JP5852385B2 - Imaging device - Google Patents
Imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5852385B2 JP5852385B2 JP2011209784A JP2011209784A JP5852385B2 JP 5852385 B2 JP5852385 B2 JP 5852385B2 JP 2011209784 A JP2011209784 A JP 2011209784A JP 2011209784 A JP2011209784 A JP 2011209784A JP 5852385 B2 JP5852385 B2 JP 5852385B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- unit
- exposure
- images
- output
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 64
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 178
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 178
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 claims description 159
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 51
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 51
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 41
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010191 image analysis Methods 0.000 description 51
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 26
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 22
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012556 adjustment buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011946 reduction process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、露光量の異なる複数枚の撮像画像を合成して、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を生成する撮像装置に関する。
The present invention combines a plurality of captured images with different exposure amounts, an image relating to that imaging device generates a wide dynamic range.
一般に、露光量の異なる複数枚の撮像画像を合成し、ダイナミックレンジを拡大した後、出力機器のダイナミックレンジに合わせて、階調圧縮を行う画像処理装置が提案されている(特許文献1)。また、入力画像を複数の解像度の画像に変換し、それらを用いて、入力画像の着目画素周囲の小領域毎に、階調圧縮特性を最適化して、入力画像のダイナミックレンジを圧縮する画像処理が提案されている(特許文献2)。 In general, there has been proposed an image processing apparatus that synthesizes a plurality of captured images with different exposure amounts, expands the dynamic range, and then performs gradation compression in accordance with the dynamic range of the output device (Patent Document 1). Image processing that converts the input image into multiple resolution images and uses them to optimize the tone compression characteristics for each small area around the pixel of interest in the input image and compress the dynamic range of the input image Has been proposed (Patent Document 2).
しかし、特許文献1に記載された技術では、露光量の異なる複数枚の画像を合成したダイナミックレンジの広い画像を、図9のように、画面内の輝度に応じた一様な特性で、出力機器のダイナミックレンジに収まるよう階調圧縮を行う。そのため、階調再現性の損なわれる輝度領域が発生するという課題がある。
However, in the technique described in
一方、特許文献2に記載された技術では、階調圧縮特性を生成するために、多重解像度処理を必要とする。すなわち、入力画像から生成した複数種類の解像度の画像を同じタイミングで参照しなければならない。そのため、低解像度画像を生成する間、高解像度画像をフレームメモリにバッファリングしてタイミングを調整する必要がある。フレームメモリを使った画像のバッファリングは、特に、動画撮影時や、画像サイズ、ビット幅が大きい場合に撮像システムへの負荷が高くなるという課題がある。
On the other hand, the technique described in
本発明は、上記の課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、露光量の異なる複数枚の撮像画像を合成し、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を生成する場合のシステム負荷の増大を抑えることにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object thereof is to suppress an increase in system load when a plurality of captured images with different exposure amounts are combined to generate an image with a wide dynamic range. It is in.
上記の目的を達成するための本発明の一態様による撮像装置は以下の構成を備える。すなわち、
露光量の異なる2つの画像を合成してダイナミックレンジが拡張された画像を生成する撮像装置であって、
異なる2つの露光量を順次に適用した撮影により第1の画像とこれに後続する第2の画像を出力する撮像手段と、
前記第1の画像と前記第2の画像を合成してダイナミックレンジが拡張された合成画像を生成する合成手段と、
前記第1の画像と前記第1の画像を低解像度化した画像とに基づいて階調圧縮特性を生成する生成手段と、
前記生成手段で生成された前記階調圧縮特性を用いて前記合成画像の階調を圧縮する階調圧縮手段と、
前記階調圧縮特性の生成に使用される画像の露光量として前記2つの露光量のいずれが適切かを判定するために、前記第1の画像を解析する解析手段と、
前記解析手段が適切と判定した露光量で撮影された画像を前記生成手段が用いるように、前記第1および第2の画像と前記2つの露光量との対応を制御する制御手段と、を備える。
In order to achieve the above object, an imaging apparatus according to an aspect of the present invention has the following arrangement. That is,
An imaging apparatus that generates an image with an expanded dynamic range by combining two images having different exposure amounts,
Imaging means for outputting a first image and a second image following the first image by photographing in which two different exposure amounts are sequentially applied;
Synthesizing means for synthesizing the first image and the second image to generate a synthesized image having an extended dynamic range;
Generating means for generating gradation compression characteristics based on the first image and an image obtained by reducing the resolution of the first image;
Gradation compression means for compressing the gradation of the composite image using the gradation compression characteristic generated by the generation means;
Analyzing means for analyzing the first image in order to determine which of the two exposure amounts is appropriate as an exposure amount of the image used for generating the gradation compression characteristic;
Control means for controlling correspondence between the first and second images and the two exposure amounts so that the generation unit uses an image taken with an exposure amount determined to be appropriate by the analysis unit. .
本発明によれば、露光量の異なる複数枚の撮像画像を合成し、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を生成する場合のシステム負荷の増大を抑えることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to suppress an increase in system load when a plurality of captured images with different exposure amounts are combined to generate an image with a wide dynamic range.
以下、添付の図面を参照しながら、本発明の好適な実施形態を説明する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[第1実施形態]
第1実施形態では、露光量の異なる2つのフレームの画像を合成して、ダイナミックレンジの拡大された1フレーム分の画像を出力する画像処理装置を有する撮像装置について説明する。
[First Embodiment]
In the first embodiment, an imaging apparatus having an image processing apparatus that synthesizes images of two frames with different exposure amounts and outputs an image of one frame with an expanded dynamic range will be described.
図1は、第1実施形態の撮像装置100の構成を示すブロック図である。図1において、光学系1は撮像レンズ、絞り等の光学素子を含む。撮像素子2は光学系1により撮像面上に結像された光学像を電気信号に変換して画像信号を出力する。本実施意形態の撮像素子2は複数種類の露光量を切り替えて撮像を行うことが可能であり、露光量の切り替えは、例えば光電変換素子における電荷蓄積時間の切り替えにより実現される。フレームメモリ3は、撮像素子2から出力される画像の1フレーム分をバッファリングするためのメモリである。合成部4は、フレームメモリ3から読み出した画像と、撮像素子2から出力される現フレームの画像とを所定の演算によって合成し、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を生成する。階調圧縮特性生成部5は、合成部4により合成された画像に対する階調圧縮特性を生成する。階調圧縮部6は、合成部4の出力画像が、所定のダイナミックレンジに収まるよう、階調圧縮特性生成部5から出力された階調圧縮特性を用いて階調圧縮を行う。画像解析部7は、撮像素子2から出力される2種類の露光量の画像のうちいずれの露光量の画像を階調圧縮特性の生成に使用すべきかを判定するために、撮像素子2から出力される画像を解析する。システム制御部8は、撮像装置100の全体の動作を制御する。
FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
次に、第1実施形態による撮像装置100の動作の概要について説明する。撮像装置100において撮影が開始されると、システム制御部8は、フレーム毎に、指示された露光量の画像が撮像素子2から出力されるよう、光学系1、撮像素子2を制御する。光学系1を介して撮像素子2から出力された画像は、フレームメモリ3、合成部4、階調圧縮特性生成部5および、画像解析部7に入力される。フレームメモリ3では、撮像素子2からの出力画像の1フレーム分を保持する。
Next, an outline of the operation of the
合成部4は、フレームメモリ3に保持された画像と撮像素子2から出力される画像とを、ダイナミックレンジを拡張するように合成する。この結果、フレームメモリ3から読み出された1フレーム前の撮像素子2の出力画像と、撮像素子2から現在出力されている撮像素子2の現フレームの出力画像とが合成される。フレームメモリ3から読み出された1フレーム前の撮像素子2の出力画像と、撮像素子2からの現フレームの出力画像は、それぞれ露光量が異なる。そのため、合成前に露光量の差に応じたゲイン処理を実施し、現フレームおよび1フレーム前の撮像素子2の出力画像のレベル調整を行う。
The synthesizing
階調圧縮特性生成部5は、フレームメモリ3から読み出された1フレーム前の出力画像と、撮像素子2からの現フレームの出力画像とを用いて、合成部4の出力画像のための階調圧縮特性を生成する。階調圧縮部6は、階調圧縮特性生成部5から出力される階調圧縮特性を用いることにより、撮影中の画像が好ましい階調再現となり、かつ出力映像フォーマットのダイナミックレンジに収まるよう、合成部4から出力される画像の階調圧縮を行う。
The gradation compression
次に、階調圧縮特性生成部5の構成について、図2を参照して説明する。階調圧縮特性生成部5では、着目画素を含む小領域の輝度レベルを参照することにより、画素毎に階調圧縮特性を決定する。
Next, the configuration of the gradation compression
図2において、入力端子58にはフレームメモリ3の出力画像が、入力端子59には撮像素子2の出力画像が入力される。輝度生成部51、輝度生成部52は、それぞれ、入力端子58、入力端子59から入力された画像から輝度信号を生成する。フレームメモリ3の出力画像と撮像素子2の出力画像は、いずれも、RAWデータであり、RGBベイヤー等、画素毎に色フィルタによるレベル差がある。したがって、輝度生成部51、52では、補間処理、マトリクス演算を行い、色フィルタによるレベル差を解消した輝度信号を生成する。
In FIG. 2, the output image of the
画像縮小部53は、輝度生成部52から出力される1フレーム分の輝度画像を、×1/64、×1/128等の高い縮小率で縮小し、結果を第2のメモリとしてのメモリ54に格納する。なお、縮小後の画像を格納するメモリ54の容量は、入力画像1フレーム分をバッファリングするフレームメモリ3と比較して十分に小さく、メモリ54を用いても撮像システムへの負荷は問題にならない。また、フレームメモリ3とメモリ54は別個のメモリであってもよいし、同じメモリの異なるメモリ領域であってもよい。画像拡大部55は、メモリ54に格納された縮小画像を、輝度生成部51から出力される輝度画像と等しい画像サイズになるよう、線形補間等を用いて拡大する。
The
局所輝度レベル推定部56は、輝度生成部51から出力される高解像度の輝度画像と、画像拡大部55から出力される低解像度の輝度画像を用いた演算により、着目画素を含む小領域の輝度レベルを推定する。このような推定演算の一例としては、
・画素毎に、解像度の異なる複数枚の画像の出力を比較し、
・高解像度画像と低解像度画像の差分が小さい場合には、低解像度画像の出力を着目画素における輝度レベルとして出力し、
・高解像度画像と低解像度画像の差分が大きい場合には、低解像度画像と高解像度画像を加重加算して、着目画素における輝度レベルとして出力する、という方法等が挙げられる。このような推定演算を用いることで、ノイズや被写体のエッジ等の影響は排除しつつ、図4(a)、図4(b)のように様々な輝度レベルの小領域が混在する画像において、各領域の分離精度を高められる。なお、本実施形態では、2種類の解像度の画像を用いて局所輝度レベルの推定を行ったが、これに限られるものではなく、3種類以上の異なる解像度の画像を用いてもよい。
The local luminance
・ Compare the output of multiple images with different resolutions for each pixel,
When the difference between the high resolution image and the low resolution image is small, the output of the low resolution image is output as the luminance level at the pixel of interest,
-When the difference between the high-resolution image and the low-resolution image is large, a method of weighting and adding the low-resolution image and the high-resolution image and outputting the luminance level at the pixel of interest can be used. By using such an estimation calculation, in an image in which small areas of various luminance levels are mixed as shown in FIGS. The separation accuracy of each region can be increased. In the present embodiment, the local luminance level is estimated using images of two types of resolutions, but the present invention is not limited to this, and images of three or more types of different resolutions may be used.
階調圧縮特性決定部57は、局所輝度レベル推定部56の出力を参照して、画素ごとに、適切な階調圧縮特性を決定する。例えば、
・着目画素を含む小領域の輝度レベルが適正露光よりも暗い場合には、着目画素の輝度レベルをゲインアップするような階調圧縮特性を生成し、
・着目画素を含む小領域の輝度レベルが、適正露光よりも明るい場合には、着目画素の輝度レベルをゲインダウンするような階調圧縮特性を生成する。
The gradation compression
When the brightness level of the small area including the target pixel is darker than the appropriate exposure, a gradation compression characteristic that increases the brightness level of the target pixel is generated,
When the luminance level of the small area including the target pixel is brighter than the appropriate exposure, a gradation compression characteristic that reduces the luminance level of the target pixel is generated.
ところで、局所輝度レベル推定部56では、低解像度画像と高解像度画像を同じタイミングで参照する必要がある。したがって、画像縮小部53で、1フレーム分の画像を縮小している間、1フレーム分の高解像度画像をバッファリングして、遅延する必要がある。このような画像のバッファリングは、特に、画像サイズが大きい場合や、撮影画像のフレームレートが高い場合に、撮像装置のシステム負荷を増大させる。そこで、本実施形態の撮像装置100では、合成部4で用いるフレームメモリ3を、階調圧縮特性生成部5での遅延調整用バッファとして共用することで、システム負荷が増大するのを防いでいる。
Incidentally, the local luminance
一方、合成部4で用いるフレームメモリ3にバッファリングできるのは1フレーム分の画像である。本実施形態では、低露光画像と高露光画像を合成する場合、低露光画像と高露光画像の2つのフレームの画像のうち、最初に撮影された方、すなわち1フレーム目の画像がフレームメモリ3にバッファリングされる。そして、その次に撮像素子2から出力される2フレーム目の画像と、フレームメモリ3にバッファリングされた1フレーム目の画像が合成される。上述したように、2つのフレームの画像は、光学系1、撮像素子2により異なる露光量が適用されて撮影された画像である。したがって、合成用にバッファリングされている画像を、階調圧縮特性生成部5で共用する場合、合成前の1フレーム目の画像、すなわち合成前の低露光画像または高露光画像のいずれかで階調圧縮特性が生成することになる。
On the other hand, an image for one frame can be buffered in the
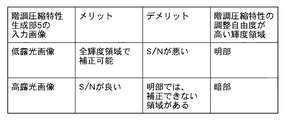
図5に、低露光画像、高露光画像のそれぞれを用いて階調圧縮特性を生成した場合のメリット、デメリットを示す。低露光画像は、暗部のS/Nが高露光画像よりも低いが、明部でも飽和していないため、低露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を生成すると暗部から明部まで全ての輝度領域にわたる階調圧縮特性を生成できる。一方、高露光画像は、明部の飽和領域では階調圧縮特性を生成できないが、暗部のS/Nは低露光画像よりも高いため、高露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を生成すると暗部でS/Nの良い階調圧縮特性を生成できる。すなわち、低露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を生成すると明部に適した階調圧縮処理となり、高露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を生成すると暗部に適した階調圧縮処理となるといえる。 FIG. 5 shows merits and demerits when the gradation compression characteristic is generated using each of the low exposure image and the high exposure image. The low-exposure image has a dark S / N lower than that of the high-exposure image, but is not saturated even in the bright part. A wide range of gradation compression characteristics can be generated. On the other hand, a high-exposure image cannot generate a gradation compression characteristic in a saturated area in a bright part, but a dark part has a higher S / N than a low-exposure image. Can generate tone compression characteristics with good S / N. In other words, generating gradation compression characteristics using a low-exposure image results in gradation compression processing suitable for bright areas, and generating gradation compression characteristics using a high-exposure image results in gradation compression processing suitable for dark areas. .
そこで、本実施形態の撮像装置100では、撮影中の画像において、支配的な輝度領域が、図4(a)のように暗部なのか、図4(b)のように明部なのかを判定する。そして、撮影中の画像において、少なくとも、支配的な輝度領域では、好ましい階調圧縮特性で、階調圧縮処理が行われるよう、階調圧縮特性生成部5で用いる画像、すなわち、フレームメモリ3に保持させる画像を決定する。
Therefore, in the
撮影中の画像において、支配的な輝度領域を判定する方法としては、以下で説明するように、画像解析部7が撮影中の画像の輝度分布を解析して判定してもよいし、例えば露出設定等の撮影条件や、ユーザの指示などを参照して、システム制御部8が決定してもよい。以下、画像内の輝度分布を解析し、暗部が支配的な画像か、明部が支配的な画像かを判定する画像解析部7の動作について説明する。
As a method for determining a dominant luminance region in an image being shot, as described below, the
画像解析部7における解析方法の一例としては、所定の輝度レベル毎に、当該輝度レベルを持つ画素領域の面積を算出し、最も面積の大きい輝度レベルを、画面内で支配的な輝度レベルとみなす方法がある。この場合、支配的な輝度レベルが所定の閾値よりも低い場合には撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的であると判定する。また、支配的な輝度レベルが所定の値よりも高い場合には撮影中の画像において明部が支配的であると判定する。
As an example of the analysis method in the
また、画像解析部7による別の解析方法として、画面中央の所定の画素領域で輝度の平均値を求め、当該画素領域の平均輝度が所定の値よりも低い場合に、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的であると判定する。また、当該画素領域の平均輝度が所定の値よりも高い場合には、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的であると判定する。
As another analysis method by the
さらに、画像解析部7による別の解析方法として、画像の輝度、色、動き、エッジ量等から、顔やペットなど特定被写体が画面内に存在するかを検出し、特定被写体領域の平均輝度を求める。そして、特定被写体領域の平均輝度が所定の値よりも低い場合には、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的であると判定し、特定被写体の平均輝度が所定の値よりも高い場合には、撮影中の画像において、明部が支配的であると判定する。
Further, as another analysis method by the
以上のようにして、画像解析部7は撮影中の画像を解析し、その解析結果をシステム制御部8に送出する。システム制御部8は、画像解析部7の解析結果出力に基づき、撮像素子2の駆動を制御する。例えば、画像解析部7による解析の結果、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的と判定された場合には、フレームメモリ3に高露光画像が保持されるようにする。本実施形態では、暗部が支配的な画像に対して、合成対象の連続した2つのフレームの画像のうち、露光量の高い画像の方が先に撮影されるよう、撮像素子2を駆動制御する。一方、画像解析部7による解析の結果、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的と判定された場合には、フレームメモリ3に低露光画像が保持されるようにする。本実施形態では、合成対象の連続した2つのフレームの画像のうち、露光量の低い画像の方が先に撮影されるよう撮像素子2を駆動制御する。
As described above, the
撮影中の画像において支配的な領域が明部から暗部に変化した際の撮像動作の一例を、図3のタイミングチャートを参照して説明する。図3において、時刻t1、t2、t3、・・・、t7の間隔は、それぞれ、1フレーム期間(以下1Vと表記する。)を示す。撮像素子2からは、1V毎に、低露光画像または高露光画像が出力され、合成部4において合成される画像は図2の破線で囲まれた組み合わせとなる。
An example of the imaging operation when the dominant region in the image being shot changes from the bright part to the dark part will be described with reference to the timing chart of FIG. In FIG. 3, the intervals between times t1, t2, t3,..., T7 each indicate one frame period (hereinafter referred to as 1V). A low-exposure image or a high-exposure image is output from the
すなわち、時刻t1からt3の期間では、撮像素子2から出力された低露光画像L1と高露光画像H1が合成されて合成画像(H1+L1)が生成される。同様に、時刻t3からt5の期間では、撮像素子2から出力された低露光画像L2と高露光画像H2が合成され、時刻t5からt7の期間では、撮像素子2出力の低露光画像L3と高露光画像H3が合成される。
That is, in the period from time t1 to t3, the low exposure image L1 and the high exposure image H1 output from the
制御信号S1〜S3は、システム制御部8が制御、出力する信号である。制御信号S1は、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込み、及び、階調圧縮特性生成部5での処理のOn/Offを制御する2値の制御信号である。制御信号S1が“1”の場合には撮像素子2の出力画像が1V期間かけてフレームメモリ3に書き込まれる。同時に、撮像素子2の出力画像が、階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力され、1V期間かけてその縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。制御信号S1が“0”の場合には、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込みは停止され、階調圧縮特性生成部5では、フレームメモリ3に保持されている画像とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像とを用いて階調圧縮特性が生成され、順次に出力される。
The control signals S1 to S3 are signals that the
制御信号S2は、フレームメモリ3からの画像の読み出し、及び、合成部4での処理のon/off、及び、階調圧縮部6での処理のon/offを制御する2値の信号である。制御信号S2が“0”の場合は、フレームメモリ3からの画像の読み出しが停止され、合成部4、及び、階調圧縮部6での処理はoffとなる。制御信号S2が“1”の場合には、フレームメモリ3に保持されている画像が読み出される。そして、合成部4は、撮像素子2から出力される現フレームの画像と、フレームメモリ3から読み出した画像(現フレームの一つ前の画像)を用いて、ダイナミックレンジを拡張する合成処理を行う。そして、階調圧縮部6は、合成部4から逐次出力される合成後の画像に対して、階調圧縮特性生成部5から逐次出力される階調圧縮特性の出力を用いて、階調圧縮処理を行う。
The control signal S <b> 2 is a binary signal that controls reading of an image from the
制御信号S3は、合成される2つのフレームの画像、すなわち、低露光画像と高露光画像のうち、どちらを先に撮像素子2により撮影するかを決定する2値の制御信号である。制御信号S3は、例えば画像解析部7での解析結果に基づいて更新される。制御信号S3が“0”になるのは、画像解析部7の解析の結果、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的であると判定された場合である。制御信号S3が“0”の場合、次の合成用画像の撮影時には低露光画像が先に撮影されるよう撮像素子2が制御される。他方、制御信号S3が“1”になるのは、画像解析部7の解析の結果、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的であると判定された場合である。制御信号S3が“1”の場合、次の合成用画像の撮影時には、高露光画像が先に撮影されるよう撮像素子2が制御される。
The control signal S3 is a binary control signal that determines which of the two frames to be combined, that is, the low-exposure image or the high-exposure image, is to be captured first by the
図3において、時刻t1からt2の期間では、制御信号S3が“0”であるので、合成対象の2つのフレームの画像は、1フレーム目が低露光画像L1、2フレーム目が高露光画像H1の順となるように撮像素子2から出力される。そして、時刻t1からt2までの1V期間で、低露光画像L1がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれ、それと並行して低露光画像L1の縮小画像が生成されメモリ54に保持される。時刻t2からt3では、合成部4がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれた低露光画像L1と撮像素子2から出力される高露光画像H1を合成して、画像H1+L1を出力する。それと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5がフレームメモリ3に保持されている低露光画像L1とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像から階調圧縮特性g(L1)を順次生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が合成後の画像H1+L1に対し階調圧縮特性g(L1)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行って最終的な画像を生成する。
In FIG. 3, since the control signal S3 is “0” in the period from time t1 to t2, the images of the two frames to be combined are the low exposure image L1 for the first frame and the high exposure image H1 for the second frame. Are output from the
また、時刻t1からt3の期間では、画像解析部7は、合成される低露光画像L1と高露光画像H1のうち先に撮影された低露光画像L1について解析を行い、その解析結果A(L1)を出力する。そして、システム制御部8は、解析結果A(L1)に基づいて、時刻t3からの合成で参照する制御信号S3を“0”に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果明部が支配的であると判断できるので、次の合成処理の際も、低露光画像を先に撮影して、明部での階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が好ましい画質になると考えられるためである。
In the period from time t1 to time t3, the
時刻t3からt5の期間においても、制御信号S3が“0”であるので、合成対象の2つのフレームの画像は、低露光画像L2、高露光画像H2の順に撮像素子2から出力される。そして、時刻t3からt4までの1V期間で、低露光画像L2がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれ、それと並行して低露光画像L1の縮小画像が生成されメモリ54に保持される。時刻t4からt5では、合成部4が、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれた低露光画像L2と撮像素子2から出力される高露光画像H2を合成して、画像H2+L2を出力する。それと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5がフレームメモリ3に保持されている低露光画像L2とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像から階調圧縮特性g(L2)を順次生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が合成後の画像H2+L2に対し階調圧縮特性g(L2)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行って最終的な画像を生成する。
Since the control signal S3 is “0” also during the period from the time t3 to the time t5, the images of the two frames to be synthesized are output from the
また、時刻t3からt5の期間では、画像解析部7は、合成される2つのフレームの画像、すなわち低露光画像L2と高露光画像H2のうち、先に撮影された低露光画像L2について解析を行い、その解析結果A(L2)を出力する。今度は、画像解析部7において暗部が支配的であると判断されたとする。この場合、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、暗部が支配的になってきていると判断できるので、次の合成処理の際は、高露光画像を先に撮影し、暗部での階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が、好ましい画質となると考えられる。そのため、システム制御部8は、A(L2)に基づいて、時刻t5からの合成で参照する制御信号S3を“1”に更新する。
In the period from time t3 to time t5, the
時刻t5からt7の期間では、制御信号S3が“1”なので、合成対象の2つのフレームの画像は、高露光画像H3、低露光画像L3の順に撮像素子2から出力される。そして、時刻t5からt6までの1V期間で、高露光画像H3がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれ、それと並行して、高露光画像H3の縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。時刻t6からt7では、合成部4がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれた高露光画像H3と撮像素子2から出力される低露光画像L3を合成して、画像H3+L3を出力する。そして、それと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5がフレームメモリ3に保持されている高露光画像H3とメモリ54に保持された縮小画像を用いて階調圧縮特性g(H3)を順次生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が合成後の画像H3+L3に対し階調圧縮特性g(H3)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行って最終的な画像を生成する。
Since the control signal S3 is “1” during the period from time t5 to time t7, the images of the two frames to be combined are output from the
また、時刻t5からt7の期間では、画像解析部7は、合成される2つのフレーム、すなわち低露光画像L3と高露光画像H3のうち、先に撮影された高露光画像H3を用いて、での処理を行い、解析結果A(H3)を出力する。そして、システム制御部8は、この解析結果A(H3)に基づいて、時刻t7からの合成で参照する制御信号S3を1に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、暗部が支配的であると判断できるので、次の合成処理の際も、高露光画像を先に撮影し、暗部での階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が、好ましい画質となると考えられるためである。
In the period from time t5 to t7, the
以上のような一連の撮像制御を行うことにより、露光量を変えた複数枚の画像を合成し、合成後の画像に適した階調圧縮特性で、階調圧縮を行って、映像信号を出力することができる。 By performing a series of imaging control as described above, multiple images with different exposure amounts are combined, and gradation compression is performed with gradation compression characteristics suitable for the combined image, and a video signal is output. can do.
以上説明したように、本実施形態の撮像装置100では、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を生成する合成処理のためにフレームメモリ3にバッファリングする画像と同じ画像を用いて合成後の画像に対する階調圧縮特性を生成することができる。そのため、メモリアクセスによるシステム負荷の増大を回避できる。また、撮影中の画像の特徴を解析して、階調圧縮特性の生成に用いる画像を決定することにより、撮影中の画像に適した階調圧縮処理を行うことができる。
As described above, in the
[第2実施形態]
次に、第2実施形態の撮像装置について説明する。第1実施形態では、画像解析部7の解析結果に基づいて合成対象の2つのフレームの1フレーム目と2フレーム目の露光量を切り替える際に、撮像素子2から連続して出力される2つのフレームの露光量の適用の順序を入れ替える構成を示した。例えば、低露光画像L→高露光画像Hから、高露光画像H→低露光画像Lのように順番を切り替えることで、1フレーム目及び2フレーム目が対応する露光量を切り替える構成を採用した。しかしながら、露光量を切り替えるための構成は、第1実施形態に限られるものではない。たとえば、フレームメモリ3が保持するフレームを1フレームずらすことにより、1フレーム目と2フレーム目の露光量を切り替える構成としてもよい。第2実施形態では、このような構成について説明する。
[Second Embodiment]
Next, an imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment will be described. In the first embodiment, when the exposure amounts of the first frame and the second frame of the two frames to be synthesized are switched based on the analysis result of the
第2実施形態も、露光量の異なる2フレーム分の画像を合成して、ダイナミックレンジの拡大された1フレーム分の画像を出力する撮像装置である。第2実施形態の撮像装置100の構成は第1実施形態と同じで図1のようになる。第1実施形態と同様、合成部4と階調圧縮特性生成部5でフレームメモリ3を共用するため、合成対象の2つのフレームの画像のうち、フレームメモリ3にバッファリングされる方の画像で合成後の画像用の階調圧縮特性が生成される。
The second embodiment is also an imaging apparatus that synthesizes images for two frames with different exposure amounts and outputs an image for one frame with an expanded dynamic range. The configuration of the
しかし、第2実施形態では、第1実施形態のように、画像解析部7の結果に基づいて、低露光画像を先に撮影するか、高露光画像を先に撮影するかを選択するしくみは不要である。すなわち、第2実施形態の撮像素子2は、常に、低露光画像、または、高露光画像が先に撮影されるよう撮像素子2の駆動が制御される。第2実施形態では、画像解析部7の結果に基づいて合成対象となる2つのフレームの画像のうち、好ましい階調圧縮特性が生成できる方の画像がフレームメモリ3にバッファリングされるよう、フレームメモリ3への画像書き込みのタイミングを制御する。
However, in the second embodiment, as in the first embodiment, a mechanism for selecting whether to shoot a low-exposure image or a high-exposure image first is based on the result of the
システム制御部8は、画像解析部7の解析の結果、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的な場合には、高露光画像がフレームメモリ3にバッファリングされ、明部が支配的な場合には、低露光画像がフレームメモリ3にバッファリングされるように制御する。ここで、撮影中の画像において、支配的な輝度領域が、暗部から明部、または、明部から暗部に変化した場合には、撮像素子2から出力される高露光画像と低露光画像を2フレーム連続してフレームメモリ3にバッファリングする。
As a result of the analysis by the
そのため、撮像素子2の出力画像をフレームメモリ3にバッファリングしている1V期間内に、画像解析部7での画像解析処理を終了し、次の1V期間でフレームメモリ3に画像をバッファリングする必要があるか判断する必要がある。そのため、第2実施形態では、撮像素子2からの信号読み出しを、2ラインずつ間引いて、2回に分けて行う。
Therefore, the image analysis processing in the
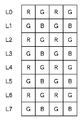
例えば、撮像素子2の画素配置が図10に示すようである場合、1V期間の前半では、撮像素子2のL0、L1、L4、L5、・・・のラインの信号を読み出し、当該1V期間の後半では、撮像素子2のL2、L3、L6、L7、・・・のラインの信号を読み出す。画像解析部7では、1V期間の前半で撮像素子2から読み出された垂直方向1/2に間引かれた画像を入力し、当該1V期間の後半で解析処理を行う。したがって、1フレーム分の画像をフレームメモリ3に書き込んでいる間に、次の1V期間で画像をフレームメモリ3にバッファリングすべきかを決定することができる。
For example, when the pixel arrangement of the
以下、図6を参照して、第2実施形態の撮像装置の制御について説明する。撮像素子2からは、常に、低露光画像、高露光画像の順で合成前の画像が出力される。制御信号S1は、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込み、及び、階調圧縮特性生成部5での処理のOn/Offを制御する2値の制御信号であり、1V期間毎に更新される。制御信号S1が“1”の場合には、撮像素子2の出力画像が1V期間かけてフレームメモリ3に書き込まれる。同時に、撮像素子2の出力画像が階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力され、1V期間かけて、縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。制御信号S1が“0”の場合には、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込みは停止され、階調圧縮特性生成部5での縮小画像の生成処理はoffとなる。
Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 6, control of the imaging apparatus of the second embodiment will be described. The
ここで、ある1V期間で制御信号S1が“0”の場合には、次の1V期間では制御信号S1は常に“1”となる。また、ある1V期間で制御信号S1が“1”の場合には、次の1V期間で制御信号S1が“0”、“1”のどちらの値をとるかは、画像解析部7に入力された画像に対する解析結果によって決まる。
Here, when the control signal S1 is “0” in a certain 1V period, the control signal S1 is always “1” in the next 1V period. In addition, when the control signal S1 is “1” in a certain 1V period, whether the control signal S1 takes “0” or “1” in the next 1V period is input to the
ある1V期間の制御信号S1が“1”で、画像解析部7の入力画像が低露光画像であり、かつ、画像解析部7での解析結果で明部が支配的と判定された場合、システム制御部8は次の1V期間で制御信号S1を“0”にする。これは、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的な場合には、フレームメモリ3にバッファリングされている低露光画像で、階調圧縮特性を生成すればよいので、次の1V期間で、高露光画像をバッファリングする必要がないからである。
When the control signal S1 for a certain 1V period is “1”, the input image of the
一方、ある1V期間の制御信号S1が“1”で、画像解析部7の入力画像が低露光画像であり、かつ、画像解析部7での解析結果で暗部が支配的と判定された場合、システム制御部8は、次の1V期間で制御信号S1を“1”にする。これは、撮影中の画像において暗部が支配的な場合には、次の1V期間でフレームメモリ3に高露光画像をバッファリングし、暗部重視の階調圧縮特性を生成する必要があるためである。
On the other hand, when the control signal S1 for a certain 1V period is “1”, the input image of the
また、ある1V期間の制御信号S1が“1”で、画像解析部7の入力画像が高露光画像であり、かつ、画像解析部7での解析結果で暗部が支配的と判定された場合、システム制御部8は、次の1V期間で制御信号S1を“0”にする。これは、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的な場合には、フレームメモリ3にバッファリングされている高露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を生成すればよいので、次の1V期間で、低露光画像をバッファリングする必要がないからである。
Further, when the control signal S1 for a certain 1V period is “1”, the input image of the
さらに、ある1V期間の制御信号S1が“1”で、画像解析部7の入力画像が高露光画像であり、かつ、画像解析部7での解析結果で明部が支配的と判定された場合、システム制御部8は、次の1V期間で制御信号S1を“1”にする。これは、撮影中の画像において明部が支配的な場合には、次の1V期間でフレームメモリ3に低露光画像をバッファリングし、明部重視の階調圧縮特性を生成する必要があるためである。
Furthermore, when the control signal S1 for a certain 1V period is “1”, the input image of the
制御信号S2は、フレームメモリ3からの画像の読み出し、及び、合成部4での処理のon/off、及び、階調圧縮部6での処理のon/offを制御する2値の信号である。制御信号S2が“0”の場合は、フレームメモリ3からの画像の読み出しが停止され、合成部4、及び、階調圧縮部6での処理はoffとなる。制御信号S2が“1”の場合には、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれている画像を読み出し、合成部4において撮像素子2から出力される画像と、フレームメモリ3から読み出した画像を用いて、ダイナミックレンジを拡張する合成処理を行う。そして、階調圧縮特性部5は、フレームメモリ3から読み出した画像とメモリ54から読み出した縮小画像を用いて階調特性を生成し、出力する。階調圧縮部6は、合成部4からの合成後の画像に対して、階調圧縮特性生成部5からの階調特性を用いて階調圧縮処理を行う。
The control signal S <b> 2 is a binary signal that controls reading of an image from the
また、制御信号S2で制御されるフレームメモリ3からの読み出し処理、合成部4、階調圧縮部6での処理は、制御信号S1で制御されるフレームメモリ3への画像の書き込み処理と階調圧縮特性生成部5での処理が終了した1V後に実行される。したがって、制御信号S2は制御信号S1の波形を1V遅延させたものとなっている。
Further, the reading process from the
図6において、時刻t1では、制御信号S1が1であるので、時刻t1からt2までの1V期間で、低露光画像L1をフレームメモリ3に書き込み、それと、並行して、時刻t2までに、低露光画像L1の縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。時刻t2からt3において、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3に保持されている低露光画像L1と撮像素子2から出力される高露光画像H1を合成して、画像H1+L1を出力する。これと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5はフレームメモリ3に保持されている低露光画像L1とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像とから階調圧縮特性g(L1)を生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が、合成後の画像H1+L1に対して階調圧縮特性g(L1)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行う。
In FIG. 6, since the control signal S1 is 1 at time t1, the low-exposure image L1 is written to the
また、時刻t1からt2の1V期間の前半で、垂直方向1/2に間引かれた低露光画像L1が、画像解析部7に入力され、時刻t1からt2の1V期間の後半で、画像解析結果A(L1)を生成する。そして、A(L1)に基づき、時刻t2での制御信号S1を“0”に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、明部が支配的であると判断できるので、次の合成処理でも、低露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が好ましく、時刻t2からt3の期間で、高露光画像をバッファリングする必要はないと判断したためである。
Further, the low-exposure image L1 thinned out in the
時刻t2からt3の1V期間、制御信号S1は“0”なので、時刻t3からt4までの1V期間で、制御信号S1は“1”に更新される。時刻t3からt4の期間では、制御信号S1が“1”であるので、撮像素子2から出力される低露光画像L2をフレームメモリ3に書き込み、それと、並行して、時刻t4までに、低露光画像L2の縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。
Since the control signal S1 is “0” in the 1V period from the time t2 to the time t3, the control signal S1 is updated to “1” in the 1V period from the time t3 to the time t4. Since the control signal S1 is “1” during the period from the time t3 to the time t4, the low exposure image L2 output from the
また、時刻t3からt4の1V期間の前半で、垂直方向1/2に間引かれた低露光画像L2が画像解析部7に入力され、時刻t3からt4の1V期間の後半で、画像解析結果A(L2)が生成される。そして、解析結果A(L2)に基づき、システム制御部8は、時刻t4での制御信号S1を“1”に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、暗部が支配的になってきたと判断され、次の合成処理では、高露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が好ましく、時刻t4からt5の期間で高露光画像をバッファリングする必要があると判断されたためである。
Further, in the first half of the 1V period from time t3 to t4, the low-exposure image L2 thinned out in the
時刻t4からt5において、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれた低露光画像L2と撮像素子2から出力される高露光画像H2を合成して、画像H2+L2を出力する。これと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5はフレームメモリ3に保持されている低露光画像L1とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像とから階調圧縮特性g(L2)を生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が、合成後の画像H2+L2に対して階調圧縮特性g(L2)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行う。
From time t4 to t5, the synthesizing
また、時刻t4からt5では、制御信号S1が“1”であるので、フレームメモリ3では、前述の合成処理のために低露光画像L2が読み出されると、順次、高露光画像H2で上書きされる。それと、並行して、時刻t5までに、低露光画像L2の縮小画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。なお、縮小画像のメモリ54への書き込みは、時刻43〜t4で生成した圧縮画像がメモリ54から読み出されてから、順次に上書きされる。
Further, since the control signal S1 is “1” from time t4 to t5, when the low-exposure image L2 is read out for the above-described composition processing, the
さらに、時刻t4からt5の1V期間の前半で、垂直方向1/2に間引かれた低露光画像H2が、画像解析部7に入力され、時刻t4からt5の1V期間の後半で、画像解析結果A(H2)が生成される。そして、解析結果A(H2)に基づき、システム制御部8は、時刻t5での制御信号S1を“0”に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、暗部が支配的であると判断でき、次の合成処理でも高露光画像を用いて階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が好ましく、時刻t5からt6の期間で低露光画像をバッファリングする必要はないと判断したためである。
Further, the low-exposure image H2 thinned out in the
時刻t5からt6において、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれた高露光画像H2と撮像素子2から出力される低露光画像L3を合成して、画像H2+L3を出力する。これと並行して、階調圧縮特性生成部5はフレームメモリ3に保持されている高露光画像H2とメモリ54に保持されている縮小画像とから階調圧縮特性g(H2)を生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6が、合成後の画像H2+L3に対して階調圧縮特性g(H2)を用いて階調圧縮処理を行う。なお、時刻t5からt6の1V期間、制御信号S1は“0”なので、時刻t6からt7までの1V期間で、制御信号S1は“1”に更新される。
From time t5 to t6, the synthesizing
以上のような一連の撮像制御を行うことにより、第2実施形態においても露光量を変えた複数枚の画像を合成し、合成後の画像に適した階調圧縮特性で、階調圧縮を行って、映像信号を出力することができる。 By performing a series of imaging control as described above, a plurality of images with different exposure amounts are combined in the second embodiment, and gradation compression is performed with gradation compression characteristics suitable for the combined image. Video signals can be output.
以上のように、第2実施形態の撮像装置においても、合成処理のためにフレームメモリ3にバッファリングする画像と同じ画像を用いて、合成後の画像に対する階調圧縮特性を生成することができ、メモリアクセスによるシステム負荷の増大を回避できる。
As described above, also in the imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment, it is possible to generate the gradation compression characteristics for the combined image using the same image as the image buffered in the
また、撮影中の画像の特徴を解析して、階調圧縮特性の生成に用いる画像を決定することにより、撮影中の画像に適した階調圧縮処理を行うことができる。また、撮像素子2においては、低露光画像と高露光画像の取得順を切り替えるような構成を持たせる必要がなくなる。
In addition, by analyzing the characteristics of the image being shot and determining the image used to generate the tone compression characteristics, tone compression processing suitable for the image being shot can be performed. Further, the
なお、上記第2実施形態では、1フレーム目の画像の入力を終えるまでに1フレーム目と2フレーム目の露光量を切り替えるか否かを決定し、切り替えが必要であれば次のフレームで切り替えを実行するようにした(例えば、t3〜t4)。このように構成することで、合成に使用されない無駄なフレームが発生しなくなる。しかしながら、画像解析部7の解析結果に応じて1フレーム目と2フレーム目の路光量を入れ替えるという観点からすれば、このような構成に限られるものではない。例えば、画像解析部7による解析を1フレームの期間かけて行ない、2つのフレームにおける路光量の順序の切り替えを、その2フレーム後に実施するようにしてもよい。例えば、図6において、t3〜t4の期間で画像を解析して、高露光量の画像をフレームメモリ3に保持するように決定されると、t6のタイミングで制御信号S1を“1”にするようにしてもよい。
In the second embodiment, it is determined whether or not to switch the exposure amounts of the first frame and the second frame until the input of the image of the first frame is completed. (For example, t3 to t4). With this configuration, useless frames that are not used for synthesis are not generated. However, from the viewpoint of switching the road light amounts of the first frame and the second frame according to the analysis result of the
[第3実施形態]
次に、第3実施形態の撮像装置について説明する。第3実施形態では、露光量の異なるnフレーム分の画像を合成して、ダイナミックレンジの拡大された1フレーム分の画像を出力する撮像装置について説明する。ここで、nは3以上の自然数であり、本実施形態では、その一例としてn=3の場合について説明する。
[Third Embodiment]
Next, an imaging apparatus according to a third embodiment will be described. In the third embodiment, an imaging apparatus that synthesizes images of n frames with different exposure amounts and outputs an image of one frame with an expanded dynamic range will be described. Here, n is a natural number of 3 or more, and in this embodiment, a case where n = 3 will be described as an example.
第3実施形態の撮像装置101の構成を図7に示す。撮像装置101では、第1実施形態の撮像装置100の構成に対して、選択部9が追加されている。また、選択部9の出力がフレームメモリ3と階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力される点が第1実施形態と異なる。
FIG. 7 shows the configuration of the
次に、第3実施形態の撮像装置101の動作の概要について説明する。撮影が開始されると、システム制御部8は、撮像素子2から出力される画像の露光量が3V周期で変化するよう、光学系1、および、撮像素子2を制御する。光学系1を介して撮像撮像素子2から出力された画像は、選択部9、合成部4、および、画像解析部7に入力される。
Next, an outline of the operation of the
選択部9には、撮像素子2の出力画像とともに、合成部4からの出力画像も入力され、システム制御部8からの制御信号に基づいて合成部4からの出力画像または撮像素子2からの出力画像のいずれかを選択する。選択部9によって選択された出力画像は、フレームメモリ3および階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力される。フレームメモリ3では、選択部9からの出力画像を1フレーム分バッファリングする。選択部9は合成対象のn個のフレームのうち1つ目のフレームのタイミングでは、撮像素子2からの信号をフレームメモリ3に保持させ、2つ目以降、n−1個目までは、合成部4が出力する合成画像をフレームメモリ3に保持させる。合成部4では、フレームメモリ3から読み出された画像と、撮像素子2からの出力画像とを合成する。その結果、フレームメモリ3には、撮像素子2から連続して出力される合成対象のn個のフレームのうち、1つ目のフレームの画像、または現フレームの1つ前のフレームまで合成を終えた画像が保持される。
In addition to the output image of the
階調圧縮特性生成部5では、フレームメモリ3から読み出された画像と、選択部9からの出力画像とを用いて、合成部4の出力画像に対する、階調圧縮特性を生成する。階調圧縮部6では、階調圧縮特性生成部5から出力される階調圧縮特性を用いて、撮影中の画像に対して好ましい階調再現となり、かつ出力映像フォーマットのダイナミックレンジに収まるよう、合成部4の出力画像に階調圧縮を行う。即ち、フレームメモリ3にn−1フレーム目まで合成を終えた画像が保持されると、階調圧縮特性生成部5は、フレームメモリ3に保持された画像とその保持された画像の低解像度化された画像とに基づいて階調圧縮特性を生成する。そして、階調圧縮部6は、生成された階調圧縮特性を用いて合成部4から出力されたnフレーム目まで合成された画像の階調を圧縮する。
The tone compression
第3実施形態でも、第1実施形態と同様、フレームメモリ3は、1フレーム分の画像をバッファリングする構成となっている。したがって、3フレーム分以上の画像を合成する際には、2フレーム分ずつ、順次画像を合成するような動作となる。3枚合成の場合は、1フレーム目と2フレーム目を合成した後、1フレーム目と2フレーム目の合成結果と3フレーム目の入力画像を合成する。そのため、本実施形態のフレームメモリ3には、合成後の拡張されたダイナミックレンジを有する1フレーム分の画像、すなわち1画素あたりのビット数が増加した1フレーム分の画像を保持できる容量が必要である。nフレーム分の画像を合成する場合には、2フレームずつ、n−1回合成を行った後に、階調圧縮処理が行われる。
Also in the third embodiment, as in the first embodiment, the
このため、第3実施形態では、図7に示すように、フレームメモリ3の前段に選択部9が設けられている。そして、nフレーム分の画像を合成する際、初回の合成時には、撮像素子2の出力画像をフレームメモリ3に書き込み、2回目以降n−1回目までの合成時には、合成部4の出力画像をフレームメモリ3に書き込むようにしている。
For this reason, in the third embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7, the selection unit 9 is provided in the previous stage of the
階調圧縮特性生成部5の内部構成は第1実施形態と同様であるが、入力信号が一部異なり、図2の入力端子58にフレームメモリ3の出力画像が入力され、入力端子59には、選択部9の出力画像が入力される。
The internal configuration of the gradation compression
前述のように、本実施形態でnフレーム分の画像を合成する場合には、フレームメモリ3に、合成途中の画像をバッファリングして、2フレーム分ずつ合成し、nフレーム分全ての合成が終了した後に、階調圧縮処理を行う。そのため、階調圧縮特性は、n−1フレーム目までの合成処理(n−2回目の合成処理)で生成された画像を用いて生成される。入力端子59(図2)には、選択部9から出力される、n−2回目の合成処理後の画像が入力されて、縮小処理が行なわれ、縮小画像がメモリ54に格納される。また、フレームメモリ3には、n−2回目の合成処理後の画像が格納される。
As described above, when images for n frames are combined in the present embodiment, the image being combined is buffered in the
入力端子59から画像拡大部55までの処理は、第1実施形態と同様、1V期間かかる。低解像度画像と、フレームメモリ3から入力端子58を介して入力され、輝度生成部51を経て得られた高解像度画像とは、タイミングが一致した状態で、局所輝度レベル推定部56に入力される。局所輝度レベル推定部56、階調圧縮特性決定部57の処理は、第1実施形態と同様である。
The processing from the
また、第3実施形態においても、1フレーム分の画像をバッファリングするフレームメモリ3を、合成部4と階調圧縮特性部5で共用している。したがって、撮影中の画像に適した階調圧縮特性が生成できるよう、画像解析部7での解析結果に基づいて、階調圧縮特性生成部5で用いるn−1フレーム目までの合成後画像の組成を決定する。
Also in the third embodiment, the
例えば、図4(a)のように、明部が支配的な場合には、次の合成用画像撮影時に、露光量の低い画像から順に撮影するように撮像素子2の駆動を制御する。これにより、階調圧縮特性生成部5で参照されるn−2回目までの合成後画像(n−1フレーム目までの合成後画像)は、低露光画像をベースに生成されることになるので、明部に対して適した階調圧縮特性を生成できるようになる。
For example, as shown in FIG. 4A, when the bright part is dominant, the drive of the
また、図4(b)のように、暗部が支配的な場合には、次の合成用画像撮影時に、露光量の高い画像から順に撮影するよう、撮像素子2の駆動を制御する。これにより、階調圧縮特性生成部5で参照されるn−2回目までの合成後画像(n−1フレーム目までの合成後画像)は、高露光画像をベースに生成されることになるので、暗部に対して適した階調圧縮特性を生成できるようになる。
Also, as shown in FIG. 4B, when the dark part is dominant, the drive of the
以上のように、合成対象となるnフレームの露光量の順番の変更は、少なくとも、n個のフレームのうちのn番目のフレームの画像の露光量が最大の露光量もしくは最小の露光量になるように露光量の順番を切り替えればよい。例えば、本実施形態のように、合成対象が3個のフレームである場合、少なくとも3フレーム目の画像を最大の露光量にするか最小の露光量にするかが、画像解析部7による解析の結果に基づいて決定されればよい。
As described above, the change in the order of the exposure amounts of the n frames to be combined is at least the exposure amount of the image of the nth frame among the n frames becomes the maximum exposure amount or the minimum exposure amount. Thus, the order of exposure amounts may be switched. For example, when the synthesis target is three frames as in the present embodiment, whether the image of at least the third frame has the maximum exposure amount or the minimum exposure amount is analyzed by the
尚、本実施形態では、画像解析部7において、合成前の撮像素子2からの出力画像を参照しているがこれに限られるものではない。合成部4から出力される合成途中の画像を参照して画像解析を行なってもよい。画像解析部7による解析方法は、第1実施形態と同様である。
In the present embodiment, the
次に、第3実施形態の撮像制御の一例を図8のタイミングチャートを参照して説明する。撮像素子2からは、1V期間毎に、露光量の異なる画像が出力され、1枚の合成画像を生成するために用いられる合成前の画像の組み合わせは、図8の破線で囲まれたものとなる。すなわち、時刻t1からt4の期間では、撮像素子2の出力画像L1、M1、H1が合成され、時刻t4からt7の期間では、撮像素子2の出力画像H2、M2、L2が合成される。なお、合成される画像の組み合わせの中で、Lが表記されている画像は、最も露光量が小さく、Hが表記されている画像は、最も露光量が大きく、Mが表記されている画像は、LとHの中間の露光量となる。
Next, an example of the imaging control of the third embodiment will be described with reference to the timing chart of FIG. Images with different exposure amounts are output from the
制御信号S1は、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込みを制御する2値の制御信号である。制御信号S1が“0”の場合には、フレームメモリ3への画像の書き込みは停止され、制御信号S1が“1”の場合には、選択部9からの出力画像が、1V期間かけて、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれる。
The control signal S <b> 1 is a binary control signal that controls writing of an image into the
識別信号Iは、nフレームの画像のうち、何フレーム目までの画像を合成したかを示す識別信号であり、3枚合成の場合には、0、1、2、0、1、2、・・・と周期的に変化する。識別信号Iも、システム制御部8によって制御される信号である。識別信号Iが“0”の場合には、選択部9が撮像素子2からの画像を選択して出力し、撮像素子2から出力される画像がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれる。また、識別信号Iが“1”の場合には、選択部9が合成部4からの出力画像(合成途中の画像)を選択して出力し、合成部4の出力画像がフレームメモリ3に書き込まれる。識別信号Iが“2”の場合は、制御信号S1が“0”となり、フレームメモリへの画像の書き込みは停止される。
The identification signal I is an identification signal indicating how many frames of the n frames of images have been combined. In the case of combining three images, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2,.・ ・ Changes periodically. The identification signal I is also a signal controlled by the
また、識別信号Iは、階調圧縮特性生成部5においても参照される。階調圧縮特性生成部5は、識別信号Iが1のとき(合成対象がnフレームの場合はIが“n−2”のとき)に、選択部9からの合成画像(n−1個目のフレームまでの合成画像)を取り込み、縮小画像を生成し、メモリ54に保持する。したがって、露光量の異なるnフレームの画像を合成した結果に対して、階調圧縮を行う際、n−1フレーム目までの画像を合成した結果を参照して、階調圧縮特性を作ることになる。本実施形態のように3枚合成の場合には、2枚目までの画像の合成結果から、階調圧縮特性が生成される。
The identification signal I is also referred to in the gradation compression
制御信号S2は、フレームメモリ3からの画像の読み出しと、合成部4、及び、階調圧縮部6での処理のon/offを制御する2値の信号である。制御信号S2が“1”の場合、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3に書き込まれている画像を読み出し、撮像素子2から出力される画像と、フレームメモリ3から読み出した画像を用いて、合成処理が行う。また、制御信号S2が“1”の場合、階調圧縮部6は、前述の識別信号Iを参照し、n枚合成において識別信号Iが“n−1”(3枚合成の場合には、I=“2”)の場合に、合成部4の出力に対して階調圧縮処理を行う。
The control signal S <b> 2 is a binary signal that controls reading of an image from the
制御信号S3は、合成される露光量の異なる3フレーム分の画像を、どのような順序で撮影するかを決定する制御信号であり、画像解析部7の結果に基づいて決定される。制御信号S3が“0”になるのは、撮影中の画像において、明部が支配的であると判定された場合であり、制御信号S3が“1”になるのは、撮影中の画像において、暗部が支配的であると判定された場合である。制御信号S3が“0”の場合には、合成される3フレームの画像のうち、露光量の小さい2フレーム分の画像が先に撮影されるよう、撮像素子2が制御される。また、制御信号S3が“1”の場合には、合成される3フレームの画像のうち、露光量の大きい2フレーム分の画像が先に撮影されるよう、撮像素子2が制御される。
The control signal S3 is a control signal that determines in what order the images for three frames with different exposure amounts to be combined are taken, and is determined based on the result of the
また、図8では、識別信号Iが“0”のときに、撮像素子2から出力された画像を用いて、画像解析部7での処理を行っているが、識別信号Iが“1”のときに撮像素子2から出力される画像、または、合成途中の画像を用いてもよい。
In FIG. 8, when the identification signal I is “0”, the
図8において、時刻t1からt4までの期間では、制御信号S3が“0”であるので、合成対象の3フレーム分の画像は、露光量の小さいものから順に、L1、M1、H1と撮像素子2から出力される。 In FIG. 8, since the control signal S3 is “0” in the period from time t1 to time t4, the images for three frames to be combined are L1, M1, H1, and the image sensor in order of increasing exposure amount. 2 is output.
時刻t1からt2の期間で、フレームメモリ3には、画像L1が書き込まれ、時刻t2からt3までの期間で合成部4はフレームメモリ3から読み出された画像L1と、撮像素子2から出力される画像M1とを合成する。合成後の画像L1+M1は、フレームメモリ3に上書きされるとともに、階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力され、1V期間かけて低解像度画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。
In the period from time t1 to t2, the image L1 is written in the
時刻t3からt4までの期間で、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3から合成途中の画像L1+M1を読み出し、それと、撮像素子2から出力される画像H1を合成して、合成後の画像L1+M1+H1を出力する。また、階調圧縮特性生成部5は、フレームメモリ3から読み出された合成途中の画像L1+M1とその縮小画像(1V前でメモリ54に保持されている)を用いて階調圧縮特性g(L1+M1)を生成し、出力する。階調圧縮部6は、合成部4から出力される合成後の画像L1+M1+H1に対して、階調圧縮特性生成部5からの階調圧縮特性g(L1+M1)を用いて、階調圧縮を行う。
During the period from time t3 to t4, the
また、時刻t1からt4の期間では、画像解析部7は、合成対象の複数フレームの画像の中で、最初に撮像素子2から出力された画像L1を用いて解析を行い、解析結果A(L1)を出力する。そして、解析結果A(L1)に基づいて、時刻t4からの合成で参照する制御信号S3を“1”に更新する。これは、現在撮影中の画像を解析した結果、暗部が支配的になってきたと判断でき、時刻t4からの合成処理は、高露光画像を先に撮影して、暗部での階調圧縮特性を最適化した方が好ましいと考えられるためである。
In the period from time t1 to time t4, the
時刻t4からt7までの期間においては、制御信号S3が“1”であるので、合成対象の3フレーム分の画像は、露光量の大きいものから順に、すなわちH2、M2、L2の順に撮像素子2から出力される。
Since the control signal S3 is “1” during the period from time t4 to t7, the image for the three frames to be synthesized is
時刻t4からt5の期間で、フレームメモリ3には、画像H2が書き込まれ、時刻t5からt6までの期間で合成部4はフレームメモリ3から読み出された画像H2と、撮像素子2から出力される画像M2とを合成する。合成後の画像H2+M2は、フレームメモリ3に上書きされるとともに、階調圧縮特性生成部5に入力され、1V期間かけて低解像度画像が生成され、メモリ54に保持される。
In the period from time t4 to t5, the image H2 is written in the
時刻t6からt7までの期間で、合成部4は、フレームメモリ3から読み出された画像H2+M2と、撮像素子2から出力される画像L2とを合成して、合成後の画像H2+M2+L2を出力する。また、階調圧縮特性生成部5は、フレームメモリ3から読み出された合成途中の画像H2+M2とその縮小画像(1V前でメモリ54に保持されている)を用いて階調圧縮特性g(H2+M2)を生成し、出力する。階調圧縮部6は、合成部4から出力される合成後の画像H2+M2+L2に対して、階調圧縮特性生成部5からの階調圧縮特性g(L1+M1)を用いて、階調圧縮を行う。
In the period from time t6 to t7, the
また、時刻t4からt7の期間において、画像解析部7は、合成される複数フレームの画像の中で最初に撮像素子2から出力された画像H2を用いて解析処理を行い、その解析結果A(H2)を出力する。システム制御部8は、A(H2)に基づいて、時刻t7からの合成で参照する制御信号S3を更新する。以上のような、一連の撮像制御を行うことにより、露光量を変えた複数枚の画像を合成し、合成後の画像に適した階調圧縮特性で、階調圧縮を行って、映像信号を出力することができる。
In the period from time t4 to time t7, the
以上のように、nフレームの画像を合成対象とした場合にも、合成処理のためにフレームメモリ3にバッファリングする画像と同じ画像を用いて、合成後の画像に対する階調圧縮特性を生成することができる。そのため、メモリアクセスによるシステム負荷の増大を回避できる。また、撮影中の画像の特徴を解析して、階調圧縮特性の生成に用いる画像を決定することにより、撮影中の画像に適した階調圧縮処理を行うことができる。
As described above, even when an image of n frames is selected as a synthesis target, tone compression characteristics for the synthesized image are generated using the same image as the image buffered in the
また、本発明は、以下の処理を実行することによっても実現される。即ち、上述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェア(プログラム)を、ネットワーク又は各種記憶媒体を介してシステム或いは装置に供給し、そのシステム或いは装置のコンピュータ(またはCPUやMPU等)がプログラムを読み出して実行する処理である。 The present invention can also be realized by executing the following processing. That is, software (program) that realizes the functions of the above-described embodiments is supplied to a system or apparatus via a network or various storage media, and a computer (or CPU, MPU, or the like) of the system or apparatus reads the program. It is a process to be executed.
Claims (8)
異なる2つの露光量を順次に適用した撮影により第1の画像とこれに後続する第2の画像を出力する撮像手段と、
前記第1の画像と前記第2の画像を合成してダイナミックレンジが拡張された合成画像を生成する合成手段と、
前記第1の画像と前記第1の画像を低解像度化した画像とに基づいて階調圧縮特性を生成する生成手段と、
前記生成手段で生成された前記階調圧縮特性を用いて前記合成画像の階調を圧縮する階調圧縮手段と、
前記階調圧縮特性の生成に使用される画像の露光量として前記2つの露光量のいずれが適切かを判定するために、前記第1の画像を解析する解析手段と、
前記解析手段が適切と判定した露光量で撮影された画像を前記生成手段が用いるように、前記第1および第2の画像と前記2つの露光量との対応を制御する制御手段と、を備えることを特徴とする撮像装置。 An imaging apparatus that generates an image with an expanded dynamic range by combining two images having different exposure amounts,
Imaging means for outputting a first image and a second image following the first image by photographing in which two different exposure amounts are sequentially applied;
Synthesizing means for synthesizing the first image and the second image to generate a synthesized image having an extended dynamic range;
Generating means for generating gradation compression characteristics based on the first image and an image obtained by reducing the resolution of the first image;
Gradation compression means for compressing the gradation of the composite image using the gradation compression characteristic generated by the generation means;
Analyzing means for analyzing the first image in order to determine which of the two exposure amounts is appropriate as an exposure amount of the image used for generating the gradation compression characteristic;
Control means for controlling correspondence between the first and second images and the two exposure amounts so that the generation unit uses an image taken with an exposure amount determined to be appropriate by the analysis unit. An imaging apparatus characterized by that.
前記生成手段は、前記第1の画像が前記メモリに保持されていくのと並行して前記低解像度化した画像を生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の撮像装置。 A holding means for holding the first image in a memory;
The imaging apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the generation unit generates the reduced-resolution image in parallel with the first image being held in the memory.
前記制御手段は、前記撮像手段における前記2つの露光量の適用の順序を入れ替えることを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の撮像装置。 The imaging means continuously outputs images obtained by imaging by alternately applying the two exposure amounts,
It said control means, the image pickup apparatus according to claim 1 or 2, characterized in that switching the order of application of the two exposure amount in the imaging means.
前記制御手段は、前記撮像手段から連続して出力される画像からの前記第1および第2の画像として用いる画像の抽出を1画像分ずらすことを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の撮像装置。 The imaging means continuously outputs images obtained by imaging by alternately applying the two exposure amounts,
Wherein, imaging according to claim 1 or 2, characterized in that shifting one image to extract image used as the first and second images from images continuously output from the imaging means apparatus.
n個の異なる露光量を順次に適用して撮影することにより得られた画像を連続して出力する撮像手段と、
前記撮像手段から連続して出力されたn個の画像を順次に合成して、ダイナミックレンジが拡張された合成画像を得る合成手段と、
前記合成手段よりn−1番目以前の段階で得られる中間合成画像と、該中間合成画像を低解像度化した画像とに基づいて階調圧縮特性を生成する生成手段と、
前記生成手段で生成された前記階調圧縮特性を用いて前記合成手段により得られた前記合成画像の階調を圧縮する階調圧縮手段と、
前記n個の画像のうちのn番目の画像を前記n個の露光量のうちの最大の露光量が適用された画像とするか、最小の露光量が適用された画像とするかを判定するために、前記n個のフレームの1フレーム目の画像または前記合成手段が出力した前記中間合成画像を解析する解析手段と、
前記解析手段による前記判定に基づいて、前記n個の画像と前記n個の露光量との対応を制御する制御手段と、を備えることを特徴とする撮像装置。 An imaging apparatus that generates an image with an expanded dynamic range by combining n images (n is a natural number of 3 or more) with different exposure amounts,
imaging means for continuously outputting images obtained by sequentially applying and shooting n different exposure amounts;
Synthesis means for sequentially synthesizing n images continuously output from the imaging means to obtain a synthesized image with an extended dynamic range;
Generating means for generating a gradation compression characteristic based on an intermediate composite image obtained at the stage before the (n−1) th from the synthesis means, and an image obtained by reducing the resolution of the intermediate composite image;
A gradation compression means for compressing the gradation of the composite image obtained by the composition means using the gradation compression characteristic generated by the generation means;
It is determined whether the nth image among the n images is an image to which the maximum exposure amount among the n exposure amounts is applied or an image to which the minimum exposure amount is applied. Therefore, analysis means for analyzing the first frame image of the n frames or the intermediate synthesized image output by the synthesizing means,
An imaging apparatus comprising: control means for controlling correspondence between the n images and the n exposure amounts based on the determination by the analysis means .
前記合成手段は、前記撮像手段から現在出力されている画像と前記メモリに保持されている画像を合成して前記保持手段に出力し、
前記生成手段は、前記中間合成画像が前記メモリに保持されるのと並行して、該中間合成画像を低解像度化した画像を生成することを特徴とする請求項7に記載の撮像装置。 A holding unit that holds the first image of the n images to be combined output from the imaging unit or the intermediate combined image output from the combining unit in a memory;
The synthesizing unit synthesizes an image currently output from the imaging unit and an image held in the memory, and outputs the synthesized image to the holding unit.
The imaging apparatus according to claim 7 , wherein the generation unit generates an image obtained by reducing the resolution of the intermediate composite image in parallel with the intermediate composite image being held in the memory.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011209784A JP5852385B2 (en) | 2011-09-26 | 2011-09-26 | Imaging device |
| US13/617,772 US9049380B2 (en) | 2011-09-26 | 2012-09-14 | Image processing apparatus for generating an image having an expanded dynamic range and method thereof, and image capture apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011209784A JP5852385B2 (en) | 2011-09-26 | 2011-09-26 | Imaging device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013074334A JP2013074334A (en) | 2013-04-22 |
| JP2013074334A5 JP2013074334A5 (en) | 2014-10-30 |
| JP5852385B2 true JP5852385B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 |
Family
ID=48478509
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011209784A Expired - Fee Related JP5852385B2 (en) | 2011-09-26 | 2011-09-26 | Imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5852385B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6635722B2 (en) * | 2015-09-01 | 2020-01-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
| JP7204480B2 (en) | 2018-12-27 | 2023-01-16 | キヤノン株式会社 | IMAGING DEVICE, IMAGING SYSTEM, MOVING OBJECT, AND IMAGING DEVICE CONTROL METHOD |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4214457B2 (en) * | 2003-01-09 | 2009-01-28 | ソニー株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and method, recording medium, and program |
| JP2011010108A (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2011-01-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Imaging control apparatus, imaging apparatus, and imaging control method |
-
2011
- 2011-09-26 JP JP2011209784A patent/JP5852385B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013074334A (en) | 2013-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9049380B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus for generating an image having an expanded dynamic range and method thereof, and image capture apparatus | |
| JP5898466B2 (en) | Imaging device, control method thereof, and program | |
| US8009337B2 (en) | Image display apparatus, method, and program | |
| US8149283B2 (en) | Image processing device, electronic camera, image processing method, and image processing program | |
| US8570334B2 (en) | Image processing device capable of efficiently correcting image data and imaging apparatus capable of performing the same | |
| JP2007201985A (en) | Wide dynamic range imaging apparatus | |
| JP5325745B2 (en) | Moving image processing program, apparatus and method, and imaging apparatus equipped with moving image processing apparatus | |
| JP4821626B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, electronic camera, and image processing program | |
| JP6304293B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| US6867805B2 (en) | Image pickup device and video signal processing method | |
| JP2018160777A (en) | Imaging device and control method thereof, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2005311743A (en) | Image processing device | |
| KR20230175155A (en) | Image processing apparatus and method thereof | |
| US8699827B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, signal processing method, and program | |
| JP5852385B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP5829122B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and evaluation value generation apparatus | |
| JP6152009B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and recording medium | |
| JP4225241B2 (en) | Image display device | |
| US8077226B2 (en) | Data processing apparatus having parallel processing zoom processors | |
| JP5820213B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and method, and imaging apparatus | |
| US8411181B2 (en) | Image pick-up apparatus for controlling generation of an electronic shutter pulse signal based on one of a detected brightness of an imaging object and an obtained current exposure value, and method and non-transitory computer readable recording medium therefor | |
| JP5195973B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, electronic camera, and image processing program | |
| JP7545238B2 (en) | Imaging device and control method thereof | |
| JP4610488B2 (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP2022119630A (en) | Image processing device, image processing method, imaging device, and control method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140912 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140912 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150522 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150626 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150821 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20151106 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20151204 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5852385 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |