JP6155179B2 - Rectifier, alternator and power converter - Google Patents
Rectifier, alternator and power converter Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6155179B2 JP6155179B2 JP2013252875A JP2013252875A JP6155179B2 JP 6155179 B2 JP6155179 B2 JP 6155179B2 JP 2013252875 A JP2013252875 A JP 2013252875A JP 2013252875 A JP2013252875 A JP 2013252875A JP 6155179 B2 JP6155179 B2 JP 6155179B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- voltage
- mosfet
- rectifier
- terminal
- current
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Rectifiers (AREA)
- Power Conversion In General (AREA)
Description
本発明は、自律型の同期整流MOSFET(Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)の整流装置と、この整流装置を用いたオルタネータおよび電力変換装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a rectifier of an autonomous synchronous rectifier MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor), an alternator using the rectifier, and a power converter.
自動車にて発電を行うオルタネータには、整流素子としてこれまでダイオードが用いられてきた。ダイオードは安価ではあるが、順方向電圧降下があり、損失が大きい。これに対し、近年、ダイオードに代わり、順方向電圧降下がなく0Vから順方向電流が立ち上がるMOSFETがオルタネータ用の整流素子として使われ始めている。 A diode has been used as a rectifying element in an alternator that generates electricity in an automobile. Although the diode is inexpensive, it has a forward voltage drop and a large loss. On the other hand, in recent years, MOSFETs in which forward current rises from 0 V without forward voltage drop instead of diodes have begun to be used as rectifiers for alternators.
電源装置は、交流電力の周波数が一定である。よって、電源装置の整流素子としてMOSFETを用いる場合、クロックに同期させてMOSFETのオン・オフ制御を行うこともできる。しかし、オルタネータは、コイルで発電される交流電力の周波数が一定ではない。よって、オルタネータの整流素子としてMOSFETを用いる場合、電源装置等で用いる場合のように単にクロックに同期させるのではなく、その時々の周波数に同期させてMOSFETのオン・オフ制御を行う必要がある。
そこで、ホール素子を用いてモータの位置を検知してMOSFETの制御を行う方式が考えられるが、ホール素子を要するため、現状の整流素子をそのまま置き換えることができず、オルタネータを大きく変更しなければならない。
In the power supply device, the frequency of the AC power is constant. Therefore, when a MOSFET is used as the rectifying element of the power supply device, the MOSFET on / off control can be performed in synchronization with the clock. However, in the alternator, the frequency of the AC power generated by the coil is not constant. Therefore, when a MOSFET is used as the rectifier element of the alternator, it is necessary to perform on / off control of the MOSFET in synchronization with the frequency at that time, not simply in synchronization with the clock as in the case of use in a power supply device or the like.
Therefore, a method of controlling the MOSFET by detecting the position of the motor using a Hall element can be considered, but since the Hall element is required, the current rectifier cannot be replaced as it is, and the alternator must be changed greatly. Don't be.
特許文献1の請求項1には、「カソード端子(K1)、アノード端子(A1)および前記カソード端子と前記アノード端子の間に設けられている電子回路を備え、該電子回路には、逆ダイオード(Inversdiode)(D6)が組み込まれたMOSトランジスタ(T1)、コンデンサ(C1)および差動増幅器(T2,T3,R1,R2,R3)が含まれていることを特徴とする、整流器回路。」と記載されている。特許文献1の段落0018には、「整流器回路のカソード端子K1の電位が整流器回路のアノード端子A1の電位より正の極性にあり、その電位差がツェナダイオードD4によってセットされている値を超過すると、トランジスタT4,T5から成る電流増幅段の入力側の電位が上昇させられる。これによって、MOSトランジスタT1のゲートソース間の電圧も上昇し、MOSトランジスタT1のドレインとソースの間を電流が流れるようになる。」と記載されている。ここでは、特許文献1に記載された方式を自律型と呼ぶことにする。
特許文献1に記載の自律型の同期整流MOSFETには、安価に整流素子(整流装置)を提供できるメリットがある。しかし、MOSFETがオンとオフとを繰り返すチャタリングが問題となる。
The autonomous synchronous rectification MOSFET described in
チャタリングは、具体的には、次のように引き起こされる。整流動作の開始時にMOSFETをオンに制御するとき、まず、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオードに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなる。オン電圧がMOSFETをオンする判定基準に達すると、MOSFETがオンされて同期整流が開始する。同期整流により、低抵抗のMOSFETに電流が流れてオン電圧が下がる。オン電圧が下がりすぎてMOSFETをオフする判定基準に達すると、MOSFETがオフされて同期整流が終了する。同期整流の終了により、内蔵ダイオードに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなる。オン電圧は、MOSFETをオンする判定基準に達し、MOSFETがオンされて同期整流が開始する。このように、MOSFETのオンとオフの判定を繰り返してしまう。整流動作の終了時にMOSFETをオフに制御するときも同様である。
チャタリングにより、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオードに電流が流れて電力の効率が低下する。チャタリングによりコンパレータやゲートドライバがオンとオフとを繰り返すので、自律型の整流装置の電源であるコンデンサは、大容量のものが必要となる。更に、チャタリングによるノイズが電子部品の動作に悪影響を及ぼす虞がある。
Specifically, chattering is caused as follows. When the MOSFET is turned on at the start of the rectifying operation, first, a current flows through the high-resistance built-in diode, and the on-voltage increases. When the on-voltage reaches a determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET, the MOSFET is turned on and synchronous rectification starts. As a result of synchronous rectification, a current flows through the low-resistance MOSFET and the on-voltage decreases. When the criterion for turning off the MOSFET is reached because the on-voltage is too low, the MOSFET is turned off and the synchronous rectification ends. Upon completion of the synchronous rectification, a current flows through the built-in diode and the on-voltage increases. The on-voltage reaches a criterion for turning on the MOSFET, the MOSFET is turned on, and synchronous rectification starts. In this way, the ON / OFF determination of the MOSFET is repeated. The same applies when the MOSFET is controlled to be turned off at the end of the rectification operation.
Chattering causes a current to flow through the high-resistance built-in diode, reducing the power efficiency. Since the comparator and the gate driver are repeatedly turned on and off by chattering, a capacitor that is a power source of the autonomous rectifier is required to have a large capacity. Further, noise due to chattering may adversely affect the operation of the electronic component.
チャタリングを防止する方法として、チャタリングを起こす期間において、ゲートドライバの出力を固定することが考えられる。しかし、これをオルタネータの整流素子に適用しようとすると、オルタネータの幅広い周期の交流電力に対応しなければならないため、ゲートドライバの出力を固定する期間の設定が極めて困難である。
他のチャタリングを防止する方法として、チャタリングのノイズを除去する方法があるが、ノイズ除去の回路を加えなければならず、回路規模が大きくなってしまう。
As a method for preventing chattering, it is conceivable to fix the output of the gate driver during a period in which chattering occurs. However, if this is applied to the rectifier of the alternator, it is necessary to cope with a wide range of AC power of the alternator, and therefore it is extremely difficult to set a period for fixing the output of the gate driver.
As another method for preventing chattering, there is a method for removing chattering noise. However, a circuit for removing noise has to be added, which increases the circuit scale.
そこで、本発明は、簡易な回路構成でチャタリングを容易に防止可能な整流装置と、この整流装置を用いたオルタネータおよび電力変換装置を提供することを課題とする。 Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide a rectifier capable of easily preventing chattering with a simple circuit configuration, and an alternator and a power converter using the rectifier.
前記した課題を解決する第1の発明は、直流端子がエネルギ蓄積部に、交流端子が交流電源に接続されるブリッジ型の整流回路のハイサイドおよびロウサイドにそれぞれ接続される整流装置である。整流装置は、ドレインが正極側主端子に接続され、ソースが負極側主端子に接続されるMOSFETと、前記MOSFETをオンオフ制御するゲートドライバと、前記MOSFETの前記正極側主端子から前記負極側主端子への主端子間電圧と基準電圧とを比較した比較信号を生成して前記ゲートドライバに出力することにより、前記主端子間電圧が前記基準電圧以下ならば前記MOSFETをオンさせる比較部と、を備える。前記基準電圧は0Vより大きく、前記正極側主端子から前記負極側主端子への前記主端子間電圧が負である場合、前記MOSFETは順方向の電流を流し、前記主端子間電圧が正であり、かつ、前記基準電圧以下である場合、前記MOSFETは逆方向の電流を流す。 A first invention for solving the above-described problem is a rectifier connected to a high side and a low side of a bridge-type rectifier circuit in which a DC terminal is connected to an energy storage unit and an AC terminal is connected to an AC power supply. Rectifier has a drain connected to the positive electrode side main terminal, a MOSFET having a source connected to the negative electrode side main terminal, the negative electrode side of said MOSFET and a gate driver for on-off control, from the positive electrode side main terminal of the pre-Symbol MOSFET A comparator that turns on the MOSFET if the voltage between the main terminals is equal to or lower than the reference voltage by generating a comparison signal that compares the voltage between the main terminals to the main terminal and a reference voltage and outputting the comparison signal to the gate driver; . When the reference voltage is greater than 0V and the main-terminal voltage from the positive-side main terminal to the negative-side main terminal is negative, the MOSFET passes a forward current and the main-terminal voltage is positive. If the voltage is lower than the reference voltage, the MOSFET passes a current in the reverse direction.
第2の発明は、オルタネータであり、直流端子が前記エネルギ蓄積部に、交流端子が交流電源に接続されるブリッジ型の前記整流回路と、前記整流回路のハイサイドおよびロウサイドにそれぞれ接続される前記整流装置とを備える。エネルギ蓄積部はバッテリである。 The second invention is an alternator, wherein a DC terminal is connected to the energy storage unit, an AC terminal is connected to an AC power supply, the bridge type rectifier circuit, and the rectifier circuit connected to the high side and the low side, respectively. A rectifier. The energy storage unit is a battery.
第3の発明は電力変換装置であり、直流端子が前記エネルギ蓄積部に、交流端子が交流電源に接続されるブリッジ型の前記整流回路と、前記整流回路のハイサイドおよびロウサイドにそれぞれ接続される前記整流装置とを備える。
その他の手段については、発明を実施するための形態のなかで説明する。
A third invention is a power converter, wherein a direct current terminal is connected to the energy storage unit, an alternating current terminal is connected to an alternating current power supply, the bridge type rectifier circuit, and a high side and a low side of the rectifier circuit, respectively. The rectifier is provided.
Other means will be described in the embodiment for carrying out the invention.
本発明によれば、簡易な回路構成でチャタリングを容易に防止可能な整流装置と、この整流装置を用いたオルタネータおよび電力変換装置を提供することが可能となる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, it becomes possible to provide the rectifier which can prevent chattering easily with a simple circuit structure, the alternator using this rectifier, and a power converter device.
以下、比較例と本発明の実施の形態とを各図に基づいて詳細に説明する。なお、実施形態を説明するための各図において同一機能を有するものは同一の符号を付し、その繰り返しの説明は適宜省略する。また、以下の実施形態の説明では、特に必要なとき以外は同一又は同様な部分の説明は、適宜省略する。 Hereinafter, a comparative example and an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. Note that components having the same function are denoted by the same reference symbols in the drawings for describing the embodiments, and repetitive description thereof will be omitted as appropriate. In the following description of the embodiments, the description of the same or similar parts is omitted as appropriate unless particularly necessary.
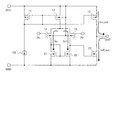
図1は、自律型の整流装置を用いたオルタネータの概略構成を示す回路図である。このオルタネータの構成は、比較例および各実施形態において共通する。
図1に示すように、自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置を用いたオルタネータ140は、回転子コイル109および固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuを含んで構成される発電部と、整流回路130とを備えている。
発電部は、回転子コイル109と、Δ結線された3本の固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuとを含んで構成される。固定子コイル110wu,110uvが結線されたノードからU相131uの中点配線が引き出される。固定子コイル110uv,110vwが結線されたノードからV相131vの中点配線が引き出される。固定子コイル110vw,110wuが結線されたノードからW相131wの中点配線が引き出される。なお、各固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの結線は、Δ結線の代わりにY結線としてもよく、限定されない。
FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a schematic configuration of an alternator using an autonomous rectifier. The configuration of this alternator is common to the comparative example and each embodiment.
As shown in FIG. 1, an
The power generation unit includes a
整流回路130は、U相131uとV相131vとW相131wとを含んで構成され、ノードNu,Nv,Nw間の三相交流を直流に整流してノードNp,Nn間に流すものである。U相131uの中点配線のノードNuは、ハイサイド側に整流装置132uhが接続され、ロウサイド側に整流装置132ulが接続される。V相131vの中点配線のノードNvは、ハイサイド側に整流装置132vhが接続され、ロウサイド側に整流装置132vlが接続される。W相131wの中点配線のノードNwは、ハイサイド側に整流装置132whが接続され、ロウサイド側に整流装置132wlが接続される。ハイサイド側の整流装置132uh,132vh,132whは、直流の正極側のノードNpを介してバッテリ111(エネルギ蓄積部)の正極側端子が接続される。ロウサイド側の整流装置132ul,132vl,132wlは、直流の負極側のノードNnを介して、バッテリ111の負極側端子が接続される。
バッテリ111(エネルギ蓄積部)は、例えば車載用バッテリであり、その動作範囲は例えば10.8Vから14V程度である。
The
The battery 111 (energy storage unit) is, for example, a vehicle-mounted battery, and its operating range is, for example, about 10.8V to 14V.
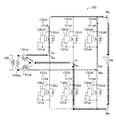
U相131uのハイサイドの整流装置132uhは、MOSFET101uhと内蔵ダイオード102uhと制御IC108uhとコンデンサ107uhとを含んで構成される。U相131uのロウサイドの整流装置132ulは、同様にMOSFET101ulと内蔵ダイオード102ulと制御IC108ulとコンデンサ107ulとを含んで構成される。
V相131vのハイサイドの整流装置132vhは、MOSFET101vhと内蔵ダイオード102vhと制御IC108vhとコンデンサ107vhとを含んで構成される。V相131vのロウサイドの整流装置132vlは、同様にMOSFET101vlと内蔵ダイオード102vlと制御IC108vlとコンデンサ107vlとを含んで構成される。
The high-side rectifier 132uh of the
The high-side rectifier 132vh of the
W相131wのハイサイドの整流装置132whは、MOSFET101whと内蔵ダイオード102whと制御IC108whとコンデンサ107whとを含んで構成される。W相131wのロウサイドの整流装置132wlは、同様にMOSFET101wlと内蔵ダイオード102wlと制御IC108wlとコンデンサ107wlとを含んで構成される。
なお、各相のロウサイドの整流装置132ul,132vl,132wlは、外部から制御IC108ul,108vl,108wlへの電源供給が容易なので、コンデンサ107ul,107vl,107wlを用いず、外部からの電源供給としてもよい。
以下、各整流装置132uh〜132wlを特に区別しないときには、比較例では整流装置132zと記載し、各実施形態では整流装置132,132a〜132cと記載する。
各制御IC108uh〜108wlを特に区別しないときには、比較例では制御IC108zと記載し、各実施形態では制御IC108,108a〜108cと記載する。
各MOSFET101uh〜101wlを特に区別しないときには、単にMOSFET101と記載する。各内蔵ダイオード102uh〜102wlを特に区別しないときには、単に内蔵ダイオード102と記載する。各コンデンサ107uh〜107wlを特に区別しないときには、単にコンデンサ107と記載する。
The high-side rectifier 132wh of the
The low-side rectifiers 132ul, 132vl, and 132wl of each phase can be supplied from the outside without using the capacitors 107ul, 107vl, and 107wl because the power supply to the control ICs 108ul, 108vl, and 108wl is easy from the outside. .
Hereinafter, when the rectifiers 132uh to 132wl are not particularly distinguished, they are described as a
When the control ICs 108uh to 108wl are not particularly distinguished, the control ICs 108uh to 108wl are described as the
When the MOSFETs 101uh to 101wl are not particularly distinguished, they are simply referred to as
図13は、比較例の自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置を示す回路図である。
図13に示すように、比較例の自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132zは、MOSFET101と、MOSFET101のチップに内蔵される内蔵ダイオード102と、コンパレータ103zと、負基準電圧発生部125と、ゲートドライバ105と、ダイオード106と、コンデンサ107とを含んで構成される。整流装置132zは、負極側主端子TLから正極側主端子THに電流を流すものである。
FIG. 13 is a circuit diagram showing a rectifier of an autonomous type synchronous rectification MOSFET of a comparative example.
As shown in FIG. 13, the autonomous synchronous
MOSFET101は、オルタネータ140の発電部が発電する大電流を流すため、パワーMOSFETが使用される。MOSFET101は、ドレインが正極側主端子THに接続され、ソースが負極側主端子TLに接続される。これによりMOSFET101の内蔵ダイオード102は、アノードが負極側主端子TLに接続され、カソードが正極側主端子THに接続される。
コンパレータ103zは、非反転入力端子IN+がMOSFET101のドレインに接続され、反転入力端子IN−が負基準電圧発生部125を介してMOSFET101のソースに接続される。コンパレータ103zの出力端子は、ゲートドライバ105の入力端子に接続される。コンパレータ103zの出力端子からは、比較信号Vcompが出力される。コンパレータ103zは、一般的な機能を有するコンパレータでよく、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−との間の電圧ΔVから、比較信号Vcompを生成するものである。これによりコンパレータ103zは、負極側主端子TLの電圧V1に負基準電圧発生部125の電圧を加算した電圧と、正極側主端子THの電圧V2との比較結果を出力する。コンパレータ103zは、性能的には高精度ものが望ましい。
The
The
ゲートドライバ105の出力端子は、MOSFET101のゲート端子に接続される。ゲートドライバ105は、ゲート電圧Vgsを出力する。
ダイオード106は、正極側主端子THからコンデンサ107の正極側端子への向きに接続される。コンデンサ107の正極側端子は、コンパレータ103zとゲートドライバ105の電源端子に接続されて、直流電力を供給する。ゲートドライバ105は、1段または2段のCMOS(Complementary MOS)の簡単な回路構成であり、一般的なゲートドライバである。
The output terminal of the
The
負基準電圧発生部125は、MOSFET101のソースに対し、コンパレータ103zの反転入力端子IN−に負の基準電圧を与える。しかし、これに限られず、整流装置132zが負基準電圧発生部125を備えず、コンパレータ103zの反転入力端子IN−は、MOSFET101のソースに直接接続されてもよい。
The negative
制御IC108zは、コンパレータ103zと、負基準電圧発生部125と、ゲートドライバ105と、ダイオード106とを含んで構成される。
The
コンデンサ107は、制御IC108zが駆動するための電源を供給するものである。コンデンサ107を電源に用いることで、整流装置132zの端子数は2個となり、オルタネータ140に用いられる従来の整流ダイオードの端子と互換性を持たせることができる。これにより、従来の整流ダイオードを整流装置132zに置き換えて、オルタネータ140の性能を向上させることができる。
The
図1に示すオルタネータ140の各相のハイサイド側は、整流装置132zの正極側主端子THが、ノードNpを介してバッテリ111の正極側端子に接続される。整流装置132zの負極側主端子TLが、各相の中点配線であるノードNu,Nv,Nwに接続される。
各相のロウサイド側は、整流装置132zの正極側主端子THが、各相の中点配線であるノードNu,Nv,Nwに接続される。整流装置132zの負極側主端子TLが、ノードNnを介してバッテリ111の負極側端子に接続される。
On the high side of each phase of the
On the low side of each phase, the positive side main terminal TH of the
図14(a)〜(g)は、比較例の自律型の整流装置132zを用いたオルタネータ140のU相131uの波形を示すグラフである。図14(a)〜(g)の横軸は、共通する時間tを示している。
図14(a)は、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuの波形を示すグラフである。
図14(b)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのコンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompHの波形を示すグラフである。
図14(c)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsHの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsHは、MOSFET101uhのソース電圧を基準としている。
図14(d)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhに流れるドレイン電流IdHを示すグラフである。
図14(e)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのコンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompLの波形を示すグラフである。
図14(f)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsLの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsLは、MOSFET101ulのソース電圧を基準としている。
図14(g)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulに流れるドレイン電流IdLを示すグラフである。
V相131vの電圧や電流は、U相131uと位相が120°シフトした同一波形である。W相131wの電圧や電流は、U相131uと位相が240°シフトした同一波形である。
FIGS. 14A to 14G are graphs showing waveforms of the
FIG. 14A is a graph showing the waveform of the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the
FIG. 14B is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompH of the
FIG. 14C is a graph showing a waveform of the gate voltage VgsH of the
FIG. 14D is a graph showing the drain current IdH flowing through the rectifier 132uh on the high side.
FIG. 14E is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompL of the
FIG. 14F is a graph showing the waveform of the gate voltage VgsL of the
FIG. 14G is a graph showing the drain current IdL flowing through the low-side rectifier 132ul.
The voltage and current of the
図1に示したオルタネータ140を適宜参照しつつ、各部の電圧と電流による動作を説明する。
オルタネータ140において、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの中を回転子コイル109が回転することで発電が行われる。このとき、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuには、交流電力が発生する。
図14(a)に示すように、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの交流電力により、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuは、周期的に上下する。
比較例の整流装置132zは、貫通電流を防ぐために、整流の方向とは逆の方向に電流を流さないように動作している。
電圧Vuが0Vよりも小さくなると、同期整流の開始時にMOSFET101ulをオンに制御する前に、先ず、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなる。
時刻t10において、電圧Vuが負の基準電圧よりも低くなり、MOSFET101ulをオンする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオンして、同期整流が開始する。すると、低抵抗のMOSFET101ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が下がる。オン電圧が下がりすぎると、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達する。MOSFET101ulはオフし、同期整流が終了する。これにより、内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなり、MOSFET101ulがオンして、再び同期整流が開始する。このように、MOSFET101ulは、電圧Vuが充分に小さくなるまで、オンとオフとを繰り返す。
時刻t11において、電圧Vuが負の基準電圧よりも高くなると、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオフして、同期整流が終了する。すると、内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなり、MOSFET101ulがオンして、再び同期整流が開始する。このように、MOSFET101ulは、電圧Vuが充分に大きくなるまで、オンとオフとを繰り返す。
時刻t12において、電圧Vuが、電圧VBから負の基準電圧を減算した閾値よりも高くなったときも、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uuのMOSFET101uhが、同様にオンとオフとを繰り返す。
時刻t13において、電圧Vuが、電圧VBから負の基準電圧を減算した閾値よりも低くなったときも、ハイサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulが、同様にオンとオフとを繰り返す。
With reference to the
In the
As shown in FIG. 14A, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the U-phase 131u periodically rises and falls by the AC power of the stator coils 110uv, 110vw, and 110wu.
The rectifying
When the voltage Vu becomes smaller than 0 V, before the MOSFET 101ul is controlled to be turned on at the start of synchronous rectification, first, a current flows through the high-resistance built-in diode 102ul, and the on-voltage increases.
At time t10, when the voltage Vu becomes lower than the negative reference voltage and reaches the determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101ul of the low-side rectifier 132ul is turned on and synchronous rectification starts. Then, a current flows through the low-resistance MOSFET 101ul, and the on-voltage decreases. If the on-voltage is too low, the criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul is reached. The MOSFET 101ul is turned off and the synchronous rectification ends. As a result, a current flows through the built-in diode 102ul to increase the on-voltage, the MOSFET 101ul is turned on, and synchronous rectification starts again. As described above, the MOSFET 101ul is repeatedly turned on and off until the voltage Vu becomes sufficiently small.
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than the negative reference voltage at time t11, when the determination criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul is reached, the MOSFET 101ul of the rectifier 132ul on the low side is turned off, and the synchronous rectification is finished. Then, a current flows through the built-in diode 102ul, the on-voltage increases, the MOSFET 101ul turns on, and synchronous rectification starts again. As described above, the MOSFET 101ul is repeatedly turned on and off until the voltage Vu becomes sufficiently large.
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than the threshold value obtained by subtracting the negative reference voltage from the voltage VB at time t12, the MOSFET 101uh of the rectifier 132uu on the high side repeats ON and OFF similarly.
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than the threshold value obtained by subtracting the negative reference voltage from the voltage VB at time t13, the MOSFET 101ul of the rectifier 132ul on the high side repeats ON and OFF in the same manner.
図14(b)に示すように、比較信号VcompHは、時刻t12以前はHレベルであり、時刻t12以降暫くはLレベルとHレベルとを繰り返したのち、Lレベルで安定する。比較信号VcompHは、時刻t13以降暫くは、LレベルとHレベルとを繰り返したのち、Hレベルで安定する。
図14(c)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t12以前はLレベルであり、時刻t12以降暫くはHレベルとLレベルとを繰り返したのち、Hレベルで安定する。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t13以降暫くは、HレベルとLレベルとを繰り返したのち、Lレベルで安定する。ゲート電圧VgsHがHレベルのとき、MOSFET101uhは同期整流を行う。
As shown in FIG. 14B, the comparison signal VcompH is at the H level before the time t12, and after the time t12, the L level and the H level are repeated for a while and then becomes stable at the L level. The comparison signal VcompH is stabilized at the H level after repeating the L level and the H level for a while after the time t13.
As shown in FIG. 14C, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before the time t12, and after the time t12, the H level and the L level are repeated for a while and then becomes stable at the H level. The gate voltage VgsH is stabilized at the L level after repeating the H level and the L level for a while after the time t13. When the gate voltage VgsH is at the H level, the MOSFET 101uh performs synchronous rectification.
図14(d)に示すように、ドレイン電流IdHは、図14(a)に示す電圧Vuが、バッテリ111の電圧VBを超えたときに流れる。
As shown in FIG. 14 (d), the drain current IdH flows when the voltage Vu shown in FIG. 14 (a) exceeds the voltage VB of the
図14(e)に示すように、比較信号VcompLは、時刻t10以前はHレベルであり、時刻t10以降暫くはLレベルとHレベルとを繰り返したのち、Lレベルで安定する。比較信号VcompLは、時刻t11以降暫くは、LレベルとHレベルとを繰り返したのち、Hレベルで安定する。
図14(f)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t10以前はLレベルであり、時刻t10以降暫くは、HレベルとLレベルとを繰り返したのち、Hレベルで安定する。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t11以降暫くは、LレベルとHレベルとを繰り返したのち、Lレベルで安定する。ゲート電圧VgsHがHレベルのとき、MOSFET101uhは同期整流を行う。
図14(g)に示すように、ドレイン電流IdLは、図14(a)に示す電圧Vuが、0Vよりも小さくなったときに流れる。
As shown in FIG. 14E, the comparison signal VcompL is at the H level before the time t10, and after the time t10, the L level and the H level are repeated for a while and then becomes stable at the L level. The comparison signal VcompL is stabilized at the H level after repeating the L level and the H level for a while after the time t11.
As shown in FIG. 14F, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before the time t10, and after the time t10 for a while, the H voltage and the L level are repeated and then stabilized at the H level. The gate voltage VgsH is stabilized at the L level after repeating the L level and the H level for a while after the time t11. When the gate voltage VgsH is at the H level, the MOSFET 101uh performs synchronous rectification.
As shown in FIG. 14 (g), the drain current IdL flows when the voltage Vu shown in FIG. 14 (a) becomes smaller than 0V.
図15(a)〜(g)は、小電流時におけるオルタネータのU相波形を示すグラフである。図15(a)〜(g)の横軸は、共通する時間tを示している。
図15(a)は、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuの波形を示すグラフである。
図15(b)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのコンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompHの波形を示すグラフである。
図15(c)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsHの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsHは、MOSFET101uhのソース電圧を基準としている。
図15(d)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhに流れるドレイン電流IdHを示すグラフである。
FIGS. 15A to 15G are graphs showing the U-phase waveform of the alternator when the current is small. The horizontal axis in FIGS. 15A to 15G shows a common time t.
FIG. 15A is a graph showing a waveform of the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the
FIG. 15B is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompH of the
FIG. 15C is a graph showing a waveform of the gate voltage VgsH of the
FIG. 15D is a graph showing the drain current IdH flowing through the rectifier 132uh on the high side.
図15(e)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのコンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompLの波形を示すグラフである。
図15(f)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsLの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsLは、MOSFET101ulのソース電圧を基準としている。
図15(g)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulに流れるドレイン電流IdLを示すグラフである。
FIG. 15E is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompL of the
FIG. 15F is a graph showing a waveform of the gate voltage VgsL of the
FIG. 15G is a graph showing the drain current IdL flowing through the low-side rectifier 132ul.
図15(a)〜(g)の基本的な動作は、図14(a)〜(g)と同じである。しかし、図14(d)の場合と比べると、図15(d)に示すドレイン電流IdHは小さい。図14(g)の場合と比べると、図15(g)に示すドレイン電流IdLは小さい。
例えば、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhを流れるドレイン電流IdHは、V相131vのロウサイドのMOSFET101vlから流れる電流と、W相131wのロウサイドのMOSFET101wlから流れる電流とから成る。これらの電流が小さいと、両電流が時間的に連続せず、よってMOSFET101uhにドレイン電流IdHが流れない期間が生じる。
The basic operations in FIGS. 15A to 15G are the same as those in FIGS. 14A to 14G. However, compared with the case of FIG. 14D, the drain current IdH shown in FIG. Compared to the case of FIG. 14G, the drain current IdL shown in FIG.
For example, the drain current IdH flowing through the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u includes a current flowing from the low-side MOSFET 101vl of the V-
図15(d)に示すように、時刻t24〜t25において、V相131vのロウサイドのMOSFET101vlから流れる電流が、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhをドレイン電流IdHとなる。
時刻t25〜t26において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhにドレイン電流IdHが流れない。
時刻t26〜t27において、W相131wのロウサイドのMOSFET101wlから流れる電流が、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhをドレイン電流IdHとなる。
As shown in FIG. 15 (d), from time t24 to t25, the current flowing from the low-side MOSFET 101vl of the V-
From time t25 to t26, the drain current IdH does not flow through the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u.
From time t26 to t27, the current flowing from the low-side MOSFET 101wl of the
図15(g)に示すU相131uのロウサイドのMOSFET101ulを流れるドレイン電流IdLも同様に、V相131vのハイサイドのMOSFET101vhから流れる電流と、W相131wのハイサイドのMOSFET101whから流れる電流とから成る。これらの電流が小さいと、両電流が時間的に連続せず、よってMOSFET101ulにドレイン電流IdLが流れない期間が生じる。
時刻t20〜t21において、V相131vのハイサイドのMOSFET101vhから流れる電流が、U相131uのロウサイドのMOSFET101ulのドレイン電流IdLとなる。
時刻t21〜t22において、U相131uのロウサイドのMOSFET101ulにドレイン電流IdLが流れない。
時刻t22〜t23において、W相131wのハイサイドのMOSFET101whから流れる電流が、U相131uのロウサイドのMOSFET101ulのドレイン電流IdLとなる。
Similarly, the drain current IdL flowing through the low-side MOSFET 101ul of the U-phase 131u shown in FIG. 15G is composed of a current flowing from the high-side MOSFET 101vh of the V-
From time t20 to t21, the current flowing from the high-side MOSFET 101vh of the V-
From time t21 to t22, the drain current IdL does not flow through the low-side MOSFET 101ul of the U-phase 131u.
From time t22 to t23, the current flowing from the high-side MOSFET 101wh of the W-
図15(a)に示すように、時刻t20以前において、電圧Vuは、電圧VB以下かつ0V以上である。
時刻t20〜t21において、電圧Vuは、0V未満である。ロウサイドのMOSFET101ulは、同期整流を行う。
時刻t21〜t22において、電圧Vuは、再び電圧VB以下かつ0V以上となる。ロウサイドのMOSFET101ulは、同期整流を終了する。
時刻t22〜t23において、電圧Vuは、再び0V未満となる。ロウサイドのMOSFET101ulは、同期整流を行う。
As shown in FIG. 15A, the voltage Vu is equal to or lower than the voltage VB and equal to or higher than 0 V before the time t20.
From time t20 to t21, the voltage Vu is less than 0V. The low-side MOSFET 101ul performs synchronous rectification.
From time t21 to t22, the voltage Vu again becomes equal to or lower than the voltage VB and equal to or higher than 0V. The low-side MOSFET 101ul finishes synchronous rectification.
From time t22 to t23, the voltage Vu again becomes less than 0V. The low-side MOSFET 101ul performs synchronous rectification.
時刻t23〜t24において、電圧Vuは、電圧VB以下かつ0V以上である。
時刻t24〜t25において、電圧Vuは、電圧VB以上である。ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhは、同期整流を行う。
時刻t25〜t26において、電圧Vuは、再び電圧VB以下かつ0V以上となる。ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhは、同期整流を停止する。
時刻t26〜t27において、電圧Vuは、再び電圧VB以上となる。ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhは、同期整流を行う。
時刻t27以降において、電圧Vuは、電圧VB以下かつ0V以上となる。
From time t23 to t24, the voltage Vu is equal to or lower than the voltage VB and equal to or higher than 0V.
From time t24 to t25, the voltage Vu is equal to or higher than the voltage VB. The high-side MOSFET 101uh performs synchronous rectification.
At times t25 to t26, the voltage Vu again becomes equal to or lower than the voltage VB and equal to or higher than 0V. The high-side MOSFET 101uh stops synchronous rectification.
From time t26 to t27, the voltage Vu becomes equal to or higher than the voltage VB again. The high-side MOSFET 101uh performs synchronous rectification.
After time t27, voltage Vu is equal to or lower than voltage VB and equal to or higher than 0V.
図15(b)に示すように、比較信号VcompHは、時刻t24以前ではHレベルである。比較信号VcompHは、時刻t24〜t25においてLレベルとなり、時刻t25〜t26においてHレベルとなり、時刻t26〜t27においてLレベルとなり、時刻t27以降はHレベルとなる。
図15(c)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t24以前ではLレベルである。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t24〜t25においてHレベルとなり、時刻t25〜t26においてLレベルとなり、時刻t26〜t27においてHレベルとなり、時刻t27以降はLレベルとなる。
As shown in FIG. 15B, the comparison signal VcompH is at the H level before time t24. The comparison signal VcompH becomes L level at times t24 to t25, becomes H level at times t25 to t26, becomes L level at times t26 to t27, and becomes H level after time t27.
As shown in FIG. 15C, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before time t24. The gate voltage VgsH becomes the H level from time t24 to t25, becomes the L level from time t25 to t26, becomes the H level from time t26 to t27, and becomes the L level after time t27.
図15(e)に示すように、比較信号VcompLは、時刻t20以前ではHレベルである。比較信号VcompLは、時刻t20〜t21においてLレベルとなり、時刻t21〜t22においてHレベルとなり、時刻t22〜t23においてLレベルとなり、時刻t23以降はHレベルとなる。 As shown in FIG. 15E, the comparison signal VcompL is at the H level before time t20. The comparison signal VcompL becomes L level at times t20 to t21, becomes H level at times t21 to t22, becomes L level at times t22 to t23, and becomes H level after time t23.
図15(f)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsLは、時刻t20以前ではLレベルである。ゲート電圧VgsLは、時刻t20〜t21においてHレベルとなり、時刻t21〜t22においてLレベルとなり、時刻t22〜t23においてHレベルとなり、時刻t23以降はLレベルとなる。 As shown in FIG. 15F, the gate voltage VgsL is at the L level before time t20. The gate voltage VgsL becomes H level at times t20 to t21, becomes L level at times t21 to t22, becomes H level at times t22 to t23, and becomes L level after time t23.
このように、コンパレータ103zが出力する比較信号VcompH,VcompLやゲート電圧VgsH,VgsLが、1回の整流動作で複数回上下すると、コンデンサ107が蓄えたエネルギ(電荷)を消費してしまう。その結果コンデンサ107をより大容量のものとしなければならず、実装面積が増大し、整流装置132zのコストが増大する。
As described above, when the comparison signals VcompH, VcompL and the gate voltages VgsH, VgsL output from the
以下、比較例の整流装置132zにおいて、チャタリングがどのように発生するかについて説明する。
整流装置132zが整流動作を開始するとき、MOSFET101はオフ状態であり、内蔵ダイオード102に整流電流が流れ始める。整流装置132zのオン電圧には、内蔵ダイオード102の順方向電圧降下(約0.7V)で決まる大きな電圧が現れる。その後、MOSFET101がオンし、整流電流は低抵抗のMOSFET101を流れる。整流装置132zのオン電圧は、MOSFET101の低いオン抵抗で決まる電圧へ急激に小さくなる。このとき、再度MOSFET101がオフする判定基準を満たすとMOSFET101はオフする。MOSFET101がオフすると、内蔵ダイオード102に整流電流が流れて、整流装置132zのオン電圧は、内蔵ダイオード102で決まる大きな電圧となる。このように、整流装置132zは、MOSFET101のオンとオフとを繰り返すので、チャタリングが発生する。
Hereinafter, how chattering occurs in the
When the
整流装置132zが整流動作を終了する直前において、MOSFET101はオン状態である。整流装置132zのオン電圧は、MOSFET101の低いオン抵抗で決まる小さな電圧である。整流装置132zが整流動作を終了するとき、整流電流がMOSFET101を流れている状態で、MOSFET101をオフする。MOSFET101をオフすると、整流の電流は、内蔵ダイオード102に流れる。整流装置132zのオン電圧は、内蔵ダイオード102で決まる大きな電圧へと急激に変わる。整流装置132zのオン電圧が大きくなり、MOSFET101がオンする判定基準を満たすと、MOSFET101はオンして、再び整流電流が流れる。MOSFET101がオンすると、整流装置132zのオン電圧は、MOSFET101の低いオン抵抗で決まる小さな電圧に変化する。整流装置132zのオン電圧がMOSFET101がオフする判定基準を満たすと、MOSFET101は再びオフする。
このように、整流装置132zは、MOSFET101のオフとオンの判定を繰り返すので、チャタリングが発生する。
Immediately before the
Thus, chattering occurs because the
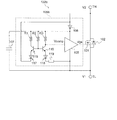
図2は、第1実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置を示す回路図である。
図2に示すように、第1実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132は、正極側主端子THと負極側主端子TLの2つの端子と、MOSFET101と、MOSFET101のチップに内蔵される内蔵ダイオード102と、コンパレータ103と、ゲートドライバ105と、ダイオード106と、コンデンサ107とを含んで構成されている。
FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram showing a rectifier of the autonomous type synchronous rectification MOSFET in the first embodiment.
As shown in FIG. 2, the autonomous synchronous
MOSFET101は、オルタネータ140の発電部が発電する大電流を流すため、パワーMOSFETが使用される。MOSFET101は、ドレインが正極側主端子THに接続され、ソースが負極側主端子TLに接続される。これによりMOSFET101の内蔵ダイオード102は、アノードが負極側主端子TLに接続され、カソードが正極側主端子THに接続される。
コンパレータ103(比較部)は、非反転入力端子IN+がMOSFET101のドレインに接続され、反転入力端子IN−が直接にMOSFET101のソースに接続される。コンパレータ103の出力端子は、ゲートドライバ105の入力端子に接続される。コンパレータ103の出力端子からは、比較信号Vcompが出力される。コンパレータ103は、回路バランスで判定レベルを変えることにより、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−とを直接比較し、電圧ΔVが基準電圧VREF以下であるか否かを判定した比較信号Vcompを生成するものである。コンパレータ103は、負極側主端子TLの電圧V1に基準電圧VREFを加算した電圧(V1+VREF)と、正極側主端子THの電圧V2との比較結果を出力する。コンパレータ103の性能は、高精度であることが望ましい。コンパレータ103は更に、オン判定とオフ判定にヒステリシスを持たせてもよい。これにより、チャタリング防止効果を更に高めることができる。
基準電圧VREFは、バッテリ111の動作範囲の最小電圧の半分未満かつ0Vよりも大きくなるように設定される。これにより、図1に示す制御回路130の貫通電流を防ぐことができる。
The
In the comparator 103 (comparator), the non-inverting input terminal IN + is connected to the drain of the
Reference voltage VREF is set to be less than half of the minimum voltage of the operating range of
ゲートドライバ105の出力端子は、MOSFET101のゲート端子に接続される。ゲートドライバ105は、ゲート電圧Vgsを出力する。ダイオード106は、正極側主端子THからコンデンサ107の正極側端子への向きに接続される。コンデンサ107の正極側端子は、コンパレータ103とゲートドライバ105の電源端子に接続されて、直流電力を供給する。ゲートドライバ105は、1段または2段のCMOSの簡単な回路構成であり、一般的なゲートドライバである。
The output terminal of the
制御IC108は、コンパレータ103と、ゲートドライバ105と、ダイオード106とを含んで構成され、かつ単一のシリコンチップから成る。このように、ワンチップのICとすることで、低コスト・底面積・高ノイズ耐性のメリットが得られる。
The
コンデンサ107は、制御IC108が駆動するための電源を供給するものである。コンデンサ107を電源に用いることで、整流装置132の端子数は2個となり、オルタネータ140に用いられる従来の整流ダイオードの端子と互換性を持たせることができる。これにより、従来の整流ダイオードを整流装置132に置き換えて、オルタネータ140の性能を向上させることができる。コンデンサ107に代えて、端子を1個追加して、外部電源から制御IC108の電源を供給してもよい。こうすることで、より安定した電源を供給することができる。
The
この整流装置132がチャタリングを起こすと、コンパレータ103が出力する比較信号Vcompや、ゲートドライバ105が出力するゲート電圧Vgsが振動する。これにより、コンデンサ107が蓄えたエネルギ(電荷)を消費してしまい、制御IC108が動作しなくなる虞がある。チャタリングが発生しても、制御IC108に確実に電源を供給するためには、コンデンサ107をより大容量のものとしなければならず、実装面積が増大し、整流装置132のコストが増大する。
第1実施形態の整流装置132は、チャタリングを防止することによりコンデンサ107を小容量にしても、制御IC108に電源を供給することが可能となり、小面積・低コストの整流装置132を実現できるようになる。更に、電圧および電流の振動に起因したノイズの発生を抑制することができる。
When the
The
整流装置132は更に、MOSFET101と並列にサージ吸収用のダイオードを接続してもよい。このように構成することで、整流装置132は、サージ吸収機能を備えることができる。
なお、整流装置132は、コンパレータ103の非反転入力端子IN+を負極側主端子TLに接続し、反転入力端子IN−を正極側主端子THに接続してもよい。すなわち、第1実施形態とは逆極性の比較信号Vcompを出力するように構成してもよい。この場合には、ゲートドライバ105は、入力信号を反転せずにゲート電圧を出力するように構成する。
The
The
図3は、第1実施形態における自律型の整流装置のコンパレータを示す回路図である。
コンパレータ103は、定電流回路122と、PMOS11,12,13,14,15と、NMOS21,22,23とを備えている。コンパレータ103のVCC端子とGND端子との間には電源が供給されて動作する。コンパレータ103は、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−との間の電圧ΔVが、基準電圧VREF以下であるか否かを判定するものである。
PMOS11,12,13は、ミラー回路を構成する。すなわち、PMOS11,12,13のドレインは、VCC端子に接続される。PMOS11,12,13のゲートとPMOS11のソースは、それぞれ接続されて、定電流回路122に接続される。この定電流回路122は、PMOS11,12,13のゲートとPMOS11のソースの接続ノードからGND端子に向けて電流を流すように接続される。
PMOS14,15のドレインは、PMOS12のソースに接続される。PMOS12,14,15のバックゲートは、VCC端子に接続される。PMOS14のゲートは、反転入力端子IN−が接続される。PMOS15のゲートは、非反転入力端子IN+が接続される。PMOS14のソースは、NMOS21のソースと、NMOS21,22のゲートに接続される。PMOS15のソースは、NMOS22のソースと、NMOS23のゲートに接続される。NMOS21,22,23のドレインは、GND端子に接続される。
PMOS13のソースとNMOS23のソースとは、OUT端子に接続される。
FIG. 3 is a circuit diagram showing a comparator of the autonomous rectifier in the first embodiment.
The
The
The drains of the
The source of the
以下、コンパレータ103の動作を説明する。
定電流回路122がPMOS11を流れる電流を決定する。PMOS11,12,13が作るミラー回路により、PMOS12,13には、PMOS11とのチャネル幅の比に応じた定電流が流れる。PMOS12に流れる電流は、PMOS15に流れる電流Iin+とPMOS14に流れる電流Iin−とに分流する。
コンパレータ103の非反転入力端子IN+の電圧が反転入力端子IN−の電圧よりも高くなると、PMOS15に流れる電流Iin+よりもPMOS14に流れる電流Iin−の方が大きくなる。PMOS14に流れる電流Iin−がNMOS21に流れることにより、NMOS21は、オンする。NMOS21と同じゲート電圧が印加されるNMOS22もオンする。NMOS22のオンにより、NMOS23のゲート電圧が下がり、オフする。その結果、PMOS13からOUT端子へと電流Ion_outが流れ、OUT端子には、Hレベルの電圧が生じる。
反対に、コンパレータ103の非反転入力端子IN+の電圧が反転入力端子IN−の電圧よりも低くなると、PMOS15に流れる電流Iin+よりもPMOS14に流れる電流Iin−が小さくなる。NMOS21に流れる電流Iin+も小さくなり、NMOS21はオフする。NMOS21と同じゲート電圧が印加されるNMOS22もオフする。NMOS22のオフにより、NMOS23のゲート電圧が上がり、オンする。その結果、OUT端子からNMOS23へと電流Ioff_outが流れ、OUT端子には、Lレベルの電圧が生じる。
Hereinafter, the operation of the
The constant
When the voltage at the non-inverting input terminal IN + of the
On the contrary, when the voltage at the non-inverting input terminal IN + of the
図3に示すコンパレータ103において、OUT端子に高電圧が出力されるときにPMOS13からOUT端子へと流れる電流Ion_outよりも、OUT端子にLレベル電圧が出力されるときにOUT端子からNMOS23へと流れる電流Ioff_outを大きくすることで、コンパレータ103の判定レベルを、基準電圧VREF分だけずらすことができる。
In the
電流Ion_outよりも電流Ioff_outを大きくするには、PMOS13のチャネル幅を小さくするか、PMOS13のチャネル長を大きくするか、NMOS23のチャネル幅を大きくするか、NMOS23のチャネル長を小さくすることが考えられる。または、電流Ion_outの経路かつ、電流Ioff_outの経路以外の位置に、PMOS13に対して直列に抵抗を設けてもよい。
In order to make the current Ioff_out larger than the current Ion_out, it is conceivable to reduce the channel width of the
別の方法として、図3に示すコンパレータ103において、非反転入力端子IN+の電圧と反転入力端子IN−が等しいときに、非反転入力端子IN+がゲートに接続されたPMOS15に流れる電流Iin+よりも反転入力端子IN−がゲートに接続されたPMOS14に流れる電流Iin−を小さくすることで、コンパレータ103の判定レベルを、基準電圧VREF分だけずらすことができる。
As another method, in the
電流Iin+よりも電流Iin−を小さくするには、PMOS14のチャネル幅をPMOS15のチャネル幅より小さくするか、PMOS14のチャネル長をPMOS15のチャネル長より大きくするか、NMOS21のチャネル幅をNMOS22のチャネル幅より小さくするか、NMOS21のチャネル長をNMOS22のチャネル長より大きくすることが考えられる。または、電流Iin−の経路かつ電流Iin+の経路以外の位置に、PMOS14またはNMOS21と直列に抵抗を設けてもよい。
In order to make the current Iin− smaller than the current Iin +, the channel width of the
図4(a)〜(g)は、第1実施形態における自律型の整流装置132を用いたオルタネータ140のU相波形を示すグラフである。図4(a)〜(g)は、図14(a)〜(g)に示した比較例のグラフに対応している。図4(a)〜(g)の横軸は、共通する時間tを示している。
図4(a)は、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuの波形を示すグラフである。
図4(b)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのコンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompHの波形を示すグラフである。
図4(c)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsHの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsHは、MOSFET101uhのソース電圧を基準としている。
図4(d)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhに流れるドレイン電流IdHを示すグラフである。
図4(e)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのコンパレータ103の比較信号VcompLの波形を示すグラフである。
図4(f)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsLの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsLは、MOSFET101ulのソース電圧を基準としている。
図4(g)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulに流れるドレイン電流IdLを示すグラフである。
FIGS. 4A to 4G are graphs showing the U-phase waveform of the
FIG. 4A is a graph showing the waveform of the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the
FIG. 4B is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompH of the
FIG. 4C is a graph showing a waveform of the gate voltage VgsH of the
FIG. 4D is a graph showing the drain current IdH flowing through the high-side rectifier 132uh.
FIG. 4E is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompL of the
FIG. 4F is a graph showing the waveform of the gate voltage VgsL of the
FIG. 4G is a graph showing the drain current IdL flowing through the low-side rectifier 132ul.
図1に示したオルタネータ140を適宜参照しつつ、各部の電圧と電流による動作を説明する。
オルタネータ140において、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの中を回転子コイル109が回転することで発電が行われる。このとき、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuには、交流電力が発生する。
With reference to the
In the
図4(a)に示すように、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの交流電力により、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuは、周期的に上下する。
電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも小さくなると、同期整流の開始時にMOSFET101ulをオンに制御するとき、まず、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなる。
時刻t30において、電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも低くなり、MOSFET101ulをオンする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオンする。このとき、MOSFET101ulには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t31において、電圧Vuが0Vよりも低くなると、MOSFET101ulには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t32において、電圧Vuが0Vよりも高くなると、MOSFET101ulには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t33において、電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも高くなり、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオフする。
負極側主端子TLから正極側主端子THへの電圧は、整流電流が流れ始めてから流れ終わるまで、MOSFET101ulのゲートをオン制御したときのオン電圧である。
As shown in FIG. 4A, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the U-phase 131u periodically rises and falls due to the AC power of the stator coils 110uv, 110vw, and 110wu.
When the voltage Vu becomes smaller than the reference voltage VREF, when the MOSFET 101ul is controlled to be turned on at the start of synchronous rectification, first, a current flows through the high-resistance built-in diode 102ul, and the on-voltage increases.
At time t30, when the voltage Vu becomes lower than the reference voltage VREF and reaches a determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101ul of the low-side rectifier 132ul is turned on. At this time, a reverse current flows through the
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than 0 V at time t31, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101ul and synchronous rectification starts.
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than 0V at time t32, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101ul and circulates in the
At time t33, when the voltage Vu becomes higher than the reference voltage VREF and reaches a determination criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101ul of the rectifier 132ul on the low side is turned off.
The voltage from the negative-side main terminal TL to the positive-side main terminal TH is an on-voltage when the gate of the MOSFET 101ul is on-controlled from when the rectified current starts to flow until it ends.
時刻t34〜t37においても、時刻t30〜t33と同様である。
時刻t34において、電圧Vuが電圧VBから基準電圧VREFを減算した電圧(VB−VREF)よりも高くなり、MOSFET101uhをオンする判定基準に達すると、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのMOSFET101uhがオンする。このとき、MOSFET101uhには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t35において、電圧Vuが電圧VBよりも高くなると、MOSFET101uhには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t36において、電圧Vuが電圧VBよりも低くなると、MOSFET101uhには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t37において、電圧Vuが電圧VBから基準電圧VREFを減算した電圧(VB−VREF)よりも低くなり、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達すると、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのMOSFET101uhがオフする。
負極側主端子TLから正極側主端子THへの電圧は、整流電流が流れ始めてから流れ終わるまで、MOSFET101uhのゲートをオン制御したときのオン電圧である。
The time t34 to t37 is the same as the time t30 to t33.
At time t34, when the voltage Vu becomes higher than the voltage (VB−VREF) obtained by subtracting the reference voltage VREF from the voltage VB and reaches the determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET 101uh, the MOSFET 101uh of the high-side rectifier 132uh is turned on. At this time, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and circulates in the
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than the voltage VB at time t35, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and synchronous rectification is started.
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than the voltage VB at time t36, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and circulates in the
At time t37, when the voltage Vu becomes lower than the voltage (VB−VREF) obtained by subtracting the reference voltage VREF from the voltage VB and reaches the determination criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101uh of the high-side rectifier 132uh is turned off.
The voltage from the negative-side main terminal TL to the positive-side main terminal TH is an on-voltage when the gate of the MOSFET 101uh is on-controlled from when the rectified current starts to flow until it ends.
図4(b)に示すように、比較信号VcompHは、時刻t34以前はHレベルであり、時刻t34において、Lレベルとなる。比較信号VcompHは、時刻t37においてHレベルとなる。
図4(c)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t34以前はLレベルであり、時刻t34において、Hレベルとなる。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t37において、Lレベルとなる。
As shown in FIG. 4B, the comparison signal VcompH is at the H level before the time t34 and becomes the L level at the time t34. Comparison signal VcompH becomes H level at time t37.
As shown in FIG. 4C, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before the time t34 and becomes the H level at the time t34. Gate voltage VgsH becomes L level at time t37.
図4(d)に示すように、時刻t34以前において、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
時刻t34〜t35において、ドレイン電流IdHは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t35〜t36において、ドレイン電流IdHは順方向に流れる。
時刻t36〜t37において、ドレイン電流IdHは逆方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t37以降、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
As shown in FIG. 4D, the drain current IdH does not flow before time t34.
From time t34 to t35, the drain current IdH flows in the reverse direction, that is, from the drain to the source. This drain current IdH circulates in the
From time t35 to t36, the drain current IdH flows in the forward direction.
From time t36 to t37, the drain current IdH flows in the reverse direction. This drain current IdH circulates in the
After time t37, the drain current IdH does not flow.
図4(e)に示すように、比較信号VcompLは、時刻t30以前はHレベルであり、時刻t30において、Lレベルとなる。比較信号VcompLは、時刻t33において、Hレベルとなる。
図4(f)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t30以前はLレベルであり、時刻t30において、Hレベルとなる。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t33において、Lレベルとなる。
図4(g)に示すように、時刻t30以前において、ドレイン電流IdLは流れない。
時刻t30〜t31において、ドレイン電流IdLは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t31〜t32において、ドレイン電流IdLは順方向に流れる。
時刻t32〜t33において、ドレイン電流IdLは逆方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdLは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t33以降、ドレイン電流IdLは流れない。
As shown in FIG. 4E, the comparison signal VcompL is at the H level before the time t30, and becomes the L level at the time t30. The comparison signal VcompL becomes H level at time t33.
As shown in FIG. 4F, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before time t30, and becomes the H level at time t30. Gate voltage VgsH becomes L level at time t33.
As shown in FIG. 4G, the drain current IdL does not flow before time t30.
From time t30 to t31, the drain current IdL flows in the reverse direction, that is, from the drain to the source. This drain current IdH circulates in the
From time t31 to t32, the drain current IdL flows in the forward direction.
From time t32 to t33, the drain current IdL flows in the reverse direction. This drain current IdL circulates in the
After time t33, the drain current IdL does not flow.
以下、適宜図1や図2を参照しつつ、オルタネータ140の各部動作を説明する。
オルタネータ140での発電は、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの中を回転子コイル109が回転することで行われる。このとき、各相の固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuには交流電力が発生する。その交流電力によってU相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuは、周期的に上下する。
The operation of each part of the
Power generation by the
U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuが上昇し、ハイサイドの整流装置132uhが整流動作する場合を説明する。
時刻t34の直前において、U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuは上昇している。
時刻t34において、電圧Vuは、この電圧Vuが印加されているハイサイドのMOSFET101uhのソースの電圧が、バッテリ111の正極側端子の電圧VBであるドレインの電圧から基準電圧VREFだけ低い電圧(VB−VREF)に達する。コンパレータ103の出力端子の比較信号VcompHは、HレベルからLレベルに変化する。これにより、MOSFET101uhのゲート電圧VgsHは、LレベルからHレベルに変化し、MOSFET101uhをオンする。コンパレータ103の基準電圧VREFは、0Vを超え、かつ、電圧VBの半分未満に設定される。
The case where the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the U-phase 131u increases and the high-side rectifier 132uh performs rectification operation will be described.
Immediately before time t34, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
At time t34, the voltage Vu is a voltage (VB−) in which the source voltage of the high-side MOSFET 101uh to which the voltage Vu is applied is lower than the drain voltage, which is the voltage VB of the positive terminal of the
第1実施形態の整流装置132uhは、MOSFET101uhのソースの電圧がドレインの電圧とクロスする前の、整流時とは逆方向の電圧がドレインとソースの間に印加された状態で、MOSFET101uhをオンする。MOSFET101uhがオンした直後において、ドレイン電流IdHは、整流方向とは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。
時刻t34以降、U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuは、更に上昇する。
The rectifier 132uh of the first embodiment turns on the MOSFET 101uh in a state where a voltage in the opposite direction to that during rectification is applied between the drain and the source before the source voltage of the MOSFET 101uh crosses the drain voltage. . Immediately after the MOSFET 101uh is turned on, the drain current IdH flows in the direction opposite to the rectification direction, that is, from the drain to the source.
After time t34, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
時刻t35において、電圧Vuは、バッテリ111の正極側端子の電圧VBを上回る。MOSFET101uhのドレインとソースとの間には、整流方向の電圧が印加される。ドレイン電流IdHは、整流方向に、すなわちソースからドレインの方向に流れる。
At time t35, the voltage Vu exceeds the voltage VB of the positive terminal of the
時刻t35以降、U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuは上昇から下降に転ずる。
時刻t36において、ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhのソースの電圧がドレインの電圧を下回ると、再び整流時とは逆方向の電圧がMOSFET101uhのドレインとソースの間に印加される。ドレイン電流IdHは、整流方向とは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。
After time t35, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
At time t36, when the source voltage of the high-side MOSFET 101uh falls below the drain voltage, a voltage in the opposite direction to that during rectification is again applied between the drain and source of the MOSFET 101uh. The drain current IdH flows in the direction opposite to the rectification direction, that is, from the drain to the source.
時刻t36以降、U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuが更に下降する。
時刻t37において、U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuが、ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhのドレインに印加される電圧VBよりも基準電圧VREFだけ低い電圧(VB−VREF)に達すると、コンパレータ103の出力端子の比較信号VcompHがLレベルからHレベルに変化する。これにより、ゲート電圧VgsHは、HレベルからLレベルに変化し、MOSFET101uhをオフ状態にする。MOSFET101uhがオフするので、ドレイン電流IdHは流れなくなる。
After time t36, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
When the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the U-phase 131u reaches a voltage (VB−VREF) lower than the voltage VB applied to the drain of the high-side MOSFET 101uh at time t37, the output terminal of the
以上、MOSFET101uhの動作を順に追うと、時刻t34において、ゲート電圧VgsHがHレベルに変化し、MOSFET101uhがオンする。
時刻t34〜t35において、MOSFET101uhには、整流時とは逆方向のドレイン電流IdHが流れる。
時刻t35〜t36において、MOSFET101uhには、整流方向のドレイン電流IdHが流れる。
時刻t36〜t37において、MOSFET101uhには、整流時とは逆方向のドレイン電流IdHが流れる。
時刻t37において、ゲート電圧VgsHがLレベルに変化し、MOSFET101uhがオフする。
As described above, when the operation of the MOSFET 101uh is sequentially followed, at time t34, the gate voltage VgsH changes to the H level, and the MOSFET 101uh is turned on.
From time t34 to t35, the drain current IdH in the direction opposite to that during rectification flows through the MOSFET 101uh.
From time t35 to t36, a drain current IdH in the rectifying direction flows through the MOSFET 101uh.
From time t36 to t37, a drain current IdH in the direction opposite to that during rectification flows through the MOSFET 101uh.
At time t37, the gate voltage VgsH changes to the L level, and the MOSFET 101uh is turned off.
この動作では、整流方向のドレイン電流IdHは、MOSFET101uhがオン状態のときにのみ流れる。オン状態のMOSFET101uhと比べて高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102uhに、ドレイン電流IdHが流れる場合はない。そのため、整流装置132uhのオン電圧は、MOSFET101uhのオン抵抗のみで決定され、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102uhで決定される場合はない。よって、整流装置132uhのオン電圧は、ドレイン電流IdHが増加するときには単調増加し、ドレイン電流IdHが減少するときには単調減少する。
U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuからバッテリ111の電圧VBを減算した電圧(Vu−VB)が、整流装置132uhのオン電圧に該当する。図4(a)に示すように、第1実施形態における整流装置132uhのオン電圧は、単調に増加し、かつ単調に減少する。比較例の整流装置132zとは異なり、ドレイン電流IdHが内蔵ダイオード102uhに流れている状態からMOSFET101uhに流れる状態に変わる場合、または、MOSFET101uhに流れている状態から内蔵ダイオード102uhに流れる状態に変わる場合はなく、オン電圧は急激に変化しない。これにより、第1実施形態における整流装置132uhは、整流動作を制御するときのオンとオフの誤判定を繰り返すチャタリングを防止できる。
In this operation, the drain current IdH in the rectifying direction flows only when the MOSFET 101uh is on. The drain current IdH does not flow through the built-in diode 102uh having a higher resistance than the MOSFET 101uh in the on state. Therefore, the on-voltage of the rectifier 132uh is determined only by the on-resistance of the MOSFET 101uh, and is not determined by the high-resistance built-in diode 102uh. Therefore, the ON voltage of the rectifier 132uh increases monotonously when the drain current IdH increases, and decreases monotonously when the drain current IdH decreases.
A voltage (Vu−VB) obtained by subtracting the voltage VB of the
なお、ゲートドライバ105の遅延で、MOSFET101uhに逆方向の電流が流れなくても、内蔵ダイオード102uhに電流が流れず、整流装置132uhのオン電圧に内蔵ダイオード102uhで決定されるオン電圧が現れなければ、同じ効果を得ることができる。
更にゲートドライバ105の遅延が大きい場合に備えて、第1実施形態のコンパレータ103は、回路バランスを調整して判定レベルを基準電圧VREFとしている。これにより、コンパレータ103は、反転入力端子IN−の電圧が非反転入力端子IN+の電圧を超える前に比較信号VcompをHレベルからLレベルに変化させ、反転入力端子IN−の電圧が非反転入力端子IN+の電圧を下回る前に比較信号VcompをLレベルからHレベルに変化させている。これにより、チャタリングの発生を防止できる。
Even if the reverse current does not flow through the MOSFET 101uh due to the delay of the
Further, in preparation for the case where the delay of the
U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuが下降し、ロウサイドの整流装置132ulが整流動作する場合も、バッテリ111の正極側端子の電圧VBが負極側端子の電圧0Vになり、かつ電圧の向きが逆になるだけで、同様に動作する。
MOSFET101ulの動作を順に追うと、時刻t30において、ゲート電圧VgsLがHレベルに変化し、MOSFET101ulがオンする。
時刻t30〜t31において、MOSFET101ulには、整流時とは逆方向のドレイン電流IdLが流れる。
時刻t31〜t32において、MOSFET101ulには、整流方向のドレイン電流IdLが流れる。
時刻t32〜t33において、MOSFET101ulには、整流時とは逆方向のドレイン電流IdLが流れる。
時刻t33において、ゲート電圧VgsLがLレベルに変化し、MOSFET101ulがオフする。
Even when the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
When the operation of the MOSFET 101ul is sequentially followed, at time t30, the gate voltage VgsL changes to the H level, and the MOSFET 101ul is turned on.
From time t30 to t31, a drain current IdL in the direction opposite to that during rectification flows through the MOSFET 101ul.
From time t31 to t32, the drain current IdL in the rectifying direction flows through the MOSFET 101ul.
From time t32 to t33, a drain current IdL in the direction opposite to that during rectification flows through the MOSFET 101ul.
At time t33, the gate voltage VgsL changes to the L level, and the MOSFET 101ul is turned off.
この動作では、整流方向のドレイン電流IdLは、MOSFET101ulがオン状態のときにのみ流れる。オン状態のMOSFET101ulと比べて高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102ulに、ドレイン電流IdLが流れる場合はない。そのため、整流装置132ulのオン電圧は、MOSFET101ulのオン抵抗のみで決定され、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102ulで決定される場合はない。よって、整流装置132ulのオン電圧は、ドレイン電流IdLが増加するときには単調増加し、ドレイン電流IdLが減少するときには単調減少する。 In this operation, the drain current IdL in the rectifying direction flows only when the MOSFET 101ul is on. The drain current IdL does not flow in the built-in diode 102ul having a higher resistance than the MOSFET 101ul in the on state. Therefore, the on-voltage of the rectifier 132ul is determined only by the on-resistance of the MOSFET 101ul, and is not determined by the high-resistance built-in diode 102ul. Therefore, the ON voltage of the rectifier 132ul increases monotonously when the drain current IdL increases, and decreases monotonously when the drain current IdL decreases.
U相131uの中点配線の電圧Vuの逆方向の電圧(−Vu)が、整流装置132ulのオン電圧に該当する。図4(a)に示すように、第1実施形態における整流装置132ulのオン電圧は、単調に増加し、かつ単調に減少する。比較例の整流装置132zとは異なり、ドレイン電流IdLが内蔵ダイオード102ulに流れている状態からMOSFET101ulに流れる状態に変わる場合、または、MOSFET101ulに流れている状態から内蔵ダイオード102ulに流れる状態に変わる場合はなく、オン電圧は急激に変化しない。これにより、第1実施形態における整流装置132ulは、整流動作を制御するときのオンとオフの誤判定を繰り返すチャタリングを防止できる。
A voltage (-Vu) in the reverse direction of the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring of the
ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhの場合と同様に、ゲートドライバ105の遅延で、MOSFET101ulに逆方向の電流が流れなくても、内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れず、整流装置132ulのオン電圧に内蔵ダイオード102ulで決まるオン電圧が現れなければ、同じ効果を得ることができる。
更にゲートドライバ105の遅延が大きい場合に備えて、第1実施形態のコンパレータ103は、回路バランスを調整して判定レベルを基準電圧VREFとしている。これにより、コンパレータ103は、反転入力端子IN−の電圧が非反転入力端子IN+の電圧を超える前に比較信号VcompをHレベルからLレベルに変化させ、反転入力端子IN−の電圧が非反転入力端子IN+の電圧を下回る前に比較信号VcompをLレベルからHレベルに変化させている。これにより、チャタリングの発生を防止できる。
As in the case of the high-side MOSFET 101uh, even if no reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101ul due to the delay of the
Further, in preparation for the case where the delay of the
コンパレータ103の判定レベルである基準電圧VREFは、0Vよりも大きく、かつ、バッテリ111の電圧VBの半分よりも小さい。
ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhがオンするとき、ハイサイドの整流装置132uhの正極側主端子THと負極側主端子TLとの間の電圧は、電圧VBの半分よりも小さい。ロウサイドの整流装置132ulの正極側主端子THと負極側主端子TLとの間の電圧は、電圧VBの半分よりも大きい。コンパレータ103の判定レベルである基準電圧VREFは、VB/2より小さいので、ロウサイドのMOSFET101ulがオン状態になることはない。ハイサイドとロウサイドが逆のときも同じである。
すなわち、第1実施形態の自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132を用いると、ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhとロウサイドのMOSFET101ulとが両方同時にオンする場合はない。よって、ハイサイドのMOSFET101uhまたはロウサイドのMOSFET101ulに逆方向の電流が流れても、バッテリ111の正極側端子から負極側端子に貫通電流が流れる場合はない。以下、図5ないし図7を用いて、逆方向の電流の動作について詳細に説明する。
The reference voltage VREF that is the determination level of the
When the high-side MOSFET 101uh is turned on, the voltage between the positive-side main terminal TH and the negative-side main terminal TL of the high-side rectifier 132uh is smaller than half of the voltage VB. The voltage between the positive-side main terminal TH and the negative-side main terminal TL of the low-side rectifier 132ul is larger than half of the voltage VB. Since the reference voltage VREF which is the determination level of the
That is, when the autonomous synchronous
図5は、第1実施形態における自律型の整流装置132を用いたオルタネータ140の充電フェーズを示す図である。太実線矢印と太破線矢印とは、それぞれオルタネータ140に流れる電流を示している。
太実線矢印で示す電流は、V相131vのロウサイドからU相131uのハイサイドに流れる整流電流である。この電流は、バッテリ111の負極側端子から、整流装置132vl・ノードNv・固定子コイル110uv・ノードNu・整流装置132uhを介して、バッテリ111の正極側端子に流れる。これにより、オルタネータ140は、バッテリ111を充電することができる。
太破線矢印で示す電流は、V相131vのロウサイドからW相131wのハイサイドに流れる整流電流である。この電流は、バッテリ111の負極側端子から、整流装置132vl・ノードNv・固定子コイル110vw・ノードNw・整流装置132whを介して、バッテリ111の正極側端子に流れる。これにより、オルタネータ140は、バッテリ111を充電することができる。
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a charging phase of the
A current indicated by a thick solid arrow is a rectified current that flows from the low side of the
A current indicated by a thick dashed arrow is a rectified current that flows from the low side of the
図6は、第1実施形態における自律型の整流装置132を用いたオルタネータ140の環流フェーズを示す図である。
オルタネータ140は、図5に示す充電フェーズの次に、図6に示す環流フェーズで動作する。
太実線矢印で示す電流は、環流電流である。この環流電流は、整流装置132uhを整流方向とは逆方向に流れて、ノードNu・固定子コイル110uv・固定子コイル110vw・ノードNw・整流装置132whを介して、再び整流装置132uhに環流する。
太破線矢印で示す電流は、図5で示した電流と同様である。
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a reflux phase of the
The
The current indicated by the thick solid arrow is a circulating current. This circulating current flows through the rectifying device 132uh in the direction opposite to the rectifying direction, and circulates again to the rectifying device 132uh via the node Nu, the stator coil 110uv, the stator coil 110vw, the node Nw, and the rectifying device 132wh.
The current indicated by the thick dashed arrow is the same as the current shown in FIG.
図7は、第1実施形態における自律型の整流装置132を用いたオルタネータ140の次の充電フェーズを示す図である。
オルタネータ140は、図6に示す環流フェーズの次に、図7に示す次の充電フェーズで動作する。
太実線矢印で示す電流は、充電電流であり、図6に示す環流電流が転流したものである。この充電電流は、バッテリ111の負極側端子から、整流装置132ul・ノードNu・固定子コイル110uv・固定子コイル110vw・ノードNw・整流装置132whを介して、バッテリ111の正極側端子に流れる。このように、整流装置132uhを整流方向とは逆方向に流れる電流は、最終的にはバッテリ111に流れて、これを充電する。
太破線矢印で示す電流は、図5で示した電流と同様である。
以上より、第1実施形態における整流装置132をブリッジ型の整流回路130に用いることで、逆方向電流がバッテリ111の正極側端子から負極側端子へと貫通電流として流れないようにすることができる。
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a next charging phase of the
The
A current indicated by a thick solid arrow is a charging current, which is a commutation of the circulating current shown in FIG. This charging current flows from the negative terminal of the
The current indicated by the thick dashed arrow is the same as the current shown in FIG.
As described above, by using the
図8(a)〜(g)は、小電流時におけるオルタネータ140のU相波形を示すグラフである。図8(a)〜(g)の横軸は、共通する時間tを示している。
図8(a)は、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuの波形を示すグラフである。
図8(b)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのコンパレータ103の比較信号VcompHの波形を示すグラフである。
図8(c)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsHの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsHは、MOSFET101uhのソース電圧を基準としている。
図8(d)は、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhに流れるドレイン電流IdHを示すグラフである。
8A to 8G are graphs showing the U-phase waveform of the
FIG. 8A is a graph showing the waveform of the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the
FIG. 8B is a graph showing a waveform of the comparison signal VcompH of the
FIG. 8C is a graph showing the waveform of the gate voltage VgsH of the
FIG. 8D is a graph showing the drain current IdH flowing through the rectifier 132uh on the high side.
図8(e)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのコンパレータ103の比較信号VcompLの波形を示すグラフである。
図8(f)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのゲートドライバ105のゲート電圧VgsLの波形を示すグラフである。ゲート電圧VgsLは、MOSFET101ulのソース電圧を基準としている。
図8(g)は、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulに流れるドレイン電流IdLを示すグラフである。
FIG. 8E is a graph showing the waveform of the comparison signal VcompL of the
FIG. 8F is a graph showing a waveform of the gate voltage VgsL of the
FIG. 8G is a graph showing the drain current IdL flowing in the low-side rectifier 132ul.
図8(a)〜(g)の基本的な動作は、図4(a)〜(g)と同じである。しかし、図4(d)の場合と比べると、図8(d)に示すドレイン電流IdHは小さい。図4(g)の場合と比べると、図8(g)に示すドレイン電流IdLは小さい。
例えば、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhを流れるドレイン電流IdHは、V相131vのロウサイドのMOSFET101vlから流れる電流と、W相131wのロウサイドのMOSFET101wlから流れる電流とから成る。これらの電流が小さいと、両電流が時間的に連続せず、よってMOSFET101uhにドレイン電流IdHが流れない期間が生じる。
The basic operations in FIGS. 8A to 8G are the same as those in FIGS. 4A to 4G. However, the drain current IdH shown in FIG. 8D is smaller than that in the case of FIG. Compared to the case of FIG. 4G, the drain current IdL shown in FIG.
For example, the drain current IdH flowing through the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u includes a current flowing from the low-side MOSFET 101vl of the V-
図8(a)に示すように、固定子コイル110uv,110vw,110wuの交流電力により、U相131uの中点配線(ノードNu)の電圧Vuは、周期的に上下する。
電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも小さくなると、同期整流の開始時にMOSFET101ulをオンに制御するとき、まず、高抵抗の内蔵ダイオード102ulに電流が流れてオン電圧が大きくなる。
As shown in FIG. 8A, the voltage Vu of the midpoint wiring (node Nu) of the
When the voltage Vu becomes smaller than the reference voltage VREF, when the MOSFET 101ul is controlled to be turned on at the start of synchronous rectification, first, a current flows through the high-resistance built-in diode 102ul, and the on-voltage increases.
時刻t40において、電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも低くなり、MOSFET101ulをオンする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオンする。このとき、MOSFET101ulには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t41において、電圧Vuが0Vよりも低くなると、MOSFET101ulには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t42において、電圧Vuが0Vよりも高くなると、MOSFET101ulには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t43において、電圧Vuが0Vよりも低くなると、MOSFET101ulには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t44において、電圧Vuがほぼ0Vとなり、MOSFET101ulには電流が流れなくなる。
時刻t45において、電圧Vuが基準電圧VREFよりも高くなり、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達すると、ロウサイド側の整流装置132ulのMOSFET101ulがオフする。
At time t40, when the voltage Vu becomes lower than the reference voltage VREF and reaches a determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101ul of the low-side rectifier 132ul is turned on. At this time, a reverse current flows through the
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than 0 V at time t41, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101ul and synchronous rectification starts.
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than 0V at time t42, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101ul and circulates in the
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than 0 V at time t43, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101ul and synchronous rectification starts.
At time t44, the voltage Vu becomes substantially 0 V, and no current flows through the MOSFET 101ul.
At time t45, when the voltage Vu becomes higher than the reference voltage VREF and reaches a determination criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101ul of the low-side rectifier 132ul is turned off.
時刻t46〜t51においても、時刻t40〜t45と同様である。
時刻t46において、電圧Vuが電圧VBから基準電圧VREFを減算した電圧(VB−VREF)よりも高くなり、MOSFET101uhをオンする判定基準に達すると、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのMOSFET101uhがオンする。このとき、MOSFET101uhには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t47において、電圧Vuが電圧VBよりも高くなると、MOSFET101uhには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t48において、電圧Vuがほぼ0Vとなり、MOSFET101uhには電流が流れなくなる。
時刻t49において、電圧Vuが電圧VBよりも高くなると、MOSFET101uhには順方向の電流が流れて同期整流を開始する。
時刻t50において、電圧Vuが電圧VBよりも低くなると、MOSFET101uhには逆方向の電流が流れ、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t51において、電圧Vuが電圧VBから基準電圧VREFを減算した電圧(VB−VREF)よりも低くなり、MOSFET101ulをオフする判定基準に達すると、ハイサイド側の整流装置132uhのMOSFET101uhがオフする。
The time t46 to t51 is the same as the time t40 to t45.
At time t46, when the voltage Vu becomes higher than the voltage obtained by subtracting the reference voltage VREF from the voltage VB (VB−VREF) and reaches the determination criterion for turning on the MOSFET 101uh, the MOSFET 101uh of the high-side rectifier 132uh is turned on. At this time, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and circulates in the
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than the voltage VB at time t47, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and synchronous rectification starts.
At time t48, the voltage Vu becomes substantially 0 V, and no current flows through the MOSFET 101uh.
When the voltage Vu becomes higher than the voltage VB at time t49, a forward current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and synchronous rectification starts.
When the voltage Vu becomes lower than the voltage VB at time t50, a reverse current flows through the MOSFET 101uh and circulates in the
At time t51, when the voltage Vu becomes lower than the voltage (VB−VREF) obtained by subtracting the reference voltage VREF from the voltage VB and reaches a determination criterion for turning off the MOSFET 101ul, the MOSFET 101uh of the high-side rectifier 132uh is turned off.
図8(b)に示すように、比較信号VcompHは、時刻t46以前はHレベルであり、時刻t46において、Lレベルとなる。比較信号VcompHは、時刻t51においてHレベルとなる。
図9(c)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t46以前はLレベルであり、時刻t46において、Hレベルとなる。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t51において、Lレベルとなる。
As shown in FIG. 8B, the comparison signal VcompH is at the H level before the time t46, and becomes the L level at the time t46. Comparison signal VcompH becomes H level at time t51.
As shown in FIG. 9C, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before time t46, and becomes the H level at time t46. Gate voltage VgsH becomes L level at time t51.
図8(d)に示すように、時刻t46以前において、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
時刻t46〜t47において、ドレイン電流IdHは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t47〜t48において、ドレイン電流IdHは順方向に流れる。
時刻t48〜t49において、ドレイン電流IdHは流れなくなる。
時刻t49〜t50において、ドレイン電流IdHは順方向に流れる。
時刻t50〜t51において、ドレイン電流IdHは逆方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t51以降、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
As shown in FIG. 8D, the drain current IdH does not flow before time t46.
From time t46 to t47, the drain current IdH flows in the reverse direction, that is, from the drain to the source. This drain current IdH circulates in the
From time t47 to t48, the drain current IdH flows in the forward direction.
From time t48 to t49, the drain current IdH stops flowing.
From time t49 to t50, the drain current IdH flows in the forward direction.
From time t50 to t51, the drain current IdH flows in the reverse direction. This drain current IdH circulates in the
After time t51, the drain current IdH does not flow.
図8(e)に示すように、比較信号VcompLは、時刻t40以前はHレベルであり、時刻t40において、Lレベルとなる。比較信号VcompLは、時刻t45において、Hレベルとなる。
図8(f)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t40以前はLレベルであり、時刻t40において、Hレベルとなる。ゲート電圧VgsHは、時刻t45において、Lレベルとなる。
As shown in FIG. 8E, the comparison signal VcompL is at the H level before the time t40 and becomes the L level at the time t40. The comparison signal VcompL becomes H level at time t45.
As shown in FIG. 8F, the gate voltage VgsH is at the L level before time t40, and becomes the H level at time t40. Gate voltage VgsH becomes L level at time t45.
図8(g)に示すように、時刻t40以前において、ドレイン電流IdLは流れない。
時刻t40〜t41において、ドレイン電流IdLは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdHは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t41〜t42において、ドレイン電流IdLは順方向に流れる。
時刻t42〜t43において、ドレイン電流IdLは流れなくなる。
時刻t41〜t42において、ドレイン電流IdLは順方向に流れる。
時刻t44〜t45において、ドレイン電流IdLは逆方向に流れる。このドレイン電流IdLは、整流回路130の中を循環する。
時刻t45以降、ドレイン電流IdLは流れない。
As shown in FIG. 8G, the drain current IdL does not flow before time t40.
From time t40 to t41, the drain current IdL flows in the reverse direction, that is, from the drain to the source. This drain current IdH circulates in the
From time t41 to t42, the drain current IdL flows in the forward direction.
From time t42 to t43, the drain current IdL stops flowing.
From time t41 to t42, the drain current IdL flows in the forward direction.
From time t44 to t45, the drain current IdL flows in the reverse direction. This drain current IdL circulates in the
After time t45, the drain current IdL does not flow.
以下、適宜図1を参照しつつ、整流回路130の電流の流れを説明する。
時刻t46の直前において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhはオフしている。このとき、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
時刻t46〜t47において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhはオンしている。このとき、ドレイン電流IdHは、整流方向とは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れて、整流回路130を環流する。
時刻t47〜t48において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhにドレイン電流IdHが流れる。これは、V相131vのロウサイドのMOSFET101vlから流れるものである。
Hereinafter, the current flow of the
Immediately before time t46, the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u is turned off. At this time, the drain current IdH does not flow.
From time t46 to t47, the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u is on. At this time, the drain current IdH flows in the direction opposite to the rectification direction, that is, in the direction from the drain to the source, and circulates through the
From time t47 to t48, the drain current IdH flows through the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u. This flows from the low-side MOSFET 101vl of the
時刻t48〜t49において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhはオンしているが、ドレイン電流IdHは流れない。
時刻t49〜t50において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhにドレイン電流IdHが流れる。これは、W相131wのロウサイドのMOSFET101wlから流れるものである。
時刻t50〜t51において、U相131uのハイサイドのMOSFET101uhはオンしている。このとき、ドレイン電流IdHは、整流方向とは逆方向に、すなわちドレインからソースの方向に流れて、整流回路130を環流する。
U相131uのロウサイドのMOSFET101ulを流れる電流も同様であり、V相131vのハイサイドのMOSFET101vhへと流れていく電流と、W相131wのハイサイドのMOSFET101whへと流れていく電流とが時間的に連続しない。
From time t48 to t49, the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u is on, but the drain current IdH does not flow.
From time t49 to t50, the drain current IdH flows through the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u. This flows from the low-side MOSFET 101wl of the
From time t50 to t51, the high-side MOSFET 101uh of the U-phase 131u is on. At this time, the drain current IdH flows in the direction opposite to the rectification direction, that is, in the direction from the drain to the source, and circulates through the
The same applies to the current flowing through the low-side MOSFET 101ul of the U-phase 131u. The current flowing to the high-side MOSFET 101vh of the V-
オルタネータ140の整流回路130に、第1実施形態の整流装置132を用いた場合、整流動作の間に電流が流れない期間があっても、図8(b),(e)に示すようにコンパレータ103の比較信号VcompH,VcompLが切り替わらない。図8(c),(f)に示すようにゲート電圧VgsH,VgsLがLレベルとなることがない。コンパレータ103は回路バランスで判定レベルを変えており、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−との間の電圧ΔVが基準電圧VREF以下でなければ、比較信号VcompH,VcompLを切り替えないからである。
When the
これに対し、オルタネータ140の整流回路130に比較例の整流装置132zを用いた場合、整流動作の間に電流が流れない期間があると、図15(b),(e)に示すように、コンパレータ103zの比較信号VcompH,VcompLが切り替わらない。図15(c),(f)に示すように、ゲート電圧VgsH,VgsLは、Lレベルになったのち、再度Hレベルとなる。コンパレータ103は、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−との間の電圧ΔVにより、比較信号VcompH,VcompLを切り替えるからである。
On the other hand, when the
比較例の整流装置132zは、比較信号VcompH,VcompLやゲート電圧VgsH,VgsLが、1回の整流動作で複数回上下する。この動作により、制御IC108zは、コンデンサ107が蓄えたエネルギ(電荷)を消費してしまう。その結果、コンデンサ107をより大容量のものとしなければならず、実装面積が増大し、整流装置132zのコストが増大する。
第1実施形態の整流装置132を用いると比較信号VcompH,VcompLやゲート電圧VgsH,VgsLが1回の整流動作で1回上下するだけとなる。制御IC108zは、コンデンサ107が蓄えた電力を有効に使用することができる。よって、コンデンサ107を小容量とすることが可能となり、小面積、低コストの整流素子を実現できる。
In the
When the
図9は、第2実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132aを示す回路図である。図2に示す第1実施形態の整流装置132と同一の要素には、同一の符号を付与している。
図9に示すように、第2実施形態の整流装置132aは、第1実施形態とは異なる制御IC108aを備えており、それ以外は、第1実施形態の整流装置132と同様である。
第2実施形態の制御IC108aは、第1実施形態とは異なるコンパレータ103aを備え、更に正基準電圧発生部104を備えている。
コンパレータ103a(比較部)は、一般的なコンパレータであり、非反転入力端子IN+と反転入力端子IN−との間の電圧ΔVが0V以上であるか否かを判定し、比較信号Vcompを生成するものである。
正基準電圧発生部104は、正の基準電圧VREFを発生する。正基準電圧発生部104は、負極側主端子TLから反転入力端子IN−への方向に正の基準電圧VREFを印加するように接続される。正基準電圧発生部104は、例えば、コンデンサ107の正極側端子側に接続された分圧抵抗や、バンドギャップリファレンス回路で構成される。
このように構成することで、第2実施形態の整流装置132aは、コンパレータ103aとして一般的なものを用いることができる。
FIG. 9 is a circuit diagram showing a
As shown in FIG. 9, the
The
The
The positive
With this configuration, the
第2実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132aを用いたオルタネータ140の整流回路130の動作を示す電圧波形と電流波形は、図4(a)〜(g)や図8(a)〜(g)と同一となる。これにより、第1実施形態の整流装置132を用いた場合と同様に、チャタリングを防止することができる。
The voltage waveform and the current waveform showing the operation of the
図10は、第3実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132bを示す回路図である。図2に示す第1実施形態の整流装置132と同一の要素には、同一の符号を付与している。
図10に示すように、第3実施形態の整流装置132bは、第1実施形態とは異なる制御IC108bを備えており、それ以外は、第1実施形態の整流装置132と同様である。
第3実施形態の制御IC108bは、第1実施形態のコンパレータ103の代わりに、一対のバイポーラトランジスタ115,116と、抵抗R1〜R3と、ダイオード117,118と、電圧降下部119とで構成された差動増幅回路(比較部)を備えている。この差動増幅回路は、MOSFET101のオンとオフの判定を行うものである。
バイポーラトランジスタ115のコレクタは、抵抗R1でプルアップされ、エミッタは順方向接続されたダイオード117を介して、MOSFET101のドレインかつ正極側主端子THに接続される。バイポーラトランジスタ115のベースは、バイポーラトランジスタ116のベースと接続され、かつ、抵抗R2でプルアップされる。
バイポーラトランジスタ116のコレクタは、抵抗R3でプルアップされ、エミッタは順方向接続されたダイオード118と電圧降下部119とを介して、MOSFET101のソースかつ負極側主端子TLに接続される。バイポーラトランジスタ116のコレクタは更に、ゲートドライバ105に比較信号Vcompを出力する。
FIG. 10 is a circuit diagram showing a
As shown in FIG. 10, the
The
The collector of the bipolar transistor 115 is pulled up by the resistor R1, and the emitter is connected to the drain of the
The collector of the
電圧降下部119は、抵抗またはダイオードで構成される。電圧降下部119を抵抗で構成する場合、制御時に流れる電流IREFによる電圧降下が、電圧VBの半分未満かつ0Vを超えるように抵抗値RREFを選択する。すなわち、電流IREFと抵抗値RREFの積が、電圧VBの半分未満かつ0Vを超えるように設定する。
電圧降下部119をダイオードで構成する場合、1または複数個のダイオードを直列に接続して構成し、これらダイオードの順方向電圧降下の合計が、電圧VBの半分未満かつ0Vを超えるように設定する。
The
When the
第3実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132bを用いたオルタネータ140の整流回路130の動作を示す電圧波形と電流波形は、図4(a)〜(g)や図8(a)〜(g)と同一となる。これにより、第1実施形態の整流装置132を用いた場合と同様に、チャタリングを防止することができる。
The voltage waveform and the current waveform showing the operation of the
図11は、第4実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132cを示す回路図である。
図11に示すように、第4実施形態の整流装置132cは、第1実施形態とは異なる制御IC108cを備えており、それ以外は、第1実施形態の整流装置132と同様である。
第4実施形態の制御IC108cは、第1実施形態のコンパレータ103の代わりに、MOSFET120(比較部)と、抵抗R4とを備えている。このMOSFET120は、MOSFET101のオンとオフの判定を行うものである。
MOSFET120のゲートは、MOSFET101のドレインに接続される。MOSFET120のソースは、MOSFET101のソースに接続される。MOSFET120のドレインは、抵抗R4を介してプルアップされる。
FIG. 11 is a circuit diagram showing a
As shown in FIG. 11, the
The
The gate of
MOSFET120のゲートの電圧VGとソースの電圧VSとの差に、MOSFET120の閾値電圧VTHを加算した電圧が、電圧VBの半分未満かつ0Vを超えるように、このMOSFET120の特性を選択して回路を構成する。これにより、極めて簡単な回路構成で、比較信号Vcompを生成することができる。
The circuit is configured by selecting the characteristics of the
第4実施形態における自律型の同期整流MOSFETの整流装置132cを用いたオルタネータ140の整流回路130の動作を示す電圧波形と電流波形は、図4(a)〜(g)や図8(a)〜(g)と同一となる。これにより、第1実施形態の整流装置132を用いた場合と同様に、チャタリングを防止することができる。
The voltage waveform and current waveform showing the operation of the
図12は、第5実施形態における自律型の整流装置を用いた電力変換装置141の概略構成を示す回路図である。図1に示す第1実施形態のオルタネータ140と同一の要素には同一の符号を付与している。
第5実施形態の電力変換装置141は、交流電源122uv,122vw,122wuと、整流回路130と、平滑コンデンサ123および直流負荷124を備えている。
交流電源122uv,122vw,122wuは、三相交流を供給する電源である。交流電源122uv,122vw,122wuは、Δ接続されている。交流電源122wu,122uvは、整流回路130のノードNuに接続される。交流電源122uv,122vwは、整流回路130のノードNvに接続される。交流電源122vw,122wuは、整流回路130のノードNwに接続される。
FIG. 12 is a circuit diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of a
The
The AC power supplies 122uv, 122vw, and 122wu are power supplies that supply three-phase AC. The AC power supplies 122uv, 122vw, and 122wu are Δ-connected.
整流回路130は、三相交流を直流に整流するブリッジ回路であり、図1に示すオルタネータ140の整流回路130と同様に構成される。整流回路130は、直流端子であるノードNp,Nn間に平滑コンデンサ123(エネルギ蓄積部)および直流負荷124が並列に接続され、直流電力を供給する。
平滑コンデンサ123は、直流電圧を平滑化するコンデンサである。直流負荷124は、直流電力を受けて駆動する任意の負荷であり、例えばモータや照明などである。
第5実施形態において、整流装置132は、平滑コンデンサ123の動作範囲の最小電圧の半分未満かつ0Vよりも大きい条件を満たすように、基準電圧VREFを設定する。
The
The smoothing
In the fifth embodiment, the
第5実施形態における電力変換装置141においても、各実施形態の整流装置132,132a〜132cを用いることができる。このとき、整流回路130の動作を示す電圧波形と電流波形は、図4(a)〜(g)や図8(a)〜(g)と同一となる。これにより、チャタリングを防止することができる。
Also in the
101 MOSFET
102 内蔵ダイオード
103 コンパレータ (比較部)
104 正基準電圧発生部
105 ゲートドライバ
106 ダイオード
107 コンデンサ
108 制御IC
109 回転子コイル
110uv,110vw,110wu 固定子コイル (交流電源)
111 バッテリ (エネルギ蓄積部)
119 電圧降下部
120 MOSFET (比較部)
122uv,122vw,122wu 交流電源
123 平滑コンデンサ (エネルギ蓄積部)
124 直流負荷
125 負基準電圧発生部
130 整流回路
131u U相
131v V相
131w W相
132 整流装置
140 オルタネータ
141 電力変換装置
Nu,Nv,Nw,Np,Nn ノード
TH 正極側主端子
TL 負極側主端子
VREF 基準電圧
RREF 抵抗値
11〜15 PMOS
21〜23 NMOS
Iin+,Iin− 電流
Ion_out,Ioff_out 電流
Vu 電圧
VB 電圧
VG 電圧
VS 電圧
ΔV 電圧
IN− 反転入力端子
IN+ 非反転入力端子
VTH 閾値電圧
Vgs,VgsH,VgsL ゲート電圧
Vcomp,VcompH,VcompL 比較信号
Id,IdH,IdL ドレイン電流
101 MOSFET
102 Built-in
104 Positive
109 Rotor coil 110uv, 110vw, 110wu Stator coil (AC power supply)
111 battery (energy storage unit)
119
122 uv, 122 vw, 122 wu
124
21-23 NMOS
Iin +, Iin− current Ion_out, Ioff_out current Vu voltage VB voltage VG voltage VS voltage ΔV voltage IN− inverting input terminal IN + non-inverting input terminal VTH threshold voltages Vgs, VgsH, VgsL gate voltages Vcomp, VcompH, VcompL, comparison signals Id, IdH, IdL drain current
Claims (15)
ドレインが正極側主端子に接続され、ソースが負極側主端子に接続されるMOSFETと、
前記MOSFETをオンオフ制御するゲートドライバと、
前記MOSFETの前記正極側主端子から前記負極側主端子への主端子間電圧と基準電圧とを比較した比較信号を生成して前記ゲートドライバに出力することにより、前記主端子間電圧が前記基準電圧以下ならば前記MOSFETをオンさせる比較部と、
を備え、
前記基準電圧は0Vより大きく、
前記正極側主端子から前記負極側主端子への前記主端子間電圧が負である場合、前記MOSFETは順方向の電流を流し、前記主端子間電圧が正であり、かつ、前記基準電圧以下である場合、前記MOSFETは逆方向の電流を流す、
ことを特徴とする整流装置。 A rectifier connected to a high side and a low side of a bridge-type rectifier circuit in which a DC terminal is connected to an energy storage unit and an AC terminal is connected to an AC power source,
A MOSFET whose drain is connected to the positive main terminal and whose source is connected to the negative main terminal ;
A gate driver for controlling on / off of the MOSFET;
By generating and outputting the comparison signal obtained by comparing the voltage with a reference voltage between the main terminals of the positive electrode side main terminal wherein the negative electrode side main terminal of the pre-Symbol MOSFET to the gate driver, the inter-main terminal voltage the A comparator that turns on the MOSFET if it is below the reference voltage;
With
The reference voltage is greater than 0V;
When the voltage between the main terminals from the positive-side main terminal to the negative-side main terminal is negative, the MOSFET passes a forward current, the main-terminal voltage is positive, and is equal to or lower than the reference voltage. The MOSFET passes a reverse current.
A rectifier characterized by that.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の整流装置。 The reference voltage is less than half the minimum voltage of the energy storage unit operating range and greater than 0V;
The rectifier according to claim 1.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の整流装置。 The comparison unit is a comparator that compares whether the voltage between the main terminals is equal to or lower than the reference voltage.
The rectifier according to claim 1.
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の整流装置。 The comparator is configured by changing the circuit balance so as to directly compare whether or not the first input terminal and the second input terminal of the comparator are equal to or lower than the reference voltage.
The rectifier according to claim 3.
前記コンパレータの第1入力端子は、前記負極側主端子に前記基準電圧発生部を介して接続され、
前記コンパレータの第2入力端子は、前記正極側主端子に接続される、
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の整流装置。 A reference voltage generator for generating the reference voltage;
The first input terminal of the comparator is connected to the negative main terminal via the reference voltage generator,
A second input terminal of the comparator is connected to the positive-side main terminal;
The rectifier according to claim 3.
ことを特徴とする請求項5に記載の整流装置。 The reference voltage generator generates the reference voltage by resistance-dividing a power supply voltage supplied to the comparator;
The rectifier according to claim 5.
ことを特徴とする請求項5に記載の整流装置。 The reference voltage generator includes a band gap reference circuit.
The rectifier according to claim 5.
ことを特徴とする請求項5に記載の整流装置。 The reference voltage generation unit is configured to include a resistor, and a voltage across the resistor is equal to or less than half of the minimum voltage of the operating range of the energy storage unit and greater than 0V.
The rectifier according to claim 5.
各前記ダイオードの順方向電圧の合計は、前記エネルギ蓄積部の最小電圧の半分以下である、
ことを特徴とする請求項5に記載の整流装置。 The reference voltage generator includes a series connection of one or a plurality of diodes,
The sum of the forward voltages of each of the diodes is less than or equal to half of the minimum voltage of the energy storage unit,
The rectifier according to claim 5.
前記判定用MOSFETのソース端子は、前記負極側主端子に接続され、
前記判定用MOSFETのゲート端子は、前記正極側主端子に接続され、
前記判定用MOSFETのドレイン端子は、プルアップされて前記ゲートドライバの入力側に接続される、
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の整流装置。 The comparison unit includes a determination MOSFET,
The source terminal of the determination MOSFET is connected to the negative electrode side main terminal,
The gate terminal of the determination MOSFET is connected to the positive-side main terminal,
The drain terminal of the determination MOSFET is pulled up and connected to the input side of the gate driver.
The rectifier according to claim 1.
ことを特徴とする請求項10に記載の整流装置。 When a threshold voltage is added to the difference between the gate voltage and the source voltage of the determination MOSFET, a condition that is less than half of the minimum voltage of the energy storage unit and greater than 0 V is satisfied.
The rectifier according to claim 10.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の整流装置。 A capacitor for storing a power supply voltage to be supplied to the comparison unit;
The rectifier according to claim 1.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の整流装置。 The voltage from the negative-side main terminal to the positive-side main terminal is an on-voltage when the MOSFET gate is on-controlled from the start of the rectification current to the end of the flow.
The rectifier according to claim 1.
前記整流回路のハイサイドおよびロウサイドにそれぞれ接続される請求項1ないし請求項12のいずれか1項に記載の整流装置と、
を備えており、
前記エネルギ蓄積部は、バッテリである、
ことを特徴とするオルタネータ。 A bridge-type rectifier circuit in which a DC terminal is connected to the energy storage unit and an AC terminal is connected to an AC power supply;
The rectifier according to any one of claims 1 to 12, connected to a high side and a low side of the rectifier circuit, respectively.
With
The energy storage unit is a battery.
An alternator characterized by that.
前記整流回路のハイサイドおよびロウサイドにそれぞれ接続される請求項1ないし請求項12のいずれか1項に記載の整流装置と、
を備えることを特徴とする電力変換装置。 A bridge-type rectifier circuit in which a DC terminal is connected to the energy storage unit, and an AC terminal is connected to an AC power supply;
The rectifier according to any one of claims 1 to 12, connected to a high side and a low side of the rectifier circuit, respectively.
A power conversion device comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013252875A JP6155179B2 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2013-12-06 | Rectifier, alternator and power converter |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013252875A JP6155179B2 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2013-12-06 | Rectifier, alternator and power converter |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015111969A JP2015111969A (en) | 2015-06-18 |
| JP2015111969A5 JP2015111969A5 (en) | 2016-06-16 |
| JP6155179B2 true JP6155179B2 (en) | 2017-06-28 |
Family
ID=53526391
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013252875A Active JP6155179B2 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2013-12-06 | Rectifier, alternator and power converter |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6155179B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6617002B2 (en) * | 2015-10-20 | 2019-12-04 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | Rectifier, alternator and power supply using it |
| US10333425B1 (en) | 2018-05-03 | 2019-06-25 | Linear Technology Holding Llc | Self-biasing ideal diode circuit |
| JP7582621B2 (en) * | 2021-09-21 | 2024-11-13 | ミネベアパワーデバイス株式会社 | Rectifier circuit and power supply using same |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002084873A1 (en) * | 2001-03-28 | 2002-10-24 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Synchronous rectifiers |
| FR2884079B1 (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2007-09-07 | Valeo Equip Electr Moteur | CONTROLLING A MOS TRANSISTOR |
| FR2908945B1 (en) * | 2006-11-16 | 2009-01-30 | Valeo Equip Electr Moteur | SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFIER BRIDGE ELEMENT, CORRESPONDING SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFIER BRIDGE AND USE. |
-
2013
- 2013-12-06 JP JP2013252875A patent/JP6155179B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015111969A (en) | 2015-06-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6617002B2 (en) | Rectifier, alternator and power supply using it | |
| JP6371053B2 (en) | Rectifier, alternator and power converter | |
| US7138786B2 (en) | Power supply driver circuit | |
| US8526202B2 (en) | System and method for synchronous rectifier | |
| US9362823B2 (en) | Switch-mode power supply, charging current source and associated method | |
| US8130521B2 (en) | On-vehicle charging generator and rectifier unit thereof | |
| CN108123623B (en) | Rectifier and alternator using the same | |
| CN101383604A (en) | Switch controls and motor drives | |
| JP2016073141A (en) | Synchronous rectification device and alternator employing the same | |
| JP2008043070A (en) | Power generation control unit for vehicle | |
| JP6155179B2 (en) | Rectifier, alternator and power converter | |
| JP2007201595A (en) | Drive device | |
| JP6942559B2 (en) | Power receiving device | |
| JP2011151788A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US20220173734A1 (en) | Drive circuit and drive system | |
| US9231508B2 (en) | Motor driver apparatus and method of controlling the same | |
| JP2012027811A (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit with voltage regulator | |
| JP6896203B2 (en) | Rectifier circuit, DC power supply synthesis circuit, and full-wave rectifier circuit | |
| JP2012005295A (en) | Motor driving circuit | |
| JP2025059836A (en) | Control circuit, isolated DC/DC converter, inverter system, and motor system | |
| JP2025059252A (en) | Switching power supply control device, switching power supply device, and electrical equipment | |
| JP2010136576A (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit and power supply apparatus | |
| CN112154597A (en) | Integrated circuit and power supply circuit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160422 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160422 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20160715 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170203 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170221 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170418 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170523 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170605 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6155179 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |