角度」という式で換算できる。この15という換算係数は、1回転で5400パルス出力という例によって定まった値だが、一般的にはKという記号で表すことにする。 However, when the magnetic pole position information MP is 5400 or more based on the output of 5400 pulses in one rotation of the electrical angle, the remainder obtained by subtracting 5400 is stored in the magnetic pole position counter 451c, and ranges from 0 to 5399. The value fluctuates at. In other words, when counting up from 0 and counting up immediately after reaching 5399, it returns to 0. Each count value that counts up from 0 and traces in one round returning to 0 is read as representing each angle traced when rounding from 0 degree to 0 degree (= 360 degrees) in electrical angle. Then, the count value and the angle can be converted by the formula “count value = 15 × angle”. The conversion factor of 15 is a value determined by the example of 5400 pulse output per rotation, but is generally represented by the symbol K.
<磁極位置の認識とその更新>
以上、<ドア制御部の周辺と内部>という見出しの段落群から記載してきたように、永久磁石同期電動機41の回転に伴ってエンコーダ46から出力されるパルスを単純カウンタ455でカウントし、そのカウント値を磁極位置カウンタ451cで読み出すことによって、永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置の変動量に対して忠実に追従した情報(磁極位置情報MP)を磁極位置カウンタ451cで保持するわけである。つまり、ドア制御部45が磁極位置を認識した結果が磁極位置カウンタ451cで保持されていることになる。この磁極位置カウンタ451cで保持する磁極位置情報MPでもってドア制御部45はd軸電流の位相を定めている。
<Recognition and update of magnetic pole position>
As described above, the pulse output from the
ただし、磁極位置と磁極位置カウンタ451cの対応関係は、磁極位置カウンタ451cの原点が磁極位置の原点に一致することの確認(磁極位置カウンタ451cの校正)を所定の時期に経た上で、上述したような、磁極位置カウンタ451cの変動量が磁極位置の変動量に対して忠実に追従することで、保証されることになる。このような磁極位置カウンタ451cの校正を、これから述べる磁極位置推定制御で実施することにする。 However, the correspondence relationship between the magnetic pole position and the magnetic pole position counter 451c is as described above after confirming that the origin of the magnetic pole position counter 451c matches the origin of the magnetic pole position (calibration of the magnetic pole position counter 451c) after a predetermined time. As described above, the variation amount of the magnetic pole position counter 451c faithfully follows the variation amount of the magnetic pole position. Such a calibration of the magnetic pole position counter 451c will be carried out by the magnetic pole position estimation control described below.
なお、磁極位置推定制御では、磁極位置カウンタ451cが保持する磁極位置情報MPを更新するのに付随して、補正情報記憶部451dが保持する補正情報MPCの更新も行なう。それによってドア制御部45は、磁極位置情報MPだけでなく補正情報MPCも加味してd軸電流の位相を定めることになる。
In the magnetic pole position estimation control, the correction information MPC held by the correction information storage unit 451d is also updated in association with updating the magnetic pole position information MP held by the magnetic pole position counter 451c. As a result, the
<磁極位置推定制御の開始、完了>
さて、これから磁極位置推定制御について詳細を述べて行くが、その前にエレベータ制御装置5とドア制御部45の間でやりとりする信号を紹介する。まずエレベータ制御装置5からドア制御部45への信号としては、戸開指令、戸閉指令、磁極位置推定指令(それぞれONとOFFの間で切換わる)。次にドア制御部45からエレベータ制御装置5への信号としては、運転状態信号(通常運転モードと磁極位置推定モードの間で切換わる)や、ドア正常信号(正常時ON、異常時OFF)や、トルク過大信号(正常時OFF、異常時ON)がある。
<Start and completion of magnetic pole position estimation control>
Now, the magnetic pole position estimation control will be described in detail. Before that, signals exchanged between the elevator control device 5 and the
エレベータ制御装置5は、ドア制御部45が異常検出した場合に、磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する。ドア制御部45が異常検出するとは、過電流(電動機へ出力する電流や、内部回路の電流について)や、オーバースピード(電動機の回転速度について)等を検出した場合である。その場合ドア制御部45は、エレベータ制御装置5に対するドア正常信号をONからOFFにするので、そのことでエレベータ制御装置5は、磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する。
When the
こういう判断をする理由は次のとおりである。すなわち、何かのきっかけで「永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置と、磁極位置カウンタ451cの対応関係が、ずれた状態」が発生してしまう場合があり、このような状態が実際に発生しているとドア制御部45において過電流やオーバースピード等の異常検出が起きてしまう可能性がある。したがって、ずれた状態を磁極位置推定制御の実施によって是正すれば、異常検出が再発しなくなる可能性があり、磁極位置推定制御を実施してみる意義があるからである。
The reason for making such a determination is as follows. That is, there is a case in which “the state where the correspondence between the magnetic pole position of the permanent
以上、ドア制御部45からドア正常信号をONからOFFにされることによって、エレベータ制御装置5が磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する場合を述べたが、エレベータ制御装置5自身が異常検出したり電源立上りを検出した場合には、磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると自身で判断する。これらの場合については後で述べる。
The case where the elevator control device 5 determines that the magnetic pole position estimation control needs to be performed by turning the door normal signal from ON to OFF from the
さて、磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断した場合、エレベータ制御装置5は、ドアセンサが作動していないならば、ドア制御部45に対する磁極位置推定指令をOFFからONにする。それと同時に、ドア制御部45に対する戸開指令または戸閉指令もOFFからONにする。逆にドアセンサが作動している場合は、作動しなくなってから磁極位置推定指令をONにする。ここでドアセンサとは、かごドア3や乗場ドア1の開閉を妨げる可能性がある人や物の存在を、接触式や非接触式で検知するために設けている種々のセンサを指しており、その作動状態をエレベータ制御装置5が常時見ているものである(図示しない)。
When it is determined that the magnetic pole position estimation control needs to be performed, the elevator control device 5 changes the magnetic pole position estimation command for the
これを受けてドア制御部45は、自身の運転状態を「通常運転モード」から「磁極位置推定モード」に切換える。そして、この切換内容を運転状態信号でもってエレベータ制御装置5に伝える。ドア制御部45においては、この磁極位置推定モードにおいて磁極位置推定制御が開始し、進行することになる。
In response to this, the
ドア制御部45において磁極位置推定制御が進行して完了すると、磁極位置推定モードから通常運転モードに切換え、それを受けてエレベータ制御装置5は磁極位置推定指令をOFFとする。しかし、戸開指令または戸閉指令はONを継続し、戸開制御または戸閉制御が開始する。
When the magnetic pole position estimation control proceeds and is completed in the
一方、ドア制御部45において磁極位置推定制御の進行中に異常検出した場合には、エレベータ制御装置5に対するドア正常信号をONからOFFにする。そして、磁極位置推定制御を中止し、磁極位置推定モードから通常運転モードに切換え、それを受けてエレベータ制御装置5は、磁極位置推定指令や、戸開指令または戸閉指令をOFFとする。
On the other hand, when the
なお、ドア制御部45が通常運転モードで過電流やオーバースピード等の異常検出をした場合にドア正常信号を変化させることを前述したが、ここで述べる磁極位置推定モードでの異常検出でも同様にドア正常信号を変化させることにしている。
As described above, the door normal signal is changed when the
この異常検出とは、例えばドアセンサが作動した場合である。他の異常検出としては、かごドア3と終端保持装置38の位置に関係するものや、エンコーダ46からドア制御部45への入力に関係するものがあり、後述の<磁極位置制御のフロー>という見出しの段落群で述べる。
This abnormality detection is, for example, when the door sensor is activated. Other abnormality detections include those related to the positions of the
異常検出したときは、ドア制御部45とエレベータ制御装置5の双方で、異常検出データをセットする。このデータは、異常検出の原因を解消し、磁極位置推定制御をやり直して完了させると、リセットされる。
When an abnormality is detected, abnormality detection data is set by both the
<電源立上りによる磁極位置推定モード>
ここで、エレベータ制御装置5が電源立上りを検出した場合に磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する場合について述べる。電源立上りを検出するとは、エレベータ制御装置5やドア制御部45を含むエレベータ全体に供給される電源が、保守作業等で一旦遮断された後に再投入されたり、停電発生後に復帰したりして立上ったことを検出することである。
<Magnetic pole position estimation mode at power-on>
Here, a case will be described in which it is determined that the magnetic pole position estimation control needs to be performed when the elevator control device 5 detects the rise of the power supply. The detection of the power supply rise means that the power supplied to the entire elevator including the elevator control device 5 and the
上記のように判断する理由は次のとおりである。すなわち、保守や停電のために給電されていない状態では、ドア(かごドア3および乗場ドア1)は、保守作業員の手で開け閉めされたり、乗場ドア1に働く自閉力によって戸閉動作が起きたりして、ドア位置が変化する可能性がある。ドア位置の変化に伴って、かごドア3に連動する永久磁石同期電動機41も回転し、エンコーダ46も回転する。しかし、給電されていない状態ではエンコーダ46からの信号は発生しないので、その信号をドア制御部45が受け取って磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPを更新することはできない。したがって、「永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置と、磁極位置カウンタ451cの対応関係が、ずれた状態」になってしまい、この状態を修正するには、磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要が出てくるのである。
The reason for judging as described above is as follows. That is, when power is not supplied due to maintenance or power failure, the doors (the
なお、エレベータ制御装置5が電源立上りを検出したとき、かご2が(階間ではなく)どこかの階に停止している場合、磁極位置推定モードに切り換えるタイミングの設計には選択の余地がある。というのは、電源立上り後、呼び登録が初めて発生する時点まで待ってから磁極位置推定モードに切換える設計も可能だからである。しかし、そうはせず、電源立上り直後の時点とする。
When the elevator controller 5 detects a power-up, and the
逆に、電源立上り直後の時点とはしない場合のほうを考えてみる。例えば、電源立上り後に呼び登録が初めて発生した時点で、その呼び登録が乗場呼び登録であり、登録された階にかご2が停止していて、ドア(かごドア3および乗場ドア1)が全閉位置にあったとき、呼び登録された時点になってから磁極位置推定モードに切換える場合を考える。すると、乗場ボタンを押してもすぐには戸開制御が始まらず、磁極位置推定制御の実施によって通常の開閉動作とは違うドアの挙動を経た上で、通常の戸開動作に移行することになる。その場合、エレベータがすぐには利用開始できず、ドアの不審な動作から始まるため、利用者を戸惑わせるおそれがある。そういう点を考えて、電源立上り直後の時点で磁極位置推定制御を開始して済ませておくようにする。すると、電源立上り後に呼び登録が初めて発生した時点では、すぐに通常の戸開制御から始めることができるので好都合である。
Conversely, let us consider the case where it is not the time immediately after the power is turned on. For example, when call registration occurs for the first time after the power is turned on, the call registration is hall call registration, the
ところで、電源立上り直後に、かご2がどこかの階に停止していてドアが全開位置にあった場合も、磁極位置推定制御の実施によって通常の開閉動作とは違うドアの挙動が始まるが、ドアの挙動は全開位置の付近で起きるだけであって、利用者としてはかご2に乗り込んでもよさそうに思ってしまうおそれがある。そして、電源立上り直後にドアが中間位置(全開位置でも全閉位置でもない位置)にあった場合も、同様のおそれがあると考えておく必要がある。
By the way, even when the
このような場合、かご内や乗場に設置した利用者への案内装置に対してエレベータ制御装置5から、エレベータの利用ができない状態であることを告知するよう指令する。例えば、「ドアから離れてください」といったアナウンスをしたり、ブザー音を鳴らしたりするよう指令する。また、「ドアから離れてください」といった文字を表示したり、かごの現在階を表示する文字周辺の表示色を通常とは違う色にしたりするよう指令する。あるいは、かごドア3や乗場ドア1に設置した発光装置(開閉動作中に点滅したりする装置)に対して点灯や点滅を指令することもできる。そうすることによって、磁極位置推定制御を実施している際にエレベータ利用者にドアが当ったり、磁極位置推定制御の進行が妨げられたりする可能性を削減することができる。
In such a case, the elevator control device 5 is instructed to notify the guidance device to the user installed in the car or the landing that the elevator cannot be used. For example, an announcement such as “Please leave the door” or a buzzer sound is issued. In addition, a command such as “Please leave the door” is displayed, or the display color around the character displaying the current floor of the car is instructed to be different from the normal color. Alternatively, lighting or blinking can be instructed to a light emitting device (a device that blinks during opening and closing operations) installed in the
なお、電源立上り直後のドア位置が全閉位置の場合には、ドアの挙動が全閉位置の付近で起きるので、利用者はかごに乗り込もうとは思わない可能性が高い。その場合、わざわざ告知すると、そのことによって逆に要らぬ懸念を与えてしまうことにもなりかねないので、告知しないほうがよい。以上のように、告知する要否を場合に応じて変えることによって、スムーズなエレベータ利用を図ることができる。 When the door position immediately after the power is turned on is the fully closed position, the door behavior occurs in the vicinity of the fully closed position, so the user is unlikely to think of getting into the car. In that case, it is better not to announce it because it may cause unnecessary concern. As described above, the elevator can be used smoothly by changing the necessity of notification depending on the case.
<戸開/閉不能による磁極位置推定モード>
ここでは、エレベータ制御装置5自身が異常検出して磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する場合について述べる。この異常検出するとは、戸開不能の検出(かごドア3に対してドア制御部45から戸開制御をさせているにもかかわらずかごドア3が全開位置に到らない状態)が連続したり、戸閉不能の検出(かごドア3に対してドア制御部45から戸閉制御をさせているにもかかわらずかごドア3が全閉位置に到らない状態)が連続したりする場合である。
<Magnetic pole position estimation mode when door cannot be opened / closed>
Here, a case will be described in which the elevator control device 5 itself detects an abnormality and determines that it is necessary to perform magnetic pole position estimation control. When this abnormality is detected, detection of the inability to open the door (a state in which the
このとき、エレベータ制御装置5がかごドア3は全開位置や全閉位置に到らないと判断するのは、ドア制御部45が、「戸開制御中や戸閉制御中には、戸開速度や戸閉速度が目標値に達する所まで電流指令値(q軸電流の振幅)を上昇させるという制御をするが、目標値に達する所まで行かない状態が何らかの不具合によって継続したために、電流指令値がとうとう設定上限値にまで達した」というトルク過大の検出をして、トルク過大信号ONを伝達してきた場合である。
At this time, the elevator control device 5 determines that the
また、戸開不能の検出が連続するとは次のことを指す。すなわち、エレベータが或る階に到着したときに全閉位置から戸開制御をしたが全開位置に到らないとき(戸開不能1回め)、戸閉制御に切り換えて全閉位置に戻してから再度の戸開制御により全開位置を目指したが不成功となり(戸開不能2回め)、同じことをもう一度繰り返したがやはり不成功となった(戸開不能3回め)という場合である。その場合、エレベータを別の階に移動して戸開制御をし、全開位置に到るかどうかを試みてやはり戸開不能3回となった場合は、エレベータを運行休止とする。なお、この3回という数は、その他の数に設定しても構わないので、以下では所定回数とする。 Further, the continuous detection of the inability to open the door means the following. In other words, when the elevator arrives at a certain floor, the door opening control is performed from the fully closed position, but when the elevator does not reach the fully opened position (the first time the door cannot be opened), switch to the door closing control and return to the fully closed position. It is a case where it aimed at the fully open position by the door opening control again, but it was unsuccessful (second opening impossible), and the same thing was repeated once again but it was still unsuccessful (third opening impossible). . In that case, the elevator is moved to another floor to perform door opening control, and if it reaches the fully opened position and the door cannot be opened three times, the elevator is put into operation suspension. Note that the number of three times may be set to other numbers, and is set to a predetermined number below.
さらに、戸閉不能の検出が連続するとは次のことを指す。すなわち、エレベータが或る階でドアが全開位置にあるときに戸閉制御をしたが全閉位置に到らないとき(戸閉不能1回め)、戸開制御によって全開位置に戻してから再度の戸閉制御により全開位置を目指したが不成功となった(戸閉不能2回め)という場合である。その後も、再度の戸閉制御により全開位置を目指すことを続けるが、例えば10回繰り返しても不成功となった場合はエレベータを運行休止とする。その後は、所定時間(例えば1分)が経過したら自動的に運行を再開して、再度の戸閉制御により全開位置を目指す。なお、この10回という数は、その他の数に設定しても構わないので、以下では所定回数とする。 Further, the continuous detection of the inability to close the door means the following. That is, when the elevator is door-closed on a certain floor and the door is in the fully open position but does not reach the fully closed position (the first time the door cannot be closed), return to the fully open position by the door open control and then again. This is a case where the fully open position is aimed at by the door closing control but is unsuccessful (the second time the door cannot be closed). After that, it continues to aim at the fully opened position by the door closing control again. However, if the operation is unsuccessful even after repeated 10 times, the elevator is stopped. Thereafter, when a predetermined time (for example, 1 minute) elapses, the operation is automatically restarted, and the fully open position is aimed at by the door closing control again. Note that the number of 10 times may be set to other numbers, and is set to a predetermined number below.
エレベータ制御装置5が戸開不能や戸閉不能を検出する場合に磁極位置推定制御を実施する必要があると判断する理由は、次のとおりである。すなわち、何かのきっかけで「永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置と、磁極位置カウンタ451cの対応関係が、ずれた状態」が発生してしまう場合があり、このような状態が実際に発生しているとドア制御部45においてトルク過大の検出が起きてしまう可能性がある。したがって、ずれた状態を磁極位置推定制御の実施によって是正すれば、異常検出が再発しなくなる可能性があり、磁極位置推定制御を実施してみる意義があるからである。
The reason why it is determined that the magnetic pole position estimation control needs to be performed when the elevator control device 5 detects that the door cannot be opened or cannot be closed is as follows. That is, there is a case in which “the state where the correspondence between the magnetic pole position of the permanent
なお、エレベータ制御装置5が戸開不能を連続検出した場合(ドアセンサも作動していない場合)に、磁極位置推定モードへと切換えるタイミングの設計には選択の余地がある。というのは、かご2が別の階に移動したときの戸開不能が1回めの後で磁極位置推定モードに切換えるか、あるいは所定回数到達後に切換えるか、あるいはその間の回数かという選択が考えられるからである。
When the elevator control device 5 continuously detects that the door cannot be opened (when the door sensor is not operating), there is room for selection in designing the timing for switching to the magnetic pole position estimation mode. This is because it is possible to select whether the inability to open the door when the
このような選択の幅がある中で「所定回数−1」回めを選ぶことにする。つまり、戸開不能が「所定回数−1」回めとなった後、全閉位置に戻して(戸開制御から始めるのではなく)まず磁極位置推定制御を実施し、その後で戸開制御を実施すると、戸開不能を検出しなくなるのではないかを試すことにする。しかし、やはり戸開不能を検出するのであればエレベータを運行休止させることになる。 Within such a range of selection, the “predetermined number minus 1” turn is selected. In other words, after the inability to open the door becomes the “predetermined number of times −1”, it is returned to the fully closed position (not starting from the door opening control), and first the magnetic pole position estimation control is performed. If implemented, it will be tested whether it will not detect the inability to open the door. However, if it is detected that the door cannot be opened, the elevator is suspended.
このように、戸開不能を検出するかどうかを試す最後の1回で、戸開制御の前に磁極位置推定制御を実施するほうが、それ以前の段階で実施するよりも、通常の開閉動作とは違うドアの挙動を利用者の目に触れさせる機会が減るので好都合である。なぜなら、戸開不能が発生した階から移動した別の階では、かごドアと係合する乗場ドアが替わることによって戸開不能が出なくなる可能性など、別の階に移ることによる改善効果が考えられるからである。そのような可能性に賭けて、戸開不能を検出するかどうかを試す最後の1回までは、磁極位置推定制御を実施せずに戸開制御だけをさせてみる。そのことで戸開不能が検出されなくなるようであれば、通常の開閉動作とは違うドアの挙動を利用者の目に触れさせる機会もなくて済み、好都合である。つまり、このような機会を最後の1回にまで先延ばししようとする意図である。 Thus, in the last attempt to detect whether or not the door cannot be opened, it is more normal to perform the magnetic pole position estimation control before the door opening control than to perform the normal opening / closing operation. This is advantageous because it reduces the chance of different door behavior being exposed to the user. This is because there is an improvement effect of moving to another floor, such as the possibility of the door not being able to open by changing the landing door that engages with the car door on another floor that has moved from the floor where the door cannot be opened. Because it is. Betting on such a possibility, only the door opening control is performed without performing the magnetic pole position estimation control until the last time of trying to detect whether the door opening failure is detected. If this makes it impossible to detect that the door cannot be opened, there is no need to let the user see the door behavior different from the normal opening / closing operation, which is convenient. In other words, the intention is to postpone such an opportunity until the last one.
また、エレベータ制御装置5が戸閉不能を連続検出した場合に、磁極位置推定モードへと切換えるタイミングの設計としては、戸閉不能の検出が所定回数に達した時とすることが考えられる。しかし、そうはせず、戸閉不能の検出が所定回数に達して運行休止とした後、所定時間が経過して自動的に運行再開となった直後とする。つまりこの時に、「まずは磁極位置推定制御を実施し、その後で戸閉制御を実施すると、戸閉不能を検出しなくなるのではないか」を試すことにする。 In addition, when the elevator control device 5 continuously detects the inability to close the door, the design of the timing for switching to the magnetic pole position estimation mode may be when the detection of the inability to close the door reaches a predetermined number of times. However, instead of doing so, it is assumed that the detection of the inability to close the door reaches a predetermined number of times and the operation is stopped, and then the operation is automatically resumed after a predetermined time has elapsed. In other words, at this time, it will be tried whether "when the magnetic pole position estimation control is performed first and then the door closing control is performed, it will not be detected that the door cannot be closed".
このように、戸閉不能の検出が所定回数に達して運行休止とするまでの段階で磁極位置推定制御を実施するよりも、運行休止とした後、所定時間が経過して自動的に運行再開となった直後に磁極位置推定制御を実施するほうが、通常の開閉動作とは違うドアの挙動を利用者の目に触れさせる機会が減るので好都合である。なぜなら、運行休止とするまでの段階で利用者がドアの挙動に注目していても、運行休止となりエレベータ利用が不可となることによって、利用者がエレベータから離れてしまい注目することがなくなるということが十分考えられるからである。 Thus, rather than performing the magnetic pole position estimation control at the stage where the detection of the inability to close the door reaches the predetermined number of times until the operation is stopped, the operation is automatically resumed after the predetermined time has elapsed after the operation is stopped. It is more convenient to perform the magnetic pole position estimation control immediately after it becomes, because the opportunity for the user to touch the door behavior different from the normal opening / closing operation is reduced. Because even if the user is paying attention to the behavior of the door at the stage until the operation is stopped, the operation is stopped and the elevator cannot be used, so that the user leaves the elevator and does not pay attention. This is because there is enough consideration.
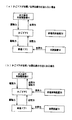
<磁極位置推定モード時のフェーズ移行>
磁極位置推定モードにおける磁極位置推定制御の実施中は、3つのフェーズ(磁極位置確認フェーズ、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズ)が移行する。その移行の仕方は、戸開指令ONを受信したときのかごドア3の位置によって変動する。
<Phase transition in magnetic pole position estimation mode>
During the execution of the magnetic pole position estimation control in the magnetic pole position estimation mode, three phases (the magnetic pole position confirmation phase, the holding zone escape phase, and the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase) shift. The transition method varies depending on the position of the
図10に示すように、戸開指令ONを受信したときのかごドア3の位置が全閉位置P1であった場合、磁極位置推定制御は、磁極位置確認フェーズ、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズという順に推移する3段階で構成される。この保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ終了時に磁極位置情報MPが書き換えられ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズの終了時に補正情報MPCが書き換えられる。なお、こういう結果に到達することが、磁極位置推定制御が完了するということの意味である。
As shown in FIG. 10, when the position of the
また、保持解除ゾーンZ3内であった場合、磁極位置推定制御は、磁極位置確認フェーズ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズという順に推移する2段階で構成される。この磁極位置確認フェーズ終了時に磁極位置情報MPが書き換えられ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズの終了時に補正情報MPCが書き換えられる。なお、こういう結果に到達することが、磁極位置推定制御が完了するということの意味である。 In addition, when it is in the holding release zone Z3, the magnetic pole position estimation control is composed of two stages that transition in the order of the magnetic pole position confirmation phase and the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase. The magnetic pole position information MP is rewritten at the end of the magnetic pole position confirmation phase, and the correction information MPC is rewritten at the end of the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase. Note that reaching such a result means that the magnetic pole position estimation control is completed.
以上のように、戸開指令ONを受信したときのかごドア3の位置は、全閉位置P1か、保持解除ゾーンZ3内かの、いずれかとなるのであるが、その理由は次のとおりである。
As described above, the position of the
かごドア3の位置は、全閉位置P1か、保持解除ゾーンZ3内か、全開位置P2かである。なぜなら、全閉位置P1以外の閉保持ゾーンZ1内では、終端保持装置38が作用して全閉位置P1に移動させられ、全開位置P2以外の開保持ゾーンZ2内では、終端保持装置38が作用して全開位置P2に移動させられるからである。
The position of the
そして、エレベータ制御装置5が戸開指令ONを発するときのかごドア3の位置は、全閉位置P1か、保持解除ゾーンZ3内かであり、全開位置P2にあることはない。なぜなら、エレベータ制御装置5は、全開位置検出部39bからの信号で、かごドア3が全開位置P2にあることを知ると、戸開指令ONを発することはないからである。
The position of the
以上、戸「開」指令ONの受信がきっかけとなって通常運転モードから磁極位置推定モードに移った場合を述べたが、戸「閉」指令ONの受信がきっかけとなる場合については説明を省略する(以降の説明でも同様とする)。なぜなら、戸「開」指令ONの受信がきっかけの場合に対し、かごドア3を動かす全局面で動かす方向を逆にしたり、かごドア3の位置を全閉位置P1との関係で見る代りに全開位置P2との関係で見るようにしたりするだけで、それ以外の点は全く同じ内容となるからである。
In the above, the case where the door “open” command ON is received as a trigger and the mode is shifted from the normal operation mode to the magnetic pole position estimation mode has been described. However, the case where the door “close” command ON is triggered is omitted. (The same applies to the following description). This is because, instead of receiving the door “open” command ON, the direction in which the
以下では、これらの各フェーズ(磁極位置確認フェーズ、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズ)それぞれで実施する内容について述べる。 The contents to be implemented in each of these phases (magnetic pole position confirmation phase, holding zone escape phase, magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase) will be described below.
<磁極位置確認フェーズ>
磁極位置確認フェーズでは、或る一つの電流位相で永久磁石同期電動機41に直流電流を流す。この電流位相と磁極位置が違っていた場合、この電流位相に対して磁極位置がほぼ一致しようとして回転子が回転するが、この回転したことを検出すると、電流位相と磁極位置の違いが基本的に解消されたと判断する。しかし、この電流位相に対して磁極位置が初めからほぼ一致していた場合には、回転子は回転しないので、改めて別の電流位相を指令することによって回転子を回転させ、回転したことを検出したら、電流位相と磁極位置の違いが基本的に解消されたと判断する(ステップS1)。
<Magnetic pole position confirmation phase>
In the magnetic pole position confirmation phase, a direct current is passed through the permanent
このような、電流位相と磁極位置の違いが基本的に解消されたと判断したときの電流位相でもって磁極位置情報MPを書き換える、としたいところではあるが、その書き換えは、戸開指令ONを受信したときのかごドア3の位置が保持解除ゾーンZ3内であった場合(ステップS2で「保持解除ゾーンZ3」を選択)のみ実施する(ステップS4)。全閉位置P1であった場合(ステップS2で「全閉位置P1」を選択)は、次の保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ終了時に書き換えることにする(ステップS3,S4)。
The magnetic pole position information MP is rewritten with the current phase when it is determined that the difference between the current phase and the magnetic pole position is basically eliminated. Only when the position of the
なお、回転したことを検出するに到るまで、いくつかの電流位相を試すのであるが、そのような電流位相のセットは、セット中のいずれかの電流位相で必ず回転が起きるといった電流位相で構成されておればよい。これらの電流位相を切換えてゆく際には、速度制御部451は、電流が途切れないように電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。 It should be noted that several current phases are tried until the rotation is detected, but such a current phase set is a current phase in which rotation always occurs at any current phase in the set. What is necessary is just to be comprised. When these current phases are switched, the speed control unit 451 continuously outputs a current command value so that the current is not interrupted.
<保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ>
保持ゾーン脱出フェーズは、戸開指令ONを受信したときのかごドア3の位置が全閉位置P1の場合のみ適用するフェーズである。このフェーズでは、電流位相と磁極位置の違いが基本的に解消されたと判断したときの電流位相から始めて電流位相を小刻みに変化させ、位相変化が所定量となる電流位相に到達すると電流位相の変化をとめる。このようにして、電流位相が寸動するのに沿って磁極位置が追従することによって回転子が寸動をくり返し、かごドア3を全閉位置P1近傍から保持解除ゾーンZ3内にまで移動させる。この移動終了時の電流位相でもって磁極位置情報MPを書き換える(ステップS3,S4)。
<Retention zone escape phase>
The holding zone escape phase is a phase applied only when the position of the
なお、電流位相を小刻みに変化させる際の位相間隔は、回転子の寸動距離が大きくなってかごドア3や乗場ドア1がギクシャクした動きになってしまわないような間隔であるのが好ましい。また、小刻みな位相変化の際、速度制御部451は、電流が途切れないよう電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。さらに、磁極位置確認フェーズから移行する際についても、電流が途切れないよう電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。
Note that the phase interval when the current phase is changed in small increments is preferably an interval that does not cause the
かごドア3を保持解除ゾーンZ3内にまで移動させるのは、終端保持装置38の力が影響しない状態にしておいてから、次の磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズを実施するようにしたいからである。また、電流位相に磁極位置が一致しようとするときに、終端保持装置38の力に影響されてズレが生じるので、そのズレがない所で、磁極位置とよく一致した状態の電流位相でもって磁極位置情報MPを書き換えるのが好ましいからである。
The reason why the
かごドア3を全閉位置P1から保持解除ゾーンZ3内にまで移動させる際は、閉保持ゾーンZ1の距離に、保持解除ゾーンZ3内に確実に入るための余裕分を加算し、その距離だけかごドア3を移動させる。この距離に相当した回転子の回転量を得るために電流位相をどれだけ変化させればよいのかという量(位相変化の所定量)は、速度制御部451内に記憶されている。
When the
<磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズ>
磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズでは、前段(磁極位置確認フェーズまたは保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ)で到達した電流位相を出発点にする。その位相(開始位相)から始めて電流位相を小刻みに変化させ、目標設定した電流位相(目標位相)に到達すると電流位相の変化をとめる。例えば、60度から始めて1度刻みに、61度、62度、……、299度、300度と変化させ、300度でとめる。
<Magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase>
In the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase, the current phase reached in the previous stage (the magnetic pole position confirmation phase or the holding zone escape phase) is used as a starting point. Starting from the phase (starting phase), the current phase is changed in small increments, and when the target current phase (target phase) is reached, the change in the current phase is stopped. For example, starting from 60 degrees, in increments of 1 degree, 61 degrees, 62 degrees,... 299 degrees, and 300 degrees are changed and stopped at 300 degrees.
このようにして、電流位相の寸動に磁極位置が追従して回転子が寸動をくり返すのであるが、電流位相と磁極位置が、ほぼ一致した状態に追従することをくり返すとはいうものの、一定のズレが生じてしまう。ズレの原因は、乗場ドア1に掛かっている自閉力である。それが、乗場ドア1と連動するかごドア3から、さらに伝達機構を通じて永久磁石同期電動機41に影響を及ぼし、電流位相と磁極位置の完全一致を妨げるのである。
In this way, the magnetic pole position follows the jogging of the current phase, and the rotor repeats the jogging, but it is said that the current phase and the magnetic pole position follow the state where they substantially match. However, a certain amount of deviation occurs. The cause of the deviation is a self-closing force applied to the landing door 1. This influences the permanent
このようなズレの量を演算して補正情報MPCを書き換えることにする。そのため、目標位相に到った時点で、磁極位置カウンタ451cから磁極位置情報MPを読みとる。以上をステップS5で実施している。 The correction information MPC is rewritten by calculating the amount of such deviation. Therefore, when the target phase is reached, the magnetic pole position information MP is read from the magnetic pole position counter 451c. The above is performed in step S5.
磁極位置情報MPの値は、目標位相に磁極位置が完全一致しているとした場合には「K×目標位相」となる。このKは、前述したように、パルスカウント値N0から位相への換算係数であり、例えば15という値になる。よって、目標位相が300度の場合は、磁極位置情報MP=15×300=4500となる。 The value of the magnetic pole position information MP is “K × target phase” when the magnetic pole position is completely coincident with the target phase. As described above, K is a conversion coefficient from the pulse count value N0 to the phase, and has a value of 15, for example. Therefore, when the target phase is 300 degrees, the magnetic pole position information MP = 15 × 300 = 4500.
ところが、磁極位置カウンタ451cから読みとった磁極位置情報MPの実際値としては4485だったとすると、4485−4500=(−15)のズレが生じていることになる。このようなズレの量でもって、補正情報記憶部451dの補正情報MPCを書き換える(ステップS6)。 However, if the actual value of the magnetic pole position information MP read from the magnetic pole position counter 451c is 4485, a deviation of 4485-4500 = (− 15) is generated. The correction information MPC in the correction information storage unit 451d is rewritten with such an amount of deviation (step S6).
以上のように、開始位相から目標位相へと電流位相を小刻みに変化させ、目標位相に達したときに磁極位置カウンタ451cから磁極位置を読みとり、そこからズレ量を演算して補正情報MPCを書き換えるという手順となる。 As described above, the current phase is changed in small increments from the start phase to the target phase, and when the target phase is reached, the magnetic pole position is read from the magnetic pole position counter 451c, the deviation amount is calculated therefrom, and the correction information MPC is rewritten. It becomes the procedure.
この手順においては、かごドア3が戸「開」する方向に回転させたのか、戸「閉」する方向に回転させたのかという違いにこだわることも可能である。つまり、永久磁石同期電動機41に対する自閉力の影響が、戸「開」方向と戸「閉」方向とで何らかの違いを生じるので、この点を考慮することが好ましい。
In this procedure, it is possible to stick to the difference between whether the
そこで代表的な実施例としては、戸「開」方向の回転1回と、戸「閉」方向の回転1回とで、上記手順を2回行うことにする。その場合、戸「開」方向で目標位相(第1位相と称する)に達したときに読みとった磁極位置カウンタ451cの値を第1計測位置と名づけ、戸「閉」方向で目標位相(第2位相と称する)に達したときに読みとった磁極位置カウンタ451cの値を第2計測位置と名づける。そして、第1計測位置から演算したズレ量と、第2計測位置から演算したズレ量とを平均した値でもって補正情報MPCを書き換えることにする。 Therefore, as a typical embodiment, the above procedure is performed twice for one rotation in the door “open” direction and one rotation in the door “closed” direction. In that case, the value of the magnetic pole position counter 451c read when the target phase (referred to as the first phase) is reached in the door “open” direction is named the first measurement position, and the target phase (second phase) in the door “closed” direction. The value of the magnetic pole position counter 451c read when the phase reaches (referred to as phase) is named the second measurement position. Then, the correction information MPC is rewritten with a value obtained by averaging the amount of deviation calculated from the first measurement position and the amount of deviation calculated from the second measurement position.
あるいは、戸「開」方向と戸「閉」方向の違いをもっと活かすやり方も考えられる。すなわち、第1計測位置から演算したズレ量でもって書き換える補正情報MPC1と、第2計測位置から演算したズレ量でもって書き換える補正情報MPC2とを設け、通常運転モードの戸「開」制御では、スタート時のd軸電流の位相を「MP+MPC1」を用いて決定し、戸「閉」制御では「MP+MPC2」を用いて決定するというわけである。 Alternatively, a method of making more use of the difference between the door “open” direction and the door “closed” direction can be considered. That is, the correction information MPC1 to be rewritten with the amount of deviation calculated from the first measurement position and the correction information MPC2 to be rewritten with the amount of deviation calculated from the second measurement position are provided. The phase of the d-axis current at that time is determined using “MP + MPC1”, and the door “closed” control is determined using “MP + MPC2”.
なお、戸開方向の回転と戸閉方向の回転の、両方を実施する場合は、戸開方向を先に実施したほうが、エレベータ利用者が誤って乗込もうとするようなことがあったとしても、ドアに衝突する確率が減らせるので、好ましい。この点は、戸「開」指令ONの受信で磁極位置推定制御を開始した場合だけでなく、戸「閉」指令ONの受信で磁極位置推定制御を開始した場合も同様である。先述した箇所では、戸「開」指令の場合と戸「閉」指令の場合で、「開」と「閉」を逆にすれば同じ動作になるという趣旨を述べたが、本件については逆にするのではなくて、どちらの場合も「開」のほうを「閉」よりも優先して実施するのが好ましい。 In addition, when carrying out both the rotation in the door opening direction and the rotation in the door closing direction, it was assumed that the elevator user tried to get in by mistake if the door opening direction was carried out first. However, it is preferable because the probability of collision with the door can be reduced. This is the same not only when the magnetic pole position estimation control is started by receiving the door “open” command ON, but also when the magnetic pole position estimation control is started by receiving the door “close” command ON. In the above-mentioned part, it was stated that the same operation would be achieved by reversing "open" and "closed" in the case of door "open" command and door "closed" command. Instead, in either case, it is preferable to implement “open” in preference to “close”.
目標位相の設定は、開始位相から目標位相への変化量をどうするかで決ってくる。この変化量については、少なすぎると、上記ズレ量の計測値のバラつきが大きくなると考えられるので、そうならない程度の量以上とする。また、磁極位置推定制御の実施中は、エレベータの一般利用を中断している状態となるため、誤ってかごに乗り降りすることを招かないように、かごドア3の移動量をなるべく小さくできる程度の量に留めるのが好ましい。
The setting of the target phase is determined depending on the amount of change from the start phase to the target phase. If the amount of change is too small, the variation in the measured value of the amount of deviation is considered to be large. Further, during the execution of the magnetic pole position estimation control, the general use of the elevator is interrupted, so that the amount of movement of the
電流位相を小刻みに変化させる際の位相間隔は、回転子の寸動距離が大きくなってかごドア3や乗場ドア1がギクシャクした動きになってしまわないような間隔であるのが好ましい。そして、小刻みな位相変化の際に速度制御部451は、電流が途切れないよう電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。
The phase interval when the current phase is changed in small increments is preferably an interval that does not cause the
また、戸「開」する方向の回転から、戸「閉」する方向の回転へと切換わる際にも、電流が途切れないよう電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。さらに、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズから移行する際についても、電流が途切れないよう電流指令値を出し続けるものとする。 Further, it is assumed that the current command value is continuously output so that the current is not interrupted when switching from the rotation in the door “open” direction to the rotation in the door “closed” direction. Further, even when shifting from the holding zone escape phase, the current command value is continuously output so that the current is not interrupted.
<磁極位置推定制御のフロー>
上記のように、磁極位置推定制御の各フェーズ(磁極位置確認フェーズ、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズ、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズ)について詳細を述べたが、その内容を制御手順の流れに沿って述べ直すことにする。それを図示したものが図11ないし図13である。そこでは、磁極位置推定部456を構成部位に分けて役割分担を示してある。構成部位とは、図9に示すように、磁極固定部456aと、磁極情報取得部456bと、磁極情報演算部456cである。
<Flow of magnetic pole position estimation control>
As described above, the details of each phase of the magnetic pole position estimation control (the magnetic pole position confirmation phase, the holding zone escape phase, and the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase) have been described, but the contents will be rewritten along the flow of the control procedure. To do. This is illustrated in FIGS. 11 to 13. Here, the magnetic pole position estimation unit 456 is divided into constituent parts and role sharing is shown. As shown in FIG. 9, the component parts are a magnetic pole fixing unit 456a, a magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b, and a magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c.
図11は、磁極位置確認フェーズにおいて磁極位置推定部456の各部(磁極固定部456a、磁極情報取得部456b、磁極情報演算部456c)がそれぞれどうふるまうのかを示している。 FIG. 11 shows how each part (the magnetic pole fixing part 456a, the magnetic pole information acquisition part 456b, and the magnetic pole information calculation part 456c) of the magnetic pole position estimation part 456 behaves in the magnetic pole position confirmation phase.
まず、磁極固定部456aは、0度の位相指令を速度制御部451に発する(ステップS11)。すると、電機子巻線に0度位相の直流電流が流れて起磁力が発生し、起磁力の方向に磁極位置が一致すべく回転子が回転しようとする。磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報取得部456bは、位相指令が発された前と後に磁極位置カウンタ451cを読みとって、それぞれの値を磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS12)。磁極情報演算部456cは、前の値に比べ、後の値に変化があったかどうかを見て、回転子が回転動作を起したのかどうかを判断し、結果を磁極固定部456aに送る(ステップS13)。 First, the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a issues a phase command of 0 degree to the speed control unit 451 (step S11). Then, a DC current having a phase of 0 degrees flows through the armature winding to generate a magnetomotive force, and the rotor attempts to rotate so that the magnetic pole position coincides with the direction of the magnetomotive force. In response to a command from the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a, the magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b reads the magnetic pole position counter 451c before and after the phase command is issued, and sends each value to the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c (step S12). The magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c determines whether or not the rotor has been rotated by checking whether or not the subsequent value has changed compared to the previous value, and sends the result to the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a (step S13). ).
磁極固定部456aは、回転動作が起きていた場合、磁極位置確認フェーズの終了へと進める(ステップS20)。 If the rotation operation has occurred, the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a proceeds to the end of the magnetic pole position confirmation phase (step S20).
一方、回転動作が起きていなかった場合は、先ほどの0度から変更した120度の位相指令を、速度制御部451に発する(ステップS21)。磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報取得部456bは、位相指令が発された前と後に磁極位置カウンタ451cを読みとって、それぞれの値を磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS22)。磁極情報演算部456cは、前の値に比べ、後の値に変化があったかどうかを見て、回転子が回転動作を起したのかどうかを判断し、結果を磁極固定部456aに送る(ステップS23)。 On the other hand, if the rotation operation has not occurred, a phase command of 120 degrees changed from the previous 0 degrees is issued to the speed control unit 451 (step S21). In response to a command from the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a, the magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b reads the magnetic pole position counter 451c before and after the phase command is issued, and sends each value to the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c (step S22). The magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c determines whether or not the rotor has been rotated by checking whether or not the subsequent value has changed compared to the previous value, and sends the result to the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a (step S23). ).
磁極固定部456aは、回転動作が起きていた場合、磁極位置確認フェーズの終了へと進める(ステップS30)。回転動作が起きていなかった場合は、先ほどの0度や120度から変更した240度の位相指令を、速度制御部451に発する(ステップS31)。今度は必ず回転動作が起きるはずなので、磁極位置確認フェーズの終了へと進める(ステップS32)。 When the rotation operation is occurring, the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a proceeds to the end of the magnetic pole position confirmation phase (step S30). If the rotation operation has not occurred, a phase command of 240 degrees changed from the previous 0 degree or 120 degrees is issued to the speed control unit 451 (step S31). Since a rotation operation should surely occur this time, the process proceeds to the end of the magnetic pole position confirmation phase (step S32).
次に移るフェーズが、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズではなくて磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズの場合のみ、磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報演算部456cは、磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPを書き換える。書き換える値は、フェーズ終了直前に位相指令されていた角度を換算係数K=15でもってカウント値に換算した値であり、0(15×0度)か、1800(15×120度)か、3600(15×240度)となる(ステップS40)。 The magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c rewrites the magnetic pole position information MP of the magnetic pole position counter 451c only in response to a command from the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a only when the next phase is not the holding zone escape phase but the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase. The value to be rewritten is a value obtained by converting the angle commanded immediately before the end of the phase into a count value with a conversion coefficient K = 15, and is 0 (15 × 0 degrees), 1800 (15 × 120 degrees), 3600 (15 × 240 degrees) (step S40).
図12は、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズにおいて磁極位置推定部456の各部(磁極固定部456a、磁極情報取得部456b、磁極情報演算部456c)がそれぞれどうふるまうのかを示している。 FIG. 12 shows how each part of the magnetic pole position estimation unit 456 (the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a, the magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b, and the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c) behaves in the holding zone escape phase.
磁極固定部456aは、120度から359度まで、続いて0度から60度まで、1度刻みの位相指令を、次々に速度制御部451に発する(ステップS51)。すると、電機子巻線に流れる直流電流の位相が変化すると共に、発生する起磁力の方向も変化する。このような起磁力の方向の寸動に磁極位置が追従して、回転子が全閉位置P1近傍から戸開方向に回転し、かごドア3は閉保持ゾーンZ1を脱出して保持解除ゾーンZ3に突入する。この移動終了時の位相60度という値を、磁極固定部456aは磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS52)。磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報演算部456cは、15×60=900という値でもって、磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPを書き換える(ステップS53)。
The magnetic pole fixing unit 456a sequentially issues phase commands in increments of 1 degree from 120 degrees to 359 degrees and subsequently from 0 degrees to 60 degrees to the speed control section 451 (step S51). Then, the phase of the direct current flowing through the armature winding changes and the direction of the magnetomotive force generated also changes. The position of the magnetic pole follows such inching in the direction of the magnetomotive force, the rotor rotates in the door opening direction from the vicinity of the fully closed position P1, and the
上記のように、磁極固定部456aが1度刻みの位相指令を次々に速度制御部451に発すると回転子が回転し、それに伴って磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPが変化するはずであるが、位相指令の変化量に見合っただけの変化がないとか、全く変化しないとかといった異常が発生する可能性がある。このような場合は、磁極位置推定制御を中止する(<磁極位置推定制御の開始、完了>という見出しの段落群で挙げていた一例である)。そうすることにより、回転子が到達した位置を誤認してしまう(磁極位置カウンタ451cから、妥当でない値を読みとってしまう)ことを防止することができる。 As described above, when the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a sequentially issues a phase command in increments of 1 degree to the speed control unit 451, the rotor rotates, and the magnetic pole position information MP of the magnetic pole position counter 451c should change accordingly. However, there is a possibility that an abnormality such as no change corresponding to the change amount of the phase command or no change at all occurs. In such a case, the magnetic pole position estimation control is stopped (this is an example given in the group of paragraphs entitled <Start and completion of magnetic pole position estimation control>). By doing so, it is possible to prevent misrecognizing the position where the rotor has reached (reading an invalid value from the magnetic pole position counter 451c).
このような異常が発生するのは、回転子が実際に回転している場合と、回転子が回転していない場合がある。回転子が実際に回転している場合の原因としては、例えばエンコーダ46の故障が考えられる。また、回転子が回転していない場合の原因としては、かごドア3や乗場ドア1の動きが悪いこと等が考えられる。例えば、ドアの据付・調整状態が機械的に万全でなかったり、開閉する行路に何らかの物体が挟まっていたりする場合である。
Such an abnormality may occur when the rotor is actually rotating or when the rotor is not rotating. As a cause when the rotor is actually rotating, for example, a failure of the
図13は、磁極位置ズレ計測フェーズにおいて磁極位置推定部456の各部(磁極固定部456a、磁極情報取得部456b、磁極情報演算部456c)がそれぞれどうふるまうのかを示している。 FIG. 13 shows how each part of the magnetic pole position estimation unit 456 (the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a, the magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b, and the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c) behaves in the magnetic pole position deviation measurement phase.
(磁極位置確認フェーズから移行した場合ではなく、保持ゾーン脱出フェーズから移行した場合の、最後の位相60度を例にとると、)磁極固定部456aは、60度から300度まで1度刻みの位相指令を、次々に速度制御部451に発する(ステップS61)。すると、電機子巻線に流れる直流電流の位相が変化すると共に、発生する起磁力の方向も変化する。このような起磁力の方向の寸動に磁極位置が追従して、かごドア3が戸開する方向に回転子が回転する。終了時の位相300度という値を、磁極固定部456aは磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS62)。磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報取得部456bは、磁極位置カウンタ451cを読みとって(例えば4485という値)、磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS63)。
(Take the last phase of 60 degrees as an example when shifting from the holding zone escape phase, not when shifting from the magnetic pole position confirmation phase) The magnetic pole fixing portion 456a is incremented by 1 degree from 60 degrees to 300 degrees. Phase commands are issued to the speed controller 451 one after another (step S61). Then, the phase of the direct current flowing through the armature winding changes and the direction of the magnetomotive force generated also changes. The position of the magnetic pole follows the inching in the direction of the magnetomotive force, and the rotor rotates in the direction in which the
次に、磁極固定部456aは、300度から180度まで1度刻みの位相指令を、次々に速度制御部451に発する(ステップS71)。すると、電機子巻線に流れる直流電流の位相が変化すると共に、発生する起磁力の方向も変化する。このような起磁力の方向の寸動に磁極位置が追従して、かごドア3が戸閉する方向に回転子が回転する。終了時の位相180度という値を、磁極固定部456aは磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS72)。磁極固定部456aからの指令により磁極情報取得部456bは、磁極位置カウンタ451cを読みとって(例えば2655という値)、磁極情報演算部456cに送る(ステップS73)。
Next, the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a sequentially issues a phase command in increments of 1 degree from 300 degrees to 180 degrees to the speed control unit 451 (step S71). Then, the phase of the direct current flowing through the armature winding changes and the direction of the magnetomotive force generated also changes. The position of the magnetic pole follows the inching in the direction of the magnetomotive force, and the rotor rotates in the direction in which the
かごドア3が戸閉する方向に回転子が回転した際、何かの見当違い等で、閉保持ゾーンZ1に突入してしまうことも発生する可能性がある。そのような場合は、磁極位置推定制御を中止する(<磁極位置推定制御の開始、完了>という見出しの段落群で挙げていた一例である)。なぜなら、閉保持ゾーンZ1内では終端保持装置38の力によってかごドア3が動いてしまい、それに連動して永久磁石同期電動機41の回転子の位置も、最後の電流位相指令に見合った位置からずれてしまうので、磁極位置カウンタ451cから読みとった値が妥当なものではないからである。
When the rotor rotates in the direction in which the
また上記のように、磁極固定部456aが1度刻みの位相指令を次々に速度制御部451に発すると回転子が回転し、それに伴って磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPが変化するはずであるが、位相指令の変化量に見合っただけの変化がないとか、全く変化しないとかといった異常が発生する可能性がある。このような場合は、磁極位置推定制御を中止する(<磁極位置推定制御の開始、完了>という見出しの段落群で挙げていた一例である)。そうすることにより、回転子が到達した位置を誤認してしまう(磁極位置カウンタ451cから、妥当でない値を読みとってしまう)ことを防止することができる。 Further, as described above, when the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a issues phase commands in increments of 1 degree to the speed control unit 451 one after another, the rotor rotates, and the magnetic pole position information MP of the magnetic pole position counter 451c should change accordingly. However, there is a possibility that an abnormality such as no change corresponding to the change amount of the phase command or no change at all occurs. In such a case, the magnetic pole position estimation control is stopped (this is an example given in the group of paragraphs entitled <Start and completion of magnetic pole position estimation control>). By doing so, it is possible to prevent misrecognizing the position where the rotor has reached (reading an invalid value from the magnetic pole position counter 451c).
このような異常が発生するのは、回転子が実際に回転している場合と、回転子が回転していない場合がある。回転子が実際に回転している場合の原因としては、例えばエンコーダ46の故障が考えられる。また、回転子が回転していない場合の原因としては、かごドア3や乗場ドア1の動きが悪いこと等が考えられる。例えば、ドアの据付・調整状態が機械的に万全でなかったり、開閉する行路に何らかの物体が挟まっていたりする場合である。
Such an abnormality may occur when the rotor is actually rotating or when the rotor is not rotating. As a cause when the rotor is actually rotating, for example, a failure of the
上記のようにして磁極情報取得部456bが磁極位置カウンタ451cから読みとった値を基にして、磁極情報演算部456cは、磁極固定部456aからの指令を受けて以下3段階の演算をする。まず、1回目に読みとった値4485と、換算係数K=15と、1回目の終了時の位相300度を使って、4485−15×300=(−15)と演算する(ステップS81)。次に、磁極情報演算部456cは、2回目に読みとった値2655と、換算係数K=15と、2回目の終了時の位相180度を使って、2655−15×180=(−45)と演算する(ステップS82)。最後に、磁極情報演算部456cは、演算結果(−15)と(−45)を使って、{(−15)+(−45)}÷2=(−30)と演算する(ステップS83)。磁極情報演算部456cは、上記で得た(−30)でもって、補正情報記憶部451dの補正情報MPCを書き換える(ステップS84)。 Based on the value read from the magnetic pole position counter 451c by the magnetic pole information acquisition unit 456b as described above, the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c receives the command from the magnetic pole fixing unit 456a and performs the following three steps of calculation. First, 4485-15 × 300 = (− 15) is calculated using the value 4485 read at the first time, the conversion coefficient K = 15, and the phase at the end of the first time 300 degrees (step S81). Next, the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c uses the value 2655 read at the second time, the conversion coefficient K = 15, and the phase 180 degrees at the end of the second time, 2655-15 × 180 = (− 45). Calculation is performed (step S82). Finally, the magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c calculates {(−15) + (− 45)} ÷ 2 = (− 30) using the calculation results (−15) and (−45) (step S83). . The magnetic pole information calculation unit 456c rewrites the correction information MPC in the correction information storage unit 451d with (−30) obtained above (step S84).
<本実施形態が発揮する効果>
以上、特に<電源立上りによる磁極位置推定モード>という見出しの段落群で述べたように、エレベータ制御装置5やドア制御部45を含むエレベータ全体が、保守や停電のために給電されていない状態で、かごドア3や乗場ドア1が保守作業員の手で開け閉めされたり、乗場ドア1に働く自閉力によって戸閉動作が起きたりしてドア位置が変化した場合は、かごドア3に連動する永久磁石同期電動機41も回転し、エンコーダ46も回転する。しかし、給電されていない状態ではエンコーダ46からの信号は発生しないので、その信号をドア制御部45が受け取って磁極位置カウンタ451cの磁極位置情報MPを更新することはできず、永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置と、それをドア制御部45が認識するための磁極位置カウンタ451cとが、ずれた状態になってしまう。それに対してエレベータ制御装置5は、給電されていない状態から給電されている状態に切換ったと検出された際に、ドア制御部45に磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう指令して、磁極位置をドア制御部45が認識するための磁極位置カウンタ451cを更新させるので、ずれた状態を解消することができる。
<Effects of this embodiment>
As described above, in particular, as described in the paragraph group entitled <Magnetic pole position estimation mode by power supply startup>, the entire elevator including the elevator control device 5 and the
また、特に<戸開/閉不能による磁極位置推定モード>という見出しの段落群で述べたように、ドア制御部45が戸開制御をしているのにかごドア3が全開位置に到らないとか、戸閉制御をしているのにかごドア3が全閉位置に到らないことを、エレベータ制御装置5が、ドア制御部4によるトルク過大検出を受けて判断した場合、永久磁石同期電動機41の磁極位置と、それをドア制御部45が認識するための磁極位置カウンタ451cとが、何かのきっかけでずれてしまったことが一原因だと想定できる。したがって、ドア制御部45に磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう指令して、磁極位置をドア制御部45が認識するための磁極位置カウンタ451cを更新させることによって、全開位置に到らないとか全閉位置に到らないという現象を解消できる可能性が出てくる。
In particular, as described in the paragraph group heading <Magnetic pole position estimation mode when door cannot be opened / closed>, the
<他の実施形態>
なお、本発明に係るエレベータのドア制御システムは、上記実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で種々の変更を加えることができる。
<Other embodiments>
The elevator door control system according to the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the gist of the present invention.
例えば、ドア開閉装置4がダイレクトドライブ方式であって、水平方向の一方側に動作して開閉するサイドオープンタイプのドアに適用される例を説明したが、これに限定されるものではない。ドア開閉装置が後述する従来方式であって、水平方向の両側に動作して開閉するセンターオープンタイプのドアに適用されてもよい。ダイレクトドライブ方式とセンターオープンタイプを組み合わせたり、従来方式とサイドオープンタイプを組合せたりすることも可能である。サイドオープンタイプでは、開閉するドアの数量が2枚に限定されず、1枚若しくは3枚以上であってもよい。センターオープンタイプでは、左右のドアのそれぞれが2枚以上であってもよい。
For example, although the door opening /
従来方式のドア開閉装置4は、図14に示すように、永久磁石同期電動機41と、モータプーリ47と、減速ベルト48と、減速プーリ49と、駆動プーリ42と、従動プーリ43と、駆動ベルト44とを備える。永久磁石同期電動機41は、かご2の出入口の間口方向(図14の左右方向)に沿って延びる上部フレーム21の上面に取り付けられている。モータプーリ47は、永久磁石同期電動機41の駆動軸に取り付けられている。減速ベルト48は、モータプーリ47及び減速プーリ49間に巻き掛けられている。減速プーリ49は、上部フレーム21の正面の一端側に取り付けられ、モータプーリ47よりも径が大きい。駆動プーリ42は、減速プーリ49と同軸且つ一体に設けられている。駆動ベルト44は、駆動プーリ42及び従動プーリ43間に巻き掛けられている。従動プーリ43は、上部フレーム21の正面の他端側に取り付けられている。以上の従来方式に対し、永久磁石同期電動機41が、モータプーリ47、減速ベルト48、減速プーリ49を介することなく、駆動プーリ42と同軸で直結されるのが、ダイレクトドライブ方式である。
As shown in FIG. 14, the conventional door opening /
また、センターオープンタイプのドアは、図14に示すように、上部フレーム21の正面にドアレール33が取り付けられている。かごドア3は、ドアハンガ32に取り付けられた一対のローラ34,34がドアレール33上に載置されている。そして、ドアハンガ32を介してドアレール33に吊り下げられている。かかる状態で、かごドア3は、ドアハンガ32及び該ドアハンガ32に取り付けられた連結具35を介してドア開閉装置4の駆動ベルト44に連結されている。
Further, as shown in FIG. 14, the center open type door has a
従って、永久磁石同期電動機41によりモータプーリ47が回転すると、減速ベルト48を介して減速プーリ49に回転が伝達され、減速プーリ49と共に駆動プーリ42が回転し、これに伴い、駆動ベルト44が循環し、連結具35及びドアハンガ32を介してかごドア3がドアレール33に沿って往復動して、かごドア3が開閉される。尚、図14に示すエレベータは、駆動ベルト44の一辺側に一方のかごドア3が連結され、駆動ベルト44の他辺側に他方のかごドア3が連結されているため、一対のかごドア3,3が互いに相反する方向に移動する構成となっている。
Therefore, when the
また、自閉装置14がスプリング形である例を説明したが、これに限定されるものではない。例えば、自閉装置がウエイト形であってもよいし、スプリングリール形であってもよい。
Moreover, although the self-closing
また、回転角計測器がインクリメンタルタイプのエンコーダ46(若しくはパルスジェネレータ)である例を説明したが、これに限定するものではない。アブソリュートタイプのエンコーダやレゾルバを採用してもよい。 Further, the example in which the rotation angle measuring instrument is the incremental type encoder 46 (or pulse generator) has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this. An absolute type encoder or resolver may be employed.
1…乗場ドア、2…かご、3,3f,3s…かごドア、4…ドア開閉装置、5…エレベータ制御装置、11…被係合部、12・・・支持部材、13…ドア吊り部材、14…自閉装置、15…フレーム、21…上部フレーム、31…係合部、32f、32s…ドアハンガ、33f,33s…ドアレール、34f、34s…ローラ、35f,35s…連結具、37…減速機構、37a…アーム、37b…減速プーリ、37c…減速ワイヤ、37d…ブラケット、38…終端保持装置、38a…ベース、38b…ローラ、38c…レバー、38d…弾性部、38e…ガイドレール、38f…軸、38g,38h…傾斜部、38i…平坦部、39a…全閉位置検出部、39b…全開位置検出部、41…永久磁石同期電動機、42…駆動プーリ、43…従動プーリ、44…駆動ベルト、45…ドア制御部、46…エンコーダ、47…モータプーリ、48…減速ベルト、49…減速プーリ、451…速度制御部、451a…ドア位置カウンタ、451b…ドア速度カウンタ、451c…磁極位置カウンタ、451d…補正情報記憶部、452…電流制御部、453…電力変換部、454…電流検出部、455…単純カウンタ、456…磁極位置推定部、456a…磁極固定部、456b…磁極情報取得部、456c…磁極情報演算部、P1…全閉位置、P2…全開位置、P3…閉側保持解除位置、P4…開側保持解除位置、Z1…閉保持ゾーン、Z2…開保持ゾーン、Z3…保持解除ゾーン
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 ... Platform door, 2 ... Car, 3, 3f, 3s ... Car door, 4 ... Door opening and closing device, 5 ... Elevator control device, 11 ... Engagement part, 12 ... Support member, 13 ... Door suspension member, DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
前記ドアを開ける方向や閉める方向に前記回転子を回転させるために前記電機子巻線に電流を流すドア制御部と、
前記ドア制御部に対して前記ドアを開けるための戸開指令および前記ドアを閉めるための戸閉指令を出すエレベータ制御装置を備えたエレベータ制御システムであって、
前記エレベータ制御装置は、エレベータが給電されていない状態から給電されている状態に切換ったと検出した直後、呼び登録が発生する前に、前記永久磁石の磁極位置の認識を更新するための磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう前記ドア制御部に指令することを特徴とするエレベータ制御システム。 A permanent magnet synchronous motor that has a rotor with a permanent magnet and a stator with an armature winding, and that opens and closes and opens and closes an elevator door as the rotor rotates;
A door control unit for passing a current through the armature winding to rotate the rotor in a direction to open or close the door;
An elevator control system comprising an elevator control device that issues a door opening command for opening the door and a door closing command for closing the door to the door control unit,
Immediately after detecting that the elevator control device has switched from a state where the elevator is not powered to a state where power is being fed, and before call registration occurs , the magnetic pole position for updating the recognition of the magnetic pole position of the permanent magnet An elevator control system that commands the door control unit to perform estimation control.
前記ドアを開ける方向や閉める方向に前記回転子を回転させるために前記電機子巻線に電流を流すドア制御部と、
前記ドア制御部に対して前記ドアを開けるための戸開指令および前記ドアを閉めるための戸閉指令を出すエレベータ制御装置を備えたエレベータ制御システムであって、
前記エレベータ制御装置は、前記戸開指令を出しても前記ドアが全開位置にならないと検出した場合、または前記戸閉指令を出しても前記ドアが全閉位置にならないと検出した場合、それらの検出によってエレベータを運行休止にしようとする直前、または運行休止にした後で運行を再開した直後に、前記永久磁石の磁極位置の認識を更新するための磁極位置推定制御を実施するよう前記ドア制御部に指令することを特徴とするエレベータ制御システム。 A permanent magnet synchronous motor that has a rotor with a permanent magnet and a stator with an armature winding, and that opens and closes and opens and closes an elevator door as the rotor rotates;
A door control unit for passing a current through the armature winding to rotate the rotor in a direction to open or close the door;
An elevator control system comprising an elevator control device that issues a door opening command for opening the door and a door closing command for closing the door to the door control unit,
If the elevator control device detects that the door is not in the fully open position even if the door opening command is issued, or if the door is not in the fully closed position even if the door close command is issued , The door control to perform magnetic pole position estimation control for updating the recognition of the magnetic pole position of the permanent magnet immediately before attempting to stop the elevator by detection or immediately after restarting operation after having stopped operation. An elevator control system characterized by instructing a section.
請求項2に記載されたエレベータ制御システム。 The elevator control device continuously detects a number of times less than the predetermined number of times when the elevator is put into operation stoppage when the door is not fully opened for a predetermined number of times even when the door opening command is issued. When the door control unit is instructed to carry out the magnetic pole position estimation control,
The elevator control system according to claim 2 .
請求項2に記載されたエレベータ制御システム。 When the elevator control device detects that the door will not be fully closed even after issuing the door closing command for a predetermined number of times, the elevator control device resumes operation after a predetermined time has elapsed. Immediately after, it is characterized by instructing the door control unit to perform the magnetic pole position estimation control,
The elevator control system according to claim 2 .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015021402A JP6435895B2 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2015-02-05 | Elevator control system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015021402A JP6435895B2 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2015-02-05 | Elevator control system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016141564A JP2016141564A (en) | 2016-08-08 |
| JP2016141564A5 JP2016141564A5 (en) | 2017-09-14 |
| JP6435895B2 true JP6435895B2 (en) | 2018-12-12 |
Family
ID=56569574
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015021402A Active JP6435895B2 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2015-02-05 | Elevator control system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6435895B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6568505B2 (en) * | 2016-09-05 | 2019-08-28 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Video surveillance system |
| CN110088024B (en) * | 2016-12-28 | 2020-09-18 | 三菱电机大楼技术服务株式会社 | Remote recovery system for elevator fault |
| JP7582543B1 (en) | 2024-04-25 | 2024-11-13 | 三菱電機ビルソリューションズ株式会社 | Elevator System |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000191248A (en) * | 1998-12-25 | 2000-07-11 | Toshiba Elevator Co Ltd | Elevator control device |
| JP2007308231A (en) * | 2006-05-17 | 2007-11-29 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | Inverter device for elevators and method of controlling brake of inverter device |
| JP5125079B2 (en) * | 2006-11-29 | 2013-01-23 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Elevator door control device |
| CN101729001B (en) * | 2008-10-16 | 2012-05-30 | 鸿富锦精密工业(深圳)有限公司 | Positioning system and method for magnetic pole angle of motor |
| JP5651322B2 (en) * | 2009-11-04 | 2015-01-07 | 株式会社日立産機システム | Power converter |
| JP5761243B2 (en) * | 2013-03-29 | 2015-08-12 | 株式会社安川電機 | Motor control device and magnetic pole position estimation method |
-
2015
- 2015-02-05 JP JP2015021402A patent/JP6435895B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016141564A (en) | 2016-08-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6435895B2 (en) | Elevator control system | |
| US10246809B2 (en) | Washing machine and method of controlling the same using an AC motor | |
| WO2015152118A1 (en) | Electric curtain control device and program for same | |
| US10570549B2 (en) | Washing machine and control method of the same | |
| US10584436B2 (en) | Washing machine and method for controlling same | |
| JP6464710B2 (en) | Elevator door control system | |
| JP2017093535A (en) | Washing machine | |
| JP2011063405A (en) | Door control device of elevator | |
| JP2009127347A (en) | Automatic door driving device and automatic door device | |
| US10800237B2 (en) | Method and device for determining a position of an actuating element | |
| JP5837337B2 (en) | Breaker | |
| JP5445254B2 (en) | Robot controller | |
| KR101870373B1 (en) | Semi-automatic sliding door system | |
| CA2544181C (en) | Drive motor reversal for a barrier operator or the like | |
| JP5658910B2 (en) | Switchgear | |
| JP6448934B2 (en) | Switchgear | |
| JP6042388B2 (en) | Automatic door device | |
| US10954708B2 (en) | Movable barrier opener with brushless DC motor | |
| JP6130632B2 (en) | Automatic door open / close control device and open / close control method | |
| JP7421042B1 (en) | Opening/closing device for opening/closing body and its control method | |
| JP6265686B2 (en) | Opening and closing body device | |
| JP2023158587A (en) | Electric opening/closing body control device, electric opening/closing system, program | |
| JP2023031762A (en) | Electric opening/closing body control device, electric opening/closing system, and program | |
| JP2001231282A (en) | Opening/closing member controller | |
| JP2005076319A (en) | Power sliding door device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170802 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170802 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20180522 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180605 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20180724 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180920 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20181016 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20181029 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6435895 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |