JP6109791B2 - 監視カメラの位置および向きを選択するための方法およびシステム - Google Patents
監視カメラの位置および向きを選択するための方法およびシステム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6109791B2 JP6109791B2 JP2014152478A JP2014152478A JP6109791B2 JP 6109791 B2 JP6109791 B2 JP 6109791B2 JP 2014152478 A JP2014152478 A JP 2014152478A JP 2014152478 A JP2014152478 A JP 2014152478A JP 6109791 B2 JP6109791 B2 JP 6109791B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- area
- camera
- surveillance
- orientation
- monitoring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 73
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 claims description 99
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000012804 iterative process Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 claims 4
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- 125000002057 carboxymethyl group Chemical group [H]OC(=O)C([H])([H])[*] 0.000 claims 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 53
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 17
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 16
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 244000144992 flock Species 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 241000251468 Actinopterygii Species 0.000 description 2
- 238000013528 artificial neural network Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000256837 Apidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000238631 Hexapoda Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000257303 Hymenoptera Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000256856 Vespidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001149 cognitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012854 evaluation process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 244000144980 herd Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008520 organization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010422 painting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003252 repetitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003997 social interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009827 uniform distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N7/00—Television systems
- H04N7/18—Closed-circuit television [CCTV] systems, i.e. systems in which the video signal is not broadcast
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/18—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength
- G08B13/189—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems
- G08B13/194—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems
- G08B13/196—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems using television cameras
- G08B13/19639—Details of the system layout
- G08B13/19641—Multiple cameras having overlapping views on a single scene
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/18—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength
- G08B13/189—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems
- G08B13/194—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems
- G08B13/196—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems using television cameras
- G08B13/19639—Details of the system layout
- G08B13/19645—Multiple cameras, each having view on one of a plurality of scenes, e.g. multiple cameras for multi-room surveillance or for tracking an object by view hand-over
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/90—Arrangement of cameras or camera modules, e.g. multiple cameras in TV studios or sports stadiums
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N7/00—Television systems
- H04N7/18—Closed-circuit television [CCTV] systems, i.e. systems in which the video signal is not broadcast
- H04N7/181—Closed-circuit television [CCTV] systems, i.e. systems in which the video signal is not broadcast for receiving images from a plurality of remote sources
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/10—Geometric CAD
- G06F30/13—Architectural design, e.g. computer-aided architectural design [CAAD] related to design of buildings, bridges, landscapes, production plants or roads
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/18—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength
- G08B13/189—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems
- G08B13/194—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems
- G08B13/196—Actuation by interference with heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength; Actuation by intruding sources of heat, light, or radiation of shorter wavelength using passive radiation detection systems using image scanning and comparing systems using television cameras
- G08B13/19639—Details of the system layout
- G08B13/19652—Systems using zones in a single scene defined for different treatment, e.g. outer zone gives pre-alarm, inner zone gives alarm
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Closed-Circuit Television Systems (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
は、時刻tにおける次元dの粒子iの速度ベクトルであり、
は、時刻tにおける次元dの粒子iの位置であり、
Pbest,iは、これまでに見つかった粒子iの個体最良位置であり、
Gbestは、群れによってこれまでに見つかった最適の粒子であり、
C1は、ノスタルジア構成要素の寄与を決定する加速度定数であり、
C2は、社会構成要素の寄与を決定する加速度定数であり、
r1およびr2は、0.0〜1.0の間の一様分布からの乱数である。
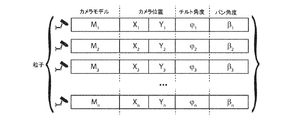
1:問題空間内でのd次元において、ランダムな速度および位置で、粒子の全個体群を初期化する。
2:While maxIterationに達するか、十分に良好な適合度が達成されると、以下を実行する。
3:各粒子について適合度関数を評価する。
4:粒子の適合度と粒子のpBestとを比較する。現在値がpBestよりも良好である場合、pBestをd次元空間内の現在の粒子に設定する。
5:適合度評価と個体群全体の以前の最良値とを比較する。現在値がgBestよりも良好である場合、gBestを現在の粒子に設定する。
6:式(1)および(2)に従って、粒子の速度および位置を変更する。
7:End While
8:gBest粒子が、この最適化プロセスを用いて達成された、十分に良好な適合度である。
ヒットテスト:
pBestは、これまでの因子の最良性能であり(個体最良)、
lBestは、これまでの近隣区域での最良性能の粒子の因子であり(局所最良)、
ω=0.975に設定された慣性係数、
c1=2.01に設定されたノスタルジア係数、
c2=2.01に設定された社会係数、
ζ=c1r1+c2r2、
r1、r2=0〜1の間の乱数。
更新適合度:
104 FoV
106 区域
108 監視区域
110 入射視野角
112 入射視野角
202 空白区域
302 非監視区域
402 監視区域
404 入射視野角
406 入射視野角
408 監視カメラ
412 入射視野角
602 カバレージエリア、FoV
610 縁部
612 縁部
614 向き
702 カバレージエリア
704 区域
706 障害物
S502 区域に関するデータを受信するステップ
S504 仮想区域をモデル化するステップ
S506 適合度関数の繰返し処理を評価するステップ
S508 適合解を選択するステップ
Claims (12)
- 少なくとも監視区域(108、402)および非監視区域(302)を含む区域(106)内の複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の位置および向きを選択するための方法であって、
前記区域(106)に関するデータをプロセッサによって受信するステップ(S502)と、
前記データを用いて仮想区域の多角形表現を前記プロセッサによってモデル化するステップ(S504)と、
適合度関数の繰返し処理を前記プロセッサによって評価するステップ(S506)であって、前記適合度関数が、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のシミュレーションされたカバレージエリアを計算し、かつ前記監視区域(108、402)のシミュレーションされた入射視野角(112、412)を計算するための、前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の位置および向きを含む、評価するステップと、
前記適合度関数に対する適合解を前記プロセッサによって選択するステップ(S508)であって、前記適合解が、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の前記位置および向きを含み、前記選択するステップが、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の前記シミュレーションされ計算されたカバレージエリア(602、702)、前記監視区域(108、402)における前記シミュレーションされ計算された入射視野角(112、412)、および前記監視区域(108、402)の所要の入射視野角(110、404、406)に基づく、選択するステップとを含み、
前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のうちの少なくとも1台の監視カメラの前記位置および前記向きのうち少なくとも1つが、各繰返し処理において変更され、前記適合度関数の繰返し処理は、前記適合解が、前記監視区域(108、402)を完全にカバーし、前記非監視区域(302)をカバーしない、シミュレーションされたカバレージエリア(602、702)を含むまで評価され、前記適合解は、前記監視区域(108、402)の前記所要の入射視野角(110、404、406)を満たし、
各繰返し処理での前記変更が、粒子群最適化(PSO)アルゴリズムによって実行され、前記複数の監視カメラの数がn個であり、PSOアルゴリズムの初期段階がn個の粒子の生成を含み、各粒子が前記複数台の監視カメラのうちの特定の1台の監視カメラに対応し、n個の粒子のそれぞれの初期配置が、前記仮想区域内の孔を表す内部の多角形を除く前記仮想区域の主要な外部の多角形の内部に各粒子を配置するヒットテストアルゴリズムの使用を含む、方法。 - 前記PSOアルゴリズムの繰返しが、前記n個の粒子のクラスタリングを含み、前記粒子のクラスタリングが、前記粒子が対応する前記監視カメラの向きではなく、仮想環境における各粒子の位置に基づく、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 適合解を選択する前記ステップ(S508)がさらに、前記監視区域(108、402)を監視する前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のうちの少なくとも1台の監視カメラが取り込んだ画像の所要の解像度に基づいている、請求項1または2に記載の方法。
- 前記区域(106)がさらに空白区域(202)を含み、適合解を選択する前記ステップ(S508)がさらに、監視される前記空白区域(202)の割合に基づく、請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 前記適合度関数が、複数の監視カメラ(102、408)を含み、前記適合解がさらに、前記監視カメラ(102、408)の数を含む、請求項1から4のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 前記仮想区域内の前記監視カメラ(102、408)の数、ならびに前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のうち少なくとも1台の監視カメラの前記位置および前記向きのうち少なくとも1つが、各繰返し処理において変更される、請求項5に記載の方法。
- 前記少なくとも1台の監視カメラ(102、408)のそれぞれがカメラ機能を含み、前記カメラ機能が、視野およびズームレベルのうち少なくとも1つを含み、前記適合解が、前記少なくとも1台の監視カメラ(102、408)の前記カメラ機能を含む、請求項1から6のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 前記仮想区域内の前記少なくとも1台の監視カメラ(102、408)の前記カメラ機能、ならびに前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のうち少なくとも1台の監視カメラの前記位置および前記向きのうち少なくとも1つが、各繰返し処理において変更される、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記適合度関数がさらに、少なくとも2台の監視カメラ(102、408)を備え、適合解を選択する前記ステップ(S508)がさらに、前記少なくとも2台の監視カメラ(102、408)のそれぞれに対する前記監視区域(402)の所要の入射視野角(404、406)に基づく、請求項1から8のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 前記シミュレーションされたカバレージエリアが、アクティブエッジアルゴリズムを使用して計算される、請求項1から9のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 処理機能を有する装置上で実行されるときに、請求項1から10のいずれか一項に記載の方法を実行するためのプログラムが記録された、コンピュータ可読記録媒体。
- 少なくとも監視区域(108、402)および非監視区域(302)を含む区域(106)内の複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の位置および向きを選択するためのシステムであって、
前記区域(106)に関するデータを受信することと(S502)、
前記データを用いて仮想区域の多角形表現をモデル化することと(S504)、
適合解を計算するために適合度関数の繰返し処理を評価することであって(S506)、前記適合度関数が、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のシミュレーションされたカバレージエリアを計算し、かつ前記監視区域(108、402)のシミュレーションされた入射視野角(112、412)を計算するための、前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の位置および向きを含む、評価することと、
前記適合度関数に適合解を選択することであって(S508)、前記適合解が、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)の前記位置および向きを含み、前記選択が、前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のシミュレーションされ計算されたカバレージエリア(602、702)、前記監視区域(108、402)の前記シミュレーションされ計算された入射視野角(112、412)、および前記監視区域(108、402)の所要の入射視野角(110、404、406)に基づく、選択することと
を行うように構成された1つまたは複数のコンピュータプロセッサを備え、
前記仮想区域内の前記複数台の監視カメラ(102、408)のうちの少なくとも1台の監視カメラの前記位置および前記向きのうち少なくとも1つが、各繰返し処理において変更され、前記適合度関数の繰返し処理は、前記適合解が前記監視区域(108、402)を完全にカバーし、前記非監視区域(302)をカバーしない、シミュレーションされたカバレージエリア(602、702)を含むまで評価され、前記適合解は、前記監視区域(108、402)の前記所要の入射視野角(110、404、406)を満たし、
各繰返し処理での前記変更が、粒子群最適化(PSO)アルゴリズムによって実行され、前記複数の監視カメラの数がn個であり、PSOアルゴリズムの初期段階がn個の粒子の生成を含み、各粒子が前記複数台の監視カメラのうちの特定の1台の監視カメラに対応し、n個の粒子のそれぞれの初期配置が、前記仮想区域内の孔を表す内部の多角形を除く前記仮想区域の主要な外部の多角形の内部に各粒子を配置するヒットテストアルゴリズムの使用を含む、システム。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13179569.2A EP2835792B1 (en) | 2013-08-07 | 2013-08-07 | Method and system for selecting position and orientation for a monitoring camera |
| EP13179569.2 | 2013-08-07 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015035806A JP2015035806A (ja) | 2015-02-19 |
| JP2015035806A5 JP2015035806A5 (ja) | 2017-01-19 |
| JP6109791B2 true JP6109791B2 (ja) | 2017-04-05 |
Family
ID=48948291
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014152478A Active JP6109791B2 (ja) | 2013-08-07 | 2014-07-28 | 監視カメラの位置および向きを選択するための方法およびシステム |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9536019B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2835792B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6109791B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101710149B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104349134B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI624181B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2835792B1 (en) * | 2013-08-07 | 2016-10-05 | Axis AB | Method and system for selecting position and orientation for a monitoring camera |
| CN103630072B (zh) * | 2013-10-25 | 2016-01-13 | 大连理工大学 | 双目视觉测量系统中摄像机的布局优化方法 |
| KR101701974B1 (ko) * | 2015-11-10 | 2017-02-03 | 주식회사 슈어컴 | 감시 카메라의 los 시뮬레이션 장치 및 방법 |
| CN108259817B (zh) * | 2016-12-28 | 2021-03-19 | 南宁富桂精密工业有限公司 | 图片拍摄系统及方法 |
| CN106789312A (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2017-05-31 | 南京理工大学 | 一种基于云计算的安全资源优化分配方法 |
| CN107356975B (zh) * | 2017-07-12 | 2019-08-13 | 电子科技大学 | 基于粒子群优化算法的水下二维空间主动电场定位方法 |
| TWI636428B (zh) * | 2017-12-29 | 2018-09-21 | 晶睿通訊股份有限公司 | 影像分析方法、攝影機及其攝影系統 |
| CN108174162B (zh) * | 2018-01-05 | 2019-12-31 | 河南大学 | 一种基于签到poi的城市视频监控空间优化方法 |
| CN108989796A (zh) * | 2018-08-09 | 2018-12-11 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | 一种图像采集设备选择方法及装置 |
| CN109308547B (zh) * | 2018-09-01 | 2020-09-15 | 中国人民解放军61646部队 | 一种面阵凝视型光学遥感卫星区域覆盖路径优化方法 |
| TWI681166B (zh) * | 2018-12-05 | 2020-01-01 | 晶睿通訊股份有限公司 | 資訊量測方法及資訊量測系統 |
| CN111242271A (zh) * | 2020-01-13 | 2020-06-05 | 北京工业大学 | 一种基于改进惯性权重粒子群算法的装配序列规划方法 |
| CN111405253B (zh) * | 2020-04-16 | 2022-04-26 | 国网湖南省电力有限公司 | 户外变电站一次设备监视摄像头选点布置方法、系统及介质 |
| US12053875B2 (en) * | 2021-01-07 | 2024-08-06 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Method and system for determining sensor placement for a workspace based on robot pose scenarios |
| CN115529437A (zh) * | 2021-06-25 | 2022-12-27 | 青岛海信智慧生活科技股份有限公司 | 一种监控设备布置信息确定方法、装置、设备及介质 |
| CN113489952B (zh) * | 2021-06-30 | 2022-03-22 | 电子科技大学 | 一种面向室内三维场景的视频监控设施布设方法 |
| DE102021207641A1 (de) | 2021-07-16 | 2023-01-19 | Robert Bosch Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Überwachungsvorrichtung mit einer Mehrzahl an Kameras, Verfahren und Computerprogramm zur Überwachung |
| CN113674356B (zh) * | 2021-07-20 | 2024-08-02 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | 相机筛选方法及相关装置 |
| CN113645632B (zh) * | 2021-07-26 | 2023-11-07 | 长江大学 | 基于人工免疫优化和可视多边形算法的5g基站布局方法 |
| US20230370579A1 (en) * | 2022-05-12 | 2023-11-16 | AiFi Corp | Methods of visual camera planning |
| US20240193849A1 (en) * | 2022-12-13 | 2024-06-13 | Schlumberger Technology Corporation | Quantification of sensor coverage using synthetic modeling and uses of the quantification |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5123085A (en) * | 1990-03-19 | 1992-06-16 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method and apparatus for rendering anti-aliased polygons |
| AU3249600A (en) * | 1999-03-18 | 2000-10-04 | Showbites, Inc. | Method for optimization of video coverage |
| JP2005505209A (ja) * | 2001-09-27 | 2005-02-17 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | コンピュータベースの視覚監視用の最適マルチカメラセットアップ |
| US20030058342A1 (en) | 2001-09-27 | 2003-03-27 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Optimal multi-camera setup for computer-based visual surveillance |
| US7558762B2 (en) * | 2004-08-14 | 2009-07-07 | Hrl Laboratories, Llc | Multi-view cognitive swarm for object recognition and 3D tracking |
| JP3915805B2 (ja) * | 2004-08-31 | 2007-05-16 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 駐車場におけるカメラ設置条件の自動決定方法及び装置 |
| US20080291278A1 (en) * | 2005-04-05 | 2008-11-27 | Objectvideo, Inc. | Wide-area site-based video surveillance system |
| US8184157B2 (en) * | 2005-12-16 | 2012-05-22 | Siemens Corporation | Generalized multi-sensor planning and systems |
| KR101187909B1 (ko) * | 2007-10-04 | 2012-10-05 | 삼성테크윈 주식회사 | 감시 카메라 시스템 |
| US8345101B2 (en) | 2008-10-31 | 2013-01-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Automatically calibrating regions of interest for video surveillance |
| JP5190970B2 (ja) * | 2009-10-13 | 2013-04-24 | 国立大学法人 鹿児島大学 | 監視カメラ配置位置評価装置 |
| JP5269002B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-28 | 2013-08-21 | 株式会社日立製作所 | カメラ配置決定支援装置 |
| EP2580738A4 (en) * | 2010-08-10 | 2018-01-03 | LG Electronics Inc. | Region of interest based video synopsis |
| US8514283B2 (en) * | 2010-09-20 | 2013-08-20 | Ajou University Industry Cooperation Foundation | Automatic vision sensor placement apparatus and method |
| US8830230B2 (en) | 2011-01-31 | 2014-09-09 | Honeywell International Inc. | Sensor placement and analysis using a virtual environment |
| US8934017B2 (en) | 2011-06-01 | 2015-01-13 | Honeywell International Inc. | System and method for automatic camera placement |
| EP2600316A1 (en) * | 2011-11-29 | 2013-06-05 | Inria Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et en Automatique | Method, system and software program for shooting and editing a film comprising at least one image of a 3D computer-generated animation |
| EP2835792B1 (en) * | 2013-08-07 | 2016-10-05 | Axis AB | Method and system for selecting position and orientation for a monitoring camera |
| US20160188756A1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2016-06-30 | Invent.ly LLC | Deployment Strategy For Sensors Using Linked-Guard-Covers |
-
2013
- 2013-08-07 EP EP13179569.2A patent/EP2835792B1/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-06-30 TW TW103122572A patent/TWI624181B/zh active
- 2014-07-21 CN CN201410347759.7A patent/CN104349134B/zh active Active
- 2014-07-28 JP JP2014152478A patent/JP6109791B2/ja active Active
- 2014-08-04 US US14/450,443 patent/US9536019B2/en active Active
- 2014-08-07 KR KR1020140101899A patent/KR101710149B1/ko active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2835792A1 (en) | 2015-02-11 |
| KR20150017687A (ko) | 2015-02-17 |
| TW201511568A (zh) | 2015-03-16 |
| CN104349134B (zh) | 2018-08-17 |
| KR101710149B1 (ko) | 2017-02-24 |
| JP2015035806A (ja) | 2015-02-19 |
| TWI624181B (zh) | 2018-05-11 |
| US9536019B2 (en) | 2017-01-03 |
| EP2835792B1 (en) | 2016-10-05 |
| US20150046129A1 (en) | 2015-02-12 |
| CN104349134A (zh) | 2015-02-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6109791B2 (ja) | 監視カメラの位置および向きを選択するための方法およびシステム | |
| Wu et al. | Building generalizable agents with a realistic and rich 3d environment | |
| KR102219276B1 (ko) | 인테리어 공간의 3d 그리드 표현에서 2d 플로어 플랜 추출 | |
| JP6977730B2 (ja) | 人流推定装置、人流推定方法およびプログラム | |
| CN111260031B (zh) | 一种基于深度强化学习的无人机集群目标防卫方法 | |
| US7599894B2 (en) | Object recognition using a cognitive swarm vision framework with attention mechanisms | |
| Gao et al. | Object tracking using firefly algorithm | |
| KR101650799B1 (ko) | 가변 자세를 포함하는 이미지를 컴퓨터를 사용하여 실시간으로 분석하는 방법 | |
| CN108983823B (zh) | 一种植保无人机集群协同控制方法 | |
| Hahn et al. | Emergent escape-based flocking behavior using multi-agent reinforcement learning | |
| Zhai et al. | Peanut: Predicting and navigating to unseen targets | |
| Chrysostomou et al. | A bio-inspired multi-camera system for dynamic crowd analysis | |
| Kirik et al. | The shortest time and/or the shortest path strategies in a CA FF pedestrian dynamics model | |
| CN114692397A (zh) | 基于多机制组合策略的集群分布式抓捕方法 | |
| US20240161377A1 (en) | Physics-based simulation of human characters in motion | |
| Chen et al. | Controlling the movement of crowds in computer graphics by using the mechanism of particle swarm optimization | |
| Farid et al. | Effective UAV patrolling for swarm of intruders with heterogeneous behavior | |
| Sirakoulis | Cellular automata for crowd dynamics | |
| Chen et al. | Vision-assisted Arm Motion Planning for Freeform 3D Printing | |
| Johansson et al. | Knowledge-based probability maps for covert pathfinding | |
| WO2024156093A1 (en) | Systems, methods, and media for generating point cloud frame training data | |
| CN113298847B (zh) | 基于视场感知的共识自主性追捕与逃逸方法和装置 | |
| Taguchi et al. | Reward for Exploration based on View Synthesis | |
| Ho et al. | Fame, soft flock formation control for collective behavior studies and rapid games development | |
| JP2021047618A (ja) | データ生成装置およびその制御方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161205 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20161205 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20161205 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20170125 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170207 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170308 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6109791 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |