JP6007409B2 - Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method - Google Patents
Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6007409B2 JP6007409B2 JP2012249005A JP2012249005A JP6007409B2 JP 6007409 B2 JP6007409 B2 JP 6007409B2 JP 2012249005 A JP2012249005 A JP 2012249005A JP 2012249005 A JP2012249005 A JP 2012249005A JP 6007409 B2 JP6007409 B2 JP 6007409B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- node
- arrival determination
- autonomous mobile
- determination area
- mobile device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 19
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Position, Course, Altitude, Or Attitude Of Moving Bodies (AREA)
Description
本発明は、複数のノードを用いて目的地へ移動するための経路を生成し、この経路に沿って目的地へ移動する自律移動装置及び自律移動方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an autonomous mobile device and an autonomous mobile method for generating a route for moving to a destination using a plurality of nodes and moving to the destination along the route.
建物(例えば、病院又は商業施設等)内の通路を移動する自律移動装置が提案されている。自律移動装置は、自己位置と目的地との間に、複数のノードを通る経路を生成する。そして、自律移動装置は、その経路に沿って移動する。詳細には、自律移動装置は、経路上のノードを当面の通過点目標として移動し、そのノードに到達すると、到達したノードに接続する経路上の次のノードを当面の通過点目標に切り替える。そして、次のノードに向って移動する。このように、自律移動装置は、当面の通過点目標を順々に変え、当面の通過点目標のノードに向って移動し続けることで、経路に沿って移動する。 An autonomous mobile device that moves through a passage in a building (for example, a hospital or a commercial facility) has been proposed. The autonomous mobile device generates a route passing through a plurality of nodes between its own position and the destination. Then, the autonomous mobile device moves along the route. Specifically, the autonomous mobile device moves a node on the route as a passing point target for the time being, and when that node is reached, switches the next node on the route connected to the reached node to the current passing point target. Then, it moves toward the next node. In this way, the autonomous mobile device moves along the route by changing the current passing point target in order and continuing to move toward the current passing point target node.
しかし、例えば、当面の通過点目標のノードの位置に人又は他の移動装置が存在し、自律移動装置が目的地に到達できない場合がある。この場合、自律移動装置は、人又は移動装置を障害物とみなして障害物に接近することを避けるため、ノードに近づくことができない。そのため、自律移動装置は、障害物が当面の通過点目標の位置から別の位置へ移動するまで、当面の通過点目標のノードに近づいたり離れたりして、そのノードの手前で待機したような状態になる。 However, for example, there may be a person or other mobile device at the location of the current target node of the passing point, and the autonomous mobile device cannot reach the destination. In this case, the autonomous mobile device cannot approach the node to avoid approaching the obstacle by regarding the person or the mobile device as an obstacle. Therefore, the autonomous mobile device approaches or leaves the node of the current pass point target and waits in front of that node until the obstacle moves from the current pass point target position to another position. It becomes a state.
そこで、ノードに予め定めた距離に近づくとノードに到達したと判定する自律移動装置が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 Then, the autonomous mobile apparatus which determines with having reached the node when approaching the predetermined distance to a node is proposed (for example, refer patent document 1).
図11は、経路に沿って移動する従来の自律移動装置を説明する平面図である。図11に示すように、従来の自律移動装置1は、まず、当面の通過点目標であるノードn1に向って移動する。そして、ノードn1に接近して、ノードn1からの距離が所定距離rに達したとき、ノードn1に到達したと判断する。すると、自律移動装置1は、次のノードn2を当面の通過点目標に切り替え、ノードn2に向って移動する。このように、自律移動装置1は、ノードn1、n2、n3により生成される経路2に沿って、目的地へ移動する。この自律移動装置1は、ノードに到達したか否かを、ノードから所定距離rだけ離れた位置で判定することで、障害物がノードn1、n2、n3上に存在したとしても、その障害物を避けて、次のノードへ向って移動することができる。
FIG. 11 is a plan view illustrating a conventional autonomous mobile device that moves along a route. As shown in FIG. 11, the conventional autonomous
しかしながら、ノードは曲がり角又は交差点等の方向転換のための場所に設定されることが多いため、ノードn1より所定距離rだけ手前で次のノードn2へ向って方向転換すると、通路の角に接近してしまうことがある。逆に、その対策として所定距離rを短くすると、自律移動装置1は、障害物とすれ違うことができなくなることがある。すなわち、従来の自律移動装置1は、所定距離rに近づくとノードに到達したと判定するようにしているが、ノードの位置、通路の形状、経路の形状等によっては、通路をスムーズに移動できない可能性がある。
However, since the node is often set at a turning point such as a corner or an intersection, when the direction is changed toward the next node n2 by a predetermined distance r before the node n1, the node approaches the corner of the passage. May end up. Conversely, if the predetermined distance r is shortened as a countermeasure, the autonomous
本発明は、ノードの位置、通路の形状、経路の形状等によらず、スムーズに移動することが可能な自律移動装置及び自律移動方法を提供することを目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to provide an autonomous mobile device and an autonomous mobile method that can move smoothly regardless of the position of a node, the shape of a passage, the shape of a route, and the like.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明の自律移動装置は、車体と、前記車体を移動させる移動部と、前記車体の自己位置を取得する自己位置取得部と、複数のノードの位置と前記複数のノードをそれぞれ囲む到達判定エリアの大きさと地図情報とを記憶する記憶部と、
前記複数のノードを接続して前記自己位置から目的地までの経路を生成する経路生成部と、
当面の通過点目標としたノードを囲む前記到達判定エリアに到達すると、次のノードを当面の通過点目標として切り替えて前記次のノードへ向って移動させる移動制御部と、を備え、前記到達判定エリアは、囲んでいるノードと前記地図情報に含まれる通路の壁との間隔に応じて大きさが異なることを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above problems, an autonomous mobile device of the present invention includes a vehicle body, a moving unit that moves the vehicle body, a self-position acquisition unit that acquires the self-position of the vehicle body, the positions of a plurality of nodes, and the plurality of nodes. A storage unit for storing the size of the arrival determination area surrounding each of the nodes and map information;
A route generator that connects the plurality of nodes to generate a route from the self-location to a destination;
A movement control unit that switches the next node as the current passing point target and moves it toward the next node when the arrival determining area surrounding the node that is the current passing point target is reached. The area is characterized in that the size differs according to the distance between the enclosing node and the wall of the passage included in the map information .
本発明によれば、ノードの位置箇所、通路の形状、経路の形状等によらず、スムーズに移動することが可能な自律移動装置及び自律移動方法を提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the autonomous moving apparatus and the autonomous moving method which can move smoothly irrespective of the position location of a node, the shape of a channel | path, the shape of a path | route, etc. can be provided.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、同じ構成要素には同じ符号を付しており、説明を省略する場合もある。また、図面は理解しやすくするために、それぞれの構成要素を主体に模式的に示している。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the same component and description may be abbreviate | omitted. In addition, for easy understanding, the drawings schematically show each component mainly.
(実施の形態1)
図1(a)、図1(b)は、本発明の実施の形態1にかかる自律移動装置11を説明するための図である。図1(a)は、通路における自律移動装置の移動を説明するための模式図であり、図1(b)は、自律移動装置11のブロック図である。この自律移動装置11は、建物(例えば、病院又は商業施設等)内の通路21を移動するものである。
(Embodiment 1)
Fig.1 (a) and FIG.1 (b) are the figures for demonstrating the autonomous
図1(a)、図1(b)に示すように、自律移動装置11は、車体12と、移動部13と、自己位置取得部14と、記憶部15と、経路生成部16と、移動制御部17と、を備える。さらに、自律移動装置11は、外部の障害物および建物内の通路の壁20等を検出する外部環境情報取得部18と、電池19と、到達判定エリア生成部31を備える。なお、上述した、自己位置取得部14、記憶部15、経路生成部16、移動制御部17、及び、到達判定エリア生成部31は、制御部23に含まれる。
As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, the autonomous
最初に、自律移動装置11の各構成について説明する。
First, each configuration of the autonomous
移動部13は、電池19で駆動されるモータ(図示せず)と、このモータにより回転する4つの駆動輪(図示せず)を有する。このモータには、その回転数及び回転速度を計測するエンコーダ(図示せず)が設けられている。移動制御部17は、このエンコーダの出力によって移動距離および移動方向を知ることができる。
The moving
自己位置取得部14は、移動部13のエンコーダの出力より、自律移動装置11の位置を算出する。具体的には、自己位置取得部14は、エンコーダの出力、外部環境情報取得部18で得られるセンサ情報、及び、地図情報記憶部に記憶された建物内の通路の壁20の位置情報などを比較することにより、自律移動装置11の車体12の位置を取得する。
The self
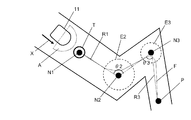
記憶部15は、地図情報記憶部に、ノードN1、N2、N3の位置、及び、ノードN2、N3を囲む到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさ、を記憶している。到達判定エリアE2、E3は、後述する到達判定エリア生成部31により生成される。地図情報記憶部は、ノードN1、N2、N3及び到達判定エリアE2、E3以外に、建物内の通路21の壁20の配置等の地図情報を記録している。記憶部15は、複数の到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさを記憶する。なお、本実施の形態においては、複数の到達判定エリアの大きさには、少なくとも異なる2つの大きさがある。記憶部15に記憶される到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさは、ノードの配置位置、通路21の形状又は移動経路の形状に合わせて設定されている。本実施の形態においては、到達判定エリアの形状は、円形状である。
The
経路生成部16は、自律移動装置11の位置から目的地Pまでの移動経路を生成する。移動経路は、自律移動装置11を自律移動させるための経路である。経路生成部16は、まず、自己位置取得部14で取得される自律移動装置11の位置(以下、現在位置)からのコストが一番小さなノードN1を、現在位置から最初に到達すべきノードである始点ノードとして選択する。ここでのコストとは、現在位置から各ノードN1、N2、N3に到達するための距離を示し、コストが小さいとは、距離が短いことを示す。そして、経路生成部16は、始点ノードから目的地Pのノードまでの間において、所定の条件に従ってノードN1、N2、N3を選択し、これらのノードより移動経路を生成する。図1(a)において、自律移動装置11が移動経路に沿って移動した軌跡を、移動跡Fとして示す。
The
移動制御部17は、移動部13を制御して自律移動装置11を移動経路に沿って目的地Pに向けて移動させる。具体的に、移動制御部17は、移動経路において一番コストが小さいノードを当面の通過点目標Tとし、この当面の通過点目標Tに向かって移動する。そして、移動制御部17は、当面の通過点目標TとしたノードN1に到達すると、当面の通過点目標Tを次のノードN2に切り替え、次のノードN2へ向って移動するように移動部13を制御する。そして、ノードN2の到達判定エリアE2に車体12が入ると、移動制御部17は、当面の通過点目標Tを、次のノードN3に切り替える。すると、自律移動装置11は、新たな当面の通過点目標TとなるノードN3に向って移動する。ノードN3の到達判定エリアE3に、車体12が入ると、移動制御部17は、当面の通過点目標Tを、経路を形成する次のノード(目的地P)に切り替える。
The
外部環境情報取得部18は、車体12の前面下部中央に備えられてその前方周辺をスキャンするライダー(Light Detection And Ranging)で構成されている。ライダー(別名、レーザレーダ)は、そのスキャン面内でレーザビームを振ることで、所定の半径を有する半円形の障害物検出エリアAにおいて、物体までの距離を取得する。外部環境情報取得部18は、一定の周期のもとで間欠的にスキャンを行ない、1回のスキャン毎に取得する距離データの集合を各時点におけるセンサ情報として時系列的に記憶部15に記憶させる。また、外部環境情報取得部18は、ライダー(レーザレーダ)の他に、超音波センサなどを備えてもよい。
The external environment
到達判定エリア生成部31は、各ノードN2、N3において、それらノードに到達したと判定するための所定半径の円形状(又は)の到達判定エリアを生成する。到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさは、移動経路の形状に合わせて変わるものであり、円形状の到達判定エリアE2、E3の中心は、ノードN2、N3である。なお、到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさは、移動経路で隣り合う第1ノード及び第2ノードを直線で結ぶことで形成されるリンク間角度θ2、θ3に応じて異なる。ここで、ノードN2を中心に隣り合う第1ノードはN3であり、ノードN2を中心に隣り合う第2ノードはN1である。また、ノードN1とノードN2とを結ぶ直線をリンクR1とし、ノードN2とノードN3を結ぶ直線をリンクR2とすると、リンクR1とリンクR2との間に形成される狭い方の角度がリンク間角度θ2である。また、ノードN3を中心に隣り合う第1ノードは目的地Pであり、ノードN3を中心に隣り合う第2ノードはノードN2である。ノードN3と目的地Pとを結ぶ直線をリンクR3とすると、リンクR2とリンクR3との間に形成される狭い方の角度がリンク間角度θ3である。到達判定エリアE2、E3の半径は、リンク間角度θ2、θ3に略比例した長さである。よって、リンク間角度θ2がリンク間角度θ3よりも大きいと、到達判定エリアE2の半径は、到達判定エリアE3の半径よりも長くなる。そのため、通路21の曲り角度が小さい(リンク間角度が大きい)と、到達判定エリアE2の半径は長くなり、自律移動装置11は、ノードN2より離れた位置で当面の通過点目標Tを目的地Pに設定することになる。また、通路21の曲り角度が大きい(リンク間角度が小さい)と、到達判定エリアE3の半径は短くなり、自律移動装置11は、ノードN3の手前で当面の通過点目標Tを目的地Pに設定することになる。
The arrival determination
このように、本実施の形態1の自律移動装置11では、ノード間を結ぶリンク間角度が小さい場合、到達判定エリアを小さくすることで、自律移動装置11が移動方向を大きく変えてもノードより離れた箇所で移動方向を変えないようにして、通路21の角22に接近することを防止している。つまり、本実施の形態1の自律移動装置11は、到達判定エリアの大きさをリンク間角度に基づいて変えることで、通路21の角22によって移動を妨げられることがなくなり、スムーズに移動することができる。これは、ノードN1、N2、N3は、通路21の交差点及び曲り角に設定されることが多いため、通路21が大きく曲る場合、曲り角の到達判定エリアを小さくすることで、自律移動装置11が角22より離れて移動することができるためである。
As described above, in the autonomous
ここで、到達判定エリアE2、E3が同じ大きさであると、自律移動装置11の進路方向S3に角22が重なることがあり、自律移動装置11のスムーズな移動の妨げとなる場合がある。この場合について、図2を用いて説明する。
Here, if the arrival determination areas E2 and E3 have the same size, the
図2は、到達判定エリアE2と到達判定エリアE3の大きさが同じ場合の通路の模式図である。図2に示すように、到達判定エリアE3に到達した自律移動装置11の進路方向S3には、通路21の角22が存在する。その結果、自律移動装置11は、進路方向S3へ移動する途中に外部環境情報取得部18で通路21の角22を検出し、通路21の角22を回避して移動するため、スムーズに通路を移動することができない。
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a passage when the arrival determination area E2 and the arrival determination area E3 have the same size. As shown in FIG. 2, a
それに対し、本実施の形態1の自律移動装置11は、到達判定エリアの大きさを通路の形状又は経路の形状に合わせて変えることで、スムーズな移動を可能としている。
On the other hand, the autonomous
さらに、本実施の形態1の自律移動装置11は、リンク間角度に応じて到達判定エリアの大きさを変えることで、到達判定エリアを経路の形状にさらに適した大きさにして、さらにスムーズに通路を移動することができる。なお、到達判定エリアE2、E3の大きさは、自律移動装置11の到達判定エリア生成部31で、自動的にリンク間角度θ2、θ3により設定される。具体的には、図1(a)に示すように、到達判定エリア生成部31は、ノードN2を中心に経路の隣り合う第1ノードとなるノードN3及び第2ノードとなるノードN1を直線で結ぶことで形成されるリンク間角度θ2に応じて、ノードN2の到達判定エリアE2の大きさを設定する。
Furthermore, the autonomous
本実施の形態1にかかる自律移動装置11の自律移動方法のフローチャートについて、図3、図4を用いて説明する。図3は、本実施の形態1にかかる自律移動装置11の移動開始前のフローチャートであり、図4は、本実施の形態1にかかる自律移動装置11の移動途中のフローチャートである。
The flowchart of the autonomous movement method of the autonomous
まず、図3のフローチャートについて説明する。 First, the flowchart of FIG. 3 will be described.
図3に示すように、最初に、自律移動装置11が移動準備を開始すると(ステップS01)、記憶部15の地図情報記憶部から地図情報を読み込む(ステップS02)。
As shown in FIG. 3, first, when the autonomous
次に、ユーザにより予め設定されて記憶部15に記憶された目的地Pを取得する(ステップS03)。
Next, the destination P preset by the user and stored in the
次に、目的地Pに基づいて、経路生成部16で、始点ノードを設定し、経路を生成する(ステップS04)。ここで、始点ノードは、例えば、自己位置取得部14で算出される車体12の位置から到達するためのコストが一番小さなノードである。また、経路は、複数のノードを用いて、始点ノードと目的地Pとを結んだ経路である。経路生成部16で生成された経路は、記憶部15に記憶される。なお、始点ノードは、コストが一番小さいノード以外を選択することも可能である。
Next, based on the destination P, the
次に、自律移動装置11は、到達判定エリア生成部31で、ステップS02で生成された経路より、到達判定エリアを生成する(ステップS05)。
Next, the autonomous
次に、目標のノードを中心に経路の隣り合う第1ノード及び第2ノードを直線で結ぶことで形成されるリンク間角度が、第1所定値(例えば、60°)以下か否かを判定する(ステップS06)。リンク間角度が第1所定値以下の場合(ステップS06の「yes」)、到達判定エリアを小さくする(ステップS07)。 Next, it is determined whether or not the inter-link angle formed by connecting the first node and the second node adjacent to each other with a straight line around the target node is equal to or less than a first predetermined value (for example, 60 °). (Step S06). When the inter-link angle is equal to or smaller than the first predetermined value (“yes” in step S06), the arrival determination area is reduced (step S07).
また、リンク間角度が第1所定値より大きい場合(ステップS06の「no」)は、リンク間角度が第2所定値(90°)より大きいか否かを判定する(ステップS08)。リンク間角度が第2所定値より大きい場合(ステップS08の「yes」)、到達判定エリアを大きくする(ステップS09)。 If the inter-link angle is larger than the first predetermined value (“no” in step S06), it is determined whether the inter-link angle is larger than the second predetermined value (90 °) (step S08). When the inter-link angle is larger than the second predetermined value (“yes” in step S08), the arrival determination area is increased (step S09).
そして、ステップS07、S09の後、又は、リンク間角度が第1所定値以上かつ第2所定値以下の場合(ステップS06の「no」でステップS08の「no」)、ステップS10に進む。 Then, after Steps S07 and S09, or when the inter-link angle is not less than the first predetermined value and not more than the second predetermined value (“no” in Step S06 and “no” in Step S08), the process proceeds to Step S10.
本実施の形態1では、ステップS06〜S10を行うことで、リンク間角度の大きさに略比例する大きさの到達判定エリアを設定している。なお、本実施の形態1では、始点ノード及び目的地Pを除いたすべてのノードに対して、前述のステップS06〜S10を行うことで、到達判定エリアを設定している。
In this
ここで、ステップS06〜S10の具体的な判定については、例えば、リンク間角度が0°より大きく30°以下の場合に到達判定エリアの半径を0.2mとし、リンク間角度が30°より大きく60°以下の場合に到達判定エリアの半径を0.4mとし、リンク間角度が60°より大きく90°以下の場合に到達判定エリアの半径を0.6mとする。また、さらに細かく到達判定エリアを設定する場合は、到達判定エリアの半径をリンク間角度に比例した値として、 到達判定エリアの半径[m]=0.3+0.2×リンク間角度(rad) から求めても良い。 Here, for specific determinations in steps S06 to S10, for example, when the inter-link angle is greater than 0 ° and 30 ° or less, the radius of the arrival determination area is 0.2 m, and the inter-link angle is greater than 30 °. The radius of the arrival determination area is 0.4 m when the angle is 60 ° or less, and the radius of the arrival determination area is 0.6 m when the inter-link angle is greater than 60 ° and 90 ° or less. Further, when setting the arrival determination area in more detail, the radius of the arrival determination area is set to a value proportional to the inter-link angle, and the radius of the arrival determination area [m] = 0.3 + 0.2 × inter-link angle (rad) You may ask.
次に、以上算出された到達判定エリアが通路21の壁と交わっているか否かを判定する(ステップS10)。 Next, it is determined whether or not the calculated arrival determination area intersects the wall of the passage 21 (step S10).
そして、到達判定エリアが通路21の壁と交わっている場合(ステップS10の「yes9」)は、到達判定エリアの大きさを、壁に交わらなくなる大きさまで小さくした後、ステップS12に移動する。 If the arrival determination area intersects with the wall of the passage 21 (“yes9” in step S10), the size of the arrival determination area is reduced to a size that does not intersect the wall, and the process moves to step S12.
また、到達判定エリアが通路21の壁と交わっていない場合(ステップS10の「no」)は、そのままステップS12に異動する。 If the arrival determination area does not intersect with the wall of the passage 21 (“no” in step S10), the process directly moves to step S12.
このように、ステップS02〜S11を行うことで、移動準備が完了し、自律移動装置11は、移動を開始する(ステップS12)。
Thus, by performing steps S02 to S11, the preparation for movement is completed, and the autonomous
続いて、図4のフローチャートについて説明する。 Next, the flowchart of FIG. 4 will be described.
図4に示すように、最初に、自律移動装置11が移動中(ステップS21)に、次の目標のノードの自律移動装置が到着可能か否かを判定する(ステップS22)。具体的には、外部環境情報取得部18により取得した情報に基づいて、目的としている目標ノードに車体12が到達できるか否かを制御部23で判定する。
As shown in FIG. 4, first, it is determined whether or not the autonomous mobile device of the next target node can arrive while the autonomous
そして、目標のノードに到着できないと判定された場合(ステップS22の「no」)、その目標のノードの到達判定エリアの大きさを大きくする(ステップS23)。具体的には、目標のノードの周辺に障害物が存在するなどして目標のノードへ自律移動装置11の到着不可能であると判定された場合、到達判定エリアの半径を0.3mから0.4mに変更するなどすることで、目標のノードへ自律移動装置11を到着可能にする。
If it is determined that the target node cannot be reached (“no” in step S22), the size of the arrival determination area of the target node is increased (step S23). Specifically, when it is determined that the autonomous
また、目標のノードに到着可能であると判定された場合(ステップS22の「yes」)、ノード移動を開始してから所定時間以内か否かを判定する(ステップS24)。 If it is determined that the target node can be reached (“yes” in step S22), it is determined whether or not it is within a predetermined time after starting the node movement (step S24).
そして、ノード移動を開始してから所持時間以内でない場合(ステップS24の「no」)、目標のノードの到達判定エリアの大きさを大きくする(ステップS25)。これは、ノード移動を開始してから所定時間を経過している場合は、例えば、目標のノードの周辺に障害物などが存在するなどして目標のノードへ自律移動装置11が到着できないと判断するためである。
If it is not within the possession time after the start of node movement (“no” in step S24), the size of the target node arrival determination area is increased (step S25). For example, when a predetermined time has elapsed since the start of node movement, it is determined that the autonomous
次に、ステップS23、S25の後、又は、ノード移動を開始してから所定時間以内である場合(ステップS24の「yes」)、目標のノードに到着しているか否かを判定する(ステップS26)。 Next, after steps S23 and S25, or when it is within a predetermined time since the start of node movement (“yes” in step S24), it is determined whether or not the target node has been reached (step S26). ).
そして、目標のノードに到着している場合(ステップS27の「yes」)、ノード移動を完了する。 If the node has arrived at the target node (“yes” in step S27), the node movement is completed.
また、目標のノードに到着していない場合(ステップS27の「no」)、ステップS22に戻って、ノードに到着可能か否かの判定を繰り返す。 If the node has not arrived at the target node (“no” in step S27), the process returns to step S22 to repeat the determination of whether or not the node can be reached.
本実施の形態1では、図3に示す移動準備を完了した後に、各ノード間で図4に示すノード間移動を行い、目的地Pに向けて移動する。このように移動を制御することで、ノードの位置箇所、通路の形状、経路の形状等によらず、スムーズに移動することが可能な自律移動方法又は自律移動装置を提供することができる。 In the first embodiment, after the movement preparation shown in FIG. 3 is completed, the movement between nodes shown in FIG. 4 is performed between the nodes, and the movement toward the destination P is performed. By controlling the movement in this way, it is possible to provide an autonomous movement method or an autonomous mobile device that can move smoothly regardless of the location of the node, the shape of the passage, the shape of the route, and the like.
(実施の形態2)
図5は、本発明の実施の形態2にかかる自律移動装置の移動を説明するための模式図である。図6は、自律移動装置11の移動速度の変化を示す図である。図6(a)は到達判定エリアの大きさが異なる自律移動装置11の移動速度変化を示す図であり、図6(b)は到達判定エリアのない自律移動装置11の移動速度変化を示す図であり、図6(c)は到達判定エリアの大きさが同じ自律移動装置の移動速度変化を示す図である。
(Embodiment 2)
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram for explaining the movement of the autonomous mobile device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating changes in the moving speed of the autonomous
以下、本実施の形態2が実施の形態1と異なる点について、図面を参照しながら説明する。 Hereinafter, differences of the second embodiment from the first embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings.
本実施の形態2の自律移動装置11の移動制御部17は、図6(a)に示す速度変化で車体の移動速度を制御して、車体の位置と当面の通過点目標Tとの間隔が所定距離以下になると、車体12の位置と当面の通過点目標Tとの間隔に略比例した移動速度にして移動部13を制御する。
The
例えば、図5に示す経路に沿って自律移動装置11が移動跡Fを移動する場合、自律移動装置11の移動制御部17は、図6(a)に示す速度変化で移動速度を制御する。その結果、到達判定エリアE2に到達した自律移動装置11は、高速のまま大きな弧を描いて曲ってノードN3に向って移動し、到達判定エリアE3に到達して、当面の通過点目標Tを目的地Pに設定した自律移動装置11は、低速で小さな弧を描いて曲り、目的地Pに向って移動する。
For example, when the autonomous
本実施の形態2の自律移動装置11の移動制御部17は、上述したように、車体12の位置と当面の通過点目標Tとの間隔が所定距離(減速距離)以下になると、車体の位置と当面の通過点目標Tとの間隔に略比例した移動速度に制御する。そのため、減速距離が到達判定エリアの半径より短いと、高速のまま自律移動装置11は曲ることができ、減速距離が到達判定エリアの半径より長いと、減速して自律移動装置11は曲ることができる。例えば、ノードのリンク間角度が小さいと、到達判定エリアの半径が減速距離より短い場合がある。その場合、本実施の形態2の自律移動装置11は、減速して到達判定エリアに入り、減速して移動方向を変える。その結果、自律移動装置11は、当面の通過点目標Tへ向ってスムーズに移動することができる。
As described above, the
ここで、参考までに、到達判定エリアが設定されていない場合の例について図6(b)を用いて説明し、到達判定エリアの大きさが同じ場合の例について図6(c)を用いて説明する。 Here, for reference, an example in which the arrival determination area is not set will be described with reference to FIG. 6B, and an example in which the arrival determination area has the same size will be described with reference to FIG. explain.
到達判定エリアが設定されていない場合は、図6(b)に示すように、自律移動装置11の移動制御部17は、各ノードに到達する際に移動速度を減速させて、ノードに到達した時点で停止するように制御する。
When the arrival determination area is not set, as shown in FIG. 6B, the
到達判定エリアE2と到達判定エリアE3との大きさが同じであり、且つ、移動速度が一定の場合、自律移動装置11の移動速度の変化は、図6(c)に示すようになる。その場合、自律移動装置11は、高速で移動しながら移動方向を変えなければならない。リンク間角度θ3が小さい場合、自律移動装置は、高速で移動しながら移動方向を変えるため、経路より大きく離れ、通路の壁に接近する可能性がある。
When the arrival determination area E2 and the arrival determination area E3 have the same size and the movement speed is constant, the change in the movement speed of the autonomous
それに対し、本実施の形態2では、到達判定エリアを異なる大きさに設定すると共に、図6(a)に示す速度変化で移動速度を制御しているため、スムーズに自律移動装置11を移動させることができる。
On the other hand, in the second embodiment, the arrival determination areas are set to different sizes, and the moving speed is controlled by the speed change shown in FIG. 6A, so that the autonomous
(実施の形態3)
図7は、本発明の実施の形態3にかかる通路の模式図である。
(Embodiment 3)
FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of a passage according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
以下、本実施の形態3が実施の形態1と異なる点について、図面を参照しながら説明する。 Hereinafter, the differences of the third embodiment from the first embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings.
図7に示すように、本実施の形態3の自律移動装置41の記憶部15に記憶された到達判定エリアE12、E13は、地図情報に含まれる通路の壁43とノードN2、N3との間隔L2、L3に応じて大きさが異なる。この間隔L2、L3は、ノードN2、N3から壁43までが最も短い距離である。ノードN2、N3から壁43までが最も短い距離とは、隣り合うノードを結ぶ直線により形成される180°未満の角度の側における壁43との距離である。つまり、間隔L2、L3は、自律移動装置41が移動方向を変える際、曲る側の壁43の角44との距離である。
As shown in FIG. 7, the arrival determination areas E12 and E13 stored in the
そして、到達判定エリアE12、E13の半径は、壁43とノードN2、N3との間隔L2、L3に略比例した長さである。よって、間隔L2が間隔L3よりも長いと、到達判定エリアE12の半径が到達判定エリアE13の半径よりも長くなる。そして、自律移動装置41は、ノードN2より間隔L2離れた位置で当面の通過点目標TをノードN3に設定し、ノードN3より間隔L3離れた位置で、当面の通過点目標Tを目的地Pに設定する。
The radii of the arrival determination areas E12 and E13 are approximately proportional to the distances L2 and L3 between the
このように到達判定エリアE12、E13の大きさを変えることで、自律移動装置41は、通路42の角44によって移動を妨げられることなく、スムーズに移動することができる。
Thus, by changing the sizes of the arrival determination areas E12 and E13, the autonomous
ここで、到達判定エリアE12、E13が同じ大きさであると、自律移動装置41の進路S3に角44が重なることがあり、自律移動装置41のスムーズな移動の妨げとなる場合がある。つまり、自律移動装置41の進路方向S3に角44が存在する場合がある。この場合について、図8を用いて説明する。図8は、到達判定エリアの大きさを同じとした場合の通路42の模式図である。図8に示すように、到達判定エリアE13に到達した自律移動装置41の進路方向S3には、角44が存在してしまう。そのために、自律移動装置41は、進路方向S3へ移動する途中に外部環境情報取得部18で角44を検出し、角44を回避して移動する。そのため、自律移動装置41は、スムーズに通路を移動することができない。
Here, if the arrival determination areas E12 and E13 have the same size, the
本実施の形態4にかかる自律移動装置41は、地図情報に含まれる通路の壁43とノードとの壁間隔L2、L3に応じて、ノードの到達判定エリアの大きさを設定することにより、通路の形状に適した到達判定エリアを生成することができる。
The autonomous
(実施の形態4)
図9、図10は、本発明の実施の形態4にかかる到達判定エリアの変化を説明するための到達判定エリアの模式図である。
(Embodiment 4)
9 and 10 are schematic diagrams of arrival determination areas for explaining changes in the arrival determination area according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention.
以下、本実施の形態4が実施の形態1と異なる点について、図面を参照しながら説明する。 Hereinafter, differences of the fourth embodiment from the first embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings.
自律移動装置51は、当面の通過点目標TであるノードN3における到達判定エリアE31に、所定の条件で車体の位置が到達できるか否かを判定する。そして、自律移動装置51は、ノードN3に到達できないと判定した場合に、ノードN3の到達判定エリアE31の大きさを大きくする。具体的には、図9に示すように、ノードN3の位置に障害物52があり、到達判定エリアE31が障害物52よりも小さいために、自律移動装置51が近づくことができても、到達判定エリアE31に到達することができない場合がある。この場合、当面の通過点目標Tを目的地Pに変更することもできず、自律移動装置51は、目的地Pへ移動することができない。そこで、本実施の形態4では、直近の到達判定が成されてからの経過時間が所定の時間以上であることを条件に、ノードN3における到達判定エリアE31に到達できないと判定する。
The autonomous
例えば、到達判定エリアE2に到達してから10秒経過しても、自律移動装置51が到達判定エリアE31に到達しなければ、判定部は、自律移動装置51が到達判定エリアE2に到達できないと判定する。そして、到達判定エリア設定部は、到達判定エリアE31を大きくして到達判定エリアE32に変更する。到達判定エリアE32は障害物52よりも大きくなるように設定されているために、ノードN3の位置に到達判定エリアE31よりも大きな障害物52が存在しても、自律移動装置51に到達判定をさせることができる。その結果、自律移動装置51は、ノードの位置に到達判定エリアよりも大きな障害物が存在しても、次のノードである当面の通過点目標へ向ってスムーズに移動することができる。
For example, if the autonomous
また、図10に示すように、ノードN3の位置に障害物52がなくとも、ノードN3の付近に障害物53があり、この障害物53が自律移動装置51をノードN3に到達させることを妨害する場合がある。この場合も、自律移動装置51の判定部が到達できないと判定すると、ノードN3の到達判定エリアE31の大きさを大きくすることで、到達判定エリアに到達することを妨害する障害物が存在しても、次のノードである当面の通過点目標へ向ってスムーズに移動することができる。
As shown in FIG. 10, even if there is no
なお、到達判定エリア設定部は、判定部が到達できないと判定すると、ノードN3の到達判定エリアE31を時間経過と共に大きくしてもよい。 If the arrival determination area setting unit determines that the determination unit is not reachable, the arrival determination area setting unit E3 may increase the arrival determination area E31 of the node N3 over time.
また、外部環境情報取得部18で検出される環境情報から、判定部が到達できないと判定すると、到達判定エリア設定部は、ノードN3の到達判定エリアE31を大きくしてもよい。
Further, when it is determined from the environment information detected by the external environment
本発明の自律移動装置は、コミュニケーションロボット、及び、運搬、配達、警備、掃除などの作業を行う移動装置等に有用である。 The autonomous mobile device of the present invention is useful for a communication robot and a mobile device that performs operations such as transportation, delivery, security, and cleaning.
11、41、51 自律移動装置
12 車体
13 移動部
14 自己位置取得部
15 記憶部
16 経路生成部
17 移動制御部
18 外部環境情報取得部
19 電池
20、43 壁
21、42 通路
22、44 角
31 到達判定エリア生成部
52、53 障害物
N1、N2、N3 ノード
E2、E3、E12、E13、E31、E32 到達判定エリア
T 通過点目標
P 目的地
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
前記車体を移動させる移動部と、
前記車体の自己位置を取得する自己位置取得部と、
複数のノードの位置と前記複数のノードをそれぞれ囲む到達判定エリアの大きさと地図情報とを記憶する記憶部と、
前記複数のノードを接続して前記自己位置から目的地までの経路を生成する経路生成部と、
当面の通過点目標としたノードを囲む前記到達判定エリアに到達すると、次のノードを当面の通過点目標として切り替えて前記次のノードへ向って移動させる移動制御部と、を備え、
前記到達判定エリアは、囲んでいるノードと前記地図情報に含まれる通路の壁との間隔に応じて大きさが異なる、自律移動装置。 The car body,
A moving unit for moving the vehicle body;
A self-position obtaining unit for obtaining the self-position of the vehicle body;
A storage unit for storing the position of a plurality of nodes, the size of an arrival determination area surrounding each of the plurality of nodes, and map information;
A route generator that connects the plurality of nodes to generate a route from the self-location to a destination;
When reaching the arrival determination area surrounding the node as the current passing point target, a movement control unit that switches the next node as the current passing point target and moves toward the next node, and
The said arrival determination area is an autonomous mobile apparatus from which a magnitude | size differs according to the space | interval of the node and the wall of the channel | path included in the said map information.
前記判定部が、前記到達判定エリアに車体を入れることができないと判定すると、前記到達判定エリアの大きさを変える到達判定エリア設定部とを備える、
請求項1に記載の自律移動装置。 In the node that is the current passing point target, a determination unit that determines whether or not the vehicle body enters the arrival determination area of the node under a predetermined condition;
When the determination unit determines that a vehicle body cannot be put in the arrival determination area, the determination unit includes an arrival determination area setting unit that changes the size of the arrival determination area.
The autonomous mobile device according to claim 1 .
当面の通過点目標としたノードを囲む到達判定エリアに到達すると、次のノードを当面の通過点目標として切り替えて前記次のノードへ向って車体を移動させるに際し、
前記到達判定エリアは、囲んでいるノードと地図情報に含まれる通路の壁との間隔に応じて大きさが異なる、
自律移動方法。 Connect multiple nodes to create a route from your location to your destination,
When reaching the arrival judgment area surrounding the node as the current passing point target, when switching the next node as the current passing point target and moving the vehicle body toward the next node,
The arrival determination area varies in size according to the distance between the enclosing node and the wall of the passage included in the map information.
Autonomous movement method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012249005A JP6007409B2 (en) | 2012-11-13 | 2012-11-13 | Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012249005A JP6007409B2 (en) | 2012-11-13 | 2012-11-13 | Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014098948A JP2014098948A (en) | 2014-05-29 |
| JP2014098948A5 JP2014098948A5 (en) | 2015-08-20 |
| JP6007409B2 true JP6007409B2 (en) | 2016-10-12 |
Family
ID=50940937
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012249005A Active JP6007409B2 (en) | 2012-11-13 | 2012-11-13 | Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6007409B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108287544A (en) * | 2018-01-16 | 2018-07-17 | 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所 | A kind of intelligent robot route planning and the method and system along original route return |
| US10717384B2 (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2020-07-21 | Pony Ai Inc. | System and method for projecting trajectory path of an autonomous vehicle onto a road surface |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6830452B2 (en) * | 2016-02-05 | 2021-02-17 | 株式会社日立産機システム | Position detector and control device |
| SG11201811228SA (en) | 2017-06-19 | 2019-01-30 | Beijing Didi Infinity Technology & Development Co Ltd | Systems and methods for displaying movement of vehicle on map |
| CN109145065A (en) * | 2017-06-19 | 2019-01-04 | 北京嘀嘀无限科技发展有限公司 | Methods of exhibiting and device, the computer readable storage medium of vehicle driving trace |
| CN107943017B (en) | 2017-09-30 | 2023-05-09 | 北京极智嘉科技股份有限公司 | Automatic conveying unit, motion control method and device and automatic sorting system |
| CN107885206A (en) * | 2017-11-07 | 2018-04-06 | 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所 | A kind of Obstacle Avoidance and its robot of application |
| TWI714040B (en) | 2019-03-27 | 2020-12-21 | 財團法人船舶暨海洋產業研發中心 | A vessel navigation system and navigation method thereof |
| JP2020187551A (en) * | 2019-05-14 | 2020-11-19 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | Autonomous traveling vehicle |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2622579B2 (en) * | 1988-05-06 | 1997-06-18 | 株式会社小松製作所 | How to guide moving objects |
| JP4093245B2 (en) * | 2005-02-23 | 2008-06-04 | 松下電工株式会社 | Autonomous mobile device |
-
2012
- 2012-11-13 JP JP2012249005A patent/JP6007409B2/en active Active
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10717384B2 (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2020-07-21 | Pony Ai Inc. | System and method for projecting trajectory path of an autonomous vehicle onto a road surface |
| CN108287544A (en) * | 2018-01-16 | 2018-07-17 | 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所 | A kind of intelligent robot route planning and the method and system along original route return |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014098948A (en) | 2014-05-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6007409B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile device and autonomous mobile method | |
| JP7212074B2 (en) | A method for controlling edge-along running of an autonomous mobile robot | |
| CN109227533B (en) | Movement planning device, mobile robot, and movement planning program | |
| JP6863991B2 (en) | Virtual line tracking method and modification method for autonomous mobile robots and mobile robots | |
| CN110018686A (en) | A kind of paths planning method of intelligent grass-removing | |
| EP2870513B1 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot and method for operating the same | |
| CN110730931A (en) | Deadlock free multi-agent navigation roadmap annotation | |
| WO2014089922A1 (en) | Covering method of map self-established by mobile platform in unknown region | |
| WO2022142858A1 (en) | Robot moving path planning method and apparatus, method and apparatus for determining degree of deviation of planned path point from history path, and robot and computer-readable storage medium | |
| JP2008152600A (en) | Moving route generation method, autonomous moving object, and autonomous moving object control system | |
| JP2007249632A (en) | Mobile robot moving autonomously under environment with obstruction, and control method for mobile robot | |
| US9599987B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot and method for operating the same | |
| JP5380165B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile device | |
| JP4093261B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile device | |
| JP2017142659A (en) | Autonomous moving body system | |
| JPWO2019031168A1 (en) | MOBILE BODY AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING MOBILE BODY | |
| JP6709055B2 (en) | Mobile unit and server | |
| CN112631269A (en) | Autonomous mobile robot and control program for autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP2008152599A (en) | Moving route generation method, autonomous moving object, and autonomous moving object control system | |
| JP2008134744A (en) | Autonomous moving device group control system | |
| JP4893535B2 (en) | Route generating apparatus for autonomous movement and autonomous mobile apparatus using the apparatus | |
| JP2009223812A (en) | Autonomous mobile device | |
| JP2008129695A (en) | Path generation system and method for traveling object | |
| JP4093245B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile device | |
| JPH04365104A (en) | Optimum course planning device and autonomously moving robot |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20150312 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150703 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20150703 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160420 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160510 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20160518 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160608 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160802 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160815 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6007409 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |