JP5517654B2 - Lens barrel and imaging device - Google Patents
Lens barrel and imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5517654B2 JP5517654B2 JP2010024665A JP2010024665A JP5517654B2 JP 5517654 B2 JP5517654 B2 JP 5517654B2 JP 2010024665 A JP2010024665 A JP 2010024665A JP 2010024665 A JP2010024665 A JP 2010024665A JP 5517654 B2 JP5517654 B2 JP 5517654B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cam
- group
- optical axis
- cam member
- restricting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Lens Barrels (AREA)
- Structure And Mechanism Of Cameras (AREA)
Description
本発明はデジタルカメラなどの撮像装置に用いるレンズ鏡筒において、遮光性、設計自由度、動作精度を向上させる技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for improving light shielding, design freedom, and operation accuracy in a lens barrel used in an imaging apparatus such as a digital camera.
レンズ鏡筒において前群及び後群のレンズ群鏡筒をカム係合保持し、直進規制用のキーを有するガイド部材で前群及び後群の回転を規制する構成が知られている。特許文献1に開示された撮影鏡筒では、直進キーと隣接して相対的に回転運動するカム環に直進キーより半径方向の外側に位置する外周部が切り欠かれている。 In the lens barrel, a configuration is known in which the front and rear lens group barrels are cam-engaged and the rotation of the front and rear groups is regulated by a guide member having a key for regulating rectilinear advance. In the photographic lens barrel disclosed in Patent Literature 1, an outer peripheral portion located radially outward from the rectilinear key is cut out in a cam ring that rotates relatively adjacent to the rectilinear key.
従来のレンズ鏡筒は、外光に対する遮光性や、カム環の連動部配置の設計自由度について課題がある。特許文献1に示す構成では、カム環の外周部が切り欠かれているため、レンズ鏡筒内に侵入した外光がカム環の外周から通過して撮像素子まで到達した場合、撮影画像に影響を及ぼす虞がある。また隣接部材と連動するカム環の連動部配置に制限があるため、設計自由度の低さが問題となる。
そこで本発明の目的は、外光に対する遮光性や、カム環の連動部配置に関する設計自由度を高めることである。
Conventional lens barrels have problems with respect to light shielding against external light and the degree of freedom in designing the arrangement of interlocking portions of the cam ring. In the configuration shown in Patent Document 1, since the outer peripheral portion of the cam ring is cut out, if the external light that has entered the lens barrel passes through the outer periphery of the cam ring and reaches the image sensor, the captured image is affected. There is a risk of affecting. In addition, since there is a limitation on the interlocking portion arrangement of the cam ring interlocking with the adjacent member, a low degree of freedom in design becomes a problem.
Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to increase the degree of freedom in designing the light shielding property against external light and the arrangement of interlocking portions of the cam ring.
上記課題を解決するために本発明は、光軸方向に移動可能な第1のレンズ群及び第2のレンズ群を有するレンズ鏡筒であって、前記第1のレンズ群の第1の保持部材にカム係合して前記第1の保持部材を保持する第1のカム部材と、前記第1のカム部材と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって前記第1の保持部材の回転を規制する第1の規制部材と、前記第2のレンズ群の第2の保持部材にカム係合して前記第2の保持部材を保持する第2のカム部材と、前記第2のカム部材と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって前記第2の保持部材の回転を規制する第2の規制部材と、前記第1のカム部材及び第2のカム部材を案内する第3のカム部材と、を備える。前記第1の規制部材には、前記第1のレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第1のフランジ部が形成され、前記第2の規制部材には、前記第2のレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第2のフランジ部が形成され、前記第1のフランジ部は前記第3のカム部材に対してカム係合し、前記第2のフランジ部は前記第3のカム部材に対してカム係合している。 In order to solve the above problems, the present invention provides a lens barrel having a first lens group and a second lens group that are movable in the optical axis direction, the first holding member of the first lens group . in the first cam member when the cam engagement with holding the first holding member, the rotation of the a movable said to the first cam member integrally with the optical axis direction first holding member a first regulating member for regulating a second cam member for holding the second holding member cam engagement with the second holding member of the second lens group, and the second cam member A second restricting member that is integrally movable in the optical axis direction and restricts the rotation of the second holding member; and a third cam member that guides the first cam member and the second cam member. And comprising. Wherein the first regulating member, the first flange portion which extends in a direction extends to the inner peripheral surface of the third cam member which is perpendicular to the optical axis of the first lens group is formed, the first The second restricting member is formed with a second flange portion extending in a direction orthogonal to the optical axis of the second lens group and extending to the inner peripheral surface of the third cam member. The flange portion is cam-engaged with the third cam member, and the second flange portion is cam-engaged with the third cam member .
本発明によれば、レンズ鏡筒内に侵入する外光に対して内部での遮光性が高く、またカム環の連動部配置の設計自由度を高めることが可能である。 According to the present invention, it is possible to increase the degree of freedom in designing the arrangement of the interlocking portions of the cam ring, and the internal light shielding property is high with respect to external light entering the lens barrel.
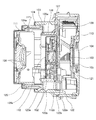
以下、本発明の撮像装置に係る実施形態として、3段沈胴式のレンズ鏡筒を備えた装置の構成例を説明する。図1はレンズ鏡筒を光軸に沿って切断した中央断面図であり、本図に基づいてレンズ鏡筒の構成の概略を説明する。撮影光学系は、第1のレンズ群(以下、1群という)101、第2のレンズ群(以下、2群という)102、第3のレンズ群(以下、3群という)103から成る。各レンズ群は一般的に複数の光学部材で構成され、3群103(本例では単レンズ)は撮像素子104の手前に位置する。撮像素子104は各レンズ群を通して結像する被写体像を電気信号に変換し、撮像信号を不図示の信号処理回路に出力する。撮像素子104の前面には光学フィルタ105が配置される。1群鏡筒111、2群鏡筒112、3群鏡筒113はそれぞれ、1群101、2群102、3群103の保持部材である。1群鏡筒(第1保持枠)111にはレンズ保護用のレンズバリアとその駆動部が設けられ、2群鏡筒(第2保持枠)112にはシャッタ機構や絞り機構が設けられているが、それらの詳細な説明は省略する。また1群101と2群102は協同して主に焦点距離調節機能をもち、3群103は主に焦点調節機能をもつ。
Hereinafter, a configuration example of an apparatus including a three-stage retractable lens barrel will be described as an embodiment according to the imaging apparatus of the present invention. FIG. 1 is a central sectional view of the lens barrel cut along the optical axis, and the outline of the configuration of the lens barrel will be described based on this drawing. The photographing optical system includes a first lens group (hereinafter referred to as “first group”) 101, a second lens group (hereinafter referred to as “second group”) 102, and a third lens group (hereinafter referred to as “third group”) 103. Each lens group is generally composed of a plurality of optical members, and the third group 103 (single lens in this example) is positioned in front of the
レンズ鏡筒の基台となるベース121は撮像素子104を保持し、支持部材である固定筒122に取り付けられている。固定筒122は円筒形を成し、内周にカム溝122aを有する。レンズ鏡筒は、第1のカム部材(1群カム環124)、第2のカム部材(2群カム環126)、第3のカム部材(移動カム環123)を備える。1群カム環124は1群鏡筒111とカム係合して保持し、2群カム環126は2群鏡筒112とカム係合して保持する。移動カム環123は1群カム環124及び2群カム環126と係合して、これらを案内する。さらに第1の規制部材(1群直進環125)、第2の規制部材(2群直進環127)と、直進環の回転を規制する直進案内部材(ガイドプレート128)が設けられている。
A
円筒状をした移動カム環123は、その外周部にカムフォロワ123zを有しており、これは固定筒122のカム溝122aと係合する。移動カム環123の内周には2種類のカム溝123a、123bが形成されており、1群直進環125や2群直進環127に形成した不図示のカムフォロワが係合する。つまりカム溝123aには1群直進環125の外周に設けたカムフォロワが係合し、またカム溝123bには2群直進環127の外周に設けたカムフォロワが係合する。1群直進環125は1群カム環124を保持しており、光軸方向において1群カム環124と一体的に移動可能であり、光軸回り方向においては相対的に回転可能である。1群カム環124の内周にはカム溝124aが形成され、1群鏡筒111の外周部に設けたカムフォロワ111zが係合する。2群直進環127は2群カム環126を保持しており、光軸方向において2群カム環126と一体的に移動可能であり、光軸回り方向においては相対的に回転可能である。2群カム環126の内周にはカム溝126aが形成され、2群鏡筒112の外周部に設けたカムフォロワ112zが係合する。ガイドプレート128は固定筒122に対して回転が規制される直進案内部材であり、後述する2本のキー(本例では長方形状の規制部)によって1群直進環125と2群直進環127の回転を規制している。
The cylindrical moving
本レンズ鏡筒は、1群鏡筒111、2群鏡筒112の光軸方向における位置がそれぞれ、3つのカム環123、124、126によって決定される3段鏡筒である。ところで本例の光学系は1群101が負のパワーを持ち、2群102が正のパワーを持ち、3群103が正のパワーを持つ光学系であり、焦点距離の変化は主に1群と2群のレンズの配置で決定される。そして2群102が光軸方向に大きく移動することで焦点距離が変化するという性質がある。近年、レンズ全長の短縮化や高倍率化によって、レンズ全長に対する2群の移動量が相対的に大きくなる傾向にある。従来は1群の移動量でレンズ鏡筒の沈胴全長が決定されていたが、近年では2群の移動量による影響が大きくなっている。
This lens barrel is a three-stage barrel in which the positions of the
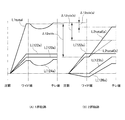
図2は、1群が負、2群と3群が正のパワーをそれぞれ有する光学系について、各レンズ群のカム軌跡を模式的に示す。図2(A)は1群101のカム軌跡を示し、図2(B)は2群レンズのカム軌跡を示しており、図の上方が被写体側、つまり撮像装置の前方を示す。「沈胴」はレンズ鏡筒が非動作時にカメラ本体に収納される状態を表し、「ワイド端」は画角変化における広角端を表し、「テレ端」は画角変化における望遠端を表している。図2中のL(122a)は固定筒122の内周に設けたカム溝122aのカム軌跡を表し、沈胴からワイド端の手前にかけて直線的に変化し、ワイド端の手前からテレ端にかけて一定位置となる。1群101、2群102ともに、これらの光軸方向の位置にはカム溝122aとこれに係合するカムフォロワ123zによるストローク分が共通の成分として加わる。図2(A)においてL(123a)は移動カム環123の内周に設けたカム溝123aのカム軌跡を表し、沈胴からワイド端の手前にかけて直線的に変化し、ワイド端の手前からテレ端にかけて一定位置となる。L(124a)は1群カム環124の内周に設けたカム溝124aのカム軌跡であり、沈胴からワイド端の手前にかけて直線的に変化し、ワイド端からテレ端までの間には下方に凸の曲線部をもつ。1群101の光軸方向の位置は、合成軌跡L1totalに示すように、L(122a)、L(123a)、L(124a)に示す各カム軌跡の位置成分の合計によって決定され、1群101はこの軌跡に従って光軸方向に移動する。
FIG. 2 schematically shows the cam locus of each lens group for an optical system in which the first group is negative and the second group and the third group have positive powers. 2A shows the cam trajectory of the
2群102については、図2(B)に示すL(123b)が移動カム環123の内周に設けたカム溝123bのカム軌跡を表し、沈胴からワイド端を超えたところまで一定位置であり、ワイド端からテレ端にかけて直線部をもつ。L(126a)は2群カム環126の内周に設けたカム溝126aのカム軌跡を表し、沈胴からワイド端にかけて負勾配(後退方向)の直線部をもち、ワイド端からテレ端にかけて直線部をもつ。合成軌跡L2total(a)は、L(122a)、L(123b)、L(126a)に示す各カム軌跡の位置成分の合計、すなわち2群102の移動軌跡を表している。
For the
図中のΔ12wideはワイド端における1群101と2群102の間隔(位置差)を表し、Δ12tele(a)はテレ端における1群101と2群102の間隔を表す。この様に各レンズ群ともに沈胴位置からの移動量は同程度必要である。そして1群101と2群102の間隔についても、ワイド端でのΔ12wideから、テレ端でのΔ12tele(a)まで大きく変化できるようにする必要がある。これは1群鏡筒111を3段カム構成とし、2群鏡筒112を3段カム構成とすることで達成される。例えば2群のカム構成においてカム軌跡L(123b)が無い2段構成を仮定する。この場合、2群の合成軌跡は破線で示すL2total(b)となり、テレ端における1群と2群の間隔はΔ12tele(a)からΔ12tele(b)に広がってしまい、画角倍率変化が低下してしまう。
In the figure, Δ12wide represents the interval (positional difference) between the
本実施形態では、ベース121から2段目の移動カム環123において1群用のカム溝123aと2群用のカム溝123bを分離して形成している。すなわち1群101と2群102との相互間隔は、1群鏡筒111のカム2段分のストローク(=L(123a)+L(124a))と、2群鏡筒112のカム2段分のストローク(=L(123b)+L(126a))の差によって決まる。これにより、短い沈胴全長のレンズ鏡筒においても1群と2群の相互間隔について大きな変化量を得ることが可能であり、薄型化に好適なレンズ鏡筒を実現できる。例えば、ベースから3段目で1群と2群のカムを分離する構成の場合、1群と2群との相互間隔は1段分のカムストロークのみで決まるので、これを大きくする事はできなくなってしまう。
In the present embodiment, the first-
次にレンズ鏡筒の構成について詳細に説明する。図3はレンズ鏡筒におけるズーム機構系の分解斜視図である。先ず1群101の保持機構を説明すると、1群カム環124の内周には1群直進環125が嵌合し、不図示の脱落規制部によって両者は光軸方向へ一体的に移動可動であって、かつ相対的に回転可能である。1群カム環124の内周面に3箇所形成されたカム溝124aには、1群鏡筒111に設けた3つのカムフォロワ111zがそれぞれ係合することで、1群鏡筒111がカム溝124aに沿って案内される。1群直進環125の円筒部の側面には直進案内溝125aが3箇所に形成されており、1群鏡筒111に設けた各カムフォロワ111zが係合することで1群鏡筒111の回転が規制される。1群直進環125自体の回転規制については、ガイドプレート128に立設した2つのキー128aが1群直進環125の側面に形成した2箇所のスリット125bにそれぞれ嵌合することで行われる。なお各キー128aは光軸を挟んで互いに対向して位置し、光軸に対して平行に延びている。ガイドプレート128にはそのフランジ部から半径方向の外方に延伸した凸部128zが3箇所形成されており、これらは固定筒122の内周に3箇所形成した直進案内溝122bにそれぞれ嵌合することで回転が規制される。
Next, the configuration of the lens barrel will be described in detail. FIG. 3 is an exploded perspective view of the zoom mechanism system in the lens barrel. First, the holding mechanism of the
2群鏡筒112の保持機構についても1群鏡筒111の場合と同様、2群カム環126の内周に2群直進環127が嵌合し、不図示の脱落規制部によって両者は光軸方向へ一体的に移動可能であって、かつ相対的に回転可能である。2群カム環126の内周に3箇所形成したカム溝126aには、2群鏡筒112に3箇所形成したカムフォロワ112zがそれぞれ係合し、2群鏡筒112はカム溝126aに沿って案内される。2群直進環127の円筒部の側面には直進案内溝127aが3箇所形成され、2群鏡筒112に3箇所形成したカムフォロワ112zがそれぞれの案内溝127aに嵌合することで2群鏡筒112の回転が規制される。2群直進環127には、円筒部から半径方向にて外方に延伸したフランジ部127fが形成され、これにはスリット孔127bが2箇所形成されている。ガイドプレート128の各キー128aを、フランジ部127fのスリット孔127bに挿通することで、2群直進環127の回転が規制される。2群カム環126には、その円筒部から半径方向にて外方に延伸したフランジ部126fが形成されており、この部分に2箇所形成された弧状の孔126cに、各キー128aがそれぞれ挿通される。
As for the holding mechanism of the
次にカム溝とカムフォロワとの係合関係を説明する。1群直進環125に形成した第1のカムフォロワ125zは、移動カム環123の内周に形成した第1のカム溝123aと係合する。2群直進環127に形成した第2のカムフォロワ127zは移動カム環123の内周に形成した第2のカム溝123bと係合する。これにより1群直進環125と2群直進環127はそれぞれカム溝123a、123bに沿って案内される。移動カム環123の内周には直進案内溝123cが円周方向において3箇所形成されている。これらの直進案内溝123cには、1群カム環124の外周の突起124z、及び2群カム環126の外周の突起126zがそれぞれ嵌合しており、1群カム環124及び2群カム環126は移動カム環123に従動して回転する。移動カム環123は固定筒122の内周に3箇所形成したカム溝122aに沿って案内される。つまり、各カムフォロワ123zがそれぞれに対応するカム溝122aに係合する。移動カム環123の外周にはギア部123gが一体的に形成されている。該ギア部には後述する駆動ギアを介して駆動モータの力が伝達され、移動カム環123は光軸回りに回転すると共に光軸方向に移動する。ガイドプレート128は移動カム環123に設けた不図示の脱落規制部によって、移動カム環123と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって、かつ光軸回り方向において相対的に回転可能である。
Next, the engagement relationship between the cam groove and the cam follower will be described. The
本構造では、移動カム環123の回転に従動して1群カム環124も回転するが、1群直進環125はガイドプレート128のキー128aによって回転が規制されているため、1群鏡筒111は光軸方向にのみ移動することになる。なお1群直進環125はその後端部にて半径方向に延伸したフランジ部125fを有しており、後述のように鏡筒の強度向上及び遮光性向上の効果を奏する。
In this structure, the first
一方、移動カム環123の回転に従動して2群カム環126も回転するが、2群直進環127はガイドプレート128のキー128aによって回転が規制されているため、2群鏡筒112は光軸方向にのみ移動することになる。なお2群カム環126、2群直進環127にはその後端部にて半径方向に延伸したフランジ部126f、127fをそれぞれ有しており、後述のように鏡筒の強度向上及び遮光性向上の効果を奏する。
On the other hand, the second
図4は、レンズ鏡筒におけるズーム機構駆動系、フォーカス駆動系、撮像素子の周辺部を示す分解斜視図である。ベース121の下方にはズーム機構の駆動源としてズームモータ401が取り付けられている。ズームモータ401の回転軸にはギア402が固定され、伝達ギア群403は、ギア402の回転力を移動カム環123のギア部123gに伝達する。ギア402に近辺に設けたフォトインタラプタ404は、ズームモータ401の回転方向及び回転数を検出する。ベース121に設けたフォトインタラプタ405は、ズーム駆動時のリセット位置を検出すする。2群直進環127に設けた不図示の遮光リブがフォトインタラプタ405を遮光することでリセット検出が行われる。
FIG. 4 is an exploded perspective view showing the periphery of the zoom mechanism drive system, focus drive system, and image sensor in the lens barrel. A
3群鏡筒113にはスリーブ113aが延設され、この部分にガイドバー407を挿通した状態でガイドバー407をベース121の保持部121aで保持することによって、スリーブ113aがベース121に支持される。これにより、3群鏡筒113はガイドバー407に沿って光軸と平行な方向に進退可能である。片寄せバネ408は、その一端が3群鏡筒113の一部に設けたフック113hに引っ掛けられ、他端はベース121の保持部121aに設けたフック121hに引っ掛けられている。フォーカス駆動機構の駆動源としてのフォーカスモータ410は、3群鏡筒113を駆動する送りネジ機構を構成する。送りネジであるフォーカスモータ410の回転軸410aと、3群鏡筒113に設けた送りナット411によって、3群鏡筒113はガイドバー407に沿って光軸と平行な方向に進退する。3群鏡筒113にはリブ113bが設けられており、これによってベース121に設けたフォトインタラプタ412が遮光される際、フォーカス駆動時における3群鏡筒113のリセット位置が検出される。撮像素子104は保持板420に固定され、複数のビス421を用いてベース121に取り付けられる。保持板420と光学フィルタ105(不図示)の間には防塵用のゴム部材422が挟持される。
A
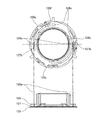
図5はガイドプレート128の両キー128aを含み光軸に沿う切断面にて、ワイド端状態のレンズ鏡筒を示した断面図である。以下、本図を用いて鏡筒構成による遮光性及び強度の向上効果について説明する。
移動カム環123と1群カム環124の間には、半径方向に僅かな隙間が存在する。太陽光など、強い光源からの光がこの隙間を通過して鏡筒内部に到達した場合、撮影画像に影響を及ぼす虞がある。そこで1群直進環125には、その一部を半径方向にて外方に延伸してフランジ部125fを形成している。フランジ部125fの外径を移動カム環123の内径とほぼ等しくすることで内部に侵入する光を遮光できる。つまり1群カム環124の外周と移動カム環123の内周との隙間を光が通過する際、面反射を繰り返すことで侵入光の強度が減衰する。その後、フランジ部125fと移動カム環123の内周面との隙間を通過する際、更に面反射が繰り返されることで、一段と減衰効果が増すことになる。本実施形態では1群直進環125にフランジ部125fを形成したが、これに代えて又はこれと併せて1群カム環124に同様のフランジ部を形成してもよい。該フランジ部はレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して移動カム環123の内周面に及んでおり、この部分をキー128aが貫通するように構成すれば、光の減衰効果が得られる。
FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view showing the lens barrel in the wide end state on a cut surface including both
A slight gap exists in the radial direction between the moving
同様に、2群カム環126のフランジ部126fと、2群直進環127のフランジ部127fについてもそれらの外径は、移動カム環123の内径とほぼ等しい。これにより上述のように減衰した光は、フランジ部126fや127fと移動カム環123の内周面との隙間にて更に減衰する。移動カム環123の後端面にはガイドプレート128が取り付けられているので、上述のように減衰した光は、最終的にガイドプレート128によって遮光される。その結果、外光は撮影画像に影響を及ぼさない程度にまで減衰する。
Similarly, the outer diameters of the
ところで沈胴時には、2群カム環126及び2群直進環127は1群鏡筒111、1群カム環124及び1群直進環125に対し、光軸と直交する半径方向の内側に収納される。このため1群鏡筒111と1群直進環125の隙間から侵入した外光があったとしても、フランジ部126fや127fによって遮光することができる。本例では、ガイドプレート128のキー128aを、フランジ部127fに形成したスリット孔127b、及びフランジ部126fに形成した弧状の孔126cを挿通させた構成を採用している。これにより、キー128aよりも半径方向の外側に各フランジ部が存在するので、遮光の効果が高まる。
以上のように、外径が移動カム環123の内径にほぼ等しいフランジ部を設け、直進キーがフランジ部を貫通するように構成すれば、光が通過し難い構造を実現できる。
By the way, when retracted, the second
As described above, if a flange portion having an outer diameter substantially equal to the inner diameter of the
キー128aよりも外側にフランジ部が存在する事は、設計レイアウトの自由度を高める効果も奏する。これは、2群カム環126の突起126zをフランジ部の全周において任意の位置に配置できるからであり、フランジ部に隣接部材との連動部を設けることによって当該連動部の位置について制限を受けなくなる。図6は2群カム環126、2群直進環127、ガイドプレート128について、ワイド端における互いの関係を示す正面図及び中央断面図である。2群直進環127は、そのスリット孔127bにキー128aが挿合されることで回転が規制される。2群カム環126には弧状の各スリット孔126cが光軸を中心に対向し、キー128aを避けて形成されている。ガイドプレート128において各キー128aは対向して2箇所にあるので、スリット孔126cについても対向した2箇所にある。移動カム環123に従動して回転する2群カム環126において、円周方向の3箇所に形成された突起126zと、スリット孔126cとの位置関係は不規則なものとなる。例えば図6のように、左上の突起126zはスリット孔126cの外側に位置している。仮にスリット孔126cよりも外側の形状部が無い簡便な形状にしてしまうと、突起126zを、円周方向において2つのスリット孔126c同士の間に配置する他は手立てがなくなってしまう。キー128aよりも外側にフランジ部を設けた場合、そうような制約を受けなくなる。本実施形態では、光軸回りの円周方向に亘って突起126zを3箇所に設けているが、その理由は設計レイアウトの自由度を考慮したことによるものである。つまり、突起126zは前述のように移動カム環123の内周に形成した直進溝123c(図3参照)に嵌合するが、内周には2種類のカム溝123a、123bが円周方向に亘ってそれぞれ3箇所形成されている。これらのカム溝を避けて直進溝123cを配置するためには、直進溝123cについても円周方向に亘って3箇所に配置することが望ましい。こうして2群カム環126のスリット孔126cよりも外側に形状部を残すことによって、設計レイアウトの自由度を高める効果が得られる。なお以上の説明は1群カム環124にフランジ部を形成して外周に突起124zを配置する場合にも同様に当てはまる。
The presence of the flange portion outside the key 128a also has an effect of increasing the degree of freedom in design layout. This is because the
次にフランジ部による鏡筒強度向上の効果について、図7を用いて説明する。図7(A)は移動カム環123と1群直進環125について、カムフォロワ125zを通る面で切断した断面形状を模式的に示す図である。通常の使用状態では、図7(A)に示すように、カムフォロワ125zがカム溝123aに対して確実に嵌合している。図7(B)は、カメラが落下して鏡筒先端から地面に衝突した時のように、鏡筒先端に正面から過大な外力が加わった状況を誇張的に示している。カムフォロワ125zとカム溝123aは、図1の断面に示すようにテーパー状の接触面をもち、光軸方向に対して勾配があるので、正面からの外力によって両者は勾配に沿って互いに滑ろうとする。図7(B)に示すように、移動カム環123のうち、カムフォロワ125zと嵌合している部分が一時的に変形して外側に膨らみ(矢印F参照)、1群直進環125ではカムフォロワ125zが変形して内側に撓んだ状態となる(矢印G参照)。矢印F、Gは変形の向きを示している。この変形が大きい場合、カムフォロワ125zはカム溝123aから脱落してしまい、鏡筒はその後、正常動作が不可能になる虞が生じる。そこで本実施形態では、1群直進環125にフランジ部125fを設けることにより、単純な円筒形状に比して剛性を増して変形し難い形状を採用している。また図7(B)に示すように、1群直進環125において、カムフォロワ125zが内側に撓むと同時に、カムフォロワ125z同士の間に位置する部分は外側に膨らむ。この外側に膨らんだフランジ部125fが移動カム環123の内周面に当接することにより、それ以上の変形が抑制される。よってカムフォロワ125zがカム溝123aから脱落し難くなるという効果が得られる。
Next, the effect of improving the barrel strength by the flange will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 7A is a diagram schematically showing a cross-sectional shape of the moving
さらに移動カム環123には、前述のように2群カム環126と2群直進環127が係合しており、それらのフランジ部126f、127fが移動カム環123の内側に撓んだ内周面と当接する。これにより移動カム環123の変形が抑制され、1群直進環125が脱落し難くなる。
また前述のようにガイドプレート128は、1群直進環125と2群直進環127の双方を共通のキー128aで規制している。よって、1群直進環125と2群直進環127の回転方向の位置ずれを低減する効果が得られる。また従来のように1群規制用と2群規制用の2種類のキー(規制部)を各2本ずつ使用する必要がなくなり、キーの本数が減るので、部品加工性の改善やコスト低減の効果が得られる。各群についてキーをそれぞれ使用する場合には動作精度を確保する上で不利となるので、本実施形態のように、両群の規制用に1種類のキーを使用することが有効である。
Further, as described above, the second
Further, as described above, the
101 第1のレンズ群
102 第2のレンズ群
104 撮像素子
123 第3のカム部材(移動カム環)
124 第1のカム部材(1群カム環)
125 第1の規制部材(1群直進環)
125f フランジ部
126 第2のカム部材(2群カム環)
126f フランジ部
127 第2の規制部材(2群直進環)
127f フランジ部
128 直進案内部材
128a 規制部
101
124 1st cam member (1 group cam ring)
125 1st regulating member (group 1 straight ring)
126f
Claims (6)
前記第1のレンズ群の第1の保持部材にカム係合して前記第1の保持部材を保持する第1のカム部材と、前記第1のカム部材と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって前記第1の保持部材の回転を規制する第1の規制部材と、前記第2のレンズ群の第2の保持部材にカム係合して前記第2の保持部材を保持する第2のカム部材と、前記第2のカム部材と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって前記第2の保持部材の回転を規制する第2の規制部材と、前記第1のカム部材及び第2のカム部材を案内する第3のカム部材と、を備え、
前記第1の規制部材には、前記第1のレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第1のフランジ部が形成され、
前記第2の規制部材には、前記第2のレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第2のフランジ部が形成され、
前記第1のフランジ部は前記第3のカム部材に対してカム係合し、前記第2のフランジ部は前記第3のカム部材に対してカム係合していることを特徴とするレンズ鏡筒。 A lens barrel having a first lens group and a second lens group movable in an optical axis direction,
A first cam member that holds the first cam engages said first holding member of the holding member of the first lens group, movable the the first cam member integrally with the optical axis second for holding the first regulating member and the second lens group of the second cam engagement with the second holding member in the holding member for restricting the rotation of the first holding member comprising a The second cam member, a second restricting member which is movable in the optical axis direction integrally with the second cam member and restricts the rotation of the second holding member, the first cam member and the second cam member A third cam member for guiding the two cam members;
The first restricting member is formed with a first flange portion extending in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the first lens group and extending to the inner peripheral surface of the third cam member,
The second restricting member is formed with a second flange portion extending in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the second lens group and extending to the inner peripheral surface of the third cam member,
The lens mirror, wherein the first flange portion is cam-engaged with the third cam member, and the second flange portion is cam-engaged with the third cam member. Tube.
前記第1のレンズ群の第1の保持部材にカム係合して前記第1の保持部材を保持する第1のカム部材と、
前記第1の保持部材の回転を規制する第1の規制部材と、
前記第2のレンズ群の第2の保持部材にカム係合して前記第2の保持部材を保持する第2のカム部材と、
前記第2の保持部材の回転を規制する第2の規制部材と、
前記第1及び第2のカム部材を案内する第3のカム部材と、
前記第3のカム部材と一体的に光軸方向へ移動可能であって、前記第1の規制部材の回転を規制する規制部を有する直進案内部材と、を備え、
前記第1のカム部材又は前記第1の規制部材には、前記第1のレンズ群の光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第1のフランジ部が形成され、前記規制部が当該第1のフランジ部を貫通し、前記第2のカム部材には、前記第2のレンズ群の前記光軸に直交する方向に延伸して前記第3のカム部材の内周面へと及ぶ第2のフランジ部が形成され、前記規制部が当該第2のフランジ部を貫通しており、
前記第3のカム部材と従動して回転するための突起が、前記第2のフランジ部の外周に配置され、前記第3のカム部材には当該突起と係合する案内溝が形成されていることを特徴とするレンズ鏡筒。 A lens barrel having a first lens group and a second lens group movable in an optical axis direction,
A first cam member that cam-engages with the first holding member of the first lens group and holds the first holding member;
A first regulating member for regulating the rotation of said first holding member,
A second cam member for holding the second holding member cam engaged with the second holding member of the second lens group,
A second restricting member for restricting rotation of the second holding member;
A third cam member for guiding the first and second cam members;
A linear guide member that is movable in the optical axis direction integrally with the third cam member and has a restricting portion that restricts rotation of the first restricting member;
The first cam member or the first regulating member has a first flange extending in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the first lens group and extending to the inner peripheral surface of the third cam member. A portion is formed, the restricting portion penetrates the first flange portion, and the second cam member extends in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the second lens group, and the third cam member A second flange portion extending to the inner peripheral surface of the cam member is formed, and the restricting portion passes through the second flange portion;
A protrusion for rotating by rotating with the third cam member is disposed on the outer periphery of the second flange portion, and a guide groove for engaging with the protrusion is formed on the third cam member. A lens barrel characterized by that.
前記レンズ鏡筒を通して結像する被写体像を電気信号に変換する撮像素子を備えたことを特徴とする撮像装置。
The lens barrel according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
Imaging device being characterized in that an imaging device for converting a subject image imaged through the lens barrel to an electrical signal.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010024665A JP5517654B2 (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2010-02-05 | Lens barrel and imaging device |
| US13/010,288 US8520328B2 (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2011-01-20 | Lens barrel and imaging apparatus |
| CN2011100347649A CN102147554B (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2011-01-31 | Lens barrel and imaging apparatus |
| US13/950,960 US20130342721A1 (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2013-07-25 | Lens barrel and imaging apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010024665A JP5517654B2 (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2010-02-05 | Lens barrel and imaging device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011164215A JP2011164215A (en) | 2011-08-25 |
| JP2011164215A5 JP2011164215A5 (en) | 2013-03-21 |
| JP5517654B2 true JP5517654B2 (en) | 2014-06-11 |
Family
ID=44594996
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010024665A Active JP5517654B2 (en) | 2010-02-05 | 2010-02-05 | Lens barrel and imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5517654B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6135460B2 (en) * | 2013-10-30 | 2017-05-31 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Lens unit |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4524507B2 (en) * | 2000-01-31 | 2010-08-18 | コニカミノルタオプト株式会社 | Zoom lens barrel |
| JP3689379B2 (en) * | 2002-03-20 | 2005-08-31 | 株式会社タムロン | High magnification zoom lens |
| JP4181896B2 (en) * | 2003-02-26 | 2008-11-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | Lens barrel and imaging device |
| JP4971647B2 (en) * | 2006-02-17 | 2012-07-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging tube and imaging device |
| JP4933420B2 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2012-05-16 | 日本電産コパル株式会社 | Lens barrel |
-
2010
- 2010-02-05 JP JP2010024665A patent/JP5517654B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011164215A (en) | 2011-08-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7929228B2 (en) | Image pickup apparatus having lens barrel | |
| US8520328B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging apparatus | |
| US8477430B2 (en) | Image pickup apparatus having lens barrel | |
| JP6949684B2 (en) | Lens device and imaging device | |
| CN114755796A (en) | Lens barrel and image pickup apparatus | |
| US8456753B2 (en) | Zoom lens barrel and image pickup apparatus having the same | |
| US7872810B2 (en) | Light shielding structure of an optical device | |
| US11022775B2 (en) | Lens apparatus and optical apparatus | |
| JP5517654B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging device | |
| JP4763342B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging device | |
| US7373082B2 (en) | Light shielding structure of a zoom lens barrel | |
| JP5517653B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging device | |
| JP5570098B2 (en) | Lens barrel and camera | |
| JP7268688B2 (en) | Lens barrels and optical equipment | |
| JP4693797B2 (en) | Lens drive device | |
| JP5441744B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2004198499A (en) | Optical equipment | |
| JP2010262177A (en) | Camera unit | |
| JP2008197455A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP6544598B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2007333764A (en) | Lens barrel and camera | |
| JP4710340B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2005084406A (en) | Zoom lens barrel and optical equipment | |
| JP7435630B2 (en) | Lens barrel and optical equipment | |
| JP4763341B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130205 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130205 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131129 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131210 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140210 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140304 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140401 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5517654 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |