JP5446134B2 - Sound absorbing structure - Google Patents
Sound absorbing structure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5446134B2 JP5446134B2 JP2008146826A JP2008146826A JP5446134B2 JP 5446134 B2 JP5446134 B2 JP 5446134B2 JP 2008146826 A JP2008146826 A JP 2008146826A JP 2008146826 A JP2008146826 A JP 2008146826A JP 5446134 B2 JP5446134 B2 JP 5446134B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vibrating body
- sound absorbing
- sound
- absorbing structure
- air layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Soundproofing, Sound Blocking, And Sound Damping (AREA)
Description
本発明は、音を吸音する技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for absorbing sound.
特許文献1に開示された吸音構造のように、板状(または膜状)の振動体と、この振動体の背後の空気層により音を吸収する吸音構造(以下、板・膜振動型吸音構造という)がある。この板・膜振動型吸音構造においては、振動体の質量成分と空気層のバネ成分によってバネマス系の吸音メカニズムが形成されて音が吸音される。 As in the sound absorbing structure disclosed in Patent Document 1, a sound absorbing structure that absorbs sound by a plate-like (or film-like) vibrating body and an air layer behind the vibrating body (hereinafter referred to as a plate / membrane vibrating type sound absorbing structure) Called). In this plate / membrane vibration type sound absorption structure, a sound absorption mechanism of a spring mass system is formed by the mass component of the vibrating body and the spring component of the air layer, and the sound is absorbed.
ところで、板・膜振動型吸音構造においては、空気層の厚さや振動体の素材を替えることにより、吸音する音の周波数を変えることができる。しかしながら、吸音率が高い周波数帯が狭いため、幅広い帯域で効率良く吸音することができないという問題がある。 By the way, in the plate / membrane vibration type sound absorbing structure, the frequency of the sound to be absorbed can be changed by changing the thickness of the air layer or the material of the vibrating body. However, since the frequency band with a high sound absorption rate is narrow, there is a problem that sound cannot be efficiently absorbed in a wide band.
本発明は、上述した背景の下になされたものであり、板・膜振動型の吸音構造において、吸音率が高い周波数帯を広げて効率良く吸音する技術を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made under the above-described background, and an object of the present invention is to provide a technique for efficiently absorbing sound by expanding a frequency band having a high sound absorption coefficient in a plate / membrane vibration type sound absorbing structure.
上述した課題を解決するために本発明は、複数の板状または膜状の振動体と、中空部を備える管の形状の側壁とを有し、前記中空部を塞ぐように前記振動体が前記側壁に固着され、前記複数の振動体は、非平行で配置され、距離をおいて表面が他の振動体の表面に面し、前記振動体と空気層とが交互に積層された吸音構造体を提供する。 In order to solve the above-described problem, the present invention has a plurality of plate-like or membrane-like vibrators and a side wall in the shape of a tube having a hollow portion, and the vibrator has the above-described shape so as to close the hollow portion. The sound absorbing structure fixed to the side wall, wherein the plurality of vibrators are arranged non-parallel, the surface faces the surface of another vibrator at a distance, and the vibrators and air layers are alternately stacked. I will provide a.
本発明においては、前記振動体の数が3つ以上であってもよい。
また、本発明においては、前記複数の振動体の厚さが各々異なっていてもよい。
また、本発明においては、前記空気層に多孔質吸音材を有していてもよい。
また、本発明においては、空気層と交互に重なっている前記複数の振動体のうち最も外側にある2つの振動体の一方に対して前記振動体より高い剛性を有する非振動体が面していてもよい。
In the present invention, the number of the vibrators may be three or more.
In the present invention, the plurality of vibrators may have different thicknesses.
In the present invention, the air layer may have a porous sound absorbing material.
In the present invention, the non-vibrating body having higher rigidity than the vibrating body faces one of the two outermost vibrating bodies among the plurality of vibrating bodies that alternately overlap the air layer. May be.
本発明によれば、板・膜振動型の吸音構造において、吸音率が高い周波数帯を広げて効率良く吸音することができる。 According to the present invention, in a plate / membrane vibration type sound absorbing structure, it is possible to efficiently absorb sound by expanding a frequency band having a high sound absorption coefficient.
[第1実施形態]
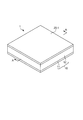
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る吸音構造体1の外観図、図2は、吸音構造体1の分解斜視図、図3は吸音構造体1のA−A線断面矢視図である。なお、図面においては、本実施形態の構成を分かりやすく図示するために、吸音構造体1の寸法を実際の寸法とは異ならせてある。
[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 is an external view of a sound absorbing structure 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view of the sound absorbing structure 1, and FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line AA of the sound absorbing structure 1. is there. In the drawings, the dimensions of the sound absorbing structure 1 are different from the actual dimensions in order to illustrate the configuration of the present embodiment in an easy-to-understand manner.
(各部の構成)
吸音構造体1は、図に示したように大別すると筐体10、第1振動体20−1および第2振動体20−2で構成されている。
金属板で形成されている筐体10は、正方形で板状の底面部11と、角管の形状で断面形状が正方形の側壁12とを有している。なお、本実施形態においては筐体10は金属で形成されているが、素材は金属に限定されず、第1振動体20−1と第2振動体20−2を支持して前記第1振動体20−1及び第2振動体20−2に振動を発現させるものであれば、金属以外の合成樹脂や木質材料、繊維板など他の素材であってもよい。
(Configuration of each part)
The sound absorbing structure 1 is roughly composed of a
A
第1振動体20−1は、ポリエチレンを薄い膜状にしたものであり、形状が正方形となっている。第1振動体20−1は、弾性を有しており、力(音圧)を加えると変形し、弾性により復元力を発生して振動する。なお、本実施形態においては、第1振動体20−1の素材はポリエチレンとしているが、素材はポリエチレンに限定されず、弾性を有し振動が生じるのであればポリエチレン以外の合成樹脂、紙、金属、繊維板など他の素材であってもよい。 The 1st vibrating body 20-1 makes polyethylene thin film shape, and the shape is a square. The first vibrating body 20-1 has elasticity, deforms when a force (sound pressure) is applied, and vibrates by generating a restoring force by elasticity. In the present embodiment, the material of the first vibrating body 20-1 is polyethylene, but the material is not limited to polyethylene. If the material has elasticity and vibration occurs, synthetic resin other than polyethylene, paper, metal Other materials such as fiberboard may be used.
第2振動体20−2は、ABS(Acrylonitrile:アクリロニトリル、Butadiene:ブタジエン、Styrene:スチレンの共重合合成樹脂)樹脂を板状にしたものである。第2振動体20−2は、形状が正方形となっており、その面積は側壁12の中空部の断面積と同じとなっている。そして、第2振動体20−2も弾性を有しており、力(音圧)を加えると変形し、弾性により復元力を発生して振動する。なお、本実施形態においては、第2振動体20−2の素材はABS樹脂としているが、素材はABS樹脂に限定されず、弾性を有し振動が生じるのであればABS樹脂以外の合成樹脂、紙、金属、繊維板など他の素材であってもよい。
The second vibrating body 20-2 is a plate of ABS (Acrylonitrile: acrylonitrile, Butadiene: butadiene, Styrene: styrene copolymer synthetic resin) resin. The second vibrating body 20-2 has a square shape, and the area thereof is the same as the cross-sectional area of the hollow portion of the
(全体構成)
吸音構造体1においては、側壁12の一方(裏側)の開口部に底面部11が固着され、他方(表側)の開口部に第1振動体20−1が固着されて底面部11と第1振動体20−1が平行となっている。また、側壁12の内側であって底面部11から第1振動体20−1側へ所定距離離れた位置には、底面部11と平行となるようにして第2振動体20−2が側壁12に固着されている。
(overall structure)
In the sound absorbing structure 1, the
これにより、第1振動体20−1、側壁12および第2振動体20−2とで囲まれて第1振動体20−1の直ぐ背後には長方体の形状に区画された第1空気層30−1が形成されており、第2振動体20−2、側壁12および底面部11とで囲まれて第2振動体20−2の直ぐ背後には長方体の形状に区画された第2空気層30−2が形成されている。
なお、本実施形態において第1空気層30−1と第2空気層30−2は密閉されているが、側壁12や底面部11に孔を設けて第1空気層30−1や第2空気層30−2が吸音構造体1の外側の空間と通じるようにしてもよい。
As a result, the first air surrounded by the first vibrating body 20-1, the
In addition, in this embodiment, although the 1st air layer 30-1 and the 2nd air layer 30-2 are sealed, the hole is provided in the
このように構成された吸音構造体1においては、第1振動体20−1の質量成分、第2振動体20−2の質量成分、第1空気層30−1のバネ成分および第2空気層30−2のバネ成分によって、以下(1)〜(5)に示したように複数のバネマス系の吸音メカニズムがそれぞれ単独または相互に連成して吸音構造体1の吸音メカニズムが形成される。
(1)第1振動体20−1と第1空気層30−1で形成される吸音メカニズム。
(2)第2振動体20−2と第2空気層30−2で形成される吸音メカニズム。
(3)第1振動体20−1と、第1空気層30−1および第2空気層30−2が一体となった空気層で形成される吸音メカニズム。
(4)第2振動体20−2と第1空気層30−1で形成される吸音メカニズム。
(5)第1振動体20−1と第2振動体20−2と第2空気層30−2で形成される吸音メカニズム。
また、第1振動体20−1と第2振動体20−2は弾性を有しており、これらの振動体が屈曲振動する場合には、屈曲振動(固有振動)による屈曲系の吸音メカニズムも形成される。なお、本実施形態においては底面部11及び筐体10は第1振動体20−1と第2振動体20−2より高い剛性を有しており、振動しない部材(非振動体)として機能する。
In the sound absorbing structure 1 configured as described above, the mass component of the first vibrating body 20-1, the mass component of the second vibrating body 20-2, the spring component of the first air layer 30-1, and the second air layer. As shown in the following (1) to (5), the sound absorbing mechanism of the sound absorbing structure 1 is formed by a plurality of spring mass sound absorbing mechanisms individually or in combination with each other by the spring component 30-2.
(1) A sound absorbing mechanism formed by the first vibrating body 20-1 and the first air layer 30-1.
(2) A sound absorbing mechanism formed by the second vibrating body 20-2 and the second air layer 30-2.
(3) A sound absorbing mechanism formed by an air layer in which the first vibrating body 20-1 is integrated with the first air layer 30-1 and the second air layer 30-2.
(4) A sound absorbing mechanism formed by the second vibrating body 20-2 and the first air layer 30-1.
(5) A sound absorbing mechanism formed by the first vibrating body 20-1, the second vibrating body 20-2, and the second air layer 30-2.
Further, the first vibrating body 20-1 and the second vibrating body 20-2 have elasticity, and when these vibrating bodies vibrate, the bending sound absorption mechanism by bending vibration (natural vibration) is also provided. It is formed. In the present embodiment, the
ここで、(1)〜(5)の各吸音メカニズムでは、吸音メカニズム毎に吸音率のピークが発現するが、各吸音メカニズムは質量成分又はバネ成分が各々異なるため、吸音率がピークとなる音の周波数も各吸音メカニズムで異なる。つまり、吸音構造体1では複数の周波数で吸音率のピークが発現し、広帯域で効率よく吸音を行うこととなる。 Here, in each of the sound absorption mechanisms (1) to (5), a peak of the sound absorption coefficient appears for each sound absorption mechanism, but each sound absorption mechanism has a different mass component or spring component. The frequency of is also different for each sound absorption mechanism. That is, in the sound absorbing structure 1, the sound absorption coefficient peaks appear at a plurality of frequencies, and sound is efficiently absorbed in a wide band.
図4は、吸音構造体1の垂直入射吸音率のオクターブ分析(1/3オクターブバンド)の測定結果を示したグラフ(図4の(2))である(垂直入射吸音率の測定は、JIS A 1405-2(音響管による吸音率及びインピーダンスの測定−第2部:伝達関数法)による)。この吸音率の測定においては、吸音構造体1は、図5(a)に示したように第1振動体20−1の厚さが0.85[mm]、第1空気層30−1の厚さが30[mm]、第2振動体20−2の厚さが3[mm]、第2空気層30−2の厚さが30[mm]となっており、第1振動体20−1の面密度は第2振動体20−2の面密度より小さく設定され、音波が入射する表側の第1振動体20−1の共振周波数が、裏側の第2振動体20−2の共振周波数より相対的に高く設定されている。 FIG. 4 is a graph ((2) in FIG. 4) showing the measurement result of the octave analysis (1/3 octave band) of the normal incident sound absorption coefficient of the sound absorbing structure 1 (measurement of the normal incident sound absorption coefficient is JIS A 1405-2 (Acoustic tube sound absorption coefficient and impedance measurement-Part 2: Transfer function method). In the measurement of the sound absorption coefficient, the sound absorbing structure 1 has a thickness of the first vibrating body 20-1 of 0.85 [mm] and a first air layer 30-1 as shown in FIG. The thickness is 30 [mm], the thickness of the second vibrating body 20-2 is 3 [mm], the thickness of the second air layer 30-2 is 30 [mm], and the first vibrating body 20- 1 is set to be smaller than the surface density of the second vibrating body 20-2, and the resonance frequency of the first vibrating body 20-1 on the front side on which the sound wave enters is the resonance frequency of the second vibrating body 20-2 on the back side. It is set relatively higher.
なお、図4においては比較のため、第2振動体20−2および第2空気層30−2を備えない他の吸音構造体(図5(b)、図5(c))の垂直入射吸音率の測定結果のグラフも示している。
図5(b)に示した吸音構造体は、第2振動体20−2を備えず、第1振動体20−1の厚さが0.85[mm]、第1振動体20−1の背後の空気層の厚さが30[mm]であり、図5(c)に示した吸音構造体は、第2振動体20−2を備えず、第1振動体20−1の素材をABS樹脂に替えてその厚さを3[mm]とし、第1振動体20−1の背後の空気層の厚さを30[mm]としたものである。
For comparison, in FIG. 4, the normal incident sound absorption of other sound absorbing structures (FIGS. 5B and 5C) that do not include the second vibrating body 20-2 and the second air layer 30-2. A graph of the rate measurement results is also shown.
The sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5B does not include the second vibrating body 20-2, the thickness of the first vibrating body 20-1 is 0.85 [mm], and the first vibrating body 20-1 The thickness of the air layer behind is 30 [mm], and the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5C does not include the second vibrating body 20-2, and the material of the first vibrating body 20-1 is ABS. Instead of resin, the thickness is 3 [mm], and the thickness of the air layer behind the first vibrating body 20-1 is 30 [mm].
図5(b)に示した吸音構造体の場合、第1振動体20−1の質量成分と空気層のバネ成分とで吸音メカニズムが形成され、音波が第1振動体20−1に到達すると吸音がされる。図4の(1)のグラフが図5(b)に示した吸音構造体の測定結果であるが、この吸音構造体においては、400[Hz]付近が吸音率のピークとなっている。一方、250[Hz]以下では吸音率が低く、広い帯域で吸音が行えていないことが分かる。 In the case of the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5B, when the sound absorbing mechanism is formed by the mass component of the first vibrating body 20-1 and the spring component of the air layer, and the sound wave reaches the first vibrating body 20-1. Sound is absorbed. The graph of (1) in FIG. 4 shows the measurement result of the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5B. In this sound absorbing structure, the sound absorption coefficient peak is in the vicinity of 400 [Hz]. On the other hand, at 250 [Hz] or less, the sound absorption coefficient is low, and it can be seen that sound absorption cannot be performed in a wide band.
また、図5(c)に示した吸音構造体の場合、図4の(3)のグラフが図5(c)に示した吸音構造体の測定結果であるが、この吸音構造体においては、250[Hz]付近で吸音率のピークが表れているが、これより高いまたは低い周波数では吸音率が低くなっている。つまり、250[Hz]付近については吸音が行えるものの、これ以外の周波数帯については吸音率が低く、広い帯域で吸音が行えていないことが分かる。 In the case of the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5C, the graph of FIG. 4C is the measurement result of the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5C. In this sound absorbing structure, The peak of the sound absorption coefficient appears in the vicinity of 250 [Hz], but the sound absorption coefficient is low at frequencies higher or lower than this. That is, it can be seen that although sound absorption can be performed in the vicinity of 250 [Hz], the sound absorption rate is low in other frequency bands and sound absorption cannot be performed in a wide band.
一方、図5(a)に示した本実施形態に係る吸音構造体1の場合、図4の(2)のグラフに示されているように235[Hz]付近で吸音率のピークが表れつつ、315[Hz]以上においても図5(b)に示した吸音構造体と同等の吸音率が得られている。従って、図5(b)や図5(c)のように振動体と空気層が一つの吸音構造と比較して、図5(b)や図5(c)の吸音特性を包含する広い周波数帯で吸音がなされていることが分かる。 On the other hand, in the case of the sound absorbing structure 1 according to the present embodiment shown in FIG. 5A, a peak of the sound absorption coefficient appears near 235 [Hz] as shown in the graph of FIG. 4B. Even at 315 [Hz] or higher, a sound absorption coefficient equivalent to that of the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 5B is obtained. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 5B and FIG. 5C, compared with a sound absorbing structure in which the vibrating body and the air layer are one, a wide frequency including the sound absorption characteristics of FIG. 5B and FIG. 5C. It can be seen that sound is absorbed by the belt.
なお、自動車において車室を構成する各種パネルなどの境界面や、一般家屋、ビルの会議室や居室などの部屋、防音室、音楽室、ホール、劇場、音響機器のリスニングルームなどの音響室など各種部屋の境界面(壁、床、天井など)において、吸音構造体1の第1振動体20−1を音場に向け、底面部11を境界面に接触させて固定して設置すると、各振動体の共振周波数以外の音波は、例えば以下の(a)〜(d)ように各振動体を透過する成分と各振動体に反射される成分に別れる。
(a)第1振動体20−1で反射される反射波。
(b)第1振動体20−1を透過して第2振動体20−2で反射され、第1振動体20−1を透過する反射波。
(c)第1振動体20−1と第2振動体20−2とを透過して底面部11で反射され第2振動体20−2と第1振動体20−1を透過する反射波。
(d)第1振動体20−1を透過して第2振動体20−2で反射され、第1振動体20−1で再び反射された後、第2振動体20−2で再度反射されて第1振動体20−1を透過する反射波。
これらの反射波は、少しずつ位相がずれて音場に到達する。すると、これら位相がずれた反射波が重畳された音場においては、音圧分布の偏り(定在波)が緩和されるため、吸音だけでなく車室や音響室などの部屋の騒音を低減することもできる。また、オーディオや楽音、音声などの音質を改善することもできる。
In addition, the boundary surfaces of various panels that make up the cabin in automobiles, rooms such as general houses, building conference rooms and living rooms, soundproof rooms, music rooms, halls, theaters, acoustic rooms such as listening rooms for audio equipment, etc. When the first vibration body 20-1 of the sound absorbing structure 1 is directed to the sound field on the boundary surfaces (walls, floors, ceilings, etc.) of various rooms, Sound waves other than the resonance frequency of the vibrating body are divided into, for example, components that pass through each vibrating body and components that are reflected by each vibrating body as shown in (a) to (d) below.
(A) A reflected wave reflected by the first vibrating body 20-1.
(B) A reflected wave that passes through the first vibrating body 20-1, is reflected by the second vibrating body 20-2, and passes through the first vibrating body 20-1.
(C) A reflected wave that passes through the first vibrating body 20-1 and the second vibrating body 20-2, is reflected by the
(D) After passing through the first vibrating body 20-1, reflected by the second vibrating body 20-2, reflected again by the first vibrating body 20-1, and then reflected again by the second vibrating body 20-2. The reflected wave which permeate | transmits the 1st vibrating body 20-1.
These reflected waves are gradually shifted in phase and reach the sound field. Then, in the sound field where these reflected waves that are out of phase are superimposed, the bias of the sound pressure distribution (standing wave) is alleviated, reducing not only the sound absorption but also the noise in the rooms such as the vehicle compartment and the acoustic room. You can also It is also possible to improve sound quality such as audio, musical sound, and voice.
また、比較的容積の小さい車室などにおいては各種騒音(ロードノイズ、風切り音、エンジン音など)が入射することにより、車室内に孤立した固有振動モードが励起されやすく、特定の周波数帯域で騒音が大きくなるが、吸音構造体1によって少しずつ位相のずれた反射波が形成されて車室内に再入射すると車室内の孤立した固有振動モードが緩和されるため、車室の騒音を低減することもできる。 Also, in a cabin with a relatively small volume, various noises (road noise, wind noise, engine noise, etc.) are incident, so that an isolated natural vibration mode is easily excited in the cabin, and noise is generated in a specific frequency band. However, when a reflected wave that is gradually shifted in phase is formed by the sound absorbing structure 1 and re-enters the vehicle interior, the isolated natural vibration mode in the vehicle interior is relaxed, so that the vehicle interior noise is reduced. You can also.
なお、吸音構造体1においては、第1空気層30−1または第2空気層30−2にグラスウール、フェルト、発泡ポリウレタン、不織布など多孔質の吸音材を配置し、上述したバネマス系の吸音メカニズムが吸音する音をさらに広帯域に吸音するようにしてもよい。 In the sound-absorbing structure 1, a porous sound-absorbing material such as glass wool, felt, foamed polyurethane, and nonwoven fabric is disposed in the first air layer 30-1 or the second air layer 30-2, and the above-described spring mass-based sound absorbing mechanism. The sound absorbed by the sound may be absorbed in a wider band.
[第2実施形態]
次に、本発明の第2実施形態に係る吸音構造体1Aについて説明する。
吸音構造体1Aは、第1実施形態の吸音構造体1と同様に、底面部11と側壁12で構成された筐体10、第1振動体20−1および第2振動体20−2を備えており、外観については第1実施形態の吸音構造体1と同じである。吸音構造体1Aが第1実施形態の吸音構造体1と異なる点は、図6(吸音構造体1Aの断面図)に示したように側壁12の内側に複数の振動体を有している点である。なお、図面においては、本実施形態の構成を分かりやすく図示するために、吸音構造体1の寸法を実際の寸法とは異ならせてある。また、下の説明においては、第1実施形態と同じ構成の部材については第1実施形態と同じ符号を付し、その詳細については説明を省略する。
[Second Embodiment]
Next, the
Similar to the sound absorbing structure 1 of the first embodiment, the sound absorbing structure 1 </ b> A includes a
第3振動体20−3、第4振動体20−4および第5振動体20−5は、ポリエチレンを薄い膜状にしたものであり、形状が第2振動体20−2と同じであるが各々厚さが異なっている。第3振動体20−3〜第5振動体20−5は、弾性を有しており、力を加えると変形し、弾性により復元力を発生して振動する。なお、本実施形態においては、第3振動体20−3〜第5振動体20−5の素材はポリエチレンとしているが、素材はポリエチレンに限定されず、弾性を有し振動が生じるのであればポリエチレン以外の合成樹脂、紙、金属、繊維板など他の素材であってもよい。 The third vibrating body 20-3, the fourth vibrating body 20-4, and the fifth vibrating body 20-5 are made of polyethylene in a thin film shape, and have the same shape as the second vibrating body 20-2. Each has a different thickness. The third vibrating body 20-3 to the fifth vibrating body 20-5 have elasticity, and are deformed when a force is applied, and vibrate by generating a restoring force by the elasticity. In the present embodiment, the material of the third vibrating body 20-3 to the fifth vibrating body 20-5 is polyethylene. However, the material is not limited to polyethylene, and polyethylene can be used if it has elasticity and vibrations are generated. Other materials such as synthetic resin, paper, metal, fiberboard, etc. may be used.
吸音構造体1Aにおいては、第1実施形態と同様に側壁12の一方の開口部に底面部11が固着され、もう一方の開口部に第1振動体20−1が固着されて底面部11と第1振動体20−1が平行となっている。また、側壁12の内側においては、底面部11と平行で底面部11から距離をおいて第2振動体20−2が側壁12に固着されている。さらに側壁12の内側においては、第2振動体20−2から距離をおいて平行に第3振動体20−3が固着され、第3振動体20−3から距離をおいて平行に第4振動体20−4が固着され、第4振動体20−4から距離をおいて平行に第5振動体20−5が固着されている。
In the
これにより、筐体10の内側が区画され、第1振動体20−1の直ぐ背後に第1空気層30−11、第5振動体20−5の直ぐ背後に第2空気層30−12、第4振動体20−4の直ぐ背後に第3空気層30−13、第3振動体20−3の直ぐ背後に第4空気層30−14、第2振動体20−2の直ぐ背後に第5空気層30−15が形成されている。
なお、本実施形態において各空気層は密閉されているが、側壁12や底面部11に孔を設けて各空気層が吸音構造体1Aの外側の空間と通じるようにしてもよい。
Thus, the inside of the
In the present embodiment, each air layer is hermetically sealed, but holes may be provided in the
このように構成された吸音構造体1Aにおいても、各振動体および各空気層の組み合わせにより共振周波数の異なる複数のバネマス系の吸音メカニズムが形成され、吸音メカニズム毎に吸音率のピークが発現する。ここで各吸音メカニズムは質量成分又はバネ成分が各々異なるため、吸音率がピークとなる音の周波数も各吸音メカニズムで異なる。つまり、吸音構造体1Aにおいても広帯域で効率よく吸音を行うことができる。
Also in the
また、各種部屋の境界面において第1振動体20−1を音場に向け、底面部11を境界面に接触させて固定して設置すると、吸音構造体1と同様にして複数の振動体により少しずつ位相のずれた多重反射波が形成される。そして、この反射波が音場に到達すると音場における定在波や部屋の固有振動モードが緩和され、吸音だけでなく車室や音響室などの部屋の騒音を低減することもできる。
Further, when the first vibrating body 20-1 is directed to the sound field at the boundary surfaces of various rooms and the
なお、本実施形態においては、第1振動体20−1〜第5振動体20−5について、それぞれ異なる素材としてもよい。また、第1振動体20−1〜第5振動体20−5について、全て同じ素材とする一方、振動体毎に厚さを異ならせるようにしてもよい。また、側壁12の内側に位置する第2振動体20−2〜第5振動体20−5については、側壁12の断面形状である正方形とは異なる形状(長方形、多角形など)としてもよく、また、第2振動体20−2〜第5振動体20−5毎に形状を異ならせてもよい。また、本実施形態においても、底面部11と第2振動体20−2との間に多孔質の吸音材を配置してもよい。
In the present embodiment, the first vibrating body 20-1 to the fifth vibrating body 20-5 may be different materials. In addition, the first vibrating body 20-1 to the fifth vibrating body 20-5 may be made of the same material, but may have different thicknesses for each vibrating body. Further, the second vibrating body 20-2 to the fifth vibrating body 20-5 located inside the
[第3実施形態]
次に本発明の第3実施形態に係る吸音構造体1Bについて説明する。
図7は、吸音構造体1Bの外観図、図8は、吸音構造体1Bの分解斜視図、図9は吸音構造体1BのB−B線断面矢視図である。なお、図面においては、本実施形態の構成を分かりやすく図示するために、吸音構造体1Bの寸法を実際の寸法とは異ならせてある。
[Third Embodiment]
Next, a
7 is an external view of the
(各部の構成)
吸音構造体1Bは、図に示したように側壁12、第1振動体20−11および第2振動体20−12で構成されている。
側壁12は、第1実施形態の側壁12と同じ構成である。第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12は、合成樹脂を薄い膜状にしたものであり、形状が正方形となっている。第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12は、弾性を有しており、力を加えると変形し、弾性により復元力を発生して振動する。
(Configuration of each part)
As shown in the drawing, the
The
(全体構成)
吸音構造体1Bにおいては、側壁12の一方の開口部に第2振動体20−12が固着され、もう一方の開口部に第1振動体20−11が固着されて第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12が平行となっている。
そして、吸音構造体1Bは、いずれか一方の振動体が車室や音響室などの部屋の境界面の側に向けられ、境界面の側に向けられた振動体と境界面との間に空間(空気層)が形成されるようにして配置される。
なお、吸音構造体1Bを境界面から離れた位置に配置する方法としては、一例として柱状の支持部材の一方の端部を吸音構造体1Bの四隅に固着し、支持部材のもう一方の端部を境界面に固着して振動体と境界面との間に空間を形成する方法などがある。
(overall structure)
In the
In the
In addition, as a method of disposing the
図9のように吸音構造体1Bを境界面から離して配置した吸音構造では、第1振動体20−11、側壁12および第2振動体20−12とで囲まれて第1振動体20−11の背後には長方体の形状に区画された第1空気層30−1が位置し、第2振動体20−12と境界面との間に第2空気層30−2が位置する。
なお、本実施形態において第1空気層30−1は密閉されているが、側壁12に孔を設けて第1空気層30−1が吸音構造1の外側の空間と通じるようにしてもよい。
In the sound absorbing structure in which the
In the present embodiment, the first air layer 30-1 is hermetically sealed, but a hole may be provided in the
吸音構造体1Bを境界面から離した構成の吸音構造においても、第1振動体20−11および第2振動体20−12という2つの振動体と、第1空気層30−1および第2空気層30−2という2つの空気層があるため、第1実施形態と同様にバネマス系の吸音メカニズムが複数形成される。
そして、複数の吸音メカニズム毎に吸音率のピークが発現し、各吸音メカニズムでは質量成分やバネ成分が各々異なるため、吸音率がピークとなる音の周波数帯も各吸音メカニズムで異なる。つまり、図9のように吸音構造体1Bを境界面から離れた位置に配置した吸音構造においても、広帯域で効率よく吸音を行うことができる。
Also in the sound absorbing structure in which the
The sound absorption rate peaks for each of the plurality of sound absorption mechanisms, and each sound absorption mechanism has a different mass component and spring component. Therefore, the frequency band of the sound at which the sound absorption rate reaches a peak also differs for each sound absorption mechanism. That is, even in the sound absorbing structure in which the
図10の(1)のグラフは、吸音構造体1Bにおいて、第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12の素材をPVC(polyvinyl chloride:ポリ塩化ビニル)として厚さを0.5[mm]とし、第1空気層30−1の縦と横の大きさが100[mm]×100[mm]で厚さが10[mm]であり、第2空気層30−2の厚さが20[mm]の吸音構造(図11(a))のランダム入射吸音率のオクターブ分析(1/3オクターブバンド)の測定結果を示したグラフである。
なお、比較のため図10においては、第1振動体20−11の素材をPVCとして厚さを0.5[mm]とし、第2振動体20−12に替えて底面部11を側壁12に固着し、第1空気層30−1の縦と横の大きさが100[mm]×100[mm]で第1空気層30−1の厚さが30[mm]であり、第2空気層30−2を備えない吸音構造(図11(b))のランダム入射吸音率の測定結果のグラフ(図10の(2)のグラフ)も示している。
The graph of (1) in FIG. 10 shows that in the
For comparison, in FIG. 10, the material of the first vibrating body 20-11 is PVC, the thickness is 0.5 [mm], and the
図11(b)に示したように、振動体が第1振動体20−11のみで第1空気層30−1の厚さを厚くした場合には、400[Hz]付近で吸音率のピークが表れていることが分かる。
一方、図11(a)に示した吸音構造の場合には、図11(b)のように第1空気層30−1の厚さを厚くした構成と比較すると、400[Hz]に加えて315[Hz]付近でも吸音率が高くなっており、図11(b)の構成より広い帯域で吸音が行えていることが分かる。
また、図10(a)に示した本実施形態に係る吸音構造では、図11(b)に示した吸音構造体より薄い吸音構造体で低域の音を吸音することが可能となっており、小さな体積の吸音構造体で効率良く吸音ができるという効果も得られる。
As shown in FIG. 11B, when the vibration body is only the first vibration body 20-11 and the thickness of the first air layer 30-1 is increased, the sound absorption coefficient peak is around 400 [Hz]. It can be seen that appears.
On the other hand, in the case of the sound absorption structure shown in FIG. 11A, in addition to 400 [Hz] as compared with the configuration in which the thickness of the first air layer 30-1 is increased as shown in FIG. The sound absorption rate is high even in the vicinity of 315 [Hz], and it can be seen that sound absorption can be performed in a wider band than the configuration of FIG.
Further, in the sound absorbing structure according to the present embodiment shown in FIG. 10A, it is possible to absorb low-frequency sound with a sound absorbing structure thinner than the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. In addition, it is possible to obtain an effect that sound absorption can be efficiently performed with a sound absorbing structure having a small volume.
なお、吸音構造体1Bを各種部屋の境界面から離れた位置に配置した吸音構造でも、各振動体の共振周波数以外の音波は、各振動体を透過する成分と各振動体に反射される成分に別れ、吸音構造体1と同様にして少しずつ位相のずれた多重反射波が形成される。そして、この反射波が音場に到達すると、音場における定在波や部屋の固有振動モードが緩和され、吸音だけでなく車室や音響室などの部屋の騒音を低減することもできる。
Even in the sound absorbing structure in which the
(第3実施形態の変形例)
上述した吸音構造体1Bにおいては、第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12との間に多孔質の吸音材を配置するようにしてもよい。
(Modification of the third embodiment)
In the
上述した吸音構造体1Bでは、第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12が平行となっているが、図12(a)に示したように、断面で見て第1振動体20−11が第2振動体20−12に対して所定の角度を為して非平行となるようにしてもよい。
なお、図12(a)に示した吸音構造体を配置する場合、図12(a)に示したように第2振動体20−12が境界面と平行になるように配置してもよく、図12(b)に示したように第1振動体20−11が境界面と平行になるように配置してもよい。
また、図12(c)に示したように第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12の両方が境界面と平行にならないように配置してもよい。
なお、振動体を境界面と平行にしないという観点では、第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12が平行な吸音構造体について、図12(d)に示したように第1振動体20−11と第2振動体20−12の両方が境界面と平行にならないように配置してもよい。
In the
In addition, when arrange | positioning the sound absorption structure shown to Fig.12 (a), as shown to Fig.12 (a), you may arrange | position so that the 2nd vibrating body 20-12 may become parallel to a boundary surface, As shown in FIG. 12B, the first vibrating body 20-11 may be arranged so as to be parallel to the boundary surface.
Moreover, as shown in FIG.12 (c), you may arrange | position so that both the 1st vibrating body 20-11 and the 2nd vibrating body 20-12 may not become parallel to a boundary surface.
From the standpoint that the vibrating body is not parallel to the boundary surface, the first sound-absorbing structure in which the first vibrating body 20-11 and the second vibrating body 20-12 are parallel as shown in FIG. You may arrange | position so that both the vibrating body 20-11 and the 2nd vibrating body 20-12 may not become parallel to a boundary surface.
また、上述した実施形態では、第2振動体20−12は板状で平面となっているが、図13(a)に示した第2振動体20−13のように断面で見て上下に起伏のある形状としてもよい。なお、第2振動体20−13の起伏は正弦波や方形波のように周期的に規則的な起伏であってもよいし、不規則な起伏であってもよい。
また、図13(a)に示した吸音構造体を配置する場合、第1振動体20−11が境界面に対して平行となるようにしてもよく、第1振動体20−11が境界面に対して平行にならないようにしてもよい。
また、図13(a)に示した吸音構造体を使用する場合、第1振動体20−11を境界面に平行に対向させ、第2振動体20−13を音場に向けて配置するようにしてもよく、また、第1振動体20−11を境界面に対向させる場合、第1振動体20−11が境界面に対して平行にならないように対向させて、第2振動体20−13を音場に向けて配置するようにしてもよい。
Further, in the above-described embodiment, the second vibrating body 20-12 is plate-like and flat, but when viewed in cross section like the second vibrating body 20-13 shown in FIG. It may be a undulating shape. The undulations of the second vibrating body 20-13 may be periodically undulations such as sine waves and square waves, or may be irregular undulations.
When the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 13A is disposed, the first vibrating body 20-11 may be parallel to the boundary surface, and the first vibrating body 20-11 is the boundary surface. You may make it not parallel to.
When the sound absorbing structure shown in FIG. 13A is used, the first vibrating body 20-11 is opposed to the boundary surface in parallel, and the second vibrating body 20-13 is arranged facing the sound field. In addition, when the first vibrating body 20-11 is opposed to the boundary surface, the first vibrating body 20-11 is opposed so as not to be parallel to the boundary surface, and the second vibrating body 20- You may make it arrange |
また、上述した実施形態では、平面となっている境界面に対向させて吸音構造体1Bを配置しているが、図13(b)に示したように断面で見て起伏のある非平面の境界面に対向させて吸音構造体1Bを配置するようにしてもよい。
また、吸音構造体1Bにおいても、側壁12の内側に複数の振動体を固着して、側壁12の内側に複数の空気層を設けるようにしてもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the
Also in the sound absorbing structure 1 </ b> B, a plurality of vibrating bodies may be fixed inside the
[変形例]
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上述した実施形態に限定されることなく、他の様々な形態で実施可能である。例えば、上述の実施形態を以下のように変形して本発明を実施してもよい。
[Modification]
As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described, this invention is not limited to embodiment mentioned above, It can implement with another various form. For example, the present invention may be implemented by modifying the above-described embodiment as follows.
本発明において振動体は、弾性を有して振動するのであれば、板状または膜の形状(フィルム状やシート状)のいずれであってもよい。なお、板状とは、直方体(立体)に対して相対的に厚さが薄く2次元的な広がりをもつことを意味し、膜状(フィルム状、シート状)とは、板状よりもさらに相対的に厚さが薄く、張力により復元力を発生することを意味する。 In the present invention, the vibrating body may be either plate-shaped or film-shaped (film-shaped or sheet-shaped) as long as it has elasticity and vibrates. The plate shape means that the thickness is relatively thin with respect to a rectangular parallelepiped (solid) and has a two-dimensional extension, and the film shape (film shape, sheet shape) is more than the plate shape. It means that the thickness is relatively thin and a restoring force is generated by tension.
本発明においては、振動体の素材は塩素化ポリエチレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリエチレンテレフタラート、ポリエステル、合成ゴム(イソプレンゴム、ニトリルゴム、フッ素ゴム、ブタジエンスチレン共重合体、共重合体ポリマなど)、ポリアミドなど有機高分子を主体とするものであってもよく、また、シリコーンゴムなど無機高分子を主体とするものであってもよい。
また、これらの素材においては、有機低分子(可塑剤、架橋剤、架橋促進剤、酸化防止剤)や、無機充填剤がふくまれていてもよい。
In the present invention, the material of the vibrator is chlorinated polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate, polyester, synthetic rubber (isoprene rubber, nitrile rubber, fluororubber, butadiene styrene copolymer, copolymer polymer, etc.), polyamide It may be mainly composed of an organic polymer, or may be composed mainly of an inorganic polymer such as silicone rubber.
In addition, these materials may contain organic small molecules (plasticizers, crosslinking agents, crosslinking accelerators, antioxidants) and inorganic fillers.
また、筐体10の素材は、ABSではなく、ポリプロピレン、ポリアミドなどの熱可塑性プラスチック、エポキシ樹脂などの熱硬化性プラスチック、繊維強化プラスチックなど他の素材であってもよい。
The material of the
上述した本発明に係る吸音構造体は、上方から見た時の形状が正方形となっているが、上方から見た時の形状が、長方形、台形、多角形、円形、楕円形など、他の形状となるように振動体や筐体を形成してもよい。 The sound absorbing structure according to the present invention described above has a square shape when viewed from above, but the shape when viewed from above is rectangular, trapezoidal, polygonal, circular, elliptical, or the like. You may form a vibrating body and a housing | casing so that it may become a shape.
なお、上述した実施形態または変形例に係る吸音構造体を配置する場合、大きさの同じ吸音構造体を複数組み合わせた吸音体群を配置してもよい。
また、吸音構造体を複数組み合わせる場合には、組み合わせる吸音構造体毎に振動体の素材や厚さ、密度、ヤング率、損失正接(tanδ)を異ならせてもよい。
また、吸音構造体を複数組み合わせる場合には、吸音構造体毎に空気層の厚さを異ならせてもよい。また、空気層のサイズを各々異ならせてもよく、空気層の厚さとサイズの両方を各々異ならせてもよい。
In addition, when arrange | positioning the sound-absorbing structure which concerns on embodiment mentioned above or a modification, you may arrange | position the sound-absorbing body group which combined two or more sound-absorbing structures with the same magnitude | size.
Further, when a plurality of sound absorbing structures are combined, the material, thickness, density, Young's modulus, and loss tangent (tan δ) of the vibrator may be different for each sound absorbing structure to be combined.
When a plurality of sound absorbing structures are combined, the thickness of the air layer may be varied for each sound absorbing structure. Further, the size of the air layer may be varied, and both the thickness and the size of the air layer may be varied.
また、本発明に係る吸音構造体においては、筐体10の内部を図14に示したように仕切部材13で格子状に区切り、側壁12の内側で複数の空気層が形成されるようにしてもよい。
Further, in the sound absorbing structure according to the present invention, the inside of the
上述した実施形態においては、振動体は、側壁12に固着されて固定支持されており、固着部位においては変位(移動)も回転も拘束されているが、振動体は、側壁12に対して変位が拘束され、回転が許容されている単純支持状態であってもよい。また、変位が許容されている支持状態や自由支持など他の支持状態であってもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the vibrating body is fixedly supported by being fixed to the
上述した本発明に係る吸音構造体を、吸音構造体の吸音率のピークの周波数の音が騒音として発生している場所に配置して騒音を低減させてもよい。このように吸音構造体を騒音の発生場所に配置して騒音を低減させる騒音低減方法によれば、振動体が振動して騒音のエネルギが消費されて騒音が低減されることとなる。なお、騒音の発生場所としては、例えば車両や飛行機など各種輸送機器の内部、工場や工事現場などで運転されている各種機械などがある。 The above-described sound absorbing structure according to the present invention may be disposed in a place where the sound having the peak frequency of the sound absorption coefficient of the sound absorbing structure is generated as noise to reduce noise. As described above, according to the noise reduction method in which the sound absorbing structure is arranged at a place where noise is generated to reduce noise, the vibration body vibrates, noise energy is consumed, and noise is reduced. Note that the noise generation location includes, for example, various machines operating in factories, construction sites, etc., inside various transportation equipment such as vehicles and airplanes.
1,1A,1B・・・吸音構造、10・・・筐体、11・・・底面部、12・・・側壁、13・・・仕切部材、20−1〜20−5,20−11〜20−13・・・振動体、30−1,30−2,30−11〜30−15・・・空気層。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
中空部を備える管の形状の側壁と
を有し、
前記中空部を塞ぐように前記振動体が前記側壁に固着され、
前記複数の振動体は、非平行で配置され、距離をおいて表面が他の振動体の表面に面し、
前記振動体と空気層とが交互に積層された吸音構造体。 A plurality of plate-like or film-like vibrators;
A side wall in the shape of a tube with a hollow portion, and
The vibrating body is fixed to the side wall so as to close the hollow portion,
The plurality of vibrators are arranged non-parallel, and the surface faces the surface of another vibrator at a distance,
A sound absorbing structure in which the vibrating body and the air layer are alternately stacked.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008146826A JP5446134B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2008-06-04 | Sound absorbing structure |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008146826A JP5446134B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2008-06-04 | Sound absorbing structure |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009293252A JP2009293252A (en) | 2009-12-17 |
| JP2009293252A5 JP2009293252A5 (en) | 2011-07-14 |
| JP5446134B2 true JP5446134B2 (en) | 2014-03-19 |
Family
ID=41541675
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008146826A Expired - Fee Related JP5446134B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2008-06-04 | Sound absorbing structure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5446134B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5326472B2 (en) | 2007-10-11 | 2013-10-30 | ヤマハ株式会社 | Sound absorption structure |
| EP2085962A2 (en) | 2008-02-01 | 2009-08-05 | Yamaha Corporation | Sound absorbing structure and vehicle component having sound absorbing properties |
| KR101574015B1 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2015-12-02 | 박창열 | The sound absorbent device |
| JP6684106B2 (en) * | 2016-02-12 | 2020-04-22 | 株式会社 いそのボデー | Security panel, box body and vehicle body using the same |
| JP7127073B2 (en) * | 2018-02-06 | 2022-08-29 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | soundproof structure |
| WO2019167795A1 (en) * | 2018-02-27 | 2019-09-06 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Soundproof structure |
| EP3761305B1 (en) | 2018-02-27 | 2024-10-09 | FUJIFILM Corporation | Soundproof structure |
| JP6982762B2 (en) * | 2018-09-28 | 2021-12-17 | マツダ株式会社 | Automotive panel structure |
| CN113643678B (en) * | 2021-07-06 | 2024-09-03 | 洛阳拖拉机研究所有限公司 | Sound absorption and insulation composite structure |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5448918A (en) * | 1977-09-20 | 1979-04-17 | Shingo Kizai Kk | Sound insulation wall unit |
| JPS5595999A (en) * | 1979-01-16 | 1980-07-21 | Showa Koji Kk | Sound absorption structrre consisting of transparent synthetic rubber film material |
| JPH0976391A (en) * | 1995-09-19 | 1997-03-25 | Mitsubishi Motors Corp | Sound insulation structure |
| JP4381081B2 (en) * | 2003-09-29 | 2009-12-09 | 住友林業株式会社 | Sound insulation door structure |
-
2008
- 2008-06-04 JP JP2008146826A patent/JP5446134B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009293252A (en) | 2009-12-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5446134B2 (en) | Sound absorbing structure | |
| JP5056385B2 (en) | Sound absorber | |
| JP5326472B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure | |
| US9369805B2 (en) | Acoustic absorber, acoustic transducer, and method for producing an acoustic absorber or an acoustic transducer | |
| EP2764509B1 (en) | High bandwidth antiresonant membrane | |
| JP5402025B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure and acoustic room | |
| JP5245641B2 (en) | Sound absorbing structure | |
| JP4754836B2 (en) | Double wall structure | |
| US20090223738A1 (en) | Sound absorbing structure and vehicle component having sound absorption property | |
| JP5167751B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure | |
| JP2009198902A (en) | Sound absorbing structure, sound absorbing structure group, acoustic chamber, method of adjusting sound absorbing structure and noise reduction method | |
| WO2007029697A1 (en) | Double wall structure | |
| US10878794B2 (en) | Soundproofing structure | |
| JP5493378B2 (en) | Sound absorbing structure | |
| JP2016170194A (en) | Sound absorber, and sound absorbing structure | |
| KR20210001934U (en) | sound insulation panel | |
| JP6791620B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure | |
| JP2009167702A (en) | Sound absorbing body and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2009198901A (en) | Sound absorption structure, sound absorption structure group, acoustic chamber, method of adjusting sound absorption structure and noise reduction method | |
| JP5286949B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure | |
| JP2010052632A (en) | Vehicle body structure and instrument panel | |
| JP4747589B2 (en) | Sound absorber | |
| JP2009204836A (en) | Sound absorption structure, sound absorption structure group, sound box, method of adjusting sound structure and noise reduction method | |
| JP5262800B2 (en) | Sound absorbing structure | |
| JP5223608B2 (en) | Sound absorbing structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110601 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110602 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120906 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120911 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121029 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130507 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20131203 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20131216 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5446134 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |