JP5452437B2 - Route search device - Google Patents
Route search device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5452437B2 JP5452437B2 JP2010220233A JP2010220233A JP5452437B2 JP 5452437 B2 JP5452437 B2 JP 5452437B2 JP 2010220233 A JP2010220233 A JP 2010220233A JP 2010220233 A JP2010220233 A JP 2010220233A JP 5452437 B2 JP5452437 B2 JP 5452437B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- route
- partial
- driver
- cost
- vehicle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、車両に搭載されたセンサから取得したデータに基づき経路探索を行う経路探索方法,経路探索システムおよびナビゲーション装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a route search method, a route search system, and a navigation device that perform route search based on data acquired from a sensor mounted on a vehicle.
経路探索はカーナビゲーション装置の必須機能であり、目的地までの経路や旅行時間を算出してドライバーに提供する。経路探索においては、一般道優先,高速道路優先といった経路算出の条件が選択ができる。従来の経路の算出方法は、出発地から目的地までの所要時間あるいは距離が最小の経路を算出する方法が一般的である。ところが、所要時間最小/距離最小の制約条件も下で算出される経路の中には、道幅の狭い道や見通しの悪い道等、地元の人もあまり通らないような道路が含まれることもある。このため、単なる時間や距離に限らず、走りやすさや安全性を考慮した経路の算出が求められている。 The route search is an essential function of the car navigation device, and calculates the route to the destination and the travel time and provides it to the driver. In route search, conditions for route calculation such as general road priority and expressway priority can be selected. As a conventional route calculation method, a method of calculating a route having the minimum required time or distance from the departure point to the destination is generally used. However, some routes calculated under the minimum required time / minimum distance constraints may include roads where local people do not pass, such as narrow roads and roads with poor visibility. . For this reason, there is a need for calculation of a route that takes into consideration ease of running and safety, not just time and distance.
特開2009−2817号公報には、車両の走行軌跡データを利用した経路探索方法として、走行回数が多い道路を走りやすい道路として評価し、経路探索に用いる発明が開示されている。また特開2004−333377号公報には、走行のしやすさ,安全性などの利便性が向上できる経路探索として、商用車両の走行回数を用いる発明が開示されている。その経路探索方法においては、商用車の走行回数による重み付けが一定値を超えるリンクを必ず含むように再探索を行うことで、商用車の運転者の経路選択ノウハウを経路探索に活かすことができるようにしている。 Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2009-2817 discloses an invention for evaluating a road having a large number of travels as an easy-to-run road and using it for a route search as a route search method using travel locus data of a vehicle. Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2004-333377 discloses an invention that uses the number of times a commercial vehicle travels as a route search that can improve convenience such as ease of travel and safety. In the route search method, it is possible to make use of the route selection know-how of the commercial vehicle driver for the route search by re-searching so as to always include a link whose weighting by the number of times the commercial vehicle has traveled exceeds a certain value. I have to.
特許文献1による発明では、多数の車両から収集されたプローブデータに基づき、車両の走行回数が多い道路を走りやすい経路として評価する。この走行回数から算出された評価値は、走行する時間帯やドライバーに依存しない一定値である。しかし、経路の好みはドライバーの性別,年齢などによって異なるため、多数のドライバーの傾向から個々のドライバーの好みに合った経路を提供することが難しい。
In the invention according to
一方、特許文献2による発明は、商用車両の運転軌跡を利用して走行回数の多い道路リンクを選択するようにしていることから、商用車両が頻繁に利用する道路を通る経路が常に最適経路として提供され、経路に偏りが生じる。商用車両の場合、営業目的や管轄、あるいは、運転者の営業活動等が商用車両の走行経路に影響する可能性があり、商用車が頻繁に利用する経路が必ずしも走りやすさなどを考慮した経路であるとは限らない。また、一般的なドライバーの場合、使用する車種や走行目的(通勤・ショッピング・レジャー等),目的地までの距離(所要時間),ドライバーの性別や年齢などにより経路の好みも異なるが、特許文献2ではそのような様々なドライバーの行動傾向が考慮されていないため、商用車の走行軌跡からドライバーの好みに合った経路を提供することは難しい。
On the other hand, since the invention according to
本発明の目的は、上記従来技術の問題点に鑑み、さまざまなドライバーの走行履歴とそのドライバーの特性を収集・分析した情報を経路探索に考慮することによりドライバーの嗜好,走りやすさ,安全性を考慮した利便性の高い経路を提供することにある。 The object of the present invention is to take into account the above-mentioned problems of the prior art, and to consider the driver's preference, ease of driving, and safety by considering various driving history and information collected / analyzed on the characteristics of the driver for route search. It is to provide a highly convenient route considering the above.
本発明は、車両に搭載された車載端末装置がその車両が備えるセンサから取得した走行履歴の情報を受信して蓄積し、この走行履歴の走行軌跡について、車両の分岐割合が所定値以上の交差点または主要道路の交差点を主要分岐点として検出する主要分岐点検出部と、各走行軌跡をこれら主要分岐点で区切った部分経路を求める部分経路生成手段と、予め求めた部分経路を用いて、指定された出発地から目的地への経路探索を行う経路計算部を有する経路探索装置であって、経路選択の要因に関する分類項目について運転者の情報を記録した運転者情報を取得して走行履歴と共に記憶したプローブ情報記憶部と、各部分経路について経路探索に用いる部分コストを求める部分コスト生成手段を備え、この部分コスト生成手段では、始端と終端が同じである部分経路について、各部分経路に対応する運転者情報の分類項目についての各部分経路の走行割合を求め、この走行割合から各部分経路の部分コストを算出し、経路計算部では、この部分コストを用いて出発地から目的地までのコスト最小経路を計算する。 The present invention receives and accumulates travel history information acquired by a vehicle-mounted terminal device mounted on a vehicle from a sensor included in the vehicle, and an intersection having a vehicle branching ratio of a predetermined value or more with respect to the travel locus of the travel history Alternatively, a main branch point detection unit that detects an intersection of a main road as a main branch point, a partial route generation unit that obtains a partial route obtained by dividing each travel locus by these main branch points, and a predetermined partial route A route search device having a route calculation unit for performing a route search from a designated departure place to a destination, obtaining driver information in which driver information is recorded for classification items relating to a route selection factor, and along with a travel history A stored probe information storage unit and a partial cost generation means for obtaining a partial cost to be used for route search for each partial path. For the same partial route, the travel ratio of each partial route for the classification item of the driver information corresponding to each partial route is obtained, and the partial cost of each partial route is calculated from this travel ratio. Calculate the minimum cost route from the starting point to the destination using the partial cost.
本発明によれば、ドライバー特性及び車両情報を考慮し、過去のドライバーのノウハウを反映した経路を生成することができるようになる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to generate a route reflecting past driver know-how in consideration of driver characteristics and vehicle information.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明を用いた経路探索システムの実施例を説明する。この経路探索システムでは、プローブ情報及びドライバーのプロファイルをもとに、ドライバー特性及び車両情報を考慮し、過去のドライバーのノウハウを反映した経路を生成する。 Embodiments of a route search system using the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In this route search system, based on the probe information and the driver profile, the driver characteristics and vehicle information are taken into consideration, and a route reflecting past driver know-how is generated.
図1に、本発明を用いた経路探索システムの機能ブロック図を示す。この経路探索システムでは、経路探索装置12を有するセンタ装置13が、プローブカー15からプローブ情報及びドライバーのプロファイルを収集し、情報利用者14にはこれらのデータを利用した経路探索結果を提供する。センタ装置13とプローブカー15や情報利用者14との間のデータ通信は、例えば、携帯電話やインターネット,無線LANを利用して行われる。
FIG. 1 shows a functional block diagram of a route search system using the present invention. In this route search system, a
プローブカー15は、車載端末装置11を備え、プローブデータを定期的(例えば30秒毎)に、もしくは、一定期間(例えば1日)蓄積後に、プローブデータとドライバープロファイルをセンタ装置13へ提供する車両である。ここでプローブデータとは、車両の走行軌跡データである。
The
センタ装置13は、サーバーとして機能する経路探索装置12を備えている。経路探索装置12は、プローブカー15から送信されてくるプローブデータ等をもとに抽出した過去のドライバーのノウハウを反映した経路情報を、情報利用者14に提供する。情報利用者14は、経路探索装置12の利用者であり、経路情報をカーナビゲーションや携帯,PC,スマートフォン等に表示させナビゲーションに利用する。
The
車載端末装置11は、センサ101,プローブデータ記憶部102,ドライバープロファイル記憶部103,通信機器104を備えている。センサ101は、ナビゲーション装置で一般的に搭載されているGPS,加速度センサ,方位角センサなどの種々のセンサを利用することができる。また、車両から取り込んだ車速パルスなどの信号をセンサデータとしても良い。プローブデータ記憶部102は、各種センサから出力されるセンサデータをもとに生成した、位置情報(緯度経度などの座標)やデータ収集時の時刻情報の他、走行速度,移動方向,ブレーキ情報等の車両情報をプローブデータとしてプローブデータ記憶部102に記憶する。
The in-
記憶されたプローブデータは、上記のように定期的もしくは一定期間後に、通信機器104を通じてセンタ装置13に送信される。この際、ドライバープロファイル記憶部103からドライバープロファイルも送信される。ただし、ドライバープロファイルはセンタ装置13で保存しているため、以前に送信した情報と変更が無ければ、毎回プローブデータと共にドライバープロファイルをセンタ装置13に送信しなくても良い。
The stored probe data is transmitted to the
ドライバープロファイルは、経路選択の要因となり得る項目であり、後述する部分経路の部分コストを分岐割合に基づき定める際に部分経路の分類に用いる分類項目である。ドライバープロファイルには、ドライバーの特性に関する情報として、ドライバーの性別,年齢,運転暦などの他、運転目的(通勤,レジャー,買い物,送迎等),地元/観光客,渋滞度などが記録される。また、ドライバープロファイルには、運転する車両の情報も含める。車両の情報とは、車両が該当する業種(一般車両/タクシー,トラック等の業務車両)や、車種(大型/普通/小型)等である。車両の情報は、予め設定されドライバープロファイル記憶部103に記憶されているものとする。運転目的は、運転開始時にドライバーにより車載端末装置に入力されドライバープロファイル記憶部103に記憶されるものとする。地元/観光客の種別は、車両毎に予め基点位置(一般車両であれば、自宅など、タクシーなどであれば営業所などの所在地)が登録されており、走行時に取得した位置がこの基点位置から所定距離以内に存在する場合には地元と判断し、そうでなければ観光客と判断してドライバープロファイル記憶部103に記録するものとする。渋滞度については、路上センサなどからの交通情報を受信し(図示せず)、走行位置の交通情報から該当する渋滞度を判断して、ドライバープロファイル記憶部103に記憶する。
The driver profile is an item that can be a factor of route selection, and is a classification item that is used for classifying a partial route when determining a partial cost of a partial route, which will be described later, based on a branching ratio. In the driver profile, information such as the driver's sex, age, driving calendar, driving purpose (commuting, leisure, shopping, pick-up, etc.), local / tourist, traffic congestion level, etc. are recorded as information on the driver characteristics. The driver profile also includes information about the vehicle being driven. The vehicle information includes the type of business (general vehicles / taxi, business vehicles such as trucks) to which the vehicle applies, the vehicle type (large / normal / small), and the like. The vehicle information is set in advance and stored in the driver
センタ装置13は、バッチ処理装置110,経路探索装置12,共通DB(データベース、以下DBと略す)140を備えている。バッチ処理装置110は、プローブデータ変換部114,プローブDB115,主要分岐点算出部116,主要分岐点DB117,部分経路生成部118,部分経路DB119,分岐コスト生成部131,分岐コストDB132を備えている。経路探索装置12は、経路計算部123を備えている。共通DB140は、地図DB141,交通情報DB142を備えている。地図DB141では、道路の交差点あるいは道路上の特定のポイントをノードと定義し、各ノード間を結ぶ道路をリンクとして定義し、地図を表すものとする。また、各リンクには、経路計算部123で経路探索を行う際に用いるため、リンクの経路長に応じたコストがリンク毎に格納されている。交通情報DB142に記憶される交通情報は、路上センサデータあるいはプローブデータから生成されたリンク単位の所要時間,速度,渋滞度などである。また、地図DB141に格納されているリンクに対応し、リンクの交通情報を反映した旅行時間コストが経路計算部123で経路探索を行う際に用いるために格納されている。なお、バッチ処理装置110,経路探索装置12,共通DB140は同じサーバー上で実現されていても良く、それぞれが異なるサーバー上で実現されていてもよい。
The
バッチ処理装置110において、通信機器111を通じて、車載端末装置11から受信したプローブデータ112及びドライバープロファイル113は、プローブデータ変換部114によって、受信したプローブデータの位置情報からプローブカーが走行した道路のリンク列またはノード列を求め、プローブDB115に保存される。プローブDB115には、プローブカーが走行した道路のリンク列またはノード列が、ドライバープロファイル113に関連付けられて格納される。
In the
主要分岐点算出部116は、プローブDB115に格納されているリンク列の情報と地図DB141を用いて、後述する主要分岐点算出処理によって主要分岐点を算出し、主要分岐点DB117に格納する。部分経路生成部118は、主要分岐点DB117及びプローブDB115から部分経路を算出し、結果を部分経路DB119に格納する。
The main branch
分岐コスト生成部131では、部分経路DB119に格納されている部分経路を用いて、分岐原因から部分経路のコストを算出し、その結果を分岐コストDB132に格納する。分岐原因とは、渋滞時には右折する経路を走行する車両が多いとか、道に慣れている地元のドライバーは左折して走行することが多い等の、分岐割合が変化するドライバープロファイルの項目のことである。
The branch
経路探索装置12では、情報利用者14からの経路探索要求を通信機器121により受信し、この経路探索要求に含まれる経路の探索条件を取り出す。経路計算部123では、取り出された探索条件122に最適な経路を、分岐コストDB132,地図DB141,交通情報DB142に格納された情報を用いて算出する。通常、経路の算出ではダイクストラ法などの数学的な手法を用いて道路リンク単位の旅行時間(速度)あるいは、距離に基づいたコスト最小経路を探索する。ドライバー特性及び車両情報を考慮した本発明の経路探索では、分岐コストDB132からドライバー特性及び車両情報が反映された部分経路のコストを読み込み、このコストも加味してコスト最小経路を探索する。探索された経路は推奨経路データ124として出力され、通信機器121により経路探索を要求した情報利用者14へ送信される。
In the
次に主要分岐点算出処理を説明する。主要分岐点算出処理は、主要分岐点算出部116における、プローブDB115に格納されたプローブデータ及び地図DB141の情報により、地図DB141に格納された地図データのノードから主要分岐点を検出する処理である。主要分岐点とは、車両の分岐が多いノードを指す。主要分岐点を検出する場合には、特許文献1に開示されている方法により、蓄積したプローブデータを基に分岐が多く発生するノードを主要分岐点とする。または、道路種別が主要な国道,県道,高速道路に該当する道路リンクが交わるノードを主要分岐点としてもよい。あるいは、このような道路種別が主要な国道,県道,高速道路に該当する道路リンクが交わるノードのうち、特許文献1に開示されている方法により求めたプローブデータにおける分岐が多く発生するノードを主要分岐点としてもよい。
Next, main branch point calculation processing will be described. The main branch point calculation process is a process of detecting the main branch point from the node of the map data stored in the
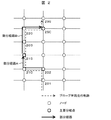
図2は、部分経路生成部118により求められる部分経路を説明する図である。部分経路は、主要分岐点から次の主要分岐点までの経路を意味する。プローブ車両が、点線で示すようにノードを201→202→210→215→203→220→250→299の順に走行したとする。このプローブ車両の走行軌跡の場合、走行軌跡が通過するノード、202,215,250が主要分岐点であるため、202→210→215と215→203→220→250の走行軌跡がそれぞれ部分経路Aと部分経路Bとなる。部分経路生成部118では、各プローブデータの走行軌跡について部分経路を求め、求められた部分経路はそれぞれプローブデータに対応したドライバープロファイルと共に部分経路DB119に保存される。
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining a partial route obtained by the
部分経路生成部118における部分経路作成の処理フローを図3に示す。部分経路作成処理は、プローブDB115が更新されたタイミングないし、例えば、1年,1月,1週間といった所定の処理周期で行われる処理により生成を開始する。処理が開始されると、まず、プローブDB115において全ての更新されたプローブデータを処理するループが開始される(S301)。ここではまず未処理の更新されたプローブデータをプローブDB115からレコード単位に読み込む(S302)。次に、読み込んだプローブデータに関連付けられたドライバープロファイルを同じプローブDB115から読み込む(S303)。そして主要分岐点DB117から主要分岐点のデータを読み込む(S304)。そしてプローブデータに含まれる全てのノードについてループ処理を開始する(S305)。ここでは、プローブデータに含まれる各ノードが、主要分岐点DB117から読み込んだ主要分岐点の何れかに該当するか判別を行う(S306)。この処理をプローブデータの全てのノードについて繰り返す(S307)。プローブデータの全てのノードについて判別が終了した後、主要分岐点と判別されたノード間の走行軌跡を部分経路として、部分経路DB119に処理対象のプローブデータに対応付けられているドライバープロファイルをこの部分経路に対応付けて保存する(S308)。以上の処理を更新されたプローブデータについて繰り返す(S309)。
FIG. 3 shows a processing flow for creating a partial path in the partial
分岐コスト生成部131では、部分経路DB119から読み込んだ部分経路について分岐原因によるコストをドライバープロファイルから算出する。例えば、ドライバープロファイルの渋滞度からコストを算出する処理の説明を図4に示す。部分経路DB119から、部分経路の始端と終端が共に一致する部分経路を抽出する。図4に示す例では、部分経路A,B,Cが抽出されたものとする。まず最初に、各部分経路について蓄積された走行数(部分経路を走行した回数)を求める。走行数は、部分経路DB119に格納されてデータのうち、部分経路が同じであるデータの個数である。この例の場合、蓄積された走行数が、それぞれ10,20,30であったとする。
The branch
次に、それぞれの走行数のデータをドライバープロファイルの渋滞度で分類する。即ち、渋滞度が順調,混雑,渋滞のそれぞれの場合に部分経路を通っていたプローブカーのデータ数を求める。この例の場合、渋滞度が順調の場合に部分経路Aを通ったプローブカーのデータが2回、部分経路Bを通ったプローブカーのデータが17回、部分経路Cを通ったプローブカーのデータが1回であったとする。渋滞度については、プローブカーの走行軌跡から速度を算出して、渋滞度(順調,混雑,渋滞)を判断してもよいし、他のセンサ情報もしくは、他の車両から生成されたプローブ交通情報から判断してもよい。 Next, the data on the number of travels is classified according to the congestion level of the driver profile. That is, the number of probe car data passing through the partial route is obtained when the degree of traffic congestion is smooth, congestion, or traffic jam. In this example, when the degree of congestion is smooth, the probe car data passing through the partial route A is 2 times, the probe car data passing through the partial route B is 17 times, and the probe car data passing through the partial route C. Is once. As for the degree of traffic congestion, the speed may be calculated from the travel trajectory of the probe car to determine the traffic congestion level (smooth, congested, traffic jam), or other sensor information or probe traffic information generated from other vehicles. You may judge from.
各渋滞度における、部分経路毎にプローブカーのデータを分類した後、分類前後の全体に占める割合を算出する。この例では部分経路Bに着目すると、分類前は、全体の33%のプローブカーが部分経路Bを通過していたのに対し、渋滞度が順調の状態で分類したデータでは、全体の80%の車両が部分経路Bを通過していたことになる。一方、部分経路Cに着目すると、分類前は、全体の33%のプローブカーが部分経路Cを通過していたのに対し、渋滞度が順調の状態で分類したデータでは、全体の5%の車両が部分経路Cを通過していたことになり、その割合は減っている。これは、道が空いているときに、最短経路となる部分経路Bを通過した方が、目的地までスムーズに早く到着できるといったケースが多いためと考えられる。 After classifying the probe car data for each partial route in each degree of congestion, the ratio of the total before and after classification is calculated. In this example, focusing on the partial route B, before the classification, 33% of the probe cars have passed the partial route B, whereas in the data classified with the degree of congestion being smooth, 80% of the total Vehicle has passed the partial route B. On the other hand, when focusing on the partial route C, before classification, 33% of the probe cars passed through the partial route C. On the other hand, in the data classified with the degree of congestion being smooth, 5% The vehicle has passed the partial route C, and the ratio is decreasing. This is considered to be because there are many cases in which a person who passes through the partial route B that is the shortest route can arrive at the destination smoothly and quickly when the road is empty.
経路探索の際には、この部分経路Bのような部分経路については、順調の場合に通常よりもコストを下げて選択されやすくすることにより、過去のドライバーのノウハウを反映したルート探索を行うことが可能となる。このための分岐コストの算出処理を以下に示す。ドライバープロファイルの各項目(渋滞度,年齢,性別,車種等)について、ドライバープロファイル項目番号をそれぞれ(1,2,3,…)と設定する。例えば、渋滞度(順調)のドライバープロファイル項目番号を1とする。部分経路Aの分類前の平均的な割合をRA、ドライバープロファイル項目番号iの項目による分類後の割合をRAiとすると、ドライバープロファイル項目番号iの項目に該当する場合の部分経路AのコストCAiは、(式1)となる。
CAi=(1−RAi+RA) …(式1)
When searching for a route, a route that reflects the know-how of past drivers is to be selected for a partial route such as this partial route B by making it easier to select at a lower cost than usual when the route is smooth. Is possible. The branch cost calculation process for this purpose is shown below. For each item of the driver profile (congestion level, age, gender, vehicle type, etc.), the driver profile item number is set to (1, 2, 3,...), Respectively. For example, the driver profile item number for the degree of traffic congestion (smooth) is set to 1. If the average ratio before classification of the partial path A is R A and the ratio after classification according to the item of the driver profile item number i is R Ai , the cost of the partial path A when it corresponds to the item of the driver profile item number i C Ai is expressed by (Formula 1).
C Ai = (1−R Ai + R A ) (Formula 1)
このドライバープロファイルの項目に該当する場合の部分経路におけるコストを、その部分経路へ分岐する場合のコストとして分岐コストと呼ぶ。この分岐コストは、ドライバープロファイルの項目による分類後の割合が大きくなれば、コストが小さくなるような算出方法とする。なお、分岐コストの算出方法は、分類後のコストが小さくなるような方法であれば、増えた走行数の逆数を用いるなどしてコストを算出しても良い。この分岐コストは、(式1)のように部分経路DB119に含まれる部分経路ごとに、ドライバープロファイルの項目数分算出する。
The cost in the partial path when corresponding to the item of the driver profile is referred to as a branching cost as a cost when branching to the partial path. This branching cost is calculated in such a way that the cost decreases as the proportion after classification according to the driver profile item increases. In addition, as long as the branch cost calculation method is a method that reduces the cost after classification, the cost may be calculated by using the reciprocal of the increased traveling number. This branching cost is calculated for the number of items in the driver profile for each partial path included in the
経路計算部123は、分岐コストDB132,地図DB141,交通情報DB142からそれぞれ、分岐コスト,経路長のコスト,旅行時間コストを読み込み、評価関数により求めたコストが最も小さくなる経路を推奨経路として算出する。リンク毎のコストを算出する評価関数は次の(式2)のようになる。
F=(W1×f1(経路長)+W2×f2(所要時間)+W3×f3(分岐コスト)…(式2)
The
F = (W 1 × f 1 (path length) + W 2 × f 2 (time required) + W 3 × f 3 (branch cost) (Equation 2)
ここでW1,W2,W3は、経路の探索条件に応じて定まる各項の重み付け係数であり、例えば、単に最短距離経路を求める場合には、W1=1、W2=0、W3=0となり、最短旅行時間経路を求める場合には、W1=0、W2=1、W3=0となる。f1( ),f2( ),f3( )は、それぞれ、経路長が短いほど、所要時間が短いほど、分岐コストが小さいほど、高い得点を出力する関数であり、例えば、道路種別毎にkとなる評価点を出力するために用いられる。なお、分岐コストの項は、過去の走行ノウハウを反映したコストであり、プローブデータが収集されていないリンクについては、ドライバープロファイルに依存しないものとして例えば分岐コスト=1として計算する。 Here, W 1 , W 2 , and W 3 are weighting factors for each term determined according to the route search condition. For example, when simply finding the shortest distance route, W 1 = 1, W 2 = 0, When W 3 = 0 and the shortest travel time route is obtained, W 1 = 0, W 2 = 1, and W 3 = 0. f1 (), f2 (), and f3 () are functions that output higher scores as the route length is shorter, the required time is shorter, and the branching cost is lower. Is used to output the evaluation score. The branch cost term is a cost reflecting past travel know-how, and a link for which probe data is not collected is calculated as a branch cost = 1, for example, assuming that it does not depend on the driver profile.
以上のようにして経路探索を行うことにより、従来の距離及び旅行時間コストの他に、経路長,所要時間等の一般的な評価基準に加えドライバー特性及び車両情報を考慮した、過去のドライバーのノウハウが反映された経路を生成することができるようになる。 By performing route search as described above, past driver's characteristics and vehicle information in addition to conventional distance and travel time cost, as well as general evaluation criteria such as route length and required time, etc. A route reflecting the know-how can be generated.
11 車載端末装置
12 経路探索装置
13 センタ装置
14 情報利用者
15 プローブカー
101 センサ
102 プローブデータ記憶部
103 ドライバープロファイル記憶部
104,111,121 通信機器
110 バッチ処理装置
112 プローブデータ
113 ドライバープロファイル
114 プローブデータ変換部
115 プローブDB
116 主要分岐点算出部
117 主要分岐点DB
118 部分経路生成部
119 部分経路DB
122 探索条件
123 経路計算部
124 推奨経路データ
131 分岐コスト生成部
132 分岐コストDB
140 共通DB
141 地図DB
142 交通情報DB
11 In-
116 Main branch
118 Partial
140 Common DB
141 Map DB
142 Traffic Information DB
Claims (4)
前記走行履歴の走行軌跡について、車両の分岐割合が所定値以上の交差点または主要道路の交差点を主要分岐点として求める主要分岐点算出部と、
前記走行軌跡を前記主要分岐点で区切った部分経路を求める部分経路生成手段と、
指定された出発地から目的地への経路探索を前記部分経路を用いて行う経路計算部を有する経路探索装置において、
経路選択の要因に関する分類項目についての運転者に関する情報を取得し、前記走行履歴と共に記憶したプローブ情報記憶部と、
前記部分経路生成手段により求めた前記部分経路について部分コストを求める部分コスト生成手段を備え、
前記部分コスト生成手段は、前記分類項目について、始端と終端が同じである複数の前記部分経路の全体における各々の前記部分経路の走行台数割合を求め、前記走行台数割合に応じた前記部分コストを前記部分経路毎に算出し、
前記経路計算部は、前記部分コストを用いて出発地から目的地までのコスト最小経路を計算することを特徴とする経路探索装置。 Collect driving histories from multiple vehicles,
For the travel locus of the travel history, a main branch point calculation unit for obtaining an intersection where the vehicle branch ratio is a predetermined value or more or an intersection of the main road as a main branch point;
Partial route generation means for obtaining a partial route obtained by dividing the travel locus by the main branch point;
In a route search device having a route calculation unit that performs a route search from a specified departure place to a destination using the partial route,
A probe information storage unit that acquires information about the driver about the classification items related to the route selection factor, and stores the information together with the travel history;
A partial cost generating means for determining a partial cost for the partial path determined by the partial path generating means;
The partial cost generation means obtains a traveling vehicle ratio of each of the partial routes in the whole of the plurality of partial routes having the same starting and ending points for the classification item, and calculates the partial cost corresponding to the traveling vehicle ratio. Calculate for each partial path ,
The route calculation unit, a route search unit and calculates the minimum cost route from the departure point to the destination using the partial costs.
始端と終端が同じである複数の前記部分経路全体における各々の前記部分経路の走行台数割合の差に応じて部分コストを算出することを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の経路探索装置。 The partial cost generating means includes
3. The route search device according to claim 1 , wherein the partial cost is calculated in accordance with a difference in a traveling number ratio of each of the partial routes in a plurality of the partial routes having the same start end and end point .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010220233A JP5452437B2 (en) | 2010-09-30 | 2010-09-30 | Route search device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010220233A JP5452437B2 (en) | 2010-09-30 | 2010-09-30 | Route search device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012073205A JP2012073205A (en) | 2012-04-12 |
| JP2012073205A5 JP2012073205A5 (en) | 2012-10-11 |
| JP5452437B2 true JP5452437B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 |
Family
ID=46169523
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010220233A Active JP5452437B2 (en) | 2010-09-30 | 2010-09-30 | Route search device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5452437B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9389089B2 (en) * | 2014-09-04 | 2016-07-12 | Visteon Global Technologies, Inc. | Determining a route based on a preference |
| CN109861923B (en) * | 2017-11-30 | 2022-05-17 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data scheduling method and TOR switch |
| WO2023148998A1 (en) * | 2022-02-07 | 2023-08-10 | 日立Astemo株式会社 | Electronic control device and vehicle control method |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4442647B2 (en) * | 2007-06-22 | 2010-03-31 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Route search method and route search system |
| JP4554653B2 (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2010-09-29 | クラリオン株式会社 | Route search method, route search system, and navigation apparatus |
| JP4985258B2 (en) * | 2007-09-14 | 2012-07-25 | 株式会社デンソー | Route guidance system |
-
2010
- 2010-09-30 JP JP2010220233A patent/JP5452437B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012073205A (en) | 2012-04-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5900454B2 (en) | Vehicle lane guidance system and vehicle lane guidance method | |
| US8694242B2 (en) | Traveling information creating device, traveling information creating method and program | |
| JP5350703B2 (en) | Traffic information generating apparatus, computer program, and traffic information generating method | |
| US20080120021A1 (en) | Guide Route Search Device, Guide Route Search Method, and Computer Program Thereof | |
| JP4983660B2 (en) | Navigation system and route search method | |
| US11022457B2 (en) | Method, apparatus, and computer program product for lane-level route guidance | |
| CN102119320A (en) | Travel route evaluation system and travel route evaluation program | |
| JP5956321B2 (en) | Destination proposal system, destination proposal method, and program | |
| US20070021910A1 (en) | Navigation apparatus | |
| JP2008242674A (en) | Traffic information system | |
| TW201031893A (en) | Method for computing an energy efficient route | |
| JP6261636B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program | |
| JP2017138179A (en) | Navigation system and center device | |
| WO2011046185A1 (en) | Vehicle-mounted device, travel characteristic data generation device, and vehicle-mounted information system | |
| JP4501619B2 (en) | Navigation system | |
| US8510036B2 (en) | Information providing device and information providing system | |
| JP2020008436A (en) | Route information assistance device and route information assistance system | |
| JP4762726B2 (en) | Navigation server and navigation device | |
| JP2014066655A (en) | Route search device and route search method | |
| JP5452437B2 (en) | Route search device | |
| JP2014009948A (en) | Route information service system and navigation device | |
| JP5355826B2 (en) | Information presentation device and navigation device | |
| WO2010113552A1 (en) | Expert route generation server and navigation device | |
| JP7264859B2 (en) | Navigation system, recommended method of its search route, and program | |
| JP4138828B2 (en) | NAVI SERVER, NAVI DEVICE, AND NAVI SYSTEM |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20120518 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120829 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120829 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120829 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130820 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131021 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131021 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20131203 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20131227 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5452437 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |