JP5828380B2 - Composite molded body and method for producing the same - Google Patents
Composite molded body and method for producing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5828380B2 JP5828380B2 JP2011141927A JP2011141927A JP5828380B2 JP 5828380 B2 JP5828380 B2 JP 5828380B2 JP 2011141927 A JP2011141927 A JP 2011141927A JP 2011141927 A JP2011141927 A JP 2011141927A JP 5828380 B2 JP5828380 B2 JP 5828380B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resin
- fiber reinforced
- reinforced resin
- fiber
- composite molded
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Moulds For Moulding Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
- Injection Moulding Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Description
本発明は、複合成形体およびその製造方法に関し、とくに、予備成形体を型内に配置してインサート成形する複合成形体の製造方法およびその方法により製造された複合成形体に関する。 The present invention relates to a composite molded body and a method for manufacturing the same, and more particularly to a method for manufacturing a composite molded body in which a preform is placed in a mold and insert molding, and a composite molded body manufactured by the method.
強化繊維にマトリックス樹脂を溶融させて含浸させた繊維強化樹脂は、その優れた力学特性を活かして各種分野で部材の補強や表面形成等に幅広く利用されている。また、優れた補強効果等を得るためには、強化繊維として連続繊維を使用する場合が多く、とくに、連続強化繊維を帯状(テープ状)に一方向に引き揃え、それに樹脂を含浸させた一方向プリプレグの態様で好ましく用いられている。例えば、特許文献1には、マトリックス樹脂に熱可塑性樹脂を用いた、実質的に平行四辺形の断面形状を有する成形材料(一方向プリプレグ)が開示されている。
A fiber reinforced resin obtained by melting and impregnating a reinforced fiber with a matrix resin is widely used for reinforcement of members and surface formation in various fields by utilizing its excellent mechanical properties. In order to obtain an excellent reinforcing effect, continuous fibers are often used as reinforcing fibers, and in particular, continuous reinforcing fibers are aligned in one direction in a strip shape (tape shape) and impregnated with resin. It is preferably used in the direction of a directional prepreg. For example,
しかしながら、このような一方向プリプレグ単独では、複雑な形状、例えば、三次元形状やリブを有する構造などを形成することは困難であった。そこで、例えば、板状の繊維強化樹脂をインサート成形(板状の繊維強化樹脂の全体または一部を覆うように熱可塑性樹脂を射出成形して結合・一体化する成形)することにより、複雑な形状を有する部材を実現する技術が広く利用されている(例えば、特許文献2〜4)。このインサート成形においては、繊維強化樹脂と後から射出成形される熱可塑性樹脂との接着性が十分でない点が問題であった。
However, it has been difficult to form a complicated shape such as a three-dimensional shape or a structure having a rib by using such a unidirectional prepreg alone. For this reason, for example, insert-molding a plate-like fiber reinforced resin (molding in which a thermoplastic resin is injection-molded so as to cover all or part of the plate-like fiber reinforced resin is combined and integrated) is complicated. A technique for realizing a member having a shape is widely used (for example,
かかる問題に対して、例えば、特許文献3、4では、物理的な係合により接着性を改善する試みが行われている。しかしながら、特に特許文献3に開示されているような、インサートされる繊維強化樹脂が例えば凸型で、金型と閉空間を形成する場合、後から射出成形される熱可塑性樹脂が、繊維強化樹脂の形態に沿って閉空間に上手く流れ込まず、本来の目的である接着性を向上させる目的を達成し難いという問題が発生していた。更には、樹脂が流れ込まずに形成された複合成形体の表面の溝や空間は、接着性の問題に留まらず、その溝や空間から水分などが侵入するという環境耐久性という面で悪影響を引き起こしていただけでなく、複合成形体の外観上の問題をも発生させていた。
For example,
そこで本発明は、上記のような実情に鑑み、とくに繊維強化樹脂と樹脂との接着性およびその信頼性、ならびに、その外観にも優れる、複合成形体およびその製造方法を提供する。 In view of the above circumstances, the present invention provides a composite molded body and a method for producing the same, which are particularly excellent in adhesion between a fiber reinforced resin and a resin, its reliability, and its appearance.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明に係る複合成形体の製造方法は、予め成形した、マトリックス樹脂が熱可塑性樹脂からなる繊維強化樹脂Aを予備成形体として型内に配置し、該型内の前記繊維強化樹脂A周りに液状化した樹脂Bを供給して前記繊維強化樹脂Aをインサート成形する複合成形体の製造方法であって、前記繊維強化樹脂Aの前記樹脂Bに接触する側面として、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面で、かつ、その側面の少なくとも一部に、深さが前記繊維強化樹脂Aの厚みTに対し0.1T〜0.9Tの範囲内にあるアンダーカット形状を有する形状の側面を、インサート成形前に形成しておき、インサート成形前に前記繊維強化樹脂Aを型の内面上に配置し、前記繊維強化樹脂Aが複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されるように前記樹脂Bを供給することを特徴とする方法(第1の方法)からなる。また、本発明は、予め成形した、マトリックス樹脂が熱可塑性樹脂からなる繊維強化樹脂Aを予備成形体として型内に配置し、該型内の前記繊維強化樹脂A周りに液状化した樹脂Bを供給して前記繊維強化樹脂Aをインサート成形する複合成形体の製造方法であって、前記繊維強化樹脂Aの前記樹脂Bに接触する側面として、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面同士が直接接続されて該傾斜面間に変曲点が形成されている形状の側面で、かつ、その側面の少なくとも一部に、深さが前記繊維強化樹脂Aの厚みTに対し0.1T〜0.9Tの範囲内にあるアンダーカット形状を有する形状の側面を、インサート成形前に形成しておき、インサート成形前に前記繊維強化樹脂Aを型の内面上に配置し、前記繊維強化樹脂Aが複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されるように前記樹脂Bを供給することを特徴とする、複合成形体の製造方法(第2の方法)も提供する。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, a method for producing a composite molded body according to the present invention includes pre-molding a fiber reinforced resin A whose matrix resin is made of a thermoplastic resin in a mold as a preform, A method of manufacturing a composite molded body in which a liquefied resin B is supplied around the fiber reinforced resin A and the fiber reinforced resin A is insert-molded, and the side surface of the fiber reinforced resin A that contacts the resin B in concave type least two distances between have a slanted surface inclined surface is maximized at a concave opening shape side of the extending obliquely in opposite directions from the opening of so as to form a concave, and A side surface having an undercut shape having a depth within a range of 0.1T to 0.9T with respect to the thickness T of the fiber reinforced resin A is formed on at least a part of the side surface before insert molding. Ii How the fiber-reinforced resin A prior insert molded placed in a mold on the inner surface, the fiber-reinforced resin A and supplying the resin B to be placed on at least one surface of the composite compact (First method) . In the present invention, a pre-molded fiber reinforced resin A whose matrix resin is made of a thermoplastic resin is placed in a mold as a preform, and a resin B liquefied around the fiber reinforced resin A in the mold is obtained. A method of manufacturing a composite molded body in which the fiber reinforced resin A is supplied and insert-molded, and the side surfaces of the fiber reinforced resin A that are in contact with the resin B are formed from the openings of the concave mold so as to form a concave mold. It is a side surface of a shape having two inclined surfaces extending in an inclined direction in the opposite direction, the inclined surfaces being directly connected to each other, and an inflection point is formed between the inclined surfaces, and at least a part of the side surface The side surface of the shape having an undercut shape whose depth is in the range of 0.1T to 0.9T with respect to the thickness T of the fiber reinforced resin A is formed before insert molding, and before the insert molding, Fiber reinforced resin A A method for producing a composite molded body (second method), wherein the resin B is supplied so that the fiber reinforced resin A is disposed on at least one surface of the composite molded body. ).
このような本発明に係る複合成形体の製造方法(第1の方法)においては、インサート成形される繊維強化樹脂Aには、樹脂Bに接触する側面として、互いに異なる角度で、とくに凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面が、インサート成形前に形成されている。インサート成形時には、樹脂Bがこの傾斜面を有する繊維強化樹脂Aの側面部にも流れ込んでくることになるが、もしこの側面部に樹脂Bが流れ込みにくい閉空間が形成されてしまうと、前述の如く繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの接着性を向上させる目的を達成し難くなり、その部位に望ましくない溝や空間が形成されて、水分の侵入などによる環境耐久性の問題を引き起こしたり、複合成形体の外観の品位を低下させたりする問題を招くおそれがある。しかし本発明では、繊維強化樹脂Aの側面が少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有する形状の側面に形成されており、これら2つの傾斜面は凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延び該傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面からなるので、両傾斜面間の角度は、例えば一つの面からなる側面(例えば一つの傾斜面からなる側面)と、繊維強化樹脂Aが配置された型の内面(例えば、繊維強化樹脂Aの上下面のいずれか一方の面が接する型の内面)との間の角度に比べ、容易にはるかに大きな角度とされる。しかも、傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面であるので、両傾斜面間には、樹脂Bが流れ込みにくい閉空間は形成され難くなり、樹脂Bは繊維強化樹脂Aの側面全面にわたって良好に接触するまで流れ込むことが可能になる。その結果、繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの接着性およびその信頼性が確保され、かつ、得られる複合成形体の外観の品位の低下も防止される。そして、繊維強化樹脂Aの側面が互いに逆方向に凹型に傾斜する少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有し、かつ、両傾斜面間には上記の如く樹脂Bが望ましくない閉空間を形成することなく良好に流れ込んでくるので、複合成形体として、樹脂Bから繊維強化樹脂A部が極めて脱落しにくい形態が達成され(つまり、繊維強化樹脂Aの側面部には繊維強化樹脂A本体側に入り込んだ凹型形状、とくに本発明ではアンダーカット形状が形成される形態が達成され)、繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの間の接合強度が極めて高い複合成形体が実現される。上記第2の方法としての本発明に係る複合成形体の製造方法においても、繊維強化樹脂Aの樹脂Bに接触する側面として、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面同士が直接接続されて該傾斜面間に変曲点が形成されている形状の側面(つまり、後述の図1や図2に示すような形状の側面)に形成されるので、必然的に、両傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面となり、両傾斜面間には、樹脂Bが流れ込みにくい閉空間は形成され難くなって、樹脂Bは繊維強化樹脂Aの側面全面にわたって良好に接触するまで流れ込むことが可能になる。その結果、上記同様、繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの接着性およびその信頼性が確保され、かつ、得られる複合成形体の外観の品位の低下も防止される。また、アンダーカット形状の形成により、繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの間の接合強度が極めて高い複合成形体が実現される。 In the manufacturing method (first method) of the composite molded body according to the present invention as described above, in the fiber reinforced resin A to be insert-molded, a concave shape is formed at different angles as side surfaces in contact with the resin B, in particular. side shape distance between have at least two inclined surfaces extending obliquely in opposite directions from the opening of the concave type inclined surface is maximized at a recessed opening such that is formed before the insert molding Has been. At the time of insert molding, the resin B also flows into the side surface portion of the fiber reinforced resin A having the inclined surface. If a closed space in which the resin B does not easily flow into the side surface portion is formed, As described above, it is difficult to achieve the purpose of improving the adhesion between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B, and undesirable grooves and spaces are formed in the portion, causing environmental durability problems due to intrusion of moisture, etc. There is a possibility of causing a problem of deteriorating the appearance quality of the molded body. In the present invention, however, the side surface of the fiber reinforced resin A is formed on the side surface of the shape having at least two inclined surfaces, the two inclined surfaces in the opposite directions from the opening of the concave type so as to form a concave since the distance between the extending inclined surface inclined to become from the side of the shape becomes maximum in recessed openings, the angle between the two inclined surfaces, for example, a side surface (e.g., one of the inclined surface made of one surface side ) And the inner surface of the mold on which the fiber reinforced resin A is disposed (for example, the inner surface of the mold on which one of the upper and lower surfaces of the fiber reinforced resin A is in contact) is easily a much larger angle. It is said. Moreover, since the distance between the inclined surfaces is a side surface having a maximum shape at the concave opening, it is difficult to form a closed space in which the resin B hardly flows between the inclined surfaces, and the resin B is a fiber-reinforced resin A. It becomes possible to flow in until it makes good contact over the entire side surface. As a result, the adhesion between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B and the reliability thereof are ensured, and the deterioration of the appearance of the resulting composite molded article is also prevented. The side surface of the fiber reinforced resin A has at least two inclined surfaces inclined in a concave shape in opposite directions, and the resin B is good without forming an undesired closed space between the inclined surfaces as described above. As a composite molded body, a form in which the fiber reinforced resin A portion hardly falls off from the resin B is achieved (that is, the side surface of the fiber reinforced resin A has a concave shape that has entered the fiber reinforced resin A main body side. Shape, in particular, a form in which an undercut shape is formed is achieved in the present invention), and a composite molded body having extremely high bonding strength between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B is realized. Also in the method for producing a composite molded body according to the present invention as the second method, the side surfaces of the fiber reinforced resin A that are in contact with the resin B are inclined in opposite directions from the opening of the concave mold so as to form a concave mold. The side surfaces of the shape in which the inclined surfaces are directly connected to each other and the inflection points are formed between the inclined surfaces (that is, the shapes as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 described later). Therefore, the distance between the two inclined surfaces is inevitably a side surface having a maximum shape at the concave opening, and a closed space in which the resin B does not easily flow is formed between the two inclined surfaces. It becomes difficult, and the resin B can flow in until it contacts well over the entire side surface of the fiber reinforced resin A. As a result, as described above, the adhesion between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B and the reliability thereof are ensured, and the deterioration of the appearance of the resulting composite molded article is also prevented. Moreover, the composite molded body in which the bonding strength between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B is extremely high is realized by forming the undercut shape.
なお、上記繊維強化樹脂Aの側面に形成される、互いに異なる角度で凹型に傾斜する少なくとも2つの傾斜面は、上記第2の方法のように両傾斜面の端部同士が直接接続されて両傾斜面間に角度の変曲点を有する形態とすることもできるし、両傾斜面間に両傾斜面の中間の角度の側面部分を有する形態とすることもできるし、両傾斜面間を断面形状が円弧状の側面部分で接続した形態とすることもできる。また、互いに異なる角度で凹型に傾斜する少なくとも2つの傾斜面は、必ずしも、逆方向に同じ角度で傾斜している必要はなく、互いに異なる角度で逆方向に傾斜していてもよい。 Note that at least two inclined surfaces formed on the side surfaces of the fiber reinforced resin A and inclined in a concave shape at different angles are directly connected to each other at the ends of both inclined surfaces as in the second method. It can be configured to have an inflection point of an angle between the inclined surfaces, or can be configured to have a side surface portion having an intermediate angle between the inclined surfaces, or a cross section between the inclined surfaces. It can also be set as the form which the shape connected in the side part of circular arc shape. In addition, the at least two inclined surfaces inclined concavely at different angles do not necessarily have to be inclined at the same angle in the opposite direction, but may be inclined in the opposite direction at different angles.
上記本発明に係る複合成形体の製造方法においては、前記繊維強化樹脂Aの側面として、互いに逆方向に傾斜する少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有し、該側面のいずれかの部分が多かれ少なかれ繊維強化樹脂A本体側に入り込んだアンダーカット形状が形成されることになるが、この側面の少なくとも一部に、深さが繊維強化樹脂Aの厚みTに対し0.1T〜0.9Tの範囲内にあるアンダーカット形状をインサート成形前に形成しておく。アンダーカット形状の深さが0.1T未満であると、上述の閉空間を形成する可能性が残るだけでなく、アンダーカット形状による樹脂Bの繊維強化樹脂Aの保持強度が低くなり、成形後における繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの間の接合強度が低下するおそれがある。アンダーカット形状の深さが0.9Tを超えると、同様にアンダーカット形状による樹脂Bの繊維強化樹脂Aの保持強度が低くなるだけでなく、繊維強化樹脂Aの厚みTに対してアンダーカット形状の深さが深くなりすぎ、また、傾斜面の傾斜角も大きくなりすぎるおそれがあるため、この繊維強化樹脂Aの側面部に樹脂Bが流れ込みにくくなるおそれがある。 In the method for producing a composite molded article according to the present invention, as the side surface of the fiber-reinforced resin A, have at least two inclined surfaces inclined in opposite directions to each other, more or less fiber reinforced any part of the side surface An undercut shape that enters the resin A main body side is formed, but the depth is within a range of 0.1 T to 0.9 T with respect to the thickness T of the fiber reinforced resin A at least part of the side surface. All clauses to form a certain undercut shape before insert molding. If the depth of the undercut shape is less than 0.1T, not only the possibility of forming the above-mentioned closed space remains, but also the holding strength of the fiber reinforced resin A of the resin B due to the undercut shape becomes low, and after molding There is a possibility that the bonding strength between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B at the time may decrease. If the depth of the undercut shape exceeds 0.9T, not only the retention strength of the fiber reinforced resin A of the resin B due to the undercut shape is lowered, but also the undercut shape with respect to the thickness T of the fiber reinforced resin A Since the depth of the resin is too deep and the inclination angle of the inclined surface may be too large, the resin B may not easily flow into the side surface portion of the fiber reinforced resin A.
そして、繊維強化樹脂Aが成形されるべき複合成形体中のどの位置に配置されるかについては、本発明では、インサート成形前に上記繊維強化樹脂Aを型の内面上に配置し、上記繊維強化樹脂Aが複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されるように前記樹脂Bを供給することとしている。すなわち、上記繊維強化樹脂Aが複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されていると、インサート成形前に繊維強化樹脂Aを型の内面上に配置すればよいことになるので、型内への繊維強化樹脂Aの配置、ひいては、樹脂Bの供給によるインサート成形が容易化される。 And in which position in the composite molded body in which the fiber reinforced resin A is to be molded , in the present invention, the fiber reinforced resin A is disposed on the inner surface of the mold before insert molding, and the fiber The resin B is supplied so that the reinforced resin A is disposed on at least one surface of the composite molded body. That is, when the fiber reinforced resin A is disposed on at least one surface of the composite molded body, the fiber reinforced resin A may be disposed on the inner surface of the mold before insert molding. The arrangement of the fiber reinforced resin A, and hence the insert molding by supplying the resin B is facilitated.
また、上記繊維強化樹脂A自体の構成は特に限定されず、例えば1枚物の繊維強化樹脂からなる構成であってもよく、複数枚の繊維強化樹脂を積層・一体化して得られたものであってもよい。特に後者の形態では、繊維強化樹脂Aの形状の自由度を拡大でき、かつ、その所望の側面形状の形成も容易化できる。 The configuration of the fiber reinforced resin A itself is not particularly limited. For example, the configuration may be a single fiber reinforced resin, which is obtained by laminating and integrating a plurality of fiber reinforced resins. There may be. In particular, in the latter form, the degree of freedom of the shape of the fiber reinforced resin A can be expanded, and the formation of the desired side surface shape can be facilitated.
また、上記繊維強化樹脂Aの強化繊維の形態については、特に限定されず、不連続な繊維から連続繊維まで、さらには織物の形態まで採用することが可能である。ただし、繊維強化樹脂Aをインサート成形する本発明の複合成形体の製造においては、繊維強化樹脂Aには補強材の機能が要求されることから、繊維強化樹脂A自体があるレベル以上の機械特性を有していることが好ましく、この面からは、繊維強化樹脂Aが、数平均繊維長2mm以上の強化繊維を含む繊維強化樹脂からなることが好ましい。 Moreover, it does not specifically limit about the form of the reinforced fiber of the said fiber reinforced resin A, It is possible to employ | adopt from the discontinuous fiber to the continuous fiber, and also the form of a textile fabric. However, in the production of the composite molded body of the present invention in which the fiber reinforced resin A is insert-molded, the fiber reinforced resin A is required to have a function of a reinforcing material. From this aspect, it is preferable that the fiber reinforced resin A is made of a fiber reinforced resin containing reinforced fibers having a number average fiber length of 2 mm or more.
とくに、上記繊維強化樹脂Aの強化繊維が連続繊維であり、かつ、一方向に配向されている形態であると、その特定の一方向の機械特性を効率よく高めることが可能である。したがって、このような形態は、複合成形体の特定方向の機械特性の向上が求められる場合に、とくに有効である。 In particular, when the reinforcing fiber of the fiber reinforced resin A is a continuous fiber and is oriented in one direction, it is possible to efficiently enhance the mechanical characteristics in that specific one direction. Therefore, such a form is particularly effective when improvement of mechanical properties in a specific direction of the composite molded body is required.
また、上記液状化した樹脂Bの型内への供給方法についてもとくに限定されないが、良好な成形性、生産性を実現するためには、溶融した樹脂Bを射出成形または射出圧縮成形により型内に供給する方法が好ましい。 Further, the method for supplying the liquefied resin B into the mold is not particularly limited, but in order to achieve good moldability and productivity, the molten resin B is injected into the mold by injection molding or injection compression molding. The method of supplying to is preferable.
また、上記繊維強化樹脂Aのマトリックス樹脂の種類は熱可塑性樹脂であるが、上記樹脂Bの種類としては、熱可塑性樹脂、熱硬化性樹脂の両方が可能である。特に上記樹脂Bが熱可塑性樹脂からなる場合、良好な成形性、生産性が得られるため、より好ましい。とりわけ繊維強化樹脂Aのマトリックス樹脂と同種の熱可塑性樹脂からなる場合、優れた接着性が得られ易いため、本発明における最も好ましい態様といえる。本発明で繊維強化樹脂A、および/または、樹脂Bに用いる熱可塑性樹脂の種類はとくに限定されず、例えば、ポリアミド(ナイロン6、ナイロン66、芳香族ポリアミド等)、ポリオレフィン(ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン等)、ポリエステル(ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリブチレンテレフタレート等)、ポリカーボネート、ポリフェニレンサルファイド、ポリフェニレンオキシド、ポリスルホン、ポリエーテルスルホン、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルケトンケトン、ポリケトン、ポリイミド、ポリエーテルイミド、ポリスチレン、ABS、液晶ポリエステルや、アクリロニトリルとスチレンの共重合体等を用いることができる。これらの混合物でもよい。また、ナイロン6とナイロン66との共重合ナイロンのように共重合したものであってもよい。特に、ポリフェニレンサルファイド、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルケトンケトン、ポリエーテルイミド、芳香族ポリアミドであると、優れた補強効果を奏する連続した強化繊維を用いる必然性が高まるため、本発明での好ましい態様といえる。さらに得たい成形品の要求特性に応じて、難燃剤、耐候性改良剤、その他酸化防止剤、熱安定剤、紫外線吸収剤、可塑剤、滑剤、着色剤、相溶化剤、導電性フィラー等を添加しておくことができる。本発明で樹脂Bに用いる熱硬化性樹脂の種類はとくに限定されず、例えば、エポキシ、フェノール、ポリベンゾイミダゾール、ベンゾオキサジン、シアネートエステル、不飽和ポリエステル、ビニルエステル、ユリア、メラミン、ビスマレイミド、ポリイミド、ポリアミドイミド等や、これらの共重合体、変性体および2種類以上ブレンドした樹脂、更にエラストマーやゴム成分、硬化剤、硬化促進剤、触媒等を添加した樹脂等を使用することができる。 Moreover, although the kind of matrix resin of the said fiber reinforced resin A is a thermoplastic resin, as a kind of the said resin B, both a thermoplastic resin and a thermosetting resin are possible. In particular, when the resin B is made of a thermoplastic resin, it is more preferable because good moldability and productivity can be obtained. In particular, when it is made of the same kind of thermoplastic resin as the matrix resin of the fiber reinforced resin A, it can be said that it is the most preferable embodiment in the present invention because excellent adhesiveness is easily obtained. In the present invention, the type of the thermoplastic resin used for the fiber reinforced resin A and / or the resin B is not particularly limited. For example, polyamide (nylon 6, nylon 66, aromatic polyamide, etc.), polyolefin (polyethylene, polypropylene, etc.) , Polyester (polyethylene terephthalate, polybutylene terephthalate, etc.), polycarbonate, polyphenylene sulfide, polyphenylene oxide, polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketoneketone, polyketone, polyimide, polyetherimide, polystyrene, ABS, liquid crystal polyester Alternatively, a copolymer of acrylonitrile and styrene can be used. A mixture of these may also be used. Moreover, what was copolymerized like the copolymer nylon of nylon 6 and nylon 66 may be used. In particular, polyphenylene sulfide, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketoneketone, polyetherimide, and aromatic polyamide increase the necessity of using continuous reinforcing fibers having an excellent reinforcing effect. I can say that. Furthermore, depending on the required properties of the molded product to be obtained, flame retardants, weather resistance improvers, other antioxidants, heat stabilizers, UV absorbers, plasticizers, lubricants, colorants, compatibilizers, conductive fillers, etc. It can be added. The kind of thermosetting resin used for the resin B in the present invention is not particularly limited. For example, epoxy, phenol, polybenzimidazole, benzoxazine, cyanate ester, unsaturated polyester, vinyl ester, urea, melamine, bismaleimide, polyimide Polyamideimide and the like, copolymers thereof, modified products and resins blended in two or more types, and resins added with elastomers, rubber components, curing agents, curing accelerators, catalysts, and the like can be used.
また、上記樹脂Bは、樹脂のみからなる形態も可能であるし、強化繊維を含む樹脂からなる形態も可能である。後者の場合、良好な成形性を確保し、かつ、樹脂Bの良好な流動性を確保するために、樹脂Bが数平均繊維長2mm未満の強化繊維を含む樹脂からなることが好ましい。 In addition, the resin B may be formed of a resin alone, or may be formed of a resin containing reinforcing fibers. In the latter case, in order to ensure good moldability and ensure good fluidity of the resin B, it is preferable that the resin B is made of a resin containing reinforcing fibers having a number average fiber length of less than 2 mm.
さらに、繊維強化樹脂Aの強化繊維、および/または、樹脂Bの強化繊維としては、炭素繊維をはじめ、ガラス繊維やアラミド繊維など、あらゆる強化繊維を使用可能であるが炭素繊維を含むことが好ましい。但し、ガラス繊維やアラミド繊維等の他の強化繊維、さらにはこれら他の強化繊維と炭素繊維との混合形態、混在形態の採用も可能である。中でも、最終成形物の強度等の機械特性の向上が望まれる場合には、炭素繊維を使用することが好ましい。炭素繊維の中でも、繊維束厚み縮小工程や樹脂含浸工程において毛羽を発生させにくい、高強度のものを用いるのがさらに好ましい。具体的には、引張強度が4,500MPa以上、更には5,000MPa以上の引張強度を有するものを指す。また、強化繊維に付与するサイジング剤としては、300℃における熱減量が5%以下のものを用いるのが好ましい。更に好ましくは、350℃における熱減量が15%以下のものである。熱分解し難いサイジング剤を用いると、繊維束厚み縮小工程や樹脂含浸工程において毛羽を発生させにくく、かつ、ダイ内でのガス発生を最小限に抑制でき、本発明の効果を最大限に発現することができる。かかる効果は、特に、加工温度が300℃近傍を超える耐熱性の熱可塑性樹脂(例えば、ポリフェニレンサルファイド、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルケトンケトン、ポリエーテルイミド、芳香族ポリアミドなど)において格段の効果を奏する。サイジング剤を付与しない炭素繊維を用いた場合、ガス発生は殆どなくなる利点があるが、毛羽の発生が著しく、高品位なシート状のプリプレグを得られないだけでなく、高生産性も実現することが困難な場合がある。なお、上記熱減量とは、TG(熱重量分析)法において大気雰囲気下にて昇温速度10℃/分で25℃から400℃まで加熱し、300℃、350℃それぞれにおけるサイジング剤が減量した比率を指す。 Furthermore, as the reinforcing fiber of the fiber reinforced resin A and / or the reinforcing fiber of the resin B, any reinforcing fiber such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, and aramid fiber can be used, but it is preferable to include carbon fiber. . However, other reinforcing fibers such as glass fibers and aramid fibers, and further mixed forms and mixed forms of these other reinforcing fibers and carbon fibers are also possible. Among these, when it is desired to improve mechanical properties such as strength of the final molded product, it is preferable to use carbon fibers. Among carbon fibers, it is more preferable to use a high-strength one that hardly generates fuzz in the fiber bundle thickness reduction step or the resin impregnation step. Specifically, it refers to those having a tensile strength of 4,500 MPa or more, and further 5,000 MPa or more. Moreover, as a sizing agent provided to the reinforcing fiber, it is preferable to use a sizing agent having a heat loss at 300 ° C. of 5% or less. More preferably, the heat loss at 350 ° C. is 15% or less. Use of a sizing agent that is difficult to thermally decompose makes it difficult to generate fluff in the fiber bundle thickness reduction process and the resin impregnation process, and can minimize the generation of gas in the die, thereby maximizing the effects of the present invention. can do. This effect is particularly remarkable in heat-resistant thermoplastic resins whose processing temperature exceeds about 300 ° C. (for example, polyphenylene sulfide, polyether ether ketone, polyether ketone ketone, polyether imide, aromatic polyamide, etc.). Play. When carbon fiber that does not have a sizing agent is used, there is an advantage that almost no gas is generated. However, fluffing is remarkable and not only a high-quality sheet-like prepreg cannot be obtained, but also high productivity is realized. May be difficult. The above heat loss is a TG (thermogravimetric analysis) method that is heated from 25 ° C. to 400 ° C. at a rate of temperature increase of 10 ° C./min in the air atmosphere, and the sizing agent is reduced at 300 ° C. and 350 ° C. Refers to the ratio.
本発明に係る複合成形体は、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる少なくとも2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面で、かつ、その側面の少なくとも一部に、厚みTに対し深さが0.1Tから0.9Tの範囲内にあるアンダーカット形状を有する形状の側面を有する、マトリックス樹脂が熱可塑性樹脂からなる繊維強化樹脂Aが、液状化した樹脂Bの供給により複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されるようにインサート成形されていることを特徴とするものからなる。また、本発明は、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる2つの傾斜面を有し該傾斜面同士が直接接続されて該傾斜面間に変曲点が形成されている形状の側面で、かつ、その側面の少なくとも一部に、厚みTに対し深さが0.1Tから0.9Tの範囲内にあるアンダーカット形状を有する形状の側面を有する、マトリックス樹脂が熱可塑性樹脂からなる繊維強化樹脂Aが、液状化した樹脂Bの供給により複合成形体の少なくとも一方の表面に配置されるようにインサート成形されていることを特徴とする複合成形体も提供する。これらの本発明に係る複合成形体は、上述したような方法により製造できる。 Composite compact according to the present invention, the maximum distance between have at least two inclined surfaces extending obliquely in opposite directions from the opening of the concave type so as to form a concave inclined surface is in concave openings in the composed shape aspect, and at least a portion of its side surface, the depth to the thickness T has a side surface shape having an undercut shape in the range of 0.9T from 0.1 T, the matrix resin The fiber reinforced resin A made of a thermoplastic resin is insert-molded so as to be disposed on at least one surface of the composite molded body by supplying the liquefied resin B. In addition, the present invention has two inclined surfaces extending in an opposite direction from the concave opening so as to form a concave shape, and the inclined surfaces are directly connected to each other so that an inflection point is formed between the inclined surfaces. And at least a part of the side surface has a side surface having an undercut shape having a depth in the range of 0.1 T to 0.9 T with respect to the thickness T. A composite molded body characterized in that the fiber reinforced resin A whose matrix resin is a thermoplastic resin is insert-molded so as to be disposed on at least one surface of the composite molded body by supplying the liquefied resin B. provide. These composite molded bodies according to the present invention can be produced by the method as described above.
また、本発明に係る複合成形体においては、上記繊維強化樹脂Aが繊維強化樹脂を積層・一体化されたものであることも好ましい形態である。 Moreover, in the composite molded body which concerns on this invention, it is also a preferable form that the said fiber reinforced resin A is what laminated | stacked and integrated the fiber reinforced resin.
また、上記繊維強化樹脂Aが、数平均繊維長2mm以上の強化繊維を含む繊維強化樹脂からなることも好ましい形態である。 Moreover, it is also a preferable form that the said fiber reinforced resin A consists of fiber reinforced resin containing the reinforced fiber whose number average fiber length is 2 mm or more.
また、上記繊維強化樹脂Aの強化繊維が連続繊維であり、かつ、一方向に配向されていることも好ましい形態である。 Moreover, it is also a preferable form that the reinforcing fiber of the fiber reinforced resin A is a continuous fiber and is oriented in one direction.
また、上記液状化した樹脂Bが射出成形または射出圧縮成形により型内に供給されることも好ましい形態である。 It is also a preferred form that the liquefied resin B is supplied into the mold by injection molding or injection compression molding.
また、上記樹脂Bが熱可塑性樹脂からなることも好ましい形態である。 It is also a preferred form that the resin B is made of a thermoplastic resin.
また、上記樹脂Bが数平均繊維長2mm未満の強化繊維を含む樹脂からなることも好ましい形態である。 It is also a preferred embodiment that the resin B is made of a resin containing reinforcing fibers having a number average fiber length of less than 2 mm.
さらに、上記繊維強化樹脂Aの強化繊維、および/または、上記樹脂Bの強化繊維が炭素繊維を含むことも好ましい形態である。 Furthermore, it is also a preferable form that the reinforcing fiber of the fiber reinforced resin A and / or the reinforcing fiber of the resin B contains carbon fiber.
このように、本発明に係る複合成形体およびその製造方法によれば、インサート成形における、とくに繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bとの接着性を向上できるとともに、その接合の信頼性を向上でき、しかも優れた成形性をもってインサート成形を行うことが可能であり、外観にも優れた複合成形体を容易に得ることができる。 As described above, according to the composite molded body and the manufacturing method thereof according to the present invention, the adhesiveness between the fiber reinforced resin A and the resin B in the insert molding can be improved, and the reliability of the bonding can be improved. It is possible to perform insert molding with excellent moldability, and it is possible to easily obtain a composite molded body excellent in appearance.
以下に、本発明の実施形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。
図1は、本発明の一実施態様に係る複合成形体およびその製造方法を示している。図1において、1は、下型2と上型3からなる金型4内でインサート成形される複合成形体を示している。複合成形体1のインサート成形においては、予め成形した、マトリックス樹脂が熱可塑性樹脂からなる繊維強化樹脂A(5)が予備成形体として金型4内に配置され(本実施態様では繊維強化樹脂A(5)の一面が金型4の一内面上に配置され)、該金型4内の繊維強化樹脂A(5)周りに液状化した(本実施態様では溶融された)樹脂B(6)が供給されて繊維強化樹脂A(5)がインサート成形される。この繊維強化樹脂A(5)の樹脂B(6)に接触する側面として、互いに異なる角度で凹型に傾斜する(本実施態様では、上記金型4の一内面に対し垂直な仮想面8に対して互いに逆方向に傾斜し、アンダーカット形状の深さが0.6Tにある)少なくとも2つの傾斜面7a、7bを有する形状の側面7が、インサート成形前に形成されている。換言すれば、図1に示すように、凹型を形成するように該凹型の開口部から互いに逆方向に傾斜して延びる少なくとも2つの傾斜面7a、7bを有し該傾斜面間の距離が凹型の開口部で最大になる形状の側面7が、インサート成形前に形成されている。また、本実施態様では、傾斜面7a、7bの端部同士が直接接続されているので、傾斜面7a、7b間には変曲点9が形成されている。このように形成された傾斜面7a、7bを有する側面7を含む繊維強化樹脂A(5)周りに溶融された樹脂B(6)が流れ込み、樹脂B(6)が固化されて繊維強化樹脂A(5)と樹脂B(6)が接着一体化された複合成形体1が成形される。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 shows a composite molded body and a method for producing the same according to one embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1,
このような複合成形体1の成形においては、繊維強化樹脂A(5)の樹脂B(6)に接触する側面7として、互いに異なる角度で凹型に傾斜する少なくとも2つの傾斜面7a、7bがインサート成形前に形成されているが、互いに逆方向に傾斜する傾斜面7a、7b間の角度(開き角)は例えば図6に示すような角度αに比べ容易に大きく形成できるので、インサート成形時に樹脂B(6)がこの側面部に流れ込んでくる際に、ガスや空気が封入された閉空間を形成することなく、樹脂B(6)は、傾斜面7a、7bの全面に接するように良好に流れ込む。すなわち、図6に示す比較例では、金型4内に配置される繊維強化樹脂A(101)の側面102が一つの傾斜面に形成されているので、この側面102と下型2の内面との間に形成される角度αは小さな角度にならざるを得ず、樹脂B(6)がこの側面部に流れ込んでくる際に、ガスや空気が封入されて樹脂B(6)が流れ込みにくくなった未充填部103が形成されてしまう可能性が高くなる。しかし上記本発明の実施態様では、互いに逆方向に傾斜する2つの傾斜面7a、7b間の角度が確実に比較例における角度αよりも大きく形成されるので、ガスや空気が封入された未充填部が発生することが防止され、この部分全面にわたる繊維強化樹脂A(5)と樹脂B(6)との良好な接着が達成される。また、この部分全面にわたる良好な接着が達成される結果、接着の信頼性も確保される。さらに、図1や図6に示したように下型2の内面上に配置される場合、成形される複合成形体の外表面には繊維強化樹脂Aと樹脂Bの境界部が現れることになるので、この境界部に上記のような未充填部103が形成されていると、成形された複合成形体の外面に溝状の欠陥部として現れることになり、成形体の品位が損なわれる。しかし本発明ではこのような未充填部103の発生を防止できるので、優れた外観が得られ、成形体の品位が向上される。
In the molding of the composite molded
また、上記本発明の実施態様においては、傾斜面7a、7bが互いに逆方向に傾斜する傾斜面とされているので、両傾斜面7a、7b間部位には樹脂B(6)に対して必然的にアンダーカット形状が形成される。すなわち、繊維強化樹脂A(5)の側面7部分には繊維強化樹脂A(5)本体側に入り込んだアンダーカット形状が形成される。このようなアンダーカット形状は、成形後において物理的に樹脂B(6)部分から繊維強化樹脂A(5)部分が脱落しにくい構造を構成するので、繊維強化樹脂A(5)と樹脂B(6)との間の接合強度が一層高められることになる。ただし、アンダーカット形状の機能のみについてみれば、図6の比較例に示した形態でも同じような機能は得られるが、図6に示した一つの傾斜面のみよって形成された側面102では、上述したような未充填部103による接着不足や外観不良の問題が発生する可能性が高くなるので、結局、アンダーカット形状による脱落防止と未充填部発生防止による接着性、外観品位の向上を両立させることはできない。
In the embodiment of the present invention described above, the inclined surfaces 7a and 7b are inclined surfaces that are inclined in opposite directions, so that the portion between the inclined surfaces 7a and 7b is necessarily in relation to the resin B (6). Thus, an undercut shape is formed. That is, the undercut shape which entered the fiber reinforced resin A (5) main body side is formed in the side surface 7 portion of the fiber reinforced resin A (5). Such an undercut shape constitutes a structure in which the fiber reinforced resin A (5) portion is not easily dropped from the resin B (6) portion after molding, and therefore the fiber reinforced resin A (5) and the resin B ( The joint strength with 6) is further increased. However, if only the function of the undercut shape is seen, the same function can be obtained in the form shown in the comparative example of FIG. 6, but the
また、図7に別の比較例を示すように、繊維強化樹脂A(111)を横断面形状が長方形のものとし、その側面112と下型2の内面との間に形成される角度βが90度またはその近辺の角度となる形態も考えられるが、図1に示した互いに逆方向に傾斜する2つの傾斜面7a、7b間の角度に比べて小さな角度となるので、やはり未含浸部発生の可能性が除去されない。また、このような形態では、上述したようなアンダーカット形状による脱落防止機能の向上効果は期待できないので、この面については、図1、図6に示した両形態よりも劣ることになる。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 7, the fiber reinforced resin A (111) has a rectangular cross-sectional shape, and the angle β formed between the
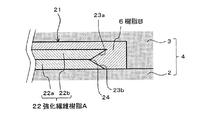
本発明の実施の形態としては、図1に示したもの以外にも種々の形態を採ることができる。例えば図2に示すように、強化繊維樹脂22aと強化繊維樹脂22bの積層構成からなる繊維強化樹脂A(22)に構成するとともに、強化繊維樹脂22a、22bに互いに逆方向に傾斜する傾斜面23a、23bを形成して、両傾斜面23a、23b間を変曲点24とした繊維強化樹脂A(22)を予備成形体として用い、複合成形体21をインサート成形することも可能である。
The embodiment of the present invention can take various forms other than that shown in FIG. For example, as shown in FIG. 2, a fiber reinforced resin A (22) composed of a laminated structure of a reinforced
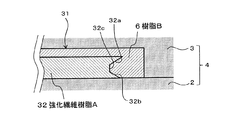
また、例えば図3に別の実施形態を示すように、繊維強化樹脂A(32)としてその側面に互いに逆方向に傾斜する傾斜面32a、32bを形成するとともに両傾斜面32a、32b間を両傾斜面32a、32bの中間の角度の面32cで接続した側面形状に形成して、繊維強化樹脂A(32)を予備成形体として用い、複合成形体31をインサート成形することも可能である。
Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 3, as the fiber reinforced resin A (32),
さらに、例えば図4にさらに別の実施形態を示すように、繊維強化樹脂A(42)としてその側面に互いに逆方向に傾斜する傾斜面42a、42bを形成するとともに両傾斜面42a、42b間を円弧状の面42cで接続した側面形状に形成して、繊維強化樹脂A(42)を予備成形体として用い、複合成形体41をインサート成形することも可能である。
Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 4, yet another embodiment of the fiber reinforced resin A (42) is formed with
本発明に係る、複合成形体をインサート成形は、特に射出成形または射出圧縮成形の適用が好適である。例えば図5に示すように、押出機52の先端部に金型53を備えた射出成形機51を使用し、上記のように予め形成された繊維強化樹脂A(54)を予備成形体として金型53内に配置し(図5(A))、金型53を閉じて押出機52から供給される溶融樹脂B(55)を金型53内に射出して樹脂B(55)により繊維強化樹脂A(54)をインサート成形する(図5(B))。冷却後、金型53を開いてインサート成形された複合成形体56を取り出す(図5(C))。このような射出成形により、本発明における繊維強化樹脂A(54)の側面形状による前述のような利点を達成しつつ、所望の成形品が量産可能な形態で容易に製造される。
The insert molding of the composite molded body according to the present invention is particularly preferably applied by injection molding or injection compression molding. For example, as shown in FIG. 5, an
本発明に係る複合成形体の製造方法は、連続強化繊維と熱可塑性樹脂を使用したあらゆる複合成形体の製造に適用できる。かかる製造方法から得られる複合成形体は、自動車、航空機、船舶等の輸送機器、レジャー・スポーツ部材、圧力容器、油田掘削、土木建築の構造部材・準構造部材などに好適に使用することができる。 The method for producing a composite molded body according to the present invention can be applied to the production of any composite molded body using continuous reinforcing fibers and a thermoplastic resin. The composite molded body obtained from such a production method can be suitably used for transportation equipment such as automobiles, airplanes, ships, etc., leisure / sports members, pressure vessels, oil field excavations, civil engineering structural / quasi-structural members. .
1、21、31、41、56 複合成形体
2 下型
3 上型
4、53 金型
5、22、32、42、54 繊維強化樹脂A
6、55 樹脂B
7 側面
7a、7b、23a、23b、32a、32b、42a、42b 傾斜面
8 金型の一内面に対し垂直な仮想面
9、24 変曲点
22a、22b 繊維強化樹脂
32c 両傾斜面の中間の角度の面
42c 円弧状の面
51 射出成形機
52 押出機
1, 21, 31, 41, 56 Composite molded
6, 55 Resin B
7
Claims (17)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011141927A JP5828380B2 (en) | 2011-06-27 | 2011-06-27 | Composite molded body and method for producing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011141927A JP5828380B2 (en) | 2011-06-27 | 2011-06-27 | Composite molded body and method for producing the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013006389A JP2013006389A (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| JP2013006389A5 JP2013006389A5 (en) | 2014-08-14 |
| JP5828380B2 true JP5828380B2 (en) | 2015-12-02 |
Family
ID=47674174
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011141927A Expired - Fee Related JP5828380B2 (en) | 2011-06-27 | 2011-06-27 | Composite molded body and method for producing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5828380B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6015583B2 (en) * | 2013-07-25 | 2016-10-26 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Manufacturing method of fiber reinforced resin composite material |
| JP6357833B2 (en) * | 2014-03-31 | 2018-07-18 | 東レ株式会社 | Manufacturing method of composite molded product |
| JP6361024B2 (en) * | 2014-08-07 | 2018-07-25 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Resin structure and electric vacuum cleaner using the same |
| CN106660349B (en) * | 2014-08-07 | 2019-08-30 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Resin tectosome and the electric dust collector for using the resin tectosome |
| EP3369566B1 (en) * | 2015-10-29 | 2020-04-08 | Asahi Kasei Kabushiki Kaisha | Composite molding and method for producing same |
| JP7091660B2 (en) * | 2016-09-26 | 2022-06-28 | 東レ株式会社 | Electronic device housing and its manufacturing method |
| US20200061952A1 (en) * | 2017-01-31 | 2020-02-27 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Integrally molded body and method of producing same |
| CN109008799B (en) * | 2017-06-09 | 2021-08-03 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Extension pipe and electric dust collector with same |
| CN113573525B (en) * | 2021-07-28 | 2023-02-28 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Shell assembly, preparation method thereof and electronic equipment |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6282791B1 (en) * | 1999-08-26 | 2001-09-04 | Asc Incorporated | Method of making an automotive vehicle convertible roof |
| JP2006010067A (en) * | 2004-05-21 | 2006-01-12 | Mitsuboshi Belting Ltd | High load transmission belt and its manufacturing method |
| JP5458529B2 (en) * | 2008-08-22 | 2014-04-02 | 東レ株式会社 | Joining method and integral molded product |
-
2011
- 2011-06-27 JP JP2011141927A patent/JP5828380B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013006389A (en) | 2013-01-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5828380B2 (en) | Composite molded body and method for producing the same | |
| EP1731282A4 (en) | Preform, frp, and processes for producing these | |
| KR101196787B1 (en) | Composite shaped article and process for manufacturing the same | |
| US11806920B2 (en) | Heat curable composite textile | |
| JP5950194B2 (en) | Method for producing composite molded body | |
| US20210162638A1 (en) | Integrated molded body and method of manufacturing same | |
| JP2013006389A5 (en) | ||
| KR102358826B1 (en) | Production of multishell composite-material components with reinforcement structure bonded thereto | |
| JP6229197B2 (en) | Molded product and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2005246902A (en) | Resin transfer molding (rtm) method | |
| KR20150009976A (en) | Manufacturing method for molded resin product with metal insert | |
| JP2014054798A (en) | Method for producing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin-molded article | |
| JP7567780B2 (en) | Integrated molding and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6596873B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of molded body | |
| JP2010076356A (en) | Preform, and molding method for fiber-reinforced plastic | |
| JP6572822B2 (en) | Method for producing fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin structure | |
| JP2020001171A (en) | Resin-injection molded article and method for manufacture the same | |
| JP2016187935A (en) | Method for manufacturing molded article | |
| JP6931850B2 (en) | Fiber reinforced resin molded body | |
| CN110877477A (en) | Composite molded article, and method for producing and use thereof | |
| JP2017206015A (en) | Method for producing composite molding | |
| KR20170143230A (en) | Method of manufacturing composite molded product by using chopped strand prepreg | |
| JP2023005555A (en) | Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin laminate molding and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2016068385A (en) | Method for manufacturing fiber-reinforced plastic | |
| EP3650191A1 (en) | Molded composite article, method for the production thereof and use thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140626 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140626 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150316 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150320 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150514 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150717 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150827 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150925 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20151008 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5828380 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |