JP5545629B2 - Ophthalmic imaging equipment - Google Patents
Ophthalmic imaging equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5545629B2 JP5545629B2 JP2010011355A JP2010011355A JP5545629B2 JP 5545629 B2 JP5545629 B2 JP 5545629B2 JP 2010011355 A JP2010011355 A JP 2010011355A JP 2010011355 A JP2010011355 A JP 2010011355A JP 5545629 B2 JP5545629 B2 JP 5545629B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- eye
- light
- fundus
- optical system
- photographing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 59
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 161
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 60
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 37
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 238000012014 optical coherence tomography Methods 0.000 description 36
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 32
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 208000014733 refractive error Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000001747 pupil Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004323 axial length Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004087 cornea Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000001061 forehead Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B3/00—Apparatus for testing the eyes; Instruments for examining the eyes
- A61B3/10—Objective types, i.e. instruments for examining the eyes independent of the patients' perceptions or reactions
- A61B3/102—Objective types, i.e. instruments for examining the eyes independent of the patients' perceptions or reactions for optical coherence tomography [OCT]
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Eye Examination Apparatus (AREA)
Description
本発明は、被検者眼の撮影画像を得る眼科撮影装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an ophthalmologic photographing apparatus that obtains a photographed image of a subject's eye.
被検者眼が覗く検査窓を介して、光源から出射した少なくとも一部の光を被検者眼の所定部位に向けて投光すると共に被検者眼の所定部位からの反射光を受光素子で受光して被検者眼の撮影画像を得る撮影光学系を有する眼科撮影装置が知られている。このような装置としては、レーザ走査検眼鏡(Scanning laser Ophthalmoscope:SLO)、光干渉断層計(Optical Coherence Tomography:OCT)、眼底カメラ、などが知られている。 A light receiving element that projects at least a part of light emitted from the light source toward a predetermined part of the subject's eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and receives reflected light from the predetermined part of the subject's eye There is known an ophthalmologic photographing apparatus having a photographing optical system that receives light and obtains a photographed image of a subject's eye. As such an apparatus, a laser scanning ophthalmoscope (SLO), an optical coherence tomography (OCT), a fundus camera, and the like are known.
そして、上記のような装置では、撮影目的に応じて光学アダプターが検査窓に装着されることにより、撮影部位に応じた焦点位置の変更(例えば、眼底から前眼部)、撮影倍率/撮影画角の変更、などが可能である(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 In the apparatus as described above, an optical adapter is attached to the examination window according to the imaging purpose, thereby changing the focal position according to the imaging region (for example, the fundus to the anterior eye), imaging magnification / imaging image. The corner can be changed (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、上記のような装置において、アダプターの装着が不十分なために、良好な撮影ができない場合がある。 However, in such a device as described above, there is a case where satisfactory photographing cannot be performed because the adapter is not sufficiently attached.
例えば、OCTにおいて、アダプターを用いて前眼部断層像の定量計測(例えば、角膜厚計測、隅角計測)を行う場合、アダプターが傾いて装着された状態では、装置本体の光学系とアダプターのレンズ系との光軸ずれにより測定光の走査範囲が変わってしまい、定量計測をしたときの結果に誤差が生じる可能性がある。 For example, in OCT, when quantitative measurement (for example, corneal thickness measurement, corner angle measurement) of an anterior segment tomogram is performed using an adapter, the optical system of the apparatus main body and the adapter are not mounted when the adapter is tilted. The scanning range of the measurement light changes due to the optical axis deviation from the lens system, and an error may occur in the result of quantitative measurement.
本発明は、上記問題点を鑑み、アダプター使用時に良好な画像を撮影可能な眼科撮影装置を提供することを技術課題とする。 In view of the above problems, an object of the present invention is to provide an ophthalmologic photographing apparatus capable of photographing a good image when using an adapter.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明は以下のような構成を備えることを特徴とする。 In order to solve the above problems, the present invention is characterized by having the following configuration.
(1)
被検者眼が覗く検査窓を介して、光源から出射した少なくとも一部の光を被検者眼の所
定部位に向けて投光すると共に被検者眼の所定部位からの反射光を受光素子で受光して被
検者眼の撮影画像を得る撮影光学系を有する眼科撮影装置において、
前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段を備え、
前記装着状態検知手段は、前記検査窓に対する前記光学アダプターの装着が適正か否かを検知する適否検知手段を有し、
前記適否検知手段による検知結果を報知する報知手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする。
(2)
光源から出射された光を測定光と参照光に分割し、測定光を被検者眼が覗く検査窓を介して被検眼の眼底又は前眼部に導き、参照光を装置内部の参照光学系に導いた後、被検眼の眼底又は前眼部で反射した測定光と参照光との合成により得られる干渉光を受光素子に受光させる干渉光学系を有し、前記受光素子の出力信号に基づいて被検眼の眼底及び前眼部の断層像を撮影可能な眼科撮影装置であって、
前記干渉光学系による被検者眼の撮影部位を切り換えるために前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段と、
眼底の断層像を撮影するための眼底撮影モードと、前眼部の断層像を撮影するための前眼部撮影モードと、に設定可能なモード設定手段と、
前記モード設定手段によって設定される撮影モードに応じて前記干渉光学系の光学配置を制御する制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする。
(3)
光源から出射された光を測定光と参照光に分割し、測定光を被検者眼が覗く検査窓を介して被検眼の眼底又は前眼部に導き、参照光を装置内部の参照光学系に導いた後、被検眼の眼底又は前眼部で反射した測定光と参照光との合成により得られる干渉光を受光素子に受光させる干渉光学系を有し、前記受光素子の出力信号に基づいて被検眼の眼底及び前眼部の断層像を撮影可能な眼科撮影装置であって、
前記干渉光学系による被検者眼の撮影部位を切り換えるために前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段と、
眼底の断層像を撮影するための眼底撮影モードと、前眼部の断層像を撮影するための前眼部撮影モードと、に設定可能なモード設定手段と、
前記干渉光学系を内蔵する筐体と、
前記筐体を電動にて移動させる電動駆動部と、
前記モード設定手段によって設定される撮影モードに応じて前記電動駆動部の駆動を制御する制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする。
(4)
(2)又は(3)の眼科撮影装置において、
前記光学アダプターは、前記干渉光学系による撮影部位を眼底から前眼部へと切り換えるためのレンズ系を持ち、
前記モード設定手段は、前記光学アダプターの装着を検知したときに前記装着状態検知手段から出力される出力信号に基づいて前記眼底撮影モードから前記前眼部撮影モードに切り換える、あるいは前記光学アダプターの装着を検知したときに前記装着状態検知手段から出力される出力信号に基づいて前眼部撮影モードへの切換を促す旨をモニタに表示することを特徴とする。
(1)
A light receiving element that projects at least a part of light emitted from the light source toward a predetermined part of the subject's eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and receives reflected light from the predetermined part of the subject's eye In an ophthalmologic photographing apparatus having a photographing optical system that receives a light and obtains a photographed image of a subject's eye,
Comprising a mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the inspection window ;
The mounting state detection means includes suitability detection means for detecting whether or not the optical adapter is properly attached to the inspection window.
Informing means for informing the detection result by the suitability detecting means,
It is characterized by providing.
(2)
The light emitted from the light source is divided into measurement light and reference light, and the measurement light is guided to the fundus or anterior eye portion of the subject eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and the reference light is a reference optical system inside the apparatus. An interference optical system that causes the light receiving element to receive interference light obtained by combining the measurement light reflected by the fundus or anterior eye portion of the eye to be examined and the reference light, and based on the output signal of the light receiving element An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus capable of photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and anterior eye of the subject eye,
A mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the examination window in order to switch the imaging part of the subject's eye by the interference optical system ;
Mode setting means that can be set to a fundus photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and an anterior eye photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the anterior eye;
Control means for controlling the optical arrangement of the interference optical system in accordance with the photographing mode set by the mode setting means;
It is characterized by providing.
(3)
The light emitted from the light source is divided into measurement light and reference light, and the measurement light is guided to the fundus or anterior eye portion of the subject eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and the reference light is a reference optical system inside the apparatus. An interference optical system that causes the light receiving element to receive interference light obtained by combining the measurement light reflected by the fundus or anterior eye portion of the eye to be examined and the reference light, and based on the output signal of the light receiving element An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus capable of photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and anterior eye of the subject eye,
A mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the examination window in order to switch the imaging part of the subject's eye by the interference optical system ;
Mode setting means that can be set to a fundus photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and an anterior eye photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the anterior eye;
A housing containing the interference optical system;
An electric drive unit for electrically moving the housing;
Control means for controlling the driving of the electric drive unit according to the photographing mode set by the mode setting means;
It is characterized by providing.
(4)
In the ophthalmologic photographing apparatus according to (2) or (3),
The optical adapter has a lens system for switching the imaging site by the interference optical system from the fundus to the anterior segment,
The mode setting means switches from the fundus photographing mode to the anterior eye photographing mode based on an output signal output from the wearing state detecting means when the wearing of the optical adapter is detected, or the wearing of the optical adapter The display device displays a message prompting the user to switch to the anterior ocular segment photographing mode based on an output signal output from the wearing state detecting means when detecting the image .
本発明によれば、アダプター使用時に良好な画像を撮影できる。 According to the present invention, a good image can be taken when the adapter is used.
本発明の実施形態を図面に基づいて説明する。図1は、本実施形態の眼科撮影装置の光学系及び制御系を示す図である。なお、本実施形態においては、被検眼の奥行き方向をZ方向(光軸L1方向)、水平方向をX方向、鉛直方向をY方向として説明する。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an optical system and a control system of the ophthalmologic photographing apparatus according to the present embodiment. In the present embodiment, the depth direction of the eye to be examined is described as the Z direction (the optical axis L1 direction), the horizontal direction is the X direction, and the vertical direction is the Y direction.
図1において、その光学系は、被検眼眼底の断層画像を光干渉の技術を用いて非侵襲で得るための干渉光学系(以下、OCT光学系とする)200と、赤外光を用いて被検眼の眼底を照明し観察するためのSLO眼底像を取得するスキャニングレーザオフサルモスコープ(SLO)光学系300と、に大別される。なお、上記各光学系は、光源から出射した少なくとも一部の光を被検者眼の所定部位に向けて投光する投光光学系と、被検者眼の所定部位からの反射光を受光素子で受光する受光光学系と、を有し、被検者眼の撮影画像を得るための撮影光学系として用いられる。なお、OCT光学系200には、スペクトラル・ドメイン型のOCT光学系が使用されている(もちろん、タイムドメイン型(TD−OCT)、スウィプト・ソース・ドメイン型(SS−OCT)でもよい)。なお、干渉光学系200及びSLO光学系300は、筐体100(図2参照)に内蔵されている。また、その筐体は、周知のアライメント用移動機構(手動又は電動)により、被検者眼Eに対して三次元的に移動される。
In FIG. 1, the optical system uses an interference optical system (hereinafter referred to as an OCT optical system) 200 for non-invasively obtaining a tomographic image of the fundus of the eye to be examined using an optical interference technique, and infrared light. A scanning laser ophthalmoscope (SLO)
なお、40は光分割部材としてのダイクロイックミラーであり、OCT光学系200に用いられる測定光源27から発せられる測定光(例えば、λ=840nm付近)を反射し、SLO光学系300に用いられる光出射部61から発せられるレーザ光(光源27とは異なる波長の光 例えば、λ=780nm付近)を透過する特性を有する。この場合、ダイクロイックミラー40は、OCT光学系200の測定光軸L2とSLO光学系300の測定光軸L1とを同軸にする。
まず、ダイクロイックミラー40の反射側に設けられたOCT光学系200の構成について説明する。OCT光学系200は、光源から出射された光束を測定光束と参照光束に分割し、測定光束を被検眼の所定部位(前眼部又は眼底)に導き,参照光束を参照光学系に導いた後、被検眼の所定部位で反射した測定光束と参照光束との合成により得られる干渉光を受光素子に受光させる。
First, the configuration of the OCT
27はOCT光学系200の測定光及び参照光として用いられる低コヒーレントな光を発するOCT光源であり、例えばSLD光源等が用いられる。OCT光源27には、例えば、中心波長840nmで50nmの帯域を持つ光源が用いられる。26は光分割部材と光結合部材としての役割を兼用するファイバーカップラーである。OCT光源27から発せられた光は、導光路としての光ファイバ38aを介して、ファイバーカップラー26によって参照光と測定光とに分割される。測定光は光ファイバ38bを介して被検眼Eへと向かい、参照光は光ファイバ38cを介して参照ミラー31へと向かう。
測定光を被検眼Eへ向けて出射する光路には、測定光を出射する光ファイバ38bの端部39b、コリメートレンズ22、被検眼眼底に対するフォーカス調整のため被検眼の屈折誤差に合わせて光軸方向に移動可能なフォーカシングレンズ24、走査駆動機構51の駆動により眼底上でXY方向に測定光を走査させることが可能な2つのガルバノミラーの組み合せからなる走査部23と、が配置されている。ダイクロイックミラー40及び対物レンズ10は、OCT光学系200からのOCT測定光を被検眼眼底へと導光する導光光学系としての役割を有する。なお、本実施形態の走査部23では、2つのガルバノミラーによって測定光の反射角度を任意に調整することにより、眼底上に走査させる測定光の走査方向を任意に設定できるような構成となっている。よって、被検眼眼底の任意の領域の断層画像を得ることが可能となる。なお、光ファイバ38bの端部39bは、被検眼眼底と共役となるように配置される。また、走査部23の2つのガルバノミラーは、被検眼瞳孔と略共役な位置に配置される。
In the optical path for emitting the measurement light toward the eye E, the optical axis is adjusted in accordance with the refractive error of the eye to be focused for adjusting the end 39b of the
上記ガルバノミラー及び走査駆動機構51は、測定光束の光路中に配置され,被検眼の所定部位上で横断方向(XY方向)に測定光束を走査させるために測定光束の進行方向を変える光スキャナ(光走査部)として用いられる。光スキャナには、ミラーの他、光の進行(偏向)方向を変化させる音響光学素子(AOM)等が用いられる。 The galvanometer mirror and scanning drive mechanism 51 are disposed in the optical path of the measurement light beam, and change the traveling direction of the measurement light beam in order to scan the measurement light beam in the transverse direction (XY direction) on a predetermined part of the eye to be examined ( Used as an optical scanning unit). The optical scanner uses an acousto-optic device (AOM) that changes the traveling (deflection) direction of light in addition to a mirror.
光ファイバ38bの端部39bから出射した測定光は、コリメートレンズ22によってコリメートされた後、フォーカシングレンズ24を介して、走査部23に達し、2つのガルバノミラーの駆動により反射方向が変えられる。そして、走査部23で反射された測定光は、ダイクロイックミラー40で反射された後、ダイクロイックミラー91及び対物レンズ10を介して、被検眼眼底に集光される。
The measurement light emitted from the end portion 39b of the
そして、眼底で反射した測定光は、対物レンズ10及びダイクロイックミラー91を介して、ダイクロイックミラー40で反射し、OCT光学系200に向かい、走査部23の2つのガルバノミラー、フォーカシングレンズ24、及びコリメートレンズ22を介して、光ファイバ38bの端部39bに入射する。端部39bに入射した測定光は、光ファイバ38b、ファイバーカップラー26、光ファイバ38dを介して、光ファイバ38dの端部84aに達する。
Then, the measurement light reflected by the fundus is reflected by the
一方、参照光を参照ミラー31に向けて出射する光路には、参照光を出射する光ファイバ38cの端部39c、コリメータレンズ29、参照ミラー31が配置されている。参照ミラー31は、参照光の光路長を変化させるべく、参照ミラー駆動機構50により光軸方向に移動可能な構成となっている。
On the other hand, an
光ファイバー38cの端部39cから出射した参照光は、コリメータレンズ29で平行光束とされ、参照ミラー31で反射された後、コリメータレンズ29により集光されて光ファイバ38cの端部39cに入射する。端部39cに入射した参照光は、光ファイバ38cを介して、ファイバーカップラー26に達する。
The reference light emitted from the
そして、光源27から発せられた光によって前述のように生成される参照光と被検眼眼底に照射された測定光による眼底反射光は、ファイバーカップラー26にて合成され干渉光とされた後、光ファイバ38dを通じて端部84aから出射される。800は周波数毎の干渉信号を得るために干渉光を周波数成分に分光する分光光学系800(スペクトロメータ部)であり、コリメータレンズ80、グレーティング(回折格子)81、集光レンズ82、受光素子83にて構成されている。受光素子83は、赤外域に感度を有する一次元素子(ラインセンサ)を用いている。
Then, the reference light generated as described above by the light emitted from the
ここで、端部84aから出射された干渉光は、コリメータレンズ80にて平行光とされた後、グレーティング81にて周波数成分に分光される。そして、周波数成分に分光された干渉光は、集光レンズ82を介して、受光素子83の受光面に集光する。これにより、受光素子83上で干渉縞のスペクトル情報が記録される。そして、そのスペクトル情報が制御部70へと入力され、フーリエ変換を用いて解析することで、被験者眼の深さ方向における情報(Aスキャン信号)が計測可能となる。ここで、制御部70は、走査部23により測定光を眼底上で所定の横断方向に走査することにより断層画像を取得できる。例えば、X方向もしくはY方向に走査することにより、被検眼眼底のXZ面もしくはYZ面における断層画像を取得できる(なお、本実施形態においては、このように測定光を眼底に対して1次元走査し、断層画像を得る方式をBスキャンとする)。なお、取得された断層画像は、制御部70に接続されたメモリ72に記憶される。さらに、測定光をXY方向に2次元的に走査することにより、被検眼眼底の3次元画像を取得することも可能である。なお、本実施形態におけるOCT画像の取得は、走査部23に設けられた2つのガルバノミラーによって行われる。
Here, the interference light emitted from the
次に、ダイクロイックミラー40の透過方向に配置されたSLO光学系(共焦点光学系)300について説明する。SLO光学系300は、被検眼眼底を照明する照明光学系と、該照明光学系によって照明された眼底反射光を受光素子により受光する受光光学系とに大別され、受光素子から出力される受光信号に基づいて被検眼眼底の正面画像を得る。
Next, the SLO optical system (confocal optical system) 300 disposed in the transmission direction of the
光出射部61は、赤外域の波長の光(例えば、λ=780nm)を発する第1の光源(SLO光源)61aと可視域の波長の光(例えば、λ=630nm)を発する第2の光源(固視光源)61b、ミラー69、ダイクロイックミラー101とを有する。なお、第1の光源61aと第2の光源61bには、輝度が高く、指向性の高い光を発する光源(レーザダイオード光源、SLD光源、等)が用いられる。第1の光源61aを出射した赤外光は、ダイクロイックミラー101を透過し、コリメートレンズ65を介してビームスプリッタ62に進む。第2の光源61bを出射した可視光は、ミラー69にて折り曲げられた後、ダイクロイックミラー101にて反射して第1の光源61aから出射した光と同軸とされる。第1の光源61aは観察用の正面眼底画像を得るために用いられ、第2の光源61bは被検眼の視線方向を誘導させるために用いられる。
The
光出射部61から発せられるレーザ光を被検眼Eに向けて出射する光路には、コリメートレンズ65、被検眼の屈折誤差に合わせて光軸方向に移動可能なフォーカシングレンズ63、走査駆動機構52の駆動により眼底上でXY方向に測定光を高速で走査させることが可能なガルバノミラーとポリゴンミラーとの組み合せからなる走査部64、対物レンズ10が配置されている。また、走査部64のガルバノミラー及びポリゴンミラーの反射面は、被検眼瞳孔と略共役な位置に配置される。
A collimating
また、光出射部61とフォーカシングレンズ63との間には、ビームスプリッタ62が配置されている。そして、ビームスプリッタ62の反射方向には、共焦点光学系を構成するための集光レンズ66と、眼底に共役な位置に置かれる共焦点開口67と、SLO用受光素子68とが設けられている。
A
ここで、光出射部61から発せられたレーザ光(測定光、又は固視光束)は、コリメートレンズ62を介してビームスプリッタ62を透過した後、フォーカシングレンズ63を介して、走査部64に達し、ガルバノミラー及びポリゴンミラーの駆動により反射方向が変えられる。そして、走査部64で反射されたレーザ光は、ダイクロイックミラー40を透過した後、ダイクロイックミラー91及び対物レンズ10を介して、被検眼眼底に集光される。
Here, the laser light (measurement light or fixation light beam) emitted from the
そして、眼底で反射したレーザ光(測定光)は、対物レンズ10、ダイクロイックミラー91、走査部64のガルバノミラー及びポリゴンミラー、フォーカシングレンズ63を経て、ビームスプリッタ62にて反射される。その後、集光レンズ66にて集光された後、共焦点開口67を介して、受光素子68によって検出される。そして、受光素子68にて検出された受光信号は制御部70へと入力される。制御部70は受光素子68にて得られた受光信号に基づいて被検眼眼底の正面画像を取得する。取得された正面画像はメモリ72に記憶される。なお、SLO画像の取得は、走査部64に設けられたガルバノミラーによるレーザ光の縦方向の走査(副走査)とポリゴンミラーによるレーザ光の横方向の走査(主走査)によって行われる。
The laser light (measurement light) reflected from the fundus is reflected by the
<アライメント指標投影光学系>
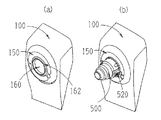
赤外光源151を持ち、被検者眼にアライメント指標を投影するための投影光学系150は、装置筐体100に設けられた検査窓(覗き窓)160の外側に配置され、眼Eの斜め前方(対物レンズ10)から指標を投影する(図2(a)の要部外観図参照)。
<Alignment index projection optical system>
A projection
より具体的には、赤外光源151が、撮影光軸L1を中心として同心円上に45度間隔で複数個配置されている。なお、図1には、便宜上、撮影光軸L1を通る垂直平面を挟んで左右対称に配置された赤外光源151(0度、及び180)が図示されている。
More specifically, a plurality of infrared
アダプター500が未装着のとき、光源151は、被検眼前眼部に向け斜め方向から光束を出射する。各赤外光源151から赤外光が発せられると、リング状に配置された輝点が眼Eの前眼部に形成される。投影された指標像は前眼部像と共にモニタ75に表示され、検者が眼Eに対して位置合わせする際に用いられる。なお、投影光学系150は、眼Eの前眼部を照明する前眼部照明としても用いられる。なお、前眼部照明は、専用の光源を設けても良い。
When the
<前眼部観察光学系>
眼Eを撮像し前眼部像を得るために配置された観察光学系90は、対物レンズ10、ダイクロイックミラー91、結像レンズ95、二次元撮像素子(二次元受光素子)97を備える。ダイクロイックミラー91は、赤外光源151から発せられた波長の光を反射し、他の光を透過する特性を有している。
<Anterior segment observation optical system>
An observation
赤外光源151による前眼部反射光及びアライメント光束は、対物レンズ10を介してダイクロイックミラー91によって反射された後、結像レンズ95を介して二次元撮像素子97により受光される。二次元撮像素子97の出力は制御部70に送信され、モニタ75には二次元撮像素子97によって撮像された前眼部像が表示される(図3参照)。
The anterior ocular segment reflected light and the alignment light beam from the infrared
なお、上記投影光学系150及び観察光学系90は、後述する前眼部アダプター500の装着状態を光学的に検知する検知光学系として兼用される。なお、本実施形態における検知光学系は、アダプター500の着脱を検知すると共に、検査窓160に適正に装着されているかを検知する構成となっている。
The projection
図2(b)は前眼部アダプター(以下、アダプター)500が検査窓150に装着された状態の図である。アダプター500は、前眼部を撮影する際に検査窓160に装着され、被検眼に対する測定光の焦点位置を眼底から前眼部へと移動させるレンズ系を持つ。これにより、前述のOCT光学系200とSLO光学系300が眼底撮像光学系から前眼部撮像光学系に切換えられる。
FIG. 2B is a view showing a state in which an anterior eye adapter (hereinafter referred to as an adapter) 500 is mounted on the
検査窓160には、溝162が設けられ、アダプター500の図示無き凸部と溝162が嵌め合い、アダプター500の回転が規制される。検者は、左右に設けられたチャック部520をつまみ、チャック部520の先端に設けられた凸部522が検査窓520の凹部165に嵌まるようにアダプター500を装着する(図4参照)。なお、アダプター500を装着させるための機構としては、ネジを用いた機構、磁石を用いた機構など種々の変容が考えられる。なお、本実施形態において、図4のような機構としたのは、アダプター500の着脱をスムーズに行えるようにするためである。
The
図5はアダプター500の内部構成について説明する光学側面図である。アダプター500は、ピントが前眼部に合うように焦点位置を装置側にシフトさせるためのレンズ系510と、装着状態の検知を行うためのミラー面(光反射部材)515aが形成された平板515(図6の正面図参照)と、を有する。
FIG. 5 is an optical side view for explaining the internal configuration of the
レンズ系510は、アダプター500と被検眼前眼部との間の適正作動距離WDに対応する焦点距離を持つレンズ系となっており、前眼部上で横断方向に走査される測定光の主光線と光軸L1が平行となるように構成されている。レンズ系510は、一枚のレンズで構成されていてもよいし、複数枚のレンズで構成されていてもよい。
The
なお、本実施形態において前眼部断層像を撮影する場合、プラスディオプター方向における所定位置(例えば、+10D位置)にフォーカシングレンズ24が移動され、OCT光学系200による測定光の焦点位置が装置側に移動される。すなわち、アダプター500の装着とプラス側へのフォーカシングレンズ24の位置調整により前眼部に対する測定光のフォーカス合わせが可能な装置状態となる。なお、撮影時には、眼Eに対する装置の作動距離(前後距離)が調整された後、前眼部に対するフォーカス合わせが行なわれる。
When an anterior segment tomogram is taken in the present embodiment, the focusing
なお、制御部70は、表示モニタ75に接続され、その表示画像を制御する。また、制御部70には、メモリ(記憶部)72、各種操作を行うための操作部74、走査駆動機構51、走査駆動機構52、参照ミラー駆動機構50、フォーカシングレンズ63を光軸方向に移動させるための第1駆動機構63a、フォーカシングレンズ24を光軸方向に移動させるための第2駆動機構24a、等が接続されている。なお、モニタ75は、アライメント観察用と撮影画像観察用で別でもよいし、もちろん一つの共用モニタであってもよい。
The
ここで、制御部70は、受光素子83から出力される受光信号に基づいて画像処理により眼底断層像を形成させると共に、受光素子68から出力される受光信号に基づいて画像処理により眼底正面像を形成させる。
Here, the
なお、本装置は、アダプター500無しで被検眼眼底の断層像及び正面像を撮像する眼底撮影モードと、アダプター500を用いて被検眼前眼部の断層像及び正面像を撮像する前眼部撮影モードと、に設定可能である。そして、制御部70は、モード切換信号が出力されると、撮影モードに応じて装置の光学配置、モニタの表示画面等を切り換える。
In addition, this apparatus has a fundus photographing mode for capturing a tomographic image and a front image of the fundus of the eye to be examined without the
<アダプター500の装着状態の光学的検出>
この場合、赤外光源151のうち少なくとも2つは、ミラー面515aに向けて検知光束を出射する検知用光源として兼用され、撮像素子97はミラー面515aからの反射光束を受光する検知用受光素子として兼用され、制御部70は、撮像素子97から出力される受光信号に基づいてアダプター500の装着状態を検知する。
<Optical detection of
In this case, at least two of the infrared
図7は、アダプター500に設けられたミラー面515aの作用について説明する図である。アダプター500が装着された場合、赤外光源151のうち、右斜め下方向と左斜め下方向に配置された2つの光源から発せられた光は、アダプター500に形成された開口部(孔)517を通過し、ミラー面515aによって反射される。そして、その反射光は、レンズ系510の一部及び対物レンズ10を介してダイクロイックミラー91によって反射された後、結像レンズ95を介して二次元撮像素子97により受光される。これにより、ミラー面515aによる輝点(反射像)KR、KLが撮像素子97上に形成される。
FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining the operation of the
図8はアダプター500の装着状態に応じて撮像素子97から出力される撮像画像の違いについて示す図である。図8(a)はアダプター500が適正に装着されたときに取得された画像である。図8(b)はアダプター500が傾いて装着されたときの画像である。図8(c)はアダプター500が装着されていないときの図である。
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating differences in captured images output from the
撮像画像の右下端と左下端に形成されたフレーム(アダプター検出枠)FR/FLは、アダプター500の装着状態を検知するために仮想的に設定された領域である。
Frames (adapter detection frames) FR / FL formed at the lower right corner and the lower left corner of the captured image are regions that are virtually set to detect the mounting state of the
アダプター500が適正に装着されている場合、図8(a)に示すように、輝点KR/KLの両方が、フレームFR/FL内の所定の位置で検出される。アダプター500が傾いた状態で装着されている場合、ミラー面515aが適正位置に対して傾斜するため、図8(b)に示すように、輝点KR/KLのうち少なくとも一つが、フレームFR/FL内に位置されるが、前述の所定の位置から外れた位置で検出される。アダプター500が未装着の場合、図8(c)に示すように、輝点KR/KLの両方が、フレームFR/FLから外れた位置で検出される(もしくは検出されない)。
When the
そこで、本装置は、撮像素子97から出力される撮像信号に基づいてアダプター500の着脱を検知すると共に、アダプター500の装着が適正か否かを検知する。(詳しくは、後述する)。なお、この前段階として、まず、アダプター500が適正に装着されているときの撮像画像上における輝点KR/KLの検出位置を予めメモリ72に記憶しておく。また、アダプター500が適正に装着されているときとアダプター500が適正に装着されていないときの輝点KR/KLの位置に基づいてフレームFR/FLの位置、大きさが予め設定される。上記ステップは、例えば、装置のキャリブレーションのタイミングにて実施すればよい。
Therefore, the present apparatus detects attachment / detachment of the
<装着状態の判定>
以下に、装着適否の検知手法について図9のフローチャートを用いて説明する。まず、制御部70は、輝点KR/KLの直径・輝度レベル等を利用して輝点KR/KLを画像処理により抽出し、抽出された輝点KR/KLの中心位置を検出する。
<Determination of wearing state>
Hereinafter, a method for detecting whether or not the apparatus is suitable will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, the
次に、制御部70は、輝点KR/KLのうち左右どちらか一方がフレームFR/FLの内側に無ければ、アダプター500が未装着であると判定し、フレームFR/FLの内側にあれば、アダプター500が装着されていると判定する。そして、制御部70は、輝点KR/KLの両方の検出位置が予めメモリ72で記憶した位置と一致していれば、アダプター500が適正に装着されていると判定し、一致していなければ、アダプター500が傾いて装着されている(装着が適正でない)と判定する。
Next, the
ここで、制御部70は、所定のフレームレートにて撮像素子97から随時出力される撮像画像に対し、前述のように装着状態の判定を連続して行う。そして、5回連続で同じ判定であれば、その判定結果を確定し、これをモニタ75上に表示する(判定処理終了)。一方、5回連続で同じ判定が得られなければ、判定結果を表示せずに、アダプター500の検出処理を一旦終了する。この場合、検出処理開始前の判定結果が反映された状態となる。
Here, the
ここで、アダプター500の装着が適正でないとの判定結果が確定されると、制御部70は、アダプター500の装着が適正でないとの検知信号を出力し、その検知信号に基づいてアダプター500の装着が適正でない旨(傾いて装着されている旨でもよい)をモニタ75に表示する。この場合、検者は、再度アダプター500の装着を行う。
Here, when the determination result that the
一方、アダプター500の装着が適正であるとの判定結果が確定されると、制御部70は、アダプター500の装着が適正であるとの検知信号を出力し、その検知信号に基づいて眼底撮像モードから前眼部撮像モードへと切換えるためのモード切換信号を発する。
On the other hand, when the determination result that the
なお、制御部70は、上記のような装着状態の検知を一定周期(例えば、1秒ごと)にて行う。
Note that the
以上示したように、アダプター500の装着の適否が検知され、その検知結果が報知されることにより、アダプター500が適正に装着されていない状態での前眼部像の撮影が回避される。また、上記構成において、投影光学系150及び観察光学系90を、アダプター500の装着の適否検知に用いることにより、専用の検知手段を設ける必要がなくなる。
As described above, whether or not the
なお、上記構成において、ミラー面515aの設置位置及び反射角度について、アダプター500が装着されたときの輝点KR/KLが撮像素子97の撮像面における端部に形成されるように設定されるのが好ましい。これは、赤外光源151による角膜輝点を輝点KR/KLであると誤って検知しないためである。その他、赤外光源151による角膜輝点より輝点KR/KLのサイズが大きくなるように構成されているので、画像処理における誤検知を回避できる。また、ミラー面515aの形状は、円形に限らず、直線、矩形、等であってもよい。
In the above configuration, the installation position and reflection angle of the
なお、上記構成において、被検者眼の前眼部にアライメント指標を投影する又は被検眼の前眼部を照明する光源を少なくとも2つ以上設け、その光源のうち少なくとも2つが、検知用光源を兼用されればよい。また、2つの輝点を用いて装着状態を判定するものとしたが、3つ以上の輝点を用いるようにしてもよい。 In the above configuration, at least two or more light sources that project the alignment index on the anterior eye portion of the subject's eye or illuminate the anterior eye portion of the subject's eye are provided, and at least two of the light sources have detection light sources. What is necessary is just to be combined. In addition, although the mounting state is determined using two bright spots, three or more bright spots may be used.
アダプター500の装着状態を検知するための構成としては、これに限るものではない。この場合、光学的手法に限らず、電気的、磁気的な検知であってもよい。例えば、検査窓520の近傍(例えば、凹部165)にフォトセンサ、押圧センサ等を設けるようにしてもよい。なお、装着の適否検知を行う場合、例えば、検査窓520の近傍に押圧センサを2つ設け、2つの押圧センサから押圧信号が出力されると、装着が適正であると検知し、一方の押圧センサからの押圧信号のみであれば、装着が適正でないと検知するようにしてもよい。
The configuration for detecting the mounting state of the
なお、アダプター500の装着が適正か否かを検知した結果を報知する構成としては、モニタ75上での表示の他、専用のランプの点灯によるものであってもよいし、音声によるものであってもよい。
In addition, as a configuration for notifying the result of detecting whether or not the
なお、上記構成においては、前記検査窓520に対するアダプター500の装着が適正か否かを検知する構成としたが、単に、検査窓520に装着されるアダプター500の着脱を検知する構成であってもよい。この場合、例えば、制御部70は、撮像素子97からの撮像信号を得て、輝点KR/KLの両方の検出位置が所定位置と一致していれば、アダプター500の装着を検知し、一致していなければ、アダプター500の未装着を検知する。そして、その検知結果をモニタ75に表示する共に、着脱の検知信号に基づいて各種設定を変更する。
In the above configuration, it is configured to detect whether or not the
また、上記構成において、アダプター500のレンズ系510は、撮影倍率を変更可能なズーム光学系としてもよい。また、ズーム光学系を持つアダプター500において、前述のようなミラー面515aを設けた場合、ズーム倍率の変更に応じて撮像素子97上の輝点KR/KLの検出位置が移動される。そこで、制御部70は、変更されるズーム倍率が適正か否かを輝点KR/KLの位置に基づいて判定するようにしてもよい。
In the above configuration, the
また、以上の説明においては、眼底撮像光学系を前眼部撮像光学系に切換えるためのアダプターを例にとって説明したが、もちろん、前眼部撮像光学系を眼底撮像光学系に切換えるためのアダプターにおいても、本発明の適用可能である。この場合、アダプターのレンズ系には、ピントが眼底に合うように焦点位置を被検者側に移動させるためのレンズ系が用いられる。なお、上記眼底撮像装置の他、眼底カメラにおいても、本発明の適用は可能である。 In the above description, the adapter for switching the fundus imaging optical system to the anterior ocular segment imaging optical system has been described as an example. Of course, in the adapter for switching the anterior ocular segment imaging optical system to the fundus imaging optical system. Also, the present invention is applicable. In this case, a lens system for moving the focal position to the subject side so that the focus is on the fundus is used for the lens system of the adapter. In addition to the above fundus imaging apparatus, the present invention can be applied to a fundus camera.
また、上記着脱検知について、眼科撮影装置の検査窓に装着される他のアダプターにおいても、本発明の適用は可能である。例えば、撮影する被検眼像の撮影倍率を変更するためのレンズ系を有する倍率変更用アダプター、撮影画角を変更するための広角レンズアダプター、強度の屈折異常眼の視度を補正するための視度補正用アダプター、等が考えられる。 In addition, the present invention can be applied to other adapters mounted on the examination window of the ophthalmologic photographing apparatus for the above-described attachment / detachment detection. For example, a magnification changing adapter having a lens system for changing the photographing magnification of the subject eye image to be photographed, a wide-angle lens adapter for changing the photographing angle of view, and a vision for correcting the diopter of an eye with abnormal refractive error. A degree correction adapter may be considered.
<モード切換時の光学配置の自動調整>
次に、本装置の全体動作について説明する。制御部70は、OCT光学系200及びSLO光学系300を駆動制御してOCT画像及びSLO画像を取得していき、モニタ75上のOCT画像及びSLO画像を随時更新する(図10、図11参照)。
<Automatic adjustment of optical arrangement when switching modes>
Next, the overall operation of this apparatus will be described. The
<眼底撮影モード>
まず、眼底撮影モードについて説明する。なお、本モードでは、アダプター500は使用されない。検者は、図示なき固視灯を注視するように被験者に指示した後、眼底に対するアライメントを行う。そして、SLO眼底像がモニタ75上に表示されるようになると、予め設定される走査パターンに基づきOCT光学系200によってOCT画像が取得され、図10に示すように、モニタ75上に表示される。この場合、制御部70は、受光素子83から出力される受光信号に基づいて駆動機構50の駆動を制御し、眼底断層画像が取得されるように測定光と参照光との光路差を調整する。この場合、参照ミラー31は、被検眼の眼軸長の違いに対応した所定の移動範囲内で移動される。
<Fundus photography mode>
First, the fundus imaging mode will be described. In this mode,
その後、検者が所望する走査位置/パターンが設定され、所定のトリガ信号が出力されると、制御部70は、設定された走査位置/パターンに基づいて断層画像を取得し、取得された画像データをメモリ72に記憶する。また、制御部70は、これに合わせて、SLO光学系300によって取得される眼底正面像をメモリ72に記憶する。
Thereafter, when a scanning position / pattern desired by the examiner is set and a predetermined trigger signal is output, the
<前眼部撮影モード>
次に、前眼部撮影モードについて説明する。前眼部撮影モードを実行する場合、検者は、アダプター500を検査窓160に装着する。制御部70は、上記のようにアダプター500の装着の適否を検知する。そして、装着が適正と検知され、眼底撮像モードから前眼部撮像モードへと切換えるための切換信号が発せられると、制御部70は、OCT光学系200及びSLO光学系300が前眼部撮影モードに対応した所定の光学配置となるように駆動機構50、第1駆動機構63a、第2駆動機構24aの駆動を制御し、各光学部材の位置を自動的に調整する。
<Anterior segment photography mode>
Next, the anterior segment imaging mode will be described. When executing the anterior ocular segment imaging mode, the examiner attaches the
<光路長調整>
制御部70は、モード切換信号に基づいて駆動機構50の駆動を制御し、前眼部撮影モードに対応する所定位置に参照ミラー31を位置させる。なお、参照ミラー31の移動完了後、参照ミラー31の移動を禁止する又は移動範囲を所定範囲内に制限してもよい。
<Optical path length adjustment>
The
なお、前述の参照ミラー31の所定位置は、予めメモリ72に記憶される。ここで、参照ミラーの位置は、測定光の焦点が眼Eの前眼部に合うように被検眼と装置(OCT光学系200)との作動距離が調整された状態で、前眼部断層像が取得可能な位置であることが好ましい。
The predetermined position of the reference mirror 31 is stored in the
例えば、作動距離の調整後、前眼部断層像(図中の角膜C参照)が所定の深さ位置にて取得されるように測定光と参照光の光路差が調整され、そのときの位置がメモリ72に記憶される。これらは、シミュレーション又は実験により求められる。
For example, after adjusting the working distance, the optical path difference between the measurement light and the reference light is adjusted so that an anterior tomogram (see cornea C in the figure) is acquired at a predetermined depth position, and the position at that time Is stored in the
上記のようにすれば、参照ミラー31の移動によって、測定光の焦点が眼Eの前眼部に十分に合っていない状態で前眼部断層像が取得されるのを回避できる。また、自動光路長調整において、アダプター500のレンズ系510からの反射光と参照光との干渉光を誤って誤検知してしまうのを回避できる。
If it does as mentioned above, it can avoid that an anterior ocular segment tomogram is acquired by the movement of reference mirror 31 in the state where the focus of measurement light is not enough in focus to the anterior segment of eye E. Further, in the automatic optical path length adjustment, it is possible to avoid erroneously detecting the interference light between the reflected light from the
なお、参照ミラー31の所定位置を移動させる場合、参照ミラー31の位置を検出するセンサ(エンコーダ、ポテンショメータ等)を設け、センサからの検出信号に基づいてメモリ72に記憶された所定位置に参照ミラー31を移動させる。また、参照ミラー31の移動範囲内における所定位置に対応する位置にセンサ(例えば、フォトセンサ)を設け、そのセンサによって参照ミラー31が所定位置に位置したことが検知されると、参照ミラー31の移動を停止するようにしてもよい。
When the predetermined position of the reference mirror 31 is moved, a sensor (an encoder, a potentiometer, or the like) that detects the position of the reference mirror 31 is provided, and the reference mirror is stored at a predetermined position stored in the
なお、上記構成においては、測定光と参照光の光路差を調整するために参照光の光路長を変更するものとしたが、これに限るものではなく、測定光の光路長の光路長を変更するようにしてもよい。例えば、コリメータレンズ22及び光ファイバー39bの端部を光軸方向に移動するようにしてもよい。
In the above configuration, the optical path length of the reference light is changed to adjust the optical path difference between the measurement light and the reference light. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the optical path length of the optical path length of the measurement light is changed. You may make it do. For example, the end portions of the
なお、前述の参照ミラー31の所定位置としては、レンズ系510による測定光の反射光と参照光との干渉光によるレンズ系510の断層画像の取得が回避可能な位置に設定するようにしてもよい。この場合、レンズ系510の断層画像が取得される位置を予め求めておき、これを避けた参照ミラー31の移動範囲を所定位置として設定すればよい。
The predetermined position of the reference mirror 31 described above may be set to a position where acquisition of a tomographic image of the
この場合、前眼部撮影モードに切換えられ、駆動機構50への駆動指令信号が出力された場合、制御部70は、レンズ系510の断層画像の取得を回避するために設定された移動範囲内において参照ミラー31を移動させ、断層像の取得が取得されると、参照ミラー31の移動を停止する。
In this case, when the mode is switched to the anterior ocular segment imaging mode and a drive command signal is output to the
<フォーカス調整>
OCT光学系200について、制御部70は、第2駆動機構24aの駆動を制御し、前眼部撮影モードに対応する所定位置にフォーカシングレンズ24を位置させる。そして、フォーカシングレンズ24が所定位置に到達したら、制御部70は、第2駆動機構24aの駆動を禁止する。
<Focus adjustment>
In the OCT
なお、フォーカシングレンズ24の所定位置は、予めメモリ72に記憶される。フォーカシングレンズ24の位置は、設定された所定の適正作動距離において、測定光の焦点が前眼部に合わせられ、かつ、前眼部に向かう測定光の主光線と光軸L1が平行となる位置であるのが好ましい。そして、その位置がメモリ72に記憶される。これらは、シミュレーション又は実験により求められる。なお、フォーカシングレンズ24を所定位置に位置させる手法としては、参照ミラー31と同様の手法を用いることができる。
The predetermined position of the focusing
また、SLO光学系300について、制御部70は、第1駆動機構63aの駆動を制御し、OCT光学系200と同様に、前眼部撮影モードに対応する所定位置にフォーカシングレンズ63を移動させる。なお、フォーカシングレンズ63の移動位置の設定手法については、上記OCT光学系200の場合と同様に設定すればよいので、説明を省略する。
In the SLO
また、モード切換信号が発せられると、制御部70は、モニタ75の表示を制御し、表示画面を眼底撮像用から前眼部撮像用に変更する。
When the mode switching signal is issued, the
制御部70は、撮影部位に合わせて複数用意された前眼部撮影用走査パターン(例えば、角膜ラインスキャン、角膜クロススキャン、隅角ラインスキャン、など)のそれぞれを選択可能に表示すると共に、走査範囲の表示を画角単位(例えば、40°)から距離単位(例えば、6.0mm)へと切換える。また、制御部70は、各フォーカシングレンズ24、63の移動が禁止されている旨を表示する共に、第1駆動機構63a及び第2駆動機構24aの駆動を禁止し、実際に各レンズの移動を禁止する。これにより、レンズ24、63の位置が所定位置に固定される。
The
また、検者は、図示なき固視灯を注視するように被験者に指示した後、前眼部に対するアライメントを行う。ここで、検者は、モニタ75上のSLO画像を見ながら、そのピントが合うように、装置筐体100を前後方向に移動させ、被検眼に対する筐体100の作動距離を調整する。なお、検者は、OCT画像が正しく表示されるように、作動距離を調整するようにしてもよい。
In addition, the examiner instructs the subject to gaze at a fixation lamp (not shown), and then performs alignment with the anterior segment. Here, the examiner moves the
なお、場合によっては、前眼部にフォーカスが合うように装置と眼Eとの作動距離を確保する必要がありうる(例えば、装置に設けられた額当ての厚みを増加させるなどの処置)。この場合、筐体100を電動にて移動させる電動駆動部を設け、制御部70は、前述のモード切換信号に基づいて電動駆動部の駆動を制御し、前眼部撮影に対応する所定の前後位置に向けて筐体100を移動させるようにしてもよい。
In some cases, it may be necessary to secure a working distance between the device and the eye E so that the anterior eye portion is in focus (for example, a treatment such as increasing the thickness of a forehead provided in the device). In this case, an electric drive unit that electrically moves the
上記のようにして、前眼部に対するアライメントが完了されると、予め設定された走査パターンに基づきOCT光学系200によって前眼部断層像が取得され、モニタ75上に動画表示される(図11参照)。
As described above, when the alignment with respect to the anterior segment is completed, an anterior segment tomogram is acquired by the OCT
その後、検者が所望する走査位置/パターンが設定され、所定のトリガ信号が出力されると、制御部70は、設定された走査位置/パターンに基づいて走査駆動機構51の駆動を制御し、前眼部断層像を取得し、取得された画像データをメモリ72に記憶する。また、制御部70は、これに合わせて、SLO光学系300によって取得される前眼部正面像をメモリ72に記憶する。
Thereafter, when the scanning position / pattern desired by the examiner is set and a predetermined trigger signal is output, the
以上示したように、アダプター500の着脱を検知する検知信号に基づいて前眼部撮影モードに対応する各設定を変更することにより、前眼部撮影をスムーズに行うことができる。
As described above, the anterior segment imaging can be performed smoothly by changing the settings corresponding to the anterior segment imaging mode based on the detection signal for detecting attachment / detachment of the
なお、制御部70は、眼底撮影モードにて撮影された断層像を眼底像、前眼部撮影モードにて撮影された断層画像を前眼部像として判別し、その判別結果と断層画像を対応づけてメモリ72に記憶するのが好ましい。
The
なお、上記のように前眼部像が撮影された後、アダプター500が装置から外されると、所定の位置で検出されていた輝点KR/KLの両方が撮像素子97の撮像面から消える。ここで、前述のアダプター500の装着状態の判定において、所定の位置で検出されていた輝点KR/KLの両方がフレームFR/FLの内側から無くなりアダプター500が未装着であると判定されると、検査窓160からのアダプター500の離脱を検知し、前眼部撮像モードから眼底撮像モードへと切換えるための切換信号を発する。
If the
切換信号が発せられると、制御部70は、OCT光学系200及びSLO光学系300が眼底撮影モードに対応した光学配置となるように駆動機構50、第1駆動機構63a、第2駆動機構24aの駆動を制御し、各光学部材の位置を自動的に調整する。この場合、参照ミラー31、各フォーカシングレンズ24、63は、所定の原点位置に移動される。
When the switching signal is issued, the
また、前述の切換信号が発せられると、制御部70は、モニタ75の表示を制御し、表示画面を前眼部撮像用から眼底撮像用に変更する。
Further, when the switching signal described above is issued, the
より具体的には、制御部70は、複数用意された眼底撮影用走査パターン(例えば、ラインスキャン、クロススキャン、ラディアルスキャン、など)のそれぞれを選択可能に表示すると共に、走査範囲の表示を距離単位(例えば、6.0mm)から画角単位(例えば、40°)へと切換える。また、制御部70は、各フォーカシングレンズ24、63の移動を許可する旨を表示する共に、実際に各レンズの移動を許可する。
More specifically, the
なお、アダプター500が装着されたときに発せられる検知信号に基づいて前眼部撮影モードに対応する変更制御を行う場合、上記手法に限るものではない。例えば、制御部70は、前眼部撮影モードへの切換を促す旨(例えば、前眼部撮影モードに移行するか否かをYES/NOで問う、など)をモニタ75に表示し、所定の選択信号に基づいて前述の変更制御を行うようにしてもよい。
In addition, when performing change control corresponding to an anterior ocular segment imaging mode based on a detection signal generated when the
なお、上記構成において、アダプター500の装着検知でなくとも、眼底撮影モードから前眼部撮影モードへ切換えるためのモード切換信号に基づいてOCT光学系200及びSLO光学系300の少なくともいずれかの光学配置が調整される制御であれば、これに限るものではない。例えば、所定のモード切換スイッチから出力される切換信号に基づいて自動的に調整制御が行われる。
In the above configuration, the optical arrangement of at least one of the OCT
なお、上記構成においては、モード切換信号に基づいて光学配置を調整するものとしたが、前眼部撮影モードにて撮影を行う場合に、駆動指令信号に基づいて光学配置が調整されるものであればよい。例えば、前眼部撮影モードへの移行後、操作部74からの操作信号に基づいて調整を開始するようにしてもよい。また、被検眼に対する装置の作動距離を検出するアライメント検出光学系を設け、その検出信号に基づいて適正作動距離に達したことが検知されたとき、断層画像を得るための参照ミラー31の自動調整を行うようにしてもよい。
In the above configuration, the optical arrangement is adjusted based on the mode switching signal. However, the optical arrangement is adjusted based on the drive command signal when shooting in the anterior segment imaging mode. I just need it. For example, the adjustment may be started based on an operation signal from the
また、上記モード切換時の光学配置の自動調整について、アダプター500の装着により眼底と前眼部の断層像を得る装置でなく、装置内部にてレンズ系の挿脱により測定光の焦点位置を前眼部と眼底とで切換える構成を有する装置においても、本発明の適用は可能である。
In addition, with regard to the automatic adjustment of the optical arrangement at the time of switching the mode, the focal position of the measurement light is not changed by inserting / removing the lens system inside the apparatus, but not by an apparatus that obtains a tomographic image of the fundus and anterior eye by attaching the
23 走査部
24 フォーカシングレンズ
24a 駆動機構
31 参照ミラー(光路長可変部材)
50 駆動機構
51 走査駆動機構
70 制御部
75 モニタ
90 前眼部観察光学系
97 撮像素子
151 赤外光源
200 干渉光学系(OCT光学系)
300 SLO光学系
500 アダプター
510 レンズ系
515a ミラー面
520 検査窓
23
DESCRIPTION OF
300 SLO
Claims (4)
定部位に向けて投光すると共に被検者眼の所定部位からの反射光を受光素子で受光して被
検者眼の撮影画像を得る撮影光学系を有する眼科撮影装置において、
前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段を備え、
前記装着状態検知手段は、前記検査窓に対する前記光学アダプターの装着が適正か否かを検知する適否検知手段を有し、
前記適否検知手段による検知結果を報知する報知手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする眼科撮影装置。 A light receiving element that projects at least a part of light emitted from the light source toward a predetermined part of the subject's eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and receives reflected light from the predetermined part of the subject's eye In an ophthalmologic photographing apparatus having a photographing optical system that receives a light and obtains a photographed image of a subject's eye,
Comprising a mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the inspection window ;
The mounting state detection means includes suitability detection means for detecting whether or not the optical adapter is properly attached to the inspection window.
Informing means for informing the detection result by the suitability detecting means,
An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus comprising:
前記干渉光学系による被検者眼の撮影部位を切り換えるために前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段と、
眼底の断層像を撮影するための眼底撮影モードと、前眼部の断層像を撮影するための前眼部撮影モードと、に設定可能なモード設定手段と、
前記モード設定手段によって設定される撮影モードに応じて前記干渉光学系の光学配置を制御する制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする眼科撮影装置。 The light emitted from the light source is divided into measurement light and reference light, and the measurement light is guided to the fundus or anterior eye portion of the subject eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and the reference light is a reference optical system inside the apparatus. An interference optical system that causes the light receiving element to receive interference light obtained by combining the measurement light reflected by the fundus or anterior eye portion of the eye to be examined and the reference light, and based on the output signal of the light receiving element An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus capable of photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and anterior eye of the subject eye,
A mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the examination window in order to switch the imaging part of the subject's eye by the interference optical system ;
Mode setting means that can be set to a fundus photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and an anterior eye photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the anterior eye;
Control means for controlling the optical arrangement of the interference optical system in accordance with the photographing mode set by the mode setting means;
An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus comprising:
前記干渉光学系による被検者眼の撮影部位を切り換えるために前記検査窓に装着される光学アダプターの装着状態を検知する装着状態検知手段と、
眼底の断層像を撮影するための眼底撮影モードと、前眼部の断層像を撮影するための前眼部撮影モードと、に設定可能なモード設定手段と、
前記干渉光学系を内蔵する筐体と、
前記筐体を電動にて移動させる電動駆動部と、
前記モード設定手段によって設定される撮影モードに応じて前記電動駆動部の駆動を制御する制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする眼科撮影装置。 The light emitted from the light source is divided into measurement light and reference light, and the measurement light is guided to the fundus or anterior eye portion of the subject eye through an inspection window through which the subject's eye looks, and the reference light is a reference optical system inside the apparatus. An interference optical system that causes the light receiving element to receive interference light obtained by combining the measurement light reflected by the fundus or anterior eye portion of the eye to be examined and the reference light, and based on the output signal of the light receiving element An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus capable of photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and anterior eye of the subject eye,
A mounting state detecting means for detecting a mounting state of an optical adapter mounted on the examination window in order to switch the imaging part of the subject's eye by the interference optical system ;
Mode setting means that can be set to a fundus photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the fundus and an anterior eye photographing mode for photographing a tomographic image of the anterior eye;
A housing containing the interference optical system;
An electric drive unit for electrically moving the housing;
Control means for controlling the driving of the electric drive unit according to the photographing mode set by the mode setting means;
An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus comprising:
前記光学アダプターは、前記干渉光学系による撮影部位を眼底から前眼部へと切り換えるためのレンズ系を持ち、
前記モード設定手段は、前記光学アダプターの装着を検知したときに前記装着状態検知手段から出力される出力信号に基づいて前記眼底撮影モードから前記前眼部撮影モードに切り換える、あるいは前記光学アダプターの装着を検知したときに前記装着状態検知手段から出力される出力信号に基づいて前眼部撮影モードへの切換を促す旨をモニタに表示することを特徴とする眼科撮影装置。 The ophthalmologic photographing apparatus according to claim 2 or 3,
The optical adapter has a lens system for switching the imaging site by the interference optical system from the fundus to the anterior segment,
The mode setting means switches from the fundus photographing mode to the anterior eye photographing mode based on an output signal output from the wearing state detecting means when the wearing of the optical adapter is detected, or the wearing of the optical adapter An ophthalmologic photographing apparatus which displays on the monitor that the user is prompted to switch to the anterior ocular segment photographing mode based on an output signal output from the wearing state detecting means when detecting the eye .
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010011355A JP5545629B2 (en) | 2010-01-21 | 2010-01-21 | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
| US13/009,940 US7980696B1 (en) | 2010-01-21 | 2011-01-20 | Ophthalmic photographing apparatus |
| EP11151579.7A EP2347701B1 (en) | 2010-01-21 | 2011-01-20 | Ophthalmic photographing apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010011355A JP5545629B2 (en) | 2010-01-21 | 2010-01-21 | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011147609A JP2011147609A (en) | 2011-08-04 |
| JP2011147609A5 JP2011147609A5 (en) | 2013-02-28 |
| JP5545629B2 true JP5545629B2 (en) | 2014-07-09 |
Family
ID=44535182
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010011355A Active JP5545629B2 (en) | 2010-01-21 | 2010-01-21 | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5545629B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3335386A1 (en) * | 1983-09-29 | 1985-04-11 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | CIRCUIT FOR CSD CODING A BINARY NUMBER SHOWN IN TWO COMPLEMENT |
| JP5220208B2 (en) | 2011-03-31 | 2013-06-26 | キヤノン株式会社 | Control device, imaging control method, and program |
| JP2013085762A (en) | 2011-10-19 | 2013-05-13 | Canon Inc | Ophthalmologic apparatus and ophthalmologic photographing method |
| JP5210443B1 (en) * | 2012-01-26 | 2013-06-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus and control method |
| JP5319799B2 (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2013-10-16 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP5210442B1 (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2013-06-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus and control method |
| JP5930757B2 (en) * | 2012-02-15 | 2016-06-08 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6143421B2 (en) * | 2012-03-30 | 2017-06-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical coherence tomography apparatus and method |
| JP6279682B2 (en) * | 2012-10-01 | 2018-02-14 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic observation device |
| WO2014084231A1 (en) | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-05 | 株式会社トプコン | Fundus photographing device |
| EP2583620B1 (en) * | 2013-01-24 | 2017-08-23 | Haag-Streit Ag | Topograph |
| JP5766225B2 (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2015-08-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus and control method |
| JP5680133B2 (en) * | 2013-04-08 | 2015-03-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP5680134B2 (en) * | 2013-04-08 | 2015-03-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6224910B2 (en) * | 2013-04-17 | 2017-11-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP6218425B2 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2017-10-25 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomography system |
| JP5777657B2 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2015-09-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6308723B2 (en) | 2013-05-02 | 2018-04-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | CONTROL DEVICE, ITS OPERATION METHOD, AND PROGRAM |
| JP6277748B2 (en) * | 2014-02-03 | 2018-02-14 | 株式会社ニデック | Fundus photographing device and wide-angle lens attachment |
| JP6080128B2 (en) | 2014-02-28 | 2017-02-15 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic photographing apparatus and optical unit that can be attached to the same |
| JP6600931B2 (en) * | 2014-07-08 | 2019-11-06 | 株式会社ニデック | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
| JP6407631B2 (en) * | 2014-08-29 | 2018-10-17 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6896048B2 (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2021-06-30 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6552200B2 (en) | 2015-01-09 | 2019-07-31 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP6652281B2 (en) | 2015-01-09 | 2020-02-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP6805539B2 (en) | 2015-05-01 | 2020-12-23 | 株式会社ニデック | Ophthalmic imaging device |
| JP6734642B2 (en) * | 2015-12-18 | 2020-08-05 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP2016182525A (en) * | 2016-07-29 | 2016-10-20 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmology imaging apparatus |
| JP6842280B2 (en) * | 2016-11-24 | 2021-03-17 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmologic imaging equipment |
| JP6809926B2 (en) * | 2017-02-07 | 2021-01-06 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmic equipment |
| JP6988133B2 (en) * | 2017-03-31 | 2022-01-05 | 株式会社ニデック | OCT device |
| JP2017159089A (en) * | 2017-05-10 | 2017-09-14 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fundus imaging apparatus |
| JP2019055106A (en) * | 2017-09-22 | 2019-04-11 | 株式会社トプコン | Ophthalmologic examination apparatus |
| JP7051041B2 (en) * | 2018-05-08 | 2022-04-11 | 株式会社ニデック | Wide-angle attachment and fundus photography device |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04204638A (en) * | 1990-11-30 | 1992-07-27 | Canon Inc | Interchangeable lens system camera apparatus |
| JP3386839B2 (en) * | 1993-02-25 | 2003-03-17 | 興和株式会社 | Ophthalmic examination device |
| JP3696949B2 (en) * | 1995-09-01 | 2005-09-21 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fundus camera |
| JP2004219812A (en) * | 2003-01-16 | 2004-08-05 | Nikon Corp | Lens accessory detecting device, lens accessory, lens barrel, and camera system |
| JP3870211B2 (en) * | 2004-12-28 | 2007-01-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fundus camera |
| JP4754945B2 (en) * | 2005-11-18 | 2011-08-24 | 興和株式会社 | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
| JP5179102B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2013-04-10 | 株式会社ニデック | Scanning laser ophthalmoscope and wide-angle lens attachment for scanning laser ophthalmoscope |
-
2010
- 2010-01-21 JP JP2010011355A patent/JP5545629B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011147609A (en) | 2011-08-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5545629B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP5545630B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP5850349B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| EP2347701B1 (en) | Ophthalmic photographing apparatus | |
| JP5511437B2 (en) | Optical tomography system | |
| US10076243B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging device | |
| JP4819478B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP6354979B2 (en) | Fundus photographing device | |
| JP2010012109A (en) | Ocular fundus photographic apparatus | |
| JP6349878B2 (en) | Ophthalmic photographing apparatus, ophthalmic photographing method, and ophthalmic photographing program | |
| JP4949504B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP2011245183A (en) | Fundus imaging apparatus | |
| JP7027698B2 (en) | Ophthalmologic photography equipment | |
| JP2015085044A (en) | Ophthalmology imaging apparatus, ophthalmology imaging system, and ophthalmology imaging program | |
| JP5830264B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP6040562B2 (en) | Attachment for fundus photography device | |
| JP5807371B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| JP6604020B2 (en) | Fundus imaging apparatus and fundus imaging program | |
| JP7181135B2 (en) | ophthalmic equipment | |
| JP2016049368A (en) | Ophthalmological photographing apparatus | |
| JP6507536B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging apparatus and ophthalmologic imaging program | |
| JP2018023675A (en) | Optical tomographic imaging apparatus | |
| JP2015085043A (en) | Fundus photographing device | |
| JP2020005672A (en) | Ocular fundus imaging apparatus | |
| JP5306554B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130111 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130111 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131022 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131025 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131218 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140408 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140507 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5545629 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |