JP6294530B2 - Shield for electronic devices - Google Patents
Shield for electronic devices Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6294530B2 JP6294530B2 JP2017055281A JP2017055281A JP6294530B2 JP 6294530 B2 JP6294530 B2 JP 6294530B2 JP 2017055281 A JP2017055281 A JP 2017055281A JP 2017055281 A JP2017055281 A JP 2017055281A JP 6294530 B2 JP6294530 B2 JP 6294530B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- shield
- trace
- traces
- decoy
- active
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 claims description 28
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 52
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 18
- 238000010146 3D printing Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013021 overheating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Shielding Devices Or Components To Electric Or Magnetic Fields (AREA)
Description
背景
セキュリティ製品は、銀行及び金融アプリケーションにおいて一般的に使用されている。業界規格及び政府規格の中には、機密データを暗号化及び暗号解除するコンピュータの構成要素に対し、セキュリティ・バリアを設けることを要求するものがある。例えば、現金自動預払機において個人識別番号が入力されたとき、入力された情報は、セキュリティ・バリアを通過する場合がある。セキュリティ・バリアは、侵入検出を提供し、それによって、機密データに対する権限のないアクセスを防止するための対応策を実施できるようにする。
Background Security products are commonly used in banking and financial applications. Some industry and government standards require a security barrier to be placed on computer components that encrypt and decrypt sensitive data. For example, when a personal identification number is input in an automatic teller machine, the input information may pass through a security barrier. The security barrier provides intrusion detection, thereby enabling implementation of countermeasures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
下記の詳細な説明では、下記の図面が参照される。
詳細な説明
既存のセキュリティ・バリアは、薄い可撓性プリント回路基板によって囲まれた金属ボックスとして設けられる場合がある。プリント回路基板は、金属ボックスの周囲で折り曲げられ、それによって、プリント回路基板を通して外部ソースによりなされる貫通を検出することができる。そのような構造は、製造に高い費用がかかり、プリント回路基板の検知層に使用される材料が熱の良好な伝導体ではないことから、金属ボックス内の電子部品により生成された熱を放散させることは難しい。したがって、プロセッサを十分に冷却することができないため、金属ボックス内のプロセッサはいずれも、比較的遅い速度で動作される場合がある。もしプロセッサを全速力で動作させようとした場合、プロセッサは、過度の熱により動作不能になる場合がある。
DETAILED DESCRIPTION Existing security barriers may be provided as a metal box surrounded by a thin flexible printed circuit board. The printed circuit board is folded around the metal box so that penetrations made by external sources through the printed circuit board can be detected. Such a structure is expensive to manufacture and dissipates the heat generated by the electronic components in the metal box because the material used for the sensing layer of the printed circuit board is not a good conductor of heat. It ’s difficult. Therefore, any processor in the metal box may be operated at a relatively slow speed because the processor cannot be cooled sufficiently. If an attempt is made to operate the processor at full speed, the processor may become inoperable due to excessive heat.
本明細書に開示される種々の実施形態は、各トレースが内側導電性部分及び外側非導電性部分を含む、複数のトレースを含むシールド(保護具)を設けることによって、それらの問題に対処する。一部の実施形態において、トレースは、三次元印刷技術を使用して生成される場合がある。シールドは、電子デバイスにセキュリティ・バリアを提供するために使用される。三次元印刷技術を使用することにより、従来技術に比べて安価にシールドを生成することができる。三次元プリンタは、導電性インク及び導電性プラスチックを使用してシールドを生成することができ、それによって、トレースは、非導電性プラスチックの中に埋め込まれた導電性プラスチックを含むように構成される場合がある。 Various embodiments disclosed herein address these issues by providing a shield that includes multiple traces, each trace including an inner conductive portion and an outer non-conductive portion. . In some embodiments, the trace may be generated using a three-dimensional printing technique. The shield is used to provide a security barrier for the electronic device. By using the three-dimensional printing technique, the shield can be generated at a lower cost than the conventional technique. A three-dimensional printer can use a conductive ink and a conductive plastic to create a shield, whereby the trace is configured to include a conductive plastic embedded in a non-conductive plastic. There is a case.
三次元印刷技術を使用すると、シールドのサイズ及び形状は、制限されない。したがって、シールドは、回路基板上の全部品を収容するようにぴったり合う形を有する場合もあれば、又は、アーチ形の表面若しくは丸みを帯びた表面を有する物体を取り囲むようにぴったり合う形を有する場合もある。また、シールド内に、空気の通路を作成することができる。シールドは、貫通保護を提供する。なぜなら、もし誰かがシールドを貫通しようと試みた場合、トレースの少なくとも1つとの間に接触が形成される場合があり、それによって、シールドに不正な変更が加えられていることを知らせることができるからである。 Using 3D printing technology, the size and shape of the shield is not limited. Thus, the shield may have a shape that fits snugly to accommodate all components on the circuit board, or it has a shape that fits snugly around an object that has an arcuate or rounded surface. In some cases. In addition, an air passage can be created in the shield. The shield provides penetration protection. Because if someone tries to penetrate the shield, a contact may be made with at least one of the traces, thereby notifying that the shield has been tampered with Because.
シールドは、熱伝導性プラスチックを用いて生成される場合もある。したがって、シールドと、プロセッサのような発熱電子部品との間に、熱結合を形成することができる。プロセッサは、かなりの量の熱を生成する場合があり、したがって、シールドの熱伝導性プラスチックは、ヒートシンクとして使用される場合がある。シールドのこのヒートシンク機能によれば、過熱を防止しつつ、プロセッサを高速に動作させることが可能となる。 The shield may be made using a thermally conductive plastic. Thus, a thermal coupling can be formed between the shield and a heat generating electronic component such as a processor. The processor may generate a significant amount of heat, and thus the thermally conductive plastic of the shield may be used as a heat sink. This heat sink function of the shield makes it possible to operate the processor at high speed while preventing overheating.
このように、本明細書に開示される種々の例示的実施形態によれば、電子デバイスにセキュリティ・バリアを提供するためのシールドが得られる。シールドは、複数のトレースを含み、各トレースは、内側導電性部分、及び外側非導電性部分を含む。トレースは、三次元印刷技術を使用して生成される場合があり、各トレースが、内側部分として電気的に導電性のプラスチックを含み、外側部分として電気的に非導電性のプラスチックを含むように生成される場合がある。トレースは、シールドが電子デバイスを取り囲む形状となるように構成される。 Thus, various exemplary embodiments disclosed herein provide a shield for providing a security barrier to an electronic device. The shield includes a plurality of traces, each trace including an inner conductive portion and an outer non-conductive portion. The traces may be generated using a three-dimensional printing technique so that each trace includes an electrically conductive plastic as the inner portion and an electrically non-conductive plastic as the outer portion. May be generated. The trace is configured such that the shield is shaped to surround the electronic device.
このアプローチによれば、トレースは、シールドの外部にあるソースによるシールドの貫通を検出するためのパターンを成すように構成される場合がある。例えば、トレースの導電性部分の抵抗値は、シールドの外部にあるソースからの接触に応答して変化する。シールドの外部にあるソースが、シールドの貫通を試みるものであることが検出された場合、電子デバイスのメモリは、消去される。 According to this approach, the traces may be configured to form a pattern for detecting penetration of the shield by a source external to the shield. For example, the resistance value of the conductive portion of the trace changes in response to contact from a source external to the shield. If it is detected that a source outside the shield is attempting to penetrate the shield, the memory of the electronic device is erased.
次に図面を参照すると、図1は、電子デバイス110の周囲に設けられた例示的シールド100を示す斜視図を、シールド100の例示的トレース120の拡大断面図とともに示している。シールド100は、他の物体を取り囲み、又はその他保護するように設計された如何なる構造であってもよい。例えば、シールド100は、電子デバイス110を取り囲むような形状を有する場合がある。図1の実施形態において、シールドは、トレース120及びトレース130を含む。シールド100は、トレース120、130を参照して説明されるが、シールド100は、もっと多くの数のトレースを含む場合もあると理解される。
Referring now to the drawings, FIG. 1 shows a perspective view of an
トレース120、130は、三次元プリンタを使用して生成される場合がある。各トレース120、130は、電子デバイス110がトレース120、130によって取り囲まれ、トレース120、130の中に収容されるように構成される場合がある。三次元プリンタは、種々の材料を用いて三次元構造を生成することができる。一例示的実施形態において、トレース120は、内側部分122、及び外側部分124を有するように生成される場合がある。内側部分122は、電気的に導電性のインクを使用して生成される場合がある一方、外側部分124は、異なる材料を使用して生成される場合があり、異なる材料から、内側部分122の周囲に形成された非導電性プラスチックカバーが生成される。同様に、トレース130は、電気的に導電性の内側部分、及び非導電性の外側部分を有するように構成される。下で説明されるように、各トレース120、130は、トレースをコントローラに接続するための端子126、136を備えている。
三次元印刷技術によれば、シールド100の形状を生成する際の自由度が得られる。図1に示されるように、シールド100は、実質的に箱形の電子デバイス110を取り囲むように生成される。ただし、下で説明されるように、シールド100は、プリント回路基板上に設けられるもののような、任意のタイプの電子デバイス、又はデバイスの組み合わせにセキュリティ・バリアを提供するために使用される任意の形状を有するように生成されてもよい。シールド100も同様に、丸みを帯びた表面若しくはアーチ形の表面を有する物体のような慣例にとらわれない形状を有する物体を取り囲むように生成される場合がある。
According to the three-dimensional printing technique, a degree of freedom in generating the shape of the
図1に示されるように、トレース120、130は、トレース120、130の各々が複数の直線を成すように構成され、かつ、各トレース120、130が実質的に90度の角度で他方のトレースと交差するようなパターンを成して、電子デバイス110を取り囲むように設けられる。このタイプのパターンは、電子デバイス110を取り囲むシールド100を得るために使用することができる多数のパターンのうちの1つであると理解される。例えば、トレース120、130は、複数の曲線又はアーチ形の線のパターンを成すように構成される場合がある。他の例において、トレース120、130は、各トレースが、自分自身の上を少なくとも一回横切るように構成される場合がある。さらに別の例では、異なる方向に延びるトレースの複数の層が得られるように、トレース120、130は、互いに繰り返し重なり合う場合がある。トレースの任意数の層を生成するために、三次元印刷技術を使用して、任意のパターンを生成することができる。電子デバイス110をトレース120、130で取り囲むために使用される実際のパターンは、トレース120、130によって電子デバイス110が実質的に包囲されることを確保するほど重要ではない。パターンは、外部ソースがトレース120、130の少なくとも一方と接触することなく、如何なる侵入角からもシールド100を貫通することができないように選択される。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
図2は、例示的コントローラ200、例示的メモリ210、及び例示的シールド220を示すブロック図である。コントローラ200は、メモリ210、及びシールド220に結合される場合がある。メモリ210は、電子デバイス110の中に含められる場合があり、シールド220のトレースは、電子デバイス110を取り囲むためのパターンを成すように構成される場合がある。一例示的実施形態では、コントローラ200もまた、電子デバイス110の中に含められる場合がある。あるいは、コントローラ200がシールド220の中に収容されないように、コントローラ200は、電子デバイス110の外部に設けられる場合がある。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating an
コントローラ200は、1以上の中央演算処理装置(CPU)であってよいし、及び/又は、シールド貫通が検出されたときにメモリ210を消去するのに適した他のハードウェア装置であってもよい。メモリ210は、データを記憶する任意の電子的、磁気的、光学的、又は他の物理的記憶装置であってよい。したがって、メモリ210は、例えば、電気的に消去可能なプログラマブル・リード・オンリー・メモリ(EEPROM)、記憶ドライブ、光ディスクなどであってもよい。後で詳細に説明されるように、トレースが、外部ソースからのシールド220の貫通を検出した場合、コントローラ200は、メモリ210を消去し、機密データをメモリ210からアクセスできないようにする。
The
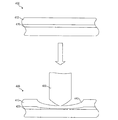
図3は、外部ソースがトレースに穴310を形成する前後における、シールドの例示的トレースを示す部分図である。トレース300は、貫通前のシールドの一部を示し、トレース300’は、穴310を生じさせた貫通後のシールドの同部分を示している。穴310は、電子デバイス110にアクセスするために、外部ソースがシールドを貫通して穴を掘り、シールドに穴をあけることを試みることによって形成される場合がある。
FIG. 3 is a partial view showing an exemplary trace of a shield before and after an external source forms a
コントローラ200は、穴をあける試みによって生じるトレース300、300’の抵抗値の変化を検知する場合がある。トレース300、300’は、貫通によって容易に検出可能な抵抗値の変化が生じるような抵抗値を有するプラスチックにより構成される場合がある。一例において、穴310は、トレース310’の内側導電性部分に破損を生じさせることができるほど十分に大きい場合があり、それによって、コントローラ200は破損を検出し、それに応答して、メモリ210の少なくとも一部を消去する。したがって、シールドを貫通しようと試みる侵入者がメモリ210にアクセスすることは、防止される。
The
他の例において、トレース300の内側導電性部分は、単位長さ当たり既知の抵抗値を有する場合がある。例えば、もしトレース300が、10センチメートルの長さ、1センチメートルの幅、及び10kΩの抵抗値を有する場合、穴310を掘ることによって、トレース310’に、約70Ωの抵抗値の低下が発生する場合がある。コントローラ200は、この抵抗値の低下を検出する場合がある。そのような抵抗値の低下に応答して、コントローラ200は、メモリ210の少なくとも一部を消去する場合があり、それによって、メモリ210上のデータへのアクセスが防止されるようにする。
In other examples, the inner conductive portion of
図4は、外部ソースがトレースに圧力を加える前後における、シールドの例示的トレースを示す部分図である。外側非導電性部分410、及び内側導電性部分420を示すために、トレース400は、断面図で示されている。非常に強力な貫通力を使用して、シールドに貫通する試みがなされる場合がある。そのような場合、人によっては、機密データを記憶していると思われる電子デバイス110の少なくとも一部をアクセスし、又は読み出すために、例えば、先の尖った物体430を使用して、シールドを貫通する穴を穿つことを試みる場合がある。例えば、侵入者は、コントローラ200がメモリ210を消去する機会を得る前に、電子デバイス110を物理的に取り外すことを試みる場合がある。
FIG. 4 is a partial view of an exemplary trace of a shield before and after an external source applies pressure to the trace.
先の尖った物体430は、トレース400に圧力を加えることができ、トレース400の幅を減少させ、外側非導電性部分410と内側導電性部分420との両方を変形させる場合がある。加えられた圧力に応答し、内側導電性部分420は、それ自体の圧電特性によって、抵抗値を変化させる場合がある。抵抗値の変化は、コントローラ200により検出される場合がある。抵抗値の変化に応答し、コントローラ200は、メモリ210の少なくとも一部を消去する場合がある。
The
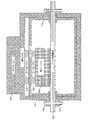
図5は、プリント回路基板510上に設けられた例示的シールド500を示す断面図である。シールド500は、クロスハッチパターンにより示されている。三次元印刷技術によれば、シールド500が任意の三次元形状となるように複数の層を成してトレースを印刷することによって、シールド500を構成することが可能となる。
FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an
シールド500は、プリント回路基板510に取り付けられる場合がある。電子デバイス520も、プリント回路基板510上に設けられる。熱伝導性材料が、シールド500の内側に取り付けられる場合がある。例えば、サーマル・パッド530が、電子デバイス520とシールド500との間に設けられる場合があり、サーマル・フィン540が、シールド500上に設けられる場合がある。シールド500は、空気穴550をさらに備える場合があり、それによって、空気はシールド500の内部を通って流れることができる場合がある。空気穴550の内部表面上には、ルーバー560が設けられる場合がある。ルーバー560は、三次元印刷技術を使用して、シールド500のトレースと共に形成される場合がある。
The
空気穴550、サーマル・パッド530、及びサーマル・フィン540は、シールド500による熱の放散を助ける。先に述べたように、シールド500は、熱伝導性材料を含む場合があり、それによって、電子デバイス520により生成された熱を、サーマル・パッド530を通してシールド500により放散させることができる場合がある。サーマル・フィン540は、シールド500から余分な熱をシールド500の内部へ放散させる場合がある。空気穴550によれば、シールド500の外部にある冷たい空気を、シールド500の内部を通して、その後シールド500の外へと通過させることが可能となる。場合によっては、空気穴550は、電子デバイス520に記憶された機密データにアクセスするための探査手段を提供する場合がある。
Air holes 550,
そのような侵入を防止するために、シールド500は、シールド500の内部へのアクセスを空気穴550によって簡単に得ることはできないように構成される。図5に示されるように、空気穴550は、複数の90度角を備え、したがって、シールド500の内部へのアクセスを獲得するためには、その付近で探査手段を巧みに操作する必要がある。三次元印刷技術を使用すれば、シールド500内を通る空気の流れを容易にするために、そのような空気穴550を容易に作成することができる。そのような構成によれば、侵入者が空気穴550を通して細いワイヤーをシールド500の内部に挿入することも、防止することができる場合がある。
To prevent such intrusion, the
シールド500の内部へのワイヤー挿入をさらに禁止するために、空気穴550の表面上には、ルーバー560が設けられる場合がある。ルーバー560は、三次元印刷技術を使用して、ヒンジ止めされる場合がある。ヒンジ止めされたルーバーは、空気穴550に挿入されたワイヤーを捕捉し、ワイヤーがシールド500の内部に進入することを防止する場合がある。また、ルーバー560は、空気穴550を通して挿入されたワイヤーを捕捉し、ワイヤーが空気穴550を通していったん挿入された後、そのワイヤーが取り除かれることを防止する場合がある。
In order to further prohibit wire insertion into the
ここまで、シールドは、導電性プラスチック材料と非導電性プラスチック材料の両方からなるトレースを含むものとして説明されてきた。環境によっては、プラスチックのみでは、シールド内部への貫通及び侵入からの十分な保護が得られない場合がある。場合によっては、熱を効率よく放散させるために、シールドによって得られる特性のほかに、より高い熱伝導性が必要となる場合がある。より強い機械的保護、及びより高い熱伝導性を得るために、プラスチック・シールドの上に金属シェルが設けられる場合がある。 So far, the shield has been described as including traces made of both conductive and non-conductive plastic materials. Depending on the environment, plastic alone may not provide sufficient protection from penetration and penetration into the shield. In some cases, in order to dissipate heat efficiently, higher thermal conductivity may be required in addition to the properties obtained by the shield. In order to obtain stronger mechanical protection and higher thermal conductivity, a metal shell may be provided over the plastic shield.
図6は、プリント回路基板600上に設けられた例示的シールド630、及び例示的金属シェル640を示す断面図である。電子デバイス610は、プリント回路基板600上に設けられる場合がある。1つのサーマル・パッド620は、電子デバイス610とシールド630との間に設けられる場合があり、もう1つのサーマル・パッド620は、電子デバイス610と金属シェル640との間に設けられる場合がある。セキュリティ向上のために、金属シェル640は、ボルト660及びナット670を使用して、プリント回路基板600に取り付けられる場合があり、また、プリント回路基板600からの金属シェル640の取り外しを検知するために、侵入者検出のさらに別の層が、接点(図示せず)を使用して設けられる場合がある。
FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an
シールド630は、金属シェル640の中に設けられる。シールド630は、サーマル・パッド620、又はサーマル・グリス(図示せず)のような熱伝導性材料を使用して、電子デバイス610に熱的に結合される場合がある。金属シェル640は、サーマル・パッド620、又はサーマル・グリス(図示せず)のような熱伝導性材料を使用して、シールド630に熱的に結合される場合がある。また、金属シェル640及びシールド630の垂直な側壁に示されてるように、金属シェル640は、シールド630に熱的に直接結合もされる。図6に示した構造では、金属シェル640、サーマル・フィン650、及びサーマル・パッド620の存在によって、熱伝導性による冷却が向上する。
A
図7は、プリント回路基板700上に設けられた例示的シールド710及び例示的金属シェル720を示す断面図である。圧力パッド730のような感圧材料が、シールド710と金属シェル720との間に設けられる場合がある。各圧力パッド730は、図4を参照して上で説明したように、シールド710のトレースの圧電特性により、測定可能な大きさの圧力をシールド710に加えることができる。金属シェル720が取り除かれた場合、又は、金属シェルを取り除く試みがなされた場合、シールド710に加えられた圧力は、シールド710のトレースの抵抗値を変化させる場合がある。圧力パッド730がある場所の圧力の変化により生じるこの抵抗値の変化に応答し、コントローラ200は、メモリ210を消去する場合がある。
FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an
例示的実施形態において、圧力パッド730は、電気的に導電性の材料を含む場合がある。この場合、圧力パッド730は、金属シェル720の一部として構成される場合がある。圧力パッド730の電気的に導電性特性によれば、圧力パッド730、金属シェル720、及びコントローラ200の間に簡単な電気的接続を形成することが可能となり、それによって、その接続が短絡され、又はその他損なわれることに応答して、金属シェルに対する不正変更を検出することができる。
In the exemplary embodiment,
図8は、例示的金属シェル810の縁部820に設けられた例示的シールド800を示す部分断面図である。トレースが可撓性回路基板上に設けられる従来のセキュリティ・バリアでは、電子デバイスの縁部に弱いスポットが存在することがあり、そのため、セキュリティ・バリアは、縁部において貫通が生じやすい場合がある。この貫通の生じやすさは、可撓性回路基板が、外部ソースによる侵入を防止するために、電子デバイスの縁部を十分に覆う能力を有していないことに起因している。例えば、セキュリティ・バリアが縁部で折り曲げられたとき、可撓性回路基板上のトレースは、壊れる場合がある。
FIG. 8 is a partial cross-sectional view illustrating an
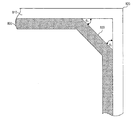
図8に示されるように、シールド800は、金属シェル810の中に設けられる。表面830は、縁部820に近接するシールド800上に形成されている。表面830は、金属シェル810の内側表面から角度θ1及びθ2を成して延びている。そのような構造は、表面830と金属シェル810の内側表面との間に、縁部820に沿って空間を形成する。
As shown in FIG. 8, the
図8において、縁部820は、実質的に90度の角度を成して形成され、そこで、金属シェル810の2つの側面が合わさっている。この場合、角度θ1及びθ2の値は、35度から55度までの範囲内にある場合がある。この構造によれば、縁部820から進入してくる侵入デバイスは、表面830に対して実質的に垂直にシールド800のトレースと接触することになるので、シールド800の表面830は、金属シェル810の縁部820からシールド800への侵入を防止することができる。
In FIG. 8, the
他の例示的実施形態において、縁部820は、90度以外の角度を成して設けられる場合があり、又は丸みを帯びている場合がある。縁部820からシールド800への侵入デバイスの侵入ラインに対して実質的に垂直になるように表面830を形成することによって、角度θ1及びθ2に、縁部820からシールド800への侵入を最も効果的に防止する値を与えることができる。実施形態によっては、表面830もまた、丸みを帯びた縁部の形状に適合するように丸みを帯びている場合がある。図8では、金属シェル810を参照して、表面830を有するシールド800について説明した。しかしながら、シールド800は、シールド800を取り囲む金属シェル810なしに、表面830を有するように形成される場合もあると理解される。図8に示した構成は、図9に示されるように、金属シェルの角部における侵入デバイスの貫通を防止するように拡張される場合がある。
In other exemplary embodiments, the
図9は、例示的金属シェル900の角部930に設けられた例示的シールド910を示す部分斜視図である。従来のセキュリティ・バリアにおける最も弱いポイントの一つは、セキュリティ・バリアの角部である。角部は、悪名高いほど貫通を検出することが難しいエリアである。なぜなら、従来の可撓性回路基板セキュリティ・バリアは、一般に、角部の付近で折り曲げられるからである。可撓性回路基板を角部の付近で複数の方向に折り曲げることによって、可撓性基板上のトレースは壊れる場合があり、それによって、侵入デバイスは、角部において検出されることなくセキュリティ・バリアに容易に貫通することが可能となる場合がある。
FIG. 9 is a partial perspective view illustrating an
図9に示されるように、シールド910は、シールド910の表面920が、金属シェル900の内側の角部930に近接するように構成される場合がある。表面920は、表面920と、角部930に近接する金属シェル900の各内側表面との間に、角度θ3、θ4及びθ5を形成している。図9において、金属シェル900の各側面は、角部930に対して実質的に垂直に延びている。この場合、角度θ3、θ4及びθ5は、35度から55度までの範囲内にある場合がある。この構造によれば、角部930に進入する侵入デバイスは、シールド920に対して実質的に垂直な方向からトレースと接触することになるので、シールド910の表面920は、金属シェル900の角部930からシールド910への侵入を防止することができる。
As shown in FIG. 9, the
他の例示的実施形態において、角部930は、金属シェル900の3つの側面により形成される場合があるが、3つの側面は、互いに垂直ではない場合があり、すなわち、角部930は、丸みを帯びている場合がある。この場合、角部930からシールド910への侵入デバイスの進入ラインに対して実質的に垂直になるように表面920を形成することによって、角度θ3、θ4及びθ5に、角部930からシールド910への侵入を最も効果的に防止する値を与えることができる。実施形態によっては、表面920もまた、丸みを帯びた角部の形状に適合するように丸みを帯びている場合がある。図9では、金属シェル900を参照して、表面920を有するシールド910について説明した。しかしながら、シールド910は、シールド910を取り囲む金属シェル900なしに、表面920を有するように形成される場合もあると理解される。
In other exemplary embodiments, the
プリント回路基板及び電子デバイスを検査するために、しばしば、スキャニング技術が使用される。例えば、X線は、回路基板製造の際に、集積回路のはんだ溶接及び接合部を検査するために一般的に使用されている。同原理を使用すれば、X線装置を使用して、プリント回路基板上の特定タイプの電子デバイスの場所を特定することができる場合がある。例えば、X線装置を備えた侵入者は、セキュリティ・キー、又は他の機密情報を記憶していることがあるフラッシュ・メモリ・デバイスを特定することができる場合がある。侵入者は、コントローラ200がセキュリティ違反を検出する能力を得る前に、それらのセキュリティ・キーを読み出すことを試みる場合がある。その理由は、特に、コントローラ200は、フラッシュ・メモリ・デバイスとは違うチップ上に設けられていることがあるからである。
Scanning techniques are often used to inspect printed circuit boards and electronic devices. For example, X-rays are commonly used to inspect integrated circuit solder welds and joints during circuit board manufacture. Using the same principle, an X-ray apparatus may be used to identify the location of a particular type of electronic device on a printed circuit board. For example, an intruder with an x-ray device may be able to identify a flash memory device that may store a security key or other sensitive information. Intruders may attempt to retrieve their security keys before the
上で説明したようなシールドは、2つの異なるタイプ、すなわち、導電性、及び非導電性のプラスチックからなるトレースを含む。トレースは、シールドを貫通する外部ソースによる攻撃を防止するように構成される。プラスチック・シールドの特性によれば、外部スキャニング装置による検出も、防止することができる。具体的には、2つの異なるタイプのプラスチックを使用してトレースを構成することによって、2つの材料の違いがほとんど知覚不能であるため、スキャニング技術の使用は、実施不可能になる場合がある。 Shields as described above include traces made of two different types: conductive and non-conductive plastic. The trace is configured to prevent attacks by external sources that penetrate the shield. According to the characteristics of the plastic shield, detection by an external scanning device can also be prevented. Specifically, by using two different types of plastic to construct the trace, the use of scanning techniques may become impractical because the difference between the two materials is almost insensitive.
図10は、例示的電子デバイス1030の上に設けられた例示的シールド1000の例示的アクティブ・トレース1010及び例示的おとりトレース1020を示している。図10では、アクティブ・トレース1010が1つの層に設けられ、おとりトレース1020が異なる層に設けられるものとして示されているが、アクティブ・トレース1010及びおとりトレース1020の多数のさらに別の層が、シールド1000に設けられる場合もあるものと理解される。
FIG. 10 illustrates an example
電流は、アクティブ・トレース1010を通って流れる場合があり、それによってアクティブ・トレース1010を使用して、外部ソースによるシールド1000内への貫通が検出される。例示的実施形態において、おとりトレース1020は、内側導電性部分を有するように構成される場合があるので、おとりトレース1020は、電流を導通する能力を有している。ただし、実際には、おとりトレース1020を通して電流は流されない場合がある。したがって、おとりトレース1020は、視覚的に、又は、何らかの他の形態の検査において、アクティブ・トレース1010と何も違いが無いように見えるように構成される場合がある。そのため、X線装置を備えた侵入者は、シールド1000のトレースの検出を試みる場合があるが、アクティブ・トレース1010とおとりトレース1020とを区別することはできない。この場合、アクティブ・トレース1010とおとりトレース1020は、同じ特性を示すように見えるので、潜在的な攻撃者は、おとりトレース1020を何らかの回避すべきものと解釈する場合がある。
Current may flow through the
一例示的実施形態において、おとりトレース1020は、アクティブ・トレース1010とは異なる材料から形成される。おとりトレース1020を形成するために使用される材料は、X線検査の際に、アクティブ・トレース1010の形成に使用される材料に比べて、より良好に視認可能である場合がある。例えば、おとりトレース1020を形成するために使用される材料は、シールド1000の非導電性部分に類似したタイプのプラスチックを使用して形成される場合がある一方、アクティブ・トレース1010は、X線装置により検出できない材料から形成される場合がある。このようにすると、攻撃者を、おとりトレース1020の貫通を避けるように仕向けることができ、攻撃者に、未検出のアクティブ・トレース1010を貫通させることができる。したがって、外部ソースに、アクティブ・トレース1010を貫通させることができ、それによって、シールド1000の侵入を検出することができる。
In one exemplary embodiment,
他の例示的実施形態では、侵入者をさらに混乱させるために、おとりトレース1020は、外部ソースによるシールド1000の貫通を実際に検出するように構成されない場合であっても、おとりトレース1020は、電流を導通する場合がある。他の例示的実施形態では、電流は、異なる時点で、アクティブ・トレース1010、及びおとりトレース1020を通して流される場合がある。この場合、アクティブ・トレース1010を通って流れる電流がないとき、アクティブ・トレース1010は、おとりトレースとして動作する場合がある。アクティブ・トレース1010を通って流れる電流がないとき、アクティブ・トレース1010は、外部ソースによるシールド1000の貫通を検出しない場合がある。同様に、おとりトレース1020を通して電流が流されていないとき、おとりトレース1020は、アクティブ・トレースとして動作する場合がある。おとりトレース1020を通って電流が流れているとき、おとりトレース1020は、いつ侵入デバイスがシールド1000を貫通するかを検出する場合がある。電流が流れるトレースを頻繁に交代することによって、潜在的な侵入者は、任意の所与の時点において、どのトレースがアクティブ・トレースとして動作していて、どのトレースがおとりトレースとして動作しているかを、簡単に検出することはできなくなる。したがって、シールド1000を貫通するための侵入者の試みを、さらに妨害することができる。
In other exemplary embodiments, to further confuse the intruder, the
図11は、電子デバイスのための例示的シールドの例示的アクティブ・トレース及び例示的おとりトレースを示している。三次元印刷技術は、平面におけるトレースの作成に限られないため、電子デバイスに対してセキュリティ・バリアを設けるためのシールドを形成するために使用可能なトレースの具体的形状に関して制限はない。図11に示されるように、アクティブ・トレース1100は、直線のような形状を有する場合があり、おとりトレース1110は、アクティブ・トレース1100を取り囲む螺旋のような形状を有する場合がある。上で述べたように、アクティブ・トレース1100を通して電流が流される場合があり、おとりトレース1110を通して電流を流すことは防止される場合がある。この構造によれば、侵入デバイスが周囲のおとりトレース1110を通過してトレース1100にアクセスすることは難しくなるため、アクティブ・トレース1100にアクセスする侵入者の試みを妨害することができる。
FIG. 11 shows an exemplary active trace and an exemplary decoy trace of an exemplary shield for an electronic device. Since three-dimensional printing techniques are not limited to creating traces in a plane, there are no restrictions on the specific shape of the traces that can be used to form a shield to provide a security barrier for electronic devices. As shown in FIG. 11, the
一例示的実施形態では、アクティブ・トレース1100がおとりトレースとして動作するようにするために、アクティブ・トレース1100を通して電流を流すことは防止され、おとりトレース1110がアクティブ・トレースとして動作するようにするために、おとりトレース1110を通して電流が流される場合がある。この実施形態では、侵入者に、直線状に設けられたトレースがアクティブ・トレースであるものと誤って思い込ませることができ、それによって、侵入者に、メモリ210を消去することなく、螺旋形のトレースを貫通することができると誤解させることができる。しかしながら、おとりトレース1110には、実際には電流が流れているため、内側のトレースにアクセスするためのこのトレースを貫通する試みはいずれも、メモリ210を消去する結果となる。
In one exemplary embodiment, in order for the
上記の開示は、電子デバイスにセキュリティ・バリアを提供するシールドの多数の例示的の実施形態について説明している。このように、本明細書に開示された実施形態によれば、外部ソースからの侵入を検出することによる、電子デバイスのメモリに記憶されたデータの保護が可能となる。 The above disclosure describes a number of exemplary embodiments of a shield that provides a security barrier to an electronic device. Thus, according to embodiments disclosed herein, it is possible to protect data stored in the memory of an electronic device by detecting intrusions from an external source.
本発明の例示的実施形態を以下に列挙する。
1.セキュリティ・バリアを提供するためのシールドであって、
各トレースが電気的に導電性の内側部分、及び電気的に非導電性の外側部分を含む、複数のトレース
を含み、
前記複数のトレースが、三次元印刷を使用して生成され、
前記複数のトレースは、当該シールドが電子デバイスを取り囲む形状となるように構成される、シールド。
2.前記内側部分は、導電性プラスチックを含む、1に記載のシールド。
3.前記外側部分は、非導電性プラスチックを含む、1に記載のシールド。
4.前記複数のトレースは、外部ソースから前記シールドへの前記シールドの貫通を検出するためのパターンを成すように構成される、1に記載のシールド。
5.前記導電性部分の抵抗値は、外部ソースから前記シールドへの接触に応答して変化する、1に記載のシールド。
6.前記複数のトレースは、前記シールドに空気の通路を規定する、1に記載のシールド。
7.前記空気の通路の中に延びる複数のルーバーをさらに含み、前記ルーバーは、三次元印刷を使用して生成される、6に記載のシールド。
8.前記シールドは、熱伝導性である、1に記載のシールド。
9.セキュリティ・バリアを提供するための装置であって、
複数のトレースを含むシールドであって、各トレースが、内側部分、及び外側部分を含み、前記内側部分が、導電性プラスチックを含み、前記外側部分が、非導電性プラスチックを含み、当該複数のトレースは、当該シールドが、電子デバイスを取り囲む形状となるように構成される、複数のトレースと、
前記シールドを取り囲む金属シェルと
を含む装置。
10.前記金属シェルと前記シールドとの間に設けられた熱伝導性材料をさらに含む、9に記載の装置。
11.前記金属シェルと前記シールドとの間に設けられた感圧材料をさらに含む、9に記載の装置。
12.前記金属シェルと前記シールドとの間に設けられた電気的に導電性の材料をさらに含む、9に記載の装置。
13.前記金属シェルは、縁部を含み、前記縁部から、前記金属シェルの2つの表面が、互いに実質的に90度の角度で延び、前記縁部に近接する前記シールドの一部が、前記金属シェルの前記2つの表面の各々との間に角度を形成する表面を形成し、前記角度が、実質的に35度から実質的に55度までの範囲内にある、9に記載の装置。
14.前記金属シェルは、角部を含み、前記角部から、前記金属シェルの3つの表面が、互いに実質的に90度の角度で延び、前記角部に近接する前記シールドの一部が、前記金属シェルの前記3つの表面との間に角度を形成する表面を有し、前記角度が、実質的に35度から実質的に55度までの範囲内にある、9に記載の装置。
15.メモリを含む電子デバイスと、
複数のトレースを含むシールドであって、各トレースが、導電性プラスチックの内側部分、及び非導電性プラスチックの外側部分を含み、当該複数のトレースは、当該シールドが前記電子デバイスを取り囲むように構成される、シールドと
を含むシステム。
16.複数のおとりトレースをさらに含み、前記複数のトレースを通して第1の電流が流され、前記複数のおとりトレースを通して第2の電流が流される、15に記載のシステム。
17.前記トレースの少なくとも一部は、螺旋のような形状を有し、前記おとりトレースの少なくとも一部は、前記螺旋の中心線に沿って延びている、16に記載のシステム。
18.前記おとりトレースの少なくとも一部は、螺旋のような形状を有し、前記トレースの少なくとも一部は、前記螺旋の中心線に沿って延びている、16に記載のシステム。
19.前記複数のトレースは、前記電子デバイスに結合され、前記シールドの外部にあるソースによる貫通の検出に応答して、前記メモリが消去される、15に記載のシステム。
20.前記複数のトレースは、三次元印刷を使用して生成される、15に記載のシステム。
Exemplary embodiments of the present invention are listed below.
1. A shield to provide a security barrier,
A plurality of traces, each trace comprising an electrically conductive inner portion and an electrically non-conductive outer portion;
The plurality of traces are generated using three-dimensional printing;
The plurality of traces are configured such that the shield has a shape surrounding the electronic device.
2. The shield of claim 1, wherein the inner portion comprises a conductive plastic.
3. The shield of claim 1, wherein the outer portion comprises a non-conductive plastic.
4). The shield of claim 1, wherein the plurality of traces are configured to form a pattern for detecting penetration of the shield from an external source to the shield.
5. The shield according to 1, wherein a resistance value of the conductive portion changes in response to contact from an external source to the shield.
6). The shield according to 1, wherein the plurality of traces define an air passage in the shield.
7). The shield of claim 6, further comprising a plurality of louvers extending into the air passage, wherein the louvers are generated using three-dimensional printing.
8). The shield according to 1, wherein the shield is thermally conductive.
9. A device for providing a security barrier comprising:
A shield including a plurality of traces, each trace including an inner portion and an outer portion, the inner portion including a conductive plastic, and the outer portion including a non-conductive plastic, the plurality of traces A plurality of traces configured such that the shield has a shape surrounding the electronic device;
And a metal shell surrounding the shield.
10. The apparatus of claim 9, further comprising a thermally conductive material provided between the metal shell and the shield.
11. The apparatus of claim 9, further comprising a pressure sensitive material provided between the metal shell and the shield.
12 The apparatus of claim 9, further comprising an electrically conductive material provided between the metal shell and the shield.
13. The metal shell includes an edge, from which two surfaces of the metal shell extend at an angle of substantially 90 degrees to each other, and a portion of the shield proximate to the edge is the metal The apparatus of claim 9, forming a surface that forms an angle with each of the two surfaces of the shell, wherein the angle is in a range of substantially 35 degrees to substantially 55 degrees.
14 The metal shell includes a corner, from which three surfaces of the metal shell extend at an angle of substantially 90 degrees with each other, and a portion of the shield proximate to the corner is the metal The apparatus of claim 9, having a surface that forms an angle with the three surfaces of the shell, wherein the angle is in a range of substantially 35 degrees to substantially 55 degrees.
15. An electronic device including a memory;
A shield including a plurality of traces, each trace including an inner portion of conductive plastic and an outer portion of non-conductive plastic, wherein the plurality of traces are configured such that the shield surrounds the electronic device. A system that includes a shield.
16. 16. The system according to 15, further comprising a plurality of decoy traces, wherein a first current is passed through the plurality of decoy traces and a second current is passed through the plurality of decoy traces.
17. The system of claim 16, wherein at least a portion of the trace has a spiral-like shape and at least a portion of the decoy trace extends along a centerline of the spiral.
18. The system of claim 16, wherein at least a portion of the decoy trace has a spiral-like shape, and at least a portion of the trace extends along a centerline of the spiral.
19. The system of claim 15, wherein the plurality of traces are coupled to the electronic device and the memory is erased in response to detection of a penetration by a source external to the shield.
20. 16. The system according to 15, wherein the plurality of traces are generated using three-dimensional printing.
Claims (9)
複数のアクティブ・トレース、及び複数のおとりトレースを含むシールドと
を含むシステムであって、
前記複数のアクティブ・トレース、及び複数のおとりトレースの各々が、導電性プラスチックの内側部分、及び非導電性プラスチックの外側部分を含み、前記複数のアクティブ・トレース、及び複数のおとりトレースは、前記シールドが前記電子デバイスを取り囲むように構成されており、
前記複数のアクティブ・トレースを使用して前記シールドの外部にあるソースからの前記シールドの貫通を検出するように、前記複数のアクティブ・トレースを通して電流が流され、
前記複数のおとりトレースは、前記シールドの外部にあるソースからの前記シールドの貫通を実際に検出するように構成されていない、システム。 An electronic device including a memory;
A system including a plurality of active traces and a shield including a plurality of decoy traces,
Each of the plurality of active traces and the plurality of decoy traces includes an inner portion of conductive plastic and an outer portion of non-conductive plastic, wherein the plurality of active traces and plurality of decoy traces are the shield Is configured to surround the electronic device,
Current is passed through the plurality of active traces to detect penetration of the shield from a source external to the shield using the plurality of active traces;
The system wherein the plurality of decoy traces are not configured to actually detect penetration of the shield from a source external to the shield.
9. The plurality of active traces are coupled to the electronic device and the memory is erased in response to detection of a penetration by a source external to the shield. System.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017055281A JP6294530B2 (en) | 2017-03-22 | 2017-03-22 | Shield for electronic devices |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017055281A JP6294530B2 (en) | 2017-03-22 | 2017-03-22 | Shield for electronic devices |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016505442A Division JP6145214B2 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2013-03-28 | Shield for electronic devices |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017146976A JP2017146976A (en) | 2017-08-24 |
| JP6294530B2 true JP6294530B2 (en) | 2018-03-14 |
Family
ID=59680839
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017055281A Active JP6294530B2 (en) | 2017-03-22 | 2017-03-22 | Shield for electronic devices |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6294530B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11881791B2 (en) * | 2018-07-04 | 2024-01-23 | Hitachi Astemo, Ltd. | Electromagnetic shielding power conversion device |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19634135C2 (en) * | 1996-08-23 | 1998-07-02 | Siemens Ag | Semiconductor circuit, in particular for use in an integrated module |
| WO2004086202A1 (en) * | 2003-03-25 | 2004-10-07 | Bourns, Inc. | A security housing for a circuit |
| JP2008065401A (en) * | 2006-09-05 | 2008-03-21 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Casing and casing constituting member |
| GB2452732A (en) * | 2007-09-12 | 2009-03-18 | Seiko Epson Corp | Smart-card chip with organic conductive surface layer for detecting invasive attack |
-
2017
- 2017-03-22 JP JP2017055281A patent/JP6294530B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017146976A (en) | 2017-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6145214B2 (en) | Shield for electronic devices | |
| US7791898B2 (en) | Security apparatus | |
| US7898413B2 (en) | Anti-tamper protected enclosure | |
| US6686539B2 (en) | Tamper-responding encapsulated enclosure having flexible protective mesh structure | |
| US8589703B2 (en) | Tamper respondent covering | |
| US8836509B2 (en) | Security device | |
| WO2009036611A1 (en) | Security protection cover | |
| US20100024046A1 (en) | Methods and systems for detecting a lateral intrusion of a secure electronic component enclosure | |
| US20170286725A1 (en) | Penetration detection boundary having a heat sink | |
| US9607172B2 (en) | Electronic data security apparatus | |
| US10489614B2 (en) | Tamper detecting cases | |
| US7701244B2 (en) | False connection for defeating microchip exploitation | |
| US8164912B2 (en) | Security protection box | |
| JP6294530B2 (en) | Shield for electronic devices | |
| WO2007018761A2 (en) | Security method for data protection | |
| EP2931011A1 (en) | A safety box for electronic circuit protection | |
| CN205608734U (en) | Finance equipment and protection device thereof | |
| EP3644209B1 (en) | Tamper sensor | |
| JP2018185588A (en) | Information processing device and data protection method | |
| US20230134349A1 (en) | Hardware protection module | |
| Dubrova | Hardware Security | |
| JP5665584B2 (en) | Electronics |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20171107 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180130 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180215 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6294530 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R360 | Written notification for declining of transfer of rights |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R360 |
|
| R360 | Written notification for declining of transfer of rights |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R360 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |