JP6109043B2 - Vehicle power supply control device - Google Patents
Vehicle power supply control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6109043B2 JP6109043B2 JP2013227572A JP2013227572A JP6109043B2 JP 6109043 B2 JP6109043 B2 JP 6109043B2 JP 2013227572 A JP2013227572 A JP 2013227572A JP 2013227572 A JP2013227572 A JP 2013227572A JP 6109043 B2 JP6109043 B2 JP 6109043B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- power
- power supply
- vehicle
- relay
- terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 35
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000001172 regenerating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium ion Chemical compound [Li+] HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002803 fossil fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001416 lithium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052987 metal hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel Substances [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 nickel metal hydride Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000008929 regeneration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011069 regeneration method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/70—Energy storage systems for electromobility, e.g. batteries
Landscapes
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
Description
本発明の実施形態は、車両の給電制御装置に関する。 Embodiments described herein relate generally to a vehicle power supply control device.
近年、原動機としてモータおよびエンジンを備え、車載の発電機から入力される電力だけでなく、車両に外部から接続される充電プラグから入力される電力によっても車載のバッテリを充電可能なプラグインハイブリッド車が実用化されている。 In recent years, a plug-in hybrid vehicle that includes a motor and an engine as a prime mover and can charge an in-vehicle battery not only with electric power input from an in-vehicle generator but also with electric power input from a charging plug connected to the vehicle from the outside Has been put to practical use.
プラグインハイブリッド車には、車両外部からの電力の入力および車両外部への電力の出力が可能な外部入出力端子と、車両の車室内に設けられ、電力の出力が可能な内部出力端子とを備えるものがある。 A plug-in hybrid vehicle has an external input / output terminal capable of inputting electric power from the outside of the vehicle and outputting electric power to the outside of the vehicle, and an internal output terminal provided in the vehicle interior of the vehicle and capable of outputting electric power. There is something to prepare.
かかるプラグインハイブリッド車として、外部入出力端子およびバッテリ間を接続する充電経路と、バッテリおよび内部出力端子間を接続する内部電経路と、充電経路および内部給電経路間を接離可能なリレーを備えるものがある(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 As such a plug-in hybrid vehicle, a charging path for connecting the external input / output terminal and the battery, an internal electric path for connecting the battery and the internal output terminal, and a relay capable of connecting / separating the charging path and the internal feeding path are provided. There are some (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、上述したリレーを備えるプラグインハイブリッド車では、リレーがON固着した場合、外部出力端子から入力される電力によってバッテリを充電中に、内部入力端子を使用すると、内部入力端子に接続される機器が破損するおそれがある。 However, in the plug-in hybrid vehicle including the above-described relay, when the relay is fixed ON, when the internal input terminal is used while the battery is being charged with the power input from the external output terminal, the device connected to the internal input terminal May be damaged.
本発明は、上記に鑑みてなされたものであって、リレーのON固着による機器の破損を防止することができる車両の給電制御装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above, and an object of the present invention is to provide a vehicle power supply control device that can prevent damage to equipment due to ON fixation of a relay.
本発明の実施形態によれば、車両の給電制御装置が提供される。車両の給電制御装置は、交流電力の入出力が可能な第1端子と、交流電力の出力が可能な第2端子とを介して、端子に接続された装置と車載のバッテリとの間で電力のやりとりが可能な車両に搭載される。車両の給電制御装置は、充電制御手段と、第1給電制御手段と、第2給電制御手段と、異常検出手段と、給電禁止制御手段とを備える。充電制御手段は、前記第1端子から第1接続部、交流電力を直流電力に変換する第1変換部、前記バッテリの順に接続する充電経路を用いて電力を供給する。第1給電制御手段は、前記バッテリから直流電力を交流電力に変換する第2変換部、第2接続部、第1リレー、前記第1接続部、前記第1端子の順に接続する第1給電経路を用いて電力を供給する。第2給電制御手段は、前記バッテリから前記第2変換部、前記第2接続部、第2リレー、前記第2端子の順に接続する第2給電経路を用いて電力を供給する。異常検出手段は、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を開始する前に、前記第1リレーのON固着を検出する。給電禁止制御手段は、前記異常検出手段によって前記第1リレーのON固着が検出された場合には、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を禁止する。 According to the embodiment of the present invention, a power supply control device for a vehicle is provided. A power supply control device for a vehicle uses a first terminal capable of inputting / outputting AC power and a second terminal capable of outputting AC power between a device connected to the terminal and a vehicle-mounted battery. It is mounted on a vehicle that can exchange The power supply control device for a vehicle includes a charge control unit, a first power supply control unit, a second power supply control unit, an abnormality detection unit, and a power supply prohibition control unit. The charge control means supplies power from the first terminal using a first connection unit, a first conversion unit that converts AC power into DC power, and a charging path that connects the battery in this order. The first power supply control unit is configured to connect a first power supply path connected in the order of a second conversion unit that converts DC power from the battery into AC power, a second connection unit, a first relay, the first connection unit, and the first terminal. To supply power. A 2nd electric power feeding control means supplies electric power using the 2nd electric power feeding path | route connected in order of the said 2nd conversion part, the said 2nd connection part, a 2nd relay, and the said 2nd terminal from the said battery. The abnormality detection means detects ON fixation of the first relay before starting to supply power by the second power supply control means. The power supply prohibition control unit prohibits the supply of power by the second power supply control unit when the abnormality detection unit detects that the first relay is ON.
本発明の実施形態によれば、リレーのON固着による機器の破損を防止することができる。 According to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to prevent the device from being damaged due to the relay being fixed ON.
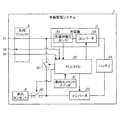
以下、実施形態に係る給電制御装置について説明する。まず、実施形態に係る給電制御装置が搭載される車両の構成について説明する。図1は、実施形態に係る給電制御装置が搭載される車両1を示す説明図である。なお、図1では、動力の伝達経路を太実線、電力の伝達経路を細点線矢印、制御信号の伝達経路を細実線矢印で示している。 Hereinafter, the power supply control device according to the embodiment will be described. First, a configuration of a vehicle on which the power supply control device according to the embodiment is mounted will be described. FIG. 1 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a vehicle 1 on which a power supply control device according to an embodiment is mounted. In FIG. 1, the power transmission path is indicated by a thick solid line, the power transmission path is indicated by a thin dotted arrow, and the control signal transmission path is indicated by a thin solid arrow.
実施形態に係る車両は、原動機としてモータおよびエンジンを備え、車載の発電機から入力される電力だけでなく、車両に外部から接続される充電プラグから入力される電力によっても車載のバッテリを充電可能なプラグインハイブリッド車である。なお、実施形態に係る給電制御装置は、プラグインハイブリッド車だけでなく、電気自動車等、車外との電力のやりとりが可能な他の車両にも適用することができる。 The vehicle according to the embodiment includes a motor and an engine as a prime mover, and can charge an in-vehicle battery not only with electric power input from an in-vehicle generator, but also with electric power input from a charging plug connected to the vehicle from the outside. Plug-in hybrid car. Note that the power supply control device according to the embodiment can be applied not only to a plug-in hybrid vehicle but also to other vehicles capable of exchanging electric power with the outside of the vehicle, such as an electric vehicle.
図1に示すように、車両1は、バッテリ10、電力供給装置11、モータ12、エンジン13、動力分割機構14、補機15、補機バッテリa、DC−DCコンバータ15b、ギヤ機構16、減速機17、共用インレット3、車内コンセント4、充電器5、および制御部6を備える。
As shown in FIG. 1, the vehicle 1 includes a
バッテリ10は、例えば、リチウムイオン電池やニッケル水素電池などの充放電が可能な蓄電池である。電力供給装置11は、インバータ21およびインバータ22を備える。
インバータ21は、車両の走行や回生に用いられるモータ12とバッテリ10との間に接続される。かかるインバータ21は、制御部6によって動作が制御され、バッテリ10から入力される直流の電力を交流の電力へ変換してモータ12へ出力する。また、インバータ21は、モータ12から出力される交流の回生電力を直流の電力へ変換してバッテリ10へ出力する。
The
The
また、インバータ22は、電力の入力側がバッテリ10に接続され、電力の出力側が共用インレット3および車内コンセント4に接続される。そして、インバータ22は、制御部6によって動作が制御され、バッテリ10から入力される直流の電力を交流の電力へ変換して共用インレット3または車内コンセント4へ出力する。
Further, the
モータ12は、例えば、三相交流の電力によって回転する回転電機である。かかるモータ12は、制御部6によって動作が制御され、インバータ21から入力される電力を動力源として駆動する。かかるモータ12は、発生させる動力をギヤ機構16へ出力する。
The
また、モータ12は、回生ブレーキが作動する場合や、動力分割14を介してエンジン13から動力が入力される場合に、発電機として機能して発電する回生電力をインバータ21へ出力する。
In addition, the
エンジン13は、例えば、ガソリンなどの化石燃料を動力源として駆動する内燃機関である。かかるエンジン13は、制御部6によって動作が制御され、発生させる動力を動力分割機構14へ出力する。動力分割機構14は、エンジン13から入力される動力をギヤ機構16およびモータ12の双方、または、いずれか一方へ出力する装置である。
The
ギヤ機構16は、モータ12および動力分割機構14の双方、または、いずれか一方から入力される動力を減速機17へ出力する装置である。減速機17は、ギヤ機構16から入力される動力(ギヤ機構16が備えるギヤの回転力)を減速して、車両1の駆動輪を回転させる車軸100へ伝達する装置である。
The gear mechanism 16 is a device that outputs power input from either or both of the
補機15は、エンジン13の始動や、エンジンの出力で発電を行うモータ(オルタネータ)である。補機バッテリ15aは、補機15、DC−DCコンバータ15b、および制御部6に接続される。かかる補機バッテリ15aは、補機15で発電される電力を蓄電する低圧バッテリである。補機バッテリ15aに蓄電される電力は、補機15の駆動に用いられる他、制御部6へも供給される。DC−DCコンバータ15bは、補機バッテリ15aとバッテリ10との間で電圧の調整を行う。
The
共用インレット3は、交流電力の入出力が可能な第1端子として機能する。かかる共用インレット3は、車両1の外部から充電プラグが接続されて、車両1のバッテリ10の充電を行う場合に、充電プラグから、例えば、100Vまたは200Vの商用の電力が入力される。
The
また、共用インレット3は、車両1の外部から電源プラグが接続されて、車両1のバッテリ10に蓄電された電力を車外の給電装置(例えば、自宅等の施設や、他車両)に供給する場合に、インバータ22から供給される交流の電力を出力する。車内コンセント4は、車室内に設けられ、交流電力の出力が可能な第2端子として機能する。
In addition, the
充電器5は、制御部6によって動作が制御され、共用インレット3から入力される交流の電力を直流の電力へ変換してバッテリ10へ出力することによって、バッテリ10を充電する装置である。
The
制御部6は、PM−ECU(Power Management-Electronic Control Unit)61と、PLG−ECU(Plug In-Electronic Control Unit)62とを備える。PM−ECU61は、主に、エンジン13、およびモータ12などといった車両1に設けられる駆動系の機器の制御を行って主に電力のマネジメントを行う制御装置である。
The control unit 6 includes a PM-ECU (Power Management-Electronic Control Unit) 61 and a PLG-ECU (Plug In-Electronic Control Unit) 62. The PM-ECU 61 is a control device that mainly performs power management by controlling drive system devices provided in the vehicle 1 such as the
一方、PLG−ECU62は、主に、電力供給装置11および充電器5などといった車両1に設けられる電気系の機器の制御を給電制御装置である。次に、かかるPLG−ECU62を含む車載配電システム7について、図2を参照して説明する。
On the other hand, the PLG-ECU 62 is a power supply control device that mainly controls electric devices provided in the vehicle 1 such as the power supply device 11 and the
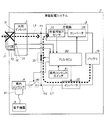
図2は、実施形態に係る車載配電システム7の構成を示す説明図である。なお、図2では、矢尻のある接続線によって信号配線を示しており、矢尻のない接続線によって電力配線を示している。また、図2では、非接地側(ライブ)の電力配線と接地側(ニュートラル)の電力配線とを1本の電力配線によって示している。 FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a configuration of the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 according to the embodiment. In FIG. 2, signal wiring is shown by connection lines with arrowheads, and power wiring is shown by connection lines without arrowheads. In FIG. 2, the non-grounded (live) power wiring and the grounded (neutral) power wiring are shown by one power wiring.
図2に示すように、車載配電システム7は、共用インレット3、充電機5、バッテリ10、インバータ22、車内コンセント4、車内コンセントスイッチ41、第1リレー30、第2リレー40、およびPLG−ECU(以下、単に「ECU」と記載する)62を含む。
As shown in FIG. 2, the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 includes a
共有インレット3は、後述の充電プラグ71(図3参照)を介して車外の充電装置が接続される場合に、電力の入力部となり、車外の給電装置の電源プラグが接続される場合に、電力の出力部となる。
The shared
そして、かかる共有インレット3は、電力配線によって充電器5および第1リレー30に接続され、信号配線によってECU62に接続される。具体的には、共有インレット3は、電力端子31、PISW端子32およびCPLT端子33を備える。なお、ここでは、図示を省略したが、共用インレット3には、接地端子も設けられる。
And this shared
電力端子31は、電力配線によって充電器5および第1リレー30に接続され、電力の入出力端子として機能する。また、PISW端子32およびCPLT端子33は、信号配線によってECU62に接続される。
The
かかるPISW端子32は、車両1の共用インレット3への充電プラグ71の接続状態(ON/OFF状態)が入力される端子であり、CPLT端子33は、車両1と車外の充電装置とを接続する接続ケーブルに設けられる制御部である後述のCCID(Charging Circuit Interrupt Device)72とECU62との間で、制御信号のやりとりを行うための端子である。
The
例えば、PISW端子32からECU62へは、充電プラグ71が接続されたことを示す信号がPISW端子32を介して出力される。また、CPLT端子33からECU62へは、例えば、電力端子31から充電器5へ入力中の電力の状態を示すコントロールパイロット信号が入力される。また、ECU62からCPLT端子33へは、例えば、充電中に何らかの問題が生じた場合に、電力の入力を遮断させる制御信号が出力される。
For example, a signal indicating that the charging
充電器5は、入力側が共用インレット3に接続され、出力側がバッテリ10に接続される。かかる充電器5は、ECU62による制御に従って動作し、共用インレット3から入力される交流の電力を直流の電力へ変換してバッテリ10へ出力する処理部である。充電器5は、充電用電圧センサ51と、コンバータ52とを備える。充電用電圧センサ51は、充電器5へ入力される電力の電圧を検出するセンサである。
The
また、コンバータ52は、入力される交流の電力を直流の電力へ変換するAC/DCコンバータである。なお、充電用電圧センサ51は、必ずしも充電器5内に設ける必要はなく、共用インレット3とコンバータ52および第1リレー30とを接続する配線部分の任意の箇所に設けてもよい。
The
バッテリ10は、入力側が充電器5に接続され、インバータ22に接続される。なお、図2では、バッテリ10の充電、共用インレット3または車内コンセント4への電力供給に関係する構成を選択的に図示している。
The
インバータ22は、入力側がバッテリ10に接続され、出力側が第2リレー40および第1リレー30に接続される。かかるインバータ22は、ECU62による制御に従って動作し、バッテリ10から入力される直流の電力を交流の電力へ変換して出力するDC/ACコンバータである。
The
第1リレー30は、ECU62による制御によってONとOFFとが切り替えられるリレーである。かかる第1リレー30は、例えば、共用インレット3に接続される給電装置へ電力を出力する場合にONとなる。
The
第2リレー40は、ECU62による制御によってONとOFFとが切り替えられるリレーである。かかる第2リレー40は、例えば、車内コンセント4に接続される電化製品へ電力を出力する場合にONとなる。
The
車内コンセント4は、車室内に設けられ、第2リレー40の出力側に接続される。かかる車内コンセント4は、一般の電化製品の電源プラグを接続することができ、家電製品へ交流の電力を供給することができる。
The vehicle interior outlet 4 is provided in the vehicle interior and is connected to the output side of the
車内コンセントスイッチ41は、ECU62に接続され、車内コンセント4の使用を所望する使用者が操作するスイッチ、もしくは、車内コンセント4への電源プラグの接続状態によってON/OFFするスイッチである。
The in-
かかる車内コンセントスイッチ41は、使用者によってONまたはOFFされる操作が行われた場合、もしくは、車内コンセント4に電源プラグが接続された場合に、その旨を示す信号をECU62へ出力する。つまり、車内コンセントスイッチ41は、車内コンセント4の使用要求を受け付ける要求受付部として機能し、使用要求を受け付けた場合に、その旨をECU62へ通知する。
The in-
ECU62は、共用インレット3、充電器5、インバータ22、車内コンセントスイッチ41、第1リレー30、および第2リレー40などに接続され、主に車外と電力のやりとりを行う際の車載配電システム7を含む車両1全体の配電制御を行う。
The
ECU62は、例えば、共用インレット3から入力される電力をバッテリ10へ充電する充電制御や、バッテリ10から共用インレット3または車内コンセント4への電力の供給制御などを行う。
The
次に、かかるECU62によって制御される車載配電システム7の動作について、図3〜図5を参照して説明する。図3〜図5は、実施形態に係る車載配電システム7の動作を説明するための説明図である。なお、以下の説明では、既に説明した車載配電システム7の各構成要素について、図2で付した符号と同様の符号を付することにより、その説明を省略する。
Next, the operation of the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 controlled by the
ここでは、車載配電システム7が奏する効果を明確にするため、まず、車載配電システム7の基本動作を説明した後に、車載配電システム7によって解決される課題を説明し、その後、課題を解決する車載配電システム7の動作を説明する。 Here, in order to clarify the effect achieved by the in-vehicle power distribution system 7, first, the basic operation of the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 will be described, and then the problem to be solved by the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 will be described, and then the in-vehicle system for solving the problem. The operation of the power distribution system 7 will be described.
図3に示すように、車載配電システム7は、充電経路L1と、第1給電経路L2と、第2給電経路L3と、とを備える。充電経路L1は、第1端子である共用インレット3から第1接続部P1、交流電力を直流電力へ変換する第1変換部として機能するコンバータ52、バッテリ10の順に接続される経路である。
As shown in FIG. 3, the on-vehicle power distribution system 7 includes a charging path L1, a first power feeding path L2, and a second power feeding path L3. The charging path L1 is a path that is connected in order from the
第1給電経路L2は、バッテリ10から直流電力を交流電力に変換する第2変換部として機能するインバータ22、第2接続部P2、第1リレー30、第1接続部P1、第1端子である共用インレット3の順に接続される経路である。第2給電経路L3は、バッテリ10からインバータ22、第2接続部P2、第2リレー40、第2端子である車内コンセント4の順に接続される経路である。
The first power supply path L2 is an
なお、図3には、共用インレット3にCCID72を備える充電プラグ71が接続され、車内コンセント4に電子機器8の電源プラグ81が接続された状態を示している。CCID72は、充電時の制御を行う制御部で、ECU62からの制御信号によって共用インレット3への電力の入力を遮断することが可能な装置である。
3 shows a state in which the charging
つまり、CCID72は、第1端子である共用インレット3よりも車外側の給電経路をECU62によって遮断可能な装置である。かかる共用インレット3には、CCID72を備えない充電プラグが接続される場合もある。
That is, the
なお、CCID72は、車両1に接続するプラグ部分ではなく、車両1側の充電プラグ71よりも車外の充電装置側(例えば、接続ケーブルの途中の部分)に設けるように構成してもよい。
Note that the
ECU62は、充電経路L1を使用してバッテリ10の充電を行う場合、第1リレー30および第2リレー40をOFFとした状態(少なくとも第1リレー30をOFFとした状態)で充電器5を動作させる。これにより、共用インレット3から入力される交流の電力は、充電器5によって直流の電力へ変換されてバッテリ10へ入力され、バッテリ10が充電される。
When the
また、ECU62は、第2給電経路L3を使用して車内コンセント4へ電力を供給する場合、第2リレー40をONとし、第1リレー30をOFFとした状態でインバータ22を動作させる。これにより、バッテリ10から出力される直流の電力は、インバータ22によって交流の電力へ変換されて車内コンセント4へ供給される。
Further, when the electric power is supplied to the in-vehicle outlet 4 using the second power supply path L3, the
第2給電経路L3を使用して電力を車内コンセント4へ電力を供給する場合、第1リレー30をOFFとすることで、充電経路L1と第2給電経路L3とが分離されるので、同時に充電経路L1を使用してバッテリ10の充電を行うことも可能である。
When power is supplied to the vehicle outlet 4 using the second power feeding path L3, the charging path L1 and the second power feeding path L3 are separated by turning off the
また、ECU62は、第1給電経路L2を使用して共用インレット3へ電力を供給する場合、第1リレー30をONとし、第2リレー40をOFFとした状態でインバータ22を動作させる。これにより、バッテリ10から出力される直流の電力は、インバータ22によって交流の電力へ変換されて共用インレット3へ供給される。なお、充電器5とバッテリ10との間に図示しない充電リレーを設けている場合には、この充電リレーについてもOFFするようにしたほうがよい。
Further, when the electric power is supplied to the
このように、ECU62は、第1給電経路L2を使用して共用インレット3へ電力を供給する場合に限り、第1リレー30をONとする。しかしながら、第1リレー30は、何らかの原因によって溶着が発生してON固着となるおそれがある。
As described above, the
そして、例えば、図4に示すように、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続され、且つ、第1リレー30がON固着しているような場合に、車内コンセント4から電子機器8へ電力を供給しようとすると、車載配電システム7には、電力の入力経路L4が形成される。
For example, as shown in FIG. 4, when the charging
かかる場合、共用インレット3から入力経路L4を経由して入力される電力と、図4に示す出力経路L5を経由してインバータ22から出力される電力との衝突が発生し、インバータ22が破損するおそれがある。
In such a case, a collision between the power input from the
また、かかる場合に、例えば、充電プラグ71から入力される電力の電圧が200Vであり、車内コンセント4に接続されている電子機器8が100Vで動作するものであると、電子機器8へ200Vの電圧がかかり、電子機器8が破損するおそれがある。
In such a case, for example, if the voltage of the electric power input from the charging
そこで、ECU62は、第2給電経路L3を使用して車内コンセント4へ電力を供給する場合、電力を供給する前に、第1リレー30がON固着しているか否かのチェックを行う。そして、ECU62は、第1リレー30がON固着していない場合に、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を許可する処理を行う。例えば、ECU62は、インバータ22を起動させる処理や、車内給電リレー40をONとする処理などを行う。一方、ECU62は、第1リレー30がON固着している場合に、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を禁止する処理を行う。
Therefore, when the electric power is supplied to the in-vehicle outlet 4 using the second power supply path L3, the
したがって、車載配電システム7によれば、第1リレー30がON固着した場合に、車部コンセント4に接続された電子機器8およびインバータ22の破損を防止することができる。
Therefore, according to the in-vehicle power distribution system 7, when the
具体的には、図5に示すように、ECU62は、充電プラグ71が共用インレット3に接続され、且つ第1リレー30がON固着している状態で、使用者が車内コンセントスイッチ41をONとした場合、まず、第1リレー30がOFF状態にないようであれば、第1リレー30をOFFする処理を行う。これにより、共用インレット3から経路L6経由で入力される電力が遮断される。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 5, the
そして、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かを判別することによって、共用インレット3から経路L6経由で入力される電力が遮断されたか否かを判定する。ここで、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51によって、0Vもしくは0V近辺の値以上の電圧が検出されているか否かを判定することによって、所定値以上の電圧が検知されたか否かを判別する。
Then, the
なお、このとき、共用インレット3に充電プラグが接続されていて充電制御を行っている場合、充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検出される。かかる場合、ECU62は、充電器5を停止させるとともに、CCID72(CPLT端子33)に対して充電プラグ71より車外側での充電経路L1の切断を指示する処理を行う。これにより、ECU62は、第1端子である共用インレット3よりも車外側の給電経路を遮断する。
At this time, when a charging plug is connected to the
そして、この処理を行っても、充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検出されるような場合には、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を禁止する処理を行う。例えば、ECU62は、インバータ22の動作を禁止する処理や、第2リレー40をOFFの状態に維持する処理などを行う。
If the
図5に示す例では、共用インレット3には、CCID72を備える充電プラグ71が接続されているため、ECU62からCCID72へ電力入力を中止させる制御信号を出力した場合、充電用電圧センサ51は、所定値以上の電圧を検知しない。
In the example illustrated in FIG. 5, since the charging
かかる場合、ECU62は、続いてインバータ22を起動し、経路L7を経由してインバータ22から第1リレー30へ電力を供給する。そして、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検知されるか否かを判別することで、第1リレー30がON固着しているか否かをチェックする。
In such a case, the
このとき、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知すれば、第1リレー30がON固着していると判定し、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知しなければ、第1リレー30がON固着していないと判定する。
At this time, if the charging
そして、ECU62は、第1リレー30がON固着していないことを条件として、第2リレー40をONとし、第2給電経路L3を使用して車内コンセント4へ電力を供給する。一方、第1リレー30がON固着していた場合、ECU62は、第2リレー40をOFFとし、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を禁止する。
Then, the
かかる車載配電システム7によれば、第1リレー30がON固着した状態で充電プラグ71が接続されている場合に、使用者が車内コンセント4を使用しようとしても、車内コンセント4に接続された電子機器8およびインバータ22の破損を防止することができる。
According to the in-vehicle power distribution system 7, when the charging
また、車載配電システム7は、第1リレー30のON固着チェックを行う前に、共用インレット3からの電力の入力を遮断する処理を行い、その結果、電力の入力が遮断されない場合にも、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を禁止する。
In addition, the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 performs a process of cutting off the power input from the
したがって、車載配電システム7によれば、第1リレー30がON固着した状態で、CCID72を備えない充電プラグが共用インレット3に接続されているような場合や、CCID72を備えた充電プラグ71が共用インレット3に接続されていても充電経路L1の遮断ができないような場合に、車内コンセント4に接続された電子機器8およびインバータ22の破損を防止することができる。
Therefore, according to the in-vehicle power distribution system 7, when the
次に、図6を参照して、ECU62が実行する処理について説明する。図6は、実施形態に係るECU62が実行する処理を示すフローチャートである。なお、ここでは、ECU62が行う第1リレー30のON固着チェックに関する処理について説明し、ECU62が行う他の処理については、説明を省略する。
Next, a process executed by the
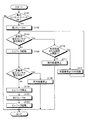
図6に示すように、ECU62は、まず、車内コンセントスイッチ41がONされたか否かを判定する(ステップS101)。そして、ECU62は、車内コンセントスイッチ41がONされていないと判定した場合(ステップS101,No)、処理を終了する。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
なお、ECU62は、処理を終了した場合、再度、図6に示す処理を開始する。このとき、基本的に第1リレー30はOFF状態にあることとし、もし、第1リレー30がOFF状態にないようであれば、第1リレー30をOFFする処理を行う。
When the process is terminated, the
一方、車内コンセントスイッチ41がONされたと判定した場合(ステップS101,Yes)、ECU62は、第2リレー40をOFFとする(ステップS102)。続いて、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かを判定する(ステップS103)。ここで、ECU62は、前述したように、充電用電圧センサ51によって、0Vもしくは0V近辺の値以上の電圧が検出されているか否かを判定することによって、所定値以上の電圧が検知されたか否かを判別する。
On the other hand, when it determines with the vehicle
そして、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知したと判定した場合(ステップS103,Yes)、処理をステップS110へ移す。一方、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知していないと判定した場合(ステップS103,No)、処理をステップS104へ移す。
If the
ステップS110において、ECU62は、判定回数または時間が閾値以下か否かの判定を行う。ここでの判定回数とは、ECU62がステップS103でYesと判定した回数である。また、時間とは、ECU62がステップS103でYesと連続して繰り返し判定した時間である。なお、判定回数と比較する閾値と、時間と比較する閾値とは異なる値である。
In step S110, the
そして、ECU62は、判定回数または時間が閾値以下でないと判定した場合、すなわち、判定回数または時間が閾値を超えたと判定した場合(ステップS110,No)、車内給電禁止を行い(ステップS111)、処理を終了する。ここでの車内給電禁止とは、第2給電経路L3を使用しての車内コンセント4への電力供給を禁止することである。
When the
一方、判定回数または時間が閾値以下であると判定した場合(ステップS110,Yes)、ECU62は、充電器5の動作を停止させるとともに、CCID72に充電プラグ71から共用インレット3への電力の入力経路を切断させることによって、第1端子である共用インレット3よりも車外側の給電経路を遮断する(ステップS112)。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the number of determinations or time is equal to or less than the threshold value (step S110, Yes), the
このように、充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検出された場合には、充電器5の停止とともにCCID72による充電プラグ51より車外側での充電経路の切断が試みられるので、CCID72を備える充電プラグが用いられている場合には、充電プラグ71が接続されている状態であっても、充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検出されない状態になって車内給電が可能な状態になる。
Thus, when the
また、CCID72を備えない充電プラグが接続されている場合には、CCID72(CPLT端子33)に対して充電プラグより車外側での充電経路の切断を指示しても充電用電圧センサ51によって所定値以上の電圧が検出されない状態にならないので、充電プラグが接続されている状態では車内給電を許可することはできないとして、車内給電を禁止する。
In addition, when a charging plug that does not include the
また、ステップS104において、ECU62は、インバータ22を起動させる。続いて、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かの判定を行う(ステップS105)。そして、ECU62は、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知した場合(ステップS105,Yes)、第1リレー30がON固着していると判定して、車内給電禁止を行い(ステップS109)、処理を終了する。
In step S104, the
一方、充電用電圧センサ51が所定値以上の電圧を検知しない場合(ステップS105,No)、ECU62は、第1リレー30がON固着していないと判定して、インバータ22を一旦停止させる(ステップS106)。
On the other hand, when the charging
続いて、ECU62は、第2リレー40をONとし(ステップS107)、その後、インバータ22を起動して(ステップS108)、処理を終了する。これにより、車内コンセント4の安全な使用が可能となる。
Subsequently, the
なお、上述した車載配電システム7の構成およびECU62が行う処理は、一例であり、種々の変形が可能である。次に、図7を参照して、変形例に係る車載配電システム7aの構成およびECU62aが行う処理について説明する。
The above-described configuration of the in-vehicle power distribution system 7 and the processing performed by the
図7は、変形例に係る車載配電システム7aの構成を示す説明図である。なお、図7では、図2に示す構成要素と同様の構成要素については、図2に示す符号と同一の符号を付している。
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing a configuration of the in-vehicle
図7に示すように、車載配電システム7aは、第1リレー30とインバータ22との間に給電用電圧センサ9を備える点を除き、図2に示す車載配電システム7と同様の構成である。かかる車載配電システム7aによれば、ECU62aは、インバータ22を起動しなくても、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続されて充電制御が行われている際のように、第1リレー30よりも共用インレット3や充電器5側の電圧が高くなっている状態にあるときに、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かを判定するだけで、第1リレー30のON固着を検知することができる。
As shown in FIG. 7, the in-vehicle
例えば、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続され、第1リレー30がON固着している場合、充電プラグ71から経路L8を経由して給電用電圧センサ9へ電力が入力される。このため、給電用電圧センサ9は、所定値以上の電圧を検知する。
For example, when the charging
一方、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続され、第1リレー30がON固着していない場合、給電用電圧センサ9は、所定値以上の電圧を検知しない。したがって、ECU62aは、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かを判定するだけで、第1リレー30のON固着を検知することができる。
On the other hand, when the charging
また、ECU62aは、給電用電圧センサ9の故障を考慮しつつ、第1リレー30がON固着していないことを検知する制御を行うこともできる。例えば、仮に、給電用電圧センサ9が故障していた場合、給電用電圧センサ9は、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続され、第1リレー30がON固着していても、所定値以上の電圧を検知しない。
Further, the
かかる場合に、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知しないからといって、使用者が車内コンセントスイッチ41をONした際に、第2リレー40をONとしてインバータ22を起動すると、図4に示す状況が発生し、電子機器8およびインバータ22が破損する。
In this case, when the power supply voltage sensor 9 does not detect a voltage higher than a predetermined value, when the user turns on the in-
そこで、ECU62aは、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続された状態で、インバータ22を駆動しておらず、第2リレー40をOFFしている状態にあるときに、第1リレー30をONに制御し、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知したか否かを判定する。
Therefore, the
ここで、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知する場合には、給電用電圧センサは正常であると判断する。なお、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知しない場合は、第1リレー30がOFF状態で固着しているか、若しくは、給電用電圧センサ9が故障しているかのいずれかである。
Here, when the power supply voltage sensor 9 detects a voltage equal to or higher than a predetermined value, it is determined that the power supply voltage sensor is normal. When the power supply voltage sensor 9 does not detect a voltage equal to or higher than a predetermined value, either the
このため、ECU62aは、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検知しない場合に、第1リレー30をOFFに制御するとともに、インバータ22を起動させる。その結果、ECU62aは、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検出すれば、給電用電圧センサ9は故障しておらず、第1リレー30がOFF状態で溶着している可能性があると判定する。
Therefore, the
なお、第1リレー30がOFF状態で固着状態にある場合には、充電電力がインバータ22や車内コンセント4側に流れてくることはないので、第2リレー40をONとして車内給電を許可するようにしてもよい。
Note that when the
なお、インバータ22を起動する前には、前述した車載配電システム7と同様に、共用インレット3へ車両1の外部から入力される電力を遮断する処理を行うことが望ましい。これにより、給電用電圧センサ9が故障している場合に、共用インレット3に充電プラグ71が接続されていても、インバータ22の起動時にインバータ22が破損することを防止することができる。
In addition, before starting the
一方、インバータ22を起動させても、給電用電圧センサ9が所定値以上の電圧を検出しなければ、給電用電圧センサ9が故障していると判定し、第1リレー30がON固着しているか否かを不明と判定して、第2リレー40をOFFとして車内給電を禁止する。なお、給電用電圧センサ9が故障している場合には、前述した車載配電システム7と同様に、給電用電圧センサ9を用いずに第1リレー30の溶着を検出するようにしてもよい。
On the other hand, even if the
かかる制御により、ECU62aは、給電用電圧センサ9の故障を考慮しつつ、第1リレー30がON固着していないことを検知して、車内給電を許可するので、車内コンセント4の安全な使用が可能となる。
By such control, the
上述したように、実施形態に係る給電制御装置は、交流電力の入出力が可能な第1端子と、交流電力の出力が可能な第2端子とを介して、端子に接続された装置と車載のバッテリとの間で電力のやりとりが可能な車両に搭載される。 As described above, the power supply control device according to the embodiment includes a device connected to a terminal and a vehicle mounted via the first terminal capable of inputting / outputting AC power and the second terminal capable of outputting AC power. It is mounted on a vehicle that can exchange power with other batteries.
給電制御装置は、前記第1端子から第1接続部、交流電力を直流電力に変換する第1変換部、前記バッテリの順に接続する充電経路を用いて電力をバッテリに充電する充電制御手段と、前記バッテリから直流電力を交流電力に変換する第2変換部、第2接続部、第1リレー、前記第1接続部、前記第1端子の順に接続する第1給電経路を用いて電力を供給する第1給電制御手段と、前記バッテリから前記第2変換部、前記第2接続部、第2リレー、前記第2端子の順に接続する第2給電経路を用いて電力を供給する第2給電制御手段とを備える。 The power supply control device includes a first connection unit from the first terminal, a first conversion unit that converts AC power into DC power, a charge control unit that charges the battery with power using a charging path that is connected in the order of the battery, Electric power is supplied from the battery by using a first power supply path that is connected in the order of a second conversion unit that converts DC power into AC power, a second connection unit, a first relay, the first connection unit, and the first terminal. First power supply control means, and second power supply control means for supplying power from the battery using a second power supply path that connects the second conversion unit, the second connection unit, the second relay, and the second terminal in this order. With.
さらに、給電制御装置は、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を開始する前に、前記第1リレーのON固着を検出する異常検出手段と、前記異常検出手段によって前記第1リレーのON固着が検出された場合には、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を禁止する給電禁止制御手段とを備える。したがって、実施形態に係る制御装置によれば、リレーのON固着による機器の破損を防止することができる。 Furthermore, the power supply control device includes an abnormality detection unit that detects ON fixation of the first relay before starting the supply of power by the second power supply control unit, and ON fixation of the first relay by the abnormality detection unit. Is detected, power supply prohibition control means for prohibiting the supply of power by the second power supply control means. Therefore, according to the control apparatus which concerns on embodiment, damage to the apparatus by ON fixation of a relay can be prevented.
なお、上述した実施形態に係る車載配電システム7、7aは、共用インレット3の内部に、車両1の外部から入力される電力を遮断するユニットを備える構成であってもよい。かかる構成によれば、CCIDを備えない充電プラグが共用インレット3に接続される場合にも、第1リレー30のON固着チェックを行う際に、共用インレット3側で車両1の外部から入力される電力を遮断することができる。
The in-vehicle
また、上述した実施形態では、共有インレット3を介して、車両1の外部から入力される電力によってバッテリ10が充電する場合について説明したが、実施形態に係る車載配電システム7、7aは、他の場合にも適用可能である。
Moreover, although embodiment mentioned above demonstrated the case where the
例えば、実施形態に係る車載配電システム7、7aは、車両に搭載されるソーラーパネルからバッテリ10へ電力が入力される場合や、非接触で車両へ電力を入力可能な施設からバッテリ10へ電力が入力される場合にも適用が可能である。
For example, in the on-vehicle
また、本願実施形態では、車載配電システムと、車外の充電装置や車内の電子機器との電力のやりとりを有線で行う場合を例に挙げて説明したが、電力のやりとりは、有線に限定するものではなく、無線によるもの(ワイヤレス給電)であってもよい。 In the embodiment of the present application, the case where power is exchanged between the in-vehicle power distribution system and the charging device outside the vehicle or the electronic device inside the vehicle is described as an example. However, the exchange of power is limited to wired. Instead, it may be wireless (wireless power feeding).
1 車両
22 インバータ
3 共用インレット
30 第1リレー
4 車内コンセント
40 第2リレー
41 車内コンセントスイッチ
5 充電器
51 充電用電圧センサ
52 コンバータ
6 制御部
62 ECU
71 充電プラグ
72 CCID
8 電子機器
81 電源プラグ
9 給電用電圧センサ
10 バッテリ
L1 充電経路
L2 第1給電経路
L3 第2給電経路
P1 第1接続部
P2 第2接続部
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
71
8
Claims (6)
前記第1端子から第1接続部、交流電力を直流電力に変換する第1変換部、前記バッテリの順に接続する充電経路を用いて電力を供給する充電制御手段と、
前記バッテリから直流電力を交流電力に変換する第2変換部、第2接続部、第1リレー、前記第1接続部、前記第1端子の順に接続する第1給電経路を用いて電力を供給する第1給電制御手段と、
前記バッテリから前記第2変換部、前記第2接続部、第2リレー、前記第2端子の順に接続する第2給電経路を用いて電力を供給する第2給電制御手段と、
前記第2接続部と前記第2変換部との間に設けられる給電用電圧センサと、
前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を開始する前に、前記第1リレーのON固着を検出する異常検出手段と、
前記異常検出手段によって前記第1リレーのON固着が検出された場合には、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を禁止する給電禁止制御手段と
を備え、
前記異常検出手段は、
前記第1リレーをOFF状態に制御し、前記第2変換部の動作を停止させた状態で、前記第1端子に充電プラグが接続されて前記充電制御手段によって充電制御が行われているときに、前記給電用電圧センサによって、所定値以上の電圧が検出された場合に、前記第1リレーがON固着状態にあると判定する
ことを特徴とする車両の給電制御装置。 To a vehicle capable of exchanging electric power between a device connected to the terminal and an in-vehicle battery via a first terminal capable of inputting / outputting AC power and a second terminal capable of outputting AC power A power supply control device installed;
A charging control means for supplying power using a charging path connected in order of the first battery, a first converter that converts AC power into DC power, a first converter that converts AC power into DC power;
Electric power is supplied from the battery by using a first power supply path that is connected in the order of a second conversion unit that converts DC power into AC power, a second connection unit, a first relay, the first connection unit, and the first terminal. First power supply control means;
Second power supply control means for supplying power from the battery using a second power supply path that connects the second converter, the second connector, the second relay, and the second terminal in this order;
A power supply voltage sensor provided between the second connection unit and the second conversion unit;
Before starting the supply of electric power by the second power supply control means, an abnormality detection means for detecting ON fixation of the first relay;
A power supply prohibition control means for prohibiting the supply of electric power by the second power supply control means when the abnormality detection means detects that the first relay is stuck on ;
The abnormality detection means includes
When the first relay is controlled to be in an OFF state and the operation of the second conversion unit is stopped, a charging plug is connected to the first terminal and charging control is performed by the charging control means A power supply control device for a vehicle, characterized in that, when a voltage equal to or higher than a predetermined value is detected by the power supply voltage sensor, the first relay is determined to be in an ON-fixed state .
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の車両の給電制御装置。 The abnormality detection means controls the first relay to be in an OFF state, and operates the second converter when the power input from the first terminal is cut off . When the voltage more than a predetermined value is detected by a charging voltage sensor provided at any position between the terminal, the first conversion unit, and the first relay, the first relay is in an ON-fixed state. The vehicle power supply control device according to claim 1, wherein the power supply control device is a vehicle power supply control device.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の車両の給電制御装置。 The abnormality detection unit is configured such that a voltage greater than a predetermined value is not detected by a charging voltage sensor provided at any position between the first terminal, the first conversion unit, and the first relay. In addition, when the second converter is operated in a state where the first relay is controlled to be in an OFF state, and when a voltage higher than a predetermined value is detected by the charging voltage sensor, the first converter The vehicle power supply control device according to claim 1, wherein the relay is determined to be in an ON-fixed state.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の車両の給電制御装置。 In the power supply prohibition control unit, a voltage greater than a predetermined value is detected by a charging voltage sensor provided at any position between the first terminal, the first conversion unit, and the first relay. In the case, the power supply control device for a vehicle according to claim 1, wherein supply of electric power by the second power supply control unit is prohibited.
ことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の車両の給電制御装置。 5. The vehicle according to claim 4, wherein when a voltage greater than or equal to a predetermined value is detected by the charging voltage sensor, control is performed so as to cut off a power feeding path outside the vehicle from the first terminal. 6. Power supply control device.
前記第1端子と前記第1変換部と前記第1リレーとの間の何れかの位置に設けられた充電用電圧センサによって、所定値以上の電圧が検出されている場合に、前記第1端子より車外側の給電経路を遮断する処理、および、前記充電用電圧センサによる電圧の検出結果を取得する処理を繰り返し、前記充電用電圧センサによって連続して所定値以上の電圧が検知された回数または時間が閾値を超えた場合に、前記第2給電制御手段による電力の供給を禁止する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の車両の給電制御装置。 The power supply prohibition control means includes
The first terminal when a voltage equal to or higher than a predetermined value is detected by a charging voltage sensor provided at any position between the first terminal, the first conversion unit, and the first relay. process for cutting off a more exterior side of the feed path, and repeats the process of acquiring the detection result of the voltage by the charging voltage sensor, number voltage higher than a predetermined value continuously by the charging voltage sensor is detected or 2. The vehicle power supply control device according to claim 1, wherein when the time exceeds a threshold value, the power supply by the second power supply control unit is prohibited . 3.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013227572A JP6109043B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2013-10-31 | Vehicle power supply control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013227572A JP6109043B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2013-10-31 | Vehicle power supply control device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015089290A JP2015089290A (en) | 2015-05-07 |
| JP6109043B2 true JP6109043B2 (en) | 2017-04-05 |
Family
ID=53051537
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013227572A Active JP6109043B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2013-10-31 | Vehicle power supply control device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6109043B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6567935B2 (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2019-08-28 | 株式会社Subaru | Vehicle power supply device and failure detection method thereof |
| JP6595934B2 (en) * | 2016-02-25 | 2019-10-23 | 株式会社Subaru | Vehicle power supply |
| CN106364429B (en) * | 2016-09-07 | 2020-04-24 | 纳恩博(北京)科技有限公司 | Charging control method, device and system |
| US20220094178A1 (en) * | 2018-11-30 | 2022-03-24 | Koki Holdings Co., Ltd. | Battery pack and electric device system |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013070474A (en) * | 2011-09-21 | 2013-04-18 | Toyota Motor Corp | Vehicle and control method of vehicle |
| JP5234159B2 (en) * | 2011-10-31 | 2013-07-10 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | A vehicle including a power storage unit capable of discharging (power feeding) to an external load, a discharge system including the vehicle and a power cable, a discharge control method for the power storage unit, and a device outside the vehicle used in the discharge system. |
| JP5821595B2 (en) * | 2011-12-09 | 2015-11-24 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Power supply system |
| JP2013169087A (en) * | 2012-02-15 | 2013-08-29 | Hitachi Vehicle Energy Ltd | Abnormality detecting device of power supply device and electric drive device of rotating electric machine provided with the same |
| JP5821715B2 (en) * | 2012-03-09 | 2015-11-24 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Power storage system, vehicle charging control device, and abnormality detection method |
-
2013
- 2013-10-31 JP JP2013227572A patent/JP6109043B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015089290A (en) | 2015-05-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10994622B2 (en) | Vehicle and control method thereof | |
| EP3046198B1 (en) | Electric power storage system | |
| KR101901798B1 (en) | Plug-in vehicle and method of controlling thereof | |
| US9114716B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for high-voltage DC charging of battery-electric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles | |
| JP5671249B2 (en) | Electric car | |
| EP2542439B1 (en) | Vehicle with external charging | |
| EP2802891B1 (en) | System and method for high voltage cable detection in hybrid vehicles | |
| US11325500B2 (en) | On-board electrical network for a motor vehicle | |
| EP2639099A1 (en) | Electric vehicle power supply system, control method thereof, and electric vehicle | |
| JP2017099250A (en) | Overdischarge prevention device and method of battery for vehicle | |
| JP2016510706A (en) | Operation method and arrangement of hybrid electric vehicle | |
| CN108604803B (en) | Integrated battery safety interlock | |
| KR20140129152A (en) | High voltage cable detection using rotating machine in hybrid vehicles | |
| CN105599711B (en) | The supply unit of vehicle | |
| JP6109043B2 (en) | Vehicle power supply control device | |
| JP2013240191A (en) | Vehicle and control method for vehicle | |
| US9108522B2 (en) | Vehicle-mounted controller | |
| EP2986466B1 (en) | Method and arrangement for error detection during charging of an energy storage system | |
| CN110816317A (en) | Vehicle-mounted control system and vehicle | |
| JP2010213552A (en) | Power supply unit and failure detection method of the same | |
| JP5918103B2 (en) | Power supply | |
| JP5884802B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP6151944B2 (en) | Power supply system | |
| JP2013034328A (en) | Electric vehicle | |
| JP5675541B2 (en) | vehicle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160119 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160905 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160913 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161109 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170214 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170307 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6109043 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |