JP5728082B2 - Topical ophthalmic suspension containing tobramycin and dexamethasone - Google Patents
Topical ophthalmic suspension containing tobramycin and dexamethasone Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5728082B2 JP5728082B2 JP2013516553A JP2013516553A JP5728082B2 JP 5728082 B2 JP5728082 B2 JP 5728082B2 JP 2013516553 A JP2013516553 A JP 2013516553A JP 2013516553 A JP2013516553 A JP 2013516553A JP 5728082 B2 JP5728082 B2 JP 5728082B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- composition
- viscosity
- xanthan gum
- sodium
- tobramycin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- NLVFBUXFDBBNBW-PBSUHMDJSA-N tobramycin Chemical compound N[C@@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CN)O[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)[C@H](N)C[C@@H]1N NLVFBUXFDBBNBW-PBSUHMDJSA-N 0.000 title claims description 88
- 229960000707 tobramycin Drugs 0.000 title claims description 79
- UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N dexamethasone Chemical compound C1CC2=CC(=O)C=C[C@]2(C)[C@]2(F)[C@@H]1[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@@](C(=O)CO)(O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H]2O UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N 0.000 title claims description 56
- 229960003957 dexamethasone Drugs 0.000 title claims description 52
- 230000000699 topical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 4
- 229940100654 ophthalmic suspension Drugs 0.000 title description 8
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 217
- 229920001285 xanthan gum Polymers 0.000 claims description 94
- 239000000230 xanthan gum Substances 0.000 claims description 92
- 229940082509 xanthan gum Drugs 0.000 claims description 92
- 235000010493 xanthan gum Nutrition 0.000 claims description 92
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 76
- 235000002639 sodium chloride Nutrition 0.000 claims description 41
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 claims description 38
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 20
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[K+] WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 14
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 13
- TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium chloride Chemical compound [Mg+2].[Cl-].[Cl-] TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 12
- LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K tripotassium phosphate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 10
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 8
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000001103 potassium chloride Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 235000011164 potassium chloride Nutrition 0.000 claims description 7
- UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca+2] UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 6
- VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium acetate Chemical compound [Na+].CC([O-])=O VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910021538 borax Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000001110 calcium chloride Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910001628 calcium chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000011148 calcium chloride Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910001629 magnesium chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000011147 magnesium chloride Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000001632 sodium acetate Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000017281 sodium acetate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000001509 sodium citrate Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K sodium citrate Chemical compound O.O.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000011083 sodium citrates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000001488 sodium phosphate Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910000162 sodium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000011008 sodium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000010339 sodium tetraborate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- BSVBQGMMJUBVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N trisodium borate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]B([O-])[O-] BSVBQGMMJUBVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- RYFMWSXOAZQYPI-UHFFFAOYSA-K trisodium phosphate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O RYFMWSXOAZQYPI-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 6
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004968 inflammatory condition Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000001508 potassium citrate Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229960002635 potassium citrate Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- QEEAPRPFLLJWCF-UHFFFAOYSA-K potassium citrate (anhydrous) Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O QEEAPRPFLLJWCF-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000011082 potassium citrates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910000160 potassium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000011009 potassium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000018044 dehydration Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 59
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 25
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 15
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 13
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 10
- 239000002953 phosphate buffered saline Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 10
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 9
- 229940035274 tobradex Drugs 0.000 description 9
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011550 stock solution Substances 0.000 description 7
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 230000006196 deacetylation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000003381 deacetylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 238000011200 topical administration Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005054 agglomeration Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 5
- LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I dipotassium trisodium dihydrogen phosphate hydrogen phosphate dichloride Chemical compound P(=O)(O)(O)[O-].[K+].P(=O)(O)([O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Cl-].[K+].[Cl-].[Na+] LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I 0.000 description 5
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000008213 purified water Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001356 surgical procedure Methods 0.000 description 5
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 206010061218 Inflammation Diseases 0.000 description 4
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000001124 body fluid Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000006196 drop Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000004054 inflammatory process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003204 osmotic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9H-xanthene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002924 anti-infective effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003110 anti-inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- NBMKJKDGKREAPL-DVTGEIKXSA-N beclomethasone Chemical compound C1CC2=CC(=O)C=C[C@]2(C)[C@]2(Cl)[C@@H]1[C@@H]1C[C@H](C)[C@@](C(=O)CO)(O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H]2O NBMKJKDGKREAPL-DVTGEIKXSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229940092705 beclomethasone Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000010839 body fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000000845 anti-microbial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229960000686 benzalkonium chloride Drugs 0.000 description 2
- CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl(dimethyl)azanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C[NH+](C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000850 deacetylating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 2
- MDYZKJNTKZIUSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyloxapol Chemical compound O=C.C1CO1.CC(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 MDYZKJNTKZIUSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960004224 tyloxapol Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229920001664 tyloxapol Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 208000002177 Cataract Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000001860 Eye Infections Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 1
- BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl tert-butyl ether Chemical compound COC(C)(C)C BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000283977 Oryctolagus Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- VZTDIZULWFCMLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonium formate Chemical compound [NH4+].[O-]C=O VZTDIZULWFCMLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001450 anions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012736 aqueous medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010338 boric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001793 charged compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960002344 dexamethasone sodium phosphate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- PLCQGRYPOISRTQ-FCJDYXGNSA-L dexamethasone sodium phosphate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].C1CC2=CC(=O)C=C[C@]2(C)[C@]2(F)[C@@H]1[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@@](C(=O)COP([O-])([O-])=O)(O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H]2O PLCQGRYPOISRTQ-FCJDYXGNSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000010494 dissociation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005593 dissociations Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000000132 electrospray ionisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000040 eye damage Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000003889 eye drop Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940124307 fluoroquinolone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000013467 fragmentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006062 fragmentation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000002484 inorganic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004895 liquid chromatography mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- FABPRXSRWADJSP-MEDUHNTESA-N moxifloxacin Chemical compound COC1=C(N2C[C@H]3NCCC[C@H]3C2)C(F)=CC(C(C(C(O)=O)=C2)=O)=C1N2C1CC1 FABPRXSRWADJSP-MEDUHNTESA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003702 moxifloxacin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000002552 multiple reaction monitoring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000005111 ocular hyperemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000002997 ophthalmic solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940054534 ophthalmic solution Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008363 phosphate buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011321 prophylaxis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002207 retinal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004007 reversed phase HPLC Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011895 specific detection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012430 stability testing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004885 tandem mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008733 trauma Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009827 uniform distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/0012—Galenical forms characterised by the site of application
- A61K9/0048—Eye, e.g. artificial tears
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/56—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids
- A61K31/57—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane or progesterone
- A61K31/573—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane or progesterone substituted in position 21, e.g. cortisone, dexamethasone, prednisone or aldosterone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7028—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages
- A61K31/7034—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin
- A61K31/7036—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin having at least one amino group directly attached to the carbocyclic ring, e.g. streptomycin, gentamycin, amikacin, validamycin, fortimicins
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/02—Inorganic compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/30—Macromolecular organic or inorganic compounds, e.g. inorganic polyphosphates
- A61K47/36—Polysaccharides; Derivatives thereof, e.g. gums, starch, alginate, dextrin, hyaluronic acid, chitosan, inulin, agar or pectin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/0012—Galenical forms characterised by the site of application
- A61K9/0048—Eye, e.g. artificial tears
- A61K9/0051—Ocular inserts, ocular implants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2121/00—Preparations for use in therapy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2300/00—Mixtures or combinations of active ingredients, wherein at least one active ingredient is fully defined in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Description
発明の背景
本発明は、眼用抗感染性/抗炎症性組成物、および哺乳類、特にヒトにおける関連する処置方法に関する。より具体的には、本発明は、トブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンを含む、新規の眼用抗感染性/抗炎症性組成物に関する。
The present invention relates to ophthalmic anti-infective / anti-inflammatory compositions and related treatment methods in mammals, particularly humans. More specifically, the present invention relates to a novel ophthalmic anti-infective / anti-inflammatory composition comprising tobramycin and dexamethasone.
眼の感染および付随する炎症を処置するために、トブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンを組み合わせて使用することが公知である。同様に、例えば眼の外科的手順と組み合わせて、炎症を処置する、および感染を予防的に処置する(すなわち、予防または寛解させる)ために、これらの化合物を組み合わせて使用することも公知である。この型の製品は、Alcon Laboratories,Inc.によって米国および他の国々において、TOBRADEX(登録商標)(トブラマイシン0.3%/デキサメタゾン0.1%)眼用懸濁液(トブラデックス点眼液)として市販されている。この製品は、米国において1988年から利用可能であった。それは長年にわたって、最先端の眼用抗感染性/抗炎症性製品であることが広く受け入れられてきた。TOBRADEX(登録商標)ブランドの眼用懸濁液の組成に関するさらなる詳細は、特許文献1において提供される。 It is known to use tobramycin and dexamethasone in combination to treat ocular infections and associated inflammation. Similarly, it is also known to use these compounds in combination to treat inflammation and prevent infection (ie, prevent or ameliorate) infection, eg, in combination with ocular surgical procedures. . This type of product is available from Alcon Laboratories, Inc. In the United States and other countries as TOBRADEX® (tobramycin 0.3% / dexamethasone 0.1%) ophthalmic suspension (tobradex ophthalmic solution). This product has been available in the United States since 1988. For many years it has been widely accepted to be a state-of-the-art ophthalmic anti-infective / anti-inflammatory product. Further details regarding the composition of the TOBRADEX® brand ophthalmic suspension are provided in US Pat.
本発明は、眼への局所投与のための、改善されたトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン組成物の提供に関する。特に、本発明は、キサンタンガムを含み、そして5から6の範囲のpHを有する組成物の提供に関する。製造のときに、および使用前の容器における保存中の組成物の粘度は、使用するキサンタンガムの濃度に基づいて通常予測されるよりもかなり低い。この使用前の粘度の低下は、組成物を患者へ投与する場合、点眼ボトル(例えばDROPTAINERTM、Alcon Laboratories,Inc.)または他の容器からの組成物の投薬と比較して有利である。製造のときおよび眼への投与前の保存中の組成物の粘度の低下は、5から6のpHで起こる、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用に起因する。それらの相互作用は、もし制御されなければ、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの集塊の形成および/またはキサンタンガムの沈殿を引き起こす。本発明は、部分的には、トブラマイシン/キサンタンガム相互作用の制御において有効であることが示された、処方成分およびパラメーターの発見に基づく。 The present invention relates to the provision of improved tobramycin / dexamethasone compositions for topical administration to the eye. In particular, the present invention relates to providing a composition comprising xanthan gum and having a pH in the range of 5-6. The viscosity of the composition during manufacture and in the container before use is considerably lower than would normally be expected based on the concentration of xanthan gum used. This reduction in viscosity prior to use is advantageous when the composition is administered to a patient compared to dispensing the composition from an eye drop bottle (eg, DROPTAINER ™ , Alcon Laboratories, Inc.) or other containers. The decrease in viscosity of the composition during manufacture and storage prior to administration to the eye is due to ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum that occur at a pH of 5-6. These interactions, if not controlled, cause tobramycin and xanthan gum agglomeration and / or xanthan gum precipitation. The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery of formulation ingredients and parameters that have been shown to be effective in controlling tobramycin / xanthan gum interactions.
上記で示したように、本発明の組成物は、キサンタンガムを含む。眼用組成物の成分としてキサンタンガムを使用することは、特許文献2;特許文献3;特許文献4;および特許文献5において記載されている。特許文献3の特許は、トブラマイシンと組み合わせたキサンタンガムの使用を記載する。それは、キサンタンガムおよびトブラマイシンは、5.0から7.8のpHで不相溶性であることを示し、そしてトブラマイシン/キサンタンガム組成物を、7.9から8.6の範囲のpHを有するように処方することによって、この不相溶性の問題が回避され得ることを教示する。特許文献3の特許に記載された発明に基づく製品が、ヨーロッパおよび他の数カ国で、Alcon Laboratories,Inc.の系列会社によって市販されている。
As indicated above, the composition of the present invention comprises xanthan gum. The use of xanthan gum as a component of an ophthalmic composition is described in Patent Document 2, Patent Document 3, Patent Document 4, and
特許文献4および特許文献5の特許は、眼への局所投与のときにゲル化する、非ゲル化液体として処方されたキサンタンベースの眼用組成物を記載する。特許文献4および特許文献5の特許の組成物は、その全イオン強度が約120mMまたはそれより低く、および好ましくは約94mMまたはそれより低くなるように処方される。約120mMより高い全イオン強度を有する特許文献4および特許文献5の特許の組成物は、眼との接触のときにゲル化しない。特許文献4および特許文献5の特許の組成物は一般的に粘稠性であり、そして眼への局所投与のときにゲル化する。対照的に、本発明の組成物は一般的に、ボトル中でより低い粘度を有するが、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間の相互作用が壊れるので、眼への投与後に粘度が有意に増加する。
The patents in US Pat. Nos. 6,057,049 and 5,037,059 describe xanthan-based ophthalmic compositions formulated as non-gelling liquids that gel upon topical administration to the eye. The patented compositions of US Pat. Nos. 6,099,036 and 5,035,059 are formulated such that their total ionic strength is about 120 mM or lower, and preferably about 94 mM or lower. The patent compositions of Patent Document 4 and
本発明のトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン組成物は、5から6のpHで処方される。このpH範囲は、デキサメタゾンの安定性を維持するために必要である。眼用トブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン組成物のためにこの範囲のpHを使用することは、特許文献1において記載されている。TOBRADEX(登録商標)(トブラマイシン0.3%/デキサメタゾン0.1%)眼用懸濁液も、この範囲のpHを有する。 The tobramycin / dexamethasone composition of the present invention is formulated at a pH of 5 to 6. This pH range is necessary to maintain the stability of dexamethasone. The use of this range of pH for ophthalmic tobramycin / dexamethasone compositions is described in US Pat. TOBRADEX® (tobramycin 0.3% / dexamethasone 0.1%) ophthalmic suspension also has a pH in this range.
本発明は、改善されたトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン処方物、特にトブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンの媒体としてキサンタンガムを使用することによって、眼への局所投与のときにトブラマイシンおよび/またはデキサメタゾンの増強された生物学的利用能を提供する組成物を生成するための努力から生じた。しかし、上記で記載したように、5から6のpHにおけるトブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用は、キサンタンガムの集塊および/または沈殿を引き起こすことが発見された。それに加えて、キサンタンガムは保存中にゆっくりと脱アセチル化を受け、それによって安定性の問題を生じることが発見された。下記でより詳細に説明するように、本発明は、これらの問題に対する解決の発見に基づく。 The present invention provides improved bioavailability of tobramycin and / or dexamethasone upon topical administration to the eye by using xanthan gum as an improved tobramycin / dexamethasone formulation, particularly tobramycin and dexamethasone vehicle. Out of efforts to produce the provided composition. However, as described above, it has been discovered that ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum at a pH of 5 to 6 cause agglomeration and / or precipitation of xanthan gum. In addition, it has been discovered that xanthan gum undergoes slow deacetylation during storage, thereby causing stability problems. As described in more detail below, the present invention is based on the discovery of solutions to these problems.
本発明は、トブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンを含み、そしてヒト患者の眼への局所投与に適切な、改善された薬学的組成物の提供に関する。本発明の組成物は、部分的には、デキサメタゾンの安定性を維持しながら、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制御する処方パラメーターの発見に基づく。それらの相互作用の制御は、本発明者らが、非常に有利な物理的性質を有する組成物を提供することを可能にした。より具体的には、本発明の組成物は、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間の、制御された相互作用の結果として、有利な流体力学的性質を有し、そしてそれらの性質は、眼に局所的に投与された薬物、特にトブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンの生物学的利用能を増強する。それに加えて、その組成物は、中でデキサメタゾンが比較的不溶性である形態の懸濁液(すなわちデキサメタゾンアルコール)と比較して有意な改善を提供し、患者がたまに眼への投与の前に組成物を含むボトルを振るという指示に従わなかったとしても、組成物中に懸濁したデキサメタゾンの利用能は有意に減少しない。 The present invention relates to the provision of an improved pharmaceutical composition comprising tobramycin and dexamethasone and suitable for topical administration to the eye of a human patient. The compositions of the present invention are based, in part, on the discovery of formulation parameters that control ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum while maintaining dexamethasone stability. Controlling their interaction has allowed us to provide compositions that have very advantageous physical properties. More specifically, the compositions of the present invention have advantageous hydrodynamic properties as a result of controlled interaction between tobramycin and xanthan gum, and these properties are locally applied to the eye. Enhance the bioavailability of administered drugs, especially tobramycin and dexamethasone. In addition, the composition provides significant improvements compared to suspensions in a form in which dexamethasone is relatively insoluble (ie, dexamethasone alcohol), and the composition is sometimes formulated by patients prior to administration to the eye. Failure to follow the instructions to shake the bottle containing the product does not significantly reduce the availability of dexamethasone suspended in the composition.
本発明において使用される濃度のキサンタンガムを含む溶液または懸濁液は、通常非常に粘稠性である。下記でより詳細に説明するように、本発明は、部分的には、陽イオン分子であるトブラマイシンが、陰性に荷電したキサンタンガム分子とイオン的に相互作用し、それによって組成物の粘度を低下させるという発見に基づく。眼への投与のときに、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用の破壊の結果として、本発明のトブラマイシン/キサンタンガム組成物の粘度は回復し(すなわち増加し)、それによって眼での保持の増加および眼での生物学的利用能の増強を引き起こす。しかし、組成物の製造中、および使用前の組成物の保存中、沈殿および集塊の形成を回避するために、および組成物中でのキサンタンガムの均一な分散を維持するために、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制御しなければならない。本発明は、部分的には、デキサメタゾンの安定性を維持しながら、製造および保存期間中のトブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制御する処方特徴およびパラメーターの同定に基づく。 The solution or suspension containing the concentration of xanthan gum used in the present invention is usually very viscous. As described in more detail below, the present invention, in part, allows the cationic molecule tobramycin to ionically interact with negatively charged xanthan gum molecules, thereby reducing the viscosity of the composition. Based on the discovery. Upon administration to the eye, as a result of disruption of the ionic interaction between tobramycin and xanthan gum, the viscosity of the tobramycin / xanthan gum composition of the present invention is restored (ie, increased), thereby increasing retention of the eye. Causes an increase and enhanced bioavailability in the eye. However, during the manufacture of the composition and during storage of the composition prior to use, to avoid the formation of precipitates and agglomerates and to maintain a uniform distribution of xanthan gum in the composition, tobramycin and xanthan gum The ionic interaction between the two must be controlled. The present invention is based, in part, on the identification of formulation features and parameters that control ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum during manufacturing and storage while maintaining dexamethasone stability.
トブラマイシンは陽性に荷電した分子であり、一方キサンタンガムは陰性に荷電している。酸性pHにおいて水溶液または懸濁液中で組み合わせた場合、トブラマイシンはキサンタンガムを沈殿させるか、または集塊を形成させる。そのような沈殿または集塊は、2つの面で容認できない。まず、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムは、もはや組成物中で均一に分布していない。適切なボトルまたは他の容器から投与されるときに、その組成物の各滴は、均一なおよび予測可能な量の、組成物の成分、特に活性成分を提供しなければならないので、これは容認できない。2番目に、キサンタンガムに対するトブラマイシンの沈殿または集塊効果は、その組成物に対するキサンタンガムの粘度増強効果の喪失を引き起こし、組成物の粘度は水と同等の値(すなわち約1センチポイズ)に逆戻りし得る。 Tobramycin is a positively charged molecule, while xanthan gum is negatively charged. When combined in aqueous solutions or suspensions at acidic pH, tobramycin precipitates xanthan gum or forms agglomerates. Such precipitation or agglomeration is unacceptable in two ways. First, tobramycin and xanthan gum are no longer uniformly distributed in the composition. This is acceptable because each drop of the composition must provide a uniform and predictable amount of the components of the composition, particularly the active ingredient, when administered from an appropriate bottle or other container. Can not. Second, the precipitation or agglomeration effect of tobramycin on xanthan gum causes a loss of xanthan gum's viscosity enhancing effect on the composition, and the viscosity of the composition can revert to a value equivalent to water (ie about 1 centipoise).
米国特許第6,352,978号は、部分的には、これらのイオン性相互作用は、アルカリ性pH(すなわち、8.0またはより高いpH)を利用することによって制御され得るという発見に基づく。しかし、デキサメタゾンはこのpHレベルにおいて不安定であるので、本発明のトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン組成物において、アルカリ性pHを使用することは不可能である。デキサメタゾンは5から6のpHにおいて安定であるが、このpHにおいて陰性に荷電したキサンタンガムおよび陽性に荷電したトブラマイシンは相互作用して物質の沈殿および/または集塊を形成する。 US Pat. No. 6,352,978 is based in part on the discovery that these ionic interactions can be controlled by utilizing alkaline pH (ie, 8.0 or higher pH). However, since dexamethasone is unstable at this pH level, it is not possible to use an alkaline pH in the tobramycin / dexamethasone composition of the present invention. Dexamethasone is stable at a pH of 5 to 6, but negatively charged xanthan gum and positively charged tobramycin interact at this pH to form a precipitate and / or agglomerate of material.
本発明者らは、沈殿または塊の形成を回避し、そして本トブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン懸濁液または溶液の粘度を、眼への投与前に許容可能な範囲内に維持するために、上記で議論した問題が、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制御するためのイオン種を使用することによって克服され得ることを発見した。この制御は、キサンタンガムまたはトブラマイシンと結合するイオン種を含み、それによってこれらの化合物間の直接的な相互作用を抑制することによって達成される。この目的のために使用するイオン種は、5から6の範囲のpHで陰イオンおよび陽イオンに解離する、あらゆる薬学的に許容可能な剤であり得るが、好ましくは塩化ナトリウム、塩化カリウム、または硫酸ナトリウムのような、無機電解質または有機緩衝剤である。 We have discussed above to avoid the formation of precipitates or lumps and to maintain the viscosity of the tobramycin / dexamethasone suspension or solution within an acceptable range prior to administration to the eye. It has been discovered that the problem can be overcome by using ionic species to control ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum. This control is achieved by including ionic species that bind xanthan gum or tobramycin, thereby inhibiting direct interactions between these compounds. The ionic species used for this purpose can be any pharmaceutically acceptable agent that dissociates into anions and cations at a pH in the range of 5 to 6, but is preferably sodium chloride, potassium chloride, or An inorganic electrolyte or organic buffer, such as sodium sulfate.
眼への投与のときに、キサンタンガムおよびトブラマイシンの間の複合体の破壊のために、本発明の組成物の粘度が回復する。すなわち、眼への投与のときに、本発明の組成物の粘度は増加し、それによって組成物が角膜表面に保持される時間の長さを増加させ、そして眼の生物学的利用能を増強する。例えば、この増強された眼の生物学的利用能の結果として、本発明の組成物中のわずか0.05w/v%のデキサメタゾン濃度が、TOBRADEX(登録商標)眼用懸濁液中の0.1w/v%のデキサメタゾン濃度と生物学的に同等である。 Upon administration to the eye, the viscosity of the composition of the present invention is restored due to the breakdown of the complex between xanthan gum and tobramycin. That is, upon administration to the eye, the viscosity of the composition of the present invention increases, thereby increasing the length of time that the composition is retained on the corneal surface and enhancing the bioavailability of the eye To do. For example, as a result of this enhanced ocular bioavailability, a concentration of only 0.05 w / v% dexamethasone in the compositions of the present invention results in a 0. 0% in TOBRADEX® ophthalmic suspension. Biologically equivalent to a dexamethasone concentration of 1 w / v%.
本発明はまた、部分的には、本発明のキサンタンガムベースの組成物は優れた懸濁性質を有するという発見に基づく。より具体的には、デキサメタゾン粒子は本発明の組成物中で、以前のTOBRADEX(登録商標)処方物と比較して、有意により長く懸濁液のままである。この改善は特に、全ての眼用懸濁液組成物にあてはまる、「使用前によく振る」という指示を時々忘れる、または見過ごす患者に関して、重要な利点を提供する。 The present invention is also based in part on the discovery that the xanthan gum-based compositions of the present invention have excellent suspending properties. More specifically, the dexamethasone particles remain in suspension significantly longer in the compositions of the present invention compared to previous TOBRADEX® formulations. This improvement provides important advantages, especially for patients who occasionally forget or overlook the “shake well before use” instructions that apply to all ophthalmic suspension compositions.
本発明はまた、部分的には、キサンタンガムは、少なくとも部分的に脱アセチル化されている場合、本発明の組成物において、粘度増強剤としてはるかにより有効であるという発見に基づく。より具体的には、キサンタンガムは、水溶液においてゆっくりと脱アセチル化を受ける。そのような脱アセチル化は、組成物のpHをさらに低下させ、それによってトブラマイシンおよびデキサメタゾンの間のイオン性相互作用を増加させることが決定された。これらの相互作用は、最初は粘度の喪失を引き起こし、そして最終的にキサンタンガムおよびトブラマイシンの集塊および/または沈殿を引き起こす。本発明者らは、本発明の組成物に含む前にキサンタンガムを脱アセチル化することによって、この問題を克服し得ることを決定した。
例えば、本発明は以下の項目を提供する。
(項目1)
局所用眼用組成物であって、該組成物は、
0.1から0.5w/v%のトブラマイシン;
0.03から0.1w/v%のデキサメタゾン;
0.3から0.9%の濃度で脱アセチル化キサンタンガムを含む、水性の眼科学的に許容されるビヒクル;および
1つ以上のイオン化可能な種であって、該組成物のインビトロ粘度が6sec −1 のせん断速度および25℃の温度において10から700cpの範囲内に維持されるように、該トブラマイシンおよび該脱アセチル化キサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制限するのに十分な量の、1つ以上のイオン化可能な種
を含み、
5から6のpHを有する、組成物。
(項目2)
前記1つ以上のイオン化可能な種が、無機電解質、有機緩衝剤、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目1に記載の組成物。
(項目3)
前記1つ以上のイオン化可能な種が、塩化ナトリウム、塩化カリウム、塩化カルシウム、塩化マグネシウム、硫酸ナトリウム、クエン酸ナトリウム、クエン酸カリウム、リン酸ナトリウム、リン酸カリウム、酢酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸/マンニトール複合体、ホウ酸/ソルビトール複合体、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目2に記載の組成物。
(項目4)
前記イオン化可能な種が、塩化ナトリウム、硫酸ナトリウム、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目3に記載の組成物。
(項目5)
前記組成物のインビトロ粘度が、10から300cpの範囲内にある、項目1に記載の組成物。
(項目6)
前記組成物が、25から175cpの初期粘度を有する、項目5に記載の組成物。
(項目7)
前記組成物が、0.01から0.65のインビトロ/インビボ粘度比を有する、項目6に記載の組成物。
(項目8)
前記1つ以上のイオン化可能な種が、無機電解質、有機緩衝剤、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目7に記載の組成物。
(項目9)
前記1つ以上のイオン化可能な種が、塩化ナトリウム、塩化カリウム、塩化カルシウム、塩化マグネシウム、硫酸ナトリウム、クエン酸ナトリウム、クエン酸カリウム、リン酸ナトリウム、リン酸カリウム、酢酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸/マンニトール複合体、ホウ酸/ソルビトール複合体、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目8に記載の組成物。
(項目10)
前記イオン化可能な種が、塩化ナトリウム、硫酸ナトリウム、およびその組み合わせからなる群より選択される、項目9に記載の組成物。
(項目11)
前記組成物が、0.3w/v%の濃度のトブラマイシン、0.6w/v%の濃度のキサンタンガム、および0.05w/v%の濃度のデキサメタゾンを含む、項目1〜10のいずれか一項に記載の組成物。
(項目12)
前記組成物のpHが、約5.7である、項目11に記載の組成物。
(項目13)
感染または感染のリスクのいずれかが存在する、眼の炎症性状態を処置する方法であって、治療上有効な量の項目1に記載の組成物を、罹患した眼に局所付与する工程を含む、方法。
(項目14)
感染または感染のリスクのいずれかが存在する、眼の炎症性状態を処置する方法であって、治療上有効な量の項目11に記載の組成物を、罹患した眼に付与する工程を含む、方法。
The invention is also based, in part, on the discovery that xanthan gum is much more effective as a viscosity enhancer in the compositions of the invention when it is at least partially deacetylated. More specifically, xanthan gum undergoes slow deacetylation in aqueous solution. Such deacetylation has been determined to further reduce the pH of the composition, thereby increasing the ionic interaction between tobramycin and dexamethasone. These interactions initially cause a loss of viscosity and ultimately agglomeration and / or precipitation of xanthan gum and tobramycin. The inventors have determined that this problem can be overcome by deacetylating xanthan gum prior to inclusion in the composition of the present invention.
For example, the present invention provides the following items.
(Item 1)
A topical ophthalmic composition comprising:
0.1 to 0.5 w / v% tobramycin;
0.03 to 0.1 w / v% dexamethasone;
An aqueous ophthalmically acceptable vehicle comprising deacetylated xanthan gum at a concentration of 0.3 to 0.9%; and
One or more ionizable species , wherein the tobramycin and the deacetylation are maintained such that the in vitro viscosity of the composition is maintained within the range of 10 to 700 cp at a shear rate of 6 sec −1 and a temperature of 25 ° C. One or more ionizable species in an amount sufficient to limit ionic interactions between the xanthane gum
Including
A composition having a pH of 5 to 6.
(Item 2)
2. The composition of item 1, wherein the one or more ionizable species is selected from the group consisting of an inorganic electrolyte, an organic buffer, and combinations thereof.
(Item 3)
The one or more ionizable species is sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium citrate, potassium citrate, sodium phosphate, potassium phosphate, sodium acetate, sodium borate, boron Item 3. The composition according to Item 2, selected from the group consisting of acid / mannitol complex, boric acid / sorbitol complex, and combinations thereof.
(Item 4)
4. The composition of item 3, wherein the ionizable species is selected from the group consisting of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, and combinations thereof.
(Item 5)
The composition of item 1, wherein the in vitro viscosity of the composition is in the range of 10 to 300 cp.
(Item 6)
6. The composition of
(Item 7)
7. A composition according to item 6, wherein the composition has an in vitro / in vivo viscosity ratio of 0.01 to 0.65.
(Item 8)
8. The composition of item 7, wherein the one or more ionizable species is selected from the group consisting of an inorganic electrolyte, an organic buffer, and combinations thereof.
(Item 9)
The one or more ionizable species is sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium citrate, potassium citrate, sodium phosphate, potassium phosphate, sodium acetate, sodium borate, boron 9. The composition of
(Item 10)
10. The composition of item 9, wherein the ionizable species is selected from the group consisting of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, and combinations thereof.
(Item 11)
Items 1-10, wherein the composition comprises tobramycin at a concentration of 0.3 w / v%, xanthan gum at a concentration of 0.6 w / v%, and dexamethasone at a concentration of 0.05 w / v%. A composition according to 1.
(Item 12)
Item 12. The composition according to Item 11, wherein the pH of the composition is about 5.7.
(Item 13)
A method of treating an inflammatory condition of the eye, wherein either an infection or a risk of infection exists, comprising topically applying a therapeutically effective amount of the composition of item 1 to the affected eye. ,Method.
(Item 14)
A method of treating an inflammatory condition of the eye, wherein either an infection or a risk of infection exists, comprising applying a therapeutically effective amount of the composition of item 11 to the affected eye. Method.
本発明の組成物は、0.1から0.5重量/体積パーセント(w/v%)、好ましくは0.3w/v%の濃度のトブラマイシン;0.03から0.1w/v%、好ましくは0.05w/v%の濃度のデキサメタゾン;0.3から0.9w/v%、好ましくは0.6w/v%の濃度の脱アシル化(deacylated)キサンタンガムを含む水性媒体;および製造日から18ヶ月の間、懸濁液の粘度が10から700センチポイズ(「cp」)、好ましくは10から300cpの範囲内に維持されるように、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間の相互作用を制限するのに十分な量のイオン種、を含む、滅菌水性懸濁液として処方される。その懸濁液は、5から6の範囲のpHを有する。 The composition of the present invention comprises tobramycin at a concentration of 0.1 to 0.5 weight / volume percent (w / v%), preferably 0.3 w / v%; 0.03 to 0.1 w / v%, preferably Dexamethasone at a concentration of 0.05 w / v%; an aqueous medium comprising a deacylated xanthan gum at a concentration of 0.3 to 0.9 w / v%, preferably 0.6 w / v%; and from the date of manufacture Sufficient to limit the interaction between tobramycin and xanthan gum so that the viscosity of the suspension is maintained within the range of 10 to 700 centipoise (“cp”), preferably 10 to 300 cp, for 18 months Formulated as a sterile aqueous suspension containing a significant amount of ionic species. The suspension has a pH in the range of 5-6.
本発明において使用されるイオン種は、5から6の範囲のpHで陽イオン成分および陰イオン成分に解離する、あらゆる薬学的に許容可能な化合物であり得る。その化合物は、無機化合物または有機化合物であり得るが、好ましくは無機電解質、有機緩衝剤、またはその組み合わせである。そのようなイオン種の例は、塩化ナトリウム、塩化カリウム、塩化カルシウム、塩化マグネシウム、硫酸ナトリウム、クエン酸ナトリウム、クエン酸カリウム、リン酸ナトリウム、リン酸カリウム、酢酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸/マンニトール複合体、ホウ酸/ソルビトール複合体、およびその組み合わせを含む。 The ionic species used in the present invention can be any pharmaceutically acceptable compound that dissociates into cationic and anionic components at a pH in the range of 5 to 6. The compound can be an inorganic compound or an organic compound, but is preferably an inorganic electrolyte, an organic buffer, or a combination thereof. Examples of such ionic species are sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium citrate, potassium citrate, sodium phosphate, potassium phosphate, sodium acetate, sodium borate, boric acid / Includes mannitol complex, boric acid / sorbitol complex, and combinations thereof.
本発明の組成物中に存在するイオン化可能な種の全量は、組成物の粘度に影響を与える。その組成物は、上記で特定した粘度の範囲を超えることなく、組成物中の沈殿または集塊の形成を回避するように、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を抑制または排除するのに十分な量で、1つ以上のイオン化可能な化合物を含まなければならない。従ってその組成物は、少なくとも10cpの製造のときにおける粘度(本明細書中で「初期粘度」と呼ばれる)を有する組成物を提供するのに十分な量で、好ましくは15cpまたはそれより高い初期粘度を提供するのに十分な量で、および最も好ましくは25cpまたはそれより高い初期粘度を提供するのに十分な量で、イオン種を含まなければならない。その組成物の初期粘度は、好ましくは25から175cpの範囲にある。 The total amount of ionizable species present in the composition of the present invention affects the viscosity of the composition. The composition is used to inhibit or eliminate ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum so as to avoid the formation of precipitates or clumps in the composition without exceeding the viscosity range specified above. A sufficient amount must contain one or more ionizable compounds. Thus, the composition is preferably in an amount sufficient to provide a composition having a viscosity at the time of manufacture of at least 10 cp (referred to herein as “initial viscosity”), preferably 15 cp or higher. The ionic species should be included in an amount sufficient to provide the most, and most preferably in an amount sufficient to provide an initial viscosity of 25 cp or higher. The initial viscosity of the composition is preferably in the range of 25 to 175 cp.
イオン強度および粘度に対するイオン種の影響は、選択された特定のイオン種に依存する。例えば、イオン強度および粘度に対する硫酸ナトリウムの影響は、塩化ナトリウムの影響より約5.3倍強い。異なるイオン化塩の相対的な影響が、本明細書中で特定されたpH範囲、トブラマイシン濃度、キサンタンガム濃度、および粘度範囲内で、日常的な実験によって決定され得る。本発明の組成物に関する限り、唯一の決定的なパラメーターは、イオン化可能な塩の量は、組成物の粘度を700cp、またはより好ましくは300cpより上に増加させることなく、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの沈殿または集塊の形成を回避するために十分でなければならないということである。 The effect of ionic species on ionic strength and viscosity depends on the particular ionic species selected. For example, the effect of sodium sulfate on ionic strength and viscosity is about 5.3 times stronger than that of sodium chloride. The relative effects of different ionized salts can be determined by routine experimentation within the pH range, tobramycin concentration, xanthan gum concentration, and viscosity range specified herein. As far as the composition of the present invention is concerned, the only critical parameter is that the amount of ionizable salt does not increase the viscosity of the composition above 700 cp, or more preferably above 300 cp, or tobramycin and xanthan gum precipitation or That is enough to avoid the formation of agglomerates.
本発明の眼用懸濁液の粘度は、組成物からの水分の喪失のために、経時的にいくらか増加し得る。従ってその懸濁液は、18ヶ月の間、その粘度を10から700cp、好ましくは10から300cpの範囲内に維持するように処方される。製造のときから眼への投与までの、本発明の組成物の粘度は、本明細書中で、その組成物の「インビトロ粘度」と呼ばれる。 The viscosity of the ophthalmic suspensions of the present invention may increase somewhat over time due to the loss of moisture from the composition. The suspension is therefore formulated to maintain its viscosity within the range of 10 to 700 cp, preferably 10 to 300 cp, for 18 months. The viscosity of the composition of the present invention from the time of manufacture to administration to the eye is referred to herein as the “in vitro viscosity” of the composition.
本明細書中で表される粘度の値は、約6sec−1のせん断速度および25℃の温度における、Brookfield粘度計の使用に基づく。約6sec−1のせん断速度は、1分あたり3回転(「rpm」)でのスピンドルCP−52、1.5rpmでのスピンドルCP−51、1.5rpmでのスピンドルCP−42、または3rpmでのスピンドルCP−41使用することにより、達成され得る。スピンドルCP−52およびCP−51は、典型的には300センチポイズ(「cp」)より高い粘度を測定するために使用される。スピンドルCP−42およびCP−41は一般的に、典型的には300cp未満の粘度を測定するために使用される。 The viscosity values represented herein are based on the use of a Brookfield viscometer at a shear rate of about 6 sec −1 and a temperature of 25 ° C. A shear rate of about 6 sec −1 is spindle CP-52 at 3 revolutions per minute (“rpm”), spindle CP-51 at 1.5 rpm, spindle CP-42 at 1.5 rpm, or 3 rpm. This can be achieved by using spindle CP-41. Spindles CP-52 and CP-51 are typically used to measure viscosities greater than 300 centipoise (“cp”). Spindles CP-42 and CP-41 are generally used to measure viscosities typically less than 300 cp.
上記で示したように、本発明の組成物の粘度は、眼への投与のときに回復し、局所眼球投与後の組成物の粘度は、容器中での保存中、製造後、および眼への投与前の粘度より高い。この増加は、その少量(すなわち1または2滴)がヒトの眼の涙液(すなわち涙)と接触した場合に、組成物のpHおよびイオン強度のシフトによって引き起こされる。すなわち、涙液中の電解質が、組成物のpHおよびイオン強度を増加させ、それが組成物の粘度を増加させ、それによって組成物の眼における保持および生物学的利用能を増強する。 As indicated above, the viscosity of the composition of the present invention is restored upon administration to the eye, and the viscosity of the composition after topical ocular administration is maintained during storage in a container, after manufacture, and to the eye. Higher than the viscosity before administration. This increase is caused by a shift in the pH and ionic strength of the composition when a small amount (ie 1 or 2 drops) comes into contact with the tears of the human eye (ie tears). That is, the electrolyte in tear fluid increases the pH and ionic strength of the composition, which increases the viscosity of the composition, thereby enhancing the retention and bioavailability of the composition in the eye.
インビボで、すなわち眼への投与後に、本発明の組成物の粘度を測定することは、容易に可能ではない。しかし、下記で説明するシミュレートされたインビボ粘度モデルが、インビボにおける本発明の組成物の粘度に対する涙液の影響を評価するために利用され得る。インビボにおける(すなわち眼への局所投与後の)本発明の組成物の粘度は、少量の以下のリン酸緩衝化食塩水を組成物へ加えることによってシミュレートされる: It is not readily possible to measure the viscosity of the composition of the invention in vivo, ie after administration to the eye. However, the simulated in vivo viscosity model described below can be utilized to assess the effect of tears on the viscosity of the compositions of the invention in vivo. The viscosity of the composition of the invention in vivo (ie after topical administration to the eye) is simulated by adding a small amount of the following phosphate buffered saline to the composition:
本明細書の目的に関して、本発明の組成物の実際のインビボ粘度は、そのような組成物のシミュレートされたインビボ粘度と同じであると仮定する。従って、本明細書中で「インビボ粘度」に対する全ての言及は、「シミュレートされたインビボ粘度」と交換可能である。本明細書中で「シミュレートされたインビボ粘度」および「インビトロ/インビボ粘度比」に対する全ての言及は、上記で記載した粘度測定手順およびシミュレートされたインビボ粘度モデルの使用に基づく。 For the purposes of this specification, it is assumed that the actual in vivo viscosity of the composition of the present invention is the same as the simulated in vivo viscosity of such composition. Thus, all references herein to “in vivo viscosity” are interchangeable with “simulated in vivo viscosity”. All references to “simulated in vivo viscosity” and “in vitro / in vivo viscosity ratio” herein are based on the use of the viscosity measurement procedure described above and a simulated in vivo viscosity model.
眼への投与前の本発明の組成物の粘度の、その1滴を眼へ投与した後の同じ組成物の粘度に対する比を、本明細書中で「インビトロ/インビボ粘度比」と呼ぶ。本発明の組成物は、好ましくは1/100から65/100または0.01から0.65の範囲のインビトロ/インビボ粘度比を有する。 The ratio of the viscosity of the composition of the present invention before administration to the eye to the viscosity of the same composition after administration of the drop to the eye is referred to herein as the “in vitro / in vivo viscosity ratio”. The compositions of the present invention preferably have an in vitro / in vivo viscosity ratio in the range of 1/100 to 65/100 or 0.01 to 0.65.
前述の比はまた、パーセンテージに関して、すなわちインビトロ粘度をシミュレートされたインビボ粘度で割って100をかけたもので表され得る。従ってシミュレートされたインビボ粘度に対するインビトロ粘度の比に関する前述の範囲は、本発明の組成物のインビトロ粘度が、当該組成物のシミュレートされたインビボ粘度の1%から65%である範囲と等価である。 The foregoing ratio can also be expressed in terms of percentage, i.e., in vitro viscosity divided by simulated in vivo viscosity multiplied by 100. Thus, the aforementioned range for the ratio of in vitro viscosity to simulated in vivo viscosity is equivalent to the range where the in vitro viscosity of the composition of the present invention is 1% to 65% of the simulated in vivo viscosity of the composition. is there.
相対的な粘度値はまた、インビトロ粘度に対するインビボ粘度の比として表し得る。本発明の組成物は、好ましくは100/1から100/65のインビボ/インビトロ粘度比を有し、それは組成物のインビボ粘度が、当該組成物のインビトロ粘度より約1.5から100倍高い範囲と等価である。 Relative viscosity values can also be expressed as the ratio of in vivo viscosity to in vitro viscosity. The composition of the present invention preferably has an in vivo / in vitro viscosity ratio of 100/1 to 100/65, which is a range where the in vivo viscosity of the composition is about 1.5 to 100 times higher than the in vitro viscosity of the composition. Is equivalent to
本発明の滅菌眼用懸濁液で利用されるトブラマイシン、デキサメタゾン、およびキサンタンガムは、公知の化合物であり、そして様々な供給源から容易に入手可能である。デキサメタゾンアルコールのような、デキサメタゾンの非塩形態が好ましい。しかし、デキサメタゾンリン酸ナトリウムのような、デキサメタゾンの塩形態も使用し得る。デキサメタゾン塩を選択する場合、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制御するために必要なイオン化可能な種の濃度を決定する場合に、デキサメタゾン塩の解離のときに形成されるイオンによって寄与されるイオン強度を考慮しなければならない。 Tobramycin, dexamethasone, and xanthan gum utilized in the sterile ophthalmic suspension of the present invention are known compounds and are readily available from a variety of sources. Non-salt forms of dexamethasone are preferred, such as dexamethasone alcohol. However, salt forms of dexamethasone, such as dexamethasone sodium phosphate, can also be used. When choosing a dexamethasone salt, it is contributed by the ions formed during the dissociation of the dexamethasone salt in determining the concentration of ionizable species required to control the ionic interaction between tobramycin and xanthan gum. Ionic strength must be considered.
医薬品グレードのキサンタンガムが使用されるべきである。そのキサンタンガムは、好ましくは、使用の前にポリッシングろ過するべきである。適切なろ過技術の選択は、当業者によって容易に決定され得る。上記で議論したように、そのキサンタンガムは、保存の間、本発明の懸濁液の安定性を増強するために、脱アセチル化されなければならない。キサンタンガムのアセテート含有量は、キサンタンガムに結合したアセテートに基づく。そのアセテート含有量は、典型的には、重量に基づいてキサンタンガムのパーセントとして表される。キサンタンガムの原材料は、典型的には6%までの結合アセテートを有する。本発明で使用される脱アセチル化キサンタンガムは、2%未満の結合アセテート、および好ましくは1%未満の結合アセテートを含む。キサンタンガムを脱アセチル化することの重要性および脱アセチル化が行われ得るプロセスは、下記の実施例1および2においてさらに説明される。 Pharmaceutical grade xanthan gum should be used. The xanthan gum should preferably be polished and filtered before use. The selection of an appropriate filtration technique can be readily determined by one skilled in the art. As discussed above, the xanthan gum must be deacetylated to enhance the stability of the suspension of the present invention during storage. The acetate content of xanthan gum is based on acetate bound to xanthan gum. The acetate content is typically expressed as a percent of xanthan gum based on weight. Xanthan gum raw materials typically have up to 6% bound acetate. The deacetylated xanthan gum used in the present invention comprises less than 2% bound acetate, and preferably less than 1% bound acetate. The importance of deacetylating xanthan gum and the process by which deacetylation can be performed are further illustrated in Examples 1 and 2 below.
上記で示したように、本発明の組成物は、5から6のpHを有する。その組成物はまた、眼科学的に許容可能な浸透圧を有し、それは典型的には水1キログラムあたり200から400ミリオスモル(mOsm/kg)の範囲にある。組成物のpHを5から6の特定した範囲に維持するために適切な緩衝剤を選択する場合、および/または浸透圧調整剤を選択する場合、そのような剤の、組成物のイオン化可能な種の含有量に対する影響が考慮されなければならない。例えば、浸透圧を調整する目的のために加えた塩化ナトリウムが、イオン種濃度を許容可能なレベルを超えて(すなわち標的粘度値と比較して)増加させるなら、塩化ナトリウムの全てまたは一部を、プロピレングリコールのような非イオン性浸透圧調整剤と置き換える必要があり得る。 As indicated above, the composition of the present invention has a pH of 5 to 6. The composition also has an ophthalmologically acceptable osmotic pressure, which is typically in the range of 200 to 400 milliosmoles per kilogram of water (mOsm / kg). When selecting an appropriate buffer to maintain the pH of the composition in the specified range of 5 to 6, and / or when selecting an osmotic pressure regulator, such agents can be ionized by the composition. The effect on the content of the species must be considered. For example, if sodium chloride added for the purpose of adjusting osmotic pressure increases the ionic species concentration beyond an acceptable level (ie compared to the target viscosity value), all or part of the sodium chloride is It may be necessary to replace a nonionic osmotic pressure regulator such as propylene glycol.
本発明の組成物は、抗菌保存剤(例えば塩化ベンザルコニウム)および湿潤剤のような、眼用薬学的組成物において典型的に使用される、様々な他の成分を含み得る。その組成物は、好ましくは複数用量製品として処方および包装されるが、従来の抗菌保存剤無しに処方され、そして密封された単位用量バイアルにも包装され得る。 The compositions of the present invention may include a variety of other ingredients typically used in ophthalmic pharmaceutical compositions, such as antimicrobial preservatives (eg, benzalkonium chloride) and wetting agents. The composition is preferably formulated and packaged as a multi-dose product, but may be formulated without conventional antimicrobial preservatives and packaged in sealed unit dose vials.
本発明の組成物は、感染または感染のリスクのいずれかが存在する、眼の炎症性状態の処置に有用である。本明細書中で使用する場合、「処置」という用語は、存在する状態の積極的な処置、および状態(例えば感染)を発症するリスクのある患者の予防的処置の両方を含む。本発明の組成物は、外傷から起こる眼の損傷に関連する眼の炎症、および眼の外科的手順(例えば白内障手術、網膜の手術、LASIK手術)および眼内注射(例えば眼球後注射、後方強膜近傍注射(posterior juxtascleral injection)、および前方強膜近傍注射)に関連する炎症の処置に特に有用である。 The compositions of the present invention are useful for the treatment of inflammatory conditions in the eye where either infection or risk of infection exists. As used herein, the term “treatment” includes both active treatment of an existing condition and prophylactic treatment of patients at risk of developing a condition (eg, infection). The compositions of the present invention may cause ocular inflammation associated with eye damage resulting from trauma, and ocular surgical procedures (eg, cataract surgery, retinal surgery, LASIK surgery) and intraocular injections (eg, post-ocular injection, posterior strength) It is particularly useful for the treatment of inflammation associated with superior juxtacular injection and anterior near scleral injection.
そのような処置を、少量(例えば1から2滴)の本発明の組成物を、1日あたり2から4回、患者の罹患した片方または両方の眼に付与することによって行われ得る。しかし、用量および投与頻度の両方は、臨床医により変更され得る。 Such treatment can be performed by applying a small amount (eg, 1 to 2 drops) of the composition of the invention to the affected eye or both of the patient 2 to 4 times per day. However, both dose and frequency of administration can be varied by the clinician.
トブラマイシン以外の選択された少数の治療剤が、実質的にトブラマイシンと同じ方式でキサンタンガムと相互作用し得、そして本発明において使用され得ることが企図される。理論に拘束されることなく、分子内に2つ以上の陽性または陽イオン性電荷を有する治療剤分子は、トブラマイシンと同じ方式でキサンタンガムと相互作用し得ると考えられる。さらに、理論に拘束されることなく、フルオロキノロン治療剤のかなりの部分が、トブラマイシンと類似の方式でキサンタンガムと相互作用し得ると考えられる。1つの例として、発明者らは、イオン種を使用してモキシフロキサシンおよびキサンタンガムの間の相互作用を制御して、上記で議論したものと実質的に同様のインビトロ/インビボ粘度比を生じ得ることを発見した。 It is contemplated that a small number of selected therapeutic agents other than tobramycin can interact with xanthan gum in substantially the same manner as tobramycin and can be used in the present invention. Without being bound by theory, it is believed that therapeutic molecules that have more than one positive or cationic charge in the molecule can interact with xanthan gum in the same manner as tobramycin. Further, without being bound by theory, it is believed that a significant portion of fluoroquinolone therapeutics can interact with xanthan gum in a manner similar to tobramycin. As one example, the inventors use ionic species to control the interaction between moxifloxacin and xanthan gum, resulting in an in vitro / in vivo viscosity ratio substantially similar to that discussed above. I found it to get.
実施例1
脱アセチル化されていないキサンタンガムを使用した、トブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン/キサンタンガム処方物の調製を下記で説明する。できた処方物の安定性も、下記で説明するように評価した。
Example 1
The preparation of a tobramycin / dexamethasone / xanthan gum formulation using non-deacetylated xanthan gum is described below. The stability of the resulting formulation was also evaluated as described below.
キサンタンガムストック溶液の調製
熱湯を容器に加えた。キサンタンガムを計量し、そして混合しながら容器にゆっくりと加えた。その温度を60℃に調節し、そしてキサンタンガムおよび水を均一になるまで混合した。精製水を加えて、組成物を最終的な標的重量にし、そして均一になるまで混合した。適切なポリッシングフィルター、例えば1.2μmフィルターを通してろ過する前に、その温度を70℃まで上げた。
Preparation of xanthan gum stock solution Hot water was added to the container. Xanthan gum was weighed and slowly added to the container with mixing. The temperature was adjusted to 60 ° C. and xanthan gum and water were mixed until uniform. Purified water was added to bring the composition to the final target weight and mixed until uniform. The temperature was raised to 70 ° C. before filtering through a suitable polishing filter, eg a 1.2 μm filter.
キサンタンガムストック溶液を用いたトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン処方物の調製
下記の表1Aで明記した量のトブラマイシン、塩化ナトリウム、ホウ酸およびエデト酸二ナトリウムを、一回分の精製水に加え、そして溶解させた。塩酸または硫酸を加えて、pHを低下させた。チロキサポールおよびデキサメタゾンを、スラリーまたは粉末として加えた。バッチ量のキサンタンガムストック溶液を加え、そしてよく混合した。1Nの塩酸または1Nの硫酸を加えて、標的pHにした。精製水を加えて最終的な体積にし、そしてよく混合した。できた処方物の粘度を、6sec−1のせん断速度で測定した。それぞれの粘度値を、下記の表1Aに示す。
Preparation of Tobramycin / Dexamethasone Formulation Using Xanthan Gum Stock Solution The amounts of tobramycin, sodium chloride, boric acid and disodium edetate specified in Table 1A below were added to a portion of purified water and dissolved. Hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid was added to lower the pH. Tyloxapol and dexamethasone were added as a slurry or powder. A batch amount of xanthan gum stock solution was added and mixed well. 1N hydrochloric acid or 1N sulfuric acid was added to reach the target pH. Purified water was added to final volume and mixed well. The viscosity of the resulting formulation was measured at a shear rate of 6 sec- 1 . The respective viscosity values are shown in Table 1A below.
脱アセチル化キサンタンガムの使用を含む、本発明の原理によるトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン処方物の調製を、下記で説明する。
The preparation of a tobramycin / dexamethasone formulation according to the principles of the present invention, including the use of deacetylated xanthan gum, is described below.
キサンタンガムストック溶液の調製および塩基による前処理
熱湯を容器に加えた。キサンタンガムを計量し、そして混合しながらゆっくりと容器に加えた。キサンタンガム1gあたり2.5mlの1N NaOHまたは等価物を加え、そして次いで20分間混合した。次いでキサンタンガム1gあたり1.66mlの1N HClまたは等価物を加えた。標的重量に調節するために精製水を加え、続いて15分間混合した。次いで脱アセチル化キサンタンガムを、適切なフィルター、例えば1.2μmのフィルターを通してろ過した。
Preparation of xanthan gum stock solution and pretreatment with base Hot water was added to the container. Xanthan gum was weighed and slowly added to the container with mixing. 2.5 ml of 1N NaOH or equivalent per gram of xanthan gum was added and then mixed for 20 minutes. Then 1.66 ml of 1N HCl or equivalent per gram of xanthan gum was added. Purified water was added to adjust to the target weight, followed by mixing for 15 minutes. The deacetylated xanthan gum was then filtered through a suitable filter, such as a 1.2 μm filter.
前処理したキサンタンガムストック溶液を用いたトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン処方物の調製
明記した量のトブラマイシン、塩化ナトリウム、硫酸ナトリウム、エデト酸二ナトリウム、およびプロピレングリコールを、一回分の精製水に加え、続いてチロキサポールおよびデキサメタゾンをスラリーまたは粉末として加えた。1Nの塩酸を用いて、pHを、標的pHよりわずかに高いpHに調節した。次いで上記で記載した脱アセチル化キサンタンガムストック溶液を加え、そしてできた懸濁液をよく混合した。pHを、HClおよび/またはNaOH溶液で、標的レベルまで調節し、そして処方物の粘度を測定した。
Preparation of Tobramycin / Dexamethasone Formulation Using Pretreated Xanthan Gum Stock Solution The specified amounts of tobramycin, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, disodium edetate, and propylene glycol are added to a batch of purified water followed by tyloxapol and Dexamethasone was added as a slurry or powder. The pH was adjusted to slightly higher than the target pH using 1N hydrochloric acid. The deacetylated xanthan gum stock solution described above was then added and the resulting suspension was mixed well. The pH was adjusted to the target level with HCl and / or NaOH solution, and the viscosity of the formulation was measured.
本発明の組成物の初期粘度に対するトブラマイシンの影響、およびその組成物を眼に投与したときの粘度の回復を、本明細書中でさらに説明する。上記の表2Aで記載した処方物番号108536の異なるロットであり、そして本発明の組成物の代表的なものである、下記の表3Aに示す処方物を、脱アセチル化キサンタンガムを用いて調製した。その処方物の初期粘度を、6sec−1のせん断速度で測定し、そして42cpであると決定した。
The effect of tobramycin on the initial viscosity of the compositions of the present invention and the restoration of viscosity when the composition is administered to the eye are further described herein. The formulations shown in Table 3A below, which are different lots of formulation number 108536 described in Table 2A above and are representative of the compositions of the present invention, were prepared using deacetylated xanthan gum. . The initial viscosity of the formulation was measured at a shear rate of 6 sec −1 and determined to be 42 cp.
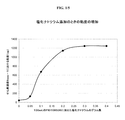
pHのわずかな上昇、または少量のイオン(例えば塩化ナトリウム、リン酸緩衝液)の添加は、トブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を抑制し、それによって処方物の粘度を回復させる。この現象を、図1〜3において図表で示す。図1は、表3Aで記載した処方物の粘度が、0.2gの塩化ナトリウムを100mLのその処方物に加えたときに、42cpから1,000cp超まで増加することを示す。図2は、その処方物の粘度が、pH5.7における42cpから、pHを6.2に上向きに調節した場合に1,100cp超まで、およびpHが6.4の場合1,300cpまで増加することを示す。図3は、その処方物の粘度が、10mLの上記で記載したPBS溶液を100mLの懸濁液に加えたときに、42cpから1,059cpまで増加することを示す。 A slight increase in pH or the addition of a small amount of ions (eg sodium chloride, phosphate buffer) suppresses ionic interactions between tobramycin and xanthan gum, thereby restoring the viscosity of the formulation. This phenomenon is shown graphically in FIGS. FIG. 1 shows that the viscosity of the formulation described in Table 3A increases from 42 cp to over 1,000 cp when 0.2 g of sodium chloride is added to 100 mL of the formulation. FIG. 2 shows that the viscosity of the formulation increases from 42 cp at pH 5.7 to over 1,100 cp when the pH is adjusted upward to 6.2 and to 1,300 cp when the pH is 6.4. It shows that. FIG. 3 shows that the viscosity of the formulation increases from 42 cp to 1,059 cp when 10 mL of the PBS solution described above is added to 100 mL of the suspension.
表3Aに示した処方物からトブラマイシンを除去した場合、その処方物の粘度は、PBS溶液と混合した後に増加しなかった。具体的には、トブラマイシンを含まない、改変されたバージョンの処方物は、10mlのリン酸緩衝化食塩水を100mlのその処方物に加えた場合、667cpの粘度を有すると決定された。言い換えると、改変された処方物の粘度は、リン酸緩衝化食塩水の添加後、836cpの初期粘度から、667cpのシミュレートされたインビボ粘度まで実際には低下した。 When tobramycin was removed from the formulation shown in Table 3A, the viscosity of the formulation did not increase after mixing with PBS solution. Specifically, a modified version of the formulation without tobramycin was determined to have a viscosity of 667 cp when 10 ml of phosphate buffered saline was added to 100 ml of the formulation. In other words, the viscosity of the modified formulation actually decreased from an initial viscosity of 836 cp to a simulated in vivo viscosity of 667 cp after addition of phosphate buffered saline.
実施例4
下記で議論および説明するように、本発明の組成物の粘度は、組成物のイオン強度およびpH、およびそれぞれ0.1から0.5w/v%および0.3から0.9w/v%の明示された範囲内で選択されるトブラマイシンおよびキサンタンガムの量によって影響される。表4A〜4Eで示すその処方物および関連するデータは、これらの因子の相互作用をさらに例証および説明するために提供される。
Example 4
As discussed and explained below, the viscosity of the composition of the present invention is the ionic strength and pH of the composition, and 0.1 to 0.5 w / v% and 0.3 to 0.9 w / v% respectively Affected by the amount of tobramycin and xanthan gum selected within the stated range. The formulations and associated data shown in Tables 4A-4E are provided to further illustrate and explain the interaction of these factors.
処方物A〜Dおよびこれらの組成物のそれぞれの粘度値の比較は、キサンタンガムを0.6w/v%の濃度で含む組成物の粘度に対するトブラマイシンの影響を示す。具体的には、トブラマイシンを0.3w/v%の濃度で含む処方物Aは、15センチポイズ(「cp」)の初期粘度を有し、一方トブラマイシンの欠如以外は処方物Aと同一である処方物Cは、919cpの初期粘度を有する。従って、処方物Aにおけるトブラマイシンの存在は、組成物の粘度の低下に寄与している。このトブラマイシンの影響はまた、処方物BおよびDの比較に基づいても明らかである。(処方物AおよびBはデキサメタゾンを含まないが、他は代表的な本発明のトブラマイシン/デキサメタゾン組成物の例である。処方物CおよびDは、比較の目的のために提供され、そして本発明の組成物の代表的な例ではない。)
処方物Aの粘度は、好ましいイオン化可能な種である、23.9mM(0.34%)の硫酸ナトリウムを含むことによって安定化される。処方物Aはまた、脱アセチル化キサンタンガムストック溶液が、脱アセチル化工程の間に水酸化ナトリウムおよび塩酸の添加によって形成された塩化ナトリウムを含むので、約10mMの塩化ナトリウムを含む。EDTA(エデト酸二ナトリウム)および塩化ベンザルコニウムからのイオン性の寄与は、それらの濃度が非常に低いので、わずかである。
Comparison of the viscosity values of formulations A to D and their respective compositions shows the effect of tobramycin on the viscosity of compositions containing xanthan gum at a concentration of 0.6 w / v%. Specifically, Formulation A containing tobramycin at a concentration of 0.3 w / v% has an initial viscosity of 15 centipoise (“cp”), while it is identical to Formulation A except for the lack of tobramycin Product C has an initial viscosity of 919 cp. Thus, the presence of tobramycin in Formulation A contributes to a decrease in the viscosity of the composition. This effect of tobramycin is also evident based on a comparison of formulations B and D. (Formulations A and B do not contain dexamethasone, but others are examples of representative tobramycin / dexamethasone compositions of the present invention. Formulations C and D are provided for comparative purposes and the present invention. It is not a representative example of the composition.)
The viscosity of Formulation A is stabilized by including 23.9 mM (0.34%) sodium sulfate, a preferred ionizable species. Formulation A also contains about 10 mM sodium chloride because the deacetylated xanthan gum stock solution contains sodium chloride formed by the addition of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid during the deacetylation process. The ionic contributions from EDTA (disodium edetate) and benzalkonium chloride are small because their concentrations are very low.
処方物Bの粘度は、これも好ましいイオン化可能な種である、138.2mMの塩化ナトリウムを含むことによって安定化される。 The viscosity of Formulation B is stabilized by including 138.2 mM sodium chloride, which is also a preferred ionizable species.
本発明の組成物の粘度は、塩化ナトリウムまたは硫酸ナトリウムを用いて安定化され得る。しかし、必要な硫酸ナトリウムの濃度は、塩化ナトリウムの濃度よりはるかに低い。約1mMの硫酸ナトリウムが、5.3mMの塩化ナトリウムと等価である。これは、実施例A、B、およびEからLによって示される。 The viscosity of the composition of the present invention can be stabilized using sodium chloride or sodium sulfate. However, the concentration of sodium sulfate required is much lower than that of sodium chloride. About 1 mM sodium sulfate is equivalent to 5.3 mM sodium chloride. This is illustrated by Examples A, B, and E through L.
処方物A、BおよびEからLの粘度対塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度が、図4にプロットされる。これらの処方物のための塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度を、「塩化ナトリウム濃度(mM)+5.3硫酸ナトリウム濃度(mM)」と定義する。0.3%のトブラマイシンおよび0.6%のキサンタンガムを含む処方物の粘度は、塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度が増加するにつれて増加する。その粘度は、134から150mMの塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度範囲に関して、10から300cpの好ましい範囲にある。 Formulations A, B and E to L viscosities versus sodium chloride equivalent ion concentration are plotted in FIG. The sodium chloride equivalent ion concentration for these formulations is defined as “sodium chloride concentration (mM) +5.3 sodium sulfate concentration (mM)”. The viscosity of a formulation containing 0.3% tobramycin and 0.6% xanthan gum increases as the sodium chloride equivalent ion concentration increases. Its viscosity is in the preferred range of 10 to 300 cp for a sodium chloride equivalent ion concentration range of 134 to 150 mM.
塩化ナトリウムまたは硫酸ナトリウムの代わりに、他のイオン化可能な種が使用され得る。好ましいイオン化される塩は、塩化ナトリウム、硫酸ナトリウム、クエン酸ナトリウム、リン酸ナトリウム、ホウ酸ナトリウム、酢酸ナトリウム、塩化カリウム、塩化カルシウム、および塩化マグネシウムである。異なるイオン化される種は、塩化ナトリウム当量濃度を決定するために、異なる係数(硫酸ナトリウムでは5.3)を必要とする。この係数は、異なる比の塩化ナトリウムおよび他の塩でサンプルを作製することによって決定され得る。次いでそれらのサンプルの粘度結果を分析して、塩化ナトリウム当量濃度を決定するための係数を決定し得る。この係数は、多価イオンを有する塩のものより高い。 Other ionizable species may be used in place of sodium chloride or sodium sulfate. Preferred ionized salts are sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium citrate, sodium phosphate, sodium borate, sodium acetate, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and magnesium chloride. Different ionized species require different coefficients (5.3 for sodium sulfate) to determine the sodium chloride equivalent concentration. This factor can be determined by making samples with different ratios of sodium chloride and other salts. The viscosity results of those samples can then be analyzed to determine a factor for determining the sodium chloride equivalent concentration. This coefficient is higher than that of salts with multivalent ions.
所定の活性部分およびその濃度に関して、比較的低い粘度を生じる塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度範囲は、pHおよびキサンタンガム濃度に依存する。0.3%のトブラマイシン溶液に関して、処方物MおよびNは、5.75のpHにおけるものと比較して、より低い5.5のpHにおいて同様の粘度を生じるためには、より高い塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度が必要であることを示す。 For a given active moiety and its concentration, the sodium chloride equivalent ion concentration range that produces a relatively low viscosity depends on the pH and xanthan gum concentration. For a 0.3% tobramycin solution, formulations M and N have higher sodium chloride equivalents to produce a similar viscosity at a lower pH of 5.5 compared to at a pH of 5.75. Indicates that ion concentration is required.
処方物O、PおよびQは、固定したpH(5.5)において、キサンタンガム濃度が0.6%から0.9%へ増加するにつれて、より低い塩化ナトリウム当量イオン濃度が必要であることを示す。 Formulations O, P and Q show that lower sodium chloride equivalent ion concentrations are required as xanthan gum concentration increases from 0.6% to 0.9% at a fixed pH (5.5) .
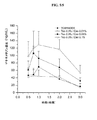
ウサギ生物学的利用能試験結果
本発明の3つの代表的な組成物の眼の生物学的利用能を、TOBRADEX(登録商標)(トブラマイシン0.3%/デキサメタゾン0.1%)眼用懸濁液と比較して評価した。本発明の組成物の処方物を、下記の表5Aに示す。TOBRADEX(登録商標)眼用懸濁液の処方物は、米国特許第5,149,694号の実施例1に示される。
Rabbit Bioavailability Test Results Ocular bioavailability of three representative compositions of the present invention was determined by TOBRADEX® (tobramycin 0.3% / dexamethasone 0.1%) ocular suspension. Evaluation was made in comparison with the liquid. The formulation of the composition of the present invention is shown in Table 5A below. A formulation of TOBRADEX® ophthalmic suspension is shown in Example 1 of US Pat. No. 5,149,694.
ウサギ水性体液中のデキサメタゾン濃度を、承認されたHPLCタンデム質量分析(HPLC/SM/MS)法を用いて測定した。この手順において、水性体液の25.0マイクロリットルのアリコートに、内部標準としてベクロメタゾンを加え、そしてメチル−t−ブチルエーテルを用いて抽出した。有機層を蒸発させて乾燥し、そして20:80の10mMギ酸アンモニウム:メタノールで再構築し、そしてサンプルの再構築に使用したものと同じ組成の移動相で、無勾配条件下で逆相HPLCカラムに注入する。カラム流出液に陽イオンエレクトロスプレーイオン化を行い、そしてデキサメタゾンおよびベクロメタゾンのプロトン化分子イオンに衝突断片化を行う。デキサメタゾンおよびベクロメタゾンの、それぞれm/z 393.1→373.4および409.3→391.4の遷移の多重反応モニタリングが、特異的な検出を可能にする。その手順の動作範囲は1.00から200ng/mLである。 Dexamethasone concentration in rabbit aqueous body fluids was measured using an approved HPLC tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC / SM / MS) method. In this procedure, to a 25.0 microliter aliquot of aqueous body fluid was added beclomethasone as an internal standard and extracted with methyl-t-butyl ether. The organic layer was evaporated to dryness and reconstituted with 20:80 10 mM ammonium formate: methanol and a reverse phase HPLC column under gradient-free conditions with a mobile phase of the same composition used to reconstitute the sample. Inject. Cation electrospray ionization is performed on the column effluent and collisional fragmentation is performed on the protonated molecular ions of dexamethasone and beclomethasone. Multiple reaction monitoring of the dexamethasone and beclomethasone transitions at m / z 393.1 → 373.4 and 409.3 → 391.4, respectively, allows specific detection. The operating range of the procedure is 1.00 to 200 ng / mL.
デキサメタゾンの平均水性体液濃度対時間は、図5にプロットされる。水性体液中のデキサメタゾンの最高濃度(Cmax)および曲線下面積(AUC)値を、下記の表5Bで示す: The average aqueous fluid concentration versus time for dexamethasone is plotted in FIG. The maximum concentration (C max ) and area under the curve (AUC) value of dexamethasone in aqueous body fluid are shown in Table 5B below:
Claims (15)
0.1から0.5w/v%のトブラマイシン;
0.03から0.1w/v%のデキサメタゾン;
0.3から0.9%の濃度で脱アセチル化キサンタンガムを含む、水性の眼科学的に許容されるビヒクル;および
1つ以上のイオン化可能な種であって、該組成物のインビトロ粘度が6sec−1のせん断速度および25℃の温度において10から700cpの範囲内に維持されるように、該トブラマイシンおよび該脱アセチル化キサンタンガムの間のイオン性相互作用を制限するのに十分な量の、1つ以上のイオン化可能な種
を含み、
5から6のpHを有し、該脱アセチル化キサンタンガムが2%未満の結合アセテートを含む、組成物。 A topical ophthalmic composition comprising:
0.1 to 0.5 w / v% tobramycin;
0.03 to 0.1 w / v% dexamethasone;
An aqueous ophthalmically acceptable vehicle comprising deacetylated xanthan gum at a concentration of 0.3 to 0.9%; and one or more ionizable species, wherein the composition has an in vitro viscosity of 6 sec. An amount of 1 sufficient to limit the ionic interaction between the tobramycin and the deacetylated xanthan gum such that it is maintained in the range of 10 to 700 cp at a shear rate of −1 and a temperature of 25 ° C. Including one or more ionizable species,
5 have a pH of 6, dehydration acetylated xanthan gum containing bound acetate of less than 2%, the composition.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2010/039618 WO2011162752A1 (en) | 2010-06-23 | 2010-06-23 | Topical ophthalmic suspensions containing tobramycin and dexamethasone |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013529632A JP2013529632A (en) | 2013-07-22 |
| JP2013529632A5 JP2013529632A5 (en) | 2013-08-29 |
| JP5728082B2 true JP5728082B2 (en) | 2015-06-03 |
Family
ID=44080140
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013516553A Expired - Fee Related JP5728082B2 (en) | 2010-06-23 | 2010-06-23 | Topical ophthalmic suspension containing tobramycin and dexamethasone |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2585037A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5728082B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20130094280A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102946855B (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2010356098B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112012033052A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2801731A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2012015051A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011162752A1 (en) |
| ZA (1) | ZA201209240B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB201208080D0 (en) * | 2012-05-09 | 2012-06-20 | Norton Healthcare Ltd | Tobramycin formulation |
| JP6527315B2 (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2019-06-05 | Dsp五協フード&ケミカル株式会社 | Fast-dissolving thickener, thickener for people with dysphagia and dysphagia, food and drink for patients with dysphagia and dysphagia |
| CN109260219B (en) * | 2018-11-30 | 2021-03-09 | 山东省药学科学院 | Articular cavity injection preparation and application thereof |
| IT202000002296A1 (en) * | 2020-02-06 | 2021-08-06 | Sifi Spa | Topical ophthalmic formulations based on xanthan with reduced dosage |
| IT202200000821A1 (en) * | 2022-01-19 | 2023-07-19 | Sifi Spa | TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC FORMULATIONS BASED ON XANTHANE WITH REDUCED DOSAGE |
| CN115006412B (en) * | 2022-05-20 | 2023-11-10 | 北京诺康达医药科技股份有限公司 | Compound tobramycin eye drops and preparation method thereof |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4136177A (en) | 1977-01-31 | 1979-01-23 | American Home Products Corp. | Xanthan gum therapeutic compositions |
| US5149694A (en) | 1988-03-09 | 1992-09-22 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Combination of tobramycin and dexamethasone for topical ophthalmic use |
| JP3979783B2 (en) * | 1997-07-29 | 2007-09-19 | アルコン ラボラトリーズ インコーポレイテッド | Ophthalmic composition comprising galactomannan polymer and borate |
| US6174524B1 (en) | 1999-03-26 | 2001-01-16 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Gelling ophthalmic compositions containing xanthan gum |
| TR200002848T2 (en) * | 1998-04-07 | 2001-02-21 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Gel ophthalmic compositions containing xanthan gum. |
| US6261547B1 (en) | 1998-04-07 | 2001-07-17 | Alcon Manufacturing, Ltd. | Gelling ophthalmic compositions containing xanthan gum |
| EP1305033B1 (en) | 2000-07-28 | 2004-10-20 | Alcon, Inc | Pharmaceutical compositions containing tobramycin and xanthan gum |
-
2010
- 2010-06-23 WO PCT/US2010/039618 patent/WO2011162752A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-06-23 AU AU2010356098A patent/AU2010356098B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2010-06-23 MX MX2012015051A patent/MX2012015051A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2010-06-23 JP JP2013516553A patent/JP5728082B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-06-23 BR BR112012033052A patent/BR112012033052A2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-06-23 CN CN201080067666.9A patent/CN102946855B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-06-23 EP EP10726406.1A patent/EP2585037A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2010-06-23 CA CA2801731A patent/CA2801731A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2010-06-23 KR KR1020137000258A patent/KR20130094280A/en active IP Right Grant
-
2012
- 2012-12-06 ZA ZA2012/09240A patent/ZA201209240B/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MX2012015051A (en) | 2013-02-15 |
| CN102946855A (en) | 2013-02-27 |
| KR20130094280A (en) | 2013-08-23 |
| BR112012033052A2 (en) | 2019-09-24 |
| JP2013529632A (en) | 2013-07-22 |
| AU2010356098A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| EP2585037A1 (en) | 2013-05-01 |
| CA2801731A1 (en) | 2011-12-29 |
| AU2010356098B2 (en) | 2014-08-14 |
| ZA201209240B (en) | 2014-02-26 |
| CN102946855B (en) | 2016-01-06 |
| WO2011162752A1 (en) | 2011-12-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8450287B2 (en) | Topical ophthalmic compositions containing tobramycin and dexamethasone | |
| JP5728082B2 (en) | Topical ophthalmic suspension containing tobramycin and dexamethasone | |
| JP4545927B2 (en) | Gelled ophthalmic composition containing xanthan gum | |
| US20110105450A1 (en) | Ophthalmic formulations of fluticasone and methods of use | |
| CA2760140C (en) | Topical solution formulations containing a corticosteroid and a cyclodextrin | |
| US20070110812A1 (en) | Ophthalmic composition for dry eye therapy | |
| JPH11510497A (en) | Formulations containing O-carboxyalkyl chitosan and methods of use in the ophthalmic field | |
| WO2010107689A1 (en) | Ophthalmic formulations of cetirizine and methods of use | |
| TW201701882A (en) | Aqueous suspension containing nano particles of GLUCOCORTICOIDS | |
| JP2001501194A (en) | Gel-forming pharmaceutical composition | |
| JP6522592B2 (en) | Topical aqueous ophthalmic composition containing 1H-indole-1-carboxamide derivatives and its use for the treatment of ocular diseases | |
| JP2808378B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of aqueous suspension | |
| WO2022238251A2 (en) | Ophthalmic pharmaceutical composition comprising atropine | |
| CA2835013C (en) | Eye drops for treatment of conjunctivochalasis | |
| WO2022238250A1 (en) | Ophthalmic pharmaceutical composition comprising atropine | |
| JPH05951A (en) | Aqueous suspension eye drop containing corticosteroid | |
| CN116847826A (en) | Ophthalmic composition comprising levofloxacin and ketorolac, preparation method and application thereof | |
| TW202342108A (en) | Multidose ophthalmic compositions | |
| JP2017178880A (en) | Artificial tear fluid type eye-drops compositions | |
| MXJL05000034A (en) | Topical ophthalmic formulation and use thereof. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130610 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130610 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140725 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141023 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150331 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150403 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5728082 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |