JP6257953B2 - Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system - Google Patents
Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6257953B2 JP6257953B2 JP2013168018A JP2013168018A JP6257953B2 JP 6257953 B2 JP6257953 B2 JP 6257953B2 JP 2013168018 A JP2013168018 A JP 2013168018A JP 2013168018 A JP2013168018 A JP 2013168018A JP 6257953 B2 JP6257953 B2 JP 6257953B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electronic medical
- display
- confirmation
- medical record
- risk level
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/10—Office automation; Time management
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H10/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data
- G16H10/60—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data for patient-specific data, e.g. for electronic patient records
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H15/00—ICT specially adapted for medical reports, e.g. generation or transmission thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/30—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for calculating health indices; for individual health risk assessment
Description
本発明の実施の形態は、電子カルテ作成装置及び電子カルテ作成システムに関する。 Embodiments described herein relate generally to an electronic medical record creation apparatus and an electronic medical record creation system.
近年、個々の患者のカルテの情報を電子化してデータベースに記憶させた電子カルテが普及している。この電子カルテは、例えば、当該電子カルテを作成する者が患者を診察してその都度作成される。 In recent years, electronic medical records in which information on medical records of individual patients is digitized and stored in a database have become widespread. This electronic medical chart is created each time a person who creates the electronic medical chart examines a patient.
但し、電子カルテへの記入事項の全てが必ずしも新規な内容ではないこともある。その場合には、過去の処方や処置、検査結果、所見等を参考に同じ処方等が入力される場合もある。また、電子カルテに記入(記録)される情報量は多くなる傾向にあり、当該電子カルテを作成する者の手間が増えることになる。 However, not all entries in the electronic medical record are necessarily new. In that case, the same prescription may be input with reference to past prescriptions and treatments, test results, findings, and the like. Further, the amount of information entered (recorded) in the electronic medical record tends to increase, and the labor of the person who creates the electronic medical record increases.
そこで、この場合、例えば、必要な内容を転記することで、簡易に情報を引き継いで記入することとしている。或いは、「Do記載(Do表示)」と言われる以前のカルテの記載内容と繰り返して入力する際にその記載内容が同じであることを示す表示を利用することもある。 Therefore, in this case, for example, by transferring necessary contents, information is simply taken over and entered. Alternatively, there may be used a display indicating that the description content is the same when the input is repeated with the description content of the previous chart called “Do description (Do display)”.
一方、例えば、記載内容が膨大な場合に処方等についてDo記載がなされると、電子カルテを作成する者による十分な確認がおろそかになる可能性もある。このような弊害をなくすべく、例えば、Do表示が適用された場合に、基礎とされた記述内容を画面上表示させる手段を持つことでDo表示の内容を簡易に確認することができるようにされている場合もある(以下の特許文献1参照)。
On the other hand, for example, if the Do is written about the prescription when the description content is enormous, sufficient confirmation by the person who creates the electronic medical record may be neglected. In order to eliminate such an adverse effect, for example, when Do display is applied, it is possible to easily check the content of the Do display by having a means for displaying the description content as a basis on the screen. (See
しかしながら、上記特許文献1において開示されている発明では、次の点について配慮がなされていない。
However, the invention disclosed in
すなわち、基礎とされた記述内容は全て表示対象となってしまい、表示される内容の重要度は考慮されない。従って、特に表示対象が多い場合には、特に確認を必要とする記述内容の確認を確実に行うことが困難となる場合が生ずる可能性がある。 That is, all the description contents that are the basis are displayed, and the importance of the displayed contents is not considered. Therefore, particularly when there are many display objects, there is a possibility that it may be difficult to surely confirm the description contents that particularly require confirmation.
本発明は上記課題を解決するためになされたものであり、本発明の目的は、電子カルテの作成においてDo表示がなされる場合に、表示される項目ごとにその確認の優先度を決定してその優先度に基づいて画面表示することによって、要確認項目のDo表示の確認を簡易かつ確実に行うことが可能な電子カルテ作成装置及び電子カルテ作成システムを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made to solve the above problems, and the object of the present invention is to determine the priority of confirmation for each displayed item when Do display is made in the creation of an electronic medical record. An object of the present invention is to provide an electronic medical record creation device and an electronic medical record creation system capable of easily and reliably confirming Do display of items to be confirmed by displaying on the screen based on the priority.
請求項1に記載の発明の特徴は、電子カルテ作成装置において、繰り返し処方またはオーダの対象となる記入項目の内容を記憶する記憶部と、記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、表示された記入項目の内容について繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、リスクレベル決定部によって要確認項目ごとに決定されたリスクレベルに応じた表示態様の表示を表示部に対して指示する表示態様決定部とを備える。 Features of the first aspect of the present invention, in the electronic medical chart creating device, a storage unit for storing the contents of the entry to be that a repetitive formulation or order, and a display unit for displaying the contents of the entry, display An input section for inputting whether to repeatedly prescribe or order the contents of the entered entry, a risk level determining section for determining the risk level of each entry, and the risk determined by the risk level determining section A determination unit that determines the confirmation conditions based on the level, and a screen level display mode for confirming whether or not to repeatedly prescribe or order the items to be confirmed according to the confirmation conditions, and a risk level determination unit And a display mode determination unit that instructs the display unit to display a display mode according to the risk level determined for each confirmation item.
請求項12に記載の発明の特徴は、電子カルテ作成装置において、繰り返し処方またはオーダの対象となる医療オーダの記入項目の内容を記憶する記憶部と、記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、表示された記入項目の内容について繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、要確認項目ごとに表示部に対して決定された表示態様の表示を指示する表示態様決定部と、を備え、決定部は、リスクレベルに応じた表示態様の表示頻度を確認条件の1つとして決定する。 According to a twelfth aspect of the present invention, in the electronic medical record creation apparatus, a storage unit that stores the contents of the entry items of the medical order that is a target of repeated prescription or order, a display unit that displays the contents of the entry items, Determined by the input section for inputting whether to repeatedly prescribe or order the contents of the displayed entry, the risk level determination section for determining the risk level of each entry, and the risk level determination section A determination unit that determines the confirmation conditions based on the risk level, and a screen display mode for confirming whether or not to repeatedly prescribe or order the required confirmation items according to the confirmation conditions, as well as the required confirmation items and a display mode decision unit for instructing the display of the determined display mode to the display unit each time, determination unit, the table示態like based on the risk level It is determined as one of the confirmation conditions the display frequency.
請求項15に記載の発明の特徴は、電子カルテ作成システムにおいて、これまでに作成された電子カルテを保存するサーバと、電子カルテの作成に当たって必要な医用画像を取得する医用画像診断装置と、繰り返し処方またはオーダの対象となる記入項目の内容を記憶する記憶部と、記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、表示された記入項目の内容について繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、リスクレベル決定部によって要確認項目ごとに決定されたリスクレベルに応じた表示態様の表示を表示部に対して指示する表示態様決定部とを備える電子カルテ作成装置とを備える。
The invention according to
請求項16に記載の発明の特徴は、電子カルテ作成システムにおいて、これまでに作成された電子カルテを保存するサーバと、電子カルテの作成に当たって必要な医用画像を取得する医用画像診断装置と、繰り返し処方またはオーダの対象となる医療オーダの記入項目の内容を記憶する記憶部と、記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、表示された記入項目の内容について繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、要確認項目ごとに表示部に対して決定された表示態様の表示を指示する表示態様決定部と、を備え、決定部は、リスクレベルに応じた表示態様の表示頻度を確認条件の1つとして決定することを特徴とする電子カルテ作成装置とを備える。 According to a sixteenth aspect of the present invention, in the electronic medical record creation system, a server for storing the electronic medical record created so far, a medical image diagnostic apparatus for acquiring a medical image necessary for creating the electronic medical record, and repetition Whether to repeat the prescription or order for the contents of the storage part that stores the contents of the entry of the medical order subject to prescription or order, the display part that displays the contents of the entry, and Input section for input, risk level determination section for determining the risk level of each entry, determination section for determining confirmation conditions based on the risk level determined by the risk level determination section, and according to the confirmation conditions Determine the display mode of the screen display for confirming the pros and cons of repeatedly prescribing or ordering the required confirmation items. Comprising a display mode decision unit for instructing the display of the display mode determined to the display unit for each item, the decision unit determines a table示態like display frequency based on the risk level as one of the confirmation conditions And an electronic medical record creation device characterized by:
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
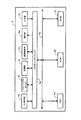
図1は、実施の形態における電子カルテ作成装置3を含む電子カルテ作成システムSの全体構成を示すブロック図である。電子カルテ作成システムSは、これまでに作成された電子カルテを保存するサーバ1と、電子カルテの作成に当たって必要な医用画像を取得する医用画像診断装置2と、電子カルテを作成する際に利用される電子カルテ作成装置3と、これらを互いに接続する通信ネットワークNから構成される。電子カルテ作成システムSは、それ自体独立したシステムとして構成されても良いが、例えば、病院情報管理システム(HIS:Hospital Information System)、放射線部門情報管理システム(RIS:Radiological Information System)、医用画像管理システム(PACS:Picture Archiving Communication System)といった医療機関内に構築された各種管理システムの全て、或いは、その一部を構成するようにされていても良い。
FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating an overall configuration of an electronic medical record creation system S including an electronic medical
サーバ1は、電子カルテ作成装置3において作成された電子カルテを保存する装置である。なお、サーバ1は、電子カルテの保存だけではなく、例えば、後述する医用画像診断装置2において取得された患者の内部情報(医用画像)を保存するようにしても良い。
The
医用画像診断装置2は、患者を撮影してその内部情報を取得する医用画像取得(撮影)装置である。医用画像診断装置2としては、例えば、例えば、X線CT装置(computed tomography:コンピュータ断層撮影装置)や、磁気共鳴診断装置(MRI:magnetic resonance imaging)等が該当する。
The medical image
電子カルテ作成装置3は、例えば、医師等が医用画像を利用して患者の診察を行ったり、或いは、医用画像の読影を行うことによって電子カルテを作成する際に使用されるワークステーションである。以下においては、特に限定することはないが、例えば、電子カルテを作成するアプリケーション等を電子カルテ作成装置3自身で保持して、当該アプリケーションを利用して電子カルテを作成しても良い。
The electronic medical
或いは、シンクライアントシステムとして当該アプリケーションはサーバ1内に記憶されており、電子カルテを作成する際には、電子カルテ作成装置3がサーバ1にアクセスしてこのアプリケーションを利用することとしても良い。この場合、電子カルテ作成装置3は、サーバ1から電子カルテを作成するに必要な情報を少なくとも要求、表示させるだけの処理能力を備えていれば足りる。
Alternatively, the application is stored in the
なお、図1に示す医用画像システムSでは、通信ネットワークNにサーバ1、医用画像診断装置2、電子カルテ作成装置3がそれぞれ1つずつ接続されている。但し、通信ネットワークNに接続されるサーバ、医用画像診断装置、或いは、電子カルテ作成装置の数は単数、或いは複数のいずれでも良く、その数は任意である。
In the medical image system S shown in FIG. 1, a
通信ネットワークNは、サーバ1と、医用画像診断装置2と、電子カルテ作成装置3とをそれぞれつなぎ、互いの間で、例えば医用画像情報のやりとりを可能とする。通信ネットワークNの例としては、LAN(Local Area Network)やインターネット等のネットワークを挙げることができる。また、この通信ネットワークNを介してやり取りされる情報に関する規格は、DICOM(Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine)等、いずれの規格であっても良い。
The communication network N connects the
図2は、本発明の実施の形態における電子カルテ作成装置3の内部構成を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an internal configuration of the electronic medical
電子カルテ作成装置3は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)3aと、ROM(Read Only Memory)3bと、RAM(Random Access Memory)3c及び入出力インターフェイス3dがバス3eを介して接続されている。入出力インターフェイス3dには、入力部3fと、表示部3gと、通信制御部3hと、記憶部3iと、リムーバブルディスク3jとが接続されている。また、Do表示を行う際に必要な処理を行うためにDo表示部10も併せて接続されている。
In the electronic medical
ここで、「「Do記載(Do表示)」とは、以前のカルテの記載されている処方やオーダを繰り返して処方、或いは、繰り返してオーダする際にその記載内容が同じであることを示す表示である。 Here, ““ Do description (Do display) ”is a display indicating that the prescription or order described in the previous chart is repeated or the description is the same when ordering repeatedly. It is.
CPU3aは、入力部3fからの入力信号に基づいてROM3bから電子カルテ作成装置3を起動するためのブートプログラムを読み出して実行し、記憶部3iに格納されている各種オペレーティングシステムを読み出す。またCPU3aは、入力部3fや入出力インターフェイス3dを介して、図3において図示していないその他の外部機器からの入力信号に基づいて各種装置の制御を行う。
The CPU 3a reads out and executes a boot program for starting the electronic medical
さらにCPU3aは、RAM3cや記憶部3i等に記憶されたプログラム及びデータを読み出してRAM3cにロードするとともに、RAM3cから読み出されたプログラムのコマンドに基づいて、Do表示を行うに当たって要確認項目の確認処理やデータの計算、加工等、一連の処理を実現する処理装置である。
Further, the CPU 3a reads the program and data stored in the
入力部3fは、電子カルテ作成装置3の操作者(例えば、医師)が各種の操作を入力するキーボード、ダイヤル等の入力デバイスにより構成されている。操作者の操作に基づいて入力部3fは入力信号を作成し、当該入力信号はバス3eを介してCPU3aに送信される。また、この他、マウス、カードリーダ、バーコードリーダ、タッチパネル、マイク、カメラ等も入力部3fの一種として挙げることができる。
The
表示部3gは、例えば液晶ディスプレイといった、モニタである。この表示部3gは、CPU3aからバス3eを介して出力信号を受信し、例えば電子カルテ作成装置3においてある画像の処理を行うに当たっての条件設定に必要な画像等、或いはCPU3aの処理結果等を表示する。またここでの表示部3gには、プリンタ、プロジェクタ、スピーカ、その他の電子カルテを作成する者の五感に訴えかける装置も含まれる。
The display unit 3g is a monitor such as a liquid crystal display. The display unit 3g receives an output signal from the CPU 3a via the
通信制御部3hは、LANカードやモデム等の手段であり、電子カルテ作成装置3をインターネットやLAN等の通信ネットワークNに接続することを可能とする手段である。通信制御部3hを介して通信ネットワークと送受信したデータは入力信号または出力信号として、入出力インターフェイス3d及びバス3eを介してCPU3aに送受信される。
The
記憶部3iは、半導体や磁気ディスクで構成されており、CPU3aで実行される、例えば、Do表示を行うためのプログラムやデータが記憶されている。また、後述する、リスクレベルに関するテーブルや確認条件についても記憶されている。
The
リムーバブルディスク3jは、光ディスクやフレキシブルディスクのことである。ディスクドライブによって読み書きされた信号は、入出力インターフェイス3d及びバス3eを介してCPU3aに送受信される。なおDo表示の処理に必要なアプリケーションは、記憶部3i、或いは、外部記憶媒体を介してリムーバブルディスク3i内に記憶されている。
The
Do表示部10は、電子カルテを作成する者である医師が電子カルテを作成する際の1つの処理である、Do表示を行うための機能を備えている。従って、電子カルテを作成する者がDo表示を行うためのきっかけとなる処理を行ったことをトリガーとして、Do表示部10の機能が実行される。
The
図3は、本発明の実施の形態におけるDo表示部10の内部構成を示すブロック図である。Do表示部10は、例えば、電子カルテを作成する者からのDoを実行するための要求を受け付ける受信部11と、判断部12と、リスクレベル決定部13と、決定部14と、表示態様決定部15と、要確認項目の確認に当たっての要確認項目の確認画面を表示部3gに対して送信する送信部16とから構成される。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an internal configuration of the
なお、これら各部の機能、働きについては、以下に説明するDo表示から当該表示内容の確認に至る流れを説明する際に併せて説明する。 The functions and functions of these units will be described together with the description of the flow from the Do display described below to the confirmation of the display content.
次に、Do表示の仕方、すなわち、Do表示の対象となる項目を選択してから電子カルテを作成する者である医師が当該項目の確認を行い、結果としてDo表示がなされるまでを順を追って説明する。なお、ここでは繰り返し行われる処方またはオーダに関するDo表示のうち、繰り返して処方する場合を例に挙げて以下説明する。 Next, the method of Do display, that is, the doctor who is the person who creates the electronic medical record after selecting the item to be displayed, confirms the item, and the order until Do display is made as a result. I will explain later. In addition, the case where it repeats and prescribes as an example among the Do display regarding the prescription or order performed repeatedly here is demonstrated below as an example.
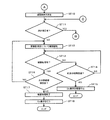
図4、図5は、実施の形態におけるDo表示から当該表示内容の確認に至る流れを示すフローチャートである。 4 and 5 are flowcharts showing a flow from Do display to confirmation of the display content in the embodiment.
電子カルテを作成する者は、電子カルテを作成するに当たって、例えば、サーバ1からカルテのひな形等を読み出して利用する。また、患者の診察やカルテの作成の役に立てるため、これまで作成された当該患者に関するカルテを読み出して電子カルテ作成装置3の表示部3gに表示させることもある。これら電子カルテを作成する流れは既知のことであるので、ここでは説明を省略する。
When creating an electronic medical chart, a person who creates an electronic medical chart, for example, reads out and uses a medical chart template from the
医師がカルテを作成する中で、例えば、処置や所見の内容、或いは、薬剤の処方についてこれまで作成された過去のカルテと同じ内容を記載することはあり得ることである。その際に、過去のカルテから該当する内容をいわばコピーアンドペーストの要領で今回のカルテに反映させることも行われる。 While a doctor prepares a medical chart, for example, it is possible to describe the contents of treatments and findings, or the same contents as past medical charts that have been created so far for prescription of drugs. At that time, the corresponding contents from the past medical record are reflected in the current medical record in a manner of copy and paste.
この背景には、カルテへの記載内容が増加する傾向にあり、全てを診察の都度記載することとするとカルテを作成する医師への負担が大きくなる。一方で、電子カルテ作成装置3の性能向上や電子カルテ作成システムSが構築される等、カルテ自体が電子カルテとなることで、処方等を紙のカルテに記載するよりも記載する行為、つまりカルテを作成する行為自体が簡易かつ便利に行える状態が作出されるようになってきている。
Against this background, there is a tendency for the contents to be described in the medical record to increase, and if all are described every time a medical examination is performed, the burden on the doctor who creates the medical chart increases. On the other hand, the medical record itself becomes an electronic medical record, such as the performance improvement of the electronic medical
従ってこのような状況の下、安易にDo表示が行えると、カルテの作成についての利便性の向上もさることながら、Do表示された内容に関してチェック(確認)が行き届かないことも考えられる。そこで電子カルテを作成する者である医師が如何に確実にDo表示をしようとする内容について確認を行うかが重要となる。 Therefore, if Do display can be easily performed under such circumstances, it is possible that the check (confirmation) regarding the Do display content is not achieved while improving the convenience of creating a chart. Therefore, it is important how a doctor who creates an electronic medical record confirms the content to be displayed Do.
Do表示がなされる場合には、まず、電子カルテを作成する者によってDo表示を行う範囲(項目)が選択されるので、電子カルテ作成装置3では、当該選択された項目を把握する(ST1)。但し、この段階ではまだ実際にDo表示を行うか否か判別できない。電子カルテ作成システムSでは、例えば、Do表示を行うボタンをクリックする等、Do表示を行うに当たって電子カルテを作成する者に何らかの意思表示を求めるからである。そこで、電子カルテ作成装置3では、選択された項目がDo表示の対象となるか否かを判断する(ST2)。
When Do display is performed, first, a range (item) in which Do display is performed is selected by a person who creates the electronic medical record, so the electronic medical
なお、選択された項目についてDo表示がなされるか否かの判断をDo表示部10において行うか否かについては、任意に設定することができる。例えば、当該判断をDo表示部10において行う場合には、判断部12が選択された項目がDo表示の対象となるか否かを判断する。また、当該判断については電子カルテ作成装置3において行うとの設定の場合には、例えば、CPU3aにおいてその判断が行われることになる。以下においては、判断部12が選択された項目がDo表示の対象となるか否かを判断することを前提に説明を行う。
Note that whether or not Do display is performed on the selected item in the
判断の結果、選択された項目についてDo表示がなされない場合には(ST2のNO)、医師は自ら電子カルテに処置や処方について記入することになる。従って、ここでは項目が選択されたことは把握したものの、Do表示はされない、ということで終了する。 If the Do is not displayed for the selected item as a result of the determination (NO in ST2), the doctor himself / herself enters the treatment and prescription in the electronic medical record. Therefore, although it is understood that the item has been selected here, the process is terminated when the Do display is not performed.
一方、医師によってDo表示をする旨の意思表示がなされた場合には(ST2のYES)、選択された項目についてDo表示を行う為の準備が開始される。Do表示部10(判断部12)は選択された項目に関する情報を記憶部3iから取得する(ST3)。当該項目に関する情報には、例えば、当該項目に示される薬剤に関する情報や当該項目を要確認項目とするか否かについての情報が含まれている。
On the other hand, when the doctor has indicated the intention to display Do (YES in ST2), preparation for performing Do display on the selected item is started. The Do display unit 10 (determination unit 12) acquires information about the selected item from the
従って、判断部12は、これらの情報を基に、選択された項目(Do表示を行う予定の項目)が要確認項目であるか否かを判断する(ST4)。ここで「要確認項目」とは、選択された項目のうち処置、処方等に関する重要な項目であるため、Do表示を行うに当たって、何らかの形で電子カルテを作成する者(医師)の確認を必要とする項目のことである。
Accordingly, the
そのため、選択された項目であっても要確認項目と判断されなければ(ST4のNO)、医師の確認がなくともそのままDo表示しても問題がないことになる。この場合には、次の項目が要確認項目であるか否かが改めて判断される。 For this reason, even if the item is selected, if it is not determined that the item needs to be confirmed (NO in ST4), there is no problem even if the Do is displayed as it is without confirmation from the doctor. In this case, it is determined again whether or not the next item is a confirmation required item.
次に、選択された項目が要確認項目であると判断された場合には(ST4のYES)、判断部12は確認対象となる項目を特定するとともに、当該要確認項目に関するリスクレベルを決定する(ST5)。判断部12は、リスクレベル決定部13を介して項目ごとにリスクレベルを決定する。
Next, when it is determined that the selected item is a confirmation required item (YES in ST4), the
すなわち、まず例えば、薬剤に関する名称、処方量といった項目に関する情報と、予め記憶部3iに記憶されている薬剤とその薬剤の標準的な処方量に関する情報とを比較する。また、薬剤の名称から当該薬剤の特性も併せて取得する。これらの情報を基にDo表示の対象となる薬剤及びその処方量に関するリスクレベルを把握する。
That is, first, for example, information related to items such as a name and prescription amount relating to a drug is compared with information related to a drug stored in advance in the
図6は、実施の形態における要確認項目のリスクレベルを示すテーブルの一例である。このテーブルによれば、縦軸に薬剤の特性が示されており、ここでは3つのレベルが示されている。リスクレベルを決定する際に薬剤の特性を把握するのは、その特性によってリスクレベルが大きく異なることになるからである。 FIG. 6 is an example of a table indicating the risk level of the items to be confirmed in the embodiment. According to this table, the vertical axis shows the characteristics of the medicine, and here, three levels are shown. The reason why the characteristics of a drug are grasped when determining the risk level is that the risk level varies greatly depending on the characteristics.
なお、当該特性については、例えば、NDP(National Demonstration Project)において定義されている特性を利用する等して設定する。ここではDo表示の対象となる処置、処方等の確認を医師に促すことを目的としていることから、当該特性の定義に当たってはいずれの定義を用いても良い。さらに特性のレベルについては、図6に示すテーブルにおいては3段階に分けて説明しているが、レベルを何段階に分けるかは任意である。 The characteristics are set using, for example, characteristics defined in NDP (National Demonstration Project). Here, since the purpose is to prompt the doctor to confirm the treatment, prescription, etc., which is the object of Do display, any definition may be used to define the characteristics. Further, the level of characteristics is described in three steps in the table shown in FIG. 6, but the number of levels is arbitrary.
また、図6に示すリスクレベルのテーブルにおいては、患者に処方した場合に重篤な結果を生じさせる可能性の低い薬剤については規定されていない。これは、ここでの実施の形態においては、このような薬剤については要確認項目には含まれないと判断されているからである。 In addition, the risk level table shown in FIG. 6 does not define drugs that are unlikely to cause serious results when prescribed to patients. This is because in this embodiment, it is determined that such a medicine is not included in the confirmation required items.
従って、薬剤の特性をどのレベルまでリスクレベルを示すテーブルに規定するかは任意に設定することが可能である。そのため、重篤な結果を生じさせる可能性の低い薬剤についてもリスクレベルを判断し、それぞれ後述する確認条件を電子カルテを作成する者に判断させることとしても良い。 Therefore, it is possible to arbitrarily set to what level the characteristics of the drug are defined in the table indicating the risk level. Therefore, it is also possible to determine the risk level of a drug that is unlikely to cause a serious result, and allow the person who creates the electronic medical record to determine the confirmation conditions described later.
一方、横軸には当該薬剤の処方量に関する適正範囲が示されている。ここでは、適正範囲内にあることを中心に、処方量が適正範囲より大きな場合、小さな場合の3つのレベルが示されている。なお、一般的に考えれば薬剤の処方量が適正範囲程度であれば患者への処方に何らの問題もないが、ここでは薬剤の特性との関係でリスクレベルを設定していることから、処方量が適正範囲程度である場合についてもリスクレベルを設定している。 On the other hand, the horizontal axis indicates an appropriate range regarding the prescription amount of the drug. Here, centering on being in the proper range, three levels are shown when the prescription amount is larger than the proper range and small. In general, there is no problem in prescribing the patient if the prescription amount of the drug is in the proper range, but here the risk level is set in relation to the characteristics of the drug, so the prescription The risk level is also set when the amount is within the appropriate range.
例えば、薬剤の特性として「成分そのものの毒性が強い薬剤」である場合には、処方量の如何に拘わらずリスクレベルは「A」と決定される。ここで図6に示すテーブルではリスクレベルを表わすものとして「A」、「B」、「C」の3つのレベルが示されており、「A」から「C」に向けてリスクレベルが低減する。例えば、薬剤の特性として「重篤な結果をもたらし得る薬物相互作用をもつ薬剤」である場合であって、処方量が「適正範囲より小さい」場合には、リスクレベルは「C」と決定される。この組み合わせは、リスクレベルがAである「成分そのものの毒性が強い薬剤」の場合よりもリスクレベルが低いと判断されるからである。 For example, when the drug characteristic is “drug with strong toxicity of the component itself”, the risk level is determined as “A” regardless of the prescription amount. Here, in the table shown in FIG. 6, three levels “A”, “B”, and “C” are shown as risk levels, and the risk level decreases from “A” to “C”. . For example, when the drug characteristic is “drug with drug interaction that can cause serious consequences” and the prescribed amount is “smaller than appropriate range”, the risk level is determined as “C”. The This is because this combination is judged to have a lower risk level than in the case of a “drug with strong toxicity of the component itself” having a risk level of A.
なお、薬剤によっては相互作用を持つ場合もある。この場合には、複数の薬剤の組み合わせをテーブルに規定しておきリスクレベルを決定しても良い。また薬剤の組み合わせについては、相互作用の他、Do表示の操作を行う時点で新たに処方される薬剤と、その時点ではまだ有効な期限を持つ、前回処方された薬剤との関係についても判断される。また、診療科が異なるとカルテも替わるので、その場合にもそれぞれの診療科で出された薬剤同士の取り合わせについても確認する必要がある。 Some drugs may interact with each other. In this case, a risk level may be determined by defining a combination of a plurality of drugs in a table. Regarding the combination of drugs, in addition to the interaction, the relationship between the newly prescribed drug at the time of performing the Do display operation and the previously prescribed drug that still has an effective deadline at that time is also judged. The In addition, since medical charts are changed when different medical departments are used, it is necessary to check the combination of medicines provided in the respective medical departments.
また、後述する表示との関係で、例えば、中位のリスクレベルと決定された薬剤が複数ある場合に、これらのリスクレベルとまとめて上げて、より高位のリスクレベルと決定し直す処理も考えられる。これは、このような高位のリスクレベルであれば医師はより注意深く確認を行うことになるからである。また、同位のリスクレベルを示す薬剤等の数が多くなると、表示が散漫になり、結果として全ての項目を表示させているのと同じになってしまい、必要とする情報を医師に届けられなくなる。そこで、いくつかの表示パターンを示すことで、特に重大なリスクレベルを持つ要確認項目の確認を確実に行わせることとしている。このような設定は予め任意に行っておくことができる。 In addition, in relation to the display described later, for example, when there are multiple drugs that have been determined to have a medium risk level, it may be possible to combine these risk levels and re-determine a higher risk level. It is done. This is because doctors will check more carefully at such high risk levels. Also, if the number of drugs that show the same level of risk increases, the display becomes diffuse, resulting in the same display as all items, and the necessary information cannot be delivered to the doctor. . Therefore, by displaying several display patterns, it is possible to ensure confirmation of items requiring confirmation having a particularly serious risk level. Such setting can be made arbitrarily in advance.
以上のリスクレベルの決定はリスクレベル決定部13においてなされる。また上述したように当該リスクレベルを規定したテーブルは本発明の実施の形態においては記憶部3iに記憶されていることから、リスクレベル決定部13から記憶部3iにアクセスして必要なリスクレベルを決定する。なお、リスクレベルを規定したテーブルは、ここでは電子カルテ作成装置3の記憶部3iに記憶されているが、例えば、Do表示部10内にデータベースを備え、このデータベース内に記憶させておいても良い。
The risk
リスクレベル決定部13は、一旦決定した要確認項目の薬剤に関するリスクレベルについて、さらに全体的なリスクレベルの調整が必要であるか否かを確認する(ST6)。ここで「全体的なリスクレベル」とは、リスクレベルを、例えば、電子カルテ作成システムSが構築されている医療機関だけではなく、当該医療機関が設置されている地域を含む広域に設置されている医療機関で共通して設定されているリスクレベルを想定している。また、例えば、当該医療機関を含む医療法人グループにおいて設定されているリスクレベルも考えられる。
The risk
仮にこのような全体的なリスクレベルが指定されている場合には、リスクレベル決定部13は一旦決定されたリスクレベルの調整を行う。例えば、「全体的なリスクレベル」として「半年間全てのリスクレベルを1レベル上げる」との指定がなされている場合には(ST6のYES)、当該指定に従ってリスクレベルの調整が行われる(ST7)。例えば、一旦決定されたリスクレベルが「B」の場合には、調整によって「A」となる。また、既にリスクレベルが「A」の場合には、例えば、リスクレベルを「AA」とする、或いは、「A」のまま据え置くといった対応が可能である。
If such an overall risk level is designated, the risk
一方、全体的なリスクレベルの調整がない場合(ST6のNO)、或いは、全体的なリスクレベルの調整が終了した場合(ST7)には、次に、個別的なリスクレベルの調整の有無を確認する(ST8)。 On the other hand, if there is no overall risk level adjustment (NO in ST6), or if the overall risk level adjustment is completed (ST7), then whether or not individual risk level adjustments are made Confirm (ST8).
この「個別的なリスクレベル」とは、例えば、電子カルテを作成する者である医師の属性に基づくものである。すなわち、電子カルテを作成する医師については、例えば、経験年数や年齢等はそれぞれである。従って、医師が例えば、経験3年未満といった経験が少ない場合や高齢である場合等には、積極的にDo表示の確認をしてもらうべく、リスクレベルを上げることとする。 This “individual risk level” is based on, for example, the attributes of a doctor who is an electronic medical record creator. That is, about the doctor who produces an electronic medical record, for example, years of experience, age, etc. are each. Therefore, for example, when the doctor has little experience such as less than 3 years of experience or is elderly, the risk level is increased so as to positively confirm the Do display.
この「個別的なリスクレベル」によるリスクレベルの調整が必要であるか否かについては、例えば、電子カルテを作成する際に入力される医師を一意的に特定することのできる、例えば医師ID等を基に判断される。当該判断は、例えば判断部12が行い、結果がリスクレベル決定部13に送信される。リスクレベル決定部13では、当該結果に基づいて、個別的なリスクレベルの調整を行い(ST8のYES、ST9)、或いは、調整を行わない(ST8のNO)。
As to whether or not the risk level needs to be adjusted based on this “individual risk level”, for example, a doctor input when creating an electronic medical record can be uniquely specified. Judgment based on. The determination is performed by, for example, the
ここでは、例えば、当該個別的なリスクレベルの調整が必要な場合には、リスクレベルを必ず1つ上げる、といった設定が可能である。また、医師の属性に合わせてリスクレベルの変動を細かく設定して調整することも可能である。さらに場合によってはリスクレベルを下げるといった設定も考えられる。 Here, for example, when the individual risk level needs to be adjusted, it is possible to set the risk level to be increased by one. It is also possible to finely set and adjust the fluctuation of the risk level according to the attributes of the doctor. In some cases, the risk level may be lowered.
以上説明したリスクレベルの決定、リスクレベルの調整については、いずれの処理が先でも、或いは、両者が並行して処理されても良い。 Regarding the determination of the risk level and the adjustment of the risk level described above, either process may be performed first or both may be performed in parallel.
最終的にリスクレベル決定部13において個々の要確認項目についてリスクレベルが決定された場合には、決定部14において確認条件が決定される(図5のST10)。ここで、「確認条件」とは、要確認項目ごとに決定されたリスクレベルに基づいた、電子カルテを作成する者である医師が行う確認の条件のことである。
When the risk level is finally determined for each item to be confirmed in the risk
図7は、実施の形態におけるリスクレベルの確認条件を示すテーブルの一例である。当該テーブルには、「リスクレベル」と紐づけられる「確認条件」が規定されている。例えば、リスクレベルが「A」の場合、確認条件としては、「操作による確認が必要」とされる。すなわち、要確認項目のリスクレベルがAである場合、電子カルテを作成する医師は、Do表示を行うに当たって、当該Do表示の対象となる項目が適切であるか否か、予め定められている確認処理を行う必要がある。また、Do表示部10としては、表示態様決定部15において医師が確認を行うための操作を行うことができる画面表示を生成して表示部3g上に表示させることになる。
FIG. 7 is an example of a table showing risk level confirmation conditions in the embodiment. In the table, “confirmation conditions” associated with “risk level” are defined. For example, when the risk level is “A”, the confirmation condition is “confirmation by operation”. That is, when the risk level of the confirmation required item is A, the doctor who creates the electronic medical record confirms whether or not the item to be displayed in the Do display is appropriate when performing the Do display. It is necessary to perform processing. In addition, as the
一方、リスクレベルが「B」の場合、「表示が3秒以上」との確認条件である。これは、表示部3g上に表示させる確認を行うための表示を「3秒以上」表示させることを意味している。表示する時間については、もちろん任意に設定することが可能である。 On the other hand, when the risk level is “B”, the confirmation condition is “display is 3 seconds or more”. This means that the display for confirming the display on the display unit 3g is displayed for “3 seconds or more”. Of course, the display time can be arbitrarily set.
リスクレベルが「C」の場合、確認条件は「2回に1回の割合で確認すれば良い」となる。ここでの回数は、電子カルテを作成する回数である。従って、「2回に1回の割合での確認」とは、今回新たに電子カルテを作成する場合を例に挙げて説明すると、前々回の電子カルテ作成の際にリスクレベルCの要確認項目について確認されている場合には、前回、今回とDo表示されている内容については、今回改めて当該要確認項目の確認を必要とする。一方で、前回の電子カルテ作成の際に確認が行われている場合には、今回の電子カルテ作成においては確認しなくても足りる、ということである。 When the risk level is “C”, the confirmation condition is “confirmation should be performed once every two times”. The number of times here is the number of times of creating an electronic medical record. Therefore, “confirmation at a rate of once every two times” will be described by taking the case of newly creating an electronic medical record as an example. For the confirmation items of risk level C at the time of the previous electronic medical chart creation, In the case of confirmation, regarding the contents previously displayed as “Do” last time, it is necessary to confirm the necessary confirmation items again this time. On the other hand, if confirmation was made at the time of the previous electronic medical record creation, it is not necessary to confirm the current electronic medical record creation.
従って、この場合には、以前いつ当該要確認項目について確認処理が行われたか否かに関する情報が把握されていなければならない。例えば、当該情報は電子カルテ作成装置3の記憶部3iに記憶されていても良い。
Therefore, in this case, information regarding whether or not the confirmation process has been performed on the necessary confirmation item before must be grasped. For example, the information may be stored in the
なお、確認条件について、上述した条件の他、例えば、一定の期間が経過した場合には必ず確認するといった条件としたり、或いは、複数の確認条件を適宜組み合わせて利用するということも可能である。 In addition to the above-described conditions, for example, the confirmation condition may be a condition that a confirmation is always performed when a certain period of time has elapsed, or a plurality of confirmation conditions may be used in appropriate combination.
例えば、「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」と「Do表示がなされる期間(患者の診察が行われる間隔)」との確認条件が存在する場合を例に挙げて説明する。図8は、実施の形態における確認条件の一例を説明するための説明図である。 For example, a case will be described as an example where there are confirmation conditions of “period in which confirmation is required for each drug” and “period in which Do display is performed (interval at which a patient is examined)”. FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram for explaining an example of the confirmation condition in the embodiment.
図8には数直線が上下2本示されており、上段の数直線αが「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」を示しており、下段の数直線βが「Do表示がなされる期間(患者の診察が行われる間隔)」を示している。「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」として、例えば、2週間ごとの確認が必要とされることを前提とする。そのため、数直線αでは、1目盛りが1週間を表わし、確認が必要とされる2週間ごとに三角形のマークが付されている。一方、患者の診察の間隔、すなわち、Do表示がなされる期間は「5日」であることを前提とする。従って、数直線βでは、Do表示がなされる期間の5日を1目盛りとして表わしている。また、数直線の始まりは、患者に対する診察が行われた時点を示している。こと時には、当然当該患者に対して初めて薬剤の処方がなされることになるため、電子カルテを作成する者である医師も新たに電子カルテに当該薬剤の処方を記入することになる。従って、この後の診察の際にDo表示がなされることになる。 FIG. 8 shows two upper and lower number lines, the upper number line α indicates the “period in which confirmation is required for each drug”, and the lower number line β indicates “Do display”. Period (interval at which the patient is examined) ". As the “period in which confirmation is required for each medicine”, for example, it is assumed that confirmation is required every two weeks. Therefore, in the number line α, one scale represents one week, and a triangular mark is added every two weeks that need to be confirmed. On the other hand, it is assumed that the interval between patient examinations, that is, the period during which Do display is performed is “5 days”. Therefore, in the number line β, 5 days of the period in which Do is displayed is represented as one scale. In addition, the beginning of the number line indicates the time point when the patient is examined. In some cases, the patient is first prescribed a medicine for the patient, and the doctor who creates the electronic medical record newly enters the prescription for the medicine in the electronic medical chart. Accordingly, Do is displayed at the subsequent examination.
上述したように、ここでは、「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」を2週間ごととしている。従って、この期間の間に2度の診察(Do表示が行われる機会)があることになる。ただ、この2度の診察の際には最初に薬剤を処方してから「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」の2週間を経過していないことから、確認の度合いを下げて対応することが可能である。一方、最初の診察から3度目(通算で4度目)の診察が行われる際には、「薬剤ごとに確認が必要とされる期間」の2週間を経過することになるため、このタイミングで電子カルテを作成する者は十分な確認を必要とする。このように複数の確認条件を適宜組み合わせて利用することで、電子カルテを作成する者はより必要かつ適切な確認を行うことができる。 As described above, here, the “period for which confirmation is required for each drug” is set every two weeks. Therefore, there are two examinations (opportunities for Do display) during this period. However, at the time of these two examinations, since the two weeks of “the period for which confirmation is required for each drug” has not elapsed since the prescription of the drug was first prescribed, the degree of confirmation should be reduced. It is possible. On the other hand, when the third examination (the fourth examination in total) is performed from the first examination, two weeks of “a period for which confirmation is required for each drug” will elapse. The person who creates the medical chart needs sufficient confirmation. Thus, by using a combination of a plurality of confirmation conditions as appropriate, a person who creates an electronic medical record can perform more necessary and appropriate confirmation.
また、上述した確認の頻度を、例えば、薬剤の種類や確認期間等によって適宜変更することによって、電子カルテを作成する者の確認対象に対する「確認の濃さ」を適切なものとすることができる。このことは、電子カルテを作成する者にとってみればメリハリの利いた確認を行うことになるため、より一層確実な確認を行うことにつながる。 In addition, by appropriately changing the above-described confirmation frequency according to, for example, the type of medicine, the confirmation period, and the like, the “concentration of confirmation” for the confirmation target of the person who creates the electronic medical record can be made appropriate. . This leads to a more reliable confirmation because it makes a clear confirmation for the person who creates the electronic medical record.
要確認項目について、決定部14において確認条件が決定された場合には、さらに要確認項目が選択されているか否か確認する(ST11)。判断部12による判断の結果、まだリスクレベル、確認条件の決定がなされていない確認項目が残っている場合には(ST11のYES)、再度ステップST4に戻って上述した一連の処理が行われる(図4参照)。
In the case where the confirmation condition is determined by the
一方、全ての項目についてリスクレベル、確認条件の決定がなされた場合には、要確認項目について表示態様決定部15において表示態様が決定されて、医師に対して確認の報知を行う(ST12)。ここでの報知については、表示部3g上に確認のための表示を挙げる方法の他、後述するように確認事項を医師に読み上げてもらう、電子カルテ作成装置3が確認事項を読み上げるといった音声による報知の方法も考えられる。従って、表示態様決定部15においては、音声による報知にも対応する。図5においては、表示部3g上に医師による確認処理を行う為の画面を表示させることを前提としてその流れを説明している。
On the other hand, when the risk level and the confirmation condition are determined for all items, the display mode is determined in the display
図9は、実施の形態における表示画面の一例を示す画面例である。表示態様決定部15では、決定部14において決定された確認条件を基に、当該確認条件に合ったDo表示を行うか否かの確認を行うための表示(報知)の態様を決定する。
FIG. 9 is a screen example showing an example of a display screen in the embodiment. The display
図9に示す当該画面例Xには、上段に患者に関する情報が表示される領域が設けられている。また、左側には診察によって得られた状況を入力する領域が、右側には処方する薬剤等が表示される領域が設けられている。ここでは、過去のカルテを基に薬剤についてDo表示された場合である。Do表示された薬剤が2種類表示されており、そのうち「アルケラン」について、電子カルテの作成者である医師に対してDo表示を行うか否かの確認を行う画面が電子カルテを作成する画面の上に表示されている。ここでは、抗がん剤である「アルケラン」を再度処方するか否か、つまりDo表示でカルテに記載するか否かの確認が行われている。 In the screen example X shown in FIG. 9, an area for displaying information about the patient is provided in the upper stage. In addition, an area for inputting a situation obtained by the examination is provided on the left side, and an area for displaying a prescription drug or the like is provided on the right side. Here, it is a case where Do is displayed about a medicine based on a past medical record. Two types of drugs displayed in Do are displayed, and the screen for confirming whether or not to display Do for the doctor who is the creator of the electronic chart for “Alkeran” is the screen for creating the electronic chart. It is displayed above. Here, it is confirmed whether or not “alkeran”, which is an anticancer agent, is prescribed again, that is, whether or not it is described in the medical chart by Do display.
医師は、当該「アルケラン」をDo表示させるには、確認ボタンをクリックして当該表示を確認、承認する必要がある。 The doctor needs to confirm and approve the display by clicking the confirmation button in order to display the “alkeran” in Do.
医師による確認処理が行われたか否かについては、判断部12において判断される(ST13)。例えば、医師によって図9に示すような画面上の確認ボタンがクリックされたか否かである。医師による確認がなされない場合には(ST13のNO)、例えば、さらに所定の時間待機した上で、さらに確認処理が行われたか否を確認する(ST14のNO)。なお、ここで確認処理が行われたか否かを判断するための待機時間を設けるか否かについては、任意に設定することができる。また待機時間についても同様に任意に設定することができる。 Whether or not the confirmation process by the doctor has been performed is determined by the determination unit 12 (ST13). For example, it is whether or not the confirmation button on the screen as shown in FIG. 9 has been clicked by the doctor. When confirmation by the doctor is not made (NO in ST13), for example, after waiting for a predetermined time, it is confirmed whether further confirmation processing has been performed (NO in ST14). Here, whether or not to provide a standby time for determining whether or not the confirmation process has been performed can be arbitrarily set. Similarly, the standby time can be arbitrarily set.
もし、所定の待機時間内に確認処理が行われなかった場合(ST14のYES)、要確認項目について医師の確認が取れなかったということになるため、Do表示を行う処理自体を中止する(ST15)。このまま確認が取れないままDo表示を行うことは、医師の承認無しに薬剤を処方することにつながるからである。具体的には、確定の処理が無効となる、或いは、例えば、Do表示を行うために選択された範囲を解除する、といった方法によってDo表示ができないように処理される。 If the confirmation process is not performed within the predetermined waiting time (YES in ST14), it means that the doctor has not confirmed the necessary confirmation item, and the process for displaying Do itself is stopped (ST15). ). This is because the Do display without confirmation can lead to prescribing the medicine without the approval of the doctor. Specifically, processing is performed so that Do display cannot be performed by a method in which the confirmation process becomes invalid or, for example, a range selected for Do display is canceled.
医師による確認処理が行われた場合には(ST13のYES)、次の要確認項目があるか否かが確認される(ST16)。判断部12によって次の要確認項目があると判断された場合には(ST16のYES)、ステップST12に戻って続けて医師による確認処理を行う。なお、ここでは要確認項目ごとに医師の確認処理を要求しているが、例えば、要確認項目の数等の条件によっては、要確認項目をまとめて確認処理に回すことも考えられる。
When the confirmation process by the doctor is performed (YES in ST13), it is confirmed whether there is a next confirmation required item (ST16). If the
また、要確認項目の表示の態様については、表示態様決定部15において、表示部3gにおける表示可能な領域の大きさを確認し、その領域を前提として表示態様を決定する。もし表示領域が大きい場合であって、Do表示を行う対象が、要確認項目も含めて全て表示可能であると判断した場合には、当該対象を全て表示させる。一方、表示領域が小さくDo表示の対象を全て表示させることが困難と判断できる場合には、要確認項目のみを抽出して当該要確認項目のみを表示させる。もちろん、表示領域の大きさに合わせて要確認項目のうちリスクレベルの高い項目のみを表示させる、といった態様を採ることも可能である。
As for the display mode of the confirmation required item, the display
また、一度に全てのDo表示を行う対象を表示することができなくとも、自動的に表示画面をスクロールさせて、要確認項目の表示がなされた場合にはそのスクロールを一時的に止めて、医師に対する確認画面を表示させるといった表示方法もある。さらには、要確認項目を別途リスト化して表示させる、要確認項目のみフォントや表示の色彩を変更して表示させる等の、医師の注意を引き確認を促す態様であればいずれの方法を採用しても良い。 In addition, even if all the Do display targets cannot be displayed at once, the display screen is automatically scrolled, and when the confirmation item is displayed, the scrolling is temporarily stopped. There is also a display method of displaying a confirmation screen for the doctor. Furthermore, any method may be adopted as long as it requires a doctor's attention and prompts confirmation, such as displaying a list of items requiring confirmation separately, or displaying only the items requiring confirmation by changing the font or display color. May be.
次の要確認項目がない場合には(ST16のNO)、これで選択された項目中、全ての要確認項目について確認処理が行われたことになるため、確認処理が終了する(ST17)。この状態で、選択された項目の全てがDo表示されることになる(ST18)。 When there is no next required confirmation item (NO in ST16), confirmation processing is completed for all the necessary confirmation items among the selected items, and thus the confirmation processing ends (ST17). In this state, all of the selected items are displayed as Do (ST18).
図10、図11は、実施の形態における表示画面の一例を示す別の画面例である。図10、図11においては、医師による確認処理が携帯情報端末(電子カルテ作成装置3A)の画面上で行われる場合を示している。
10 and 11 are other screen examples showing examples of display screens in the embodiment. 10 and 11 show a case where the confirmation process by the doctor is performed on the screen of the portable information terminal (electronic medical
今後iPad(登録商標)に代表される、携帯情報端末の一層の普及が考えられる。また、医師がこれらの携帯情報端末を利用して様々な場所、場面で利用することも考えられる。従って、医師によるDo表示の確認もよりコンパクトな画面でも確実に行われなければならない。 In the future, further spread of portable information terminals, represented by iPad (registered trademark), can be considered. In addition, doctors may use these portable information terminals in various places and scenes. Therefore, confirmation of the Do display by the doctor must be performed reliably even on a more compact screen.
例えば、図10の画面例Yでは、A及びBで示される領域に過去の処置、処方が記入されており、一方、C及びDで示される領域には、今回の処置、処方が記入されることになる。また、画面例Yの中段以下には、「処置Do」と記載されたタブと「処方Do」と記載されたタブとがそれぞれ2つずつ示されている。このタブを操作することによって、A及びBで示される領域に記載されている内容が、C及びDで示される領域にDo表示可能とされる。 For example, in the screen example Y of FIG. 10, the past treatment and prescription are entered in the areas indicated by A and B, while the current treatment and prescription are entered in the areas indicated by C and D. It will be. Further, below the middle part of the screen example Y, two tabs each having “treatment Do” and two tabs having “prescription Do” are shown. By operating this tab, the contents described in the areas indicated by A and B can be displayed Do in the areas indicated by C and D.
図11には、Do表示を行うに当たっての確認画面が示されている。ここでは、薬剤の処方に関しての確認処理に関する画面である(画面最上段に「処方Do確認」とある)。当該画面例Zでは、2種類の薬剤について表示されており、そのうち「ボナロン」という薬剤についてDo表示するに当たっての確認画面が表示されている。ここでは、対象となる要確認項目を示す領域の色を変更して対象を明確にするとともに、「劇薬が1種類(色変更)含まれています。読み上げ確認をして下さい。」とのメッセージが表示されている。従って、この画面例Zでは、医師に要確認項目を言わせることによって、Do表示を行うか否かの確認を行っている。 FIG. 11 shows a confirmation screen for performing Do display. Here, it is a screen related to the confirmation process regarding the prescription of the medicine (“prescription Do confirmation” is at the top of the screen). In the screen example Z, two types of drugs are displayed, and a confirmation screen for displaying Do for the drug “bonalon” is displayed. Here, we change the color of the area that shows the items that need confirmation, and clarify the subject, and the message “There is one kind of powerful drug (color change) included. Please read it out.” Is displayed. Accordingly, in this screen example Z, whether or not to perform Do display is confirmed by letting a doctor say an item to be confirmed.
医師が読み上げた後、「Do実行」の部分をタップすることで、確認処理がなされたことになる。なお、例えば、医師が読み上げた音声を電子カルテ作成装置3Aが把握し、確認処理を行った上で、「Do実行」を行っても良い。
After the doctor reads out, the confirmation process is performed by tapping the “Do execution” portion. In addition, for example, the electronic medical
以上説明した通り、電子カルテの作成に当たってDo表示を行う際に、単にDo表示を指示するだけではなく、表示される項目ごとにその確認の優先度を決定してその優先度に基づいて画面表示することによって、要確認項目のDo表示の確認を簡易かつ確実に行うことが可能な電子カルテ作成装置及び電子カルテ作成システムを提供することができる。 As described above, when Do display is performed in creating an electronic medical chart, not only Do display is instructed, but the confirmation priority is determined for each displayed item, and the screen display is based on the priority. By doing so, it is possible to provide an electronic medical chart creation apparatus and an electronic medical chart creation system capable of easily and reliably confirming the Do display of items to be confirmed.
これによって、Do表示を行うことに起因する指示、伝達の誤りを減少させることができる。 As a result, it is possible to reduce instruction and transmission errors due to Do display.
本発明の実施形態を説明したが、この実施形態は、例として提示したものであり、発明の範囲を限定することを意図していない。この実施形態は、その他の様々な形態で実施されることが可能であり、発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で、種々の省略、置き換え、変更を行うことができる。 Although an embodiment of the present invention has been described, this embodiment is presented as an example and is not intended to limit the scope of the invention. This embodiment can be implemented in various other forms, and various omissions, replacements, and changes can be made without departing from the spirit of the invention.
例えば、Do表示について、事前に様々な内容を確認するべく仮にDo表示を行う場合と、実際にDo表示されるべく確認の処理を行う場合とでリスクレベル及び当該リスクレベルに対応する確認条件を両者において変更する方法も採用しうる。この場合には電子カルテを作成する者に対して確認のステップが増えることになるため、はじめの段階ではリスクレベルを下げる方法も考えられる。 For example, regarding Do display, the risk level and the confirmation conditions corresponding to the risk level are determined depending on whether the Do display is performed to confirm various contents in advance or the confirmation process is performed so that the Do display is actually performed. It is also possible to adopt a method of changing both. In this case, the confirmation step for the person who creates the electronic medical record increases, so a method of lowering the risk level at the initial stage is also conceivable.
また、これまでの説明では、薬剤の処方を例に挙げて説明した。但し、当該薬剤の処方(オーダ)に限られず、例えば、注射オーダ、治療オーダ、或いは、検査オーダといった、各種の医療オーダに関してDo表示を行う場合にも適用することができる。なお、ここで「注射オーダ」とは、注射を行うという処置を行うオーダ、或いは、注射に入れられる薬剤のオーダを意味する。また、「治療オーダ」とは、診察(電子カルテが作成された)後に行われる治療のオーダである。さらに「検査オーダ」は、患者に対する検査のオーダを示している。 In the description so far, drug prescription has been described as an example. However, the present invention is not limited to the prescription (order) of the drug, and can also be applied to the case where Do display is performed for various medical orders such as an injection order, a treatment order, or a test order. Here, the “injection order” means an order for performing a treatment of performing an injection or an order of a medicine to be put into the injection. The “treatment order” is an order of treatment performed after a medical examination (an electronic medical record is created). Furthermore, the “examination order” indicates the order of the examination for the patient.
この実施形態やその変形は、発明の範囲や要旨に含まれると共に、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明とその均等の範囲に含まれる。 This embodiment and its modifications are included in the scope and gist of the invention, and are included in the invention described in the claims and the equivalents thereof.
1 サーバ
2 医用画像診断装置
3 電子カルテ作成装置
10 Do表示部
11 受信部
12 判断部
13 リスクレベル決定部
14 決定部
15 表示態様決定部
16 送信部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (16)
前記記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、
表示された前記記入項目の内容について前記繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、
前記記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、
前記リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、
前記確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を前記繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、前記リスクレベル決定部によって前記要確認項目ごとに決定された前記リスクレベルに応じた前記表示態様の表示を前記表示部に対して指示する表示態様決定部と、
を備えることを特徴とする電子カルテ作成装置。 A storage unit for storing the contents of entries to be repeatedly prescribed or ordered;
A display unit for displaying the contents of the entry;
An input unit for inputting whether to repeat the prescription or order for the content of the displayed entry;
A risk level determination unit that determines a risk level of each of the entries;
A determination unit for determining a confirmation condition based on the risk level determined in the risk level determination unit;
Depending on the check condition, and determines a screen display of the display mode for the main confirmation item to check whether to be the repeating formulation or order, it is determined for each of the principal confirmation item by the risk level determination unit A display mode determination unit that instructs the display unit to display the display mode according to the risk level ;
An electronic medical record creation apparatus comprising:
前記記入項目の内容を表示する表示部と、
表示された前記記入項目の内容について前記繰り返し処方またはオーダを行うか否かの入力を行うための入力部と、
前記記入項目それぞれのリスクレベルを決定するリスクレベル決定部と、
前記リスクレベル決定部において決定されたリスクレベルを基に確認条件を決定する決定部と、
前記確認条件に応じて、要確認項目を前記繰り返し処方またはオーダすることの是非を確認するための画面表示の表示態様を決定するとともに、要確認項目ごとに前記表示部に対して決定された前記表示態様の表示を指示する表示態様決定部と、を備え、
前記決定部は、前記リスクレベルに応じた前記表示態様の表示頻度を前記確認条件の1つとして決定することを特徴とする電子カルテ作成装置。 A storage unit for storing the contents of entries of medical orders that are subject to repeated prescriptions or orders;
A display unit for displaying the contents of the entry;
An input unit for inputting whether to repeat the prescription or order for the content of the displayed entry;
A risk level determination unit that determines a risk level of each of the entries;
A determination unit for determining a confirmation condition based on the risk level determined in the risk level determination unit;
Depending on the check conditions, a main check item and determines a screen display of the display mode for confirming whether to be the repeating formulation or order, the determined for the display unit for each main check item A display mode determination unit for instructing display of the display mode,
The determination unit determines the display frequency of the display mode according to the risk level as one of the confirmation conditions.
前記電子カルテの作成に当たって必要な医用画像を取得する医用画像診断装置と、
請求項1ないし請求項11のいずれかに記載の電子カルテ作成装置と、
を備えることを特徴とする電子カルテ作成システム。 A server for storing the electronic medical records created so far,
A medical image diagnostic apparatus for obtaining a medical image necessary for creating the electronic medical record;
An electronic medical record creation apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 11 ,
An electronic medical record creation system comprising:
前記電子カルテの作成に当たって必要な医用画像を取得する医用画像診断装置と、
請求項12ないし請求項14のいずれかに記載の電子カルテ作成装置と、
を備えることを特徴とする電子カルテ作成システム。 A server for storing the electronic medical records created so far,
A medical image diagnostic apparatus for obtaining a medical image necessary for creating the electronic medical record;
An electronic medical record creation apparatus according to any one of claims 12 to 14 ,
An electronic medical record creation system comprising:
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/071874 WO2014027661A1 (en) | 2012-08-13 | 2013-08-13 | Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system |
| JP2013168018A JP6257953B2 (en) | 2012-08-13 | 2013-08-13 | Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012179304 | 2012-08-13 | ||
| JP2012179304 | 2012-08-13 | ||
| JP2013168018A JP6257953B2 (en) | 2012-08-13 | 2013-08-13 | Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014056570A JP2014056570A (en) | 2014-03-27 |
| JP6257953B2 true JP6257953B2 (en) | 2018-01-10 |
Family
ID=50613794
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013168018A Active JP6257953B2 (en) | 2012-08-13 | 2013-08-13 | Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6257953B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2014027661A1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2201311A1 (en) * | 1994-10-28 | 1996-05-09 | Christian Mayaud | Prescription management system |
| JP2000200316A (en) * | 1998-12-29 | 2000-07-18 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Electronic clinical record device |
| JP2002334153A (en) * | 2001-05-08 | 2002-11-22 | Csi Co Ltd | Electronic chart system |
| JP2003022412A (en) * | 2001-07-10 | 2003-01-24 | Hitachi Systems & Services Ltd | Data input device and its method |
| JP4866576B2 (en) * | 2005-07-11 | 2012-02-01 | インフォコム株式会社 | Medical support system |
| JP2007037823A (en) * | 2005-08-04 | 2007-02-15 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Medicine dose dispensing support system |
| US20100161355A1 (en) * | 2008-11-20 | 2010-06-24 | Peter Stangel | Single field entry electronic clinical chart note entry system |
| JP5245954B2 (en) * | 2009-03-18 | 2013-07-24 | 富士通株式会社 | Prescription order issuing program, prescription order issuing device and method |
| US20120109686A1 (en) * | 2010-11-01 | 2012-05-03 | Oxbow Intellectual Property, LLC | Electronic medical record system and method |
-
2013
- 2013-08-13 WO PCT/JP2013/071874 patent/WO2014027661A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-08-13 JP JP2013168018A patent/JP6257953B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2014027661A1 (en) | 2014-02-20 |
| JP2014056570A (en) | 2014-03-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6280056B2 (en) | Medical support device, operating method and program for medical support device, and medical support system | |
| EP2704045A2 (en) | Apparatus and method for providing medical support | |
| JP5203627B2 (en) | Inspection reservation system and program | |
| US11216171B2 (en) | Medical image management apparatus and recording medium | |
| US20160188841A1 (en) | Medical support apparatus, system and method for medical service | |
| JP5302684B2 (en) | A system for rule-based context management | |
| JP2023073508A (en) | Medical examination support program, information processing system, information processing method, and information processor | |
| JP2013041588A (en) | Medical presentation creator | |
| JP6257953B2 (en) | Electronic medical record creation device and electronic medical record creation system | |
| CA3083090A1 (en) | Medical examination support apparatus, and operation method and operation program thereof | |
| Kuzmak et al. | Minimizing Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) modality worklist patient/study selection errors | |
| JP2008229244A (en) | Medical imaging system | |
| JP7013841B2 (en) | Interpretation report analysis device and program | |
| JP5546780B2 (en) | Medical image interpretation request device and medical image interpretation request system | |
| US20220180989A1 (en) | Medical care support device | |
| US11599319B2 (en) | Display apparatus, display system, and storage medium | |
| JP5825063B2 (en) | Medical information processing device | |
| US20230197247A1 (en) | Radiographic interpretation management apparatus, storage medium, and radiographic interpretation management method | |
| US20230245760A1 (en) | Display apparatus, image management server, and recording medium | |
| JP5662394B2 (en) | Medical support device and medical support method | |
| US20240071580A1 (en) | Medical information processing apparatus, medical information processing system, medical information processing method, and recording medium | |
| US20210007678A1 (en) | Selection support system and storage medium | |
| US20230290469A1 (en) | Recording medium, information processing apparatus, healthcare worker terminal, information processing system and healthcare worker system | |
| JP2012174015A (en) | Medical information system and radiographic report system | |
| JP5760551B2 (en) | Medical image display apparatus and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20150703 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20160527 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160614 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170829 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20171024 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20171107 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20171206 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6257953 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |